Quick filters:
Extensor muscles of foot Stock Photos and Images
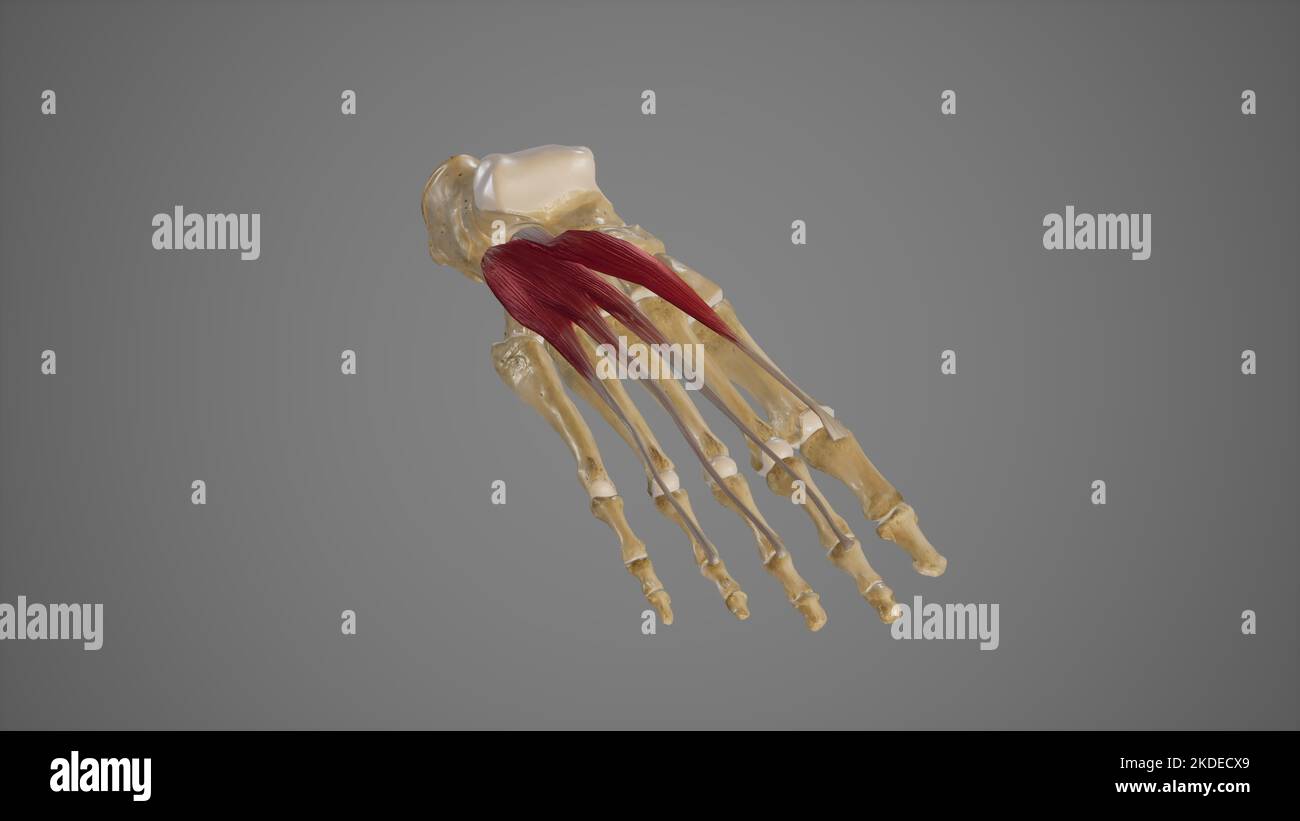 Extensor Muscles of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/extensor-muscles-of-foot-image490198305.html
Extensor Muscles of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/extensor-muscles-of-foot-image490198305.htmlRF2KDECX9–Extensor Muscles of Foot
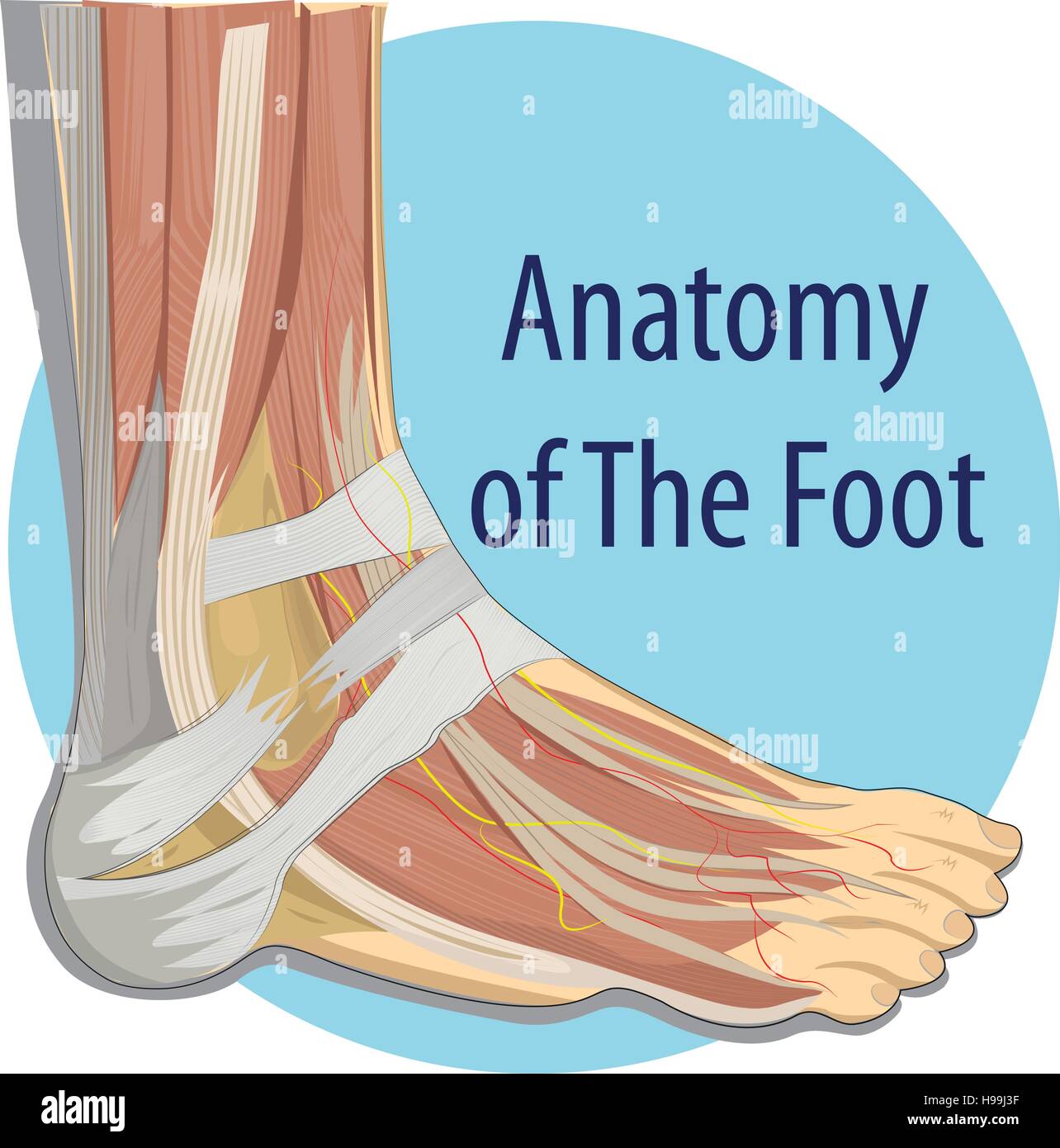 Vector illustration Anatomy of the Foot Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-vector-illustration-anatomy-of-the-foot-126216259.html
Vector illustration Anatomy of the Foot Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-vector-illustration-anatomy-of-the-foot-126216259.htmlRFH99J3F–Vector illustration Anatomy of the Foot
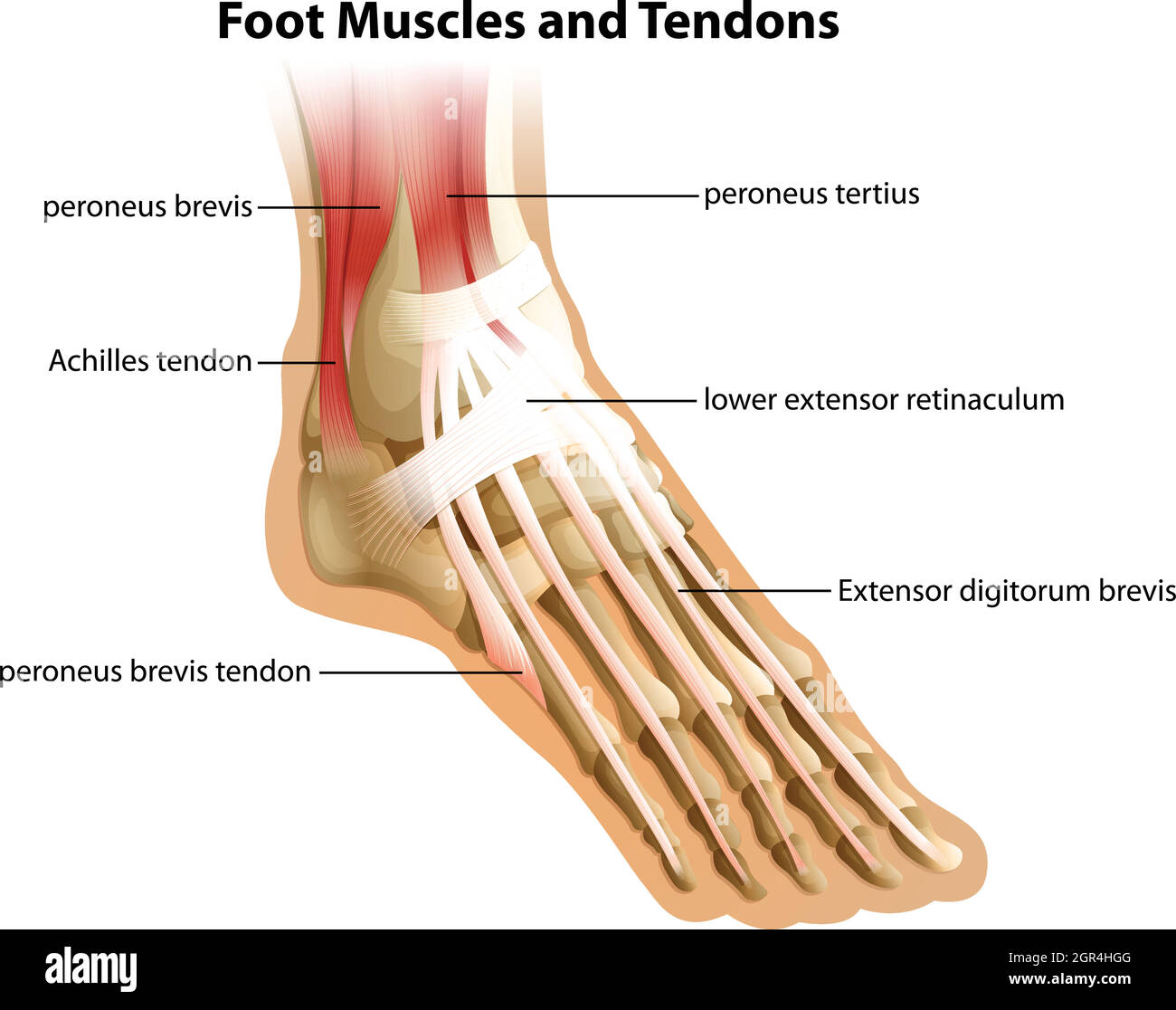 Foot Muscles and Tendons Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/foot-muscles-and-tendons-image444497888.html
Foot Muscles and Tendons Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/foot-muscles-and-tendons-image444497888.htmlRF2GR4HGG–Foot Muscles and Tendons
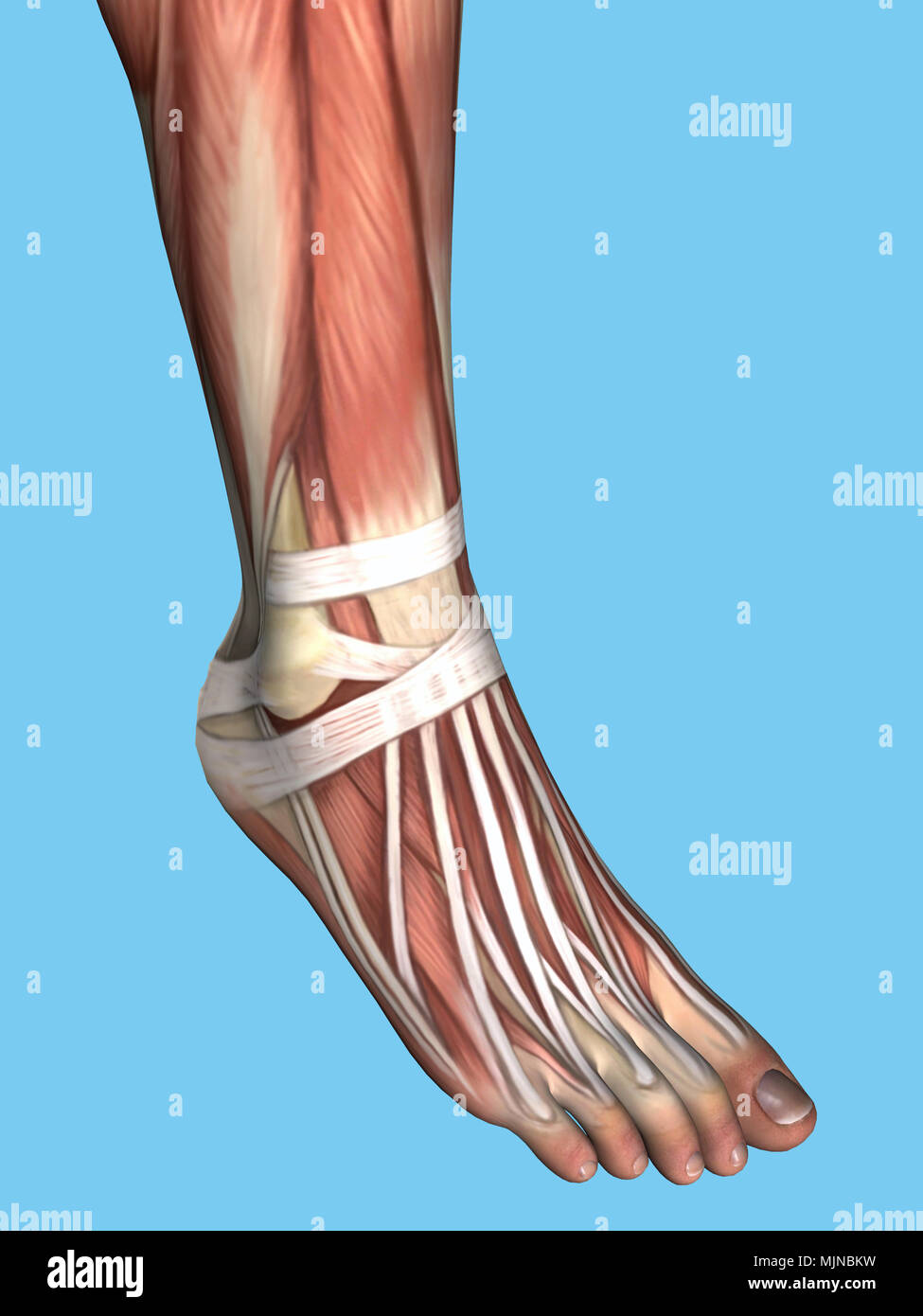 Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183637661.html
Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183637661.htmlRMMJNBKW–Anatomy of foot
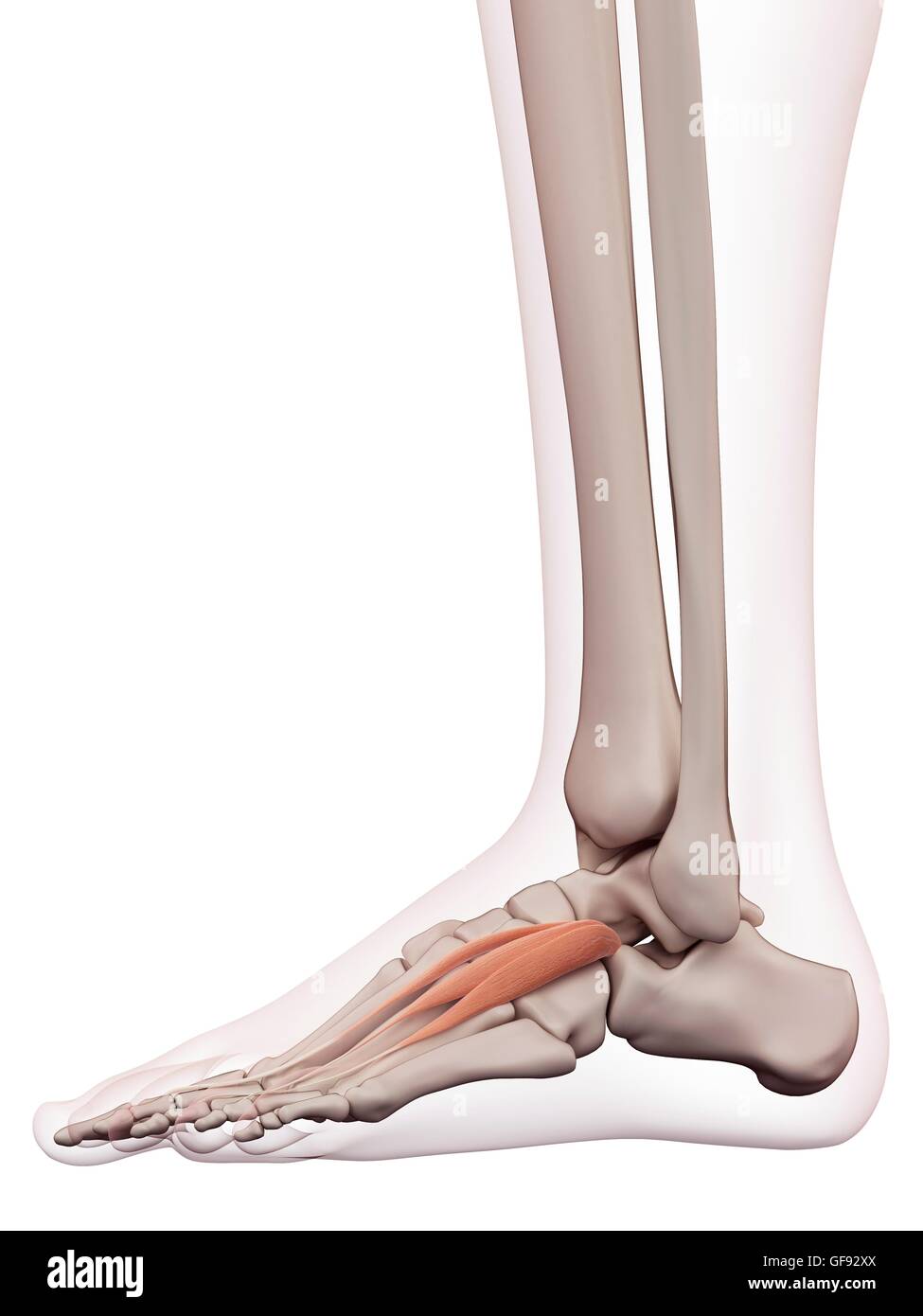 Human foot muscles, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-human-foot-muscles-illustration-112681938.html
Human foot muscles, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-human-foot-muscles-illustration-112681938.htmlRFGF92XX–Human foot muscles, illustration.
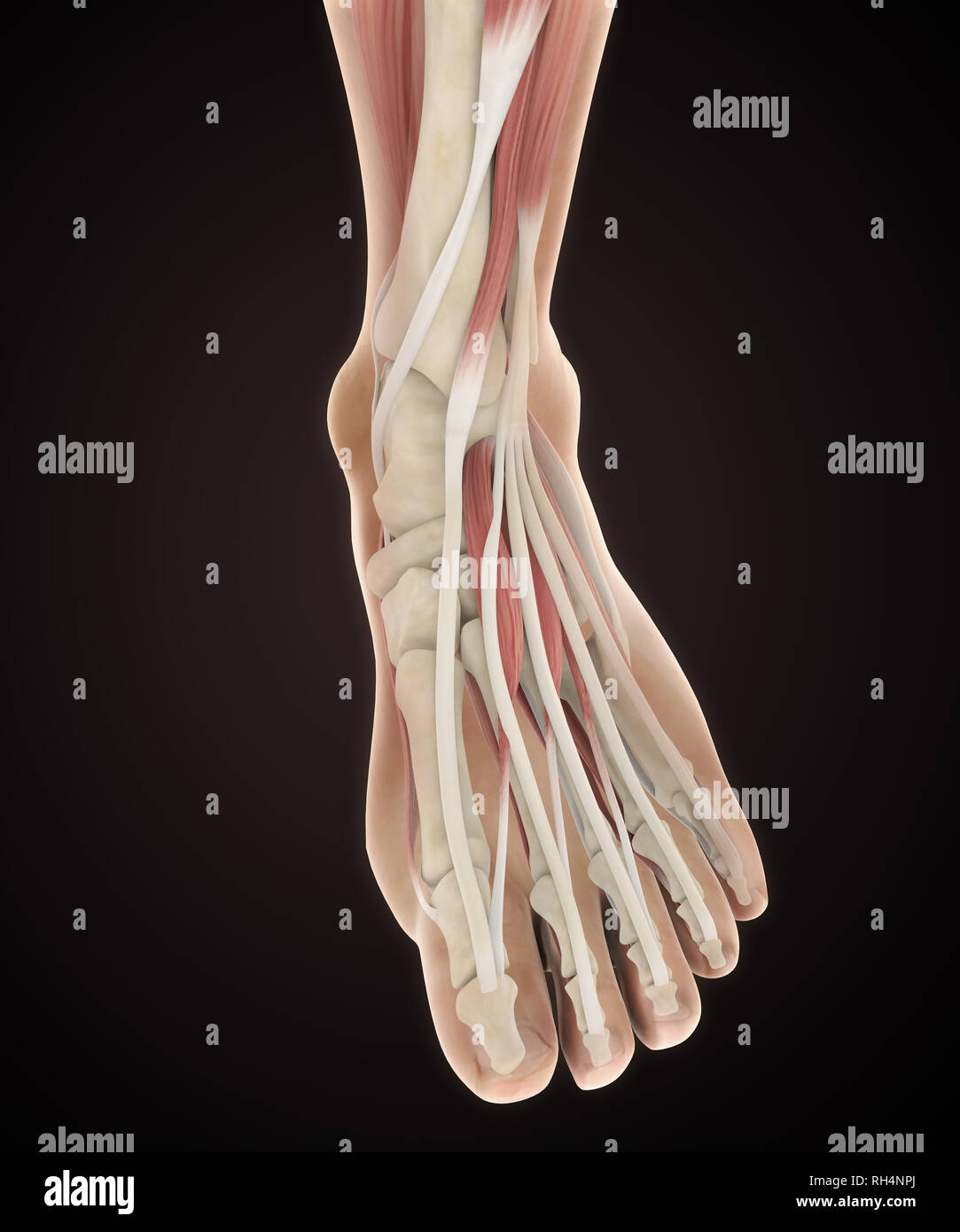 Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image234288842.html
Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image234288842.htmlRFRH4NPJ–Human Foot Muscles Anatomy
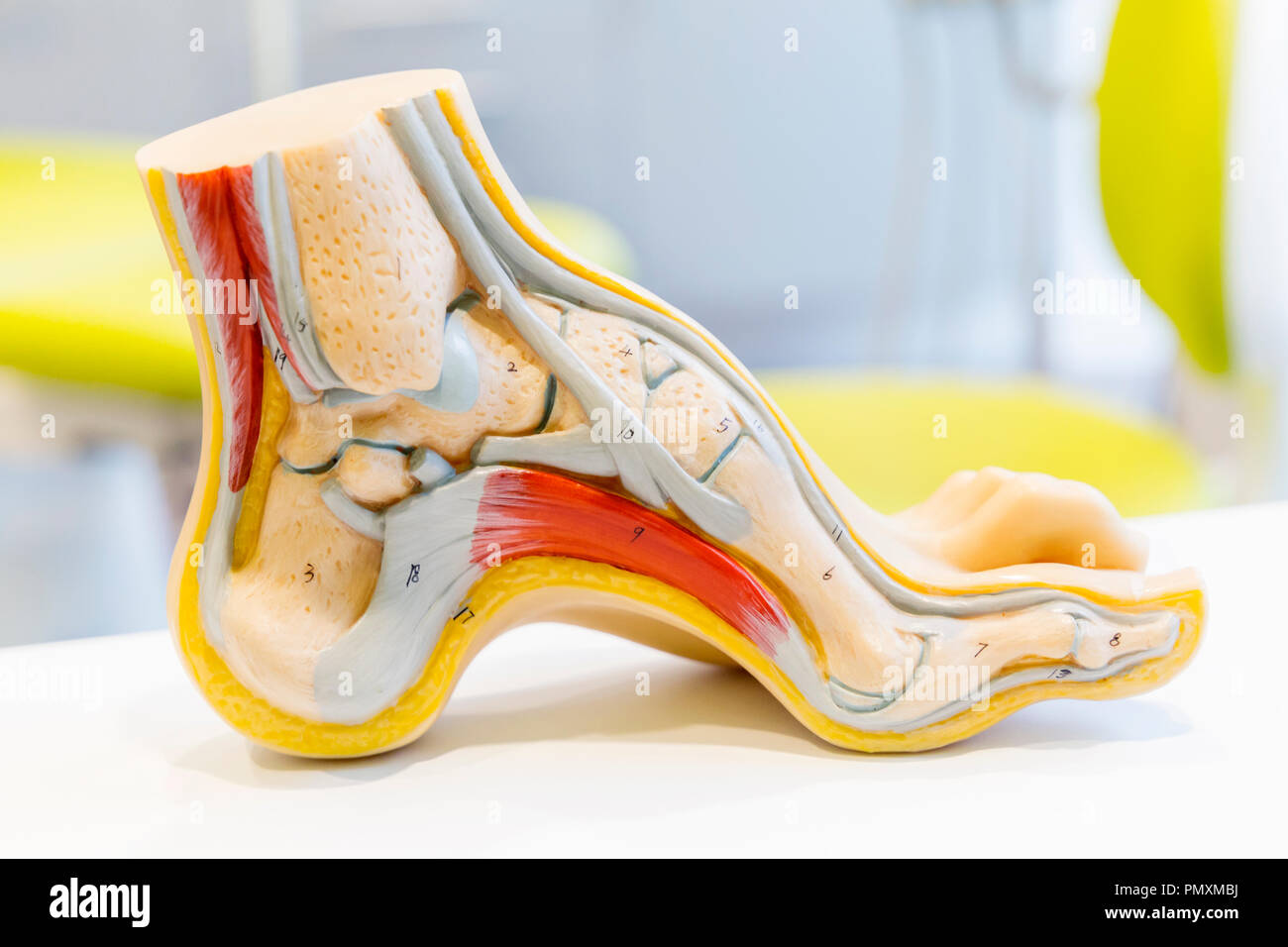 Anatomy human foot model Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-human-foot-model-image219404294.html
Anatomy human foot model Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-human-foot-model-image219404294.htmlRFPMXMBJ–Anatomy human foot model
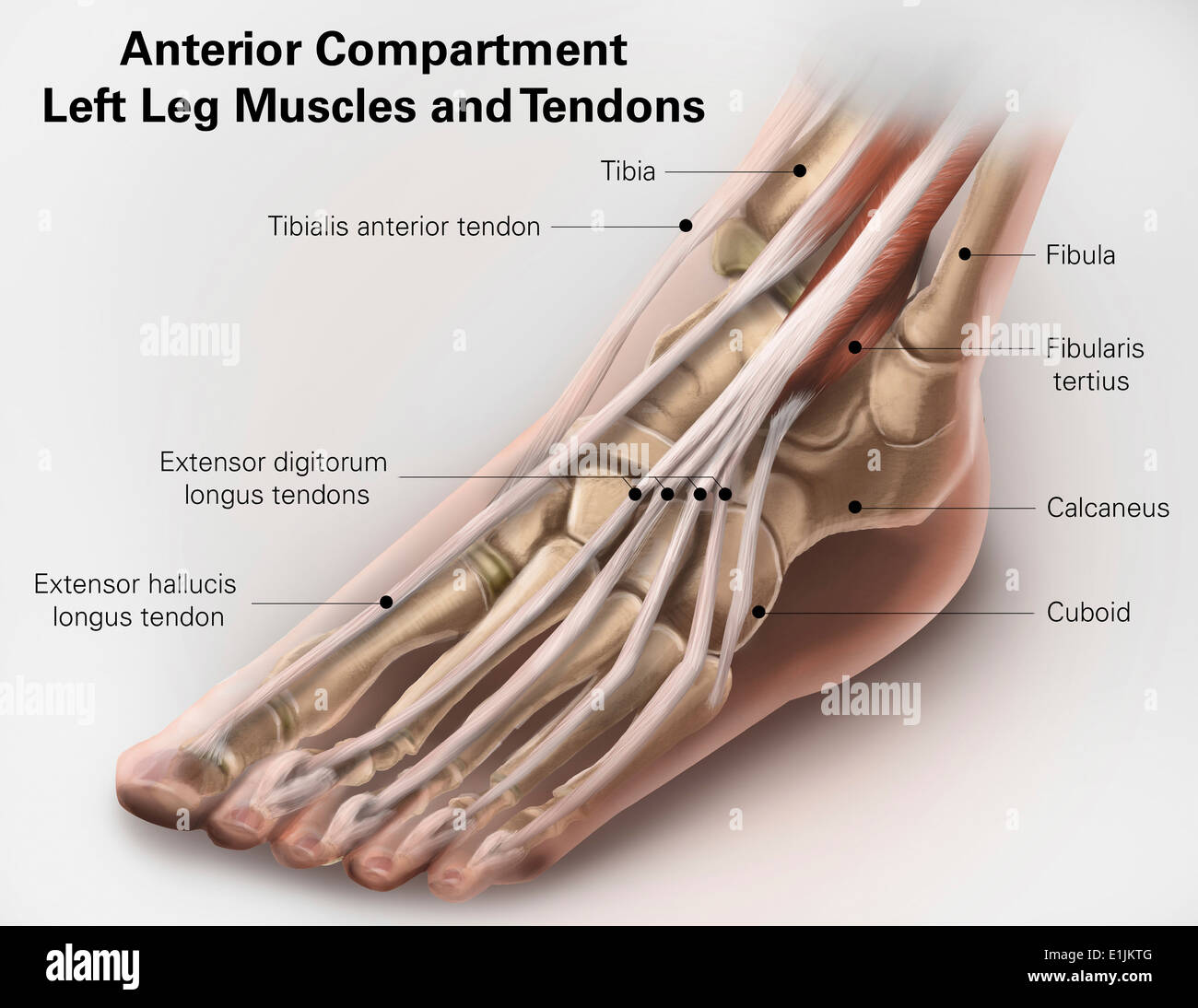 Anterior compartment anatomy of left leg muscles and tendons. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-compartment-anatomy-of-left-leg-muscles-and-tendons-image69866848.html
Anterior compartment anatomy of left leg muscles and tendons. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-compartment-anatomy-of-left-leg-muscles-and-tendons-image69866848.htmlRFE1JKTG–Anterior compartment anatomy of left leg muscles and tendons.
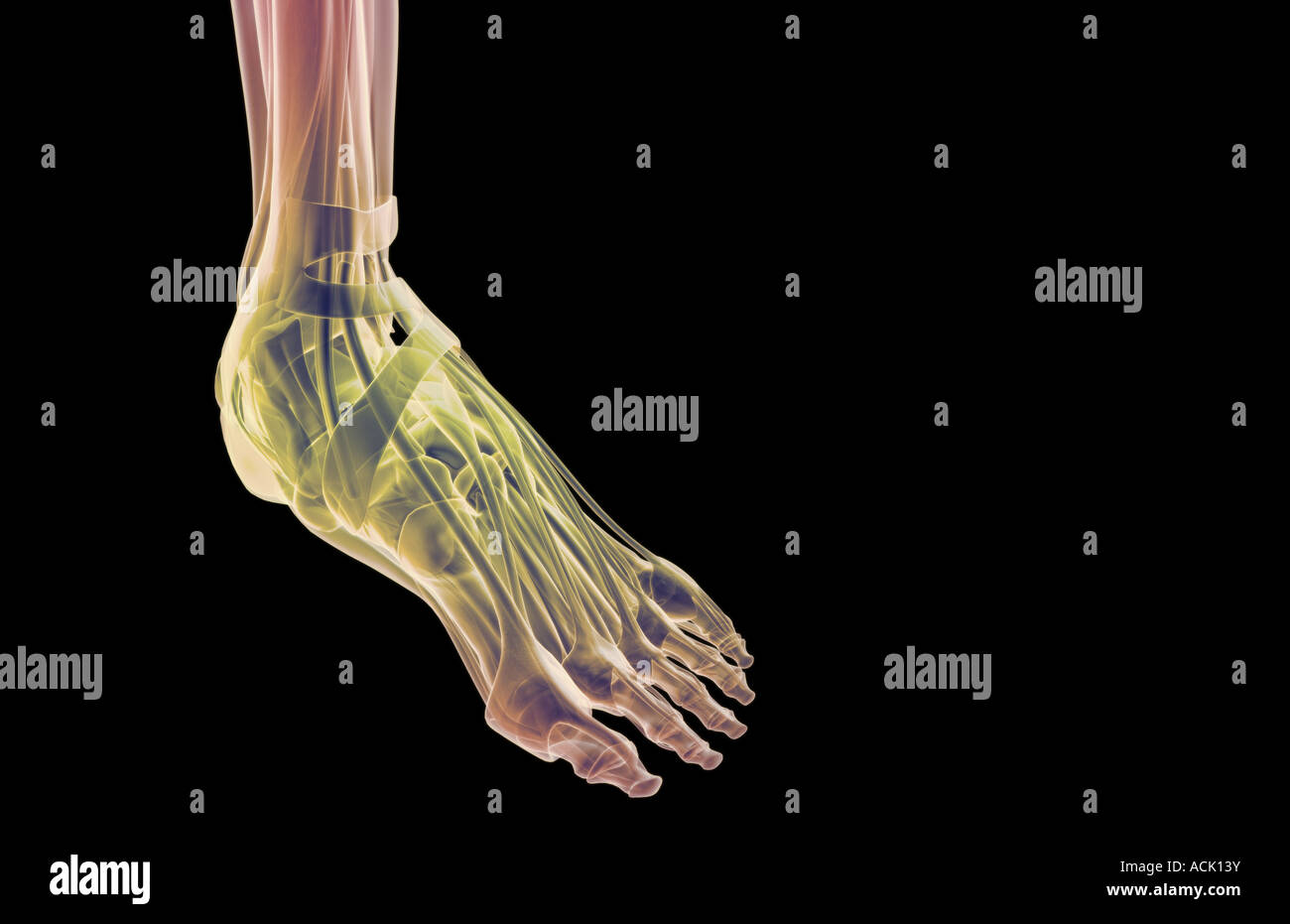 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13174718.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13174718.htmlRFACK13Y–The muscles of the foot
 Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-male-muscle-anatomy-of-the-human-legs-anterior-view-59361120.html
Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-male-muscle-anatomy-of-the-human-legs-anterior-view-59361120.htmlRFDCG3M0–Male muscle anatomy of the human legs, anterior view.
