Quick filters:
Classical mechanics Stock Photos and Images
 The title page of Isaac Newton's 'Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica' (first issue, first edition, London, 1687), one of the most important milestones in science. Lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-title-page-of-isaac-newtons-philosophiae-naturalis-principia-mathematica-104003482.html
The title page of Isaac Newton's 'Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica' (first issue, first edition, London, 1687), one of the most important milestones in science. Lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-title-page-of-isaac-newtons-philosophiae-naturalis-principia-mathematica-104003482.htmlRMG15NE2–The title page of Isaac Newton's 'Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica' (first issue, first edition, London, 1687), one of the most important milestones in science. Lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics.
RF2DHBRHD–Physics and science icons set. Classical mechanics. Experiments equipment, tools, magnet, atom, pendulum, Newton's Laws and the simplest mechanisms
 Science concept: Classical Mechanics on chalkboard background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-chalkboard-background-114381591.html
Science concept: Classical Mechanics on chalkboard background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-chalkboard-background-114381591.htmlRFGJ2ETR–Science concept: Classical Mechanics on chalkboard background
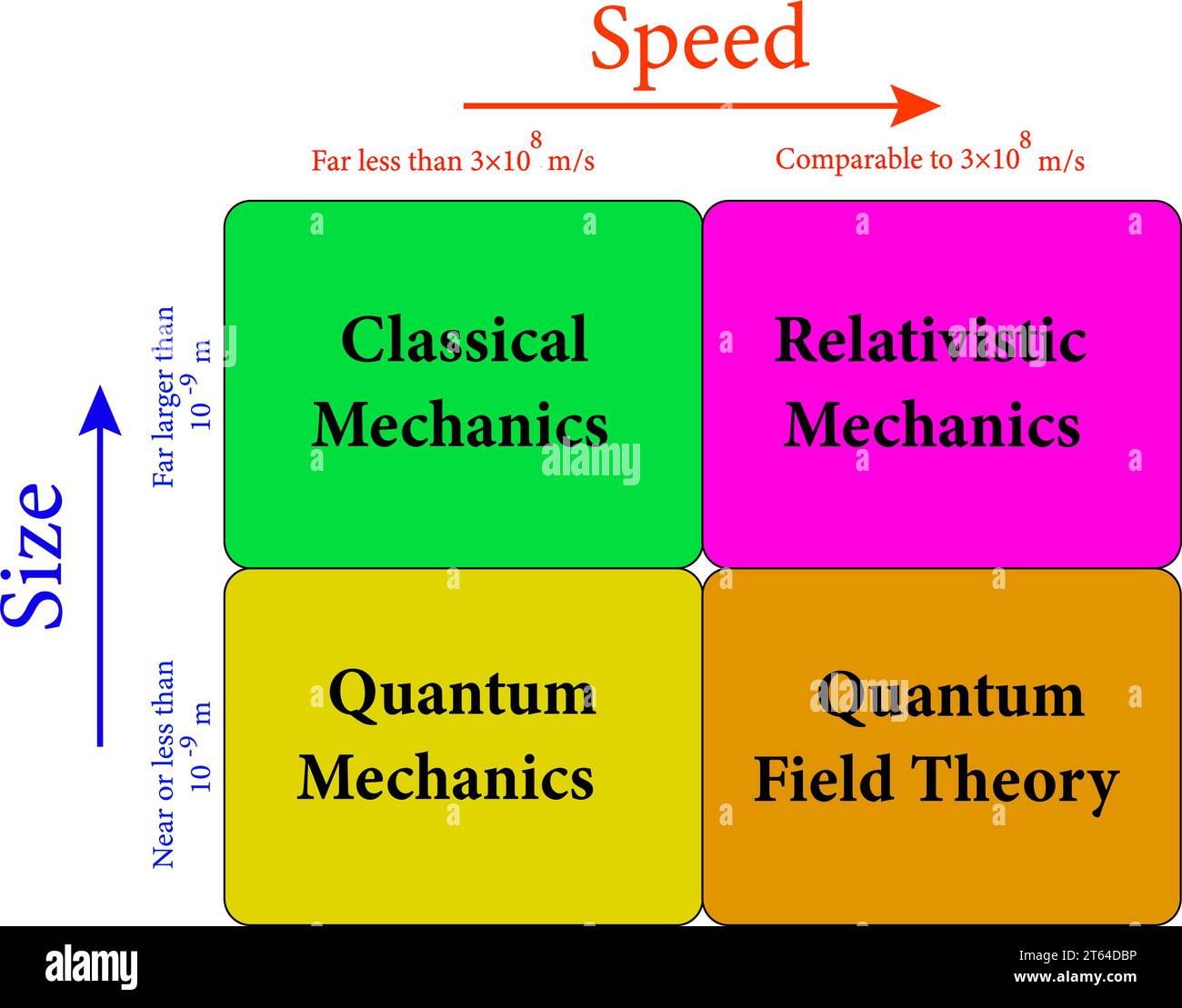 Domain of validity for classical mechanics.Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/domain-of-validity-for-classical-mechanicsvector-illustration-image571728410.html
Domain of validity for classical mechanics.Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/domain-of-validity-for-classical-mechanicsvector-illustration-image571728410.htmlRF2T64DBP–Domain of validity for classical mechanics.Vector illustration
 Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, by Isaac Newton. (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy). Title page of first edition dated July 5, 1687. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-by-isaac-newton-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-title-page-of-first-edition-dated-july-5-1687-image211140268.html
Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, by Isaac Newton. (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy). Title page of first edition dated July 5, 1687. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-by-isaac-newton-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-title-page-of-first-edition-dated-july-5-1687-image211140268.htmlRMP7E7FT–Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, by Isaac Newton. (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy). Title page of first edition dated July 5, 1687.
 Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272532.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272532.htmlRM2B02Y3G–Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus.
 Sir Isaac Newton, physicist (1643-1726) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-sir-isaac-newton-physicist-1643-1726-176097083.html
Sir Isaac Newton, physicist (1643-1726) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-sir-isaac-newton-physicist-1643-1726-176097083.htmlRMM6DWHF–Sir Isaac Newton, physicist (1643-1726)
 Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-than-the-speed-of-image382511718.html
Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-than-the-speed-of-image382511718.htmlRF2D68WGP–Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of
 NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newtons-laws-of-motion-image508193088.html
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newtons-laws-of-motion-image508193088.htmlRM2MEP5D4–NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION
 mechanics of a classical guitar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-mechanics-of-a-classical-guitar-143720544.html
mechanics of a classical guitar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-mechanics-of-a-classical-guitar-143720544.htmlRFJ9R10G–mechanics of a classical guitar
 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author, recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians, physicists, and most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica established classical mechanics. UK. Europe. Old 19th century engraved illustration from Portraits et histoire des hommes utile by Societe Montyon et Franklin 1837 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-1642-1726-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-recognised-as-one-of-the-greatest-mathematicians-physicists-and-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-he-was-a-key-figure-in-the-philosophical-revolution-known-as-the-enlightenment-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-established-classical-mechanics-uk-europe-old-19th-century-engraved-illustration-from-portraits-et-histoire-des-hommes-utile-by-societe-montyon-et-franklin-1837-image455546415.html
Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author, recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians, physicists, and most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica established classical mechanics. UK. Europe. Old 19th century engraved illustration from Portraits et histoire des hommes utile by Societe Montyon et Franklin 1837 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-1642-1726-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-recognised-as-one-of-the-greatest-mathematicians-physicists-and-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-he-was-a-key-figure-in-the-philosophical-revolution-known-as-the-enlightenment-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-established-classical-mechanics-uk-europe-old-19th-century-engraved-illustration-from-portraits-et-histoire-des-hommes-utile-by-societe-montyon-et-franklin-1837-image455546415.htmlRM2HD3X2R–Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author, recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians, physicists, and most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica established classical mechanics. UK. Europe. Old 19th century engraved illustration from Portraits et histoire des hommes utile by Societe Montyon et Franklin 1837
 Mechanics and Customers Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-and-customers-image184187536.html
Mechanics and Customers Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-and-customers-image184187536.htmlRMMKJD28–Mechanics and Customers
RF2BA2CBJ–Classical Physics: tools, equipment, experiments, concepts - lexicon illustrated table with Italian descriptions, part 2
 kinetic energy equation of classical Newtonian mechanics connecting it to mass and velocity of a point object Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-kinetic-energy-equation-of-classical-newtonian-mechanics-connecting-43931114.html
kinetic energy equation of classical Newtonian mechanics connecting it to mass and velocity of a point object Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-kinetic-energy-equation-of-classical-newtonian-mechanics-connecting-43931114.htmlRFCFD6GA–kinetic energy equation of classical Newtonian mechanics connecting it to mass and velocity of a point object
 James Clerk Maxwell FRSE FRS (1831–1879) was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell is regarded by some as the Father of Modern Physics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/james-clerk-maxwell-frse-frs-18311879-was-a-scottish-mathematician-and-theoretical-physicist-responsible-for-the-classical-theory-of-electromagnetic-radiation-which-was-the-first-theory-to-describe-electricity-magnetism-and-light-as-different-manifestations-of-the-same-phenomenon-maxwell-is-regarded-by-some-as-the-father-of-modern-physics-image475490227.html
James Clerk Maxwell FRSE FRS (1831–1879) was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell is regarded by some as the Father of Modern Physics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/james-clerk-maxwell-frse-frs-18311879-was-a-scottish-mathematician-and-theoretical-physicist-responsible-for-the-classical-theory-of-electromagnetic-radiation-which-was-the-first-theory-to-describe-electricity-magnetism-and-light-as-different-manifestations-of-the-same-phenomenon-maxwell-is-regarded-by-some-as-the-father-of-modern-physics-image475490227.htmlRM2JHGCHR–James Clerk Maxwell FRSE FRS (1831–1879) was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell is regarded by some as the Father of Modern Physics.
 Contemplative Archimedes, the founder of theoretical Mechanics with pupils and instruments of mechanical power, A diagram of the proportion of the sphere to a cylinder. Screw and wedge action, an array of pulleys, water pump based on Archimedes's screw Copperplate engraving From the Encyclopaedia Londinensis or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature; Volume XIV; Edited by Wilkes, John. Published in London in 1816 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/contemplative-archimedes-the-founder-of-theoretical-mechanics-with-pupils-and-instruments-of-mechanical-power-a-diagram-of-the-proportion-of-the-sphere-to-a-cylinder-screw-and-wedge-action-an-array-of-pulleys-water-pump-based-on-archimedess-screw-copperplate-engraving-from-the-encyclopaedia-londinensis-or-universal-dictionary-of-arts-sciences-and-literature-volume-xiv-edited-by-wilkes-john-published-in-london-in-1816-image382746005.html
Contemplative Archimedes, the founder of theoretical Mechanics with pupils and instruments of mechanical power, A diagram of the proportion of the sphere to a cylinder. Screw and wedge action, an array of pulleys, water pump based on Archimedes's screw Copperplate engraving From the Encyclopaedia Londinensis or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature; Volume XIV; Edited by Wilkes, John. Published in London in 1816 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/contemplative-archimedes-the-founder-of-theoretical-mechanics-with-pupils-and-instruments-of-mechanical-power-a-diagram-of-the-proportion-of-the-sphere-to-a-cylinder-screw-and-wedge-action-an-array-of-pulleys-water-pump-based-on-archimedess-screw-copperplate-engraving-from-the-encyclopaedia-londinensis-or-universal-dictionary-of-arts-sciences-and-literature-volume-xiv-edited-by-wilkes-john-published-in-london-in-1816-image382746005.htmlRM2D6KGC5–Contemplative Archimedes, the founder of theoretical Mechanics with pupils and instruments of mechanical power, A diagram of the proportion of the sphere to a cylinder. Screw and wedge action, an array of pulleys, water pump based on Archimedes's screw Copperplate engraving From the Encyclopaedia Londinensis or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature; Volume XIV; Edited by Wilkes, John. Published in London in 1816
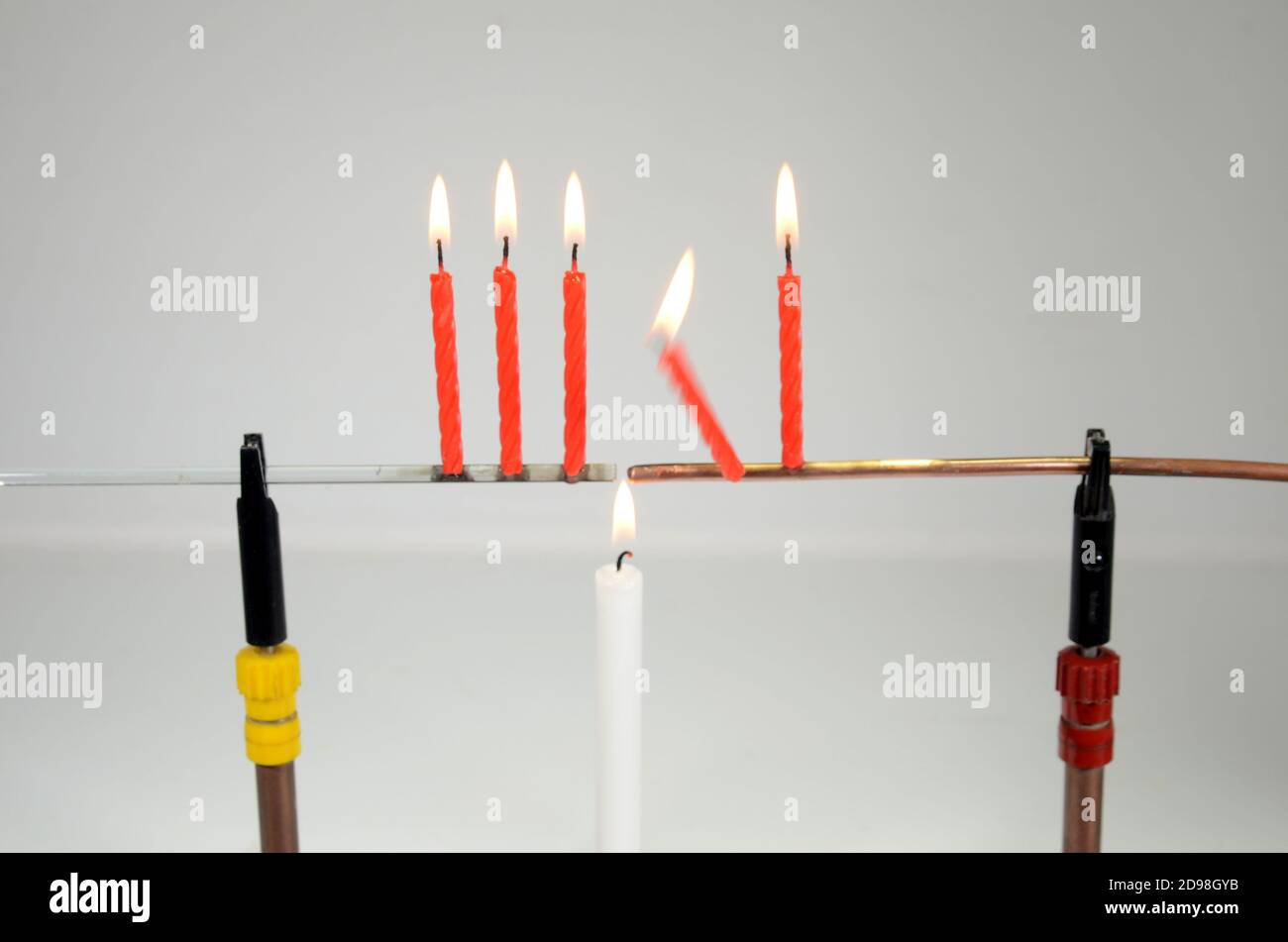 Classical physics experiment shows hat conduction. 3 red candles placed on a glass rod and a coppper rod, the rods are heated, and the candles on the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classical-physics-experiment-shows-hat-conduction-3-red-candles-placed-on-a-glass-rod-and-a-coppper-rod-the-rods-are-heated-and-the-candles-on-the-image384348927.html
Classical physics experiment shows hat conduction. 3 red candles placed on a glass rod and a coppper rod, the rods are heated, and the candles on the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classical-physics-experiment-shows-hat-conduction-3-red-candles-placed-on-a-glass-rod-and-a-coppper-rod-the-rods-are-heated-and-the-candles-on-the-image384348927.htmlRF2D98GYB–Classical physics experiment shows hat conduction. 3 red candles placed on a glass rod and a coppper rod, the rods are heated, and the candles on the
 Blue classical car undergoing roadside repairs. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-blue-classical-car-undergoing-roadside-repairs-112413578.html
Blue classical car undergoing roadside repairs. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-blue-classical-car-undergoing-roadside-repairs-112413578.htmlRMGETTJJ–Blue classical car undergoing roadside repairs.
 Inside an older grand piano with golden painted metal frame, strings, hammer, damper and red felt, showing the mechanics of the acoustic musical instr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inside-an-older-grand-piano-with-golden-painted-metal-frame-strings-hammer-damper-and-red-felt-showing-the-mechanics-of-the-acoustic-musical-instr-image443398416.html
Inside an older grand piano with golden painted metal frame, strings, hammer, damper and red felt, showing the mechanics of the acoustic musical instr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inside-an-older-grand-piano-with-golden-painted-metal-frame-strings-hammer-damper-and-red-felt-showing-the-mechanics-of-the-acoustic-musical-instr-image443398416.htmlRF2GNAF5M–Inside an older grand piano with golden painted metal frame, strings, hammer, damper and red felt, showing the mechanics of the acoustic musical instr
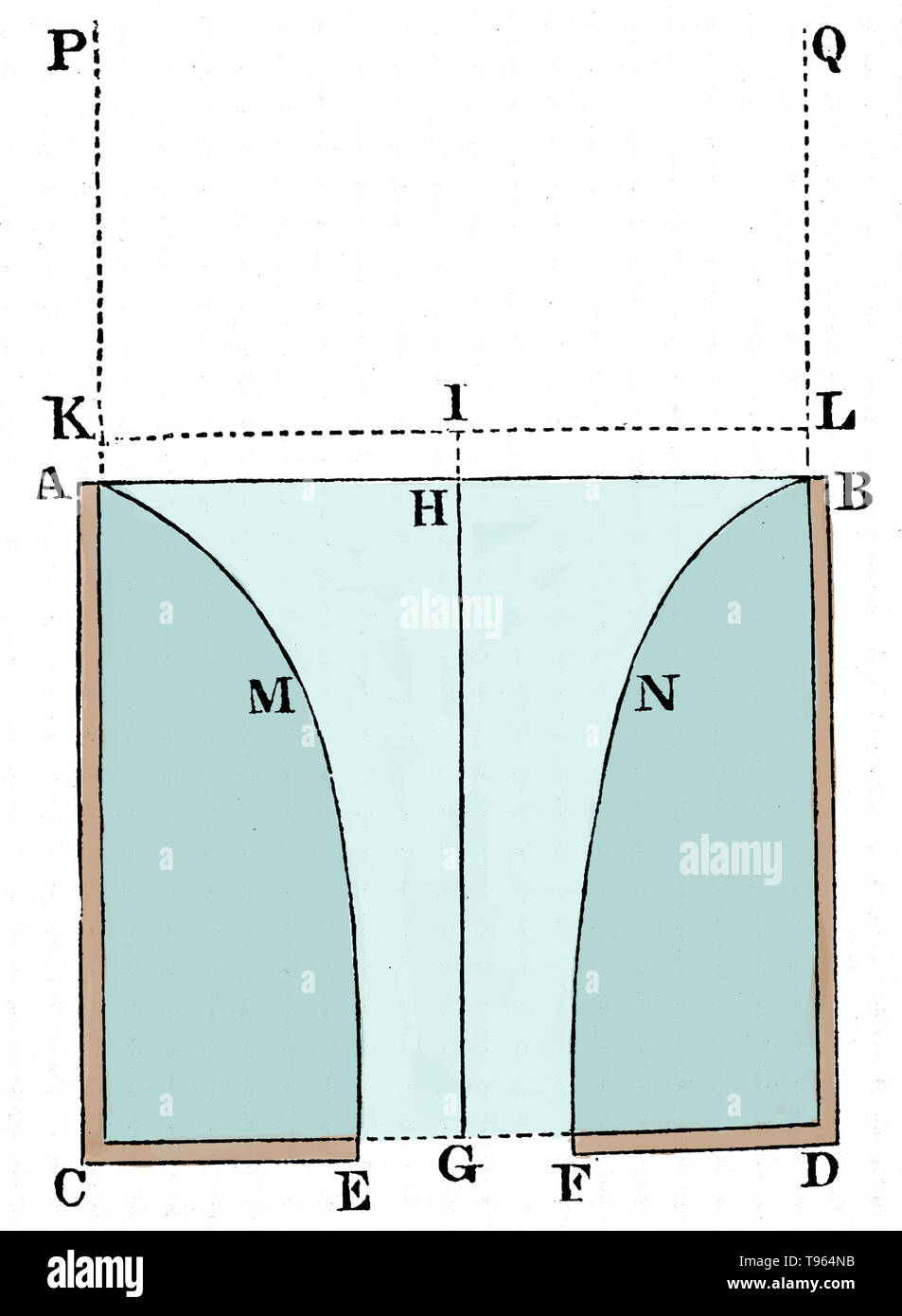 A diagram to define the motion of water running out of a cylindrical vessel through a hole made at the bottom. From The Principia: Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy by Isaac Newton. Newton (1642-1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian. His monograph Philosophae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, published in 1687, lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. In this work, Newton describes universal gravitation and the three laws of motion. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-diagram-to-define-the-motion-of-water-running-out-of-a-cylindrical-vessel-through-a-hole-made-at-the-bottom-from-the-principia-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-by-isaac-newton-newton-1642-1727-was-an-english-physicist-mathematician-astronomer-natural-philosopher-alchemist-and-theologian-his-monograph-philosophae-naturalis-principia-mathematica-published-in-1687-lays-the-foundations-for-most-of-classical-mechanics-in-this-work-newton-describes-universal-gravitation-and-the-three-laws-of-motion-image246612503.html
A diagram to define the motion of water running out of a cylindrical vessel through a hole made at the bottom. From The Principia: Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy by Isaac Newton. Newton (1642-1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian. His monograph Philosophae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, published in 1687, lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. In this work, Newton describes universal gravitation and the three laws of motion. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-diagram-to-define-the-motion-of-water-running-out-of-a-cylindrical-vessel-through-a-hole-made-at-the-bottom-from-the-principia-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-by-isaac-newton-newton-1642-1727-was-an-english-physicist-mathematician-astronomer-natural-philosopher-alchemist-and-theologian-his-monograph-philosophae-naturalis-principia-mathematica-published-in-1687-lays-the-foundations-for-most-of-classical-mechanics-in-this-work-newton-describes-universal-gravitation-and-the-three-laws-of-motion-image246612503.htmlRMT964NB–A diagram to define the motion of water running out of a cylindrical vessel through a hole made at the bottom. From The Principia: Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy by Isaac Newton. Newton (1642-1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian. His monograph Philosophae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, published in 1687, lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. In this work, Newton describes universal gravitation and the three laws of motion.
