Quick filters:
Cocci gram negative Stock Photos and Images
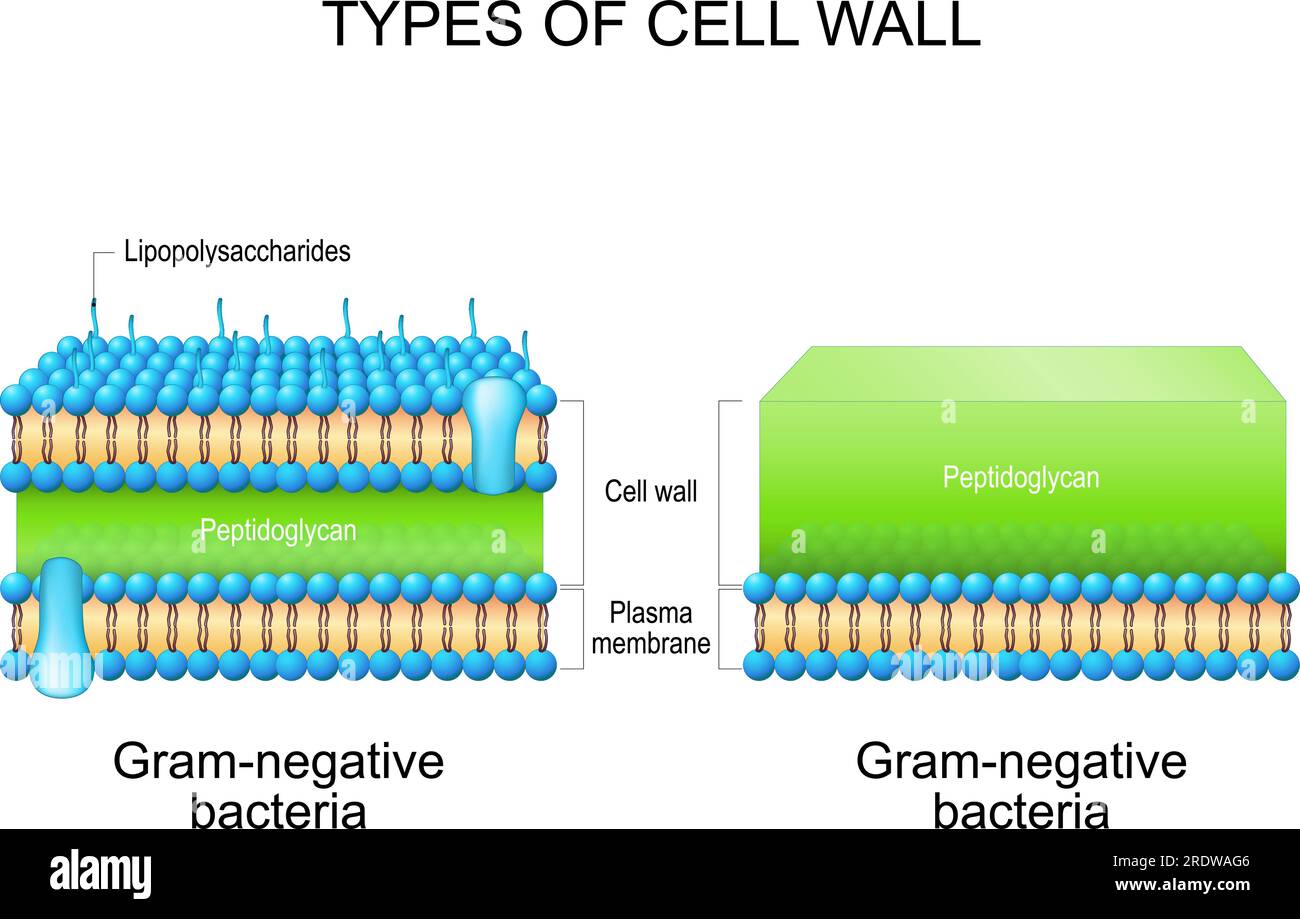 Types of bacterial cell wall. Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. comparison, structure, and composition. Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/types-of-bacterial-cell-wall-gram-negative-bacteria-and-gram-negative-bacteria-comparison-structure-and-composition-vector-illustration-image559279398.html
Types of bacterial cell wall. Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. comparison, structure, and composition. Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/types-of-bacterial-cell-wall-gram-negative-bacteria-and-gram-negative-bacteria-comparison-structure-and-composition-vector-illustration-image559279398.htmlRF2RDWAG6–Types of bacterial cell wall. Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. comparison, structure, and composition. Vector illustration
 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279049.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279049.htmlRM2AJ9XAH–Brucella
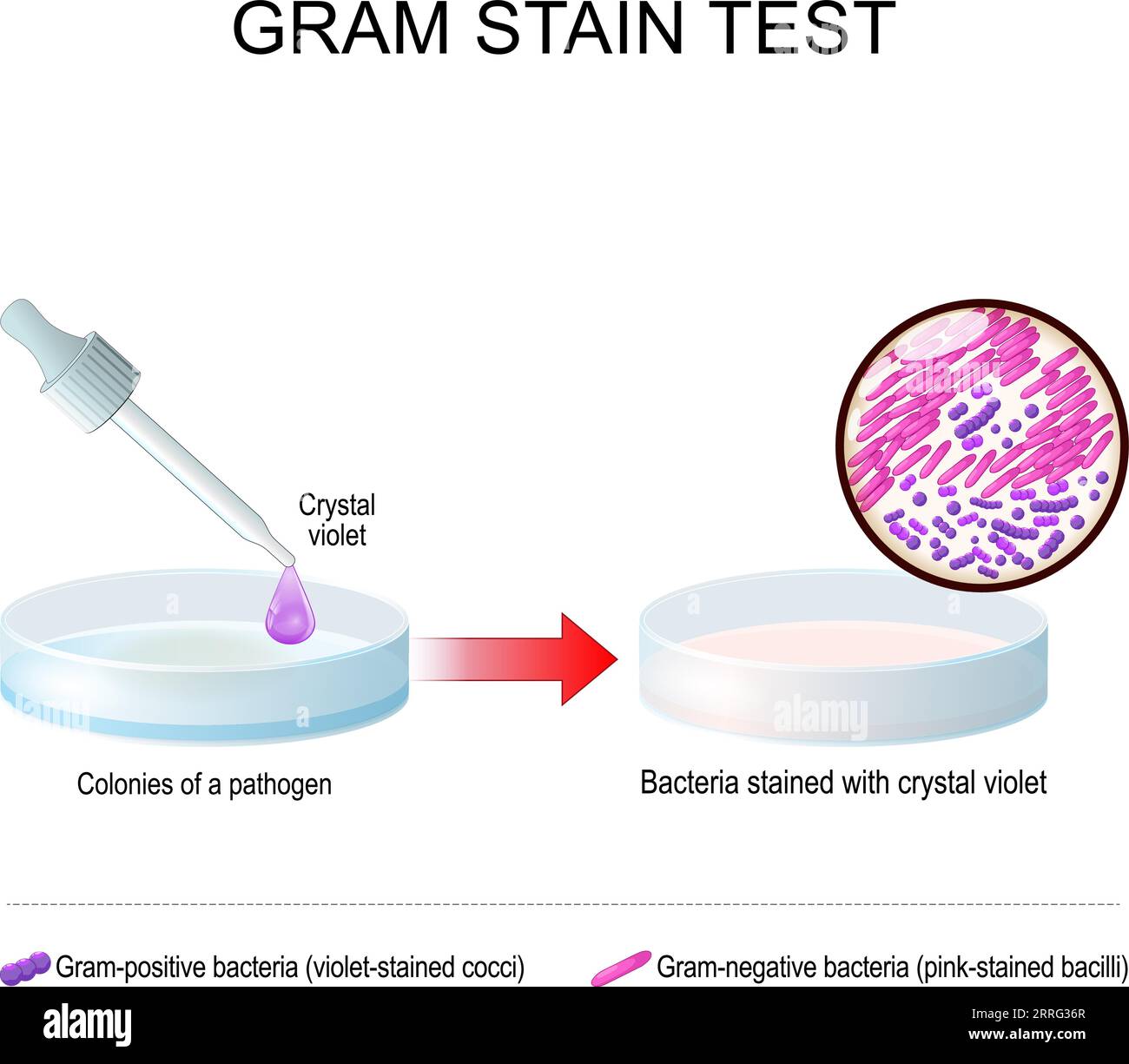 Gram stain test. A glass Petri dish with pathogen bacterial culture before and after use Crystal violet. Bacteria stained with gentian violet. Gram-po Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gram-stain-test-a-glass-petri-dish-with-pathogen-bacterial-culture-before-and-after-use-crystal-violet-bacteria-stained-with-gentian-violet-gram-po-image565222639.html
Gram stain test. A glass Petri dish with pathogen bacterial culture before and after use Crystal violet. Bacteria stained with gentian violet. Gram-po Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gram-stain-test-a-glass-petri-dish-with-pathogen-bacterial-culture-before-and-after-use-crystal-violet-bacteria-stained-with-gentian-violet-gram-po-image565222639.htmlRF2RRG36R–Gram stain test. A glass Petri dish with pathogen bacterial culture before and after use Crystal violet. Bacteria stained with gentian violet. Gram-po
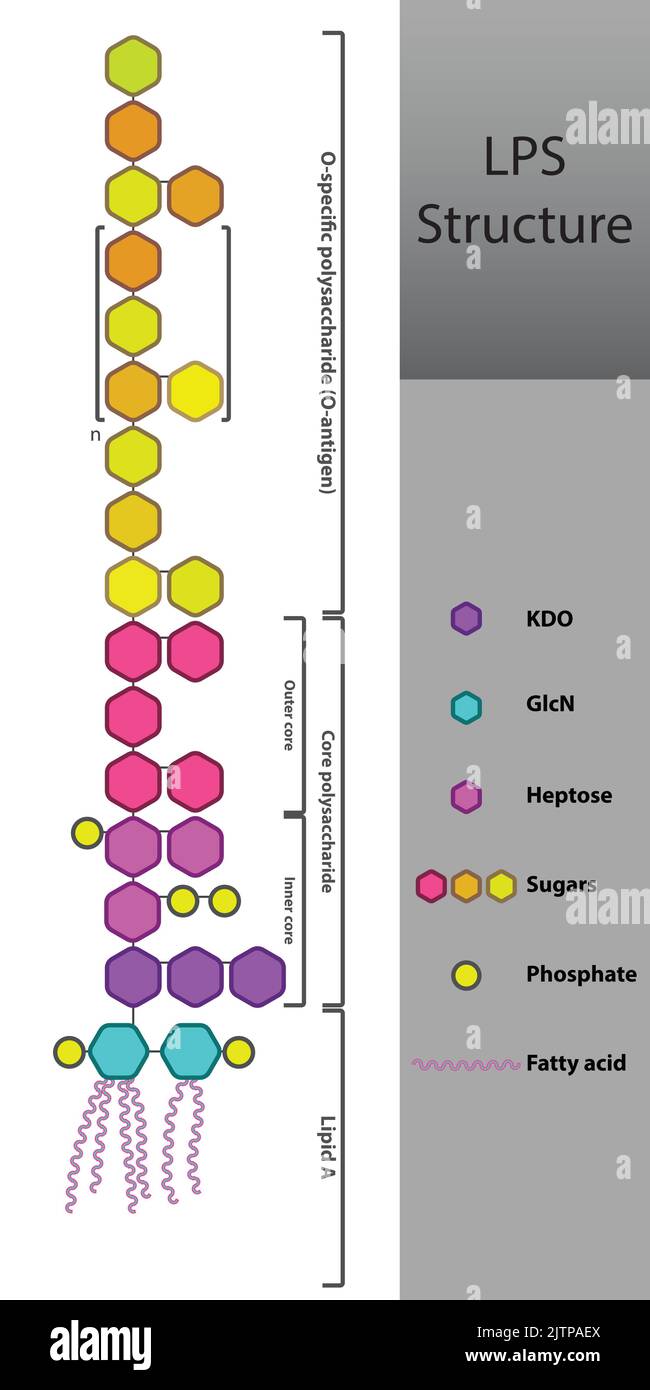 Diagram of LPS strcuture - schematic illustration of Lipopolysaccharide molecule of gram negative bacteria cell membrane. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-lps-strcuture-schematic-illustration-of-lipopolysaccharide-molecule-of-gram-negative-bacteria-cell-membrane-image479922882.html
Diagram of LPS strcuture - schematic illustration of Lipopolysaccharide molecule of gram negative bacteria cell membrane. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-lps-strcuture-schematic-illustration-of-lipopolysaccharide-molecule-of-gram-negative-bacteria-cell-membrane-image479922882.htmlRF2JTPAEX–Diagram of LPS strcuture - schematic illustration of Lipopolysaccharide molecule of gram negative bacteria cell membrane.
 Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-bacteria-moraxella-catarrhalis-computer-illustration-moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-they-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-including-pneumonia-image223398652.html
Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-bacteria-moraxella-catarrhalis-computer-illustration-moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-they-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-including-pneumonia-image223398652.htmlRFPYCK78–Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia.
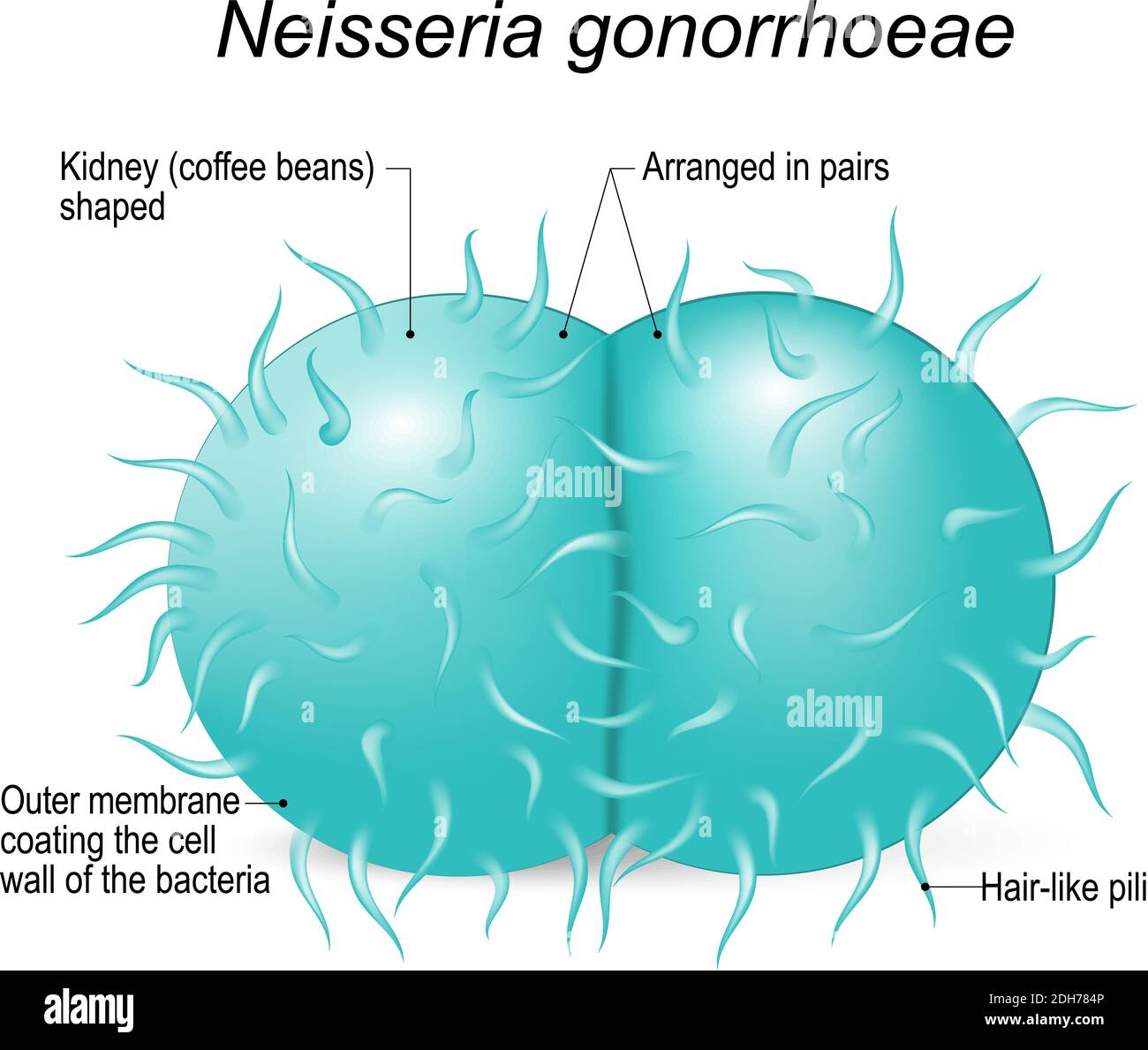 Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) is a gram-negative diplococci bacteria causes the sexually transmitted genitourinary infection - Gonorrhea Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-gonorrhoeae-gonococcus-is-a-gram-negative-diplococci-bacteria-causes-the-sexually-transmitted-genitourinary-infection-gonorrhea-image389237318.html
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) is a gram-negative diplococci bacteria causes the sexually transmitted genitourinary infection - Gonorrhea Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-gonorrhoeae-gonococcus-is-a-gram-negative-diplococci-bacteria-causes-the-sexually-transmitted-genitourinary-infection-gonorrhea-image389237318.htmlRF2DH784P–Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) is a gram-negative diplococci bacteria causes the sexually transmitted genitourinary infection - Gonorrhea
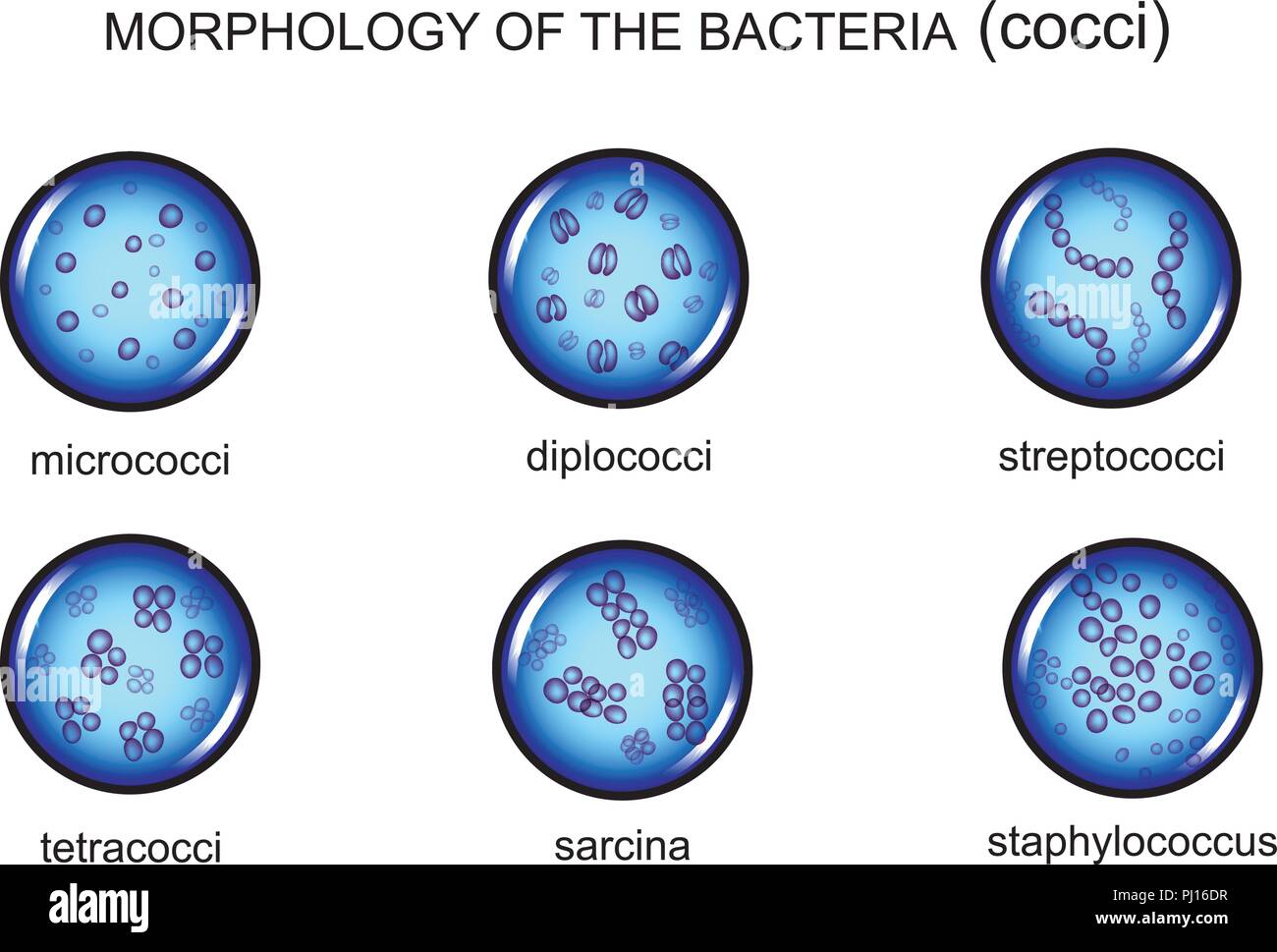 vector illustration of microorganism morphology. cocci, microbiology Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/vector-illustration-of-microorganism-morphology-cocci-microbiology-image217615267.html
vector illustration of microorganism morphology. cocci, microbiology Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/vector-illustration-of-microorganism-morphology-cocci-microbiology-image217615267.htmlRFPJ16DR–vector illustration of microorganism morphology. cocci, microbiology
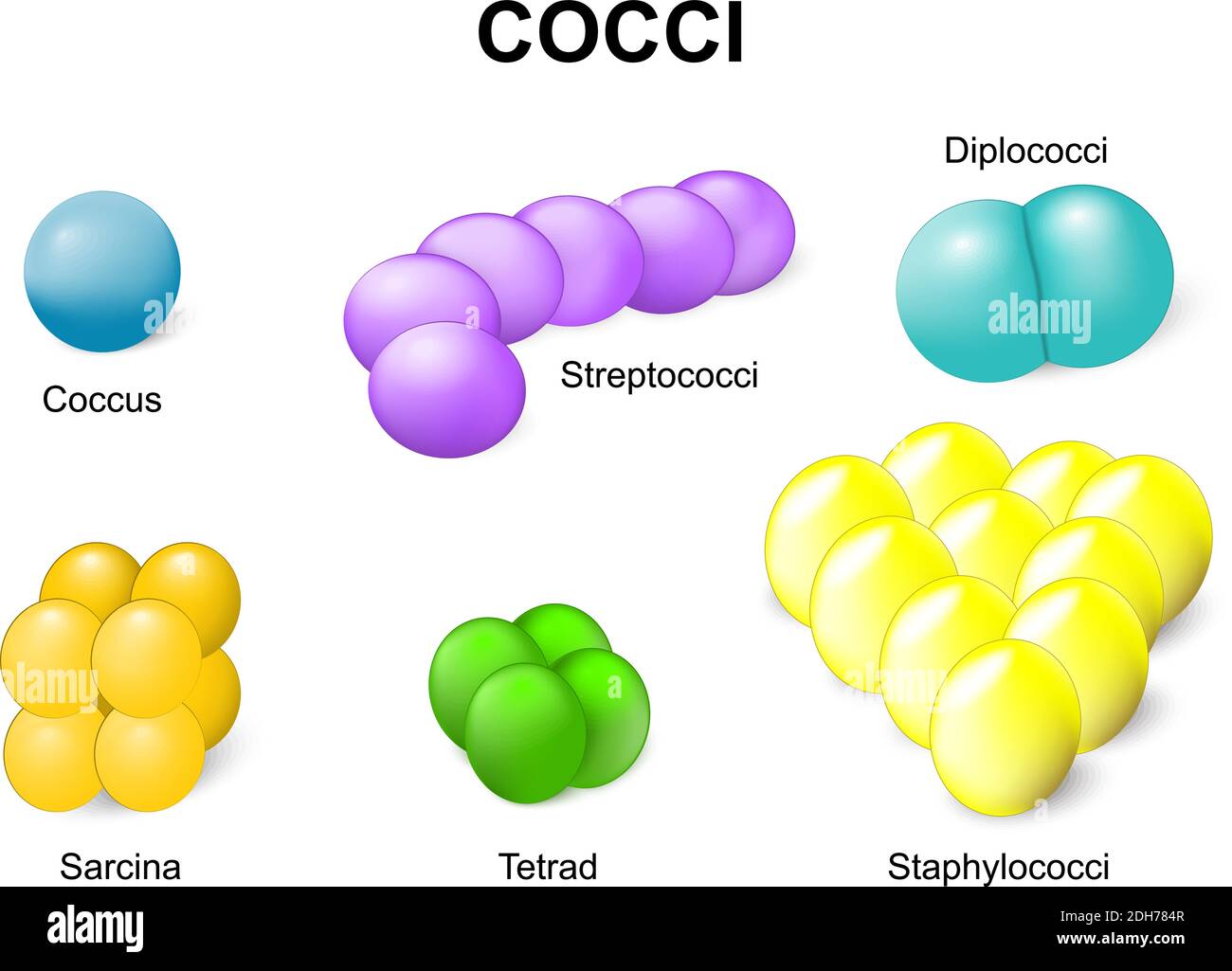 Coccus or cocci. Common bacteria infecting human. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/coccus-or-cocci-common-bacteria-infecting-human-image389237319.html
Coccus or cocci. Common bacteria infecting human. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/coccus-or-cocci-common-bacteria-infecting-human-image389237319.htmlRF2DH784R–Coccus or cocci. Common bacteria infecting human.
