Quick filters:
Fimbriae Stock Photos and Images
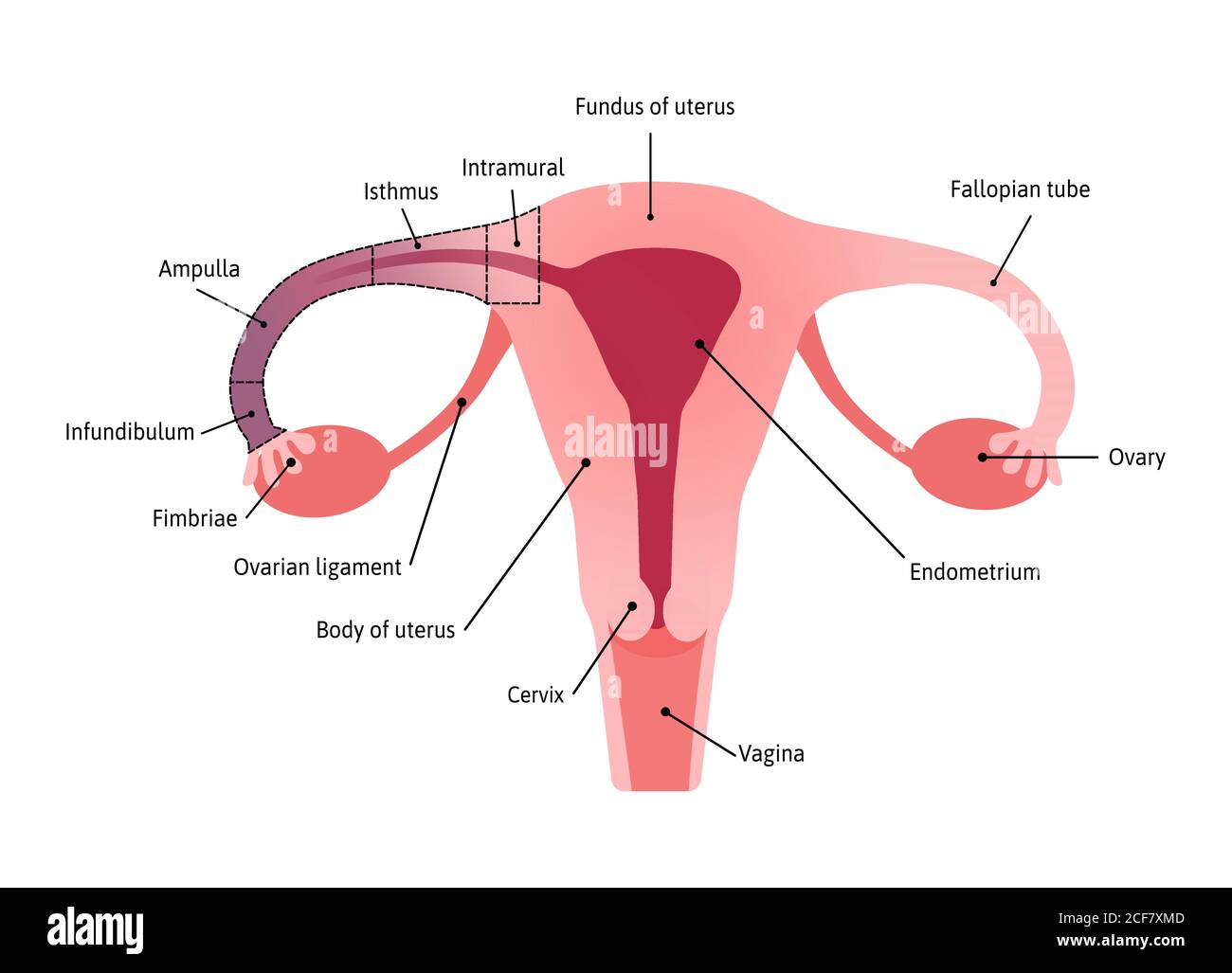 Anatomical Structure of fallopian tube. Fimbriae. Medical vector illustration marked with lines Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-structure-of-fallopian-tube-fimbriae-medical-vector-illustration-marked-with-lines-image370812189.html
Anatomical Structure of fallopian tube. Fimbriae. Medical vector illustration marked with lines Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomical-structure-of-fallopian-tube-fimbriae-medical-vector-illustration-marked-with-lines-image370812189.htmlRF2CF7XMD–Anatomical Structure of fallopian tube. Fimbriae. Medical vector illustration marked with lines
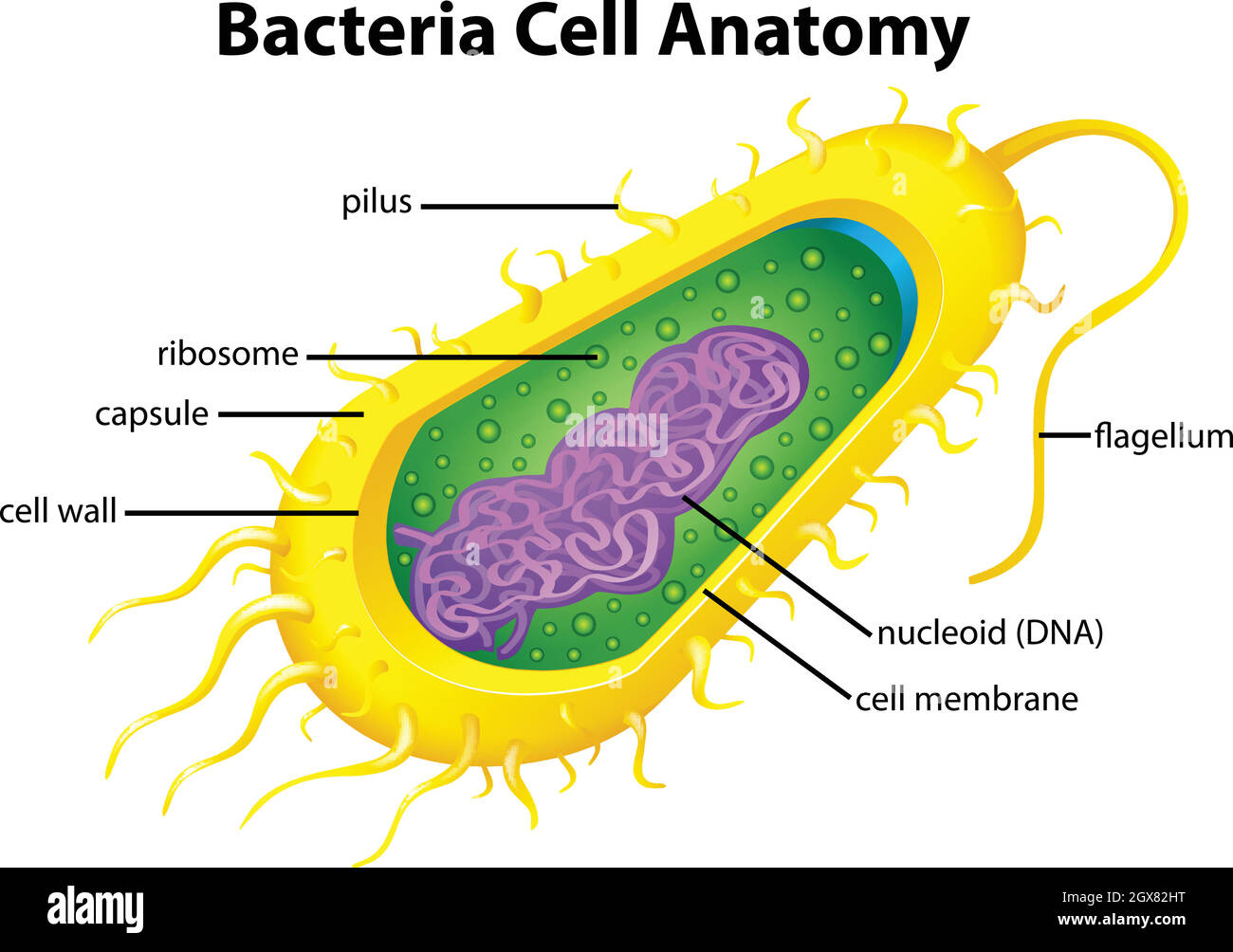 Bacteria cell structure Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-structure-image446417940.html
Bacteria cell structure Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-structure-image446417940.htmlRF2GX82HT–Bacteria cell structure
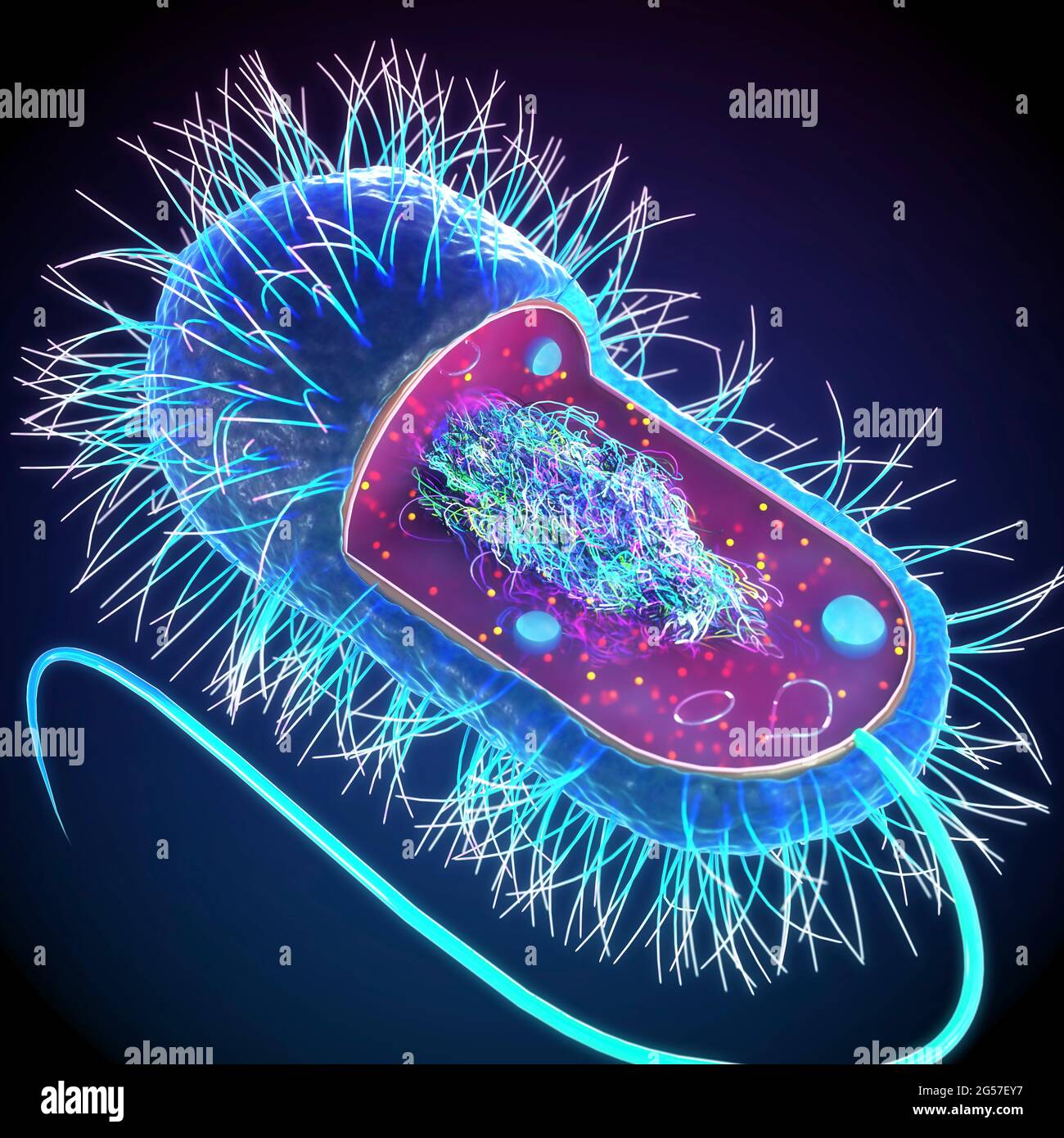
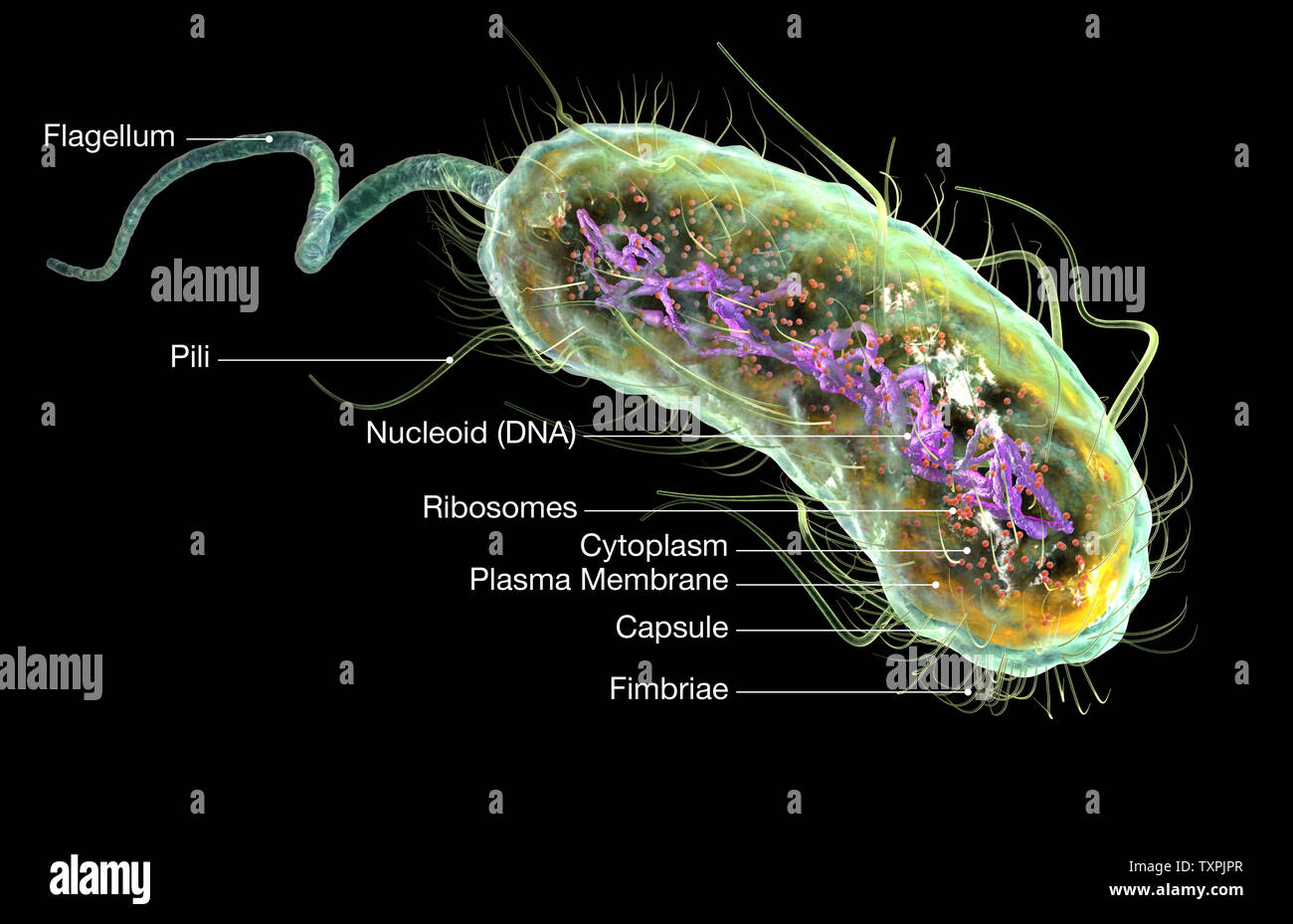 Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257423903.html
Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257423903.htmlRFTXPJPR–Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae
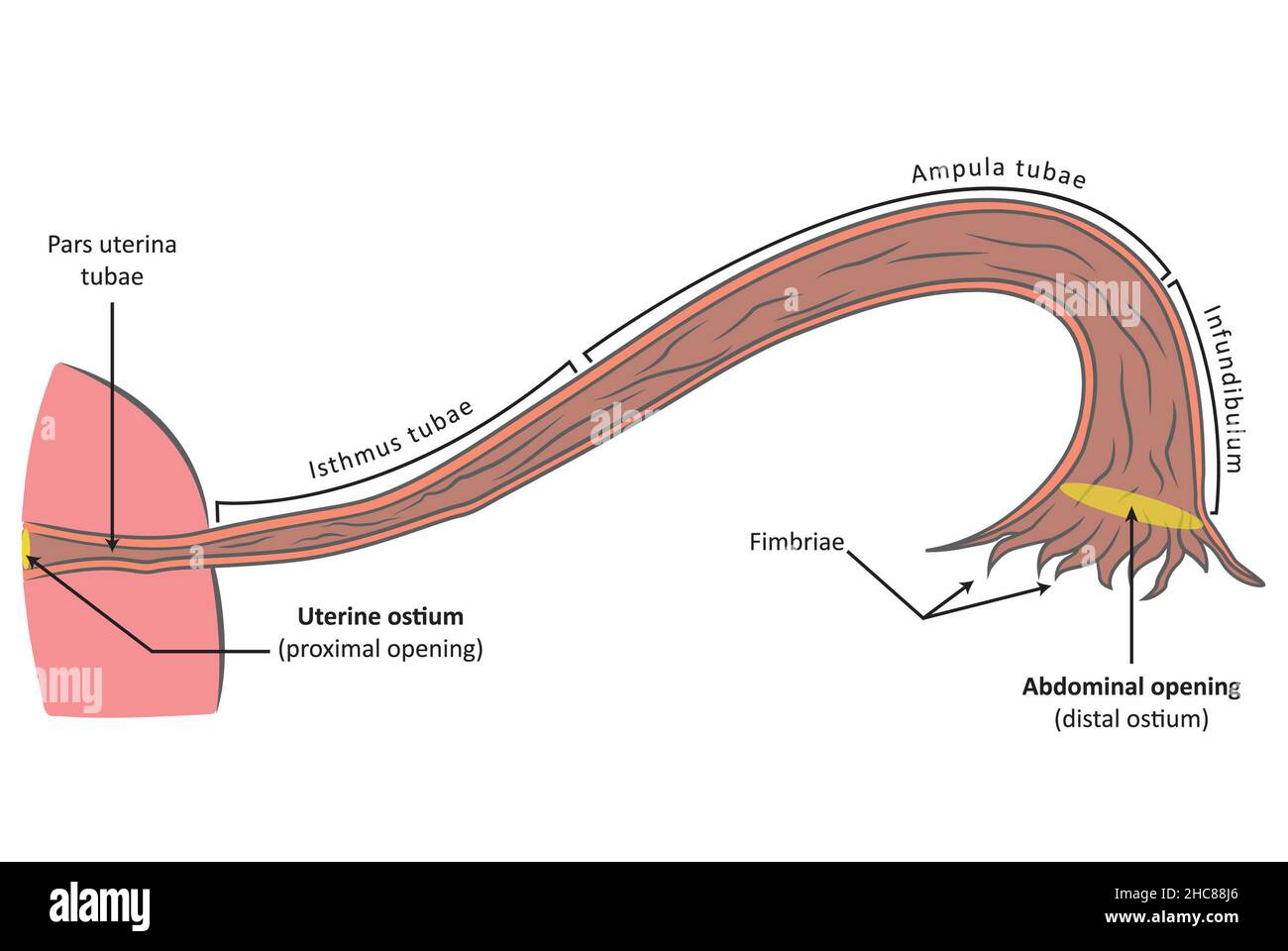 Fallopian tube (tuba uterina) frontal view, cross section. Female reproductive anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fallopian-tube-tuba-uterina-frontal-view-cross-section-female-reproductive-anatomy-image455027838.html
Fallopian tube (tuba uterina) frontal view, cross section. Female reproductive anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fallopian-tube-tuba-uterina-frontal-view-cross-section-female-reproductive-anatomy-image455027838.htmlRF2HC88J6–Fallopian tube (tuba uterina) frontal view, cross section. Female reproductive anatomy
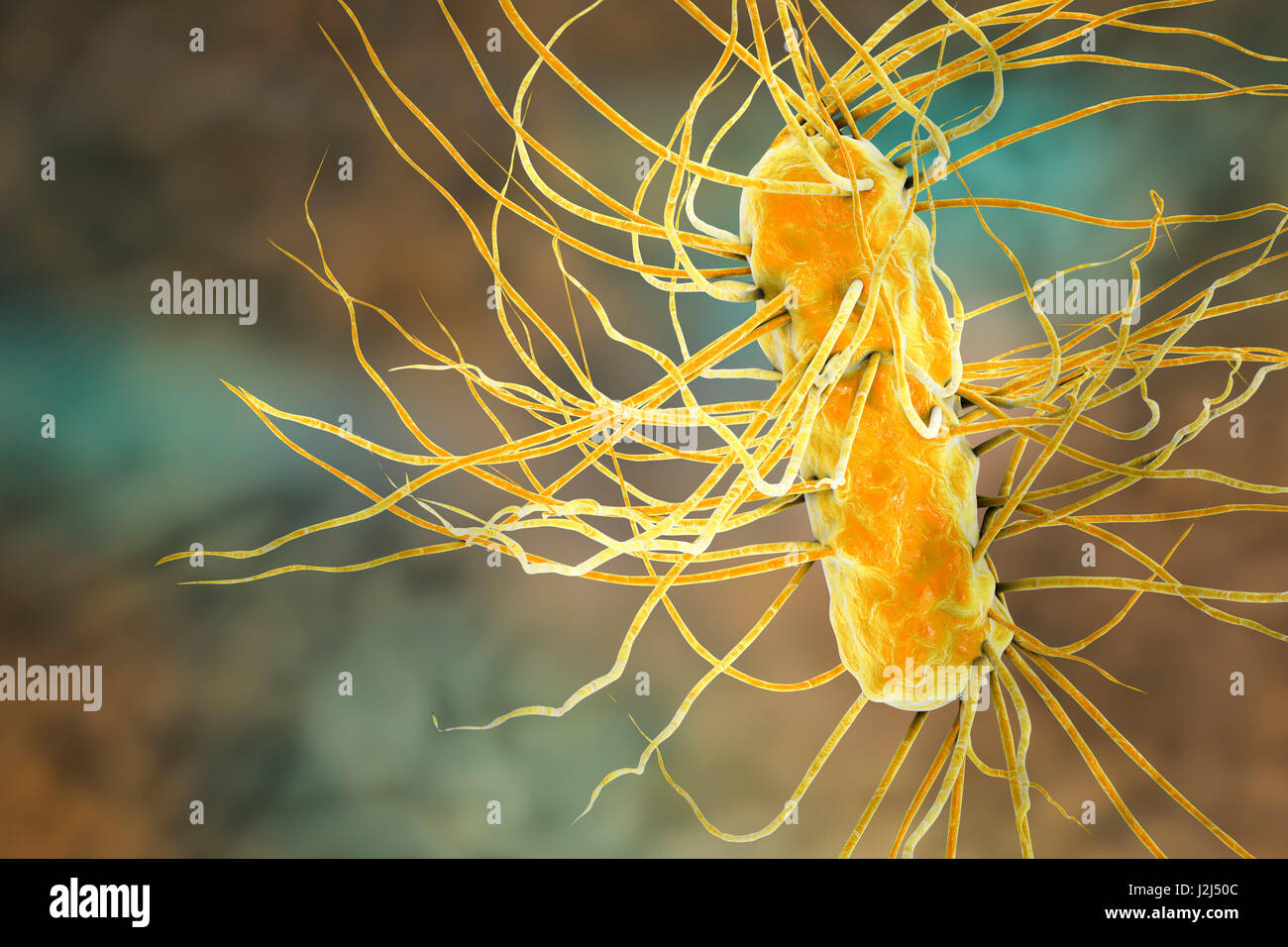 E. coli bacteria. Computer artwork of three Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod- shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacteriu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-e-coli-bacteria-computer-artwork-of-three-escherichia-coli-bacteria-139311324.html
E. coli bacteria. Computer artwork of three Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod- shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacteriu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-e-coli-bacteria-computer-artwork-of-three-escherichia-coli-bacteria-139311324.htmlRFJ2J50C–E. coli bacteria. Computer artwork of three Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod- shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacteriu
