. Bensley's Practical anatomy of the rabbit : an elementary laboratory text-book in mammalian anatomy. Rabbits -- Anatomy. THE CRANIAL NERVES 87 vertebral column through the intervertebral foramina—and the cranial or cerebral nerves—those arising from the brain and passing through the foramina of the skull—in addition to the autonomic system, described on page 74. Of these the spinal nerves (p. 73) are less modified, in both structure and distribution. N.-^ .--'^^--Y'-^. / v:- i Fig. 46. Dissection from the ventral surface of the neck. On the right side the platysma and depressor conchae poste
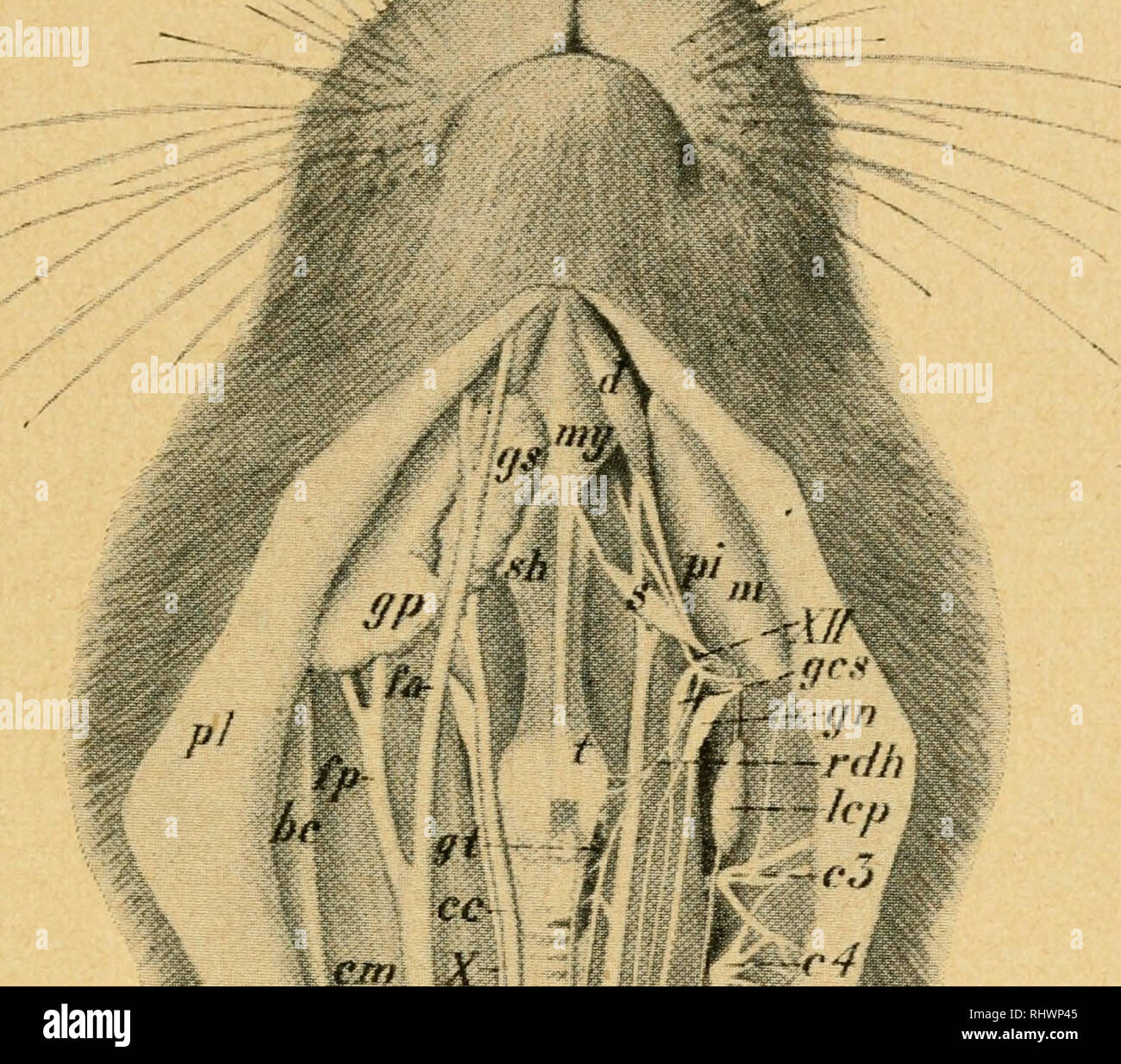
Image details
Contributor:
Library Book Collection / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RHWP45File size:
7.1 MB (548.1 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1685 x 1483 px | 28.5 x 25.1 cm | 11.2 x 9.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Bensley's Practical anatomy of the rabbit : an elementary laboratory text-book in mammalian anatomy. Rabbits -- Anatomy. THE CRANIAL NERVES 87 vertebral column through the intervertebral foramina—and the cranial or cerebral nerves—those arising from the brain and passing through the foramina of the skull—in addition to the autonomic system, described on page 74. Of these the spinal nerves (p. 73) are less modified, in both structure and distribution. N.-^ .--'^^--Y'-^. / v:- i Fig. 46. Dissection from the ventral surface of the neck. On the right side the platysma and depressor conchae posterior are reflected with the skin. The vagus nerve is in proper relation to the external jugular vein and the common carotid artery. On the left side the external jugular vein, parotid and submaxillary glands, and the sternohyoid. sternomastoid._ and cleido- mastoid muscles are removed, the common carotid displaced medially and the nerves laterally, but otherwise in proper relation. be, basioclavicularis: cc, common carotid artery; cm. cleidomastoideus; c3, c4._ c5, cervical spinal nerves; d, digastricus; fa, anterior facial vein; fp, posterior facial vein; gcs, superior cervical ganglion; gn, ganglion nodosum; gp, parotid gland; gs, submaxillary gland; gt, thyreoid^ gland; Icp. deep cervical lymph gland; m, masseter; my, mylohyoideus; pi, medial insertion portion of masseter concealing the pterygoideus internus; pi, platysma; rev, cardiac branch of vagus nerve (n. depressor); rdh, descending branch of hypoglossal nerve; s, stylohyoideus major; sh, sternohyoideus; sm_, sterno- mastoideus; st. sternothyreoideus; t, thyreohyoideus; ts, sympathetic trunk; vje. external jugular vein; vji, internal jugular vein; X, vagus nerve; XII. hypoglossal nerve. (From dissection by W. H. T. Baillie, drawing by E. B. Logier.). Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illus