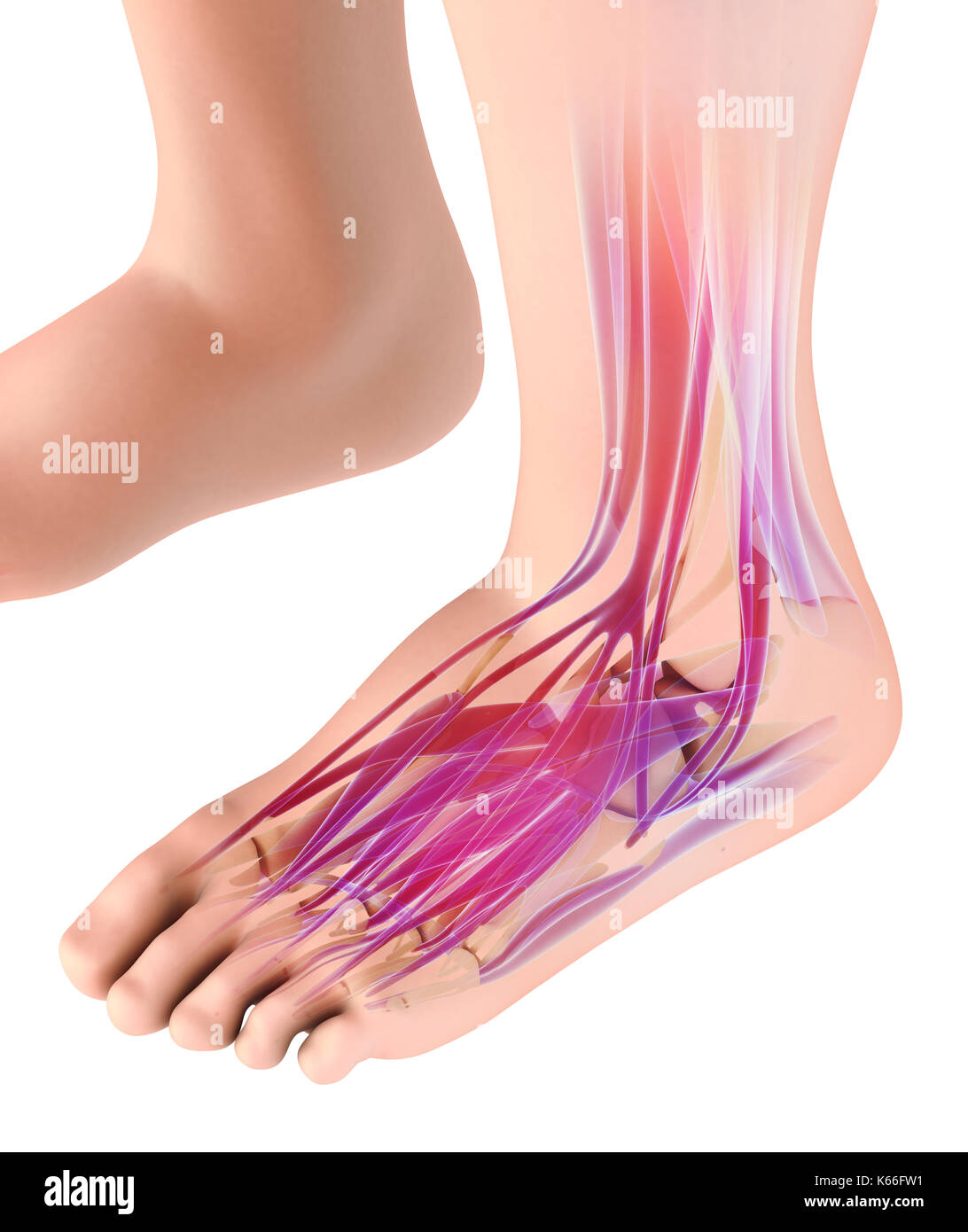 3d illustration of Medical and Scientific concept, Foot muscle - human muscular system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-medical-and-scientific-concept-foot-muscle-human-image158725421.html
3d illustration of Medical and Scientific concept, Foot muscle - human muscular system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-medical-and-scientific-concept-foot-muscle-human-image158725421.htmlRFK66FW1–3d illustration of Medical and Scientific concept, Foot muscle - human muscular system.
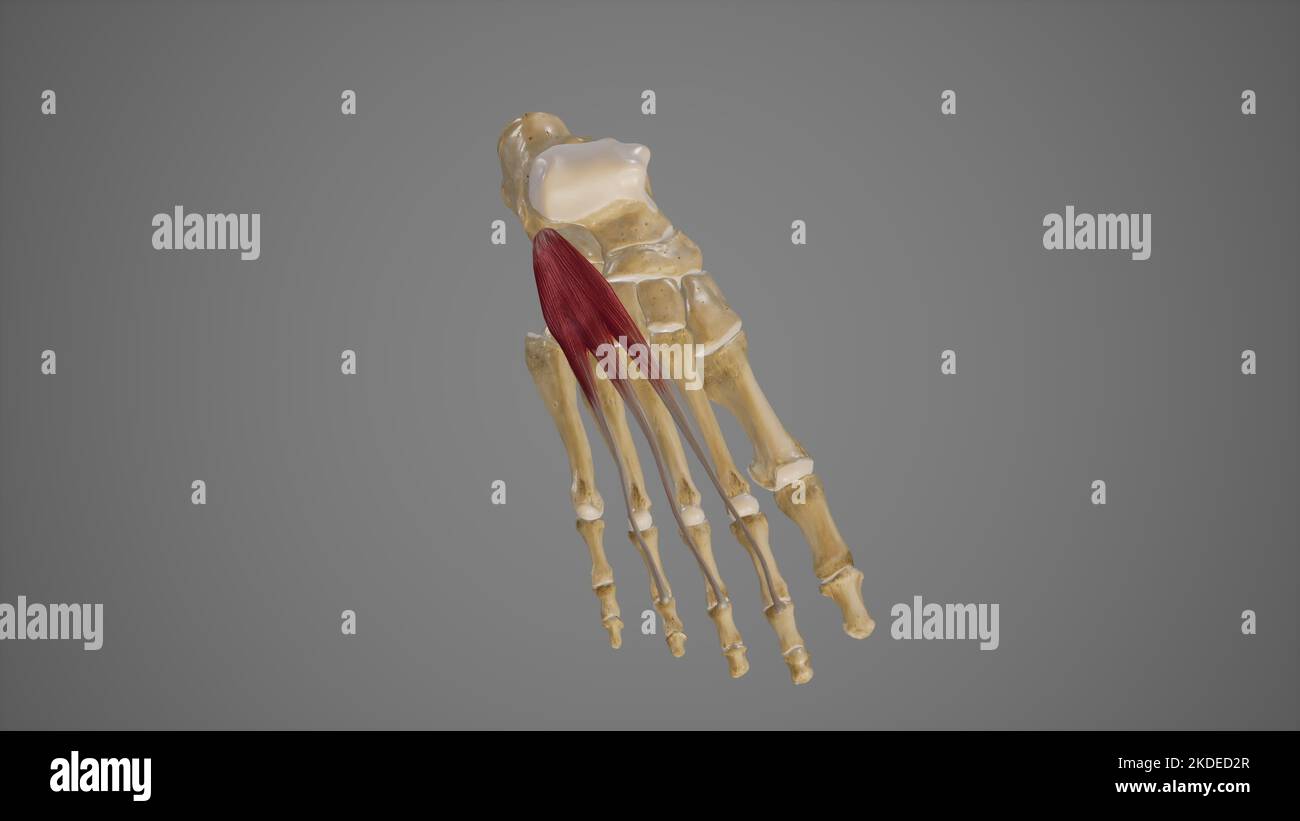
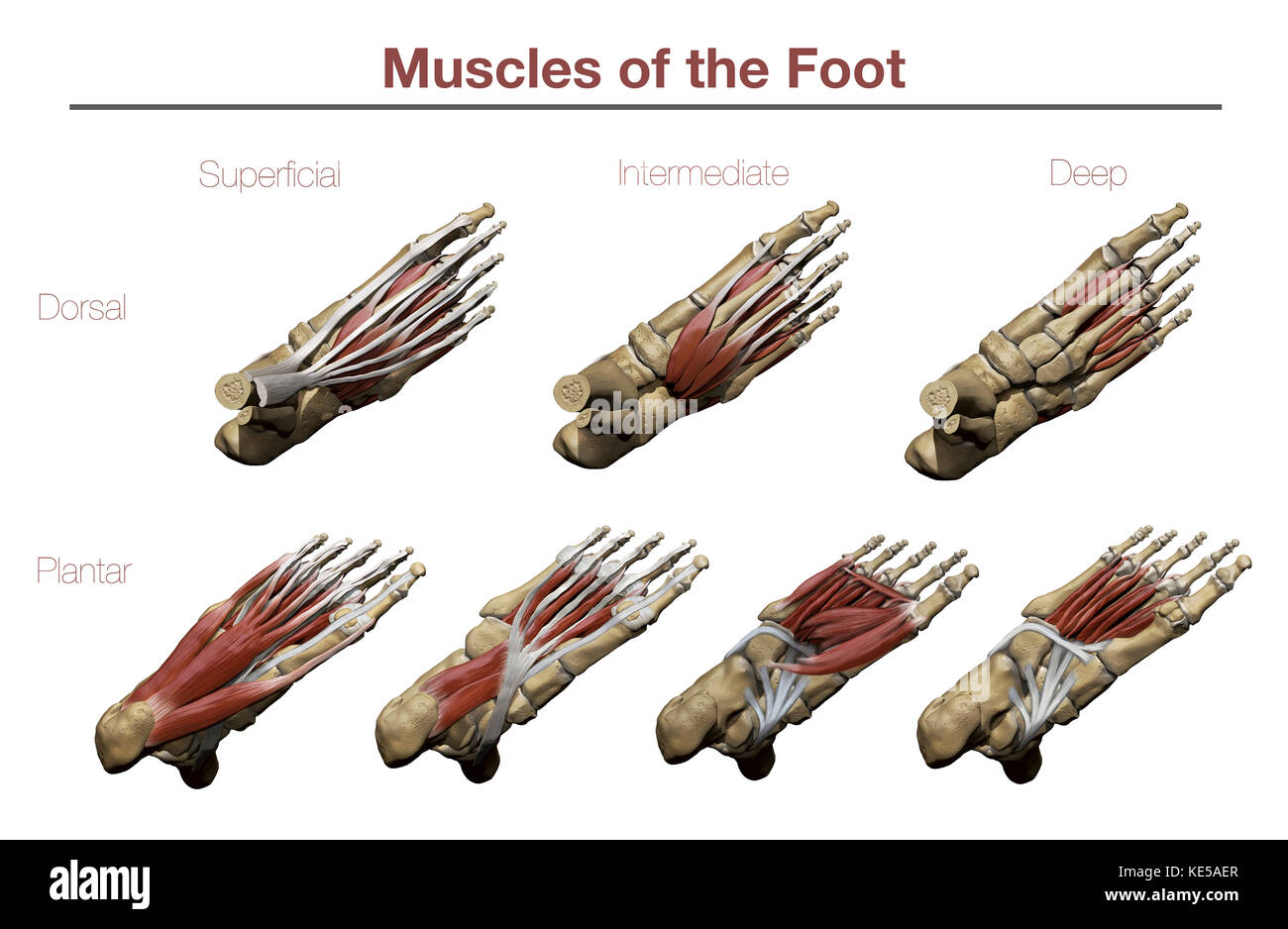 Muscles of the Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-muscles-of-the-foot-163616511.html
Muscles of the Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-muscles-of-the-foot-163616511.htmlRFKE5AER–Muscles of the Foot
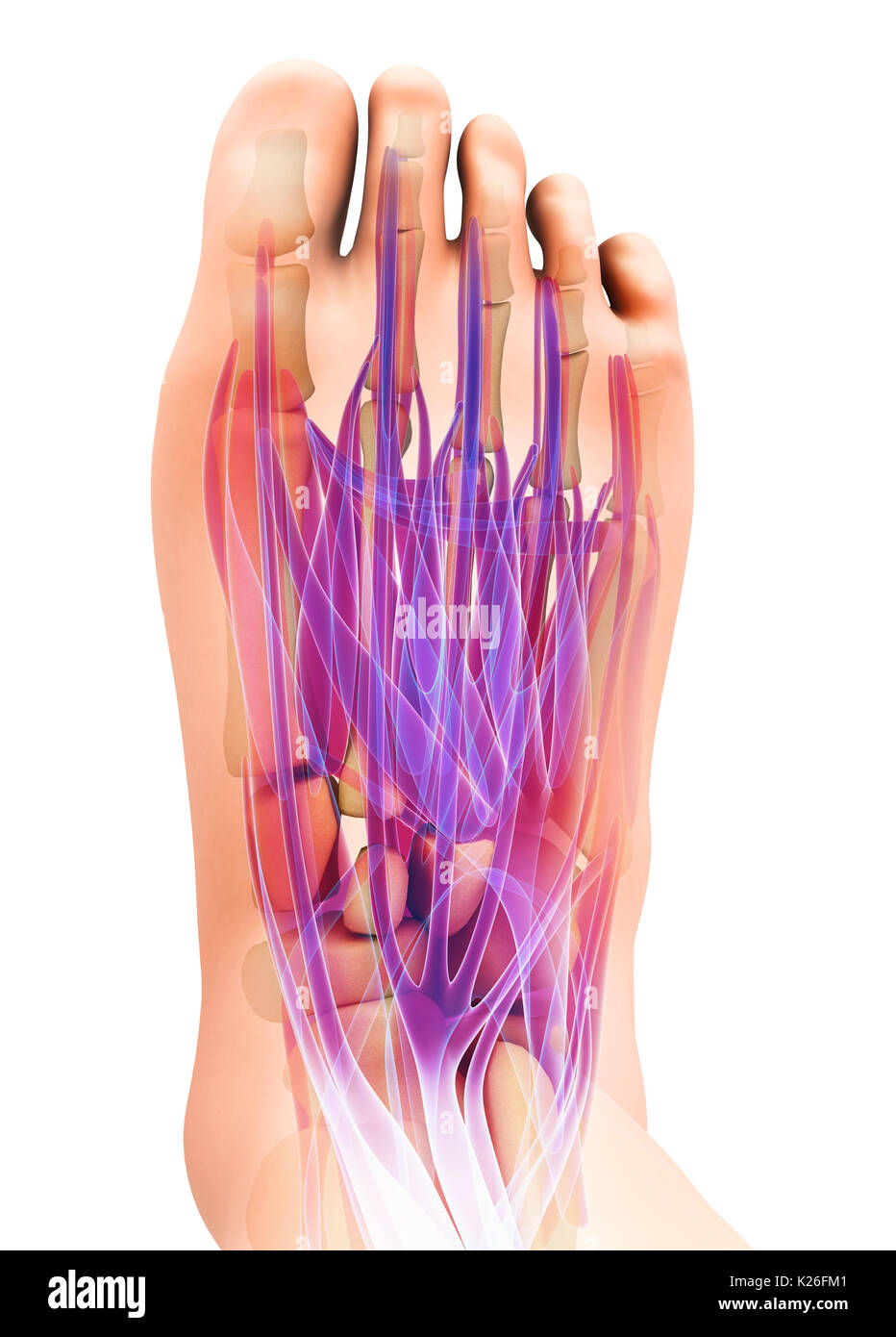 3d illustration of Medical and Scientific concept, Foot muscle - human muscular system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-medical-and-scientific-concept-foot-muscle-human-image156266657.html
3d illustration of Medical and Scientific concept, Foot muscle - human muscular system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-of-medical-and-scientific-concept-foot-muscle-human-image156266657.htmlRFK26FM1–3d illustration of Medical and Scientific concept, Foot muscle - human muscular system.
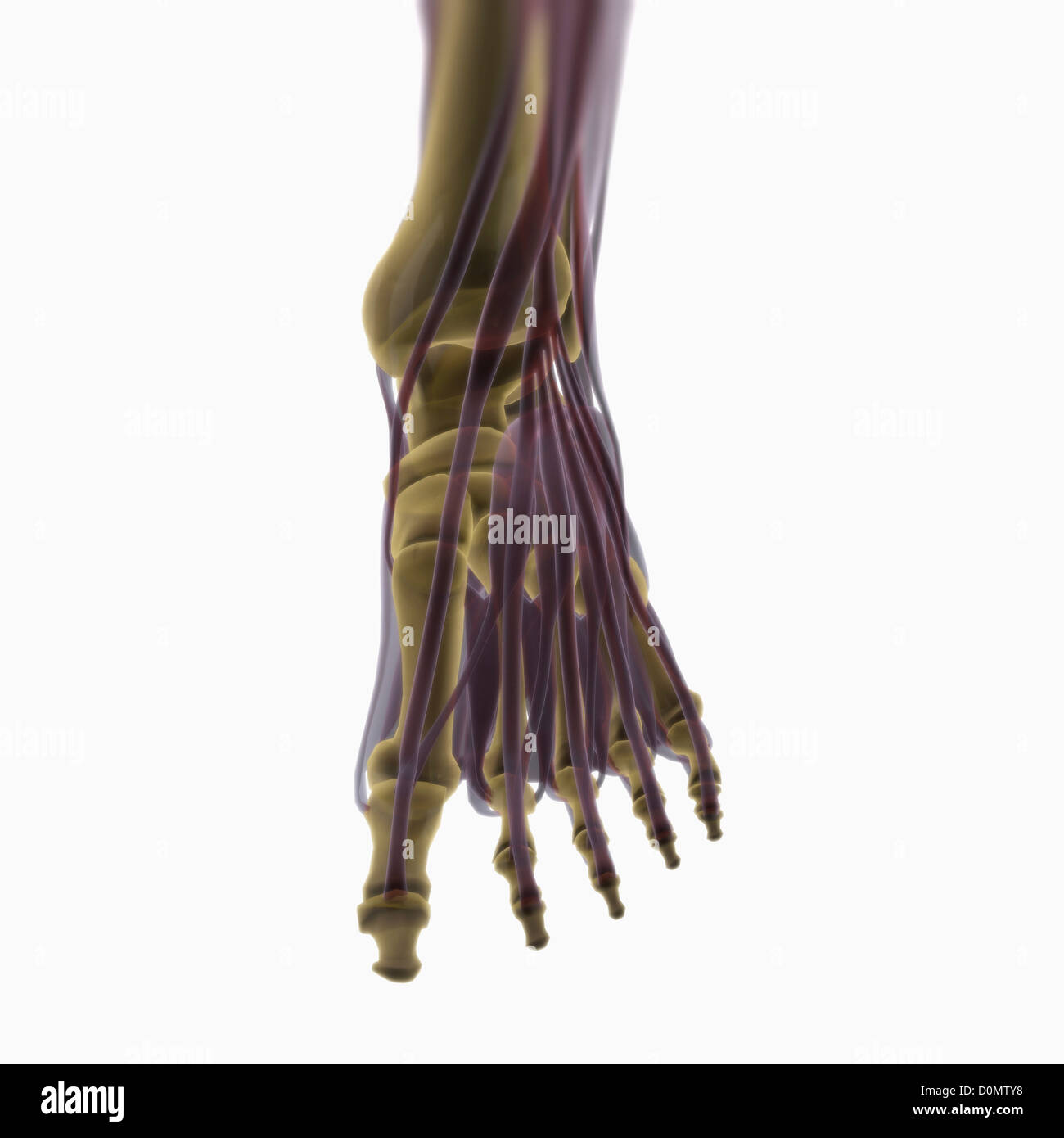 Anatomical model showing the muscles of the left foot. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomical-model-showing-the-muscles-of-the-left-foot-52089724.html
Anatomical model showing the muscles of the left foot. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomical-model-showing-the-muscles-of-the-left-foot-52089724.htmlRMD0MTY8–Anatomical model showing the muscles of the left foot.
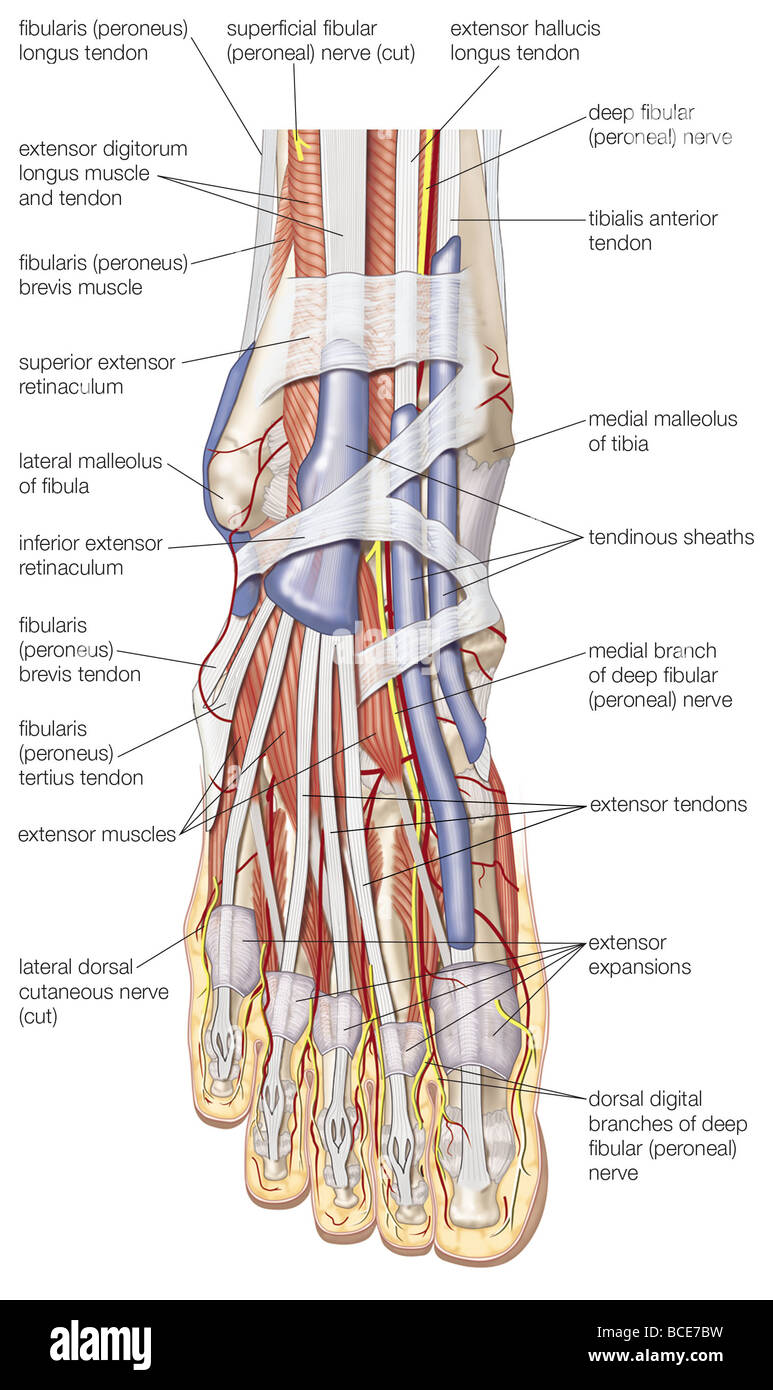 Dorsal view of the right foot, showing the major muscles, tendons, and nerves. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dorsal-view-of-the-right-foot-showing-the-major-muscles-tendons-and-24899389.html
Dorsal view of the right foot, showing the major muscles, tendons, and nerves. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dorsal-view-of-the-right-foot-showing-the-major-muscles-tendons-and-24899389.htmlRMBCE7BW–Dorsal view of the right foot, showing the major muscles, tendons, and nerves.
 Muscles of foot, Hand drawn medical illustration drawing with imitation of lithography Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-muscles-of-foot-hand-drawn-medical-illustration-drawing-with-imitation-129446871.html
Muscles of foot, Hand drawn medical illustration drawing with imitation of lithography Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-muscles-of-foot-hand-drawn-medical-illustration-drawing-with-imitation-129446871.htmlRFHEGPPF–Muscles of foot, Hand drawn medical illustration drawing with imitation of lithography
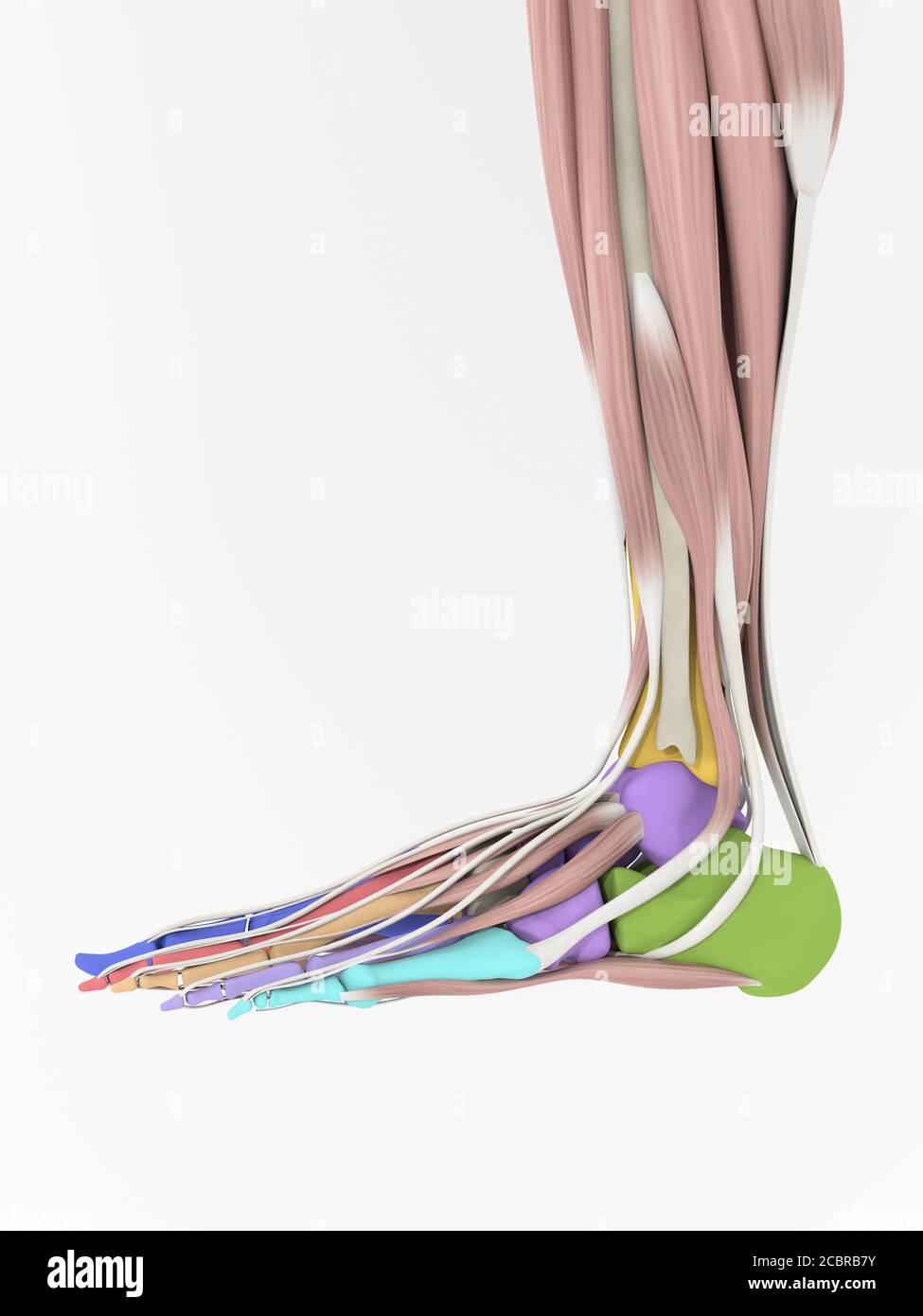 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368692687.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368692687.htmlRF2CBRB7Y–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
 Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066703.html
Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066703.htmlRFR8JTWK–Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete.
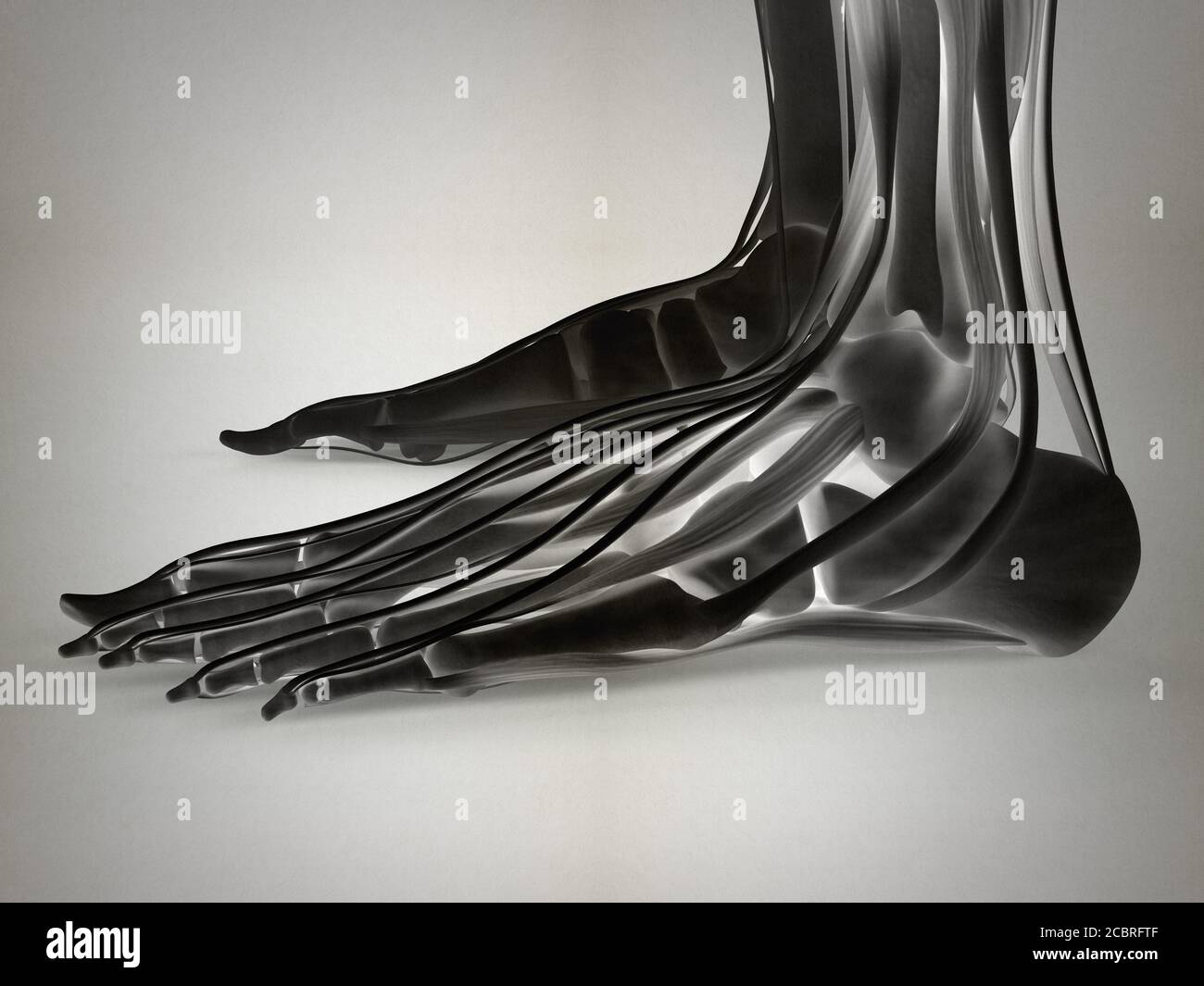 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696287.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696287.htmlRF2CBRFTF–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
 Medical Illustration of Extensor Hallucis Brevis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-hallucis-brevis-image490198434.html
Medical Illustration of Extensor Hallucis Brevis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-hallucis-brevis-image490198434.htmlRF2KDED2X–Medical Illustration of Extensor Hallucis Brevis
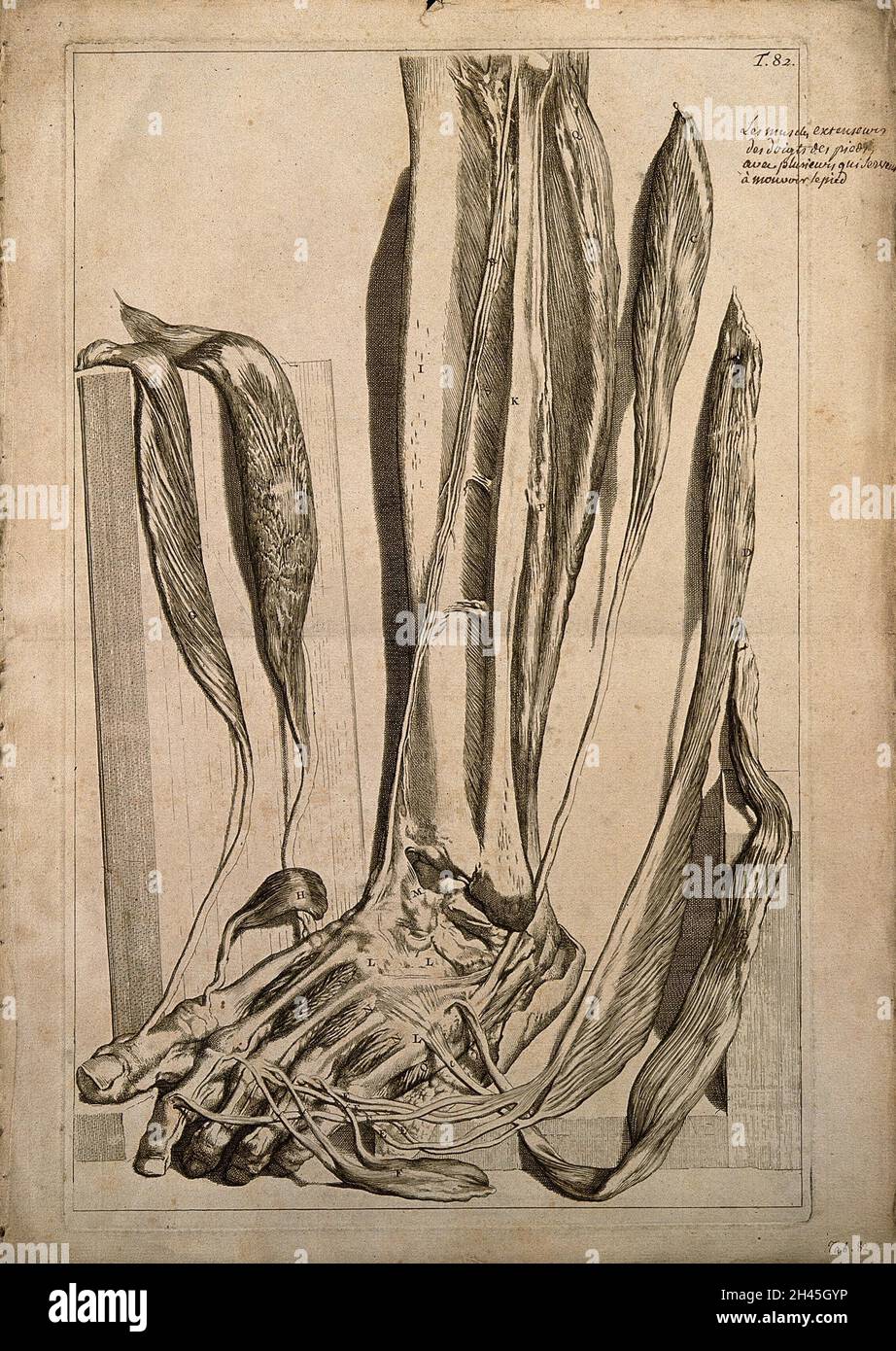 The extensor muscles of the foot dissected and left attched at their insertions. Engraving after G. de Lairesse, 1739. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-extensor-muscles-of-the-foot-dissected-and-left-attched-at-their-insertions-engraving-after-g-de-lairesse-1739-image450051274.html
The extensor muscles of the foot dissected and left attched at their insertions. Engraving after G. de Lairesse, 1739. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-extensor-muscles-of-the-foot-dissected-and-left-attched-at-their-insertions-engraving-after-g-de-lairesse-1739-image450051274.htmlRM2H45GYP–The extensor muscles of the foot dissected and left attched at their insertions. Engraving after G. de Lairesse, 1739.
![Infographic on the skeleton and muscular system of the horse. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photo Infographic on the skeleton and muscular system of the horse. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2NEBDB3/infographic-on-the-skeleton-and-muscular-system-of-the-horse-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-2NEBDB3.jpg) Infographic on the skeleton and muscular system of the horse. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-on-the-skeleton-and-muscular-system-of-the-horse-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-image525168199.html
Infographic on the skeleton and muscular system of the horse. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-on-the-skeleton-and-muscular-system-of-the-horse-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-image525168199.htmlRM2NEBDB3–Infographic on the skeleton and muscular system of the horse. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015].