 Polymo is a polychaetous annelid bearing fimbriae viewed from above, vintage line drawing or engraving illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/polymo-is-a-polychaetous-annelid-bearing-fimbriae-viewed-from-above-vintage-line-drawing-or-engraving-illustration-image244594053.html
Polymo is a polychaetous annelid bearing fimbriae viewed from above, vintage line drawing or engraving illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/polymo-is-a-polychaetous-annelid-bearing-fimbriae-viewed-from-above-vintage-line-drawing-or-engraving-illustration-image244594053.htmlRFT5X65W–Polymo is a polychaetous annelid bearing fimbriae viewed from above, vintage line drawing or engraving illustration.
 Fimbria, Print, A fimbria (plural fimbriae, adjective fimbriate) is a Latin word that literally means 'fringe.' It is commonly used in science and medicine, with its meaning depending on the field of study or the context Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fimbria-print-a-fimbria-plural-fimbriae-adjective-fimbriate-is-a-latin-word-that-literally-means-fringe-it-is-commonly-used-in-science-and-medicine-with-its-meaning-depending-on-the-field-of-study-or-the-context-image328681013.html
Fimbria, Print, A fimbria (plural fimbriae, adjective fimbriate) is a Latin word that literally means 'fringe.' It is commonly used in science and medicine, with its meaning depending on the field of study or the context Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fimbria-print-a-fimbria-plural-fimbriae-adjective-fimbriate-is-a-latin-word-that-literally-means-fringe-it-is-commonly-used-in-science-and-medicine-with-its-meaning-depending-on-the-field-of-study-or-the-context-image328681013.htmlRM2A2MKYH–Fimbria, Print, A fimbria (plural fimbriae, adjective fimbriate) is a Latin word that literally means 'fringe.' It is commonly used in science and medicine, with its meaning depending on the field of study or the context
 E. Coli Bacteria, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-image416783757.html
E. Coli Bacteria, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-image416783757.htmlRM2F623X5–E. Coli Bacteria, Illustration
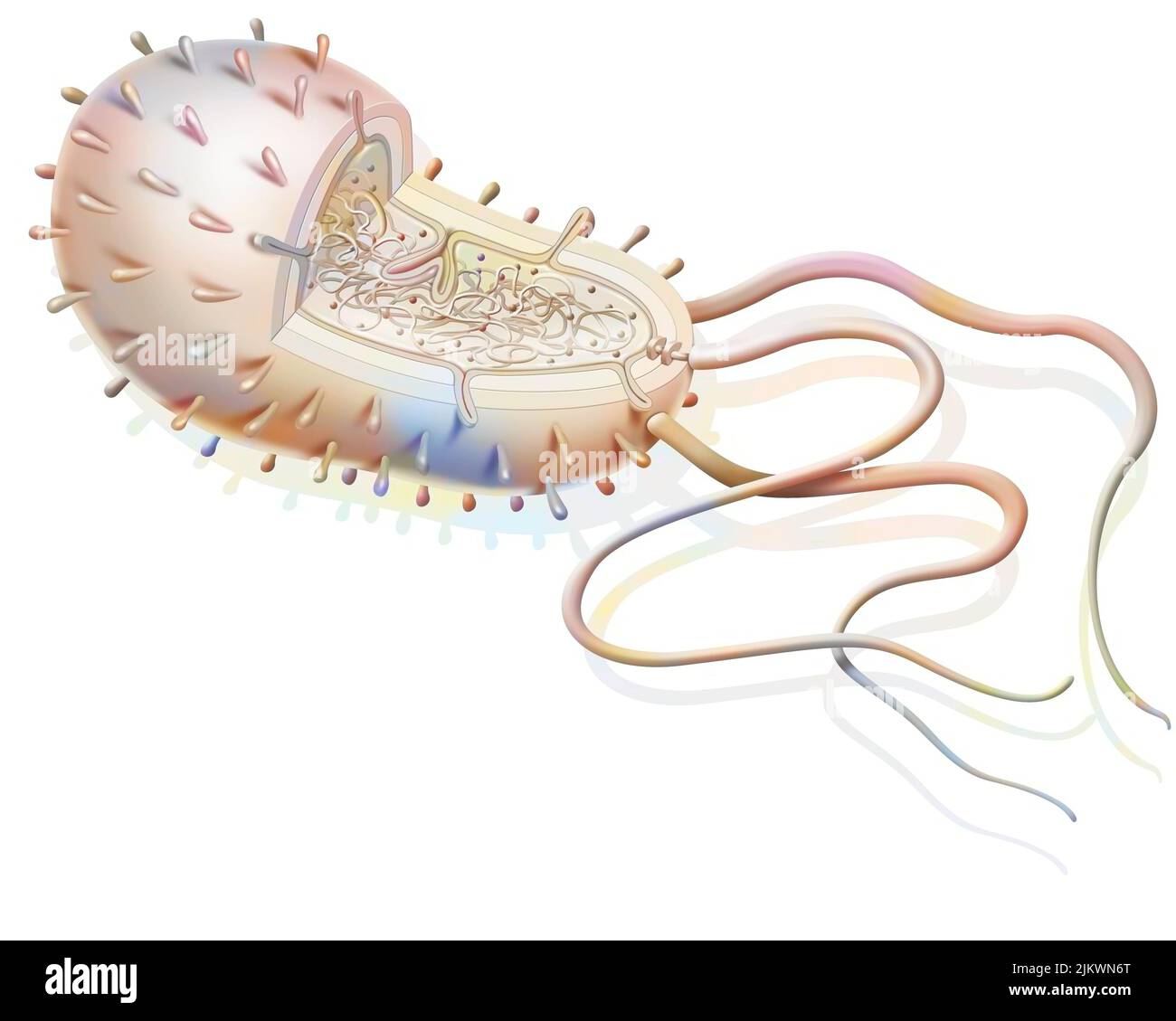 Structure of a bacterium: plasmids, ribosomes, DNA, flagella. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-a-bacterium-plasmids-ribosomes-dna-flagella-image476923856.html
Structure of a bacterium: plasmids, ribosomes, DNA, flagella. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-a-bacterium-plasmids-ribosomes-dna-flagella-image476923856.htmlRF2JKWN6T–Structure of a bacterium: plasmids, ribosomes, DNA, flagella.