 3D image of Spiramycin skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of macrolide antibiotic isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-spiramycin-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-macrolide-antibiotic-isolated-on-white-background-image500171845.html
3D image of Spiramycin skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of macrolide antibiotic isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-spiramycin-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-macrolide-antibiotic-isolated-on-white-background-image500171845.htmlRF2M1MP85–3D image of Spiramycin skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of macrolide antibiotic isolated on white background
 A typical representation of various types of Zoogloea, a genus of gram-negative and rod-shaped bacteria from the family of Zoogloeaceae, vintage line Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-typical-representation-of-various-types-of-zoogloea-a-genus-of-gram-negative-and-rod-shaped-bacteria-from-the-family-of-zoogloeaceae-vintage-line-image367213091.html
A typical representation of various types of Zoogloea, a genus of gram-negative and rod-shaped bacteria from the family of Zoogloeaceae, vintage line Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-typical-representation-of-various-types-of-zoogloea-a-genus-of-gram-negative-and-rod-shaped-bacteria-from-the-family-of-zoogloeaceae-vintage-line-image367213091.htmlRF2C9C017–A typical representation of various types of Zoogloea, a genus of gram-negative and rod-shaped bacteria from the family of Zoogloeaceae, vintage line
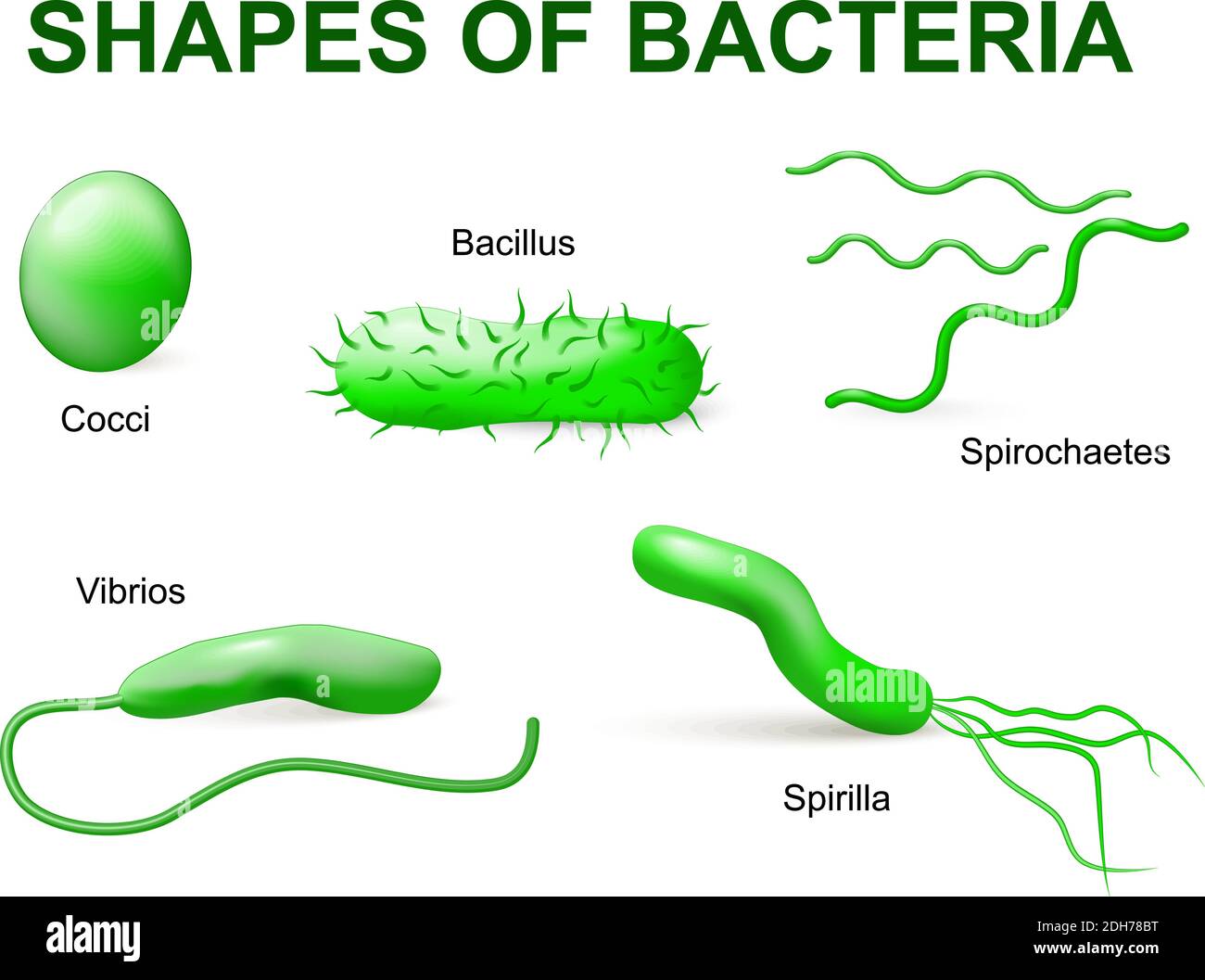 Common bacteria infecting human. vector illustration. Bacteria are classified into 5 groups according to their basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/common-bacteria-infecting-human-vector-illustration-bacteria-are-classified-into-5-groups-according-to-their-basic-shapes-spherical-cocci-rod-image389237516.html
Common bacteria infecting human. vector illustration. Bacteria are classified into 5 groups according to their basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/common-bacteria-infecting-human-vector-illustration-bacteria-are-classified-into-5-groups-according-to-their-basic-shapes-spherical-cocci-rod-image389237516.htmlRF2DH78BT–Common bacteria infecting human. vector illustration. Bacteria are classified into 5 groups according to their basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod
 3d illustration of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170789.html
3d illustration of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170789.htmlRF2C168F1–3d illustration of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus
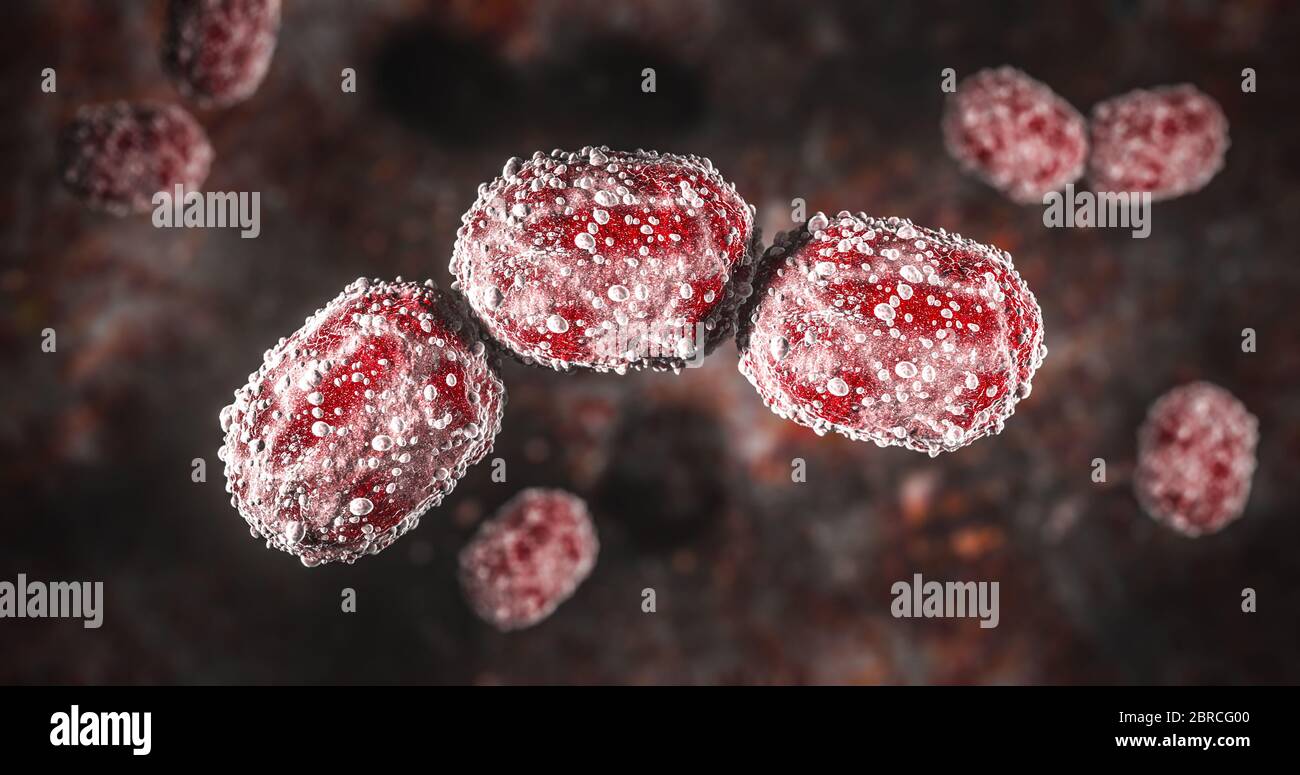 Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-photo-of-bacteria-a-coccobacillus-is-a-type-of-bacterium-with-a-shape-intermediate-between-cocci-and-bacilli-image358620416.html
Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-photo-of-bacteria-a-coccobacillus-is-a-type-of-bacterium-with-a-shape-intermediate-between-cocci-and-bacilli-image358620416.htmlRF2BRCG00–Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli
 3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-hundreds-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170739.html
3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-hundreds-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170739.htmlRF2C168D7–3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus
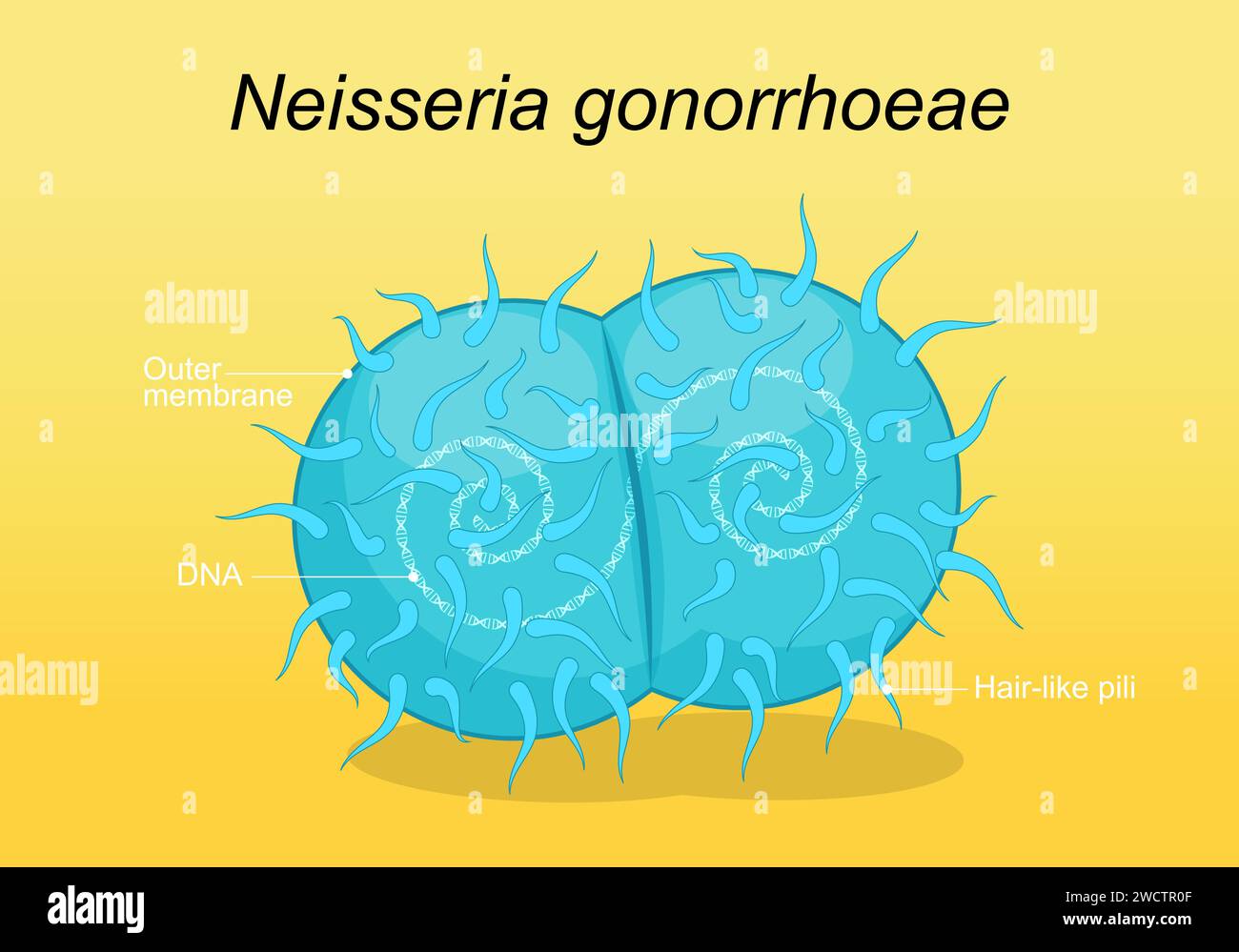 Neisseria gonorrhoeae pathogen bacteria. Sexually transmitted disease and gonococcus infection. Genital tract infection. Vector poster Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-gonorrhoeae-pathogen-bacteria-sexually-transmitted-disease-and-gonococcus-infection-genital-tract-infection-vector-poster-image593073279.html
Neisseria gonorrhoeae pathogen bacteria. Sexually transmitted disease and gonococcus infection. Genital tract infection. Vector poster Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-gonorrhoeae-pathogen-bacteria-sexually-transmitted-disease-and-gonococcus-infection-genital-tract-infection-vector-poster-image593073279.htmlRF2WCTR0F–Neisseria gonorrhoeae pathogen bacteria. Sexually transmitted disease and gonococcus infection. Genital tract infection. Vector poster
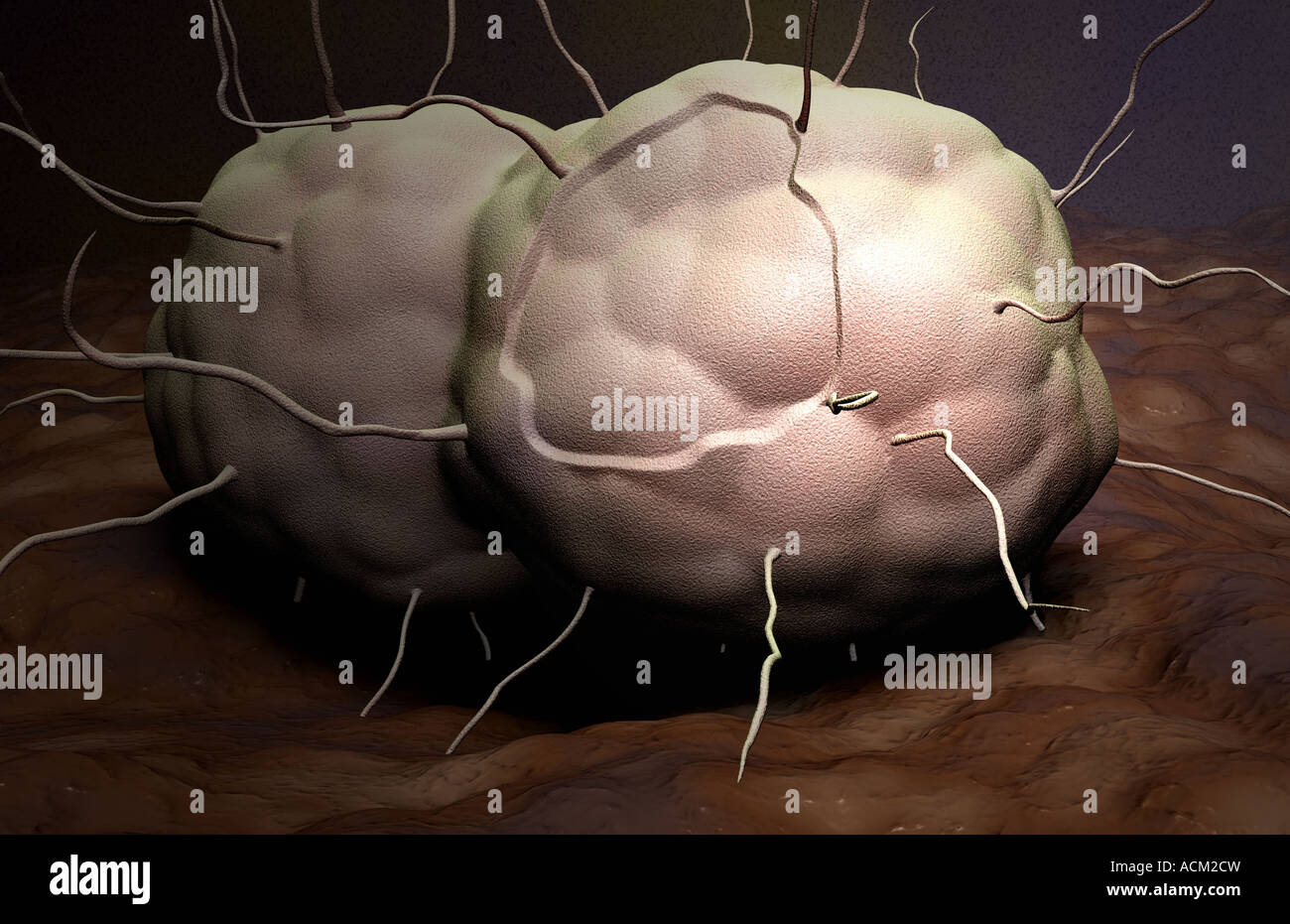 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13184568.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13184568.htmlRFACM2CW–Gonorrhea
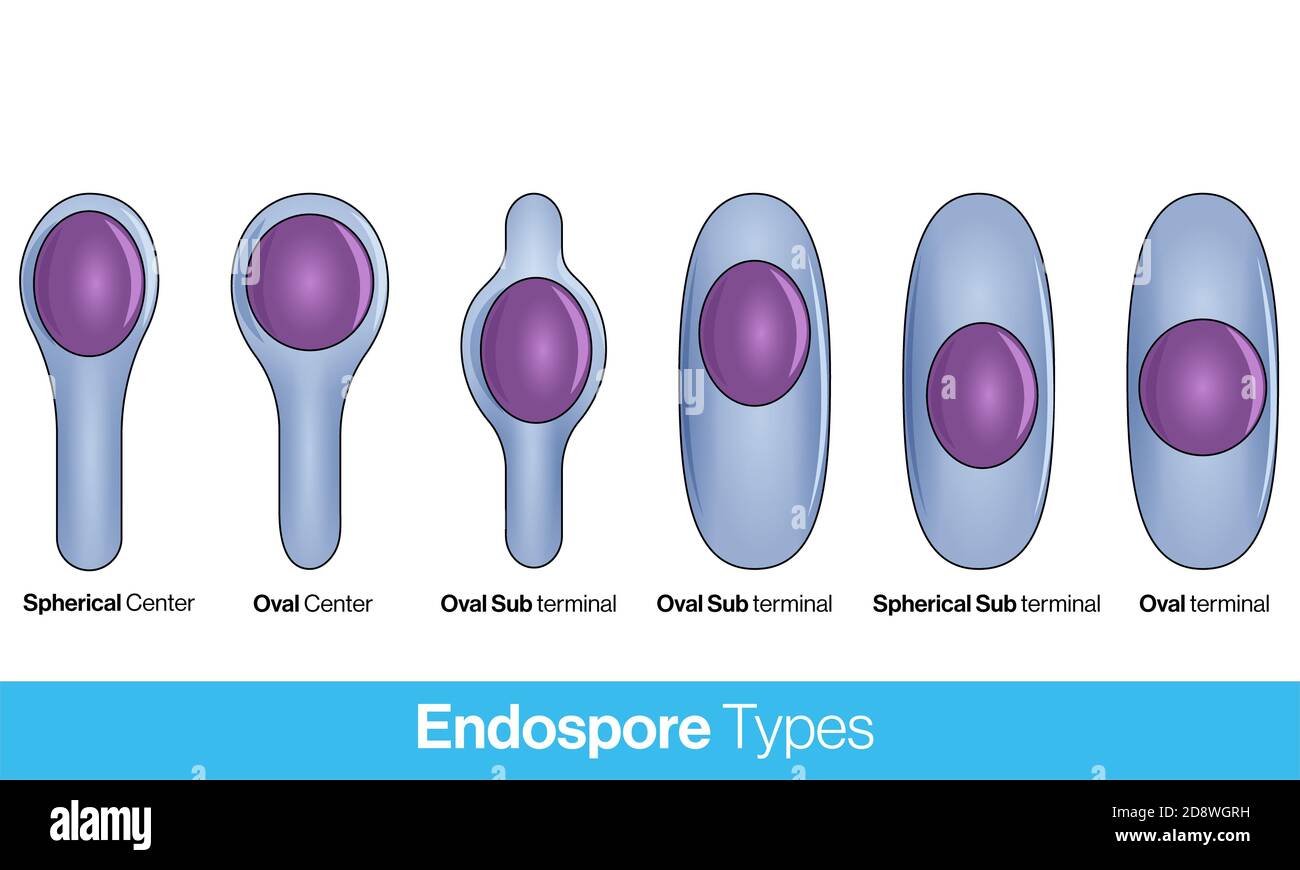 location of bacterial spores. types of endospores. Endospore structure vector illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/location-of-bacterial-spores-types-of-endospores-endospore-structure-vector-illustration-image384107349.html
location of bacterial spores. types of endospores. Endospore structure vector illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/location-of-bacterial-spores-types-of-endospores-endospore-structure-vector-illustration-image384107349.htmlRF2D8WGRH–location of bacterial spores. types of endospores. Endospore structure vector illustration.
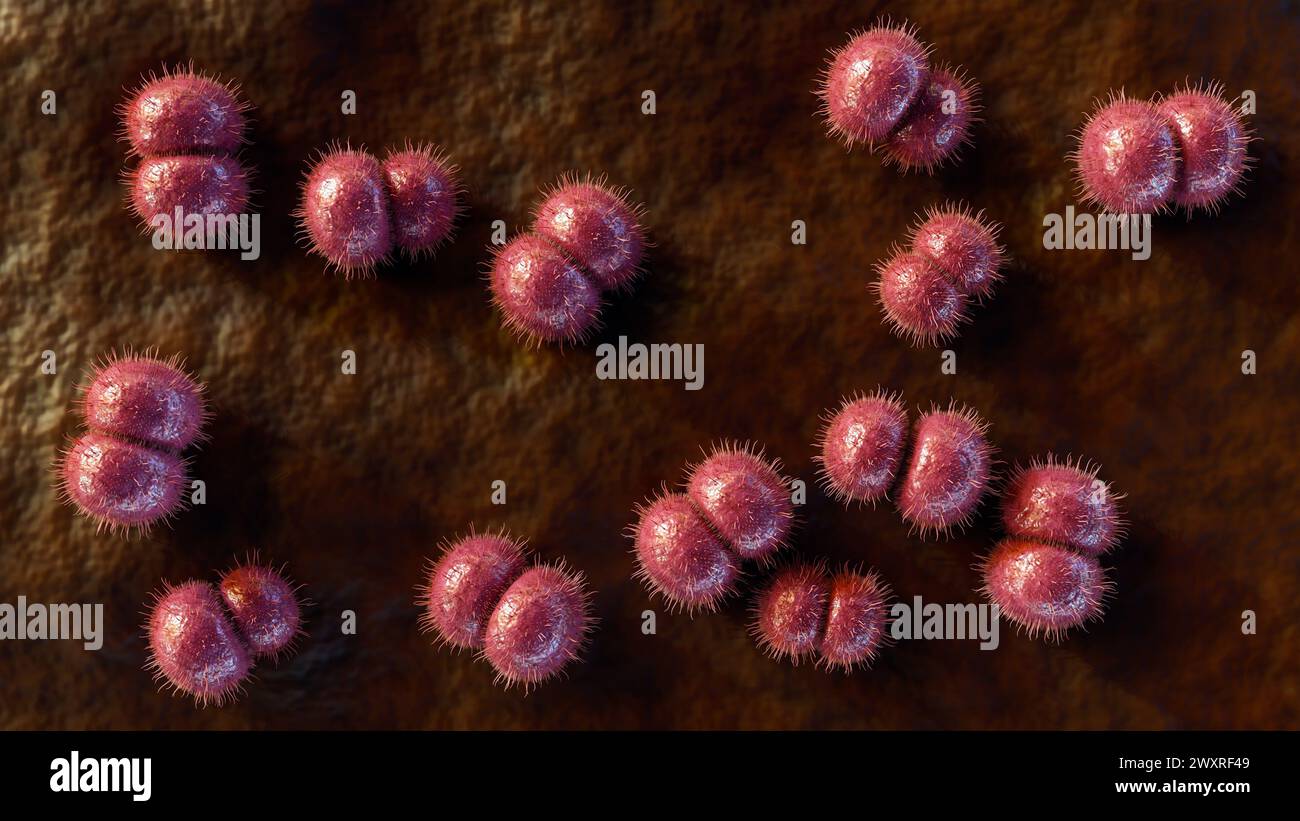 3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-neisseria-meningitidis-also-known-as-meningococcus-is-a-bacterium-that-causes-meningococcal-disease-image601650345.html
3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-neisseria-meningitidis-also-known-as-meningococcus-is-a-bacterium-that-causes-meningococcal-disease-image601650345.htmlRF2WXRF49–3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease
 Gonorrhea News.News on the phone.Mobile phone in hands. selective focus and chromatic aberration effects. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gonorrhea-newsnews-on-the-phonemobile-phone-in-hands-selective-focus-and-chromatic-aberration-effects-image430106112.html
Gonorrhea News.News on the phone.Mobile phone in hands. selective focus and chromatic aberration effects. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gonorrhea-newsnews-on-the-phonemobile-phone-in-hands-selective-focus-and-chromatic-aberration-effects-image430106112.htmlRF2FYN0MG–Gonorrhea News.News on the phone.Mobile phone in hands. selective focus and chromatic aberration effects.
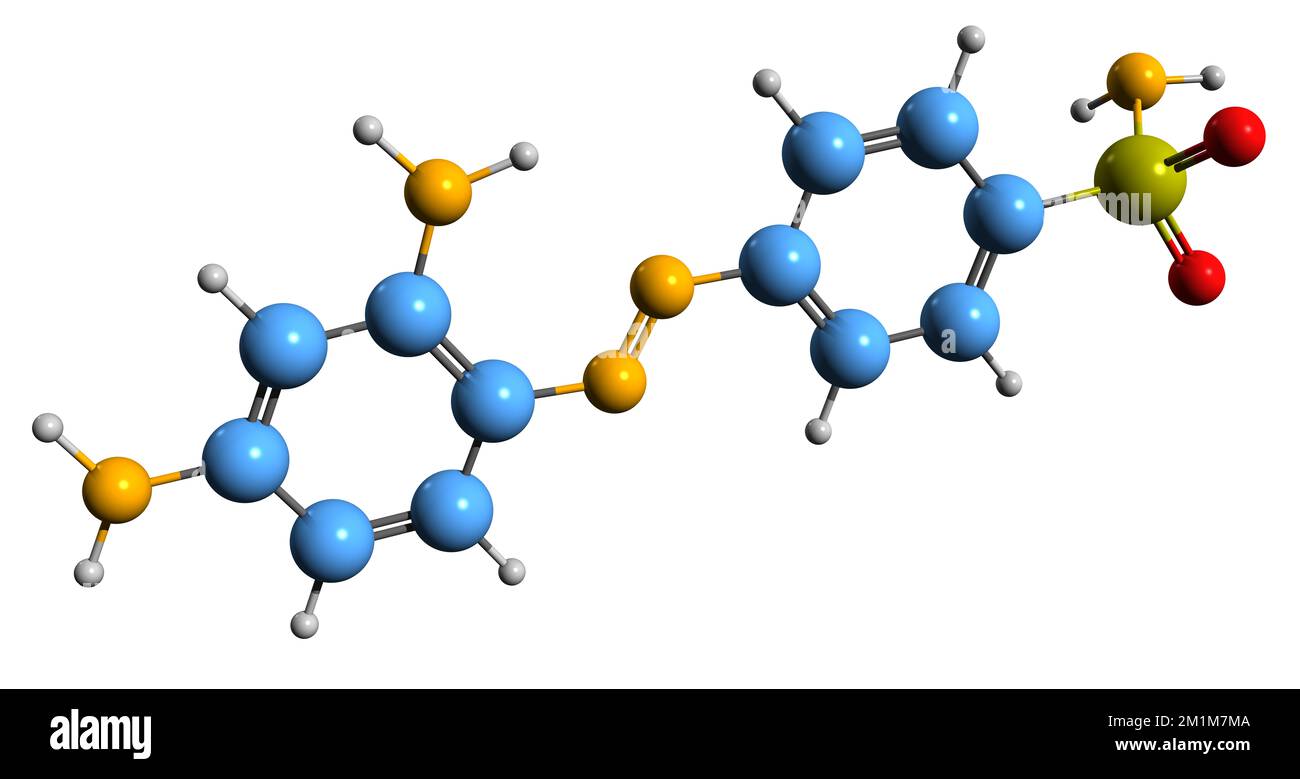 3D image of Prontosil skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of sulfonamide antibacterial drug isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-prontosil-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-sulfonamide-antibacterial-drug-isolated-on-white-background-image500160426.html
3D image of Prontosil skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of sulfonamide antibacterial drug isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-prontosil-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-sulfonamide-antibacterial-drug-isolated-on-white-background-image500160426.htmlRF2M1M7MA–3D image of Prontosil skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of sulfonamide antibacterial drug isolated on white background
 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279058.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279058.htmlRM2AJ9XAX–Brucella
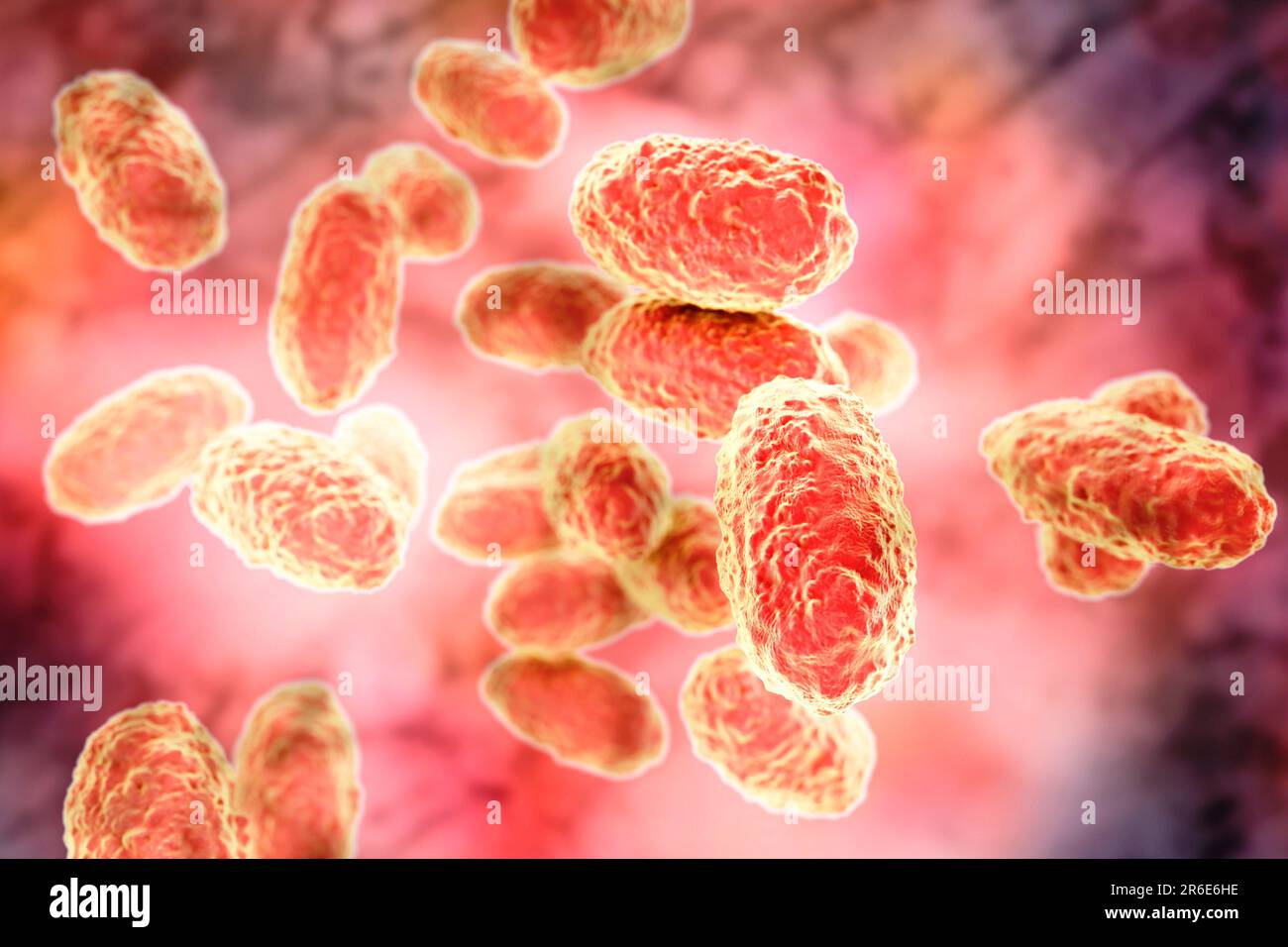 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732234.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732234.htmlRF2R6E6HE–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
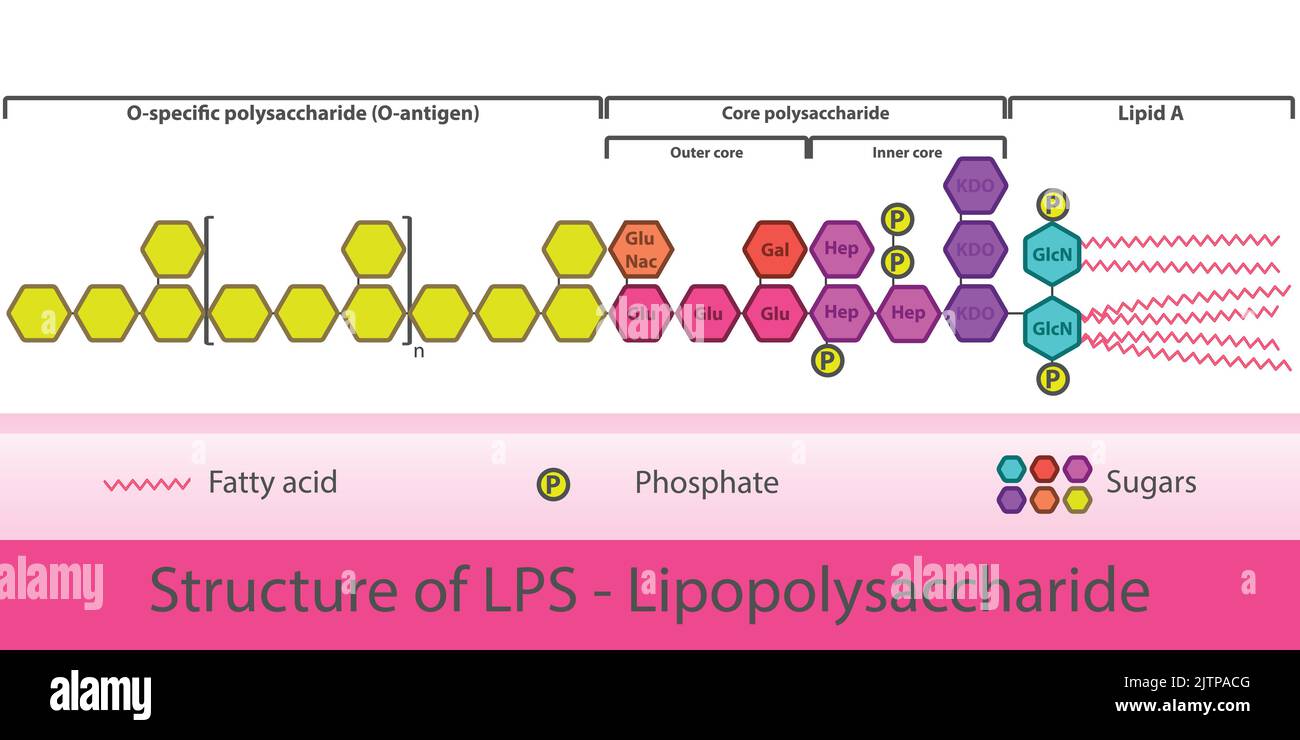 Diagram of LPS strcuture - schematic illustration of Lipopolysaccharide molecule of gram negative bacteria cell membrane. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-lps-strcuture-schematic-illustration-of-lipopolysaccharide-molecule-of-gram-negative-bacteria-cell-membrane-image479922816.html
Diagram of LPS strcuture - schematic illustration of Lipopolysaccharide molecule of gram negative bacteria cell membrane. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-lps-strcuture-schematic-illustration-of-lipopolysaccharide-molecule-of-gram-negative-bacteria-cell-membrane-image479922816.htmlRF2JTPACG–Diagram of LPS strcuture - schematic illustration of Lipopolysaccharide molecule of gram negative bacteria cell membrane.
 Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-bacteria-moraxella-catarrhalis-computer-illustration-moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-they-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-including-pneumonia-image223398654.html
Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-bacteria-moraxella-catarrhalis-computer-illustration-moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-they-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-including-pneumonia-image223398654.htmlRFPYCK7A–Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia.
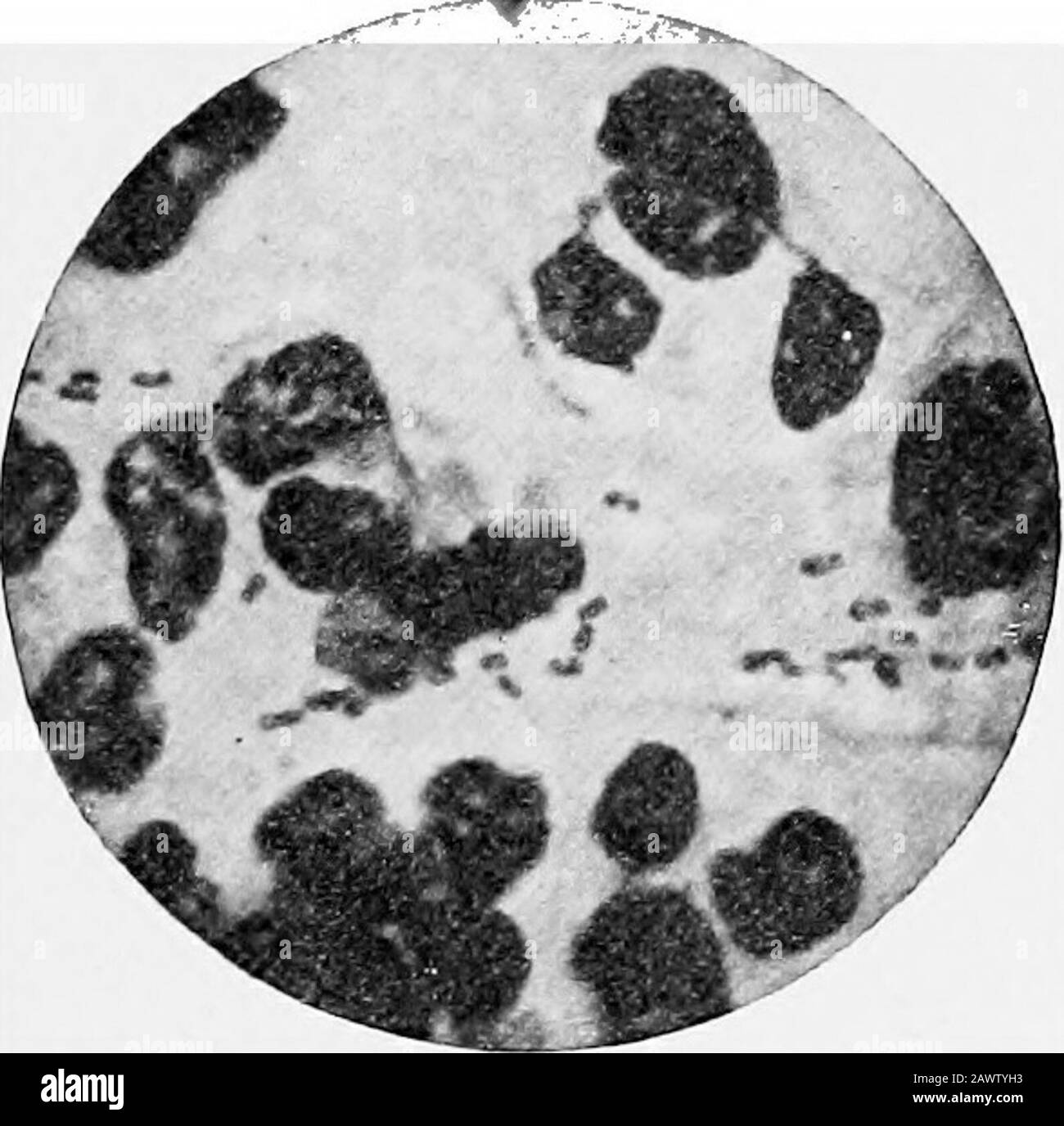 Essentials of bacteriology; being a concise and systematic introduction to the study of bacteria and allied microörganisms . ing the cocci. Bacterial Diagnosis.—By means of lumbar puncture thespinal fluid is obtained and allowed to settle. Smears madefrom sediment. Examined for bacteria. Gram-positive organisms are either pneumococci, strepto-cocci, or staphylococci. Meningococcus is Gram negative and within the leukocytes,and can be readily grown on blood-serum. If such an or-ganism is present, the disease is undoubtedly cerebrospinalmeningitis. Bacillus of Soft Chancre, Chancroid (Ducrey-Un Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/essentials-of-bacteriology-being-a-concise-and-systematic-introduction-to-the-study-of-bacteria-and-allied-microorganisms-ing-the-cocci-bacterial-diagnosisby-means-of-lumbar-puncture-thespinal-fluid-is-obtained-and-allowed-to-settle-smears-madefrom-sediment-examined-for-bacteria-gram-positive-organisms-are-either-pneumococci-strepto-cocci-or-staphylococci-meningococcus-is-gram-negative-and-within-the-leukocytesand-can-be-readily-grown-on-blood-serum-if-such-an-or-ganism-is-present-the-disease-is-undoubtedly-cerebrospinalmeningitis-bacillus-of-soft-chancre-chancroid-ducrey-un-image342911887.html
Essentials of bacteriology; being a concise and systematic introduction to the study of bacteria and allied microörganisms . ing the cocci. Bacterial Diagnosis.—By means of lumbar puncture thespinal fluid is obtained and allowed to settle. Smears madefrom sediment. Examined for bacteria. Gram-positive organisms are either pneumococci, strepto-cocci, or staphylococci. Meningococcus is Gram negative and within the leukocytes,and can be readily grown on blood-serum. If such an or-ganism is present, the disease is undoubtedly cerebrospinalmeningitis. Bacillus of Soft Chancre, Chancroid (Ducrey-Un Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/essentials-of-bacteriology-being-a-concise-and-systematic-introduction-to-the-study-of-bacteria-and-allied-microorganisms-ing-the-cocci-bacterial-diagnosisby-means-of-lumbar-puncture-thespinal-fluid-is-obtained-and-allowed-to-settle-smears-madefrom-sediment-examined-for-bacteria-gram-positive-organisms-are-either-pneumococci-strepto-cocci-or-staphylococci-meningococcus-is-gram-negative-and-within-the-leukocytesand-can-be-readily-grown-on-blood-serum-if-such-an-or-ganism-is-present-the-disease-is-undoubtedly-cerebrospinalmeningitis-bacillus-of-soft-chancre-chancroid-ducrey-un-image342911887.htmlRM2AWTYH3–Essentials of bacteriology; being a concise and systematic introduction to the study of bacteria and allied microörganisms . ing the cocci. Bacterial Diagnosis.—By means of lumbar puncture thespinal fluid is obtained and allowed to settle. Smears madefrom sediment. Examined for bacteria. Gram-positive organisms are either pneumococci, strepto-cocci, or staphylococci. Meningococcus is Gram negative and within the leukocytes,and can be readily grown on blood-serum. If such an or-ganism is present, the disease is undoubtedly cerebrospinalmeningitis. Bacillus of Soft Chancre, Chancroid (Ducrey-Un
 Neisseria gonorrhoeae Bacterium Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neisseria-gonorrhoeae-bacterium-56151653.html
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Bacterium Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neisseria-gonorrhoeae-bacterium-56151653.htmlRMD79X05–Neisseria gonorrhoeae Bacterium
 Neisseria gonorrhea (LM) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neisseria-gonorrhea-lm-134942993.html
Neisseria gonorrhea (LM) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neisseria-gonorrhea-lm-134942993.htmlRMHRF54H–Neisseria gonorrhea (LM)
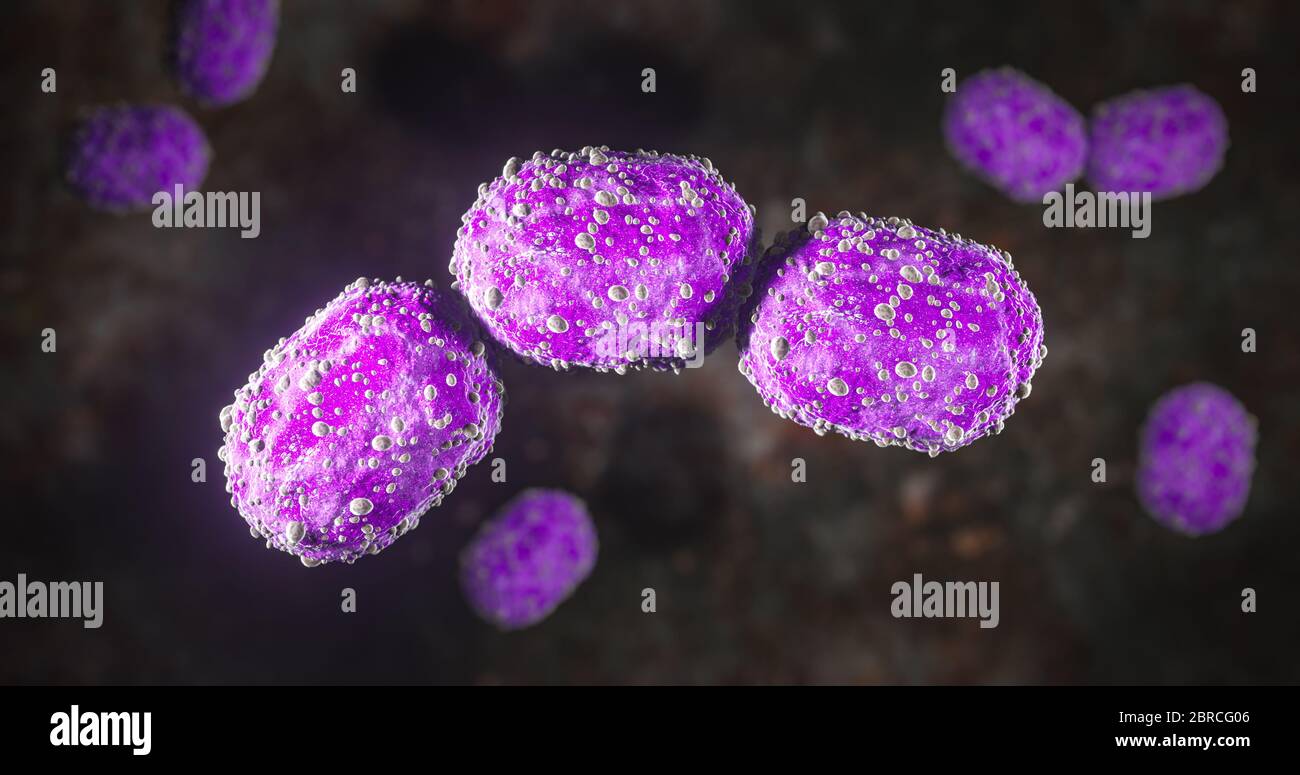 Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-photo-of-bacteria-a-coccobacillus-is-a-type-of-bacterium-with-a-shape-intermediate-between-cocci-and-bacilli-image358620422.html
Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-photo-of-bacteria-a-coccobacillus-is-a-type-of-bacterium-with-a-shape-intermediate-between-cocci-and-bacilli-image358620422.htmlRF2BRCG06–Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli
 3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-hundreds-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170736.html
3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-hundreds-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170736.htmlRF2C168D4–3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus
 3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-hundreds-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170676.html
3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-hundreds-of-meningitis-pathogens-called-menigococcus-image362170676.htmlRF2C168B0–3d illustration of hundreds of meningitis pathogens called menigococcus
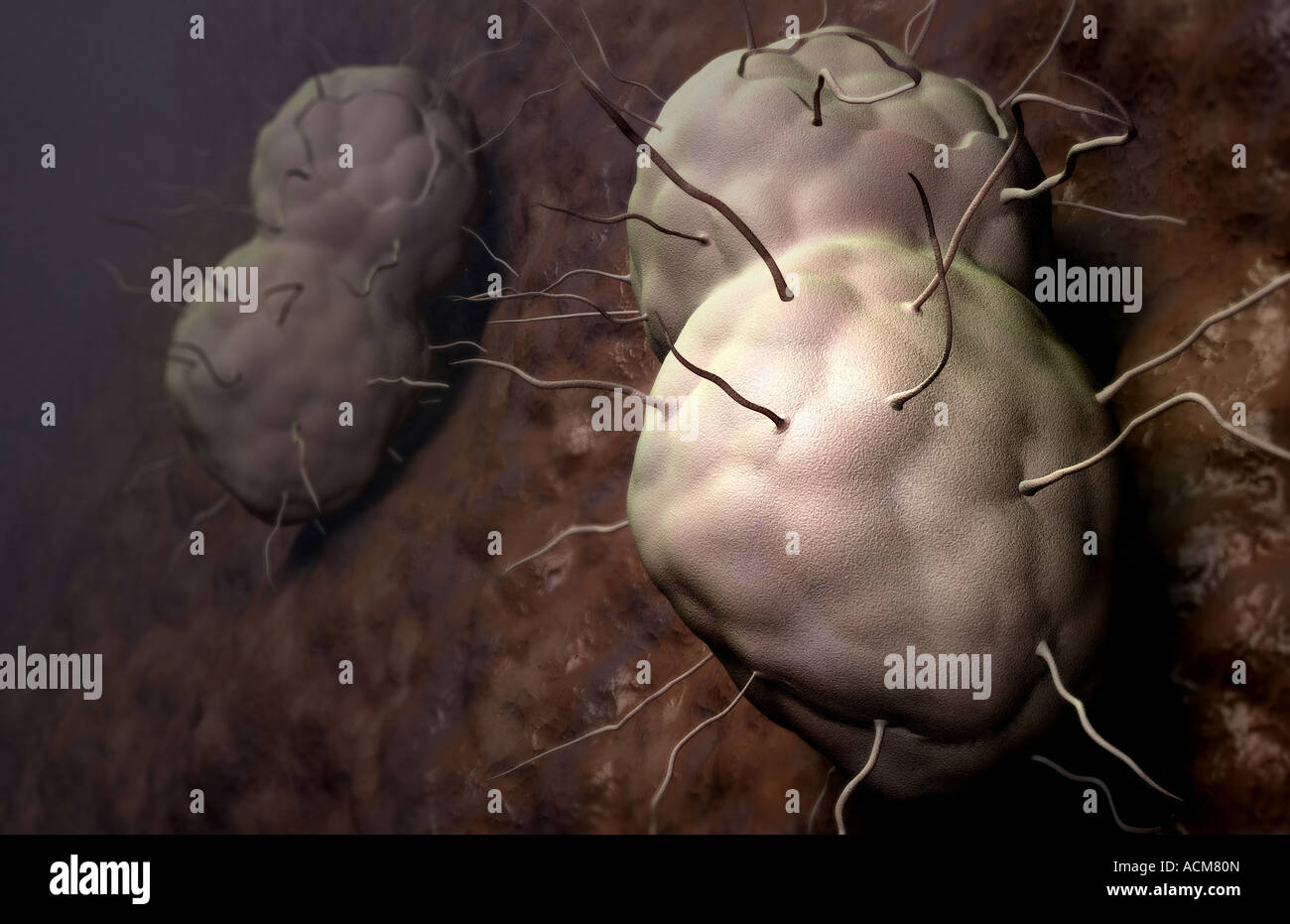 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13186436.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13186436.htmlRFACM80N–Gonorrhea
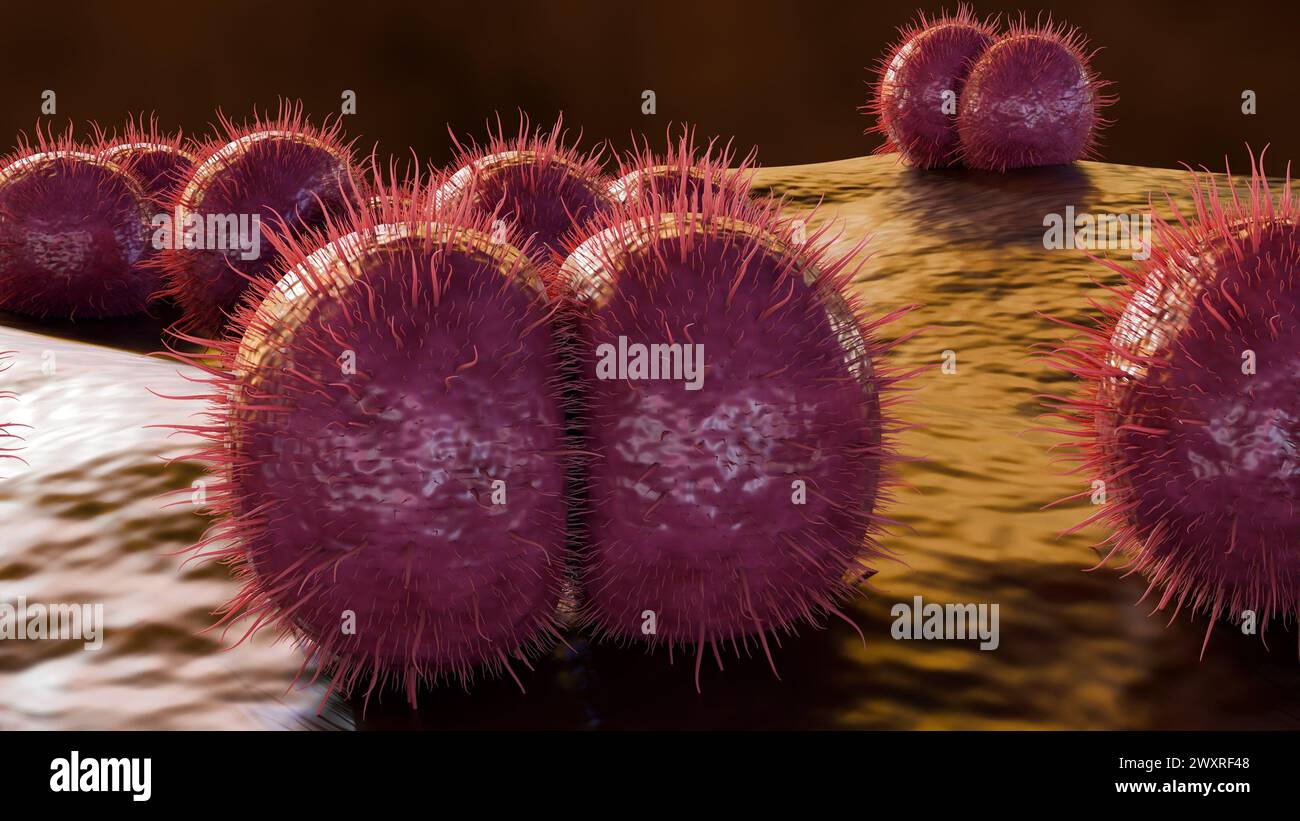 3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-neisseria-meningitidis-also-known-as-meningococcus-is-a-bacterium-that-causes-meningococcal-disease-image601650344.html
3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-neisseria-meningitidis-also-known-as-meningococcus-is-a-bacterium-that-causes-meningococcal-disease-image601650344.htmlRF2WXRF48–3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease
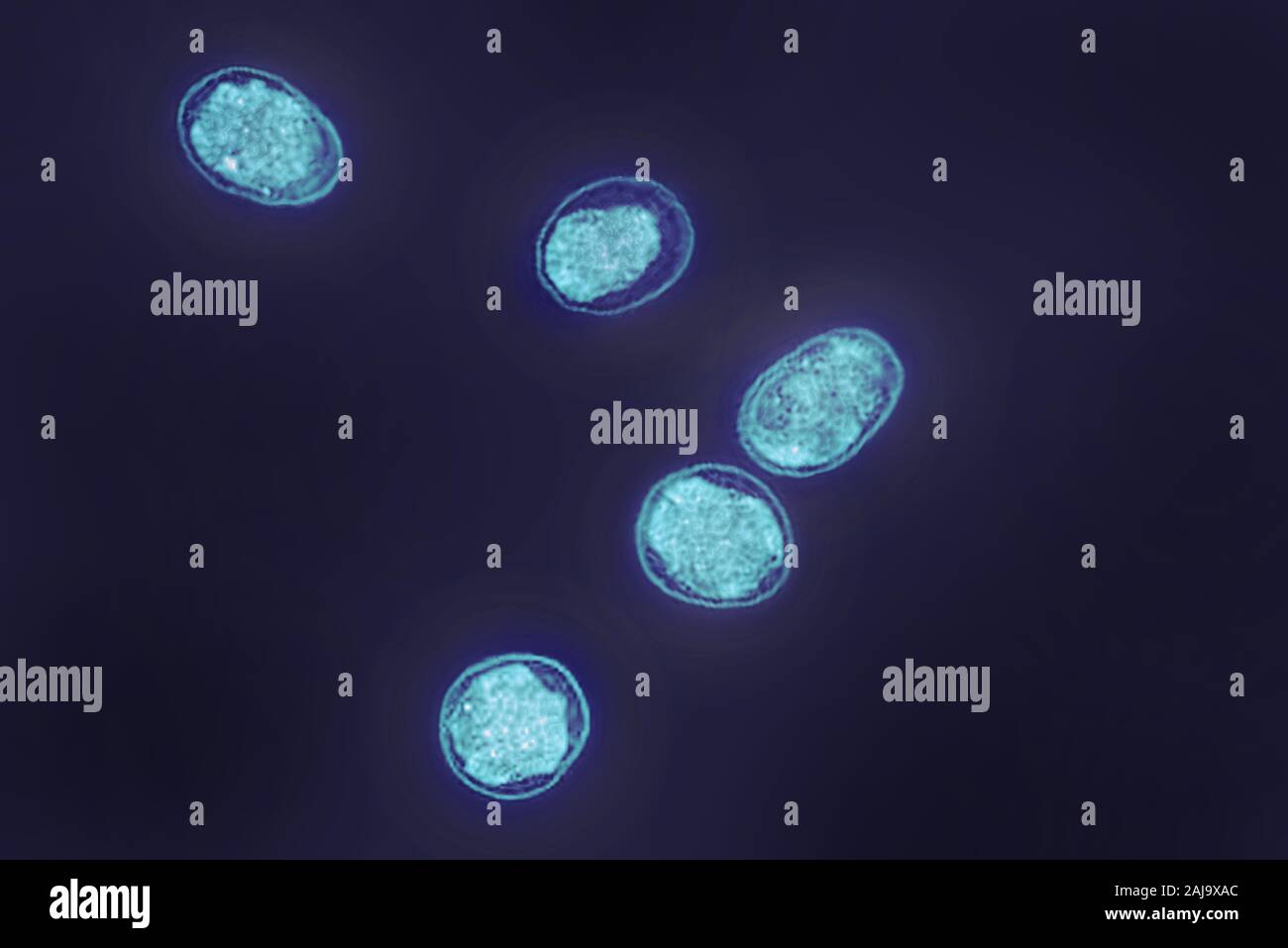 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279044.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279044.htmlRM2AJ9XAC–Brucella
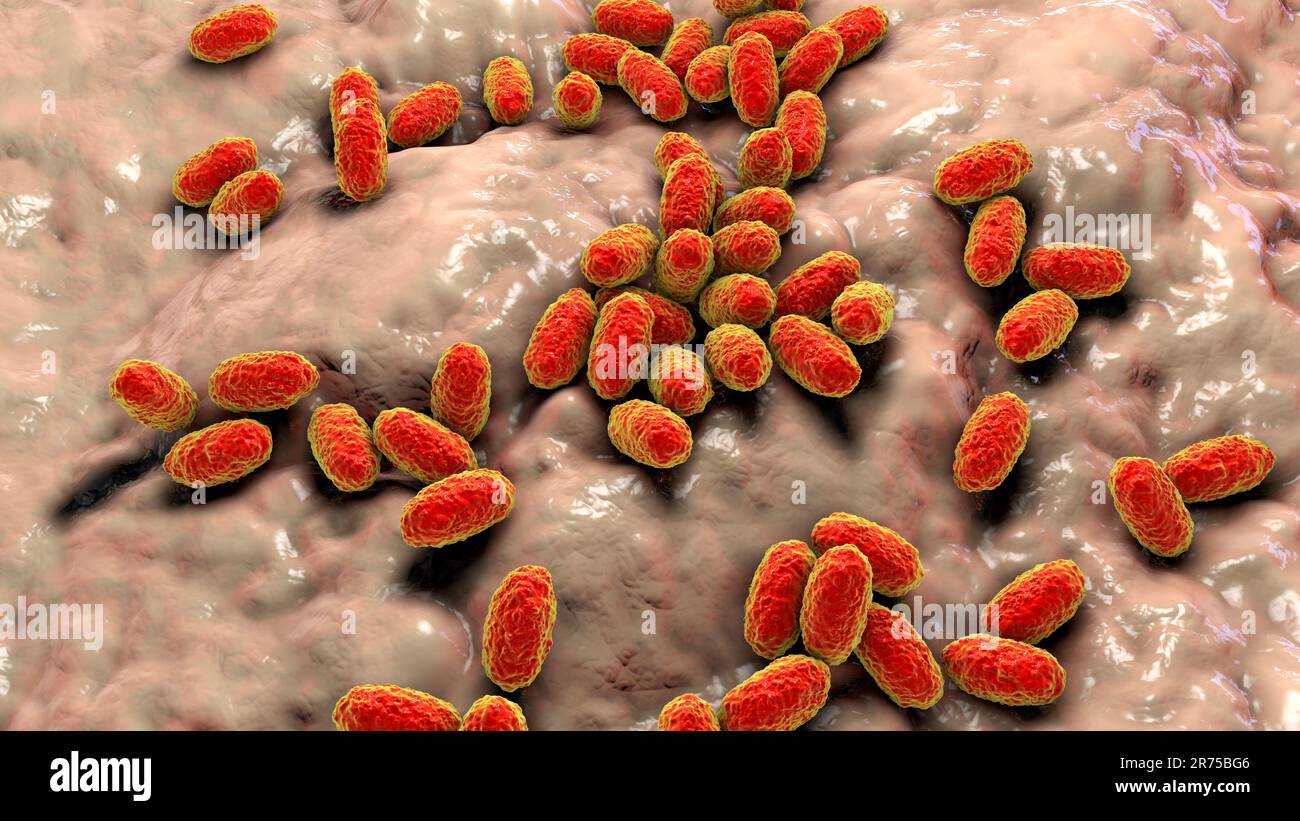 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus bacteria. Th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-bacteria-th-image555153206.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus bacteria. Th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-bacteria-th-image555153206.htmlRF2R75BG6–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus bacteria. Th
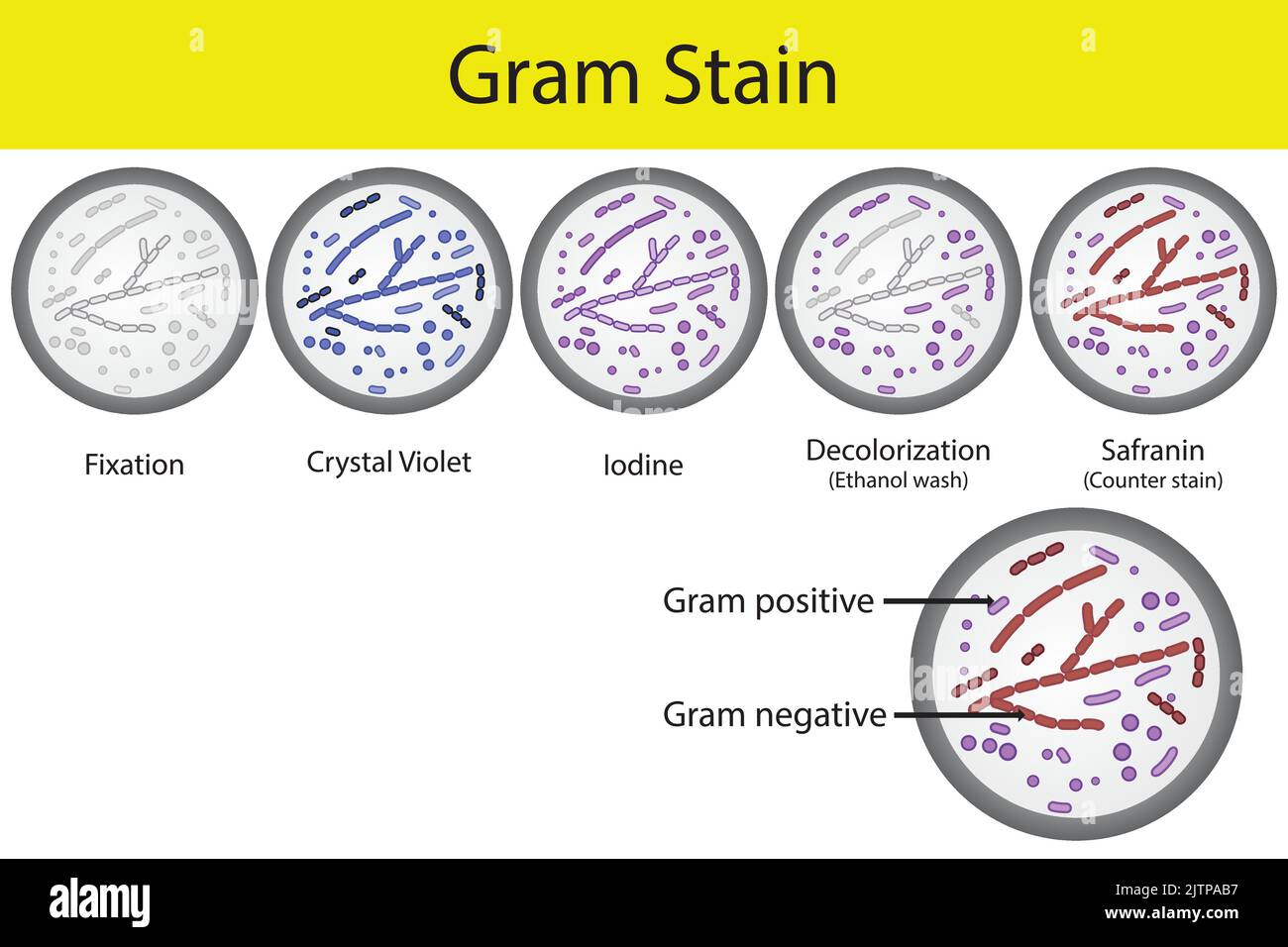 Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-showing-gram-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-microbiology-laboratory-using-crystal-violet-and-safranin-image479922779.html
Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-showing-gram-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-microbiology-laboratory-using-crystal-violet-and-safranin-image479922779.htmlRF2JTPAB7–Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin
 Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-bacteria-moraxella-catarrhalis-computer-illustration-moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-they-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-including-pneumonia-image223398653.html
Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-bacteria-moraxella-catarrhalis-computer-illustration-moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-they-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-including-pneumonia-image223398653.htmlRFPYCK79–Pneumonia caused by bacteria Moraxella catarrhalis, computer illustration. Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria). They are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia.