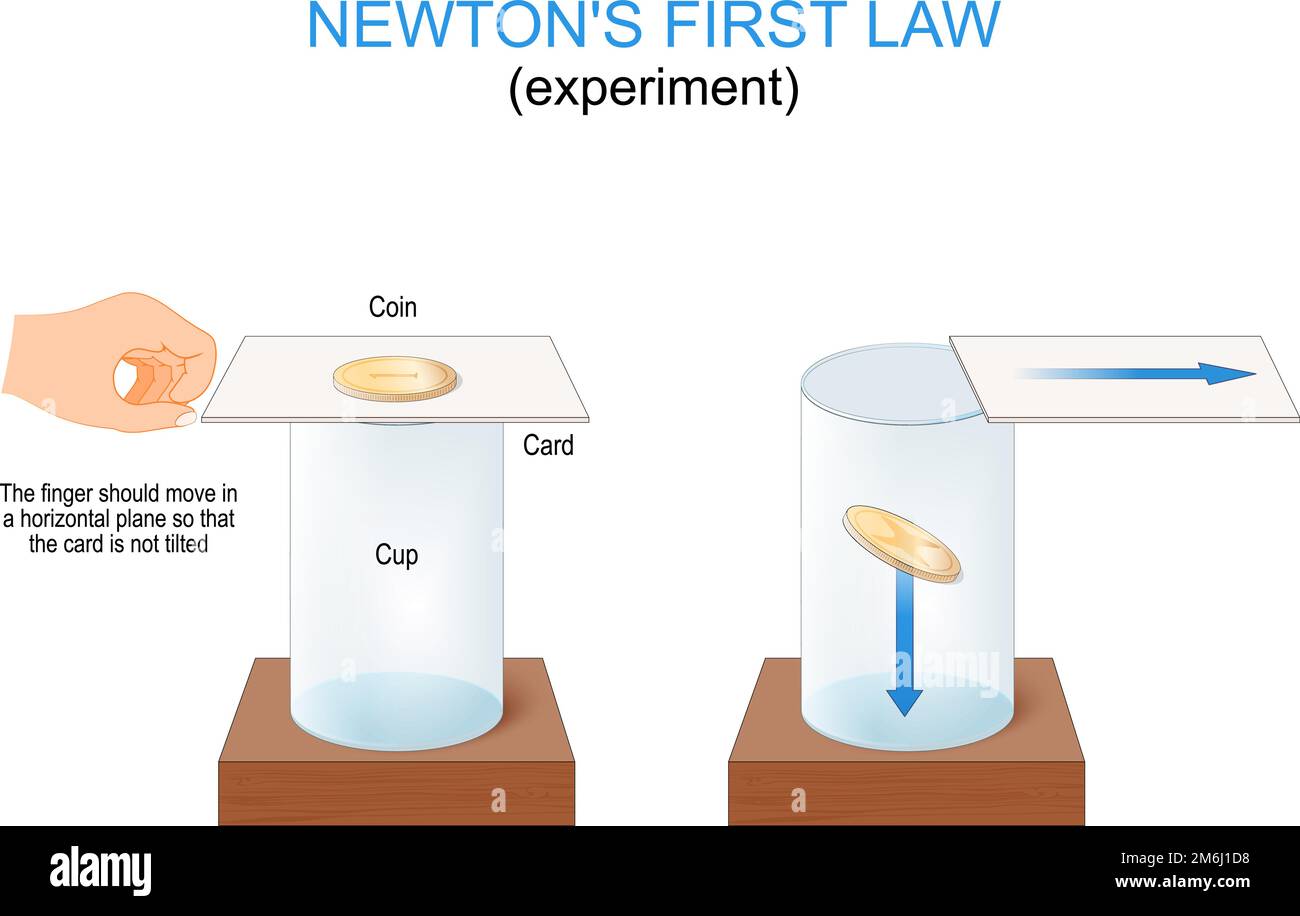 Newtons first law of motion. Forces and principle of inertia. experiment with coin, glass cup and card. classical mechanics. Vector poster Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newtons-first-law-of-motion-forces-and-principle-of-inertia-experiment-with-coin-glass-cup-and-card-classical-mechanics-vector-poster-image503184900.html
Newtons first law of motion. Forces and principle of inertia. experiment with coin, glass cup and card. classical mechanics. Vector poster Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newtons-first-law-of-motion-forces-and-principle-of-inertia-experiment-with-coin-glass-cup-and-card-classical-mechanics-vector-poster-image503184900.htmlRF2M6J1D8–Newtons first law of motion. Forces and principle of inertia. experiment with coin, glass cup and card. classical mechanics. Vector poster
 Science concept: Classical Mechanics on grunge wall background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-grunge-wall-background-image150394434.html
Science concept: Classical Mechanics on grunge wall background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-grunge-wall-background-image150394434.htmlRFJMK1HP–Science concept: Classical Mechanics on grunge wall background
 A selective focus shot of wooden keyboard hammer on strings. Inside piano mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-selective-focus-shot-of-wooden-keyboard-hammer-on-strings-inside-piano-mechanics-image476987354.html
A selective focus shot of wooden keyboard hammer on strings. Inside piano mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-selective-focus-shot-of-wooden-keyboard-hammer-on-strings-inside-piano-mechanics-image476987354.htmlRF2JM0J6J–A selective focus shot of wooden keyboard hammer on strings. Inside piano mechanics
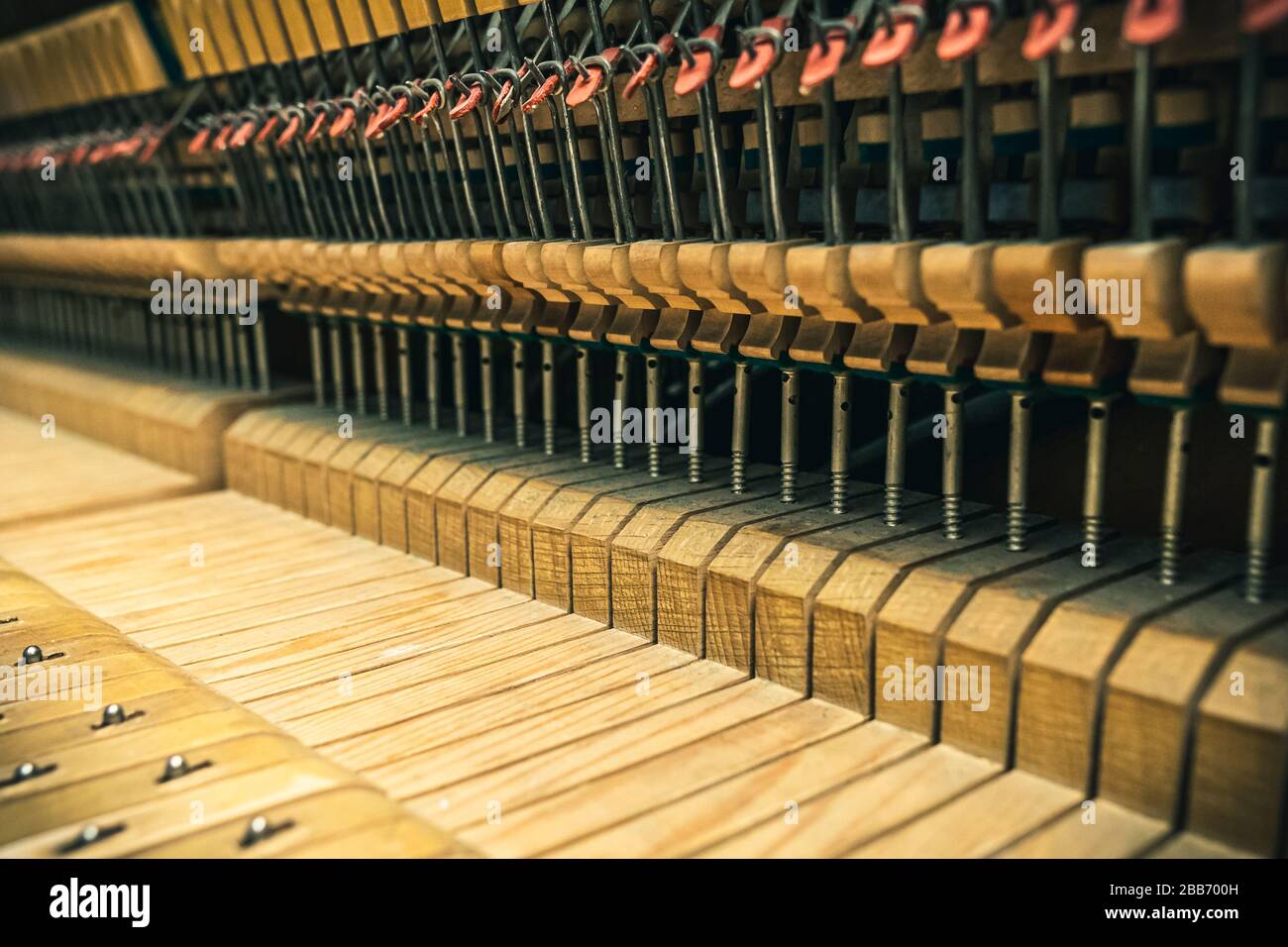 Open piano shows inside mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-piano-shows-inside-mechanics-image351122257.html
Open piano shows inside mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-piano-shows-inside-mechanics-image351122257.htmlRF2BB700H–Open piano shows inside mechanics
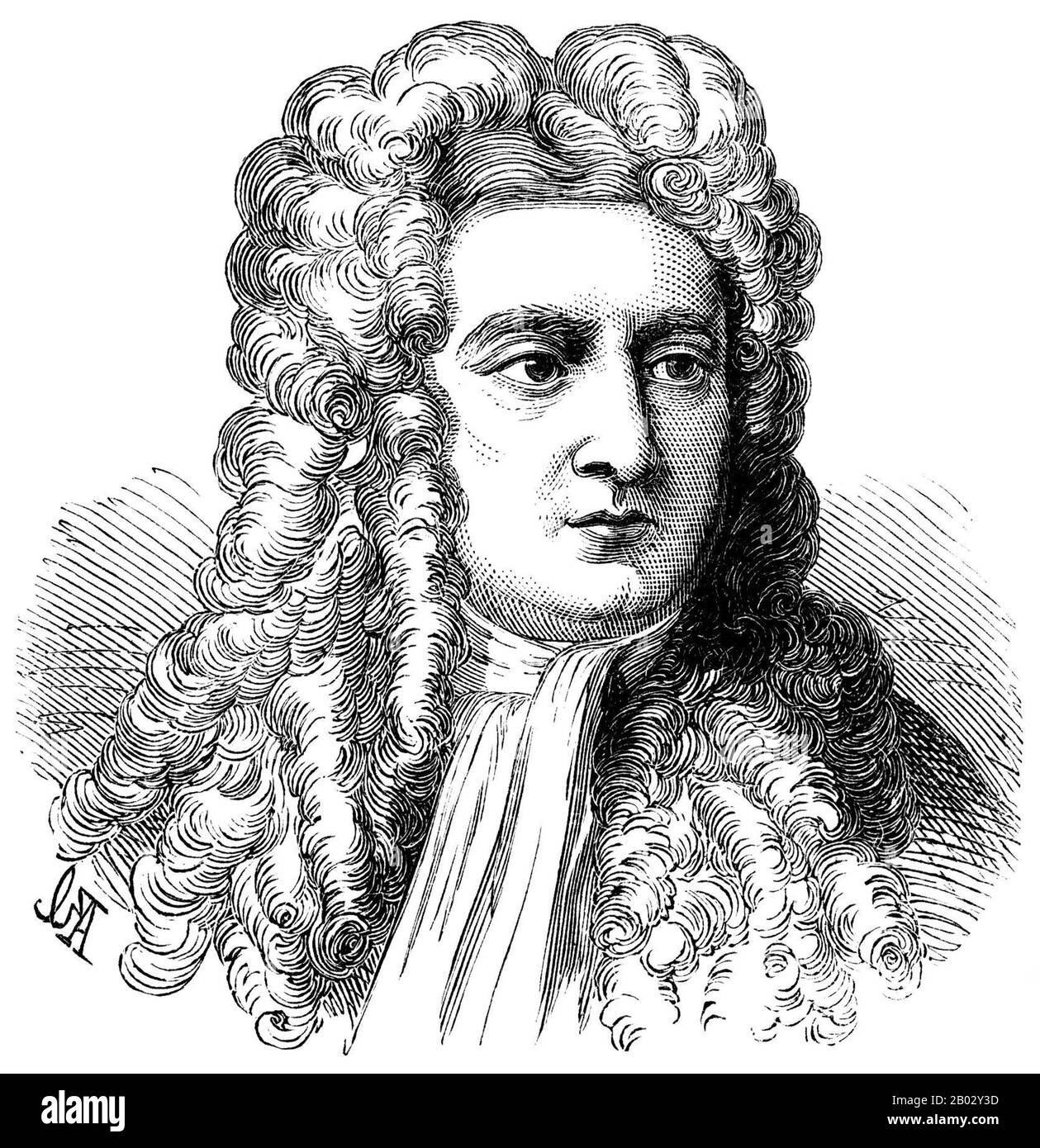 Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272529.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272529.htmlRM2B02Y3D–Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus.
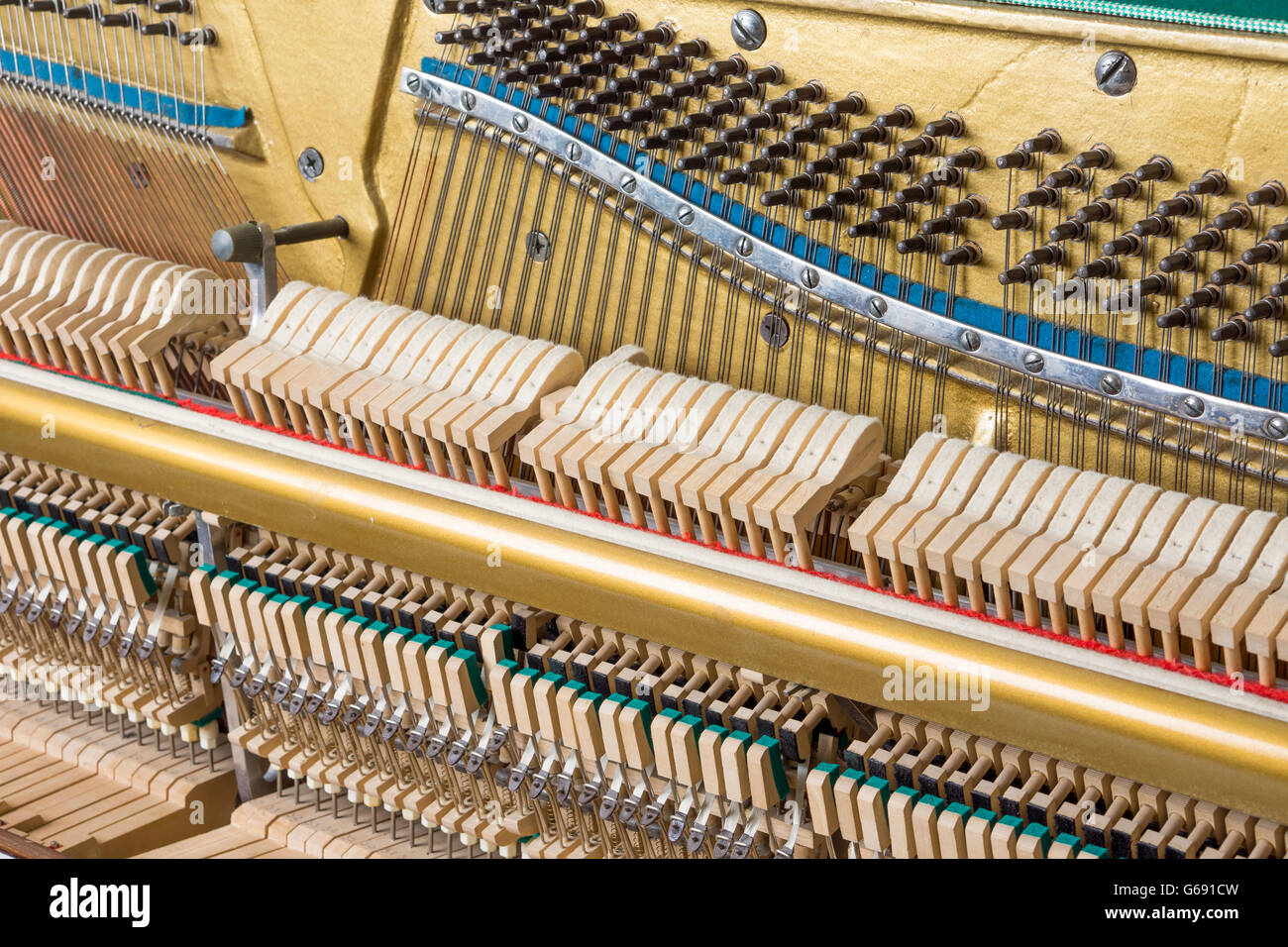 Mechanics details inside of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-mechanics-details-inside-of-an-upright-piano-107148857.html
Mechanics details inside of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-mechanics-details-inside-of-an-upright-piano-107148857.htmlRFG691CW–Mechanics details inside of an upright piano
 Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-than-the-speed-of-image382511824.html
Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-than-the-speed-of-image382511824.htmlRF2D68WMG–Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of
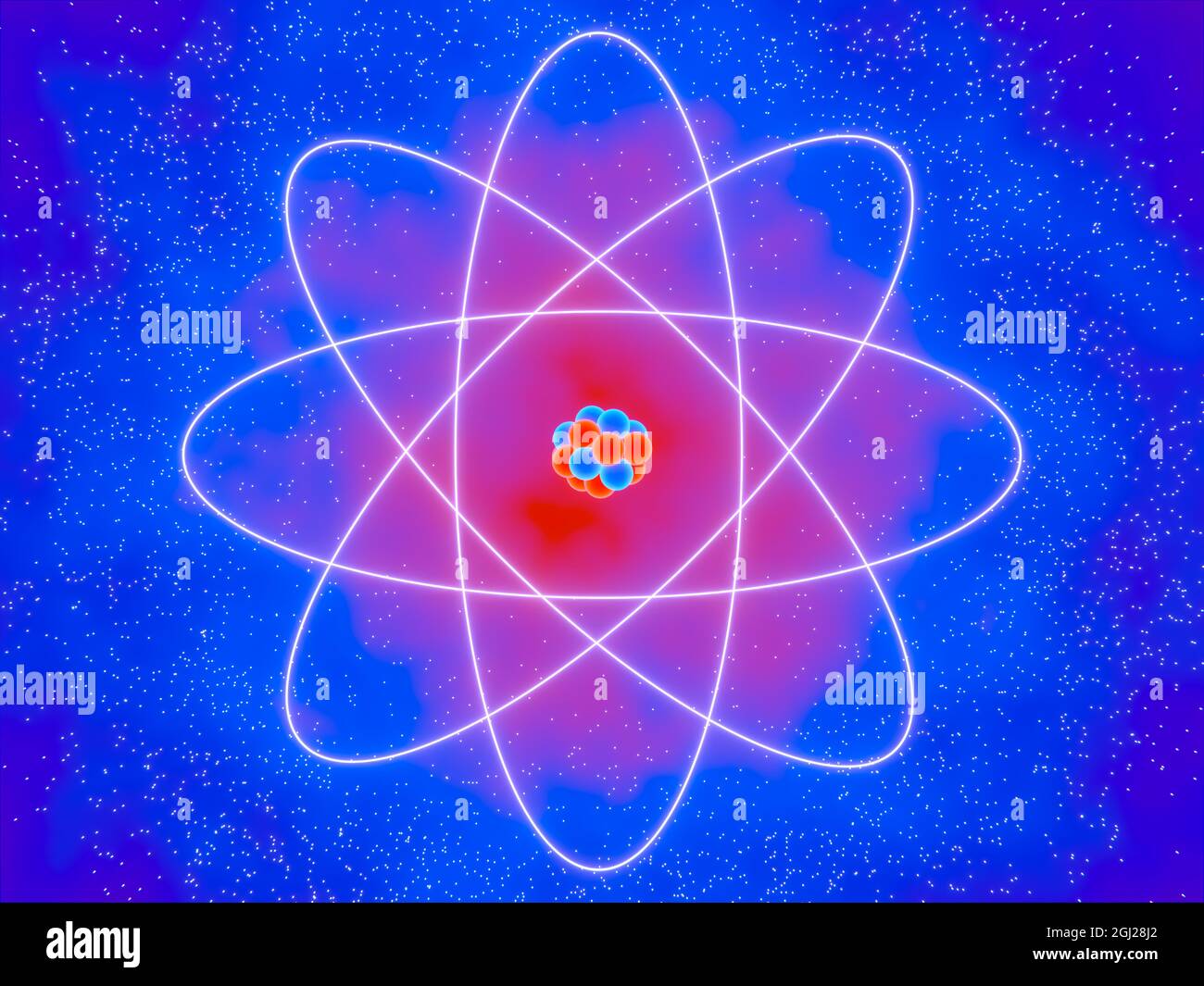 Classical Atom Symbol, with Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Conceptual Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classical-atom-symbol-with-protons-neutrons-and-electrons-conceptual-illustration-image441373690.html
Classical Atom Symbol, with Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Conceptual Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classical-atom-symbol-with-protons-neutrons-and-electrons-conceptual-illustration-image441373690.htmlRF2GJ28J2–Classical Atom Symbol, with Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Conceptual Illustration.
