Quick filters:
Brain inferior view Stock Photos and Images
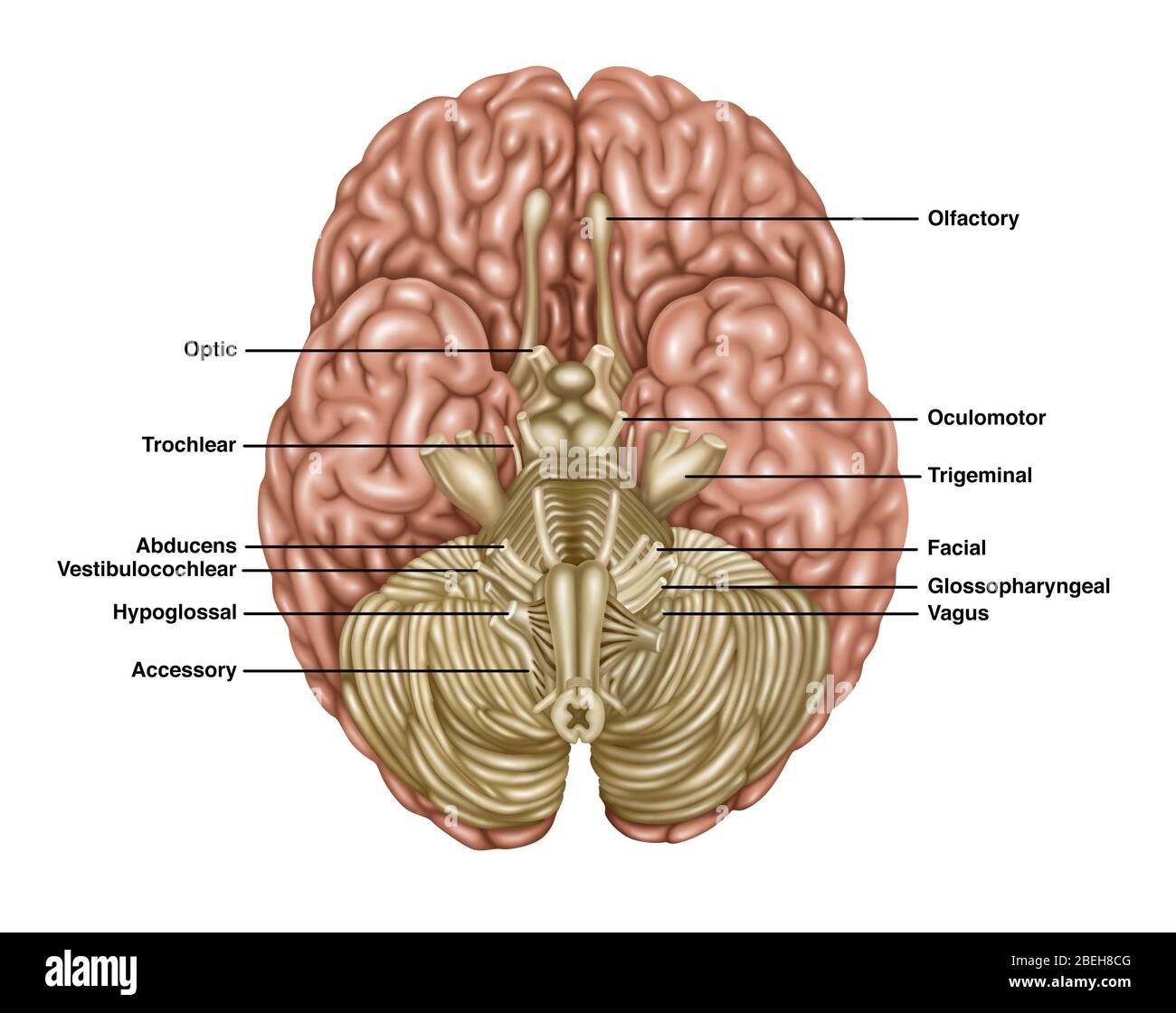 Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192352.html
Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192352.htmlRF2BEH8CG–Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration
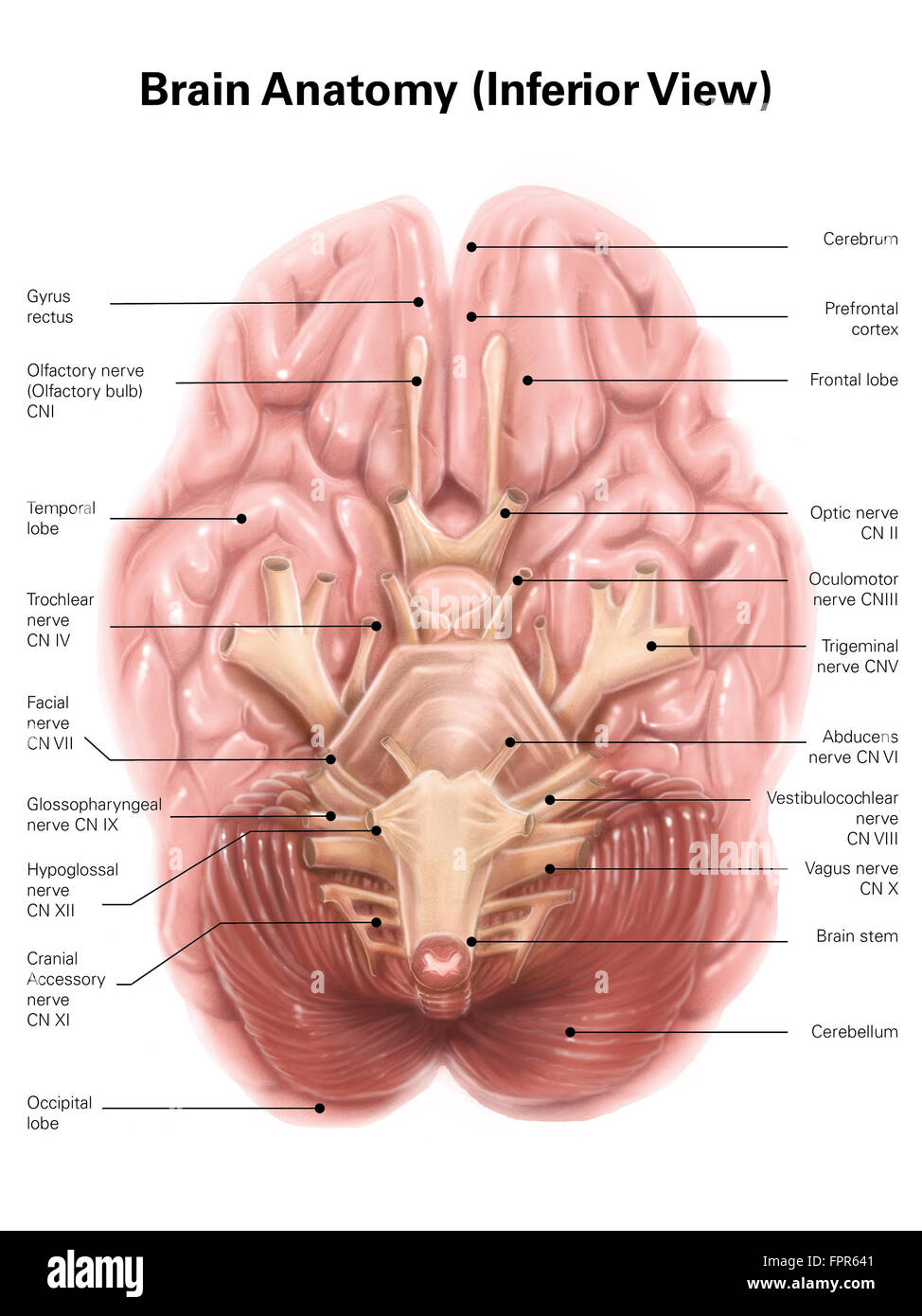 Anatomy of human brain, inferior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomy-of-human-brain-inferior-view-100083985.html
Anatomy of human brain, inferior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomy-of-human-brain-inferior-view-100083985.htmlRFFPR641–Anatomy of human brain, inferior view.
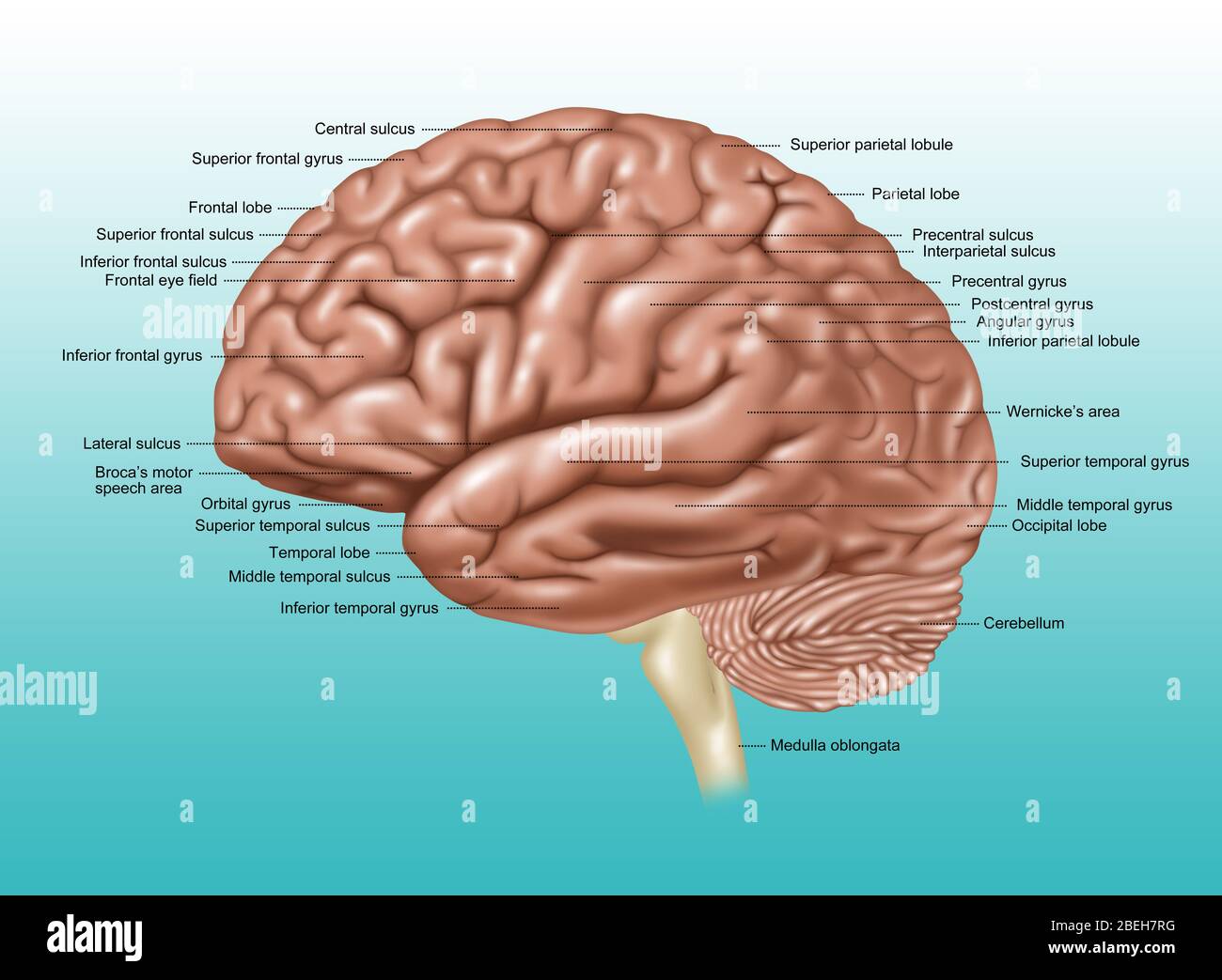
 Part of the central nervous system enclosed in the skull, consisting of the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem; it is responsible for sensory perception, most movements, memory, language, reflexes and vital functions. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/part-of-the-central-nervous-system-enclosed-in-the-skull-consisting-image156173606.html
Part of the central nervous system enclosed in the skull, consisting of the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem; it is responsible for sensory perception, most movements, memory, language, reflexes and vital functions. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/part-of-the-central-nervous-system-enclosed-in-the-skull-consisting-image156173606.htmlRMK2290P–Part of the central nervous system enclosed in the skull, consisting of the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem; it is responsible for sensory perception, most movements, memory, language, reflexes and vital functions.
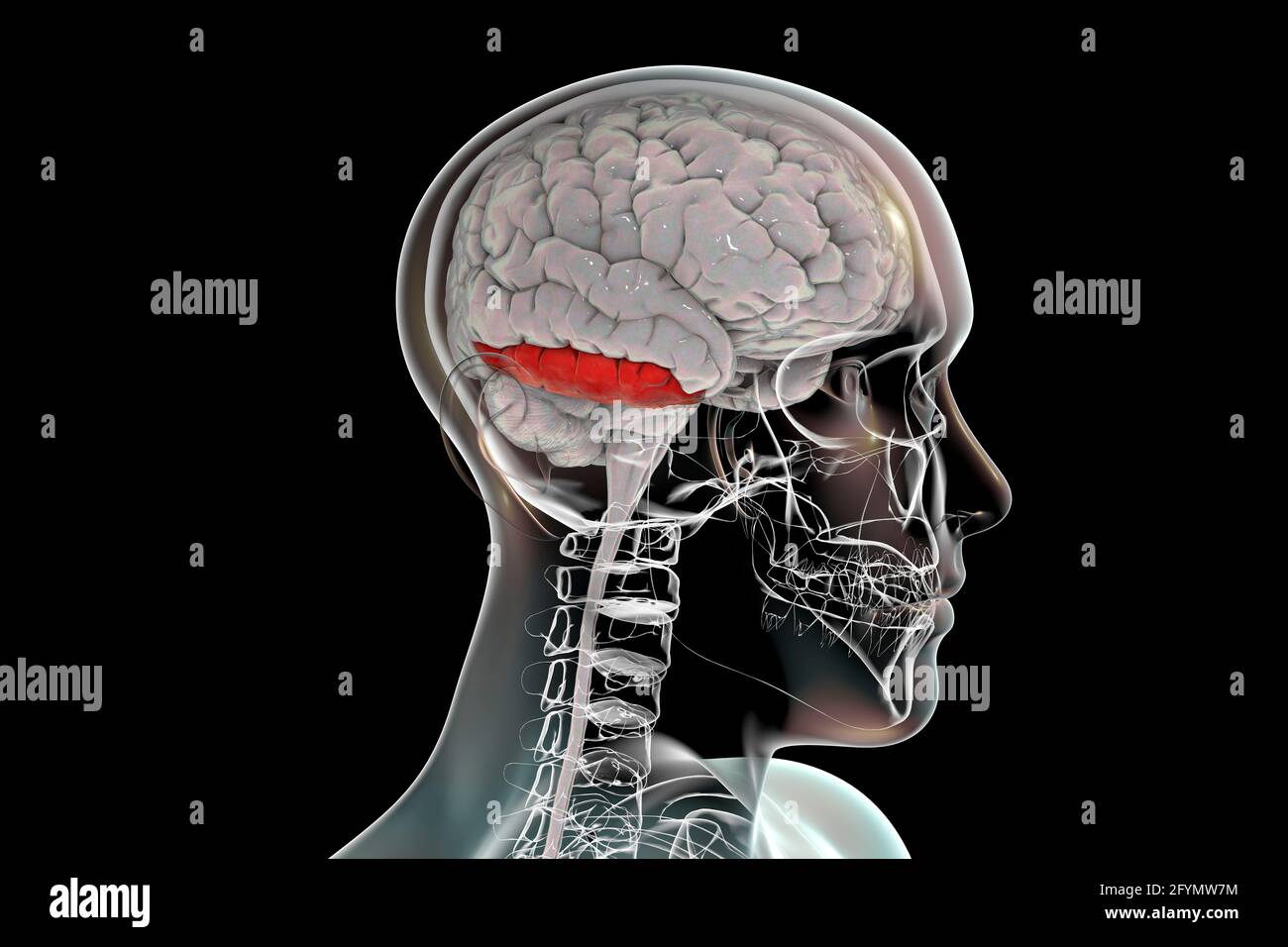 Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-temporal-gyrus-illustration-image430103400.html
Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-temporal-gyrus-illustration-image430103400.htmlRF2FYMW7M–Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration
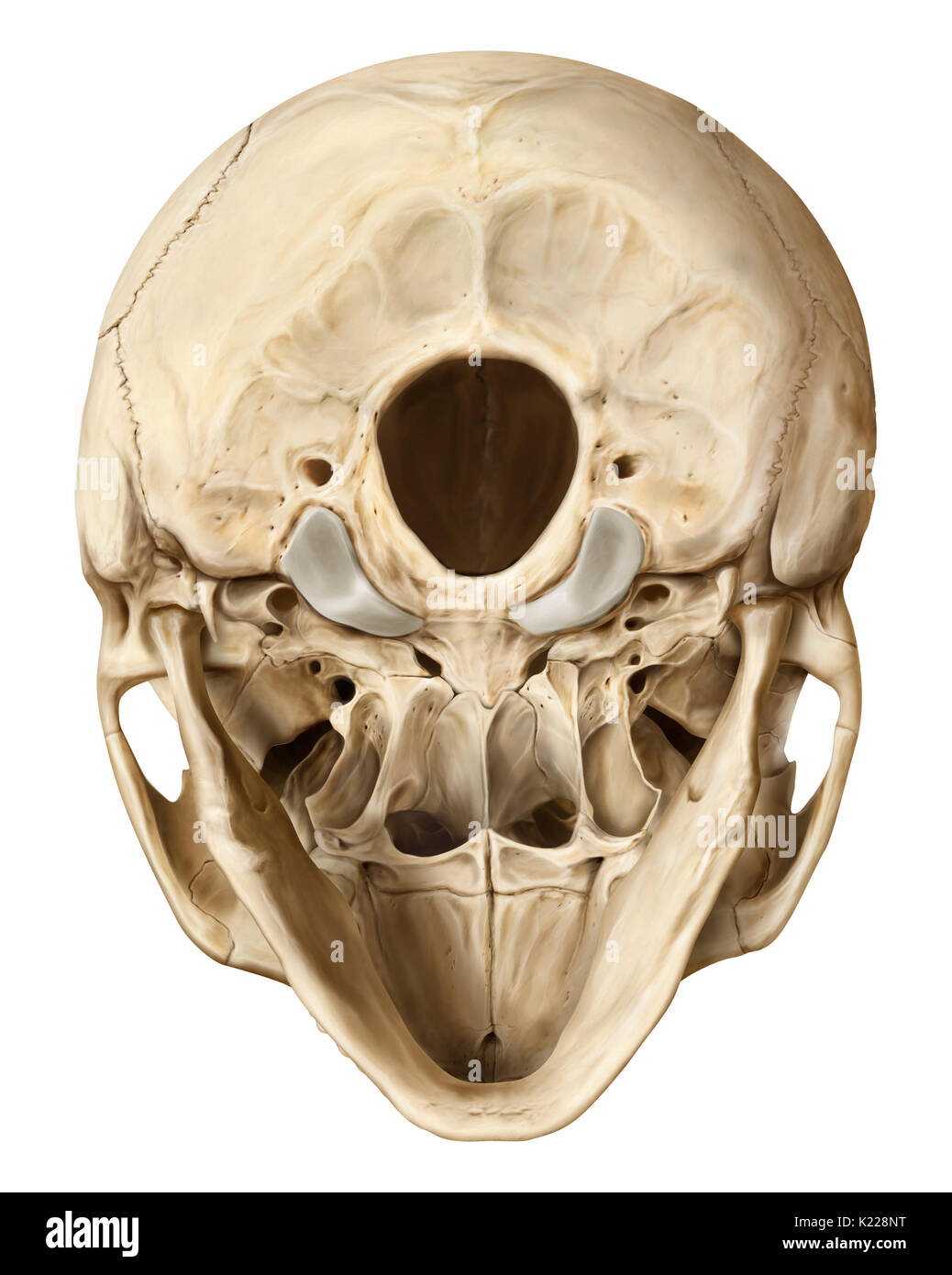 Bony structure formed of eight bones (four even bones and four odd bones) covering and protecting the brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bony-structure-formed-of-eight-bones-four-even-bones-and-four-odd-image156173412.html
Bony structure formed of eight bones (four even bones and four odd bones) covering and protecting the brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bony-structure-formed-of-eight-bones-four-even-bones-and-four-odd-image156173412.htmlRMK228NT–Bony structure formed of eight bones (four even bones and four odd bones) covering and protecting the brain.
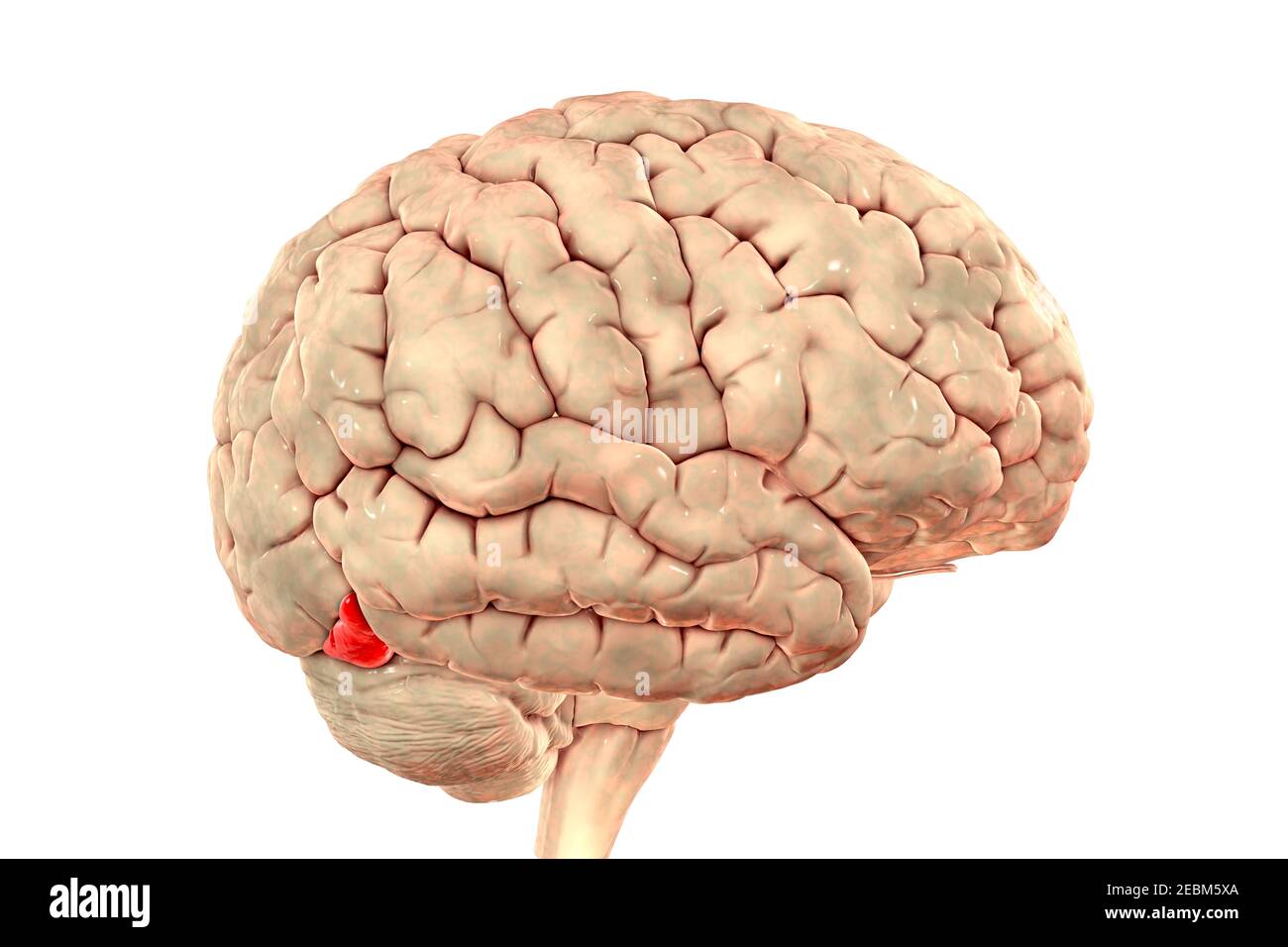
 Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043417.html
Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043417.htmlRF2EBM5YN–Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration
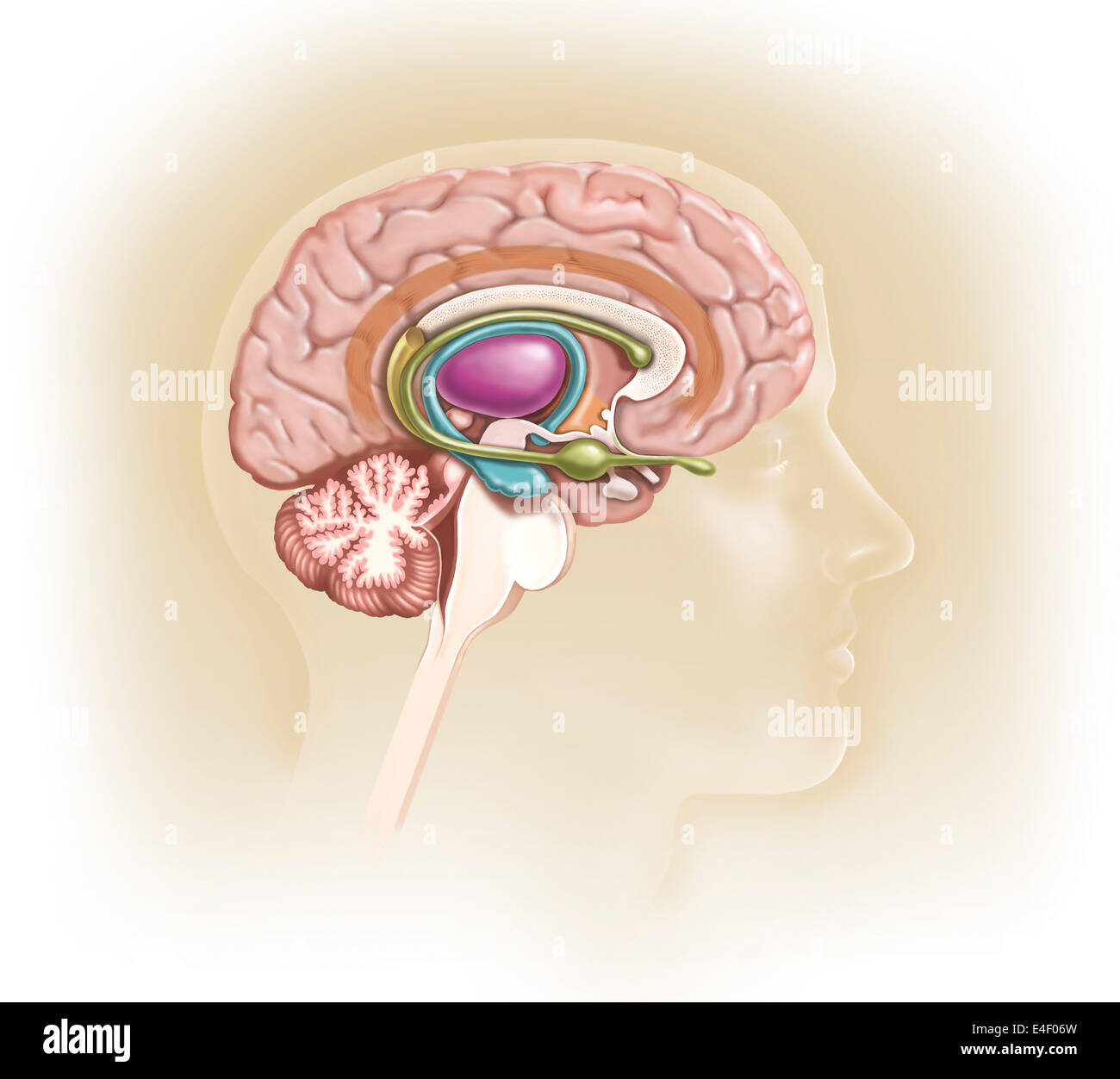 Sagittal view of human brain showing the limbic system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-sagittal-view-of-human-brain-showing-the-limbic-system-71629569.html
Sagittal view of human brain showing the limbic system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-sagittal-view-of-human-brain-showing-the-limbic-system-71629569.htmlRME4F06W–Sagittal view of human brain showing the limbic system.