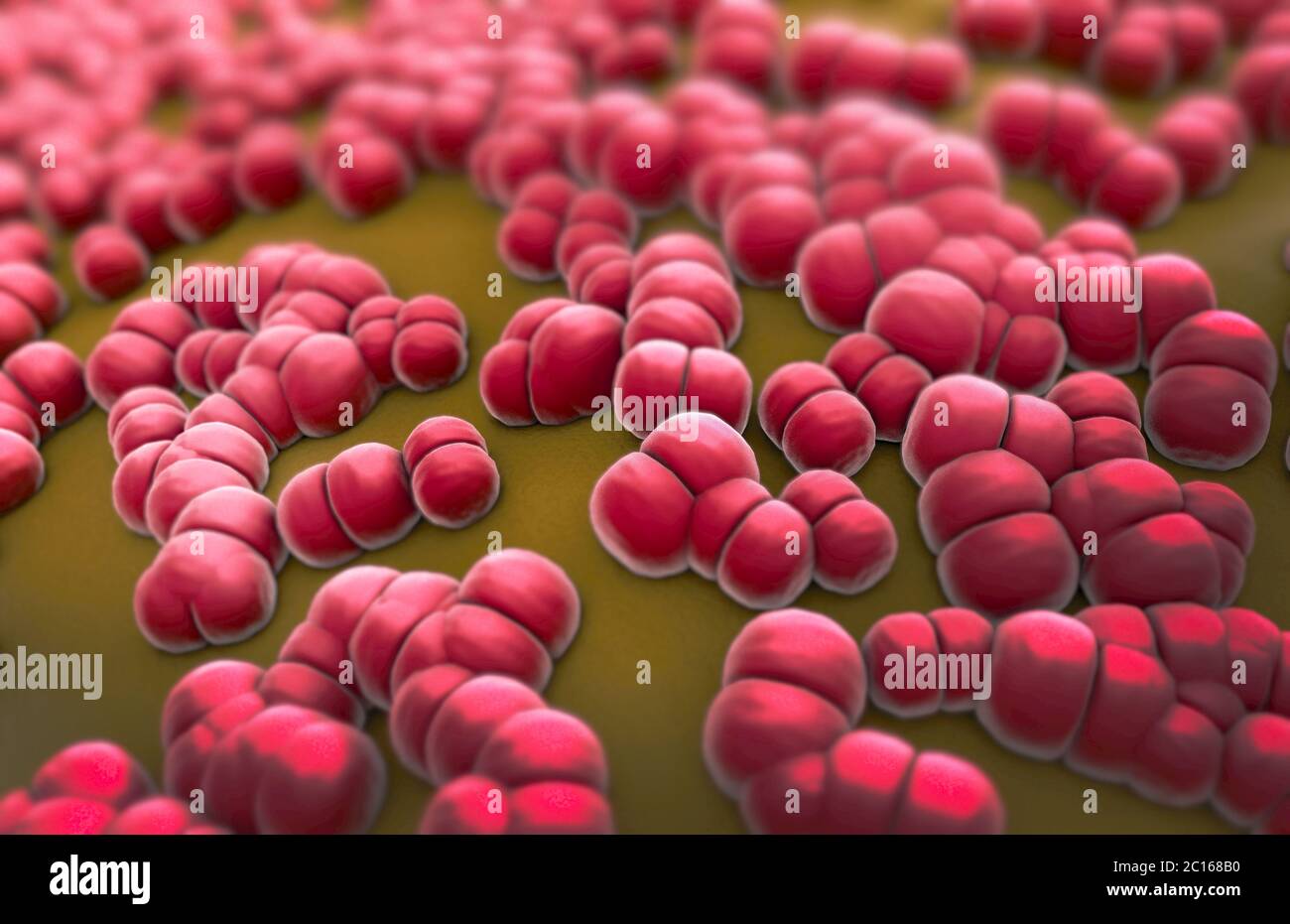
 . The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine . alveolarprocess over the apex of each tooth a rarefied area 3 to 5 mm. in diameter Avas ELECTIVE LOCALIZATIOX OF BACTERIA 715 broken into. The tissues were soft and edematous, and the pulp chamberswere filled with a dark brown, thick fluid, in which large numbers of gram-positive cocci, often in clumps, streptococci, and small gram-negative bacilliand leukocytes were found. Blood-agar-plate cultures made from these areasshowed staphylococci, green-producing streptococci and some gram-positivebacilli. The localizing power of the staphylococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-journal-of-laboratory-and-clinical-medicine-alveolarprocess-over-the-apex-of-each-tooth-a-rarefied-area-3-to-5-mm-in-diameter-avas-elective-localizatiox-of-bacteria-715-broken-into-the-tissues-were-soft-and-edematous-and-the-pulp-chamberswere-filled-with-a-dark-brown-thick-fluid-in-which-large-numbers-of-gram-positive-cocci-often-in-clumps-streptococci-and-small-gram-negative-bacilliand-leukocytes-were-found-blood-agar-plate-cultures-made-from-these-areasshowed-staphylococci-green-producing-streptococci-and-some-gram-positivebacilli-the-localizing-power-of-the-staphylococcus-image369662896.html
. The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine . alveolarprocess over the apex of each tooth a rarefied area 3 to 5 mm. in diameter Avas ELECTIVE LOCALIZATIOX OF BACTERIA 715 broken into. The tissues were soft and edematous, and the pulp chamberswere filled with a dark brown, thick fluid, in which large numbers of gram-positive cocci, often in clumps, streptococci, and small gram-negative bacilliand leukocytes were found. Blood-agar-plate cultures made from these areasshowed staphylococci, green-producing streptococci and some gram-positivebacilli. The localizing power of the staphylococcus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-journal-of-laboratory-and-clinical-medicine-alveolarprocess-over-the-apex-of-each-tooth-a-rarefied-area-3-to-5-mm-in-diameter-avas-elective-localizatiox-of-bacteria-715-broken-into-the-tissues-were-soft-and-edematous-and-the-pulp-chamberswere-filled-with-a-dark-brown-thick-fluid-in-which-large-numbers-of-gram-positive-cocci-often-in-clumps-streptococci-and-small-gram-negative-bacilliand-leukocytes-were-found-blood-agar-plate-cultures-made-from-these-areasshowed-staphylococci-green-producing-streptococci-and-some-gram-positivebacilli-the-localizing-power-of-the-staphylococcus-image369662896.htmlRM2CDBGP8–. The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine . alveolarprocess over the apex of each tooth a rarefied area 3 to 5 mm. in diameter Avas ELECTIVE LOCALIZATIOX OF BACTERIA 715 broken into. The tissues were soft and edematous, and the pulp chamberswere filled with a dark brown, thick fluid, in which large numbers of gram-positive cocci, often in clumps, streptococci, and small gram-negative bacilliand leukocytes were found. Blood-agar-plate cultures made from these areasshowed staphylococci, green-producing streptococci and some gram-positivebacilli. The localizing power of the staphylococcus
 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452213.html
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452213.htmlRFPCW3YH–Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics.
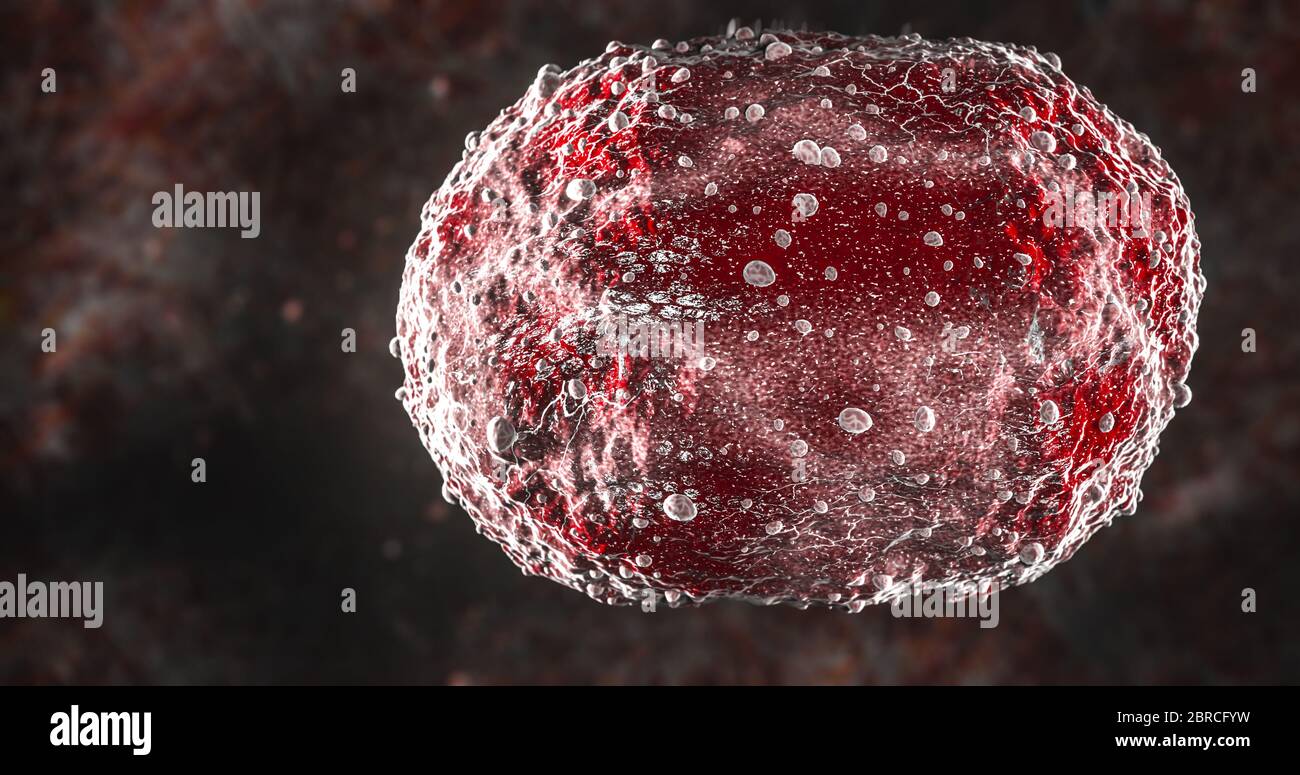 Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-photo-of-bacteria-a-coccobacillus-is-a-type-of-bacterium-with-a-shape-intermediate-between-cocci-and-bacilli-image358620413.html
Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/science-photo-of-bacteria-a-coccobacillus-is-a-type-of-bacterium-with-a-shape-intermediate-between-cocci-and-bacilli-image358620413.htmlRF2BRCFYW–Science Photo of bacteria A coccobacillus is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci and bacilli
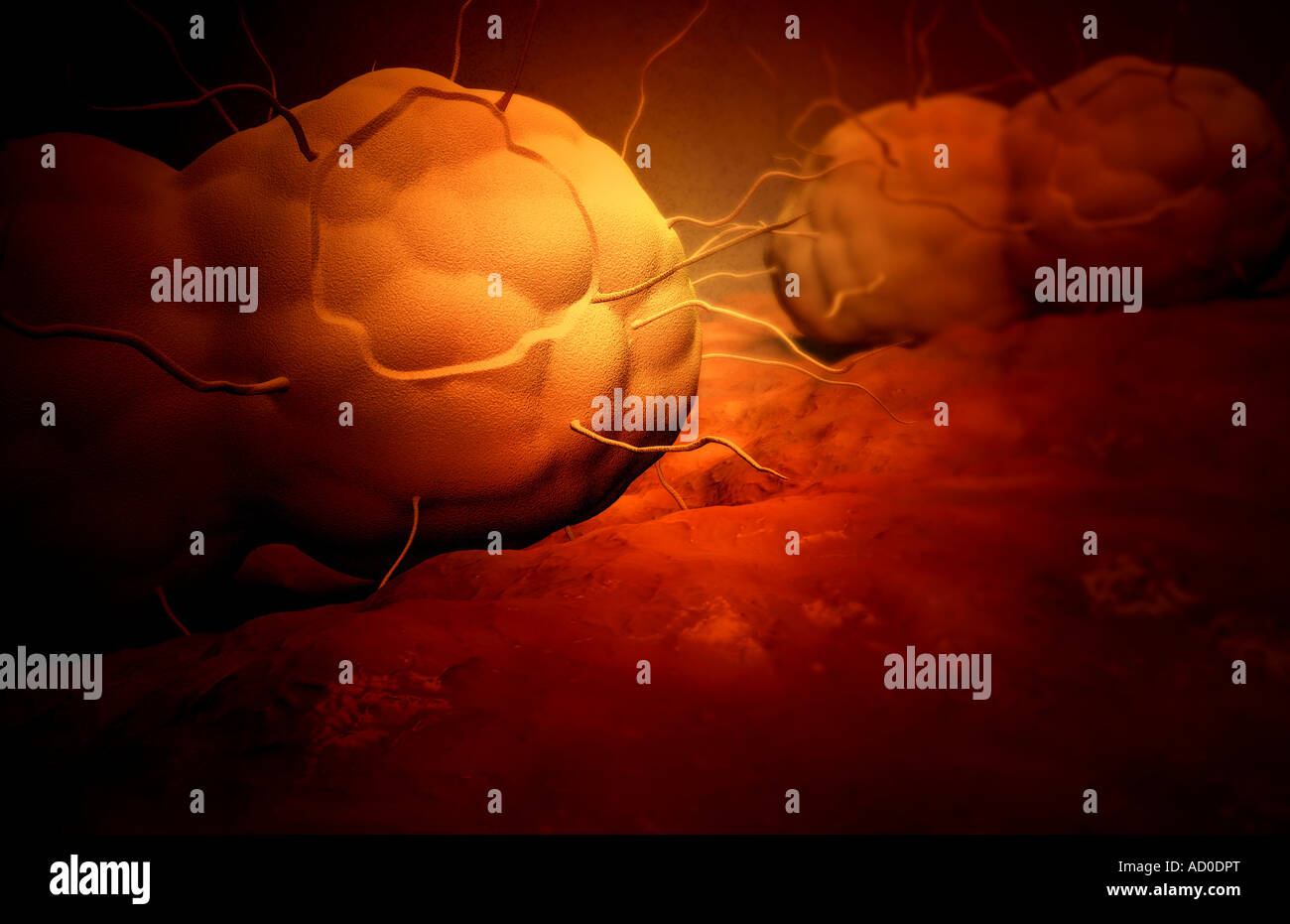 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13263647.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13263647.htmlRFAD0DPT–Gonorrhea
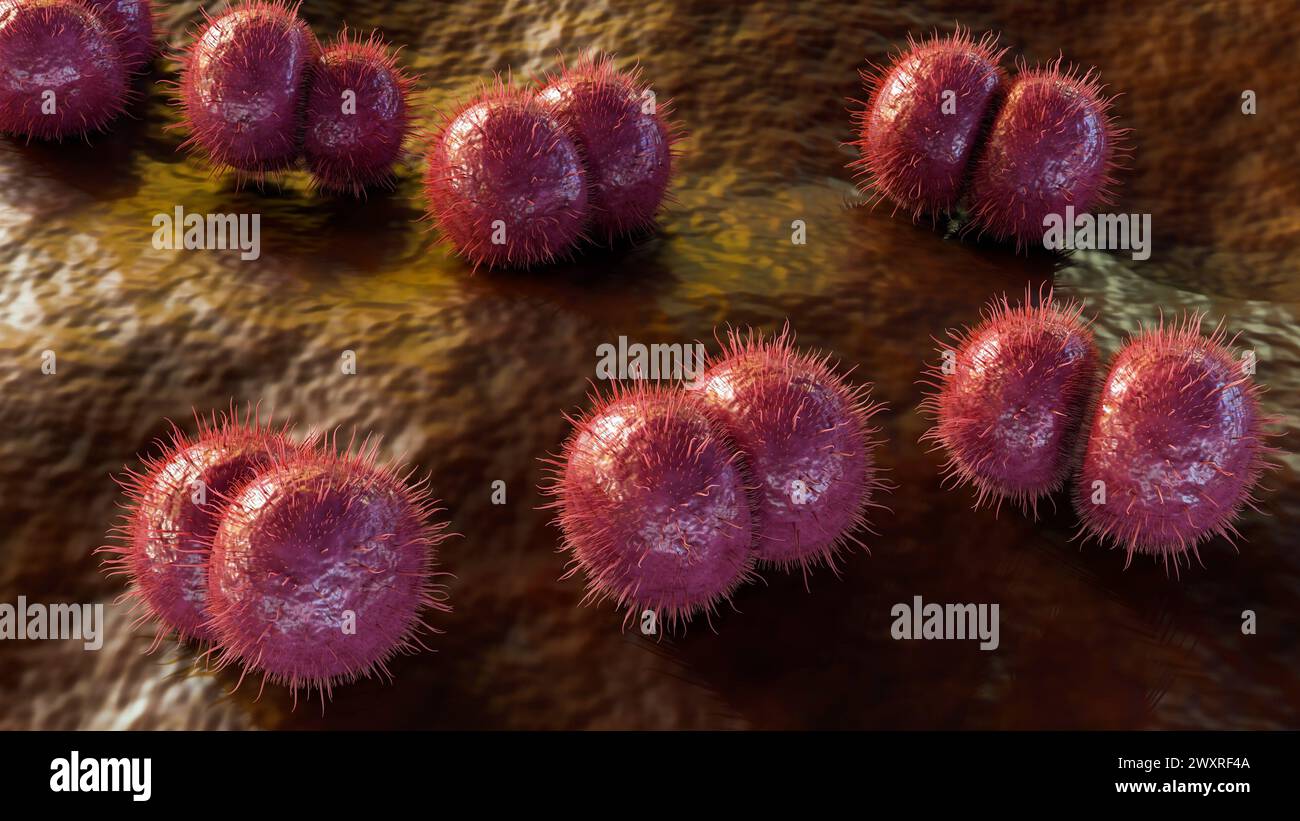 3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-neisseria-meningitidis-also-known-as-meningococcus-is-a-bacterium-that-causes-meningococcal-disease-image601650346.html
3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-neisseria-meningitidis-also-known-as-meningococcus-is-a-bacterium-that-causes-meningococcal-disease-image601650346.htmlRF2WXRF4A–3d rendering of Neisseria meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, is a bacterium that causes meningococcal disease
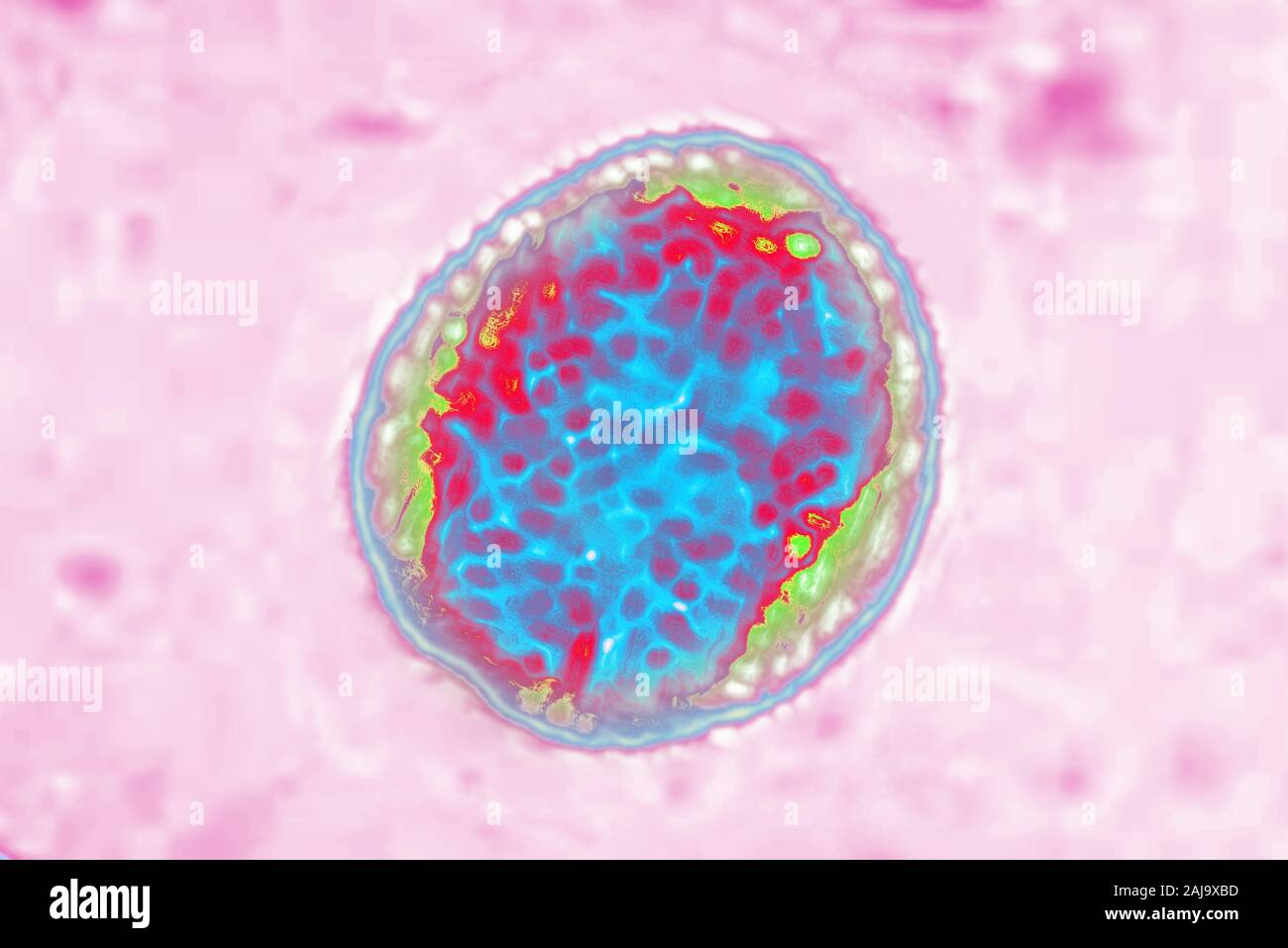 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279073.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279073.htmlRM2AJ9XBD–Brucella
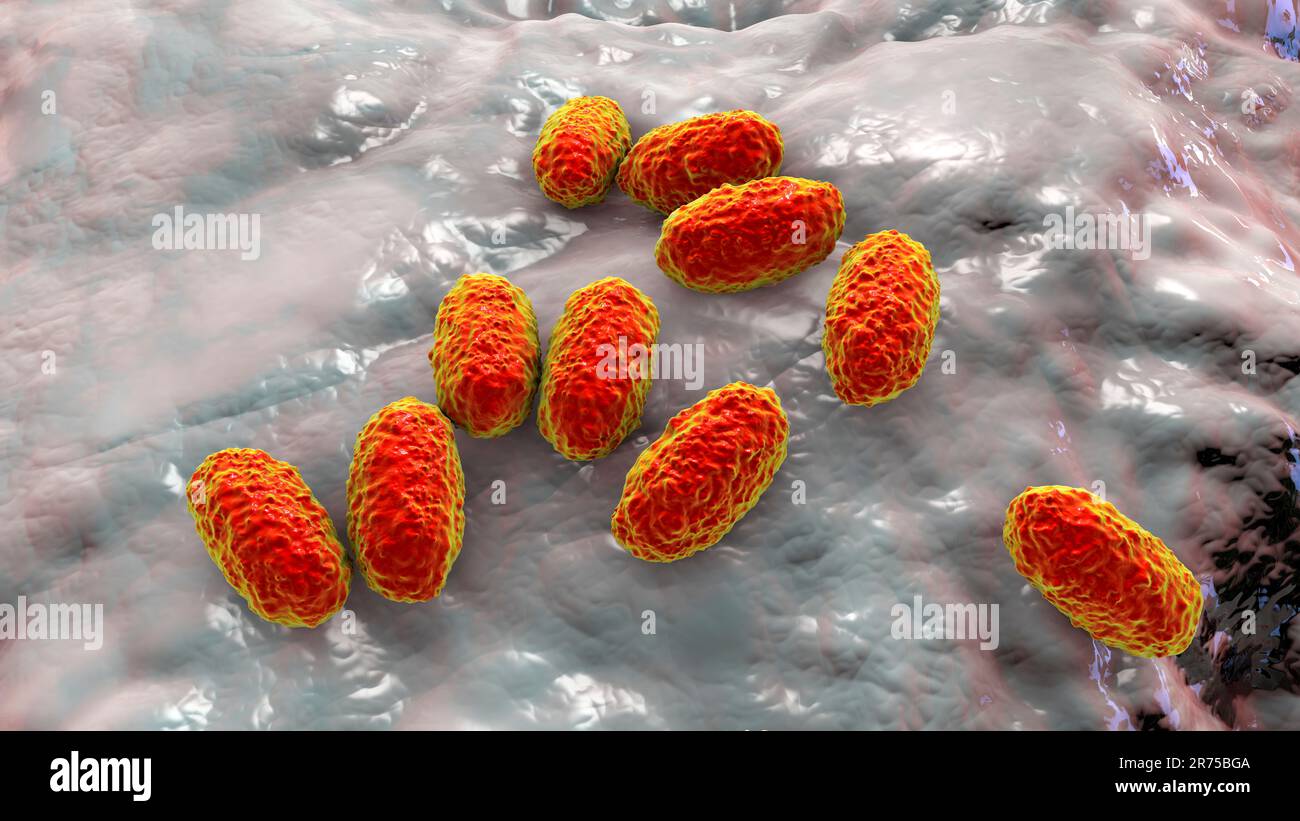 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus bacteria. Th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-bacteria-th-image555153210.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus bacteria. Th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-bacteria-th-image555153210.htmlRF2R75BGA–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus bacteria. Th
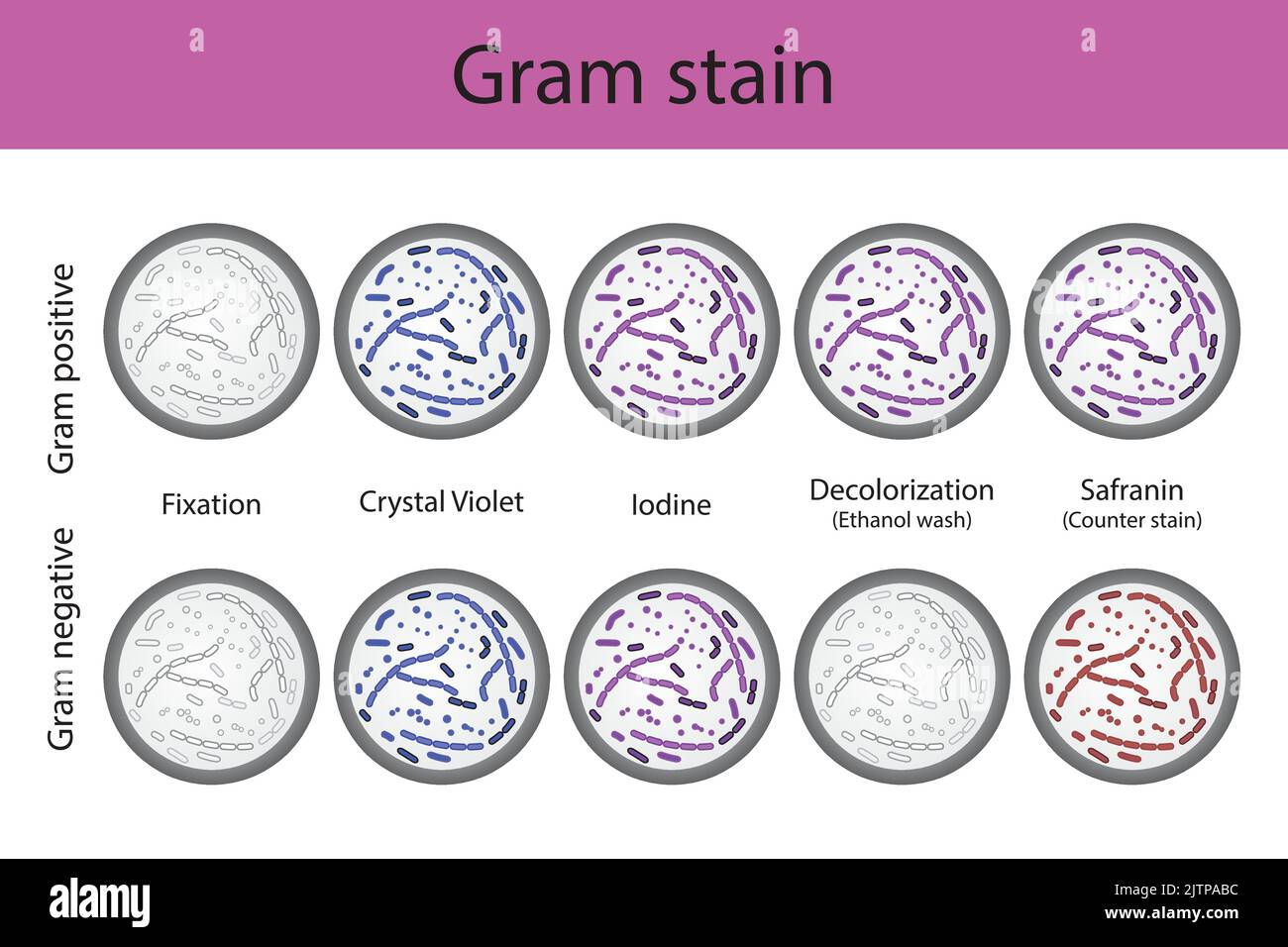 Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-showing-gram-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-microbiology-laboratory-using-crystal-violet-and-safranin-image479922784.html
Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-showing-gram-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-microbiology-laboratory-using-crystal-violet-and-safranin-image479922784.htmlRF2JTPABC–Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin
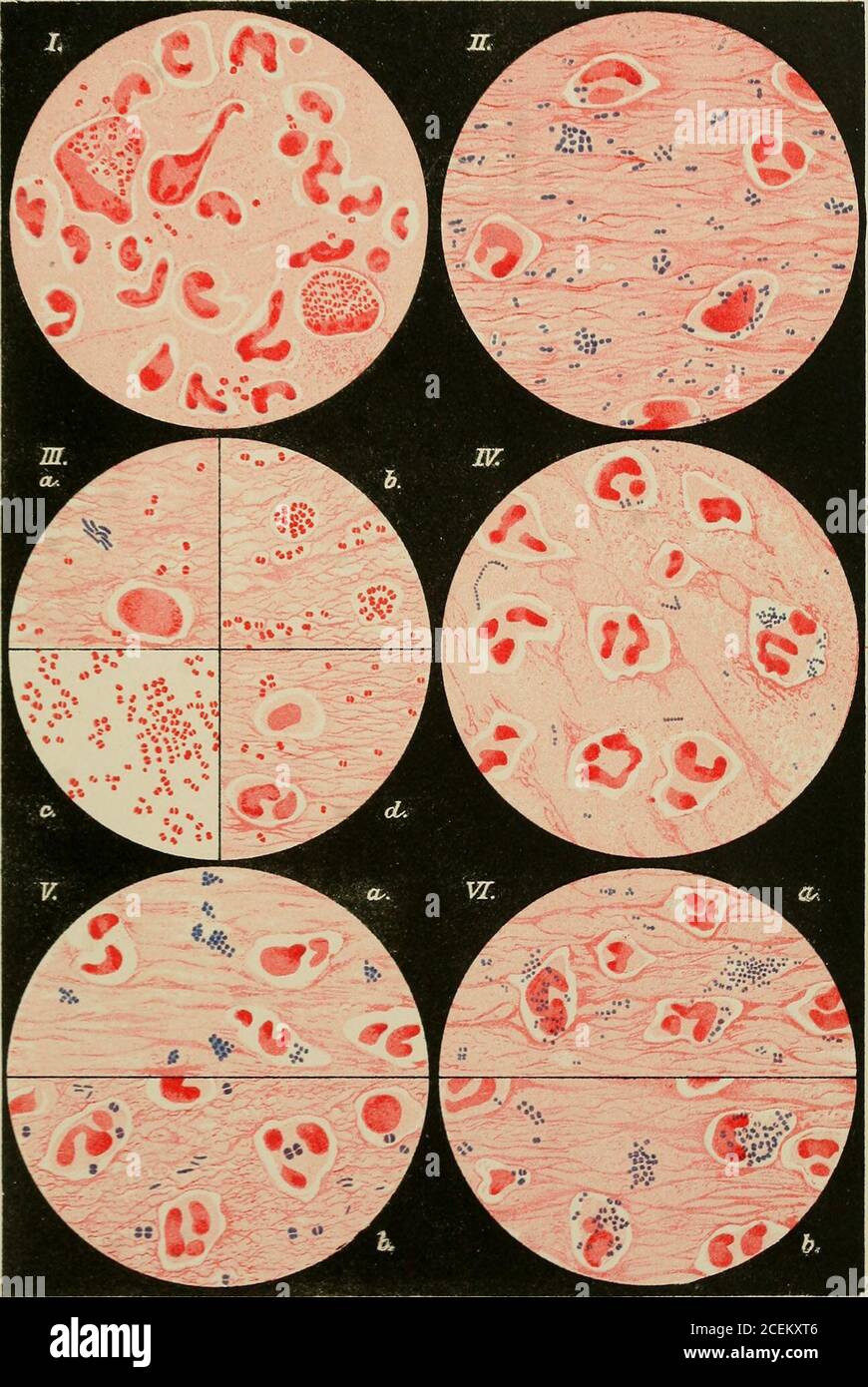 . The bacteriology of the eye. ative (red) Diplococci (Pseudo-gonococci) (fromslight cases of chronic conjunctivitis). III.a, III.c, Ill.d, MicrococcusCatarrhalis (III.c, pure culture) ; III.6, Gram negative Sarcin^e.The Diplococci are mostly larger, but some are similar to Gonococci. Fig. IV.—Streptococcal Conjunctivitis (from a case of pseudo-membranousconjunctivitis). Gram-positive (blue) round cocci, in some cases showingchains, but also in the double form. Figs. V. and VI.—Staphylococci. Gram-positive (blue) cocci. V.a. In pus from a hordeolum. Clusters. V.6. Large Diplococci and tetrads, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bacteriology-of-the-eye-ative-red-diplococci-pseudo-gonococci-fromslight-cases-of-chronic-conjunctivitis-iiia-iiic-illd-micrococcuscatarrhalis-iiic-pure-culture-iii6-gram-negative-sarcinethe-diplococci-are-mostly-larger-but-some-are-similar-to-gonococci-fig-ivstreptococcal-conjunctivitis-from-a-case-of-pseudo-membranousconjunctivitis-gram-positive-blue-round-cocci-in-some-cases-showingchains-but-also-in-the-double-form-figs-v-and-vistaphylococci-gram-positive-blue-cocci-va-in-pus-from-a-hordeolum-clusters-v6-large-diplococci-and-tetrads-image370461062.html
. The bacteriology of the eye. ative (red) Diplococci (Pseudo-gonococci) (fromslight cases of chronic conjunctivitis). III.a, III.c, Ill.d, MicrococcusCatarrhalis (III.c, pure culture) ; III.6, Gram negative Sarcin^e.The Diplococci are mostly larger, but some are similar to Gonococci. Fig. IV.—Streptococcal Conjunctivitis (from a case of pseudo-membranousconjunctivitis). Gram-positive (blue) round cocci, in some cases showingchains, but also in the double form. Figs. V. and VI.—Staphylococci. Gram-positive (blue) cocci. V.a. In pus from a hordeolum. Clusters. V.6. Large Diplococci and tetrads, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bacteriology-of-the-eye-ative-red-diplococci-pseudo-gonococci-fromslight-cases-of-chronic-conjunctivitis-iiia-iiic-illd-micrococcuscatarrhalis-iiic-pure-culture-iii6-gram-negative-sarcinethe-diplococci-are-mostly-larger-but-some-are-similar-to-gonococci-fig-ivstreptococcal-conjunctivitis-from-a-case-of-pseudo-membranousconjunctivitis-gram-positive-blue-round-cocci-in-some-cases-showingchains-but-also-in-the-double-form-figs-v-and-vistaphylococci-gram-positive-blue-cocci-va-in-pus-from-a-hordeolum-clusters-v6-large-diplococci-and-tetrads-image370461062.htmlRM2CEKXT6–. The bacteriology of the eye. ative (red) Diplococci (Pseudo-gonococci) (fromslight cases of chronic conjunctivitis). III.a, III.c, Ill.d, MicrococcusCatarrhalis (III.c, pure culture) ; III.6, Gram negative Sarcin^e.The Diplococci are mostly larger, but some are similar to Gonococci. Fig. IV.—Streptococcal Conjunctivitis (from a case of pseudo-membranousconjunctivitis). Gram-positive (blue) round cocci, in some cases showingchains, but also in the double form. Figs. V. and VI.—Staphylococci. Gram-positive (blue) cocci. V.a. In pus from a hordeolum. Clusters. V.6. Large Diplococci and tetrads,
 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452216.html
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452216.htmlRFPCW3YM–Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics.