 Close-up of a guitar head with mechanics and strings Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-a-guitar-head-with-mechanics-and-strings-image393999804.html
Close-up of a guitar head with mechanics and strings Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-a-guitar-head-with-mechanics-and-strings-image393999804.htmlRF2DW06NG–Close-up of a guitar head with mechanics and strings
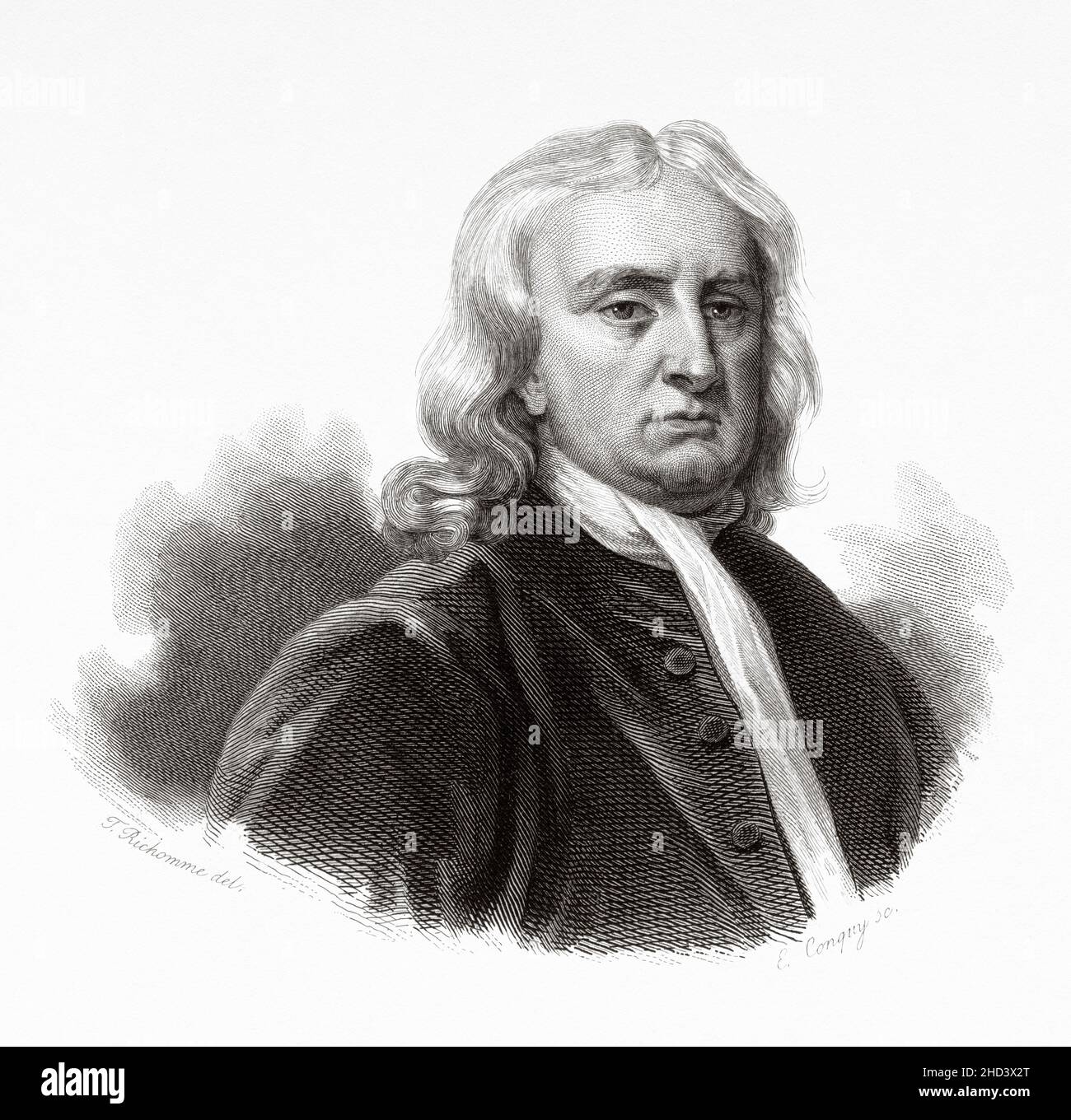 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author, recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians, physicists, and most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica established classical mechanics. UK. Europe. Old 19th century engraved illustration from Portraits et histoire des hommes utile by Societe Montyon et Franklin 1837 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-1642-1726-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-recognised-as-one-of-the-greatest-mathematicians-physicists-and-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-he-was-a-key-figure-in-the-philosophical-revolution-known-as-the-enlightenment-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-established-classical-mechanics-uk-europe-old-19th-century-engraved-illustration-from-portraits-et-histoire-des-hommes-utile-by-societe-montyon-et-franklin-1837-image455546416.html
Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author, recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians, physicists, and most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica established classical mechanics. UK. Europe. Old 19th century engraved illustration from Portraits et histoire des hommes utile by Societe Montyon et Franklin 1837 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-1642-1726-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-recognised-as-one-of-the-greatest-mathematicians-physicists-and-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-he-was-a-key-figure-in-the-philosophical-revolution-known-as-the-enlightenment-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-established-classical-mechanics-uk-europe-old-19th-century-engraved-illustration-from-portraits-et-histoire-des-hommes-utile-by-societe-montyon-et-franklin-1837-image455546416.htmlRM2HD3X2T–Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author, recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians, physicists, and most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica established classical mechanics. UK. Europe. Old 19th century engraved illustration from Portraits et histoire des hommes utile by Societe Montyon et Franklin 1837
 Mechanics Work on Plane Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-work-on-plane-image184245338.html
Mechanics Work on Plane Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-work-on-plane-image184245338.htmlRMMKN2PJ–Mechanics Work on Plane
RF2PNX6JP–Quantum physics line icons collection. Superposition, Entanglement, Wave-particle duality, Uncertainty, Quantum mechanics, Observer effect, Tunnelling
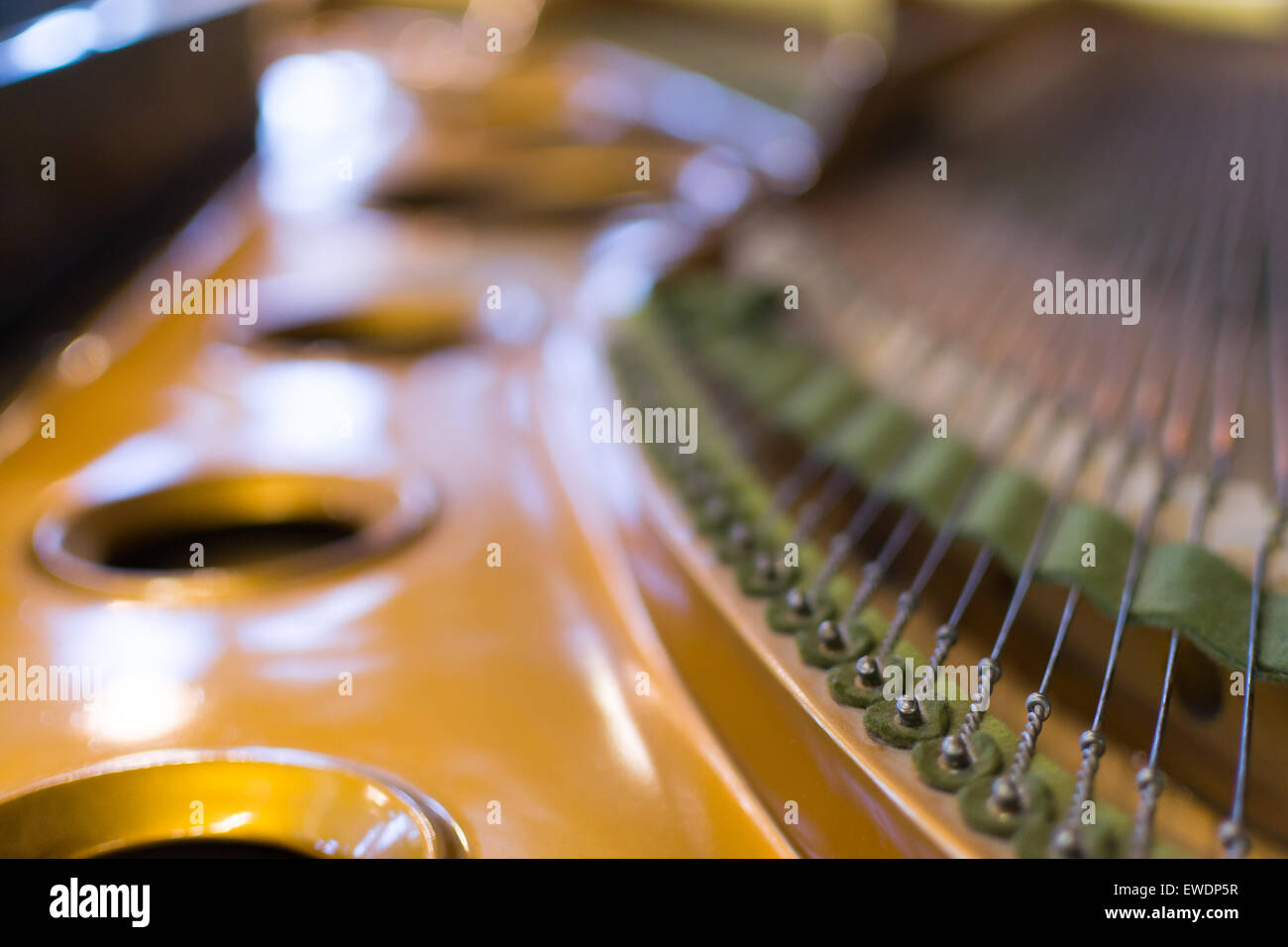 Detailed image of the strings of a classical Grand Piano in close-up Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-detailed-image-of-the-strings-of-a-classical-grand-piano-in-close-84510659.html
Detailed image of the strings of a classical Grand Piano in close-up Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-detailed-image-of-the-strings-of-a-classical-grand-piano-in-close-84510659.htmlRMEWDP5R–Detailed image of the strings of a classical Grand Piano in close-up
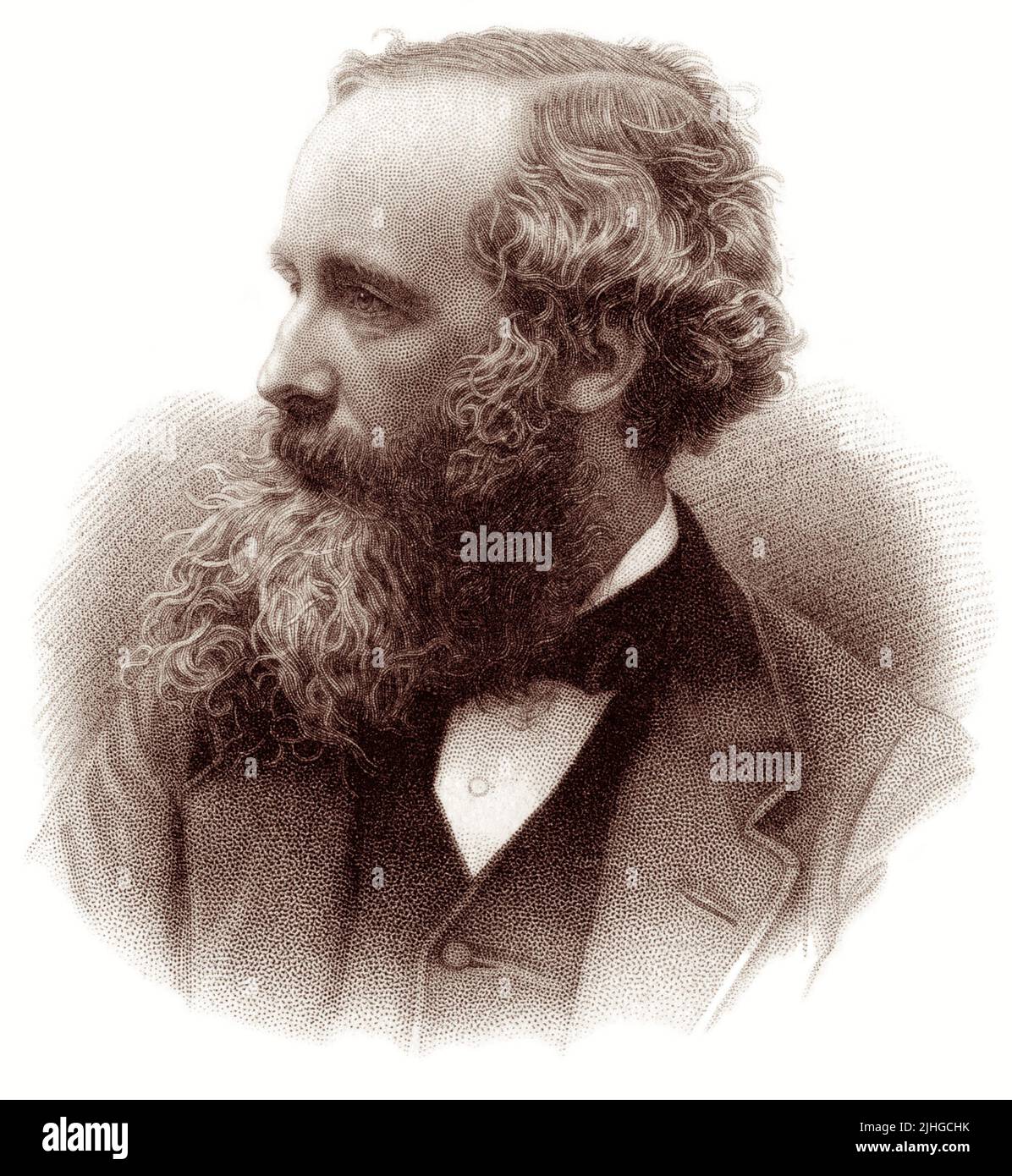 James Clerk Maxwell FRSE FRS (1831–1879) was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell is regarded by some as the Father of Modern Physics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/james-clerk-maxwell-frse-frs-18311879-was-a-scottish-mathematician-and-theoretical-physicist-responsible-for-the-classical-theory-of-electromagnetic-radiation-which-was-the-first-theory-to-describe-electricity-magnetism-and-light-as-different-manifestations-of-the-same-phenomenon-maxwell-is-regarded-by-some-as-the-father-of-modern-physics-image475490223.html
James Clerk Maxwell FRSE FRS (1831–1879) was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell is regarded by some as the Father of Modern Physics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/james-clerk-maxwell-frse-frs-18311879-was-a-scottish-mathematician-and-theoretical-physicist-responsible-for-the-classical-theory-of-electromagnetic-radiation-which-was-the-first-theory-to-describe-electricity-magnetism-and-light-as-different-manifestations-of-the-same-phenomenon-maxwell-is-regarded-by-some-as-the-father-of-modern-physics-image475490223.htmlRM2JHGCHK–James Clerk Maxwell FRSE FRS (1831–1879) was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell is regarded by some as the Father of Modern Physics.