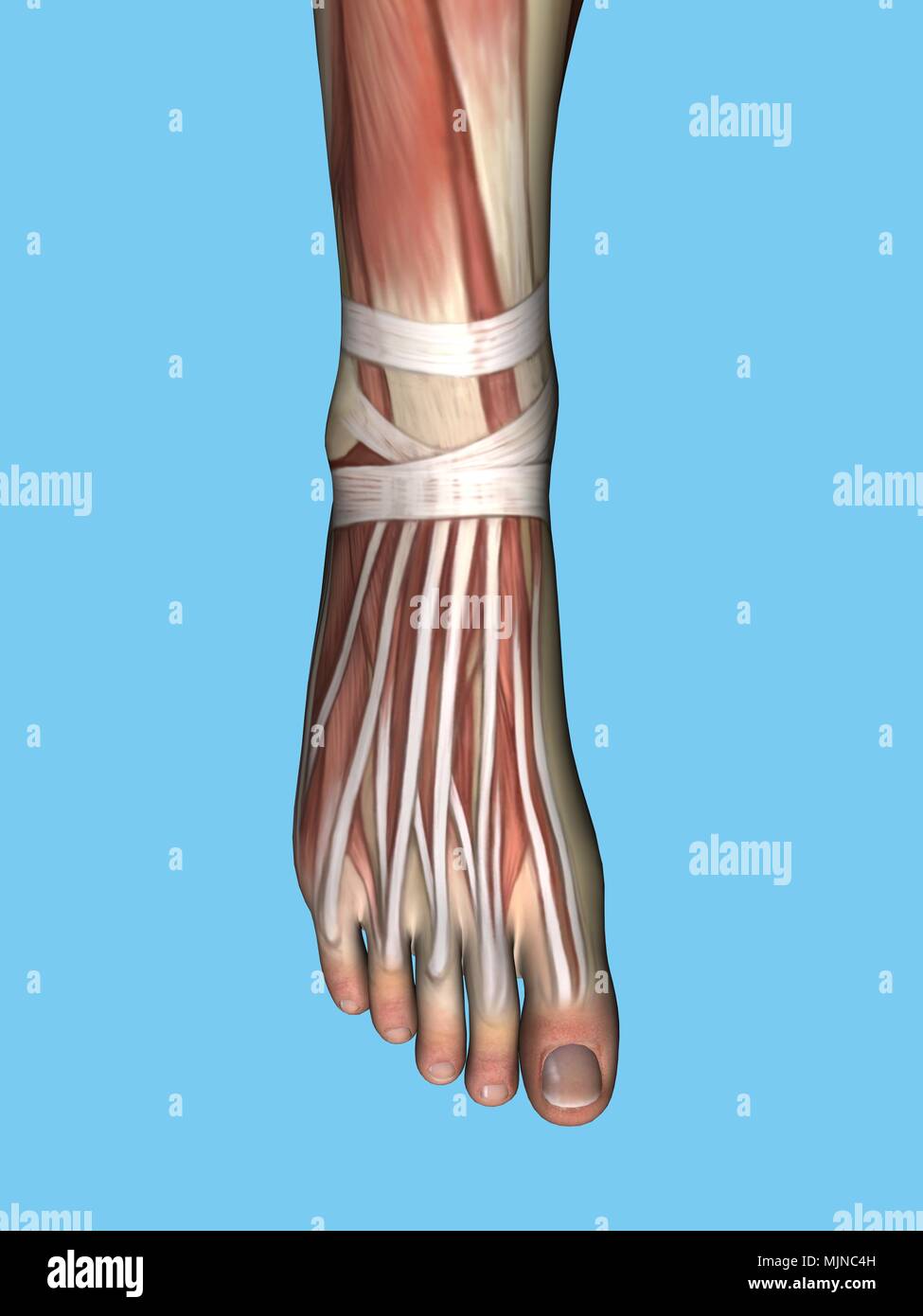 Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183638017.html
Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183638017.htmlRMMJNC4H–Anatomy of foot
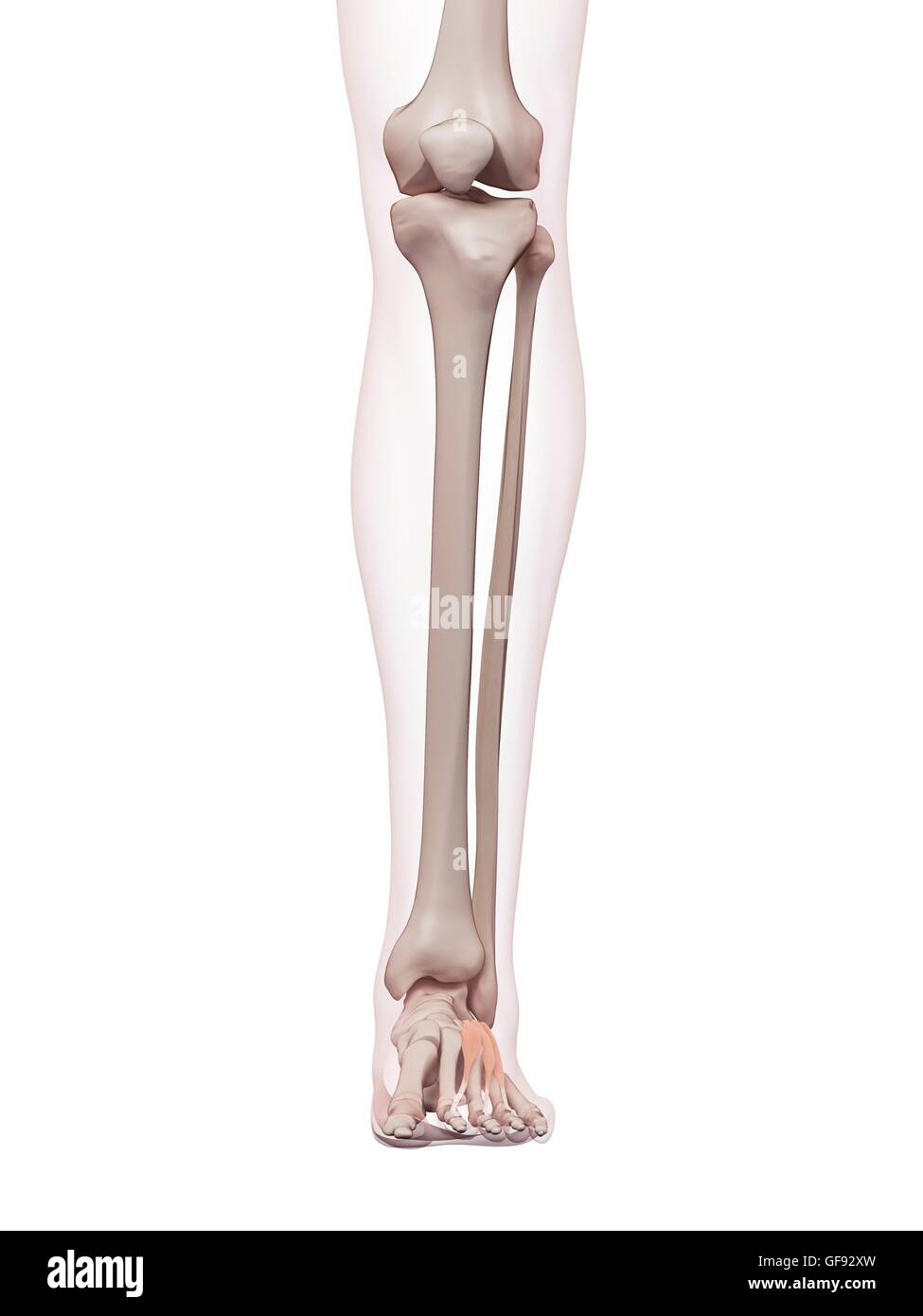 Human foot muscles, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-human-foot-muscles-illustration-112681937.html
Human foot muscles, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-human-foot-muscles-illustration-112681937.htmlRFGF92XW–Human foot muscles, illustration.
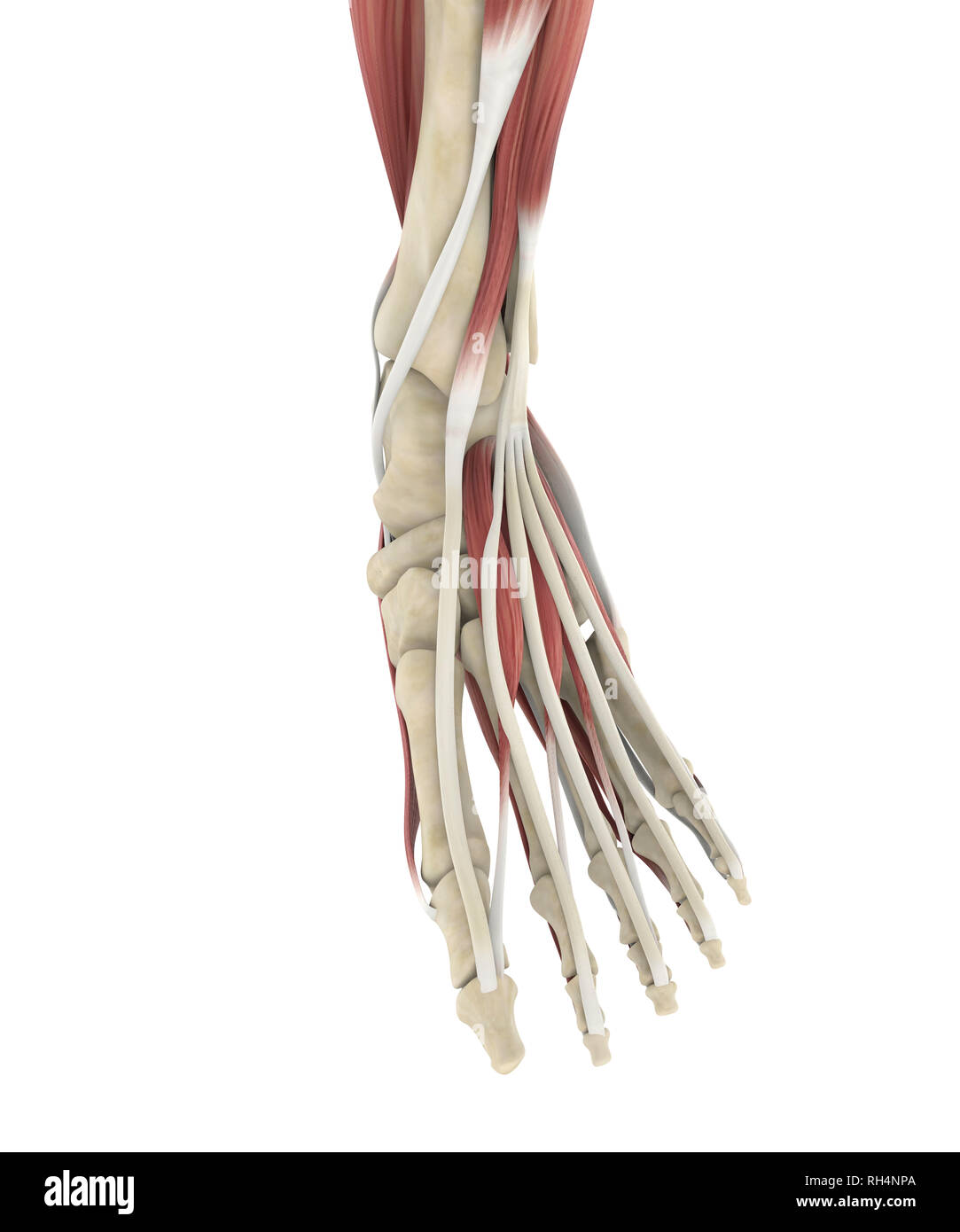 Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image234288834.html
Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image234288834.htmlRFRH4NPA–Human Foot Muscles Anatomy
 . A manual of diseases of the nervous system. le-joint,and adducts the foot. The Extensor longus digitorum (ant. tibial nerve), besidesextending the toes, flexes and abducts the foot. The abduction is in consequenceof the outward position of its tendons beneath the annular ligament. Thesetwo muscles together produce direct flexion of the foot, or flexion with adductionor abduction, as the force of one or the other preponderates. Paralysis of eitherweakens flexion, and the corresponding lateral movement is lost, flexion beingaccompanied by the deviation effected by the muscle that remains. The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-diseases-of-the-nervous-system-le-jointand-adducts-the-foot-the-extensor-longus-digitorum-ant-tibial-nerve-besidesextending-the-toes-flexes-and-abducts-the-foot-the-abduction-is-in-consequenceof-the-outward-position-of-its-tendons-beneath-the-annular-ligament-thesetwo-muscles-together-produce-direct-flexion-of-the-foot-or-flexion-with-adductionor-abduction-as-the-force-of-one-or-the-other-preponderates-paralysis-of-eitherweakens-flexion-and-the-corresponding-lateral-movement-is-lost-flexion-beingaccompanied-by-the-deviation-effected-by-the-muscle-that-remains-the-image337092447.html
. A manual of diseases of the nervous system. le-joint,and adducts the foot. The Extensor longus digitorum (ant. tibial nerve), besidesextending the toes, flexes and abducts the foot. The abduction is in consequenceof the outward position of its tendons beneath the annular ligament. Thesetwo muscles together produce direct flexion of the foot, or flexion with adductionor abduction, as the force of one or the other preponderates. Paralysis of eitherweakens flexion, and the corresponding lateral movement is lost, flexion beingaccompanied by the deviation effected by the muscle that remains. The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-diseases-of-the-nervous-system-le-jointand-adducts-the-foot-the-extensor-longus-digitorum-ant-tibial-nerve-besidesextending-the-toes-flexes-and-abducts-the-foot-the-abduction-is-in-consequenceof-the-outward-position-of-its-tendons-beneath-the-annular-ligament-thesetwo-muscles-together-produce-direct-flexion-of-the-foot-or-flexion-with-adductionor-abduction-as-the-force-of-one-or-the-other-preponderates-paralysis-of-eitherweakens-flexion-and-the-corresponding-lateral-movement-is-lost-flexion-beingaccompanied-by-the-deviation-effected-by-the-muscle-that-remains-the-image337092447.htmlRM2AGBTRY–. A manual of diseases of the nervous system. le-joint,and adducts the foot. The Extensor longus digitorum (ant. tibial nerve), besidesextending the toes, flexes and abducts the foot. The abduction is in consequenceof the outward position of its tendons beneath the annular ligament. Thesetwo muscles together produce direct flexion of the foot, or flexion with adductionor abduction, as the force of one or the other preponderates. Paralysis of eitherweakens flexion, and the corresponding lateral movement is lost, flexion beingaccompanied by the deviation effected by the muscle that remains. The
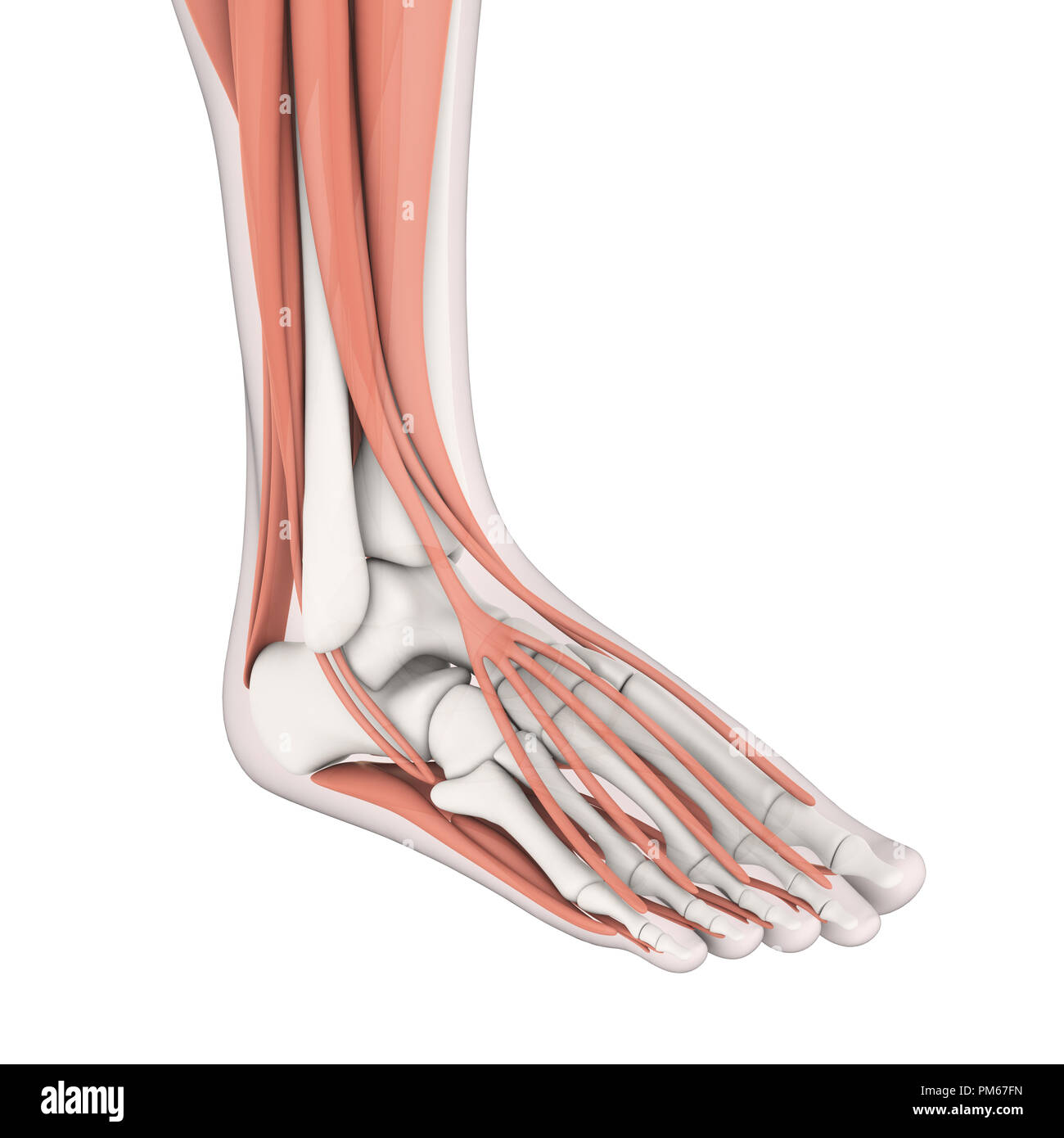 Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image218955177.html
Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image218955177.htmlRFPM67FN–Human Foot Muscles Anatomy
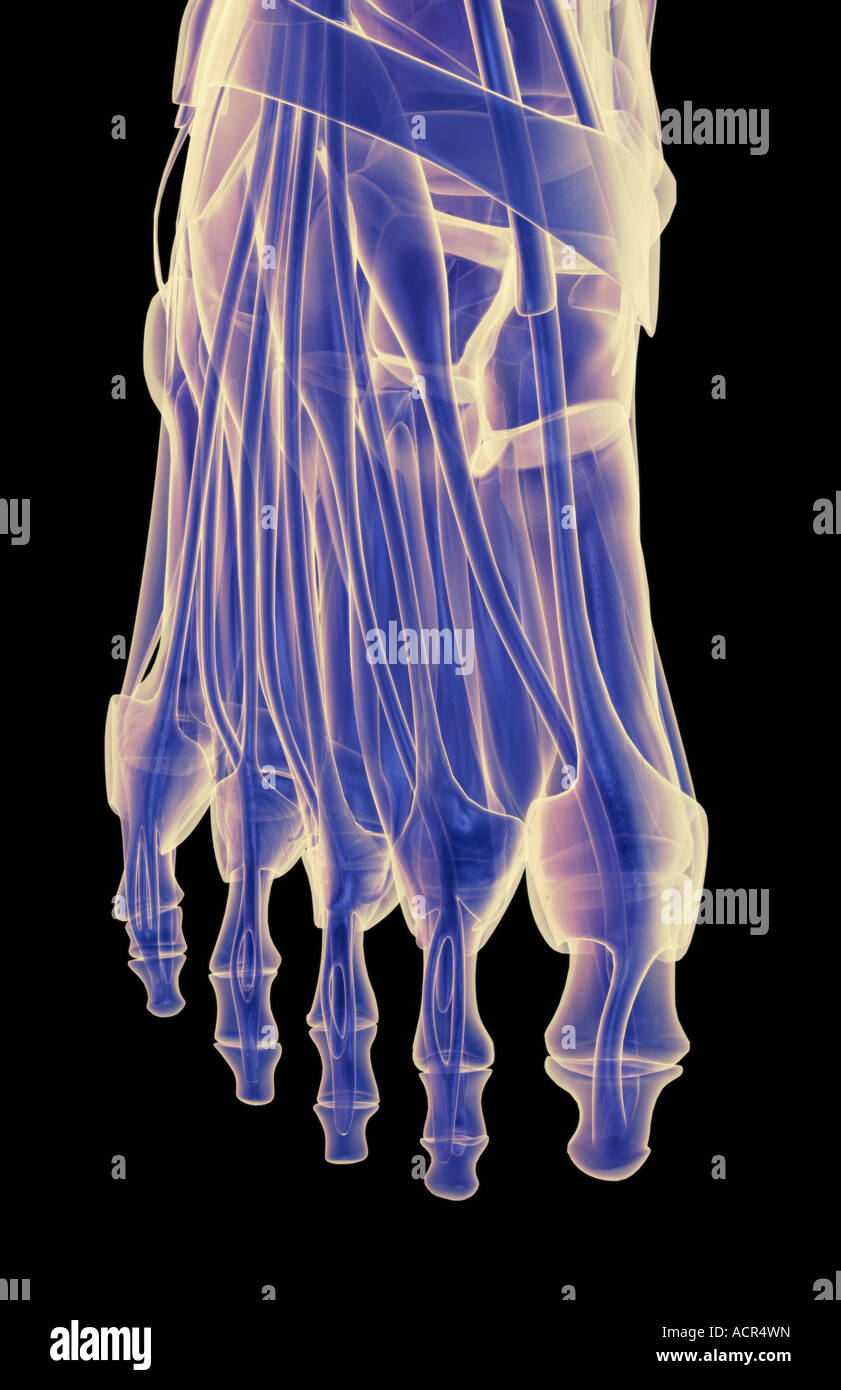 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13213616.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13213616.htmlRFACR4WN–The muscles of the foot
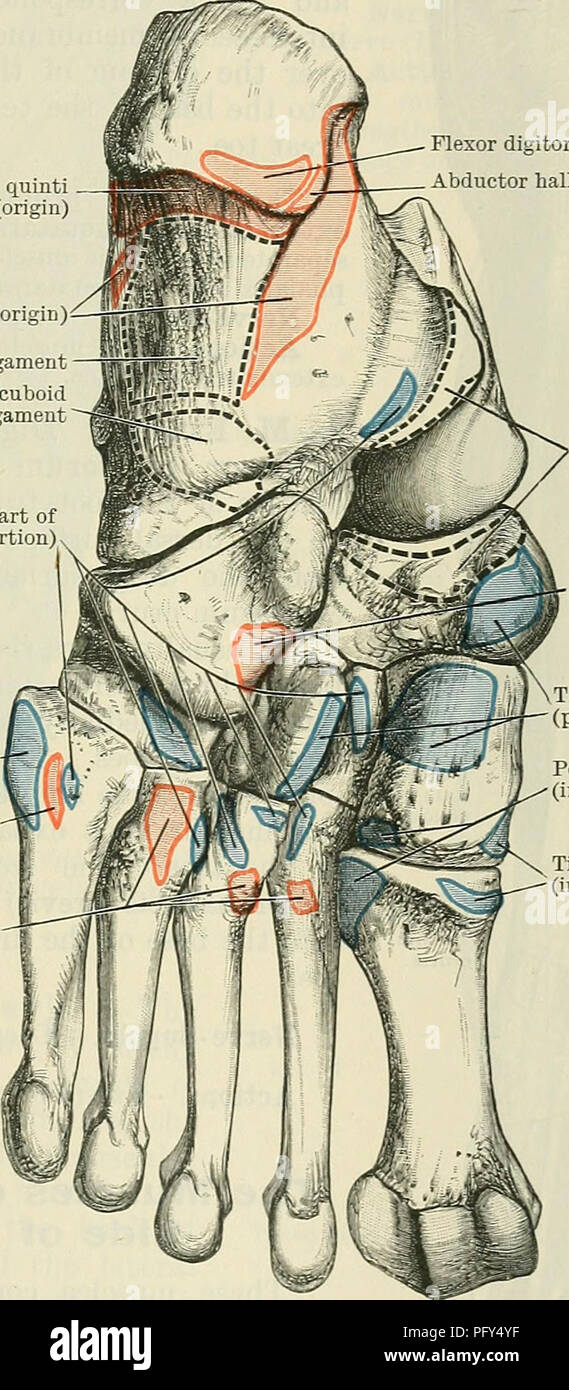
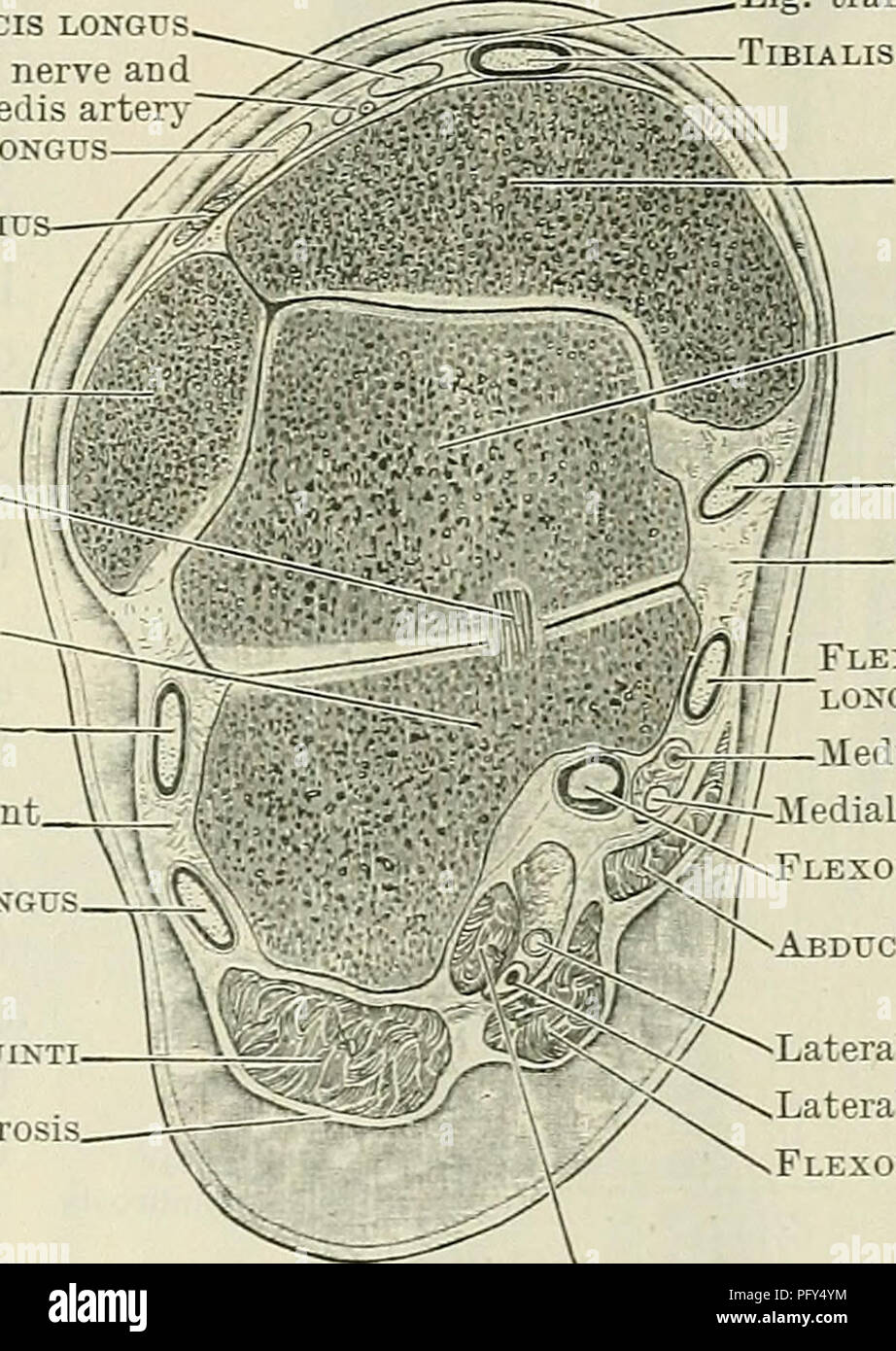 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE FASCIA AND MUSCLES OF THE LEG AND FOOT. 423 peroneal retinaculum binds them down separately on the lateral surfaces of the calcaneus. The ligamentum transversum cruris (O.T. anterior annular ligament, upper band), broad and undefined at its proximal and distal borders, stretches across the front of the ankle between the two malleoli. This band binds down to the distal end of the tibia the tendons of the tibialis anterior and extensor muscles of the toes. One synovial sheath is found beneath it, surrounding the tendon of the tibialis anterior. L Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-fascia-and-muscles-of-the-leg-and-foot-423-peroneal-retinaculum-binds-them-down-separately-on-the-lateral-surfaces-of-the-calcaneus-the-ligamentum-transversum-cruris-ot-anterior-annular-ligament-upper-band-broad-and-undefined-at-its-proximal-and-distal-borders-stretches-across-the-front-of-the-ankle-between-the-two-malleoli-this-band-binds-down-to-the-distal-end-of-the-tibia-the-tendons-of-the-tibialis-anterior-and-extensor-muscles-of-the-toes-one-synovial-sheath-is-found-beneath-it-surrounding-the-tendon-of-the-tibialis-anterior-l-image216340872.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE FASCIA AND MUSCLES OF THE LEG AND FOOT. 423 peroneal retinaculum binds them down separately on the lateral surfaces of the calcaneus. The ligamentum transversum cruris (O.T. anterior annular ligament, upper band), broad and undefined at its proximal and distal borders, stretches across the front of the ankle between the two malleoli. This band binds down to the distal end of the tibia the tendons of the tibialis anterior and extensor muscles of the toes. One synovial sheath is found beneath it, surrounding the tendon of the tibialis anterior. L Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-fascia-and-muscles-of-the-leg-and-foot-423-peroneal-retinaculum-binds-them-down-separately-on-the-lateral-surfaces-of-the-calcaneus-the-ligamentum-transversum-cruris-ot-anterior-annular-ligament-upper-band-broad-and-undefined-at-its-proximal-and-distal-borders-stretches-across-the-front-of-the-ankle-between-the-two-malleoli-this-band-binds-down-to-the-distal-end-of-the-tibia-the-tendons-of-the-tibialis-anterior-and-extensor-muscles-of-the-toes-one-synovial-sheath-is-found-beneath-it-surrounding-the-tendon-of-the-tibialis-anterior-l-image216340872.htmlRMPFY4YM–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE FASCIA AND MUSCLES OF THE LEG AND FOOT. 423 peroneal retinaculum binds them down separately on the lateral surfaces of the calcaneus. The ligamentum transversum cruris (O.T. anterior annular ligament, upper band), broad and undefined at its proximal and distal borders, stretches across the front of the ankle between the two malleoli. This band binds down to the distal end of the tibia the tendons of the tibialis anterior and extensor muscles of the toes. One synovial sheath is found beneath it, surrounding the tendon of the tibialis anterior. L
 . Kig. 27. Method of supporting thigh and foot and of recording the swing of the lower leg in the knee-jerk experiment. A, support under thigh; B, pulley; C, cross shape<l writing needle; D, rubber band, twisted so as to keep point of ipe<l writing needle against drum; E, knee-jerk hammer to swing if it is free to move. The anterior horn cells taking part in this act are in the leg areas of the third and fourth lumbar segments of the cord. The response of these cells to the sensory stimulus from the extensor muscles, is either reenforced or inhibited by other impulses reaching the anteri Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/kig-27-method-of-supporting-thigh-and-foot-and-of-recording-the-swing-of-the-lower-leg-in-the-knee-jerk-experiment-a-support-under-thigh-b-pulley-c-cross-shapeltl-writing-needle-d-rubber-band-twisted-so-as-to-keep-point-of-ipeltl-writing-needle-against-drum-e-knee-jerk-hammer-to-swing-if-it-is-free-to-move-the-anterior-horn-cells-taking-part-in-this-act-are-in-the-leg-areas-of-the-third-and-fourth-lumbar-segments-of-the-cord-the-response-of-these-cells-to-the-sensory-stimulus-from-the-extensor-muscles-is-either-reenforced-or-inhibited-by-other-impulses-reaching-the-anteri-image180051166.html
. Kig. 27. Method of supporting thigh and foot and of recording the swing of the lower leg in the knee-jerk experiment. A, support under thigh; B, pulley; C, cross shape<l writing needle; D, rubber band, twisted so as to keep point of ipe<l writing needle against drum; E, knee-jerk hammer to swing if it is free to move. The anterior horn cells taking part in this act are in the leg areas of the third and fourth lumbar segments of the cord. The response of these cells to the sensory stimulus from the extensor muscles, is either reenforced or inhibited by other impulses reaching the anteri Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/kig-27-method-of-supporting-thigh-and-foot-and-of-recording-the-swing-of-the-lower-leg-in-the-knee-jerk-experiment-a-support-under-thigh-b-pulley-c-cross-shapeltl-writing-needle-d-rubber-band-twisted-so-as-to-keep-point-of-ipeltl-writing-needle-against-drum-e-knee-jerk-hammer-to-swing-if-it-is-free-to-move-the-anterior-horn-cells-taking-part-in-this-act-are-in-the-leg-areas-of-the-third-and-fourth-lumbar-segments-of-the-cord-the-response-of-these-cells-to-the-sensory-stimulus-from-the-extensor-muscles-is-either-reenforced-or-inhibited-by-other-impulses-reaching-the-anteri-image180051166.htmlRMMCX12P–. Kig. 27. Method of supporting thigh and foot and of recording the swing of the lower leg in the knee-jerk experiment. A, support under thigh; B, pulley; C, cross shape<l writing needle; D, rubber band, twisted so as to keep point of ipe<l writing needle against drum; E, knee-jerk hammer to swing if it is free to move. The anterior horn cells taking part in this act are in the leg areas of the third and fourth lumbar segments of the cord. The response of these cells to the sensory stimulus from the extensor muscles, is either reenforced or inhibited by other impulses reaching the anteri
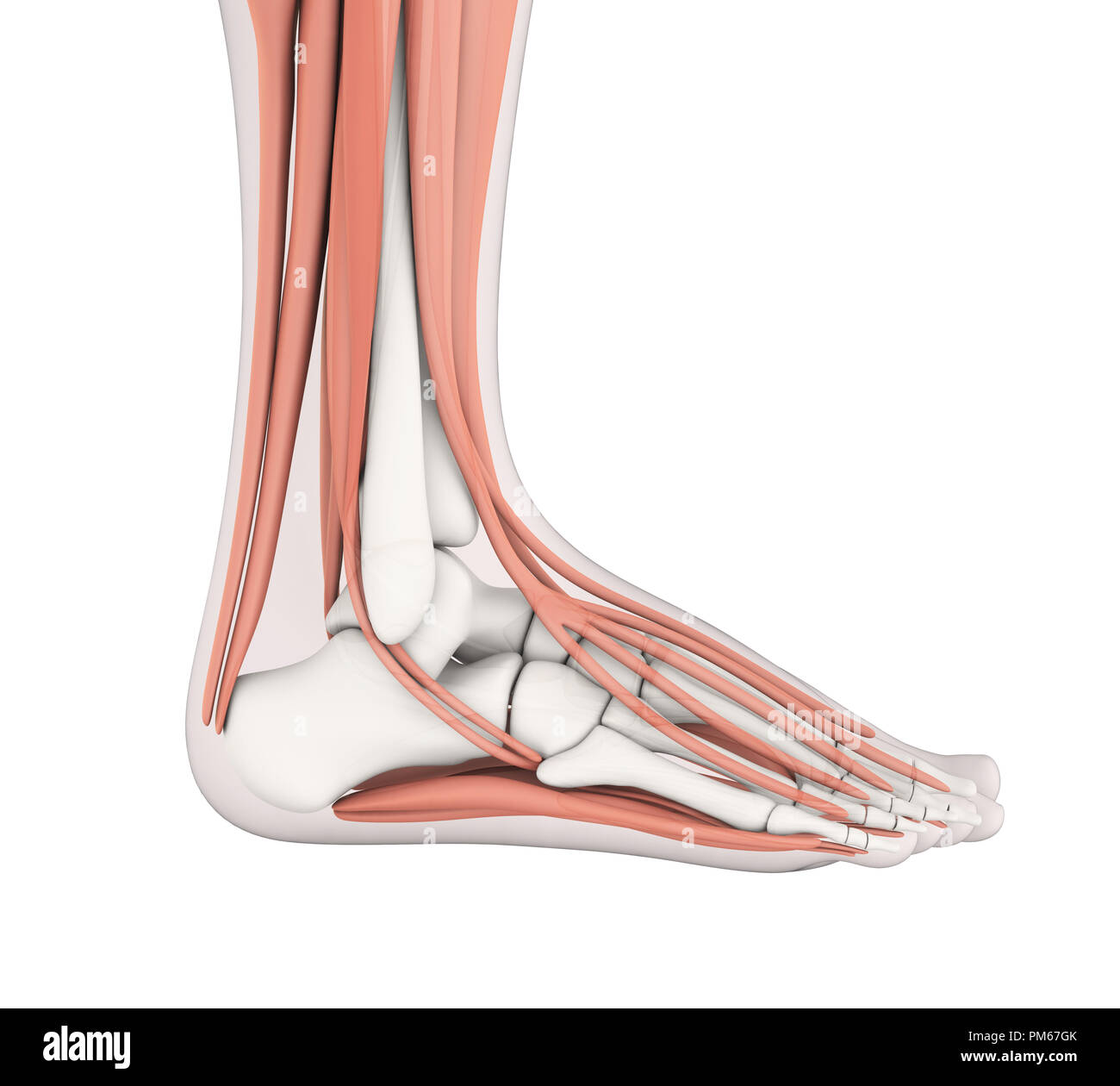
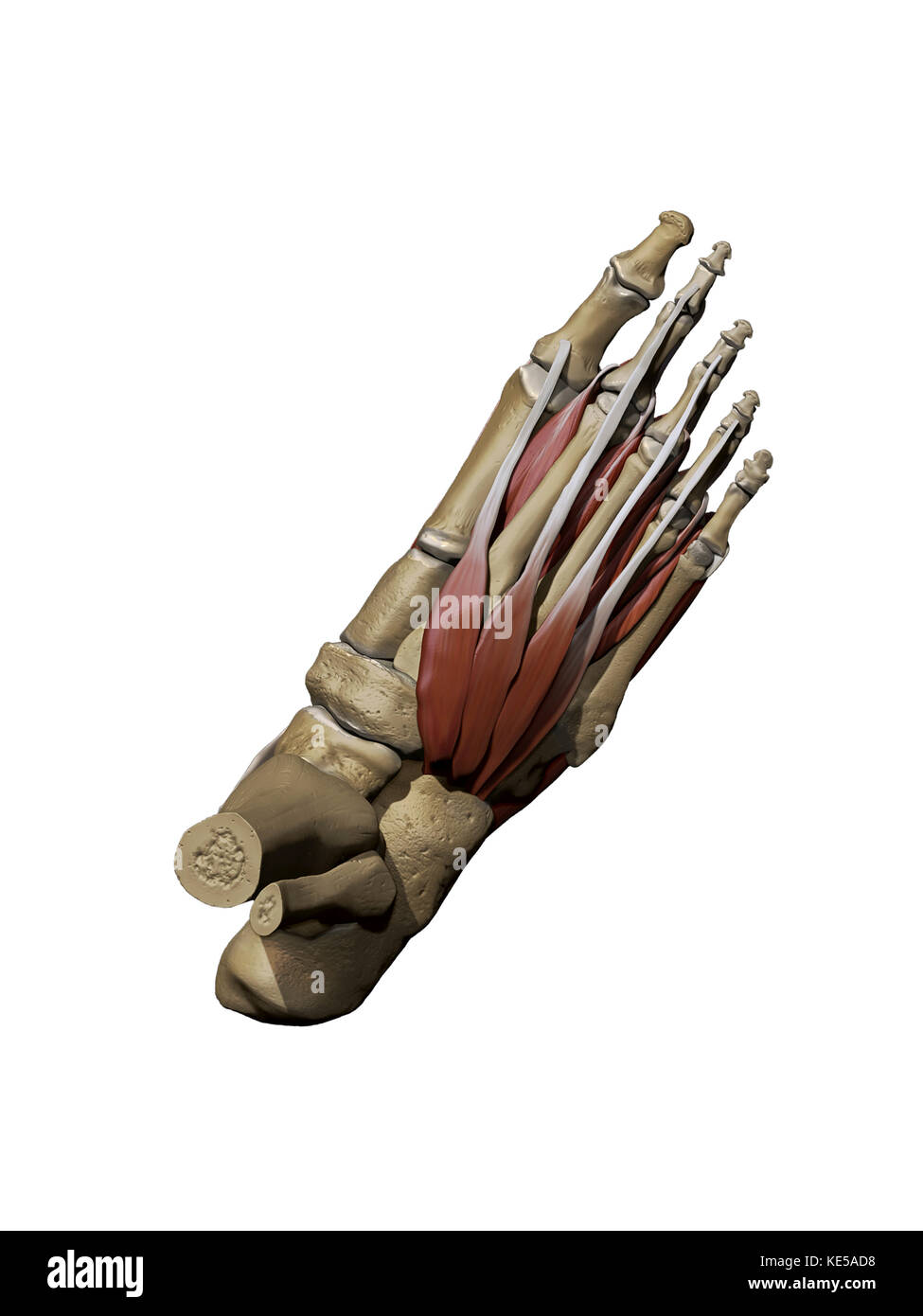 3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal intermediate muscles and bone structures. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-3d-model-of-the-foot-depicting-the-dorsal-intermediate-muscles-and-163616468.html
3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal intermediate muscles and bone structures. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-3d-model-of-the-foot-depicting-the-dorsal-intermediate-muscles-and-163616468.htmlRFKE5AD8–3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal intermediate muscles and bone structures.