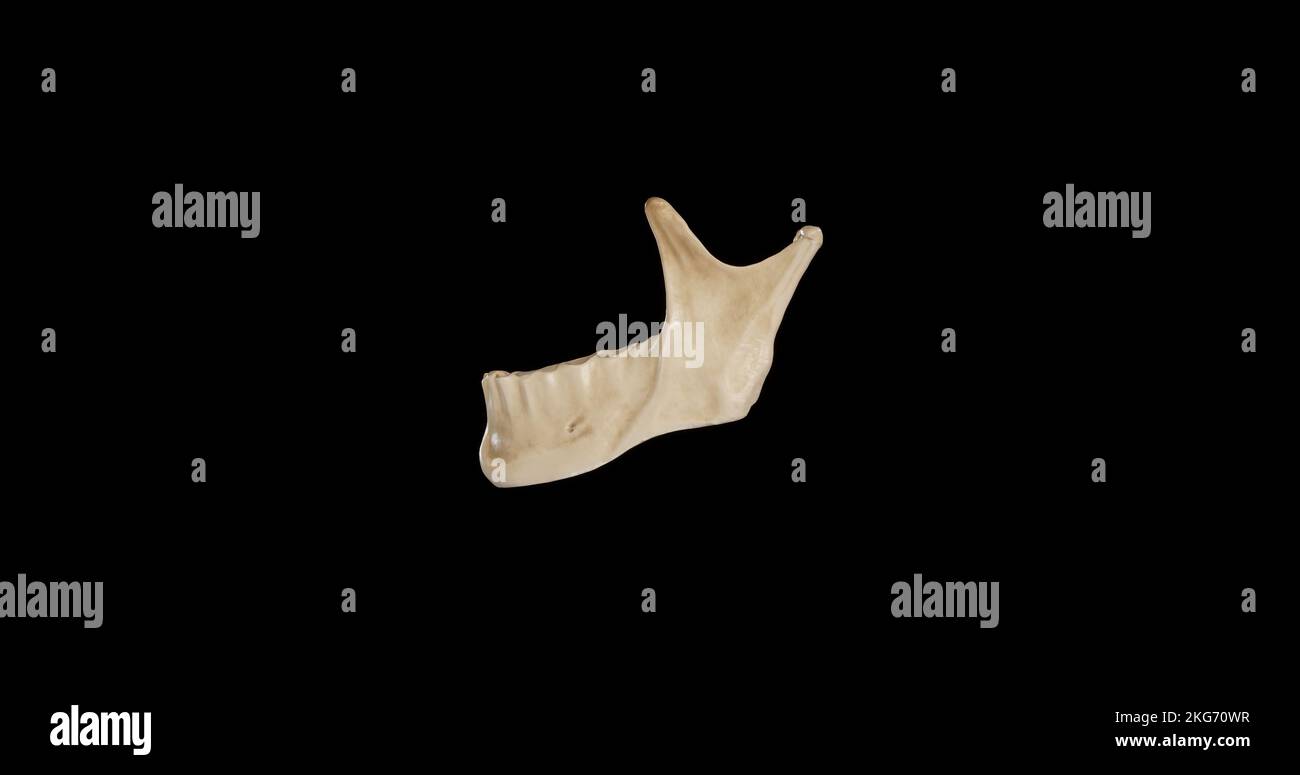
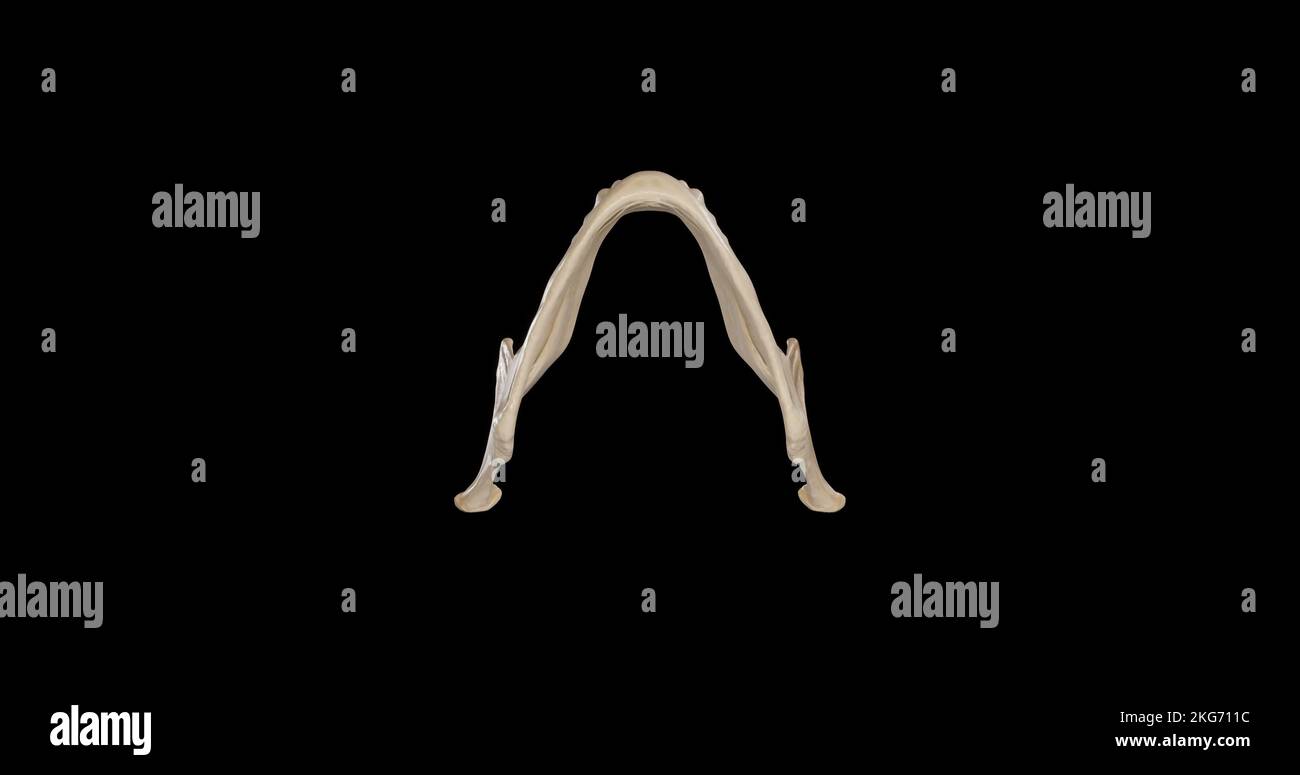 Inferior view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-mandible-image491879288.html
Inferior view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-mandible-image491879288.htmlRF2KG711C–Inferior view of Mandible
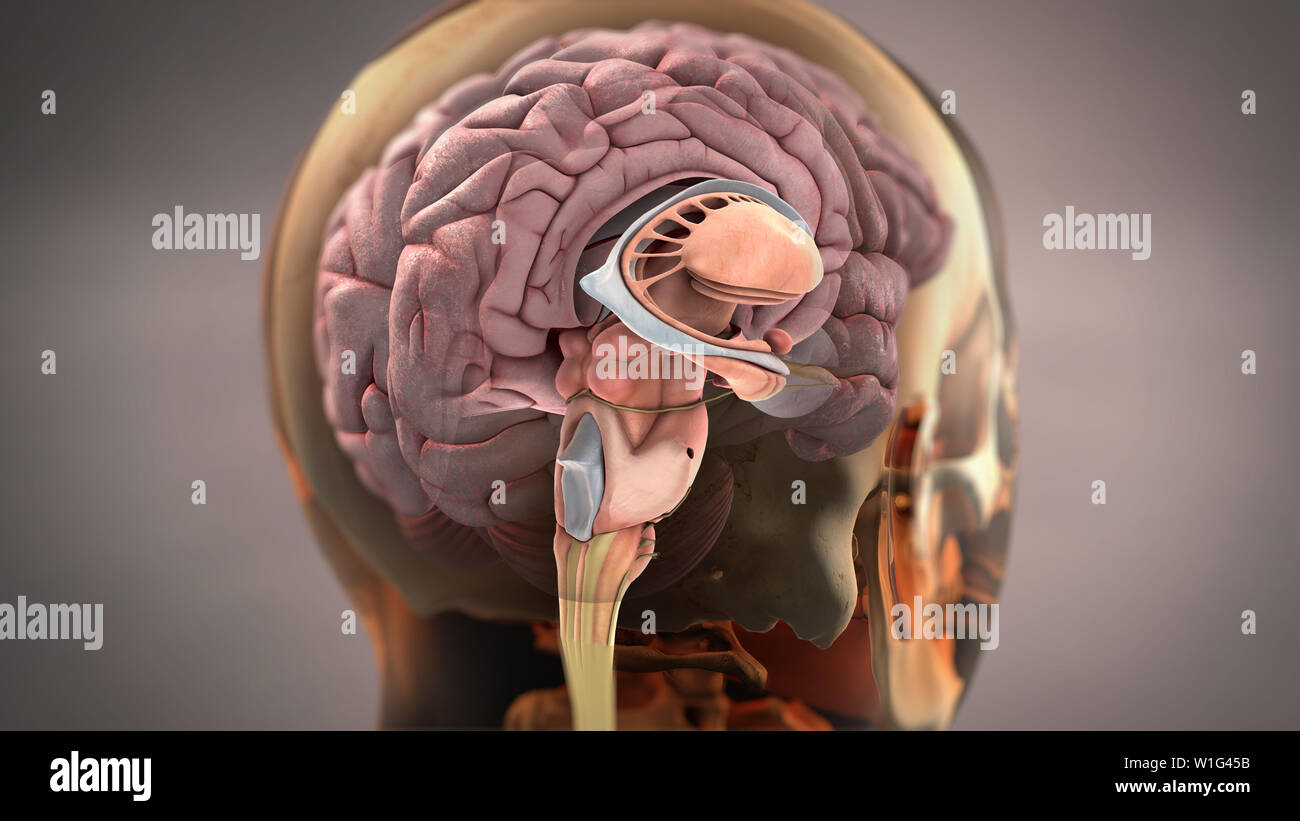 Brain Sagittal View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-sagittal-view-image259124695.html
Brain Sagittal View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-sagittal-view-image259124695.htmlRFW1G45B–Brain Sagittal View
 Inferior view of the brain and its blood supply. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-inferior-view-of-the-brain-and-its-blood-supply-52095741.html
Inferior view of the brain and its blood supply. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-inferior-view-of-the-brain-and-its-blood-supply-52095741.htmlRMD0N4J5–Inferior view of the brain and its blood supply.
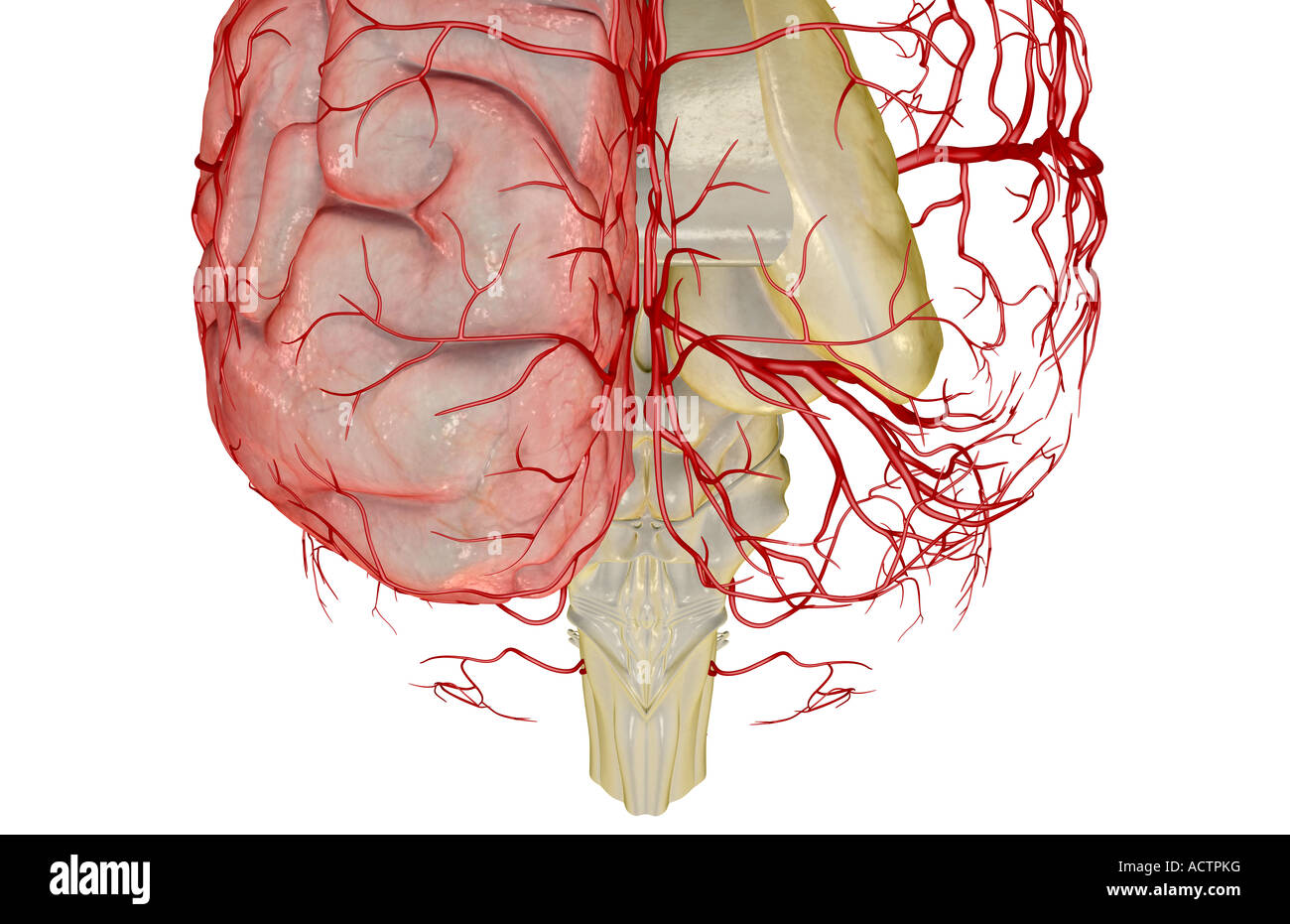 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13228995.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13228995.htmlRFACTPKG–The arteries of the brain
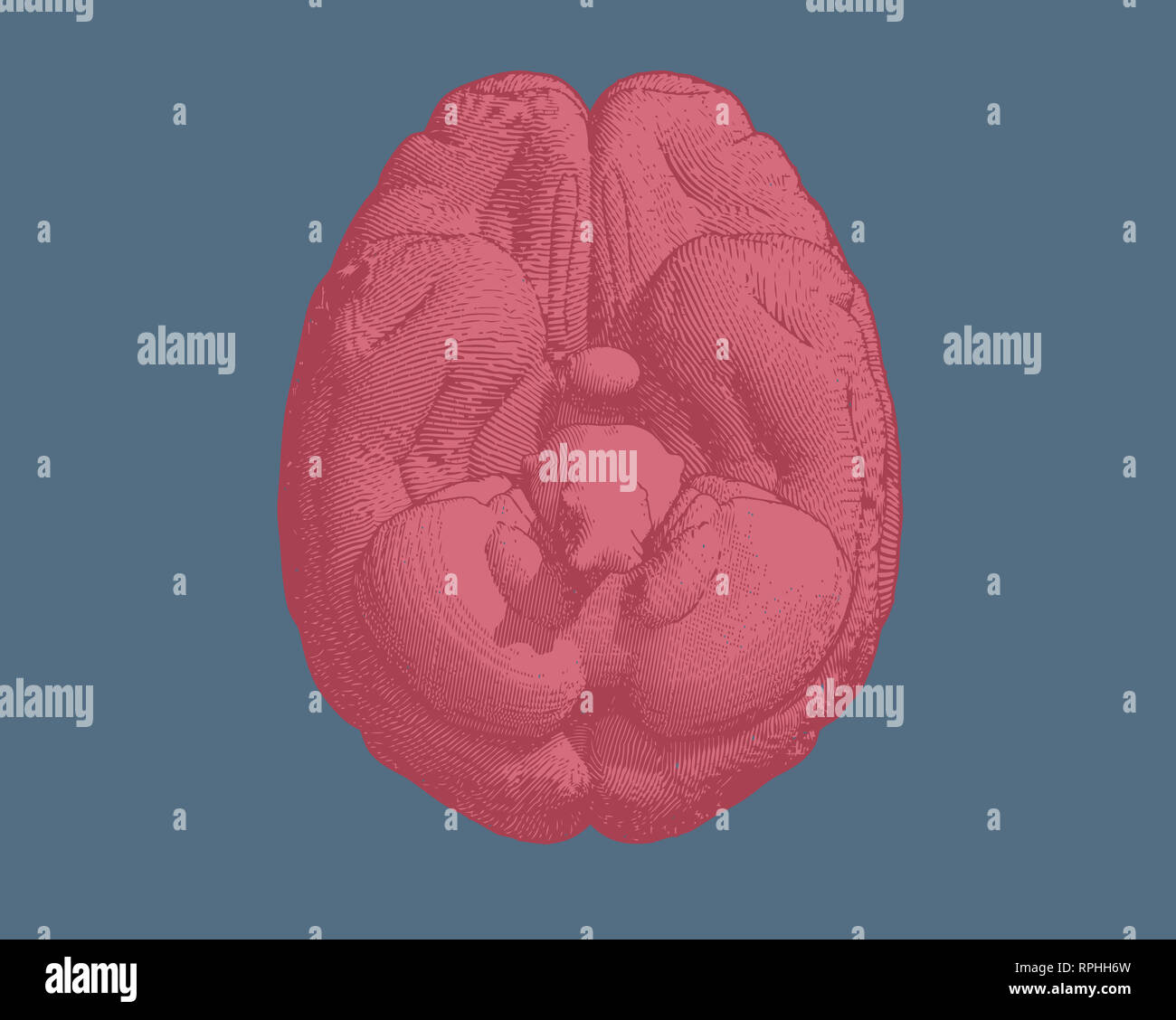 Pink engraving brain inferior view illustration isolated on blue Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pink-engraving-brain-inferior-view-illustration-isolated-on-blue-image237643921.html
Pink engraving brain inferior view illustration isolated on blue Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pink-engraving-brain-inferior-view-illustration-isolated-on-blue-image237643921.htmlRFRPHH6W–Pink engraving brain inferior view illustration isolated on blue
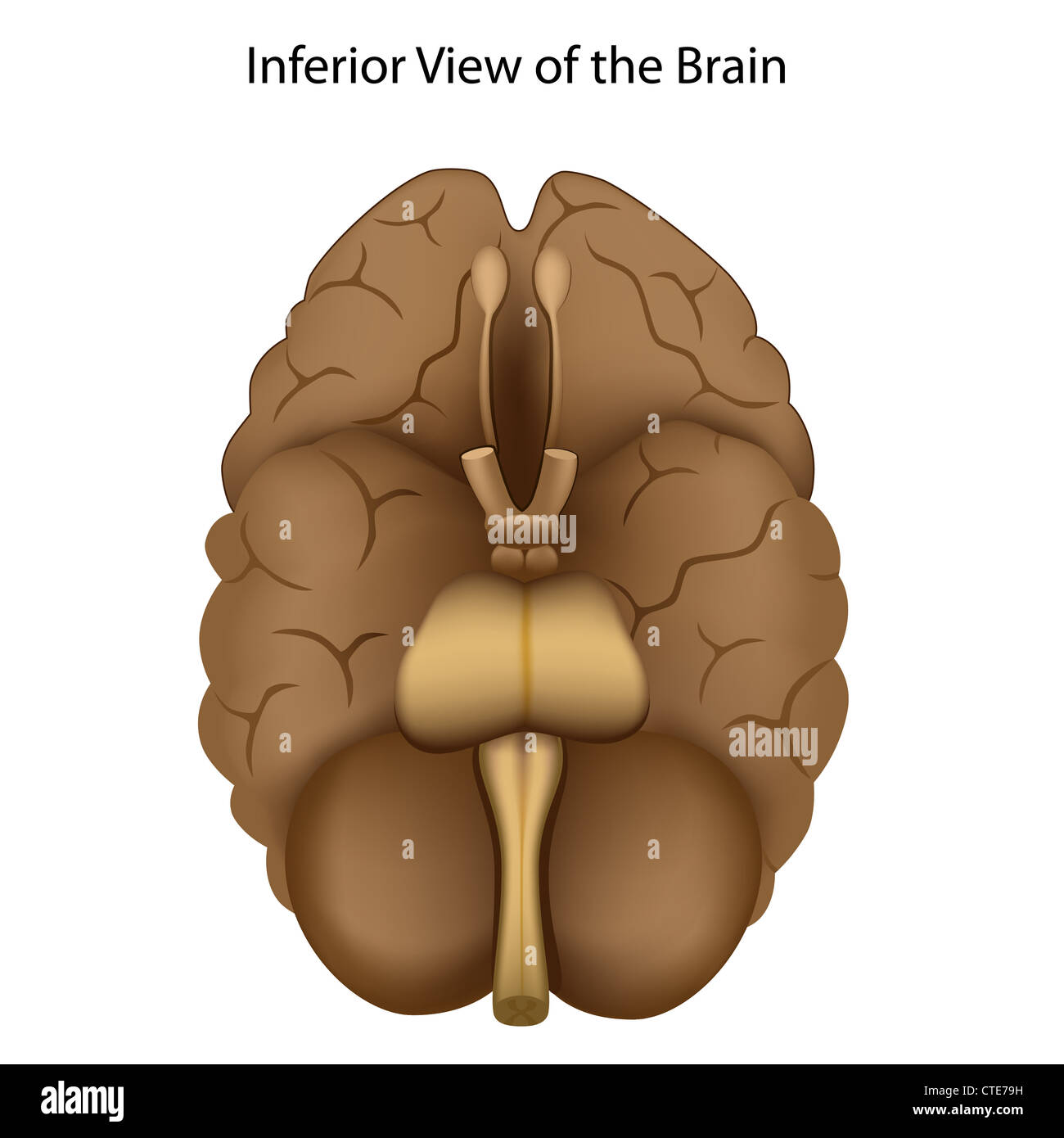 Base of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-base-of-the-brain-49485565.html
Base of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-base-of-the-brain-49485565.htmlRFCTE79H–Base of the brain
 A researcher poses with a poster describing a complex scientific experiment at the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, April 9, 2009. From the Homewood Photography collection. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-researcher-poses-with-a-poster-describing-a-complex-scientific-experiment-at-the-johns-hopkins-university-in-baltimore-maryland-april-9-2009-from-the-homewood-photography-collection-image333146918.html
A researcher poses with a poster describing a complex scientific experiment at the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, April 9, 2009. From the Homewood Photography collection. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-researcher-poses-with-a-poster-describing-a-complex-scientific-experiment-at-the-johns-hopkins-university-in-baltimore-maryland-april-9-2009-from-the-homewood-photography-collection-image333146918.htmlRM2AA0486–A researcher poses with a poster describing a complex scientific experiment at the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, April 9, 2009. From the Homewood Photography collection. ()
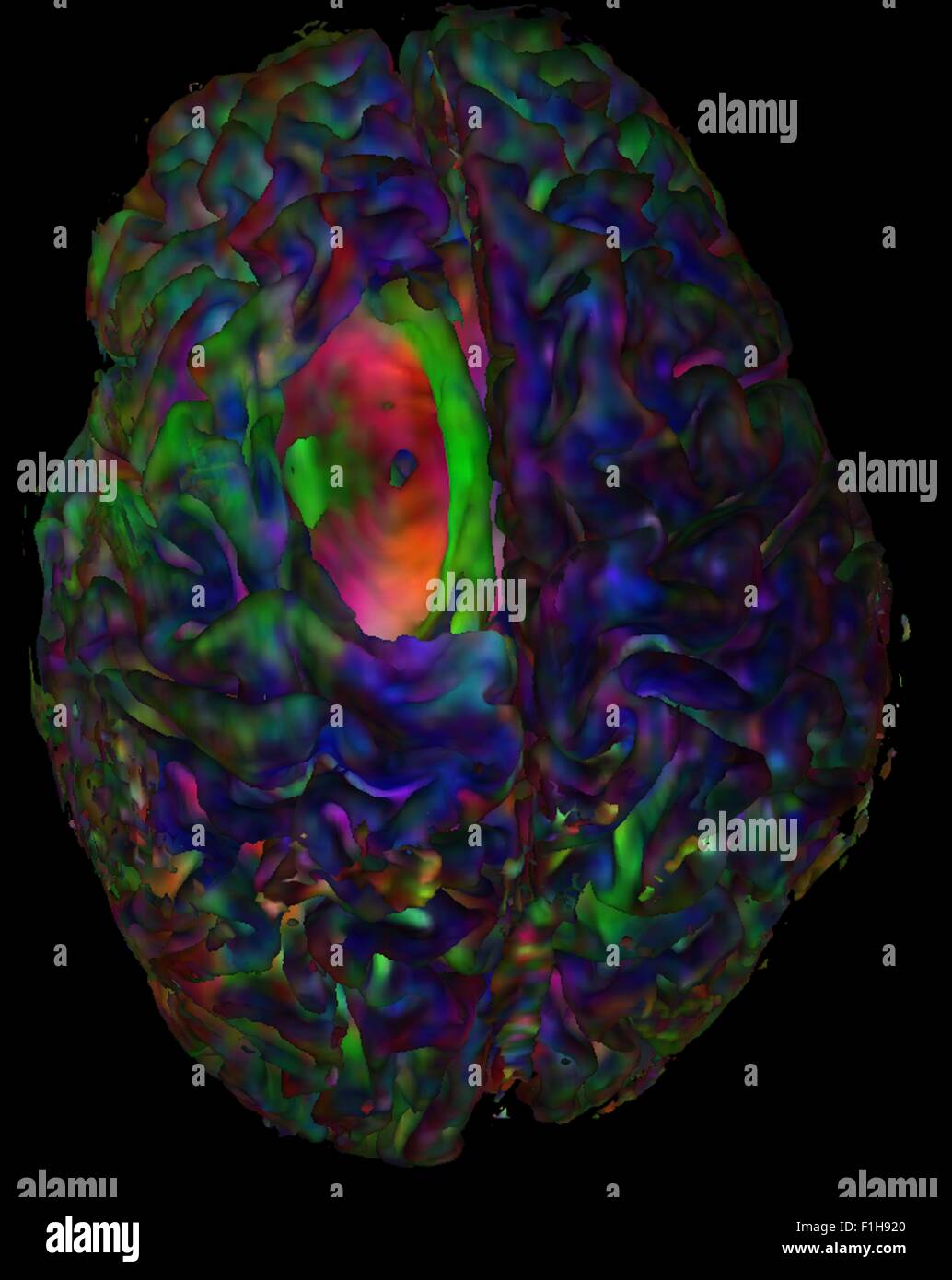 Top view cortical mesh colored diffusion orientation Red-Green-Blue tumor cavity showing hole Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-top-view-cortical-mesh-colored-diffusion-orientation-red-green-blue-87046792.html
Top view cortical mesh colored diffusion orientation Red-Green-Blue tumor cavity showing hole Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-top-view-cortical-mesh-colored-diffusion-orientation-red-green-blue-87046792.htmlRFF1H920–Top view cortical mesh colored diffusion orientation Red-Green-Blue tumor cavity showing hole
 The Plates from the Seventh Book of the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, (1514-1564) Plate 69 - this figure inasmuch as it concerns the portion of the brain remaining in the skull, also resembles the fourth and differs from the fifth in that we have freed the anterior aspect of the body constructed like a vault from the brain substance, reflecting it upwards and posteriorly so that its inferior surface might come into view, and that the vessel which is extended from the fourth sinus of the dural membrane, might be seen. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-plates-from-the-seventh-book-of-the-de-humani-corporis-fabrica-image68553468.html
The Plates from the Seventh Book of the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, (1514-1564) Plate 69 - this figure inasmuch as it concerns the portion of the brain remaining in the skull, also resembles the fourth and differs from the fifth in that we have freed the anterior aspect of the body constructed like a vault from the brain substance, reflecting it upwards and posteriorly so that its inferior surface might come into view, and that the vessel which is extended from the fourth sinus of the dural membrane, might be seen. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-plates-from-the-seventh-book-of-the-de-humani-corporis-fabrica-image68553468.htmlRMDYETJ4–The Plates from the Seventh Book of the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, (1514-1564) Plate 69 - this figure inasmuch as it concerns the portion of the brain remaining in the skull, also resembles the fourth and differs from the fifth in that we have freed the anterior aspect of the body constructed like a vault from the brain substance, reflecting it upwards and posteriorly so that its inferior surface might come into view, and that the vessel which is extended from the fourth sinus of the dural membrane, might be seen.
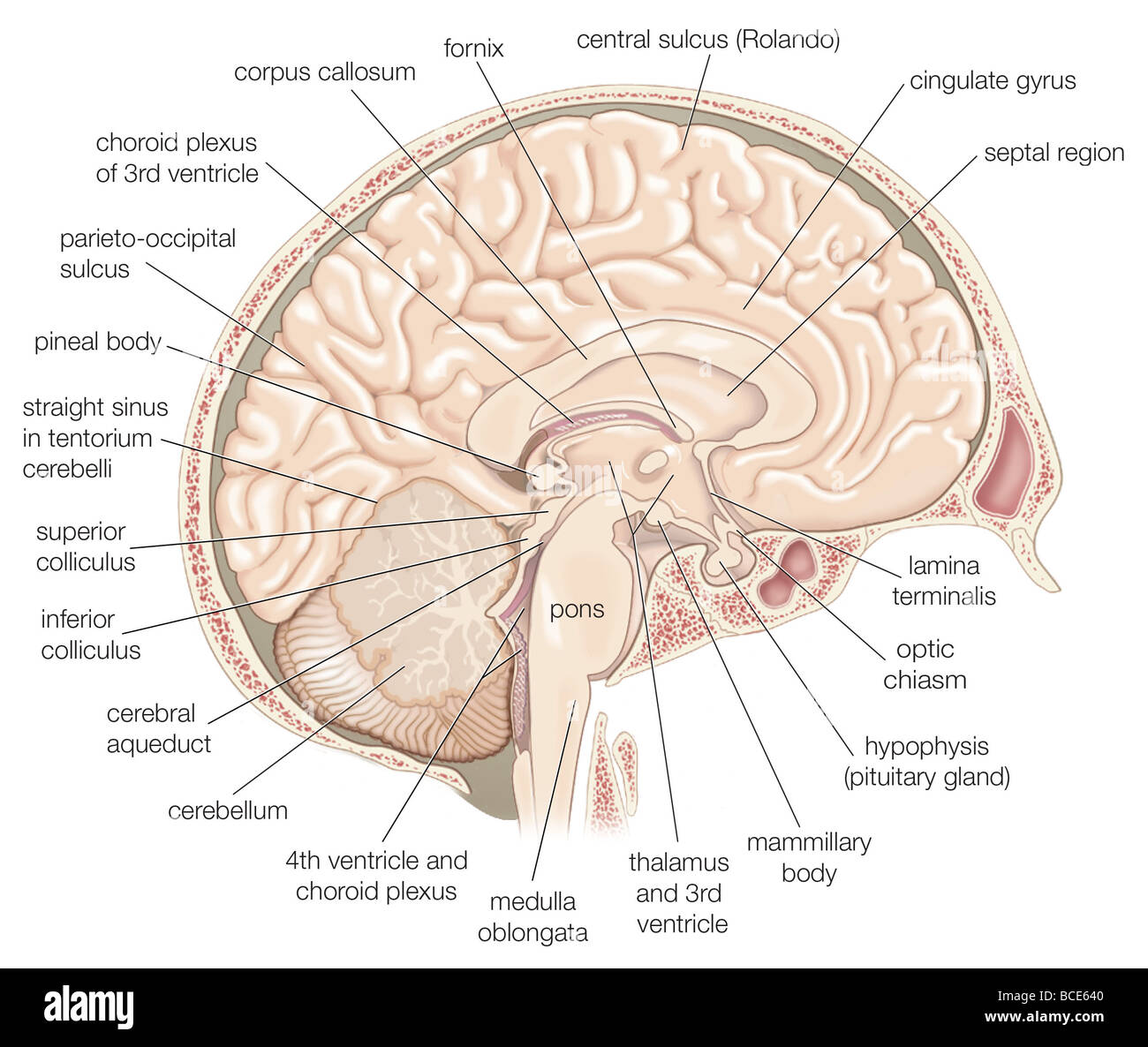 Medial view of the left hemisphere of the human brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-medial-view-of-the-left-hemisphere-of-the-human-brain-24898384.html
Medial view of the left hemisphere of the human brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-medial-view-of-the-left-hemisphere-of-the-human-brain-24898384.htmlRMBCE640–Medial view of the left hemisphere of the human brain.
 Pegs Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pegs-image226249199.html
Pegs Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pegs-image226249199.htmlRFR42F4F–Pegs
 MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image448643761.html
MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image448643761.htmlRM2H1WDKD–MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray.
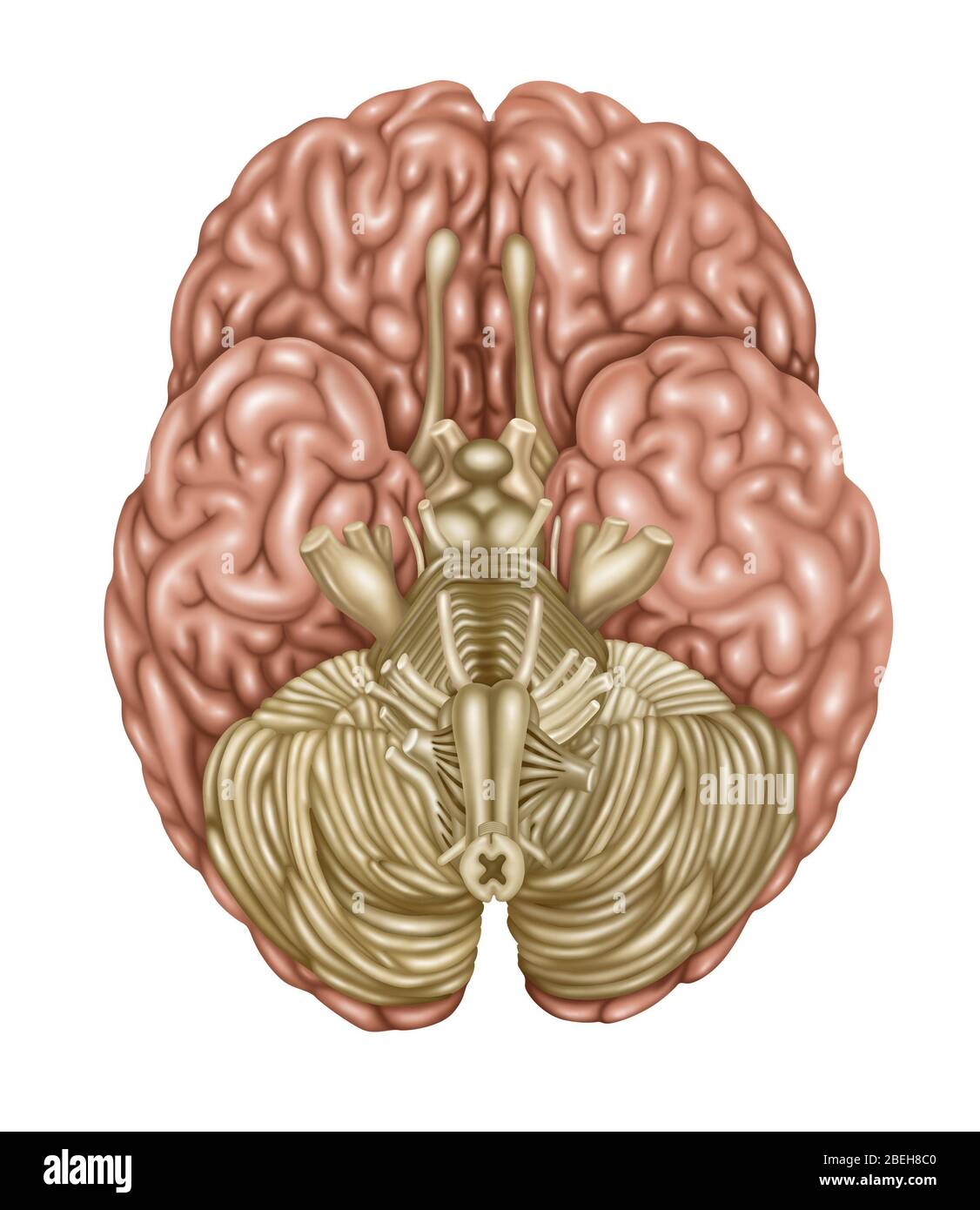 Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192336.html
Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192336.htmlRF2BEH8C0–Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration
 Pegs Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pegs-image226366931.html
Pegs Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pegs-image226366931.htmlRFR47W97–Pegs
 The Plates from the Seventh Book of the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, (1514-1564) Plate 69 - this figure inasmuch as it concerns the portion of the brain remaining in the skull, also resembles the fourth and differs from the fifth in that we have freed the anterior aspect of the body constructed like a vault from the brain substance, reflecting it upwards and posteriorly so that its inferior surface might come into view, and that the vessel which is extended from the fourth sinus of the dural membrane, might be seen. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-plates-from-the-seventh-book-of-the-de-humani-corporis-fabrica-by-andreas-vesalius-1514-1564-plate-69-this-figure-inasmuch-as-it-concerns-the-portion-of-the-brain-remaining-in-the-skull-also-resembles-the-fourth-and-differs-from-the-fifth-in-that-we-have-freed-the-anterior-aspect-of-the-body-constructed-like-a-vault-from-the-brain-substance-reflecting-it-upwards-and-posteriorly-so-that-its-inferior-surface-might-come-into-view-and-that-the-vessel-which-is-extended-from-the-fourth-sinus-of-the-dural-membrane-might-be-seen-image210323888.html
The Plates from the Seventh Book of the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, (1514-1564) Plate 69 - this figure inasmuch as it concerns the portion of the brain remaining in the skull, also resembles the fourth and differs from the fifth in that we have freed the anterior aspect of the body constructed like a vault from the brain substance, reflecting it upwards and posteriorly so that its inferior surface might come into view, and that the vessel which is extended from the fourth sinus of the dural membrane, might be seen. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-plates-from-the-seventh-book-of-the-de-humani-corporis-fabrica-by-andreas-vesalius-1514-1564-plate-69-this-figure-inasmuch-as-it-concerns-the-portion-of-the-brain-remaining-in-the-skull-also-resembles-the-fourth-and-differs-from-the-fifth-in-that-we-have-freed-the-anterior-aspect-of-the-body-constructed-like-a-vault-from-the-brain-substance-reflecting-it-upwards-and-posteriorly-so-that-its-inferior-surface-might-come-into-view-and-that-the-vessel-which-is-extended-from-the-fourth-sinus-of-the-dural-membrane-might-be-seen-image210323888.htmlRMP6527C–The Plates from the Seventh Book of the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, (1514-1564) Plate 69 - this figure inasmuch as it concerns the portion of the brain remaining in the skull, also resembles the fourth and differs from the fifth in that we have freed the anterior aspect of the body constructed like a vault from the brain substance, reflecting it upwards and posteriorly so that its inferior surface might come into view, and that the vessel which is extended from the fourth sinus of the dural membrane, might be seen.