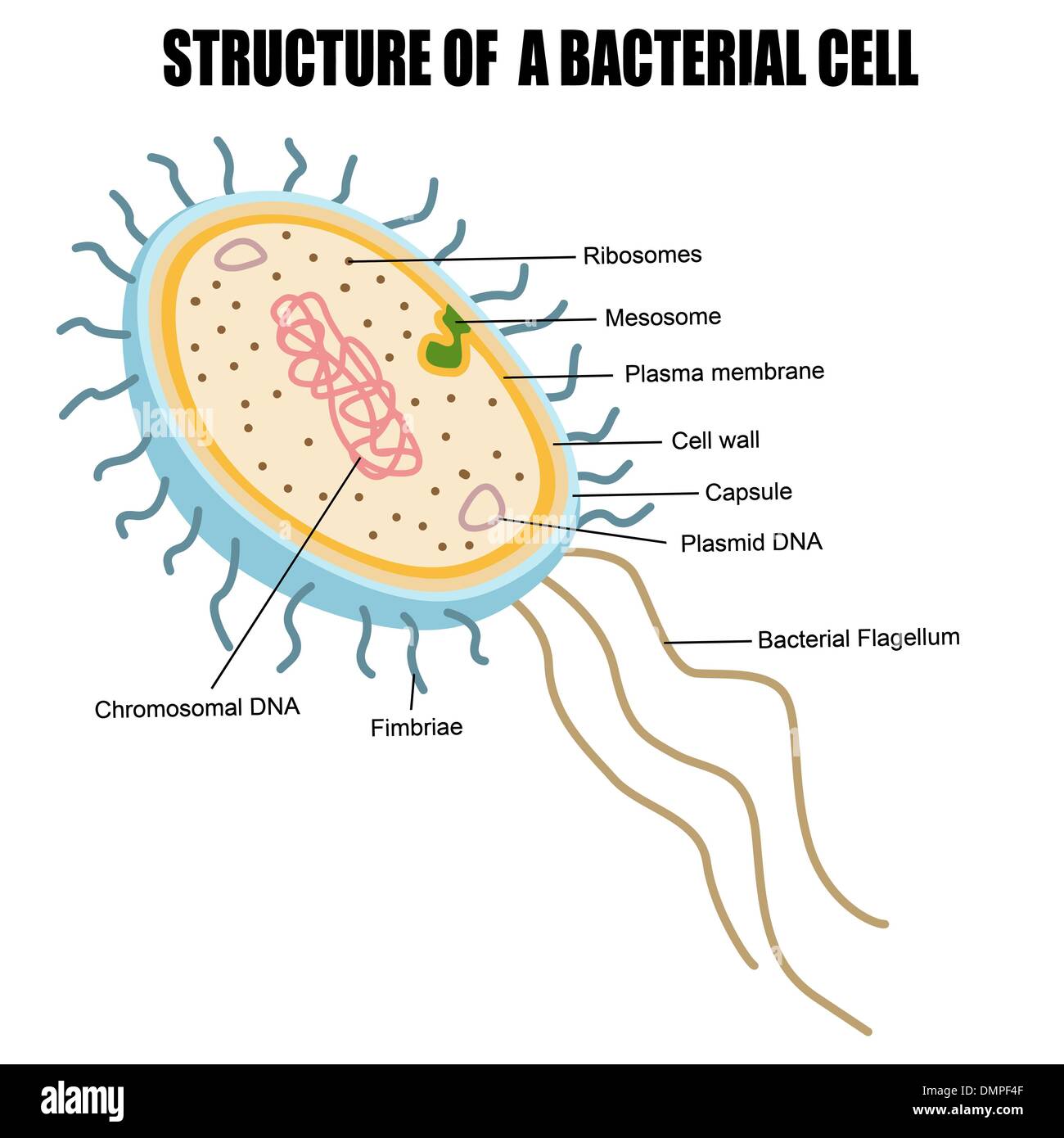 Structure of a bacterial cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-image64419055.html
Structure of a bacterial cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-image64419055.htmlRFDMPF4F–Structure of a bacterial cell
 Old leather Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/old-leather-image332861096.html
Old leather Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/old-leather-image332861096.htmlRM2A9F3M8–Old leather
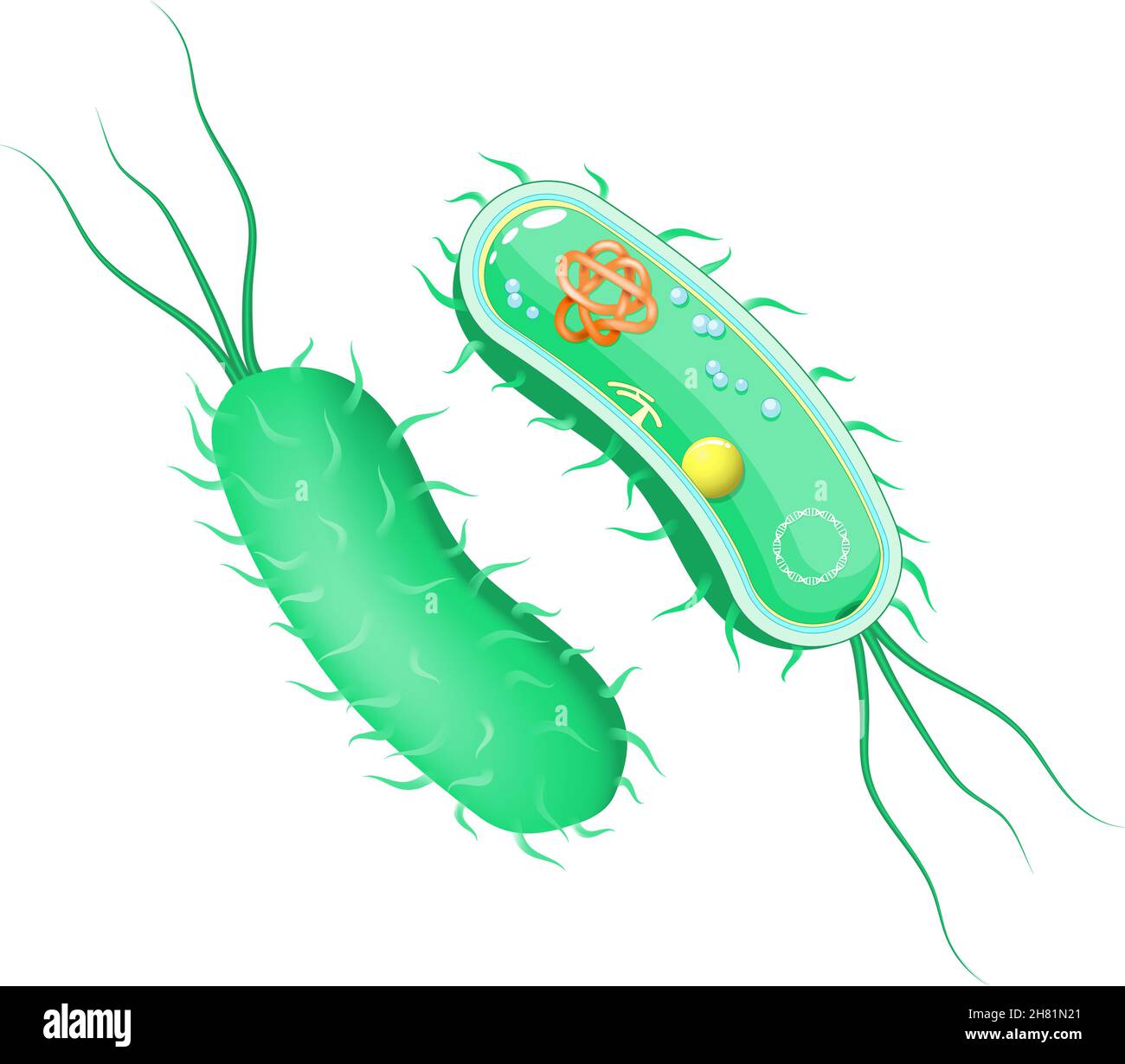 Bacteria anatomy. outside and inside view. Cross section of cell body with flagellum. Vector diagram for scientific, biological, medical, and educatio Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-anatomy-outside-and-inside-view-cross-section-of-cell-body-with-flagellum-vector-diagram-for-scientific-biological-medical-and-educatio-image452425289.html
Bacteria anatomy. outside and inside view. Cross section of cell body with flagellum. Vector diagram for scientific, biological, medical, and educatio Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-anatomy-outside-and-inside-view-cross-section-of-cell-body-with-flagellum-vector-diagram-for-scientific-biological-medical-and-educatio-image452425289.htmlRF2H81N21–Bacteria anatomy. outside and inside view. Cross section of cell body with flagellum. Vector diagram for scientific, biological, medical, and educatio
 Colorful fabrics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/colorful-fabrics-image332858048.html
Colorful fabrics Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/colorful-fabrics-image332858048.htmlRM2A9EYRC–Colorful fabrics
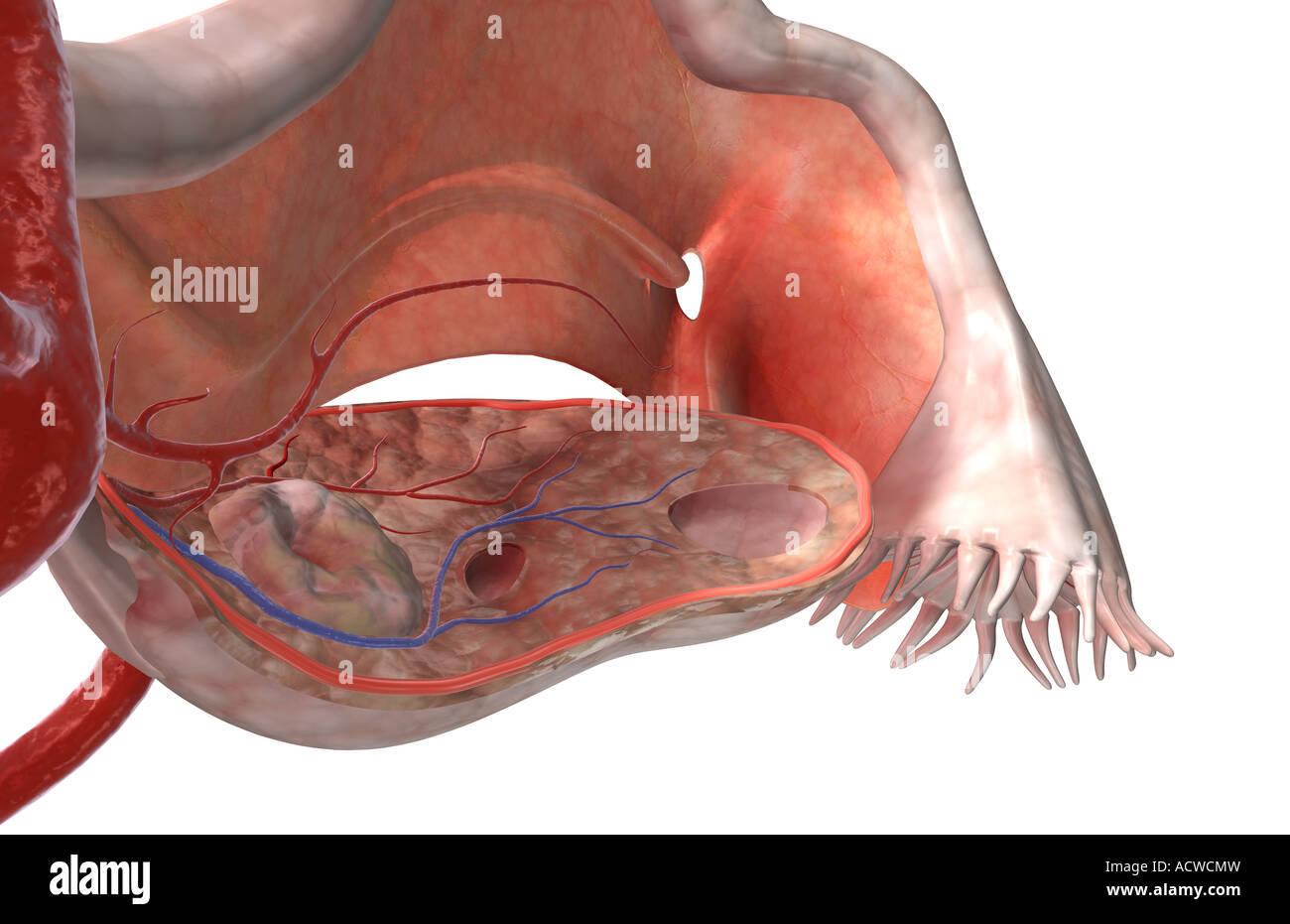 The female reproductive system Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-female-reproductive-system-13235064.html
The female reproductive system Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-female-reproductive-system-13235064.htmlRFACWCMW–The female reproductive system
 Brown sofa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brown-sofa-image332852517.html
Brown sofa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brown-sofa-image332852517.htmlRM2A9EMNW–Brown sofa
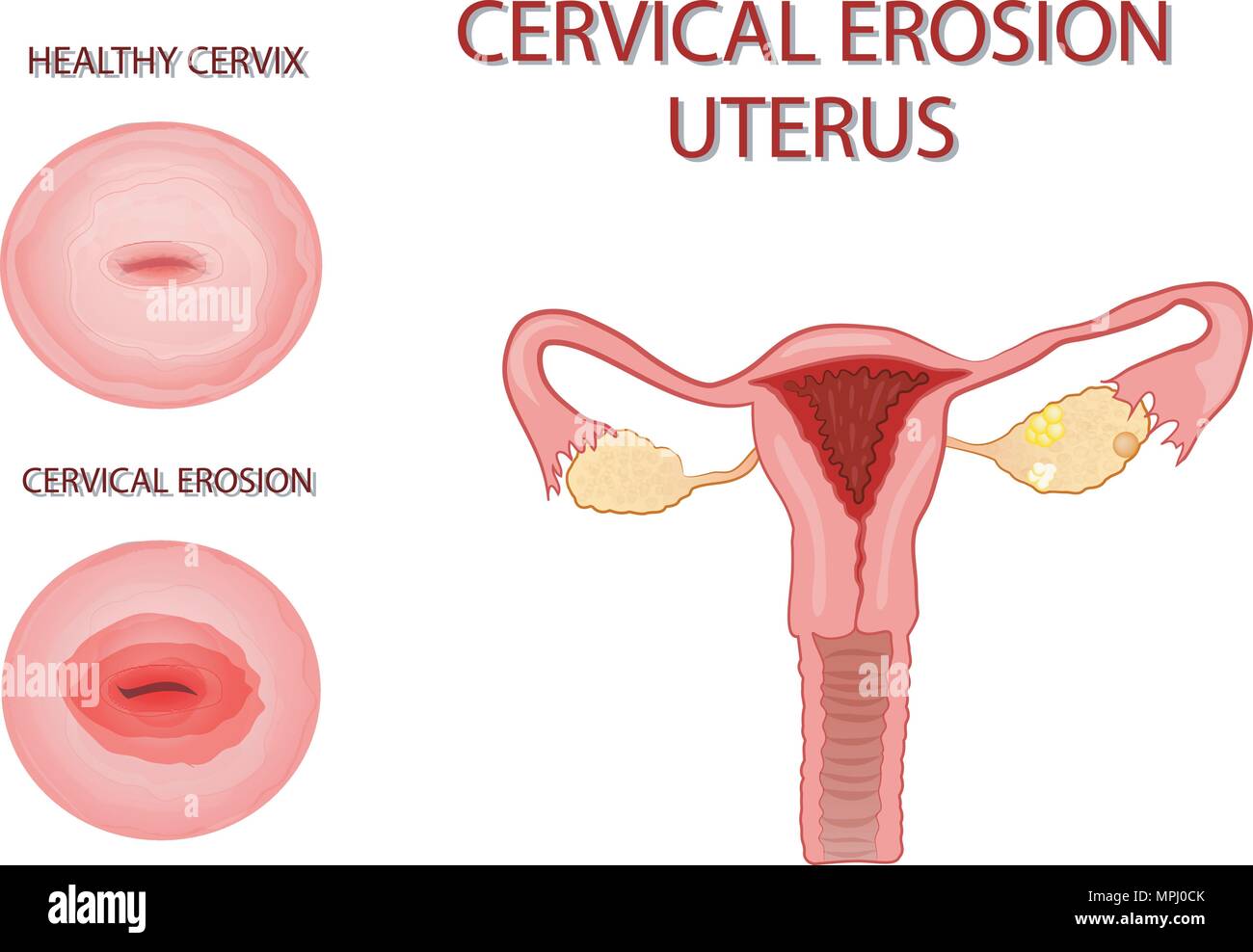 illustration of the uterus. cervical erosion Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-of-the-uterus-cervical-erosion-image186021603.html
illustration of the uterus. cervical erosion Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-of-the-uterus-cervical-erosion-image186021603.htmlRFMPJ0CK–illustration of the uterus. cervical erosion