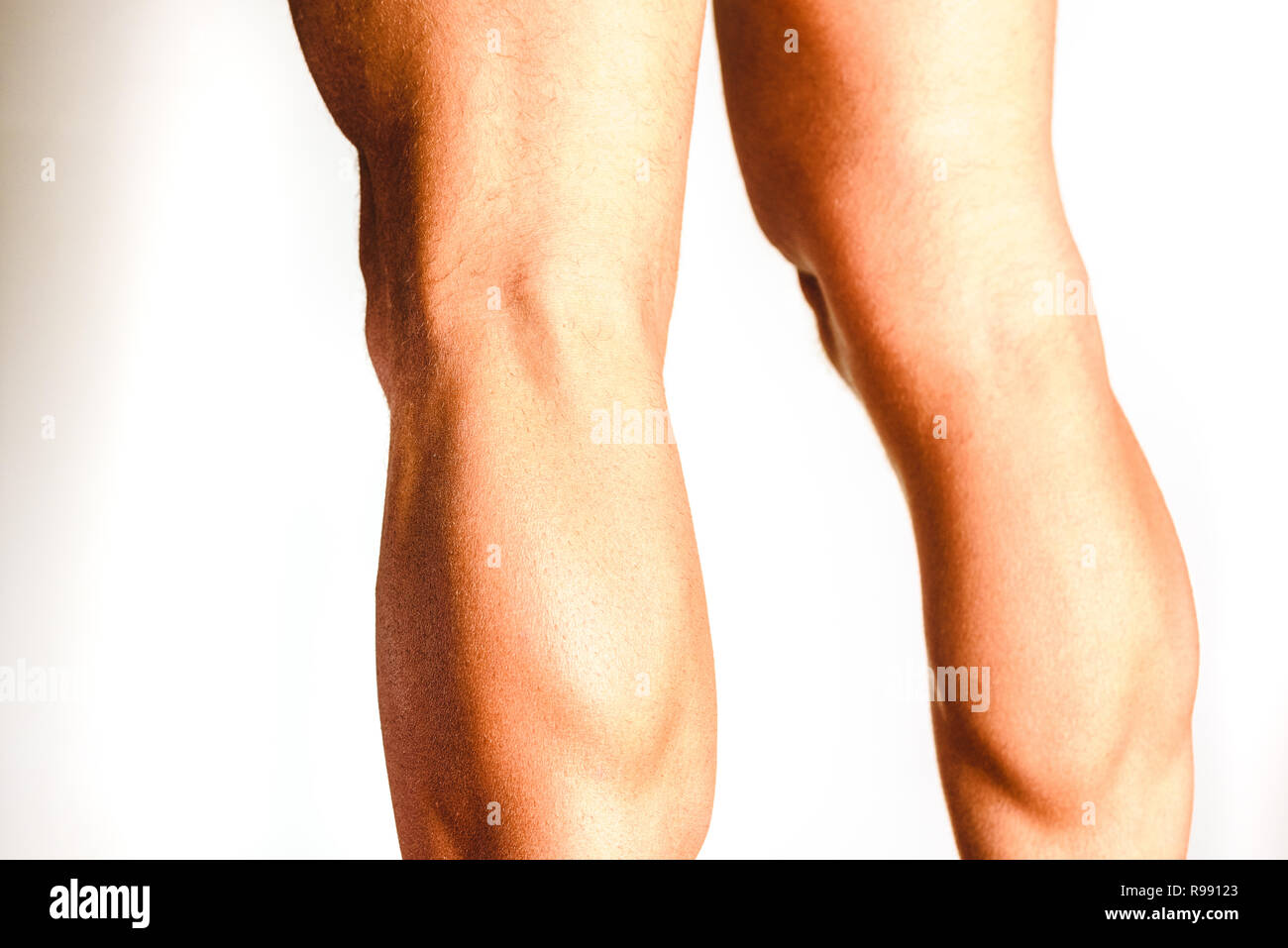 Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229465099.html
Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229465099.htmlRFR99123–Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete.
 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696270.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696270.htmlRF2CBRFRX–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
 Medical Illustration of Extensor Digitorum Brevis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-digitorum-brevis-image490198431.html
Medical Illustration of Extensor Digitorum Brevis Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-digitorum-brevis-image490198431.htmlRF2KDED2R–Medical Illustration of Extensor Digitorum Brevis
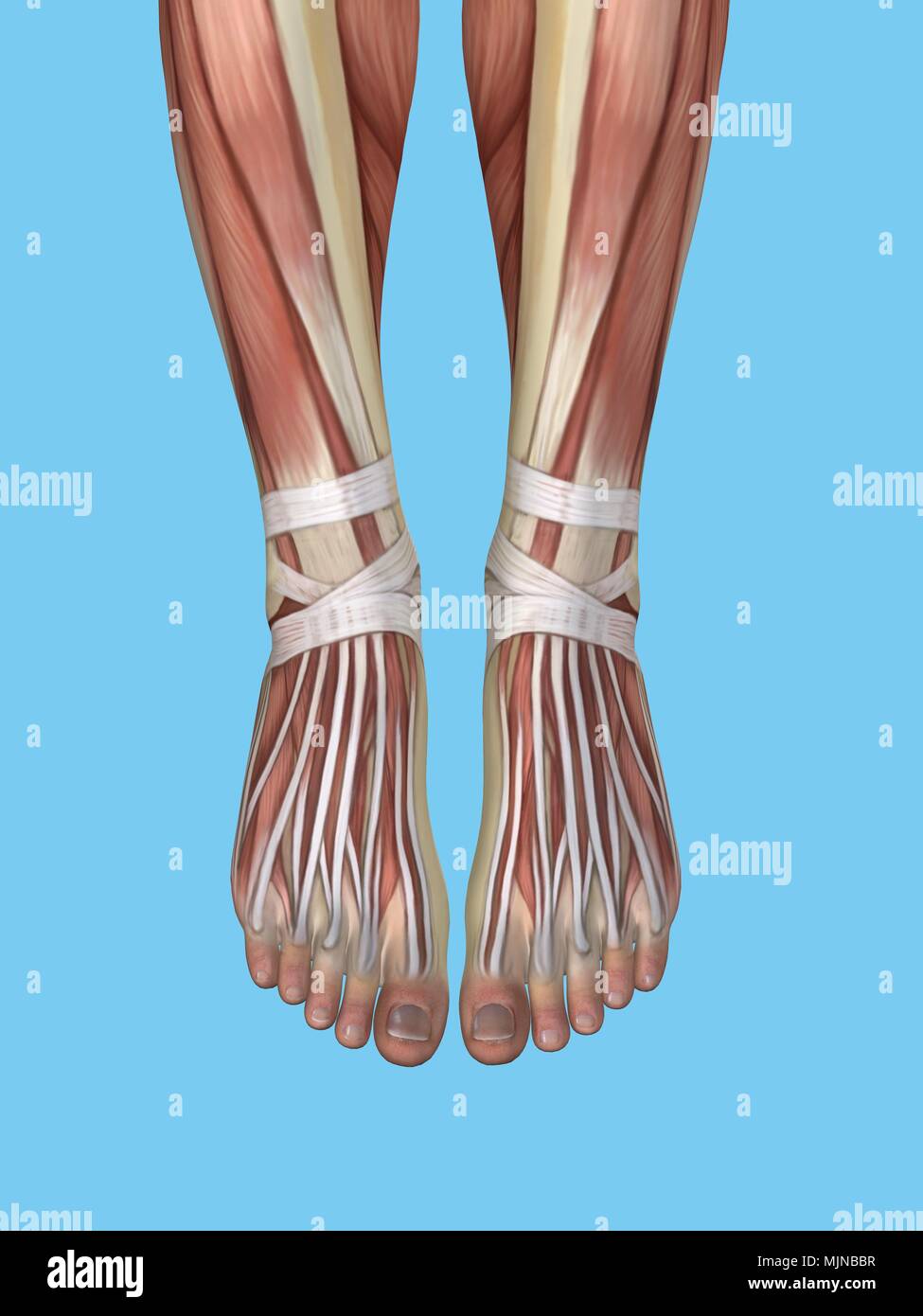 Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183637435.html
Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183637435.htmlRMMJNBBR–Anatomy of foot
 Human foot muscles, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-human-foot-muscles-illustration-112681940.html
Human foot muscles, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-human-foot-muscles-illustration-112681940.htmlRFGF92Y0–Human foot muscles, illustration.
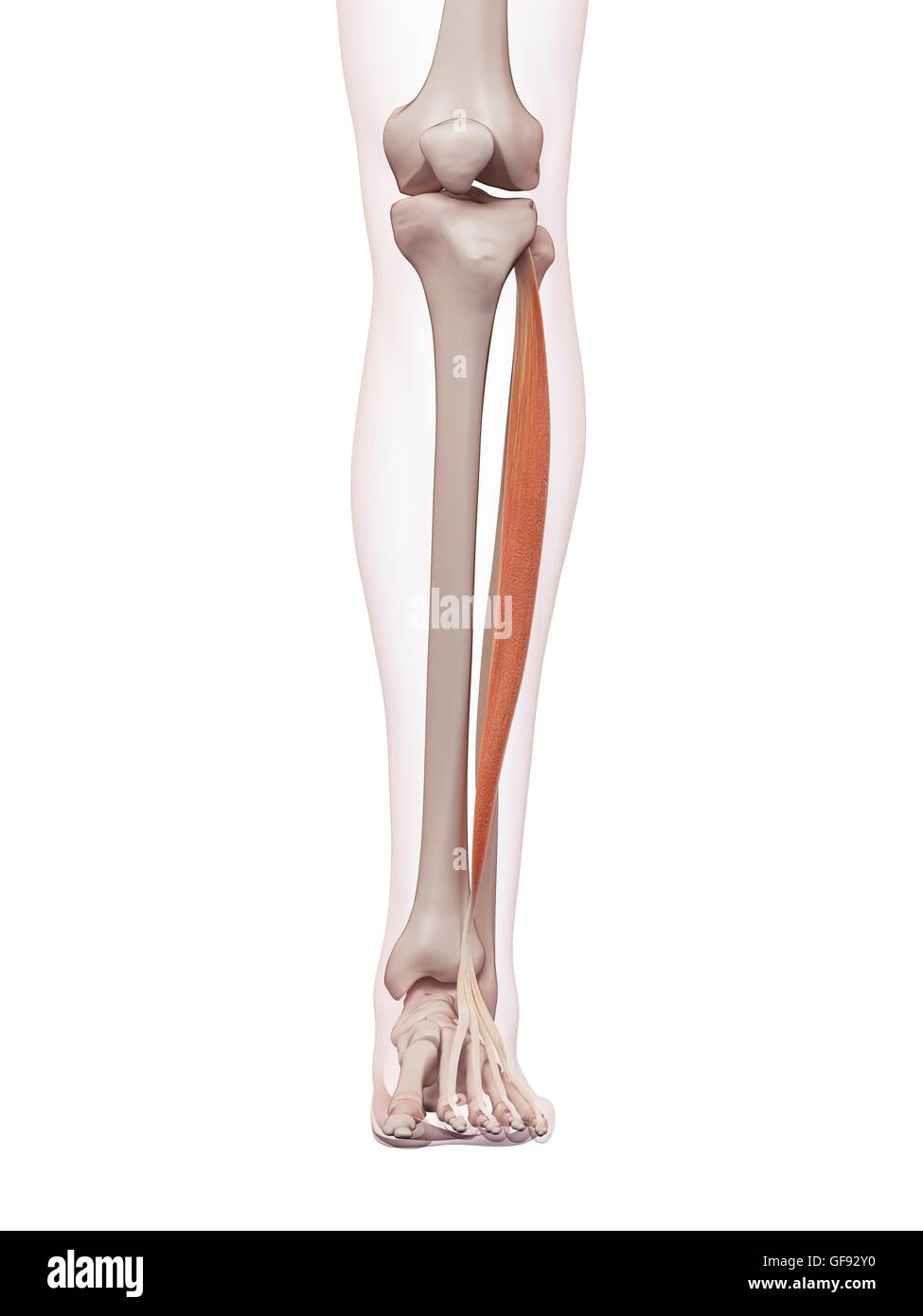
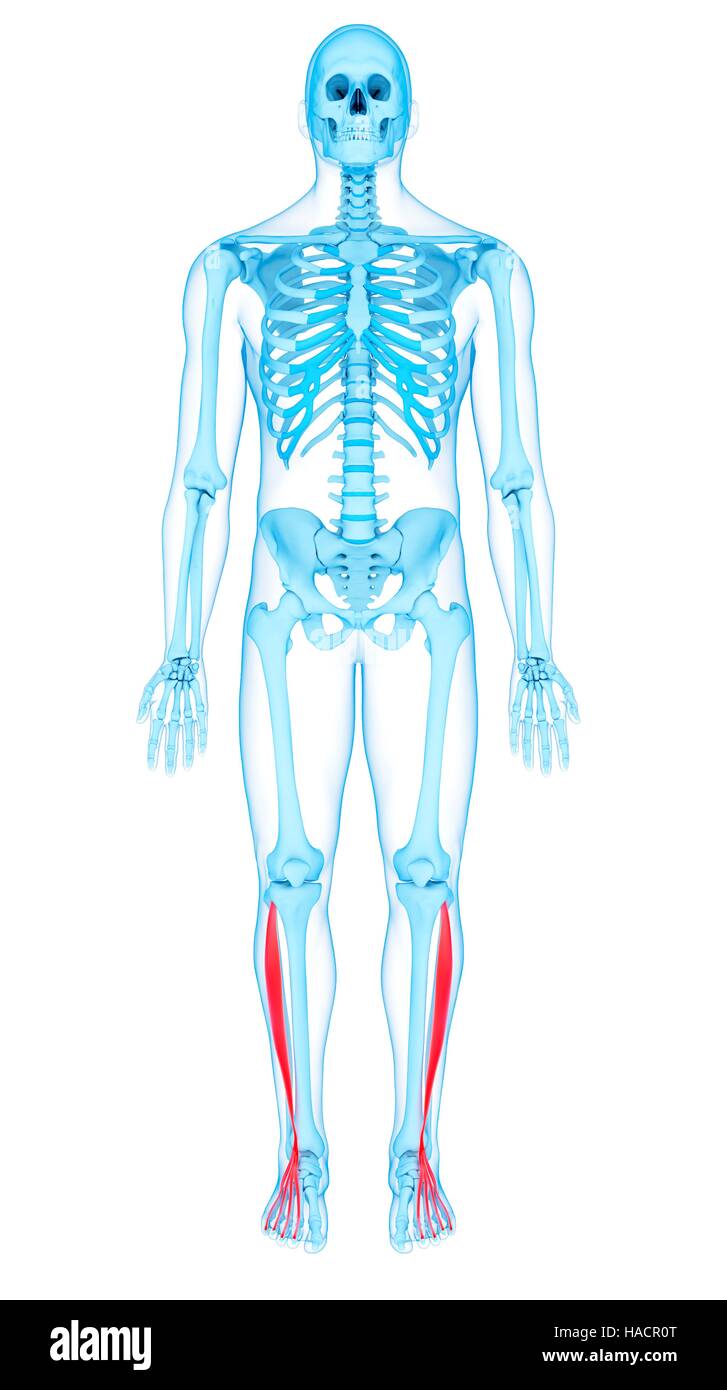 Illustration of the extensor digitorum longus muscles. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-illustration-of-the-extensor-digitorum-longus-muscles-126900616.html
Illustration of the extensor digitorum longus muscles. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-illustration-of-the-extensor-digitorum-longus-muscles-126900616.htmlRFHACR0T–Illustration of the extensor digitorum longus muscles.
 Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image218955203.html
Human Foot Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-foot-muscles-anatomy-image218955203.htmlRFPM67GK–Human Foot Muscles Anatomy
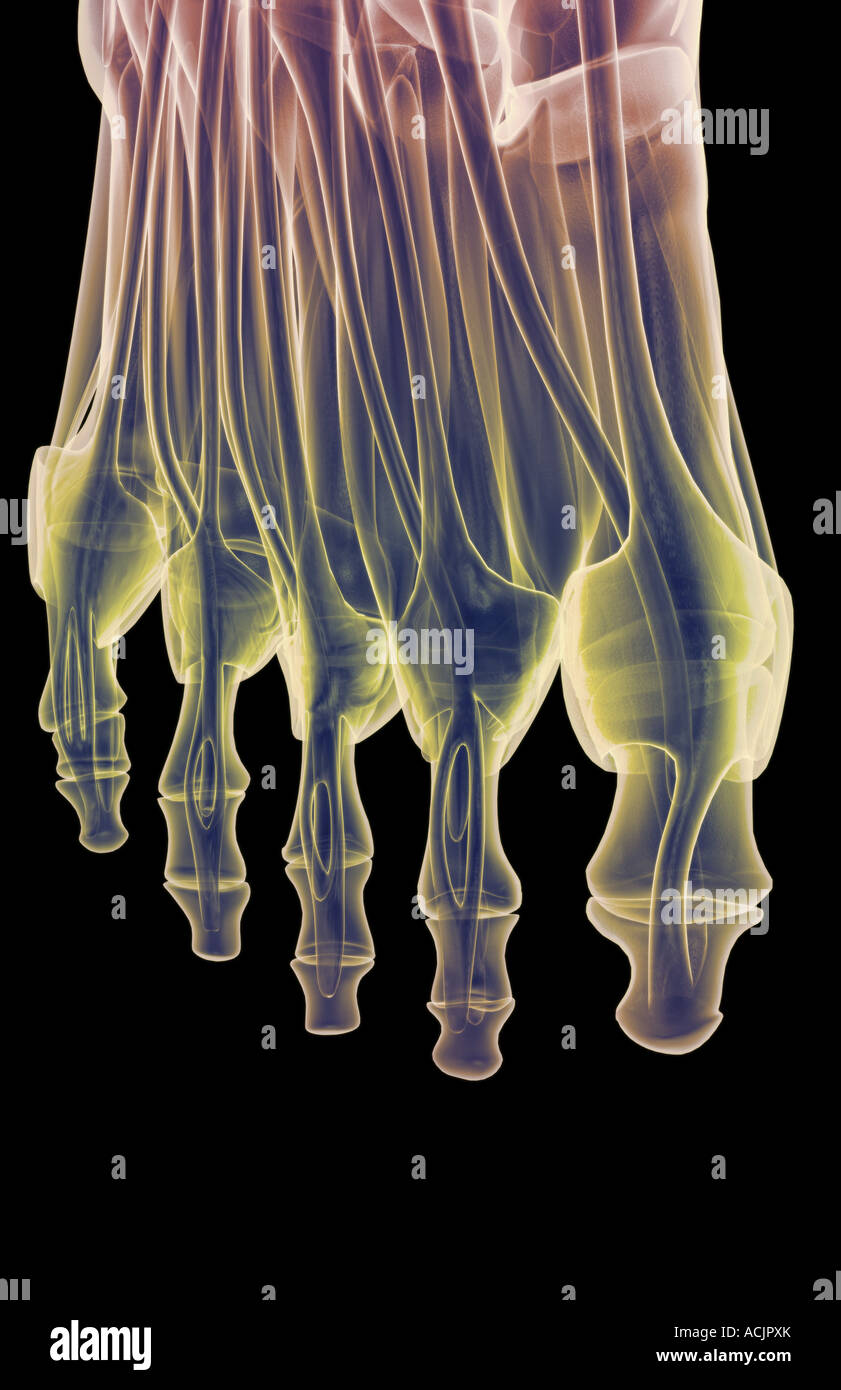 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13172634.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13172634.htmlRFACJPXK–The muscles of the foot
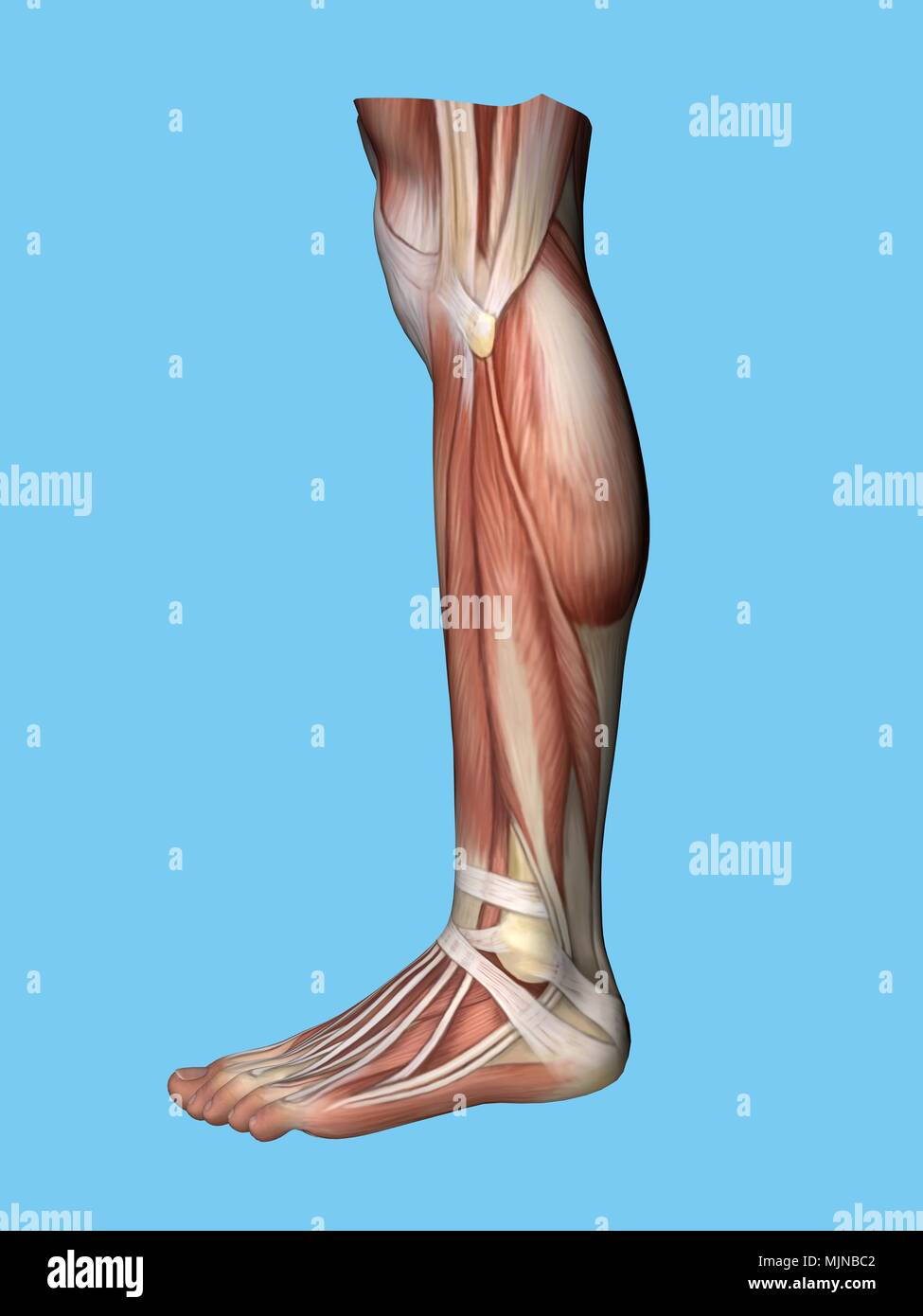
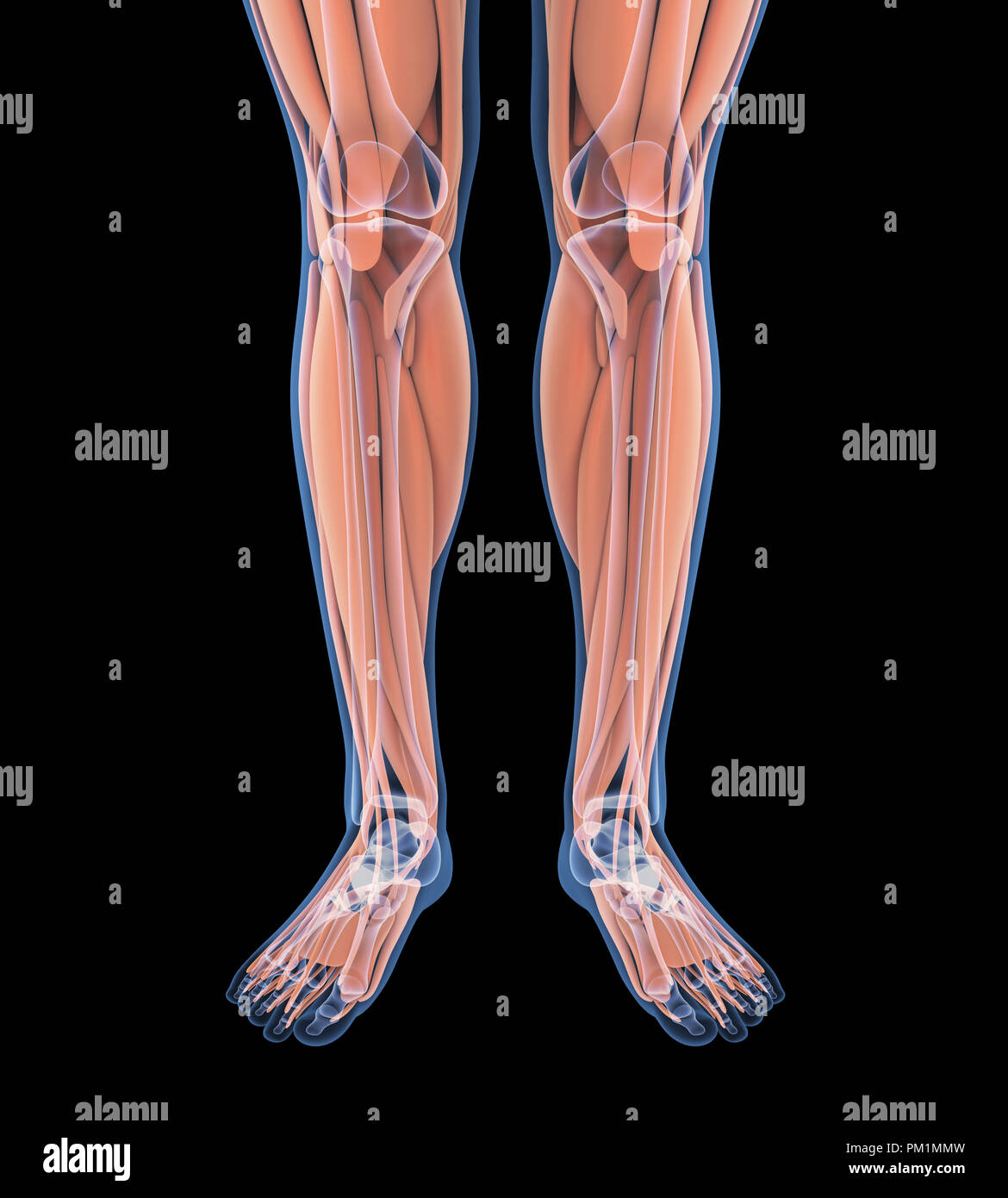 Human Leg Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-leg-muscles-anatomy-image218855753.html
Human Leg Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-leg-muscles-anatomy-image218855753.htmlRFPM1MMW–Human Leg Muscles Anatomy
 A manual of diseases of the nervous system . le-joint,and adducts the foot. The Extensor longus digitorum (ant. tibial nerve), besidesextending the toes, flexes and abducts the foot. The abduction is in consequenceof the outward position of its tendons beneath the annular ligament. Thesetwo muscles together produce direct flexion of the foot, or flexion with adductionor abduction, as the force of one or the other preponderates. Paralysis of eitherweakens flexion, and the corresponding lateral movement is lost, flexion beingaccompanied by the deviation effected by the muscle that remains. The d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-diseases-of-the-nervous-system-le-jointand-adducts-the-foot-the-extensor-longus-digitorum-ant-tibial-nerve-besidesextending-the-toes-flexes-and-abducts-the-foot-the-abduction-is-in-consequenceof-the-outward-position-of-its-tendons-beneath-the-annular-ligament-thesetwo-muscles-together-produce-direct-flexion-of-the-foot-or-flexion-with-adductionor-abduction-as-the-force-of-one-or-the-other-preponderates-paralysis-of-eitherweakens-flexion-and-the-corresponding-lateral-movement-is-lost-flexion-beingaccompanied-by-the-deviation-effected-by-the-muscle-that-remains-the-d-image338260894.html
A manual of diseases of the nervous system . le-joint,and adducts the foot. The Extensor longus digitorum (ant. tibial nerve), besidesextending the toes, flexes and abducts the foot. The abduction is in consequenceof the outward position of its tendons beneath the annular ligament. Thesetwo muscles together produce direct flexion of the foot, or flexion with adductionor abduction, as the force of one or the other preponderates. Paralysis of eitherweakens flexion, and the corresponding lateral movement is lost, flexion beingaccompanied by the deviation effected by the muscle that remains. The d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-diseases-of-the-nervous-system-le-jointand-adducts-the-foot-the-extensor-longus-digitorum-ant-tibial-nerve-besidesextending-the-toes-flexes-and-abducts-the-foot-the-abduction-is-in-consequenceof-the-outward-position-of-its-tendons-beneath-the-annular-ligament-thesetwo-muscles-together-produce-direct-flexion-of-the-foot-or-flexion-with-adductionor-abduction-as-the-force-of-one-or-the-other-preponderates-paralysis-of-eitherweakens-flexion-and-the-corresponding-lateral-movement-is-lost-flexion-beingaccompanied-by-the-deviation-effected-by-the-muscle-that-remains-the-d-image338260894.htmlRM2AJ9366–A manual of diseases of the nervous system . le-joint,and adducts the foot. The Extensor longus digitorum (ant. tibial nerve), besidesextending the toes, flexes and abducts the foot. The abduction is in consequenceof the outward position of its tendons beneath the annular ligament. Thesetwo muscles together produce direct flexion of the foot, or flexion with adductionor abduction, as the force of one or the other preponderates. Paralysis of eitherweakens flexion, and the corresponding lateral movement is lost, flexion beingaccompanied by the deviation effected by the muscle that remains. The d
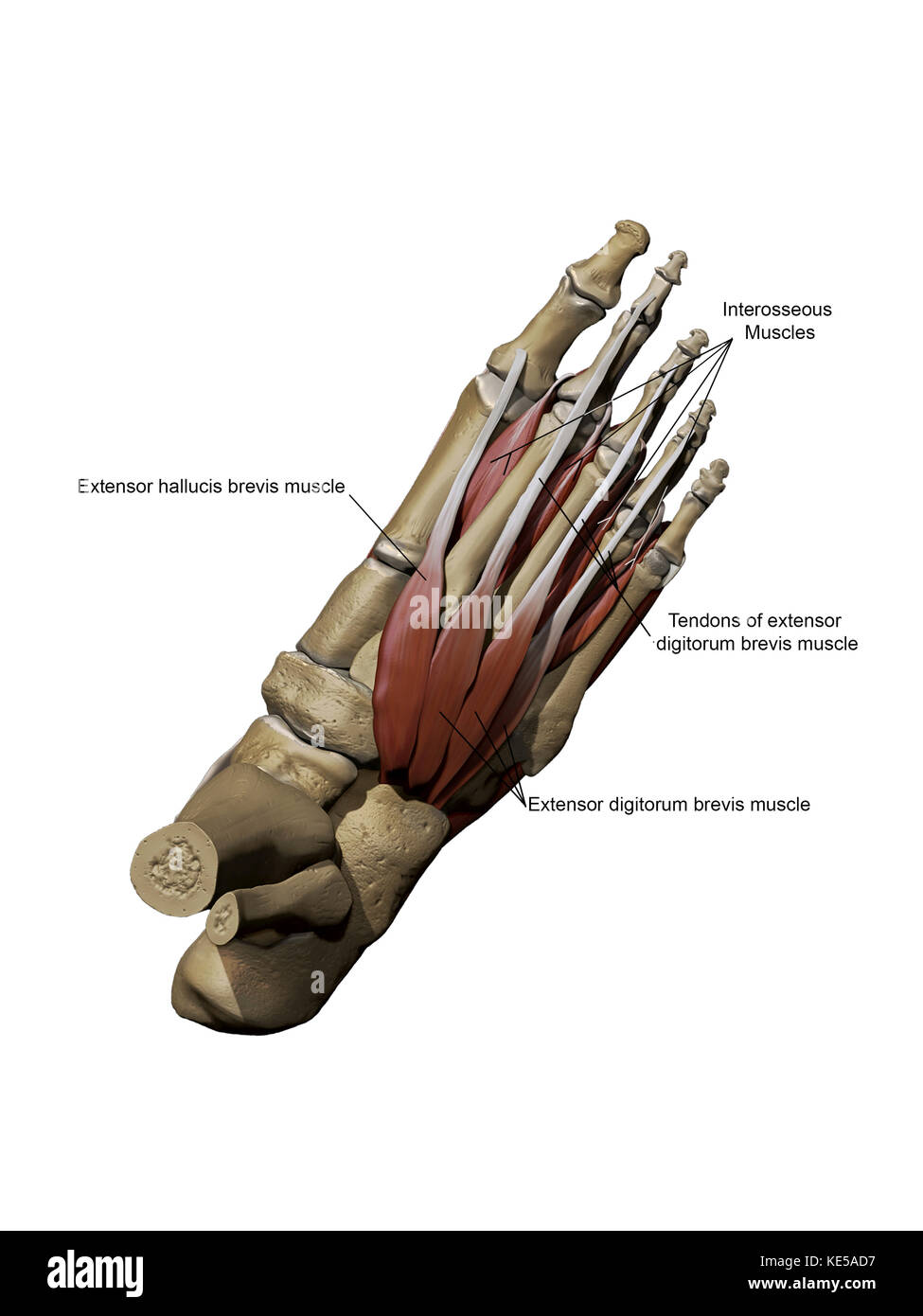 Human foot showing the dorsal intermediate muscles and bone structures with annotations. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-human-foot-showing-the-dorsal-intermediate-muscles-and-bone-structures-163616467.html
Human foot showing the dorsal intermediate muscles and bone structures with annotations. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-human-foot-showing-the-dorsal-intermediate-muscles-and-bone-structures-163616467.htmlRFKE5AD7–Human foot showing the dorsal intermediate muscles and bone structures with annotations.