 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185736.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185736.htmlRFACM5XH–Gonorrhea
 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279048.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279048.htmlRM2AJ9XAG–Brucella
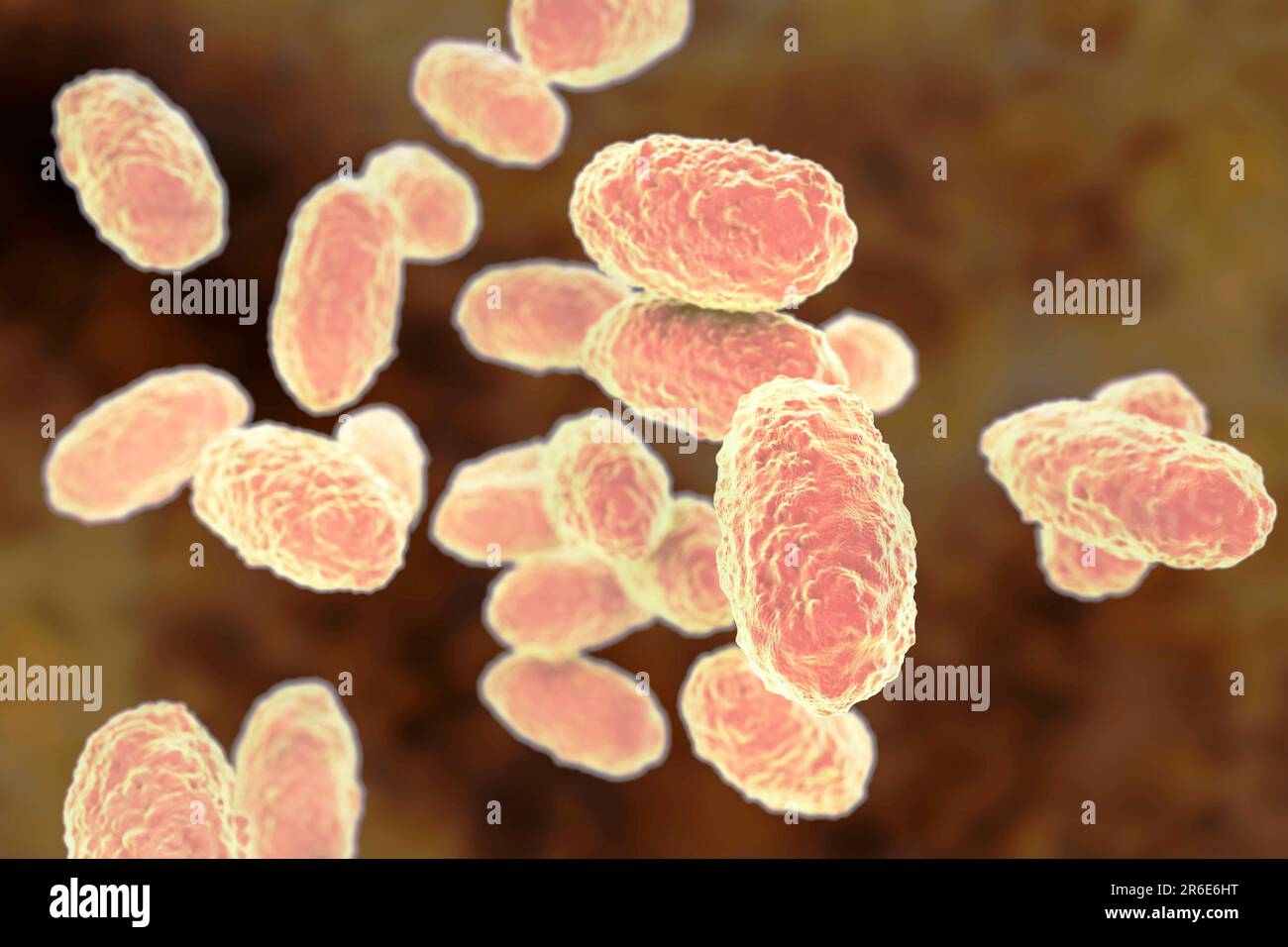 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732244.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732244.htmlRF2R6E6HT–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
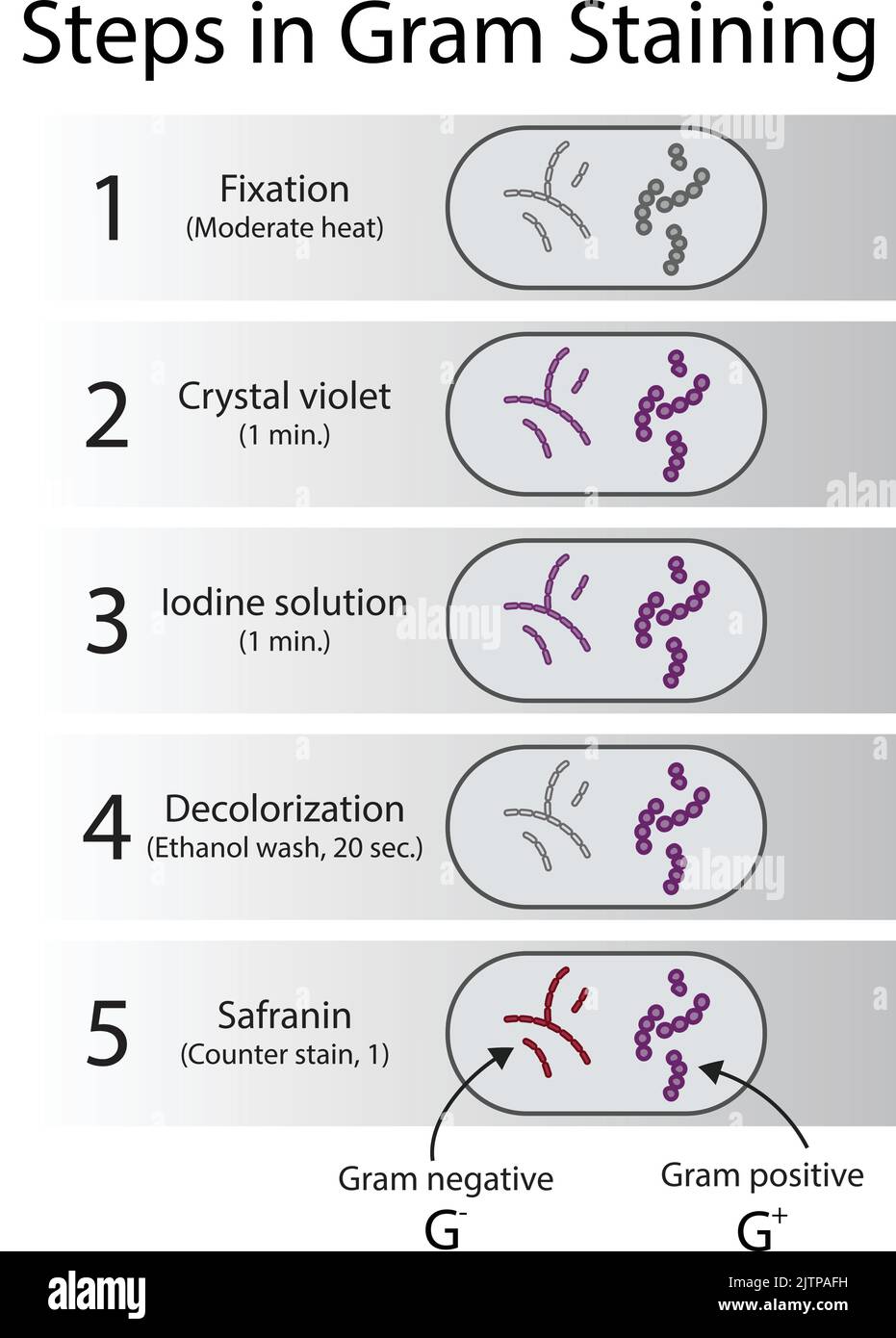 Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-showing-gram-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-microbiology-laboratory-using-crystal-violet-and-safranin-image479922901.html
Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-showing-gram-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-microbiology-laboratory-using-crystal-violet-and-safranin-image479922901.htmlRF2JTPAFH–Diagram showing gram staining microbiology lab technique steps - microbiology laboratory using Crystal violet and Safranin
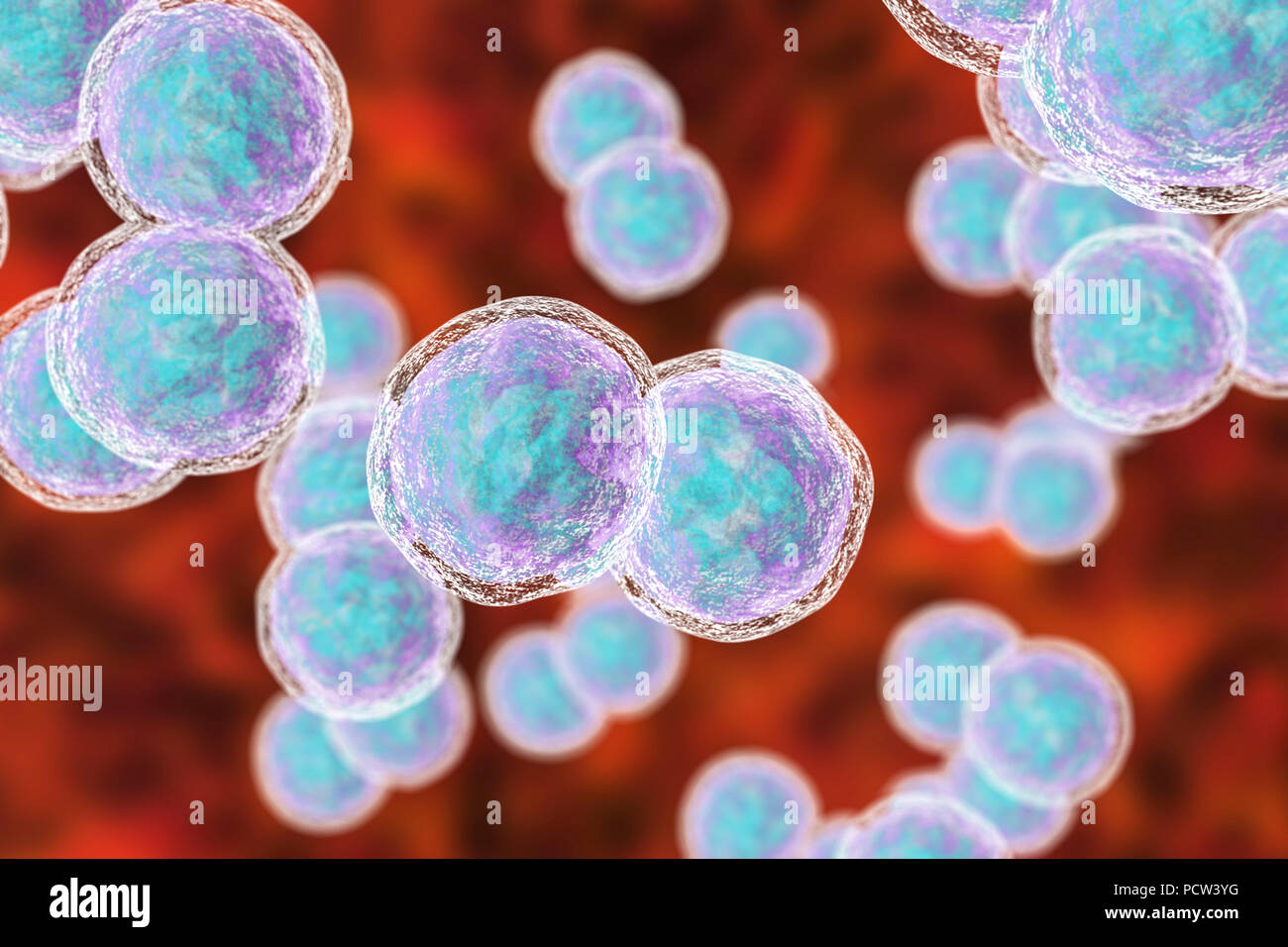 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452212.html
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452212.htmlRFPCW3YG–Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics.
 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13184899.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13184899.htmlRFACM3CM–Gonorrhea
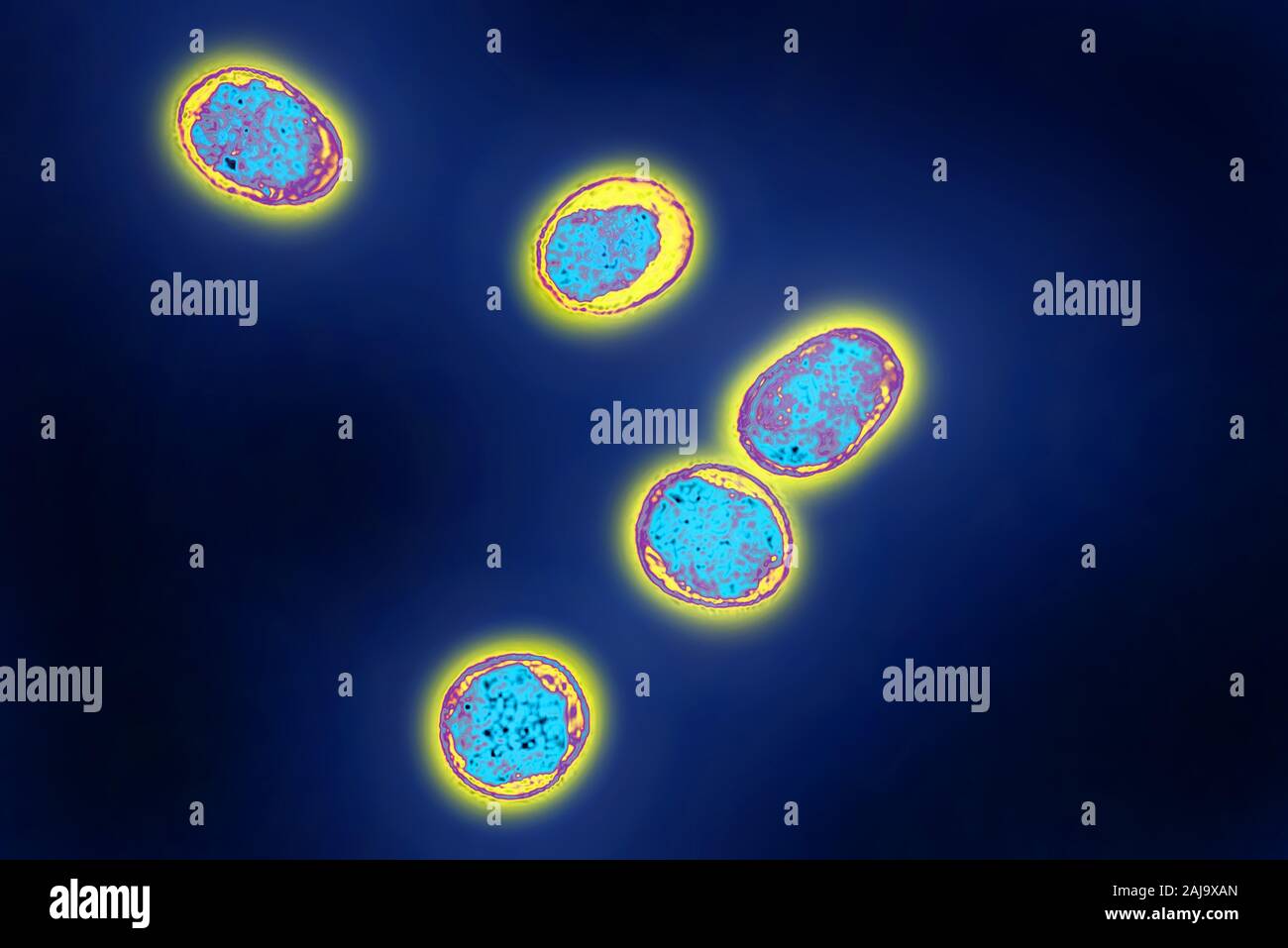 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279053.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279053.htmlRM2AJ9XAN–Brucella
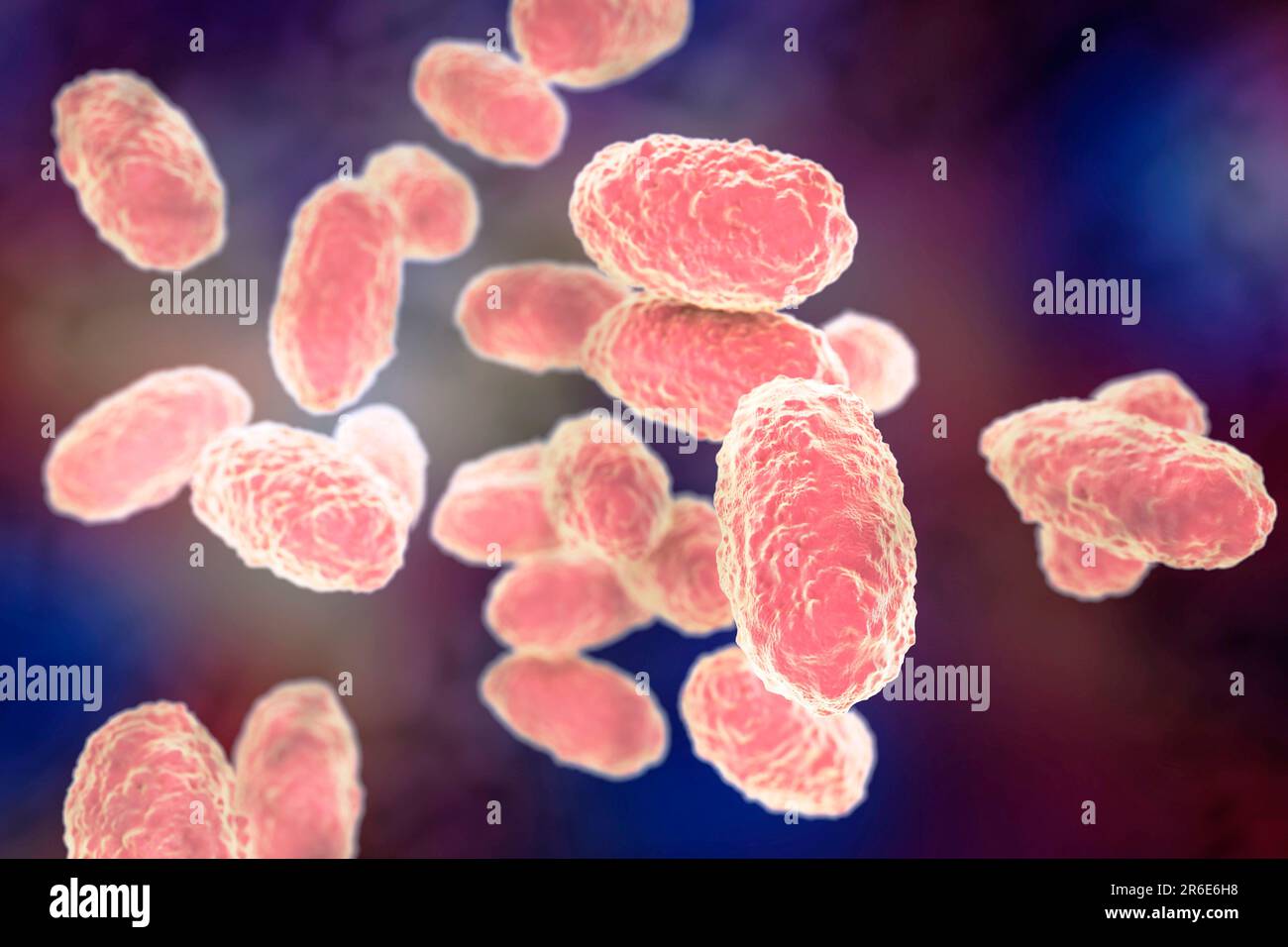 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732228.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732228.htmlRF2R6E6H8–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
 Diagram of microorganism optimal temperature range - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile growth rates with example bacteria. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-optimal-temperature-range-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-growth-rates-with-example-bacteria-image479922825.html
Diagram of microorganism optimal temperature range - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile growth rates with example bacteria. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-optimal-temperature-range-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-growth-rates-with-example-bacteria-image479922825.htmlRF2JTPACW–Diagram of microorganism optimal temperature range - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile growth rates with example bacteria.
 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452210.html
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452210.htmlRFPCW3YE–Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics.
