Modern diagnosis and treatment of diseases of childern; a treatise on the medical and surgical diseases of infancy anf childhood . the entire body is more or less involved. It closely resemblestuberculous adenitis, except that it is much less common thantuberculosis and that in the latter condition the glands show agreater tendency to caseation and suppuration. In doubtfulcases the tuberculin test may prove decisive in the diagnosis. The changes in the blood and the clinical manifestations are identical with those observed in anemia. Occasionally there are local pressure-symptoms, such as pain
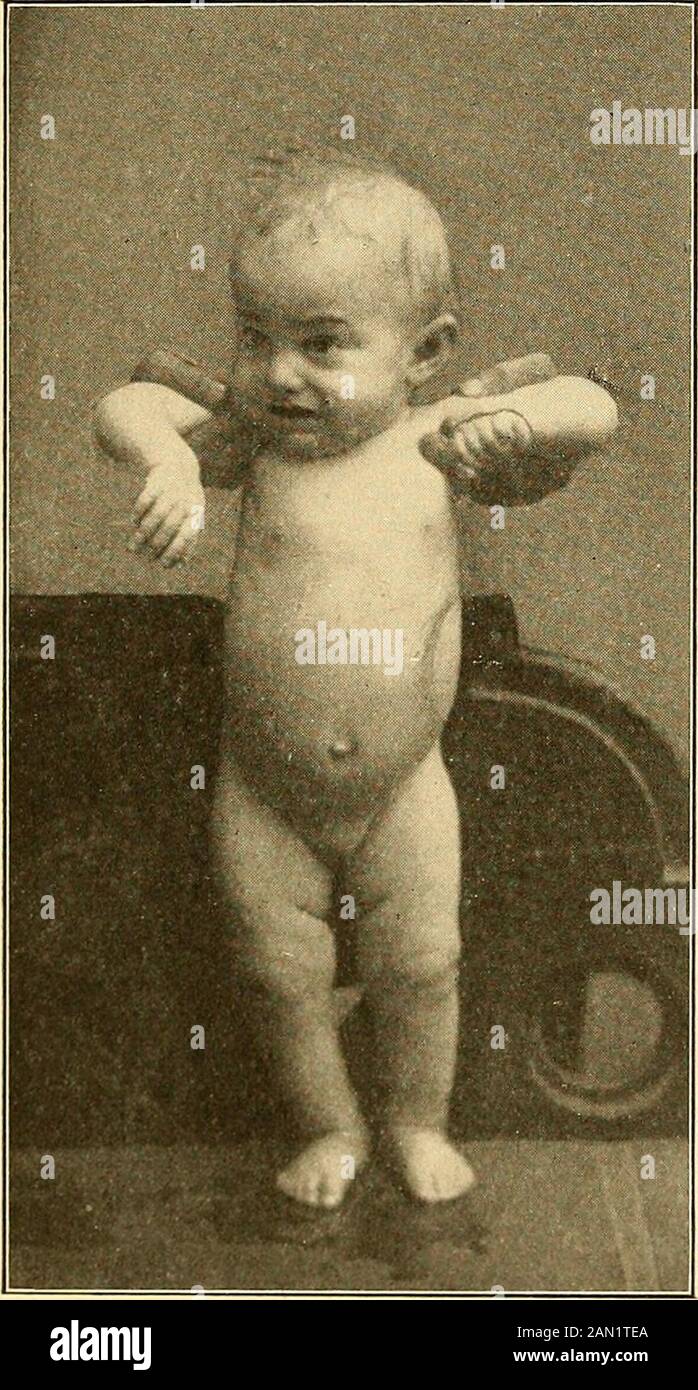
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AN1TEAFile size:
7.2 MB (509.1 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1159 x 2157 px | 19.6 x 36.5 cm | 7.7 x 14.4 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
Modern diagnosis and treatment of diseases of childern; a treatise on the medical and surgical diseases of infancy anf childhood . the entire body is more or less involved. It closely resemblestuberculous adenitis, except that it is much less common thantuberculosis and that in the latter condition the glands show agreater tendency to caseation and suppuration. In doubtfulcases the tuberculin test may prove decisive in the diagnosis. The changes in the blood and the clinical manifestations are identical with those observed in anemia. Occasionally there are local pressure-symptoms, such as pain, edema, cough and dyspnea. Under suitable treatment, which is essentiallv the same as in The same . simple simple anemia, recovery or, at least, arrest of the disease is pos- ancmia. sible. Intractable cases often terminate in leukemia. PSEUDOLEUKEMIA. 473 PSEUDOLEUKEMIA INFANTUM SPLENICA(Von Jaksch or Splenic Anemia). In contrast to genuine leukemia, pseudoleukemia splenica isof quite frequent occurrence, slow in its course and favorable in Sl0w ^ ^ , _ course. its outcome. The etiology of this affection is obscure. As a. Fig. 144.—Pseudoleukemia Infantum Splenica. Note positionof enlarged spleen. (Sheffield.) rule, it is observed in connection with pronounced forms of mal-nutrition, especially rachitis. The chief alterations in the blood are reduction of red cellsand hemoglobin, the presence of many nucleated red corpuscles, and an increase in the number of leucocytes, mostly of the mono-nuclear type. This blood picture essentially corresponds to thatof ordinary secondary anemia. In pseudoleukemia infantum. Increasedleucocytosis. 474 DISEASES OF BLOOD AXD DUCTLESS GLANDS. Enlarged however, there is marked enlargement of the spleen and occasion-spleen. ° ally also of the liver and lymphatic glands. The general symptoms differ but little from those observed insevere anemia. The same applies to the treatment. The syrupof the iodid of iron with the syrup of the hypophosphites