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES OF THE LEG AND FOOT. 425 M. Extensor Digitorum Longus.—The extensor digitorum longus arises by fleshy fibres from the lateral side of the lateral condyle of the tibia, from the proximal two-thirds or more of the anterior part of the medial surface of the shaft of the fibula, from the fascia over it, and from intermuscular septa on either side. It gives rise to a tendon which passes beneath the ligamentum transversum and cruciatum, and in front of the ankle subdivides into four tendons, inserted into the four lateral toes, exactly in the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-muscles-of-the-leg-and-foot-425-m-extensor-digitorum-longusthe-extensor-digitorum-longus-arises-by-fleshy-fibres-from-the-lateral-side-of-the-lateral-condyle-of-the-tibia-from-the-proximal-two-thirds-or-more-of-the-anterior-part-of-the-medial-surface-of-the-shaft-of-the-fibula-from-the-fascia-over-it-and-from-intermuscular-septa-on-either-side-it-gives-rise-to-a-tendon-which-passes-beneath-the-ligamentum-transversum-and-cruciatum-and-in-front-of-the-ankle-subdivides-into-four-tendons-inserted-into-the-four-lateral-toes-exactly-in-the-image216340867.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES OF THE LEG AND FOOT. 425 M. Extensor Digitorum Longus.—The extensor digitorum longus arises by fleshy fibres from the lateral side of the lateral condyle of the tibia, from the proximal two-thirds or more of the anterior part of the medial surface of the shaft of the fibula, from the fascia over it, and from intermuscular septa on either side. It gives rise to a tendon which passes beneath the ligamentum transversum and cruciatum, and in front of the ankle subdivides into four tendons, inserted into the four lateral toes, exactly in the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-muscles-of-the-leg-and-foot-425-m-extensor-digitorum-longusthe-extensor-digitorum-longus-arises-by-fleshy-fibres-from-the-lateral-side-of-the-lateral-condyle-of-the-tibia-from-the-proximal-two-thirds-or-more-of-the-anterior-part-of-the-medial-surface-of-the-shaft-of-the-fibula-from-the-fascia-over-it-and-from-intermuscular-septa-on-either-side-it-gives-rise-to-a-tendon-which-passes-beneath-the-ligamentum-transversum-and-cruciatum-and-in-front-of-the-ankle-subdivides-into-four-tendons-inserted-into-the-four-lateral-toes-exactly-in-the-image216340867.htmlRMPFY4YF–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES OF THE LEG AND FOOT. 425 M. Extensor Digitorum Longus.—The extensor digitorum longus arises by fleshy fibres from the lateral side of the lateral condyle of the tibia, from the proximal two-thirds or more of the anterior part of the medial surface of the shaft of the fibula, from the fascia over it, and from intermuscular septa on either side. It gives rise to a tendon which passes beneath the ligamentum transversum and cruciatum, and in front of the ankle subdivides into four tendons, inserted into the four lateral toes, exactly in the
 Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066784.html
Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066784.htmlRFR8JW0G–Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete.
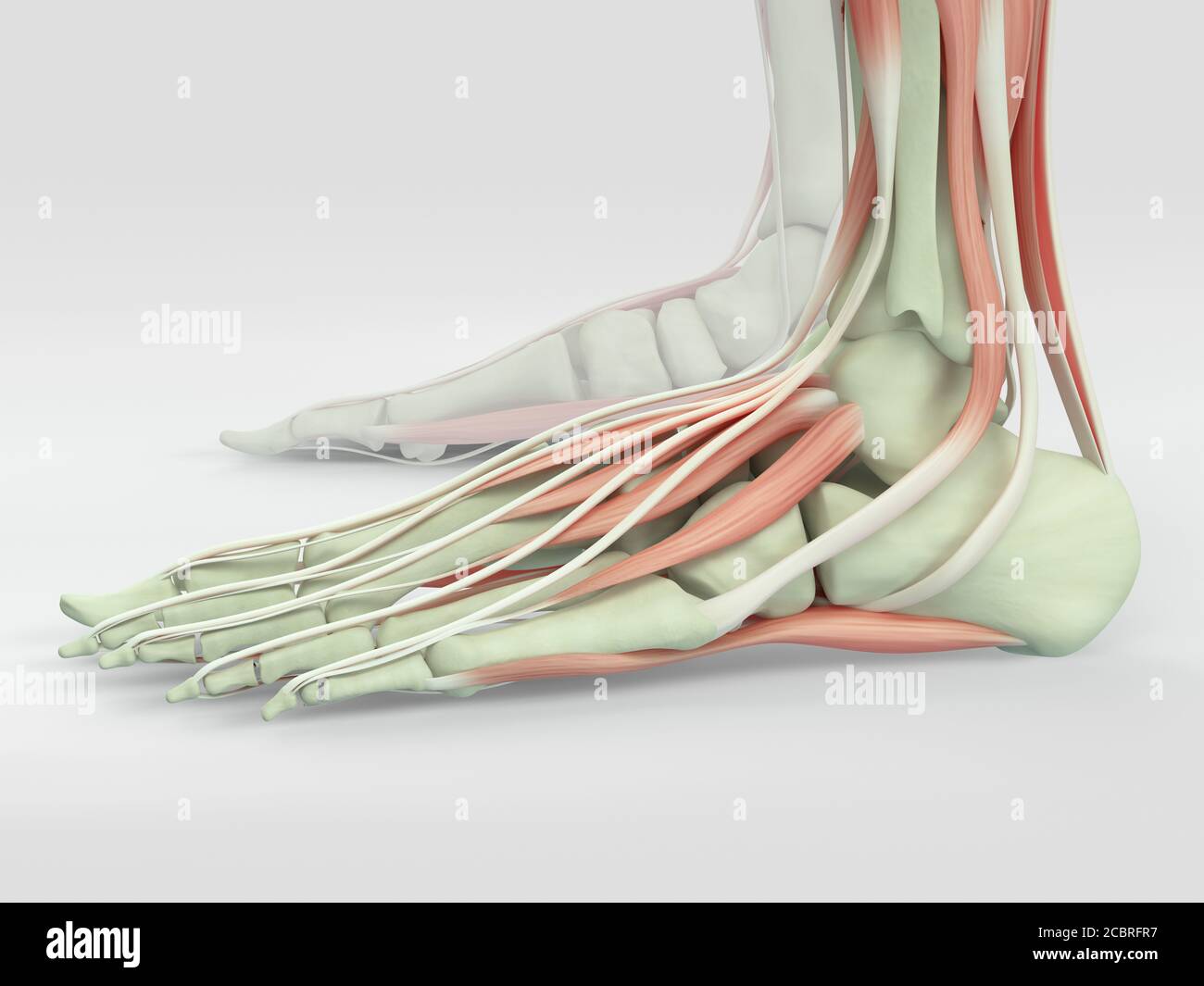 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696251.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696251.htmlRF2CBRFR7–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
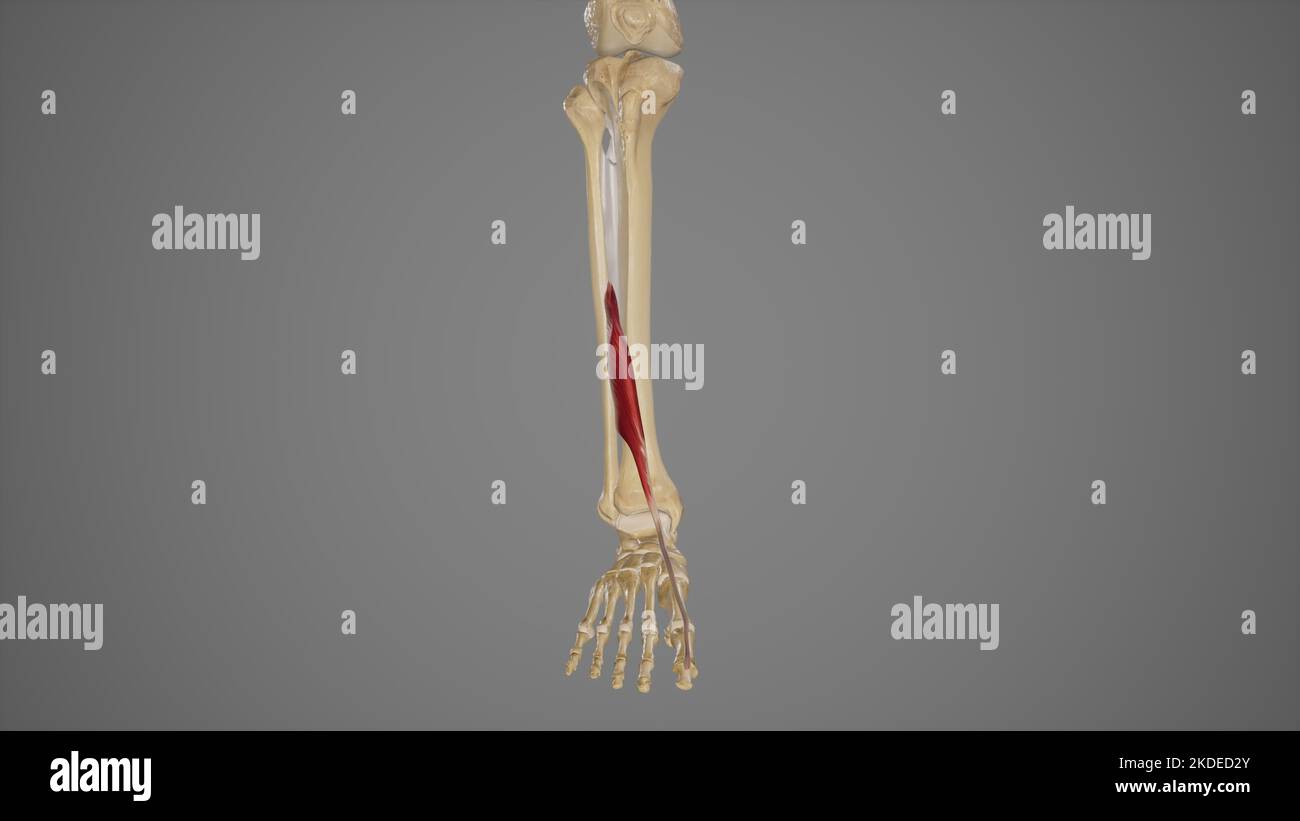 Medical Illustration of Extensor Hallucis Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-hallucis-longus-image490198435.html
Medical Illustration of Extensor Hallucis Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-hallucis-longus-image490198435.htmlRF2KDED2Y–Medical Illustration of Extensor Hallucis Longus
 Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183637442.html
Anatomy of foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-foot-image183637442.htmlRMMJNBC2–Anatomy of foot
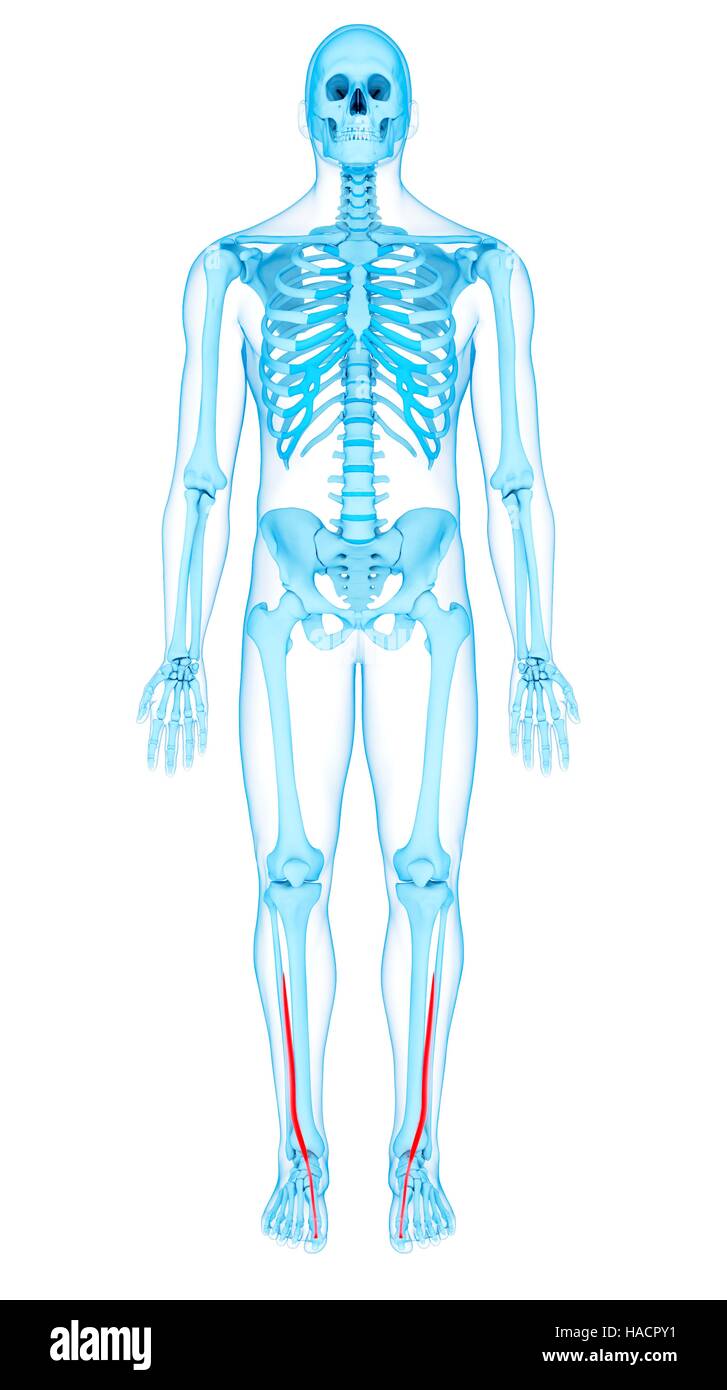 Illustration of the extensor hallucis longus muscles. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-illustration-of-the-extensor-hallucis-longus-muscles-126900565.html
Illustration of the extensor hallucis longus muscles. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-illustration-of-the-extensor-hallucis-longus-muscles-126900565.htmlRFHACPY1–Illustration of the extensor hallucis longus muscles.
 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13175587.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13175587.htmlRFACK3MM–The muscles of the foot
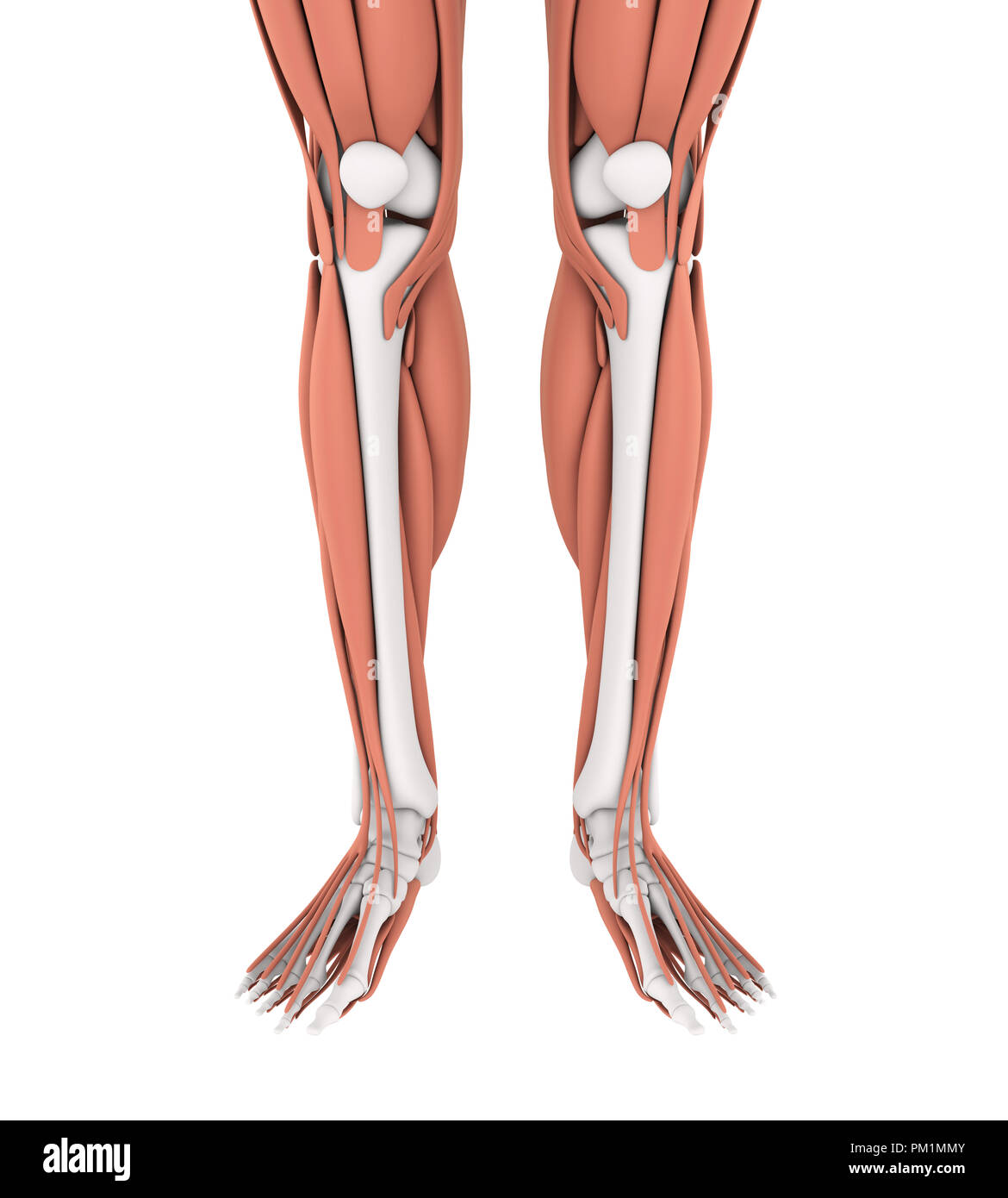 Human Leg Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-leg-muscles-anatomy-image218855755.html
Human Leg Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-leg-muscles-anatomy-image218855755.htmlRFPM1MMY–Human Leg Muscles Anatomy
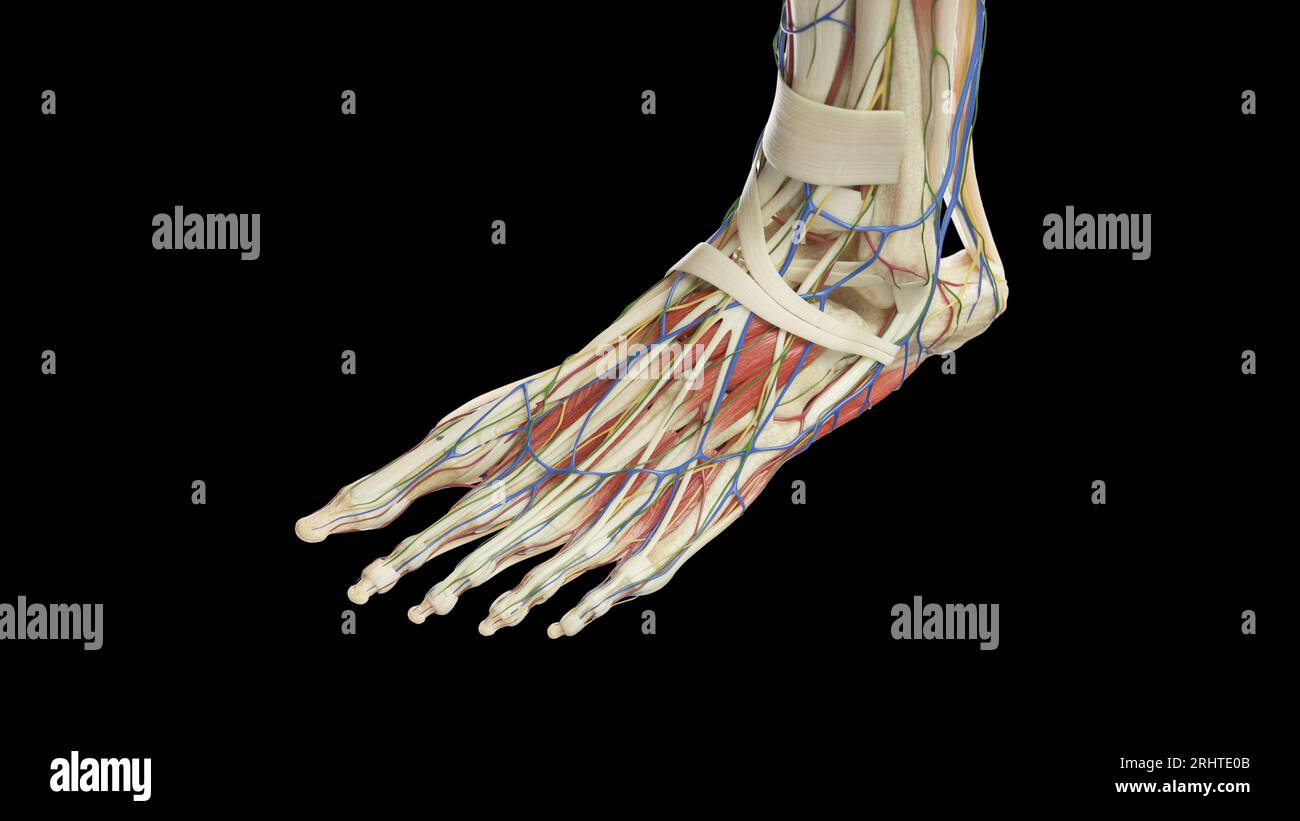 Anatomy of the left foot, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-the-left-foot-illustration-image561718763.html
Anatomy of the left foot, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-the-left-foot-illustration-image561718763.htmlRF2RHTE0B–Anatomy of the left foot, illustration
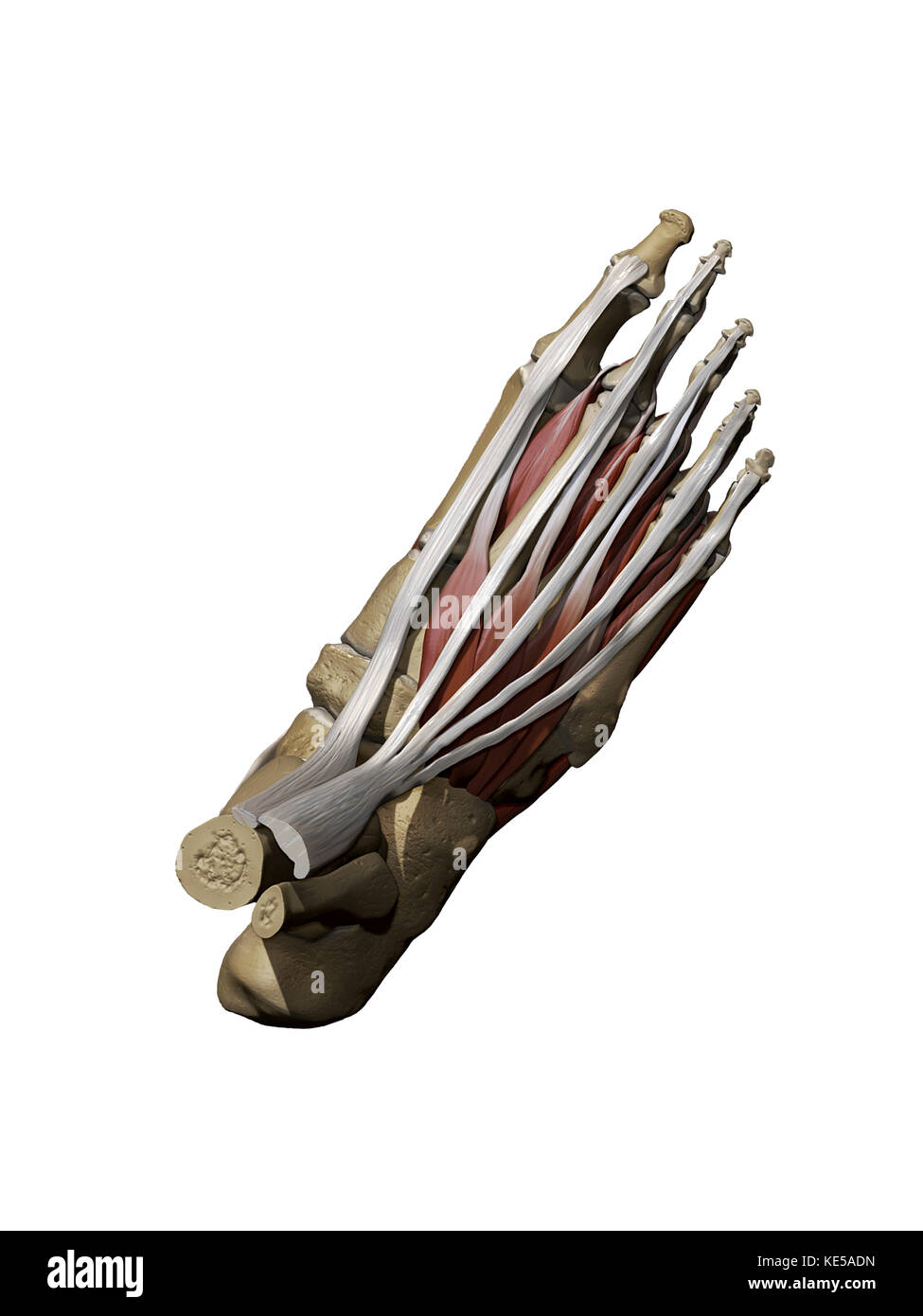 3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal superficial muscles and bone structure. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-3d-model-of-the-foot-depicting-the-dorsal-superficial-muscles-and-163616481.html
3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal superficial muscles and bone structure. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-3d-model-of-the-foot-depicting-the-dorsal-superficial-muscles-and-163616481.htmlRFKE5ADN–3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal superficial muscles and bone structure.
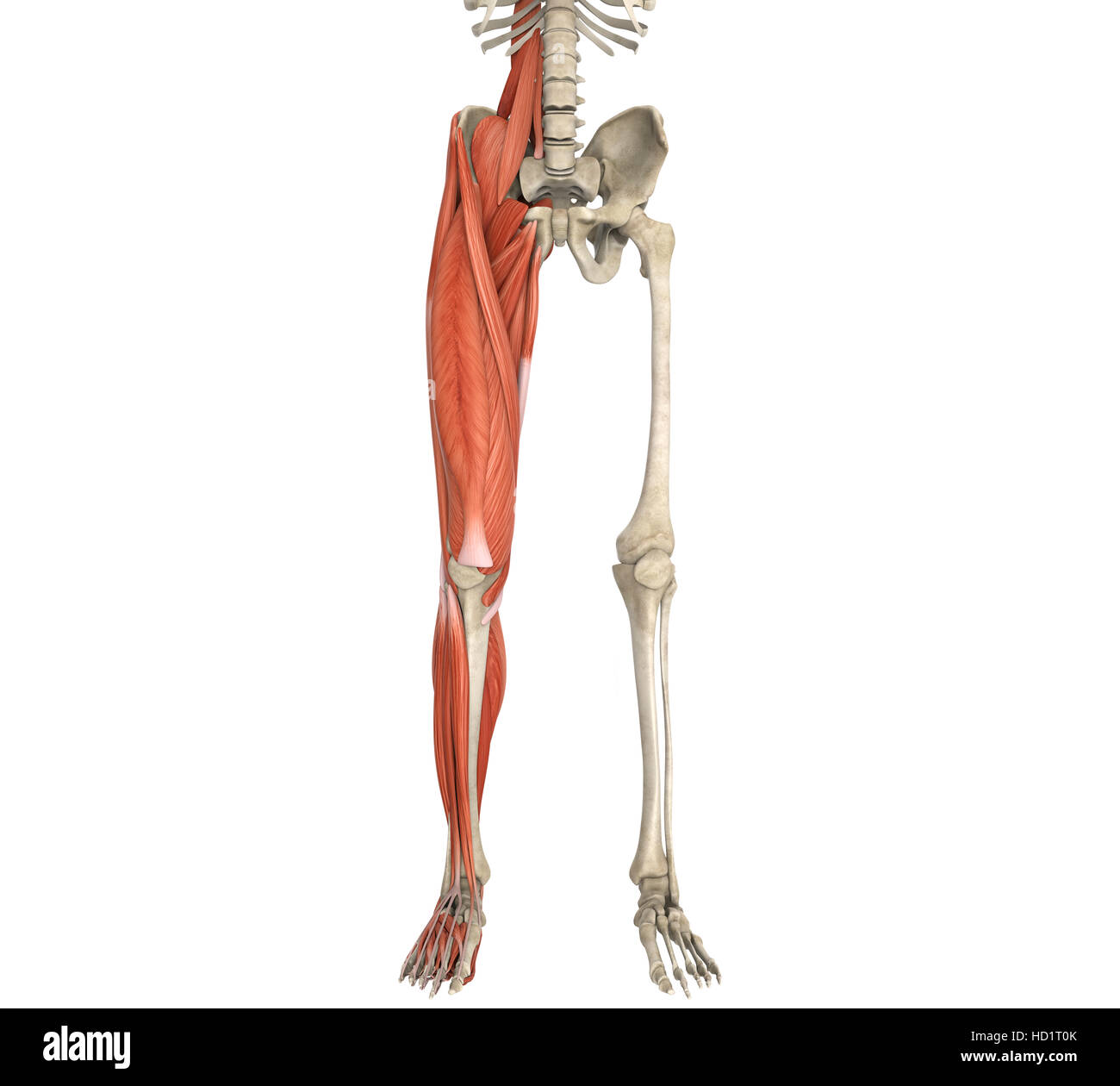 Legs Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-legs-muscles-anatomy-128503891.html
Legs Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-legs-muscles-anatomy-128503891.htmlRFHD1T0K–Legs Muscles Anatomy
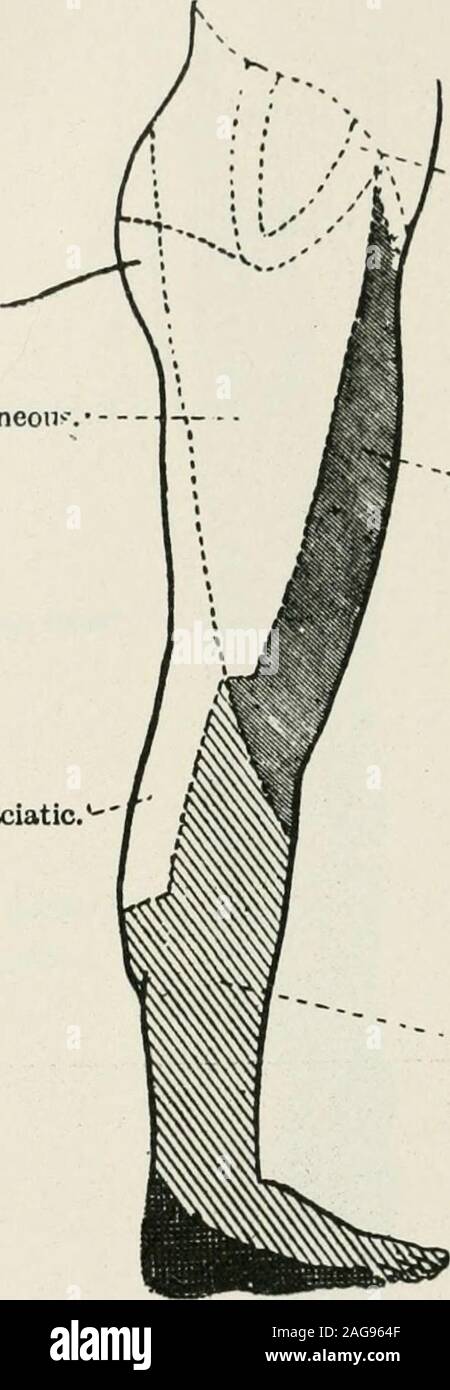 . Medical and surgical therapy. External cutaneous. Small «fiiatio. ?External popliteal. Internal popliteal. Fio. 70.—Peripheral sensory distribution of the lower extremity(posterior aspect). The peroneus hrevis abducts and everts the foot. Finally, the extensor hrevis digitorum assists the extensor longus,and extends the first phalanges of the first four toes. Muscles supplied by the Internal Popliteal Nerve.—The popUtetismuscle flexes the leg on the thigh. The plantaris is very inconstant, and has no special action. The gastrocnemius and the soleus unite to form a single muscle,the triceps o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-and-surgical-therapy-external-cutaneous-small-fiiatio-external-popliteal-internal-popliteal-fio-70peripheral-sensory-distribution-of-the-lower-extremityposterior-aspect-the-peroneus-hrevis-abducts-and-everts-the-foot-finally-the-extensor-hrevis-digitorum-assists-the-extensor-longusand-extends-the-first-phalanges-of-the-first-four-toes-muscles-supplied-by-the-internal-popliteal-nervethe-poputetismuscle-flexes-the-leg-on-the-thigh-the-plantaris-is-very-inconstant-and-has-no-special-action-the-gastrocnemius-and-the-soleus-unite-to-form-a-single-musclethe-triceps-o-image337033887.html
. Medical and surgical therapy. External cutaneous. Small «fiiatio. ?External popliteal. Internal popliteal. Fio. 70.—Peripheral sensory distribution of the lower extremity(posterior aspect). The peroneus hrevis abducts and everts the foot. Finally, the extensor hrevis digitorum assists the extensor longus,and extends the first phalanges of the first four toes. Muscles supplied by the Internal Popliteal Nerve.—The popUtetismuscle flexes the leg on the thigh. The plantaris is very inconstant, and has no special action. The gastrocnemius and the soleus unite to form a single muscle,the triceps o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-and-surgical-therapy-external-cutaneous-small-fiiatio-external-popliteal-internal-popliteal-fio-70peripheral-sensory-distribution-of-the-lower-extremityposterior-aspect-the-peroneus-hrevis-abducts-and-everts-the-foot-finally-the-extensor-hrevis-digitorum-assists-the-extensor-longusand-extends-the-first-phalanges-of-the-first-four-toes-muscles-supplied-by-the-internal-popliteal-nervethe-poputetismuscle-flexes-the-leg-on-the-thigh-the-plantaris-is-very-inconstant-and-has-no-special-action-the-gastrocnemius-and-the-soleus-unite-to-form-a-single-musclethe-triceps-o-image337033887.htmlRM2AG964F–. Medical and surgical therapy. External cutaneous. Small «fiiatio. ?External popliteal. Internal popliteal. Fio. 70.—Peripheral sensory distribution of the lower extremity(posterior aspect). The peroneus hrevis abducts and everts the foot. Finally, the extensor hrevis digitorum assists the extensor longus,and extends the first phalanges of the first four toes. Muscles supplied by the Internal Popliteal Nerve.—The popUtetismuscle flexes the leg on the thigh. The plantaris is very inconstant, and has no special action. The gastrocnemius and the soleus unite to form a single muscle,the triceps o
 Lower Legs Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-lower-legs-muscles-anatomy-128503909.html
Lower Legs Muscles Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-lower-legs-muscles-anatomy-128503909.htmlRFHD1T19–Lower Legs Muscles Anatomy
 . The development of the human body : a manual of human embryology. Embryology; Embryo, Non-Mammalian. Fig. 128.—Transverse sections through (A) the crus and (B) the foot, showing the arrangement of the layers of the flexor muscles. The shading has the same significance as in the preceding figure. AbH, abductor hallucis; AbM, abductor minimi digiti; AdH, adductor hallucis; ELD, extensor longus digitorum; F, fibula; FBD, flexor brevis digitorium; FBH, flexor brevis hallucis; FBM, flexor brevis minimi digiti; FLD, flexor longus digitorum; G, gastrocnemius; ID, interossei dorsalis; IV, interossei Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-development-of-the-human-body-a-manual-of-human-embryology-embryology-embryo-non-mammalian-fig-128transverse-sections-through-a-the-crus-and-b-the-foot-showing-the-arrangement-of-the-layers-of-the-flexor-muscles-the-shading-has-the-same-significance-as-in-the-preceding-figure-abh-abductor-hallucis-abm-abductor-minimi-digiti-adh-adductor-hallucis-eld-extensor-longus-digitorum-f-fibula-fbd-flexor-brevis-digitorium-fbh-flexor-brevis-hallucis-fbm-flexor-brevis-minimi-digiti-fld-flexor-longus-digitorum-g-gastrocnemius-id-interossei-dorsalis-iv-interossei-image215969611.html
. The development of the human body : a manual of human embryology. Embryology; Embryo, Non-Mammalian. Fig. 128.—Transverse sections through (A) the crus and (B) the foot, showing the arrangement of the layers of the flexor muscles. The shading has the same significance as in the preceding figure. AbH, abductor hallucis; AbM, abductor minimi digiti; AdH, adductor hallucis; ELD, extensor longus digitorum; F, fibula; FBD, flexor brevis digitorium; FBH, flexor brevis hallucis; FBM, flexor brevis minimi digiti; FLD, flexor longus digitorum; G, gastrocnemius; ID, interossei dorsalis; IV, interossei Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-development-of-the-human-body-a-manual-of-human-embryology-embryology-embryo-non-mammalian-fig-128transverse-sections-through-a-the-crus-and-b-the-foot-showing-the-arrangement-of-the-layers-of-the-flexor-muscles-the-shading-has-the-same-significance-as-in-the-preceding-figure-abh-abductor-hallucis-abm-abductor-minimi-digiti-adh-adductor-hallucis-eld-extensor-longus-digitorum-f-fibula-fbd-flexor-brevis-digitorium-fbh-flexor-brevis-hallucis-fbm-flexor-brevis-minimi-digiti-fld-flexor-longus-digitorum-g-gastrocnemius-id-interossei-dorsalis-iv-interossei-image215969611.htmlRMPFA7CB–. The development of the human body : a manual of human embryology. Embryology; Embryo, Non-Mammalian. Fig. 128.—Transverse sections through (A) the crus and (B) the foot, showing the arrangement of the layers of the flexor muscles. The shading has the same significance as in the preceding figure. AbH, abductor hallucis; AbM, abductor minimi digiti; AdH, adductor hallucis; ELD, extensor longus digitorum; F, fibula; FBD, flexor brevis digitorium; FBH, flexor brevis hallucis; FBM, flexor brevis minimi digiti; FLD, flexor longus digitorum; G, gastrocnemius; ID, interossei dorsalis; IV, interossei
 Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066766.html
Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066766.htmlRFR8JTYX–Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete.