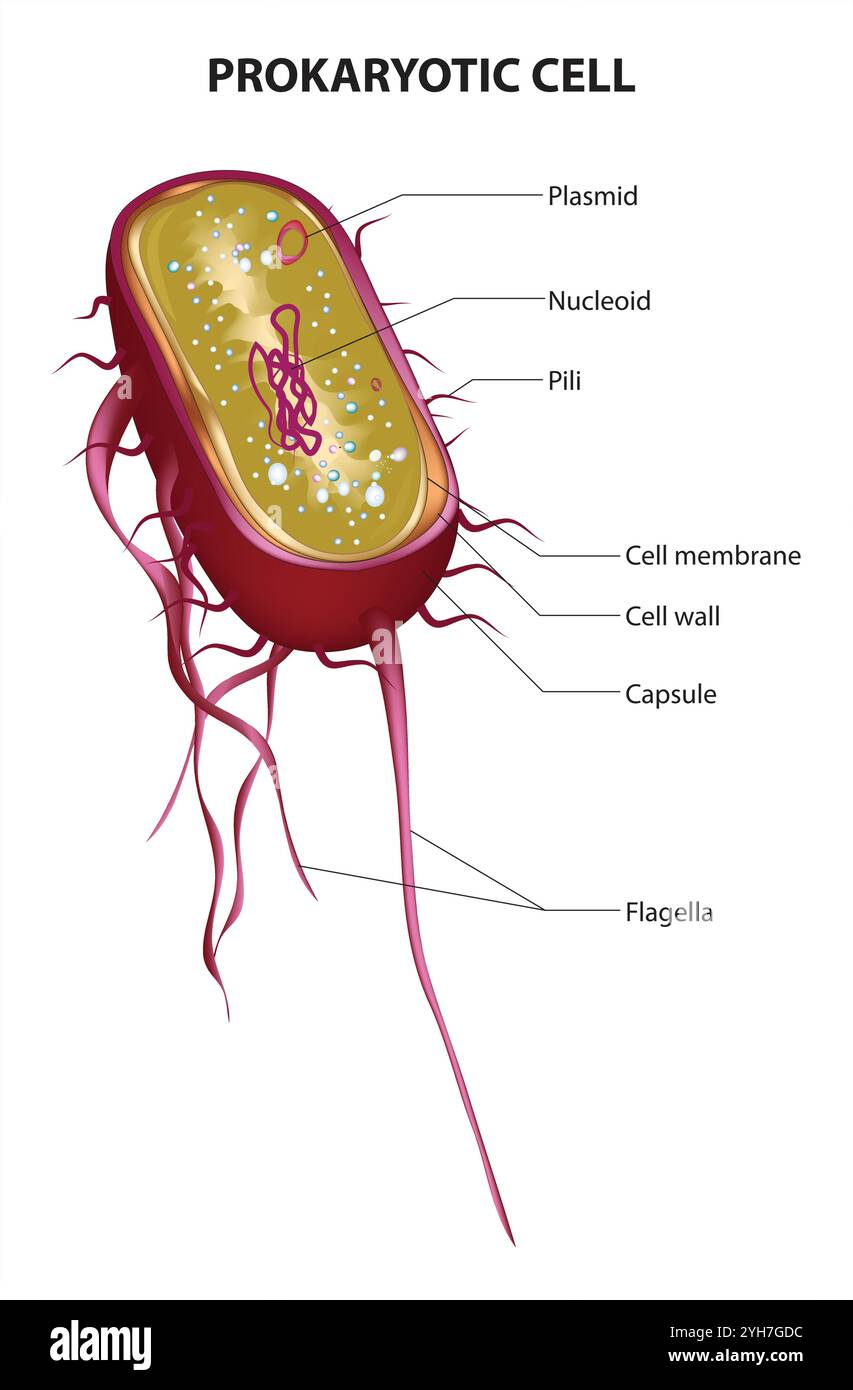 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chart, vector medical illustration, online education material. English translation text Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/prokaryotic-cell-structure-chart-vector-medical-illustration-online-education-material-english-translation-text-image630188984.html
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chart, vector medical illustration, online education material. English translation text Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/prokaryotic-cell-structure-chart-vector-medical-illustration-online-education-material-english-translation-text-image630188984.htmlRF2YH7GDC–Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chart, vector medical illustration, online education material. English translation text
 Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387299382.html
Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387299382.htmlRF2DE308P–Aksolotl
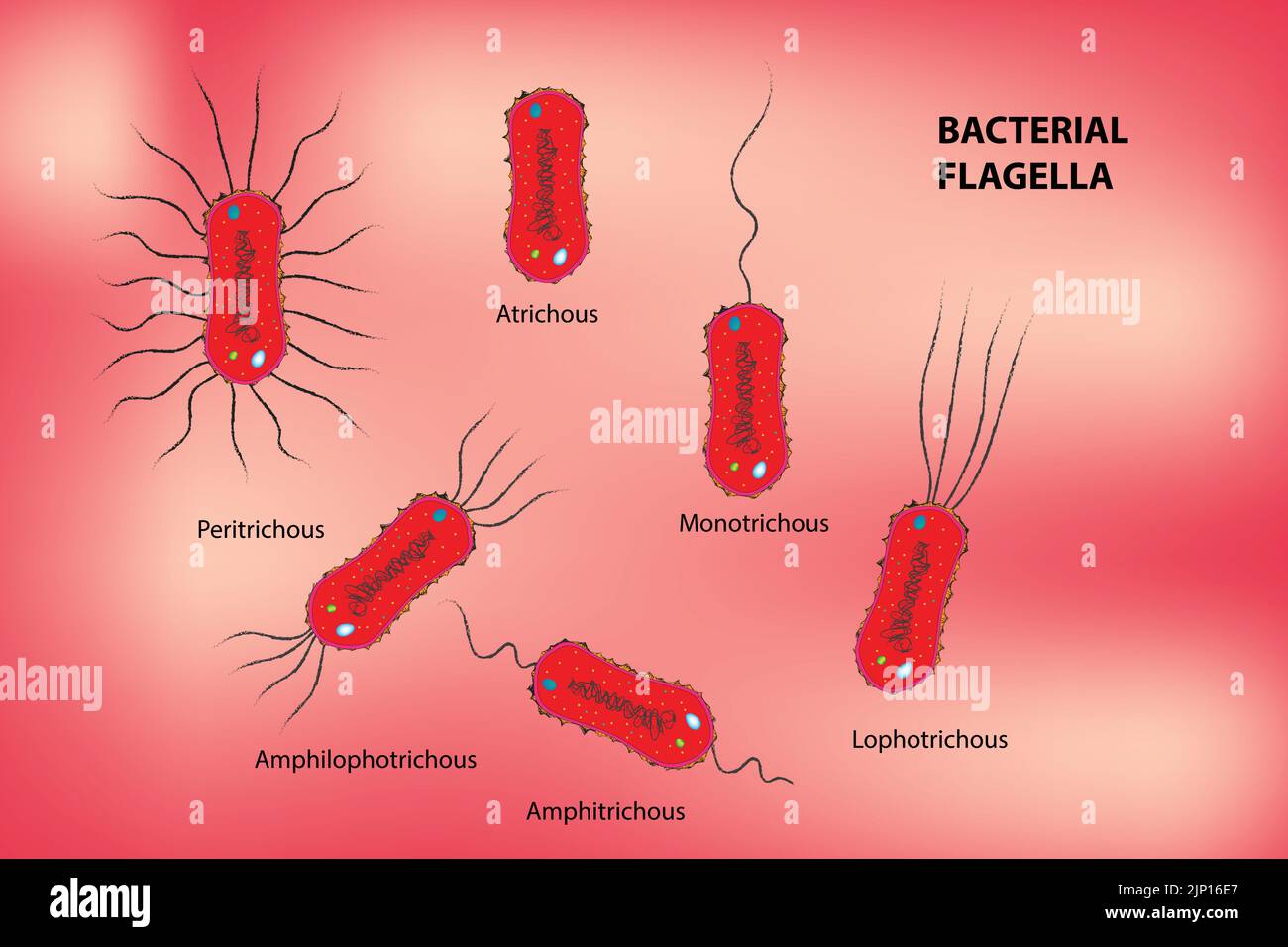 Classification of Bacterial Flagella Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classification-of-bacterial-flagella-image478229423.html
Classification of Bacterial Flagella Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/classification-of-bacterial-flagella-image478229423.htmlRF2JP16E7–Classification of Bacterial Flagella
 View of the beach Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-view-of-the-beach-32526779.html
View of the beach Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-view-of-the-beach-32526779.htmlRFBTWM6K–View of the beach
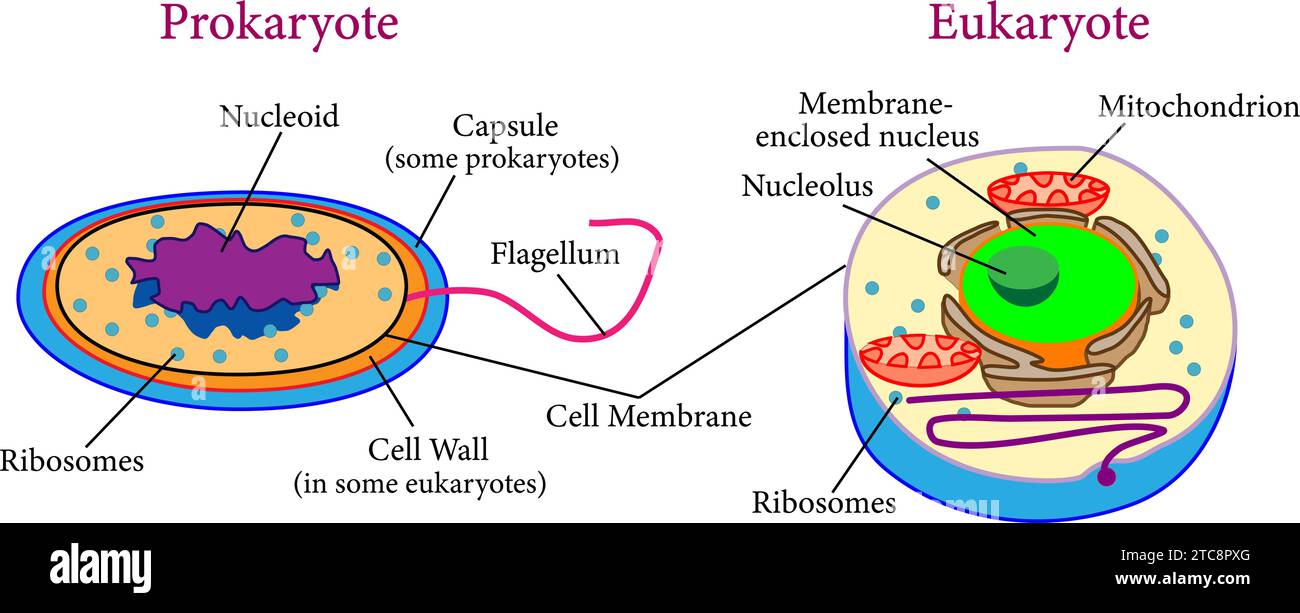 Comparison between eukaryotes and prokaryotes .Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/comparison-between-eukaryotes-and-prokaryotes-vector-illustration-image575511624.html
Comparison between eukaryotes and prokaryotes .Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/comparison-between-eukaryotes-and-prokaryotes-vector-illustration-image575511624.htmlRF2TC8PXG–Comparison between eukaryotes and prokaryotes .Vector illustration.
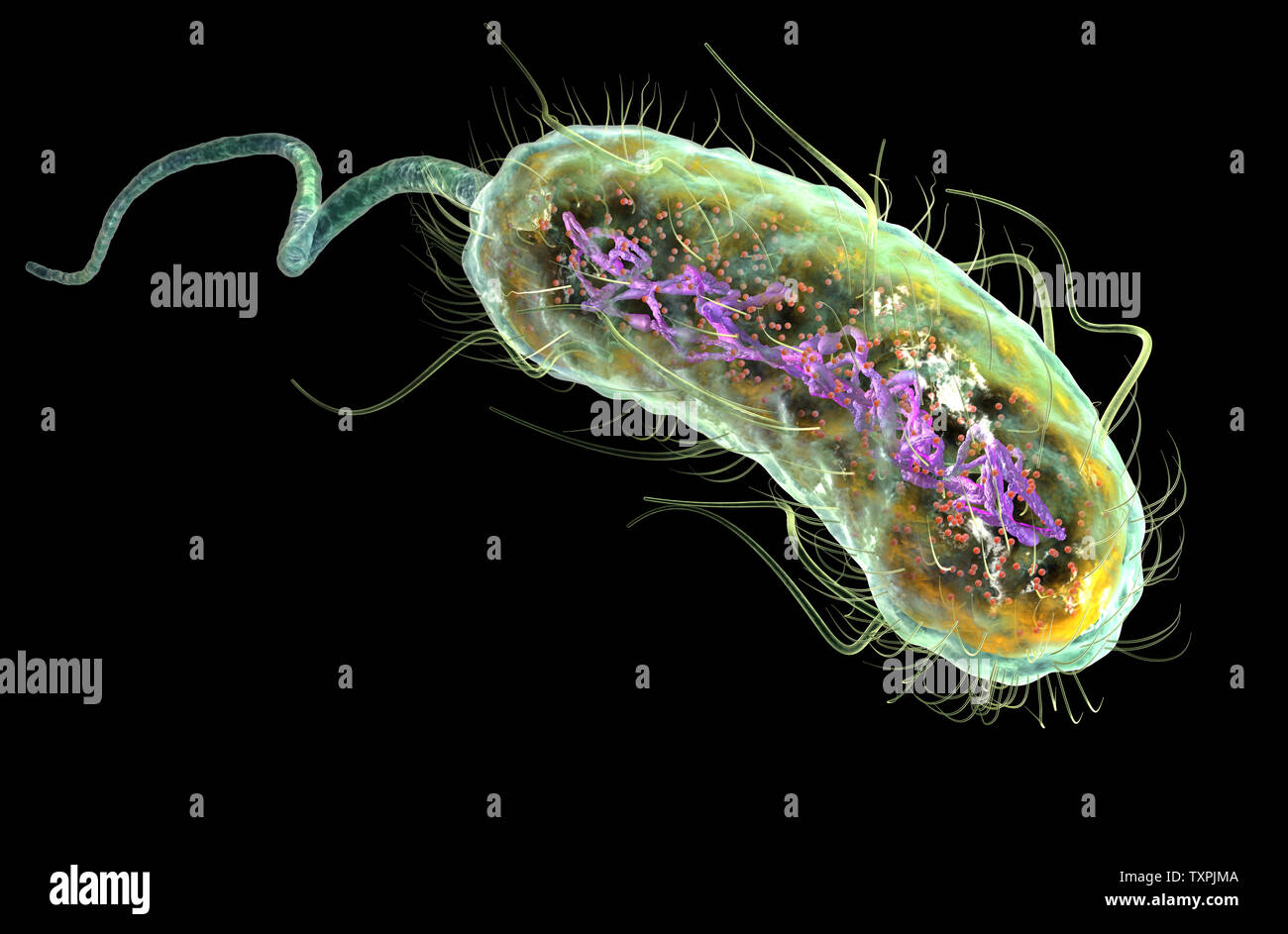 Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257423834.html
Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257423834.htmlRFTXPJMA–Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae
 Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image604289640.html
Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image604289640.htmlRF2X33NGT–Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock.
