···
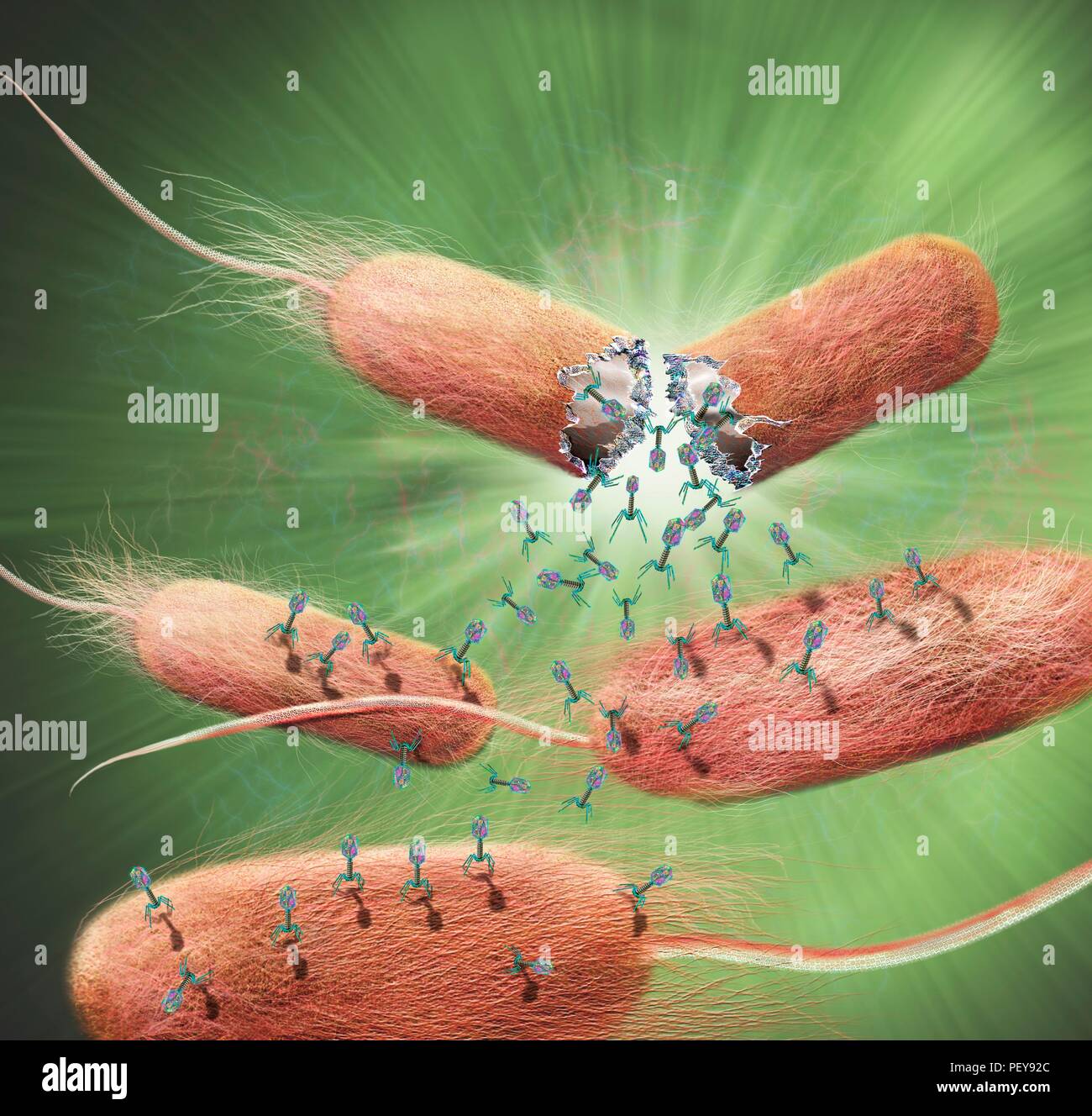
Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Image details File size:
73.2 MB (2.7 MB Compressed download)
Open your image file to the full size using image processing software.