 Pegs Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pegs-image226213538.html
Pegs Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pegs-image226213538.htmlRFR40WJX–Pegs
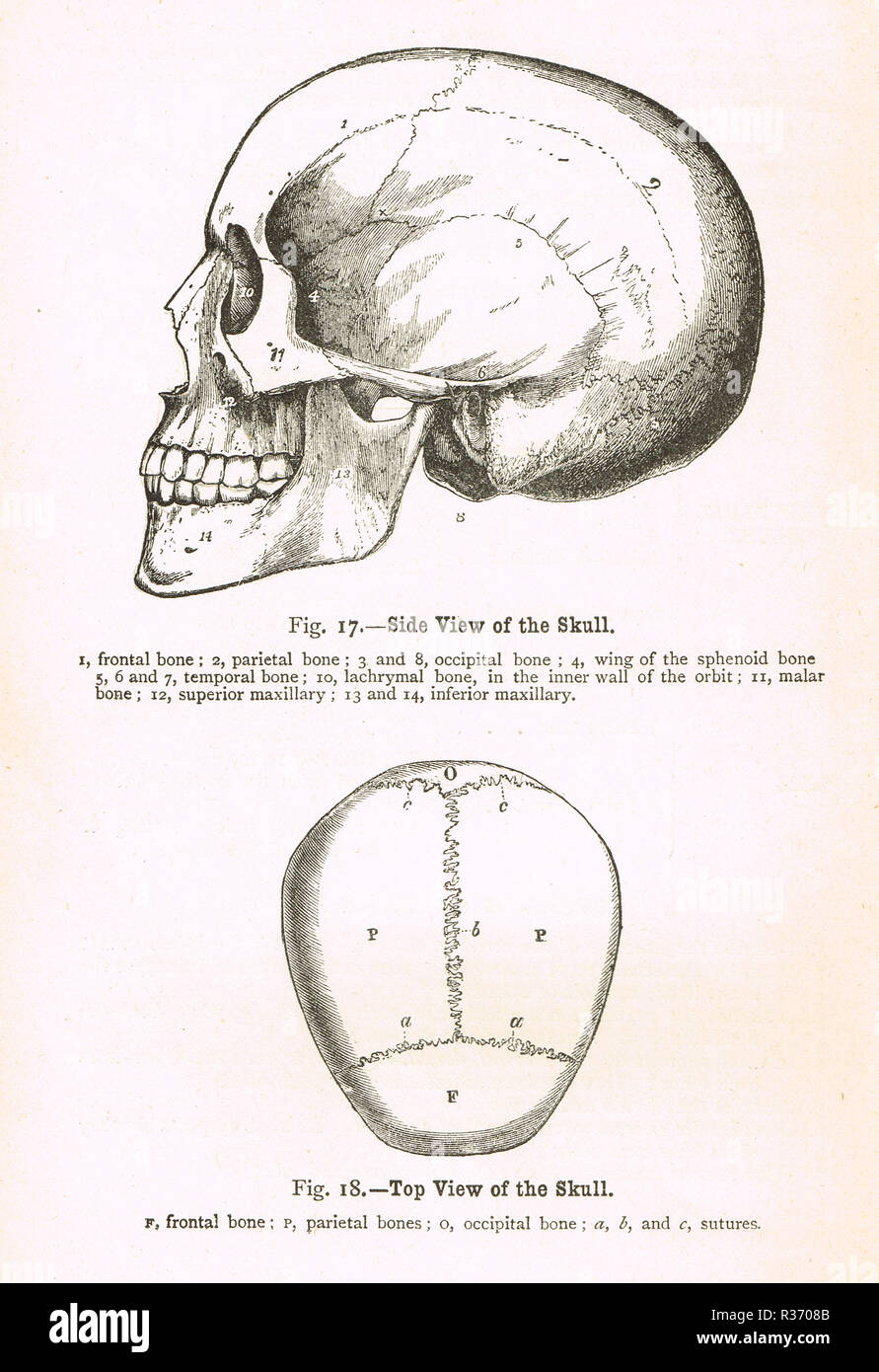 Side and top view of a human Skull. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/side-and-top-view-of-a-human-skull-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732651.html
Side and top view of a human Skull. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/side-and-top-view-of-a-human-skull-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732651.htmlRMR3708B–Side and top view of a human Skull. A 19th Century illustration
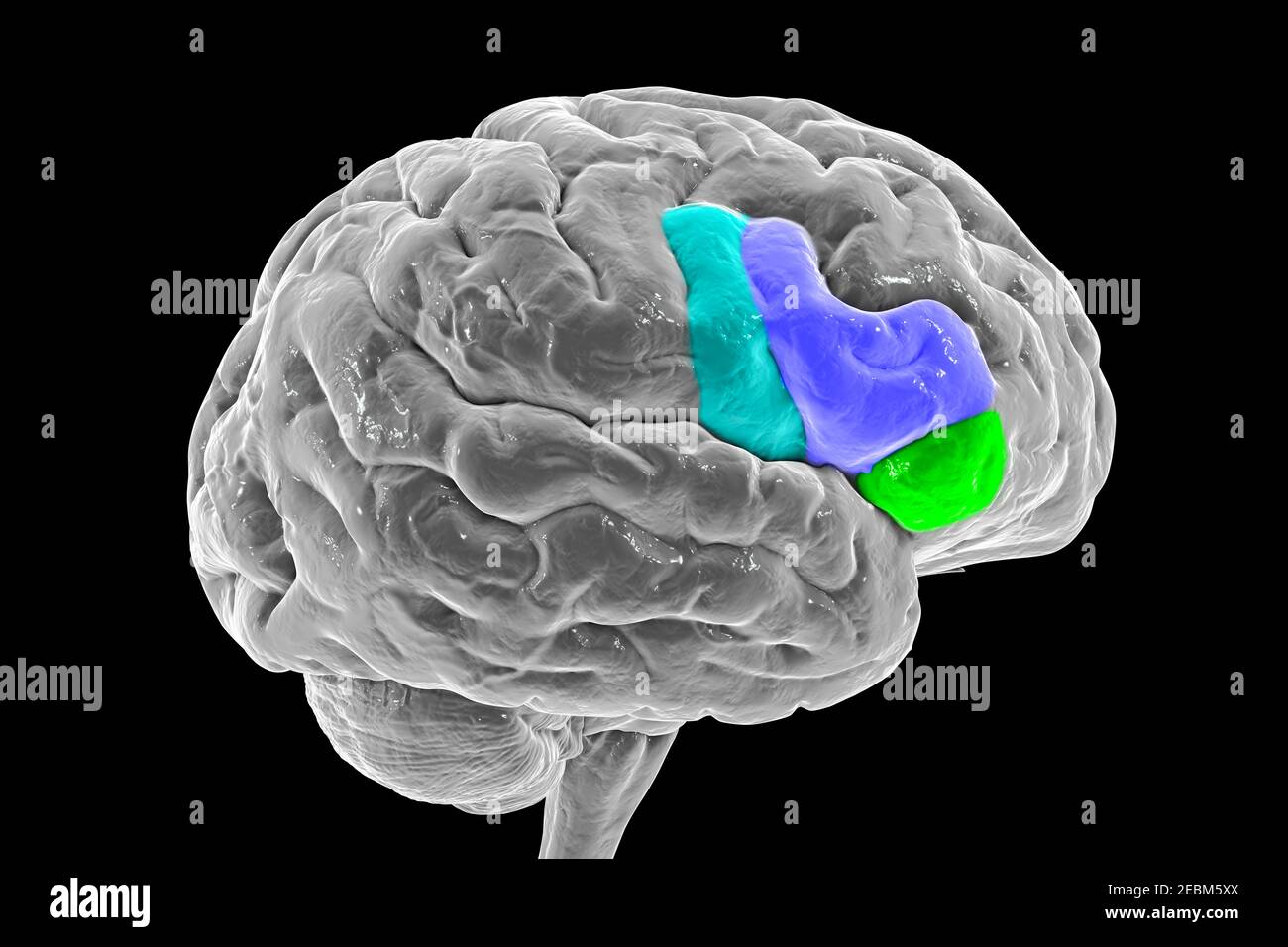 Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043394.html
Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043394.htmlRF2EBM5XX–Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration
 Serotonin released in the brain travels down the spinal cord to close the pain gates and block pain messages. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-serotonin-released-in-the-brain-travels-down-the-spinal-cord-to-close-71629390.html
Serotonin released in the brain travels down the spinal cord to close the pain gates and block pain messages. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-serotonin-released-in-the-brain-travels-down-the-spinal-cord-to-close-71629390.htmlRME4F00E–Serotonin released in the brain travels down the spinal cord to close the pain gates and block pain messages.
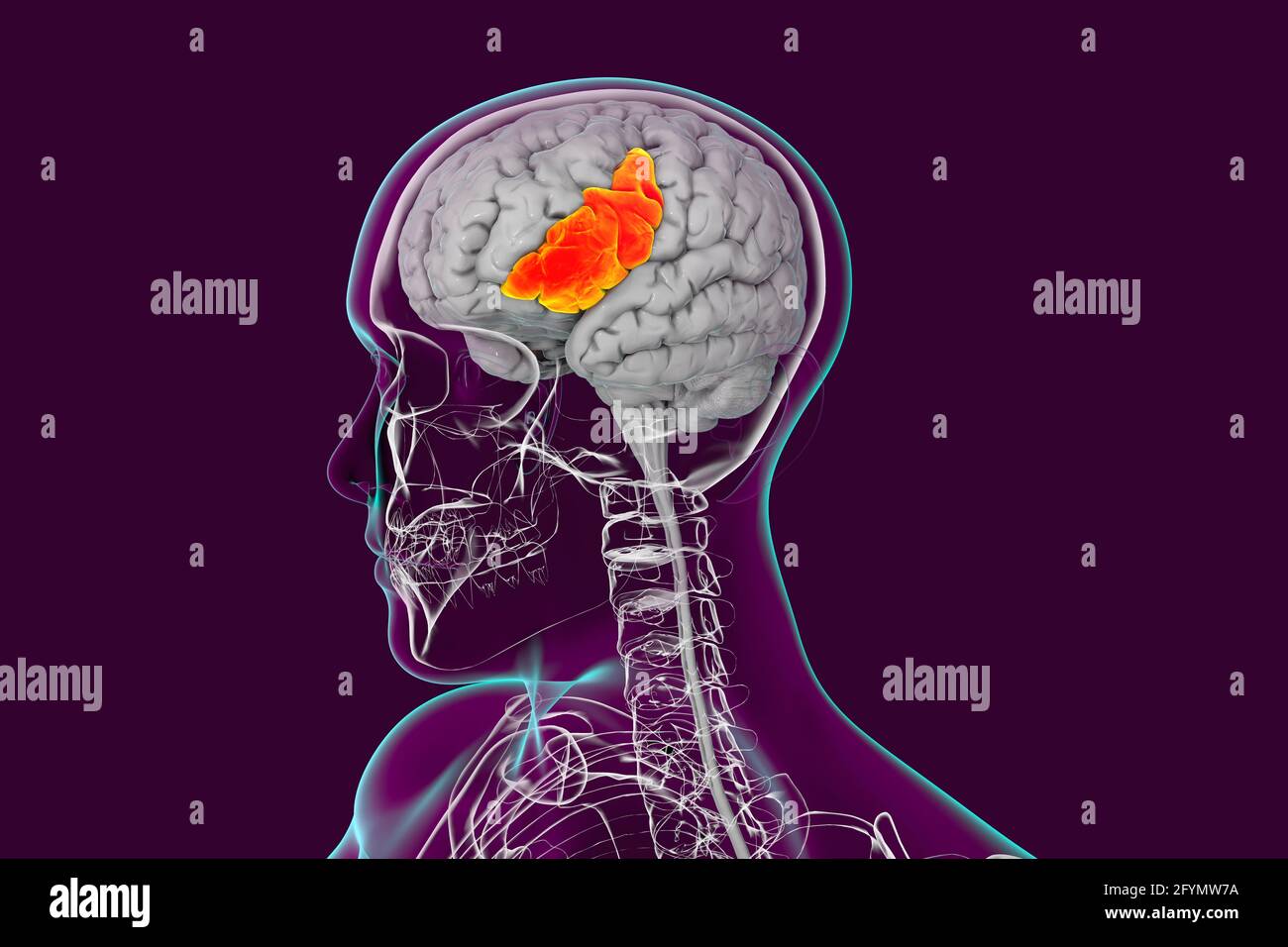 Brain with highlighted inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image430103390.html
Brain with highlighted inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image430103390.htmlRF2FYMW7A–Brain with highlighted inferior frontal gyrus, illustration
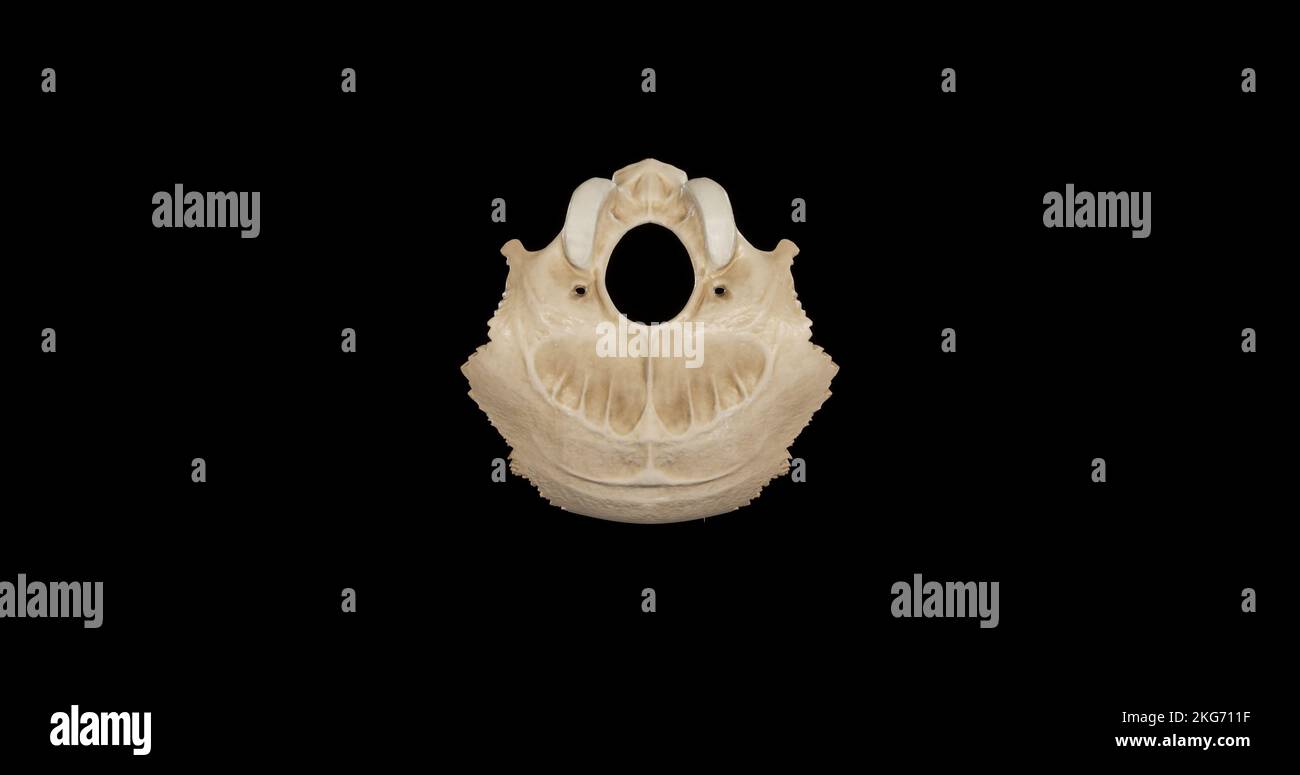 Inferior view of Occipital Bone Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-occipital-bone-image491879291.html
Inferior view of Occipital Bone Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-occipital-bone-image491879291.htmlRF2KG711F–Inferior view of Occipital Bone
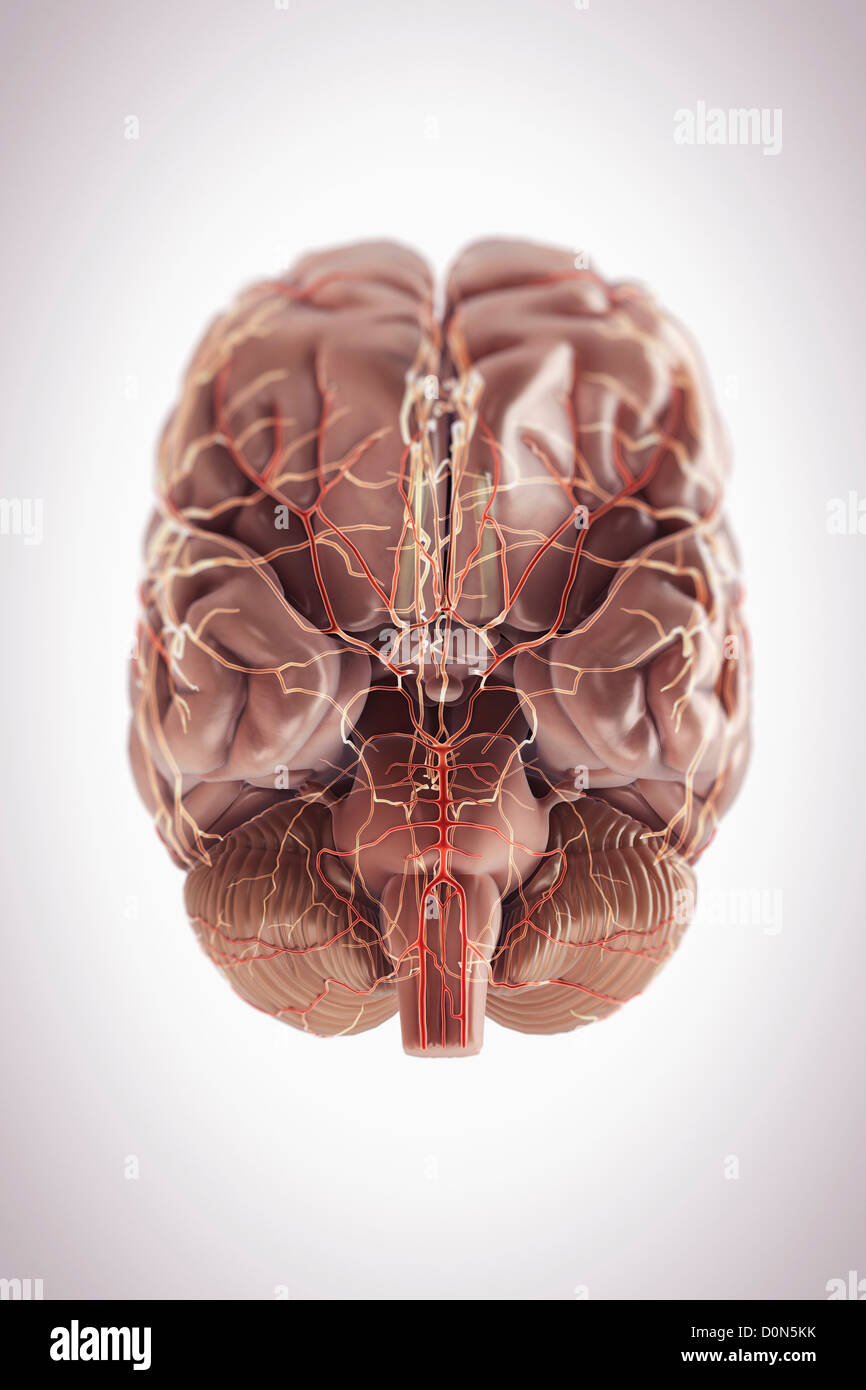 Inferior view of the brain and its blood supply. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-inferior-view-of-the-brain-and-its-blood-supply-52096567.html
Inferior view of the brain and its blood supply. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-inferior-view-of-the-brain-and-its-blood-supply-52096567.htmlRMD0N5KK–Inferior view of the brain and its blood supply.
 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13235113.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13235113.htmlRFACWCTX–The arteries of the brain
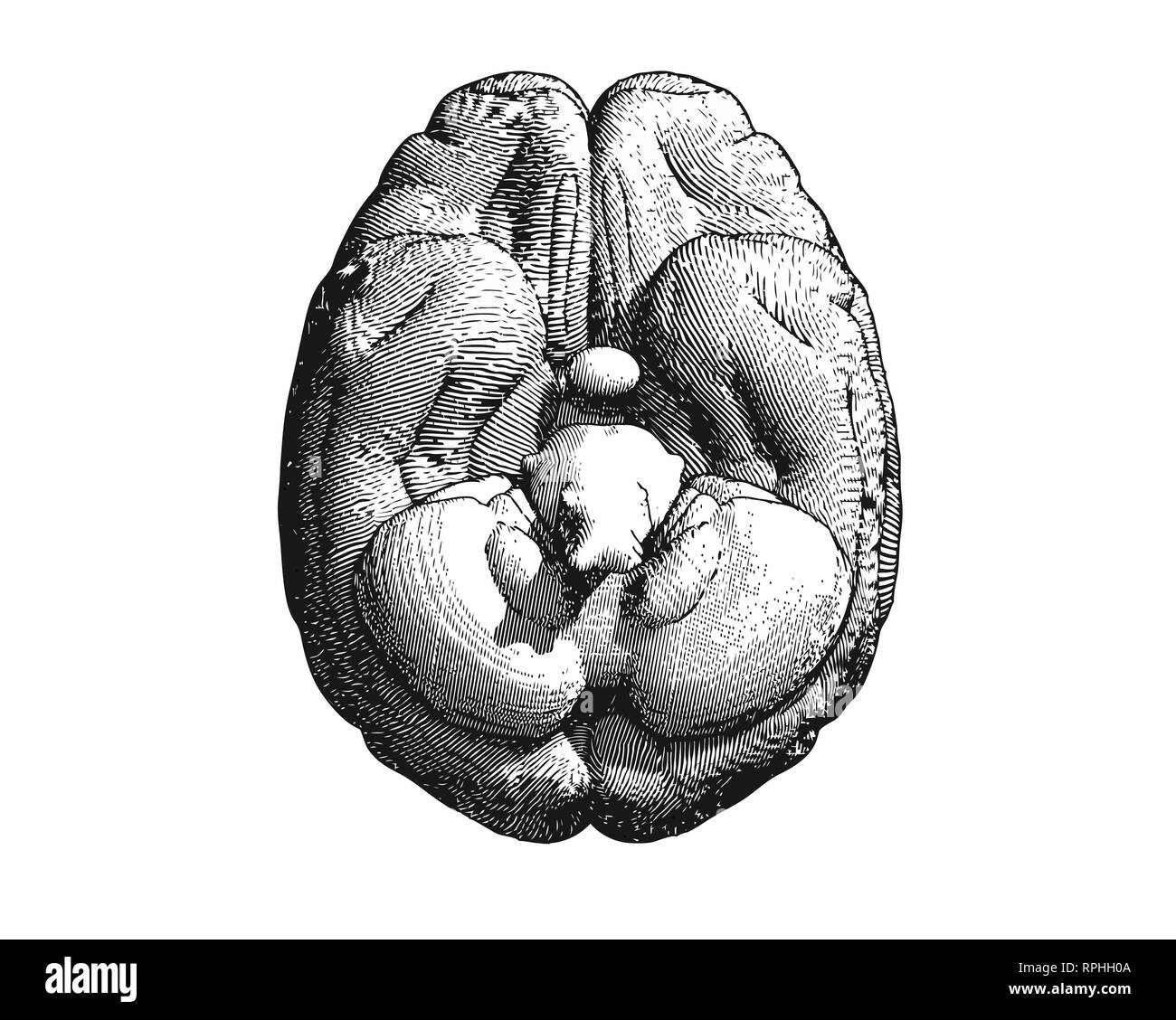 Monochrome engraving brain inferior view illustration isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monochrome-engraving-brain-inferior-view-illustration-isolated-on-white-background-image237643738.html
Monochrome engraving brain inferior view illustration isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monochrome-engraving-brain-inferior-view-illustration-isolated-on-white-background-image237643738.htmlRFRPHH0A–Monochrome engraving brain inferior view illustration isolated on white background
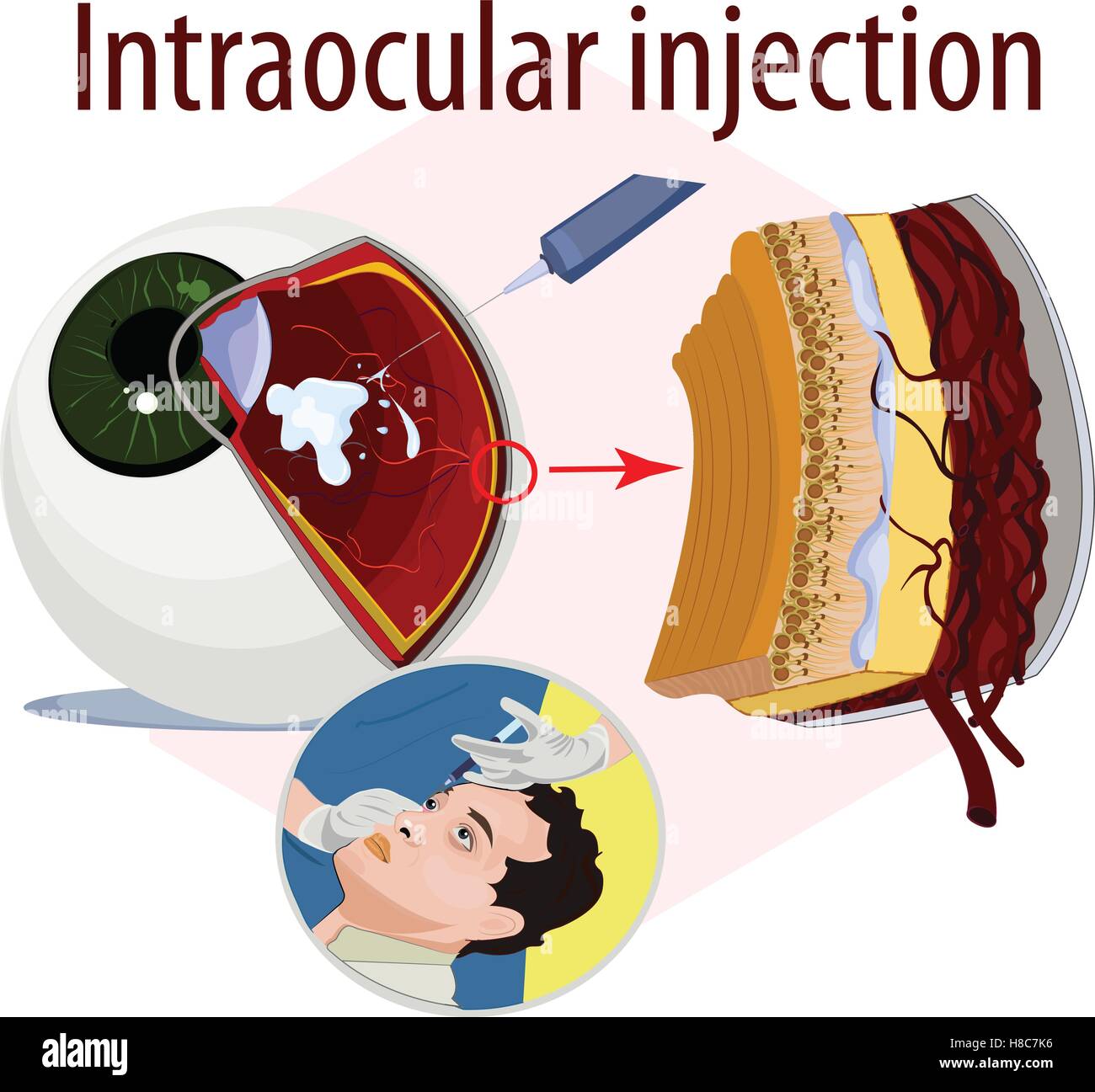 Vector illustration of intraocular injection. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-vector-illustration-of-intraocular-injection-125659274.html
Vector illustration of intraocular injection. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-vector-illustration-of-intraocular-injection-125659274.htmlRFH8C7K6–Vector illustration of intraocular injection.
 Archive image from page 331 of The cyclopædia of anatomy and. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology cyclopdiaofana0401todd Year: 1847 c, lateral view of the brain of a turtle; 1, optic tract; 2, cms cerebri. d, the same: a. portion of the optic nerve has been removed to show the crus cerebri passing upwards. {After Swan.) spinal chord. The inferior surface of the brain is almost smooth, presenting no other ele- vations than those formed by the union of the optic nerves and by the tuber cinereum. As there are no lateral lobes to the cerebellum, of course no traces of a pons varolii exist. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-331-of-the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-cyclopdiaofana0401todd-year-1847-c-lateral-view-of-the-brain-of-a-turtle-1-optic-tract-2-cms-cerebri-d-the-same-a-portion-of-the-optic-nerve-has-been-removed-to-show-the-crus-cerebri-passing-upwards-after-swan-spinal-chord-the-inferior-surface-of-the-brain-is-almost-smooth-presenting-no-other-ele-vations-than-those-formed-by-the-union-of-the-optic-nerves-and-by-the-tuber-cinereum-as-there-are-no-lateral-lobes-to-the-cerebellum-of-course-no-traces-of-a-pons-varolii-exist-image259560479.html
Archive image from page 331 of The cyclopædia of anatomy and. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology cyclopdiaofana0401todd Year: 1847 c, lateral view of the brain of a turtle; 1, optic tract; 2, cms cerebri. d, the same: a. portion of the optic nerve has been removed to show the crus cerebri passing upwards. {After Swan.) spinal chord. The inferior surface of the brain is almost smooth, presenting no other ele- vations than those formed by the union of the optic nerves and by the tuber cinereum. As there are no lateral lobes to the cerebellum, of course no traces of a pons varolii exist. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-331-of-the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-cyclopdiaofana0401todd-year-1847-c-lateral-view-of-the-brain-of-a-turtle-1-optic-tract-2-cms-cerebri-d-the-same-a-portion-of-the-optic-nerve-has-been-removed-to-show-the-crus-cerebri-passing-upwards-after-swan-spinal-chord-the-inferior-surface-of-the-brain-is-almost-smooth-presenting-no-other-ele-vations-than-those-formed-by-the-union-of-the-optic-nerves-and-by-the-tuber-cinereum-as-there-are-no-lateral-lobes-to-the-cerebellum-of-course-no-traces-of-a-pons-varolii-exist-image259560479.htmlRMW28013–Archive image from page 331 of The cyclopædia of anatomy and. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology cyclopdiaofana0401todd Year: 1847 c, lateral view of the brain of a turtle; 1, optic tract; 2, cms cerebri. d, the same: a. portion of the optic nerve has been removed to show the crus cerebri passing upwards. {After Swan.) spinal chord. The inferior surface of the brain is almost smooth, presenting no other ele- vations than those formed by the union of the optic nerves and by the tuber cinereum. As there are no lateral lobes to the cerebellum, of course no traces of a pons varolii exist.
 Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lymphatic-drainage-follows-the-course-of-the-inferior-mesenteric-vessels-3d-illustration-image596591173.html
Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lymphatic-drainage-follows-the-course-of-the-inferior-mesenteric-vessels-3d-illustration-image596591173.htmlRF2WJH23H–Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration
 Class-book of physiology : for the use of schools and families : comprising the structure and functions of the organs of man, illustrated by comparative reference to those of inferior animals . rd.—The vertebra?are cut through, so as to display a lateral view of the cord. Fioure 3. The Cerebellum.—A, Anterior view. B, Posterior view. Figure 4. A Vertical Section of the Brain, showing the Origins of its Nerves.-* a, a, The cerebrum, with its convolutions, b, The cerebellum, displaying the arbor-vita>upon its section, c, The medulla oblongata, d, The corpus callosum, a band of fibreswhich con Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/class-book-of-physiology-for-the-use-of-schools-and-families-comprising-the-structure-and-functions-of-the-organs-of-man-illustrated-by-comparative-reference-to-those-of-inferior-animals-rdthe-vertebraare-cut-through-so-as-to-display-a-lateral-view-of-the-cord-fioure-3-the-cerebelluma-anterior-view-b-posterior-view-figure-4-a-vertical-section-of-the-brain-showing-the-origins-of-its-nerves-a-a-the-cerebrum-with-its-convolutions-b-the-cerebellum-displaying-the-arbor-vitagtupon-its-section-c-the-medulla-oblongata-d-the-corpus-callosum-a-band-of-fibreswhich-con-image340235622.html
Class-book of physiology : for the use of schools and families : comprising the structure and functions of the organs of man, illustrated by comparative reference to those of inferior animals . rd.—The vertebra?are cut through, so as to display a lateral view of the cord. Fioure 3. The Cerebellum.—A, Anterior view. B, Posterior view. Figure 4. A Vertical Section of the Brain, showing the Origins of its Nerves.-* a, a, The cerebrum, with its convolutions, b, The cerebellum, displaying the arbor-vita>upon its section, c, The medulla oblongata, d, The corpus callosum, a band of fibreswhich con Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/class-book-of-physiology-for-the-use-of-schools-and-families-comprising-the-structure-and-functions-of-the-organs-of-man-illustrated-by-comparative-reference-to-those-of-inferior-animals-rdthe-vertebraare-cut-through-so-as-to-display-a-lateral-view-of-the-cord-fioure-3-the-cerebelluma-anterior-view-b-posterior-view-figure-4-a-vertical-section-of-the-brain-showing-the-origins-of-its-nerves-a-a-the-cerebrum-with-its-convolutions-b-the-cerebellum-displaying-the-arbor-vitagtupon-its-section-c-the-medulla-oblongata-d-the-corpus-callosum-a-band-of-fibreswhich-con-image340235622.htmlRM2ANF206–Class-book of physiology : for the use of schools and families : comprising the structure and functions of the organs of man, illustrated by comparative reference to those of inferior animals . rd.—The vertebra?are cut through, so as to display a lateral view of the cord. Fioure 3. The Cerebellum.—A, Anterior view. B, Posterior view. Figure 4. A Vertical Section of the Brain, showing the Origins of its Nerves.-* a, a, The cerebrum, with its convolutions, b, The cerebellum, displaying the arbor-vita>upon its section, c, The medulla oblongata, d, The corpus callosum, a band of fibreswhich con
 MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image263215995.html
MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image263215995.htmlRFW86EK7–MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray.
 foolhardy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-foolhardy-141015631.html
foolhardy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-foolhardy-141015631.htmlRFJ5BPTF–foolhardy
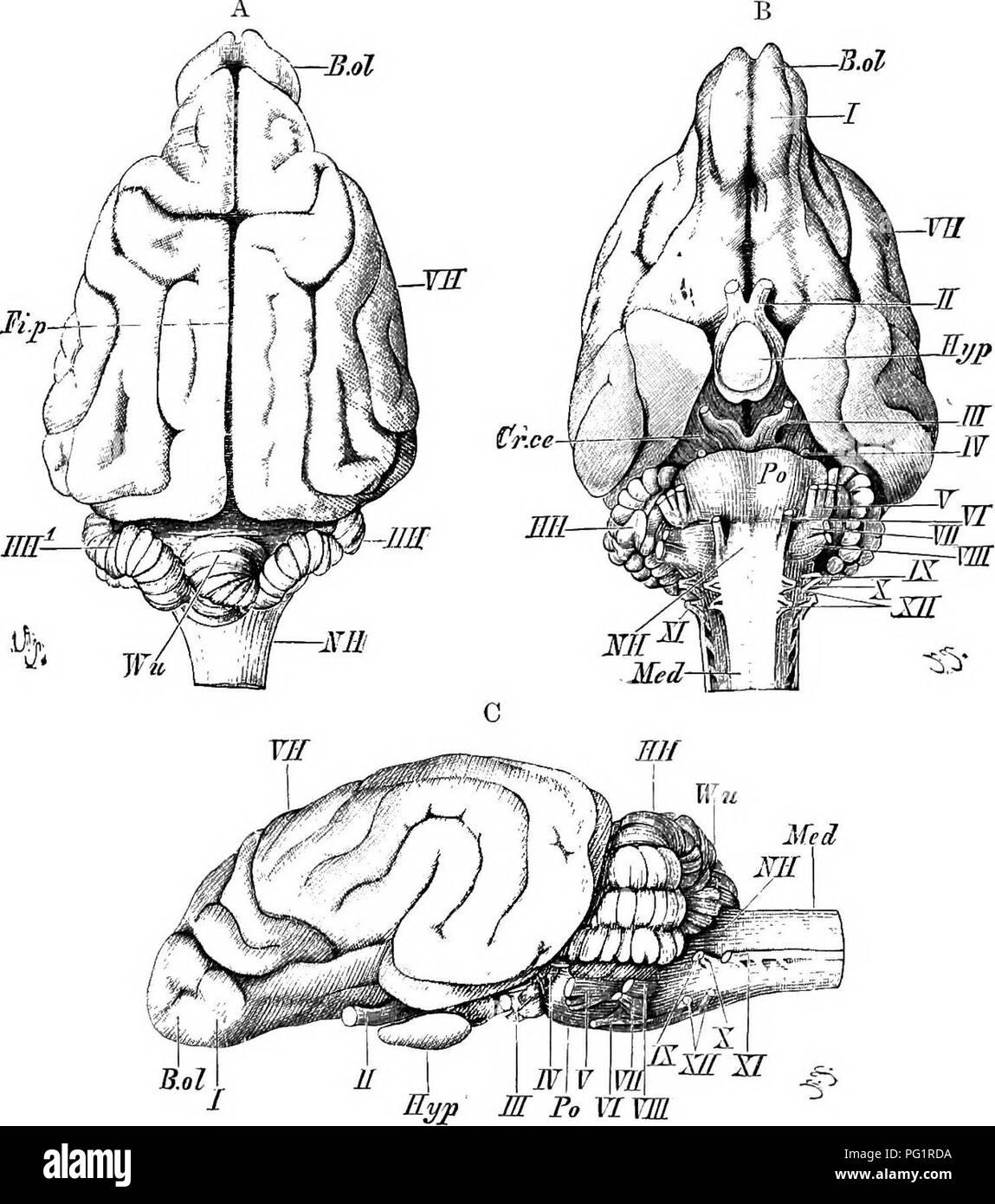 . Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. THE BRAIN 175 >SD thab an anterior, a posterior, and an inferior cornu can be dis- iipguished in each; the inferior cornu extends into what corresponds •io the hippocampal lobe of Reptiles (p. 168), and an eminence on its floor, known as the hip2Mcampus 7najor, is much more marked than in lower forms. The olfactory lobes, in which an olfactory. Fig. 144. -Bkain of Dog (Pointeb). (A, dorsal; B, ventral; and C, lateral view.) VB, cerebral hemispheres ; Mil, optic lobes; JIH, cerebellum, Wu, superior vermis ; JIH'^, la Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-the-comparative-anatomy-of-vertebrates-anatomy-comparative-the-brain-175-gtsd-thab-an-anterior-a-posterior-and-an-inferior-cornu-can-be-dis-iipguished-in-each-the-inferior-cornu-extends-into-what-corresponds-io-the-hippocampal-lobe-of-reptiles-p-168-and-an-eminence-on-its-floor-known-as-the-hip2mcampus-7najor-is-much-more-marked-than-in-lower-forms-the-olfactory-lobes-in-which-an-olfactory-fig-144-bkain-of-dog-pointeb-a-dorsal-b-ventral-and-c-lateral-view-vb-cerebral-hemispheres-mil-optic-lobes-jih-cerebellum-wu-superior-vermis-jih-la-image216399270.html
. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. THE BRAIN 175 >SD thab an anterior, a posterior, and an inferior cornu can be dis- iipguished in each; the inferior cornu extends into what corresponds •io the hippocampal lobe of Reptiles (p. 168), and an eminence on its floor, known as the hip2Mcampus 7najor, is much more marked than in lower forms. The olfactory lobes, in which an olfactory. Fig. 144. -Bkain of Dog (Pointeb). (A, dorsal; B, ventral; and C, lateral view.) VB, cerebral hemispheres ; Mil, optic lobes; JIH, cerebellum, Wu, superior vermis ; JIH'^, la Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-the-comparative-anatomy-of-vertebrates-anatomy-comparative-the-brain-175-gtsd-thab-an-anterior-a-posterior-and-an-inferior-cornu-can-be-dis-iipguished-in-each-the-inferior-cornu-extends-into-what-corresponds-io-the-hippocampal-lobe-of-reptiles-p-168-and-an-eminence-on-its-floor-known-as-the-hip2mcampus-7najor-is-much-more-marked-than-in-lower-forms-the-olfactory-lobes-in-which-an-olfactory-fig-144-bkain-of-dog-pointeb-a-dorsal-b-ventral-and-c-lateral-view-vb-cerebral-hemispheres-mil-optic-lobes-jih-cerebellum-wu-superior-vermis-jih-la-image216399270.htmlRMPG1RDA–. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. THE BRAIN 175 >SD thab an anterior, a posterior, and an inferior cornu can be dis- iipguished in each; the inferior cornu extends into what corresponds •io the hippocampal lobe of Reptiles (p. 168), and an eminence on its floor, known as the hip2Mcampus 7najor, is much more marked than in lower forms. The olfactory lobes, in which an olfactory. Fig. 144. -Bkain of Dog (Pointeb). (A, dorsal; B, ventral; and C, lateral view.) VB, cerebral hemispheres ; Mil, optic lobes; JIH, cerebellum, Wu, superior vermis ; JIH'^, la
 Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192292.html
Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192292.htmlRF2BEH8AC–Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration
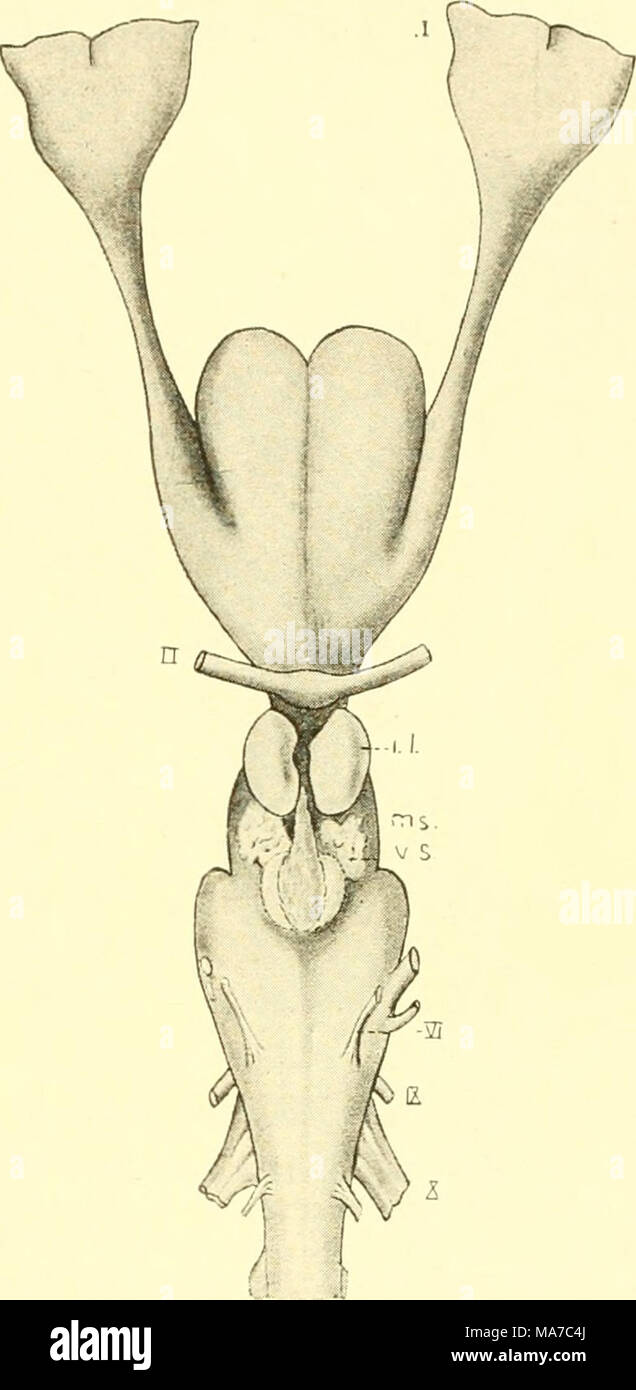 . The elasmobranch fishes . A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth cranial nerve; IX. glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagus nerve. th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-a-b-fig-210-brain-of-reterodonius-francisci-mildred-bennett-del-a-dorsal-view-b-ventral-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-dl-diencephalon-or-thalameneephalon-id-inferior-lobe-imn-median-olfactory-nucleus-mcd-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-old-olfactory-bulb-ojd-olfactory-lobe-old-olfactory-tract-opd-optic-lobe-pc-pallial-eminence-tl-telencephalon-vs-vascular-sac-7-olfactory-nerve-optic-nerve-iv-trochlearis-or-fourth-nerve-vi-alducens-or-sixth-cranial-nerve-ix-glossopharyngeal-nerve-x-vagus-nerve-th-image178413442.html
. The elasmobranch fishes . A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth cranial nerve; IX. glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagus nerve. th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-a-b-fig-210-brain-of-reterodonius-francisci-mildred-bennett-del-a-dorsal-view-b-ventral-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-dl-diencephalon-or-thalameneephalon-id-inferior-lobe-imn-median-olfactory-nucleus-mcd-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-old-olfactory-bulb-ojd-olfactory-lobe-old-olfactory-tract-opd-optic-lobe-pc-pallial-eminence-tl-telencephalon-vs-vascular-sac-7-olfactory-nerve-optic-nerve-iv-trochlearis-or-fourth-nerve-vi-alducens-or-sixth-cranial-nerve-ix-glossopharyngeal-nerve-x-vagus-nerve-th-image178413442.htmlRMMA7C4J–. The elasmobranch fishes . A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth cranial nerve; IX. glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagus nerve. th
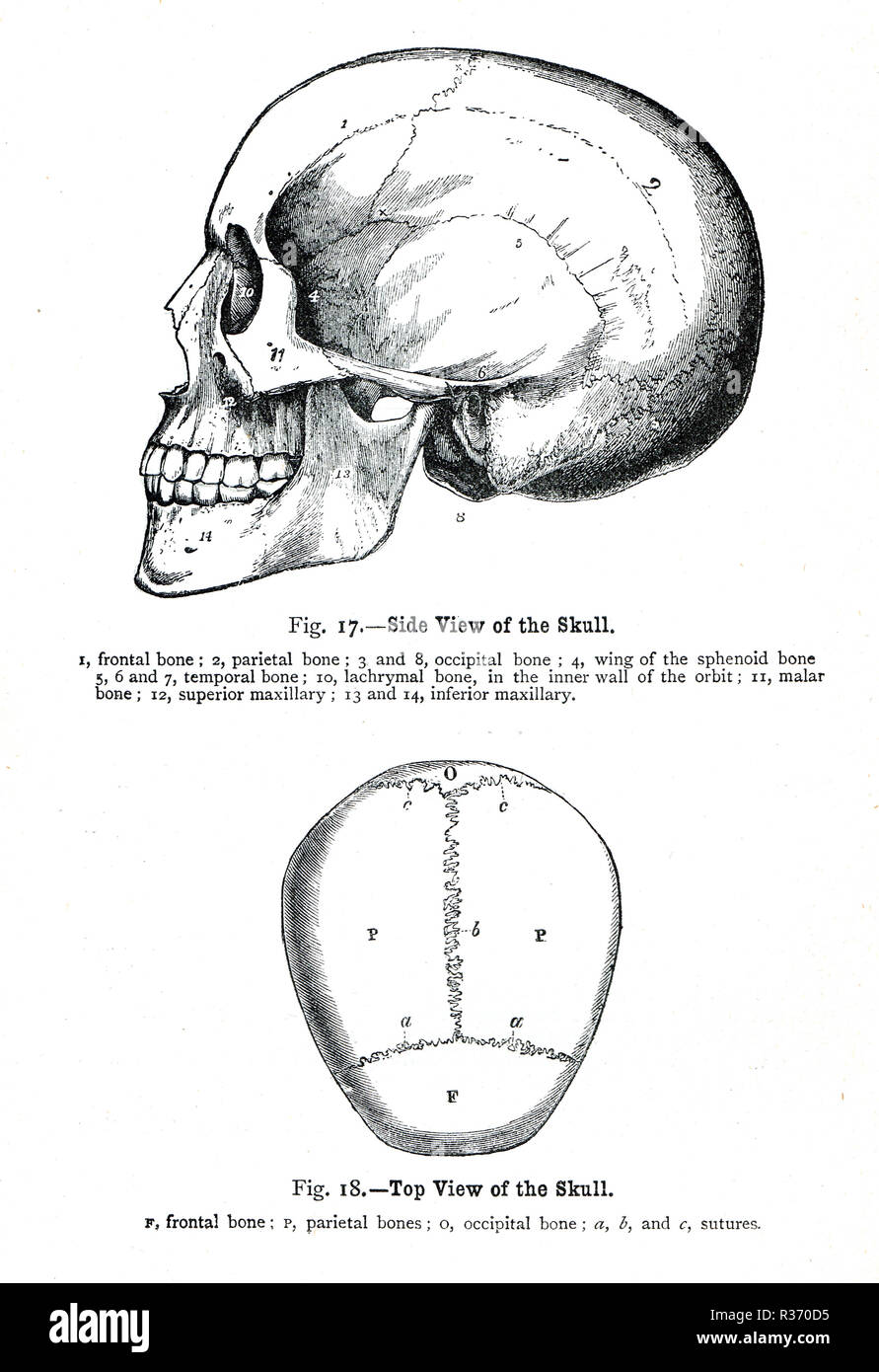 Side and top view of a human Skull. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/side-and-top-view-of-a-human-skull-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732785.html
Side and top view of a human Skull. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/side-and-top-view-of-a-human-skull-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732785.htmlRMR370D5–Side and top view of a human Skull. A 19th Century illustration
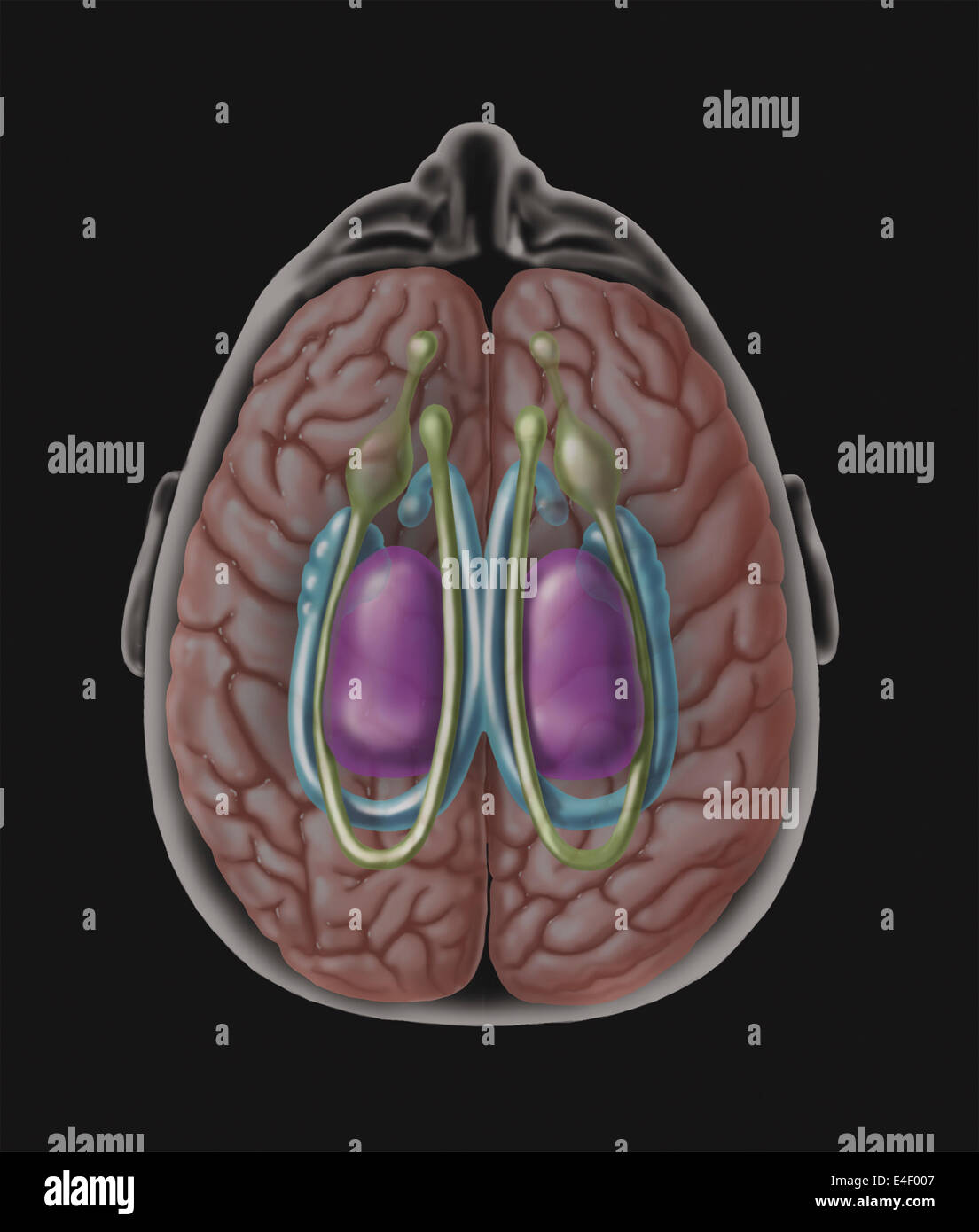 View of limbic system as seen from directly above the head. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-view-of-limbic-system-as-seen-from-directly-above-the-head-71629383.html
View of limbic system as seen from directly above the head. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-view-of-limbic-system-as-seen-from-directly-above-the-head-71629383.htmlRME4F007–View of limbic system as seen from directly above the head.
 Brain with highlighted inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image430103391.html
Brain with highlighted inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image430103391.htmlRF2FYMW7B–Brain with highlighted inferior frontal gyrus, illustration
 Inferior view of Right Parietal Bone Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-right-parietal-bone-image491879295.html
Inferior view of Right Parietal Bone Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-right-parietal-bone-image491879295.htmlRF2KG711K–Inferior view of Right Parietal Bone
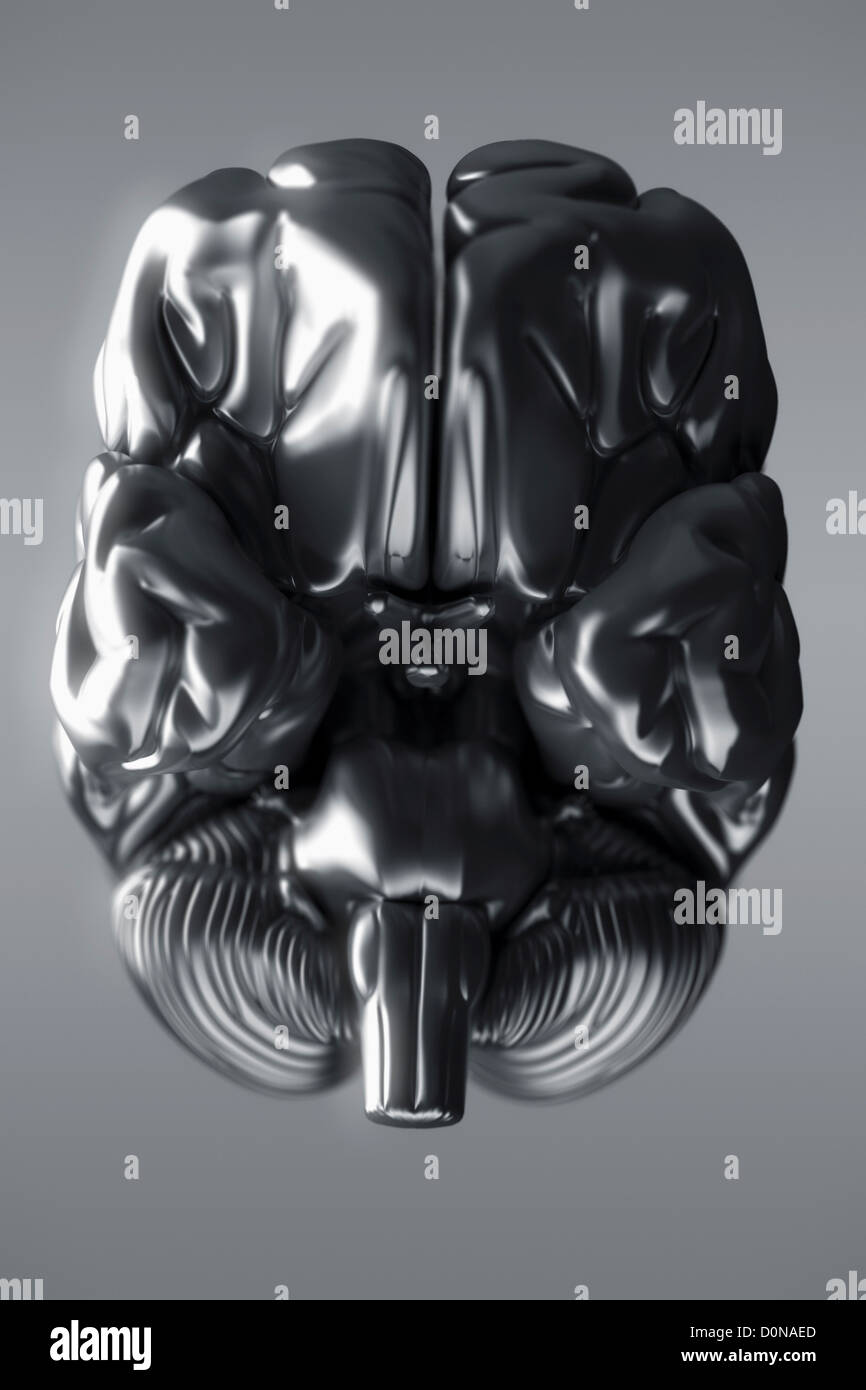 An inferior view of a metallic brain. The cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem are visible. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-an-inferior-view-of-a-metallic-brain-the-cerebral-hemispheres-cerebellum-52100341.html
An inferior view of a metallic brain. The cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem are visible. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-an-inferior-view-of-a-metallic-brain-the-cerebral-hemispheres-cerebellum-52100341.htmlRMD0NAED–An inferior view of a metallic brain. The cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem are visible.
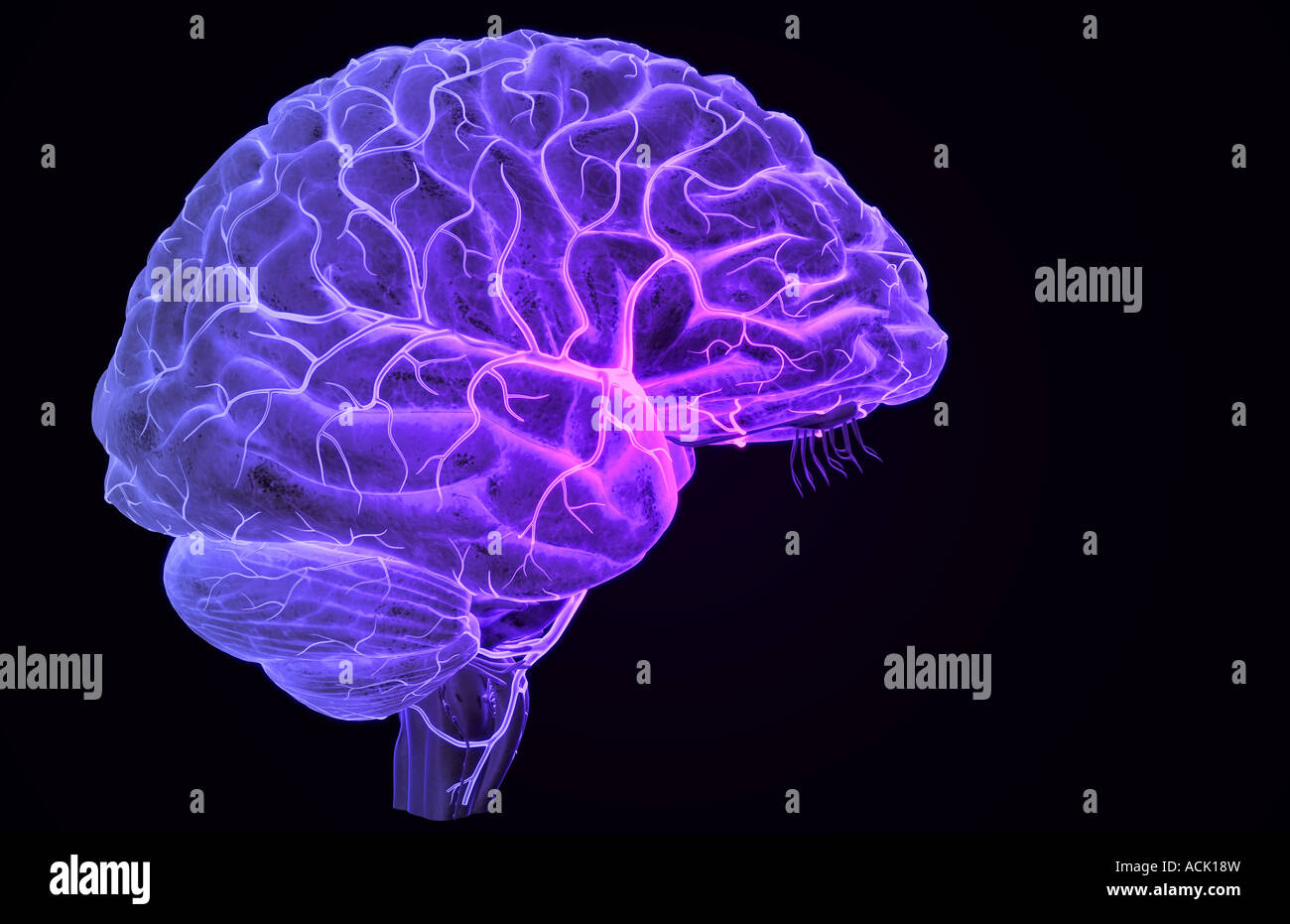 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13174776.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13174776.htmlRFACK18W–The arteries of the brain
 The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-1934-the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-a-b-fig-210-brain-of-reterodonius-francisci-mildred-bennett-del-a-dorsal-view-b-ventral-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-dl-diencephalon-or-thalameneephalon-id-inferior-lobe-imn-median-olfactory-nucleus-mcd-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-old-olfactory-bulb-ojd-olfactory-lobe-old-olfactory-tract-opd-optic-lobe-pc-pallial-eminence-tl-telencephalon-vs-vascular-sac-7-olfactory-nerve-optic-nerve-iv-trochlearis-or-fourth-nerve-vi-alducens-or-sixth-image239624424.html
The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-1934-the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-a-b-fig-210-brain-of-reterodonius-francisci-mildred-bennett-del-a-dorsal-view-b-ventral-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-dl-diencephalon-or-thalameneephalon-id-inferior-lobe-imn-median-olfactory-nucleus-mcd-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-old-olfactory-bulb-ojd-olfactory-lobe-old-olfactory-tract-opd-optic-lobe-pc-pallial-eminence-tl-telencephalon-vs-vascular-sac-7-olfactory-nerve-optic-nerve-iv-trochlearis-or-fourth-nerve-vi-alducens-or-sixth-image239624424.htmlRMRWRRB4–The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth
 Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lymphatic-drainage-follows-the-course-of-the-inferior-mesenteric-vessels-3d-illustration-image596587907.html
Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lymphatic-drainage-follows-the-course-of-the-inferior-mesenteric-vessels-3d-illustration-image596587907.htmlRF2WJGWXY–Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration
 A reference handbook of the medical sciences, embracing the entire range of scientific and practical medicine and allied science . spectively the develop-ment of the inferior and superiorcoUiculus of the corpora quad-rigemina. The development of the pro-sencephalon is much more com-plex, for here the primary seg-mental apparatus has been over-shadowed by suprasegmental cor-relation centers of the most in-tricate character. There are noperipheral motor nerves in thisregion; accordingly, the ventro-lateral lamina is greatly reduced Fio. 889.—Lateral View of the Brain of the Same Embryo Shown in Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-reference-handbook-of-the-medical-sciences-embracing-the-entire-range-of-scientific-and-practical-medicine-and-allied-science-spectively-the-develop-ment-of-the-inferior-and-superiorcouiculus-of-the-corpora-quad-rigemina-the-development-of-the-pro-sencephalon-is-much-more-com-plex-for-here-the-primary-seg-mental-apparatus-has-been-over-shadowed-by-suprasegmental-cor-relation-centers-of-the-most-in-tricate-character-there-are-noperipheral-motor-nerves-in-thisregion-accordingly-the-ventro-lateral-lamina-is-greatly-reduced-fio-889lateral-view-of-the-brain-of-the-same-embryo-shown-in-image338931811.html
A reference handbook of the medical sciences, embracing the entire range of scientific and practical medicine and allied science . spectively the develop-ment of the inferior and superiorcoUiculus of the corpora quad-rigemina. The development of the pro-sencephalon is much more com-plex, for here the primary seg-mental apparatus has been over-shadowed by suprasegmental cor-relation centers of the most in-tricate character. There are noperipheral motor nerves in thisregion; accordingly, the ventro-lateral lamina is greatly reduced Fio. 889.—Lateral View of the Brain of the Same Embryo Shown in Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-reference-handbook-of-the-medical-sciences-embracing-the-entire-range-of-scientific-and-practical-medicine-and-allied-science-spectively-the-develop-ment-of-the-inferior-and-superiorcouiculus-of-the-corpora-quad-rigemina-the-development-of-the-pro-sencephalon-is-much-more-com-plex-for-here-the-primary-seg-mental-apparatus-has-been-over-shadowed-by-suprasegmental-cor-relation-centers-of-the-most-in-tricate-character-there-are-noperipheral-motor-nerves-in-thisregion-accordingly-the-ventro-lateral-lamina-is-greatly-reduced-fio-889lateral-view-of-the-brain-of-the-same-embryo-shown-in-image338931811.htmlRM2AKBJYF–A reference handbook of the medical sciences, embracing the entire range of scientific and practical medicine and allied science . spectively the develop-ment of the inferior and superiorcoUiculus of the corpora quad-rigemina. The development of the pro-sencephalon is much more com-plex, for here the primary seg-mental apparatus has been over-shadowed by suprasegmental cor-relation centers of the most in-tricate character. There are noperipheral motor nerves in thisregion; accordingly, the ventro-lateral lamina is greatly reduced Fio. 889.—Lateral View of the Brain of the Same Embryo Shown in
 MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image261520244.html
MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image261520244.htmlRFW5D7MM–MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray.
