Pott's disease. Coloured magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of sagittal (side) sections through the spine of a patient with Pott's disease (tuberc
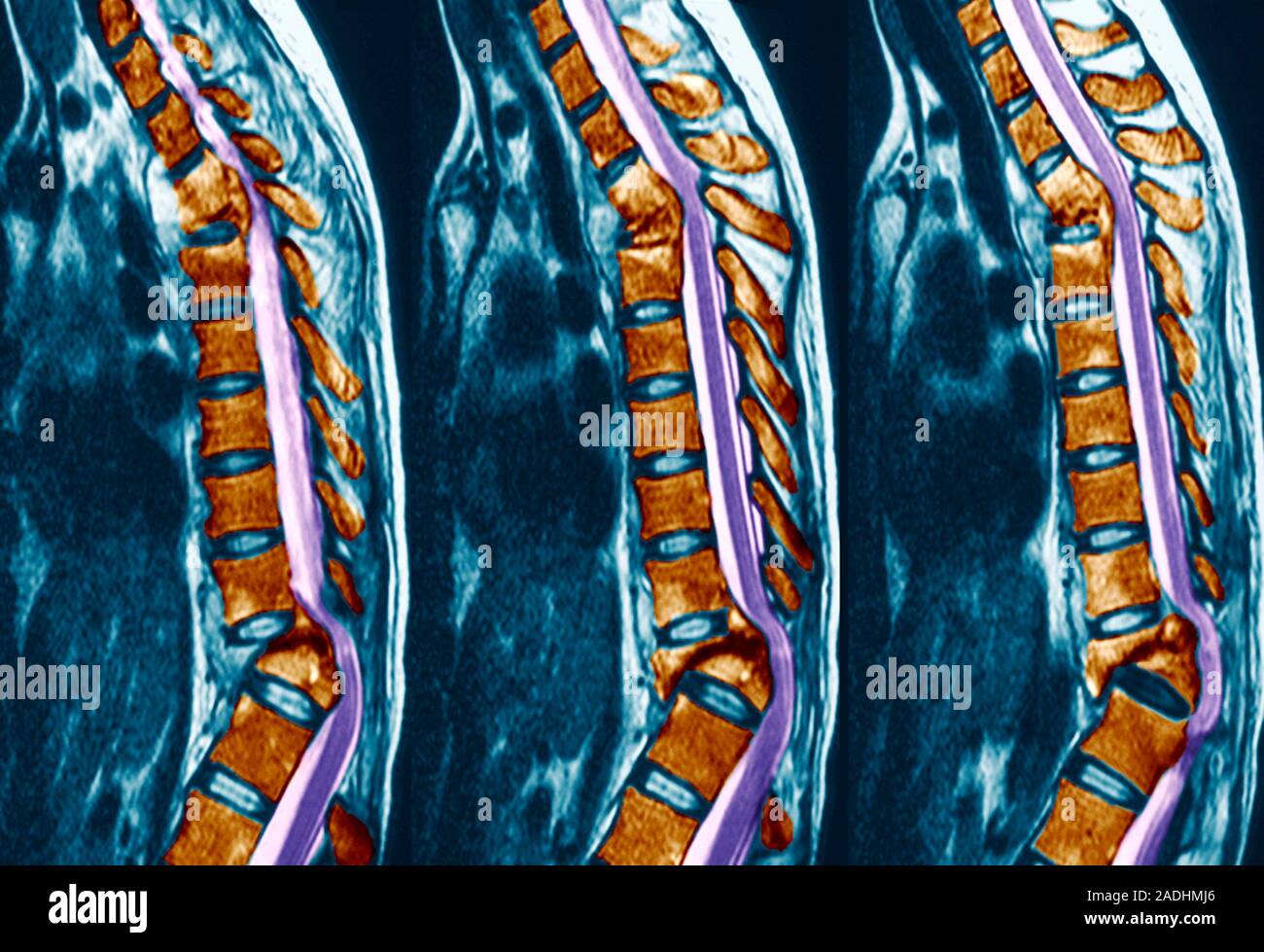
Image details
Contributor:
Science Photo Library / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2ADHMJ6File size:
28.5 MB (978.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
3813 x 2610 px | 32.3 x 22.1 cm | 12.7 x 8.7 inches | 300dpiDate taken:
9 June 2004Photographer:
ZEPHYR/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARYMore information:
Pott's disease. Coloured magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of sagittal (side) sections through the spine of a patient with Pott's disease (tuberculosis of the spine). The vertebrae (brown blocks) have become compacted, and inflamed joints are pressing on the spinal cord (purple) at the upper and lower curves. Pott's disease causes the softening, collapse and inflammation of vertebrae. It is a secondary disease to TB and is caused when the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria move from the lungs to the spine. The damage to the vertebrae often leads to a hunchback deformity, or Pott's curvature. Treatment is with antibiotics and immobilisation of the spine.