Muscle contraction. Artwork showing the mechanism for muscle contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscle. At top right troponin (T,C,I) is bound to tro
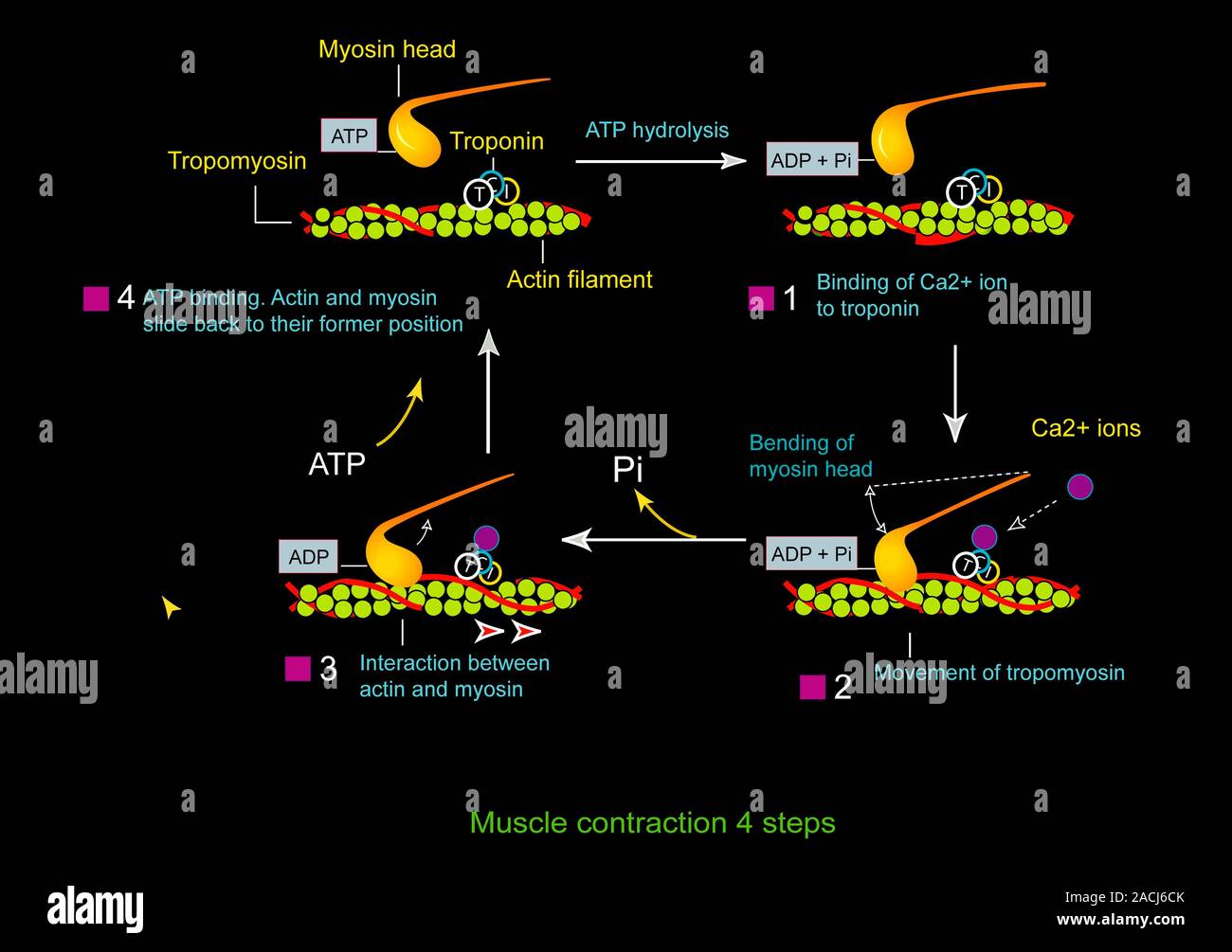
Image details
Contributor:
Science Photo Library / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2ACJ6CKFile size:
50.4 MB (588.2 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
5000 x 3523 px | 42.3 x 29.8 cm | 16.7 x 11.7 inches | 300dpiDate taken:
7 February 2011Photographer:
FRANCIS LEROY, BIOCOSMOS/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARYMore information:
Muscle contraction. Artwork showing the mechanism for muscle contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscle. At top right troponin (T, C, I) is bound to tropomyosin (red), preventing the myosin head (gold) from forming a crossbridge with the actin filament (green). The propagation of an action potential releases calcium ions (purple) into the muscle cell (bottom right). The calcium ion binds to troponin, changing its shape and exposing the myosin binding site on the actin filament. The binding of actin and mysoin causes the muscle to contract (bottom left). The myosin then binds ATP, which allows it to release the actin and return to the starting position (top left).