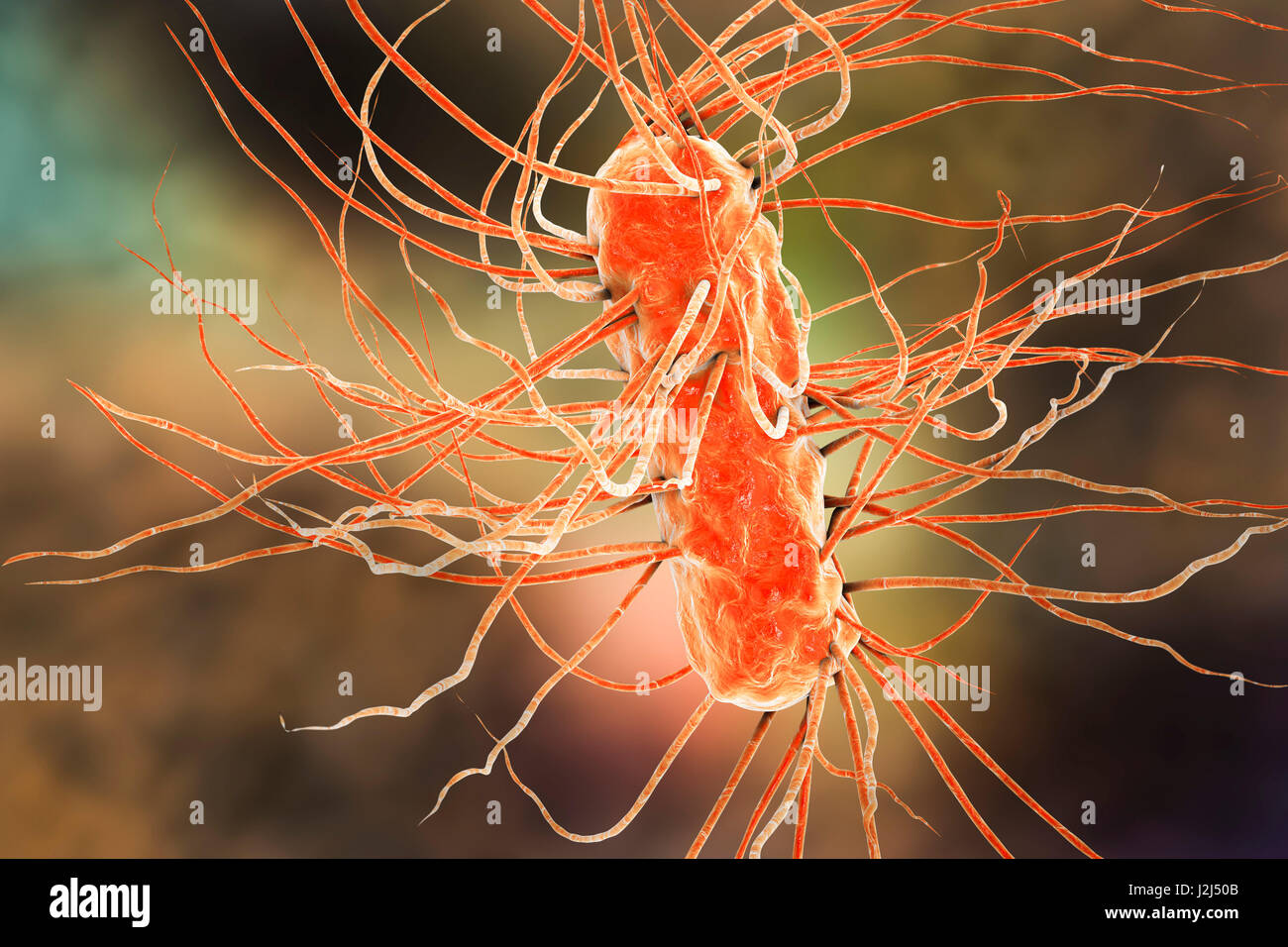 E. coli bacteria. Computer artwork of three Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod- shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacteriu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-e-coli-bacteria-computer-artwork-of-three-escherichia-coli-bacteria-139311323.html
E. coli bacteria. Computer artwork of three Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod- shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacteriu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-e-coli-bacteria-computer-artwork-of-three-escherichia-coli-bacteria-139311323.htmlRFJ2J50B–E. coli bacteria. Computer artwork of three Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod- shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacteriu
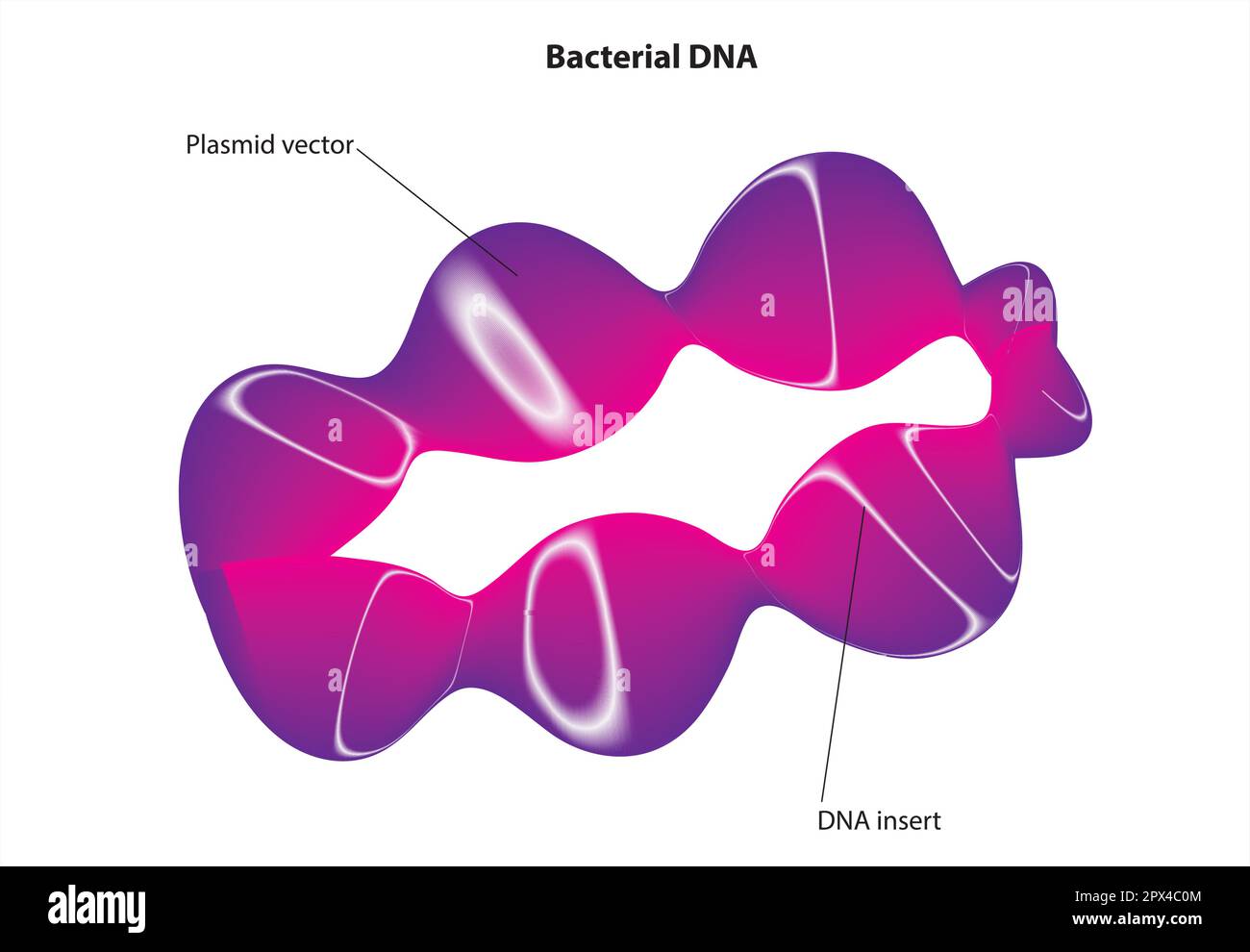 bacterial DNA Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacterial-dna-image549599700.html
bacterial DNA Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacterial-dna-image549599700.htmlRF2PX4C0M–bacterial DNA
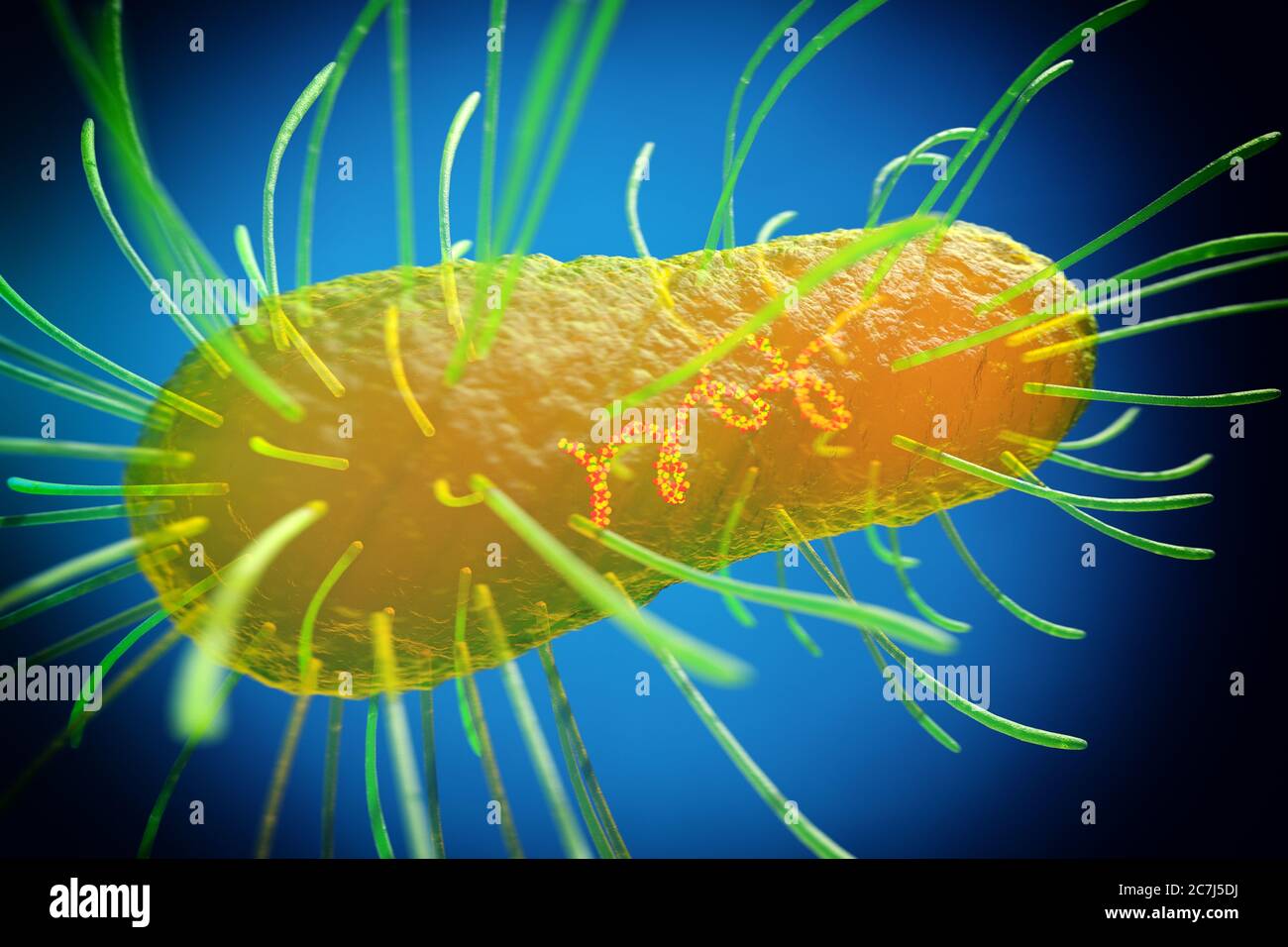 E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119758.html
E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119758.htmlRF2C7J5DJ–E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis.
 E. Coli Bacteria, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-image352801245.html
E. Coli Bacteria, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-image352801245.htmlRM2BDYDGD–E. Coli Bacteria, Illustration
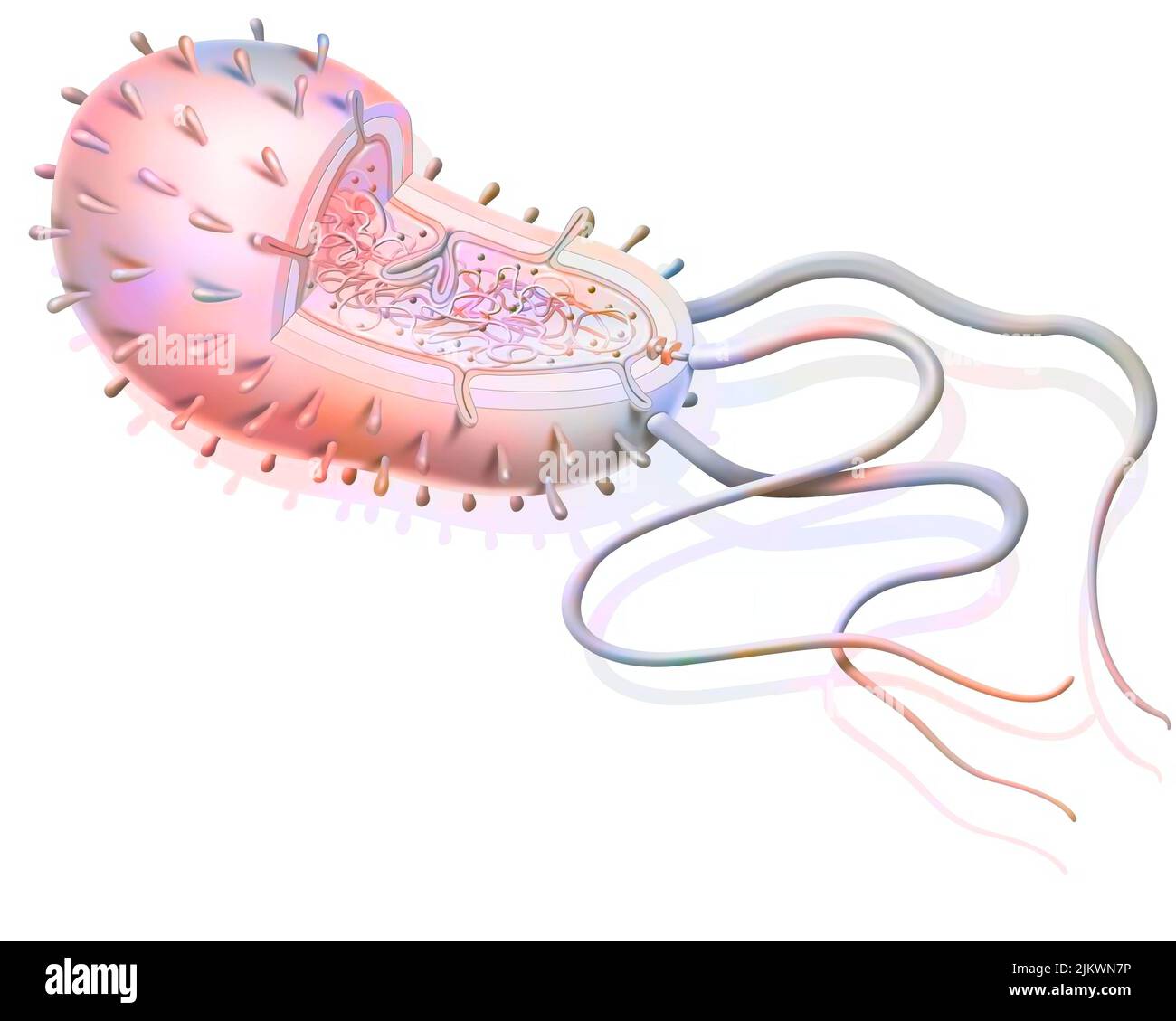 Structure of a bacterium: plasmids, ribosomes, DNA, flagella. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-a-bacterium-plasmids-ribosomes-dna-flagella-image476923882.html
Structure of a bacterium: plasmids, ribosomes, DNA, flagella. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-a-bacterium-plasmids-ribosomes-dna-flagella-image476923882.htmlRF2JKWN7P–Structure of a bacterium: plasmids, ribosomes, DNA, flagella.