 The central hall of General Society of Mechanics & Tradesmen of the City of New York with it's logo on the wall. midtown Manhattan. New York City.USA Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-central-hall-of-general-society-of-mechanics-tradesmen-of-the-city-of-new-york-with-its-logo-on-the-wall-midtown-manhattan-new-york-cityusa-image218980013.html
The central hall of General Society of Mechanics & Tradesmen of the City of New York with it's logo on the wall. midtown Manhattan. New York City.USA Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-central-hall-of-general-society-of-mechanics-tradesmen-of-the-city-of-new-york-with-its-logo-on-the-wall-midtown-manhattan-new-york-cityusa-image218980013.htmlRMPM7B6N–The central hall of General Society of Mechanics & Tradesmen of the City of New York with it's logo on the wall. midtown Manhattan. New York City.USA
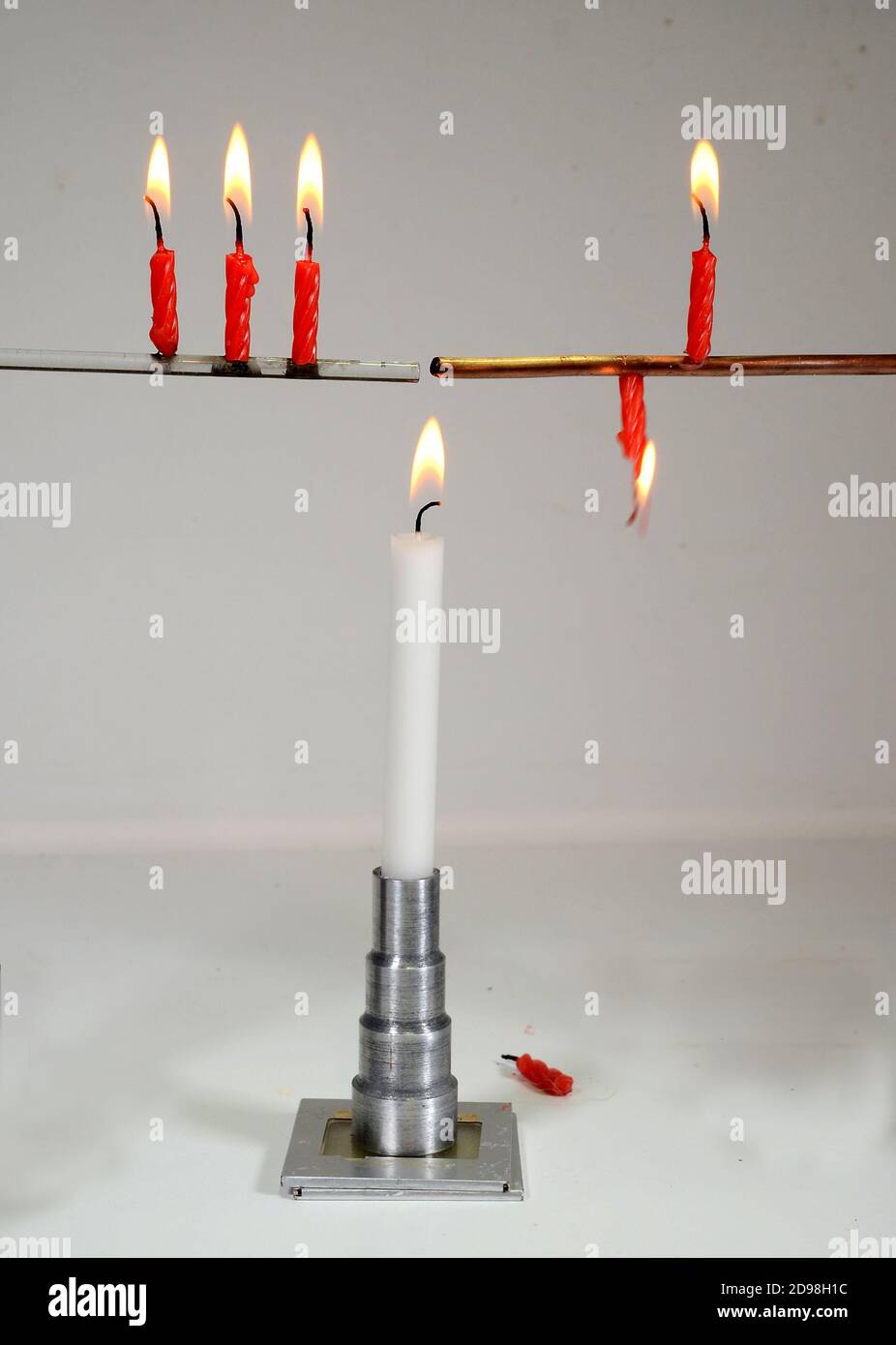 Classical physics experiment shows hat conduction. 3 red candles placed on a glass rod and a coppper rod, the rods are heated, and the candles on the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classical-physics-experiment-shows-hat-conduction-3-red-candles-placed-on-a-glass-rod-and-a-coppper-rod-the-rods-are-heated-and-the-candles-on-the-image384348984.html
Classical physics experiment shows hat conduction. 3 red candles placed on a glass rod and a coppper rod, the rods are heated, and the candles on the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classical-physics-experiment-shows-hat-conduction-3-red-candles-placed-on-a-glass-rod-and-a-coppper-rod-the-rods-are-heated-and-the-candles-on-the-image384348984.htmlRF2D98H1C–Classical physics experiment shows hat conduction. 3 red candles placed on a glass rod and a coppper rod, the rods are heated, and the candles on the
 Small hammers mechanics inside old piano with selective focus and shallow depth of field. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-small-hammers-mechanics-inside-old-piano-with-selective-focus-and-87809239.html
Small hammers mechanics inside old piano with selective focus and shallow depth of field. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-small-hammers-mechanics-inside-old-piano-with-selective-focus-and-87809239.htmlRFF2T1G7–Small hammers mechanics inside old piano with selective focus and shallow depth of field.
 View to the mechanics inside an older grand piano, hammer from below and damper from above on the strings of the acoustic musical instrument, selected Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/view-to-the-mechanics-inside-an-older-grand-piano-hammer-from-below-and-damper-from-above-on-the-strings-of-the-acoustic-musical-instrument-selected-image443397655.html
View to the mechanics inside an older grand piano, hammer from below and damper from above on the strings of the acoustic musical instrument, selected Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/view-to-the-mechanics-inside-an-older-grand-piano-hammer-from-below-and-damper-from-above-on-the-strings-of-the-acoustic-musical-instrument-selected-image443397655.htmlRF2GNAE6F–View to the mechanics inside an older grand piano, hammer from below and damper from above on the strings of the acoustic musical instrument, selected
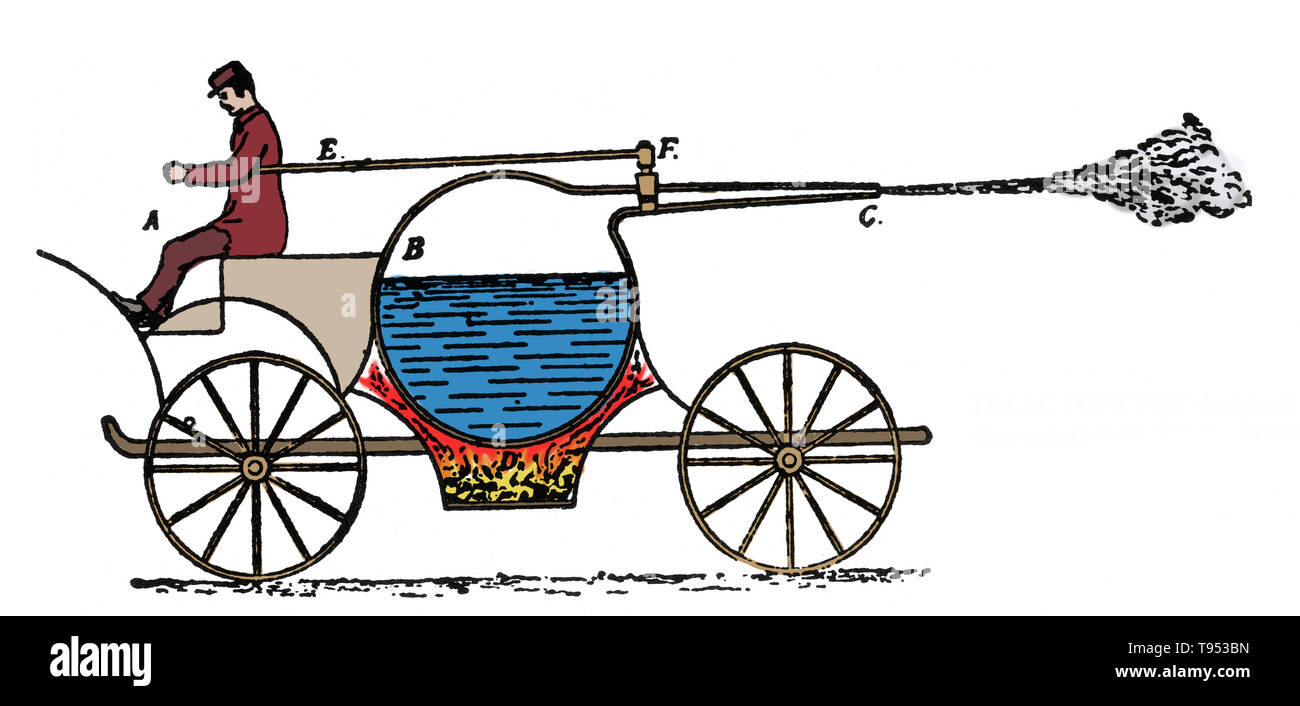 Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/steam-powered-vehicle-designed-by-gravesande-1720-willem-jacob-s-gravesande-september-26-1688-february-28-1742-was-a-dutch-lawyer-and-natural-philosopher-remembered-for-developing-experimental-demonstrations-of-the-laws-of-classical-mechanics-image246589497.html
Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/steam-powered-vehicle-designed-by-gravesande-1720-willem-jacob-s-gravesande-september-26-1688-february-28-1742-was-a-dutch-lawyer-and-natural-philosopher-remembered-for-developing-experimental-demonstrations-of-the-laws-of-classical-mechanics-image246589497.htmlRMT953BN–Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics.
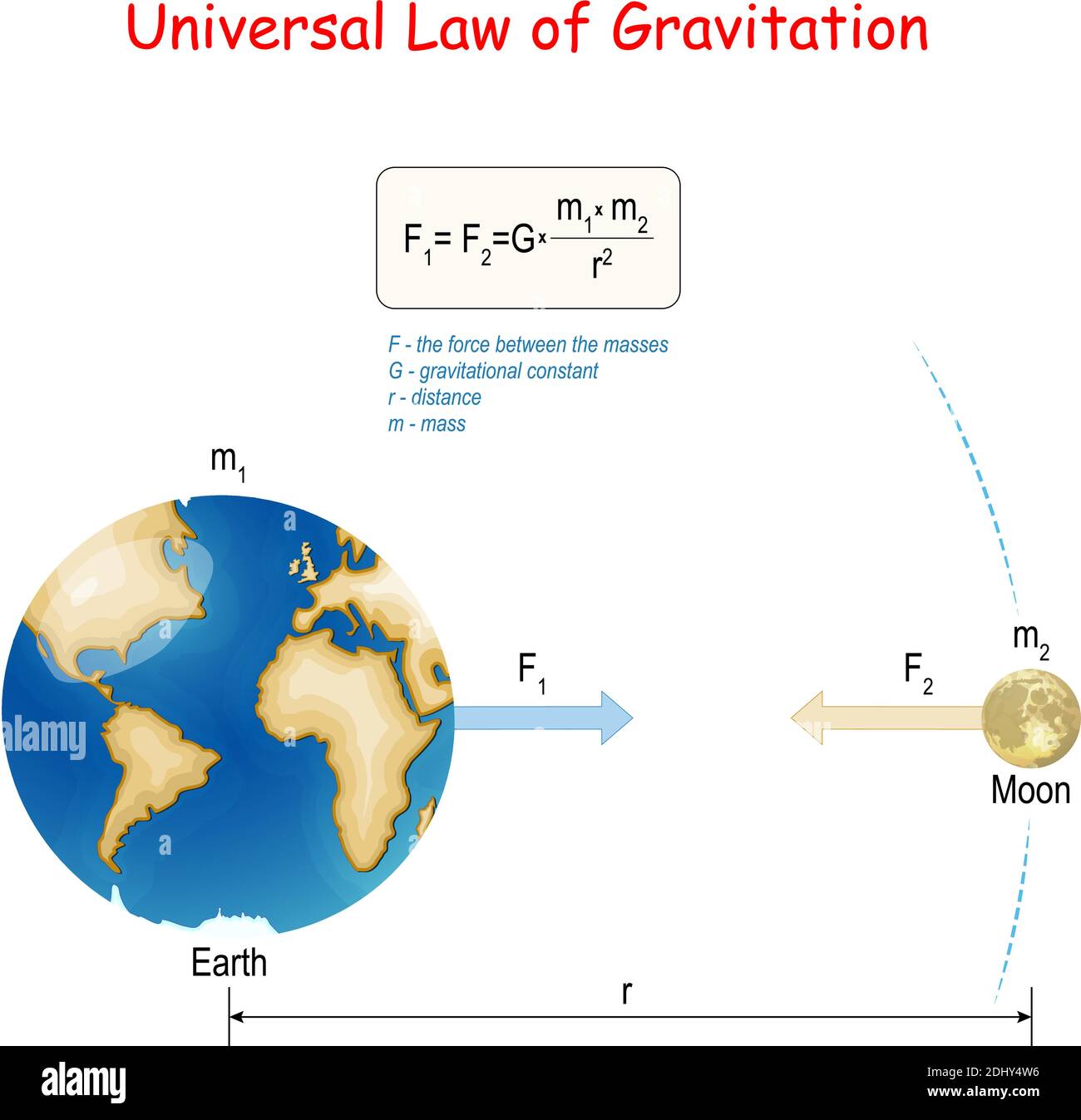 Newton's law of universal gravitation. Earth and Moon. physical law. classical mechanics. Vector Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newtons-law-of-universal-gravitation-earth-and-moon-physical-law-classical-mechanics-vector-image389673794.html
Newton's law of universal gravitation. Earth and Moon. physical law. classical mechanics. Vector Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newtons-law-of-universal-gravitation-earth-and-moon-physical-law-classical-mechanics-vector-image389673794.htmlRF2DHY4W6–Newton's law of universal gravitation. Earth and Moon. physical law. classical mechanics. Vector
 Science concept: Classical Mechanics on wall background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-wall-background-131313736.html
Science concept: Classical Mechanics on wall background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-wall-background-131313736.htmlRFHHHT08–Science concept: Classical Mechanics on wall background
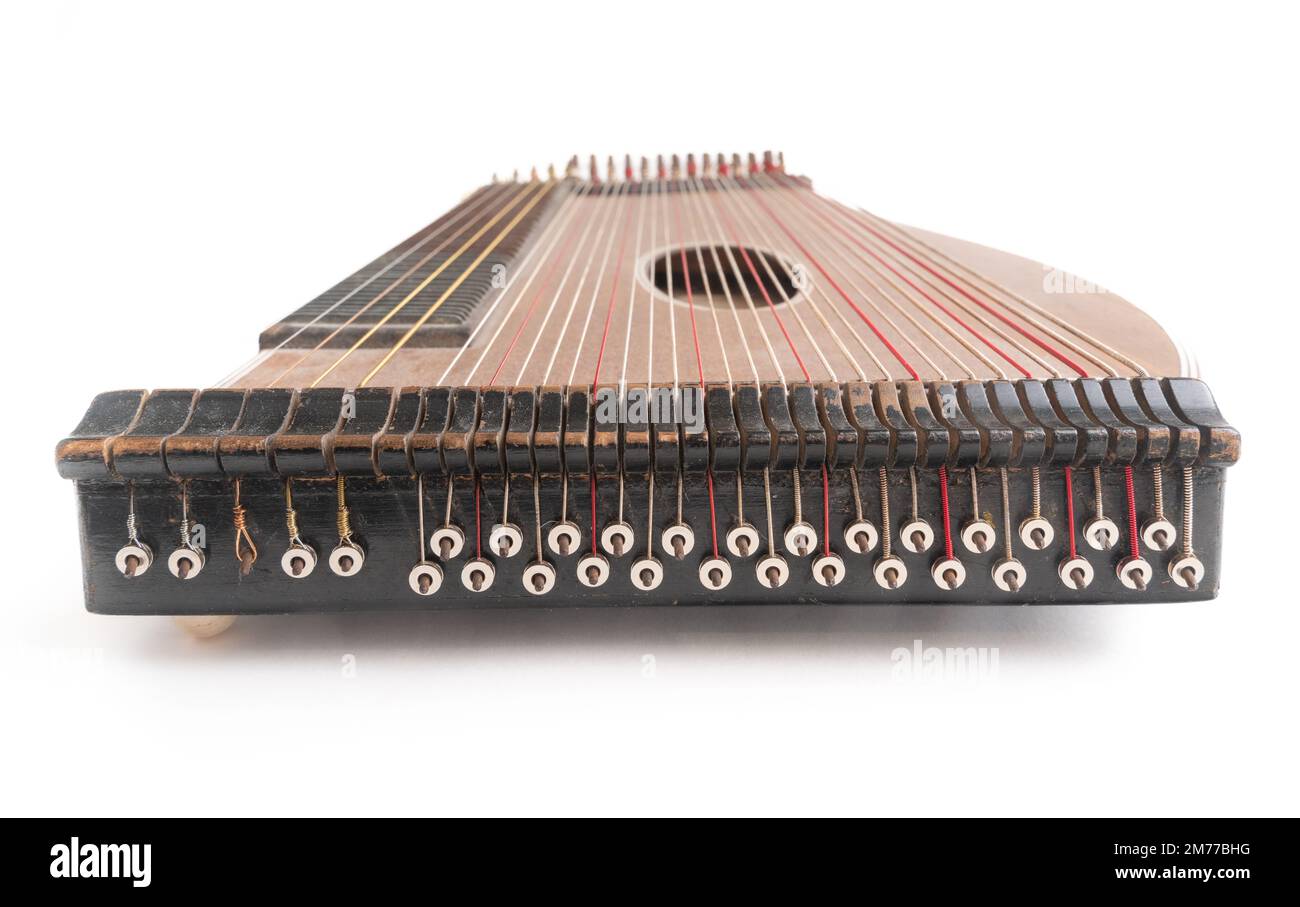 High angle closeup horizontal studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-closeup-horizontal-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-image503566044.html
High angle closeup horizontal studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-closeup-horizontal-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-image503566044.htmlRF2M77BHG–High angle closeup horizontal studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins
 Open piano shows inside mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-piano-shows-inside-mechanics-image351122464.html
Open piano shows inside mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-piano-shows-inside-mechanics-image351122464.htmlRF2BB7080–Open piano shows inside mechanics
 Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272526.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272526.htmlRM2B02Y3A–Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus.
 Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-keyboard-and-mechanics-details-of-an-upright-piano-107148800.html
Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-keyboard-and-mechanics-details-of-an-upright-piano-107148800.htmlRFG691AT–Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano
 Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-than-the-speed-of-image382511674.html
Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-than-the-speed-of-image382511674.htmlRF2D68WF6–Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of
 Burnley Mechanics, theatre and former Mechanics' Institute (built 1854-5), Burnley, Lancashire, England, UK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-burnley-mechanics-theatre-and-former-mechanics-institute-built-1854-51401639.html
Burnley Mechanics, theatre and former Mechanics' Institute (built 1854-5), Burnley, Lancashire, England, UK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-burnley-mechanics-theatre-and-former-mechanics-institute-built-1854-51401639.htmlRMCYHF8R–Burnley Mechanics, theatre and former Mechanics' Institute (built 1854-5), Burnley, Lancashire, England, UK
 Professor Albert Einstein and Louis Lewandowsky playing the violin for a Judaism Classical concert Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-professor-albert-einstein-and-louis-lewandowsky-playing-the-violin-26117344.html
Professor Albert Einstein and Louis Lewandowsky playing the violin for a Judaism Classical concert Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-professor-albert-einstein-and-louis-lewandowsky-playing-the-violin-26117344.htmlRMBEDMX8–Professor Albert Einstein and Louis Lewandowsky playing the violin for a Judaism Classical concert
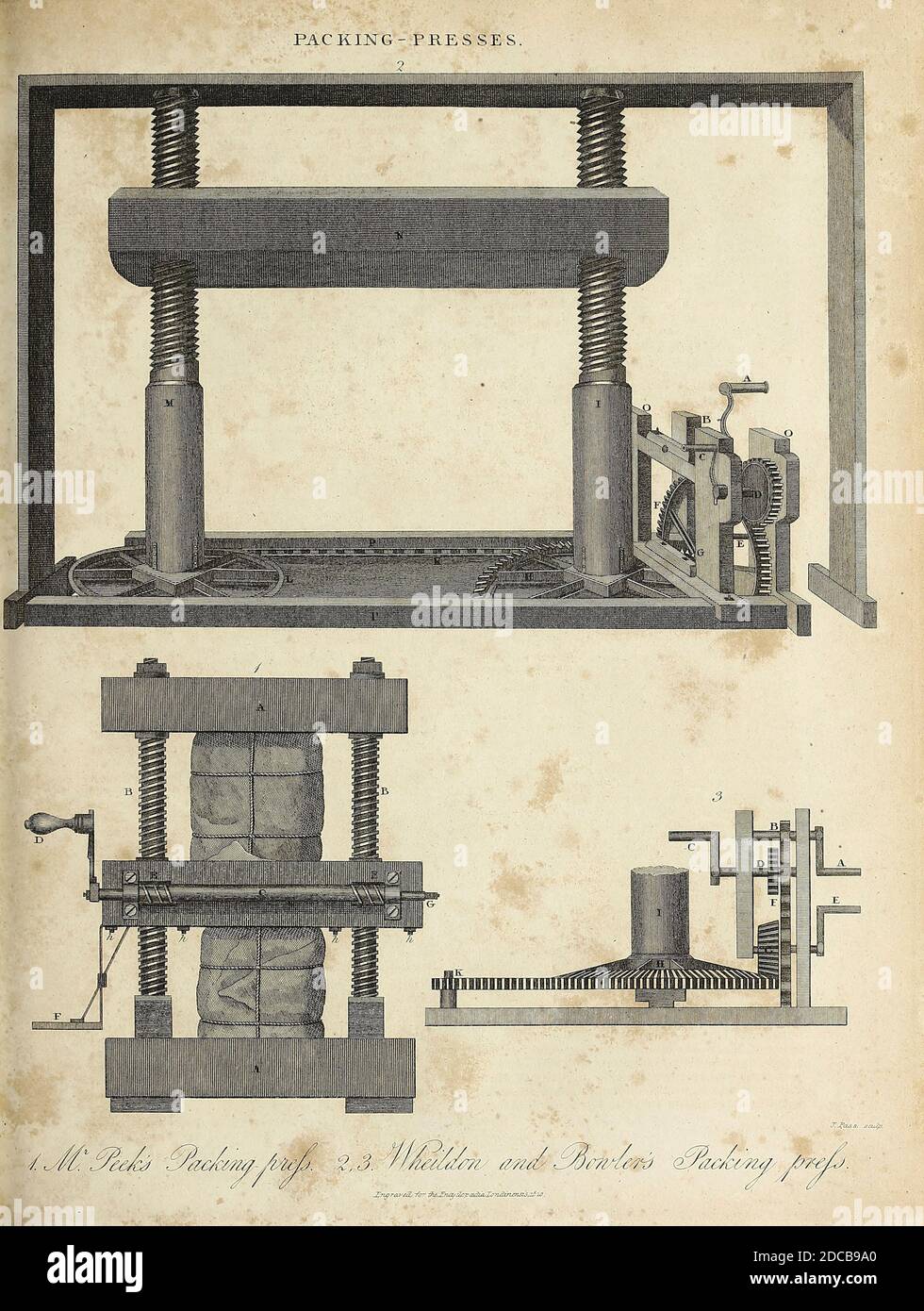 Mechanical Screw action Packing press Copperplate engraving From the Encyclopaedia Londinensis or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature; Volume XVIII; Edited by Wilkes, John. Published in London in 1821 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanical-screw-action-packing-press-copperplate-engraving-from-the-encyclopaedia-londinensis-or-universal-dictionary-of-arts-sciences-and-literature-volume-xviii-edited-by-wilkes-john-published-in-london-in-1821-image386252776.html
Mechanical Screw action Packing press Copperplate engraving From the Encyclopaedia Londinensis or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature; Volume XVIII; Edited by Wilkes, John. Published in London in 1821 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanical-screw-action-packing-press-copperplate-engraving-from-the-encyclopaedia-londinensis-or-universal-dictionary-of-arts-sciences-and-literature-volume-xviii-edited-by-wilkes-john-published-in-london-in-1821-image386252776.htmlRF2DCB9A0–Mechanical Screw action Packing press Copperplate engraving From the Encyclopaedia Londinensis or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature; Volume XVIII; Edited by Wilkes, John. Published in London in 1821
 Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/munich-germany-march-10-2016-collection-of-classical-cars-on-display-in-bmw-museum-image477500454.html
Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/munich-germany-march-10-2016-collection-of-classical-cars-on-display-in-bmw-museum-image477500454.htmlRM2JMT0KJ–Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum
RF2PP6P12–Company success line icons collection. Superposition, Entanglement, Wave-particle duality, Uncertainty, Quantum mechanics, Observer effect, Tunnelling
 acoustic audio classical close closeup coils color concert construction detail diagonal equipment grand hammer horizontal inside Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-acoustic-audio-classical-close-closeup-coils-color-concert-construction-84495910.html
acoustic audio classical close closeup coils color concert construction detail diagonal equipment grand hammer horizontal inside Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-acoustic-audio-classical-close-closeup-coils-color-concert-construction-84495910.htmlRMEWD3B2–acoustic audio classical close closeup coils color concert construction detail diagonal equipment grand hammer horizontal inside
 Vintage model of a gearshift isolated on a white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/vintage-model-of-a-gearshift-isolated-on-a-white-background-image388138845.html
Vintage model of a gearshift isolated on a white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/vintage-model-of-a-gearshift-isolated-on-a-white-background-image388138845.htmlRF2DFD71H–Vintage model of a gearshift isolated on a white background
 Upright piano hammers detail Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-upright-piano-hammers-detail-94319236.html
Upright piano hammers detail Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-upright-piano-hammers-detail-94319236.htmlRFFDCH44–Upright piano hammers detail
 Image of a string inside a musical instrument piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/image-of-a-string-inside-a-musical-instrument-piano-image559427790.html
Image of a string inside a musical instrument piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/image-of-a-string-inside-a-musical-instrument-piano-image559427790.htmlRM2RE43RX–Image of a string inside a musical instrument piano
 Classic aircraft engine Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classic-aircraft-engine-image624801471.html
Classic aircraft engine Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classic-aircraft-engine-image624801471.htmlRF2Y8E4J7–Classic aircraft engine
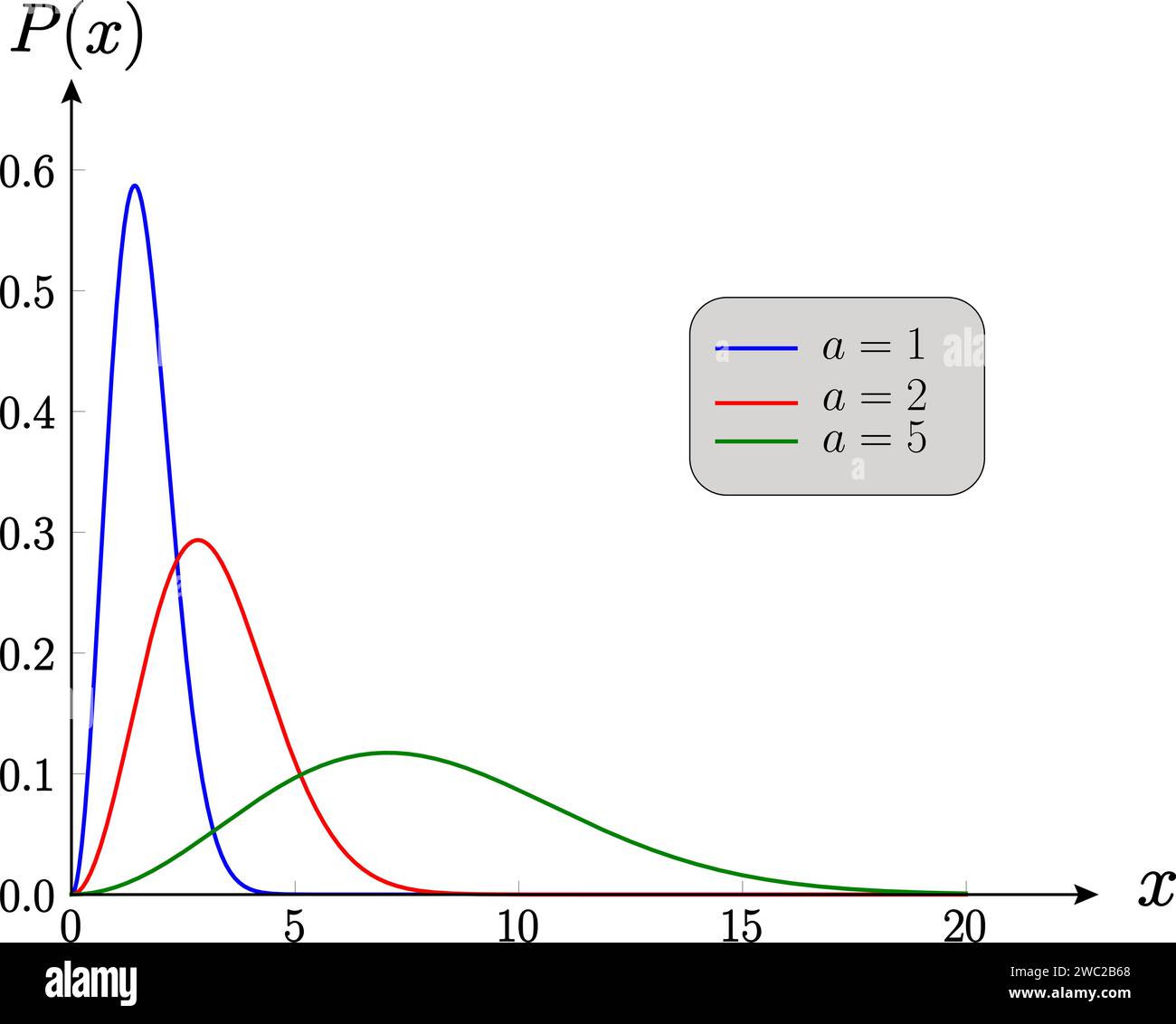 Probability distribution function, statistic ,mathematics ,analysis.Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/probability-distribution-function-statistic-mathematics-analysisvector-illustration-image592581088.html
Probability distribution function, statistic ,mathematics ,analysis.Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/probability-distribution-function-statistic-mathematics-analysisvector-illustration-image592581088.htmlRF2WC2B68–Probability distribution function, statistic ,mathematics ,analysis.Vector illustration.
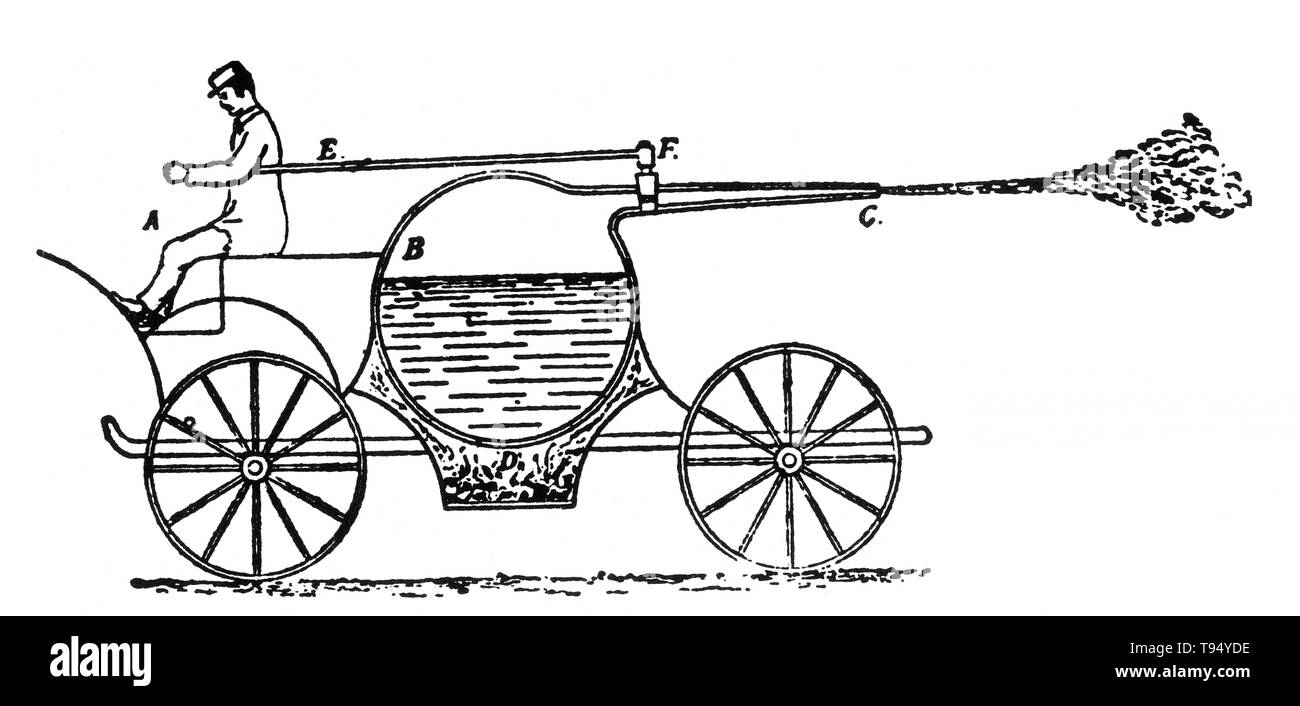 Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/steam-powered-vehicle-designed-by-gravesande-1720-willem-jacob-s-gravesande-september-26-1688-february-28-1742-was-a-dutch-lawyer-and-natural-philosopher-remembered-for-developing-experimental-demonstrations-of-the-laws-of-classical-mechanics-image246586410.html
Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/steam-powered-vehicle-designed-by-gravesande-1720-willem-jacob-s-gravesande-september-26-1688-february-28-1742-was-a-dutch-lawyer-and-natural-philosopher-remembered-for-developing-experimental-demonstrations-of-the-laws-of-classical-mechanics-image246586410.htmlRMT94YDE–Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics.
 A VW Beetle car at car mechanic repair shop, Kyoto, Japan Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-vw-beetle-car-at-car-mechanic-repair-shop-kyoto-japan-72567339.html
A VW Beetle car at car mechanic repair shop, Kyoto, Japan Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-vw-beetle-car-at-car-mechanic-repair-shop-kyoto-japan-72567339.htmlRME61MAK–A VW Beetle car at car mechanic repair shop, Kyoto, Japan
 Science concept: newspaper headline Classical Mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-newspaper-headline-classical-mechanics-172183542.html
Science concept: newspaper headline Classical Mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-newspaper-headline-classical-mechanics-172183542.htmlRFM03HT6–Science concept: newspaper headline Classical Mechanics
 High angle vertical studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins. Dusty and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-vertical-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-dusty-and-image503566330.html
High angle vertical studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins. Dusty and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-vertical-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-dusty-and-image503566330.htmlRF2M77BYP–High angle vertical studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins. Dusty and
 Open piano shows inside mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-piano-shows-inside-mechanics-image351122483.html
Open piano shows inside mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-piano-shows-inside-mechanics-image351122483.htmlRF2BB708K–Open piano shows inside mechanics
 Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272528.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344272528.htmlRM2B02Y3C–Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus.
 Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-keyboard-and-mechanics-details-of-an-upright-piano-107148780.html
Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-keyboard-and-mechanics-details-of-an-upright-piano-107148780.htmlRFG691A4–Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano
 Mechanical cranes Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanical-cranes-mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-image382511743.html
Mechanical cranes Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanical-cranes-mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significantly-less-image382511743.htmlRF2D68WHK–Mechanical cranes Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less
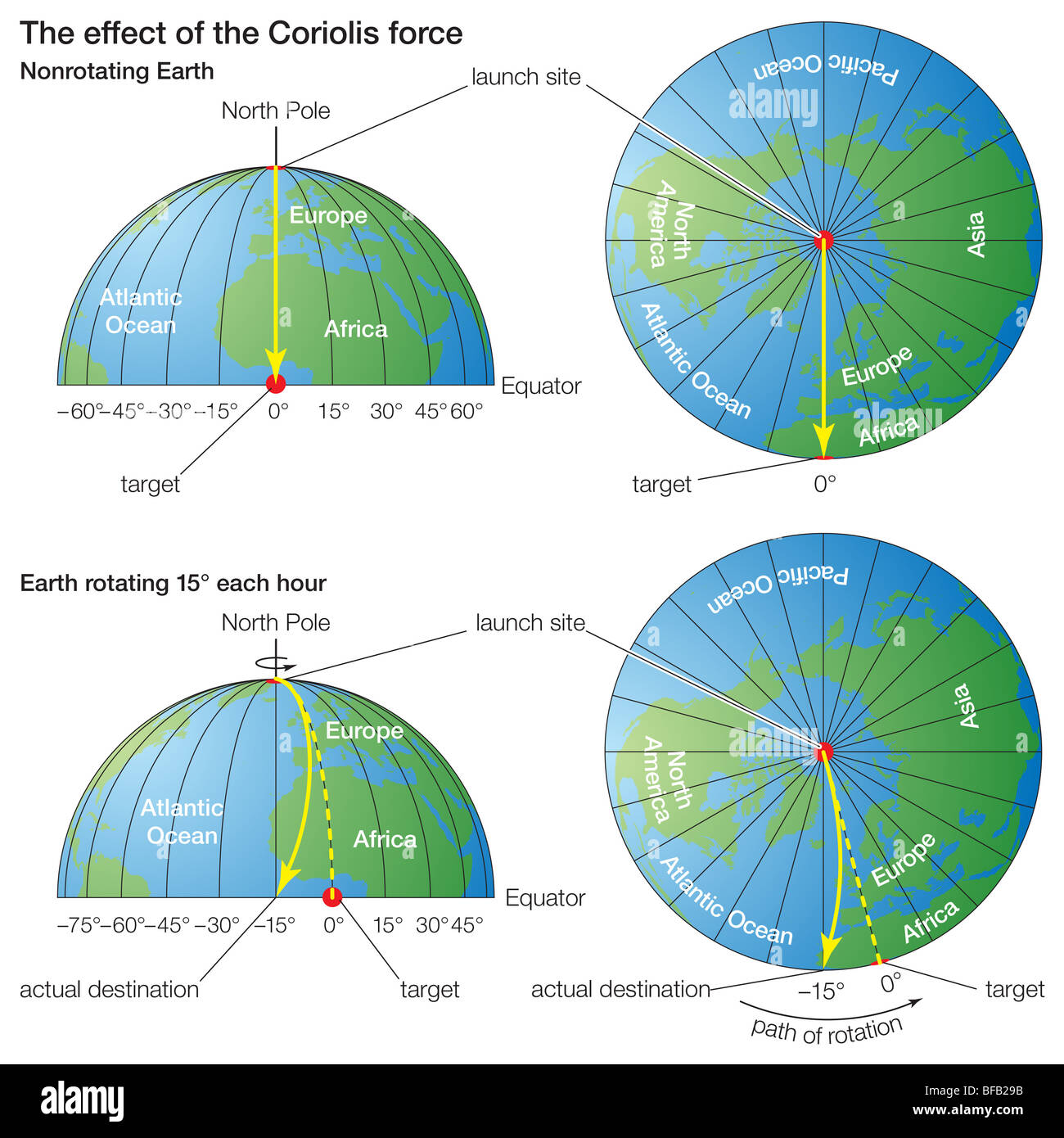 Coriolis force Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coriolis-force-26673511.html
Coriolis force Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coriolis-force-26673511.htmlRMBFB29B–Coriolis force
 Detail inside a grand piano, pins or pegs with strings and some dust in the old acoustic musical instrument, concept for music and culture, selected f Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/detail-inside-a-grand-piano-pins-or-pegs-with-strings-and-some-dust-in-the-old-acoustic-musical-instrument-concept-for-music-and-culture-selected-f-image443397613.html
Detail inside a grand piano, pins or pegs with strings and some dust in the old acoustic musical instrument, concept for music and culture, selected f Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/detail-inside-a-grand-piano-pins-or-pegs-with-strings-and-some-dust-in-the-old-acoustic-musical-instrument-concept-for-music-and-culture-selected-f-image443397613.htmlRF2GNAE51–Detail inside a grand piano, pins or pegs with strings and some dust in the old acoustic musical instrument, concept for music and culture, selected f
 Engaving of Charles Babbage from Mechanics Magazine. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/engaving-of-charles-babbage-from-mechanics-magazine-image328604133.html
Engaving of Charles Babbage from Mechanics Magazine. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/engaving-of-charles-babbage-from-mechanics-magazine-image328604133.htmlRM2A2H5WW–Engaving of Charles Babbage from Mechanics Magazine.
 Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/munich-germany-march-10-2016-collection-of-classical-cars-on-display-in-bmw-museum-image477500378.html
Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/munich-germany-march-10-2016-collection-of-classical-cars-on-display-in-bmw-museum-image477500378.htmlRM2JMT0GX–Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum
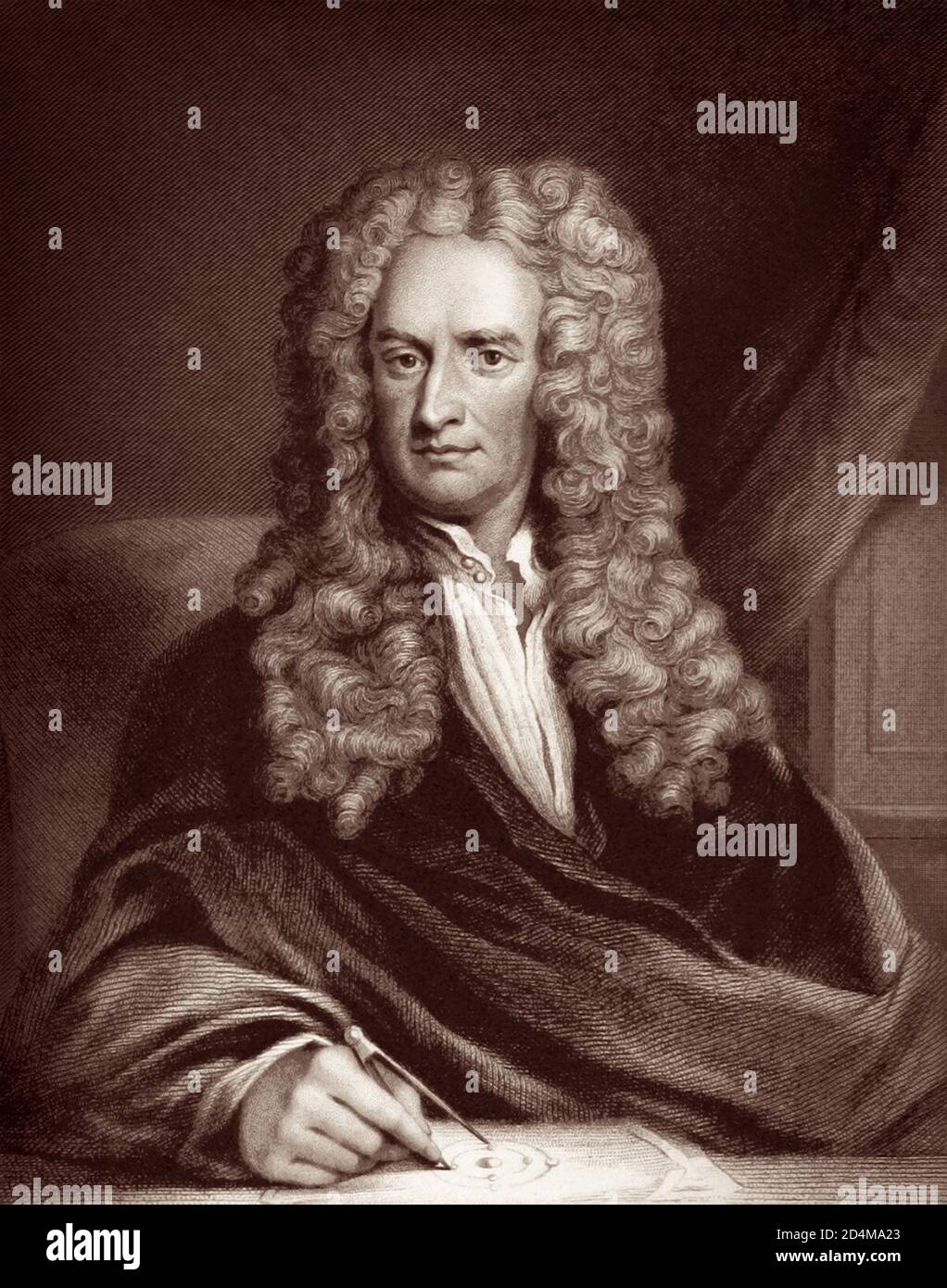 Sir Isaac Newton PRS (1642/43-1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-164243-172627-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-image381533659.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS (1642/43-1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-164243-172627-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-image381533659.htmlRM2D4MA23–Sir Isaac Newton PRS (1642/43-1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution.