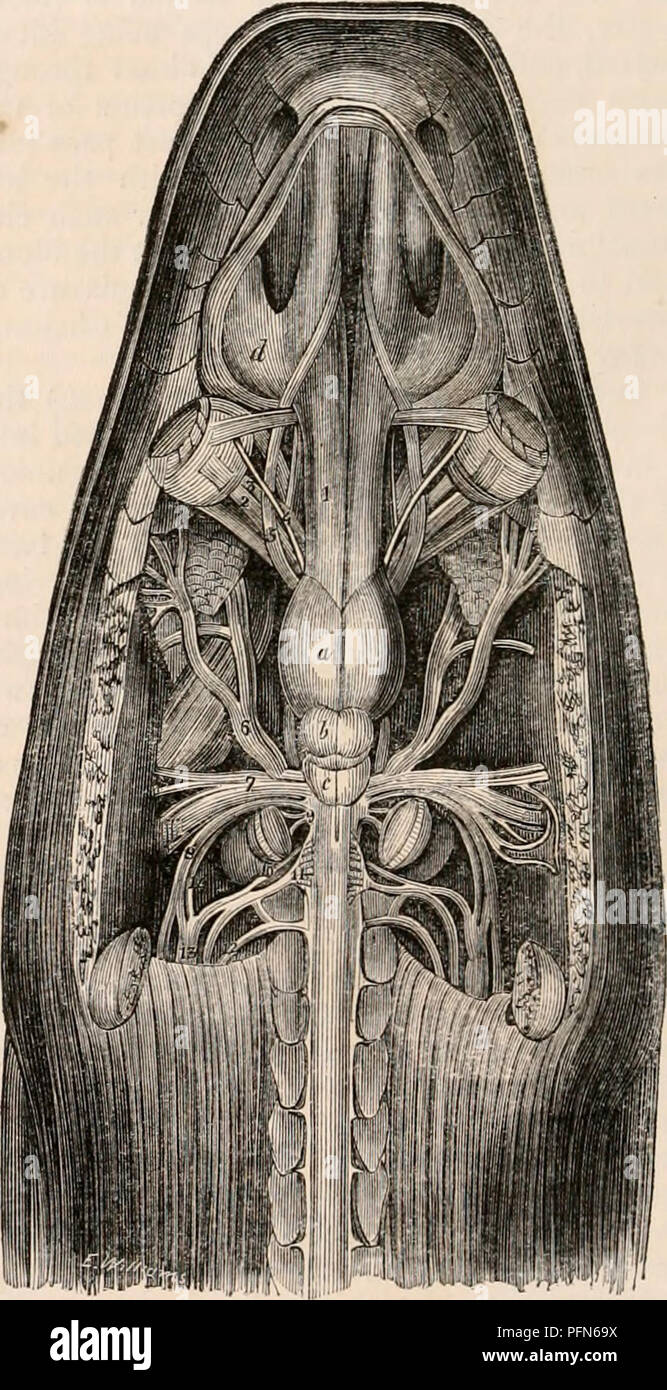 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. c, lateral view of the brain of a turtle; 1, optic tract; 2, cms cerebri. d, the same: a. portion of the optic nerve has been removed to show the crus cerebri passing upwards. {After Swan.*) spinal chord. The inferior surface of the brain is almost smooth, presenting no other ele- vations than those formed by the union of the optic nerves and by the tuber cinereum. As there are no lateral lobes to the cerebellum, of course no traces of a pons varolii exist. As in birds, a vascular inflation, which seems to represent the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-c-lateral-view-of-the-brain-of-a-turtle-1-optic-tract-2-cms-cerebri-d-the-same-a-portion-of-the-optic-nerve-has-been-removed-to-show-the-crus-cerebri-passing-upwards-after-swan-spinal-chord-the-inferior-surface-of-the-brain-is-almost-smooth-presenting-no-other-ele-vations-than-those-formed-by-the-union-of-the-optic-nerves-and-by-the-tuber-cinereum-as-there-are-no-lateral-lobes-to-the-cerebellum-of-course-no-traces-of-a-pons-varolii-exist-as-in-birds-a-vascular-inflation-which-seems-to-represent-the-image216210230.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. c, lateral view of the brain of a turtle; 1, optic tract; 2, cms cerebri. d, the same: a. portion of the optic nerve has been removed to show the crus cerebri passing upwards. {After Swan.*) spinal chord. The inferior surface of the brain is almost smooth, presenting no other ele- vations than those formed by the union of the optic nerves and by the tuber cinereum. As there are no lateral lobes to the cerebellum, of course no traces of a pons varolii exist. As in birds, a vascular inflation, which seems to represent the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-c-lateral-view-of-the-brain-of-a-turtle-1-optic-tract-2-cms-cerebri-d-the-same-a-portion-of-the-optic-nerve-has-been-removed-to-show-the-crus-cerebri-passing-upwards-after-swan-spinal-chord-the-inferior-surface-of-the-brain-is-almost-smooth-presenting-no-other-ele-vations-than-those-formed-by-the-union-of-the-optic-nerves-and-by-the-tuber-cinereum-as-there-are-no-lateral-lobes-to-the-cerebellum-of-course-no-traces-of-a-pons-varolii-exist-as-in-birds-a-vascular-inflation-which-seems-to-represent-the-image216210230.htmlRMPFN69X–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. c, lateral view of the brain of a turtle; 1, optic tract; 2, cms cerebri. d, the same: a. portion of the optic nerve has been removed to show the crus cerebri passing upwards. {After Swan.*) spinal chord. The inferior surface of the brain is almost smooth, presenting no other ele- vations than those formed by the union of the optic nerves and by the tuber cinereum. As there are no lateral lobes to the cerebellum, of course no traces of a pons varolii exist. As in birds, a vascular inflation, which seems to represent the
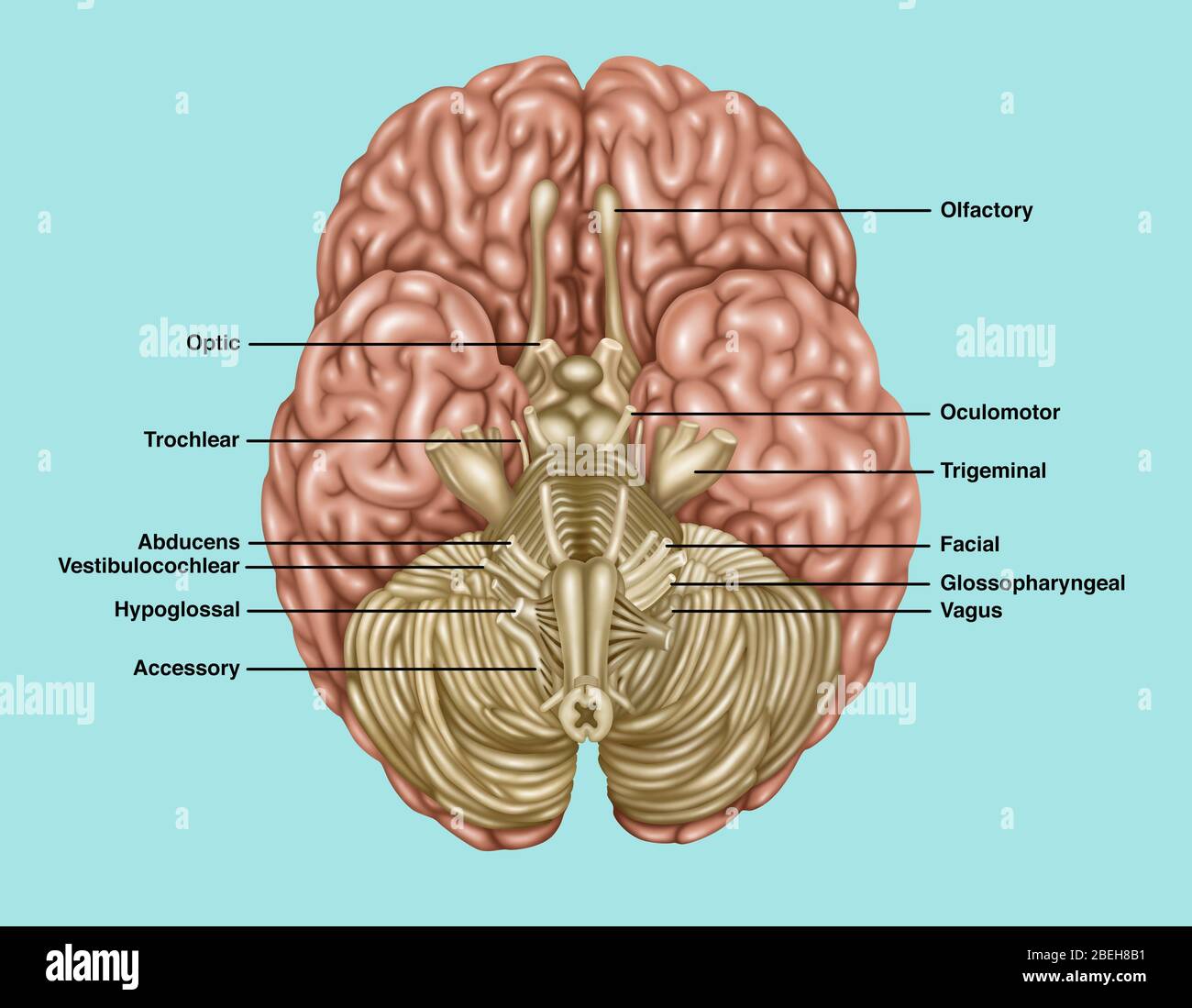 Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192309.html
Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192309.htmlRF2BEH8B1–Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration
![. The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., optic lobe; op.V, ophthalmicus pr Stock Photo . The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., optic lobe; op.V, ophthalmicus pr Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/MA7C54/the-elasmobranch-fishes-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-ojt-olfactory-tract-opl-optic-lobe-opv-ophthalmicus-pr-MA7C54.jpg) . The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., optic lobe; op.V, ophthalmicus pr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-ojt-olfactory-tract-opl-optic-lobe-opv-ophthalmicus-pr-image178413456.html
. The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., optic lobe; op.V, ophthalmicus pr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-ojt-olfactory-tract-opl-optic-lobe-opv-ophthalmicus-pr-image178413456.htmlRMMA7C54–. The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., optic lobe; op.V, ophthalmicus pr
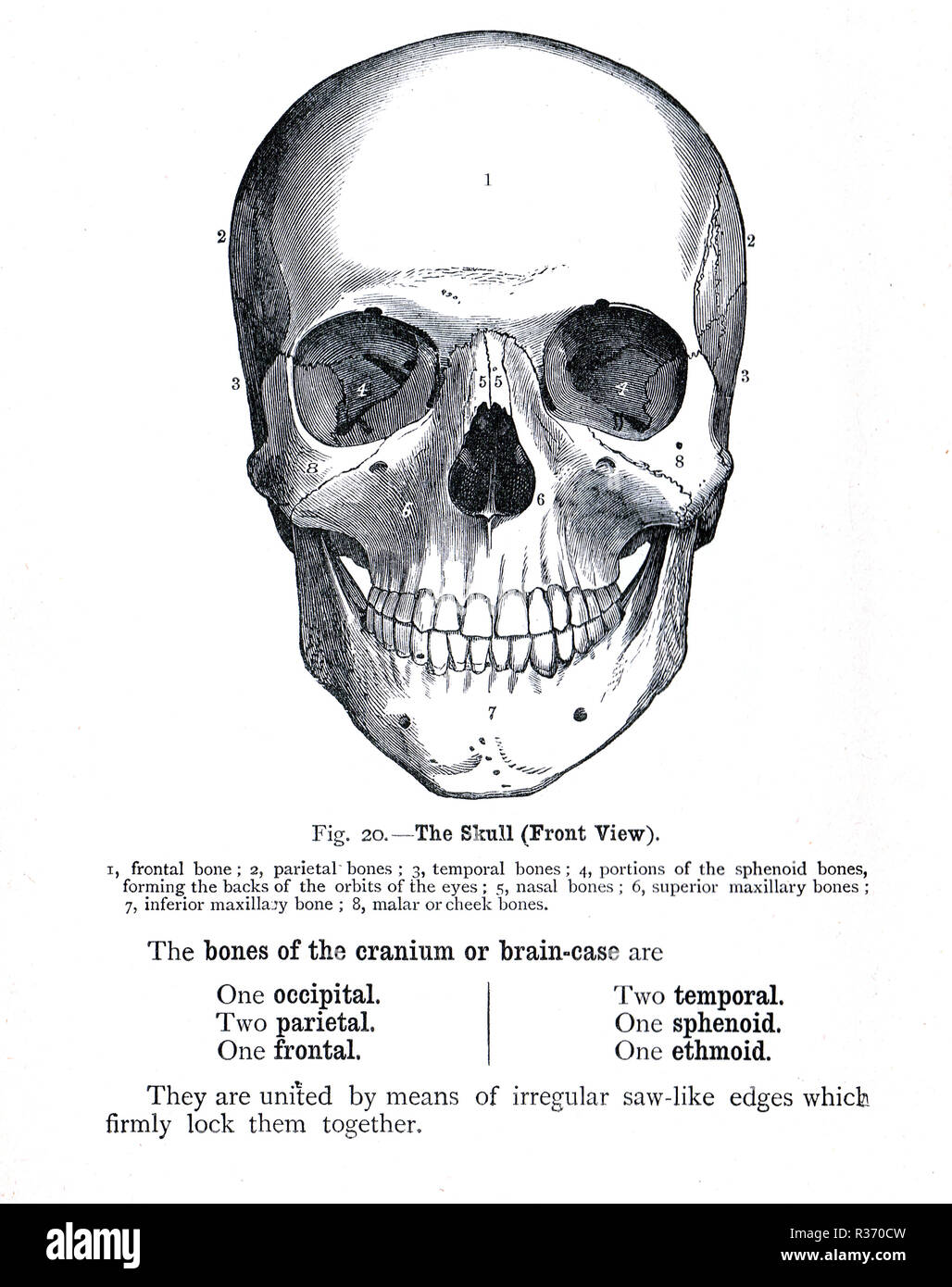
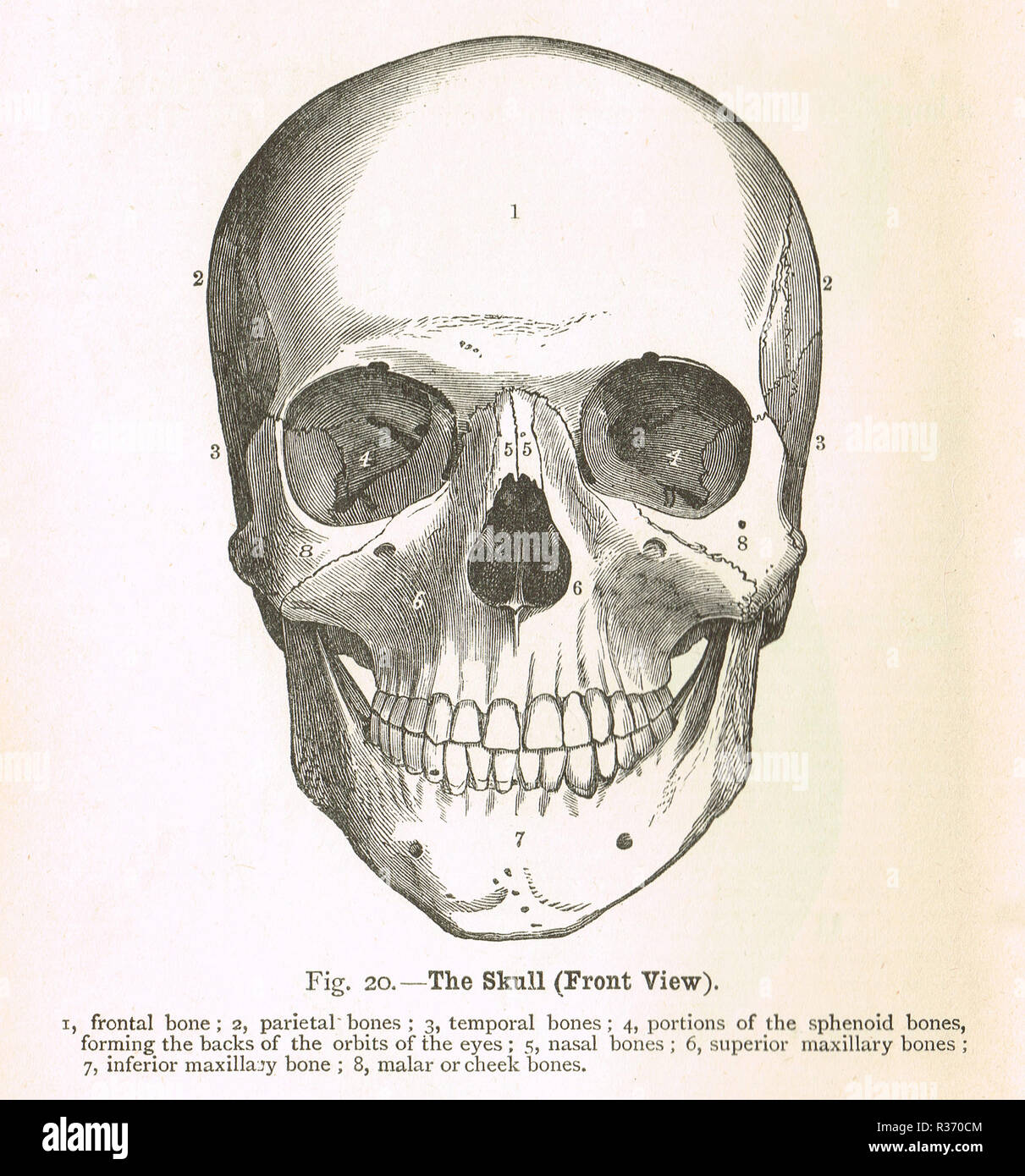 Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732772.html
Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732772.htmlRMR370CM–Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration
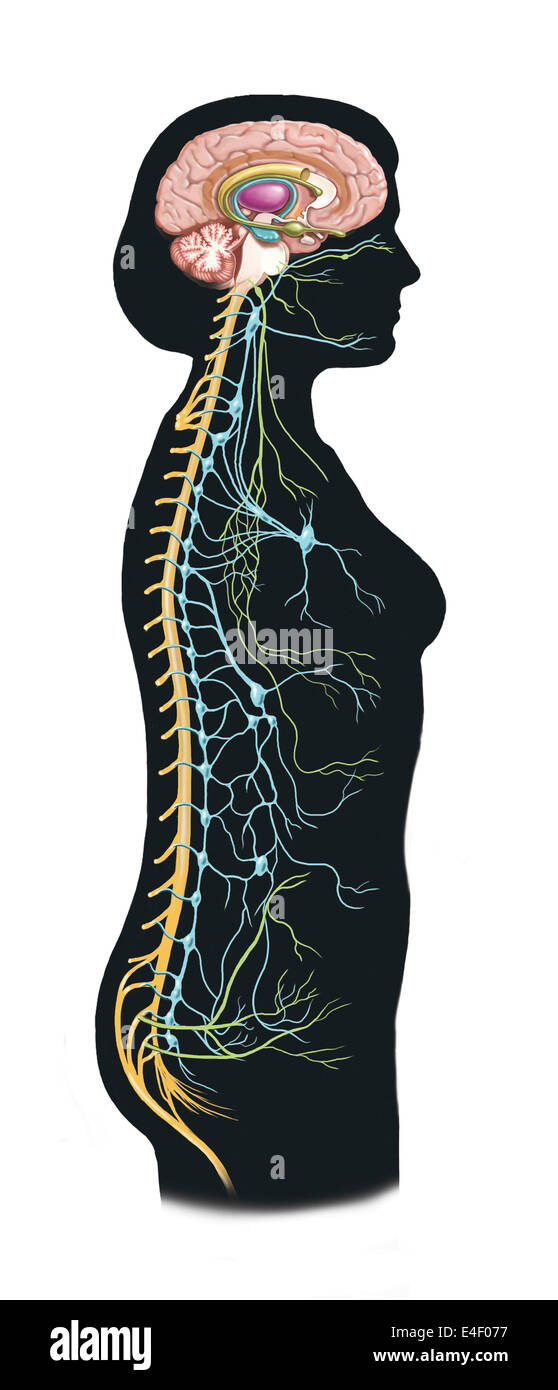 Side view of human body showing autonomic nervous system and limbic system within the brain. Green are parasympathetic nerves. B Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-side-view-of-human-body-showing-autonomic-nervous-system-and-limbic-71629579.html
Side view of human body showing autonomic nervous system and limbic system within the brain. Green are parasympathetic nerves. B Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-side-view-of-human-body-showing-autonomic-nervous-system-and-limbic-71629579.htmlRME4F077–Side view of human body showing autonomic nervous system and limbic system within the brain. Green are parasympathetic nerves. B
 Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-temporal-gyrus-illustration-image430103393.html
Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-temporal-gyrus-illustration-image430103393.htmlRF2FYMW7D–Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration
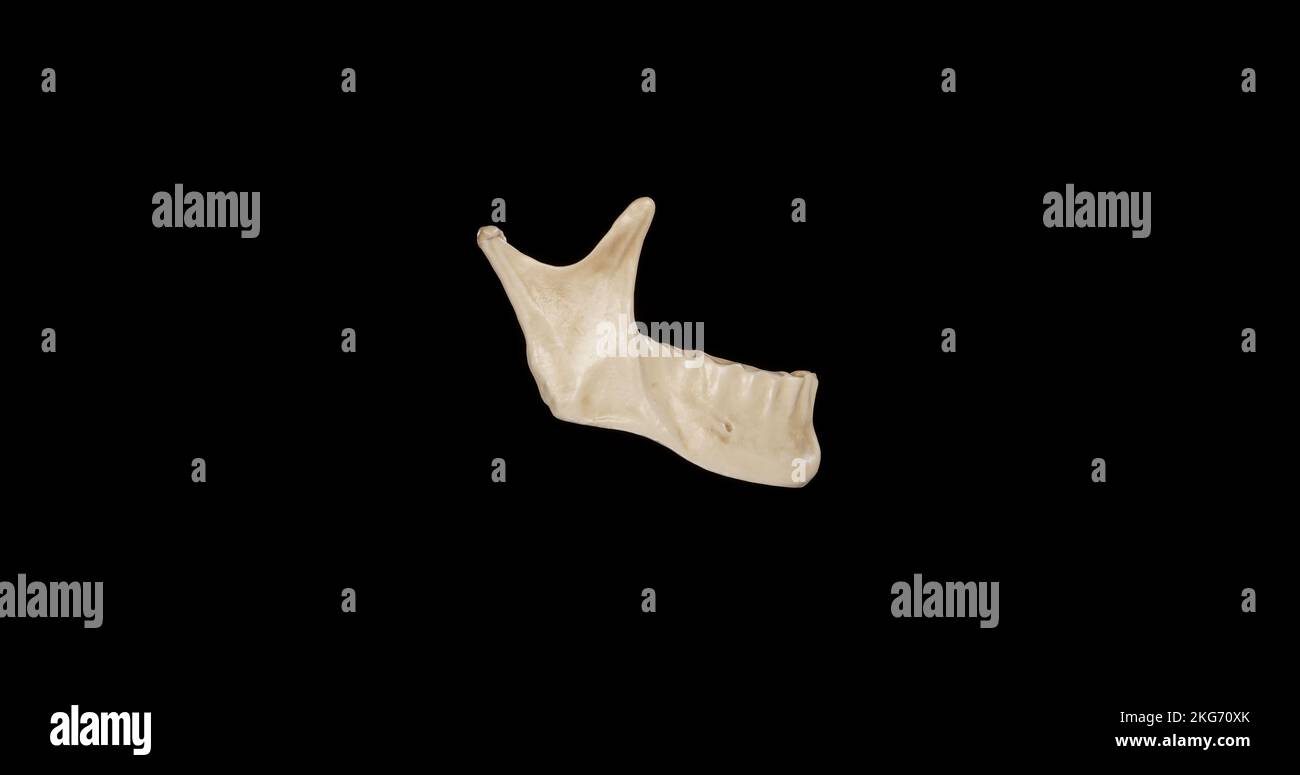 Lateral view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lateral-view-of-mandible-image491879211.html
Lateral view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lateral-view-of-mandible-image491879211.htmlRF2KG70XK–Lateral view of Mandible
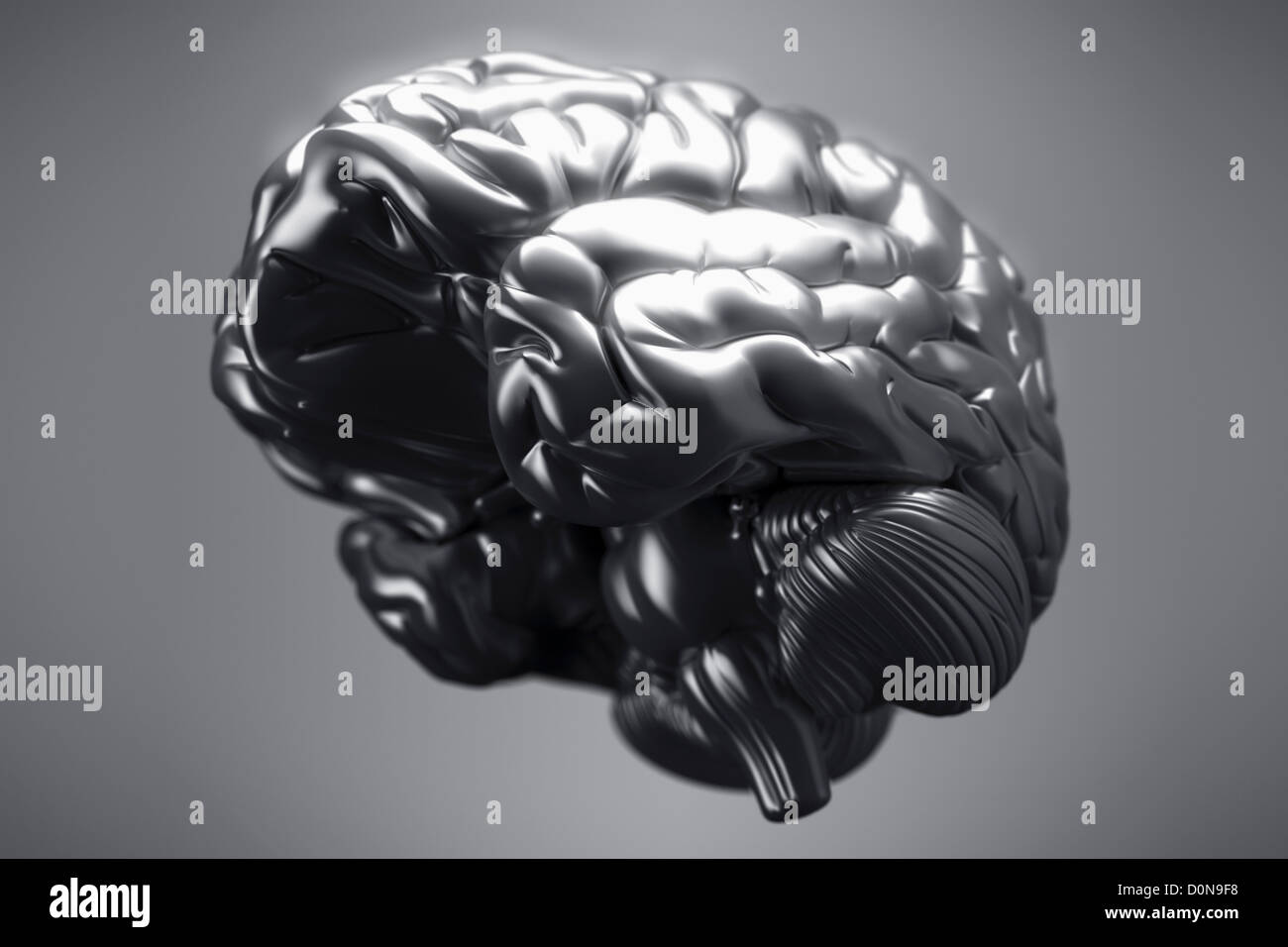 An inferior view of a metallic brain. The cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem are visible. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-an-inferior-view-of-a-metallic-brain-the-cerebral-hemispheres-cerebellum-52099580.html
An inferior view of a metallic brain. The cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem are visible. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-an-inferior-view-of-a-metallic-brain-the-cerebral-hemispheres-cerebellum-52099580.htmlRMD0N9F8–An inferior view of a metallic brain. The cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem are visible.
