. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. BOOT OF THE LUNG. 1097 Eight bronchus The pulmonary artery occupies a different position on the two sides, in relation to the main or undivided part of the bronchus. On the right side it is. placed below it, whilst on the left side it crosses the bronchus and occupies a higher level in the pulmonary root. The two pulmonary veins on both sides lie at a lower level in the root of the lung than the pulmonary artery and bronchus, whilst the superior of the two veins occupies a plane ventral to the pulmonary artery (Figs. 870 and 871). Distribution of t
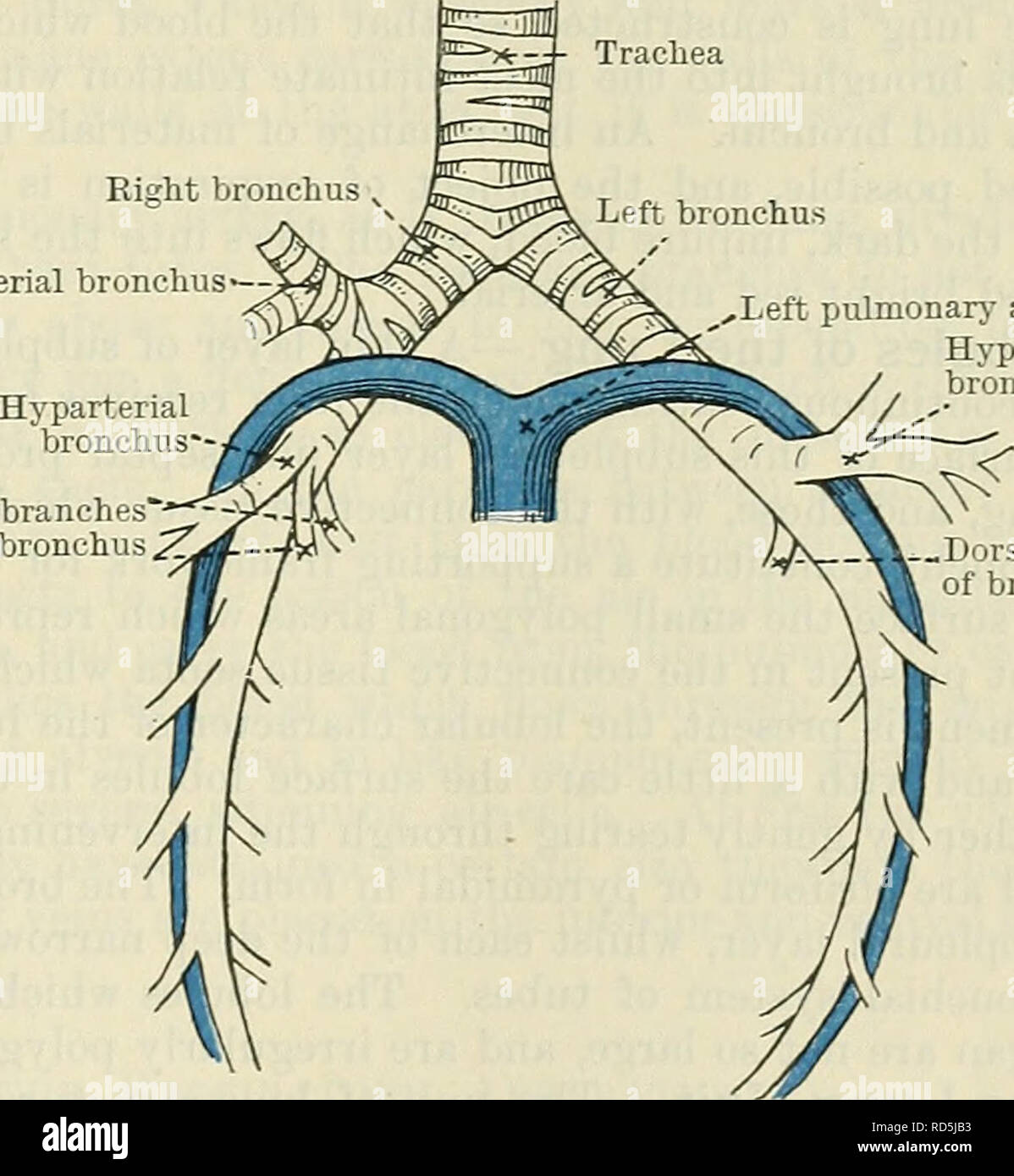
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RD5JB3File size:
7.1 MB (257.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1518 x 1646 px | 25.7 x 27.9 cm | 10.1 x 11 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. BOOT OF THE LUNG. 1097 Eight bronchus The pulmonary artery occupies a different position on the two sides, in relation to the main or undivided part of the bronchus. On the right side it is. placed below it, whilst on the left side it crosses the bronchus and occupies a higher level in the pulmonary root. The two pulmonary veins on both sides lie at a lower level in the root of the lung than the pulmonary artery and bronchus, whilst the superior of the two veins occupies a plane ventral to the pulmonary artery (Figs. 870 and 871). Distribution of the Bronchial Tubes within the Lungs.—The two lungs are not symmetrical; the right lung is subdivided into three lobes, and the left lung is cleft into two lobes. The bronchi exhibit a corresponding want of symmetry. The right bronchus, as it approaches the pulmonary hilus, gives off two branches for the superior and middle lobes of the right lung respectively, and then the main stem of the tube enters the inferior lobe. The left bronchus sends off a large branch to the superior lobe of the left lung, and then sinks into the inferior lobe. The first branch of the right bronchus, for the superior lobe, leaves the main stem about one inch from the trachea. The first branch of the left bronchus, on the other hand, takes origin about twice that distance from the trachea. The relation of the pulmonary artery to the bronchial subdivisions is different on the two sides. On the right side it turns dorsally to reach the dorsal aspect of the bronchus inferior to the first, and superior to the second, bronchial branch. On the left side the pul- monary artery turns dorsally above the level of the first bronchial branch. On the right side, therefore, the first bronchial branch is placed above the pulmonary artery, and in consequence it is termed the eparterial bronchial ramus; all the others lie below the artery, and are termed hyparterial bronchial rami. On the left side there is no epart