 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185611.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185611.htmlRFACM5FT–Gonorrhea
 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279075.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279075.htmlRM2AJ9XBF–Brucella
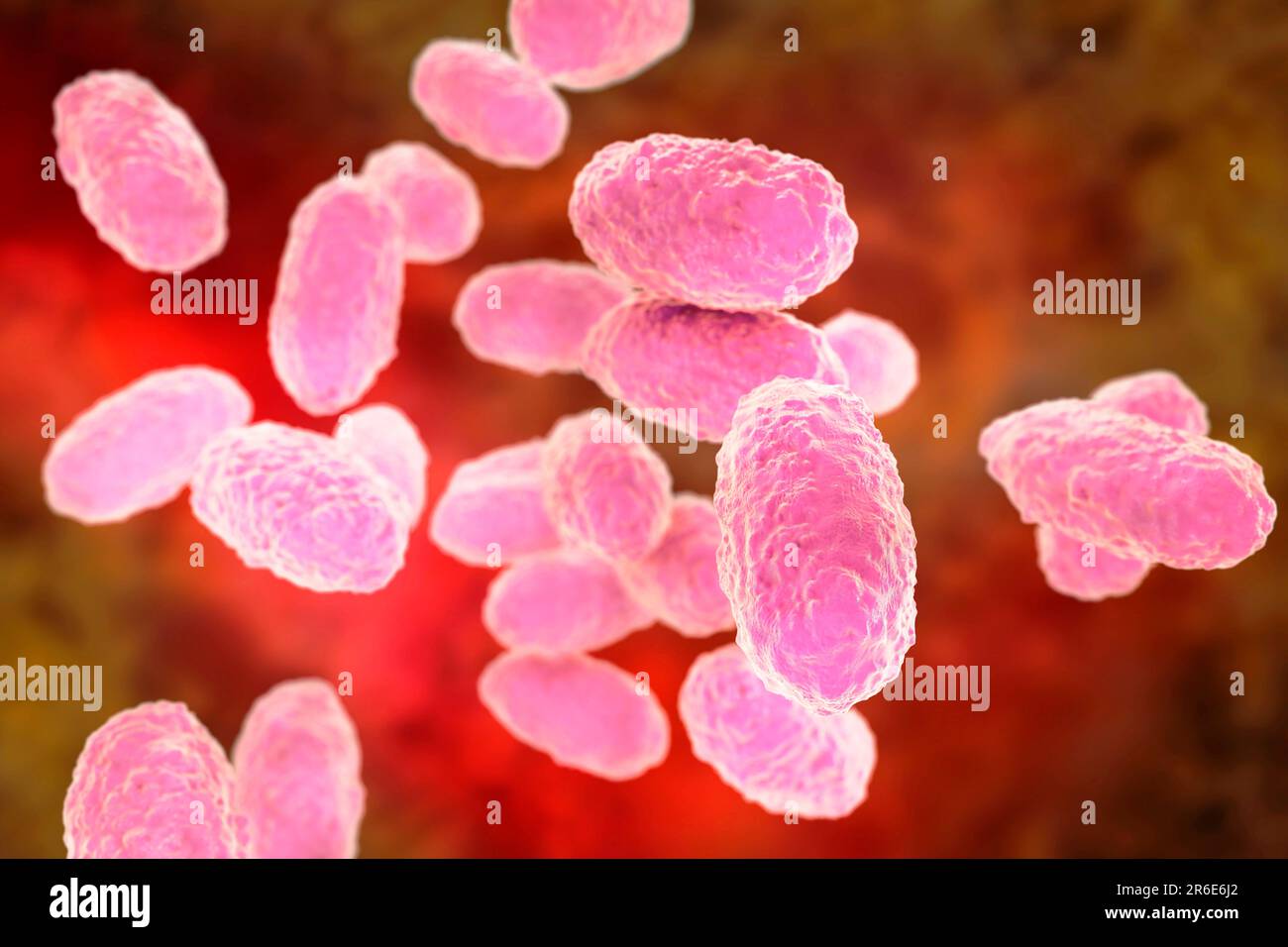 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732250.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732250.htmlRF2R6E6J2–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
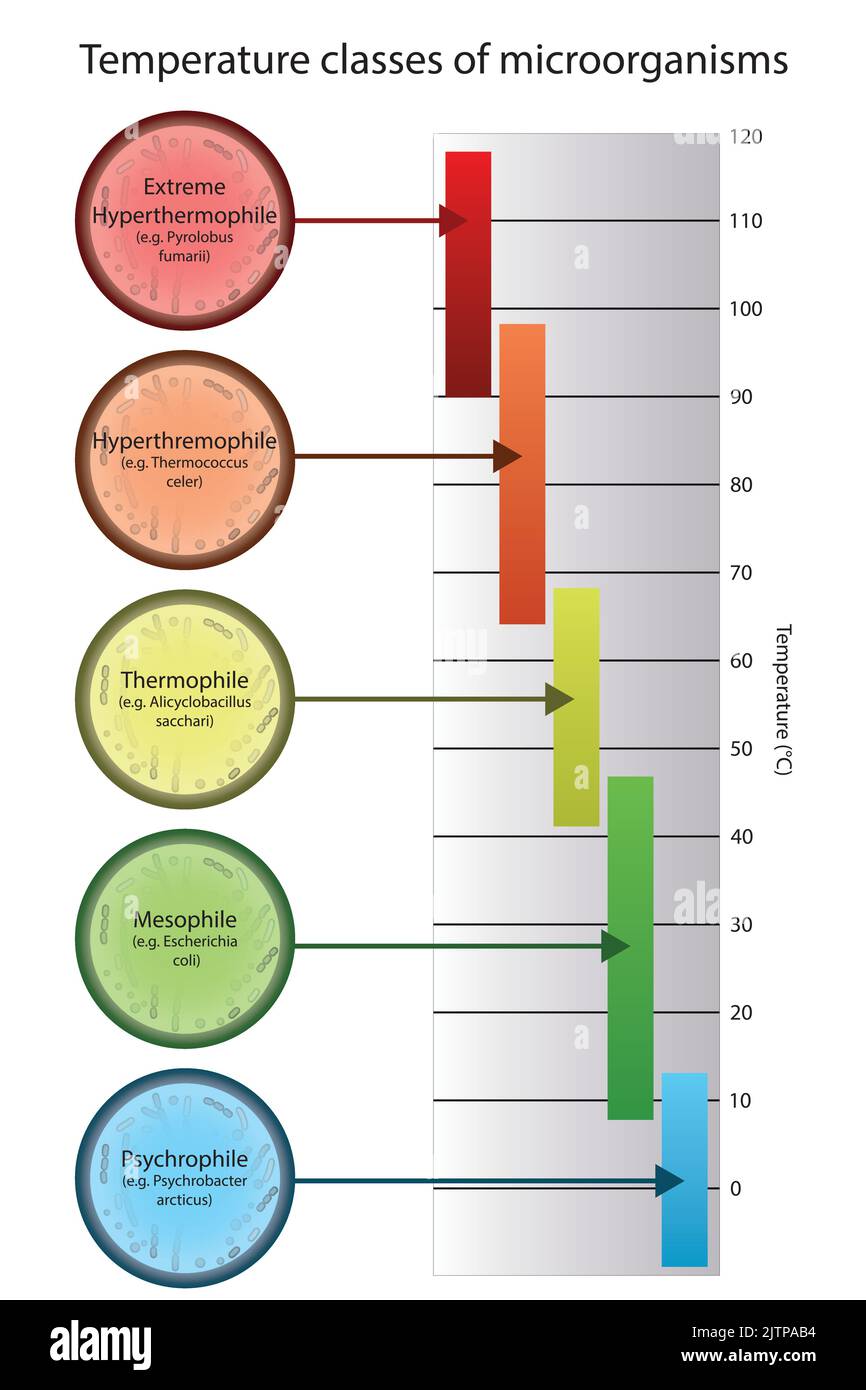 Diagram of microorganism classification by optimal growth temperature - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile with examples Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-classification-by-optimal-growth-temperature-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-with-examples-image479922776.html
Diagram of microorganism classification by optimal growth temperature - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile with examples Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-classification-by-optimal-growth-temperature-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-with-examples-image479922776.htmlRF2JTPAB4–Diagram of microorganism classification by optimal growth temperature - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile with examples
 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452211.html
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452211.htmlRFPCW3YF–Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics.
 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185397.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185397.htmlRFACM4WX–Gonorrhea
 Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279047.html
Brucella Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brucella-image338279047.htmlRM2AJ9XAF–Brucella
 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732135.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732135.htmlRF2R6E6DY–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
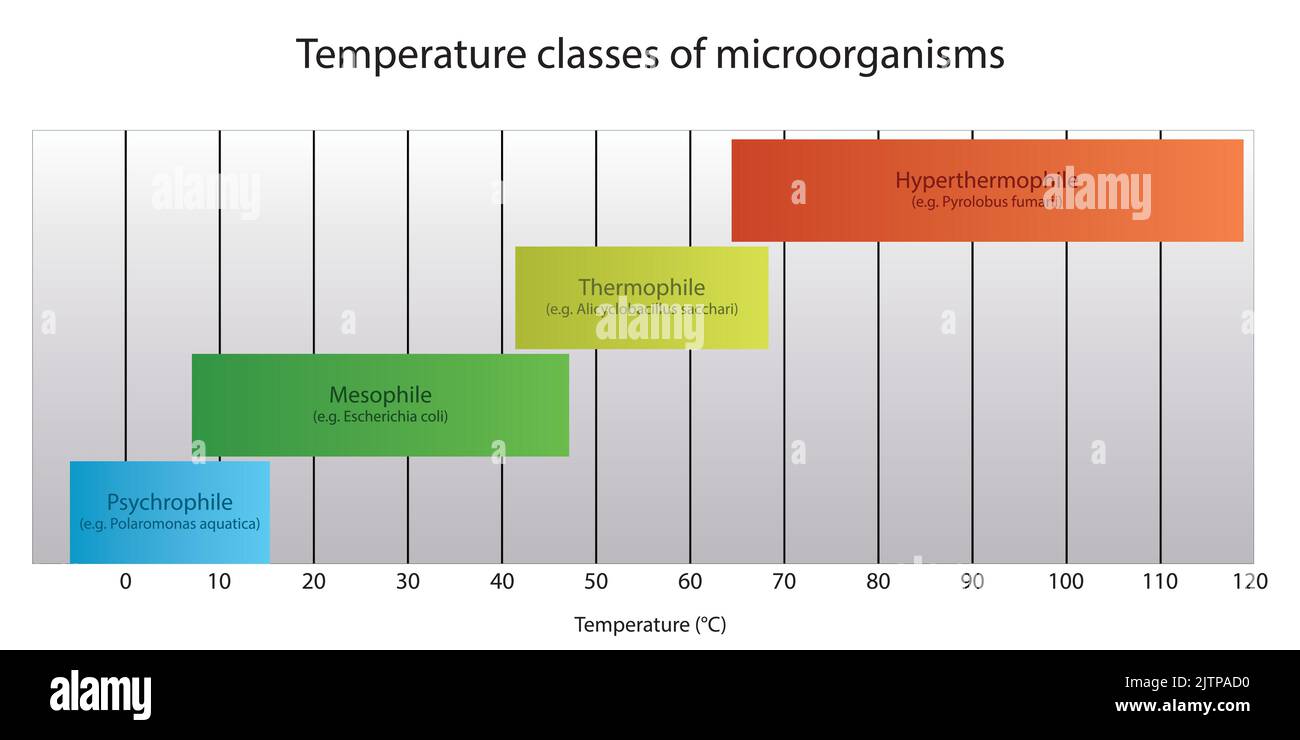 Diagram of microorganism classification by optimal growth temperature - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile with examples Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-classification-by-optimal-growth-temperature-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-with-examples-image479922828.html
Diagram of microorganism classification by optimal growth temperature - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile with examples Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-classification-by-optimal-growth-temperature-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-with-examples-image479922828.htmlRF2JTPAD0–Diagram of microorganism classification by optimal growth temperature - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile with examples
 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197206.html
NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197206.htmlRMK8HH4P–NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS
 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452217.html
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moraxella-branhamella-catarrhalis-bacteria-computer-illustration-these-are-aerobic-gram-negative-cocci-spherical-bacteria-which-are-commonly-found-in-the-mucous-membranes-of-the-respiratory-tract-of-mammals-including-humans-in-immunosuppressed-individuals-or-opportunistically-they-may-cause-respiratory-tract-infections-these-include-sinusitis-an-inflammation-of-the-sinus-membranes-this-may-also-lead-to-otitis-media-an-infection-of-the-middle-ear-treatment-is-with-antibiotics-image214452217.htmlRFPCW3YN–Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis bacteria, computer illustration. These are aerobic, Gram-negative cocci (spherical bacteria) which are commonly found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. In immunosuppressed individuals, or opportunistically, they may cause respiratory tract infections. These include sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus membranes. This may also lead to otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Treatment is with antibiotics.
 Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521058.html
Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521058.htmlRFHX3202–Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets.
 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13184442.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13184442.htmlRFACM22K–Gonorrhea
 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732265.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732265.htmlRF2R6E6JH–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
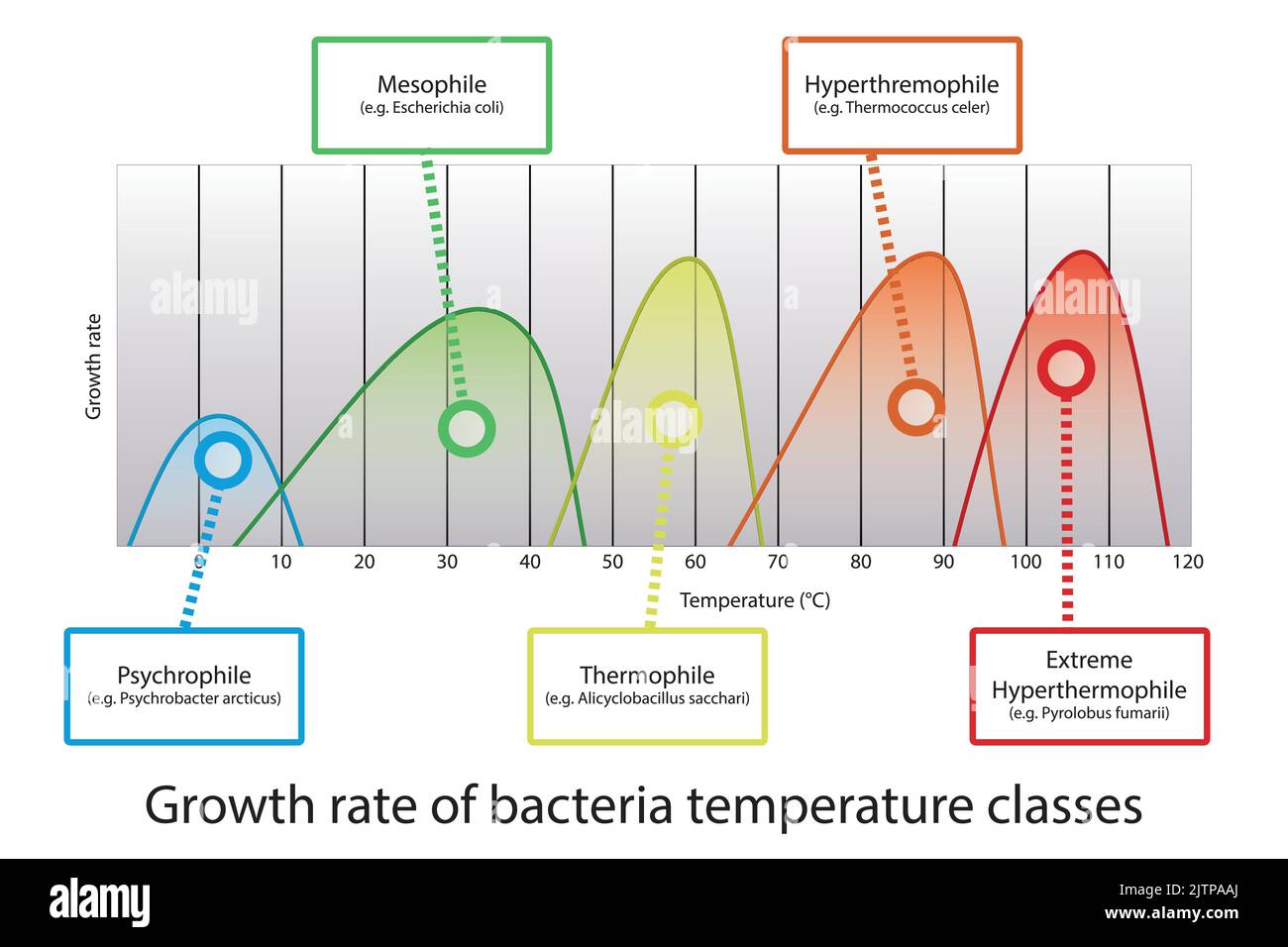 Diagram of microorganism optimal temperature range - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile growth rates with example bacteria. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-optimal-temperature-range-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-growth-rates-with-example-bacteria-image479922762.html
Diagram of microorganism optimal temperature range - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile growth rates with example bacteria. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-microorganism-optimal-temperature-range-psychrophile-mesophile-thremophile-and-hyperthermophile-growth-rates-with-example-bacteria-image479922762.htmlRF2JTPAAJ–Diagram of microorganism optimal temperature range - Psychrophile, Mesophile, Thremophile and Hyperthermophile growth rates with example bacteria.
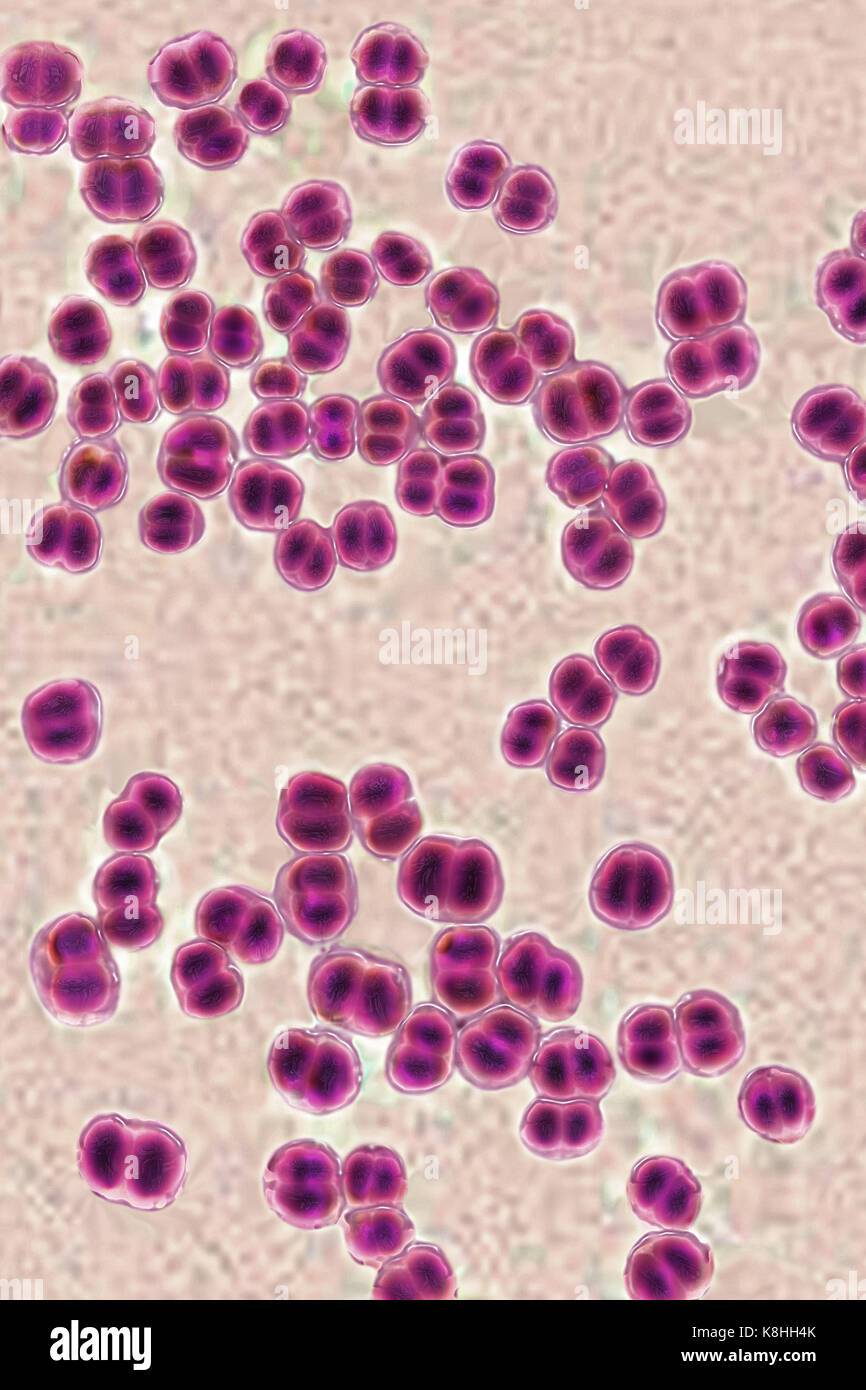 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197203.html
NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197203.htmlRMK8HH4K–NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS
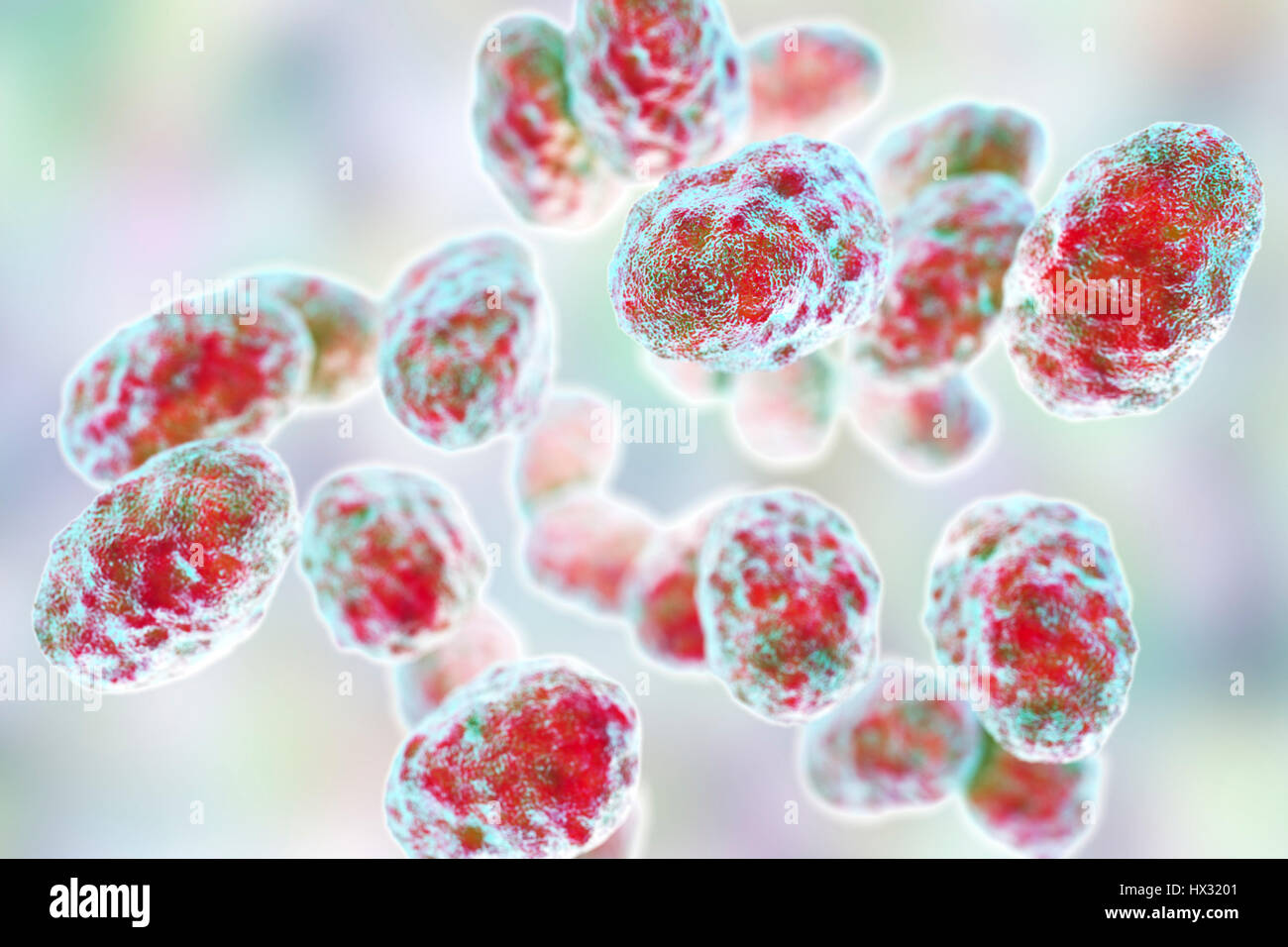 Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521057.html
Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521057.htmlRFHX3201–Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets.
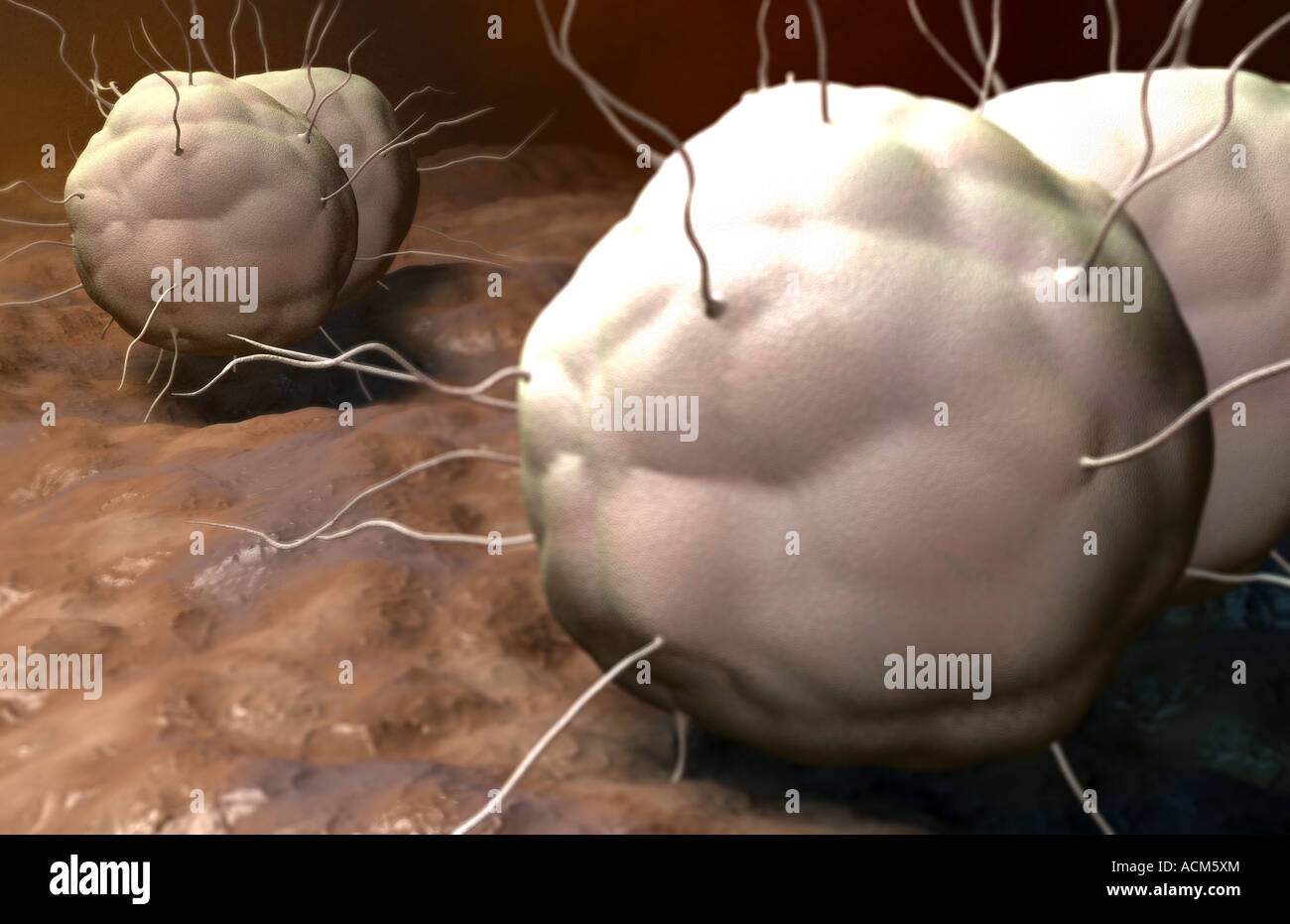 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185739.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185739.htmlRFACM5XM–Gonorrhea
 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732159.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732159.htmlRF2R6E6ER–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
RF2JTPAAA–Set of 3 petri dish icons. Colorful simple illustration with bacterial cells.
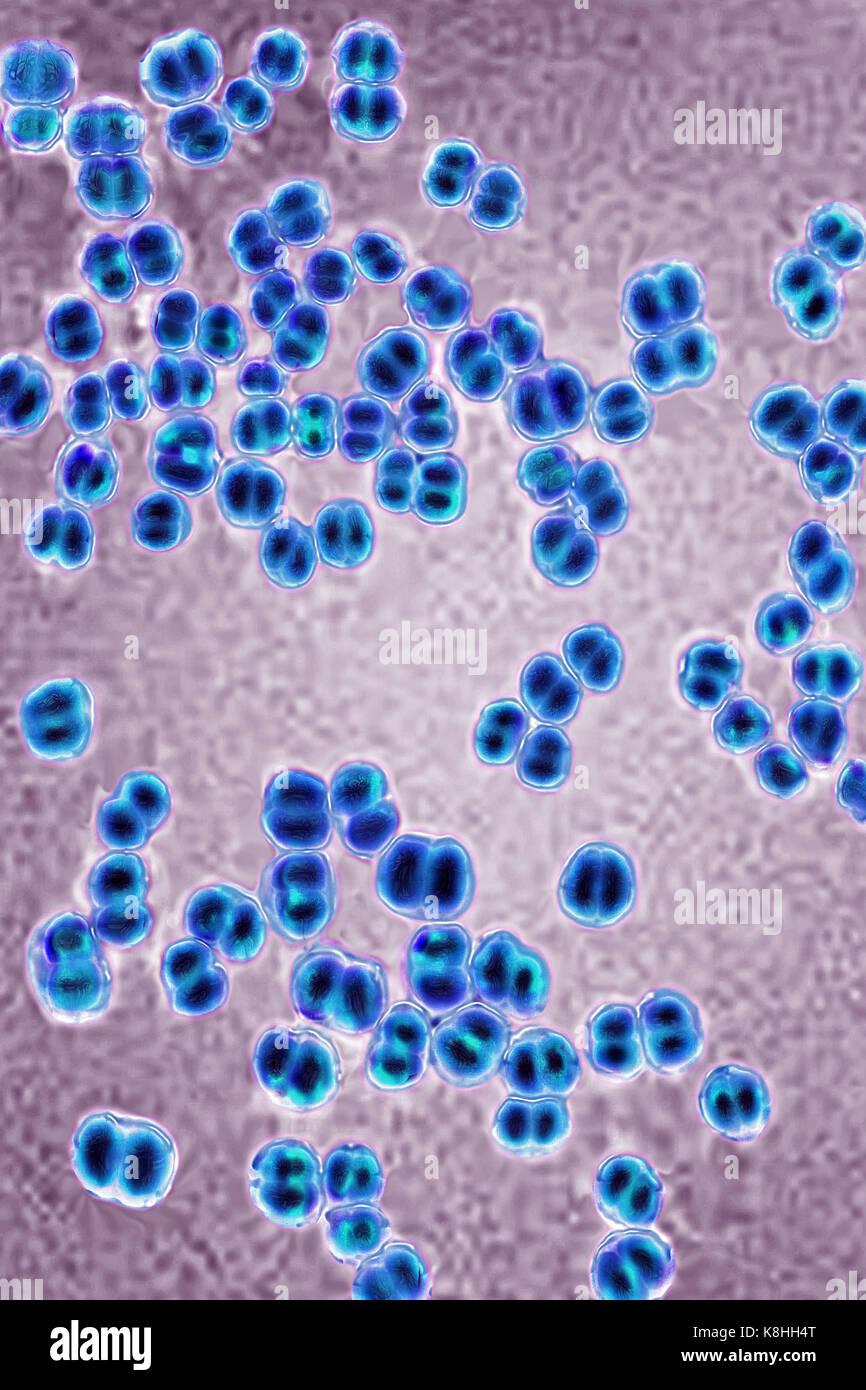 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197208.html
NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197208.htmlRMK8HH4T–NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS
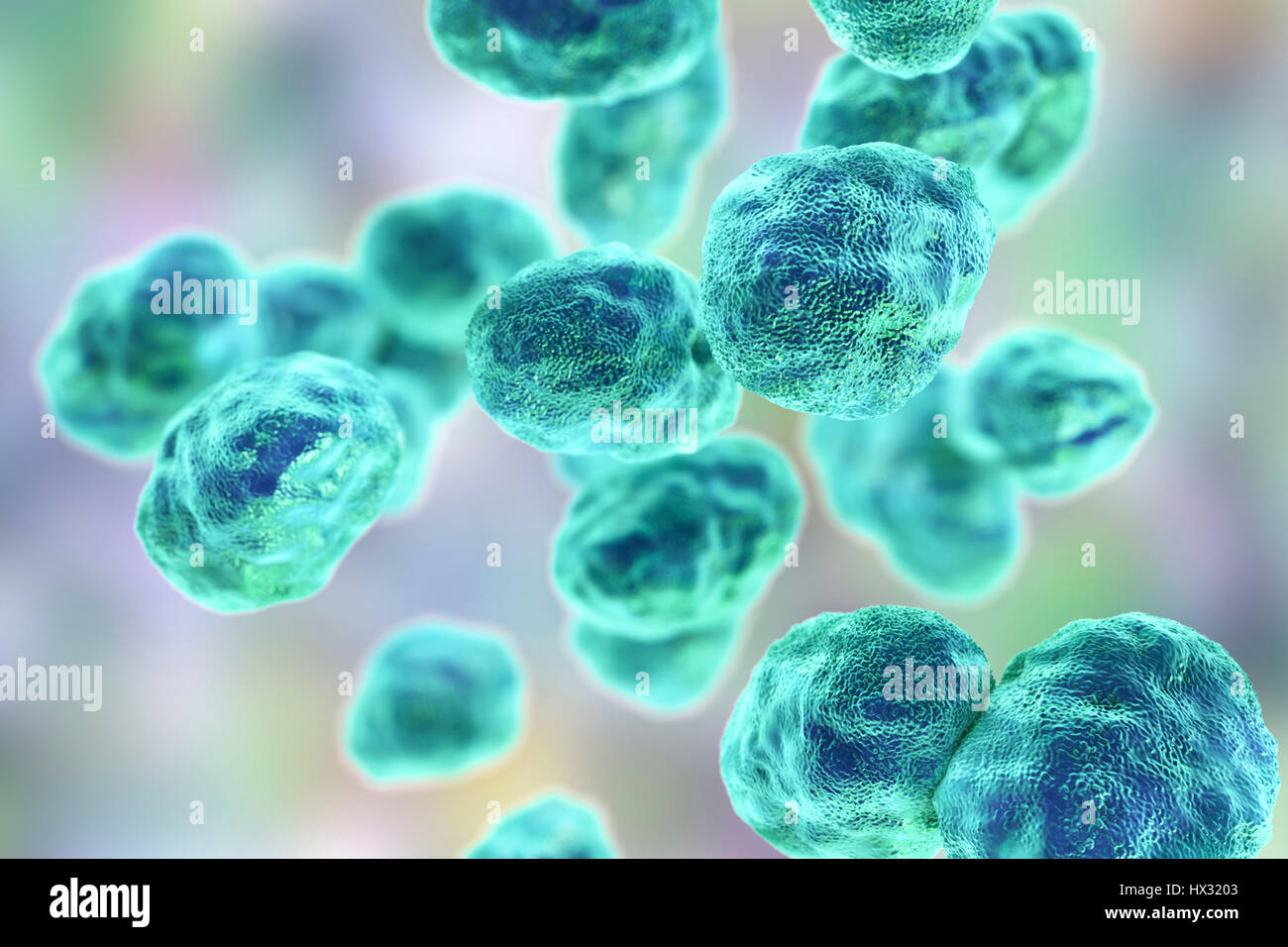 Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521059.html
Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521059.htmlRFHX3203–Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets.
