An illustrated diagram of the Ebola virus (EBOV), a virus responsible for severe hemorrhagic fever in humans and mammals, which can be transmitted through body fluids or natural reservoirs such as bats. The center of the virus contains a single-stranded,
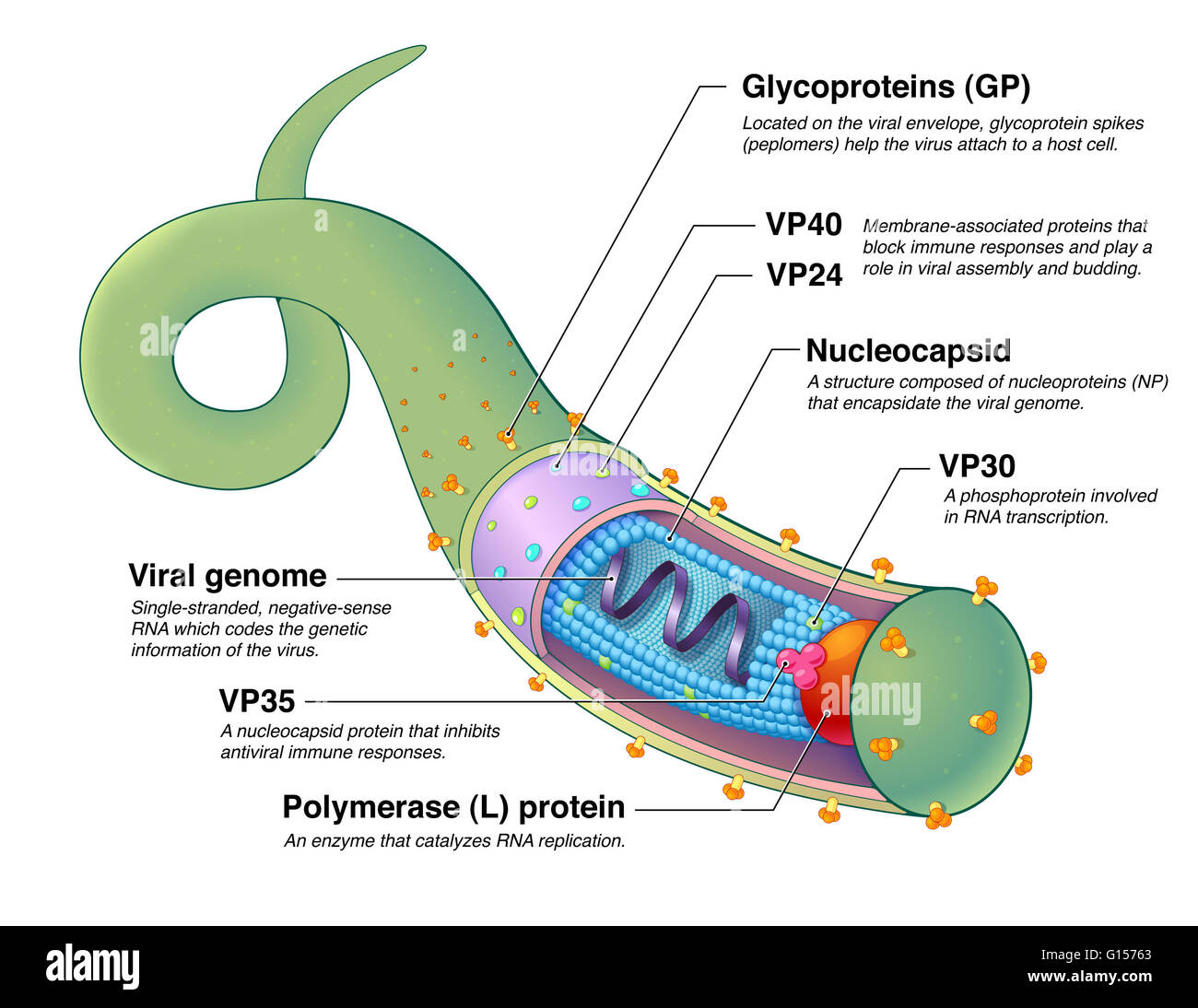
Image details
Contributor:
Science History Images / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
G15763File size:
24.1 MB (622.8 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
3300 x 2550 px | 27.9 x 21.6 cm | 11 x 8.5 inches | 300dpiPhotographer:
Evan OtoMore information:
An illustrated diagram of the Ebola virus (EBOV), a virus responsible for severe hemorrhagic fever in humans and mammals, which can be transmitted through body fluids or natural reservoirs such as bats. The center of the virus contains a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome and a nucleocapsid containing viral proteins VP35 and VP30. The matrix contains viral proteins VP40 and VP24, while the outer viral envelope uses glycoprotein (GP) spikes to attach to host cells. Once the virus enters a host cell, the viral RNA is translated to produce additional viral proteins. The viral proteins are enveloped using the host cell's plasma membrane and released through the process of budding, which destroys the cell.