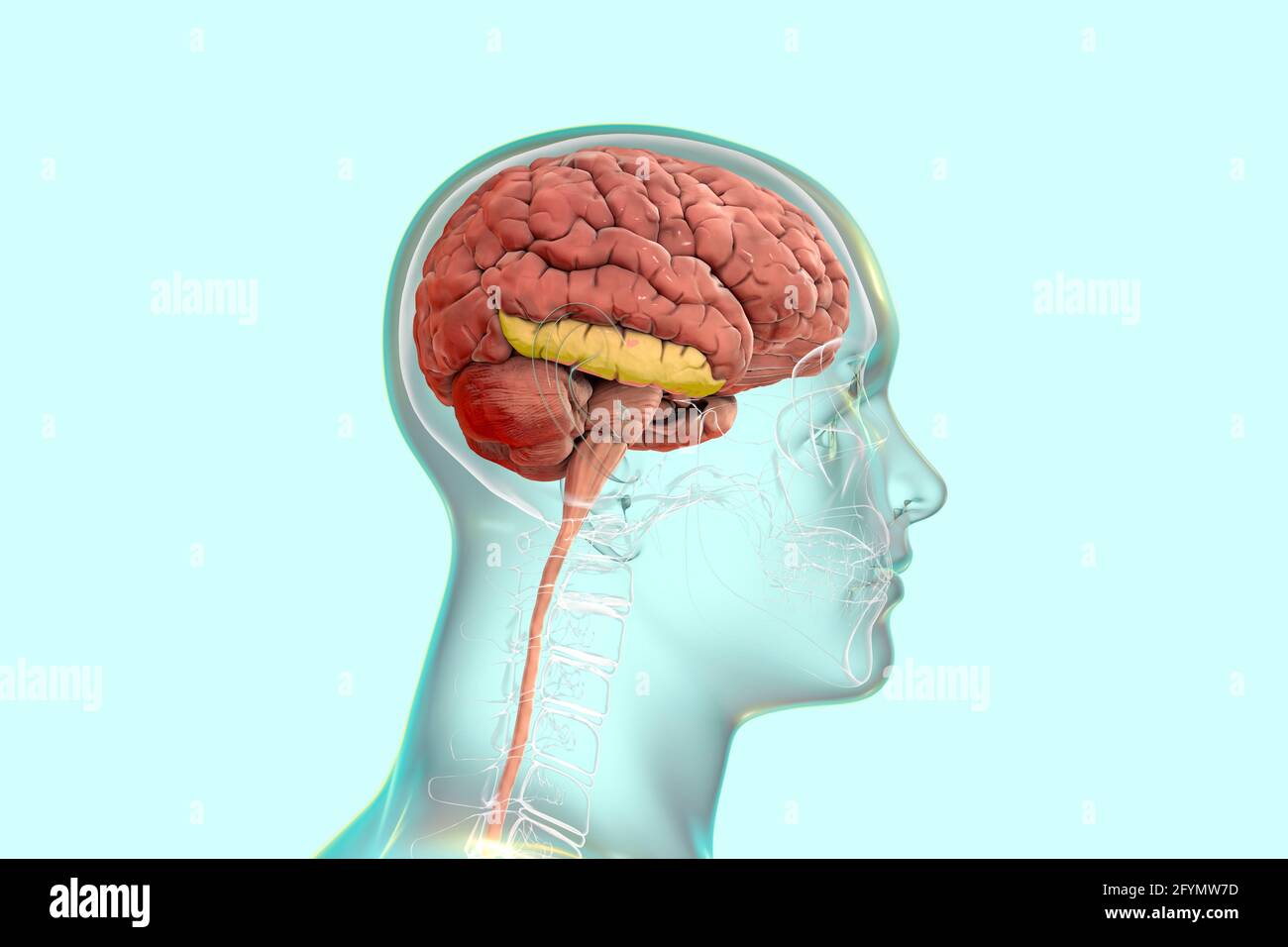
 Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715544.html
Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715544.htmlRF2A14MEG–Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain.
 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13233497.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13233497.htmlRFACW82J–The arteries of the brain
![The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ Stock Photo The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/RWT9XE/the-elasmobranch-fishes-1934-the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-oj-RWT9XE.jpg) The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-1934-the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-oj-image239635830.html
The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-1934-the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-oj-image239635830.htmlRMRWT9XE–The elasmobranch fishes (1934) The elasmobranch fishes elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ
 Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lymphatic-drainage-follows-the-course-of-the-inferior-mesenteric-vessels-3d-illustration-image596589511.html
Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lymphatic-drainage-follows-the-course-of-the-inferior-mesenteric-vessels-3d-illustration-image596589511.htmlRF2WJH007–Lymphatic drainage follows the course of the inferior mesenteric vessels 3d illustration
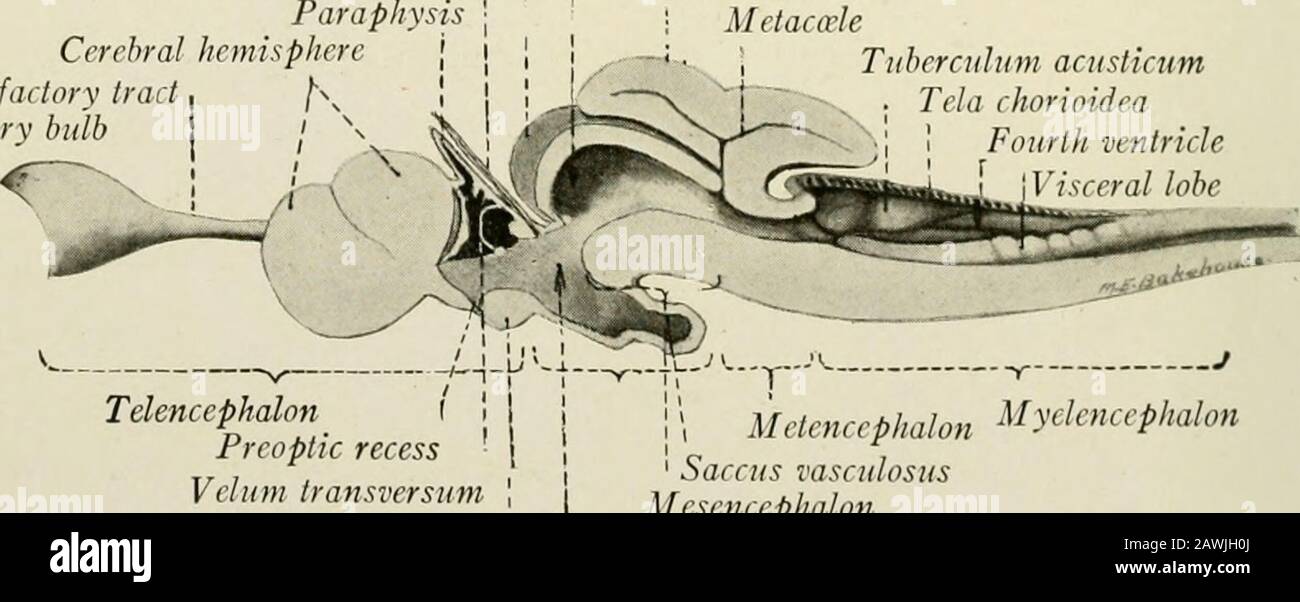 The anatomy of the nervous system, from the standpoint of development and function . Olfactory trad Optic nerve N. II Inferior lobeOculomotor nerve N. Ill . , , , . , „ „ ., Saccus vasculosus Trigeminal and facial nerves Nn. V, VII Trochlear nerve N. IV Fig. 10.—The brain of the dogfish, Squalus acanthias, lateral view. spoken of as the tectum mesencephali. Within this roof end the fibers whichcome from the retime through the optic nerves. The floor of the cavity is formedby the ventral part of the mesencephalon. This appears like a direct continua-tion of the medulla oblongata, and in the m Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-nervous-system-from-the-standpoint-of-development-and-function-olfactory-trad-optic-nerve-n-ii-inferior-lobeoculomotor-nerve-n-ill-saccus-vasculosus-trigeminal-and-facial-nerves-nn-v-vii-trochlear-nerve-n-iv-fig-10the-brain-of-the-dogfish-squalus-acanthias-lateral-view-spoken-of-as-the-tectum-mesencephali-within-this-roof-end-the-fibers-whichcome-from-the-retime-through-the-optic-nerves-the-floor-of-the-cavity-is-formedby-the-ventral-part-of-the-mesencephalon-this-appears-like-a-direct-continua-tion-of-the-medulla-oblongata-and-in-the-m-image342771874.html
The anatomy of the nervous system, from the standpoint of development and function . Olfactory trad Optic nerve N. II Inferior lobeOculomotor nerve N. Ill . , , , . , „ „ ., Saccus vasculosus Trigeminal and facial nerves Nn. V, VII Trochlear nerve N. IV Fig. 10.—The brain of the dogfish, Squalus acanthias, lateral view. spoken of as the tectum mesencephali. Within this roof end the fibers whichcome from the retime through the optic nerves. The floor of the cavity is formedby the ventral part of the mesencephalon. This appears like a direct continua-tion of the medulla oblongata, and in the m Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-nervous-system-from-the-standpoint-of-development-and-function-olfactory-trad-optic-nerve-n-ii-inferior-lobeoculomotor-nerve-n-ill-saccus-vasculosus-trigeminal-and-facial-nerves-nn-v-vii-trochlear-nerve-n-iv-fig-10the-brain-of-the-dogfish-squalus-acanthias-lateral-view-spoken-of-as-the-tectum-mesencephali-within-this-roof-end-the-fibers-whichcome-from-the-retime-through-the-optic-nerves-the-floor-of-the-cavity-is-formedby-the-ventral-part-of-the-mesencephalon-this-appears-like-a-direct-continua-tion-of-the-medulla-oblongata-and-in-the-m-image342771874.htmlRM2AWJH0J–The anatomy of the nervous system, from the standpoint of development and function . Olfactory trad Optic nerve N. II Inferior lobeOculomotor nerve N. Ill . , , , . , „ „ ., Saccus vasculosus Trigeminal and facial nerves Nn. V, VII Trochlear nerve N. IV Fig. 10.—The brain of the dogfish, Squalus acanthias, lateral view. spoken of as the tectum mesencephali. Within this roof end the fibers whichcome from the retime through the optic nerves. The floor of the cavity is formedby the ventral part of the mesencephalon. This appears like a direct continua-tion of the medulla oblongata, and in the m
 MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image261484415.html
MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mri-sacroiliac-articulation-study-of-ankylosing-spondyloarthritis-patient-the-results-of-the-study-on-the-x-ray-image261484415.htmlRFW5BJ13–MRI sacroiliac articulation. Study of ankylosing spondyloarthritis patient. The results of the study on the x-ray.
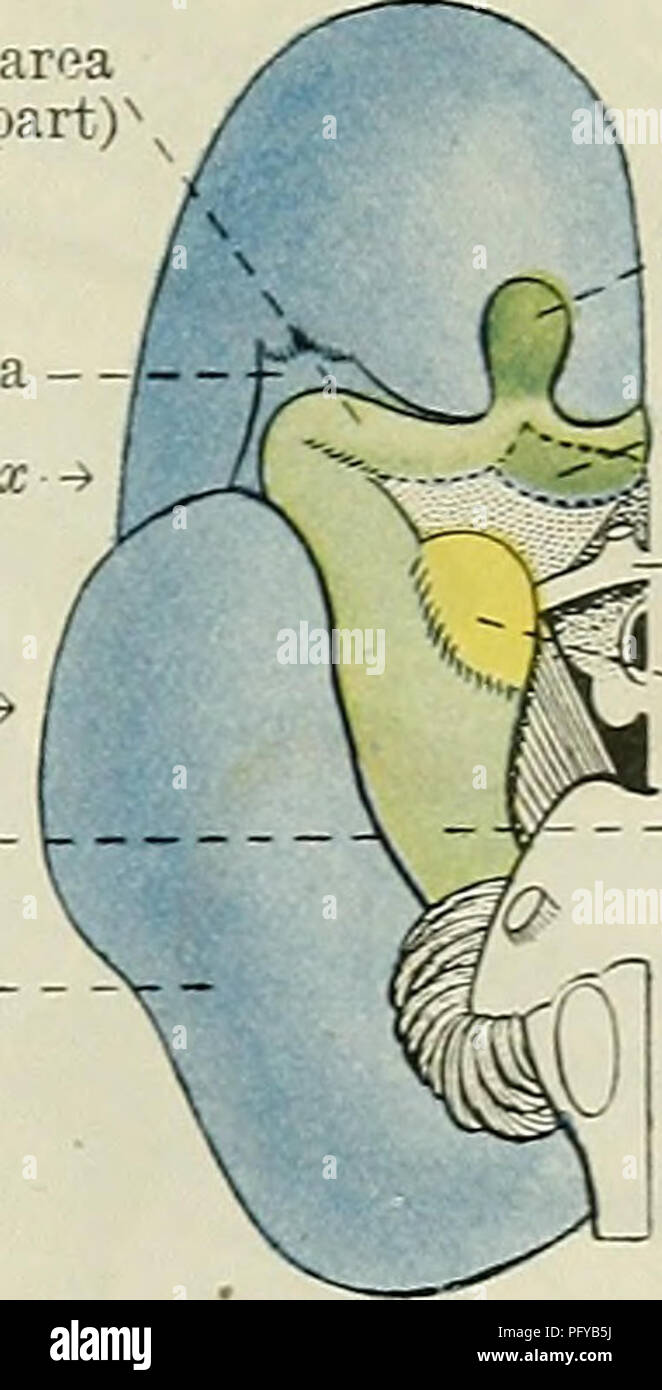 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. Piriform area (anterior part) Insula - -Olfactory tubercle •Optic ehiasma Nucleus f amygdala? Rhinal fissure— Neopallium -. ^Olfactory bulb ^Olfactory tubercle -Optic ehiasma Nucleus amygdalae Piriform area (posterior part) Fig. 553. A, The lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere of a rabbit. B, The inferior aspect of the right half of a rabbit's brain. C, The corresponding view of a human foetal brain at the fifth month. Olfactory areas, green ; neopallium, blue. excrescences; and it is whitened by a thin layer of fibres (substantia reti Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-piriform-area-anterior-part-insula-olfactory-tubercle-optic-ehiasma-nucleus-f-amygdala-rhinal-fissure-neopallium-olfactory-bulb-olfactory-tubercle-optic-ehiasma-nucleus-amygdalae-piriform-area-posterior-part-fig-553-a-the-lateral-aspect-of-the-left-cerebral-hemisphere-of-a-rabbit-b-the-inferior-aspect-of-the-right-half-of-a-rabbits-brain-c-the-corresponding-view-of-a-human-foetal-brain-at-the-fifth-month-olfactory-areas-green-neopallium-blue-excrescences-and-it-is-whitened-by-a-thin-layer-of-fibres-substantia-reti-image216345742.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. Piriform area (anterior part) Insula - -Olfactory tubercle •Optic ehiasma Nucleus f amygdala? Rhinal fissure— Neopallium -. ^Olfactory bulb ^Olfactory tubercle -Optic ehiasma Nucleus amygdalae Piriform area (posterior part) Fig. 553. A, The lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere of a rabbit. B, The inferior aspect of the right half of a rabbit's brain. C, The corresponding view of a human foetal brain at the fifth month. Olfactory areas, green ; neopallium, blue. excrescences; and it is whitened by a thin layer of fibres (substantia reti Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-piriform-area-anterior-part-insula-olfactory-tubercle-optic-ehiasma-nucleus-f-amygdala-rhinal-fissure-neopallium-olfactory-bulb-olfactory-tubercle-optic-ehiasma-nucleus-amygdalae-piriform-area-posterior-part-fig-553-a-the-lateral-aspect-of-the-left-cerebral-hemisphere-of-a-rabbit-b-the-inferior-aspect-of-the-right-half-of-a-rabbits-brain-c-the-corresponding-view-of-a-human-foetal-brain-at-the-fifth-month-olfactory-areas-green-neopallium-blue-excrescences-and-it-is-whitened-by-a-thin-layer-of-fibres-substantia-reti-image216345742.htmlRMPFYB5J–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. Piriform area (anterior part) Insula - -Olfactory tubercle •Optic ehiasma Nucleus f amygdala? Rhinal fissure— Neopallium -. ^Olfactory bulb ^Olfactory tubercle -Optic ehiasma Nucleus amygdalae Piriform area (posterior part) Fig. 553. A, The lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere of a rabbit. B, The inferior aspect of the right half of a rabbit's brain. C, The corresponding view of a human foetal brain at the fifth month. Olfactory areas, green ; neopallium, blue. excrescences; and it is whitened by a thin layer of fibres (substantia reti
 Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192355.html
Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-anatomy-inferior-view-illustration-image353192355.htmlRF2BEH8CK–Brain Anatomy, Inferior View, Illustration
 . The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 213. Brain of Scymnus. (From Burckhardt.) A. Side view. B. Median sagittal view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; (q)., pineal stalk; ffin., median longitudinal bundles; in., infundilnilum ; i.L, anterior lolie; Lv., lobe of the vagus; m-.n., median olfactory nucleus; op.l., optie lobe; p.e., pallial eminence; p.L, posterior or inferior lobe of hypophysis; v.s., vascular sacs; //, optic nerve. to be unusually large. In all forms the roof of the mesencephalon is composed of a right and a left optic lobe {op.l., figs. 210 and 213) which are hollow out- pock Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-fig-213-brain-of-scymnus-from-burckhardt-a-side-view-b-median-sagittal-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-q-pineal-stalk-ffin-median-longitudinal-bundles-in-infundilnilum-il-anterior-lolie-lv-lobe-of-the-vagus-m-n-median-olfactory-nucleus-opl-optie-lobe-pe-pallial-eminence-pl-posterior-or-inferior-lobe-of-hypophysis-vs-vascular-sacs-optic-nerve-to-be-unusually-large-in-all-forms-the-roof-of-the-mesencephalon-is-composed-of-a-right-and-a-left-optic-lobe-opl-figs-210-and-213-which-are-hollow-out-pock-image178413453.html
. The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 213. Brain of Scymnus. (From Burckhardt.) A. Side view. B. Median sagittal view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; (q)., pineal stalk; ffin., median longitudinal bundles; in., infundilnilum ; i.L, anterior lolie; Lv., lobe of the vagus; m-.n., median olfactory nucleus; op.l., optie lobe; p.e., pallial eminence; p.L, posterior or inferior lobe of hypophysis; v.s., vascular sacs; //, optic nerve. to be unusually large. In all forms the roof of the mesencephalon is composed of a right and a left optic lobe {op.l., figs. 210 and 213) which are hollow out- pock Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-fig-213-brain-of-scymnus-from-burckhardt-a-side-view-b-median-sagittal-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-q-pineal-stalk-ffin-median-longitudinal-bundles-in-infundilnilum-il-anterior-lolie-lv-lobe-of-the-vagus-m-n-median-olfactory-nucleus-opl-optie-lobe-pe-pallial-eminence-pl-posterior-or-inferior-lobe-of-hypophysis-vs-vascular-sacs-optic-nerve-to-be-unusually-large-in-all-forms-the-roof-of-the-mesencephalon-is-composed-of-a-right-and-a-left-optic-lobe-opl-figs-210-and-213-which-are-hollow-out-pock-image178413453.htmlRMMA7C51–. The elasmobranch fishes . Fig. 213. Brain of Scymnus. (From Burckhardt.) A. Side view. B. Median sagittal view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; (q)., pineal stalk; ffin., median longitudinal bundles; in., infundilnilum ; i.L, anterior lolie; Lv., lobe of the vagus; m-.n., median olfactory nucleus; op.l., optie lobe; p.e., pallial eminence; p.L, posterior or inferior lobe of hypophysis; v.s., vascular sacs; //, optic nerve. to be unusually large. In all forms the roof of the mesencephalon is composed of a right and a left optic lobe {op.l., figs. 210 and 213) which are hollow out- pock
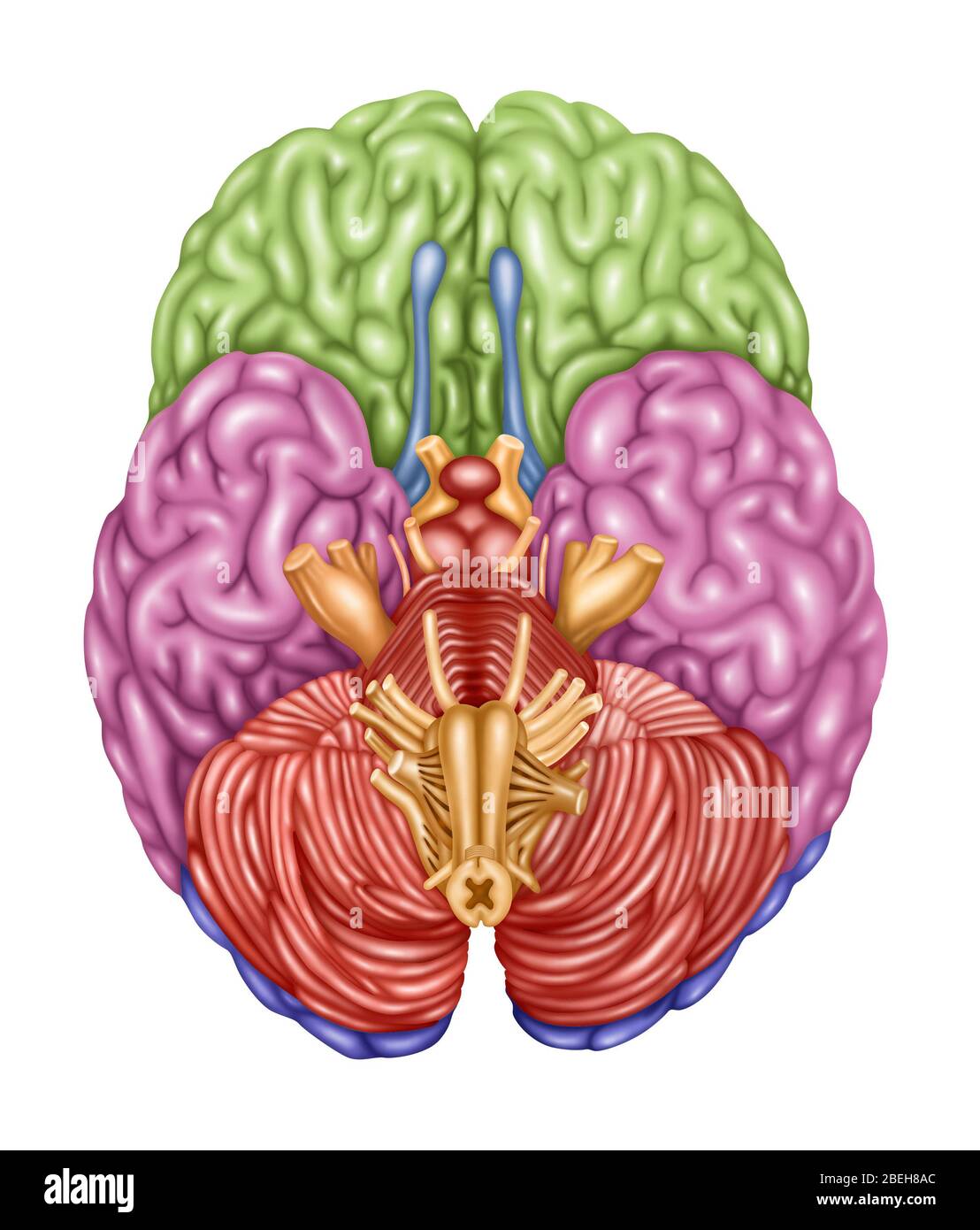
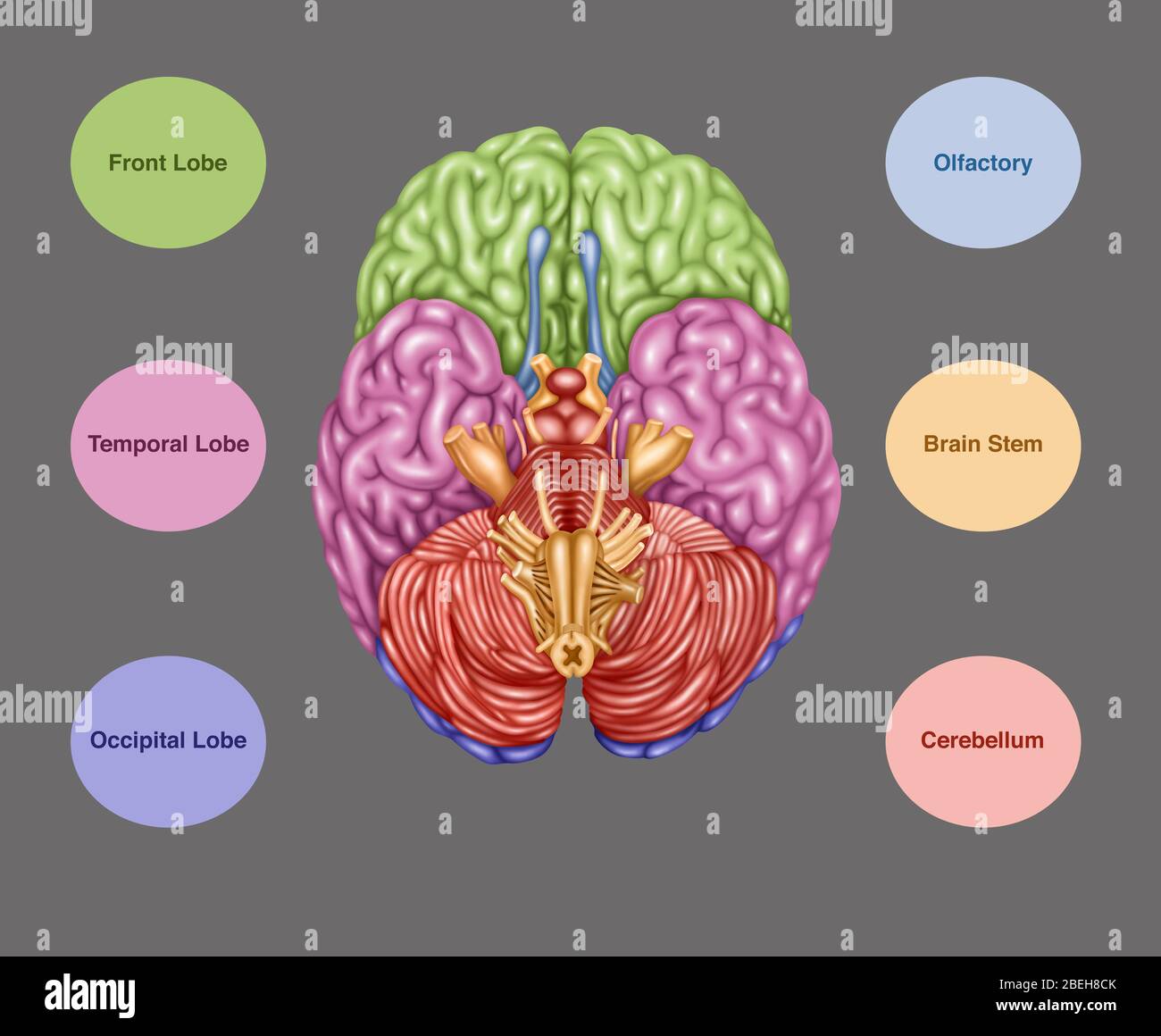
 Color coded brain depicting the following areas from an inferior view: frontal lobe (green), temporal lobe (pink), occipital lobe (purple), olfactory (blue), brain stem (orange), cerebellum (orangish-pink). Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-color-coded-brain-depicting-the-following-areas-from-an-inferior-view-103992553.html
Color coded brain depicting the following areas from an inferior view: frontal lobe (green), temporal lobe (pink), occipital lobe (purple), olfactory (blue), brain stem (orange), cerebellum (orangish-pink). Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-color-coded-brain-depicting-the-following-areas-from-an-inferior-view-103992553.htmlRMG157FN–Color coded brain depicting the following areas from an inferior view: frontal lobe (green), temporal lobe (pink), occipital lobe (purple), olfactory (blue), brain stem (orange), cerebellum (orangish-pink).
 Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732777.html
Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732777.htmlRMR370CW–Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration
 Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-temporal-gyrus-illustration-image430103394.html
Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-with-highlighted-inferior-temporal-gyrus-illustration-image430103394.htmlRF2FYMW7E–Brain with highlighted inferior temporal gyrus, illustration
 Left view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/left-view-of-mandible-image491879187.html
Left view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/left-view-of-mandible-image491879187.htmlRF2KG70WR–Left view of Mandible
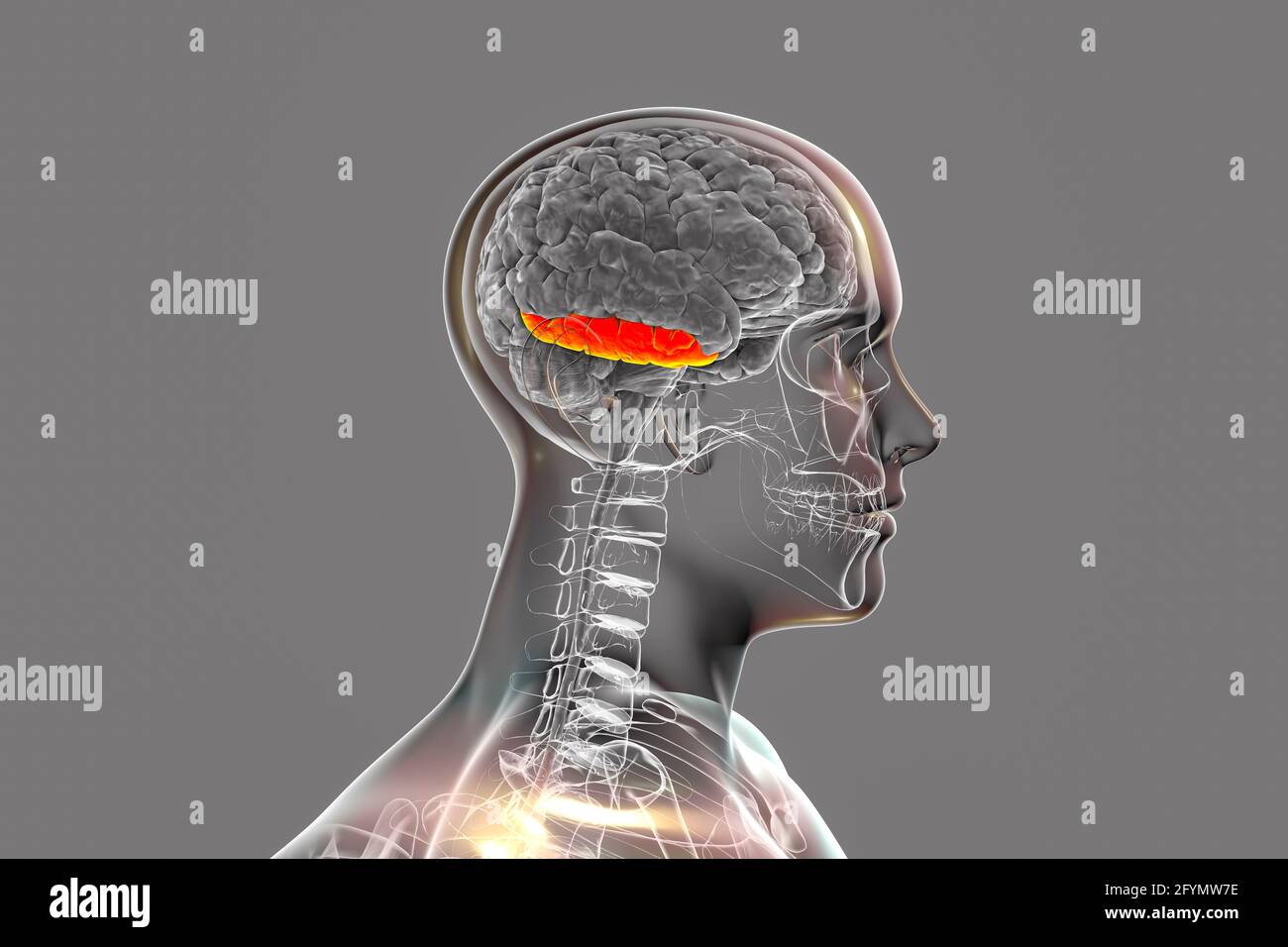
 Brain highlighting inferior occipital gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-occipital-gyrus-illustration-image403043378.html
Brain highlighting inferior occipital gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-occipital-gyrus-illustration-image403043378.htmlRF2EBM5XA–Brain highlighting inferior occipital gyrus, illustration
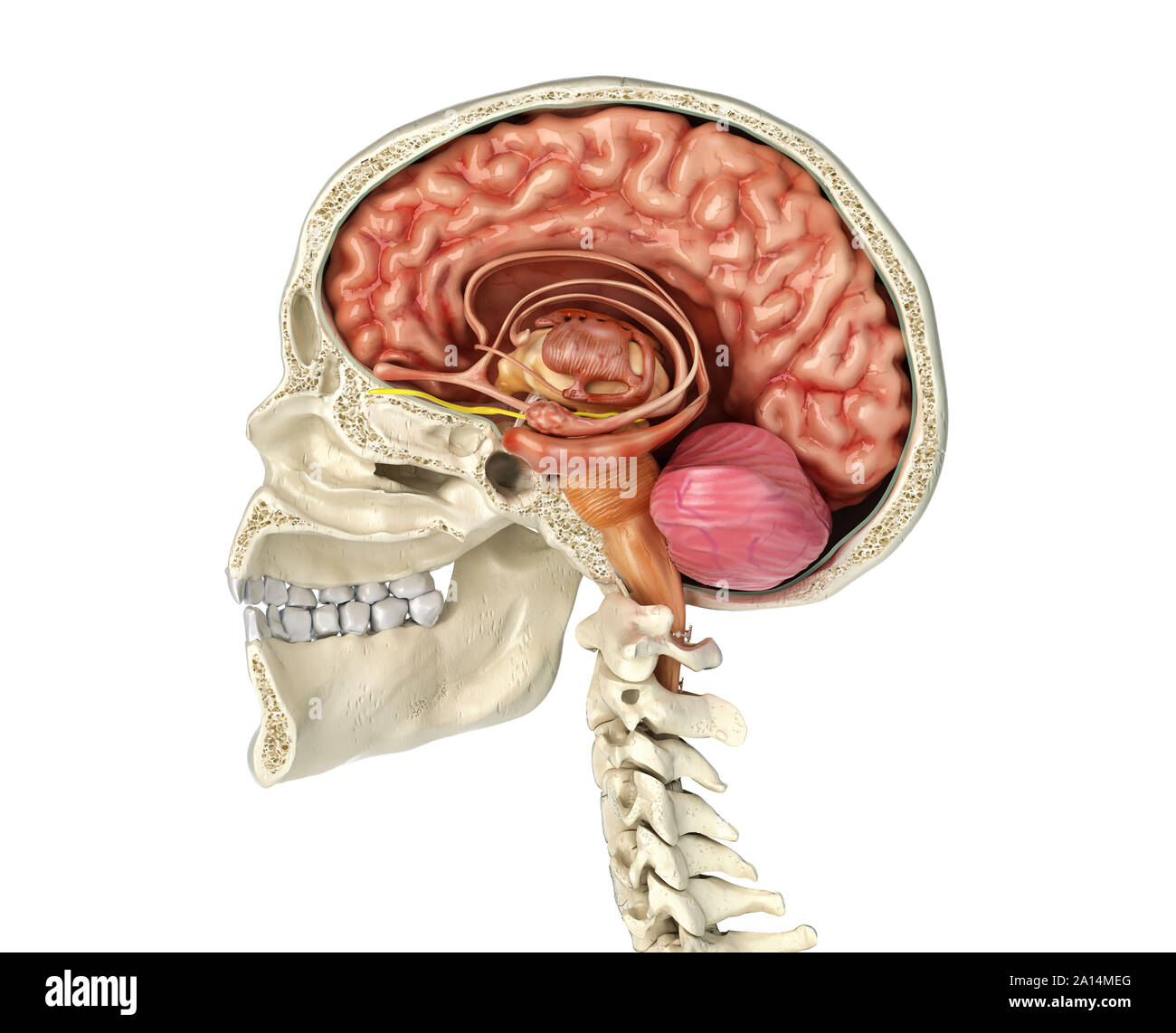
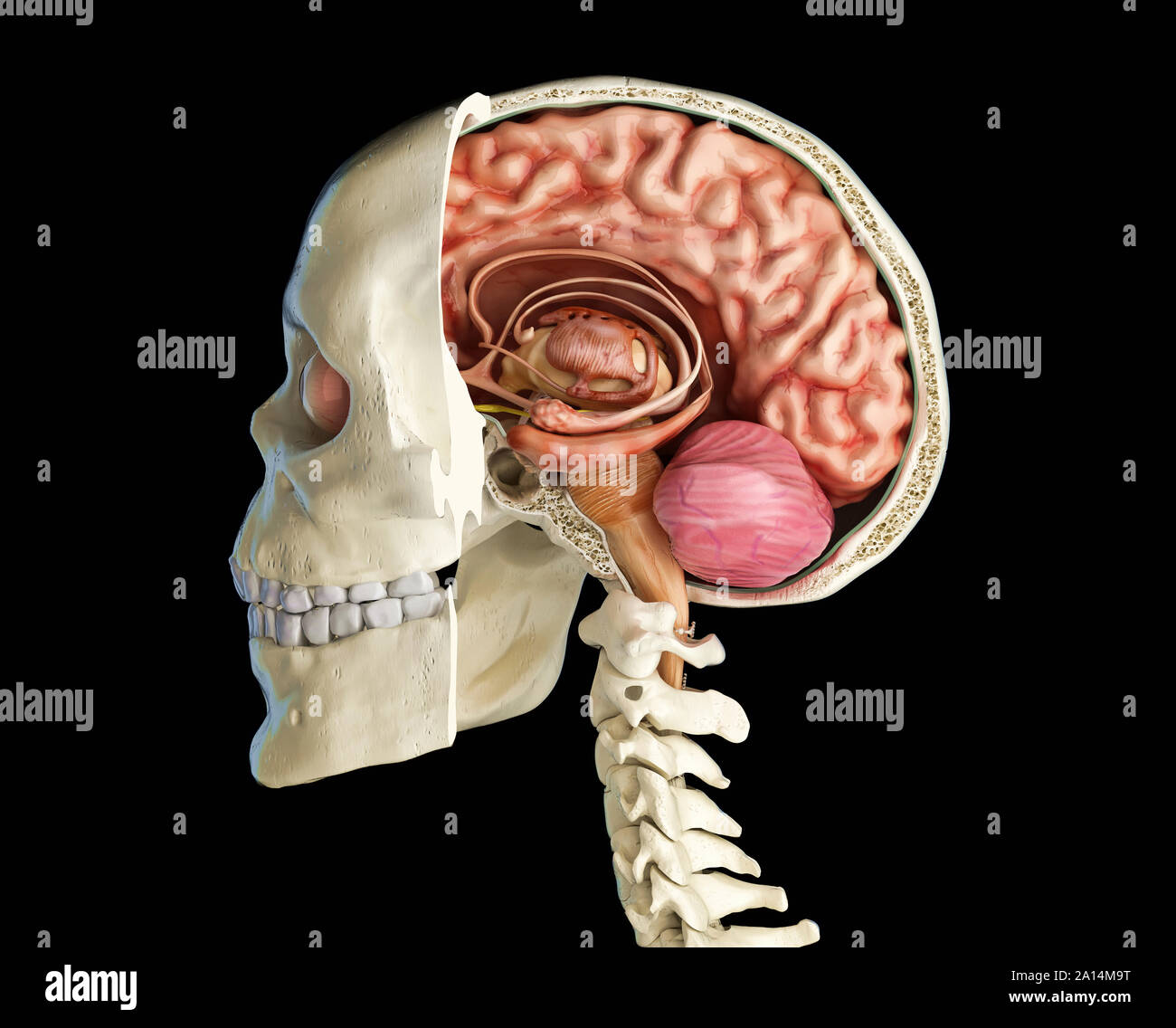 Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715412.html
Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715412.htmlRF2A14M9T–Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain.
 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13234711.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13234711.htmlRFACWBKM–The arteries of the brain
 The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth cranial nerve; IX. glossopha Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-a-b-fig-210-brain-of-reterodonius-francisci-mildred-bennett-del-a-dorsal-view-b-ventral-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-dl-diencephalon-or-thalameneephalon-id-inferior-lobe-imn-median-olfactory-nucleus-mcd-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-old-olfactory-bulb-ojd-olfactory-lobe-old-olfactory-tract-opd-optic-lobe-pc-pallial-eminence-tl-telencephalon-vs-vascular-sac-7-olfactory-nerve-optic-nerve-iv-trochlearis-or-fourth-nerve-vi-alducens-or-sixth-cranial-nerve-ix-glossopha-image241030132.html
The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth cranial nerve; IX. glossopha Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-a-b-fig-210-brain-of-reterodonius-francisci-mildred-bennett-del-a-dorsal-view-b-ventral-view-ch-cerebellum-cr-restiform-body-dl-diencephalon-or-thalameneephalon-id-inferior-lobe-imn-median-olfactory-nucleus-mcd-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-old-olfactory-bulb-ojd-olfactory-lobe-old-olfactory-tract-opd-optic-lobe-pc-pallial-eminence-tl-telencephalon-vs-vascular-sac-7-olfactory-nerve-optic-nerve-iv-trochlearis-or-fourth-nerve-vi-alducens-or-sixth-cranial-nerve-ix-glossopha-image241030132.htmlRMT03TB0–The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 A B Fig. 210. Brain of Reterodonius francisci. (Mildred Bennett, del.) A. Dorsal view. B. Ventral view. ch., cerebellum; c.r., restiform body; dL, diencephalon or thalameneephalon; id., inferior lobe; im.n., median olfactory nucleus; mcd., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; old)., olfactory bulb; oJd., olfactory lobe; old., olfactory tract; opd., optic lobe; p.c, pallial eminence; tl., telencephalon; v.s., vascular sac; 7, olfactory nerve; //, optic nerve; IV, trochlearis or fourth nerve; VI, al»ducens or sixth cranial nerve; IX. glossopha
 The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-rectum-drains-into-the-superior-rectal-lymphatics-to-the-retroperitoneal-inferior-mesenteric-lymph-nodes-3d-illustration-image596581396.html
The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-rectum-drains-into-the-superior-rectal-lymphatics-to-the-retroperitoneal-inferior-mesenteric-lymph-nodes-3d-illustration-image596581396.htmlRF2WJGHJC–The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration
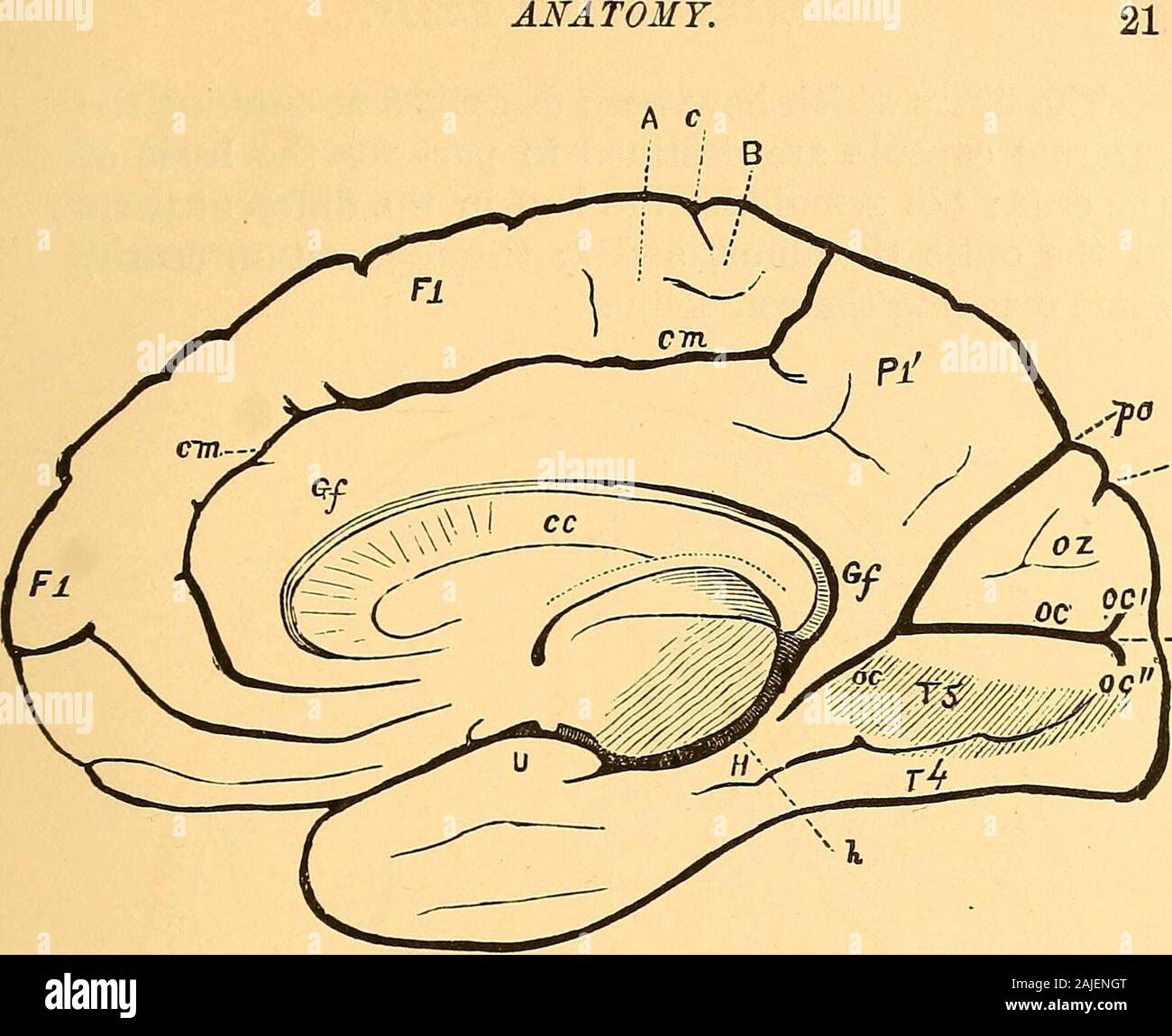 A treatise on nervous diseases; their symptoms and treatment . Fig. 8.—View of the brain from below. (Ecker.) Fu gyrus rectus, the prolongation of the first frontal convolution ; F9, middle,F3, lower frontal convolution; /4, sulcus olfactorius; /6, sulcus orbitalis; Tt,second, or middle, T3, third, or lower temporal convolution; Tt, gyrus occipito-temporalis lateralis (lobulus fusiformis), T6, gyrus occipito-temporalis medialis(lobulus lingualis); t2, middle, t3, lower temporal fissure ; r4, sulcus occipito-tem-poralis inferior; po, fissura parieto-occipitalis; oc, fissura calcarina; If, gyrus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-nervous-diseases-their-symptoms-and-treatment-fig-8view-of-the-brain-from-below-ecker-fu-gyrus-rectus-the-prolongation-of-the-first-frontal-convolution-f9-middlef3-lower-frontal-convolution-4-sulcus-olfactorius-6-sulcus-orbitalis-ttsecond-or-middle-t3-third-or-lower-temporal-convolution-tt-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-lateralis-lobulus-fusiformis-t6-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-medialislobulus-lingualis-t2-middle-t3-lower-temporal-fissure-r4-sulcus-occipito-tem-poralis-inferior-po-fissura-parieto-occipitalis-oc-fissura-calcarina-if-gyrus-image338385064.html
A treatise on nervous diseases; their symptoms and treatment . Fig. 8.—View of the brain from below. (Ecker.) Fu gyrus rectus, the prolongation of the first frontal convolution ; F9, middle,F3, lower frontal convolution; /4, sulcus olfactorius; /6, sulcus orbitalis; Tt,second, or middle, T3, third, or lower temporal convolution; Tt, gyrus occipito-temporalis lateralis (lobulus fusiformis), T6, gyrus occipito-temporalis medialis(lobulus lingualis); t2, middle, t3, lower temporal fissure ; r4, sulcus occipito-tem-poralis inferior; po, fissura parieto-occipitalis; oc, fissura calcarina; If, gyrus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-nervous-diseases-their-symptoms-and-treatment-fig-8view-of-the-brain-from-below-ecker-fu-gyrus-rectus-the-prolongation-of-the-first-frontal-convolution-f9-middlef3-lower-frontal-convolution-4-sulcus-olfactorius-6-sulcus-orbitalis-ttsecond-or-middle-t3-third-or-lower-temporal-convolution-tt-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-lateralis-lobulus-fusiformis-t6-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-medialislobulus-lingualis-t2-middle-t3-lower-temporal-fissure-r4-sulcus-occipito-tem-poralis-inferior-po-fissura-parieto-occipitalis-oc-fissura-calcarina-if-gyrus-image338385064.htmlRM2AJENGT–A treatise on nervous diseases; their symptoms and treatment . Fig. 8.—View of the brain from below. (Ecker.) Fu gyrus rectus, the prolongation of the first frontal convolution ; F9, middle,F3, lower frontal convolution; /4, sulcus olfactorius; /6, sulcus orbitalis; Tt,second, or middle, T3, third, or lower temporal convolution; Tt, gyrus occipito-temporalis lateralis (lobulus fusiformis), T6, gyrus occipito-temporalis medialis(lobulus lingualis); t2, middle, t3, lower temporal fissure ; r4, sulcus occipito-tem-poralis inferior; po, fissura parieto-occipitalis; oc, fissura calcarina; If, gyrus
 . Zoology : for students and general readers . Zoology. ANATOMY OF THE GUNNER. 441 superior (Os) and inferior (Oi), arise from the front of the orbit near the interorbital septum. The disposition of the. Pig. 400.— Anatomy of the brain of tlie Gunner, dorsal and side view.—Drawn bv C. S. Minot. recti is very constant, but tlie obhqui vary considerably in their origin in different Vertebrates. If a perch be cut through transversely, so that the section passes through the fore-part of the air-bladder, and the anterior portion then looked at from behind, a very instructive view will be obtained, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/zoology-for-students-and-general-readers-zoology-anatomy-of-the-gunner-441-superior-os-and-inferior-oi-arise-from-the-front-of-the-orbit-near-the-interorbital-septum-the-disposition-of-the-pig-400-anatomy-of-the-brain-of-tlie-gunner-dorsal-and-side-viewdrawn-bv-c-s-minot-recti-is-very-constant-but-tlie-obhqui-vary-considerably-in-their-origin-in-different-vertebrates-if-a-perch-be-cut-through-transversely-so-that-the-section-passes-through-the-fore-part-of-the-air-bladder-and-the-anterior-portion-then-looked-at-from-behind-a-very-instructive-view-will-be-obtained-image216373584.html
. Zoology : for students and general readers . Zoology. ANATOMY OF THE GUNNER. 441 superior (Os) and inferior (Oi), arise from the front of the orbit near the interorbital septum. The disposition of the. Pig. 400.— Anatomy of the brain of tlie Gunner, dorsal and side view.—Drawn bv C. S. Minot. recti is very constant, but tlie obhqui vary considerably in their origin in different Vertebrates. If a perch be cut through transversely, so that the section passes through the fore-part of the air-bladder, and the anterior portion then looked at from behind, a very instructive view will be obtained, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/zoology-for-students-and-general-readers-zoology-anatomy-of-the-gunner-441-superior-os-and-inferior-oi-arise-from-the-front-of-the-orbit-near-the-interorbital-septum-the-disposition-of-the-pig-400-anatomy-of-the-brain-of-tlie-gunner-dorsal-and-side-viewdrawn-bv-c-s-minot-recti-is-very-constant-but-tlie-obhqui-vary-considerably-in-their-origin-in-different-vertebrates-if-a-perch-be-cut-through-transversely-so-that-the-section-passes-through-the-fore-part-of-the-air-bladder-and-the-anterior-portion-then-looked-at-from-behind-a-very-instructive-view-will-be-obtained-image216373584.htmlRMPG0JM0–. Zoology : for students and general readers . Zoology. ANATOMY OF THE GUNNER. 441 superior (Os) and inferior (Oi), arise from the front of the orbit near the interorbital septum. The disposition of the. Pig. 400.— Anatomy of the brain of tlie Gunner, dorsal and side view.—Drawn bv C. S. Minot. recti is very constant, but tlie obhqui vary considerably in their origin in different Vertebrates. If a perch be cut through transversely, so that the section passes through the fore-part of the air-bladder, and the anterior portion then looked at from behind, a very instructive view will be obtained,
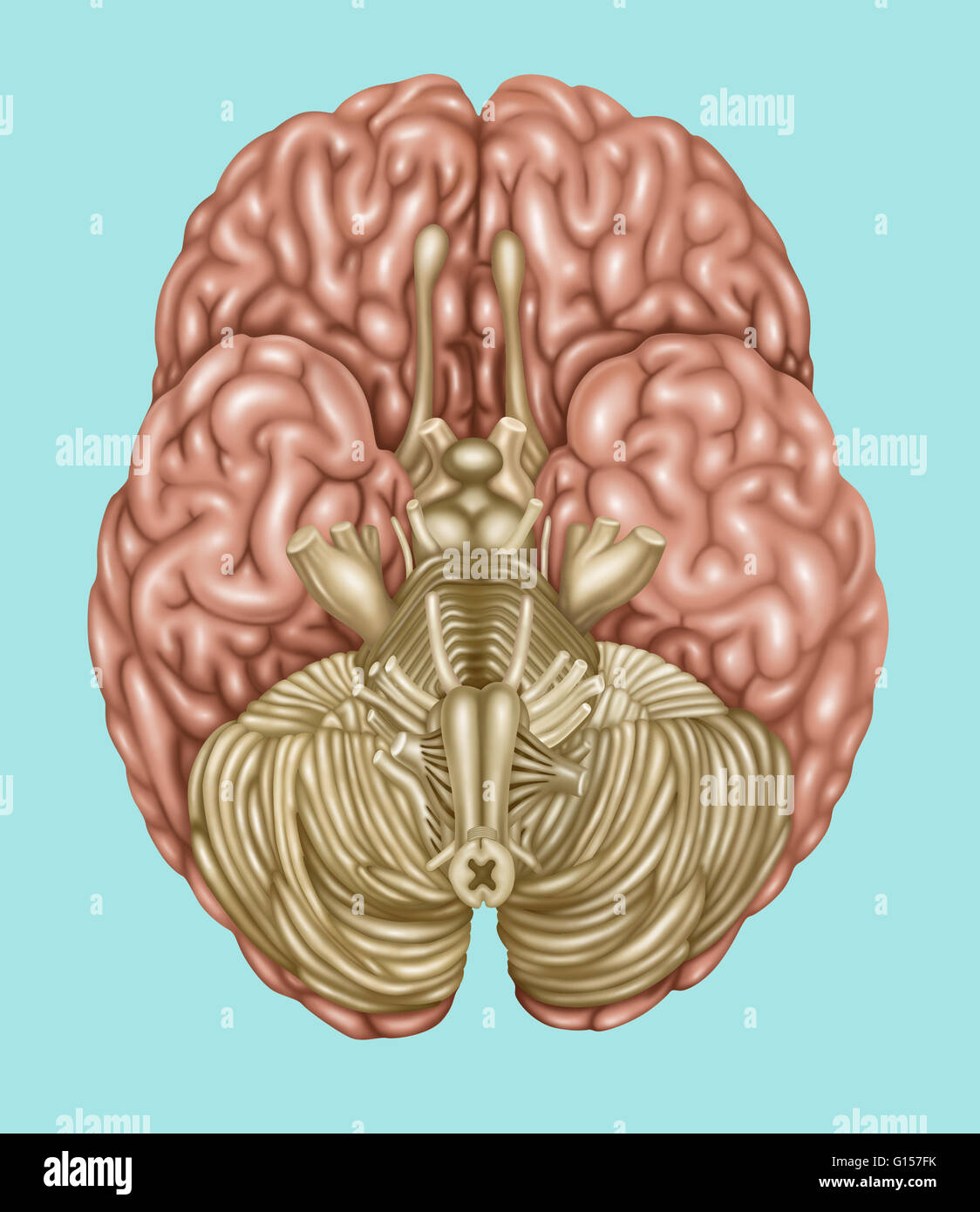 Illustration showing anatomy of the brain, inferior (underside) view. The following areas can be found in this view: olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens vestibulocochlear, hypoglossal, accessory, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vag Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-illustration-showing-anatomy-of-the-brain-inferior-underside-view-103992551.html
Illustration showing anatomy of the brain, inferior (underside) view. The following areas can be found in this view: olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens vestibulocochlear, hypoglossal, accessory, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vag Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-illustration-showing-anatomy-of-the-brain-inferior-underside-view-103992551.htmlRMG157FK–Illustration showing anatomy of the brain, inferior (underside) view. The following areas can be found in this view: olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens vestibulocochlear, hypoglossal, accessory, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vag
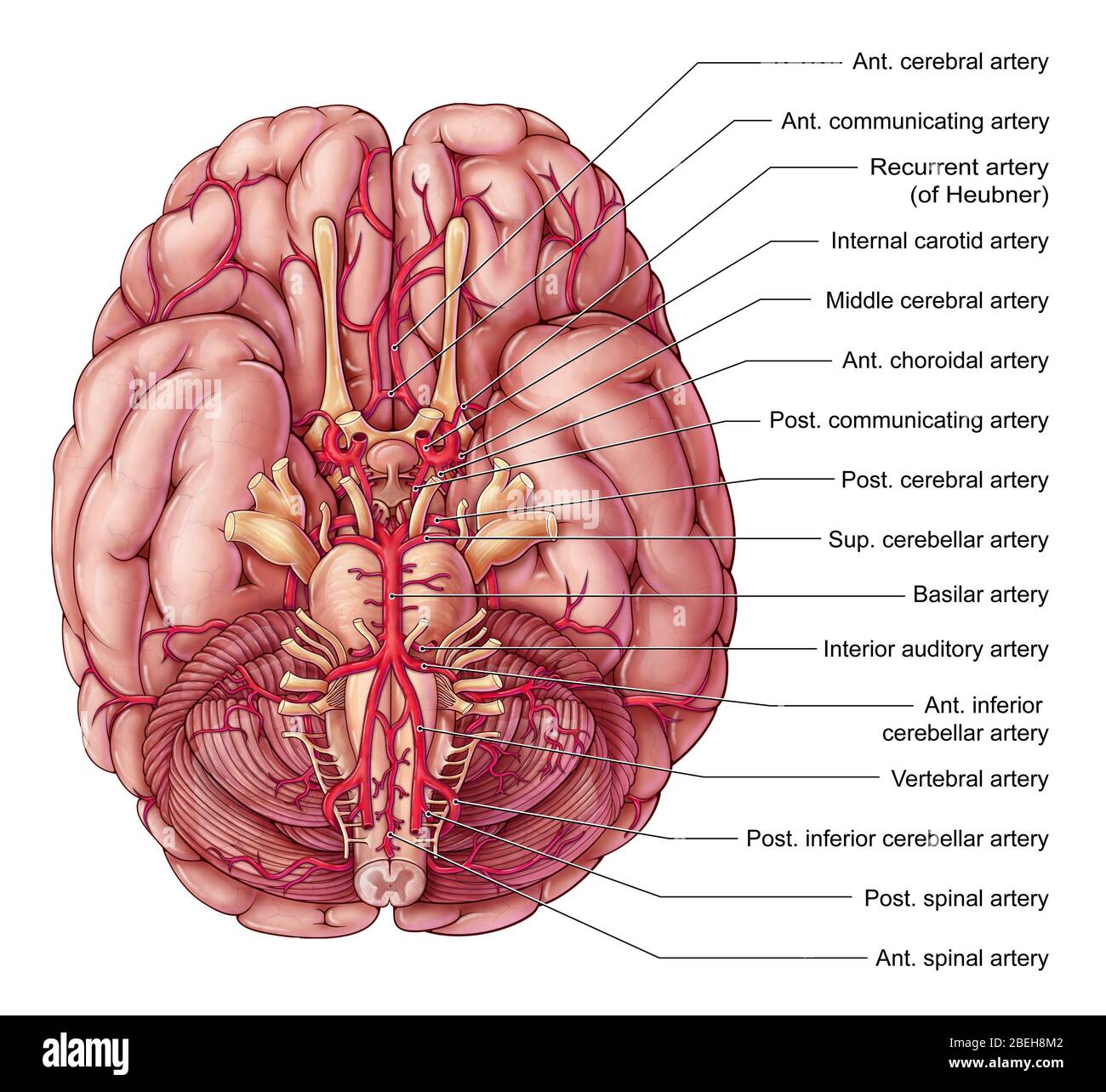 Arteries of the Brain, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/arteries-of-the-brain-illustration-image353192562.html
Arteries of the Brain, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/arteries-of-the-brain-illustration-image353192562.htmlRM2BEH8M2–Arteries of the Brain, Illustration
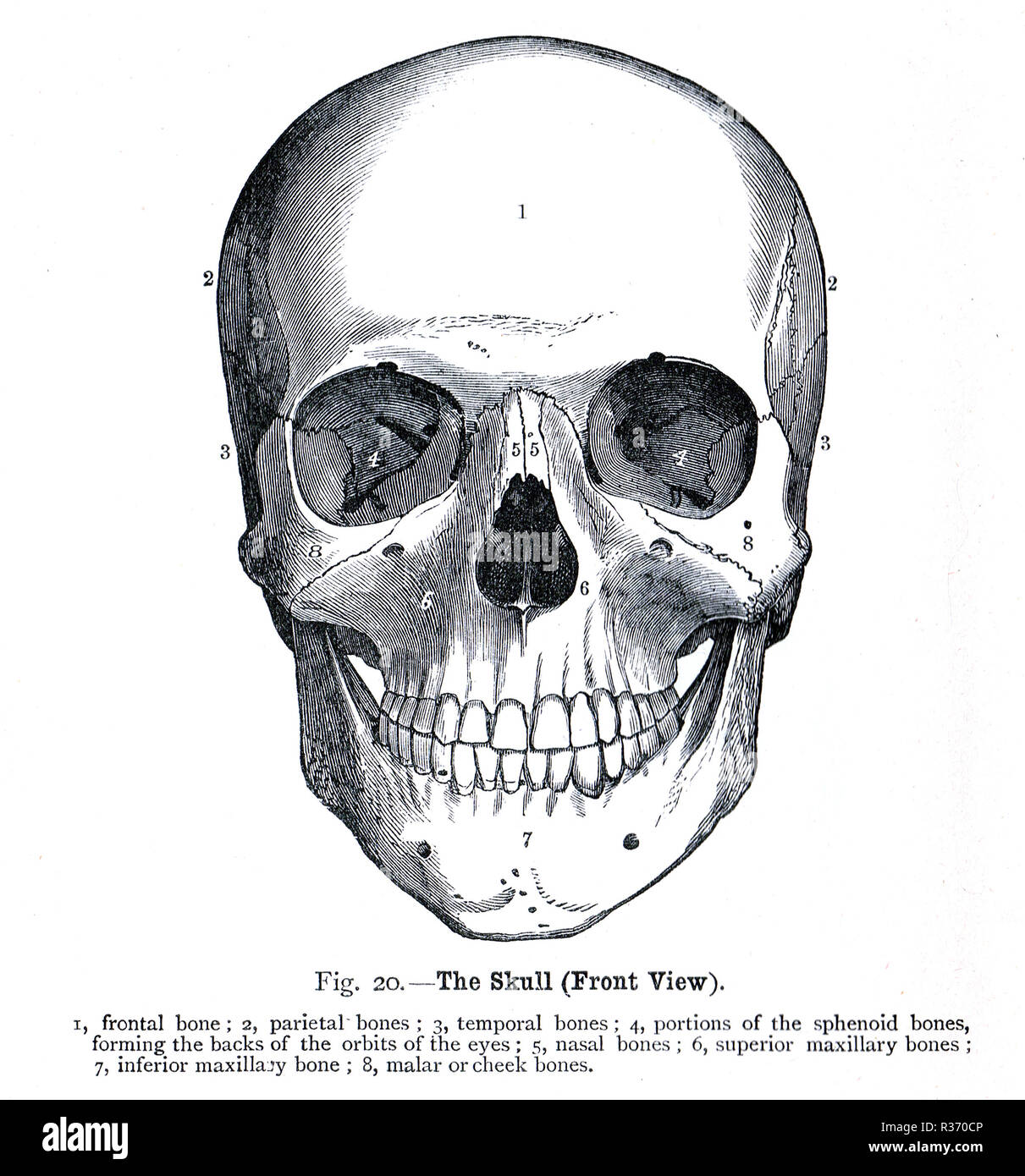 Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732774.html
Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732774.htmlRMR370CP–Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration
 Brain, Lateral View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-lateral-view-illustration-image353191819.html
Brain, Lateral View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-lateral-view-illustration-image353191819.htmlRF2BEH7NF–Brain, Lateral View, Illustration
 Superior view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superior-view-of-mandible-image491879224.html
Superior view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superior-view-of-mandible-image491879224.htmlRF2KG70Y4–Superior view of Mandible
 Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043453.html
Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043453.htmlRF2EBM611–Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration
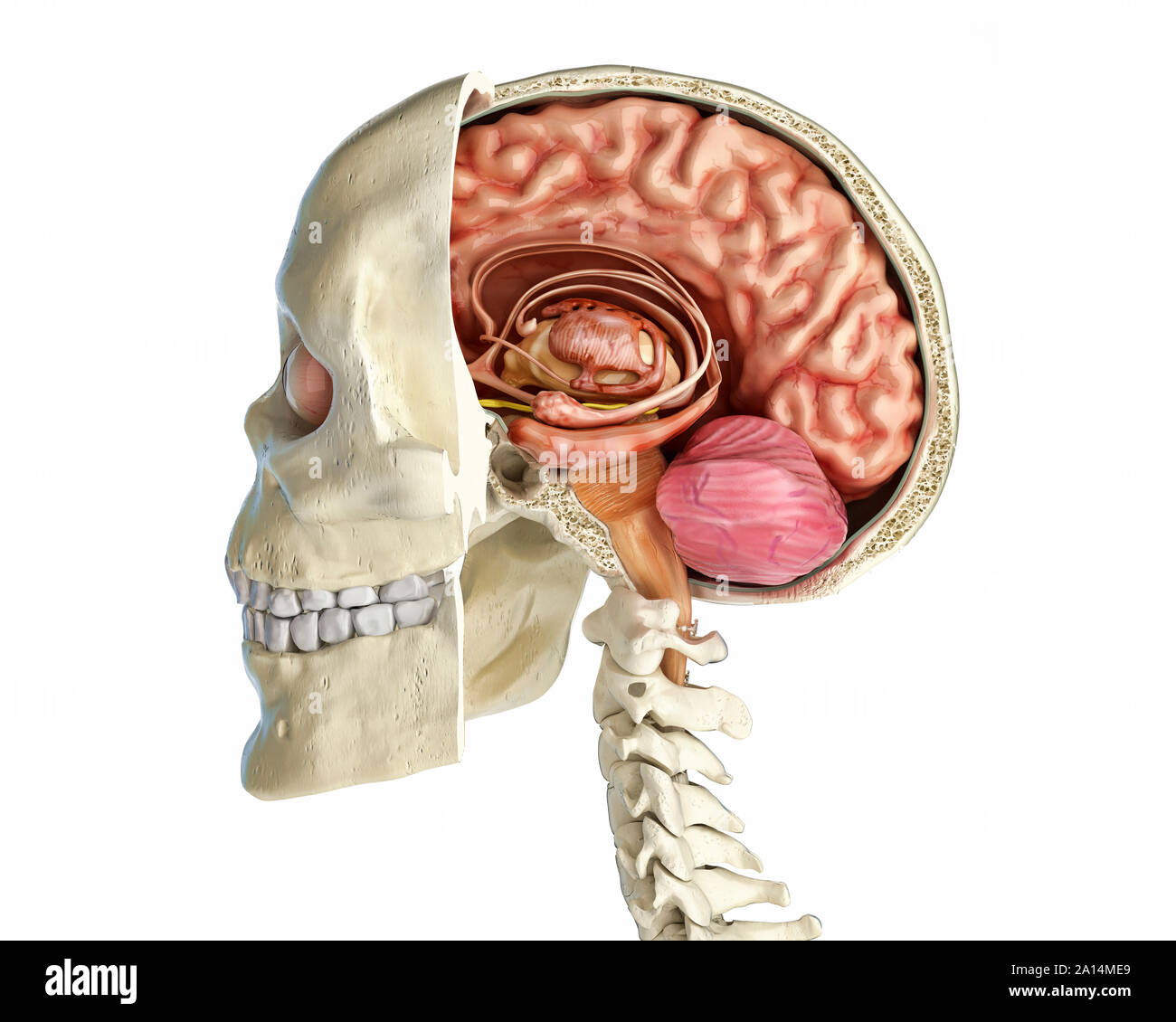 Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715537.html
Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715537.htmlRF2A14ME9–Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain.