 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696257.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696257.htmlRF2CBRFRD–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
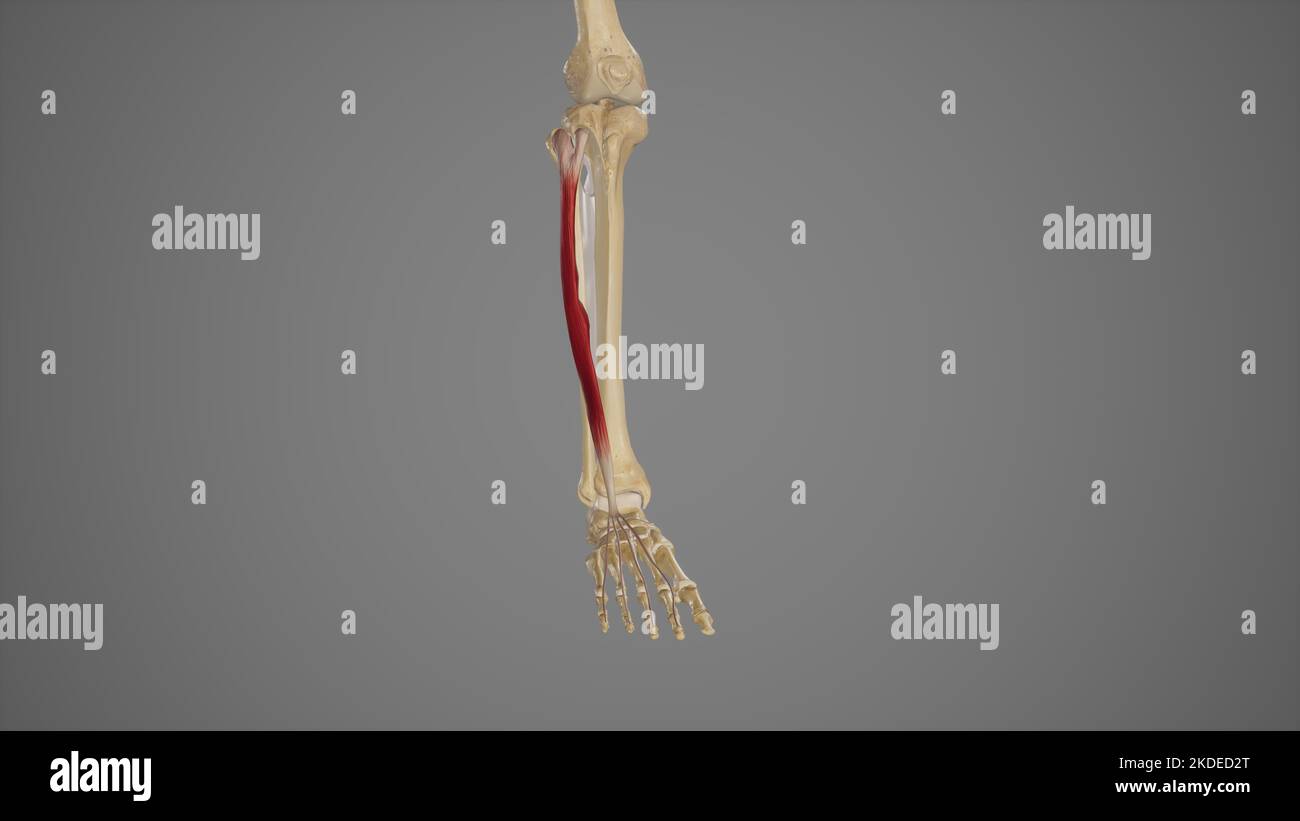 Medical Illustration of Extensor Digitorum Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-digitorum-longus-image490198432.html
Medical Illustration of Extensor Digitorum Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-extensor-digitorum-longus-image490198432.htmlRF2KDED2T–Medical Illustration of Extensor Digitorum Longus
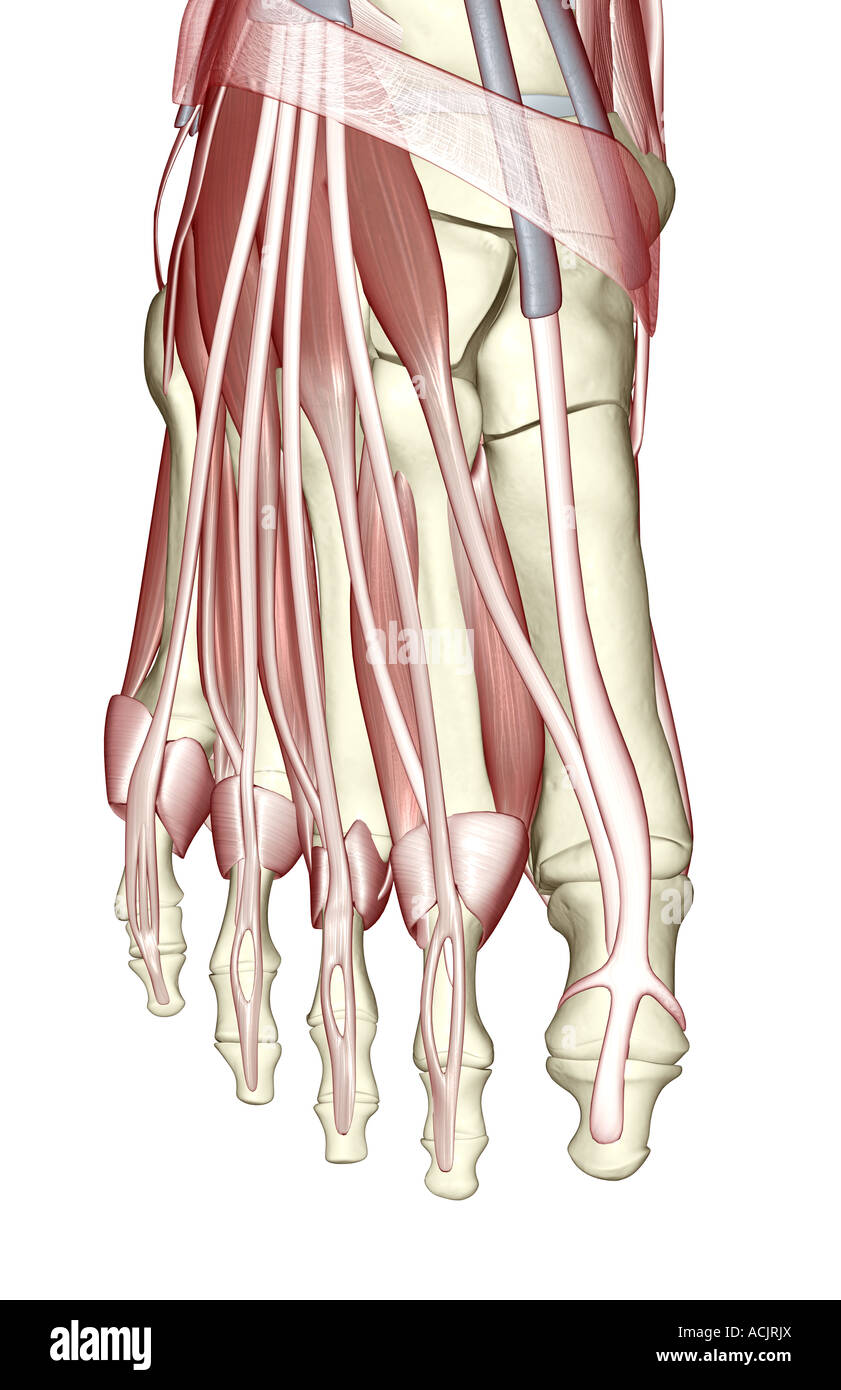 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13172881.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13172881.htmlRFACJRJX–The muscles of the foot
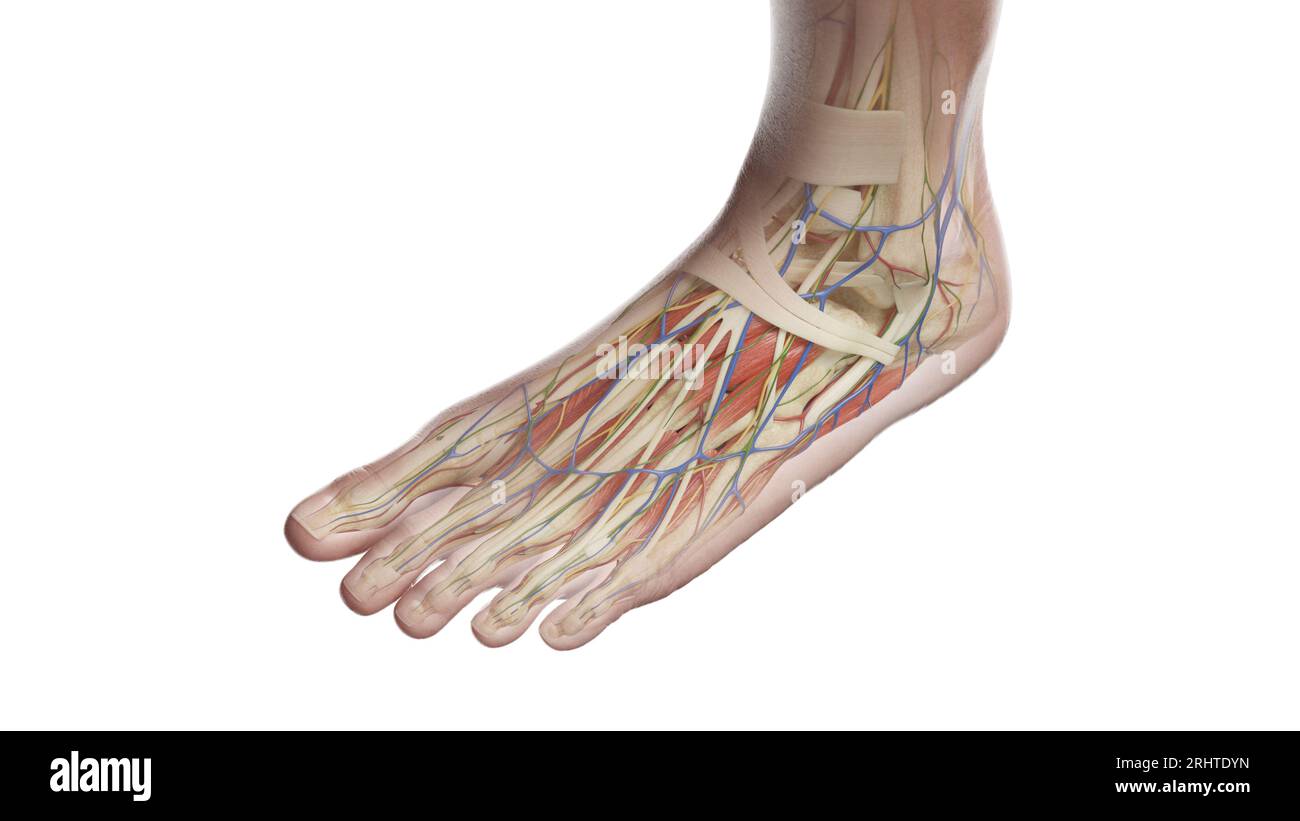 Anatomy of the left foot, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-the-left-foot-illustration-image561718745.html
Anatomy of the left foot, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-of-the-left-foot-illustration-image561718745.htmlRF2RHTDYN–Anatomy of the left foot, illustration
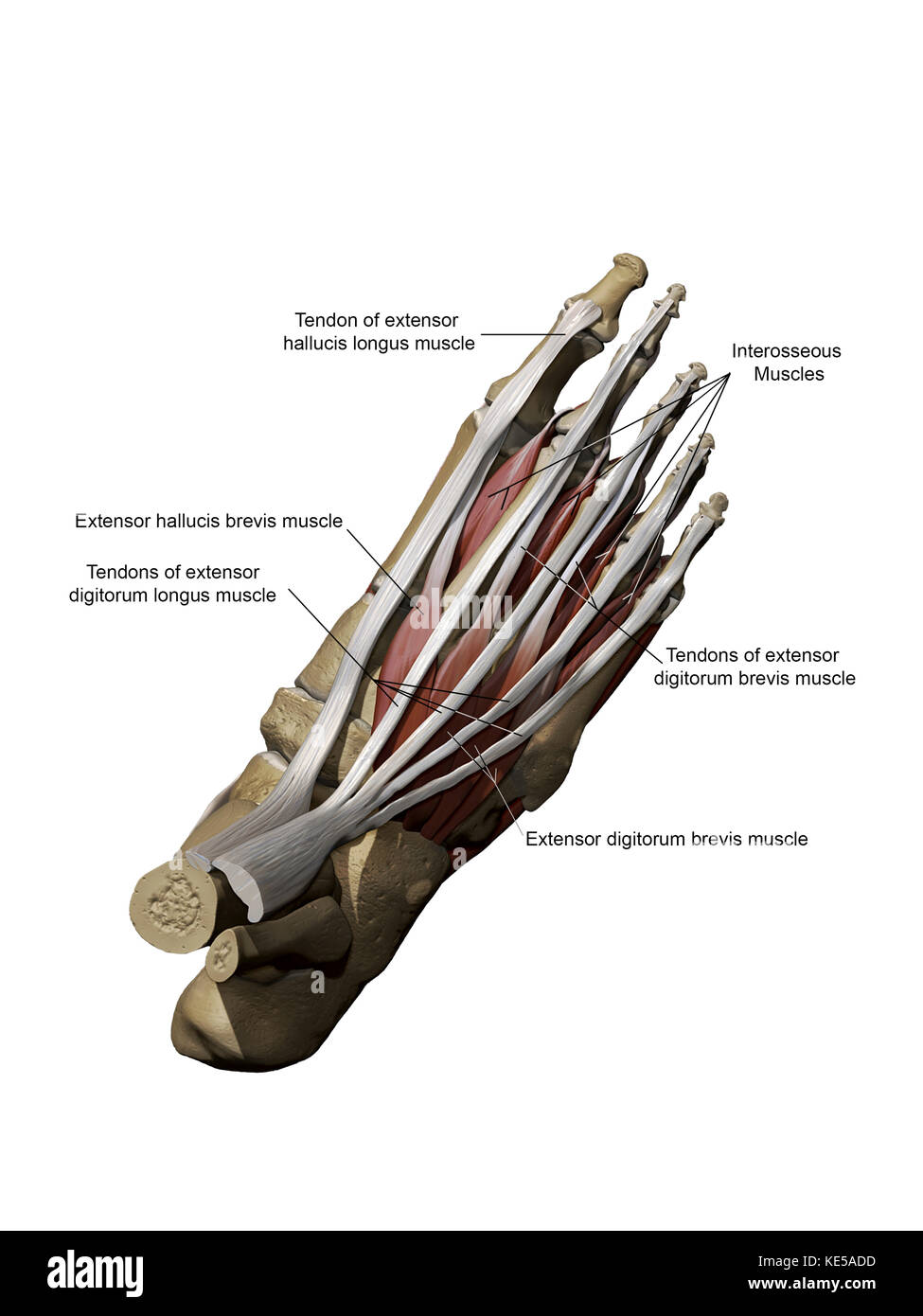 3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal superficial muscles and bone structure. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-3d-model-of-the-foot-depicting-the-dorsal-superficial-muscles-and-163616473.html
3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal superficial muscles and bone structure. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-3d-model-of-the-foot-depicting-the-dorsal-superficial-muscles-and-163616473.htmlRFKE5ADD–3D model of the foot depicting the dorsal superficial muscles and bone structure.
 Anterior compartment anatomy of left leg muscles and tendons. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-compartment-anatomy-of-left-leg-muscles-and-tendons-image69866851.html
Anterior compartment anatomy of left leg muscles and tendons. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-compartment-anatomy-of-left-leg-muscles-and-tendons-image69866851.htmlRFE1JKTK–Anterior compartment anatomy of left leg muscles and tendons.
 Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . The deep fascia is then in-cised, and working down, between the tibialis anticus on the inner sideand the extensor proprius pollicis on the outer side, with the handle ofthe scalpel, the interosseous membrane is reached. The foot is thensomewhat flexed at the ankle—dorsal flexion—to relax the muscles,and retractors are introduced deep into the wound, and the artery,with its venge comites lying upon it, is exposed. The anterior tibialnerve lies in front of the anterior tibial vessels in this part of theircourse. After the nerve has been separa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/operative-surgery-for-students-and-practitioners-the-deep-fascia-is-then-in-cised-and-working-down-between-the-tibialis-anticus-on-the-inner-sideand-the-extensor-proprius-pollicis-on-the-outer-side-with-the-handle-ofthe-scalpel-the-interosseous-membrane-is-reached-the-foot-is-thensomewhat-flexed-at-the-ankledorsal-flexionto-relax-the-musclesand-retractors-are-introduced-deep-into-the-wound-and-the-arterywith-its-venge-comites-lying-upon-it-is-exposed-the-anterior-tibialnerve-lies-in-front-of-the-anterior-tibial-vessels-in-this-part-of-theircourse-after-the-nerve-has-been-separa-image340308580.html
Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . The deep fascia is then in-cised, and working down, between the tibialis anticus on the inner sideand the extensor proprius pollicis on the outer side, with the handle ofthe scalpel, the interosseous membrane is reached. The foot is thensomewhat flexed at the ankle—dorsal flexion—to relax the muscles,and retractors are introduced deep into the wound, and the artery,with its venge comites lying upon it, is exposed. The anterior tibialnerve lies in front of the anterior tibial vessels in this part of theircourse. After the nerve has been separa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/operative-surgery-for-students-and-practitioners-the-deep-fascia-is-then-in-cised-and-working-down-between-the-tibialis-anticus-on-the-inner-sideand-the-extensor-proprius-pollicis-on-the-outer-side-with-the-handle-ofthe-scalpel-the-interosseous-membrane-is-reached-the-foot-is-thensomewhat-flexed-at-the-ankledorsal-flexionto-relax-the-musclesand-retractors-are-introduced-deep-into-the-wound-and-the-arterywith-its-venge-comites-lying-upon-it-is-exposed-the-anterior-tibialnerve-lies-in-front-of-the-anterior-tibial-vessels-in-this-part-of-theircourse-after-the-nerve-has-been-separa-image340308580.htmlRM2ANJB1T–Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . The deep fascia is then in-cised, and working down, between the tibialis anticus on the inner sideand the extensor proprius pollicis on the outer side, with the handle ofthe scalpel, the interosseous membrane is reached. The foot is thensomewhat flexed at the ankle—dorsal flexion—to relax the muscles,and retractors are introduced deep into the wound, and the artery,with its venge comites lying upon it, is exposed. The anterior tibialnerve lies in front of the anterior tibial vessels in this part of theircourse. After the nerve has been separa
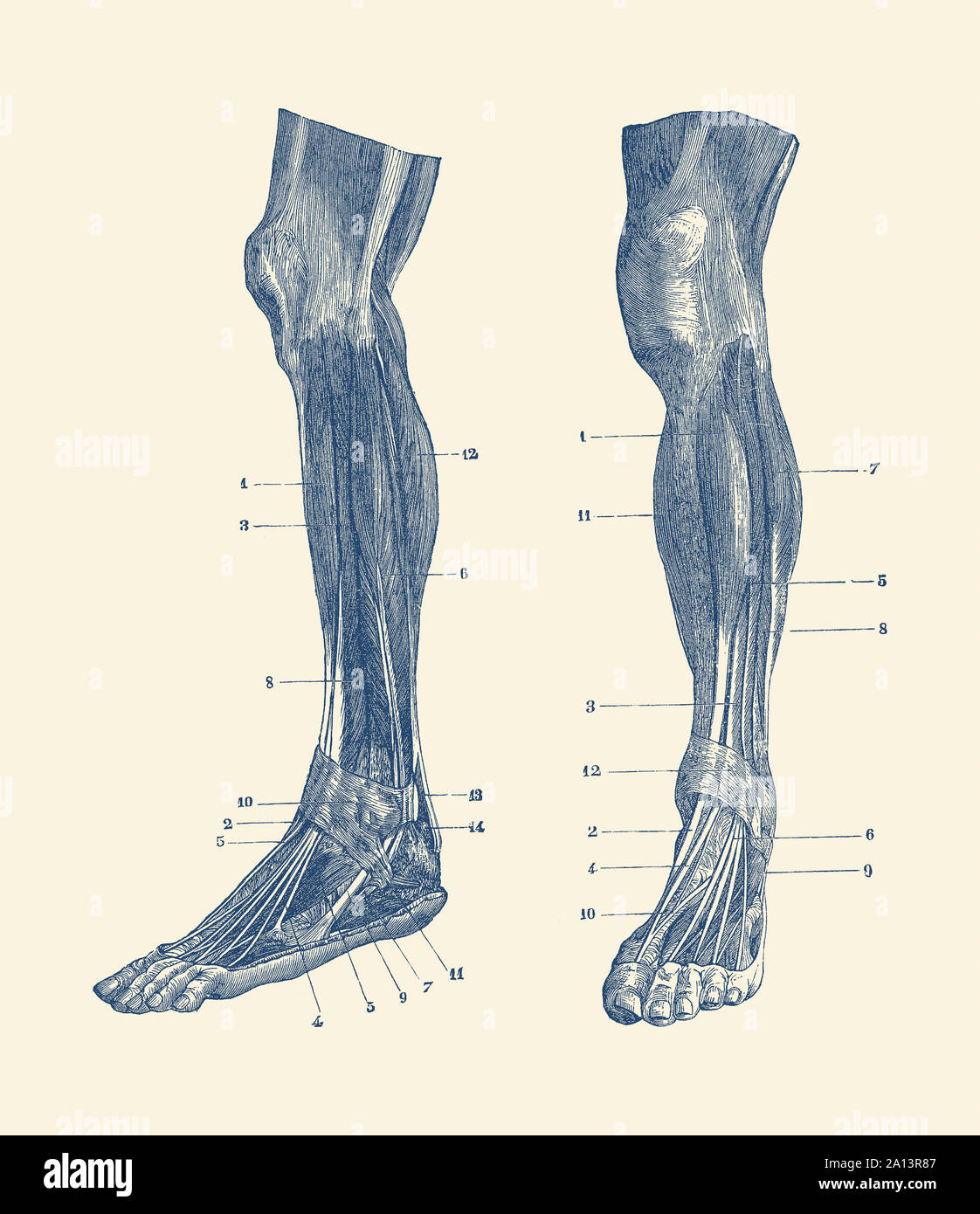 A dual view of the muscles and tendons in a human leg. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-dual-view-of-the-muscles-and-tendons-in-a-human-leg-image327695767.html
A dual view of the muscles and tendons in a human leg. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-dual-view-of-the-muscles-and-tendons-in-a-human-leg-image327695767.htmlRF2A13R87–A dual view of the muscles and tendons in a human leg.
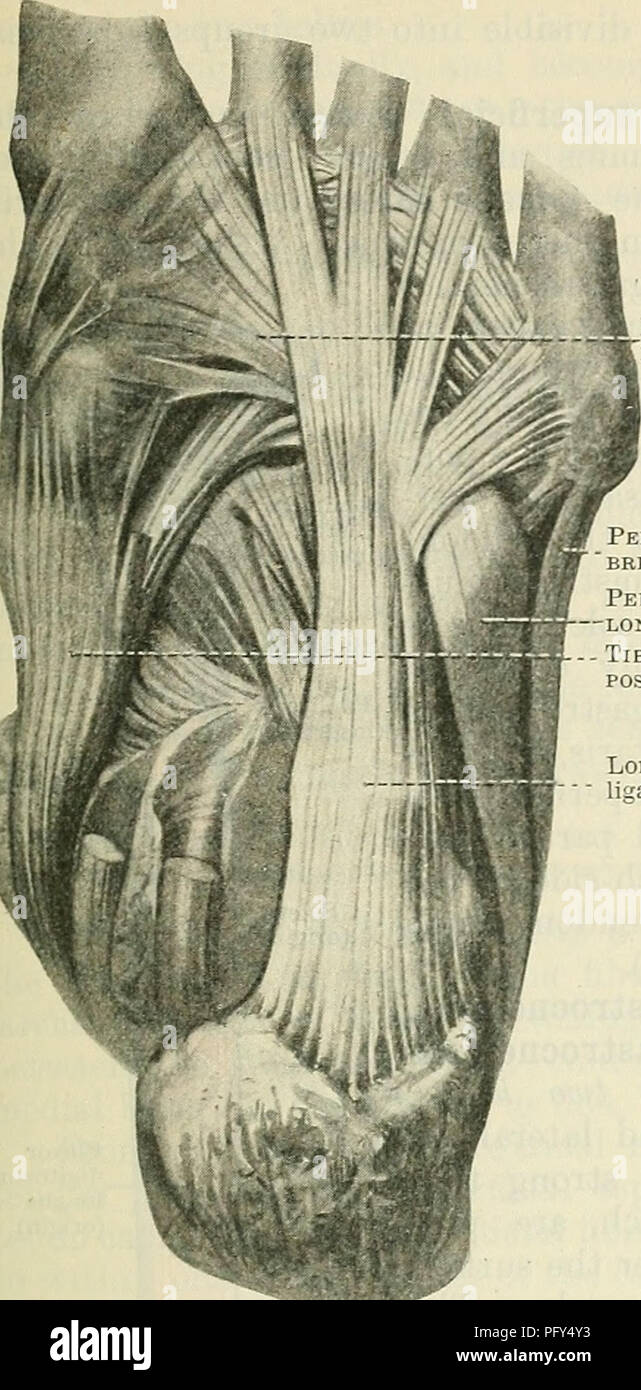 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES ON THE LATEEAL SIDE OF THE LEG. 427 base of the first metatarsal bones (Fig. 379, p. 425). As it enters the sole of the foot a fibro-cartilage is formed in the tendon, which plays over a smooth tubercle on the cuboid bone, a bursa intervening. In its passage across the foot the tendon is enclosed in a sheath derived from the long plantar (long calcaneo-cuboid) ligaments and the tibialis posterior tendon. Nerve - Supply. — Superficial peroneal nerve (L. 4. 5. S. 1.). Actions.—An extensor of the ankle ; It its. Peron.eus LONGUS 'ERON.EUS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-muscles-on-the-lateeal-side-of-the-leg-427-base-of-the-first-metatarsal-bones-fig-379-p-425-as-it-enters-the-sole-of-the-foot-a-fibro-cartilage-is-formed-in-the-tendon-which-plays-over-a-smooth-tubercle-on-the-cuboid-bone-a-bursa-intervening-in-its-passage-across-the-foot-the-tendon-is-enclosed-in-a-sheath-derived-from-the-long-plantar-long-calcaneo-cuboid-ligaments-and-the-tibialis-posterior-tendon-nerve-supply-superficial-peroneal-nerve-l-4-5-s-1-actionsan-extensor-of-the-ankle-it-its-peroneus-longus-eroneus-image216340855.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES ON THE LATEEAL SIDE OF THE LEG. 427 base of the first metatarsal bones (Fig. 379, p. 425). As it enters the sole of the foot a fibro-cartilage is formed in the tendon, which plays over a smooth tubercle on the cuboid bone, a bursa intervening. In its passage across the foot the tendon is enclosed in a sheath derived from the long plantar (long calcaneo-cuboid) ligaments and the tibialis posterior tendon. Nerve - Supply. — Superficial peroneal nerve (L. 4. 5. S. 1.). Actions.—An extensor of the ankle ; It its. Peron.eus LONGUS 'ERON.EUS Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-muscles-on-the-lateeal-side-of-the-leg-427-base-of-the-first-metatarsal-bones-fig-379-p-425-as-it-enters-the-sole-of-the-foot-a-fibro-cartilage-is-formed-in-the-tendon-which-plays-over-a-smooth-tubercle-on-the-cuboid-bone-a-bursa-intervening-in-its-passage-across-the-foot-the-tendon-is-enclosed-in-a-sheath-derived-from-the-long-plantar-long-calcaneo-cuboid-ligaments-and-the-tibialis-posterior-tendon-nerve-supply-superficial-peroneal-nerve-l-4-5-s-1-actionsan-extensor-of-the-ankle-it-its-peroneus-longus-eroneus-image216340855.htmlRMPFY4Y3–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE MUSCLES ON THE LATEEAL SIDE OF THE LEG. 427 base of the first metatarsal bones (Fig. 379, p. 425). As it enters the sole of the foot a fibro-cartilage is formed in the tendon, which plays over a smooth tubercle on the cuboid bone, a bursa intervening. In its passage across the foot the tendon is enclosed in a sheath derived from the long plantar (long calcaneo-cuboid) ligaments and the tibialis posterior tendon. Nerve - Supply. — Superficial peroneal nerve (L. 4. 5. S. 1.). Actions.—An extensor of the ankle ; It its. Peron.eus LONGUS 'ERON.EUS
 Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229465104.html
Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229465104.htmlRFR99128–Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete.
