Beginners' zoology . Fig. 38. — Hydras on the under sur-face of pondweed. 26 BEGINNERS ZOOLOGY scarce. Asexual generation (by budding) is common withthe hydra when food supply is abundant. After the bud grows to a cer-tain size, theouter layer ofcells at the baseof the bud con-stricts and theyoung hydra isdetached. Compare thesponge and thehydra in the fol-lowing respects:— many celled,or one celled;obtaining food ;breathing; tubesand cavities;openings; re-production ; loco-motion. Whichranks higher. ECTODERM CELLSINTERSTITAL 00MUSCLE LAYER FLAGELLA • •ENTERIC CAVITY* Fig. 39. ? • Longitudinal
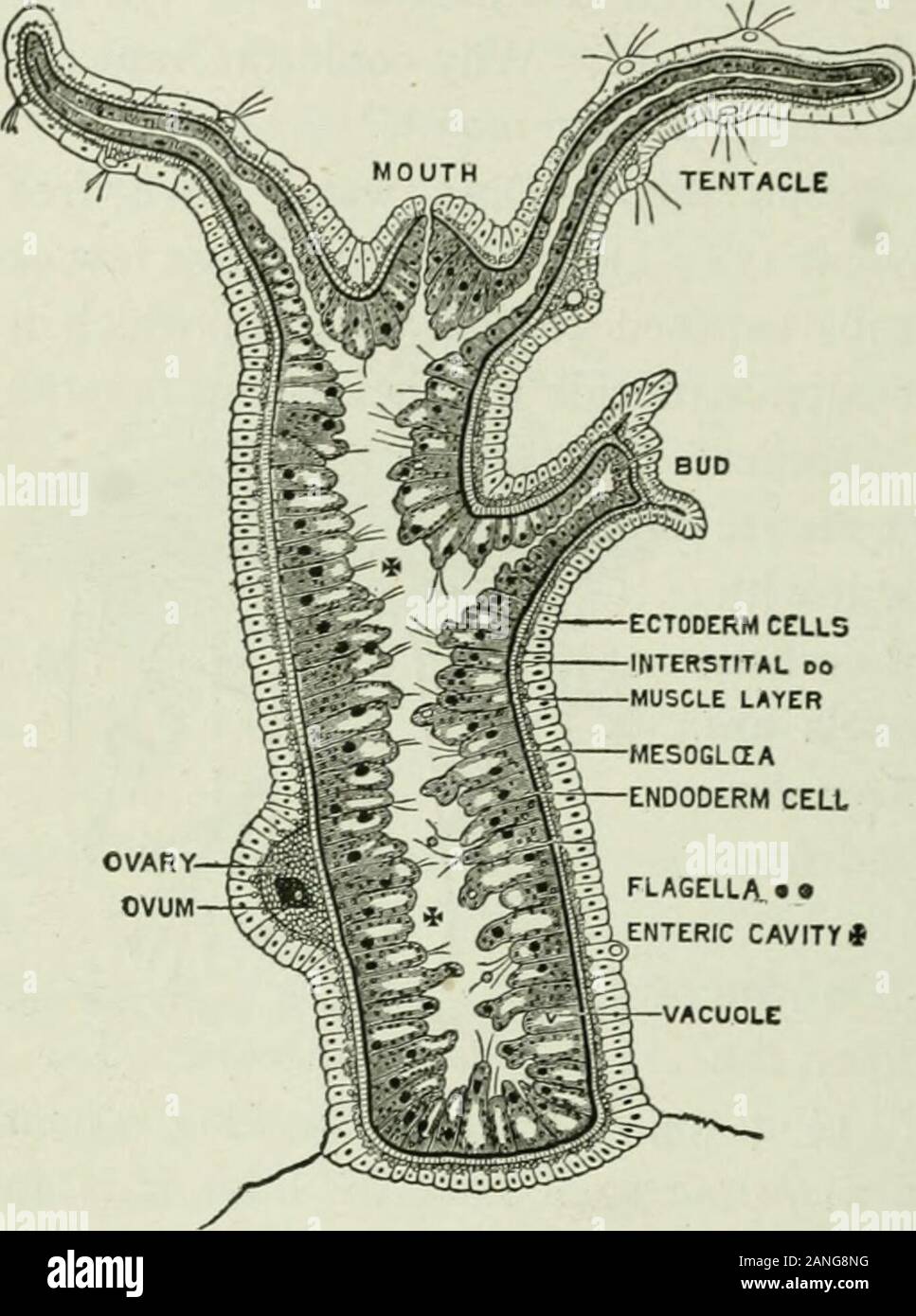
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2ANG8NGFile size:
7.1 MB (292.1 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1363 x 1832 px | 23.1 x 31 cm | 9.1 x 12.2 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
Beginners' zoology . Fig. 38. — Hydras on the under sur-face of pondweed. 26 BEGINNERS ZOOLOGY scarce. Asexual generation (by budding) is common withthe hydra when food supply is abundant. After the bud grows to a cer-tain size, theouter layer ofcells at the baseof the bud con-stricts and theyoung hydra isdetached. Compare thesponge and thehydra in the fol-lowing respects:— many celled, or one celled;obtaining food ;breathing; tubesand cavities;openings; re-production ; loco-motion. Whichranks higher. ECTODERM CELLSINTERSTITAL 00MUSCLE LAYER FLAGELLA • •ENTERIC CAVITY* Fig. 39. ? • Longitudinal section of hydra (microscopicand diagrammatic). among the metazoa . The metazoa, or many celled ani-mals, include all animals except which branch ? Figure 39 is a Microscopic view of a vertical section of a hydra toshow the structure of the body wall. There is an outer layer called theectoderm, and an inner layer called the endoderm. There is also a thinsupporting layer (black in the figure) called the viesoglea. The mesogleais the thinnest layer. Are the cells larger in the endoderm or the ectoderm ?Do both layers of cells assist in forming the reproductive bud ? The ecto-derm cells end on the inside in contractile tails which form a thin line andhave the effect of muscle fibres. They serve the hydra for its remarkablechanges of shape. When the hydra is cut in pieces, each piece makes acomplete hydra, provided it contains both endoderm and ectoderm. POLYPS (^CUPLIKE ANIMAL6) 2/ In w