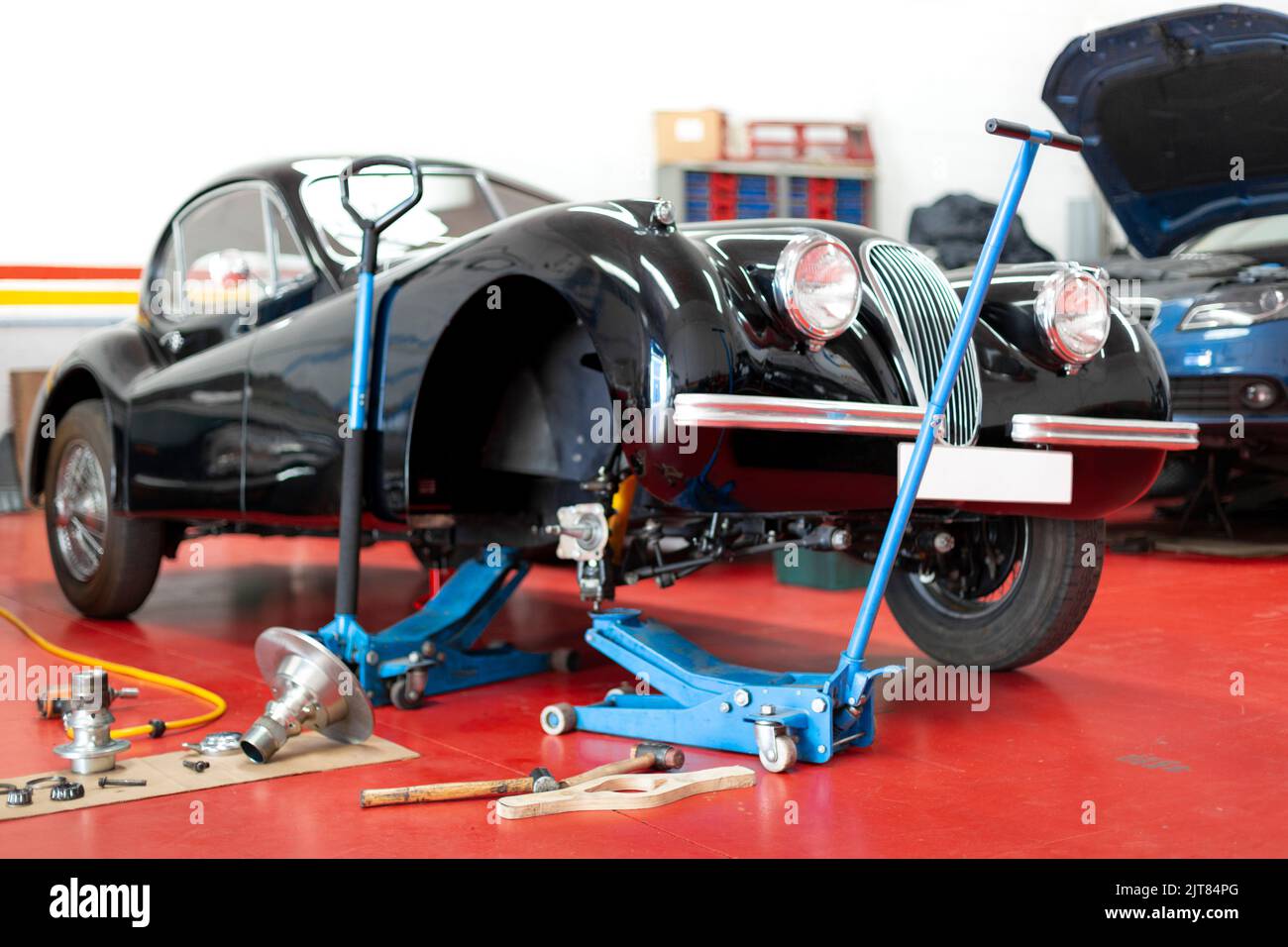 Antique automobile being repaired in the mechanic workshop. Overhaul and restoration of classic cars. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/antique-automobile-being-repaired-in-the-mechanic-workshop-overhaul-and-restoration-of-classic-cars-image479611064.html
Antique automobile being repaired in the mechanic workshop. Overhaul and restoration of classic cars. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/antique-automobile-being-repaired-in-the-mechanic-workshop-overhaul-and-restoration-of-classic-cars-image479611064.htmlRF2JT84PG–Antique automobile being repaired in the mechanic workshop. Overhaul and restoration of classic cars.
 A robot plays the violin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-robot-plays-the-violin-image366682762.html
A robot plays the violin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-robot-plays-the-violin-image366682762.htmlRF2C8FRGX–A robot plays the violin
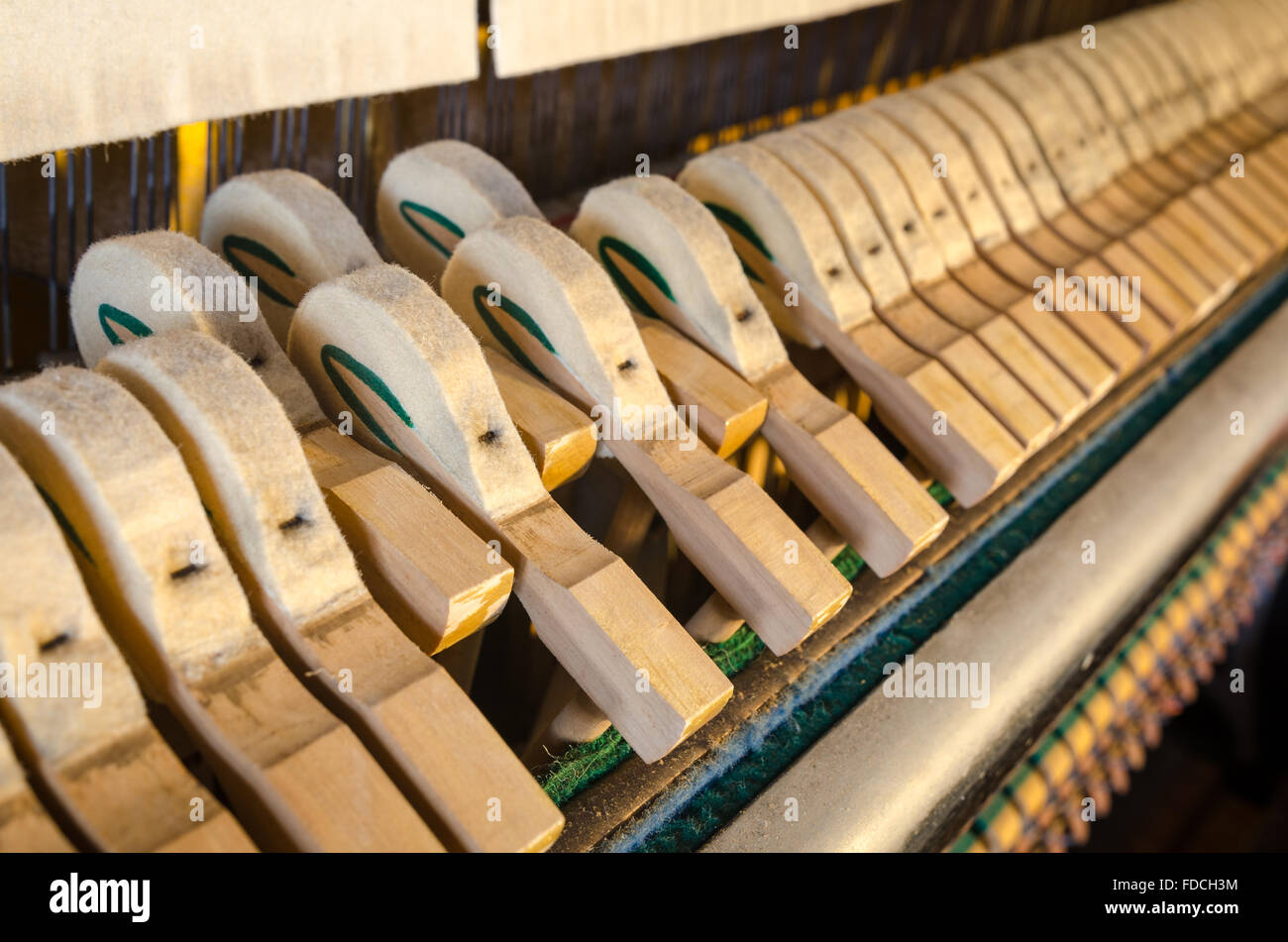 Upright piano hammers detail Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-upright-piano-hammers-detail-94319224.html
Upright piano hammers detail Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-upright-piano-hammers-detail-94319224.htmlRFFDCH3M–Upright piano hammers detail
 Inside of a piano. Close-up view of hammers and strings inside the piano. Musical instruments. Piano tuning Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inside-of-a-piano-close-up-view-of-hammers-and-strings-inside-the-piano-musical-instruments-piano-tuning-image236010884.html
Inside of a piano. Close-up view of hammers and strings inside the piano. Musical instruments. Piano tuning Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inside-of-a-piano-close-up-view-of-hammers-and-strings-inside-the-piano-musical-instruments-piano-tuning-image236010884.htmlRFRKY684–Inside of a piano. Close-up view of hammers and strings inside the piano. Musical instruments. Piano tuning
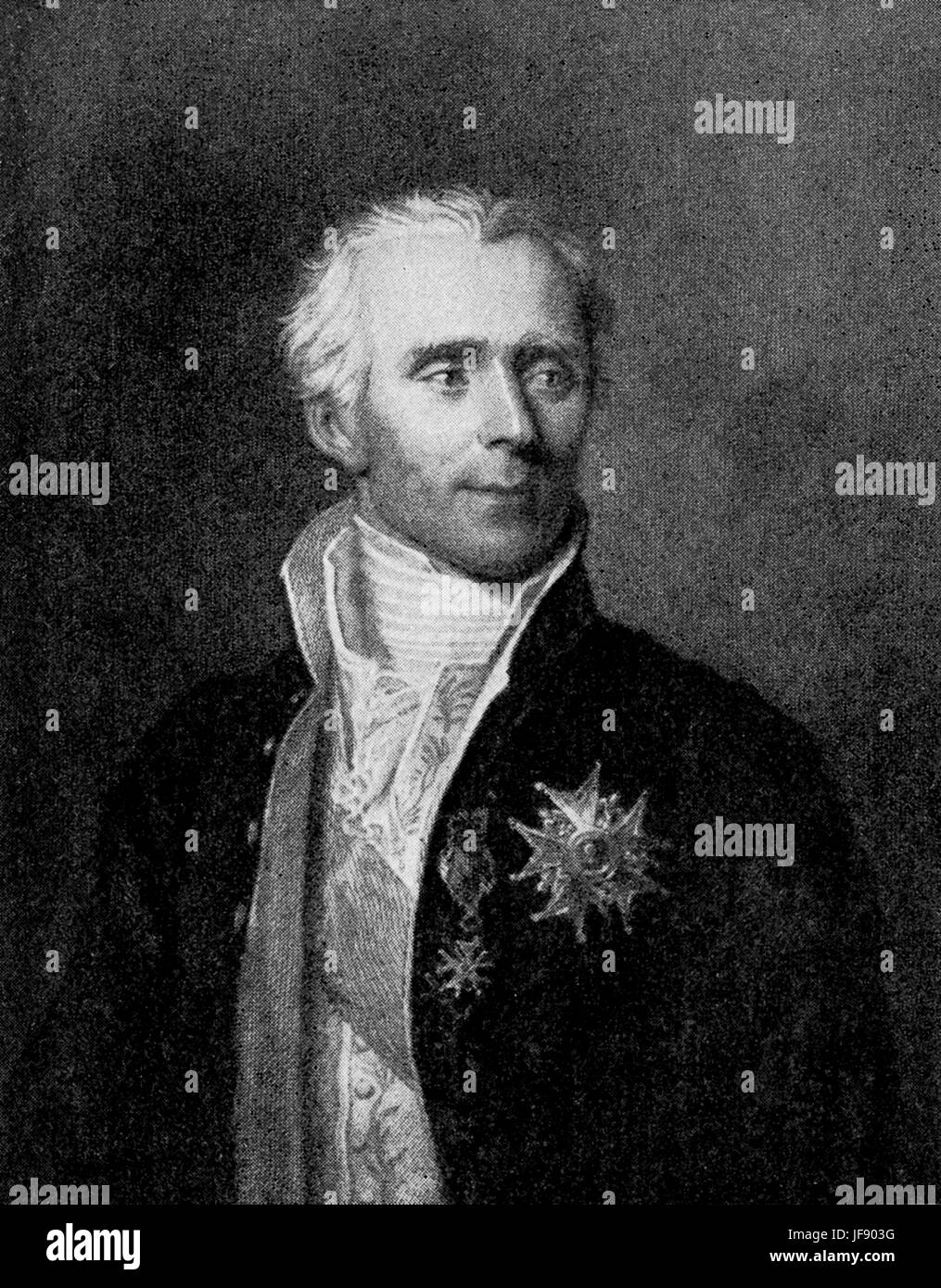 Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace. His work influenced development of mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy. Wrote five volume Mécanique Céleste (Celestial Mechanics) (1799–1825). one of the first scientists to postulate the existence of black holes and the notion of gravitational collapse 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-pierre-simon-marquis-de-laplace-his-work-influenced-development-of-147100452.html
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace. His work influenced development of mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy. Wrote five volume Mécanique Céleste (Celestial Mechanics) (1799–1825). one of the first scientists to postulate the existence of black holes and the notion of gravitational collapse 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-pierre-simon-marquis-de-laplace-his-work-influenced-development-of-147100452.htmlRMJF903G–Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace. His work influenced development of mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy. Wrote five volume Mécanique Céleste (Celestial Mechanics) (1799–1825). one of the first scientists to postulate the existence of black holes and the notion of gravitational collapse 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827
 Facade of the Mechanics' Institute in Darlington, County Durham, England. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/facade-of-the-mechanics-institute-in-darlington-county-durham-england-image470485213.html
Facade of the Mechanics' Institute in Darlington, County Durham, England. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/facade-of-the-mechanics-institute-in-darlington-county-durham-england-image470485213.htmlRM2J9CCK9–Facade of the Mechanics' Institute in Darlington, County Durham, England.
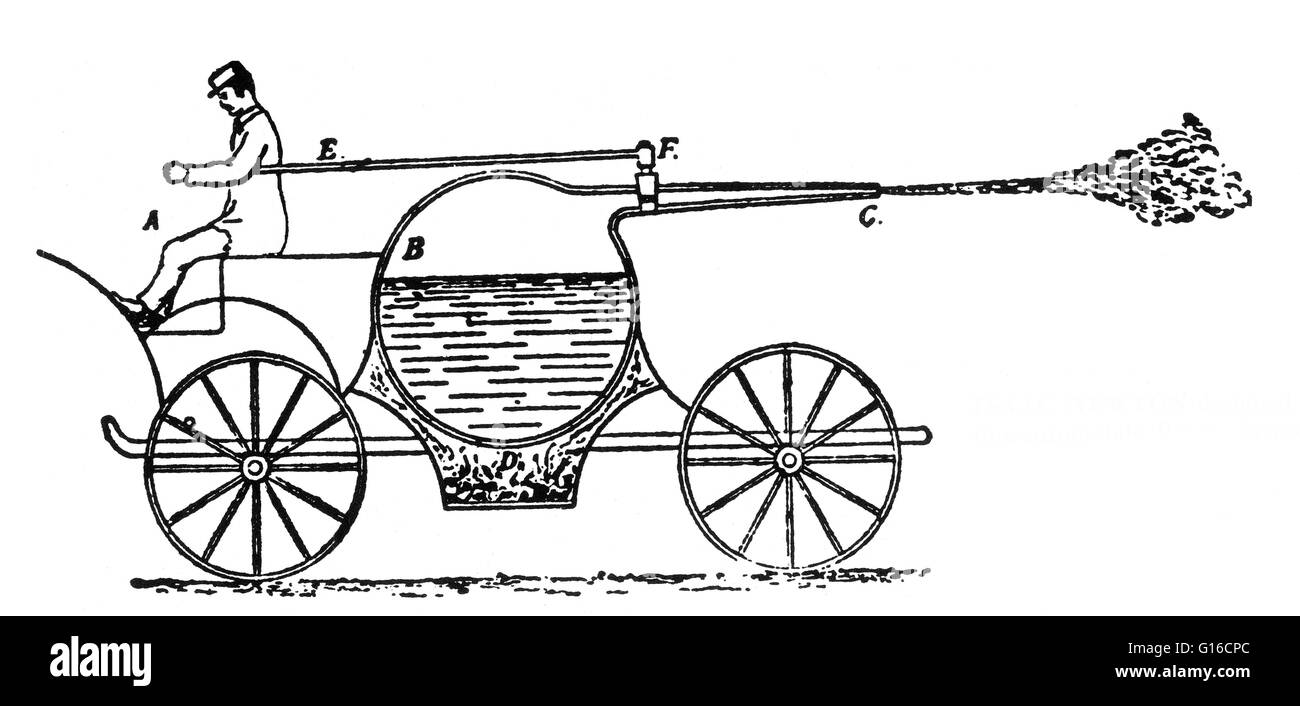 Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. H Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-steam-powered-vehicle-designed-by-gravesande-1720-willem-jacob-s-gravesande-104018612.html
Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. H Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-steam-powered-vehicle-designed-by-gravesande-1720-willem-jacob-s-gravesande-104018612.htmlRMG16CPC–Steam powered vehicle designed by Gravesande, 1720. Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (September 26, 1688 - February 28, 1742) was a Dutch lawyer and natural philosopher, remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics. H
 Isaac Newton (1642-1726/1727). English mathematician, astronomer and physicist. Chromolithography, 1876. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/isaac-newton-1642-17261727-english-mathematician-astronomer-and-physicist-chromolithography-1876-image337411042.html
Isaac Newton (1642-1726/1727). English mathematician, astronomer and physicist. Chromolithography, 1876. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/isaac-newton-1642-17261727-english-mathematician-astronomer-and-physicist-chromolithography-1876-image337411042.htmlRM2AGXB6A–Isaac Newton (1642-1726/1727). English mathematician, astronomer and physicist. Chromolithography, 1876.