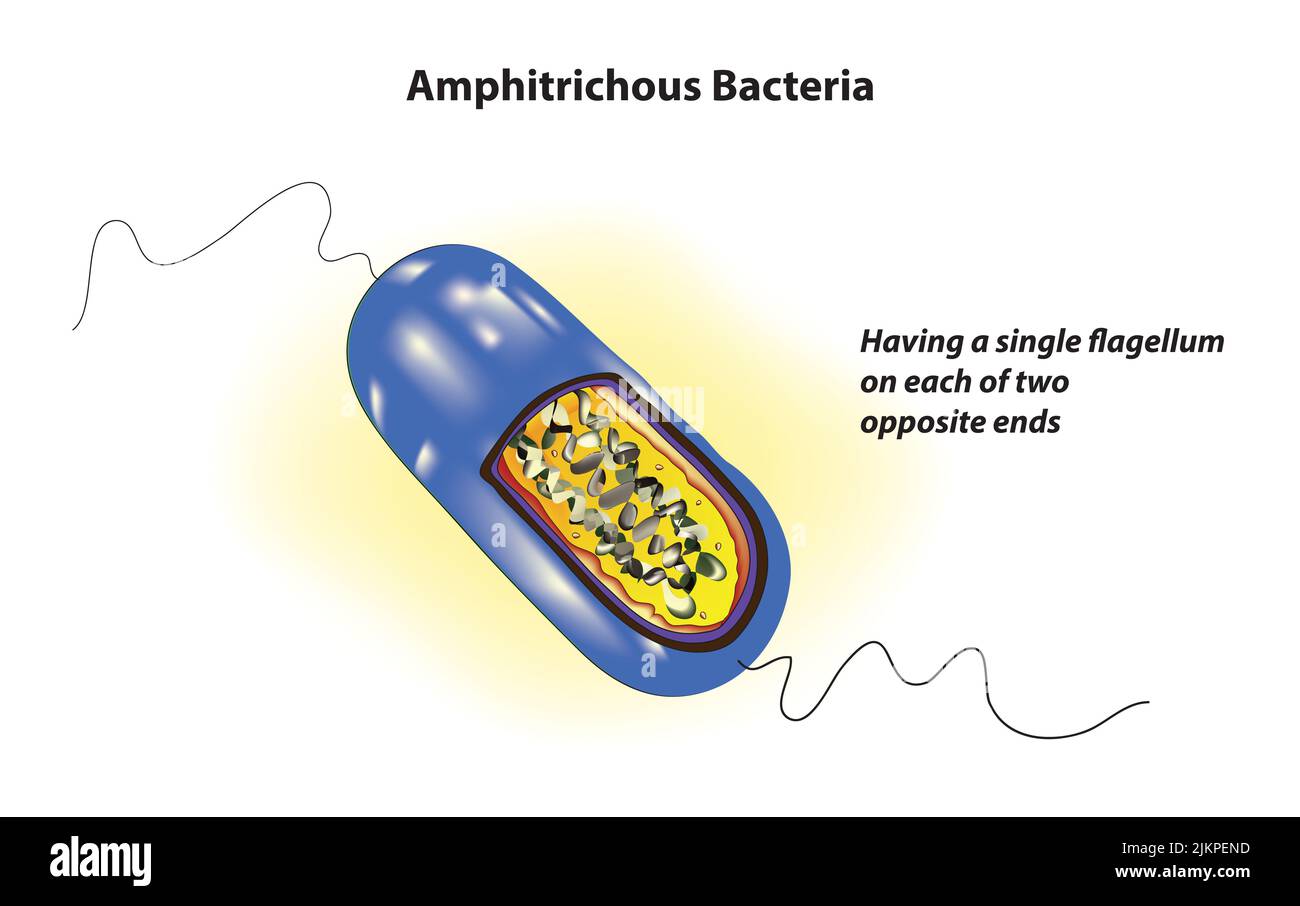 Amphitrichous Bacteria structure Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/amphitrichous-bacteria-structure-image476852921.html
Amphitrichous Bacteria structure Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/amphitrichous-bacteria-structure-image476852921.htmlRF2JKPEND–Amphitrichous Bacteria structure
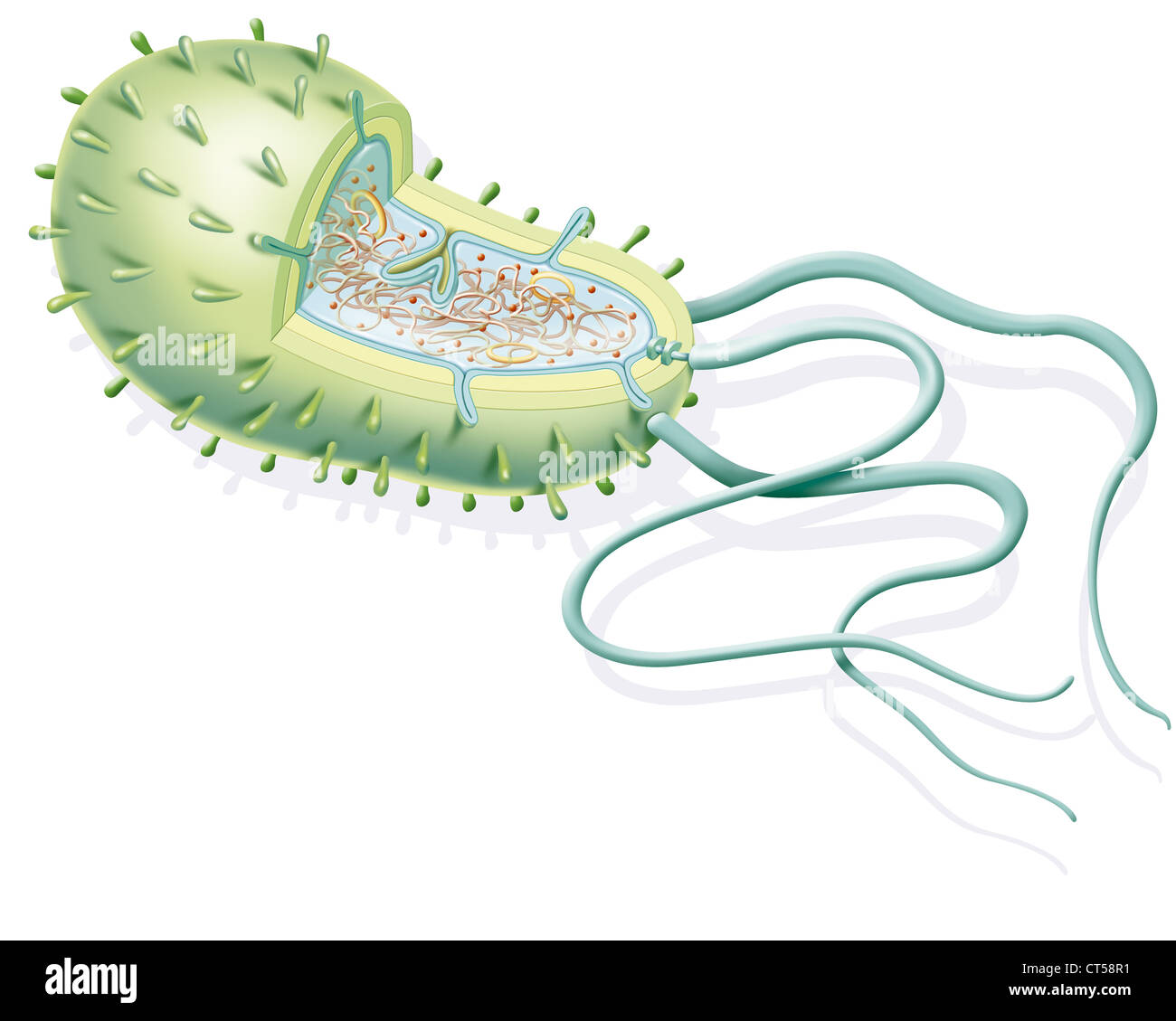 BACTERIUM, DRAWING Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacterium-drawing-49289157.html
BACTERIUM, DRAWING Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacterium-drawing-49289157.htmlRMCT58R1–BACTERIUM, DRAWING
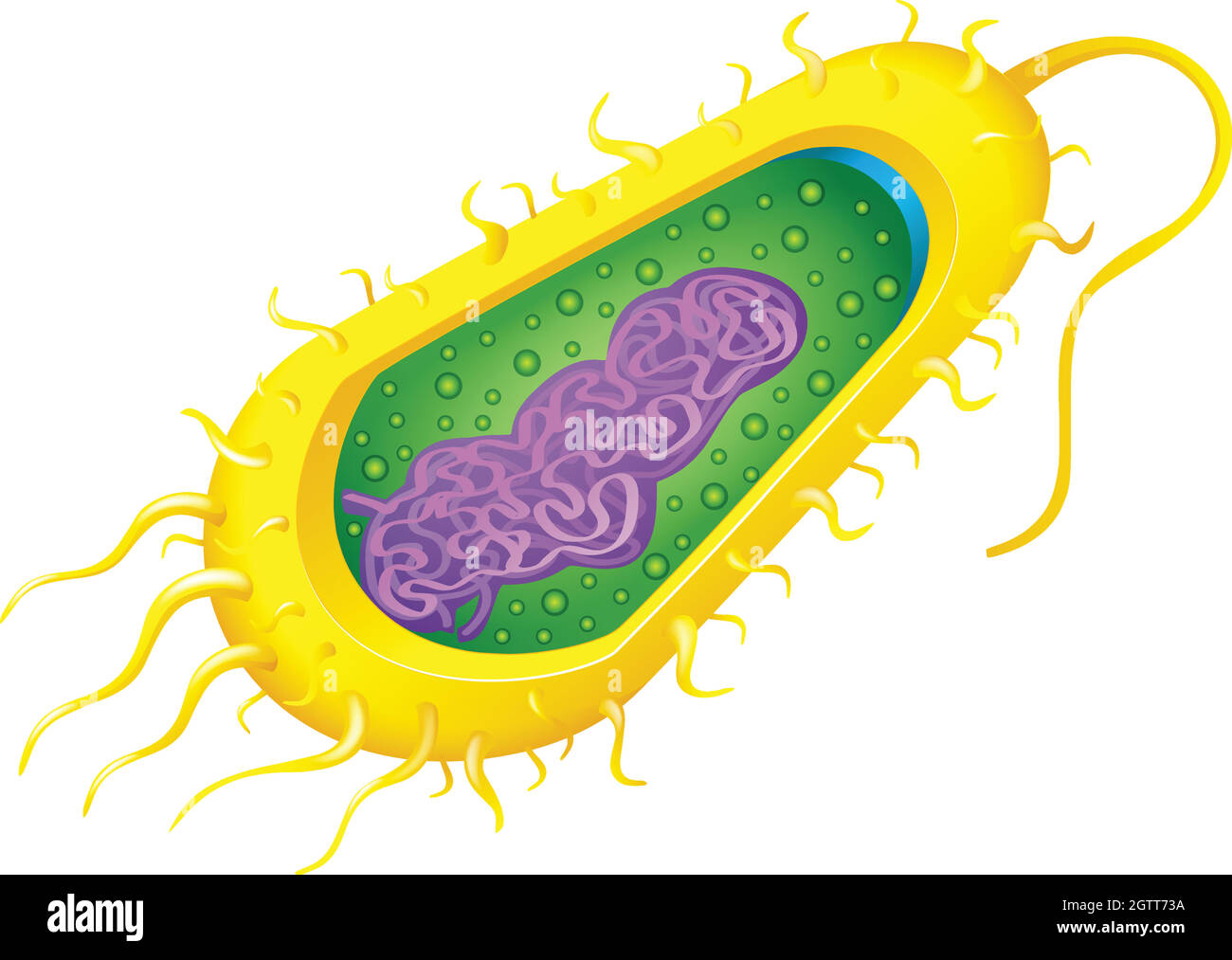 Bacteria cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-image445543374.html
Bacteria cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-image445543374.htmlRF2GTT73A–Bacteria cell
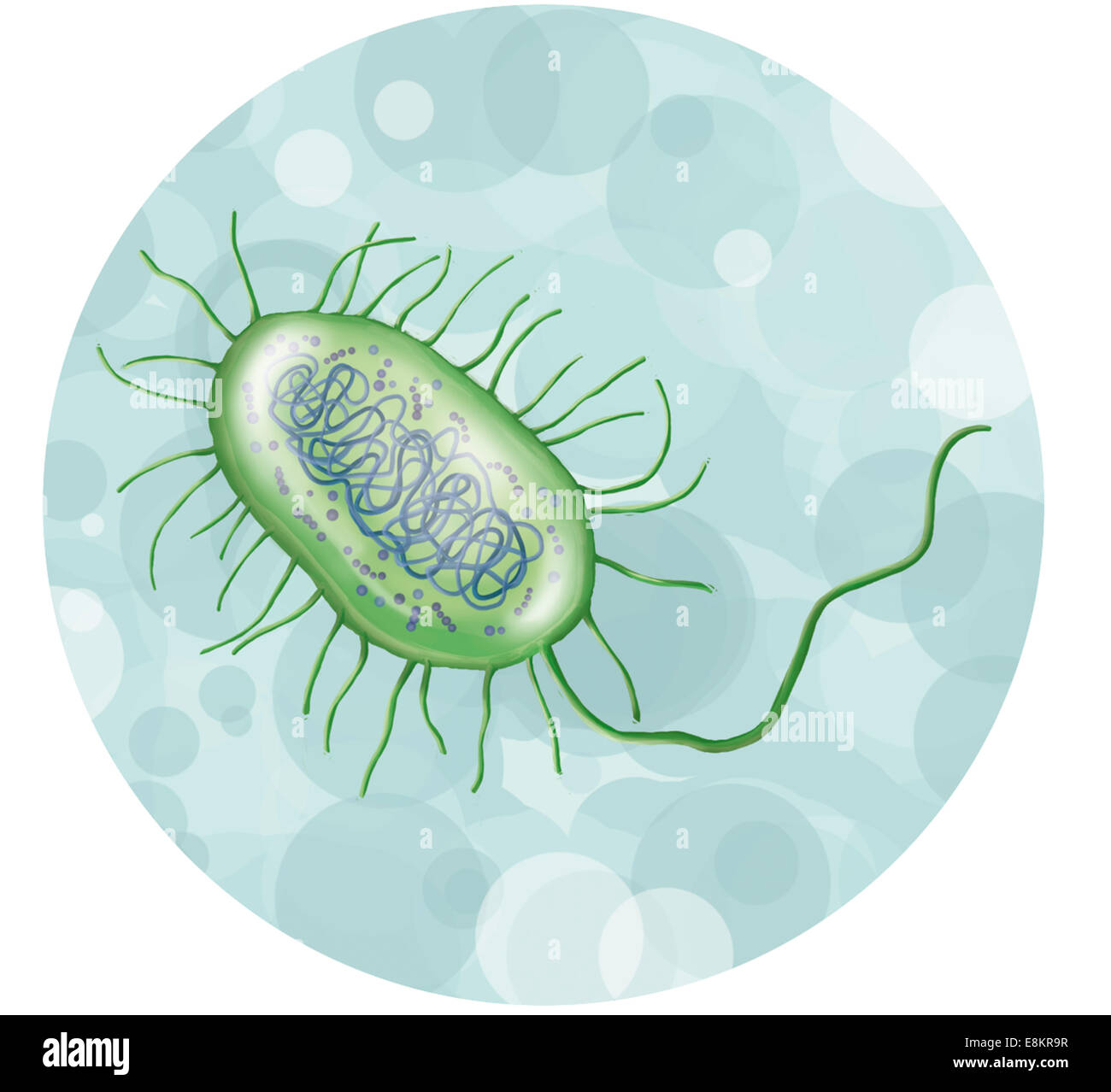 Intestinal bacterium. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-intestinal-bacterium-74194115.html
Intestinal bacterium. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-intestinal-bacterium-74194115.htmlRME8KR9R–Intestinal bacterium.