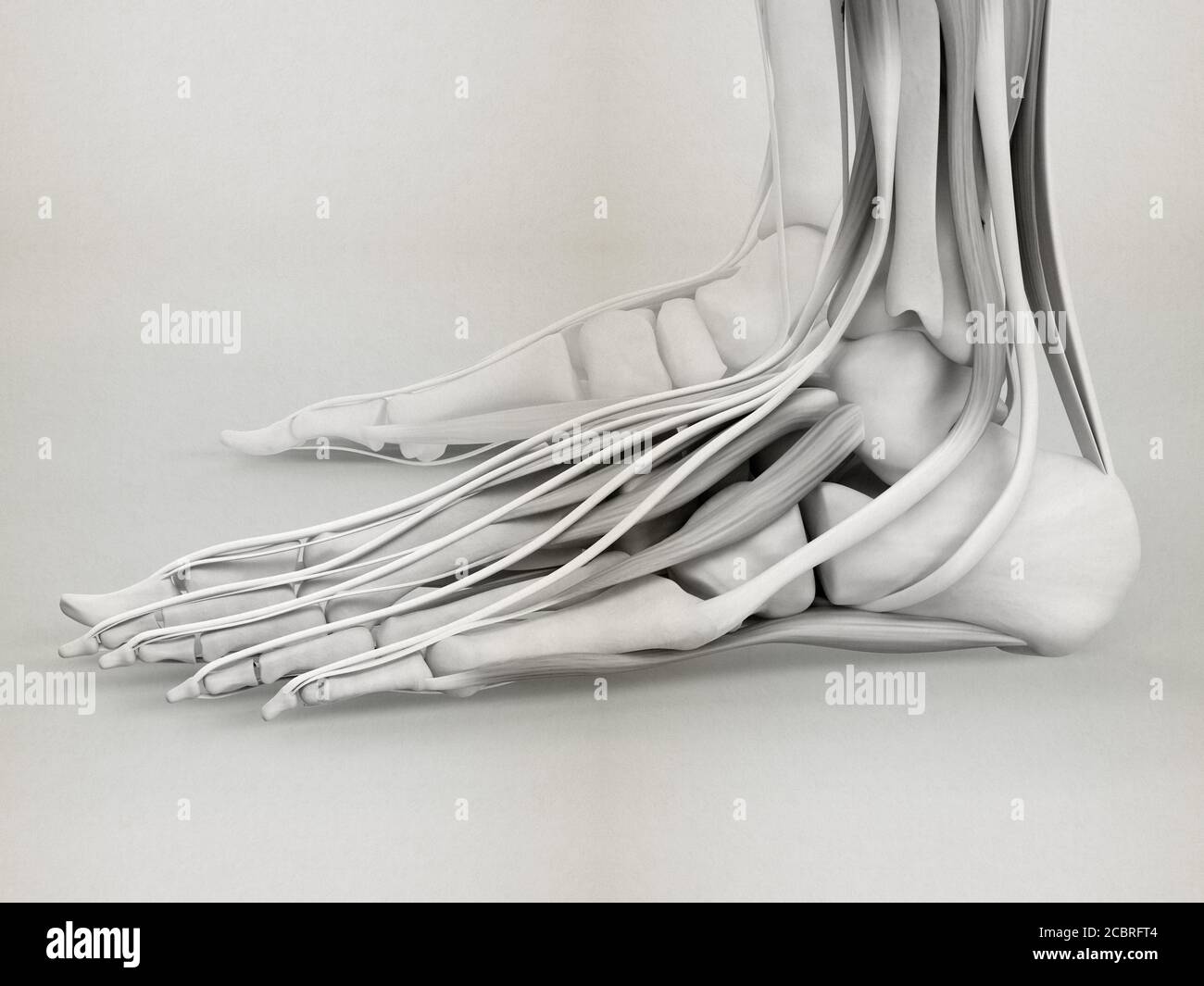 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696276.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696276.htmlRF2CBRFT4–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
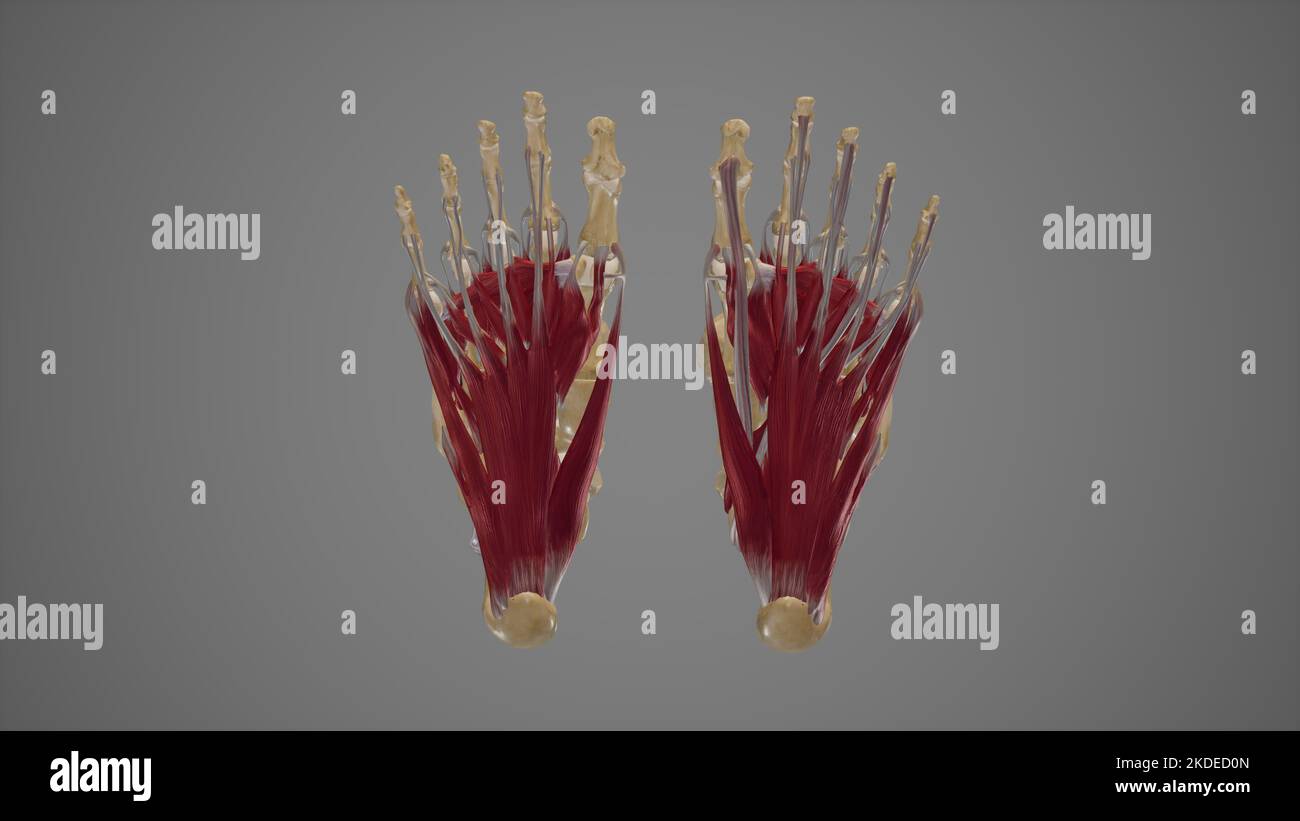 Intrinsic Muscles of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/intrinsic-muscles-of-foot-image490198373.html
Intrinsic Muscles of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/intrinsic-muscles-of-foot-image490198373.htmlRF2KDED0N–Intrinsic Muscles of Foot
 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13169731.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13169731.htmlRFACJE8M–The muscles of the foot
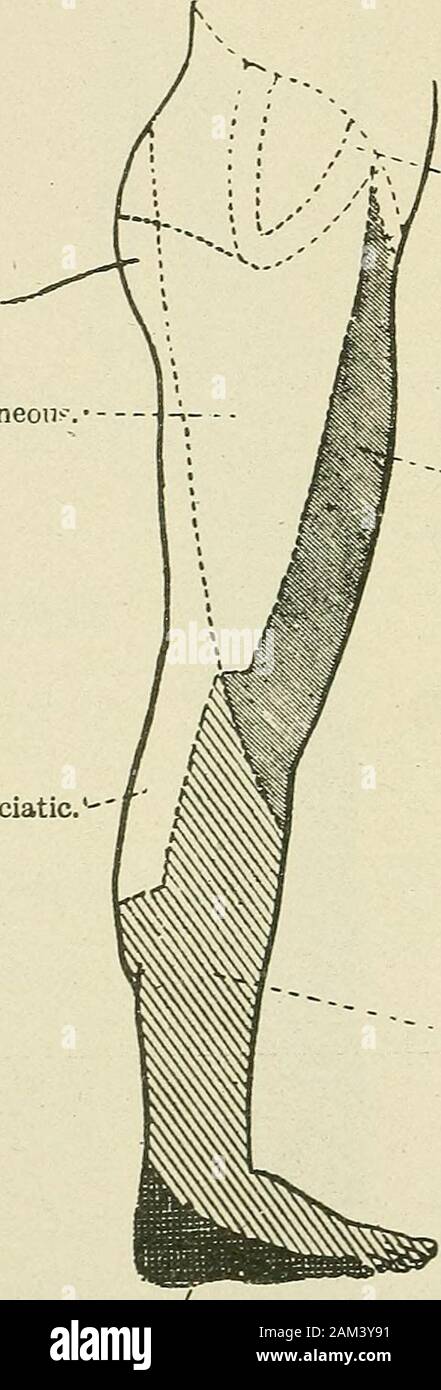 Medical and surgical therapy . ator. -^ , Anterior crural. - External cutaneous. ? Small sciatic. Interior saphenous. ?-External popliteal. Internal popliteal. Fio. 70.—^Peripheral sensory distribution of the lower extremity(posterior aspect). The peroneus hrevis abducts and everts the foot. Finally, the extensor hrevis digitorum assists the extensor longus,and extends the first phalanges of the first four toes. Muscles supplied by the Internal Popliteal Nerve.—The ^opZifewsmuscle flexes the leg on the thigh. The plantaris is very inconstant, and has no special action. The gastrocnemius and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-and-surgical-therapy-ator-anterior-crural-external-cutaneous-small-sciatic-interior-saphenous-external-popliteal-internal-popliteal-fio-70peripheral-sensory-distribution-of-the-lower-extremityposterior-aspect-the-peroneus-hrevis-abducts-and-everts-the-foot-finally-the-extensor-hrevis-digitorum-assists-the-extensor-longusand-extends-the-first-phalanges-of-the-first-four-toes-muscles-supplied-by-the-internal-popliteal-nervethe-opzifewsmuscle-flexes-the-leg-on-the-thigh-the-plantaris-is-very-inconstant-and-has-no-special-action-the-gastrocnemius-and-image339377389.html
Medical and surgical therapy . ator. -^ , Anterior crural. - External cutaneous. ? Small sciatic. Interior saphenous. ?-External popliteal. Internal popliteal. Fio. 70.—^Peripheral sensory distribution of the lower extremity(posterior aspect). The peroneus hrevis abducts and everts the foot. Finally, the extensor hrevis digitorum assists the extensor longus,and extends the first phalanges of the first four toes. Muscles supplied by the Internal Popliteal Nerve.—The ^opZifewsmuscle flexes the leg on the thigh. The plantaris is very inconstant, and has no special action. The gastrocnemius and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-and-surgical-therapy-ator-anterior-crural-external-cutaneous-small-sciatic-interior-saphenous-external-popliteal-internal-popliteal-fio-70peripheral-sensory-distribution-of-the-lower-extremityposterior-aspect-the-peroneus-hrevis-abducts-and-everts-the-foot-finally-the-extensor-hrevis-digitorum-assists-the-extensor-longusand-extends-the-first-phalanges-of-the-first-four-toes-muscles-supplied-by-the-internal-popliteal-nervethe-opzifewsmuscle-flexes-the-leg-on-the-thigh-the-plantaris-is-very-inconstant-and-has-no-special-action-the-gastrocnemius-and-image339377389.htmlRM2AM3Y91–Medical and surgical therapy . ator. -^ , Anterior crural. - External cutaneous. ? Small sciatic. Interior saphenous. ?-External popliteal. Internal popliteal. Fio. 70.—^Peripheral sensory distribution of the lower extremity(posterior aspect). The peroneus hrevis abducts and everts the foot. Finally, the extensor hrevis digitorum assists the extensor longus,and extends the first phalanges of the first four toes. Muscles supplied by the Internal Popliteal Nerve.—The ^opZifewsmuscle flexes the leg on the thigh. The plantaris is very inconstant, and has no special action. The gastrocnemius and
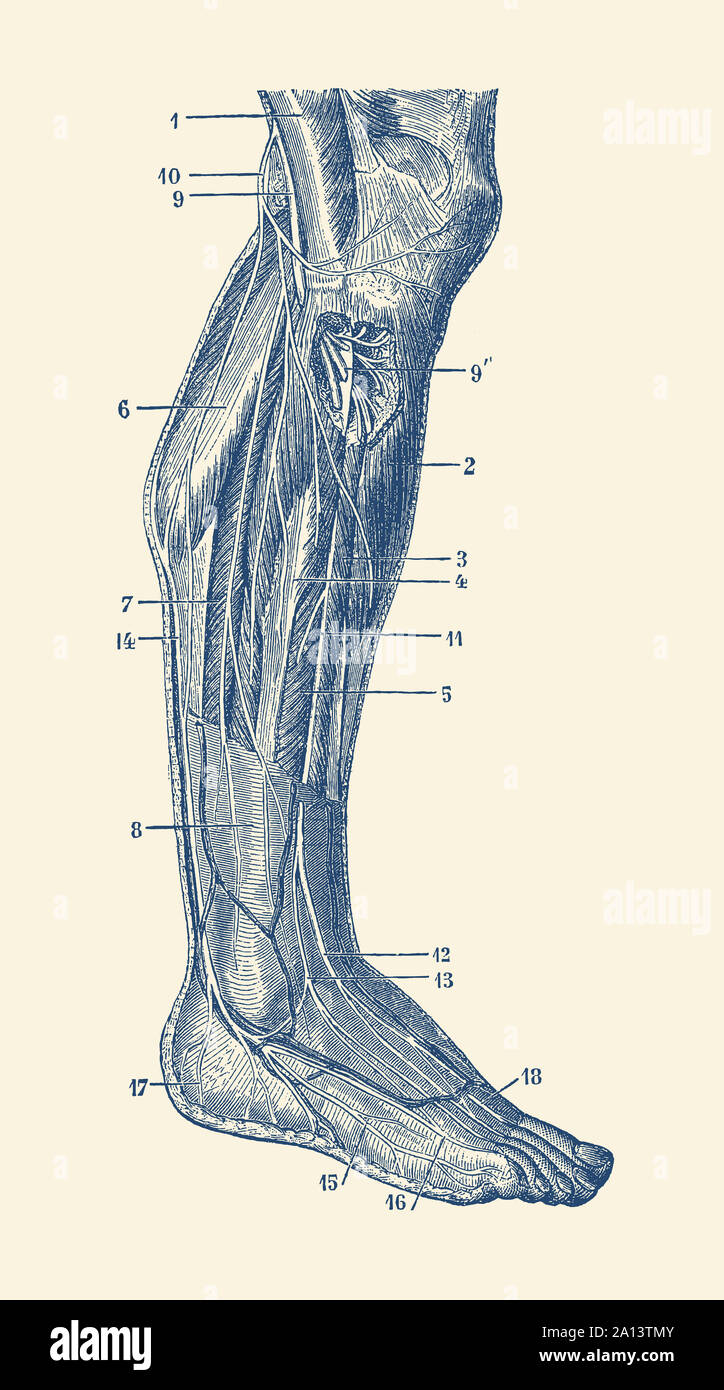 Vintage anatomy print showing the human muscular system of the right leg. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/vintage-anatomy-print-showing-the-human-muscular-system-of-the-right-leg-image327696907.html
Vintage anatomy print showing the human muscular system of the right leg. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/vintage-anatomy-print-showing-the-human-muscular-system-of-the-right-leg-image327696907.htmlRF2A13TMY–Vintage anatomy print showing the human muscular system of the right leg.
 Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066735.html
Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-the-posterior-leg-soleus-and-gastrocnemius-muscle-photo-of-an-athlete-image229066735.htmlRFR8JTXR–Muscles of the posterior leg, soleus and gastrocnemius muscle, photo of an athlete.
 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696299.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696299.htmlRF2CBRFTY–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
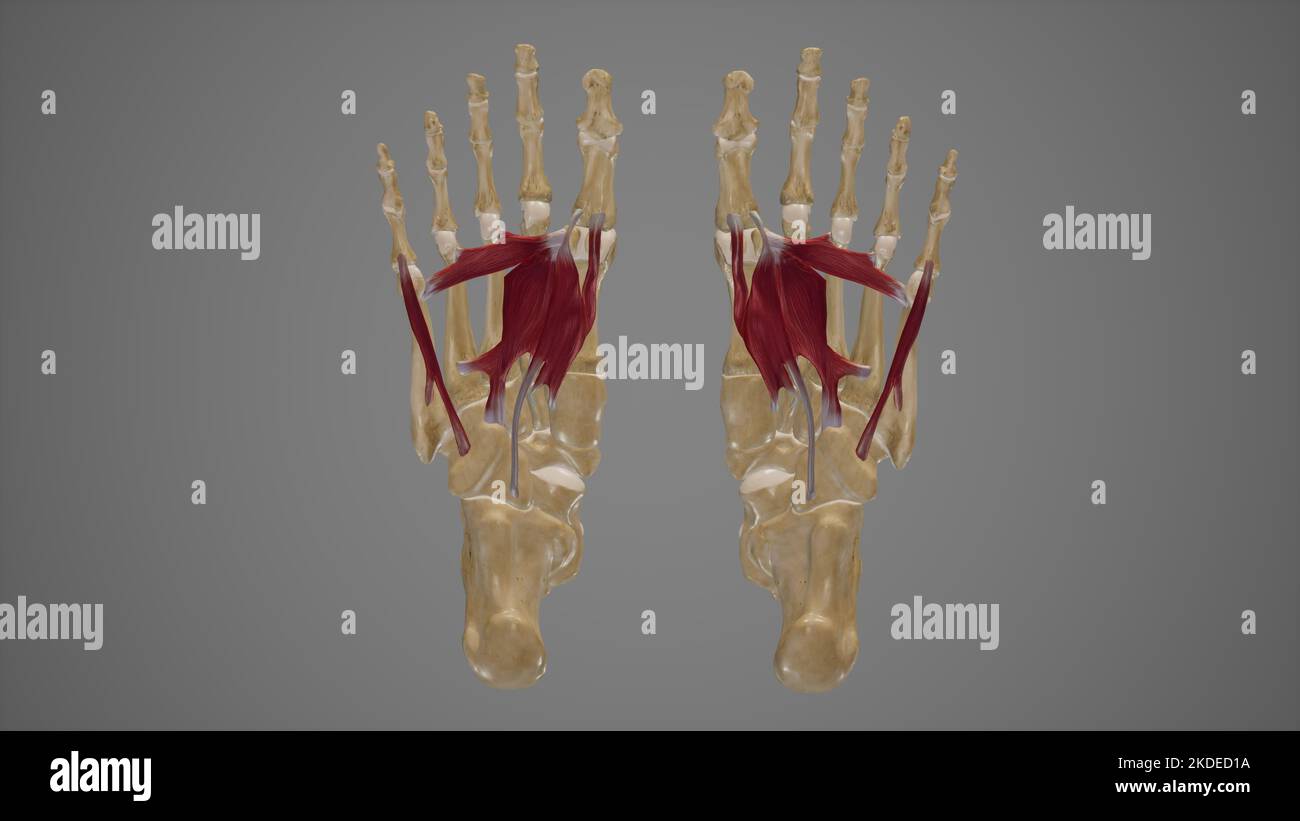 Muscles of Sole of Foot Third Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-third-layer-image490198390.html
Muscles of Sole of Foot Third Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-third-layer-image490198390.htmlRF2KDED1A–Muscles of Sole of Foot Third Layer
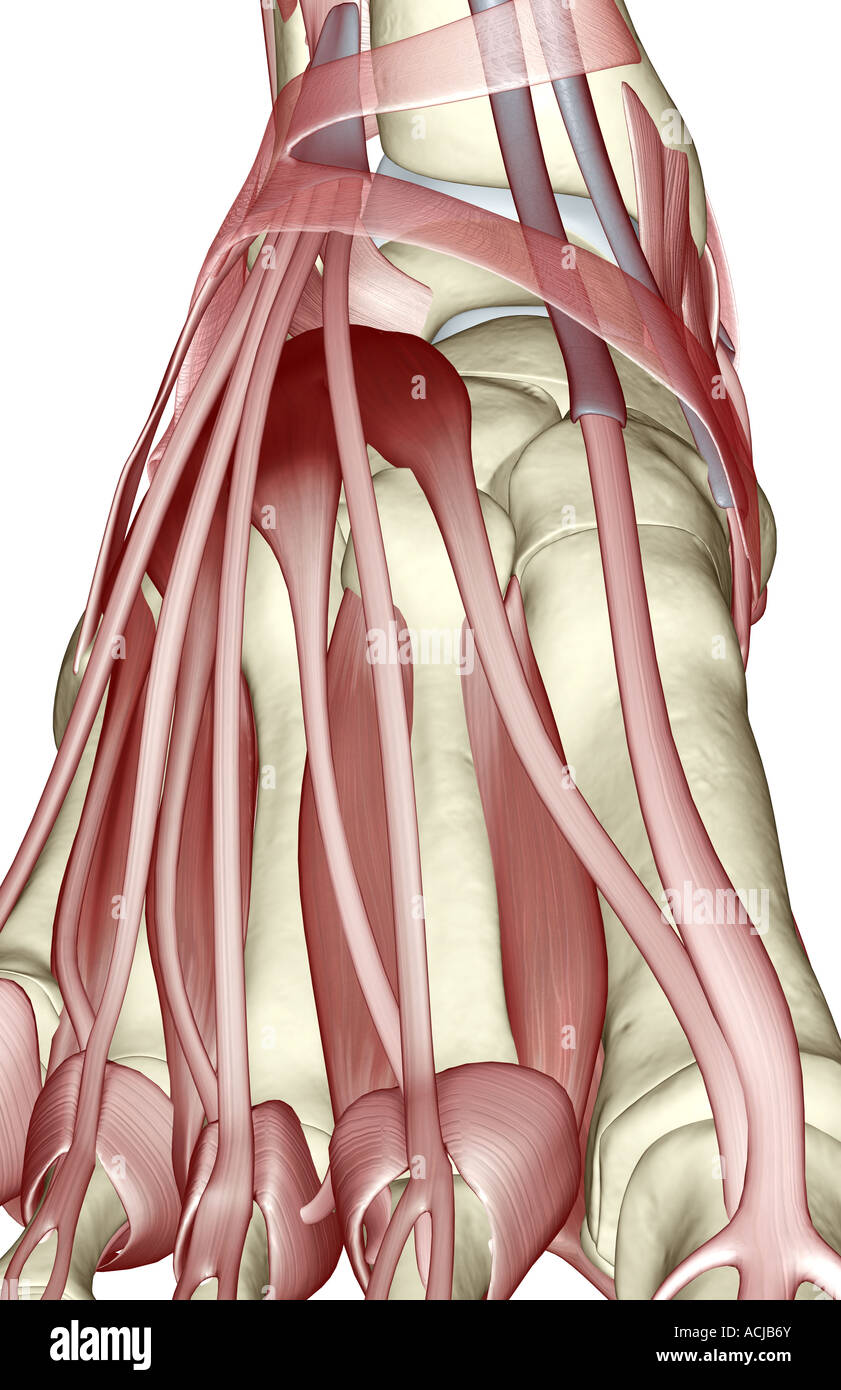 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13168706.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13168706.htmlRFACJB6Y–The muscles of the foot
 Annals of surgery . een employed in a few instances by him with success. Shortening of the Tendons of the Extensor Communis Digi-torum.—This operation I have attempted once, in a casewhere the foot dropped from the entire paralysis of the an-terior muscles. The tendons can be divided and shortenedabove the annular ligament or below it. The former is pref-erable, as the scar on the dorsum of the foot below the liga-ment would be inconvenient. TENOPLASTIC SURGERY. 157 Shortening of the Tendo Achillis.—An incision is madealong the tendon, either directly over the tendon or slightlyto the side. Th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/annals-of-surgery-een-employed-in-a-few-instances-by-him-with-success-shortening-of-the-tendons-of-the-extensor-communis-digi-torumthis-operation-i-have-attempted-once-in-a-casewhere-the-foot-dropped-from-the-entire-paralysis-of-the-an-terior-muscles-the-tendons-can-be-divided-and-shortenedabove-the-annular-ligament-or-below-it-the-former-is-pref-erable-as-the-scar-on-the-dorsum-of-the-foot-below-the-liga-ment-would-be-inconvenient-tenoplastic-surgery-157-shortening-of-the-tendo-achillisan-incision-is-madealong-the-tendon-either-directly-over-the-tendon-or-slightlyto-the-side-th-image343359204.html
Annals of surgery . een employed in a few instances by him with success. Shortening of the Tendons of the Extensor Communis Digi-torum.—This operation I have attempted once, in a casewhere the foot dropped from the entire paralysis of the an-terior muscles. The tendons can be divided and shortenedabove the annular ligament or below it. The former is pref-erable, as the scar on the dorsum of the foot below the liga-ment would be inconvenient. TENOPLASTIC SURGERY. 157 Shortening of the Tendo Achillis.—An incision is madealong the tendon, either directly over the tendon or slightlyto the side. Th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/annals-of-surgery-een-employed-in-a-few-instances-by-him-with-success-shortening-of-the-tendons-of-the-extensor-communis-digi-torumthis-operation-i-have-attempted-once-in-a-casewhere-the-foot-dropped-from-the-entire-paralysis-of-the-an-terior-muscles-the-tendons-can-be-divided-and-shortenedabove-the-annular-ligament-or-below-it-the-former-is-pref-erable-as-the-scar-on-the-dorsum-of-the-foot-below-the-liga-ment-would-be-inconvenient-tenoplastic-surgery-157-shortening-of-the-tendo-achillisan-incision-is-madealong-the-tendon-either-directly-over-the-tendon-or-slightlyto-the-side-th-image343359204.htmlRM2AXHA4M–Annals of surgery . een employed in a few instances by him with success. Shortening of the Tendons of the Extensor Communis Digi-torum.—This operation I have attempted once, in a casewhere the foot dropped from the entire paralysis of the an-terior muscles. The tendons can be divided and shortenedabove the annular ligament or below it. The former is pref-erable, as the scar on the dorsum of the foot below the liga-ment would be inconvenient. TENOPLASTIC SURGERY. 157 Shortening of the Tendo Achillis.—An incision is madealong the tendon, either directly over the tendon or slightlyto the side. Th
 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696269.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696269.htmlRF2CBRFRW–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
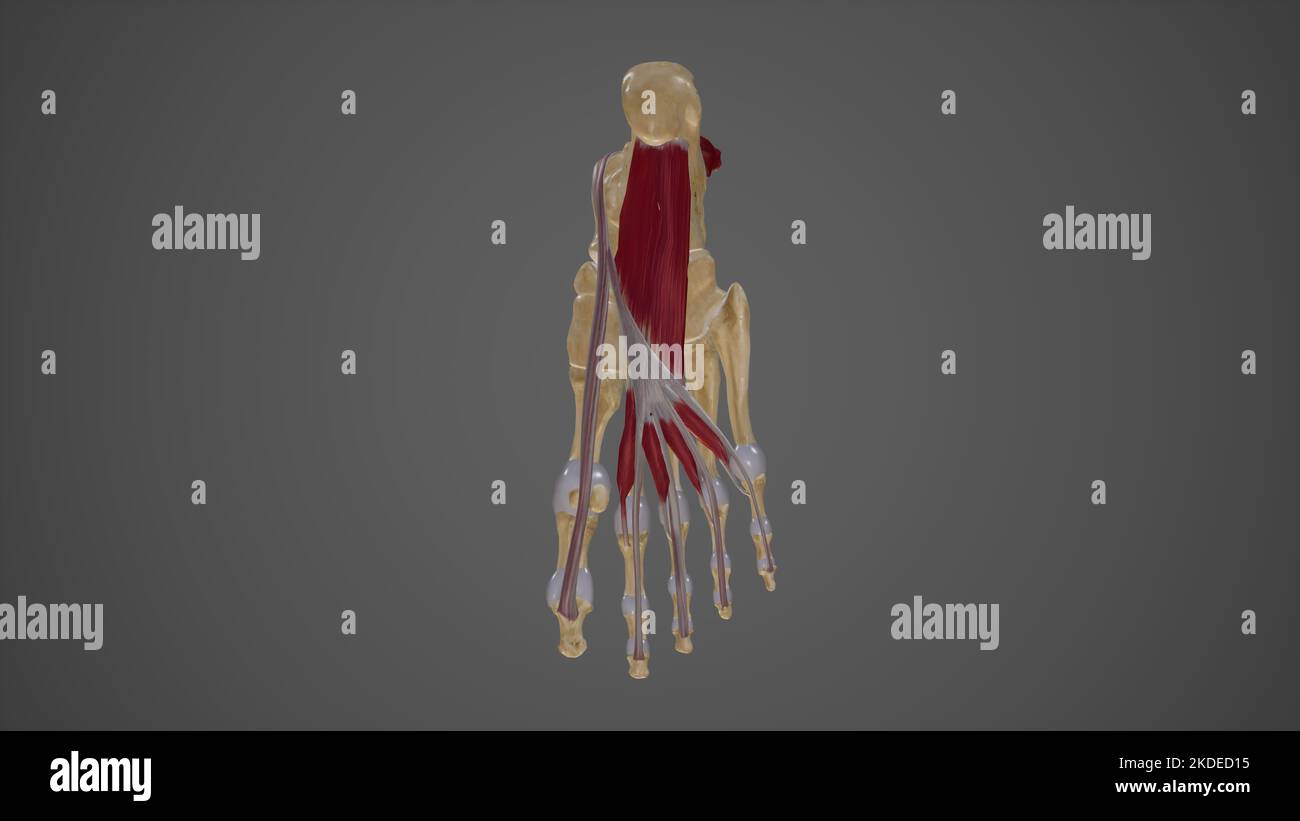 Muscles of Sole of Foot Second Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-second-layer-image490198385.html
Muscles of Sole of Foot Second Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-second-layer-image490198385.htmlRF2KDED15–Muscles of Sole of Foot Second Layer
 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13168791.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13168791.htmlRFACJBEG–The muscles of the foot
 The hydropathic encyclopedia : a system of hydropathy and hygiene in eight parts ..designed as a guide to families and students, and a text-book for physicians . these acting together maintain the foot in a flat position, as inwalking. MUSCLES OF THE FOOT. These may be arranged, according to their situation above or below,into those of the dorsal and those of the plantar regions. Dorsal Region.—Two muscles: 1. Extensor brevis digitorum;arises from the outer side of the os calcis, crosses the foot obliquely,and terminates in four tendons, one of which is inserted into the firstphalanx of the gr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-hydropathic-encyclopedia-a-system-of-hydropathy-and-hygiene-in-eight-parts-designed-as-a-guide-to-families-and-students-and-a-text-book-for-physicians-these-acting-together-maintain-the-foot-in-a-flat-position-as-inwalking-muscles-of-the-foot-these-may-be-arranged-according-to-their-situation-above-or-belowinto-those-of-the-dorsal-and-those-of-the-plantar-regions-dorsal-regiontwo-muscles-1-extensor-brevis-digitorumarises-from-the-outer-side-of-the-os-calcis-crosses-the-foot-obliquelyand-terminates-in-four-tendons-one-of-which-is-inserted-into-the-firstphalanx-of-the-gr-image342750493.html
The hydropathic encyclopedia : a system of hydropathy and hygiene in eight parts ..designed as a guide to families and students, and a text-book for physicians . these acting together maintain the foot in a flat position, as inwalking. MUSCLES OF THE FOOT. These may be arranged, according to their situation above or below,into those of the dorsal and those of the plantar regions. Dorsal Region.—Two muscles: 1. Extensor brevis digitorum;arises from the outer side of the os calcis, crosses the foot obliquely,and terminates in four tendons, one of which is inserted into the firstphalanx of the gr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-hydropathic-encyclopedia-a-system-of-hydropathy-and-hygiene-in-eight-parts-designed-as-a-guide-to-families-and-students-and-a-text-book-for-physicians-these-acting-together-maintain-the-foot-in-a-flat-position-as-inwalking-muscles-of-the-foot-these-may-be-arranged-according-to-their-situation-above-or-belowinto-those-of-the-dorsal-and-those-of-the-plantar-regions-dorsal-regiontwo-muscles-1-extensor-brevis-digitorumarises-from-the-outer-side-of-the-os-calcis-crosses-the-foot-obliquelyand-terminates-in-four-tendons-one-of-which-is-inserted-into-the-firstphalanx-of-the-gr-image342750493.htmlRM2AWHHN1–The hydropathic encyclopedia : a system of hydropathy and hygiene in eight parts ..designed as a guide to families and students, and a text-book for physicians . these acting together maintain the foot in a flat position, as inwalking. MUSCLES OF THE FOOT. These may be arranged, according to their situation above or below,into those of the dorsal and those of the plantar regions. Dorsal Region.—Two muscles: 1. Extensor brevis digitorum;arises from the outer side of the os calcis, crosses the foot obliquely,and terminates in four tendons, one of which is inserted into the firstphalanx of the gr
 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696275.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696275.htmlRF2CBRFT3–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
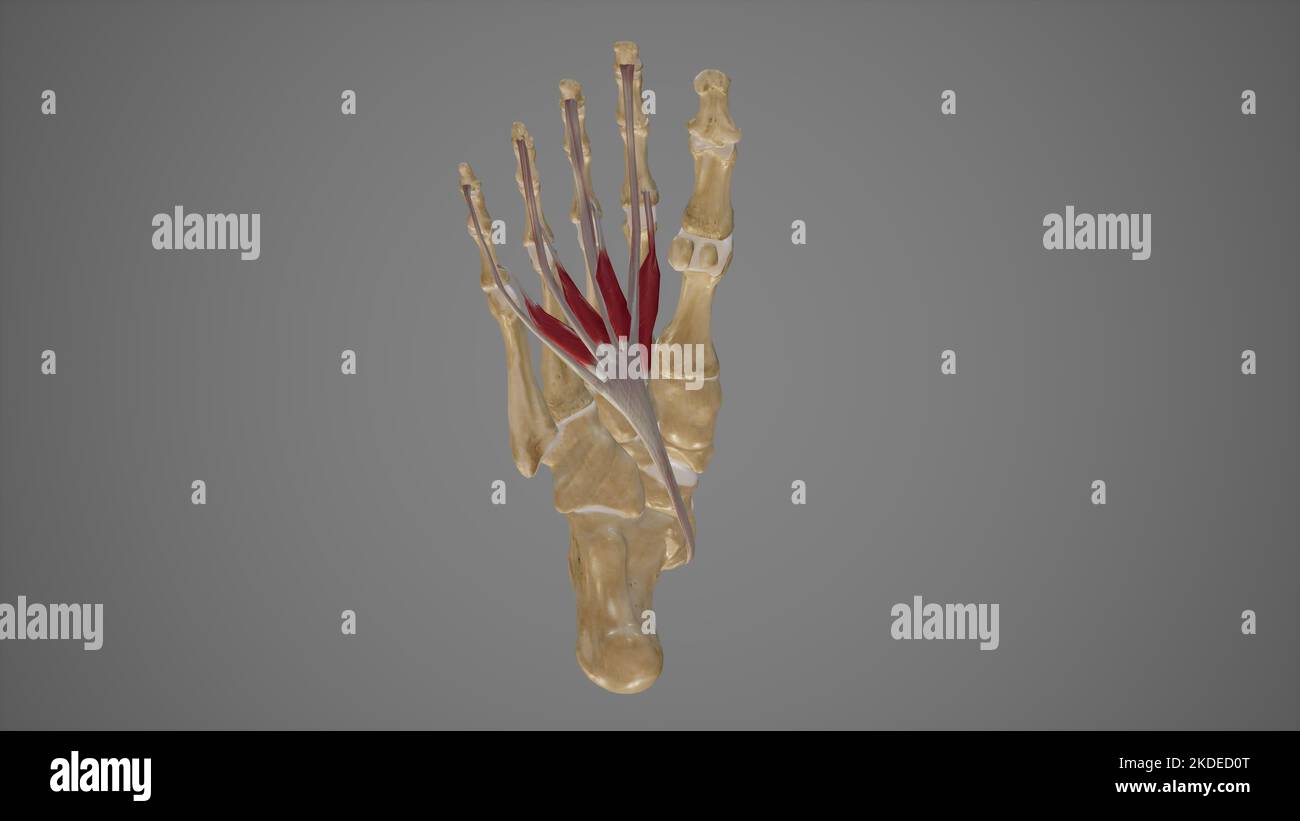 Medical Illustration of Lumbricals Muscles of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-lumbricals-muscles-of-foot-image490198376.html
Medical Illustration of Lumbricals Muscles of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-lumbricals-muscles-of-foot-image490198376.htmlRF2KDED0T–Medical Illustration of Lumbricals Muscles of Foot
 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13165777.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13165777.htmlRFACJ2EX–The muscles of the foot
 A treatise on orthopedic surgery . 3. O^ The Judson brace for paralysis of the quadriceps extensor muscle in connectionwith deformity of the foot. ary effect. In many instances, therefore, it will lie necessaryto support the knee as well as the ankle dtiring the earlier stagesof the treatment. Paralysis of the Thigh Muscles.—Paralysis of the quad-riceps extensor muscle causes primarily a peculiar gait. Thepatient, unable to extend the leg upon the thigh, throws orswings it forward, then locks the joint by direct contact of thebones and by the resistance of the posterior tissues, by incliningth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-orthopedic-surgery-3-o-the-judson-brace-for-paralysis-of-the-quadriceps-extensor-muscle-in-connectionwith-deformity-of-the-foot-ary-effect-in-many-instances-therefore-it-will-lie-necessaryto-support-the-knee-as-well-as-the-ankle-dtiring-the-earlier-stagesof-the-treatment-paralysis-of-the-thigh-musclesparalysis-of-the-quad-riceps-extensor-muscle-causes-primarily-a-peculiar-gait-thepatient-unable-to-extend-the-leg-upon-the-thigh-throws-orswings-it-forward-then-locks-the-joint-by-direct-contact-of-thebones-and-by-the-resistance-of-the-posterior-tissues-by-incliningth-image338273776.html
A treatise on orthopedic surgery . 3. O^ The Judson brace for paralysis of the quadriceps extensor muscle in connectionwith deformity of the foot. ary effect. In many instances, therefore, it will lie necessaryto support the knee as well as the ankle dtiring the earlier stagesof the treatment. Paralysis of the Thigh Muscles.—Paralysis of the quad-riceps extensor muscle causes primarily a peculiar gait. Thepatient, unable to extend the leg upon the thigh, throws orswings it forward, then locks the joint by direct contact of thebones and by the resistance of the posterior tissues, by incliningth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-orthopedic-surgery-3-o-the-judson-brace-for-paralysis-of-the-quadriceps-extensor-muscle-in-connectionwith-deformity-of-the-foot-ary-effect-in-many-instances-therefore-it-will-lie-necessaryto-support-the-knee-as-well-as-the-ankle-dtiring-the-earlier-stagesof-the-treatment-paralysis-of-the-thigh-musclesparalysis-of-the-quad-riceps-extensor-muscle-causes-primarily-a-peculiar-gait-thepatient-unable-to-extend-the-leg-upon-the-thigh-throws-orswings-it-forward-then-locks-the-joint-by-direct-contact-of-thebones-and-by-the-resistance-of-the-posterior-tissues-by-incliningth-image338273776.htmlRM2AJ9KJ8–A treatise on orthopedic surgery . 3. O^ The Judson brace for paralysis of the quadriceps extensor muscle in connectionwith deformity of the foot. ary effect. In many instances, therefore, it will lie necessaryto support the knee as well as the ankle dtiring the earlier stagesof the treatment. Paralysis of the Thigh Muscles.—Paralysis of the quad-riceps extensor muscle causes primarily a peculiar gait. Thepatient, unable to extend the leg upon the thigh, throws orswings it forward, then locks the joint by direct contact of thebones and by the resistance of the posterior tissues, by incliningth
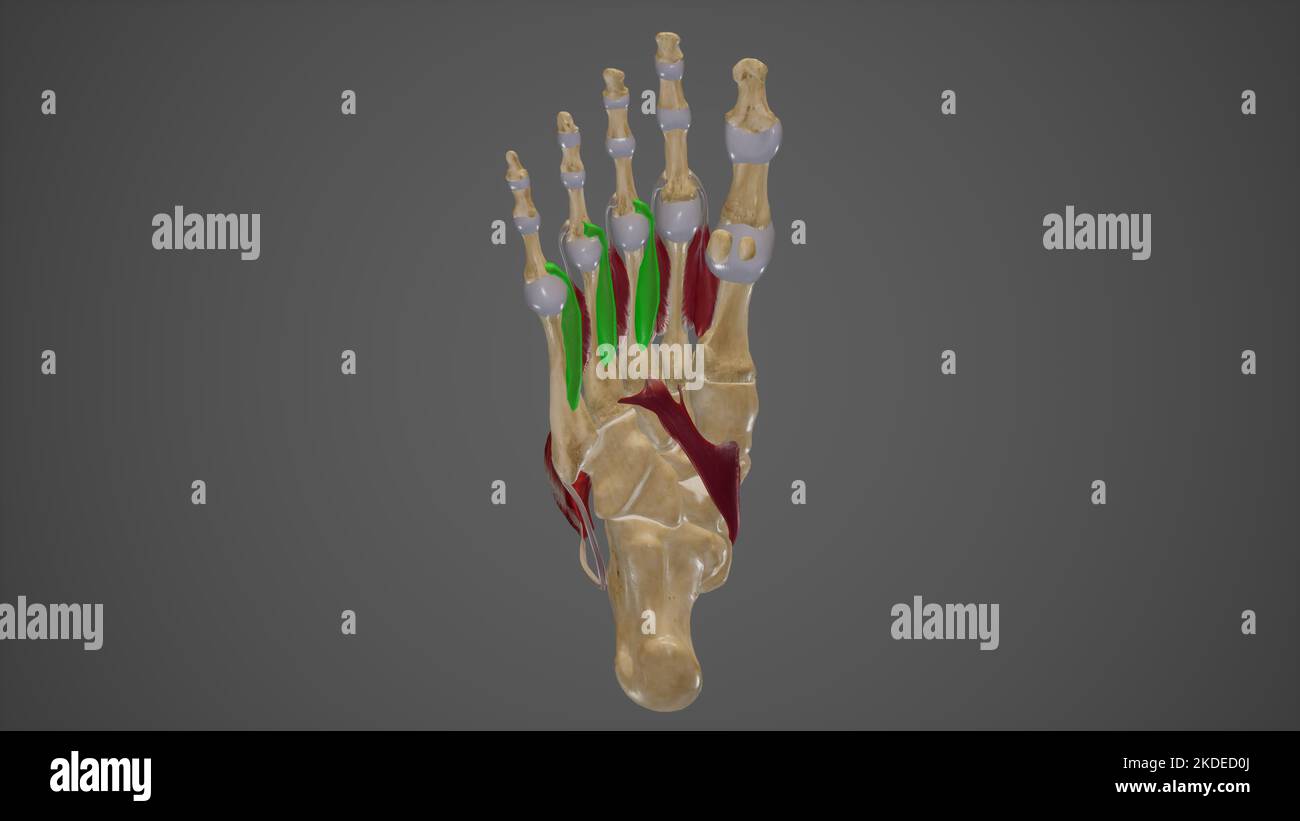
 Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696296.html
Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-illustration-of-human-foot-3d-illustration-image368696296.htmlRF2CBRFTT–Anatomy illustration of human foot 3D Illustration.