 Science concept: newspaper headline Classical Mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-newspaper-headline-classical-mechanics-142097479.html
Science concept: newspaper headline Classical Mechanics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-science-concept-newspaper-headline-classical-mechanics-142097479.htmlRFJ752NY–Science concept: newspaper headline Classical Mechanics
 High angle closeup horizontal studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-closeup-horizontal-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-image503565504.html
High angle closeup horizontal studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-closeup-horizontal-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-image503565504.htmlRF2M77AX8–High angle closeup horizontal studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins
 The house in St Martin's Street, London, England (now demolished) where Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) once lived.which appears to have been typical of the street, consisted of three storeys and basement with a tilled roof. The site is now occupied by Westminster public Reference Library. The entrance doorway had projected hood supported on carved brackets.Sir Isaac Newton, occupied the house from 1711 until 1727, the year of his death. He was still active enough to make use of a small observatory which he had built at the top of the house. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-house-in-st-martins-street-london-england-now-demolished-where-sir-isaac-newton-1642-1727-once-livedwhich-appears-to-have-been-typical-of-the-street-consisted-of-three-storeys-and-basement-with-a-tilled-roof-the-site-is-now-occupied-by-westminster-public-reference-library-the-entrance-doorway-had-projected-hood-supported-on-carved-bracketssir-isaac-newton-occupied-the-house-from-1711-until-1727-the-year-of-his-death-he-was-still-active-enough-to-make-use-of-a-small-observatory-which-he-had-built-at-the-top-of-the-house-image356891336.html
The house in St Martin's Street, London, England (now demolished) where Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) once lived.which appears to have been typical of the street, consisted of three storeys and basement with a tilled roof. The site is now occupied by Westminster public Reference Library. The entrance doorway had projected hood supported on carved brackets.Sir Isaac Newton, occupied the house from 1711 until 1727, the year of his death. He was still active enough to make use of a small observatory which he had built at the top of the house. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-house-in-st-martins-street-london-england-now-demolished-where-sir-isaac-newton-1642-1727-once-livedwhich-appears-to-have-been-typical-of-the-street-consisted-of-three-storeys-and-basement-with-a-tilled-roof-the-site-is-now-occupied-by-westminster-public-reference-library-the-entrance-doorway-had-projected-hood-supported-on-carved-bracketssir-isaac-newton-occupied-the-house-from-1711-until-1727-the-year-of-his-death-he-was-still-active-enough-to-make-use-of-a-small-observatory-which-he-had-built-at-the-top-of-the-house-image356891336.htmlRM2BMHPF4–The house in St Martin's Street, London, England (now demolished) where Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) once lived.which appears to have been typical of the street, consisted of three storeys and basement with a tilled roof. The site is now occupied by Westminster public Reference Library. The entrance doorway had projected hood supported on carved brackets.Sir Isaac Newton, occupied the house from 1711 until 1727, the year of his death. He was still active enough to make use of a small observatory which he had built at the top of the house.
 Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344280069.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-mp-25-december-1642-20-march-1726-was-an-english-physicist-and-mathematician-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-his-book-philosophi-naturalis-principia-mathematica-mathematical-principles-of-natural-philosophy-first-published-in-1687-laid-the-foundations-for-classical-mechanics-newton-made-seminal-contributions-to-optics-and-he-shares-credit-with-gottfried-leibniz-for-the-development-of-calculus-image344280069.htmlRM2B038MN–Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ('Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus.
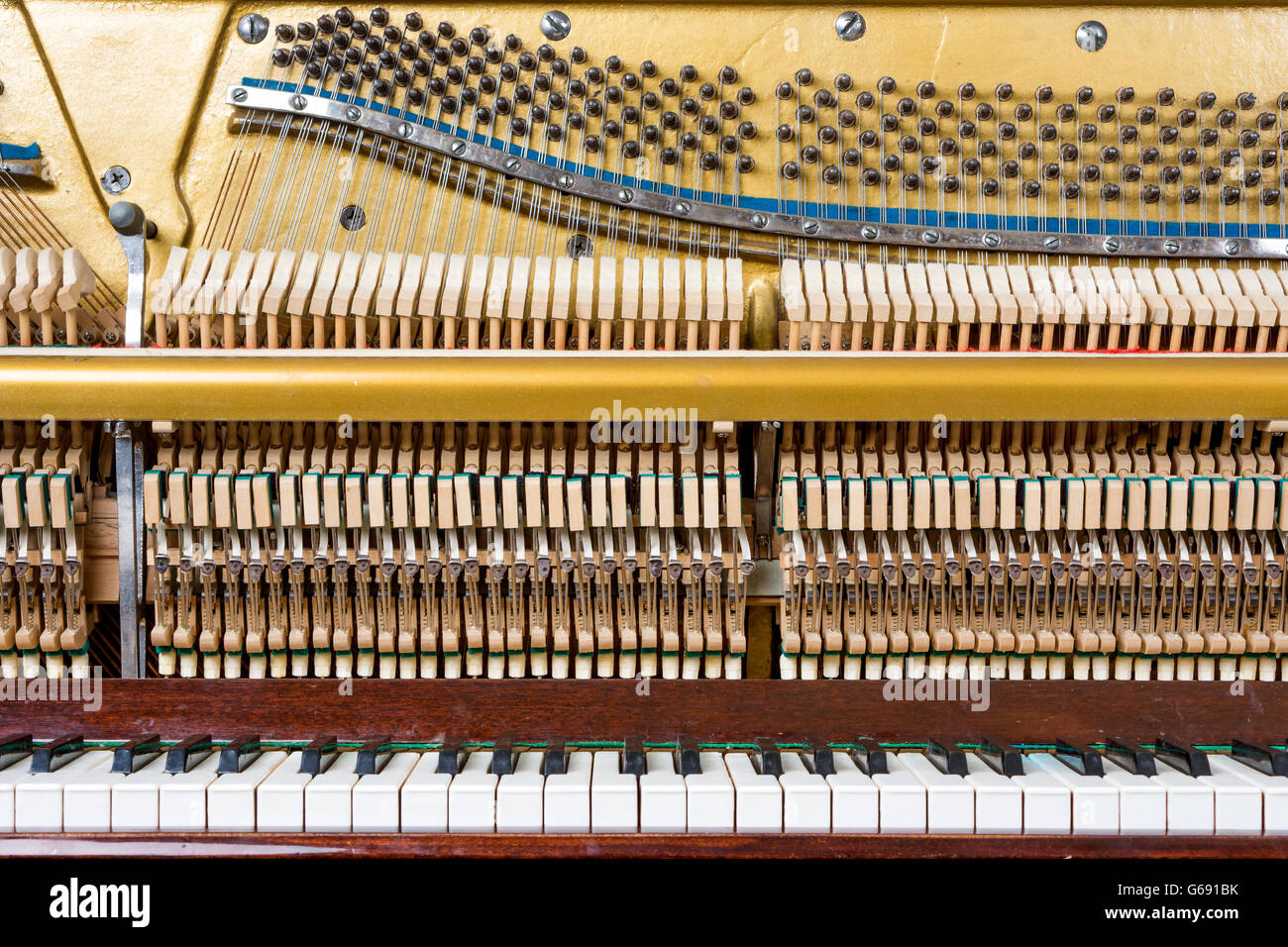 Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-keyboard-and-mechanics-details-of-an-upright-piano-107148823.html
Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-keyboard-and-mechanics-details-of-an-upright-piano-107148823.htmlRFG691BK–Keyboard and mechanics details of an upright piano
 Pumps, siphons and liquids Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pumps-siphons-and-liquids-mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significa-image382511865.html
Pumps, siphons and liquids Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pumps-siphons-and-liquids-mechanics-is-the-area-of-physics-concerned-with-the-motions-of-macroscopic-objects-forces-applied-to-objects-result-in-displacements-or-changes-of-an-objects-position-relative-to-its-environment-this-branch-of-physics-has-its-origins-in-ancient-greece-with-the-writings-of-aristotle-and-archimedes-during-the-early-modern-period-scientists-such-as-galileo-kepler-and-newton-laid-the-foundation-for-what-is-now-known-as-classical-mechanics-it-is-a-branch-of-classical-physics-that-deals-with-particles-that-are-either-at-rest-or-are-moving-with-velocities-significa-image382511865.htmlRF2D68WP1–Pumps, siphons and liquids Mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. This branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece with the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes. During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. It is a branch of classical physics that deals with particles that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significa
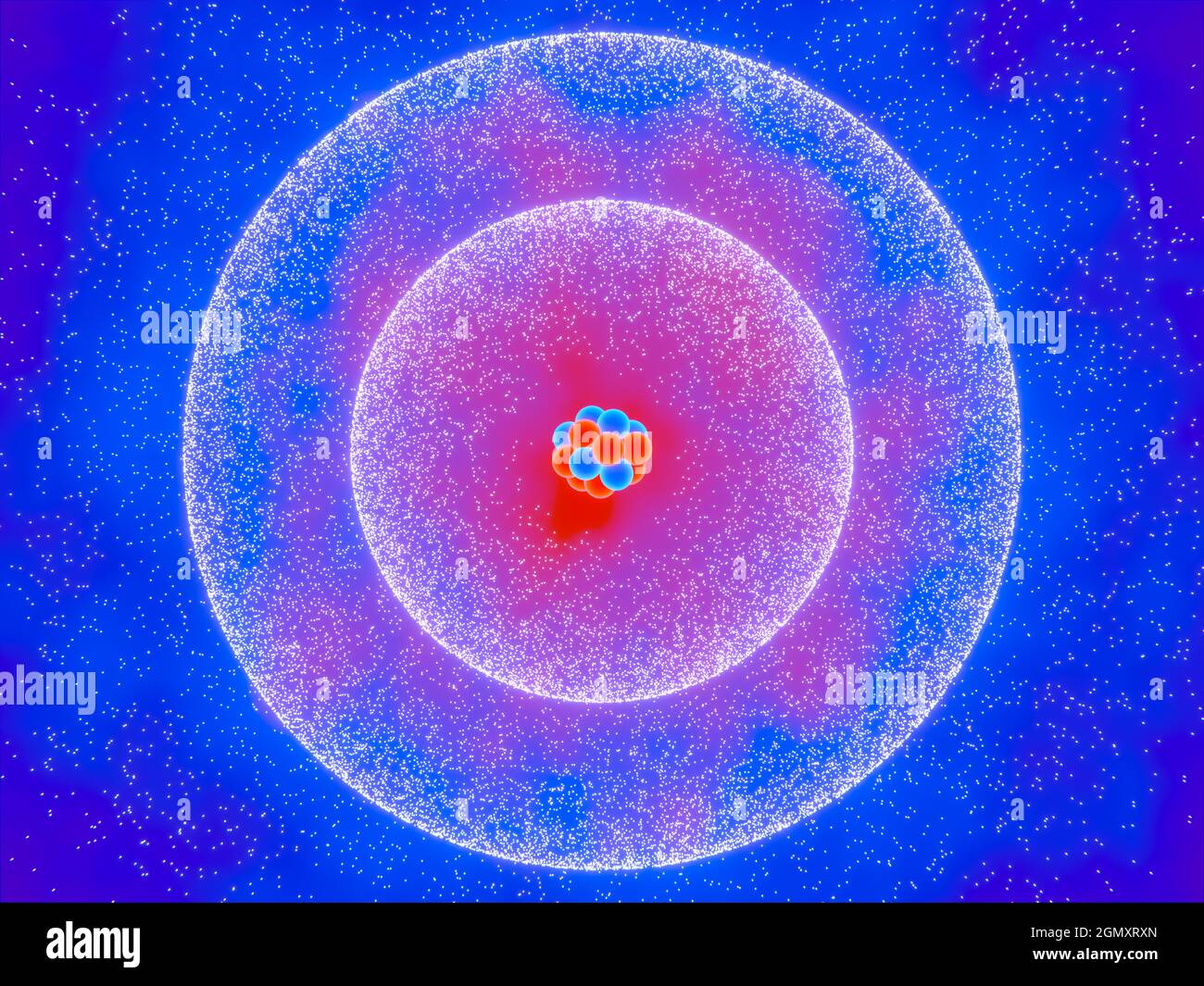 Atom with Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Conceptual Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atom-with-protons-neutrons-and-electrons-conceptual-illustration-image443141853.html
Atom with Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Conceptual Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atom-with-protons-neutrons-and-electrons-conceptual-illustration-image443141853.htmlRF2GMXRXN–Atom with Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Conceptual Illustration.
 Inside a grand piano with mirroring of frames and strings in the open lid of the musical instrument, concept for music, art and entertainment, selecte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inside-a-grand-piano-with-mirroring-of-frames-and-strings-in-the-open-lid-of-the-musical-instrument-concept-for-music-art-and-entertainment-selecte-image443397986.html
Inside a grand piano with mirroring of frames and strings in the open lid of the musical instrument, concept for music, art and entertainment, selecte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inside-a-grand-piano-with-mirroring-of-frames-and-strings-in-the-open-lid-of-the-musical-instrument-concept-for-music-art-and-entertainment-selecte-image443397986.htmlRF2GNAEJA–Inside a grand piano with mirroring of frames and strings in the open lid of the musical instrument, concept for music, art and entertainment, selecte
 Fall River Technical High - Millwrighting course Mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fall-river-technical-high-millwrighting-course-mechanics-image328926624.html
Fall River Technical High - Millwrighting course Mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fall-river-technical-high-millwrighting-course-mechanics-image328926624.htmlRM2A33W7C–Fall River Technical High - Millwrighting course Mechanics.
 Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/munich-germany-march-10-2016-collection-of-classical-cars-on-display-in-bmw-museum-image477500502.html
Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/munich-germany-march-10-2016-collection-of-classical-cars-on-display-in-bmw-museum-image477500502.htmlRM2JMT0NA–Munich, Germany - March 10, 2016: collection of classical cars on display in BMW Museum
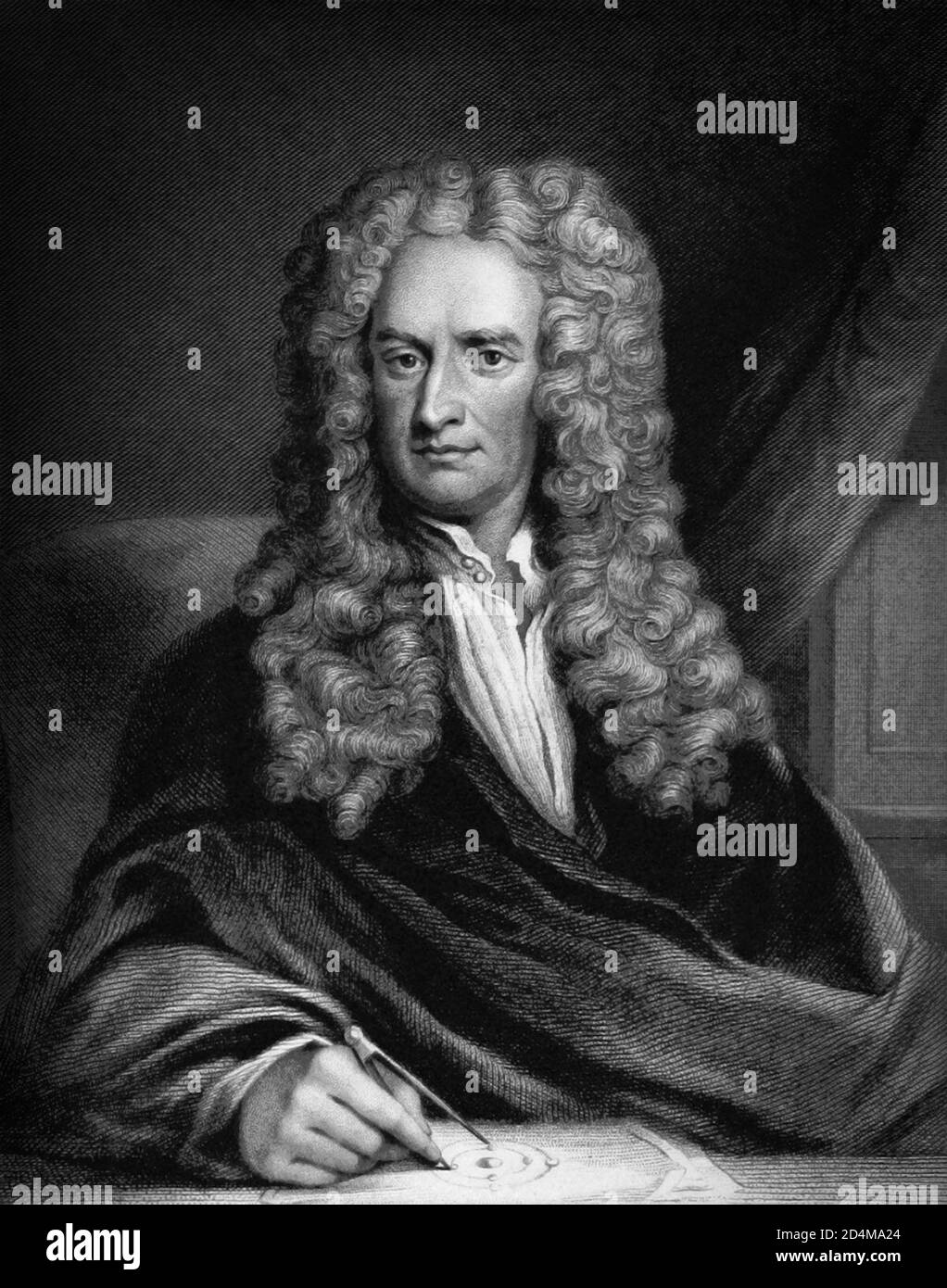 Sir Isaac Newton PRS (1642/43-1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-164243-172627-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-image381533660.html
Sir Isaac Newton PRS (1642/43-1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sir-isaac-newton-prs-164243-172627-was-an-english-mathematician-physicist-astronomer-theologian-and-author-described-in-his-own-day-as-a-natural-philosopher-who-is-widely-recognised-as-one-of-the-most-influential-scientists-of-all-time-and-as-a-key-figure-in-the-scientific-revolution-image381533660.htmlRM2D4MA24–Sir Isaac Newton PRS (1642/43-1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a 'natural philosopher') who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution.