 The ovary Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-ovary-13186119.html
The ovary Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-ovary-13186119.htmlRFACM72G–The ovary
 Brown sofa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brown-sofa-image332852478.html
Brown sofa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/brown-sofa-image332852478.htmlRM2A9EMME–Brown sofa
 Bacteria cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-image444505669.html
Bacteria cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-image444505669.htmlRF2GR4YED–Bacteria cell
 Old textile background in shabby chic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/old-textile-background-in-shabby-chic-image369145565.html
Old textile background in shabby chic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/old-textile-background-in-shabby-chic-image369145565.htmlRF2CCG0X5–Old textile background in shabby chic
 Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387298293.html
Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387298293.htmlRF2DE2XWW–Aksolotl
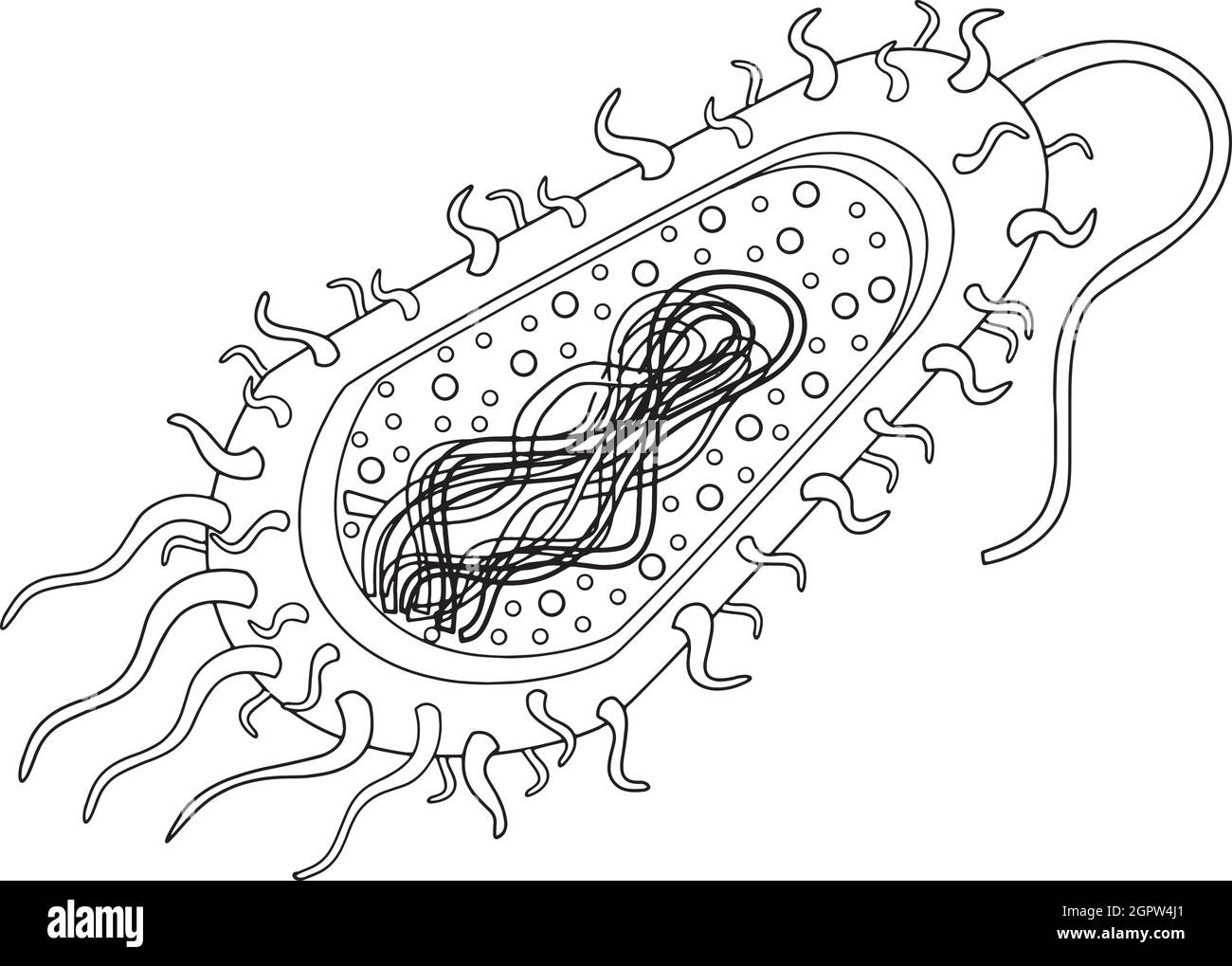 Bacteria cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-image444334073.html
Bacteria cell Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-image444334073.htmlRF2GPW4J1–Bacteria cell
 Fimbriæ Vulgo Femeren Delineatio Geometrica - Atlas Maior, vol 1, map 51 - Joan Blaeu, 1667 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fimbri-vulgo-femeren-delineatio-geometrica-atlas-maior-vol-1-map-51-joan-blaeu-1667-image592072834.html
Fimbriæ Vulgo Femeren Delineatio Geometrica - Atlas Maior, vol 1, map 51 - Joan Blaeu, 1667 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fimbri-vulgo-femeren-delineatio-geometrica-atlas-maior-vol-1-map-51-joan-blaeu-1667-image592072834.htmlRM2WB76XA–Fimbriæ Vulgo Femeren Delineatio Geometrica - Atlas Maior, vol 1, map 51 - Joan Blaeu, 1667
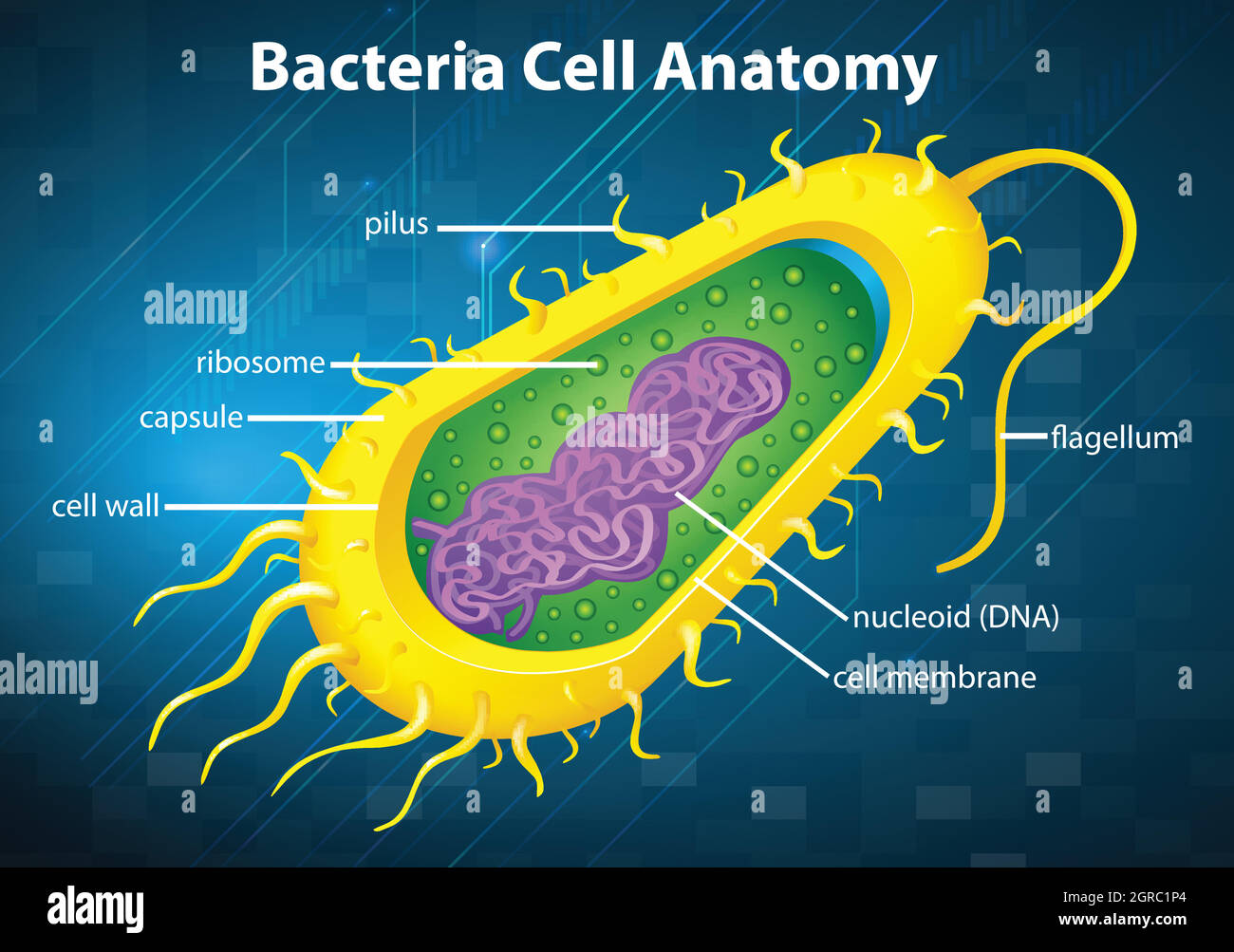 Bacteria cell structure Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-structure-image444661116.html
Bacteria cell structure Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bacteria-cell-structure-image444661116.htmlRF2GRC1P4–Bacteria cell structure
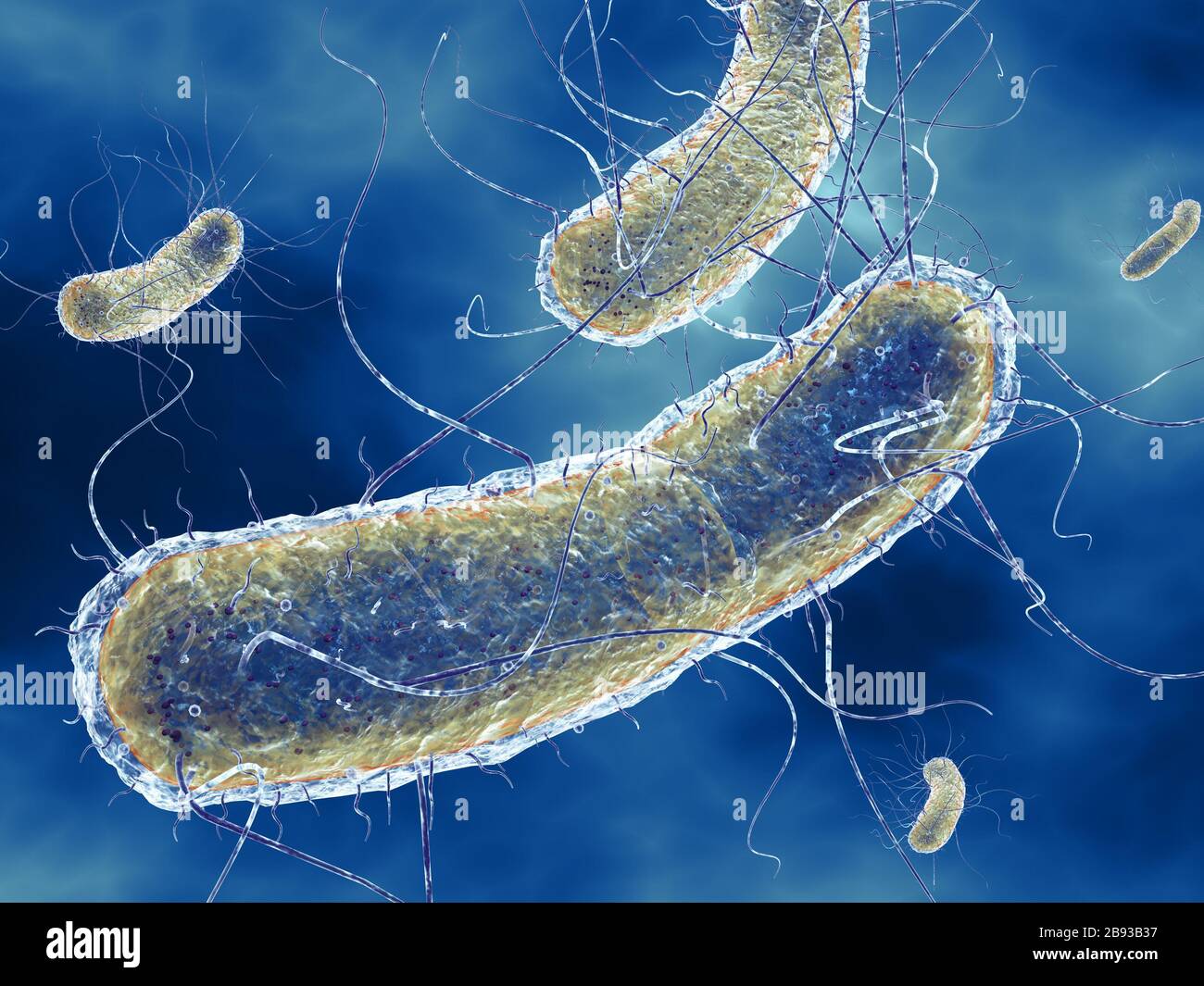 3D Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image349813835.html
3D Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image349813835.htmlRF2B93B37–3D Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae
 Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image611144356.html
Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image611144356.htmlRF2XE80T4–Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock.
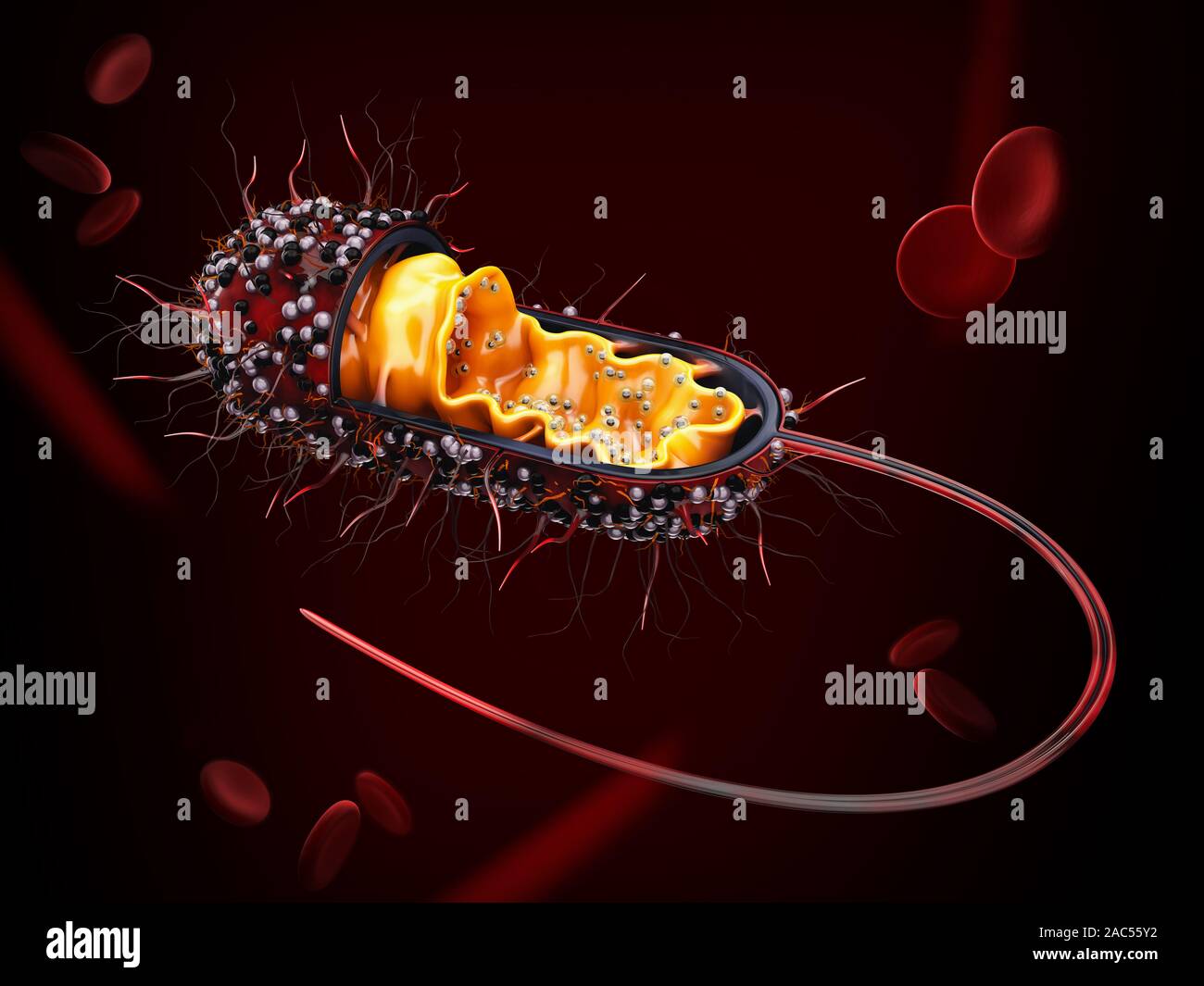 3d Rendering of Structure of a bacterial cell, clipping path included. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-clipping-path-included-image334487302.html
3d Rendering of Structure of a bacterial cell, clipping path included. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-clipping-path-included-image334487302.htmlRF2AC55Y2–3d Rendering of Structure of a bacterial cell, clipping path included.
RF2A2W43D–Cell bacteria icon. Outline cell bacteria vector icon for web design isolated on white background
 E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119764.html
E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119764.htmlRF2C7J5DT–E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis.