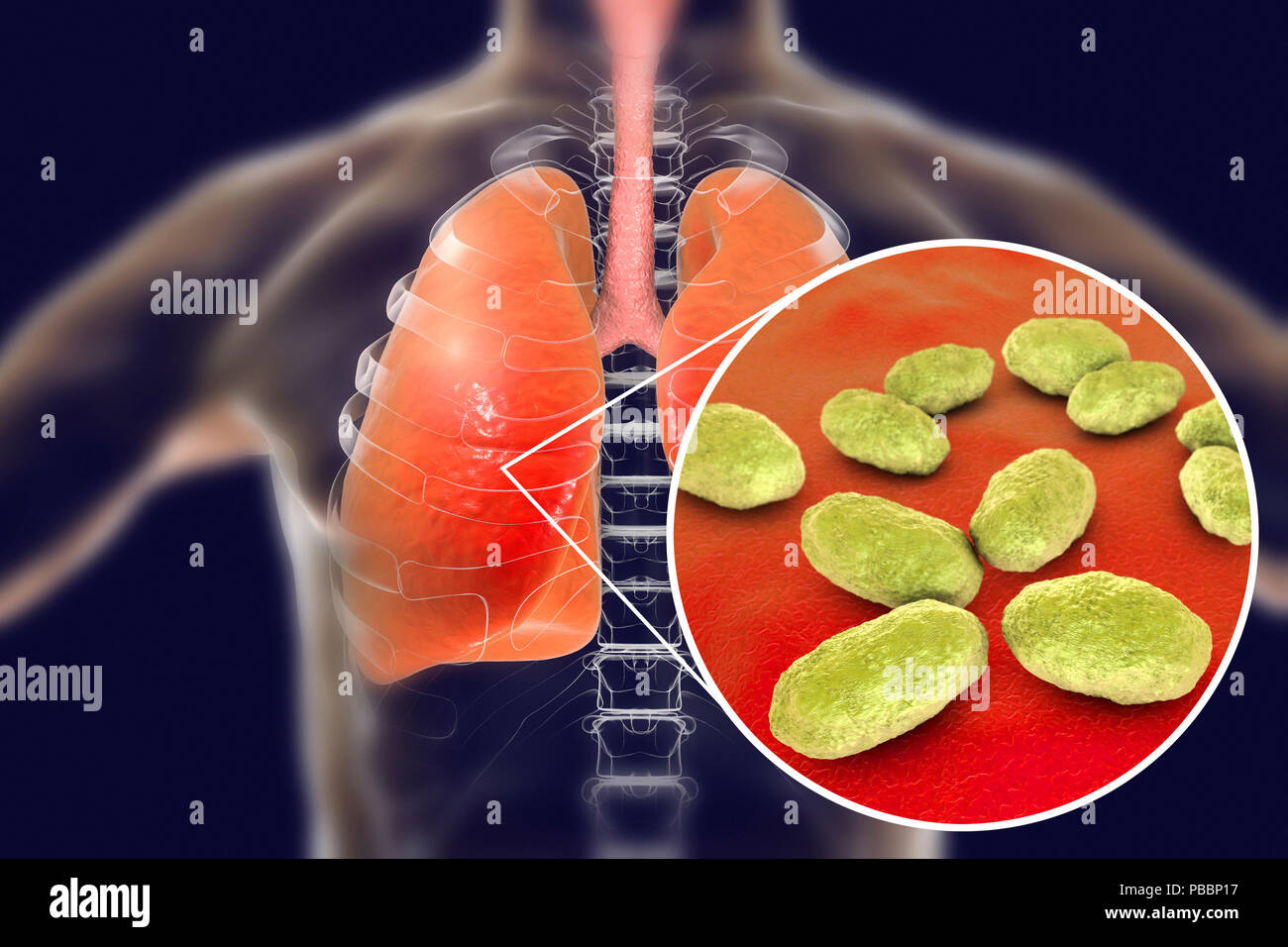 Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-haemophilus-influenzae-bacteria-computer-illustration-h-influenzae-are-coccobacillus-gram-negative-bacteria-these-bacteria-cause-a-number-of-diseases-including-meningitis-in-children-pneumonia-epiglottitis-laryngitis-conjunctivitis-neonatal-infection-otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-and-sinusitis-in-adults-h-influenzae-harmlessly-colonize-the-upper-respiratory-tract-in-most-humans-within-the-first-few-months-of-life-encapsulated-strains-spread-to-cause-diseases-such-as-bronchitis-and-pneumonia-image213544387.html
Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-haemophilus-influenzae-bacteria-computer-illustration-h-influenzae-are-coccobacillus-gram-negative-bacteria-these-bacteria-cause-a-number-of-diseases-including-meningitis-in-children-pneumonia-epiglottitis-laryngitis-conjunctivitis-neonatal-infection-otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-and-sinusitis-in-adults-h-influenzae-harmlessly-colonize-the-upper-respiratory-tract-in-most-humans-within-the-first-few-months-of-life-encapsulated-strains-spread-to-cause-diseases-such-as-bronchitis-and-pneumonia-image213544387.htmlRFPBBP17–Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185382.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185382.htmlRFACM4TR–Gonorrhea
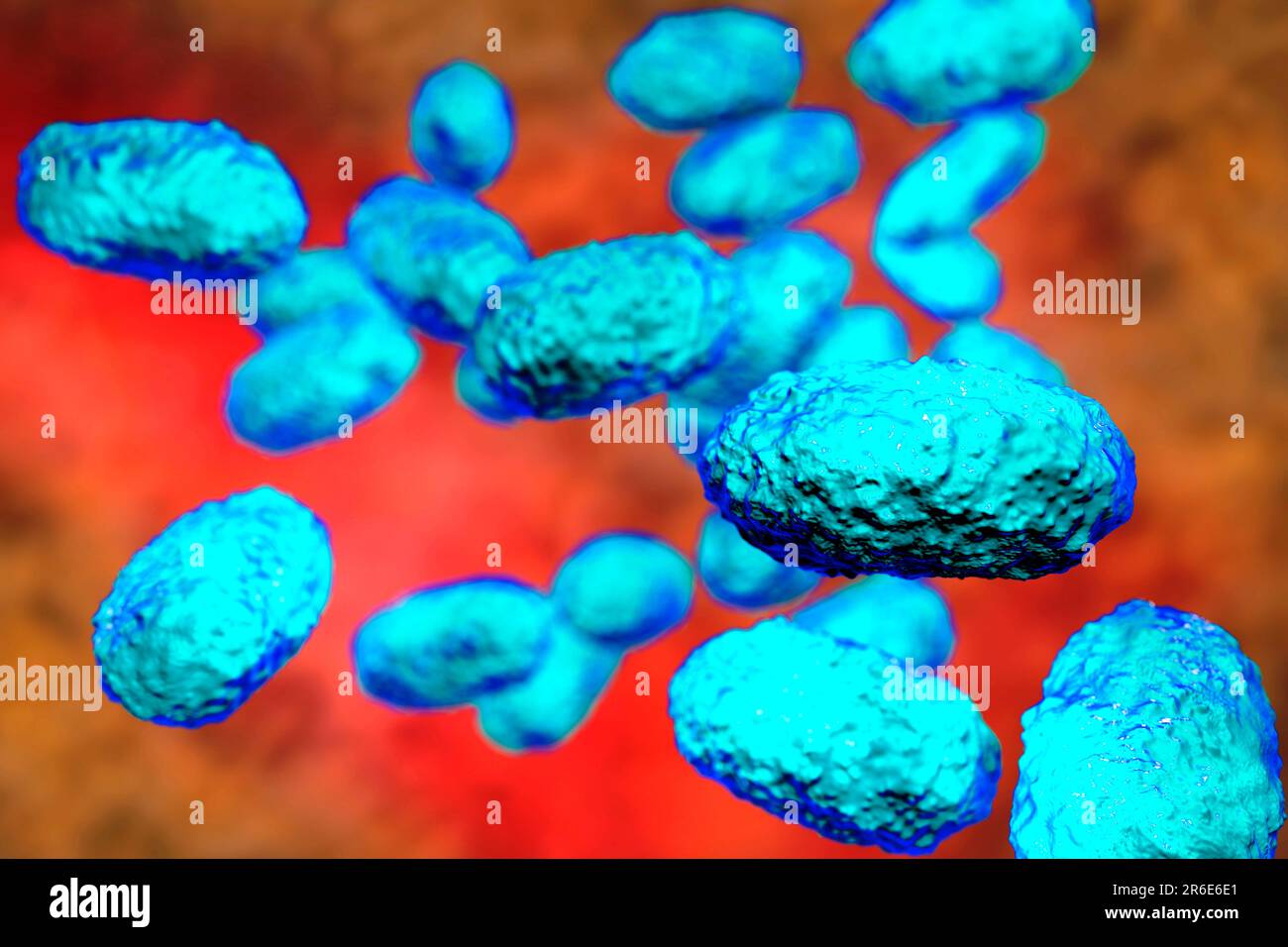 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732137.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732137.htmlRF2R6E6E1–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
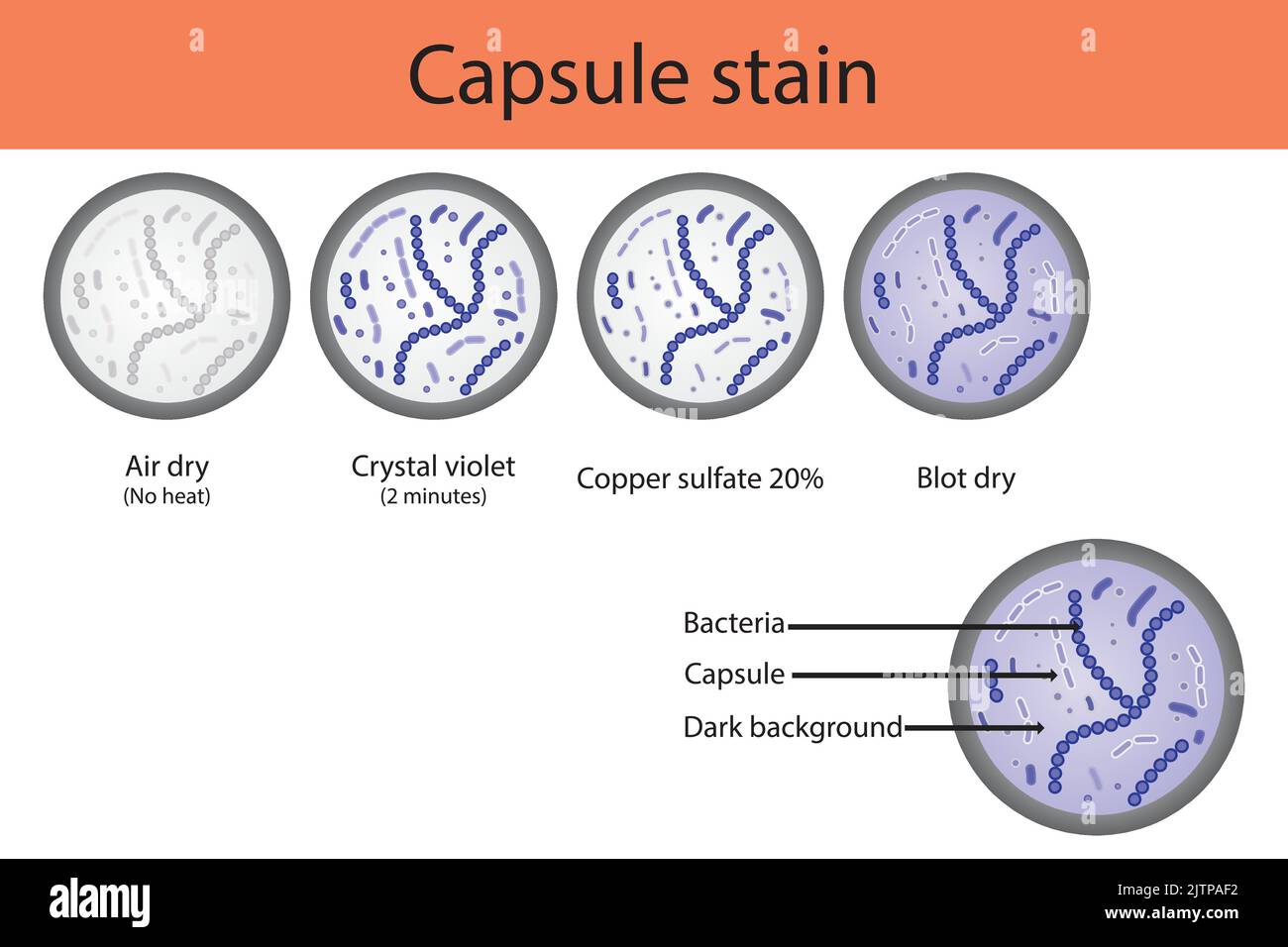 Capsule staining microbiology lab technique steps diagram, using Crystal violet and copper sulfate vector illustration eps10 Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/capsule-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-diagram-using-crystal-violet-and-copper-sulfate-vector-illustration-eps10-image479922886.html
Capsule staining microbiology lab technique steps diagram, using Crystal violet and copper sulfate vector illustration eps10 Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/capsule-staining-microbiology-lab-technique-steps-diagram-using-crystal-violet-and-copper-sulfate-vector-illustration-eps10-image479922886.htmlRF2JTPAF2–Capsule staining microbiology lab technique steps diagram, using Crystal violet and copper sulfate vector illustration eps10
 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197210.html
NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-neisseria-meningitidis-160197210.htmlRMK8HH4X–NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS
 Neisseria meningitidis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-meningitidis-image69119179.html
Neisseria meningitidis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-meningitidis-image69119179.htmlRME0CJ63–Neisseria meningitidis
 Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-haemophilus-influenzae-bacteria-computer-illustration-h-influenzae-are-coccobacillus-gram-negative-bacteria-these-bacteria-cause-a-number-of-diseases-including-meningitis-in-children-pneumonia-epiglottitis-laryngitis-conjunctivitis-neonatal-infection-otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-and-sinusitis-in-adults-h-influenzae-harmlessly-colonize-the-upper-respiratory-tract-in-most-humans-within-the-first-few-months-of-life-encapsulated-strains-spread-to-cause-diseases-such-as-bronchitis-and-pneumonia-image213544381.html
Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-haemophilus-influenzae-bacteria-computer-illustration-h-influenzae-are-coccobacillus-gram-negative-bacteria-these-bacteria-cause-a-number-of-diseases-including-meningitis-in-children-pneumonia-epiglottitis-laryngitis-conjunctivitis-neonatal-infection-otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-and-sinusitis-in-adults-h-influenzae-harmlessly-colonize-the-upper-respiratory-tract-in-most-humans-within-the-first-few-months-of-life-encapsulated-strains-spread-to-cause-diseases-such-as-bronchitis-and-pneumonia-image213544381.htmlRFPBBP11–Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
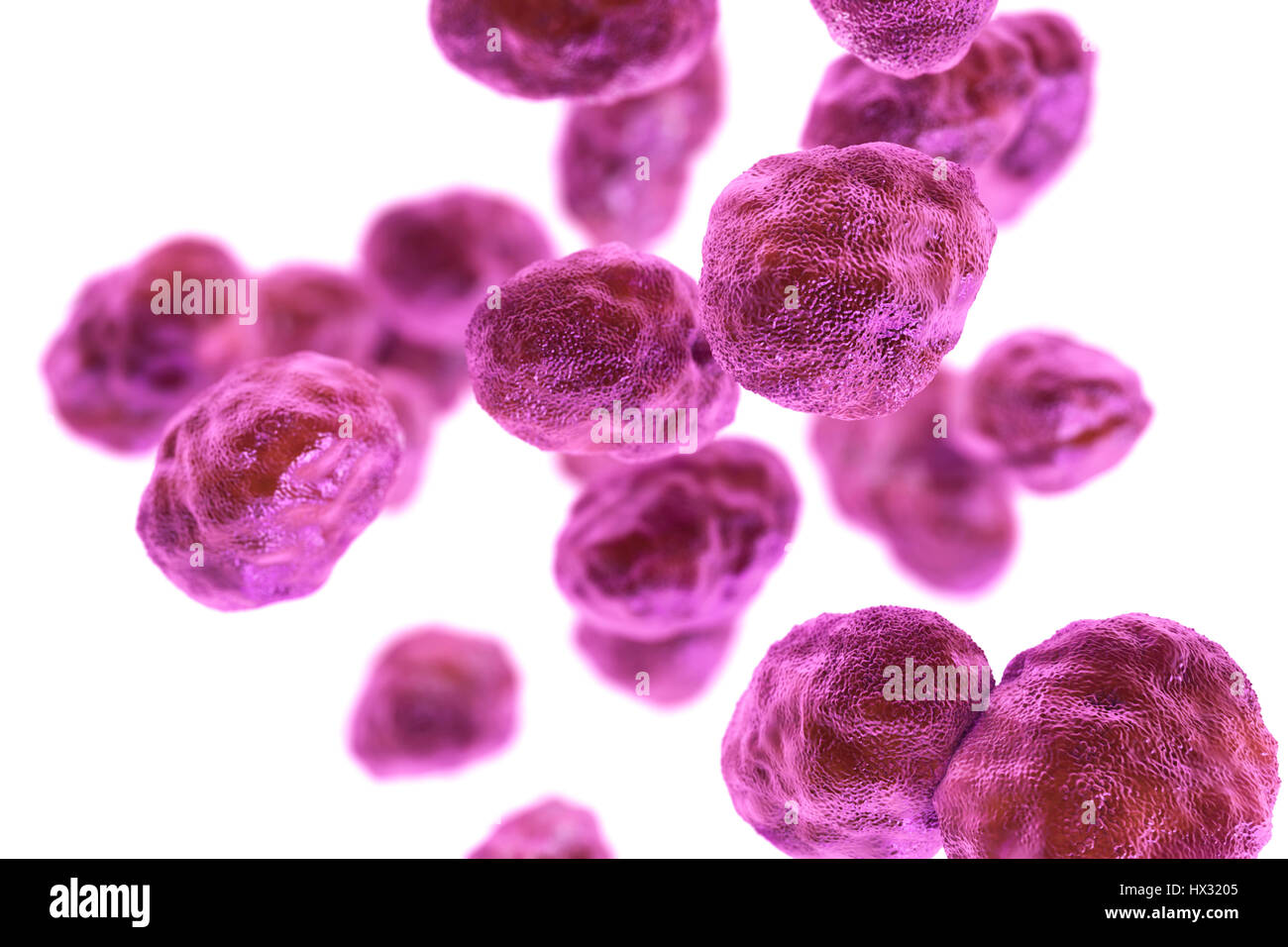 Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521061.html
Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521061.htmlRFHX3205–Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets.
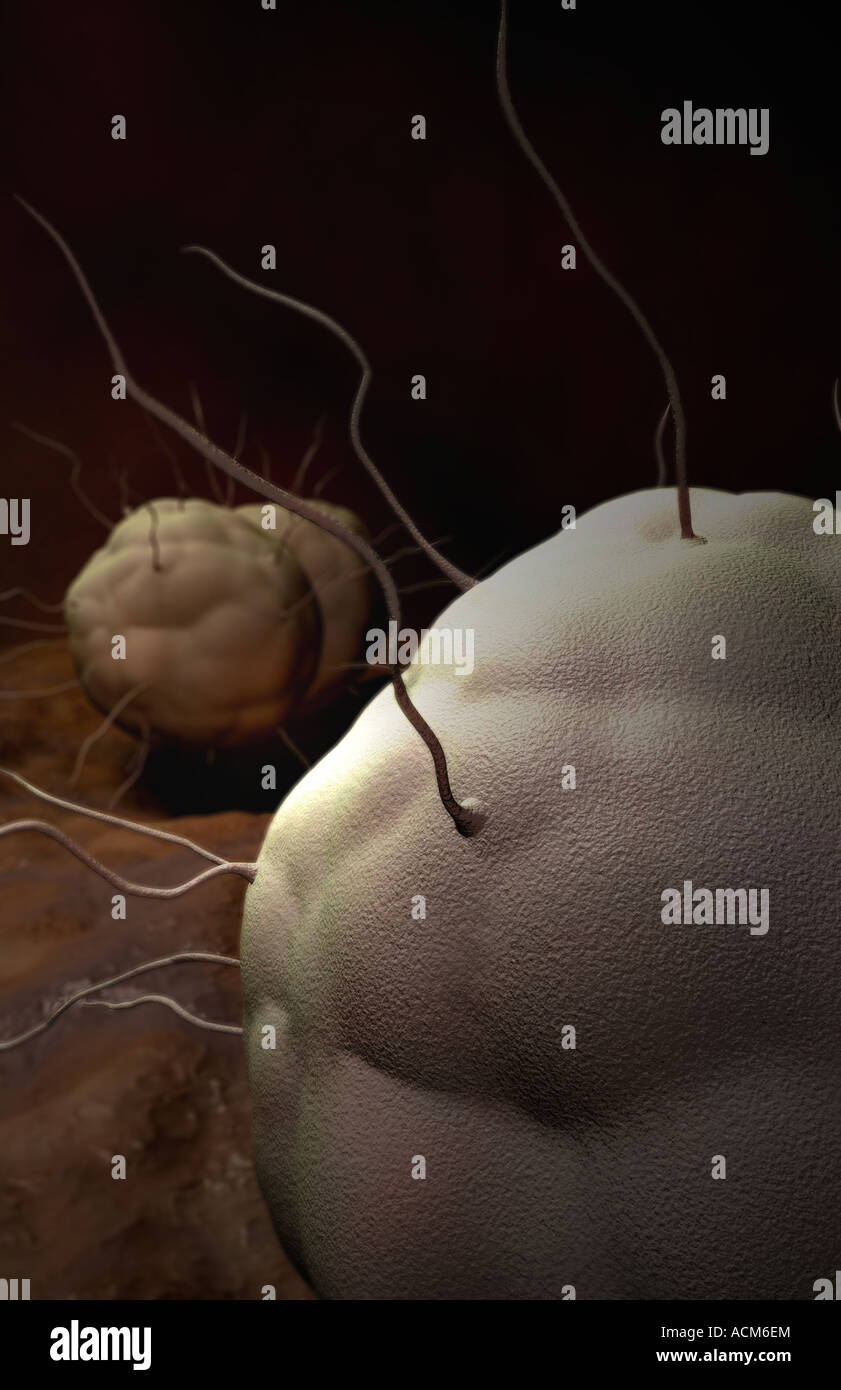 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185931.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13185931.htmlRFACM6EM–Gonorrhea
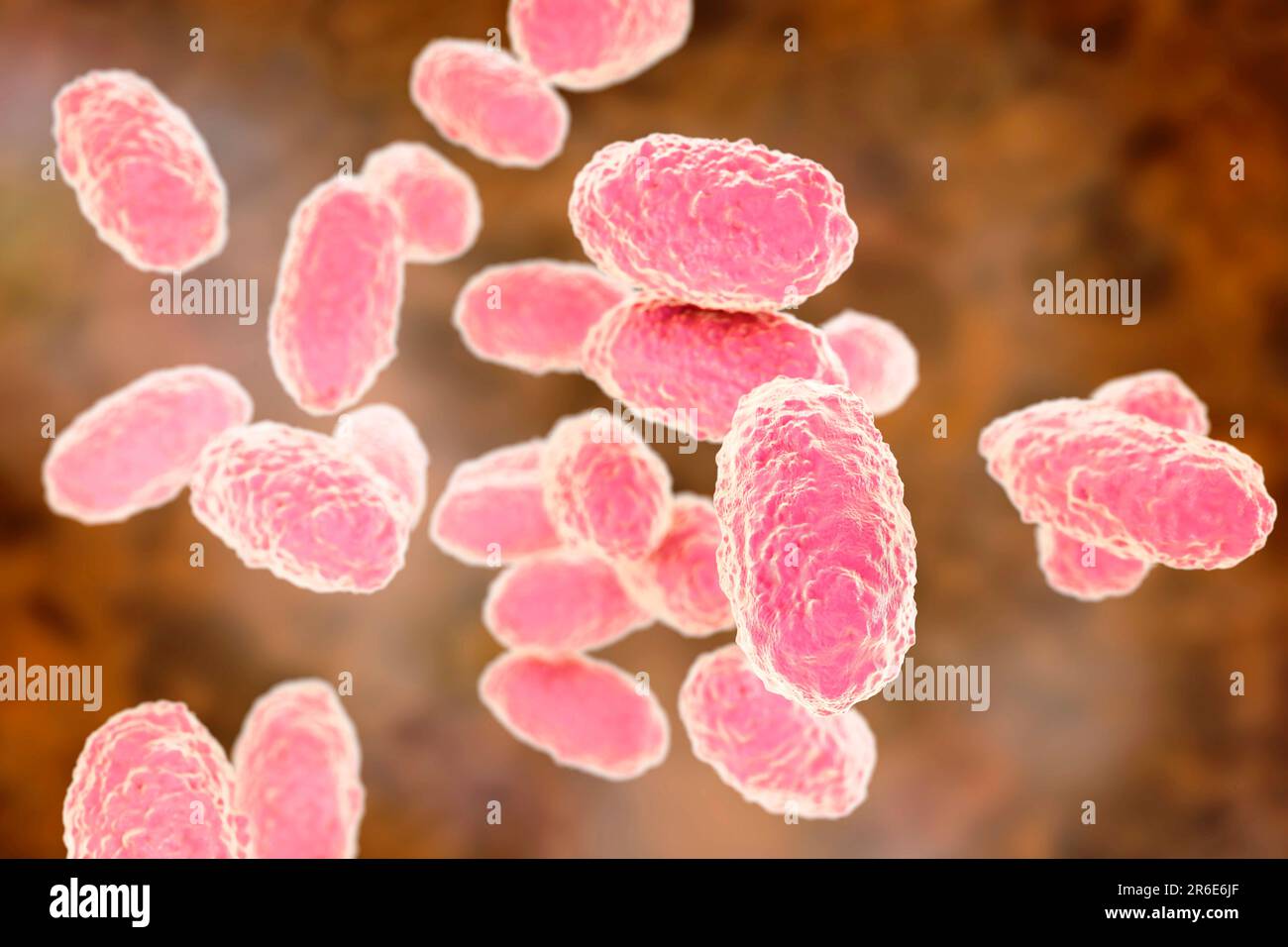 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732263.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732263.htmlRF2R6E6JF–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
RF2JTPAFM–Set of 3 petri dish icons. Colorful simple illustration with bacterial cells.