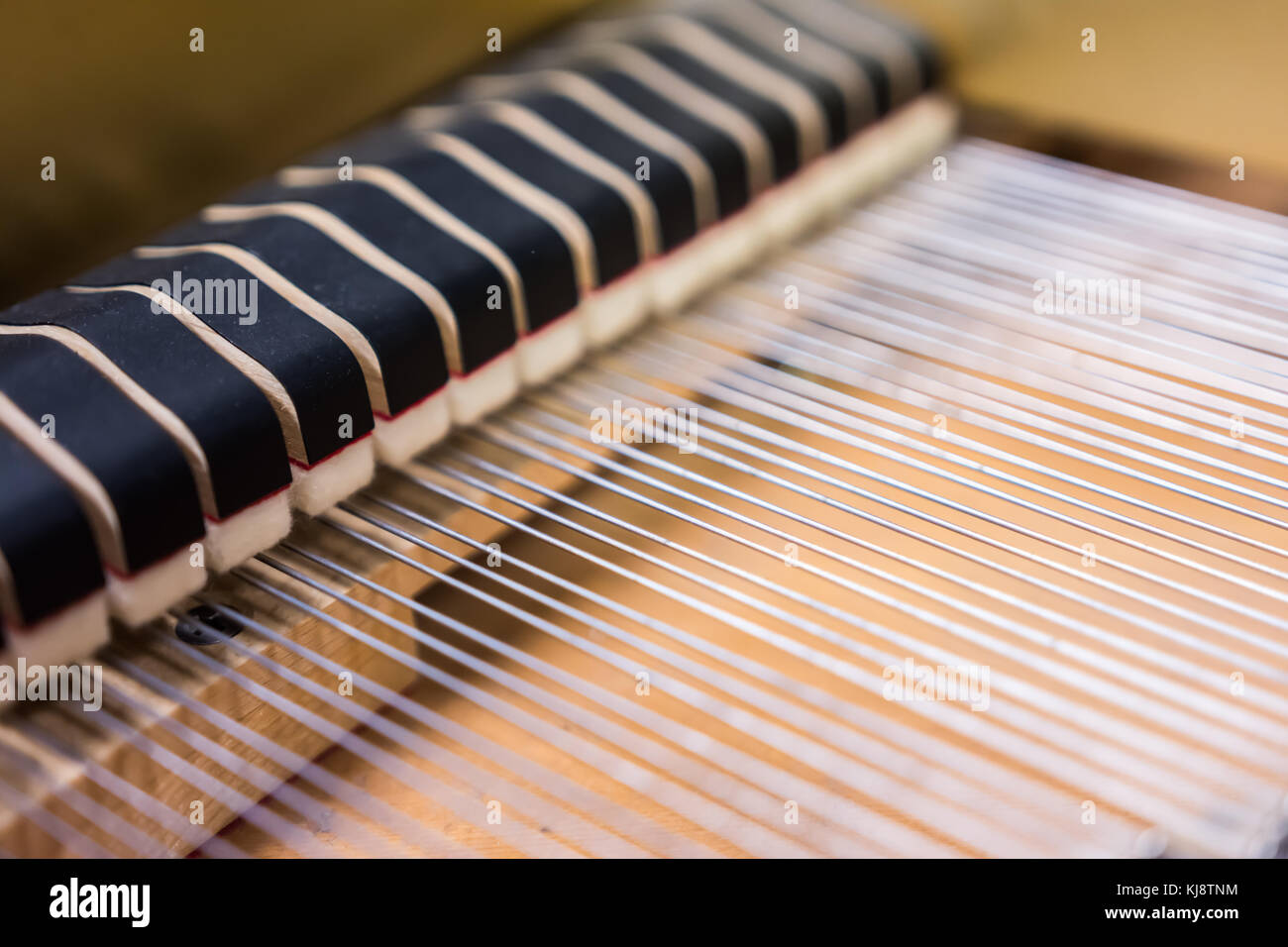 Black string dampeners inside grand piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-black-string-dampeners-inside-grand-piano-166152160.html
Black string dampeners inside grand piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-black-string-dampeners-inside-grand-piano-166152160.htmlRFKJ8TNM–Black string dampeners inside grand piano
 Close-up shot of Keys of an old piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-shot-of-keys-of-an-old-piano-image466149123.html
Close-up shot of Keys of an old piano Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-shot-of-keys-of-an-old-piano-image466149123.htmlRF2J2AWXY–Close-up shot of Keys of an old piano
 A ballista also called scorpio. Roman re enactment at Zülpich - 26th of August 2018 - Zülpich, North Rhine Westphalia, NRW, Germany, Europe Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-ballista-also-called-scorpio-roman-re-enactment-at-zlpich-26th-of-august-2018-zlpich-north-rhine-westphalia-nrw-germany-europe-image217289736.html
A ballista also called scorpio. Roman re enactment at Zülpich - 26th of August 2018 - Zülpich, North Rhine Westphalia, NRW, Germany, Europe Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-ballista-also-called-scorpio-roman-re-enactment-at-zlpich-26th-of-august-2018-zlpich-north-rhine-westphalia-nrw-germany-europe-image217289736.htmlRFPHEB7M–A ballista also called scorpio. Roman re enactment at Zülpich - 26th of August 2018 - Zülpich, North Rhine Westphalia, NRW, Germany, Europe
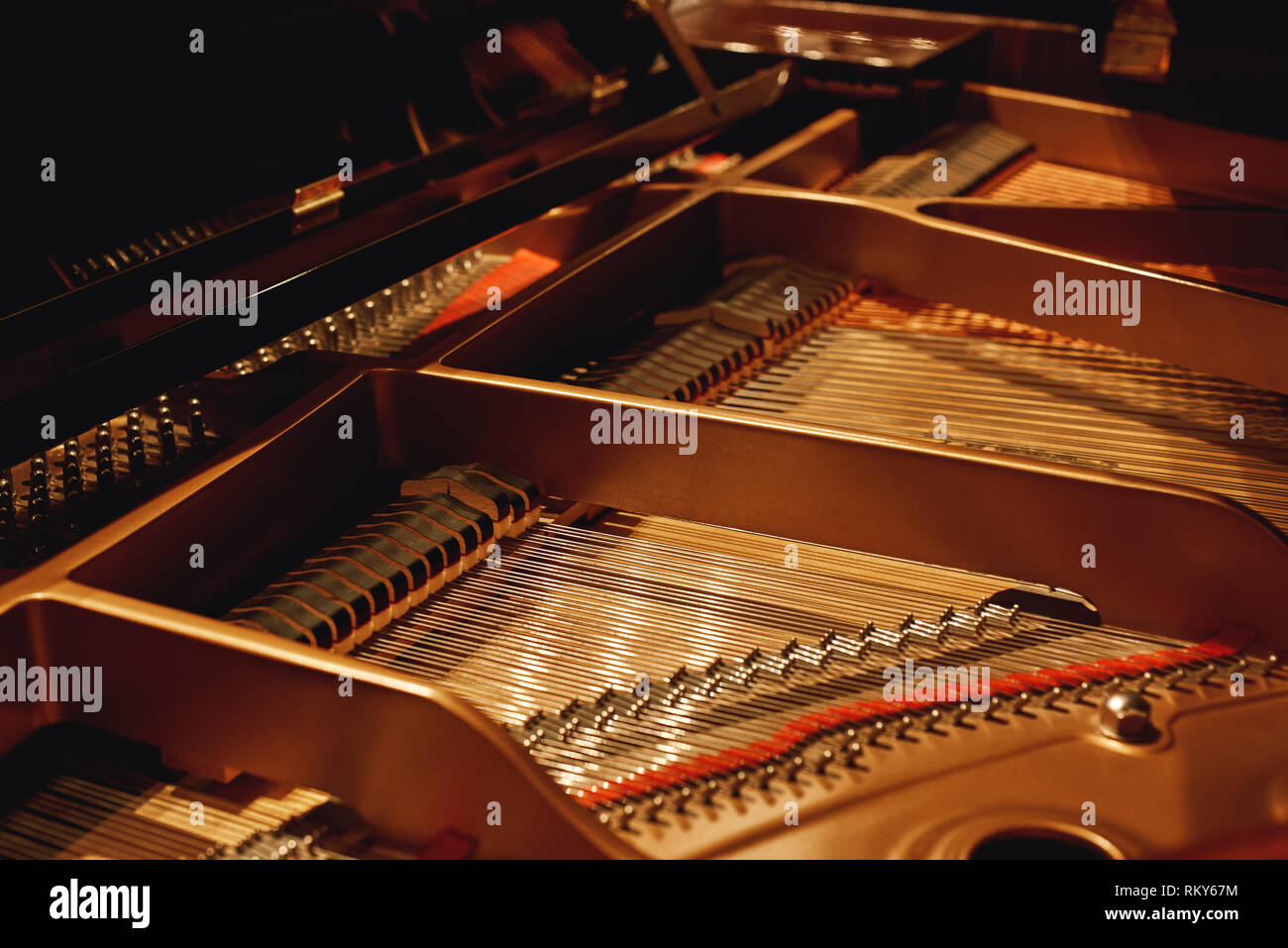 Tuning Your Piano. Close-up view of hammers, strings and pins inside the piano. Musical instruments. Piano mechanism Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tuning-your-piano-close-up-view-of-hammers-strings-and-pins-inside-the-piano-musical-instruments-piano-mechanism-image236010872.html
Tuning Your Piano. Close-up view of hammers, strings and pins inside the piano. Musical instruments. Piano mechanism Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tuning-your-piano-close-up-view-of-hammers-strings-and-pins-inside-the-piano-musical-instruments-piano-mechanism-image236010872.htmlRFRKY67M–Tuning Your Piano. Close-up view of hammers, strings and pins inside the piano. Musical instruments. Piano mechanism
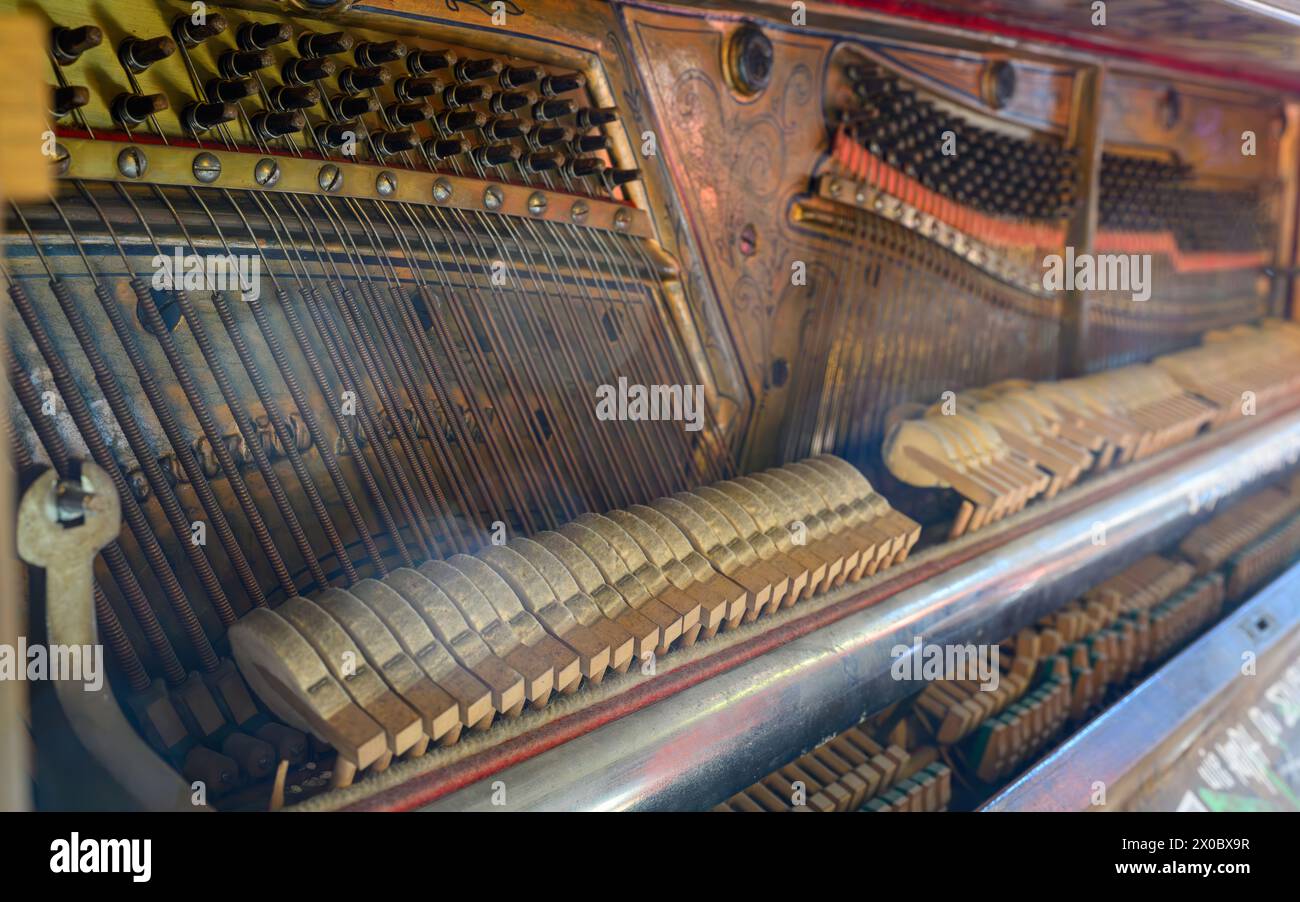 Interior of an old broken piano with defective hammers Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/interior-of-an-old-broken-piano-with-defective-hammers-image602625011.html
Interior of an old broken piano with defective hammers Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/interior-of-an-old-broken-piano-with-defective-hammers-image602625011.htmlRF2X0BX9R–Interior of an old broken piano with defective hammers
 Interior under the lid of grand piano: pins and moderators Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/interior-under-the-lid-of-grand-piano-pins-and-moderators-image380636927.html
Interior under the lid of grand piano: pins and moderators Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/interior-under-the-lid-of-grand-piano-pins-and-moderators-image380636927.htmlRF2D37E7Y–Interior under the lid of grand piano: pins and moderators
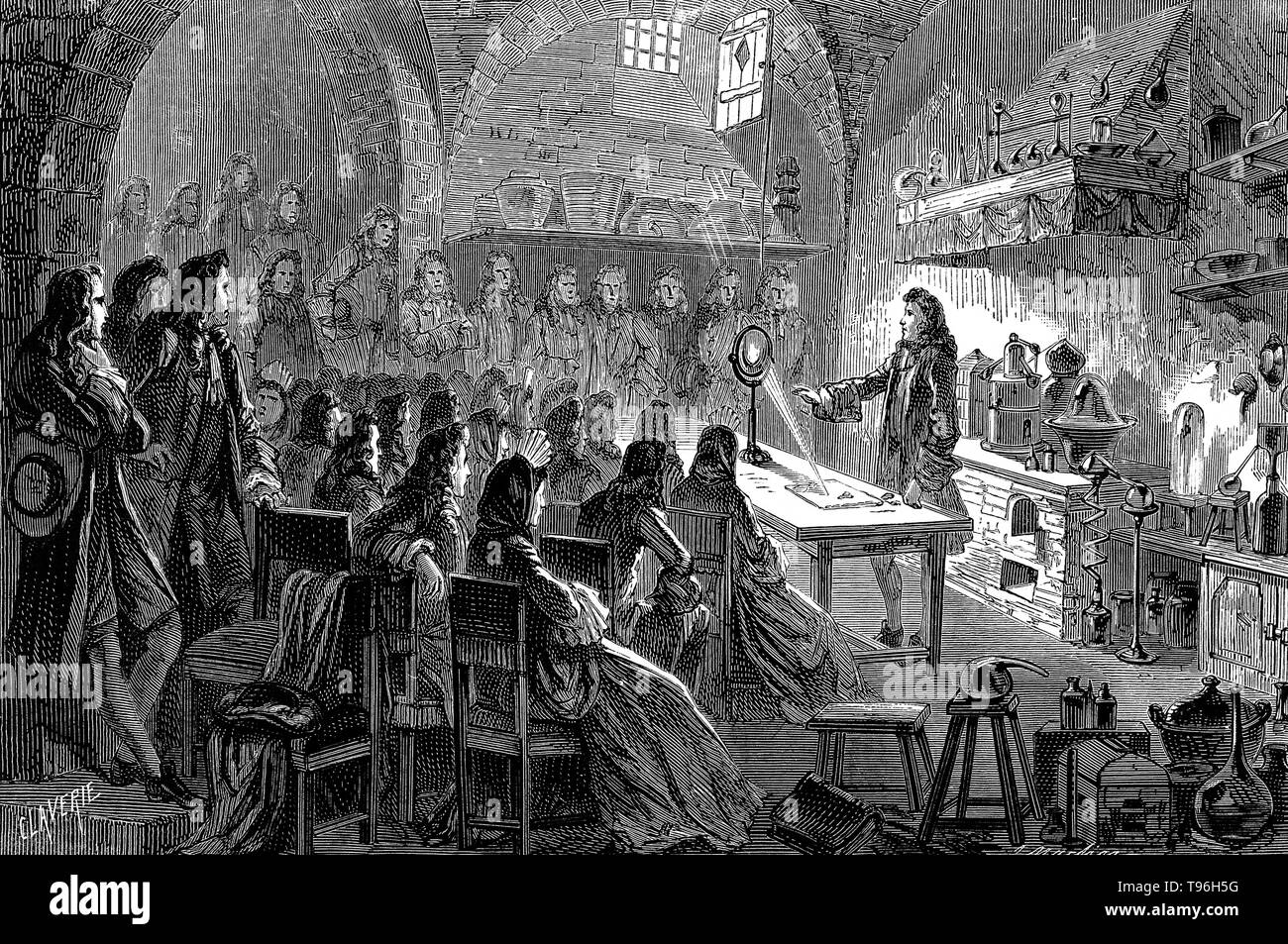 Newton showing an optical experiment to an audience in his laboratory. Isaac Newton (December 25, 1642 - March 20, 1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian. His monograph ''Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica'', published in 1687, lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newton-showing-an-optical-experiment-to-an-audience-in-his-laboratory-isaac-newton-december-25-1642-march-20-1727-was-an-english-physicist-mathematician-astronomer-natural-philosopher-alchemist-and-theologian-his-monograph-philosophiae-naturalis-principia-mathematica-published-in-1687-lays-the-foundations-for-most-of-classical-mechanics-image246622252.html
Newton showing an optical experiment to an audience in his laboratory. Isaac Newton (December 25, 1642 - March 20, 1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian. His monograph ''Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica'', published in 1687, lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/newton-showing-an-optical-experiment-to-an-audience-in-his-laboratory-isaac-newton-december-25-1642-march-20-1727-was-an-english-physicist-mathematician-astronomer-natural-philosopher-alchemist-and-theologian-his-monograph-philosophiae-naturalis-principia-mathematica-published-in-1687-lays-the-foundations-for-most-of-classical-mechanics-image246622252.htmlRMT96H5G–Newton showing an optical experiment to an audience in his laboratory. Isaac Newton (December 25, 1642 - March 20, 1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian. His monograph ''Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica'', published in 1687, lays the foundations for most of classical mechanics.
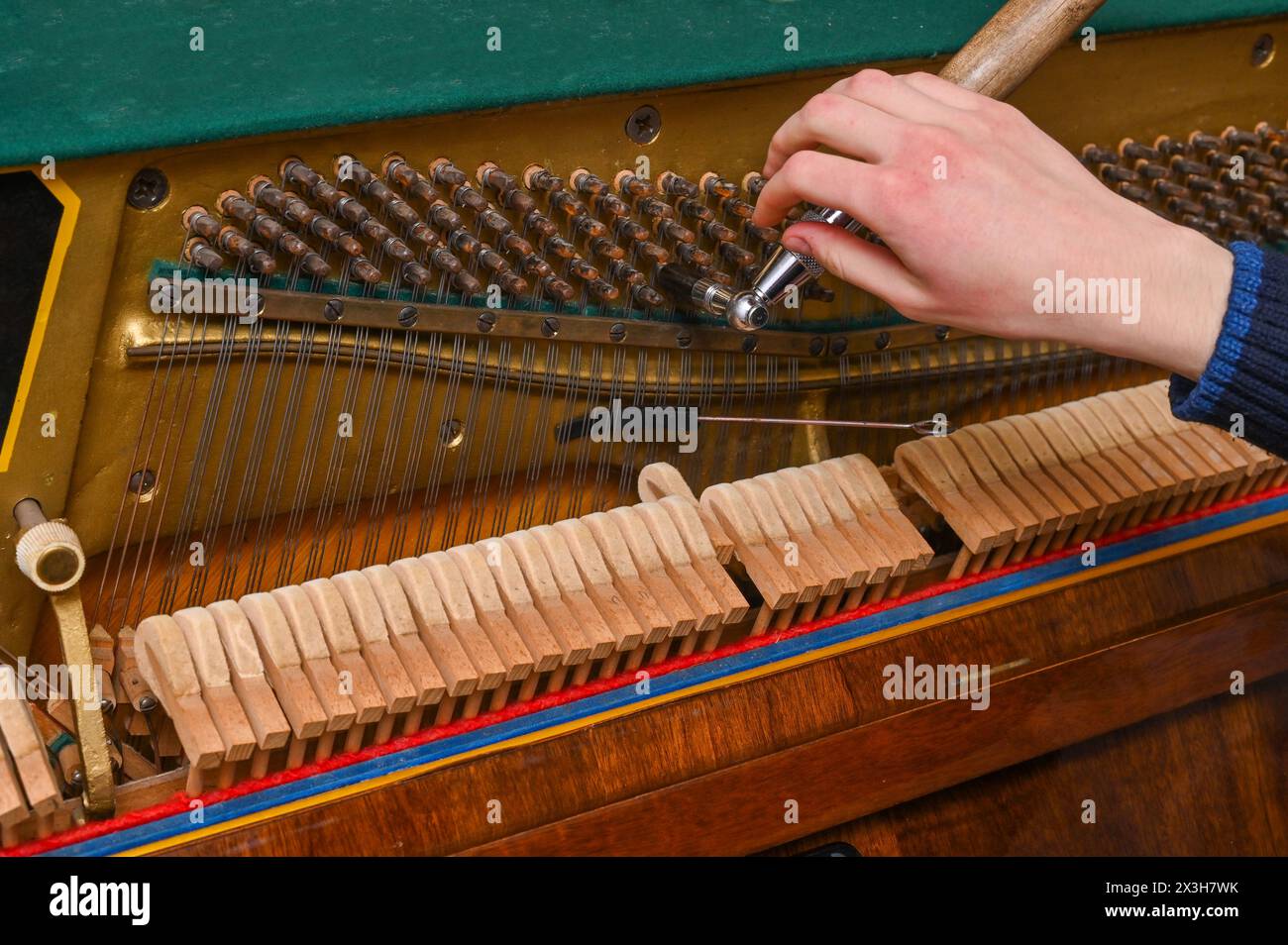 The tuner has a piano tuning instrument in his hand. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-tuner-has-a-piano-tuning-instrument-in-his-hand-image604586239.html
The tuner has a piano tuning instrument in his hand. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-tuner-has-a-piano-tuning-instrument-in-his-hand-image604586239.htmlRF2X3H7WK–The tuner has a piano tuning instrument in his hand.
 Science concept: Classical Mechanics on chalkboard background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-chalkboard-background-image155024045.html
Science concept: Classical Mechanics on chalkboard background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-concept-classical-mechanics-on-chalkboard-background-image155024045.htmlRFK05XN1–Science concept: Classical Mechanics on chalkboard background
 High angle studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins. Dusty and scratched Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-dusty-and-scratched-image503566239.html
High angle studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins. Dusty and scratched Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/high-angle-studio-shot-of-vintage-old-wooden-zither-isolated-on-white-background-detail-of-zither-mechanics-and-tuning-pins-dusty-and-scratched-image503566239.htmlRF2M77BTF–High angle studio shot of vintage, old wooden zither isolated on white background. Detail of zither mechanics and tuning pins. Dusty and scratched
 Free body physics vector. weights with rope and pulley experiment. physics string tension force Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/free-body-physics-vector-weights-with-rope-and-pulley-experiment-physics-string-tension-force-image618773670.html
Free body physics vector. weights with rope and pulley experiment. physics string tension force Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/free-body-physics-vector-weights-with-rope-and-pulley-experiment-physics-string-tension-force-image618773670.htmlRF2XXKG3J–Free body physics vector. weights with rope and pulley experiment. physics string tension force