 Muscles of Sole of Foot Fourth Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-fourth-layer-image490198370.html
Muscles of Sole of Foot Fourth Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-fourth-layer-image490198370.htmlRF2KDED0J–Muscles of Sole of Foot Fourth Layer
 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13226479.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13226479.htmlRFACTF5M–The muscles of the foot
 Electro-diagnosis and electro-therapeutics : a guide for practitioners and students . ion of the foot.Muscles of the rjyi^Q exteiisov digitorum communis longus muscle can Plantar Region not regularly be isolated between the tibialis anticus andperoneus longus; about in the middle, but farther distal,about a hand breadth below the patella, it causes a footabduction and dorsal flexion, and extends the toe feebly;at the same time the affected tendon stands out at theback of the foot and over the ankle. The extensor hallucis longus muscle, at different pointsabove the ankle-joint on the inside, ve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/electro-diagnosis-and-electro-therapeutics-a-guide-for-practitioners-and-students-ion-of-the-footmuscles-of-the-rjyiq-exteiisov-digitorum-communis-longus-muscle-can-plantar-region-not-regularly-be-isolated-between-the-tibialis-anticus-andperoneus-longus-about-in-the-middle-but-farther-distalabout-a-hand-breadth-below-the-patella-it-causes-a-footabduction-and-dorsal-flexion-and-extends-the-toe-feeblyat-the-same-time-the-affected-tendon-stands-out-at-theback-of-the-foot-and-over-the-ankle-the-extensor-hallucis-longus-muscle-at-different-pointsabove-the-ankle-joint-on-the-inside-ve-image342702400.html
Electro-diagnosis and electro-therapeutics : a guide for practitioners and students . ion of the foot.Muscles of the rjyi^Q exteiisov digitorum communis longus muscle can Plantar Region not regularly be isolated between the tibialis anticus andperoneus longus; about in the middle, but farther distal,about a hand breadth below the patella, it causes a footabduction and dorsal flexion, and extends the toe feebly;at the same time the affected tendon stands out at theback of the foot and over the ankle. The extensor hallucis longus muscle, at different pointsabove the ankle-joint on the inside, ve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/electro-diagnosis-and-electro-therapeutics-a-guide-for-practitioners-and-students-ion-of-the-footmuscles-of-the-rjyiq-exteiisov-digitorum-communis-longus-muscle-can-plantar-region-not-regularly-be-isolated-between-the-tibialis-anticus-andperoneus-longus-about-in-the-middle-but-farther-distalabout-a-hand-breadth-below-the-patella-it-causes-a-footabduction-and-dorsal-flexion-and-extends-the-toe-feeblyat-the-same-time-the-affected-tendon-stands-out-at-theback-of-the-foot-and-over-the-ankle-the-extensor-hallucis-longus-muscle-at-different-pointsabove-the-ankle-joint-on-the-inside-ve-image342702400.htmlRM2AWFCBC–Electro-diagnosis and electro-therapeutics : a guide for practitioners and students . ion of the foot.Muscles of the rjyi^Q exteiisov digitorum communis longus muscle can Plantar Region not regularly be isolated between the tibialis anticus andperoneus longus; about in the middle, but farther distal,about a hand breadth below the patella, it causes a footabduction and dorsal flexion, and extends the toe feebly;at the same time the affected tendon stands out at theback of the foot and over the ankle. The extensor hallucis longus muscle, at different pointsabove the ankle-joint on the inside, ve
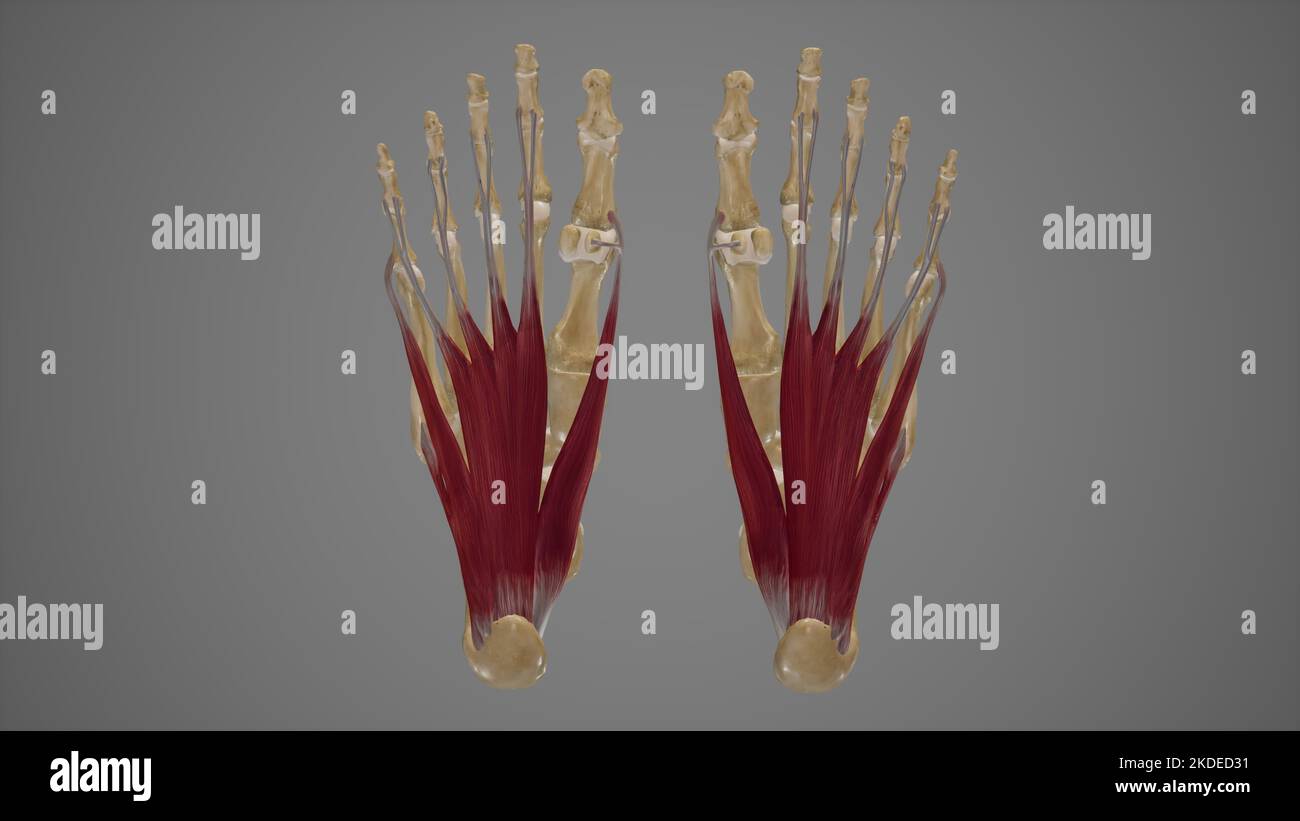 Muscles of Sole of Foot First Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-first-layer-image490198437.html
Muscles of Sole of Foot First Layer Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscles-of-sole-of-foot-first-layer-image490198437.htmlRF2KDED31–Muscles of Sole of Foot First Layer
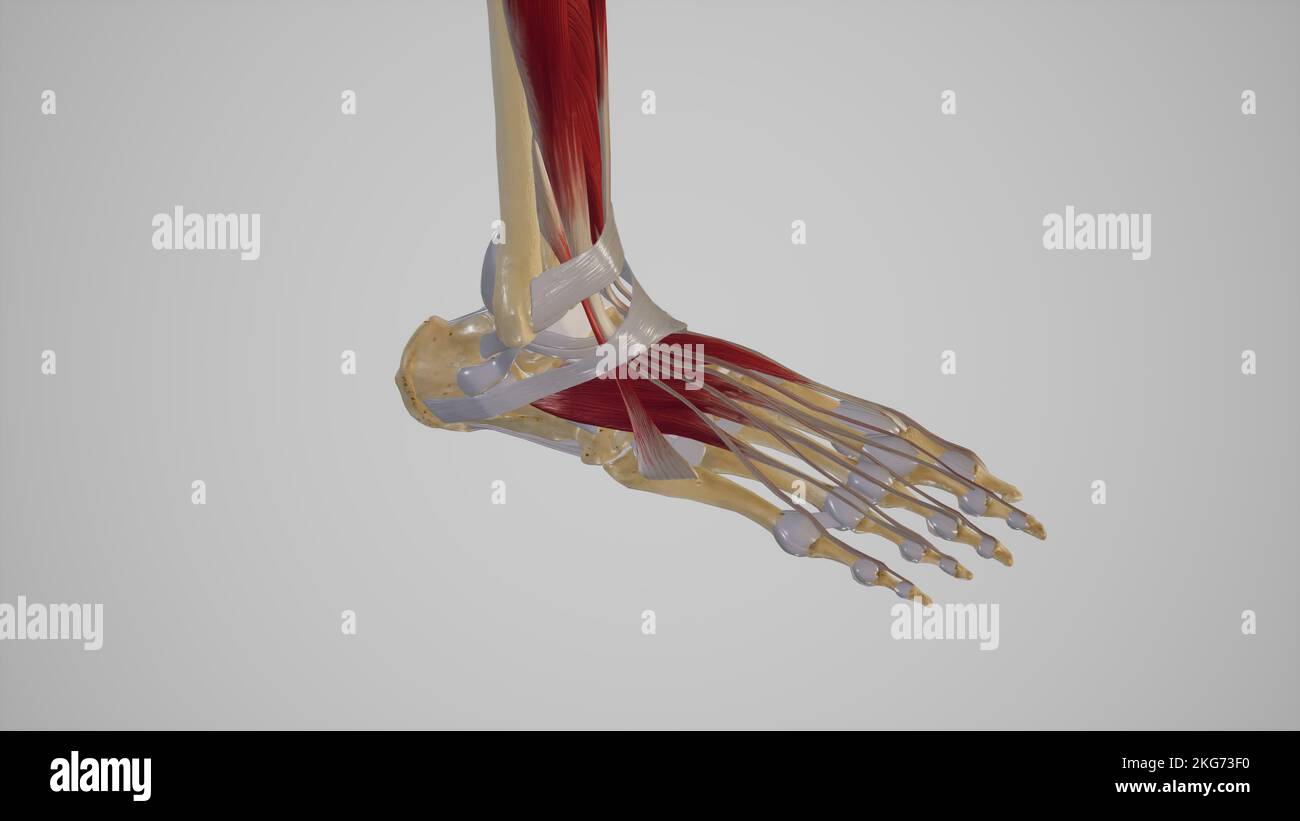 Foot Ligaments Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/foot-ligaments-image491881236.html
Foot Ligaments Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/foot-ligaments-image491881236.htmlRF2KG73F0–Foot Ligaments
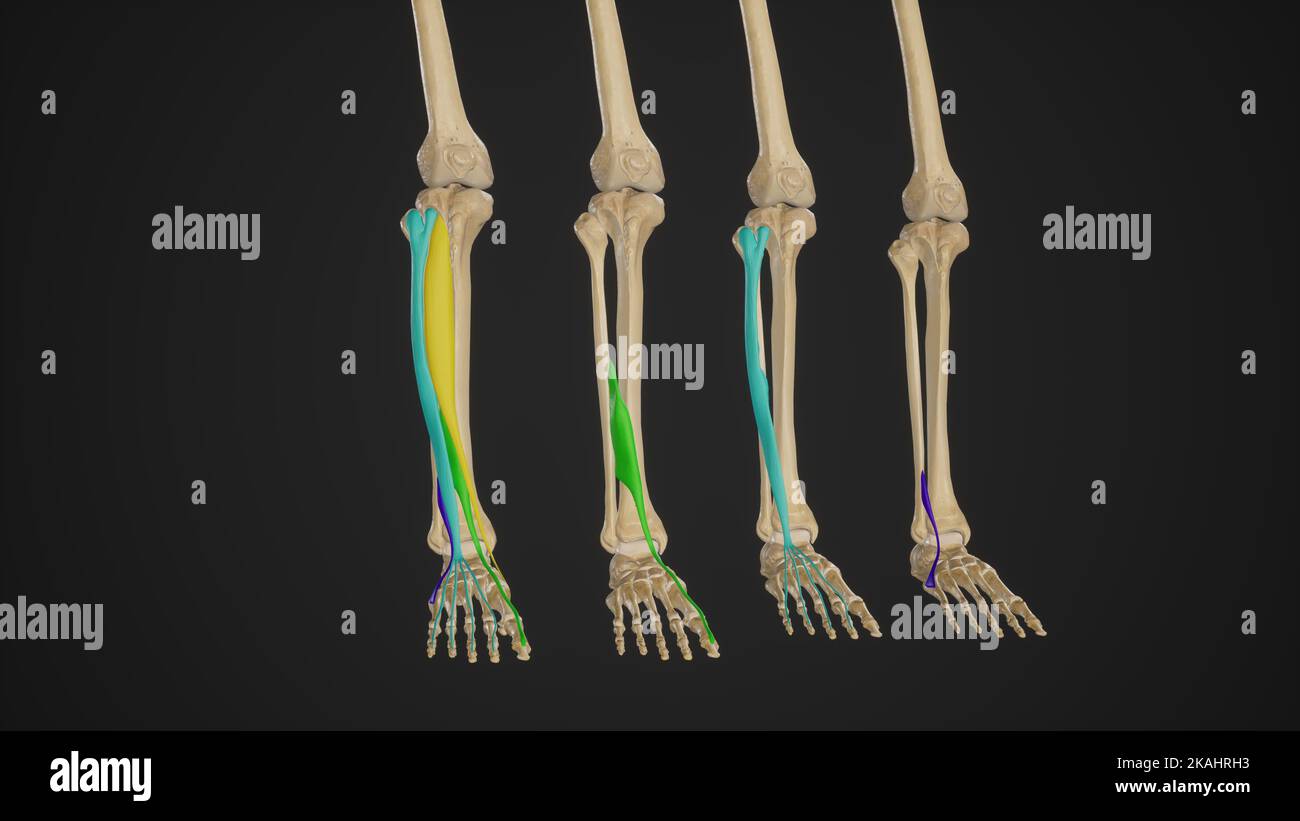 Medical Illustration of Anterior Muscles of The Leg (Dorsiflexors) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-anterior-muscles-of-the-leg-dorsiflexors-image488428559.html
Medical Illustration of Anterior Muscles of The Leg (Dorsiflexors) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-anterior-muscles-of-the-leg-dorsiflexors-image488428559.htmlRF2KAHRH3–Medical Illustration of Anterior Muscles of The Leg (Dorsiflexors)
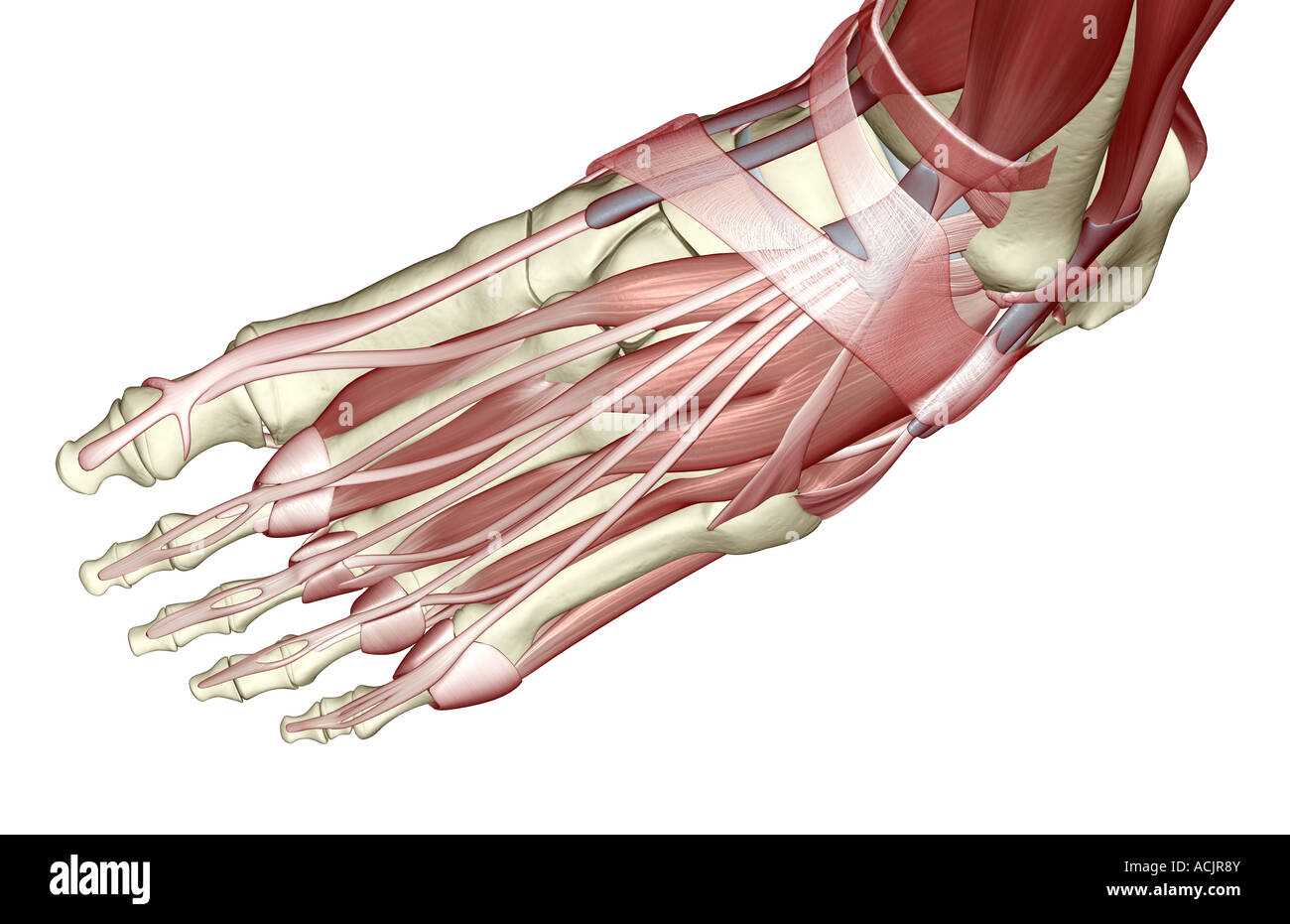 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13172762.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13172762.htmlRFACJR8Y–The muscles of the foot
 Electro-diagnosis and electro-therapeutics : a guide for practitioners and students . he foot.Muscles of the rpi^^ exteiisor digitorum communis longus muscle can Plantar Region not regularly be isolated between the tibialis anticus andperoneus longus; about in the middle, but farther distal,about a hand breadth below the patella, it causes a footabduction and dorsal flexion, and extends the toe feebly;at the same time the affected tendon stands out at theback of the foot and over the ankle. The extensor Jiallucis longus muscle, at different pointsabove the ankle-joint on the inside, very near Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/electro-diagnosis-and-electro-therapeutics-a-guide-for-practitioners-and-students-he-footmuscles-of-the-rpi-exteiisor-digitorum-communis-longus-muscle-can-plantar-region-not-regularly-be-isolated-between-the-tibialis-anticus-andperoneus-longus-about-in-the-middle-but-farther-distalabout-a-hand-breadth-below-the-patella-it-causes-a-footabduction-and-dorsal-flexion-and-extends-the-toe-feeblyat-the-same-time-the-affected-tendon-stands-out-at-theback-of-the-foot-and-over-the-ankle-the-extensor-jiallucis-longus-muscle-at-different-pointsabove-the-ankle-joint-on-the-inside-very-near-image342702501.html
Electro-diagnosis and electro-therapeutics : a guide for practitioners and students . he foot.Muscles of the rpi^^ exteiisor digitorum communis longus muscle can Plantar Region not regularly be isolated between the tibialis anticus andperoneus longus; about in the middle, but farther distal,about a hand breadth below the patella, it causes a footabduction and dorsal flexion, and extends the toe feebly;at the same time the affected tendon stands out at theback of the foot and over the ankle. The extensor Jiallucis longus muscle, at different pointsabove the ankle-joint on the inside, very near Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/electro-diagnosis-and-electro-therapeutics-a-guide-for-practitioners-and-students-he-footmuscles-of-the-rpi-exteiisor-digitorum-communis-longus-muscle-can-plantar-region-not-regularly-be-isolated-between-the-tibialis-anticus-andperoneus-longus-about-in-the-middle-but-farther-distalabout-a-hand-breadth-below-the-patella-it-causes-a-footabduction-and-dorsal-flexion-and-extends-the-toe-feeblyat-the-same-time-the-affected-tendon-stands-out-at-theback-of-the-foot-and-over-the-ankle-the-extensor-jiallucis-longus-muscle-at-different-pointsabove-the-ankle-joint-on-the-inside-very-near-image342702501.htmlRM2AWFCF1–Electro-diagnosis and electro-therapeutics : a guide for practitioners and students . he foot.Muscles of the rpi^^ exteiisor digitorum communis longus muscle can Plantar Region not regularly be isolated between the tibialis anticus andperoneus longus; about in the middle, but farther distal,about a hand breadth below the patella, it causes a footabduction and dorsal flexion, and extends the toe feebly;at the same time the affected tendon stands out at theback of the foot and over the ankle. The extensor Jiallucis longus muscle, at different pointsabove the ankle-joint on the inside, very near
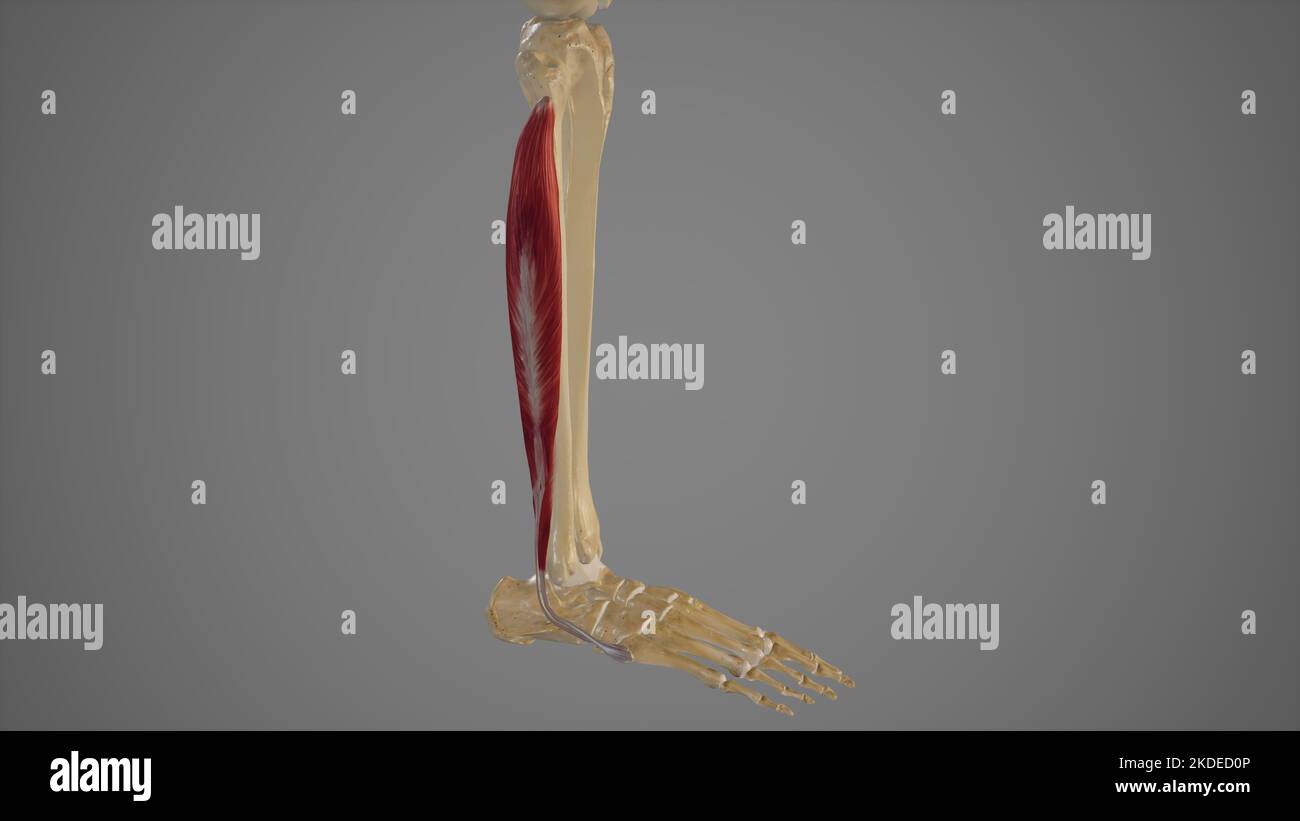 Lateral Muscles of Lower Leg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lateral-muscles-of-lower-leg-image490198374.html
Lateral Muscles of Lower Leg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lateral-muscles-of-lower-leg-image490198374.htmlRF2KDED0P–Lateral Muscles of Lower Leg
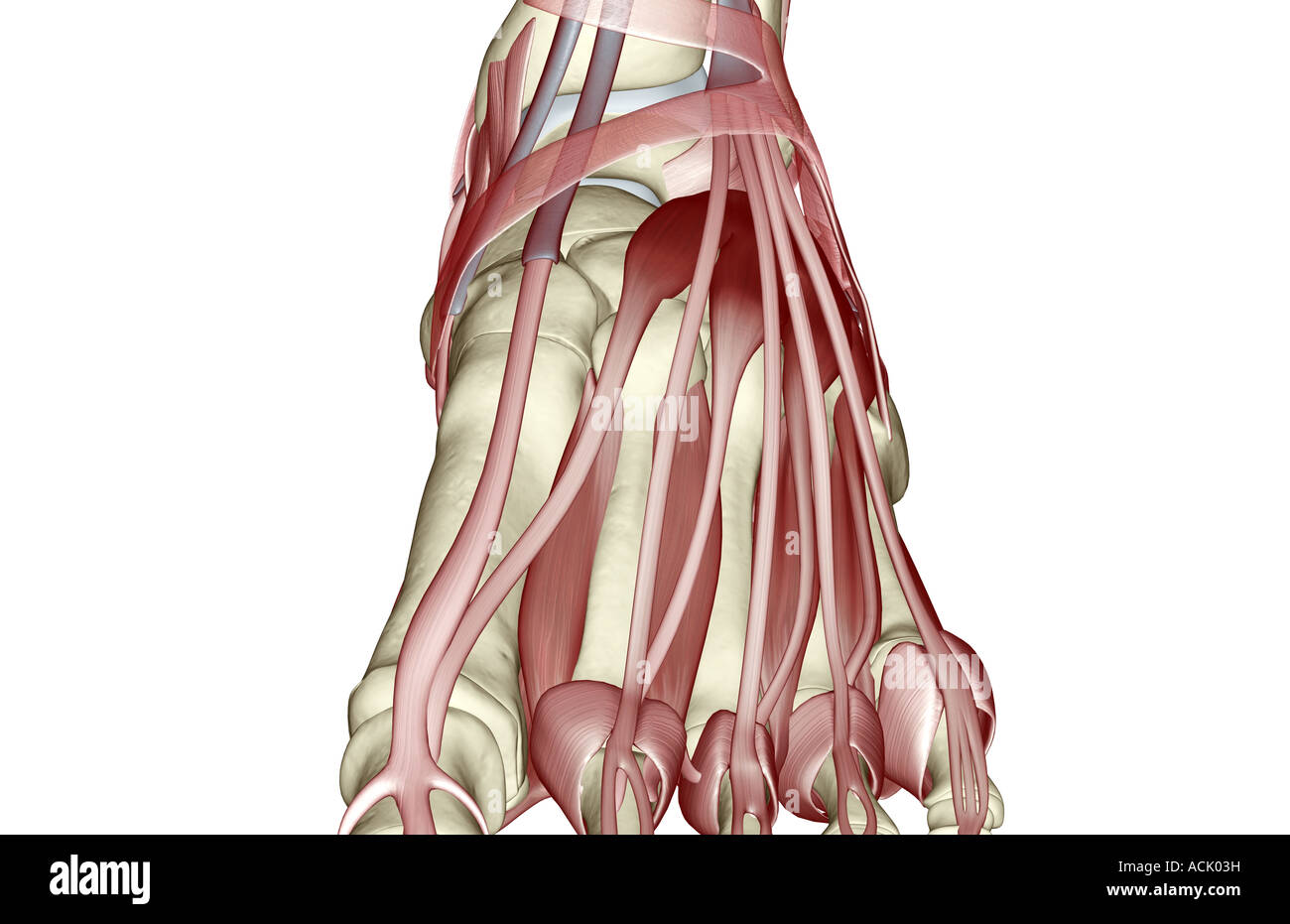 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13174372.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13174372.htmlRFACK03H–The muscles of the foot
 A manual of operative surgery . artery (Fig. 332). The deepfascia is exposed. The interval between thetibialis anticus and extensor communis isindicated by a yellowish white line. Thisis due, not to a distinct septum, but to aline of fatty tissue lodged between the twomuscles. In emaciated subjects the linemay not be apparent. The deep fascia isdivided along this line. The two musclesabove named are found lying close to-gether. The outer edge of the tibialisanticus is still muscular, but the inner edge of the commonextensor is now tendinous. Flex the foot. Separate the muscles with the handle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-operative-surgery-artery-fig-332-the-deepfascia-is-exposed-the-interval-between-thetibialis-anticus-and-extensor-communis-isindicated-by-a-yellowish-white-line-thisis-due-not-to-a-distinct-septum-but-to-aline-of-fatty-tissue-lodged-between-the-twomuscles-in-emaciated-subjects-the-linemay-not-be-apparent-the-deep-fascia-isdivided-along-this-line-the-two-musclesabove-named-are-found-lying-close-to-gether-the-outer-edge-of-the-tibialisanticus-is-still-muscular-but-the-inner-edge-of-the-commonextensor-is-now-tendinous-flex-the-foot-separate-the-muscles-with-the-handle-image343325803.html
A manual of operative surgery . artery (Fig. 332). The deepfascia is exposed. The interval between thetibialis anticus and extensor communis isindicated by a yellowish white line. Thisis due, not to a distinct septum, but to aline of fatty tissue lodged between the twomuscles. In emaciated subjects the linemay not be apparent. The deep fascia isdivided along this line. The two musclesabove named are found lying close to-gether. The outer edge of the tibialisanticus is still muscular, but the inner edge of the commonextensor is now tendinous. Flex the foot. Separate the muscles with the handle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-operative-surgery-artery-fig-332-the-deepfascia-is-exposed-the-interval-between-thetibialis-anticus-and-extensor-communis-isindicated-by-a-yellowish-white-line-thisis-due-not-to-a-distinct-septum-but-to-aline-of-fatty-tissue-lodged-between-the-twomuscles-in-emaciated-subjects-the-linemay-not-be-apparent-the-deep-fascia-isdivided-along-this-line-the-two-musclesabove-named-are-found-lying-close-to-gether-the-outer-edge-of-the-tibialisanticus-is-still-muscular-but-the-inner-edge-of-the-commonextensor-is-now-tendinous-flex-the-foot-separate-the-muscles-with-the-handle-image343325803.htmlRM2AXFRFR–A manual of operative surgery . artery (Fig. 332). The deepfascia is exposed. The interval between thetibialis anticus and extensor communis isindicated by a yellowish white line. Thisis due, not to a distinct septum, but to aline of fatty tissue lodged between the twomuscles. In emaciated subjects the linemay not be apparent. The deep fascia isdivided along this line. The two musclesabove named are found lying close to-gether. The outer edge of the tibialisanticus is still muscular, but the inner edge of the commonextensor is now tendinous. Flex the foot. Separate the muscles with the handle
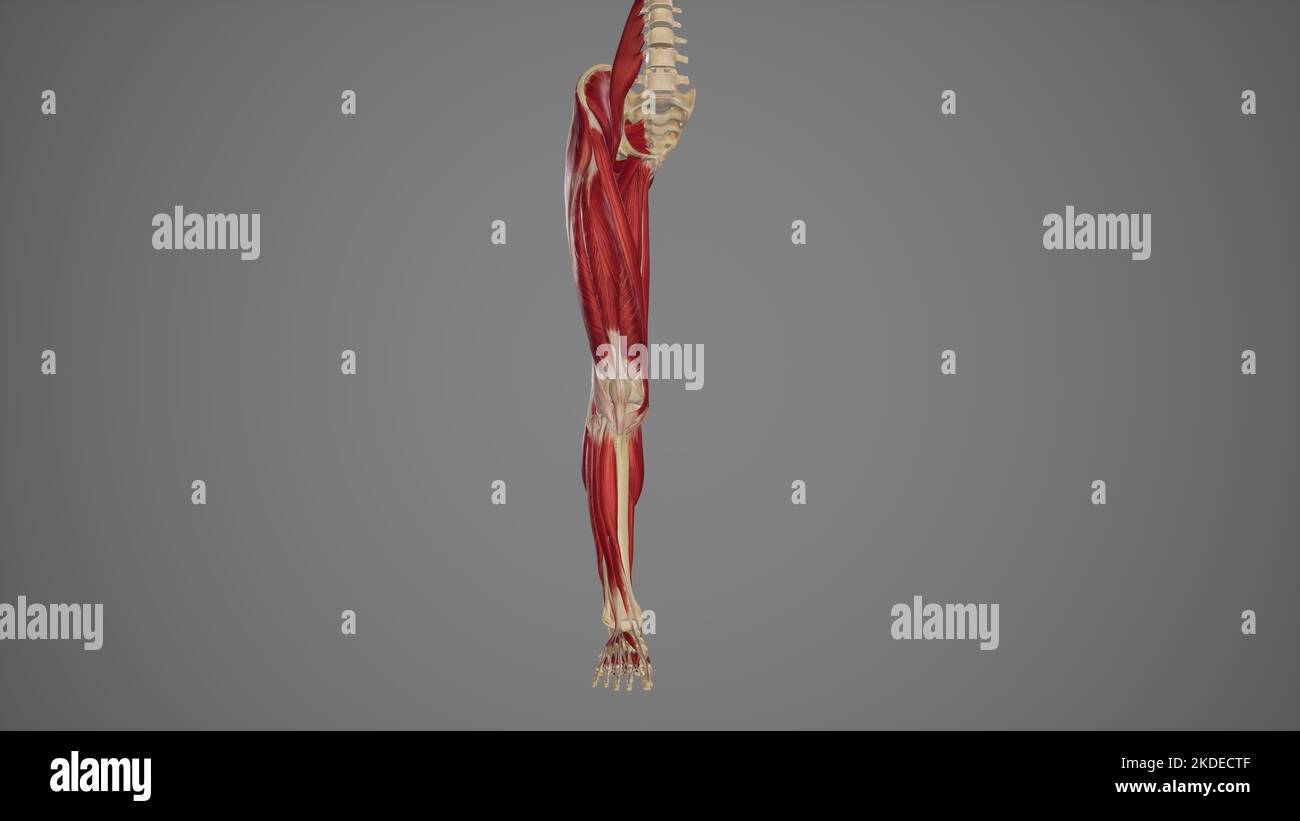 Anterior View of Lower Limb Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-view-of-lower-limb-muscles-image490198255.html
Anterior View of Lower Limb Muscles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anterior-view-of-lower-limb-muscles-image490198255.htmlRF2KDECTF–Anterior View of Lower Limb Muscles
 The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13197277.html
The muscles of the foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-muscles-of-the-foot-13197277.htmlRFACNC7X–The muscles of the foot
 The human body A beginner's text-book of anatomy, physiology and hygiene .. . scles). 31. Muscles that extend or straighten the Leg (Extensor Muscles). The muscles that bend the leg are placed on the back of the thigh, so thatthey cannot be seen in the figure. Muscles of the leg and foot: 32. Muscles that bend the Foot upon the Leg, and extend the Toes. 33. Muscles that raise the Heel—these form the prominence of the calf of the Leg. 34. Muscles that turn the Foot outwards. 35. A band of membrane which retains in position the tendons which pass from the leg to the foot. 36. A short muscle whic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-human-body-a-beginners-text-book-of-anatomy-physiology-and-hygiene-scles-31-muscles-that-extend-or-straighten-the-leg-extensor-muscles-the-muscles-that-bend-the-leg-are-placed-on-the-back-of-the-thigh-so-thatthey-cannot-be-seen-in-the-figure-muscles-of-the-leg-and-foot-32-muscles-that-bend-the-foot-upon-the-leg-and-extend-the-toes-33-muscles-that-raise-the-heelthese-form-the-prominence-of-the-calf-of-the-leg-34-muscles-that-turn-the-foot-outwards-35-a-band-of-membrane-which-retains-in-position-the-tendons-which-pass-from-the-leg-to-the-foot-36-a-short-muscle-whic-image338424944.html
The human body A beginner's text-book of anatomy, physiology and hygiene .. . scles). 31. Muscles that extend or straighten the Leg (Extensor Muscles). The muscles that bend the leg are placed on the back of the thigh, so thatthey cannot be seen in the figure. Muscles of the leg and foot: 32. Muscles that bend the Foot upon the Leg, and extend the Toes. 33. Muscles that raise the Heel—these form the prominence of the calf of the Leg. 34. Muscles that turn the Foot outwards. 35. A band of membrane which retains in position the tendons which pass from the leg to the foot. 36. A short muscle whic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-human-body-a-beginners-text-book-of-anatomy-physiology-and-hygiene-scles-31-muscles-that-extend-or-straighten-the-leg-extensor-muscles-the-muscles-that-bend-the-leg-are-placed-on-the-back-of-the-thigh-so-thatthey-cannot-be-seen-in-the-figure-muscles-of-the-leg-and-foot-32-muscles-that-bend-the-foot-upon-the-leg-and-extend-the-toes-33-muscles-that-raise-the-heelthese-form-the-prominence-of-the-calf-of-the-leg-34-muscles-that-turn-the-foot-outwards-35-a-band-of-membrane-which-retains-in-position-the-tendons-which-pass-from-the-leg-to-the-foot-36-a-short-muscle-whic-image338424944.htmlRM2AJGGD4–The human body A beginner's text-book of anatomy, physiology and hygiene .. . scles). 31. Muscles that extend or straighten the Leg (Extensor Muscles). The muscles that bend the leg are placed on the back of the thigh, so thatthey cannot be seen in the figure. Muscles of the leg and foot: 32. Muscles that bend the Foot upon the Leg, and extend the Toes. 33. Muscles that raise the Heel—these form the prominence of the calf of the Leg. 34. Muscles that turn the Foot outwards. 35. A band of membrane which retains in position the tendons which pass from the leg to the foot. 36. A short muscle whic