 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13228114.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13228114.htmlRFACTM1R–The arteries of the brain
![The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., Stock Photo The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/T03PHK/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-ojt-olfactory-tract-opl-T03PHK.jpg) The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-ojt-olfactory-tract-opl-image241028751.html
The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l., Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-fig-200a-tlie-brain-and-associated-sense-organs-jipiaic-nis-maculalvs-dorsal-view-duncan-dunning-del-iuvii-buccal-branch-of-facial-nerve-ch-cerclielluni-el-ciliary-nerve-cr-restiform-body-di-diencephalon-hmd-hyomandilular-division-of-the-facial-nerve-il-inferior-lobe-mdv-mandibular-division-of-the-fifth-nerve-mn-median-olfactory-nucleus-med-medulla-ms-mesencephalon-mxv-maxillary-division-of-trigeminal-nerve-olh-olfactory-bulb-oll-olfactory-lobe-ojt-olfactory-tract-opl-image241028751.htmlRMT03PHK–The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 Fig. 200a. Tlie brain and associated sense organs, JI(pia)ic]nis maculalvs, dorsal view. (Duncan Dunning, del.) iu.VII, buccal branch of facial nerve; ch., cerclielluni; el., ciliary nerve; c.r., restiform body; di., diencephalon; hmd., hyomandil»ular division of the facial nerve; i.l., inferior lobe; md.V, mandibular division of the fifth nerve; m.n., median olfactory nucleus; med., medulla; ms., mesencephalon; mx.V, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve; ol.h., olfactory bulb; ol.l., olfactory lobe; oJ.t., olfactory tract; op.l.,
 The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-rectum-drains-into-the-superior-rectal-lymphatics-to-the-retroperitoneal-inferior-mesenteric-lymph-nodes-3d-illustration-image596581071.html
The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-rectum-drains-into-the-superior-rectal-lymphatics-to-the-retroperitoneal-inferior-mesenteric-lymph-nodes-3d-illustration-image596581071.htmlRF2WJGH6R–The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration
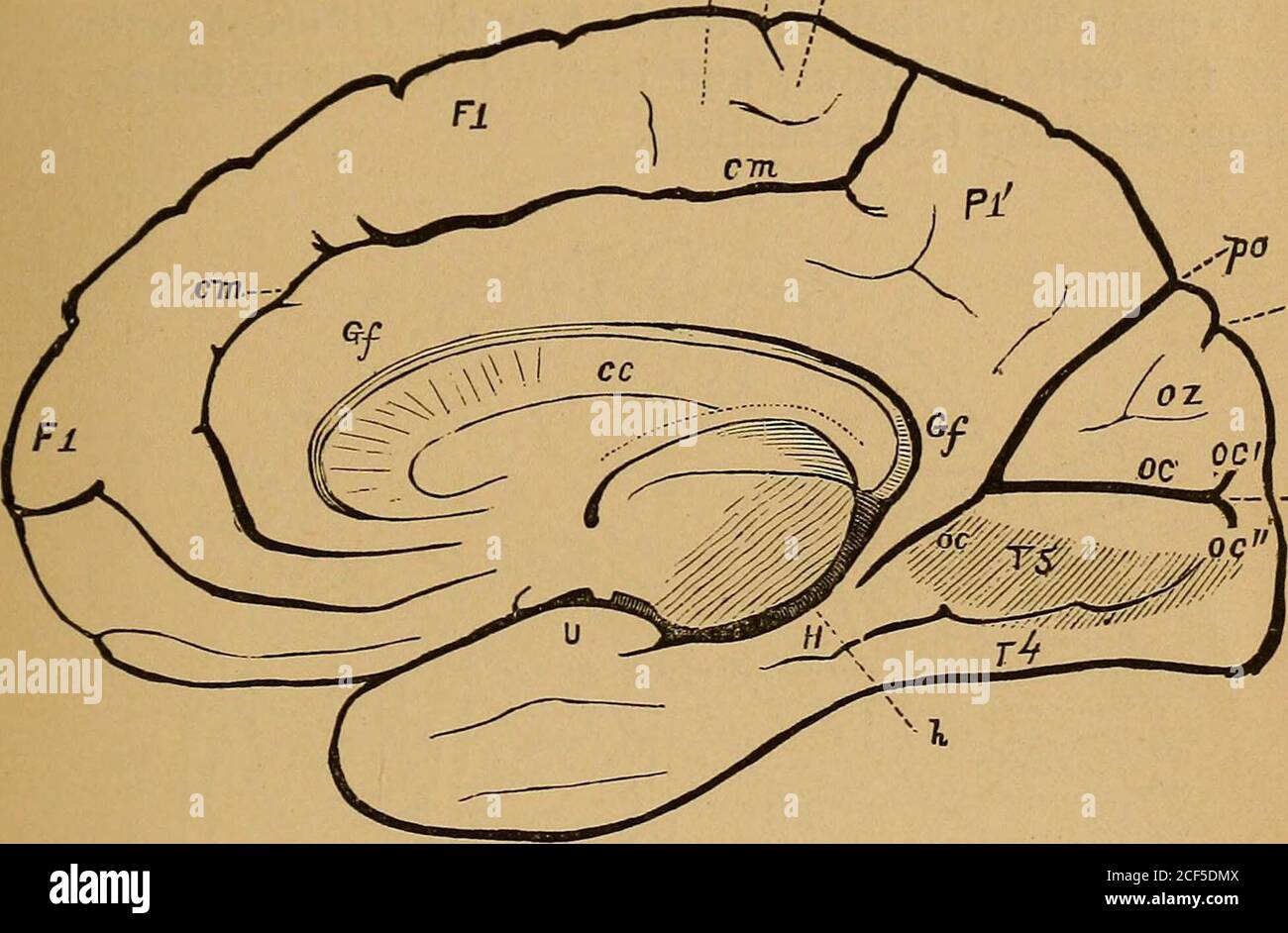 . A treatise on nervous diseases : their symptoms and treatment : a text-book for students and practitioners. Fig. 3.—^View of the brain from below. (Eckee.) -^1) gy™s rectus, the prolongation of the first frontal convolution ; i^j, middle,7^3, lower frontal convolution; fi, sulcus olfactorius; f^^ sulcus orbitalis; Tj,second, or middle, T3, third, or lower temporal convolution; Ti, gyrus occipito-temporalis lateralis (lobulus fusiformis), 7*6, gyrus occipito-temporalis medialis(lobulus lingualis); ^2, middle, 1^3, lower temporal fissure; t^, sulcus occipito-tem-poralis inferior; po, fissura p Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-nervous-diseases-their-symptoms-and-treatment-a-text-book-for-students-and-practitioners-fig-3view-of-the-brain-from-below-eckee-1-gys-rectus-the-prolongation-of-the-first-frontal-convolution-ij-middle73-lower-frontal-convolution-fi-sulcus-olfactorius-f-sulcus-orbitalis-tjsecond-or-middle-t3-third-or-lower-temporal-convolution-ti-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-lateralis-lobulus-fusiformis-76-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-medialislobulus-lingualis-2-middle-13-lower-temporal-fissure-t-sulcus-occipito-tem-poralis-inferior-po-fissura-p-image370758106.html
. A treatise on nervous diseases : their symptoms and treatment : a text-book for students and practitioners. Fig. 3.—^View of the brain from below. (Eckee.) -^1) gy™s rectus, the prolongation of the first frontal convolution ; i^j, middle,7^3, lower frontal convolution; fi, sulcus olfactorius; f^^ sulcus orbitalis; Tj,second, or middle, T3, third, or lower temporal convolution; Ti, gyrus occipito-temporalis lateralis (lobulus fusiformis), 7*6, gyrus occipito-temporalis medialis(lobulus lingualis); ^2, middle, 1^3, lower temporal fissure; t^, sulcus occipito-tem-poralis inferior; po, fissura p Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-nervous-diseases-their-symptoms-and-treatment-a-text-book-for-students-and-practitioners-fig-3view-of-the-brain-from-below-eckee-1-gys-rectus-the-prolongation-of-the-first-frontal-convolution-ij-middle73-lower-frontal-convolution-fi-sulcus-olfactorius-f-sulcus-orbitalis-tjsecond-or-middle-t3-third-or-lower-temporal-convolution-ti-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-lateralis-lobulus-fusiformis-76-gyrus-occipito-temporalis-medialislobulus-lingualis-2-middle-13-lower-temporal-fissure-t-sulcus-occipito-tem-poralis-inferior-po-fissura-p-image370758106.htmlRM2CF5DMX–. A treatise on nervous diseases : their symptoms and treatment : a text-book for students and practitioners. Fig. 3.—^View of the brain from below. (Eckee.) -^1) gy™s rectus, the prolongation of the first frontal convolution ; i^j, middle,7^3, lower frontal convolution; fi, sulcus olfactorius; f^^ sulcus orbitalis; Tj,second, or middle, T3, third, or lower temporal convolution; Ti, gyrus occipito-temporalis lateralis (lobulus fusiformis), 7*6, gyrus occipito-temporalis medialis(lobulus lingualis); ^2, middle, 1^3, lower temporal fissure; t^, sulcus occipito-tem-poralis inferior; po, fissura p
 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Brain of a Hake, ( From nature.) Side view seen from below. a a, optic nerves ; b, oblique crossing of ditto ; c, ootic lobe of left side, being the. chief source of the right optic nerve ; d d, two inferior lobes from wliicn the nerves of vision ia fishes generally derive roots. in fish very generally bear proportion to the size of the optic nerves (a proof of their physiological relations); and this proportion becomes par- ticularly apparent in fish which possess either unusually small organs of vision, as the Eel; or Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-brain-of-a-hake-from-nature-side-view-seen-from-below-a-a-optic-nerves-b-oblique-crossing-of-ditto-c-ootic-lobe-of-left-side-being-the-chief-source-of-the-right-optic-nerve-d-d-two-inferior-lobes-from-wliicn-the-nerves-of-vision-ia-fishes-generally-derive-roots-in-fish-very-generally-bear-proportion-to-the-size-of-the-optic-nerves-a-proof-of-their-physiological-relations-and-this-proportion-becomes-par-ticularly-apparent-in-fish-which-possess-either-unusually-small-organs-of-vision-as-the-eel-or-image216209363.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Brain of a Hake, ( From nature.) Side view seen from below. a a, optic nerves ; b, oblique crossing of ditto ; c, ootic lobe of left side, being the. chief source of the right optic nerve ; d d, two inferior lobes from wliicn the nerves of vision ia fishes generally derive roots. in fish very generally bear proportion to the size of the optic nerves (a proof of their physiological relations); and this proportion becomes par- ticularly apparent in fish which possess either unusually small organs of vision, as the Eel; or Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-brain-of-a-hake-from-nature-side-view-seen-from-below-a-a-optic-nerves-b-oblique-crossing-of-ditto-c-ootic-lobe-of-left-side-being-the-chief-source-of-the-right-optic-nerve-d-d-two-inferior-lobes-from-wliicn-the-nerves-of-vision-ia-fishes-generally-derive-roots-in-fish-very-generally-bear-proportion-to-the-size-of-the-optic-nerves-a-proof-of-their-physiological-relations-and-this-proportion-becomes-par-ticularly-apparent-in-fish-which-possess-either-unusually-small-organs-of-vision-as-the-eel-or-image216209363.htmlRMPFN56Y–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Brain of a Hake, ( From nature.) Side view seen from below. a a, optic nerves ; b, oblique crossing of ditto ; c, ootic lobe of left side, being the. chief source of the right optic nerve ; d d, two inferior lobes from wliicn the nerves of vision ia fishes generally derive roots. in fish very generally bear proportion to the size of the optic nerves (a proof of their physiological relations); and this proportion becomes par- ticularly apparent in fish which possess either unusually small organs of vision, as the Eel; or
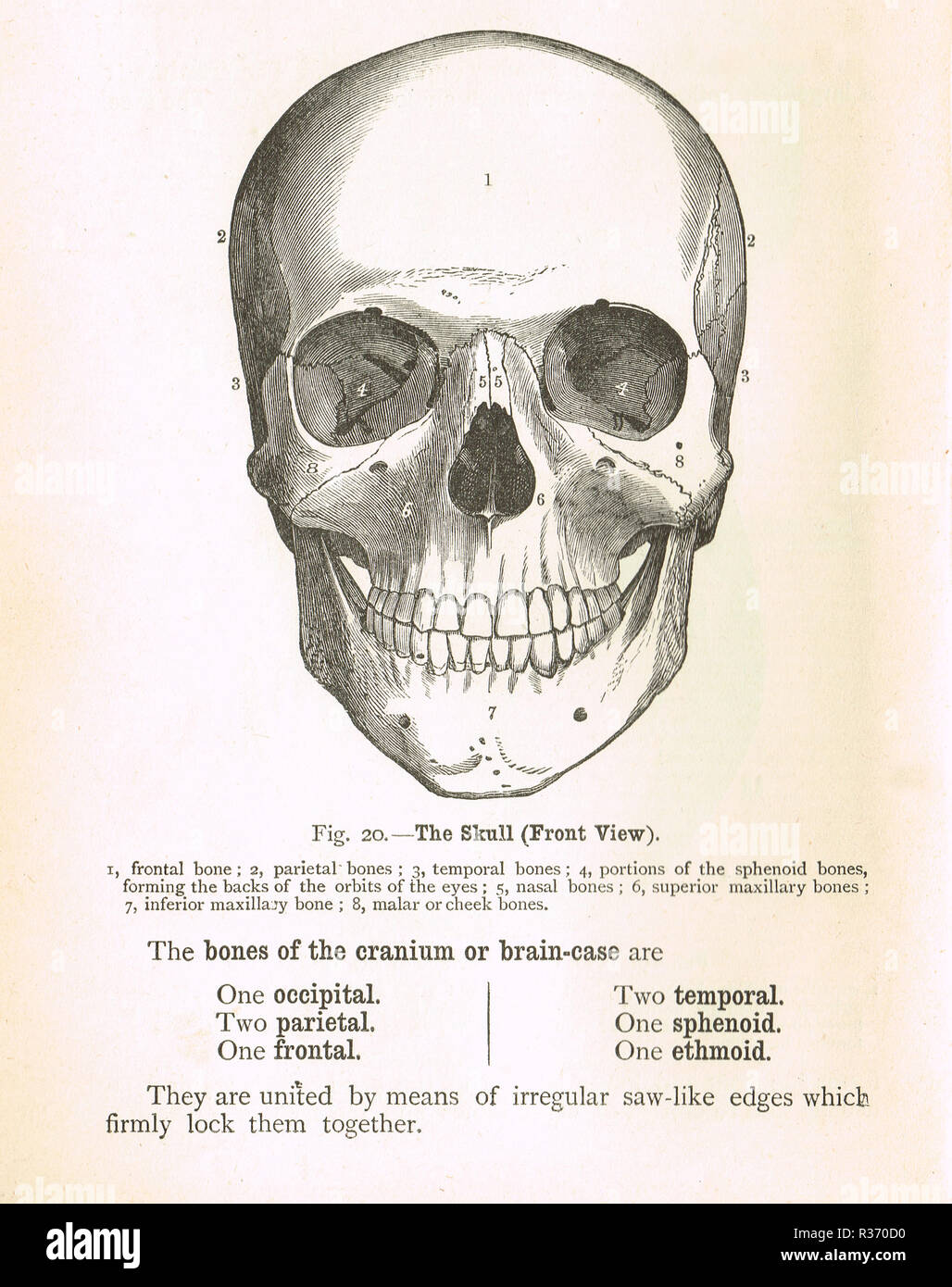 Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732780.html
Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-front-view-a-19th-century-illustration-image225732780.htmlRMR370D0–Human Skull, front view. A 19th Century illustration
 Brain, Lateral View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-lateral-view-illustration-image353191801.html
Brain, Lateral View, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-lateral-view-illustration-image353191801.htmlRF2BEH7MW–Brain, Lateral View, Illustration
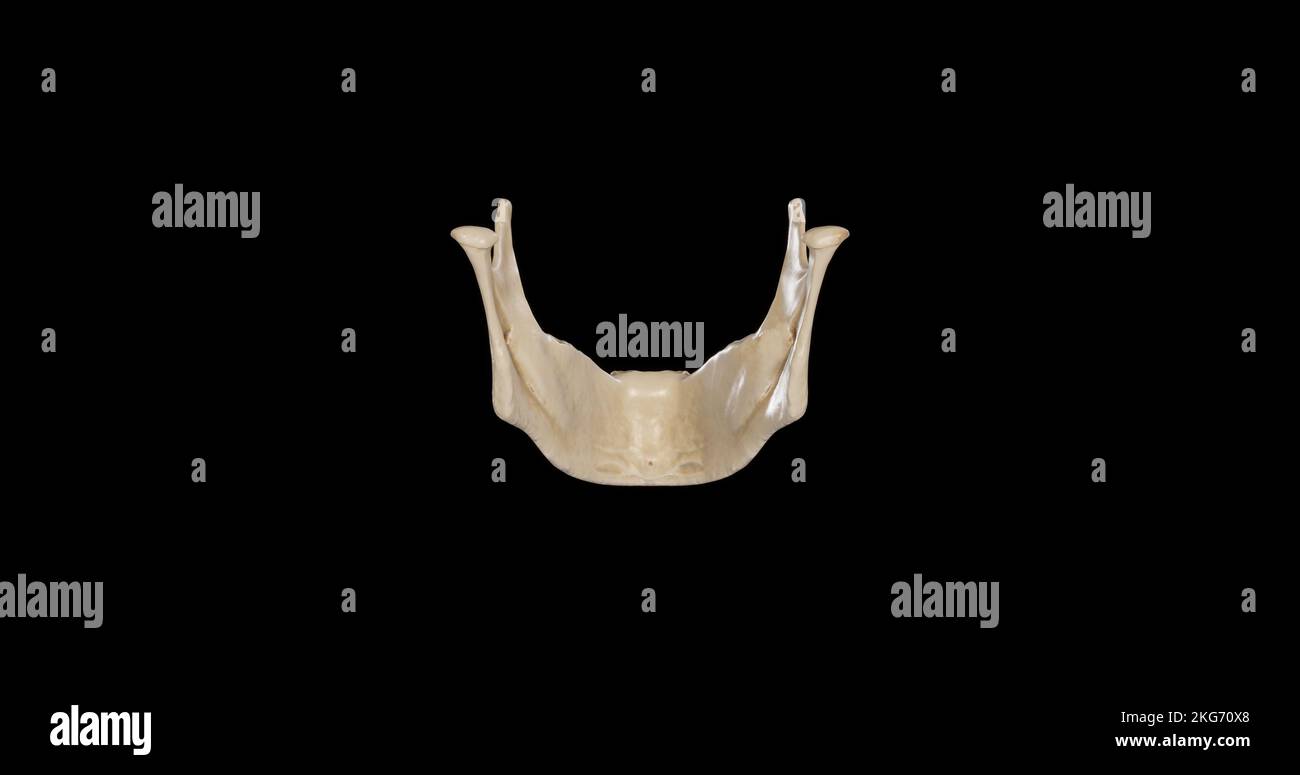 Posterior view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/posterior-view-of-mandible-image491879200.html
Posterior view of Mandible Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/posterior-view-of-mandible-image491879200.htmlRF2KG70X8–Posterior view of Mandible
 Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043406.html
Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brain-highlighting-inferior-frontal-gyrus-illustration-image403043406.htmlRF2EBM5YA–Brain highlighting inferior frontal gyrus, illustration
 Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715547.html
Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-skull-mid-sagittal-cross-section-with-brain-image327715547.htmlRF2A14MEK–Human skull mid sagittal cross-section with brain.
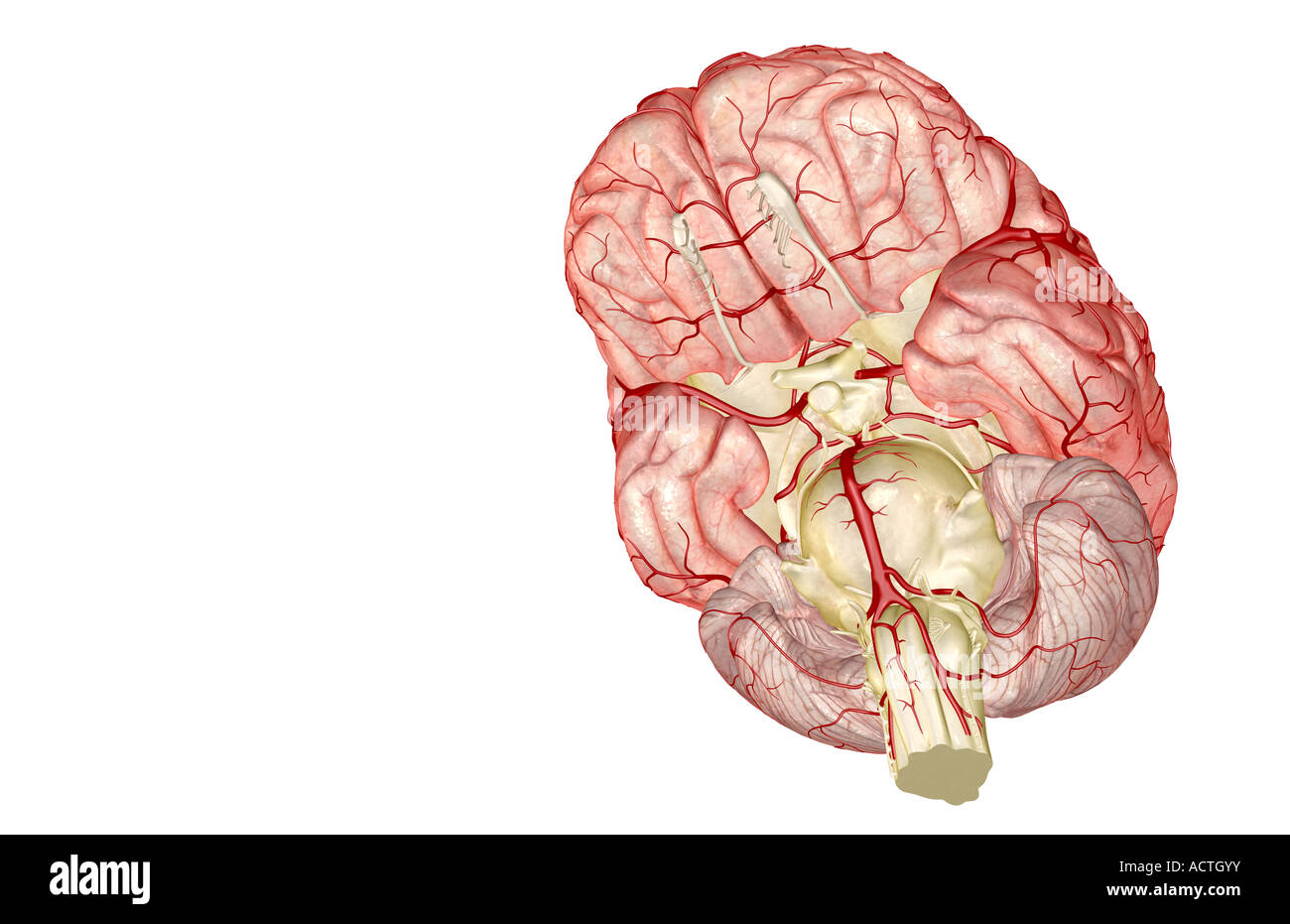 The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13227086.html
The arteries of the brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-arteries-of-the-brain-13227086.htmlRFACTGYY–The arteries of the brain
 The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 234 THE ELASMOBRANCH FISHES anterior (a.l.), intermediate (i.l.), and inferior lobes (i.l.h.). To these parts are to be added the paired suj^erior lobes (s.l.) which lie at the sides of and above the intermediate lobes. The mesencephalon (fig. 213, op.l.) is a conservative segment and yet it varies considerably in different forms. In many it is relatively inconspicuous because of the extreme development of the cerebellum, while in others it comes Fig. 213. Brain of Scymnus. (From Burckhardt.) A. Side view. B. Median sagittal view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-234-the-elasmobranch-fishes-anterior-al-intermediate-il-and-inferior-lobes-ilh-to-these-parts-are-to-be-added-the-paired-sujerior-lobes-sl-which-lie-at-the-sides-of-and-above-the-intermediate-lobes-the-mesencephalon-fig-213-opl-is-a-conservative-segment-and-yet-it-varies-considerably-in-different-forms-in-many-it-is-relatively-inconspicuous-because-of-the-extreme-development-of-the-cerebellum-while-in-others-it-comes-fig-213-brain-of-scymnus-from-burckhardt-a-side-view-b-median-sagittal-view-image241030519.html
The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 234 THE ELASMOBRANCH FISHES anterior (a.l.), intermediate (i.l.), and inferior lobes (i.l.h.). To these parts are to be added the paired suj^erior lobes (s.l.) which lie at the sides of and above the intermediate lobes. The mesencephalon (fig. 213, op.l.) is a conservative segment and yet it varies considerably in different forms. In many it is relatively inconspicuous because of the extreme development of the cerebellum, while in others it comes Fig. 213. Brain of Scymnus. (From Burckhardt.) A. Side view. B. Median sagittal view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elasmobranch-fishes-elasmobranchfish03dani-year-1934-234-the-elasmobranch-fishes-anterior-al-intermediate-il-and-inferior-lobes-ilh-to-these-parts-are-to-be-added-the-paired-sujerior-lobes-sl-which-lie-at-the-sides-of-and-above-the-intermediate-lobes-the-mesencephalon-fig-213-opl-is-a-conservative-segment-and-yet-it-varies-considerably-in-different-forms-in-many-it-is-relatively-inconspicuous-because-of-the-extreme-development-of-the-cerebellum-while-in-others-it-comes-fig-213-brain-of-scymnus-from-burckhardt-a-side-view-b-median-sagittal-view-image241030519.htmlRMT03TTR–The elasmobranch fishes . elasmobranchfish03dani Year: 1934 234 THE ELASMOBRANCH FISHES anterior (a.l.), intermediate (i.l.), and inferior lobes (i.l.h.). To these parts are to be added the paired suj^erior lobes (s.l.) which lie at the sides of and above the intermediate lobes. The mesencephalon (fig. 213, op.l.) is a conservative segment and yet it varies considerably in different forms. In many it is relatively inconspicuous because of the extreme development of the cerebellum, while in others it comes Fig. 213. Brain of Scymnus. (From Burckhardt.) A. Side view. B. Median sagittal view.
 The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-rectum-drains-into-the-superior-rectal-lymphatics-to-the-retroperitoneal-inferior-mesenteric-lymph-nodes-3d-illustration-image596582458.html
The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-rectum-drains-into-the-superior-rectal-lymphatics-to-the-retroperitoneal-inferior-mesenteric-lymph-nodes-3d-illustration-image596582458.htmlRF2WJGK0A–The rectum drains into the superior rectal lymphatics to the retroperitoneal inferior mesenteric lymph nodes 3d illustration
 . Human physiology. Fig. 17.—Side View of the Skull. 1, frontal bone : 2, parietal bone ; 3 and 8, occipital bone ; 4, wing of the sphenoid bone;5, 6 and 7, temporal bone ; 10, lachrymal bone, in the inner wall of the orbit; n, malarbone ; i2, superior maxillary ; 13 and 14, inferior maxillary.. Fig. 18.—Top View of the Skull. T, frontal bone: t, parietal bones; o, occipital bone; a. i, and c, sutures. 19 LESSON III.THE SKELETON [continued). The Skull. The skull consists of the cranium and the face. The cranium isa large and hollow bony case which encloses the brain. The face Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-physiology-fig-17side-view-of-the-skull-1-frontal-bone-2-parietal-bone-3-and-8-occipital-bone-4-wing-of-the-sphenoid-bone5-6-and-7-temporal-bone-10-lachrymal-bone-in-the-inner-wall-of-the-orbit-n-malarbone-i2-superior-maxillary-13-and-14-inferior-maxillary-fig-18top-view-of-the-skull-t-frontal-bone-t-parietal-bones-o-occipital-bone-a-i-and-c-sutures-19-lesson-iiithe-skeleton-continued-the-skull-the-skull-consists-of-the-cranium-and-the-face-the-cranium-isa-large-and-hollow-bony-case-which-encloses-the-brain-the-face-image370650093.html
. Human physiology. Fig. 17.—Side View of the Skull. 1, frontal bone : 2, parietal bone ; 3 and 8, occipital bone ; 4, wing of the sphenoid bone;5, 6 and 7, temporal bone ; 10, lachrymal bone, in the inner wall of the orbit; n, malarbone ; i2, superior maxillary ; 13 and 14, inferior maxillary.. Fig. 18.—Top View of the Skull. T, frontal bone: t, parietal bones; o, occipital bone; a. i, and c, sutures. 19 LESSON III.THE SKELETON [continued). The Skull. The skull consists of the cranium and the face. The cranium isa large and hollow bony case which encloses the brain. The face Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-physiology-fig-17side-view-of-the-skull-1-frontal-bone-2-parietal-bone-3-and-8-occipital-bone-4-wing-of-the-sphenoid-bone5-6-and-7-temporal-bone-10-lachrymal-bone-in-the-inner-wall-of-the-orbit-n-malarbone-i2-superior-maxillary-13-and-14-inferior-maxillary-fig-18top-view-of-the-skull-t-frontal-bone-t-parietal-bones-o-occipital-bone-a-i-and-c-sutures-19-lesson-iiithe-skeleton-continued-the-skull-the-skull-consists-of-the-cranium-and-the-face-the-cranium-isa-large-and-hollow-bony-case-which-encloses-the-brain-the-face-image370650093.htmlRM2CF0FY9–. Human physiology. Fig. 17.—Side View of the Skull. 1, frontal bone : 2, parietal bone ; 3 and 8, occipital bone ; 4, wing of the sphenoid bone;5, 6 and 7, temporal bone ; 10, lachrymal bone, in the inner wall of the orbit; n, malarbone ; i2, superior maxillary ; 13 and 14, inferior maxillary.. Fig. 18.—Top View of the Skull. T, frontal bone: t, parietal bones; o, occipital bone; a. i, and c, sutures. 19 LESSON III.THE SKELETON [continued). The Skull. The skull consists of the cranium and the face. The cranium isa large and hollow bony case which encloses the brain. The face