Dimensions:
5182 x 4935 px | 43.9 x 41.8 cm | 17.3 x 16.5 inches | 300dpi
Date taken:
16 August 2018
Search stock photos by tags
Similar stock images Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1 https://www.alamy.com/computer-illustration-of-t-bacteriophages-or-phages-leaving-bacteria-phages-are-viruses-that-infect-bacteria-t-phages-consist-of-an-icosahedral-20-sided-head-which-contains-the-genetic-material-either-dna-or-rna-and-a-thick-tail-with-several-bent-tail-fibres-the-tail-is-used-to-inject-the-genetic-material-into-the-host-cell-to-infect-it-the-phage-then-uses-the-bacteriums-genetic-machinery-to-replicate-itself-when-a-sufficient-number-have-been-produced-the-phages-exit-the-cell-by-lysis-a-process-that-kills-the-cell-image215729436.html RF PEY92M – Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving a bacterium. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1 https://www.alamy.com/computer-illustration-of-t-bacteriophages-or-phages-leaving-a-bacterium-phages-are-viruses-that-infect-bacteria-t-phages-consist-of-an-icosahedral-20-sided-head-which-contains-the-genetic-material-either-dna-or-rna-and-a-thick-tail-with-several-bent-tail-fibres-the-tail-is-used-to-inject-the-genetic-material-into-the-host-cell-to-infect-it-the-phage-then-uses-the-bacteriums-genetic-machinery-to-replicate-itself-when-a-sufficient-number-have-been-produced-the-phages-exit-the-cell-by-lysis-a-process-that-kills-the-cell-image215729426.html RF PEY92A – Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving a bacterium. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1 https://www.alamy.com/computer-illustration-of-t-bacteriophages-or-phages-leaving-bacteria-phages-are-viruses-that-infect-bacteria-t-phages-consist-of-an-icosahedral-20-sided-head-which-contains-the-genetic-material-either-dna-or-rna-and-a-thick-tail-with-several-bent-tail-fibres-the-tail-is-used-to-inject-the-genetic-material-into-the-host-cell-to-infect-it-the-phage-then-uses-the-bacteriums-genetic-machinery-to-replicate-itself-when-a-sufficient-number-have-been-produced-the-phages-exit-the-cell-by-lysis-a-process-that-kills-the-cell-image215729438.html RF PEY92P – Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving a bacterium. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1 https://www.alamy.com/computer-illustration-of-t-bacteriophages-or-phages-leaving-a-bacterium-phages-are-viruses-that-infect-bacteria-t-phages-consist-of-an-icosahedral-20-sided-head-which-contains-the-genetic-material-either-dna-or-rna-and-a-thick-tail-with-several-bent-tail-fibres-the-tail-is-used-to-inject-the-genetic-material-into-the-host-cell-to-infect-it-the-phage-then-uses-the-bacteriums-genetic-machinery-to-replicate-itself-when-a-sufficient-number-have-been-produced-the-phages-exit-the-cell-by-lysis-a-process-that-kills-the-cell-image215729424.html RF PEY928 – Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving a bacterium. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1 https://www.alamy.com/computer-illustration-of-t-bacteriophages-or-phages-leaving-bacteria-phages-are-viruses-that-infect-bacteria-t-phages-consist-of-an-icosahedral-20-sided-head-which-contains-the-genetic-material-either-dna-or-rna-and-a-thick-tail-with-several-bent-tail-fibres-the-tail-is-used-to-inject-the-genetic-material-into-the-host-cell-to-infect-it-the-phage-then-uses-the-bacteriums-genetic-machinery-to-replicate-itself-when-a-sufficient-number-have-been-produced-the-phages-exit-the-cell-by-lysis-a-process-that-kills-the-cell-image215729427.html RF PEY92B – Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving a bacterium. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell. Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1 https://www.alamy.com/computer-illustration-of-t-bacteriophages-or-phages-leaving-a-bacterium-phages-are-viruses-that-infect-bacteria-t-phages-consist-of-an-icosahedral-20-sided-head-which-contains-the-genetic-material-either-dna-or-rna-and-a-thick-tail-with-several-bent-tail-fibres-the-tail-is-used-to-inject-the-genetic-material-into-the-host-cell-to-infect-it-the-phage-then-uses-the-bacteriums-genetic-machinery-to-replicate-itself-when-a-sufficient-number-have-been-produced-the-phages-exit-the-cell-by-lysis-a-process-that-kills-the-cell-image215729425.html RF PEY929 – Computer illustration of T-bacteriophages, or phages, leaving a bacterium. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria. T-phages consist of an icosahedral (20-sided) head, which contains the genetic material (either DNA or RNA), and a thick tail with several bent tail fibres. The tail is used to inject the genetic material into the host cell to infect it. The phage then uses the bacterium's genetic machinery to replicate itself. When a sufficient number have been produced the phages exit the cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell.