Quick filters:
Adductor canal Stock Photos and Images
 Adductor West - Work PAC 2 - responsible for water supply in the region Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-adductor-west-work-pac-2-responsible-for-water-supply-in-the-region-101303268.html
Adductor West - Work PAC 2 - responsible for water supply in the region Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-adductor-west-work-pac-2-responsible-for-water-supply-in-the-region-101303268.htmlRMFTPN9T–Adductor West - Work PAC 2 - responsible for water supply in the region
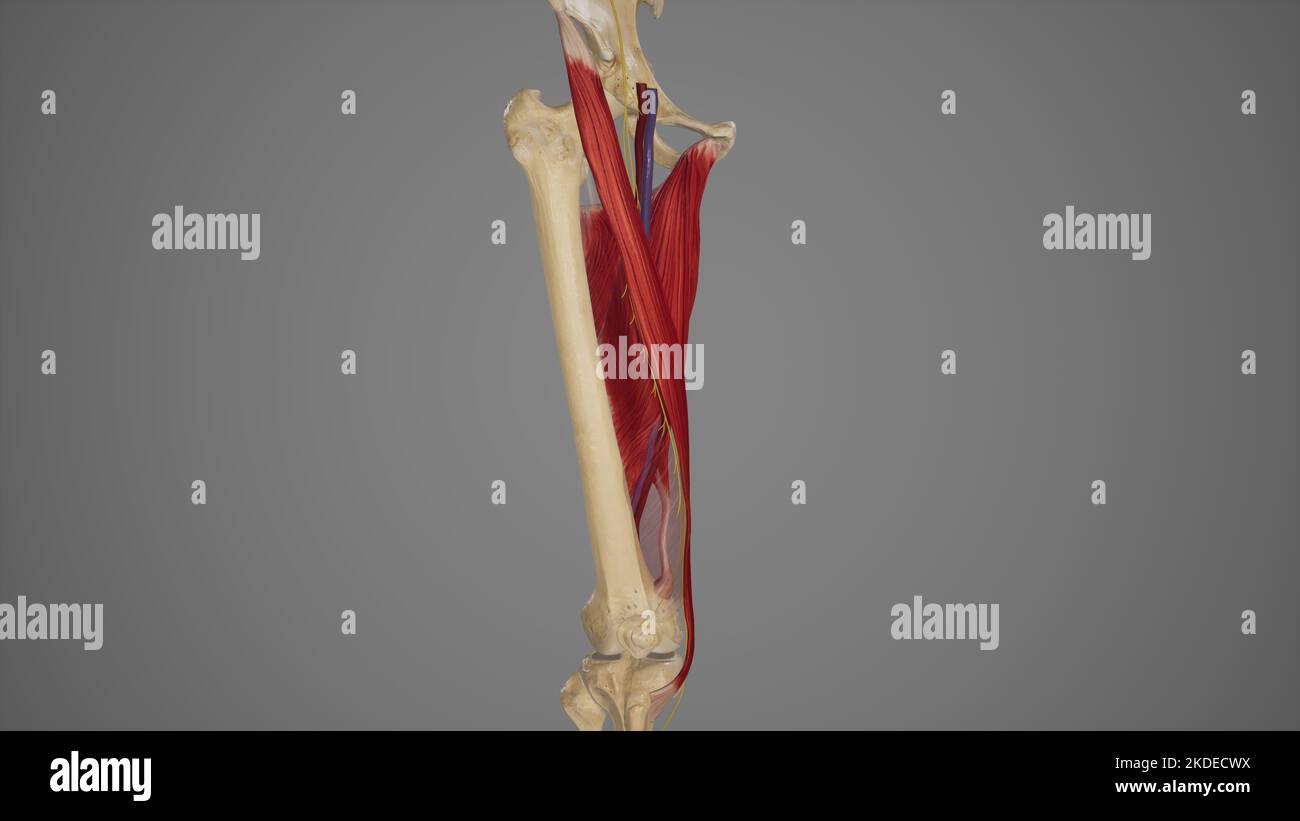 Anatomical Illustration of Adductor Canal Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-adductor-canal-image490198294.html
Anatomical Illustration of Adductor Canal Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-adductor-canal-image490198294.htmlRF2KDECWX–Anatomical Illustration of Adductor Canal
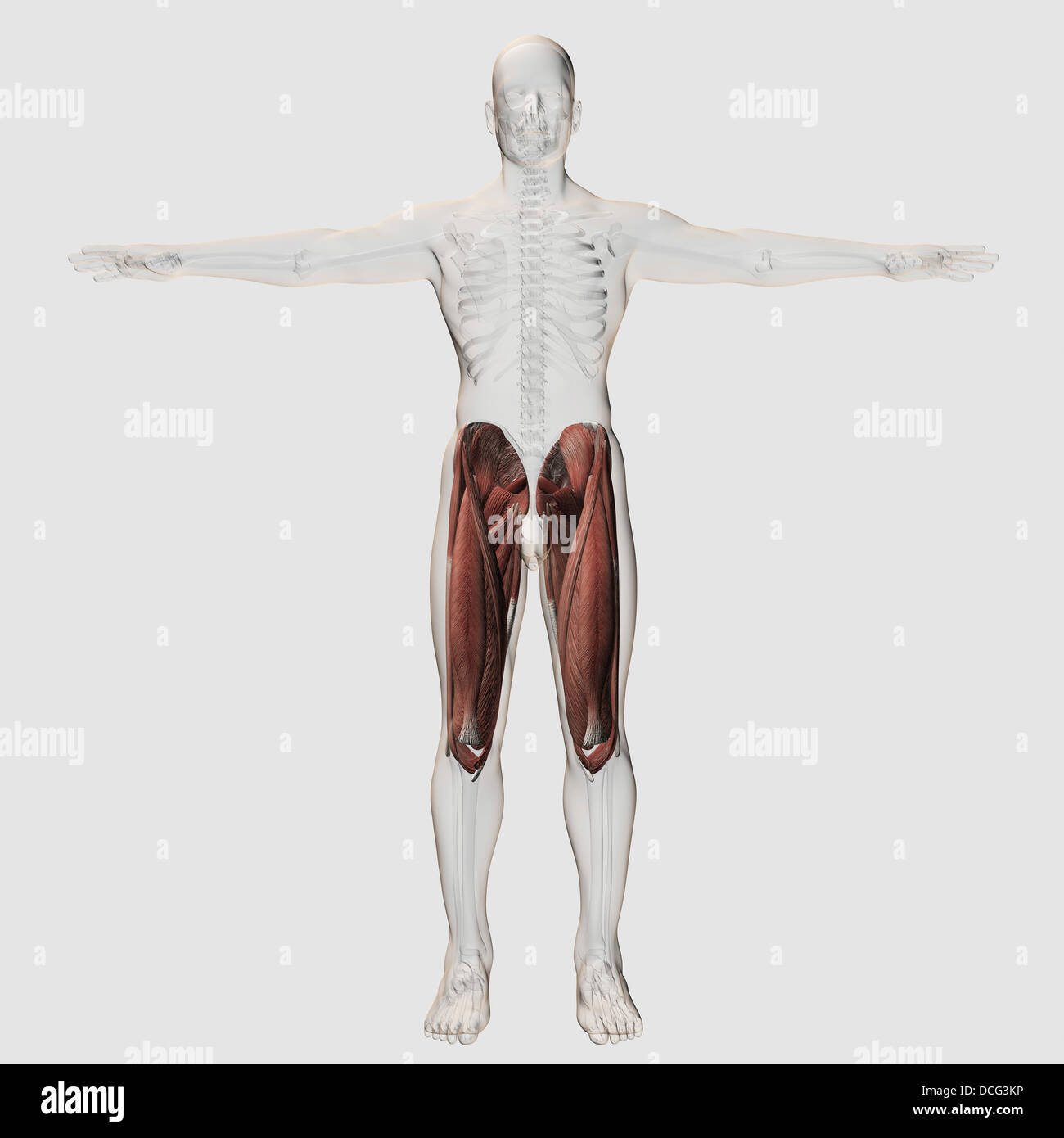 Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-male-muscle-anatomy-of-the-human-legs-anterior-view-59361114.html
Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-male-muscle-anatomy-of-the-human-legs-anterior-view-59361114.htmlRFDCG3KP–Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view.
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 406 THE MUSCULAK SYSTEM. the middle third of the thigh, the roof of Hunter's adductor canal. The ilio-psoas, passing into the thigh beneath the inguinal liga- ment, assists along with the pectineus and adductor muscles in forming the floor of the femoral triangle. M. Sartorius.—The sartor- ius, a long strap-like muscle, arises from the superior anterior spine of the ilium and half of the notch below it (Fig. 360). It passes distally in the thigh to the medial side of the knee, where it is inserted by aponeurotic fibres into the medial surface of th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-406-the-musculak-system-the-middle-third-of-the-thigh-the-roof-of-hunters-adductor-canal-the-ilio-psoas-passing-into-the-thigh-beneath-the-inguinal-liga-ment-assists-along-with-the-pectineus-and-adductor-muscles-in-forming-the-floor-of-the-femoral-triangle-m-sartoriusthe-sartor-ius-a-long-strap-like-muscle-arises-from-the-superior-anterior-spine-of-the-ilium-and-half-of-the-notch-below-it-fig-360-it-passes-distally-in-the-thigh-to-the-medial-side-of-the-knee-where-it-is-inserted-by-aponeurotic-fibres-into-the-medial-surface-of-th-image231880958.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 406 THE MUSCULAK SYSTEM. the middle third of the thigh, the roof of Hunter's adductor canal. The ilio-psoas, passing into the thigh beneath the inguinal liga- ment, assists along with the pectineus and adductor muscles in forming the floor of the femoral triangle. M. Sartorius.—The sartor- ius, a long strap-like muscle, arises from the superior anterior spine of the ilium and half of the notch below it (Fig. 360). It passes distally in the thigh to the medial side of the knee, where it is inserted by aponeurotic fibres into the medial surface of th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-406-the-musculak-system-the-middle-third-of-the-thigh-the-roof-of-hunters-adductor-canal-the-ilio-psoas-passing-into-the-thigh-beneath-the-inguinal-liga-ment-assists-along-with-the-pectineus-and-adductor-muscles-in-forming-the-floor-of-the-femoral-triangle-m-sartoriusthe-sartor-ius-a-long-strap-like-muscle-arises-from-the-superior-anterior-spine-of-the-ilium-and-half-of-the-notch-below-it-fig-360-it-passes-distally-in-the-thigh-to-the-medial-side-of-the-knee-where-it-is-inserted-by-aponeurotic-fibres-into-the-medial-surface-of-th-image231880958.htmlRMRD72EP–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 406 THE MUSCULAK SYSTEM. the middle third of the thigh, the roof of Hunter's adductor canal. The ilio-psoas, passing into the thigh beneath the inguinal liga- ment, assists along with the pectineus and adductor muscles in forming the floor of the femoral triangle. M. Sartorius.—The sartor- ius, a long strap-like muscle, arises from the superior anterior spine of the ilium and half of the notch below it (Fig. 360). It passes distally in the thigh to the medial side of the knee, where it is inserted by aponeurotic fibres into the medial surface of th
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. terior surface of the proximal part^of the Left Femur. Vastus mediai Saphenous nerve^ Femoral vessel: Sartorius Adductor lokgus Adductor magnds Gracilis. Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Femur Femoris (short head) SEMIMEMBRANOSUS' Biceps Femoris (long head) Semitendinostj Sciatic nerve Fig. 362.—Transverse Section of the Thigh (Hunter's Adductor Canal). M. Vastus Lateralis.—The vastus lateralis has an origin, partly fleshy, partly membranous, from (1) the capsule of the hip-joint) (2) the tubercle of the femur, (3) a concave surfa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-terior-surface-of-the-proximal-partof-the-left-femur-vastus-mediai-saphenous-nerve-femoral-vessel-sartorius-adductor-lokgus-adductor-magnds-gracilis-rectus-femoris-vastus-lateralis-vastus-intermedius-femur-femoris-short-head-semimembranosus-biceps-femoris-long-head-semitendinostj-sciatic-nerve-fig-362transverse-section-of-the-thigh-hunters-adductor-canal-m-vastus-lateralisthe-vastus-lateralis-has-an-origin-partly-fleshy-partly-membranous-from-1-the-capsule-of-the-hip-joint-2-the-tubercle-of-the-femur-3-a-concave-surfa-image216340965.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. terior surface of the proximal part^of the Left Femur. Vastus mediai Saphenous nerve^ Femoral vessel: Sartorius Adductor lokgus Adductor magnds Gracilis. Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Femur Femoris (short head) SEMIMEMBRANOSUS' Biceps Femoris (long head) Semitendinostj Sciatic nerve Fig. 362.—Transverse Section of the Thigh (Hunter's Adductor Canal). M. Vastus Lateralis.—The vastus lateralis has an origin, partly fleshy, partly membranous, from (1) the capsule of the hip-joint) (2) the tubercle of the femur, (3) a concave surfa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-terior-surface-of-the-proximal-partof-the-left-femur-vastus-mediai-saphenous-nerve-femoral-vessel-sartorius-adductor-lokgus-adductor-magnds-gracilis-rectus-femoris-vastus-lateralis-vastus-intermedius-femur-femoris-short-head-semimembranosus-biceps-femoris-long-head-semitendinostj-sciatic-nerve-fig-362transverse-section-of-the-thigh-hunters-adductor-canal-m-vastus-lateralisthe-vastus-lateralis-has-an-origin-partly-fleshy-partly-membranous-from-1-the-capsule-of-the-hip-joint-2-the-tubercle-of-the-femur-3-a-concave-surfa-image216340965.htmlRMPFY531–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. terior surface of the proximal part^of the Left Femur. Vastus mediai Saphenous nerve^ Femoral vessel: Sartorius Adductor lokgus Adductor magnds Gracilis. Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Femur Femoris (short head) SEMIMEMBRANOSUS' Biceps Femoris (long head) Semitendinostj Sciatic nerve Fig. 362.—Transverse Section of the Thigh (Hunter's Adductor Canal). M. Vastus Lateralis.—The vastus lateralis has an origin, partly fleshy, partly membranous, from (1) the capsule of the hip-joint) (2) the tubercle of the femur, (3) a concave surfa
 Adductor West - Work PAC 2 - responsible for water supply in the region Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-adductor-west-work-pac-2-responsible-for-water-supply-in-the-region-101303269.html
Adductor West - Work PAC 2 - responsible for water supply in the region Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-adductor-west-work-pac-2-responsible-for-water-supply-in-the-region-101303269.htmlRMFTPN9W–Adductor West - Work PAC 2 - responsible for water supply in the region
 Medical Accurate Illustration of Adductor Brevis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-accurate-illustration-of-adductor-brevis-image490198500.html
Medical Accurate Illustration of Adductor Brevis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-accurate-illustration-of-adductor-brevis-image490198500.htmlRF2KDED58–Medical Accurate Illustration of Adductor Brevis
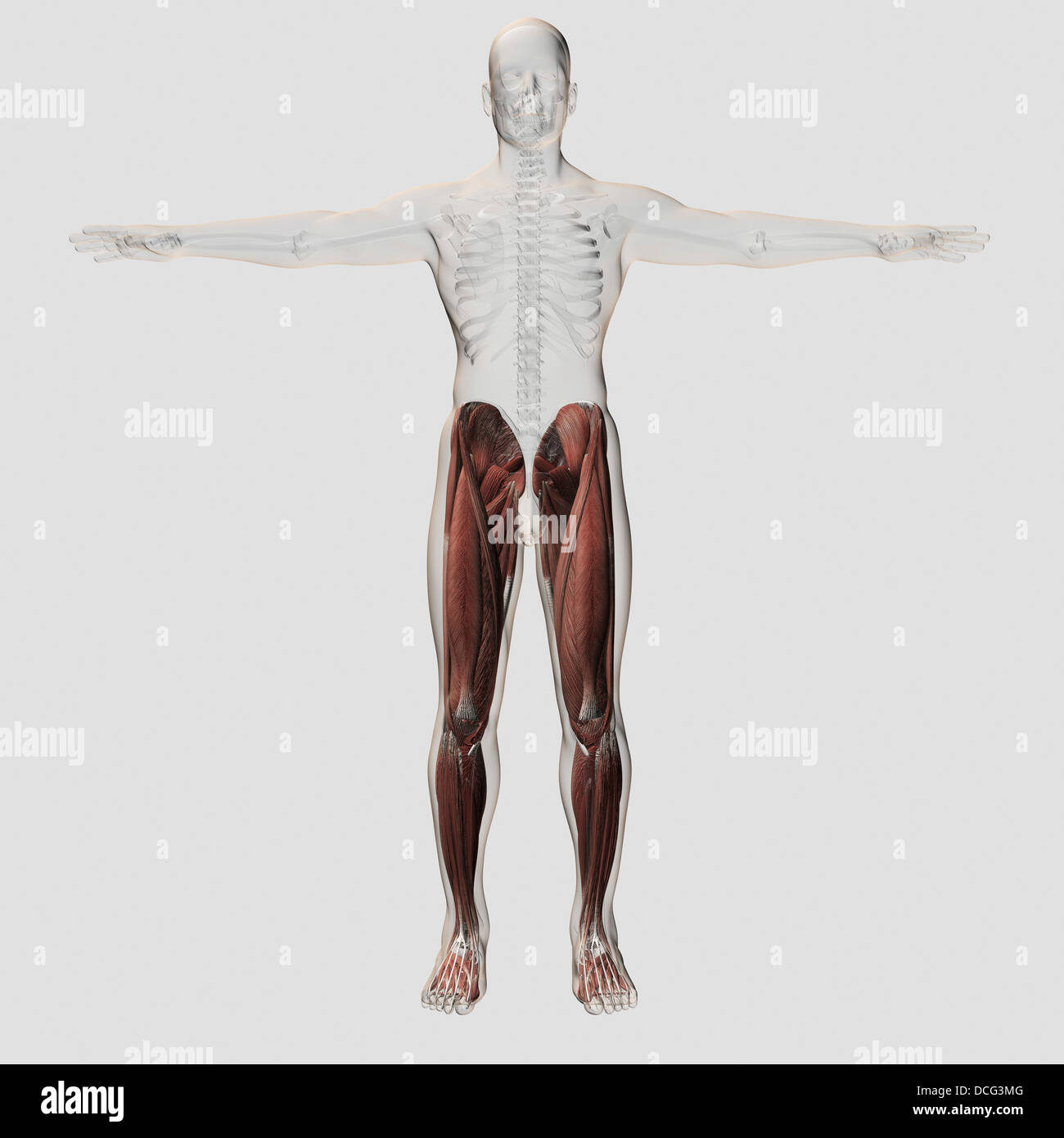 Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-male-muscle-anatomy-of-the-human-legs-anterior-view-59361136.html
Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-male-muscle-anatomy-of-the-human-legs-anterior-view-59361136.htmlRFDCG3MG–Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view.
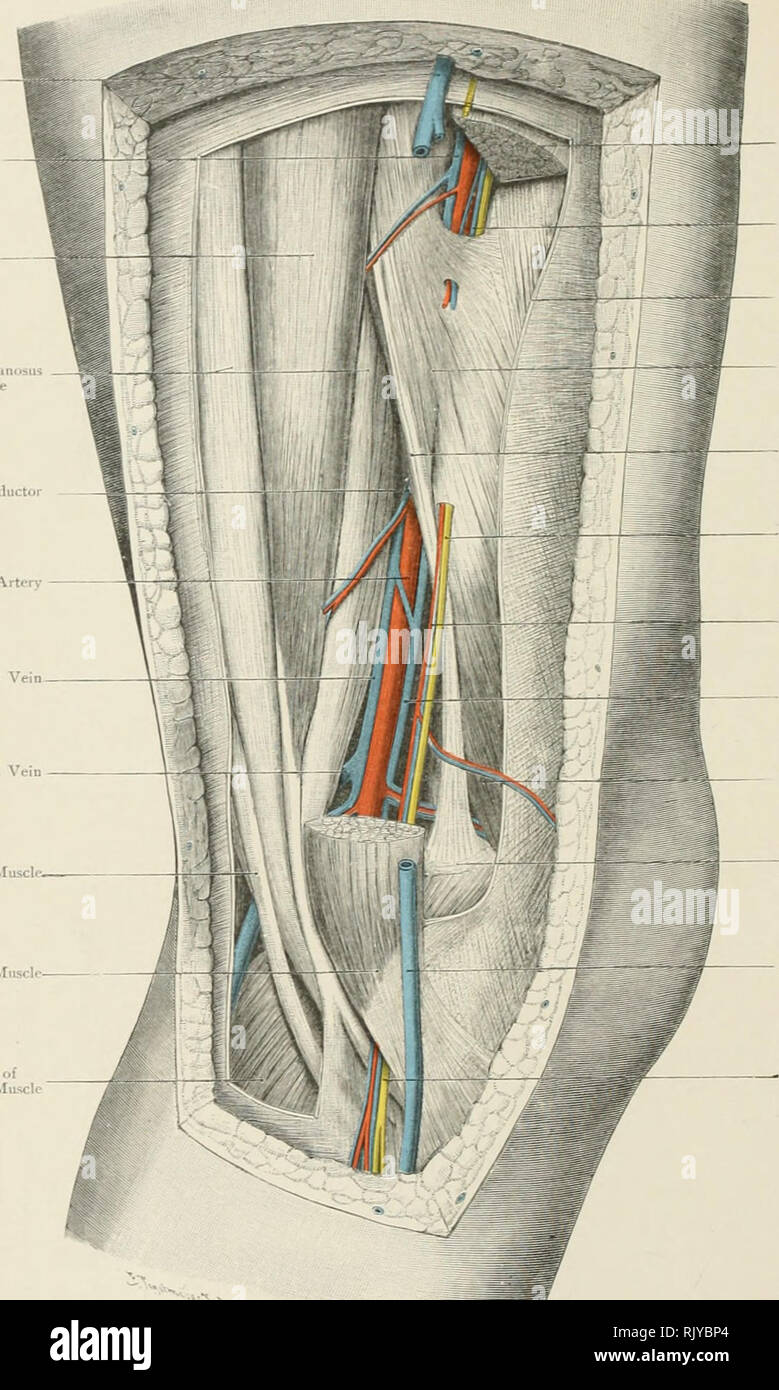 . Atlas of applied (topographical) human anatomy for students and practitioners. Anatomy. I^ong Saplienous F(-iTH»r;il Vein f-.rarilK ^r.lS.â Ie Seiiiiinembranosu^ Muscle Opening in Adductor Ma^us Poplitt-al Artery Popliteal Vein Short Saphenous Vein Semitendinosus Muscle. Sartorius fust:l loner Head of Gastrocnemius Muscl. I^'ppcr pnrt of Sartorius Muscle Vein accompanyintr the Superficial Femoral Vein Fascia Lata IIl'xter*s (Adductor) Canal Tendon of Adductor Magnus Saphenous Xervc Anastomotica ^fagna Arter>' Vein accompanying the Popliteal Vein Intfrnal Vastus Muscle Adductor Tubercle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-of-applied-topographical-human-anatomy-for-students-and-practitioners-anatomy-iong-saplienous-f-ithril-vein-f-rarilk-rls-ie-seiiiiinembranosu-muscle-opening-in-adductor-maus-poplitt-al-artery-popliteal-vein-short-saphenous-vein-semitendinosus-muscle-sartorius-fustl-loner-head-of-gastrocnemius-muscl-ippcr-pnrt-of-sartorius-muscle-vein-accompanyintr-the-superficial-femoral-vein-fascia-lata-iilxters-adductor-canal-tendon-of-adductor-magnus-saphenous-xervc-anastomotica-fagna-artergt-vein-accompanying-the-popliteal-vein-intfrnal-vastus-muscle-adductor-tubercle-image235400540.html
. Atlas of applied (topographical) human anatomy for students and practitioners. Anatomy. I^ong Saplienous F(-iTH»r;il Vein f-.rarilK ^r.lS.â Ie Seiiiiinembranosu^ Muscle Opening in Adductor Ma^us Poplitt-al Artery Popliteal Vein Short Saphenous Vein Semitendinosus Muscle. Sartorius fust:l loner Head of Gastrocnemius Muscl. I^'ppcr pnrt of Sartorius Muscle Vein accompanyintr the Superficial Femoral Vein Fascia Lata IIl'xter*s (Adductor) Canal Tendon of Adductor Magnus Saphenous Xervc Anastomotica ^fagna Arter>' Vein accompanying the Popliteal Vein Intfrnal Vastus Muscle Adductor Tubercle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-of-applied-topographical-human-anatomy-for-students-and-practitioners-anatomy-iong-saplienous-f-ithril-vein-f-rarilk-rls-ie-seiiiiinembranosu-muscle-opening-in-adductor-maus-poplitt-al-artery-popliteal-vein-short-saphenous-vein-semitendinosus-muscle-sartorius-fustl-loner-head-of-gastrocnemius-muscl-ippcr-pnrt-of-sartorius-muscle-vein-accompanyintr-the-superficial-femoral-vein-fascia-lata-iilxters-adductor-canal-tendon-of-adductor-magnus-saphenous-xervc-anastomotica-fagna-artergt-vein-accompanying-the-popliteal-vein-intfrnal-vastus-muscle-adductor-tubercle-image235400540.htmlRMRJYBP4–. Atlas of applied (topographical) human anatomy for students and practitioners. Anatomy. I^ong Saplienous F(-iTH»r;il Vein f-.rarilK ^r.lS.â Ie Seiiiiinembranosu^ Muscle Opening in Adductor Ma^us Poplitt-al Artery Popliteal Vein Short Saphenous Vein Semitendinosus Muscle. Sartorius fust:l loner Head of Gastrocnemius Muscl. I^'ppcr pnrt of Sartorius Muscle Vein accompanyintr the Superficial Femoral Vein Fascia Lata IIl'xter*s (Adductor) Canal Tendon of Adductor Magnus Saphenous Xervc Anastomotica ^fagna Arter>' Vein accompanying the Popliteal Vein Intfrnal Vastus Muscle Adductor Tubercle
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 406 THE MUSCULAK SYSTEM. the middle third of the thigh, the roof of Hunter's adductor canal. The ilio-psoas, passing into the thigh beneath the inguinal liga- ment, assists along with the pectineus and adductor muscles in forming the floor of the femoral triangle. M. Sartorius.—The sartor- ius, a long strap-like muscle, arises from the superior anterior spine of the ilium and half of the notch below it (Fig. 360). It passes distally in the thigh to the medial side of the knee, where it is inserted by aponeurotic fibres into the medial surface of th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-406-the-musculak-system-the-middle-third-of-the-thigh-the-roof-of-hunters-adductor-canal-the-ilio-psoas-passing-into-the-thigh-beneath-the-inguinal-liga-ment-assists-along-with-the-pectineus-and-adductor-muscles-in-forming-the-floor-of-the-femoral-triangle-m-sartoriusthe-sartor-ius-a-long-strap-like-muscle-arises-from-the-superior-anterior-spine-of-the-ilium-and-half-of-the-notch-below-it-fig-360-it-passes-distally-in-the-thigh-to-the-medial-side-of-the-knee-where-it-is-inserted-by-aponeurotic-fibres-into-the-medial-surface-of-th-image216340981.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 406 THE MUSCULAK SYSTEM. the middle third of the thigh, the roof of Hunter's adductor canal. The ilio-psoas, passing into the thigh beneath the inguinal liga- ment, assists along with the pectineus and adductor muscles in forming the floor of the femoral triangle. M. Sartorius.—The sartor- ius, a long strap-like muscle, arises from the superior anterior spine of the ilium and half of the notch below it (Fig. 360). It passes distally in the thigh to the medial side of the knee, where it is inserted by aponeurotic fibres into the medial surface of th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-406-the-musculak-system-the-middle-third-of-the-thigh-the-roof-of-hunters-adductor-canal-the-ilio-psoas-passing-into-the-thigh-beneath-the-inguinal-liga-ment-assists-along-with-the-pectineus-and-adductor-muscles-in-forming-the-floor-of-the-femoral-triangle-m-sartoriusthe-sartor-ius-a-long-strap-like-muscle-arises-from-the-superior-anterior-spine-of-the-ilium-and-half-of-the-notch-below-it-fig-360-it-passes-distally-in-the-thigh-to-the-medial-side-of-the-knee-where-it-is-inserted-by-aponeurotic-fibres-into-the-medial-surface-of-th-image216340981.htmlRMPFY53H–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 406 THE MUSCULAK SYSTEM. the middle third of the thigh, the roof of Hunter's adductor canal. The ilio-psoas, passing into the thigh beneath the inguinal liga- ment, assists along with the pectineus and adductor muscles in forming the floor of the femoral triangle. M. Sartorius.—The sartor- ius, a long strap-like muscle, arises from the superior anterior spine of the ilium and half of the notch below it (Fig. 360). It passes distally in the thigh to the medial side of the knee, where it is inserted by aponeurotic fibres into the medial surface of th
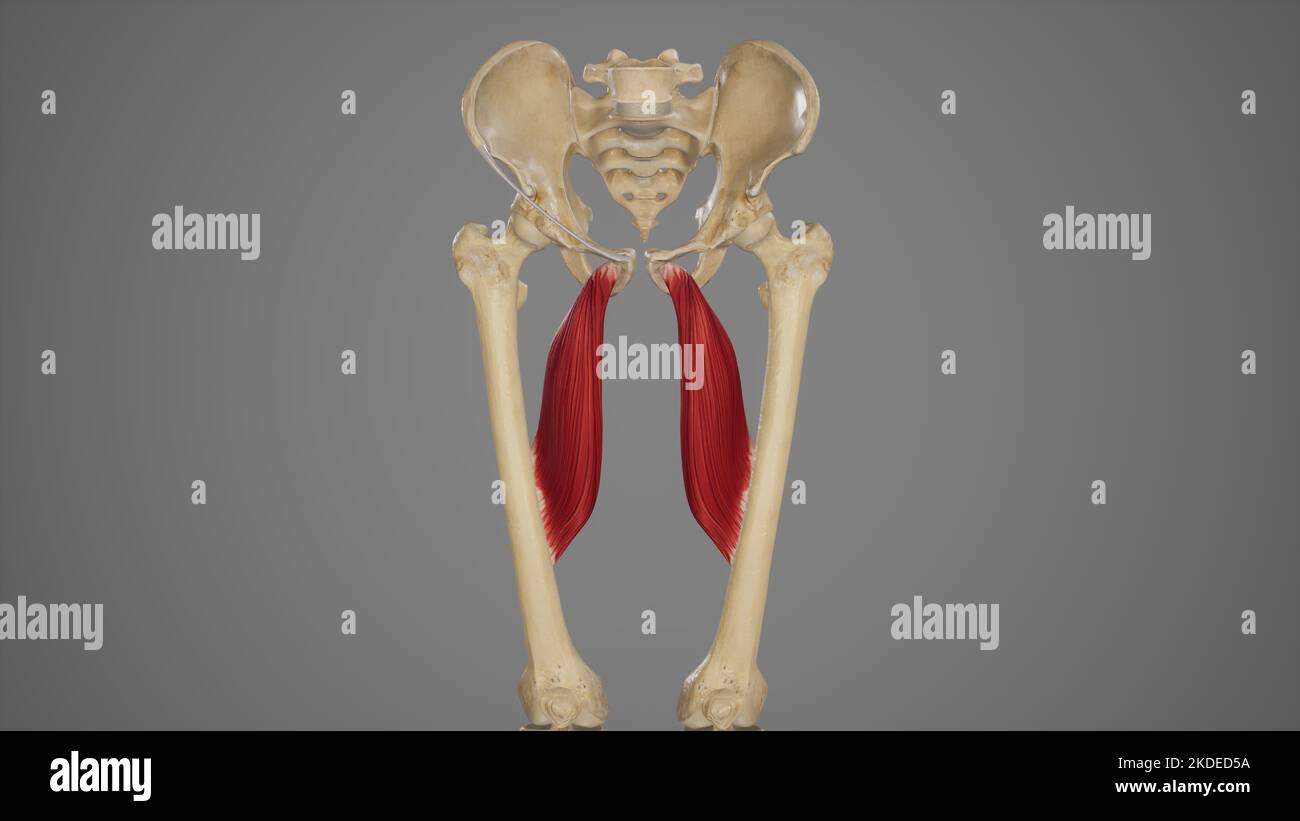 Medical Accurate Illustration of Adductor Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-accurate-illustration-of-adductor-longus-image490198502.html
Medical Accurate Illustration of Adductor Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-accurate-illustration-of-adductor-longus-image490198502.htmlRF2KDED5A–Medical Accurate Illustration of Adductor Longus
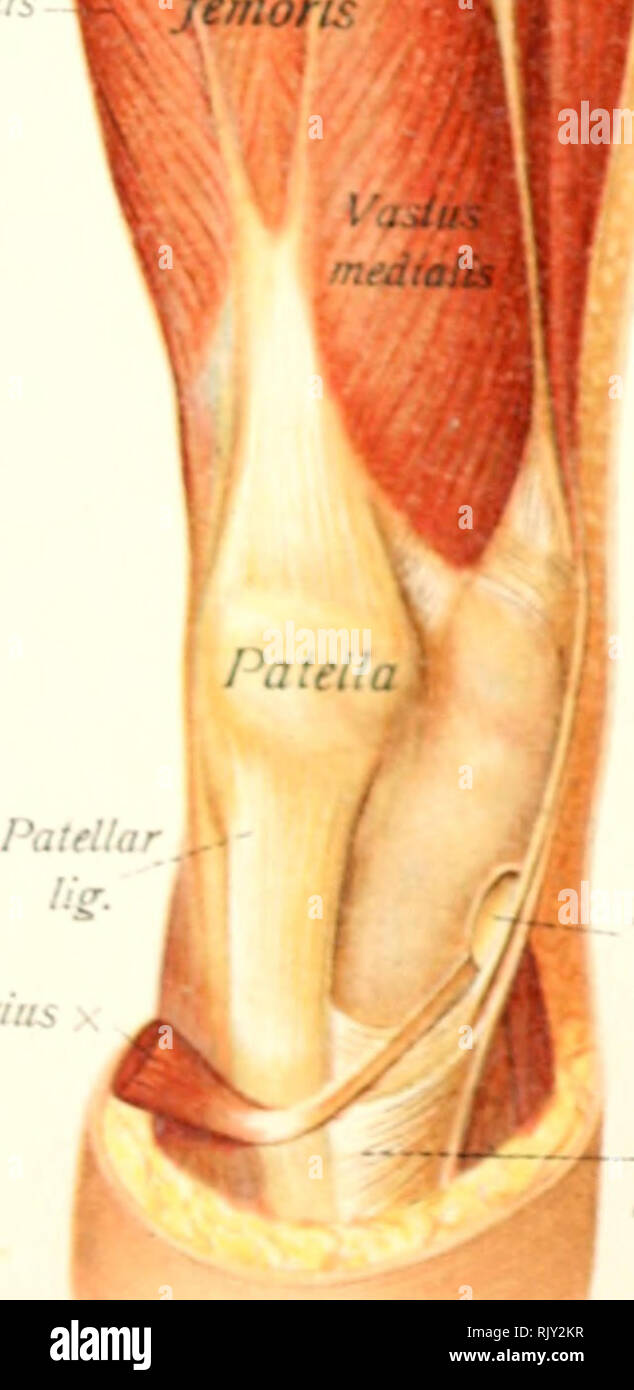 . Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. I end on of sartorius I'rndon of gracilis Tendon of 'nitendinosus QuadrL femoi Sario. nhyseal wface pubis Adductor magnus Adductor canal (^femoral vessHs) Gracilis rius Sartorial bursa -^Pes anserinus Fig. 296. Fio 297.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta, Johannes, 1869-1945; McMurrich, J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939. Philadelphia, Sa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-i-end-on-of-sartorius-irndon-of-gracilis-tendon-of-nitendinosus-quadrl-femoi-sario-nhyseal-wface-pubis-adductor-magnus-adductor-canal-femoral-vesshs-gracilis-rius-sartorial-bursa-pes-anserinus-fig-296-fio-297-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-work-sobotta-johannes-1869-1945-mcmurrich-j-playfair-james-playfair-1859-1939-philadelphia-sa-image235393419.html
. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. I end on of sartorius I'rndon of gracilis Tendon of 'nitendinosus QuadrL femoi Sario. nhyseal wface pubis Adductor magnus Adductor canal (^femoral vessHs) Gracilis rius Sartorial bursa -^Pes anserinus Fig. 296. Fio 297.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta, Johannes, 1869-1945; McMurrich, J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939. Philadelphia, Sa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-i-end-on-of-sartorius-irndon-of-gracilis-tendon-of-nitendinosus-quadrl-femoi-sario-nhyseal-wface-pubis-adductor-magnus-adductor-canal-femoral-vesshs-gracilis-rius-sartorial-bursa-pes-anserinus-fig-296-fio-297-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-work-sobotta-johannes-1869-1945-mcmurrich-j-playfair-james-playfair-1859-1939-philadelphia-sa-image235393419.htmlRMRJY2KR–. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. I end on of sartorius I'rndon of gracilis Tendon of 'nitendinosus QuadrL femoi Sario. nhyseal wface pubis Adductor magnus Adductor canal (^femoral vessHs) Gracilis rius Sartorial bursa -^Pes anserinus Fig. 296. Fio 297.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta, Johannes, 1869-1945; McMurrich, J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939. Philadelphia, Sa
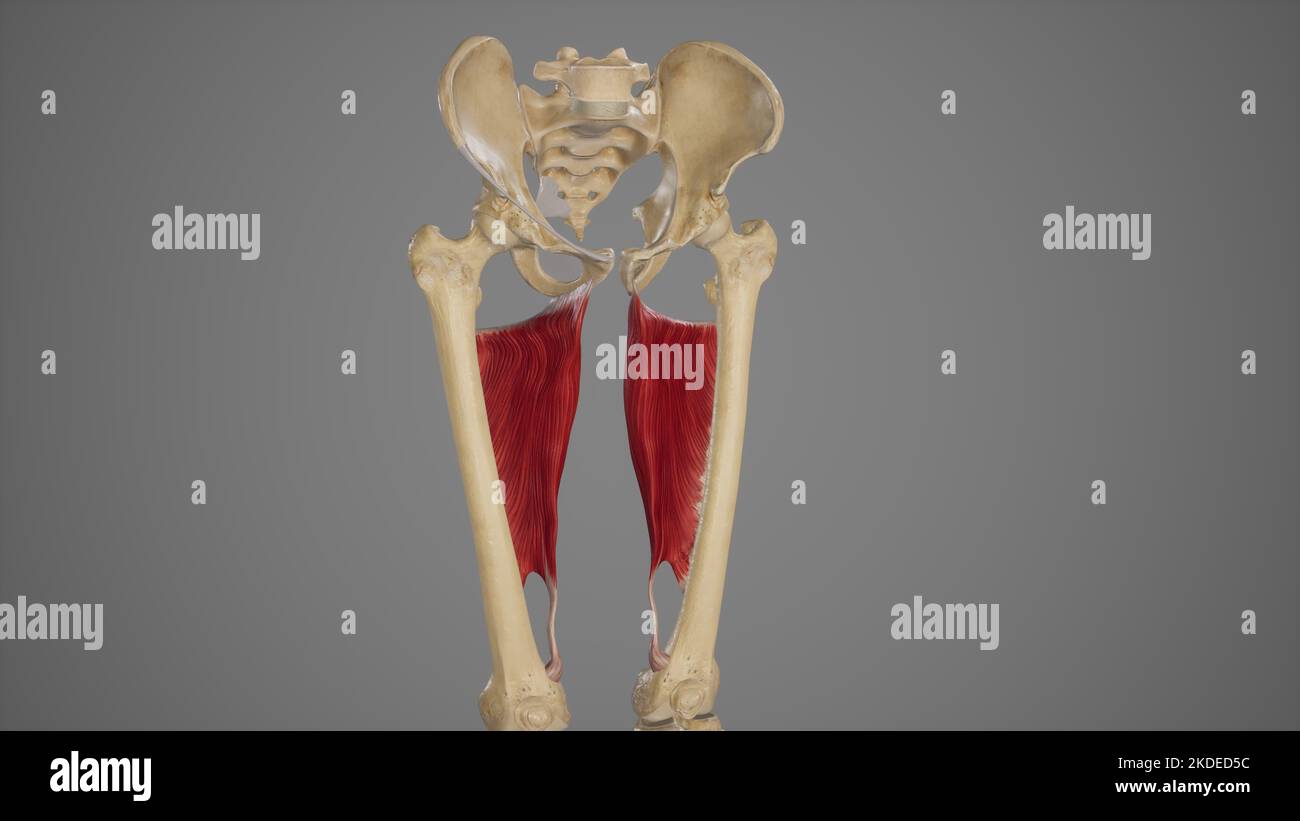 Medical Acurate Illustration of Adductor Magnus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-acurate-illustration-of-adductor-magnus-image490198504.html
Medical Acurate Illustration of Adductor Magnus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-acurate-illustration-of-adductor-magnus-image490198504.htmlRF2KDED5C–Medical Acurate Illustration of Adductor Magnus
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. terior surface of the proximal part^of the Left Femur. Vastus mediai Saphenous nerve^ Femoral vessel: Sartorius Adductor lokgus Adductor magnds Gracilis. Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Femur Femoris (short head) SEMIMEMBRANOSUS' Biceps Femoris (long head) Semitendinostj Sciatic nerve Fig. 362.—Transverse Section of the Thigh (Hunter's Adductor Canal). M. Vastus Lateralis.—The vastus lateralis has an origin, partly fleshy, partly membranous, from (1) the capsule of the hip-joint) (2) the tubercle of the femur, (3) a concave surfa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-terior-surface-of-the-proximal-partof-the-left-femur-vastus-mediai-saphenous-nerve-femoral-vessel-sartorius-adductor-lokgus-adductor-magnds-gracilis-rectus-femoris-vastus-lateralis-vastus-intermedius-femur-femoris-short-head-semimembranosus-biceps-femoris-long-head-semitendinostj-sciatic-nerve-fig-362transverse-section-of-the-thigh-hunters-adductor-canal-m-vastus-lateralisthe-vastus-lateralis-has-an-origin-partly-fleshy-partly-membranous-from-1-the-capsule-of-the-hip-joint-2-the-tubercle-of-the-femur-3-a-concave-surfa-image231880935.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. terior surface of the proximal part^of the Left Femur. Vastus mediai Saphenous nerve^ Femoral vessel: Sartorius Adductor lokgus Adductor magnds Gracilis. Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Femur Femoris (short head) SEMIMEMBRANOSUS' Biceps Femoris (long head) Semitendinostj Sciatic nerve Fig. 362.—Transverse Section of the Thigh (Hunter's Adductor Canal). M. Vastus Lateralis.—The vastus lateralis has an origin, partly fleshy, partly membranous, from (1) the capsule of the hip-joint) (2) the tubercle of the femur, (3) a concave surfa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-terior-surface-of-the-proximal-partof-the-left-femur-vastus-mediai-saphenous-nerve-femoral-vessel-sartorius-adductor-lokgus-adductor-magnds-gracilis-rectus-femoris-vastus-lateralis-vastus-intermedius-femur-femoris-short-head-semimembranosus-biceps-femoris-long-head-semitendinostj-sciatic-nerve-fig-362transverse-section-of-the-thigh-hunters-adductor-canal-m-vastus-lateralisthe-vastus-lateralis-has-an-origin-partly-fleshy-partly-membranous-from-1-the-capsule-of-the-hip-joint-2-the-tubercle-of-the-femur-3-a-concave-surfa-image231880935.htmlRMRD72DY–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. terior surface of the proximal part^of the Left Femur. Vastus mediai Saphenous nerve^ Femoral vessel: Sartorius Adductor lokgus Adductor magnds Gracilis. Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Femur Femoris (short head) SEMIMEMBRANOSUS' Biceps Femoris (long head) Semitendinostj Sciatic nerve Fig. 362.—Transverse Section of the Thigh (Hunter's Adductor Canal). M. Vastus Lateralis.—The vastus lateralis has an origin, partly fleshy, partly membranous, from (1) the capsule of the hip-joint) (2) the tubercle of the femur, (3) a concave surfa
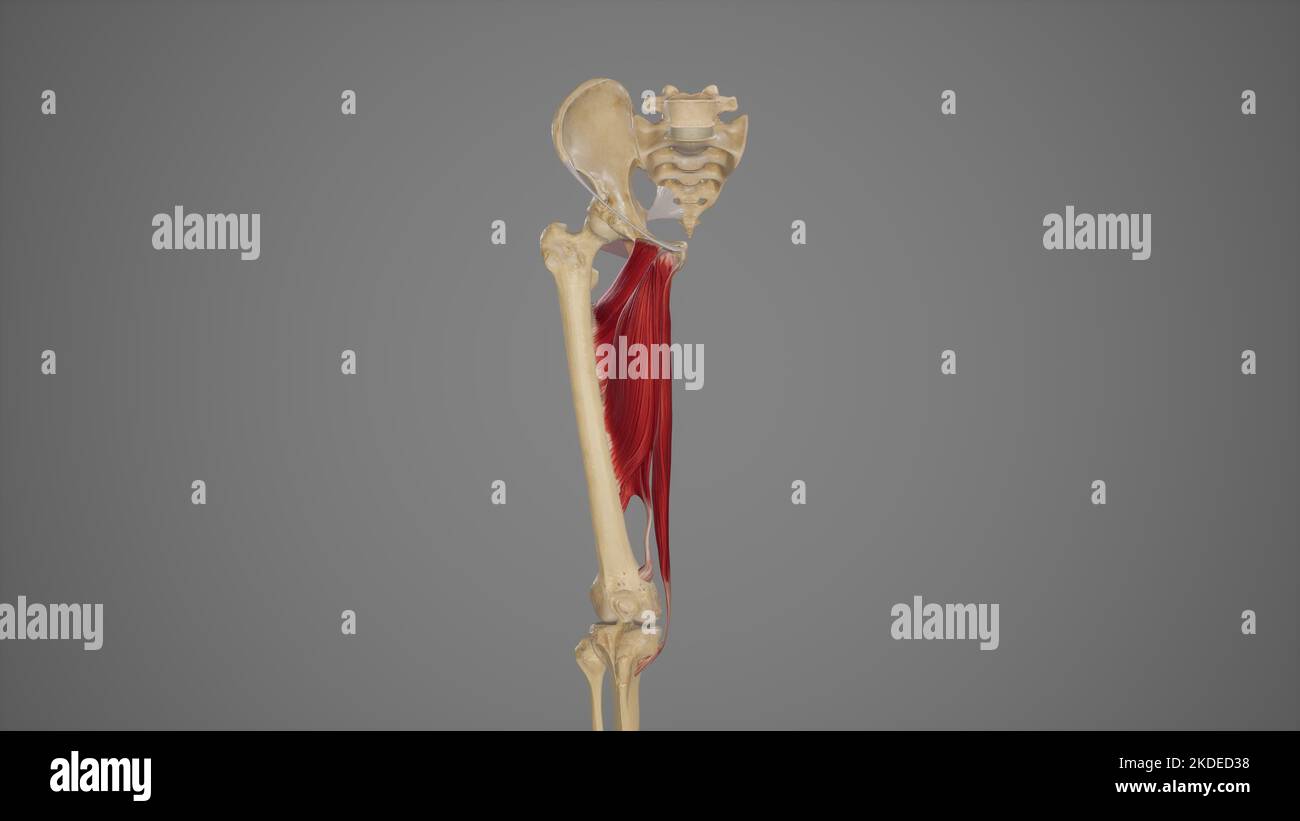 Medical Illustration of Hip Adductor Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-hip-adductor-muscles-image490198444.html
Medical Illustration of Hip Adductor Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-hip-adductor-muscles-image490198444.htmlRF2KDED38–Medical Illustration of Hip Adductor Muscles
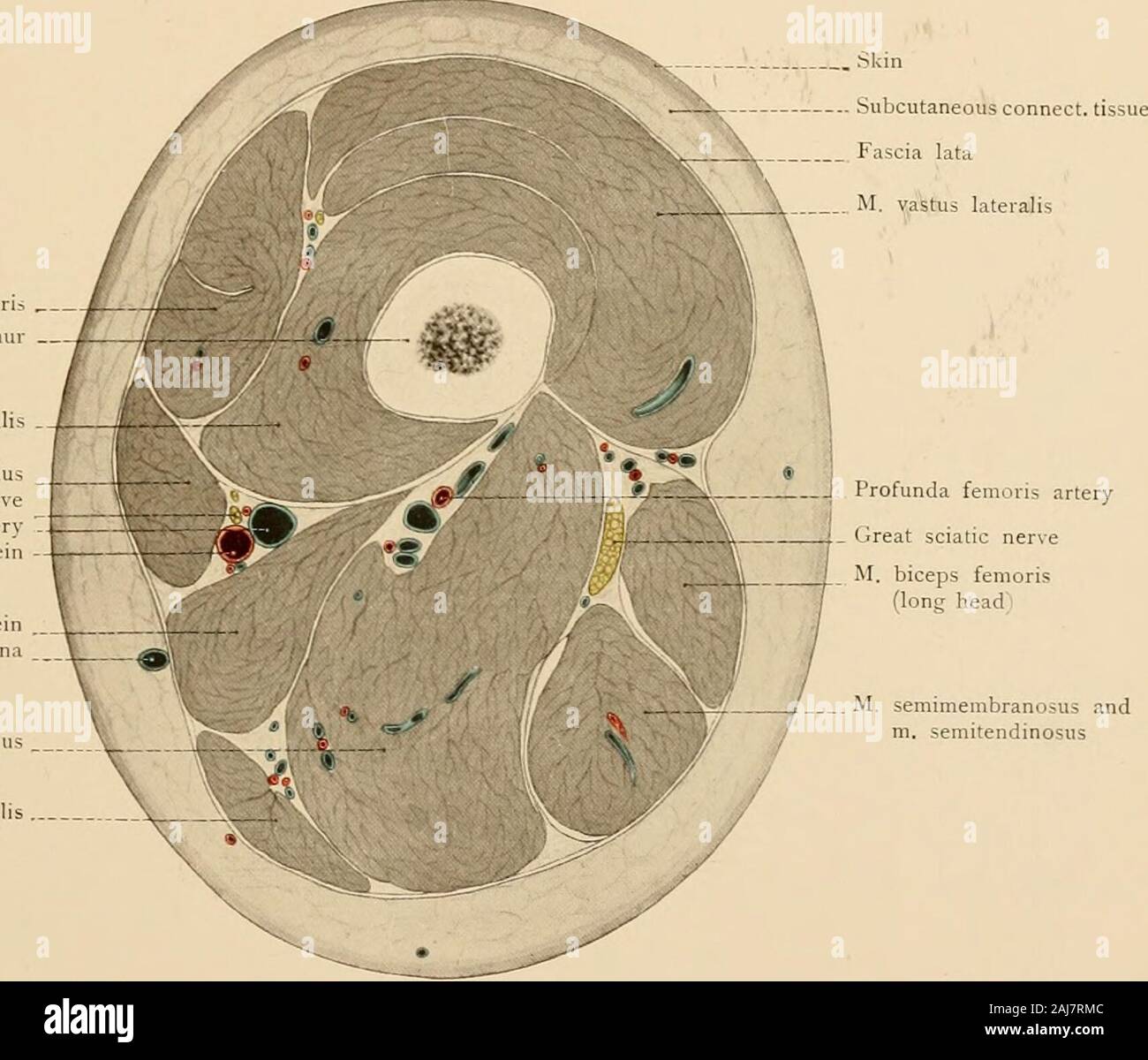 Atlas and text-book of topographic and applied anatomy . tedabove this tendon. At the junction of the middle and lower thirds of the femur an aponeurosis isstretched across from the tendon of the adductor magnus to the vastus internus; this aponeurosisforms the anterior and internal wall (Fig. 80) of a canal ending at the hiatus adductorius, thecanalis adductorius or canal of Hunter. The posterior wall of this canal is formed by the asso-ciated tendons of the adductor longus and magnus muscles and it is bounded externally by thevastus internus and the femur. This canal gives passage to the fem Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-topographic-and-applied-anatomy-tedabove-this-tendon-at-the-junction-of-the-middle-and-lower-thirds-of-the-femur-an-aponeurosis-isstretched-across-from-the-tendon-of-the-adductor-magnus-to-the-vastus-internus-this-aponeurosisforms-the-anterior-and-internal-wall-fig-80-of-a-canal-ending-at-the-hiatus-adductorius-thecanalis-adductorius-or-canal-of-hunter-the-posterior-wall-of-this-canal-is-formed-by-the-asso-ciated-tendons-of-the-adductor-longus-and-magnus-muscles-and-it-is-bounded-externally-by-thevastus-internus-and-the-femur-this-canal-gives-passage-to-the-fem-image338233068.html
Atlas and text-book of topographic and applied anatomy . tedabove this tendon. At the junction of the middle and lower thirds of the femur an aponeurosis isstretched across from the tendon of the adductor magnus to the vastus internus; this aponeurosisforms the anterior and internal wall (Fig. 80) of a canal ending at the hiatus adductorius, thecanalis adductorius or canal of Hunter. The posterior wall of this canal is formed by the asso-ciated tendons of the adductor longus and magnus muscles and it is bounded externally by thevastus internus and the femur. This canal gives passage to the fem Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-topographic-and-applied-anatomy-tedabove-this-tendon-at-the-junction-of-the-middle-and-lower-thirds-of-the-femur-an-aponeurosis-isstretched-across-from-the-tendon-of-the-adductor-magnus-to-the-vastus-internus-this-aponeurosisforms-the-anterior-and-internal-wall-fig-80-of-a-canal-ending-at-the-hiatus-adductorius-thecanalis-adductorius-or-canal-of-hunter-the-posterior-wall-of-this-canal-is-formed-by-the-asso-ciated-tendons-of-the-adductor-longus-and-magnus-muscles-and-it-is-bounded-externally-by-thevastus-internus-and-the-femur-this-canal-gives-passage-to-the-fem-image338233068.htmlRM2AJ7RMC–Atlas and text-book of topographic and applied anatomy . tedabove this tendon. At the junction of the middle and lower thirds of the femur an aponeurosis isstretched across from the tendon of the adductor magnus to the vastus internus; this aponeurosisforms the anterior and internal wall (Fig. 80) of a canal ending at the hiatus adductorius, thecanalis adductorius or canal of Hunter. The posterior wall of this canal is formed by the asso-ciated tendons of the adductor longus and magnus muscles and it is bounded externally by thevastus internus and the femur. This canal gives passage to the fem
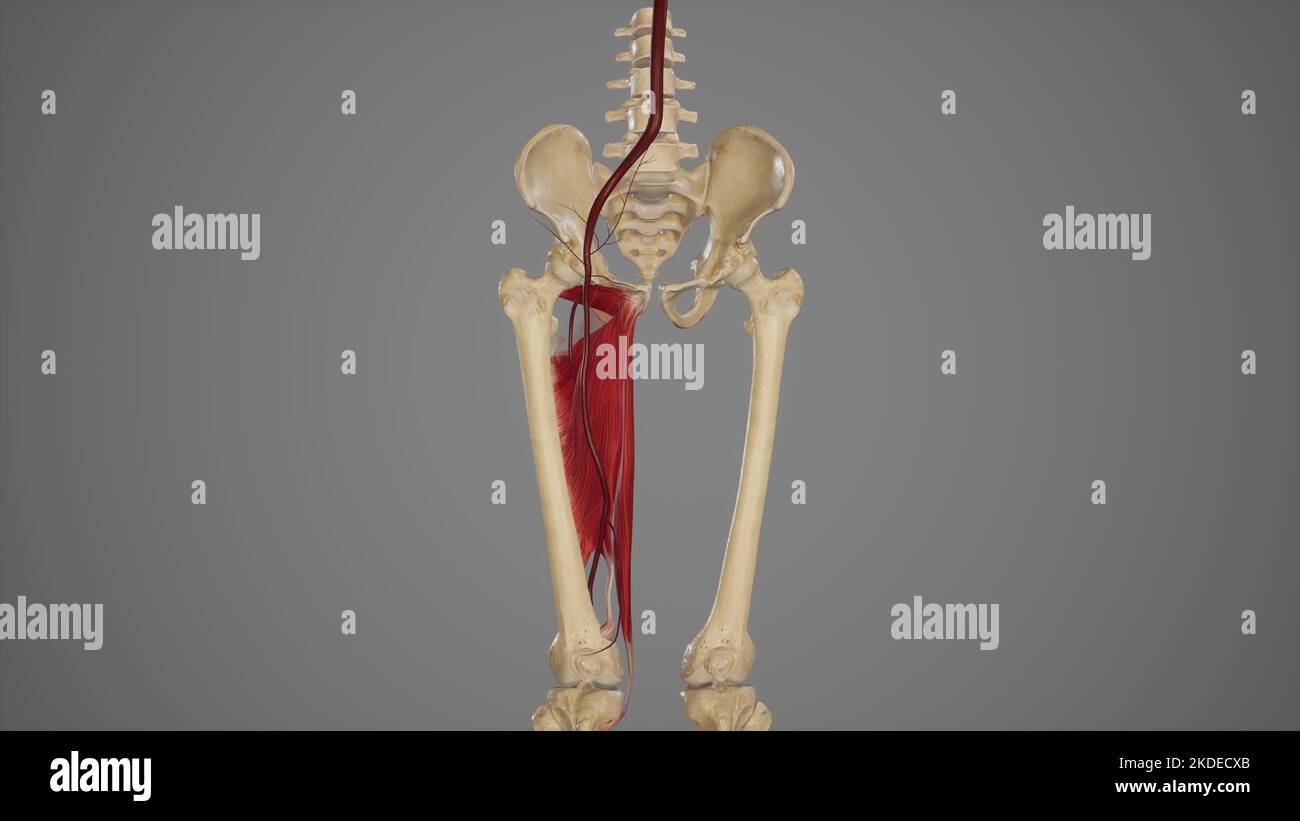 Anatomical Illustration of Femoral Artery Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-femoral-artery-image490198307.html
Anatomical Illustration of Femoral Artery Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-femoral-artery-image490198307.htmlRF2KDECXB–Anatomical Illustration of Femoral Artery
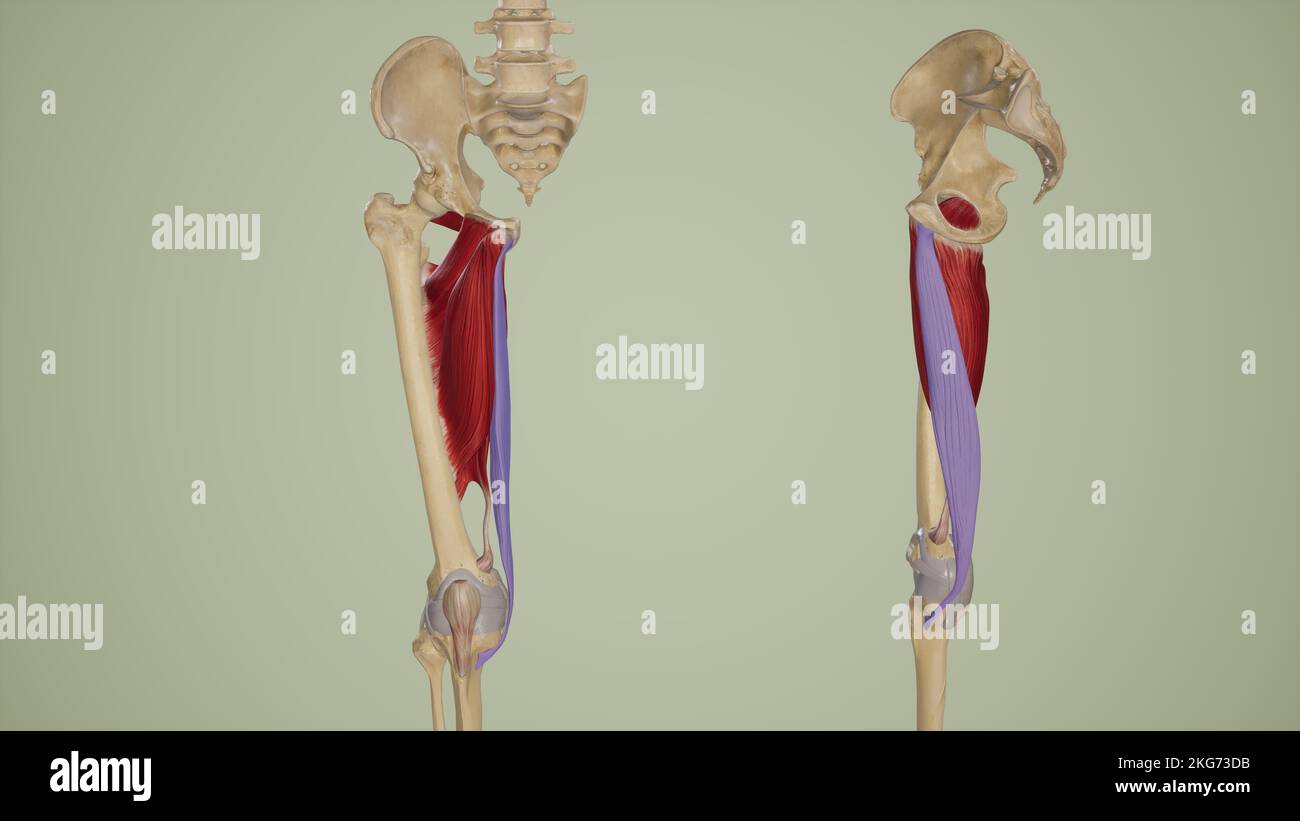 Gracilis Anterior and Lateral View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gracilis-anterior-and-lateral-view-image491881191.html
Gracilis Anterior and Lateral View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gracilis-anterior-and-lateral-view-image491881191.htmlRF2KG73DB–Gracilis Anterior and Lateral View
 Annals of the South African MuseumAnnale van die Suid-Afrikaanse Museum . muscle inserts into the medial groove (Figs 10, 17). The surangular (Figs 9-12, 17) lies posteromedially to the dentary, postero-laterally to the coronoid, dorsally to the prearticular and anteriorly to thearticular. Laterally it forms the posterior section of the mandibular shelf(Fig. 11) and dorsally it bears a ridge extending between the coronoid and thearticular processes. Its anterior extremity underlies the coronoid process whilein addition to covering the Meckelian canal up to the adductor fossa, theposterodorsal Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/annals-of-the-south-african-museumannale-van-die-suid-afrikaanse-museum-muscle-inserts-into-the-medial-groove-figs-10-17-the-surangular-figs-9-12-17-lies-posteromedially-to-the-dentary-postero-laterally-to-the-coronoid-dorsally-to-the-prearticular-and-anteriorly-to-thearticular-laterally-it-forms-the-posterior-section-of-the-mandibular-shelffig-11-and-dorsally-it-bears-a-ridge-extending-between-the-coronoid-and-thearticular-processes-its-anterior-extremity-underlies-the-coronoid-process-whilein-addition-to-covering-the-meckelian-canal-up-to-the-adductor-fossa-theposterodorsal-image343272924.html
Annals of the South African MuseumAnnale van die Suid-Afrikaanse Museum . muscle inserts into the medial groove (Figs 10, 17). The surangular (Figs 9-12, 17) lies posteromedially to the dentary, postero-laterally to the coronoid, dorsally to the prearticular and anteriorly to thearticular. Laterally it forms the posterior section of the mandibular shelf(Fig. 11) and dorsally it bears a ridge extending between the coronoid and thearticular processes. Its anterior extremity underlies the coronoid process whilein addition to covering the Meckelian canal up to the adductor fossa, theposterodorsal Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/annals-of-the-south-african-museumannale-van-die-suid-afrikaanse-museum-muscle-inserts-into-the-medial-groove-figs-10-17-the-surangular-figs-9-12-17-lies-posteromedially-to-the-dentary-postero-laterally-to-the-coronoid-dorsally-to-the-prearticular-and-anteriorly-to-thearticular-laterally-it-forms-the-posterior-section-of-the-mandibular-shelffig-11-and-dorsally-it-bears-a-ridge-extending-between-the-coronoid-and-thearticular-processes-its-anterior-extremity-underlies-the-coronoid-process-whilein-addition-to-covering-the-meckelian-canal-up-to-the-adductor-fossa-theposterodorsal-image343272924.htmlRM2AXDC38–Annals of the South African MuseumAnnale van die Suid-Afrikaanse Museum . muscle inserts into the medial groove (Figs 10, 17). The surangular (Figs 9-12, 17) lies posteromedially to the dentary, postero-laterally to the coronoid, dorsally to the prearticular and anteriorly to thearticular. Laterally it forms the posterior section of the mandibular shelf(Fig. 11) and dorsally it bears a ridge extending between the coronoid and thearticular processes. Its anterior extremity underlies the coronoid process whilein addition to covering the Meckelian canal up to the adductor fossa, theposterodorsal
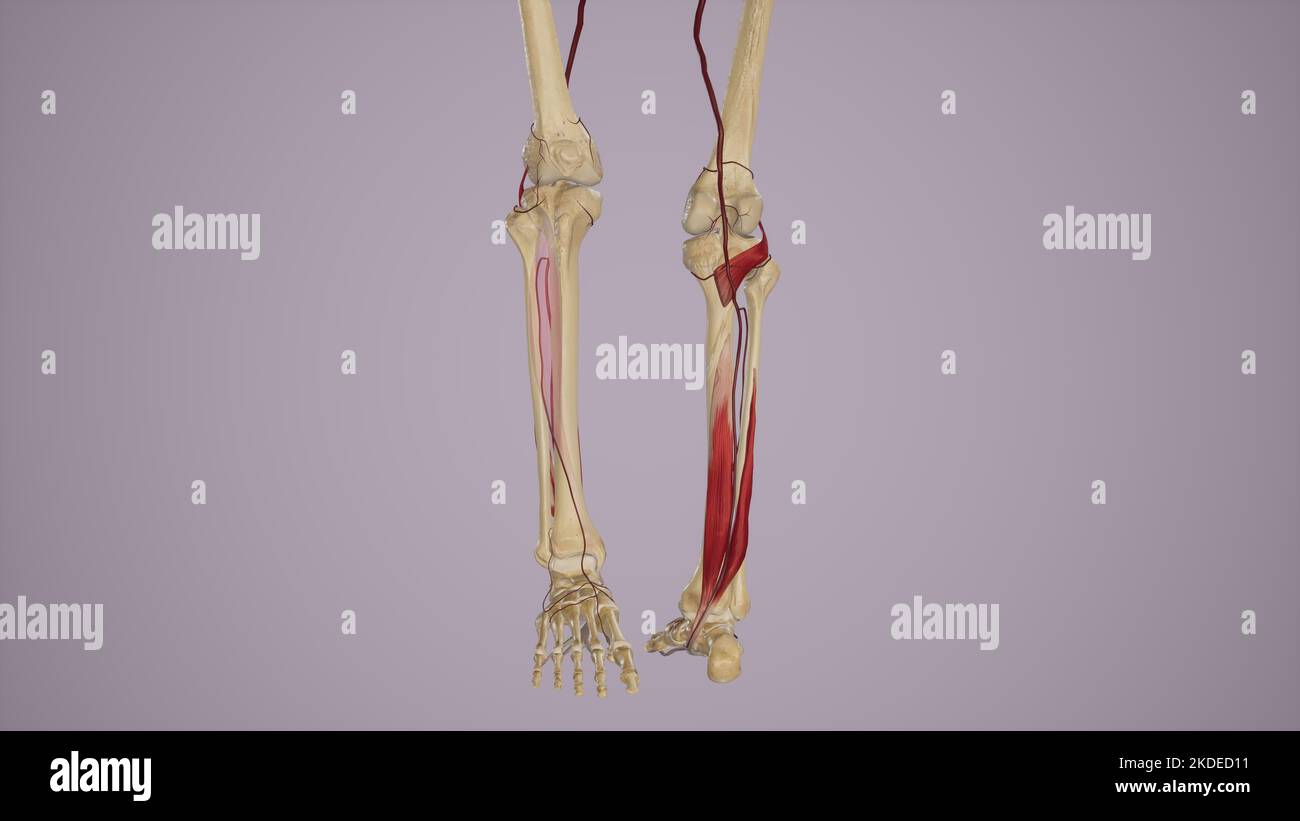 Arterial Supply to the Anterior and Posterior Leg Via Popliteal Artery and Its Branches Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/arterial-supply-to-the-anterior-and-posterior-leg-via-popliteal-artery-and-its-branches-image490198381.html
Arterial Supply to the Anterior and Posterior Leg Via Popliteal Artery and Its Branches Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/arterial-supply-to-the-anterior-and-posterior-leg-via-popliteal-artery-and-its-branches-image490198381.htmlRF2KDED11–Arterial Supply to the Anterior and Posterior Leg Via Popliteal Artery and Its Branches
 The practice of surgery . mphysis and theanterior superior spine of the ilium. The line of the femoral artery runsfrom the midpoint of Pouparts liga-ment to the internal tuberosity of thefemur at the knee. We tie it either high at the apex of Scarpastriangle, or in Hunters canal beneath the long saphenous vein, nearthe outer edge of the sartorius muscle, between the adductor magnusand the vastus intemus muscles. The posterior tibial artery lies in a line between the middle of thepopliteal space and a point midway between the internal malleolus. Fig. 475. -LifTation of brachialartery. LIGATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-surgery-mphysis-and-theanterior-superior-spine-of-the-ilium-the-line-of-the-femoral-artery-runsfrom-the-midpoint-of-pouparts-liga-ment-to-the-internal-tuberosity-of-thefemur-at-the-knee-we-tie-it-either-high-at-the-apex-of-scarpastriangle-or-in-hunters-canal-beneath-the-long-saphenous-vein-nearthe-outer-edge-of-the-sartorius-muscle-between-the-adductor-magnusand-the-vastus-intemus-muscles-the-posterior-tibial-artery-lies-in-a-line-between-the-middle-of-thepopliteal-space-and-a-point-midway-between-the-internal-malleolus-fig-475-liftation-of-brachialartery-ligation-image340308764.html
The practice of surgery . mphysis and theanterior superior spine of the ilium. The line of the femoral artery runsfrom the midpoint of Pouparts liga-ment to the internal tuberosity of thefemur at the knee. We tie it either high at the apex of Scarpastriangle, or in Hunters canal beneath the long saphenous vein, nearthe outer edge of the sartorius muscle, between the adductor magnusand the vastus intemus muscles. The posterior tibial artery lies in a line between the middle of thepopliteal space and a point midway between the internal malleolus. Fig. 475. -LifTation of brachialartery. LIGATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-surgery-mphysis-and-theanterior-superior-spine-of-the-ilium-the-line-of-the-femoral-artery-runsfrom-the-midpoint-of-pouparts-liga-ment-to-the-internal-tuberosity-of-thefemur-at-the-knee-we-tie-it-either-high-at-the-apex-of-scarpastriangle-or-in-hunters-canal-beneath-the-long-saphenous-vein-nearthe-outer-edge-of-the-sartorius-muscle-between-the-adductor-magnusand-the-vastus-intemus-muscles-the-posterior-tibial-artery-lies-in-a-line-between-the-middle-of-thepopliteal-space-and-a-point-midway-between-the-internal-malleolus-fig-475-liftation-of-brachialartery-ligation-image340308764.htmlRM2ANJB8C–The practice of surgery . mphysis and theanterior superior spine of the ilium. The line of the femoral artery runsfrom the midpoint of Pouparts liga-ment to the internal tuberosity of thefemur at the knee. We tie it either high at the apex of Scarpastriangle, or in Hunters canal beneath the long saphenous vein, nearthe outer edge of the sartorius muscle, between the adductor magnusand the vastus intemus muscles. The posterior tibial artery lies in a line between the middle of thepopliteal space and a point midway between the internal malleolus. Fig. 475. -LifTation of brachialartery. LIGATION
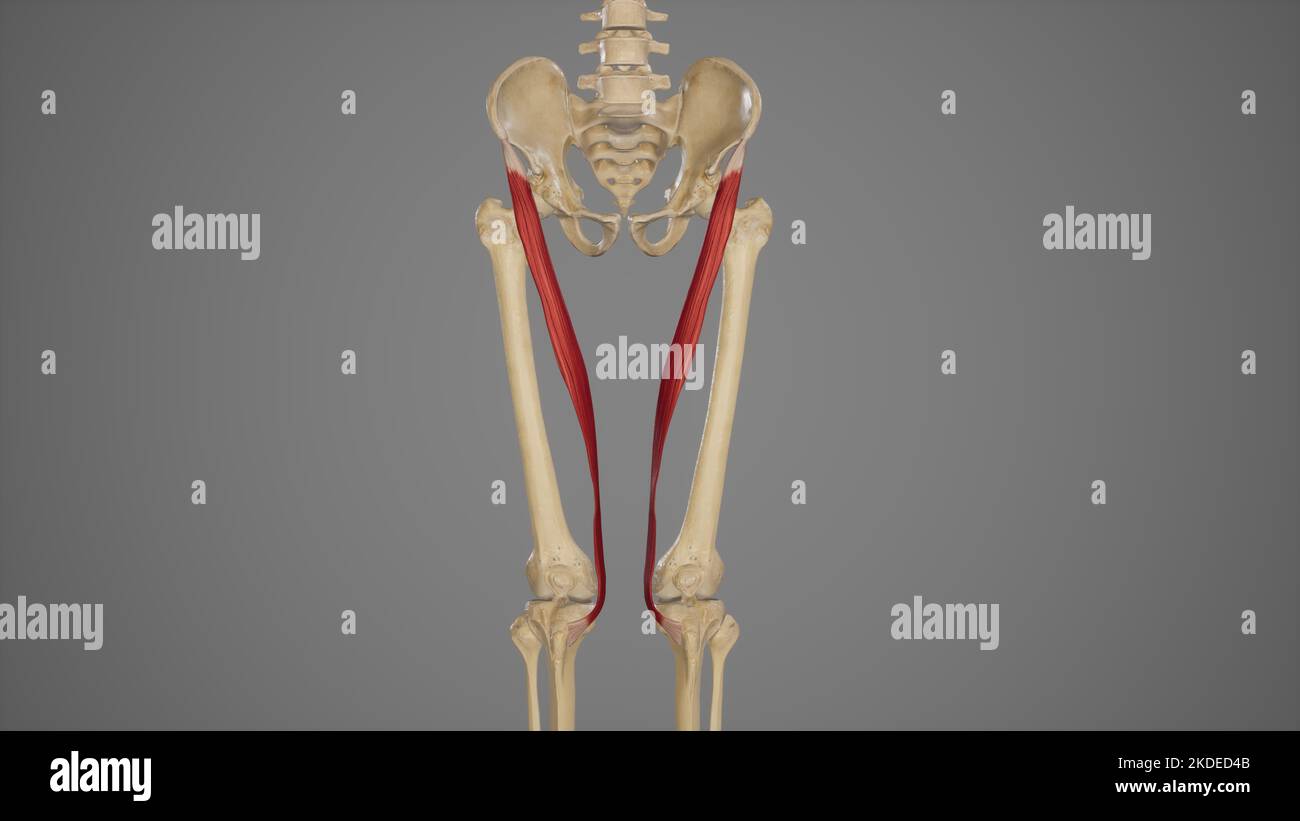 Medical Illustration of Sartorius Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-sartorius-muscle-image490198475.html
Medical Illustration of Sartorius Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-sartorius-muscle-image490198475.htmlRF2KDED4B–Medical Illustration of Sartorius Muscle
 . Manual of operative surgery. Selig (Arch. f. Klin.Chir., ciii, 994) advocates division of the obturator nerve before its entranceinto the obturator canal. The fact that the adductor magnus gains part of itsnerve supply from the sciatic nerve explains why after section of the obturatornerve, while spastic contraction is prevented, active contraction remains pos-sible. The obturator nerve arises from the second, third and fourth lumbarnerves, crosses the sacro-iliac joint and the internal iliac artery to find its way DIVISION OBTURATOR NERVE 77.3 along the lateral wall of the true pelvis until Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/manual-of-operative-surgery-selig-arch-f-klinchir-ciii-994-advocates-division-of-the-obturator-nerve-before-its-entranceinto-the-obturator-canal-the-fact-that-the-adductor-magnus-gains-part-of-itsnerve-supply-from-the-sciatic-nerve-explains-why-after-section-of-the-obturatornerve-while-spastic-contraction-is-prevented-active-contraction-remains-pos-sible-the-obturator-nerve-arises-from-the-second-third-and-fourth-lumbarnerves-crosses-the-sacro-iliac-joint-and-the-internal-iliac-artery-to-find-its-way-division-obturator-nerve-773-along-the-lateral-wall-of-the-true-pelvis-until-image336814898.html
. Manual of operative surgery. Selig (Arch. f. Klin.Chir., ciii, 994) advocates division of the obturator nerve before its entranceinto the obturator canal. The fact that the adductor magnus gains part of itsnerve supply from the sciatic nerve explains why after section of the obturatornerve, while spastic contraction is prevented, active contraction remains pos-sible. The obturator nerve arises from the second, third and fourth lumbarnerves, crosses the sacro-iliac joint and the internal iliac artery to find its way DIVISION OBTURATOR NERVE 77.3 along the lateral wall of the true pelvis until Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/manual-of-operative-surgery-selig-arch-f-klinchir-ciii-994-advocates-division-of-the-obturator-nerve-before-its-entranceinto-the-obturator-canal-the-fact-that-the-adductor-magnus-gains-part-of-itsnerve-supply-from-the-sciatic-nerve-explains-why-after-section-of-the-obturatornerve-while-spastic-contraction-is-prevented-active-contraction-remains-pos-sible-the-obturator-nerve-arises-from-the-second-third-and-fourth-lumbarnerves-crosses-the-sacro-iliac-joint-and-the-internal-iliac-artery-to-find-its-way-division-obturator-nerve-773-along-the-lateral-wall-of-the-true-pelvis-until-image336814898.htmlRM2AFY6RE–. Manual of operative surgery. Selig (Arch. f. Klin.Chir., ciii, 994) advocates division of the obturator nerve before its entranceinto the obturator canal. The fact that the adductor magnus gains part of itsnerve supply from the sciatic nerve explains why after section of the obturatornerve, while spastic contraction is prevented, active contraction remains pos-sible. The obturator nerve arises from the second, third and fourth lumbarnerves, crosses the sacro-iliac joint and the internal iliac artery to find its way DIVISION OBTURATOR NERVE 77.3 along the lateral wall of the true pelvis until
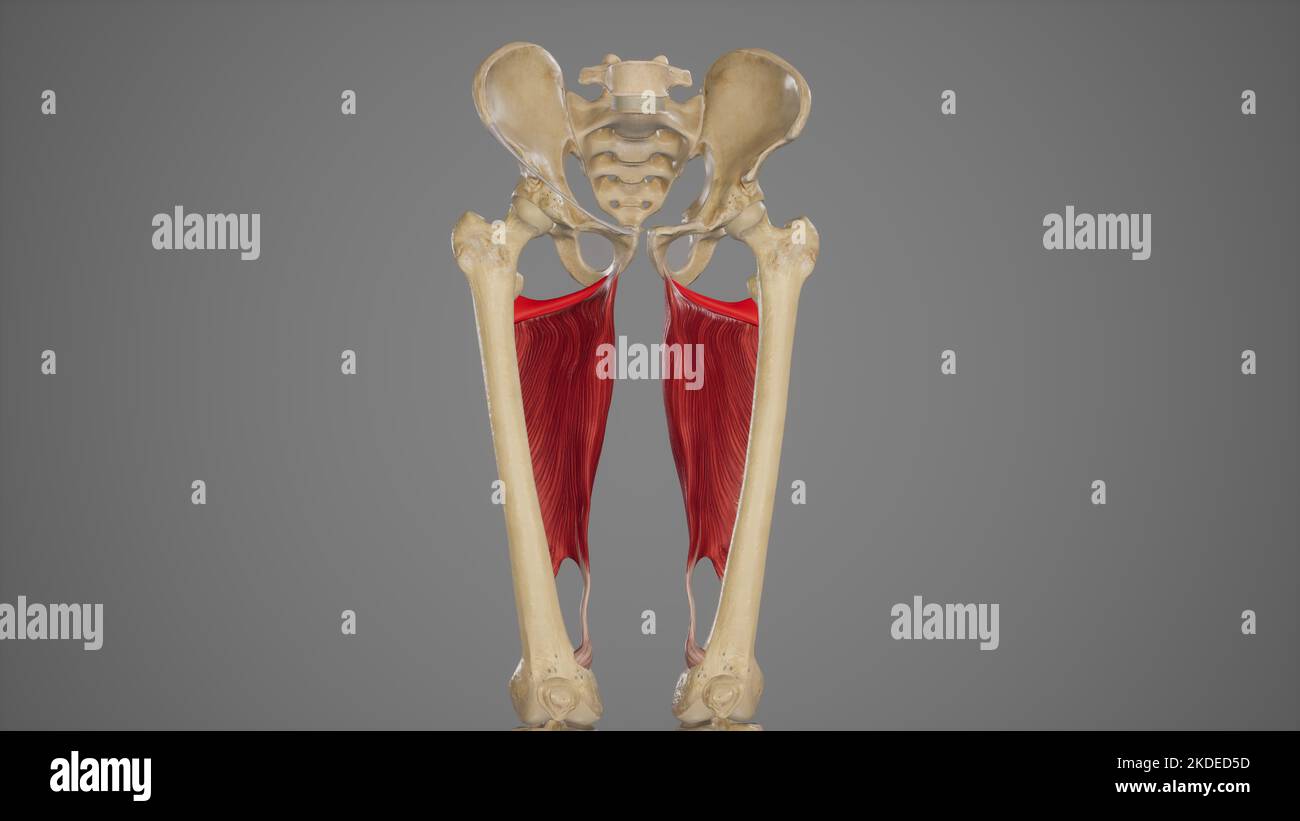 Medical Acurate Illustration of Adductor Minimus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-acurate-illustration-of-adductor-minimus-image490198505.html
Medical Acurate Illustration of Adductor Minimus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-acurate-illustration-of-adductor-minimus-image490198505.htmlRF2KDED5D–Medical Acurate Illustration of Adductor Minimus
 Atlas and text-book of topographic and applied anatomy . Obturator nerve(anterior branch)M. adductor longus ^ M. adductor ma M. vastus medial Femoral artei Long ! iaphenous nerv al vein (almost entire cone ealed) M. sartorh Anastomotica magnTendon of adductor Pouparts ligame Femoral veFemoralSuperficial external pudarteryProfunda femoris Fascia lat. THE THIGH. 159 Fig. 79.—The anterior femoral region. Fig. 80.—The exposure of the femoral artery before its entrance into Hunters canal. Fig. 81.—The subperitoneal exposure of the external iliac artery. Below Pouparts ligament the femoral vesselsha Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-topographic-and-applied-anatomy-obturator-nerveanterior-branchm-adductor-longus-m-adductor-ma-m-vastus-medial-femoral-artei-long-!-iaphenous-nerv-al-vein-almost-entire-cone-ealed-m-sartorh-anastomotica-magntendon-of-adductor-pouparts-ligame-femoral-vefemoralsuperficial-external-pudarteryprofunda-femoris-fascia-lat-the-thigh-159-fig-79the-anterior-femoral-region-fig-80the-exposure-of-the-femoral-artery-before-its-entrance-into-hunters-canal-fig-81the-subperitoneal-exposure-of-the-external-iliac-artery-below-pouparts-ligament-the-femoral-vesselsha-image338233293.html
Atlas and text-book of topographic and applied anatomy . Obturator nerve(anterior branch)M. adductor longus ^ M. adductor ma M. vastus medial Femoral artei Long ! iaphenous nerv al vein (almost entire cone ealed) M. sartorh Anastomotica magnTendon of adductor Pouparts ligame Femoral veFemoralSuperficial external pudarteryProfunda femoris Fascia lat. THE THIGH. 159 Fig. 79.—The anterior femoral region. Fig. 80.—The exposure of the femoral artery before its entrance into Hunters canal. Fig. 81.—The subperitoneal exposure of the external iliac artery. Below Pouparts ligament the femoral vesselsha Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-topographic-and-applied-anatomy-obturator-nerveanterior-branchm-adductor-longus-m-adductor-ma-m-vastus-medial-femoral-artei-long-!-iaphenous-nerv-al-vein-almost-entire-cone-ealed-m-sartorh-anastomotica-magntendon-of-adductor-pouparts-ligame-femoral-vefemoralsuperficial-external-pudarteryprofunda-femoris-fascia-lat-the-thigh-159-fig-79the-anterior-femoral-region-fig-80the-exposure-of-the-femoral-artery-before-its-entrance-into-hunters-canal-fig-81the-subperitoneal-exposure-of-the-external-iliac-artery-below-pouparts-ligament-the-femoral-vesselsha-image338233293.htmlRM2AJ7T0D–Atlas and text-book of topographic and applied anatomy . Obturator nerve(anterior branch)M. adductor longus ^ M. adductor ma M. vastus medial Femoral artei Long ! iaphenous nerv al vein (almost entire cone ealed) M. sartorh Anastomotica magnTendon of adductor Pouparts ligame Femoral veFemoralSuperficial external pudarteryProfunda femoris Fascia lat. THE THIGH. 159 Fig. 79.—The anterior femoral region. Fig. 80.—The exposure of the femoral artery before its entrance into Hunters canal. Fig. 81.—The subperitoneal exposure of the external iliac artery. Below Pouparts ligament the femoral vesselsha
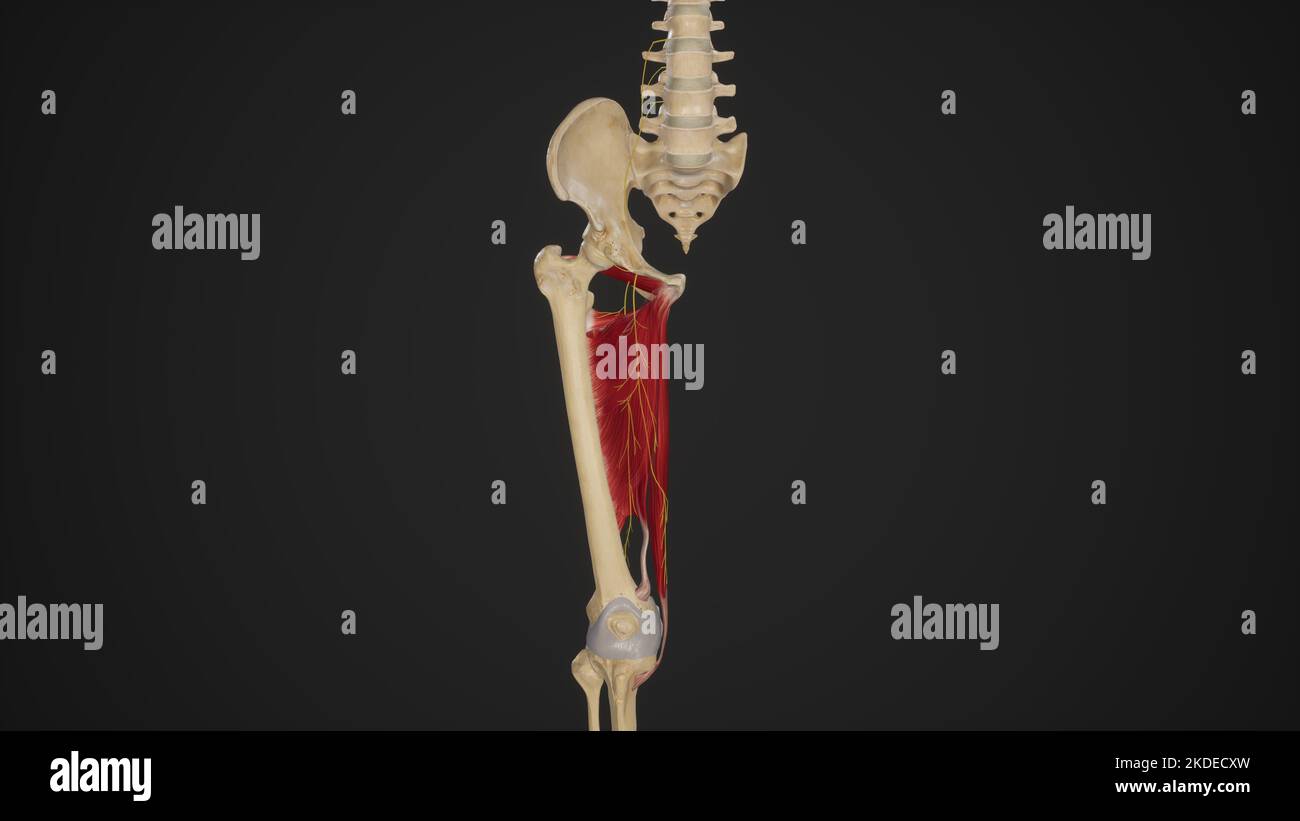 Anatomical Illustration of Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-obturator-nerve-image490198321.html
Anatomical Illustration of Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-obturator-nerve-image490198321.htmlRF2KDECXW–Anatomical Illustration of Obturator Nerve
 . Regional anesthesia : its technic and clinical application . s course along the anterolateral wall of thepelvis, below the iliopectineal line, upon the inner surface of the pelvisfascia, leaves the pelvis through the obturator canal, and divides into itsterminal branches, which are separated from each other by the obtu-rator extemus muscle and later by the adductor brevis muscle. Thesebranches supply the adductor muscles, the hip- and knee-joints, andthe integument of the medial aspect of the thigh. Sometimes a fila-ment is given off which inosculates with the saphenous internus or itsaccess Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/regional-anesthesia-its-technic-and-clinical-application-s-course-along-the-anterolateral-wall-of-thepelvis-below-the-iliopectineal-line-upon-the-inner-surface-of-the-pelvisfascia-leaves-the-pelvis-through-the-obturator-canal-and-divides-into-itsterminal-branches-which-are-separated-from-each-other-by-the-obtu-rator-extemus-muscle-and-later-by-the-adductor-brevis-muscle-thesebranches-supply-the-adductor-muscles-the-hip-and-knee-joints-andthe-integument-of-the-medial-aspect-of-the-thigh-sometimes-a-fila-ment-is-given-off-which-inosculates-with-the-saphenous-internus-or-itsaccess-image370061457.html
. Regional anesthesia : its technic and clinical application . s course along the anterolateral wall of thepelvis, below the iliopectineal line, upon the inner surface of the pelvisfascia, leaves the pelvis through the obturator canal, and divides into itsterminal branches, which are separated from each other by the obtu-rator extemus muscle and later by the adductor brevis muscle. Thesebranches supply the adductor muscles, the hip- and knee-joints, andthe integument of the medial aspect of the thigh. Sometimes a fila-ment is given off which inosculates with the saphenous internus or itsaccess Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/regional-anesthesia-its-technic-and-clinical-application-s-course-along-the-anterolateral-wall-of-thepelvis-below-the-iliopectineal-line-upon-the-inner-surface-of-the-pelvisfascia-leaves-the-pelvis-through-the-obturator-canal-and-divides-into-itsterminal-branches-which-are-separated-from-each-other-by-the-obtu-rator-extemus-muscle-and-later-by-the-adductor-brevis-muscle-thesebranches-supply-the-adductor-muscles-the-hip-and-knee-joints-andthe-integument-of-the-medial-aspect-of-the-thigh-sometimes-a-fila-ment-is-given-off-which-inosculates-with-the-saphenous-internus-or-itsaccess-image370061457.htmlRM2CE1N4H–. Regional anesthesia : its technic and clinical application . s course along the anterolateral wall of thepelvis, below the iliopectineal line, upon the inner surface of the pelvisfascia, leaves the pelvis through the obturator canal, and divides into itsterminal branches, which are separated from each other by the obtu-rator extemus muscle and later by the adductor brevis muscle. Thesebranches supply the adductor muscles, the hip- and knee-joints, andthe integument of the medial aspect of the thigh. Sometimes a fila-ment is given off which inosculates with the saphenous internus or itsaccess
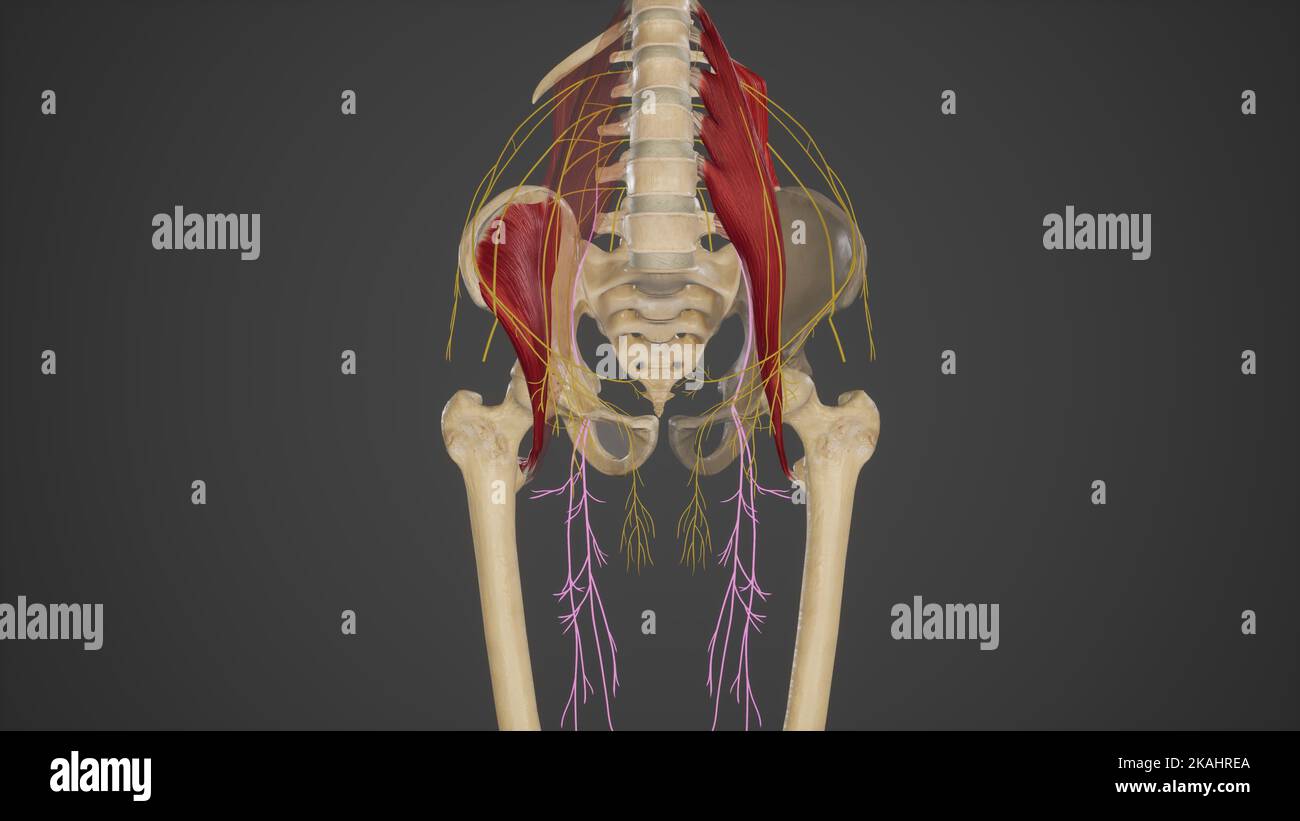 Anatomical Illustration of Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-obturator-nerve-image488428482.html
Anatomical Illustration of Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-obturator-nerve-image488428482.htmlRF2KAHREA–Anatomical Illustration of Obturator Nerve
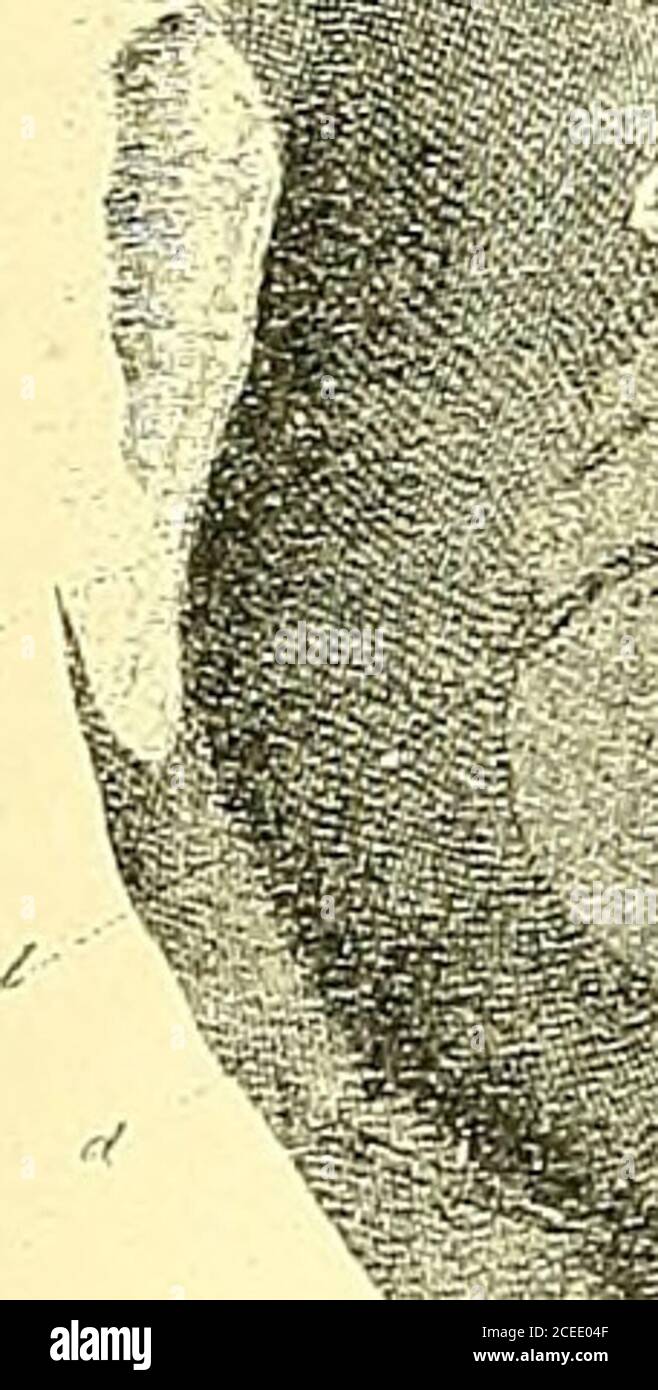 . The anatomy and surgical treatment of hernia. aused death. It produced no visible external swelling. The tumor was aboutthe size of a small hens egg, and contained sphacelated intestine and omentum. Itwas covered by the pectineus and adductor longus, and rested on the vessels andnerve. In the very large number of dissections which Cloquet made for the purposeof studying hernia, he naturally examined the thyroideal canal, and gave it as his opin-ion that this variety of hernia was much more common than is generally supposed.In post-mortem examinations, as usually conducted, I am sure the peri Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-and-surgical-treatment-of-hernia-aused-death-it-produced-no-visible-external-swelling-the-tumor-was-aboutthe-size-of-a-small-hens-egg-and-contained-sphacelated-intestine-and-omentum-itwas-covered-by-the-pectineus-and-adductor-longus-and-rested-on-the-vessels-andnerve-in-the-very-large-number-of-dissections-which-cloquet-made-for-the-purposeof-studying-hernia-he-naturally-examined-the-thyroideal-canal-and-gave-it-as-his-opin-ion-that-this-variety-of-hernia-was-much-more-common-than-is-generally-supposedin-post-mortem-examinations-as-usually-conducted-i-am-sure-the-peri-image370330367.html
. The anatomy and surgical treatment of hernia. aused death. It produced no visible external swelling. The tumor was aboutthe size of a small hens egg, and contained sphacelated intestine and omentum. Itwas covered by the pectineus and adductor longus, and rested on the vessels andnerve. In the very large number of dissections which Cloquet made for the purposeof studying hernia, he naturally examined the thyroideal canal, and gave it as his opin-ion that this variety of hernia was much more common than is generally supposed.In post-mortem examinations, as usually conducted, I am sure the peri Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-and-surgical-treatment-of-hernia-aused-death-it-produced-no-visible-external-swelling-the-tumor-was-aboutthe-size-of-a-small-hens-egg-and-contained-sphacelated-intestine-and-omentum-itwas-covered-by-the-pectineus-and-adductor-longus-and-rested-on-the-vessels-andnerve-in-the-very-large-number-of-dissections-which-cloquet-made-for-the-purposeof-studying-hernia-he-naturally-examined-the-thyroideal-canal-and-gave-it-as-his-opin-ion-that-this-variety-of-hernia-was-much-more-common-than-is-generally-supposedin-post-mortem-examinations-as-usually-conducted-i-am-sure-the-peri-image370330367.htmlRM2CEE04F–. The anatomy and surgical treatment of hernia. aused death. It produced no visible external swelling. The tumor was aboutthe size of a small hens egg, and contained sphacelated intestine and omentum. Itwas covered by the pectineus and adductor longus, and rested on the vessels andnerve. In the very large number of dissections which Cloquet made for the purposeof studying hernia, he naturally examined the thyroideal canal, and gave it as his opin-ion that this variety of hernia was much more common than is generally supposed.In post-mortem examinations, as usually conducted, I am sure the peri
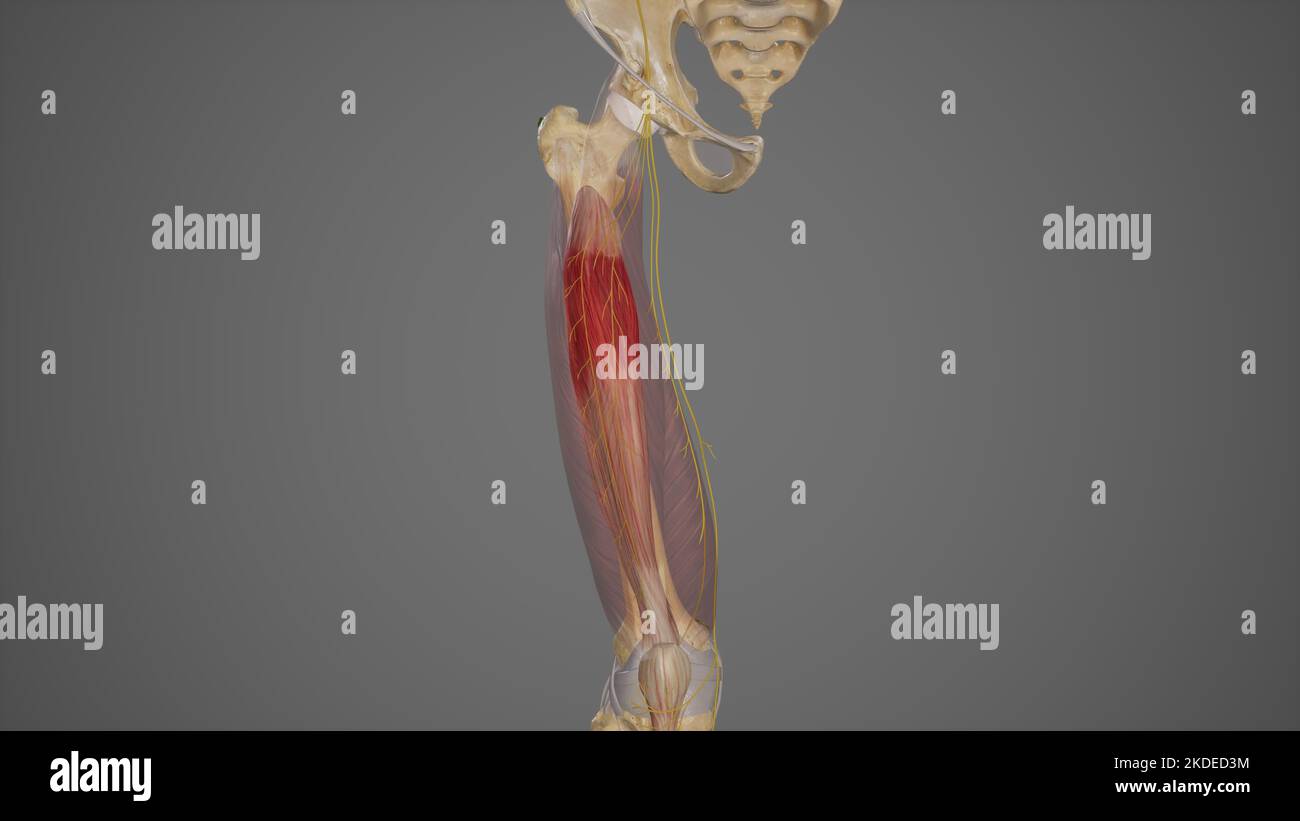 Branches of Posterior Division of Femoral Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/branches-of-posterior-division-of-femoral-nerve-image490198456.html
Branches of Posterior Division of Femoral Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/branches-of-posterior-division-of-femoral-nerve-image490198456.htmlRF2KDED3M–Branches of Posterior Division of Femoral Nerve
 . Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. of thesartorius, the medial border by the adductor longus, and the apex bythe crossing of these two muscles on the medial side of the thigh atabout the middle. The most important structures in the triangle are the femoralartery and vein lying side by side, in a line from the middle of the 302 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR NURSES. base to the apex. The femoral nerve and branches are to thelateral side of the artery. Order of structures as they pass under the inguinal ligament:V-ein, A-rtery, N-erve, the vein being medialward. Hunters Canal (Adducto Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-of-thesartorius-the-medial-border-by-the-adductor-longus-and-the-apex-bythe-crossing-of-these-two-muscles-on-the-medial-side-of-the-thigh-atabout-the-middle-the-most-important-structures-in-the-triangle-are-the-femoralartery-and-vein-lying-side-by-side-in-a-line-from-the-middle-of-the-302-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-base-to-the-apex-the-femoral-nerve-and-branches-are-to-thelateral-side-of-the-artery-order-of-structures-as-they-pass-under-the-inguinal-ligamentv-ein-a-rtery-n-erve-the-vein-being-medialward-hunters-canal-adducto-image370327652.html
. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. of thesartorius, the medial border by the adductor longus, and the apex bythe crossing of these two muscles on the medial side of the thigh atabout the middle. The most important structures in the triangle are the femoralartery and vein lying side by side, in a line from the middle of the 302 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR NURSES. base to the apex. The femoral nerve and branches are to thelateral side of the artery. Order of structures as they pass under the inguinal ligament:V-ein, A-rtery, N-erve, the vein being medialward. Hunters Canal (Adducto Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-of-thesartorius-the-medial-border-by-the-adductor-longus-and-the-apex-bythe-crossing-of-these-two-muscles-on-the-medial-side-of-the-thigh-atabout-the-middle-the-most-important-structures-in-the-triangle-are-the-femoralartery-and-vein-lying-side-by-side-in-a-line-from-the-middle-of-the-302-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-base-to-the-apex-the-femoral-nerve-and-branches-are-to-thelateral-side-of-the-artery-order-of-structures-as-they-pass-under-the-inguinal-ligamentv-ein-a-rtery-n-erve-the-vein-being-medialward-hunters-canal-adducto-image370327652.htmlRM2CEDTKG–. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. of thesartorius, the medial border by the adductor longus, and the apex bythe crossing of these two muscles on the medial side of the thigh atabout the middle. The most important structures in the triangle are the femoralartery and vein lying side by side, in a line from the middle of the 302 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR NURSES. base to the apex. The femoral nerve and branches are to thelateral side of the artery. Order of structures as they pass under the inguinal ligament:V-ein, A-rtery, N-erve, the vein being medialward. Hunters Canal (Adducto
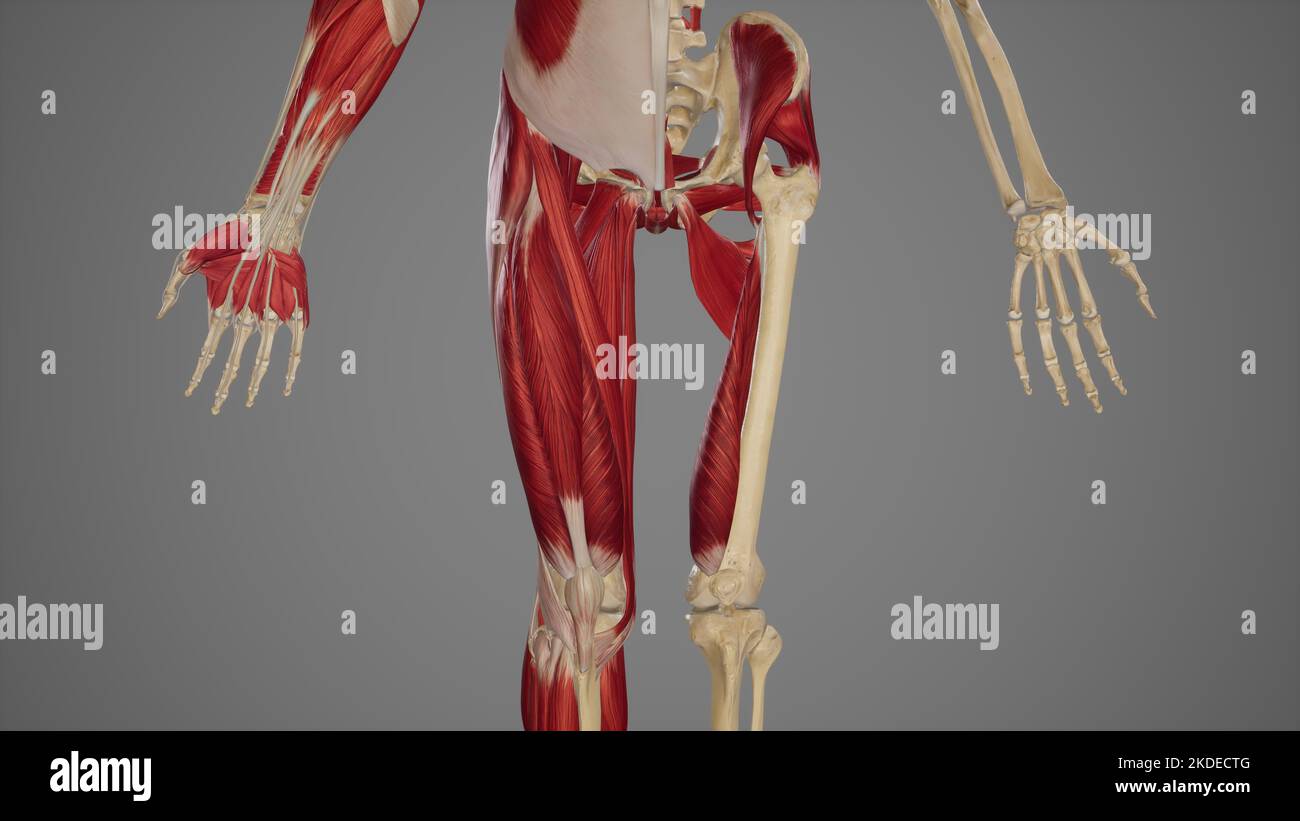 Thigh Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/thigh-muscles-image490198256.html
Thigh Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/thigh-muscles-image490198256.htmlRF2KDECTG–Thigh Muscles
 . Smithsonian miscellaneous collections. ong maxillary palpiare doubled up at its sides. The broad labrum (A, Lm) tapers toa spiny point (F) ; the mandibles (present only in the female) arebladelike (D), finely toothed near the ends (H), and each is providedwith an abductor and an adductor muscle (D, 27, 28) inserted onopposite sides of an articular point (a) ; the broad hypopharynx istraversed to its tip by the salivary canal (G). The maxillae differfrom those of the mosquito in that they are suspended by a pair ofslender rods lying in the membranous posterior wall of the head(C, St) and atta Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/smithsonian-miscellaneous-collections-ong-maxillary-palpiare-doubled-up-at-its-sides-the-broad-labrum-a-lm-tapers-toa-spiny-point-f-the-mandibles-present-only-in-the-female-arebladelike-d-finely-toothed-near-the-ends-h-and-each-is-providedwith-an-abductor-and-an-adductor-muscle-d-27-28-inserted-onopposite-sides-of-an-articular-point-a-the-broad-hypopharynx-istraversed-to-its-tip-by-the-salivary-canal-g-the-maxillae-differfrom-those-of-the-mosquito-in-that-they-are-suspended-by-a-pair-ofslender-rods-lying-in-the-membranous-posterior-wall-of-the-headc-st-and-atta-image370709005.html
. Smithsonian miscellaneous collections. ong maxillary palpiare doubled up at its sides. The broad labrum (A, Lm) tapers toa spiny point (F) ; the mandibles (present only in the female) arebladelike (D), finely toothed near the ends (H), and each is providedwith an abductor and an adductor muscle (D, 27, 28) inserted onopposite sides of an articular point (a) ; the broad hypopharynx istraversed to its tip by the salivary canal (G). The maxillae differfrom those of the mosquito in that they are suspended by a pair ofslender rods lying in the membranous posterior wall of the head(C, St) and atta Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/smithsonian-miscellaneous-collections-ong-maxillary-palpiare-doubled-up-at-its-sides-the-broad-labrum-a-lm-tapers-toa-spiny-point-f-the-mandibles-present-only-in-the-female-arebladelike-d-finely-toothed-near-the-ends-h-and-each-is-providedwith-an-abductor-and-an-adductor-muscle-d-27-28-inserted-onopposite-sides-of-an-articular-point-a-the-broad-hypopharynx-istraversed-to-its-tip-by-the-salivary-canal-g-the-maxillae-differfrom-those-of-the-mosquito-in-that-they-are-suspended-by-a-pair-ofslender-rods-lying-in-the-membranous-posterior-wall-of-the-headc-st-and-atta-image370709005.htmlRM2CF3739–. Smithsonian miscellaneous collections. ong maxillary palpiare doubled up at its sides. The broad labrum (A, Lm) tapers toa spiny point (F) ; the mandibles (present only in the female) arebladelike (D), finely toothed near the ends (H), and each is providedwith an abductor and an adductor muscle (D, 27, 28) inserted onopposite sides of an articular point (a) ; the broad hypopharynx istraversed to its tip by the salivary canal (G). The maxillae differfrom those of the mosquito in that they are suspended by a pair ofslender rods lying in the membranous posterior wall of the head(C, St) and atta
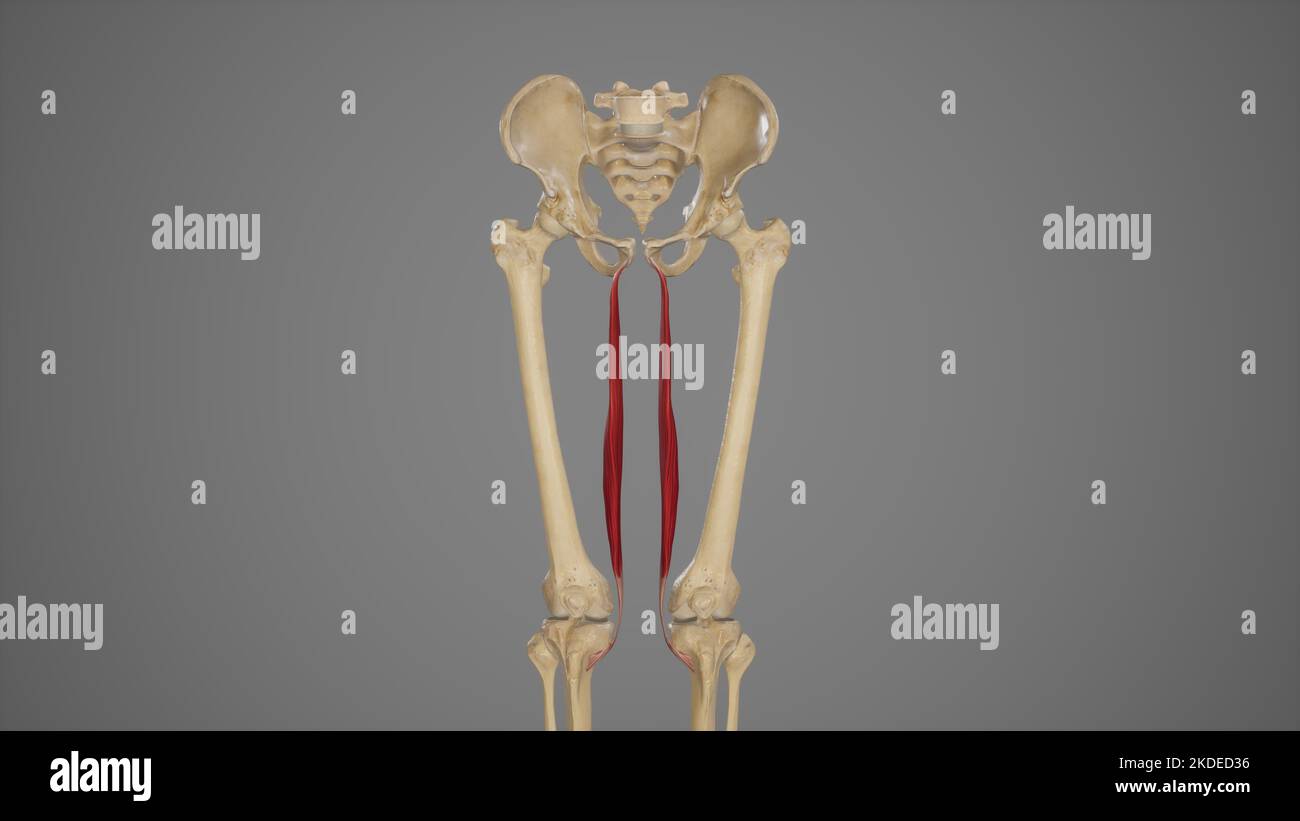 Medical Illustration of Gracilis Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-gracilis-muscle-image490198442.html
Medical Illustration of Gracilis Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-gracilis-muscle-image490198442.htmlRF2KDED36–Medical Illustration of Gracilis Muscle
![. Die Anatomie des Menschen : Mit Hinweisen auf die ärztliche Praxis : Abt. 1-6. Text und Atlas . M. pectin. X M. adductor long. X M. giacilis XM. obturat. ext. W. adductor brevis M. adductor magn.S], pectineus X A. profunda fem. X M. adductor long. XVasa femoral. X Canal. adductorius Hunteri M. vastus medial. -M. rectus fem. X M. sartor. X Muskeln an der orderseite des Oberschenkels. Außer den in der origen Abbildung schonabgeschnittenen ^luskeln ist noch der Musculus rectus femoris, Musculus pectineus, adductor longus und gracilis abgeschnitten. Musculi extremitatis inferioris. mo. 100 Spi Stock Photo . Die Anatomie des Menschen : Mit Hinweisen auf die ärztliche Praxis : Abt. 1-6. Text und Atlas . M. pectin. X M. adductor long. X M. giacilis XM. obturat. ext. W. adductor brevis M. adductor magn.S], pectineus X A. profunda fem. X M. adductor long. XVasa femoral. X Canal. adductorius Hunteri M. vastus medial. -M. rectus fem. X M. sartor. X Muskeln an der orderseite des Oberschenkels. Außer den in der origen Abbildung schonabgeschnittenen ^luskeln ist noch der Musculus rectus femoris, Musculus pectineus, adductor longus und gracilis abgeschnitten. Musculi extremitatis inferioris. mo. 100 Spi Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2CE04AB/die-anatomie-des-menschen-mit-hinweisen-auf-die-rztliche-praxis-abt-1-6-text-und-atlas-m-pectin-x-m-adductor-long-x-m-giacilis-xm-obturat-ext-w-adductor-brevis-m-adductor-magns-pectineus-x-a-profunda-fem-x-m-adductor-long-xvasa-femoral-x-canal-adductorius-hunteri-m-vastus-medial-m-rectus-fem-x-m-sartor-x-muskeln-an-der-orderseite-des-oberschenkels-auer-den-in-der-origen-abbildung-schonabgeschnittenen-luskeln-ist-noch-der-musculus-rectus-femoris-musculus-pectineus-adductor-longus-und-gracilis-abgeschnitten-musculi-extremitatis-inferioris-mo-100-spi-2CE04AB.jpg) . Die Anatomie des Menschen : Mit Hinweisen auf die ärztliche Praxis : Abt. 1-6. Text und Atlas . M. pectin. X M. adductor long. X M. giacilis XM. obturat. ext. W. adductor brevis M. adductor magn.S], pectineus X A. profunda fem. X M. adductor long. XVasa femoral. X Canal. adductorius Hunteri M. vastus medial. -M. rectus fem. X M. sartor. X Muskeln an der orderseite des Oberschenkels. Außer den in der origen Abbildung schonabgeschnittenen ^luskeln ist noch der Musculus rectus femoris, Musculus pectineus, adductor longus und gracilis abgeschnitten. Musculi extremitatis inferioris. mo. 100 Spi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/die-anatomie-des-menschen-mit-hinweisen-auf-die-rztliche-praxis-abt-1-6-text-und-atlas-m-pectin-x-m-adductor-long-x-m-giacilis-xm-obturat-ext-w-adductor-brevis-m-adductor-magns-pectineus-x-a-profunda-fem-x-m-adductor-long-xvasa-femoral-x-canal-adductorius-hunteri-m-vastus-medial-m-rectus-fem-x-m-sartor-x-muskeln-an-der-orderseite-des-oberschenkels-auer-den-in-der-origen-abbildung-schonabgeschnittenen-luskeln-ist-noch-der-musculus-rectus-femoris-musculus-pectineus-adductor-longus-und-gracilis-abgeschnitten-musculi-extremitatis-inferioris-mo-100-spi-image370026339.html
. Die Anatomie des Menschen : Mit Hinweisen auf die ärztliche Praxis : Abt. 1-6. Text und Atlas . M. pectin. X M. adductor long. X M. giacilis XM. obturat. ext. W. adductor brevis M. adductor magn.S], pectineus X A. profunda fem. X M. adductor long. XVasa femoral. X Canal. adductorius Hunteri M. vastus medial. -M. rectus fem. X M. sartor. X Muskeln an der orderseite des Oberschenkels. Außer den in der origen Abbildung schonabgeschnittenen ^luskeln ist noch der Musculus rectus femoris, Musculus pectineus, adductor longus und gracilis abgeschnitten. Musculi extremitatis inferioris. mo. 100 Spi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/die-anatomie-des-menschen-mit-hinweisen-auf-die-rztliche-praxis-abt-1-6-text-und-atlas-m-pectin-x-m-adductor-long-x-m-giacilis-xm-obturat-ext-w-adductor-brevis-m-adductor-magns-pectineus-x-a-profunda-fem-x-m-adductor-long-xvasa-femoral-x-canal-adductorius-hunteri-m-vastus-medial-m-rectus-fem-x-m-sartor-x-muskeln-an-der-orderseite-des-oberschenkels-auer-den-in-der-origen-abbildung-schonabgeschnittenen-luskeln-ist-noch-der-musculus-rectus-femoris-musculus-pectineus-adductor-longus-und-gracilis-abgeschnitten-musculi-extremitatis-inferioris-mo-100-spi-image370026339.htmlRM2CE04AB–. Die Anatomie des Menschen : Mit Hinweisen auf die ärztliche Praxis : Abt. 1-6. Text und Atlas . M. pectin. X M. adductor long. X M. giacilis XM. obturat. ext. W. adductor brevis M. adductor magn.S], pectineus X A. profunda fem. X M. adductor long. XVasa femoral. X Canal. adductorius Hunteri M. vastus medial. -M. rectus fem. X M. sartor. X Muskeln an der orderseite des Oberschenkels. Außer den in der origen Abbildung schonabgeschnittenen ^luskeln ist noch der Musculus rectus femoris, Musculus pectineus, adductor longus und gracilis abgeschnitten. Musculi extremitatis inferioris. mo. 100 Spi
 Obturator Nerve in Medial Thigh Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/obturator-nerve-in-medial-thigh-image488428444.html
Obturator Nerve in Medial Thigh Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/obturator-nerve-in-medial-thigh-image488428444.htmlRF2KAHRD0–Obturator Nerve in Medial Thigh
 . Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology Supplement. 76 ELOPIFORM FISHES narrow dorsally, but ventrally it widens considerably. The concave anterior margin of the preopercular is thickened mid-way along its length to receive part of the super- ficial adductor mandibulae musculature. The preopercular sensory canal ran close to the anterior margin and opened to the surface of the bone by several large pores. The operculum is a large bone showing a rounded dorsal margin. The ventral margin is inclined. Like the other opercular bones the surface is marked by ridges radiating from Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-british-museum-natural-history-geology-supplement-76-elopiform-fishes-narrow-dorsally-but-ventrally-it-widens-considerably-the-concave-anterior-margin-of-the-preopercular-is-thickened-mid-way-along-its-length-to-receive-part-of-the-super-ficial-adductor-mandibulae-musculature-the-preopercular-sensory-canal-ran-close-to-the-anterior-margin-and-opened-to-the-surface-of-the-bone-by-several-large-pores-the-operculum-is-a-large-bone-showing-a-rounded-dorsal-margin-the-ventral-margin-is-inclined-like-the-other-opercular-bones-the-surface-is-marked-by-ridges-radiating-from-image233957157.html
. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology Supplement. 76 ELOPIFORM FISHES narrow dorsally, but ventrally it widens considerably. The concave anterior margin of the preopercular is thickened mid-way along its length to receive part of the super- ficial adductor mandibulae musculature. The preopercular sensory canal ran close to the anterior margin and opened to the surface of the bone by several large pores. The operculum is a large bone showing a rounded dorsal margin. The ventral margin is inclined. Like the other opercular bones the surface is marked by ridges radiating from Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-british-museum-natural-history-geology-supplement-76-elopiform-fishes-narrow-dorsally-but-ventrally-it-widens-considerably-the-concave-anterior-margin-of-the-preopercular-is-thickened-mid-way-along-its-length-to-receive-part-of-the-super-ficial-adductor-mandibulae-musculature-the-preopercular-sensory-canal-ran-close-to-the-anterior-margin-and-opened-to-the-surface-of-the-bone-by-several-large-pores-the-operculum-is-a-large-bone-showing-a-rounded-dorsal-margin-the-ventral-margin-is-inclined-like-the-other-opercular-bones-the-surface-is-marked-by-ridges-radiating-from-image233957157.htmlRMRGHJMN–. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology Supplement. 76 ELOPIFORM FISHES narrow dorsally, but ventrally it widens considerably. The concave anterior margin of the preopercular is thickened mid-way along its length to receive part of the super- ficial adductor mandibulae musculature. The preopercular sensory canal ran close to the anterior margin and opened to the surface of the bone by several large pores. The operculum is a large bone showing a rounded dorsal margin. The ventral margin is inclined. Like the other opercular bones the surface is marked by ridges radiating from
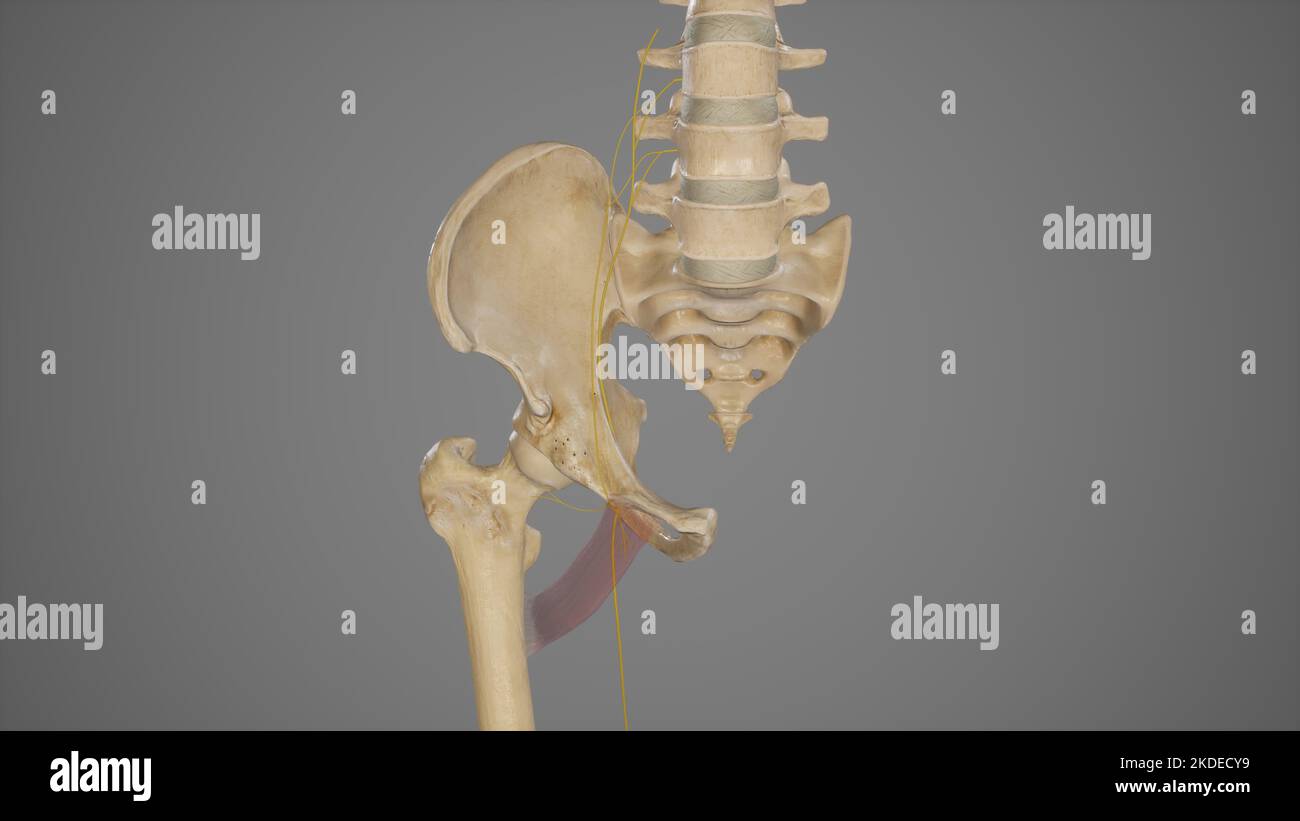 Anatomy of Accessory Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-accessory-obturator-nerve-image490198333.html
Anatomy of Accessory Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-accessory-obturator-nerve-image490198333.htmlRF2KDECY9–Anatomy of Accessory Obturator Nerve
 . A textbook in general zoology. Zoology. 108 MUSSELS, CLAMS, OYSTERS, SNAILS, SQUIDS slowly extended outward and downward into the mud and anchored there. Then the retractor muscles contract and pull the shell and body up to the foot, as it were. By a repetition of these movements of the foot the mussel covers considerable distances in the course of time. The alimentary canal and digestion. — The mouth is just under the anterior adductor muscle and between two pairs of soft flaps, the labial palps. It leads by a short gullet to the spherical stomach, which is surrounded by a dark green mass, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-textbook-in-general-zoology-zoology-108-mussels-clams-oysters-snails-squids-slowly-extended-outward-and-downward-into-the-mud-and-anchored-there-then-the-retractor-muscles-contract-and-pull-the-shell-and-body-up-to-the-foot-as-it-were-by-a-repetition-of-these-movements-of-the-foot-the-mussel-covers-considerable-distances-in-the-course-of-time-the-alimentary-canal-and-digestion-the-mouth-is-just-under-the-anterior-adductor-muscle-and-between-two-pairs-of-soft-flaps-the-labial-palps-it-leads-by-a-short-gullet-to-the-spherical-stomach-which-is-surrounded-by-a-dark-green-mass-image232089319.html
. A textbook in general zoology. Zoology. 108 MUSSELS, CLAMS, OYSTERS, SNAILS, SQUIDS slowly extended outward and downward into the mud and anchored there. Then the retractor muscles contract and pull the shell and body up to the foot, as it were. By a repetition of these movements of the foot the mussel covers considerable distances in the course of time. The alimentary canal and digestion. — The mouth is just under the anterior adductor muscle and between two pairs of soft flaps, the labial palps. It leads by a short gullet to the spherical stomach, which is surrounded by a dark green mass, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-textbook-in-general-zoology-zoology-108-mussels-clams-oysters-snails-squids-slowly-extended-outward-and-downward-into-the-mud-and-anchored-there-then-the-retractor-muscles-contract-and-pull-the-shell-and-body-up-to-the-foot-as-it-were-by-a-repetition-of-these-movements-of-the-foot-the-mussel-covers-considerable-distances-in-the-course-of-time-the-alimentary-canal-and-digestion-the-mouth-is-just-under-the-anterior-adductor-muscle-and-between-two-pairs-of-soft-flaps-the-labial-palps-it-leads-by-a-short-gullet-to-the-spherical-stomach-which-is-surrounded-by-a-dark-green-mass-image232089319.htmlRMRDGG87–. A textbook in general zoology. Zoology. 108 MUSSELS, CLAMS, OYSTERS, SNAILS, SQUIDS slowly extended outward and downward into the mud and anchored there. Then the retractor muscles contract and pull the shell and body up to the foot, as it were. By a repetition of these movements of the foot the mussel covers considerable distances in the course of time. The alimentary canal and digestion. — The mouth is just under the anterior adductor muscle and between two pairs of soft flaps, the labial palps. It leads by a short gullet to the spherical stomach, which is surrounded by a dark green mass,
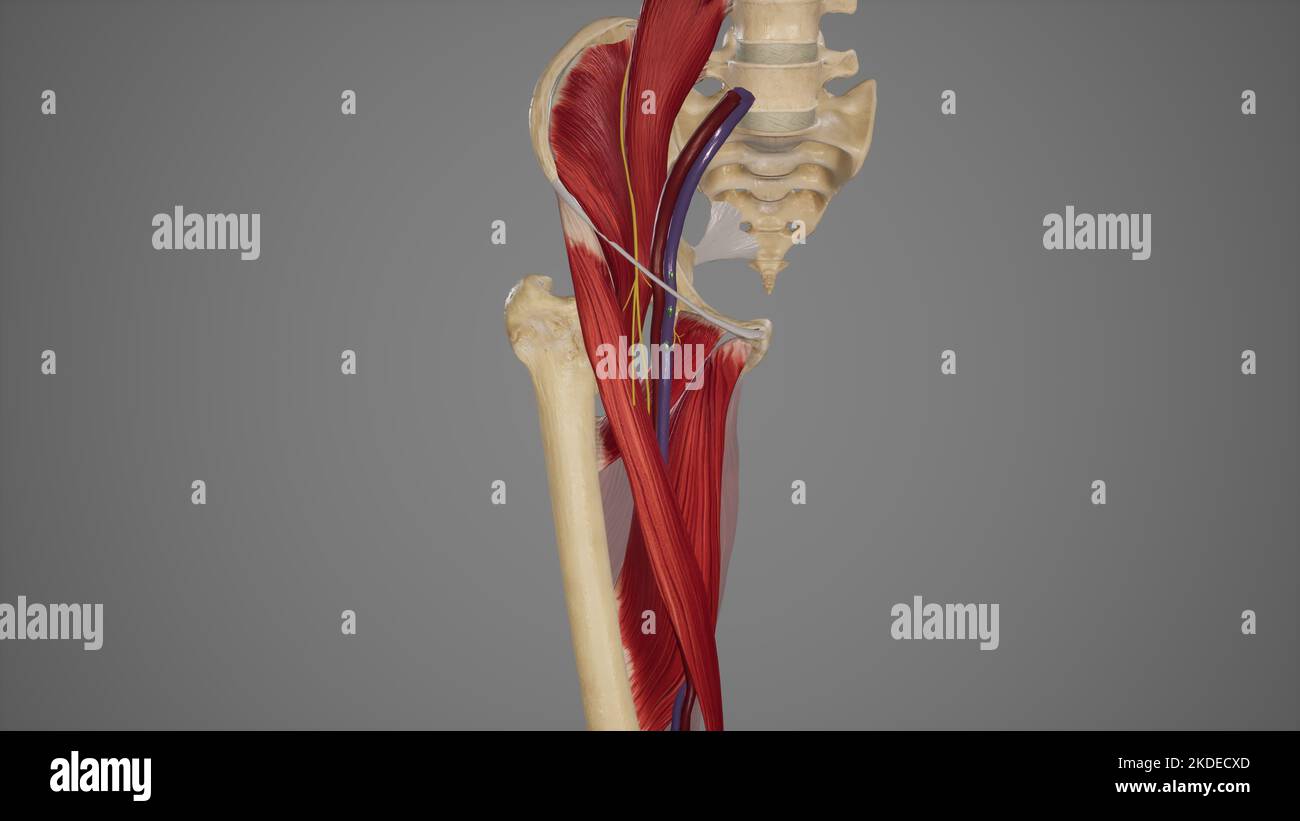 Anatomical Illustration of Femoral Triangle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-femoral-triangle-image490198309.html
Anatomical Illustration of Femoral Triangle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-illustration-of-femoral-triangle-image490198309.htmlRF2KDECXD–Anatomical Illustration of Femoral Triangle
 . Anatomy, descriptive and applied. Anatomy. THE FEMORAL ARTERY 687 it for triangle into Hunter's canal, the Iliacus and Pectineus muscles lie heliiiu a short distance (Fig. 482). That portion of the femoral artery which extends from Poupart's ligament to the origin of the profunda is sometimes named the common femoral. Plan of the Relations of the Femoral Artery in Hunter's Canal. In front. Skin, superficial and deep fasciie. Internal cutaneous nerve. Sartorius. Aponeurotic covering of Hunter's canal. Internal saphenous nerve. Inner side. Adductor longus. Adductor magnus. Sartorius.. • Behind Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-descriptive-and-applied-anatomy-the-femoral-artery-687-it-for-triangle-into-hunters-canal-the-iliacus-and-pectineus-muscles-lie-heliiiu-a-short-distance-fig-482-that-portion-of-the-femoral-artery-which-extends-from-pouparts-ligament-to-the-origin-of-the-profunda-is-sometimes-named-the-common-femoral-plan-of-the-relations-of-the-femoral-artery-in-hunters-canal-in-front-skin-superficial-and-deep-fasciie-internal-cutaneous-nerve-sartorius-aponeurotic-covering-of-hunters-canal-internal-saphenous-nerve-inner-side-adductor-longus-adductor-magnus-sartorius-behind-image236793547.html
. Anatomy, descriptive and applied. Anatomy. THE FEMORAL ARTERY 687 it for triangle into Hunter's canal, the Iliacus and Pectineus muscles lie heliiiu a short distance (Fig. 482). That portion of the femoral artery which extends from Poupart's ligament to the origin of the profunda is sometimes named the common femoral. Plan of the Relations of the Femoral Artery in Hunter's Canal. In front. Skin, superficial and deep fasciie. Internal cutaneous nerve. Sartorius. Aponeurotic covering of Hunter's canal. Internal saphenous nerve. Inner side. Adductor longus. Adductor magnus. Sartorius.. • Behind Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-descriptive-and-applied-anatomy-the-femoral-artery-687-it-for-triangle-into-hunters-canal-the-iliacus-and-pectineus-muscles-lie-heliiiu-a-short-distance-fig-482-that-portion-of-the-femoral-artery-which-extends-from-pouparts-ligament-to-the-origin-of-the-profunda-is-sometimes-named-the-common-femoral-plan-of-the-relations-of-the-femoral-artery-in-hunters-canal-in-front-skin-superficial-and-deep-fasciie-internal-cutaneous-nerve-sartorius-aponeurotic-covering-of-hunters-canal-internal-saphenous-nerve-inner-side-adductor-longus-adductor-magnus-sartorius-behind-image236793547.htmlRMRN6TGB–. Anatomy, descriptive and applied. Anatomy. THE FEMORAL ARTERY 687 it for triangle into Hunter's canal, the Iliacus and Pectineus muscles lie heliiiu a short distance (Fig. 482). That portion of the femoral artery which extends from Poupart's ligament to the origin of the profunda is sometimes named the common femoral. Plan of the Relations of the Femoral Artery in Hunter's Canal. In front. Skin, superficial and deep fasciie. Internal cutaneous nerve. Sartorius. Aponeurotic covering of Hunter's canal. Internal saphenous nerve. Inner side. Adductor longus. Adductor magnus. Sartorius.. • Behind
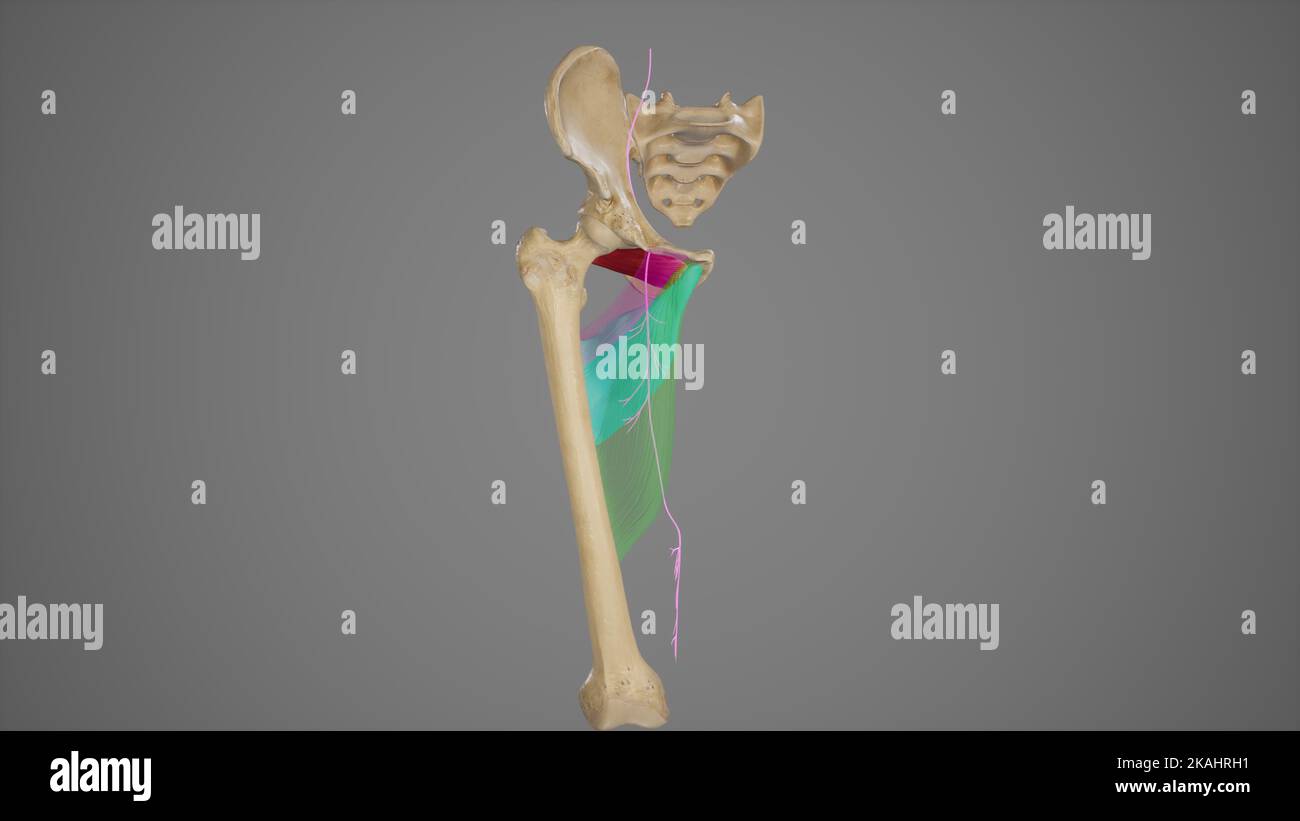 Anterior Branch of Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-branch-of-obturator-nerve-image488428557.html
Anterior Branch of Obturator Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-branch-of-obturator-nerve-image488428557.htmlRF2KAHRH1–Anterior Branch of Obturator Nerve
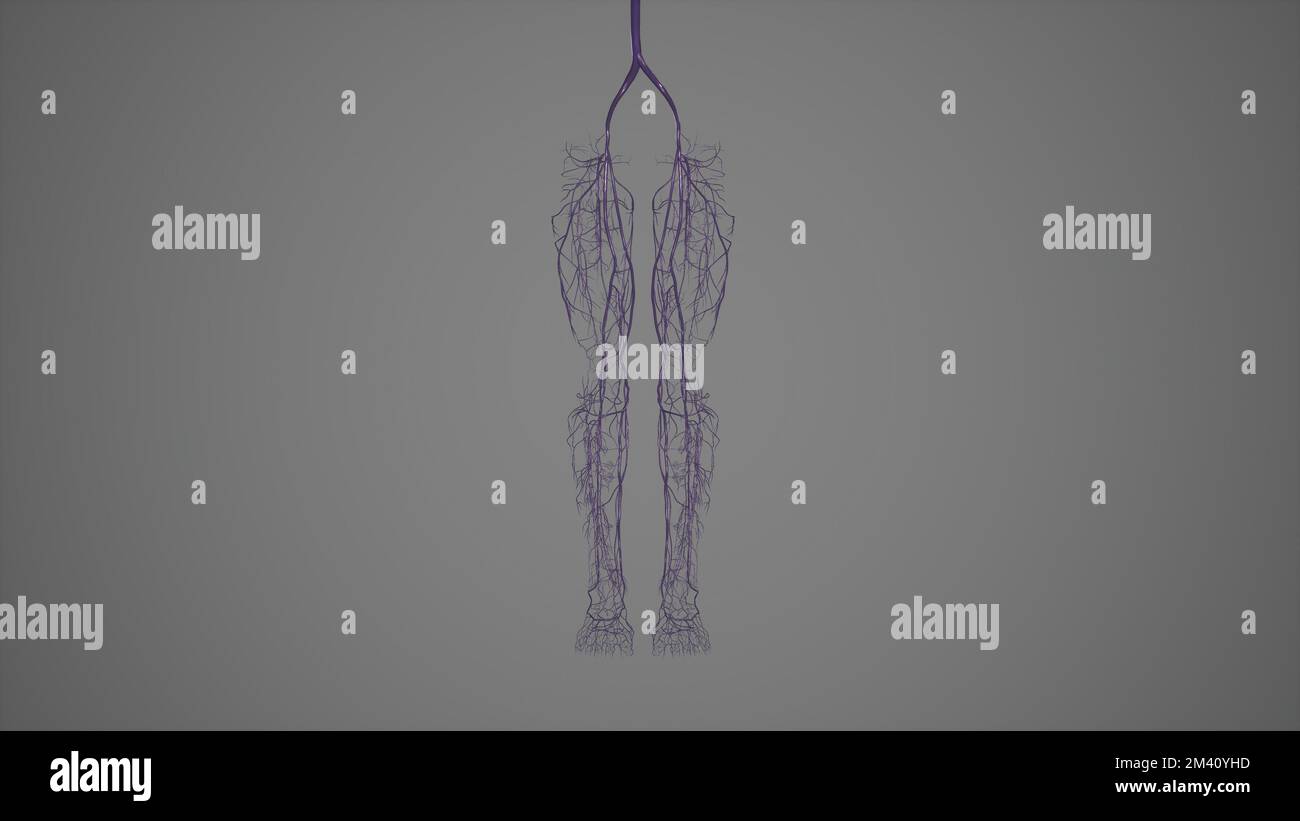 Superficial and Deep Veins of Lower Limb.3d rendering Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superficial-and-deep-veins-of-lower-limb3d-rendering-image501580953.html
Superficial and Deep Veins of Lower Limb.3d rendering Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superficial-and-deep-veins-of-lower-limb3d-rendering-image501580953.htmlRF2M40YHD–Superficial and Deep Veins of Lower Limb.3d rendering
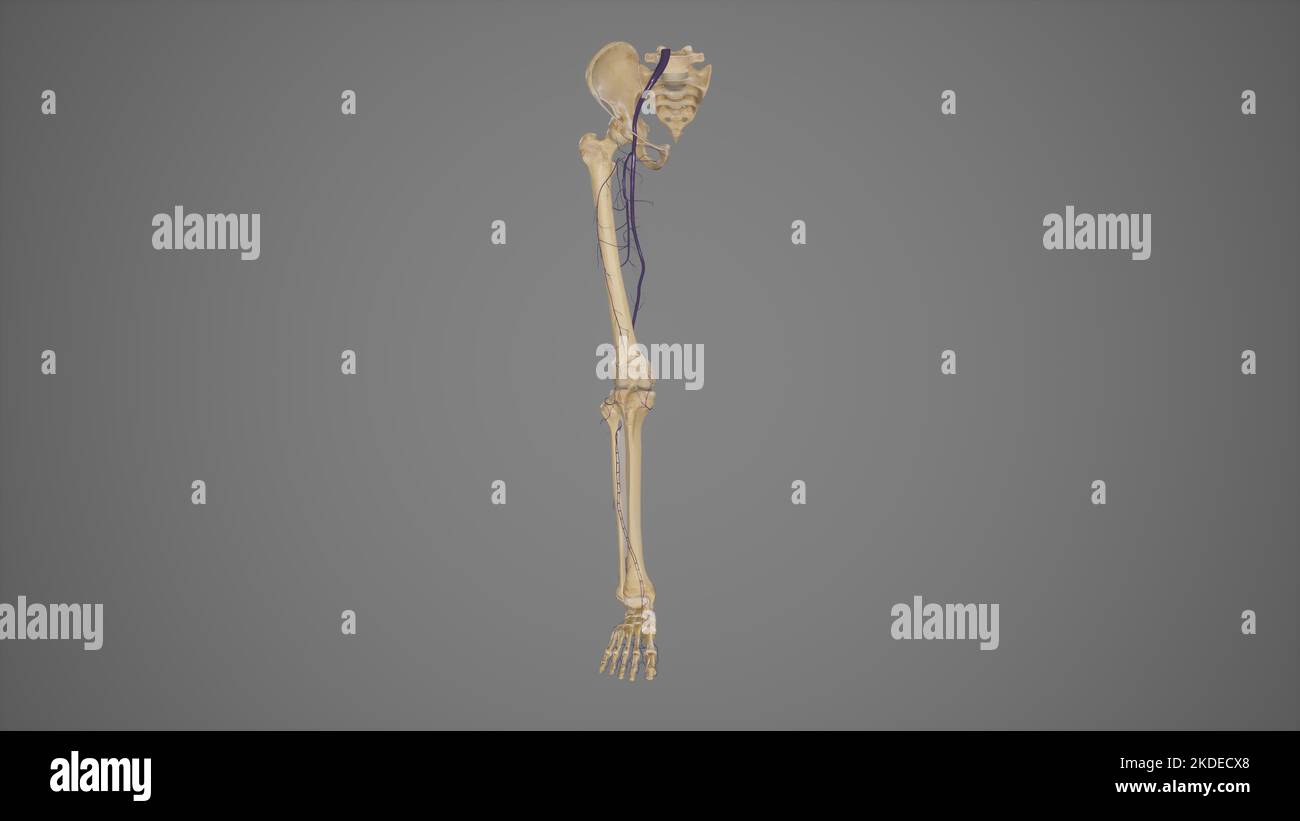 Deep Veins of Lower Limb Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/deep-veins-of-lower-limb-image490198304.html
Deep Veins of Lower Limb Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/deep-veins-of-lower-limb-image490198304.htmlRF2KDECX8–Deep Veins of Lower Limb
 . Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology Supplement. ORDOVICIAN BRACHIOPODA 69. Fig. 6. Diagrammatic views of (A) the ventral and (B) the dorsal interiors of Astraborthis. submedial lobes of diductor scars impressed on the floor of a strong pseudospondy- lium ; mantle canal pattern saccate. Dorsal interior with a simple plate-like cardinal process and short, blade-like outward-curving brachiophores embedded in a thick deposit of secondary shell; sockets oblique, notothyrial platform weak, fused with median ridge ; adductor scars quadripartite with smaller posterior pair ; man Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-british-museum-natural-history-geology-supplement-ordovician-brachiopoda-69-fig-6-diagrammatic-views-of-a-the-ventral-and-b-the-dorsal-interiors-of-astraborthis-submedial-lobes-of-diductor-scars-impressed-on-the-floor-of-a-strong-pseudospondy-lium-mantle-canal-pattern-saccate-dorsal-interior-with-a-simple-plate-like-cardinal-process-and-short-blade-like-outward-curving-brachiophores-embedded-in-a-thick-deposit-of-secondary-shell-sockets-oblique-notothyrial-platform-weak-fused-with-median-ridge-adductor-scars-quadripartite-with-smaller-posterior-pair-man-image233949744.html
. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology Supplement. ORDOVICIAN BRACHIOPODA 69. Fig. 6. Diagrammatic views of (A) the ventral and (B) the dorsal interiors of Astraborthis. submedial lobes of diductor scars impressed on the floor of a strong pseudospondy- lium ; mantle canal pattern saccate. Dorsal interior with a simple plate-like cardinal process and short, blade-like outward-curving brachiophores embedded in a thick deposit of secondary shell; sockets oblique, notothyrial platform weak, fused with median ridge ; adductor scars quadripartite with smaller posterior pair ; man Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-british-museum-natural-history-geology-supplement-ordovician-brachiopoda-69-fig-6-diagrammatic-views-of-a-the-ventral-and-b-the-dorsal-interiors-of-astraborthis-submedial-lobes-of-diductor-scars-impressed-on-the-floor-of-a-strong-pseudospondy-lium-mantle-canal-pattern-saccate-dorsal-interior-with-a-simple-plate-like-cardinal-process-and-short-blade-like-outward-curving-brachiophores-embedded-in-a-thick-deposit-of-secondary-shell-sockets-oblique-notothyrial-platform-weak-fused-with-median-ridge-adductor-scars-quadripartite-with-smaller-posterior-pair-man-image233949744.htmlRMRGH980–. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology Supplement. ORDOVICIAN BRACHIOPODA 69. Fig. 6. Diagrammatic views of (A) the ventral and (B) the dorsal interiors of Astraborthis. submedial lobes of diductor scars impressed on the floor of a strong pseudospondy- lium ; mantle canal pattern saccate. Dorsal interior with a simple plate-like cardinal process and short, blade-like outward-curving brachiophores embedded in a thick deposit of secondary shell; sockets oblique, notothyrial platform weak, fused with median ridge ; adductor scars quadripartite with smaller posterior pair ; man
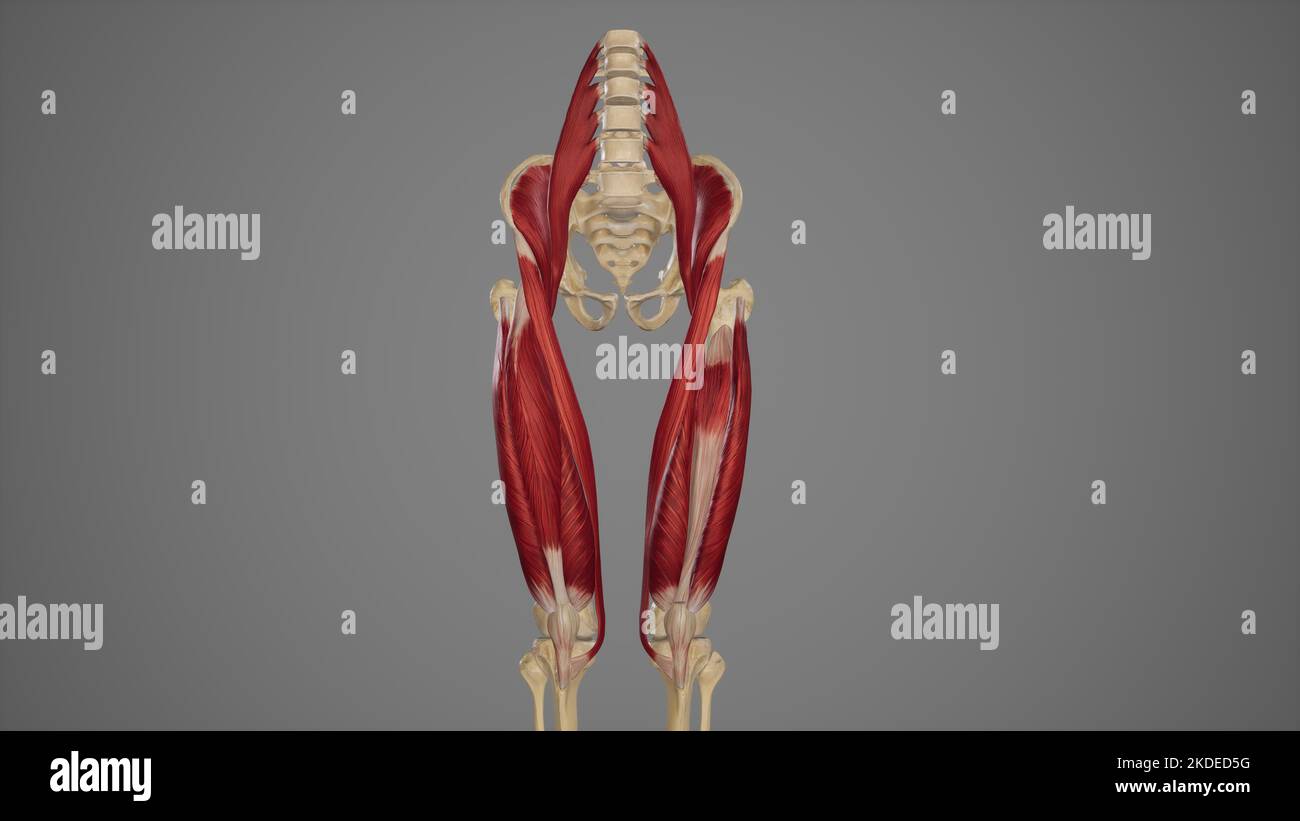 Anterior View of Anterior Thigh Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-view-of-anterior-thigh-muscles-image490198508.html
Anterior View of Anterior Thigh Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-view-of-anterior-thigh-muscles-image490198508.htmlRF2KDED5G–Anterior View of Anterior Thigh Muscles
 . Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College. Zoology. Xylophagainae • Turner 271. Plate 2. Xylophaga gerda Turner n. sp. from Gerda, station 499. Figure 1. Lateral view of holotype showing the attachment of the posterior adductor muscle through the thin valve, the mesoplax that does not extend above the umbos, and the fecal cylinder in the excurrent canal. Figure 2. Dorsal view of the holotype showing the mesoplax. Figure 3. Enlargement of the posterior end of the siphons. Figure 4. Diagrammatic cross-section through the siphons and the fecal cylinder. Figure 5. Three-qu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-museum-of-comparative-zoology-at-harvard-college-zoology-xylophagainae-turner-271-plate-2-xylophaga-gerda-turner-n-sp-from-gerda-station-499-figure-1-lateral-view-of-holotype-showing-the-attachment-of-the-posterior-adductor-muscle-through-the-thin-valve-the-mesoplax-that-does-not-extend-above-the-umbos-and-the-fecal-cylinder-in-the-excurrent-canal-figure-2-dorsal-view-of-the-holotype-showing-the-mesoplax-figure-3-enlargement-of-the-posterior-end-of-the-siphons-figure-4-diagrammatic-cross-section-through-the-siphons-and-the-fecal-cylinder-figure-5-three-qu-image233861290.html
. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College. Zoology. Xylophagainae • Turner 271. Plate 2. Xylophaga gerda Turner n. sp. from Gerda, station 499. Figure 1. Lateral view of holotype showing the attachment of the posterior adductor muscle through the thin valve, the mesoplax that does not extend above the umbos, and the fecal cylinder in the excurrent canal. Figure 2. Dorsal view of the holotype showing the mesoplax. Figure 3. Enlargement of the posterior end of the siphons. Figure 4. Diagrammatic cross-section through the siphons and the fecal cylinder. Figure 5. Three-qu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-museum-of-comparative-zoology-at-harvard-college-zoology-xylophagainae-turner-271-plate-2-xylophaga-gerda-turner-n-sp-from-gerda-station-499-figure-1-lateral-view-of-holotype-showing-the-attachment-of-the-posterior-adductor-muscle-through-the-thin-valve-the-mesoplax-that-does-not-extend-above-the-umbos-and-the-fecal-cylinder-in-the-excurrent-canal-figure-2-dorsal-view-of-the-holotype-showing-the-mesoplax-figure-3-enlargement-of-the-posterior-end-of-the-siphons-figure-4-diagrammatic-cross-section-through-the-siphons-and-the-fecal-cylinder-figure-5-three-qu-image233861290.htmlRMRGD8CX–. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College. Zoology. Xylophagainae • Turner 271. Plate 2. Xylophaga gerda Turner n. sp. from Gerda, station 499. Figure 1. Lateral view of holotype showing the attachment of the posterior adductor muscle through the thin valve, the mesoplax that does not extend above the umbos, and the fecal cylinder in the excurrent canal. Figure 2. Dorsal view of the holotype showing the mesoplax. Figure 3. Enlargement of the posterior end of the siphons. Figure 4. Diagrammatic cross-section through the siphons and the fecal cylinder. Figure 5. Three-qu
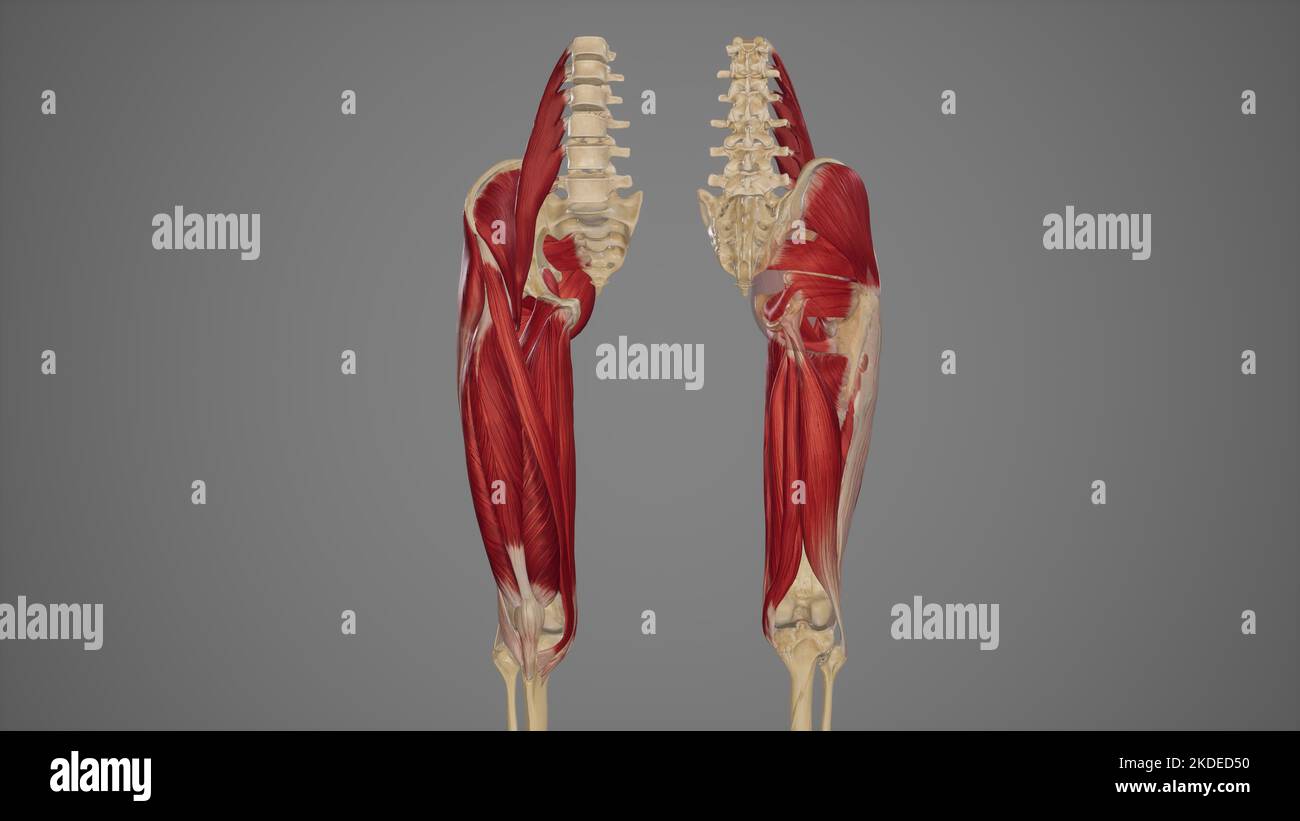 Anterior and Posterior View of Thigh Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-and-posterior-view-of-thigh-muscles-image490198492.html
Anterior and Posterior View of Thigh Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-and-posterior-view-of-thigh-muscles-image490198492.htmlRF2KDED50–Anterior and Posterior View of Thigh Muscles
 . Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. P Adduftor iongui ⢠â npHyseal urfacr f pubis /'iftjormi^ ( orcvecus Ice trochanter Sacrotahrrvus ligament rifr. 29Q. dductor opening. Tendon of adductor magnus Semimembranosus Obturator canal hiternal intermuscular septum Sartorial bursa â .serine bursa. icral cam: icrotuberous Uganienl tig. 300. Fis. 29S.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-p-adduftor-iongui-nphyseal-urfacr-f-pubis-iftjormi-orcvecus-ice-trochanter-sacrotahrrvus-ligament-rifr-29q-dductor-opening-tendon-of-adductor-magnus-semimembranosus-obturator-canal-hiternal-intermuscular-septum-sartorial-bursa-serine-bursa-icral-cam-icrotuberous-uganienl-tig-300-fis-29s-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-work-sobotta-image235393371.html
. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. P Adduftor iongui ⢠â npHyseal urfacr f pubis /'iftjormi^ ( orcvecus Ice trochanter Sacrotahrrvus ligament rifr. 29Q. dductor opening. Tendon of adductor magnus Semimembranosus Obturator canal hiternal intermuscular septum Sartorial bursa â .serine bursa. icral cam: icrotuberous Uganienl tig. 300. Fis. 29S.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-p-adduftor-iongui-nphyseal-urfacr-f-pubis-iftjormi-orcvecus-ice-trochanter-sacrotahrrvus-ligament-rifr-29q-dductor-opening-tendon-of-adductor-magnus-semimembranosus-obturator-canal-hiternal-intermuscular-septum-sartorial-bursa-serine-bursa-icral-cam-icrotuberous-uganienl-tig-300-fis-29s-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-work-sobotta-image235393371.htmlRMRJY2J3–. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. P Adduftor iongui ⢠â npHyseal urfacr f pubis /'iftjormi^ ( orcvecus Ice trochanter Sacrotahrrvus ligament rifr. 29Q. dductor opening. Tendon of adductor magnus Semimembranosus Obturator canal hiternal intermuscular septum Sartorial bursa â .serine bursa. icral cam: icrotuberous Uganienl tig. 300. Fis. 29S.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta
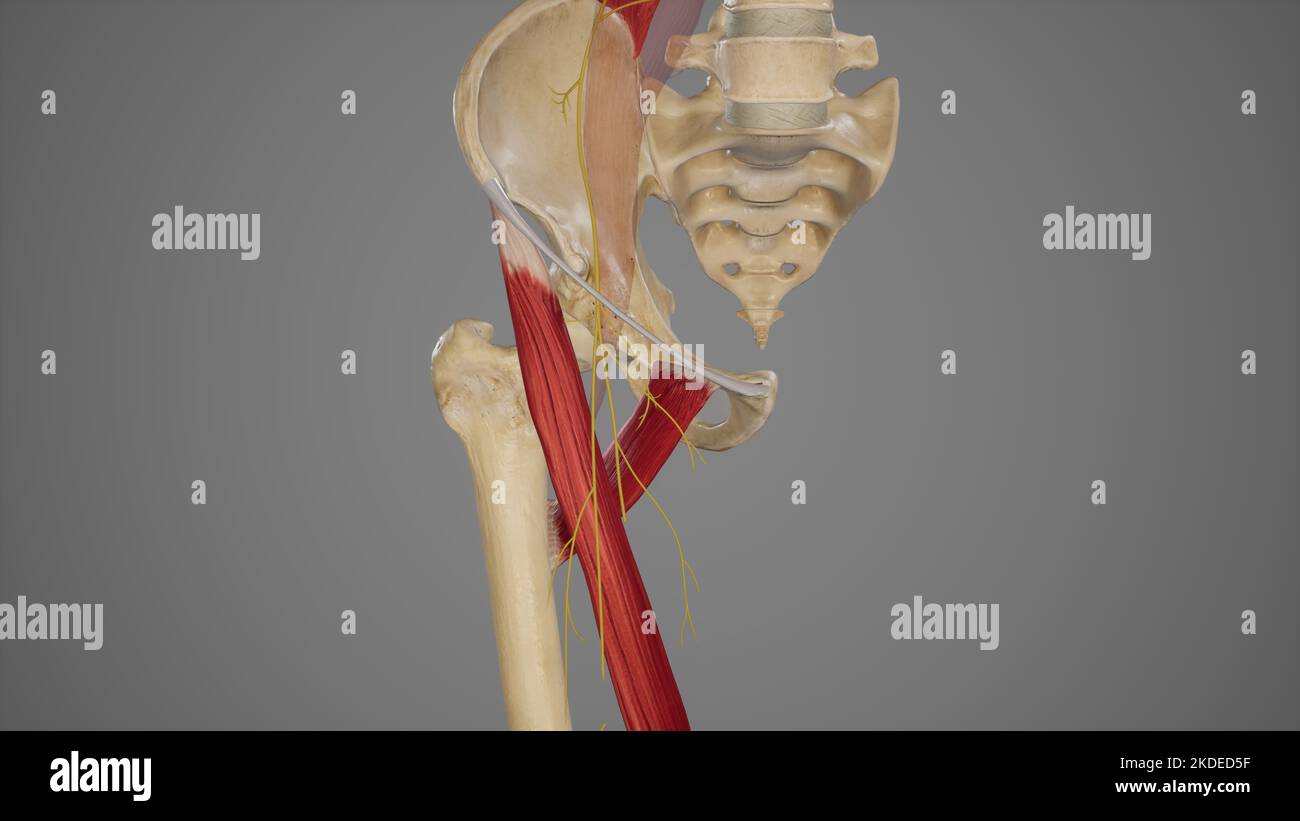 Branches of Anterior Division of Femoral Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/branches-of-anterior-division-of-femoral-nerve-image490198507.html
Branches of Anterior Division of Femoral Nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/branches-of-anterior-division-of-femoral-nerve-image490198507.htmlRF2KDED5F–Branches of Anterior Division of Femoral Nerve
 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY 357 Pectineus muscle Obturator canal I Canalis obturatorius Obturator extemus muscle Iliopsoas muscle Pectineus muscle — Adductor brevis muscle Subcrureus muscle M. articularis genu Vastus intemus muscle M. vastus medialis. Adductor longus muscle -Adductor brevis muscle -Inferior or descending ramus of the pubis Ramus inferior ossis pubis Quadratus femoris muscle Adductor brevis muscle Adductor magnus muscle Adductor longus muscle Openmg in the adductor magnus muscle through which the femoral v Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-muscles-of-the-lower-extremity-357-pectineus-muscle-obturator-canal-i-canalis-obturatorius-obturator-extemus-muscle-iliopsoas-muscle-pectineus-muscle-adductor-brevis-muscle-subcrureus-muscle-m-articularis-genu-vastus-intemus-muscle-m-vastus-medialis-adductor-longus-muscle-adductor-brevis-muscle-inferior-or-descending-ramus-of-the-pubis-ramus-inferior-ossis-pubis-quadratus-femoris-muscle-adductor-brevis-muscle-adductor-magnus-muscle-adductor-longus-muscle-openmg-in-the-adductor-magnus-muscle-through-which-the-femoral-v-image235399731.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY 357 Pectineus muscle Obturator canal I Canalis obturatorius Obturator extemus muscle Iliopsoas muscle Pectineus muscle — Adductor brevis muscle Subcrureus muscle M. articularis genu Vastus intemus muscle M. vastus medialis. Adductor longus muscle -Adductor brevis muscle -Inferior or descending ramus of the pubis Ramus inferior ossis pubis Quadratus femoris muscle Adductor brevis muscle Adductor magnus muscle Adductor longus muscle Openmg in the adductor magnus muscle through which the femoral v Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-muscles-of-the-lower-extremity-357-pectineus-muscle-obturator-canal-i-canalis-obturatorius-obturator-extemus-muscle-iliopsoas-muscle-pectineus-muscle-adductor-brevis-muscle-subcrureus-muscle-m-articularis-genu-vastus-intemus-muscle-m-vastus-medialis-adductor-longus-muscle-adductor-brevis-muscle-inferior-or-descending-ramus-of-the-pubis-ramus-inferior-ossis-pubis-quadratus-femoris-muscle-adductor-brevis-muscle-adductor-magnus-muscle-adductor-longus-muscle-openmg-in-the-adductor-magnus-muscle-through-which-the-femoral-v-image235399731.htmlRMRJYAN7–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY 357 Pectineus muscle Obturator canal I Canalis obturatorius Obturator extemus muscle Iliopsoas muscle Pectineus muscle — Adductor brevis muscle Subcrureus muscle M. articularis genu Vastus intemus muscle M. vastus medialis. Adductor longus muscle -Adductor brevis muscle -Inferior or descending ramus of the pubis Ramus inferior ossis pubis Quadratus femoris muscle Adductor brevis muscle Adductor magnus muscle Adductor longus muscle Openmg in the adductor magnus muscle through which the femoral v
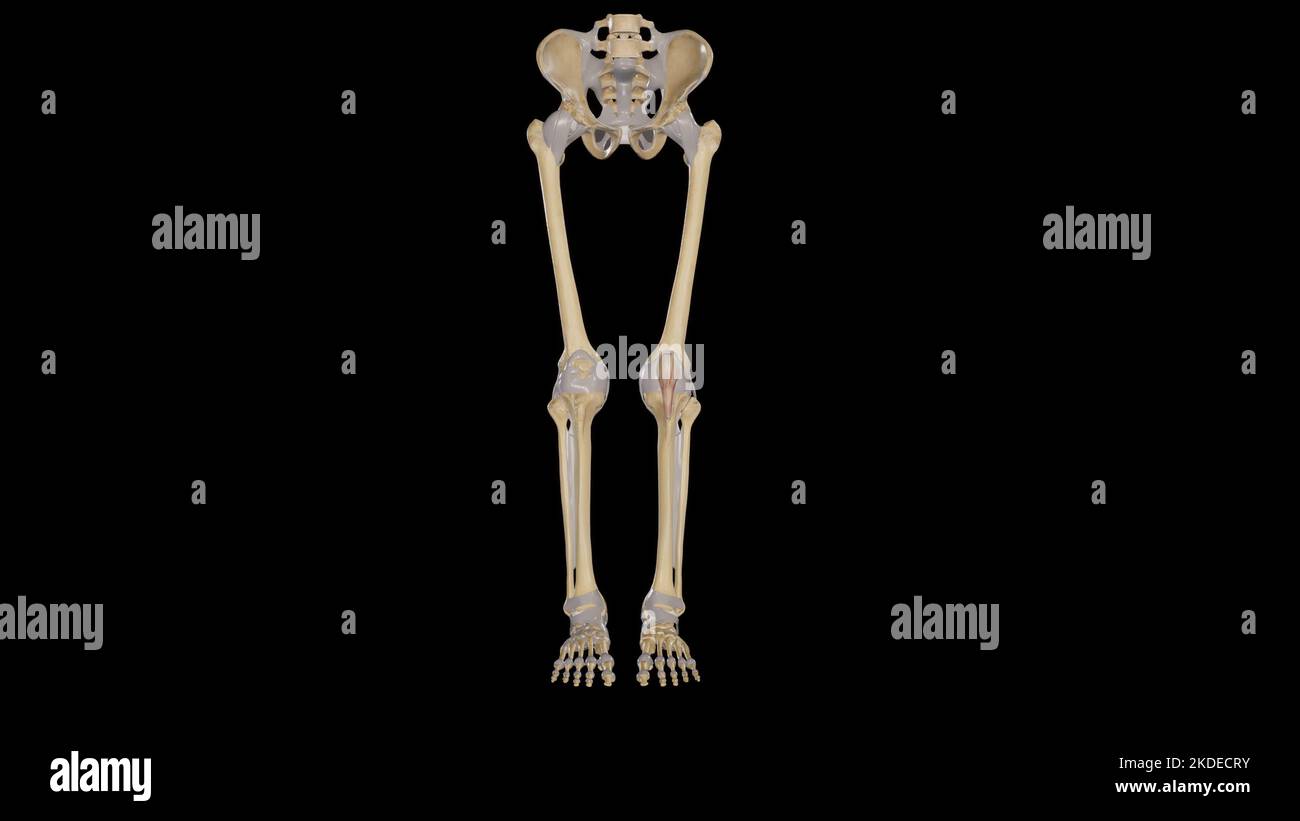 Joints of lower limb anterior view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/joints-of-lower-limb-anterior-view-image490198239.html
Joints of lower limb anterior view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/joints-of-lower-limb-anterior-view-image490198239.htmlRF2KDECRY–Joints of lower limb anterior view
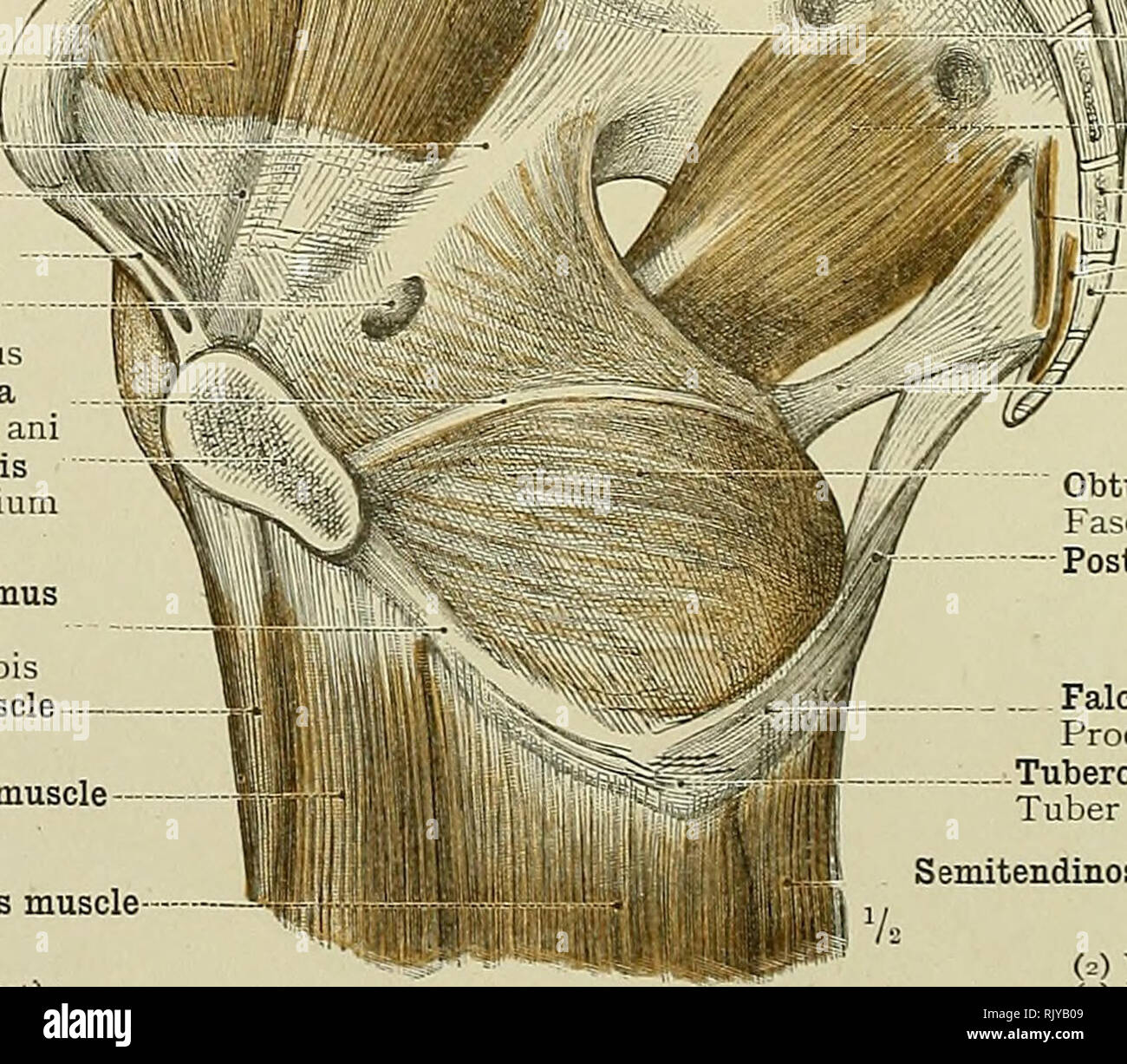 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. 346 THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY Promontory of the sacrum Promontorium Psoas magnus muscle. M. psoas major Iliacus muscle *Linea arcuata' Iliac fascia Fascia iliaca Poupart's ligament (superficial femoral archXi) Obturator canal Canalis obturatorius White line of the pelvic fascia Arcus tendineus m. levatoris am Pubic symphysis Symphysis ossium pubis Inferior or descending ramus of the pubis Ramus inferior ossis pubis Adductor longus muscle - Gracilis muscle Adductor magnus muscle (i) Lig. inguinale (Pouparti. -. Sacro-i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-346-the-muscles-of-the-lower-extremity-promontory-of-the-sacrum-promontorium-psoas-magnus-muscle-m-psoas-major-iliacus-muscle-linea-arcuata-iliac-fascia-fascia-iliaca-pouparts-ligament-superficial-femoral-archxi-obturator-canal-canalis-obturatorius-white-line-of-the-pelvic-fascia-arcus-tendineus-m-levatoris-am-pubic-symphysis-symphysis-ossium-pubis-inferior-or-descending-ramus-of-the-pubis-ramus-inferior-ossis-pubis-adductor-longus-muscle-gracilis-muscle-adductor-magnus-muscle-i-lig-inguinale-pouparti-sacro-i-image235399929.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. 346 THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY Promontory of the sacrum Promontorium Psoas magnus muscle. M. psoas major Iliacus muscle *Linea arcuata' Iliac fascia Fascia iliaca Poupart's ligament (superficial femoral archXi) Obturator canal Canalis obturatorius White line of the pelvic fascia Arcus tendineus m. levatoris am Pubic symphysis Symphysis ossium pubis Inferior or descending ramus of the pubis Ramus inferior ossis pubis Adductor longus muscle - Gracilis muscle Adductor magnus muscle (i) Lig. inguinale (Pouparti. -. Sacro-i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-346-the-muscles-of-the-lower-extremity-promontory-of-the-sacrum-promontorium-psoas-magnus-muscle-m-psoas-major-iliacus-muscle-linea-arcuata-iliac-fascia-fascia-iliaca-pouparts-ligament-superficial-femoral-archxi-obturator-canal-canalis-obturatorius-white-line-of-the-pelvic-fascia-arcus-tendineus-m-levatoris-am-pubic-symphysis-symphysis-ossium-pubis-inferior-or-descending-ramus-of-the-pubis-ramus-inferior-ossis-pubis-adductor-longus-muscle-gracilis-muscle-adductor-magnus-muscle-i-lig-inguinale-pouparti-sacro-i-image235399929.htmlRMRJYB09–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. 346 THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY Promontory of the sacrum Promontorium Psoas magnus muscle. M. psoas major Iliacus muscle *Linea arcuata' Iliac fascia Fascia iliaca Poupart's ligament (superficial femoral archXi) Obturator canal Canalis obturatorius White line of the pelvic fascia Arcus tendineus m. levatoris am Pubic symphysis Symphysis ossium pubis Inferior or descending ramus of the pubis Ramus inferior ossis pubis Adductor longus muscle - Gracilis muscle Adductor magnus muscle (i) Lig. inguinale (Pouparti. -. Sacro-i
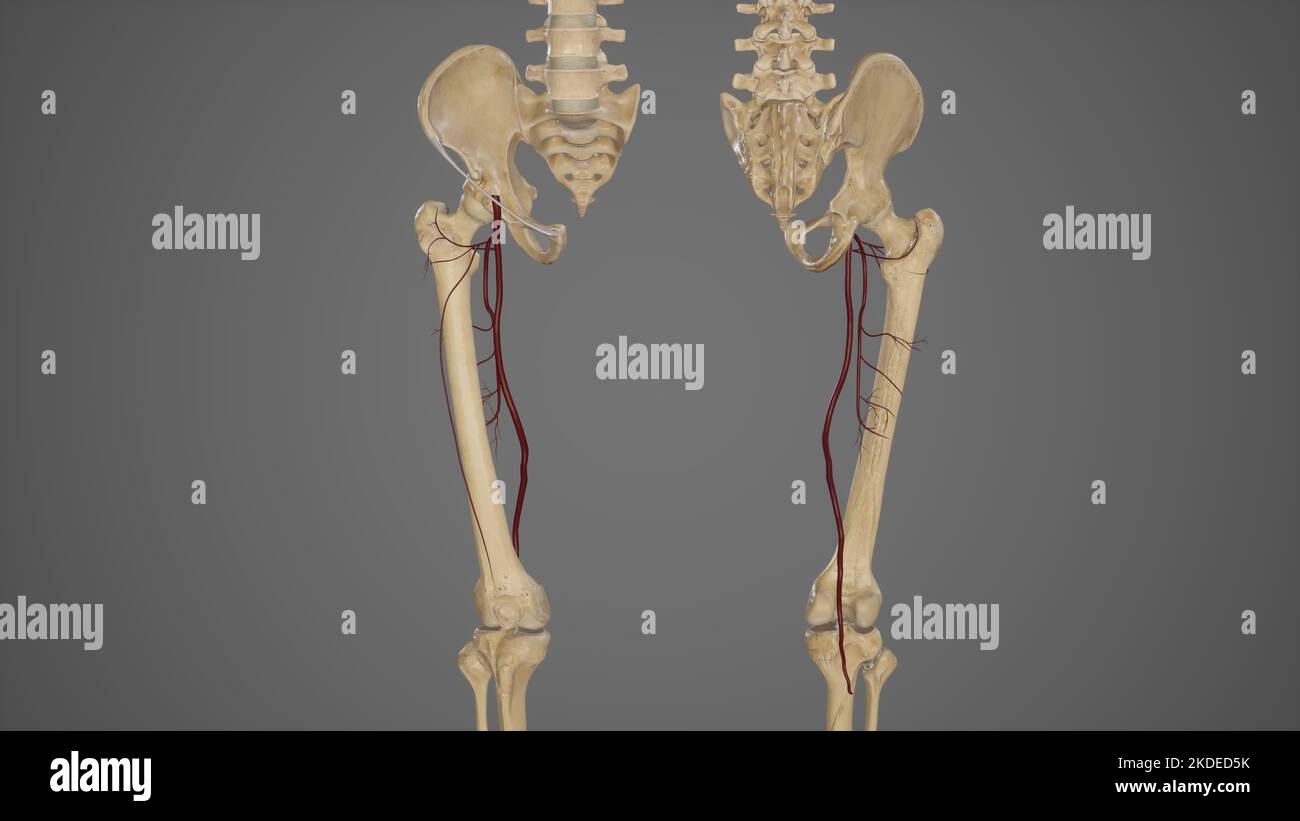 Anterior and Posterior View of Profunda Femoris Artery and Its Branches Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-and-posterior-view-of-profunda-femoris-artery-and-its-branches-image490198511.html
Anterior and Posterior View of Profunda Femoris Artery and Its Branches Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-and-posterior-view-of-profunda-femoris-artery-and-its-branches-image490198511.htmlRF2KDED5K–Anterior and Posterior View of Profunda Femoris Artery and Its Branches
 . Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. H ';a ipsoas ' >bturator externum fF^' V Obturator extern u... P Adduftor iongui ⢠â npHyseal urfacr f pubis /'iftjormi^ ( orcvecus Ice trochanter Sacrotahrrvus ligament rifr. 29Q. dductor opening. Tendon of adductor magnus Semimembranosus Obturator canal hiternal intermuscular septum Sartorial bursa â .serine bursa. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original wo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-h-a-ipsoas-gtbturator-externum-ff-v-obturator-extern-u-p-adduftor-iongui-nphyseal-urfacr-f-pubis-iftjormi-orcvecus-ice-trochanter-sacrotahrrvus-ligament-rifr-29q-dductor-opening-tendon-of-adductor-magnus-semimembranosus-obturator-canal-hiternal-intermuscular-septum-sartorial-bursa-serine-bursa-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-wo-image235393380.html
. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. H ';a ipsoas ' >bturator externum fF^' V Obturator extern u... P Adduftor iongui ⢠â npHyseal urfacr f pubis /'iftjormi^ ( orcvecus Ice trochanter Sacrotahrrvus ligament rifr. 29Q. dductor opening. Tendon of adductor magnus Semimembranosus Obturator canal hiternal intermuscular septum Sartorial bursa â .serine bursa. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original wo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-h-a-ipsoas-gtbturator-externum-ff-v-obturator-extern-u-p-adduftor-iongui-nphyseal-urfacr-f-pubis-iftjormi-orcvecus-ice-trochanter-sacrotahrrvus-ligament-rifr-29q-dductor-opening-tendon-of-adductor-magnus-semimembranosus-obturator-canal-hiternal-intermuscular-septum-sartorial-bursa-serine-bursa-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-wo-image235393380.htmlRMRJY2JC–. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. H ';a ipsoas ' >bturator externum fF^' V Obturator extern u... P Adduftor iongui ⢠â npHyseal urfacr f pubis /'iftjormi^ ( orcvecus Ice trochanter Sacrotahrrvus ligament rifr. 29Q. dductor opening. Tendon of adductor magnus Semimembranosus Obturator canal hiternal intermuscular septum Sartorial bursa â .serine bursa. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original wo
 . Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Geology. . Fig. 5. Mantle canal patterns in the pedicle valve of Eoplectodonta duplicata. The figures are drawn as internal moulds and the adductor muscle scars coloured black, (a) from BB 31990 (Plate 8, figs. 3, 4), Woodland Point, Girvan, (b) from GSM 37579, Plate 8, fig. 7), Gasworks Sandstone, Union Hill, Pembrokeshire, (c) to (f) all from Gasworks Mudstone, the Gasworks, Haverfordwest, Pembrokeshire (c) BB 31753 (Plate 6, fig. 8), (d) and (e) both BB 31732 (Plate 6, fig. 3), (f) BB 31740 (Plate 6, fig. 7). would have been to some degree Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-british-museum-natural-history-geology-fig-5-mantle-canal-patterns-in-the-pedicle-valve-of-eoplectodonta-duplicata-the-figures-are-drawn-as-internal-moulds-and-the-adductor-muscle-scars-coloured-black-a-from-bb-31990-plate-8-figs-3-4-woodland-point-girvan-b-from-gsm-37579-plate-8-fig-7-gasworks-sandstone-union-hill-pembrokeshire-c-to-f-all-from-gasworks-mudstone-the-gasworks-haverfordwest-pembrokeshire-c-bb-31753-plate-6-fig-8-d-and-e-both-bb-31732-plate-6-fig-3-f-bb-31740-plate-6-fig-7-would-have-been-to-some-degree-image233983507.html
. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Geology. . Fig. 5. Mantle canal patterns in the pedicle valve of Eoplectodonta duplicata. The figures are drawn as internal moulds and the adductor muscle scars coloured black, (a) from BB 31990 (Plate 8, figs. 3, 4), Woodland Point, Girvan, (b) from GSM 37579, Plate 8, fig. 7), Gasworks Sandstone, Union Hill, Pembrokeshire, (c) to (f) all from Gasworks Mudstone, the Gasworks, Haverfordwest, Pembrokeshire (c) BB 31753 (Plate 6, fig. 8), (d) and (e) both BB 31732 (Plate 6, fig. 3), (f) BB 31740 (Plate 6, fig. 7). would have been to some degree Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-british-museum-natural-history-geology-fig-5-mantle-canal-patterns-in-the-pedicle-valve-of-eoplectodonta-duplicata-the-figures-are-drawn-as-internal-moulds-and-the-adductor-muscle-scars-coloured-black-a-from-bb-31990-plate-8-figs-3-4-woodland-point-girvan-b-from-gsm-37579-plate-8-fig-7-gasworks-sandstone-union-hill-pembrokeshire-c-to-f-all-from-gasworks-mudstone-the-gasworks-haverfordwest-pembrokeshire-c-bb-31753-plate-6-fig-8-d-and-e-both-bb-31732-plate-6-fig-3-f-bb-31740-plate-6-fig-7-would-have-been-to-some-degree-image233983507.htmlRMRGJT9R–. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Geology. . Fig. 5. Mantle canal patterns in the pedicle valve of Eoplectodonta duplicata. The figures are drawn as internal moulds and the adductor muscle scars coloured black, (a) from BB 31990 (Plate 8, figs. 3, 4), Woodland Point, Girvan, (b) from GSM 37579, Plate 8, fig. 7), Gasworks Sandstone, Union Hill, Pembrokeshire, (c) to (f) all from Gasworks Mudstone, the Gasworks, Haverfordwest, Pembrokeshire (c) BB 31753 (Plate 6, fig. 8), (d) and (e) both BB 31732 (Plate 6, fig. 3), (f) BB 31740 (Plate 6, fig. 7). would have been to some degree
 . A course of practical instruction in elementary biology. Biology. INDEX. L»J. A. ABDUCENTES, nervi, 189 Acetabulum, 224 Acrogenous growth, 47 Adductor muscles, 108, 116, 123 Alse, 84 Alcoholic fermentation, 5, 9, 10 Algce, 48 Alimentary canal, of Anodonta, no, 121; of Crayfish, 131, 148; of Frog, 167, 173, 205; of Lob- ster, 131, 148; of Tadpole, 163 Alinasal process, 171 Alternation of generations, 37, 47, 61 Ambulatory limbs, 129, 151 Amoeba, 17 ; Laboratory work, 21 Amoeboid movements, 20, 105 Anacharis, protoplasmic move- ments in, 54 Angulo-splenial, 220 Annulus, 66 Anodonta cygncza, 10 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-course-of-practical-instruction-in-elementary-biology-biology-index-lj-a-abducentes-nervi-189-acetabulum-224-acrogenous-growth-47-adductor-muscles-108-116-123-alse-84-alcoholic-fermentation-5-9-10-algce-48-alimentary-canal-of-anodonta-no-121-of-crayfish-131-148-of-frog-167-173-205-of-lob-ster-131-148-of-tadpole-163-alinasal-process-171-alternation-of-generations-37-47-61-ambulatory-limbs-129-151-amoeba-17-laboratory-work-21-amoeboid-movements-20-105-anacharis-protoplasmic-move-ments-in-54-angulo-splenial-220-annulus-66-anodonta-cygncza-10-image232496867.html
. A course of practical instruction in elementary biology. Biology. INDEX. L»J. A. ABDUCENTES, nervi, 189 Acetabulum, 224 Acrogenous growth, 47 Adductor muscles, 108, 116, 123 Alse, 84 Alcoholic fermentation, 5, 9, 10 Algce, 48 Alimentary canal, of Anodonta, no, 121; of Crayfish, 131, 148; of Frog, 167, 173, 205; of Lob- ster, 131, 148; of Tadpole, 163 Alinasal process, 171 Alternation of generations, 37, 47, 61 Ambulatory limbs, 129, 151 Amoeba, 17 ; Laboratory work, 21 Amoeboid movements, 20, 105 Anacharis, protoplasmic move- ments in, 54 Angulo-splenial, 220 Annulus, 66 Anodonta cygncza, 10 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-course-of-practical-instruction-in-elementary-biology-biology-index-lj-a-abducentes-nervi-189-acetabulum-224-acrogenous-growth-47-adductor-muscles-108-116-123-alse-84-alcoholic-fermentation-5-9-10-algce-48-alimentary-canal-of-anodonta-no-121-of-crayfish-131-148-of-frog-167-173-205-of-lob-ster-131-148-of-tadpole-163-alinasal-process-171-alternation-of-generations-37-47-61-ambulatory-limbs-129-151-amoeba-17-laboratory-work-21-amoeboid-movements-20-105-anacharis-protoplasmic-move-ments-in-54-angulo-splenial-220-annulus-66-anodonta-cygncza-10-image232496867.htmlRMRE743F–. A course of practical instruction in elementary biology. Biology. INDEX. L»J. A. ABDUCENTES, nervi, 189 Acetabulum, 224 Acrogenous growth, 47 Adductor muscles, 108, 116, 123 Alse, 84 Alcoholic fermentation, 5, 9, 10 Algce, 48 Alimentary canal, of Anodonta, no, 121; of Crayfish, 131, 148; of Frog, 167, 173, 205; of Lob- ster, 131, 148; of Tadpole, 163 Alinasal process, 171 Alternation of generations, 37, 47, 61 Ambulatory limbs, 129, 151 Amoeba, 17 ; Laboratory work, 21 Amoeboid movements, 20, 105 Anacharis, protoplasmic move- ments in, 54 Angulo-splenial, 220 Annulus, 66 Anodonta cygncza, 10