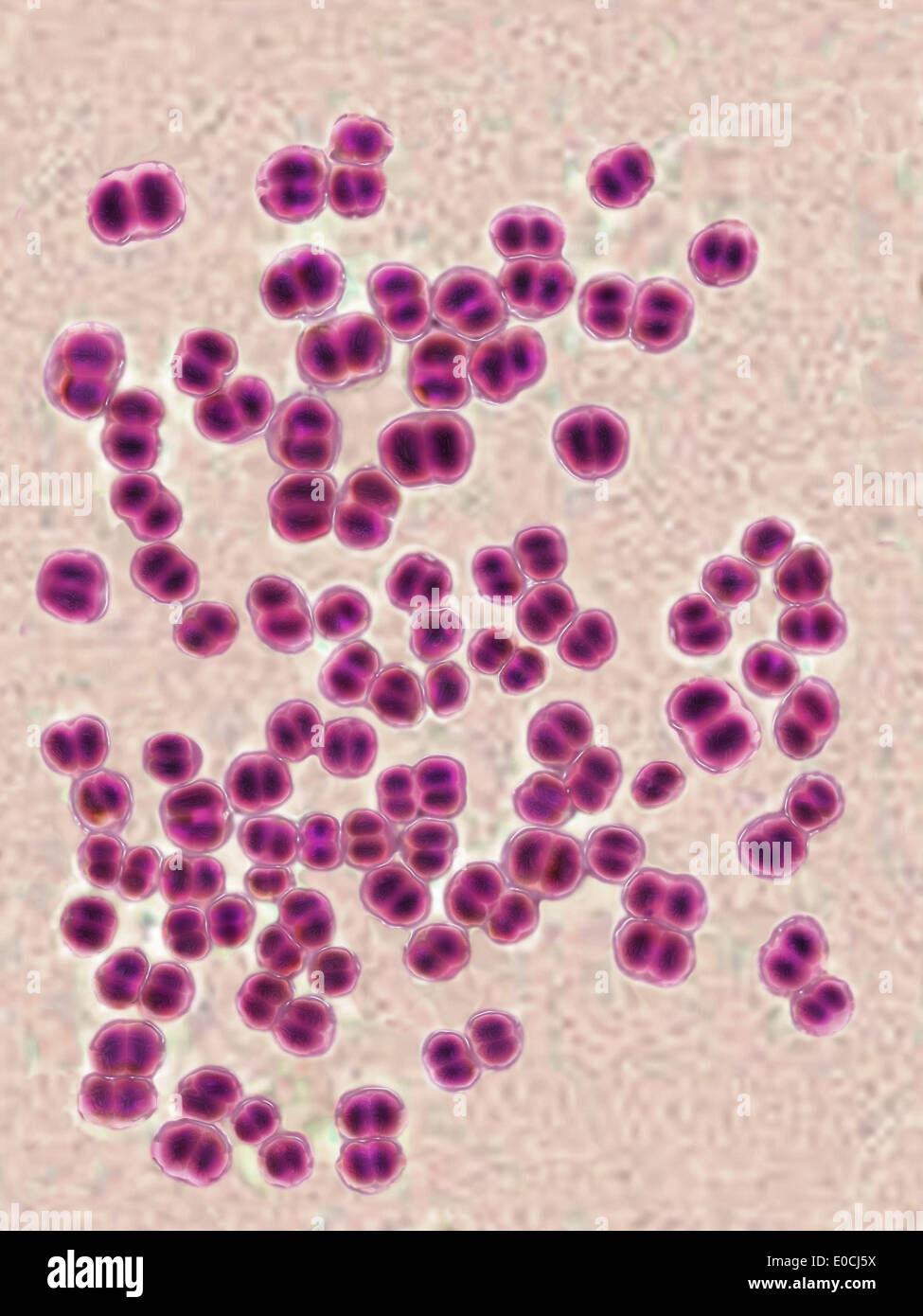 Neisseria meningitidis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-meningitidis-image69119174.html
Neisseria meningitidis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-meningitidis-image69119174.htmlRME0CJ5X–Neisseria meningitidis
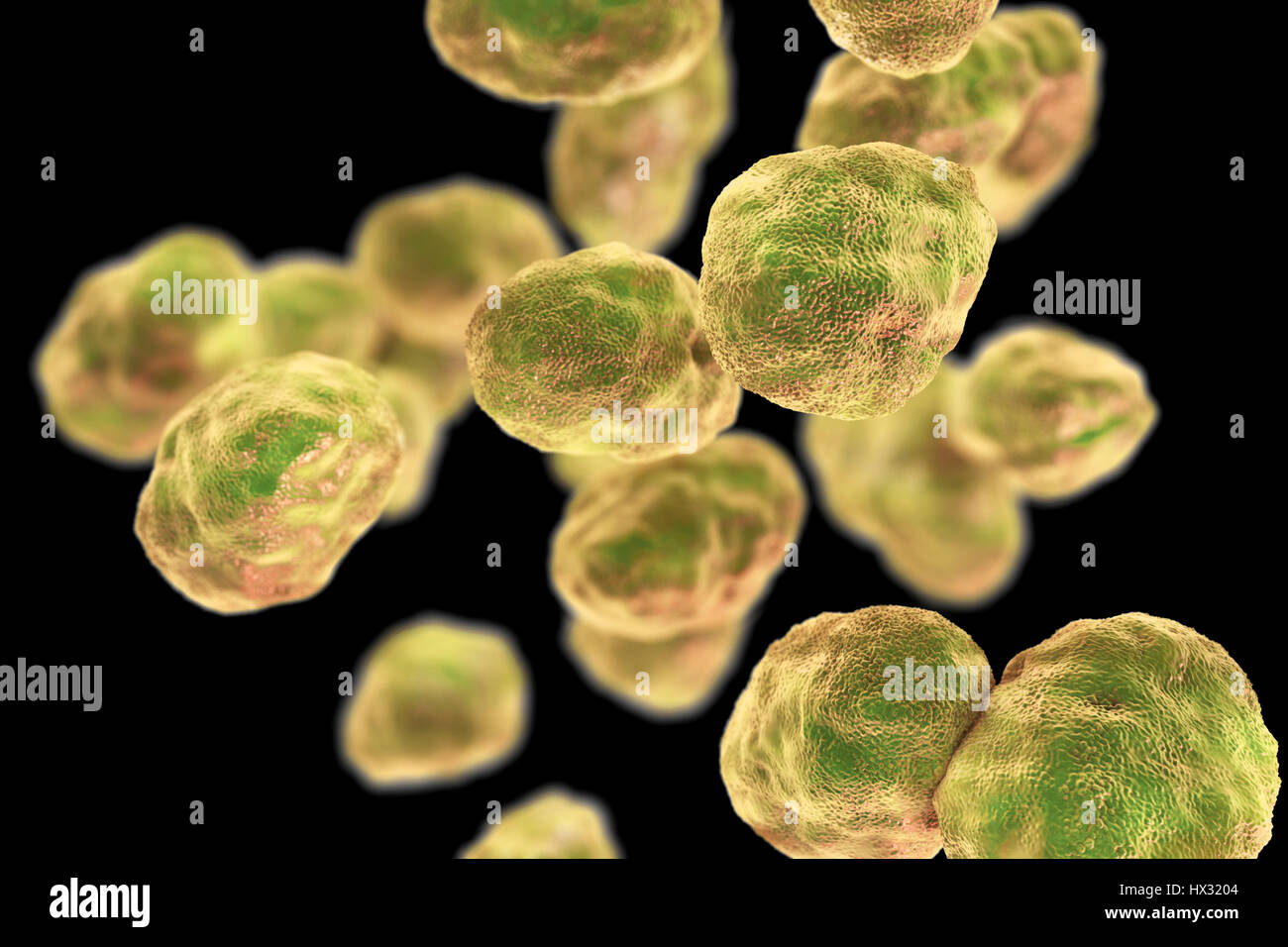 Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521060.html
Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521060.htmlRFHX3204–Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets.
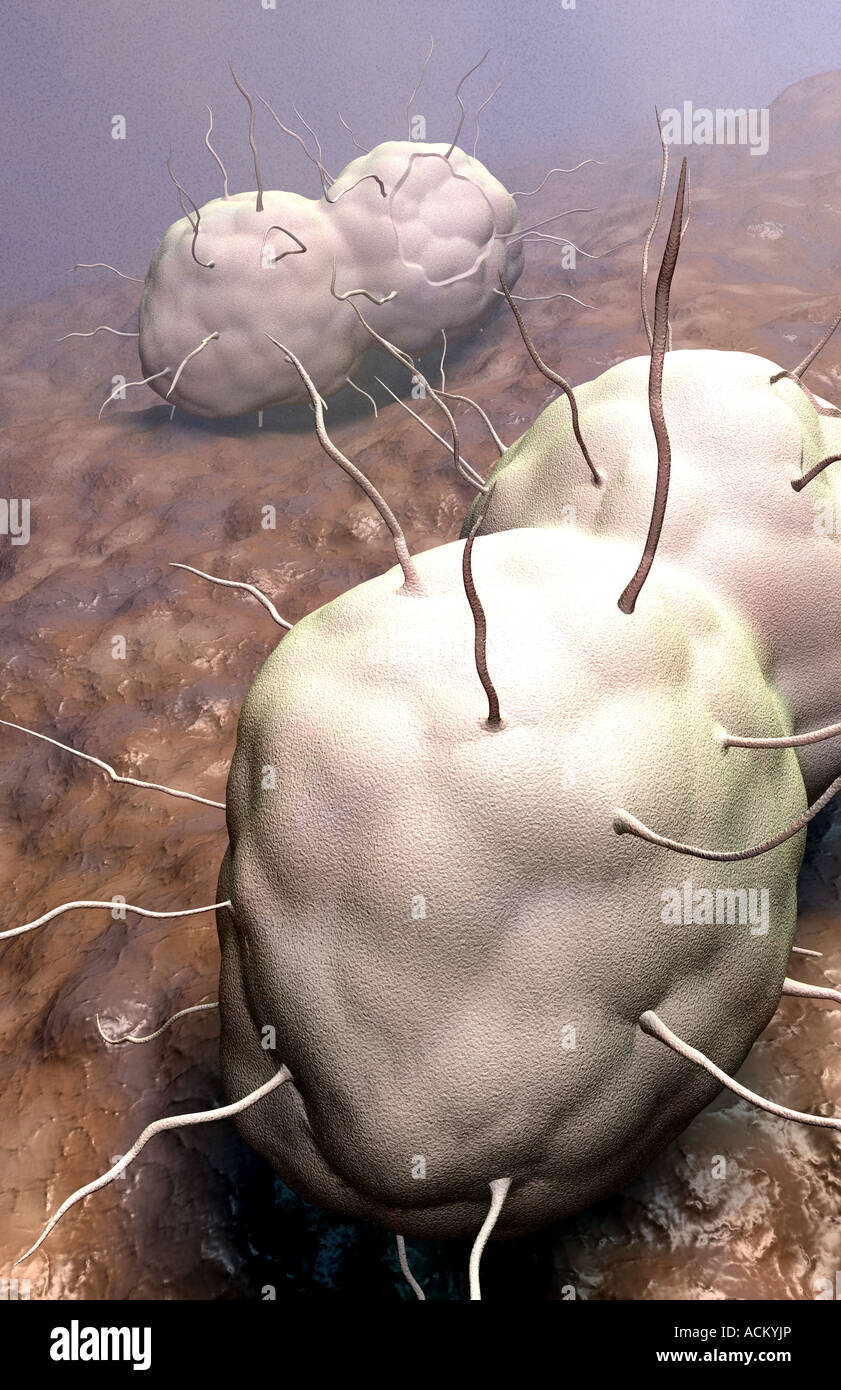 Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13183629.html
Gonorrhea Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-gonorrhea-13183629.htmlRFACKYJP–Gonorrhea
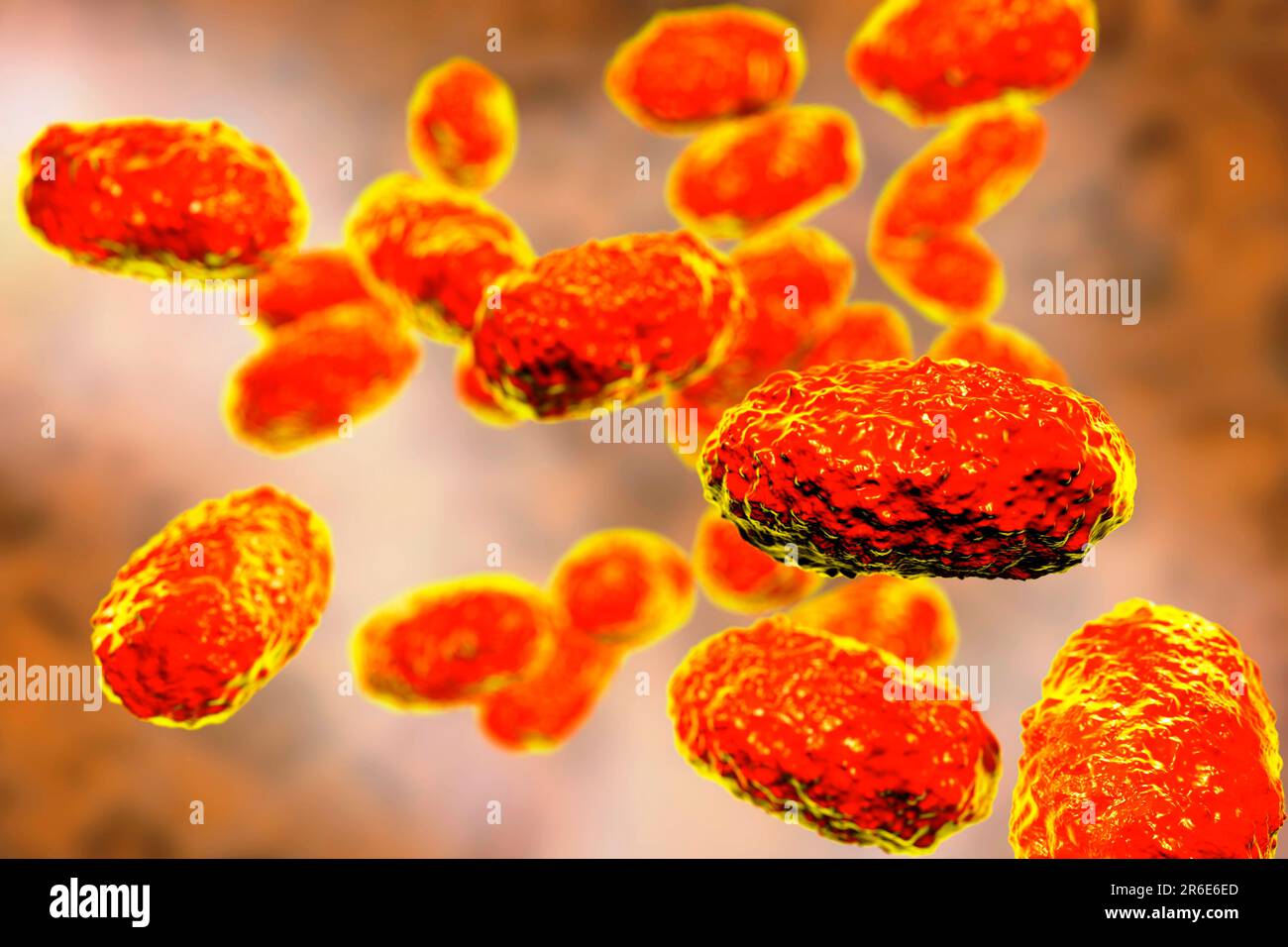 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732149.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732149.htmlRF2R6E6ED–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
RF2JTPABA–Set of 3 petri dish icons. Colorful simple illustration with bacterial cells.
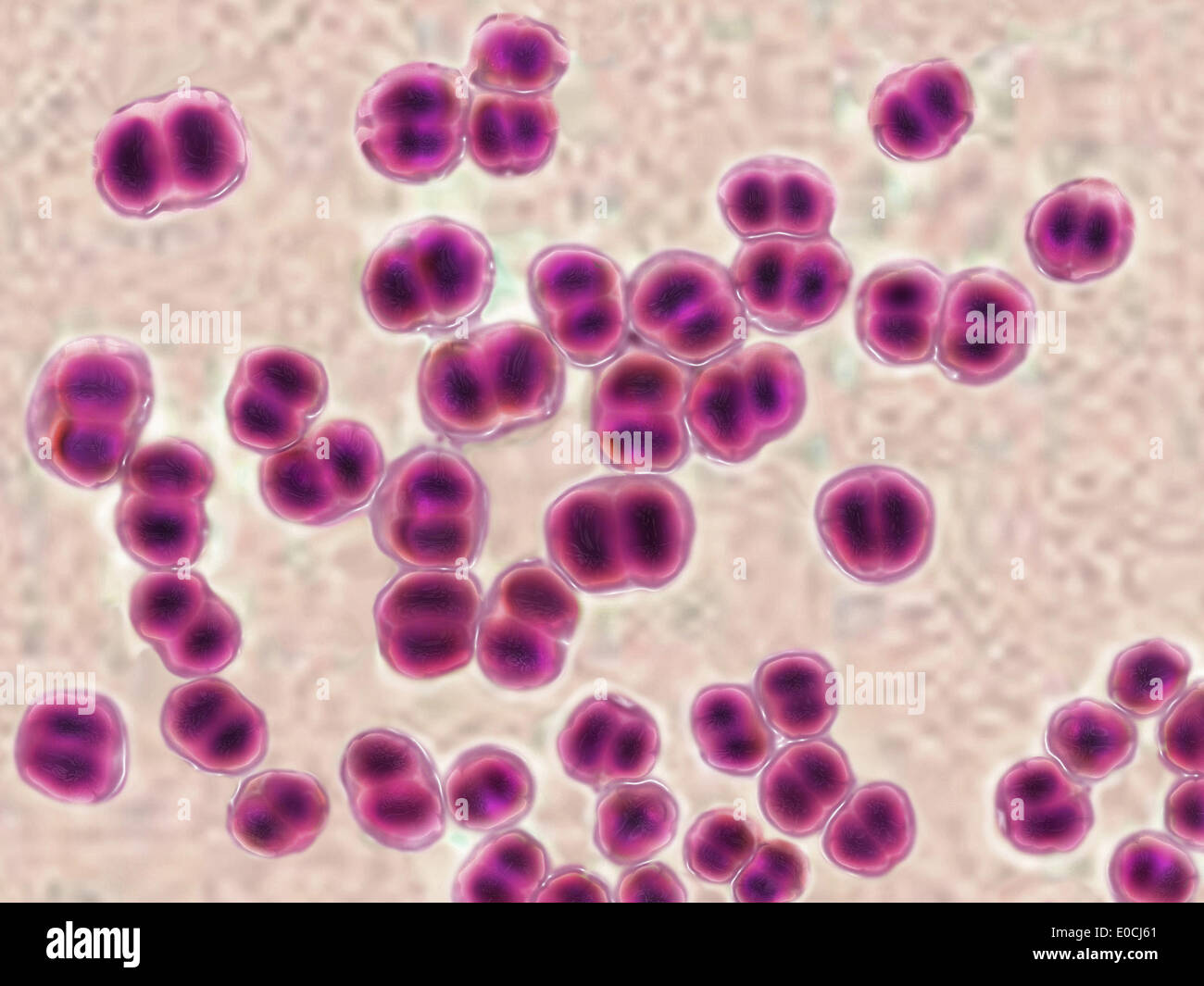 Neisseria meningitidis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-meningitidis-image69119177.html
Neisseria meningitidis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neisseria-meningitidis-image69119177.htmlRME0CJ61–Neisseria meningitidis
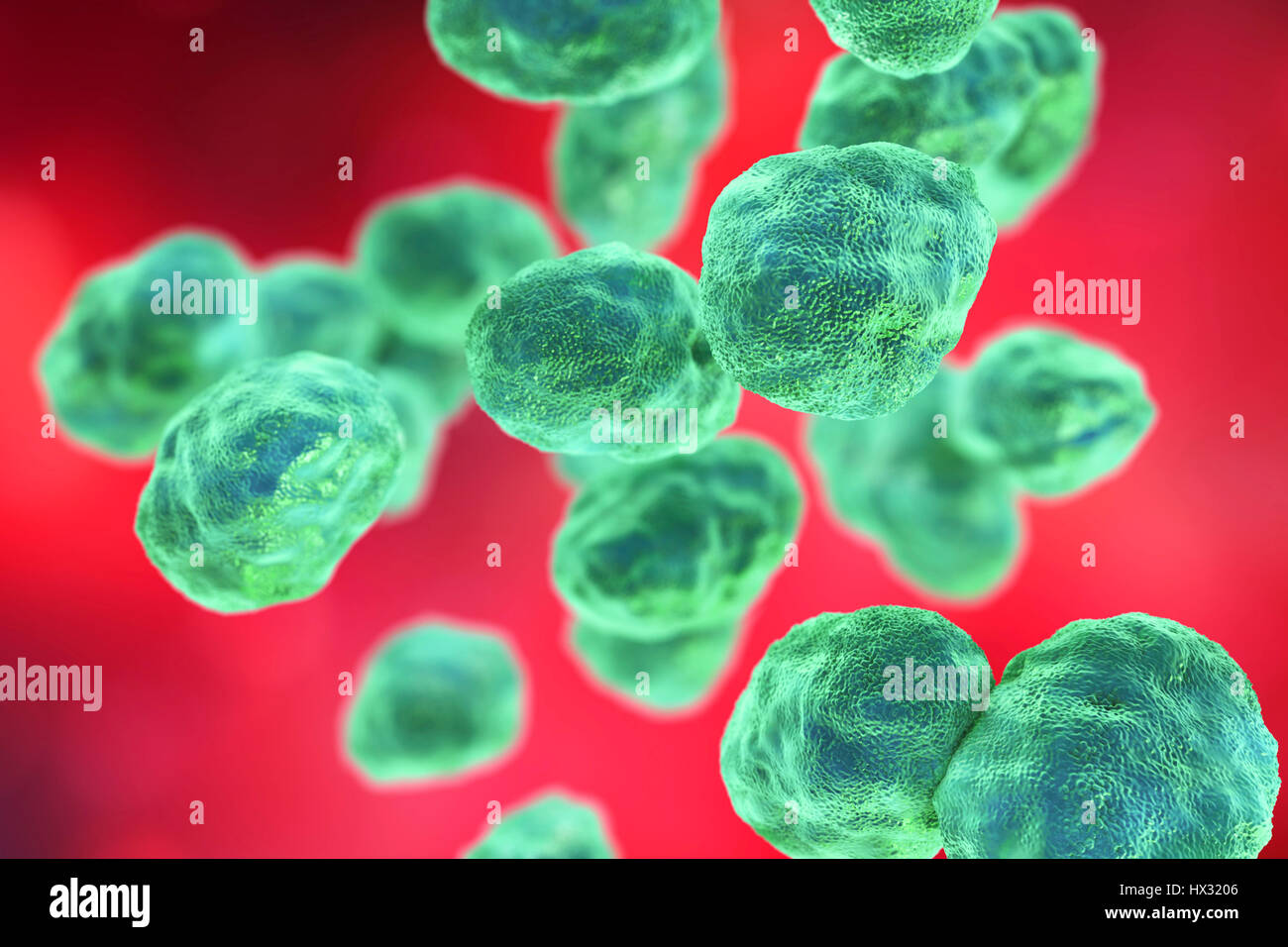 Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521062.html
Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tularaemia-bacteria-francisella-tularensis-illustration-f-tularensis-136521062.htmlRFHX3206–Tularaemia bacteria (Francisella tularensis), illustration. F. tularensis is Gram-negative, coccobacillus prokaryote. A zoonotic microorganism that causes tularaemia, a disease of wild rodents and rabbits that can be transmitted to humans and domesticated pets.
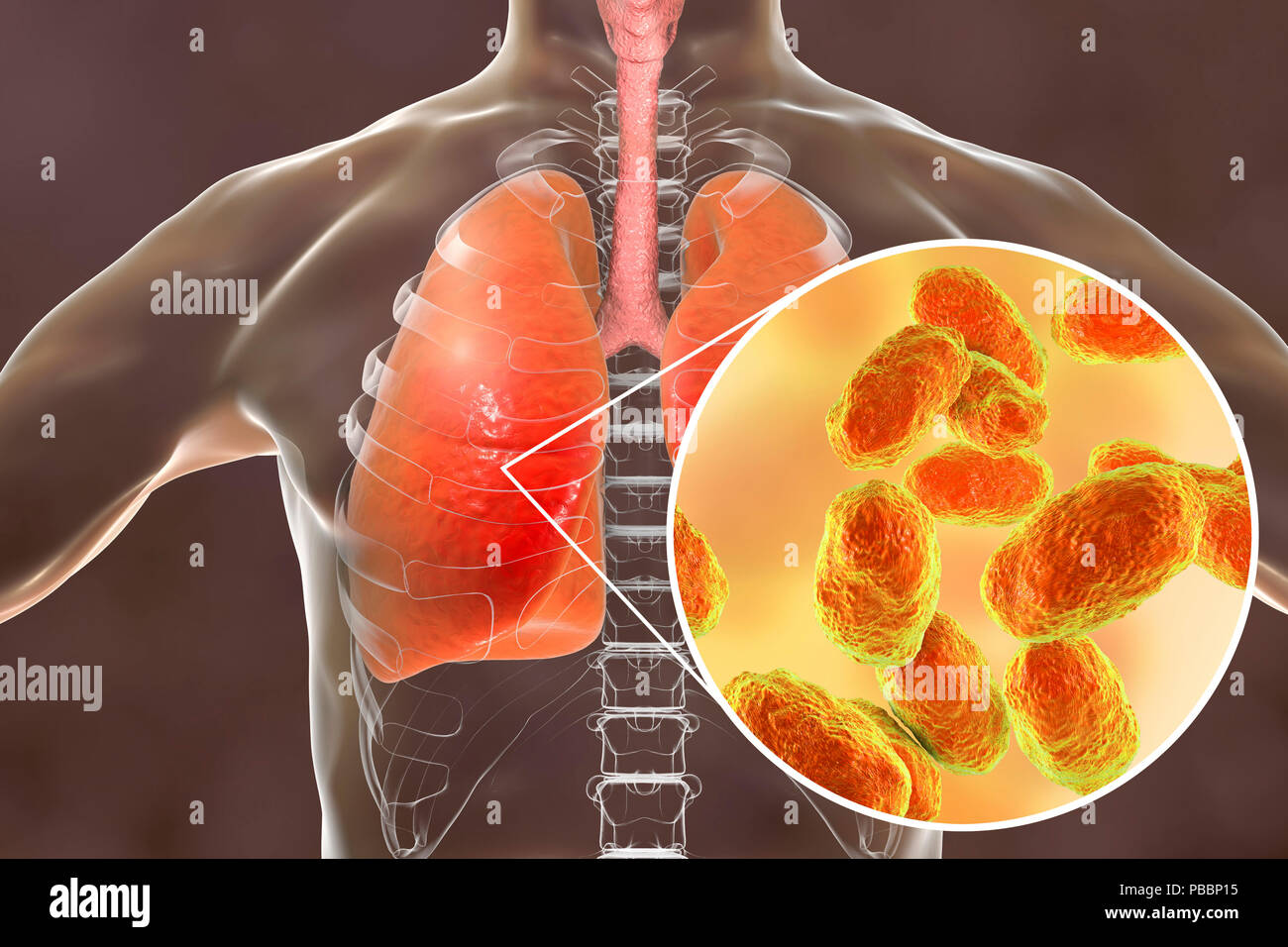 Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-haemophilus-influenzae-bacteria-computer-illustration-h-influenzae-are-coccobacillus-gram-negative-bacteria-these-bacteria-cause-a-number-of-diseases-including-meningitis-in-children-pneumonia-epiglottitis-laryngitis-conjunctivitis-neonatal-infection-otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-and-sinusitis-in-adults-h-influenzae-harmlessly-colonize-the-upper-respiratory-tract-in-most-humans-within-the-first-few-months-of-life-encapsulated-strains-spread-to-cause-diseases-such-as-bronchitis-and-pneumonia-image213544385.html
Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pneumonia-caused-by-haemophilus-influenzae-bacteria-computer-illustration-h-influenzae-are-coccobacillus-gram-negative-bacteria-these-bacteria-cause-a-number-of-diseases-including-meningitis-in-children-pneumonia-epiglottitis-laryngitis-conjunctivitis-neonatal-infection-otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-and-sinusitis-in-adults-h-influenzae-harmlessly-colonize-the-upper-respiratory-tract-in-most-humans-within-the-first-few-months-of-life-encapsulated-strains-spread-to-cause-diseases-such-as-bronchitis-and-pneumonia-image213544385.htmlRFPBBP15–Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae bacteria, computer illustration. H. influenzae are coccobacillus Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria cause a number of diseases including meningitis in children, pneumonia, epiglottitis, laryngitis, conjunctivitis, neonatal infection, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sinusitis in adults. H. influenzae harmlessly colonize the upper respiratory tract in most humans within the first few months of life. Encapsulated strains spread to cause diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
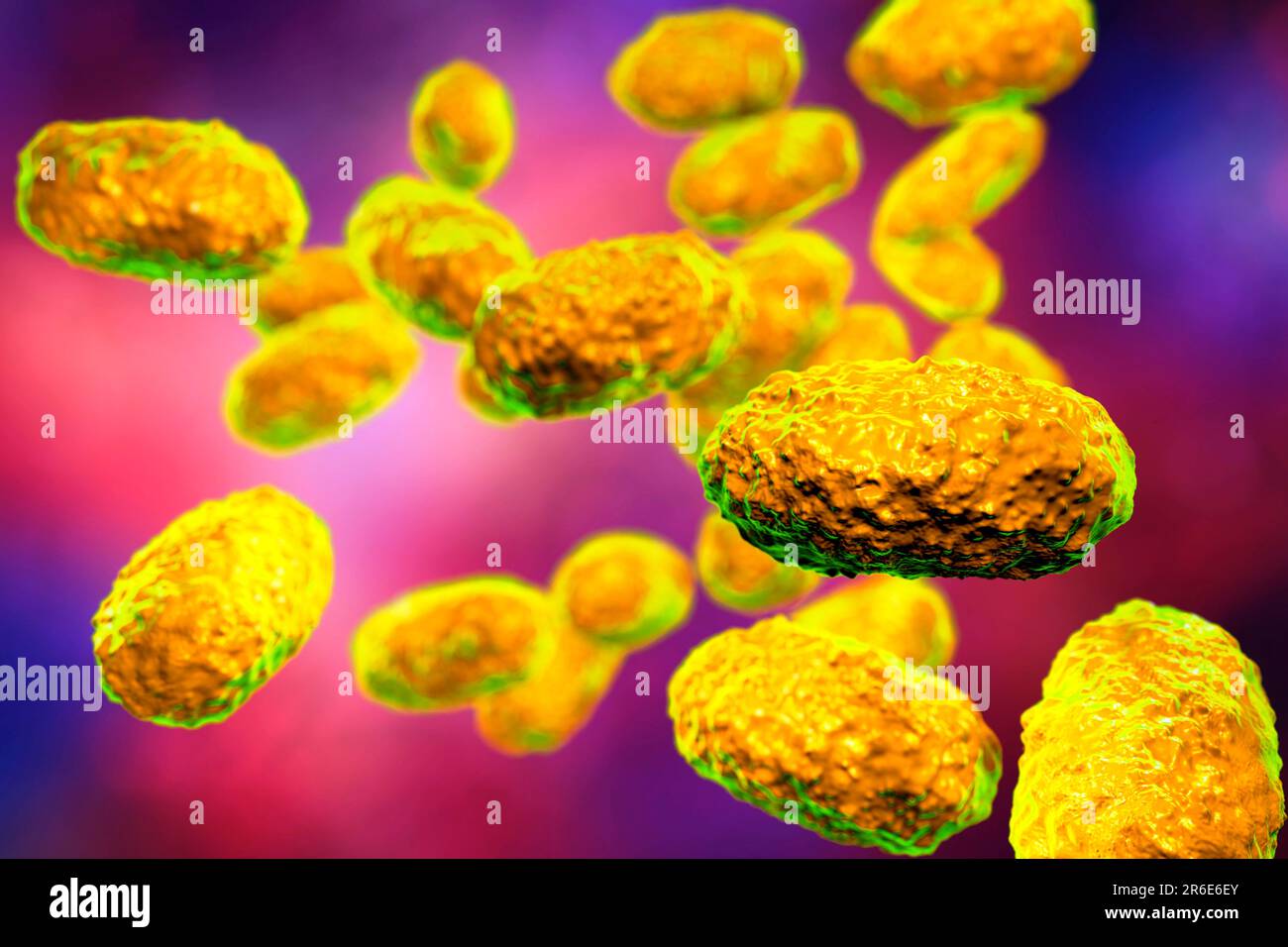 Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732163.html
Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote ( Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whooping-cough-bacteria-bordetella-pertussis-computer-illustration-b-pertussis-are-gram-negative-aerobic-non-motile-coccobacillus-prokaryote-image554732163.htmlRF2R6E6EY–Whooping cough bacteria (Bordetella pertussis), computer illustration. B. pertussis are gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, coccobacillus prokaryote (
RF2JTPAA6–Set of 3 petri dish icons. Colorful simple illustration with bacterial cells.
