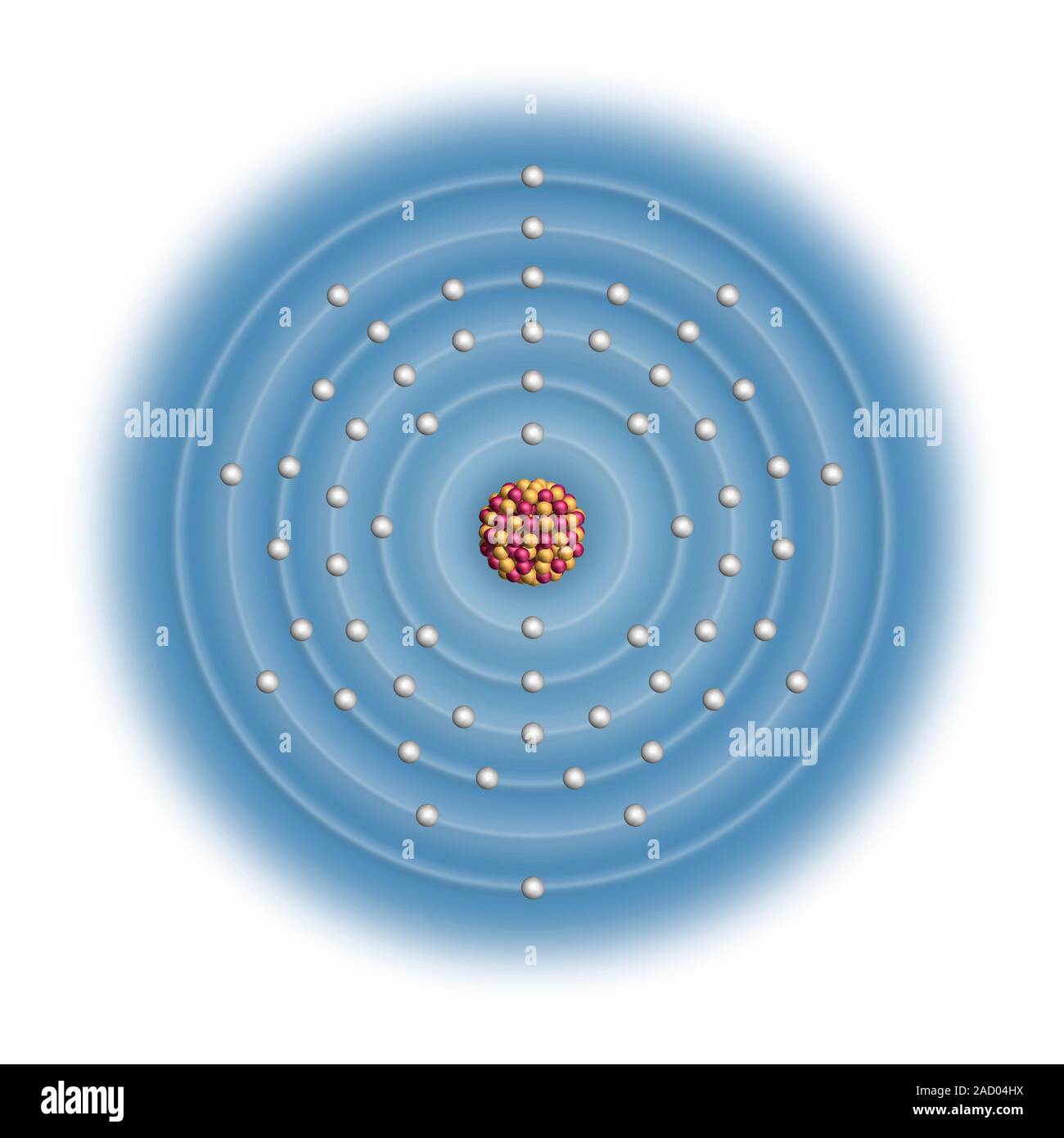
Cerium (Ce). Diagram of the nuclear composition and electron configuration of an atom of cerium-140 (atomic number: 58), the most common isotope of th
RMID:Image ID:2AD04HX
Image details
Contributor:
Science Photo Library / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AD04HXFile size:
50 MB (441.2 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
4180 x 4180 px | 35.4 x 35.4 cm | 13.9 x 13.9 inches | 300dpiDate taken:
14 January 2015Photographer:
CARLOS CLARIVAN/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARYMore information:
Cerium (Ce). Diagram of the nuclear composition and electron configuration of an atom of cerium-140 (atomic number: 58), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 58 protons (red) and 82 neutrons (yellow). 58 electrons (white) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Cerium is a lanthanide in period 6, and the f-block of the periodic table. It melts at 795 degrees Celsius. The trend across the lanthanide series arises from the failure of electrons filling an inner f-subshell (here, within the 4th ring) to shield outer electrons from increasing nuclear charge.