 E. Coli with Flagella, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-with-flagella-illustration-image352801238.html
E. Coli with Flagella, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-with-flagella-illustration-image352801238.htmlRM2BDYDG6–E. Coli with Flagella, Illustration
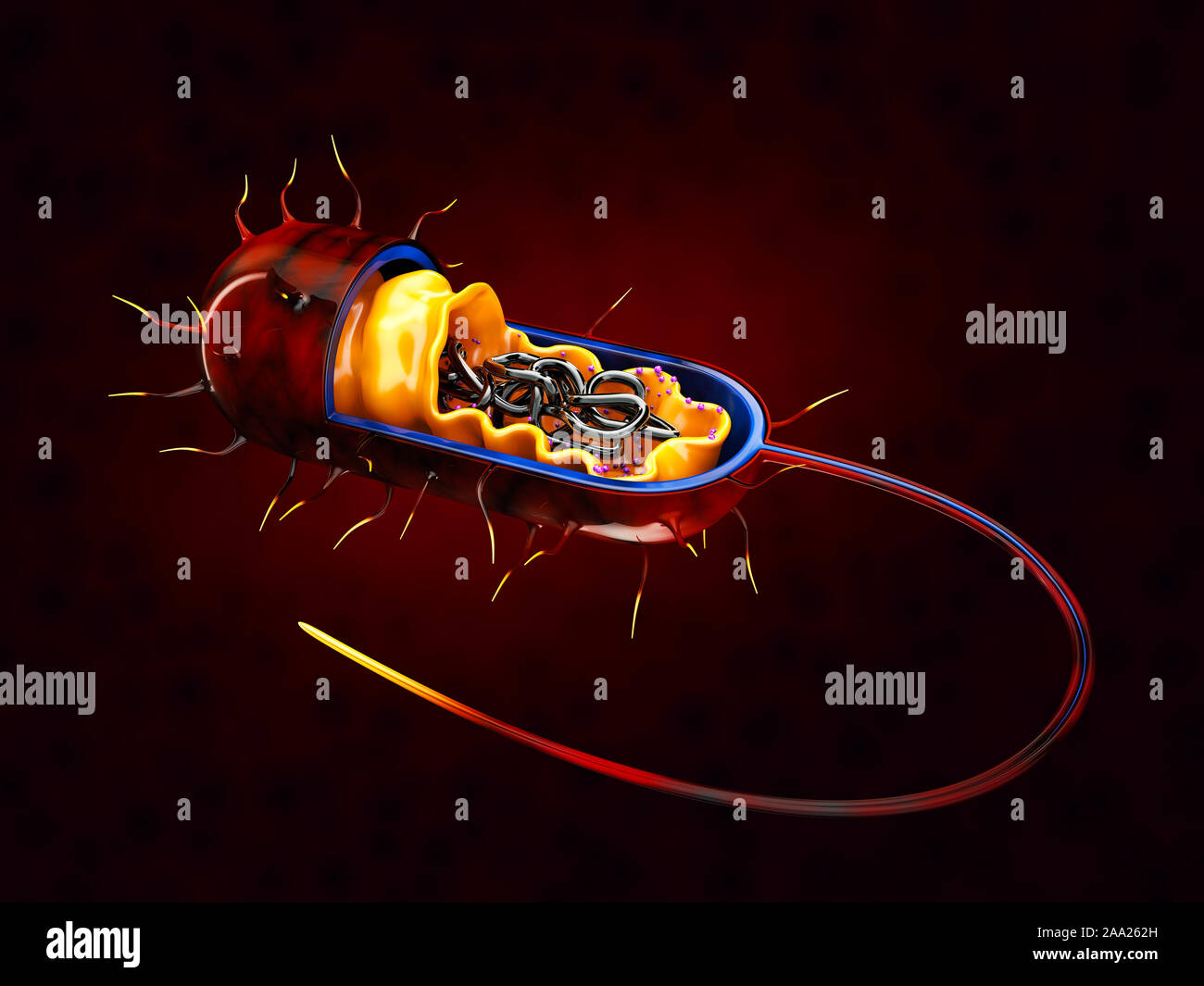 3d Rendering of Structure of a bacterial cell, isolated red. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-isolated-red-image333192233.html
3d Rendering of Structure of a bacterial cell, isolated red. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendering-of-structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-isolated-red-image333192233.htmlRF2AA262H–3d Rendering of Structure of a bacterial cell, isolated red.
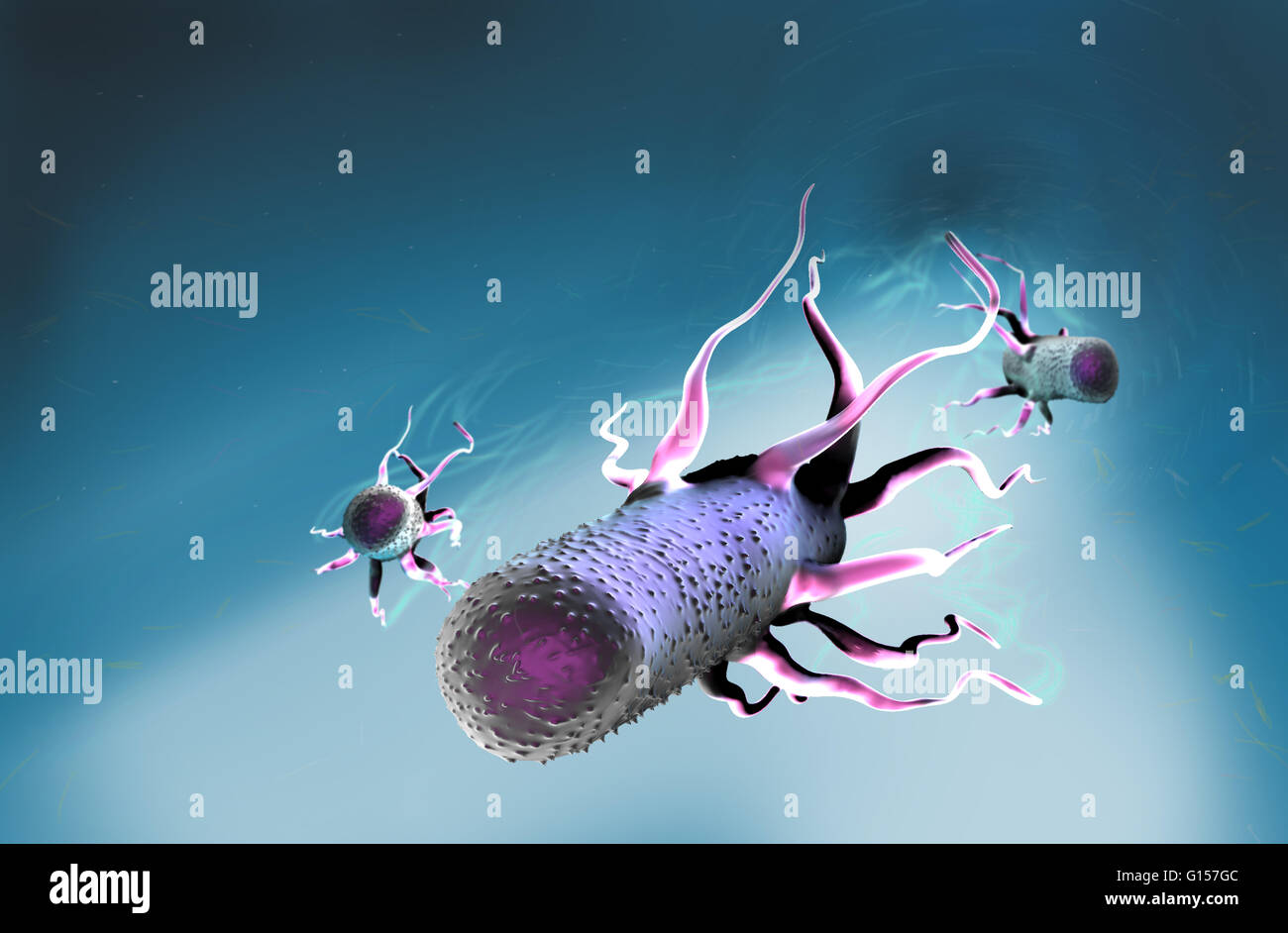 Computer artwork of Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments call pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to mak Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-computer-artwork-of-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-103992572.html
Computer artwork of Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments call pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to mak Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-computer-artwork-of-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-103992572.htmlRMG157GC–Computer artwork of Escherichia coli bacteria. E. coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments call pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to mak
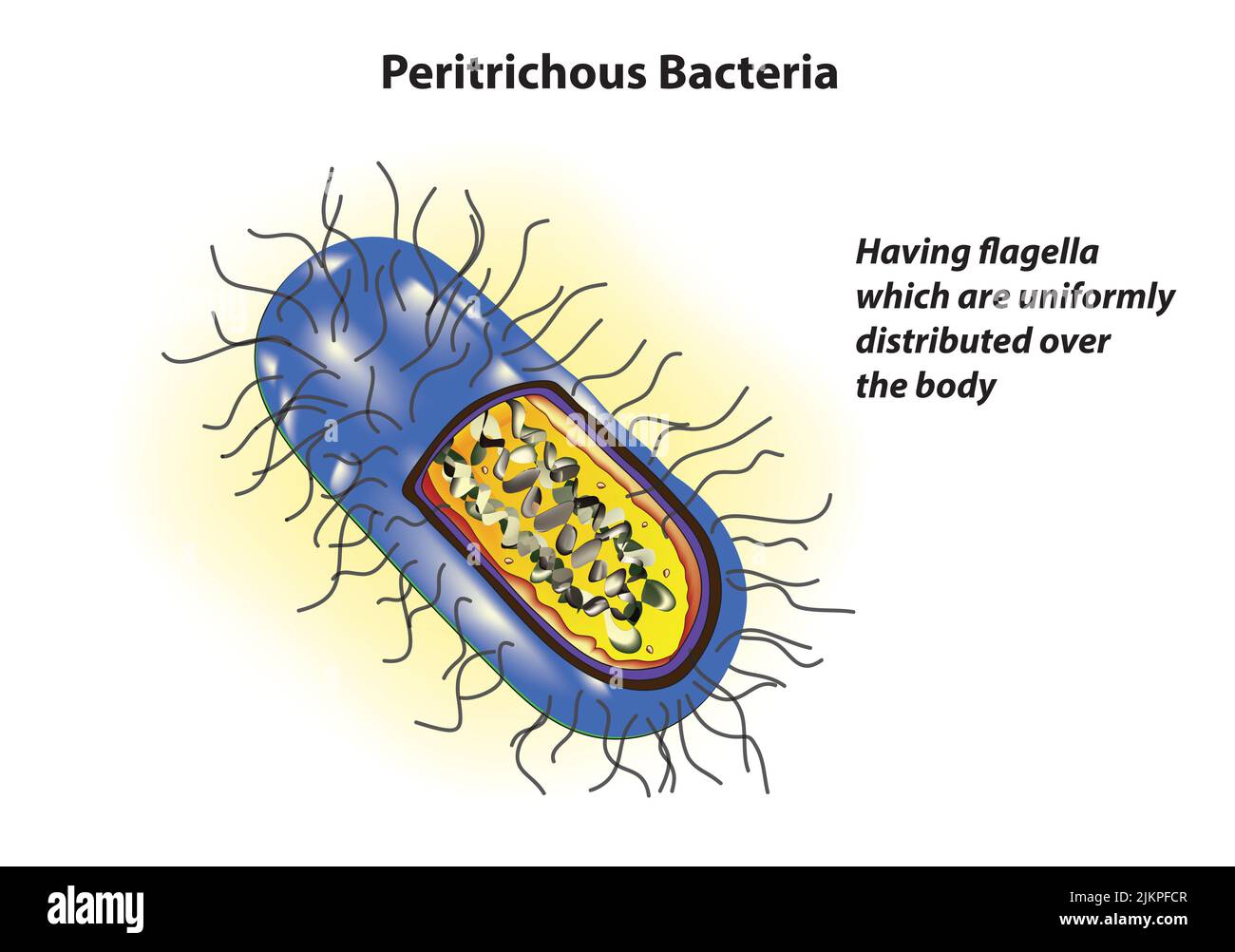 Peritrichous Bacteria anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/peritrichous-bacteria-anatomy-image476853463.html
Peritrichous Bacteria anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/peritrichous-bacteria-anatomy-image476853463.htmlRF2JKPFCR–Peritrichous Bacteria anatomy
![Infographic about virus and bacteria, microorganisms that sometimes can be harmful for the organism where they live. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 4960x3188]. Stock Photo Infographic about virus and bacteria, microorganisms that sometimes can be harmful for the organism where they live. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 4960x3188]. Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2NEC0JC/infographic-about-virus-and-bacteria-microorganisms-that-sometimes-can-be-harmful-for-the-organism-where-they-live-quarkxpress-qxp-4960x3188-2NEC0JC.jpg) Infographic about virus and bacteria, microorganisms that sometimes can be harmful for the organism where they live. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 4960x3188]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-about-virus-and-bacteria-microorganisms-that-sometimes-can-be-harmful-for-the-organism-where-they-live-quarkxpress-qxp-4960x3188-image525180164.html
Infographic about virus and bacteria, microorganisms that sometimes can be harmful for the organism where they live. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 4960x3188]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-about-virus-and-bacteria-microorganisms-that-sometimes-can-be-harmful-for-the-organism-where-they-live-quarkxpress-qxp-4960x3188-image525180164.htmlRM2NEC0JC–Infographic about virus and bacteria, microorganisms that sometimes can be harmful for the organism where they live. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 4960x3188].
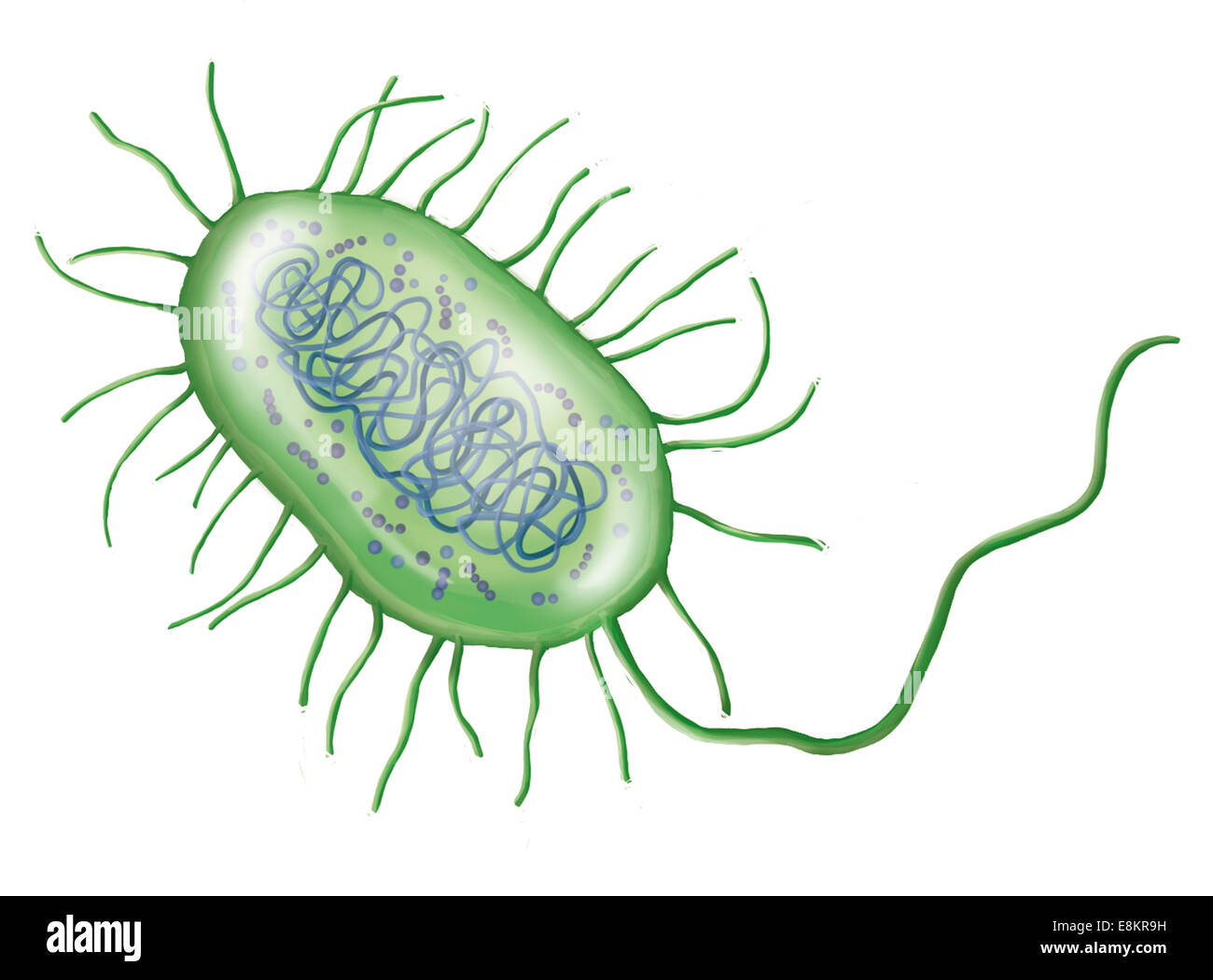 Intestinal bacterium. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-intestinal-bacterium-74194109.html
Intestinal bacterium. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-intestinal-bacterium-74194109.htmlRME8KR9H–Intestinal bacterium.
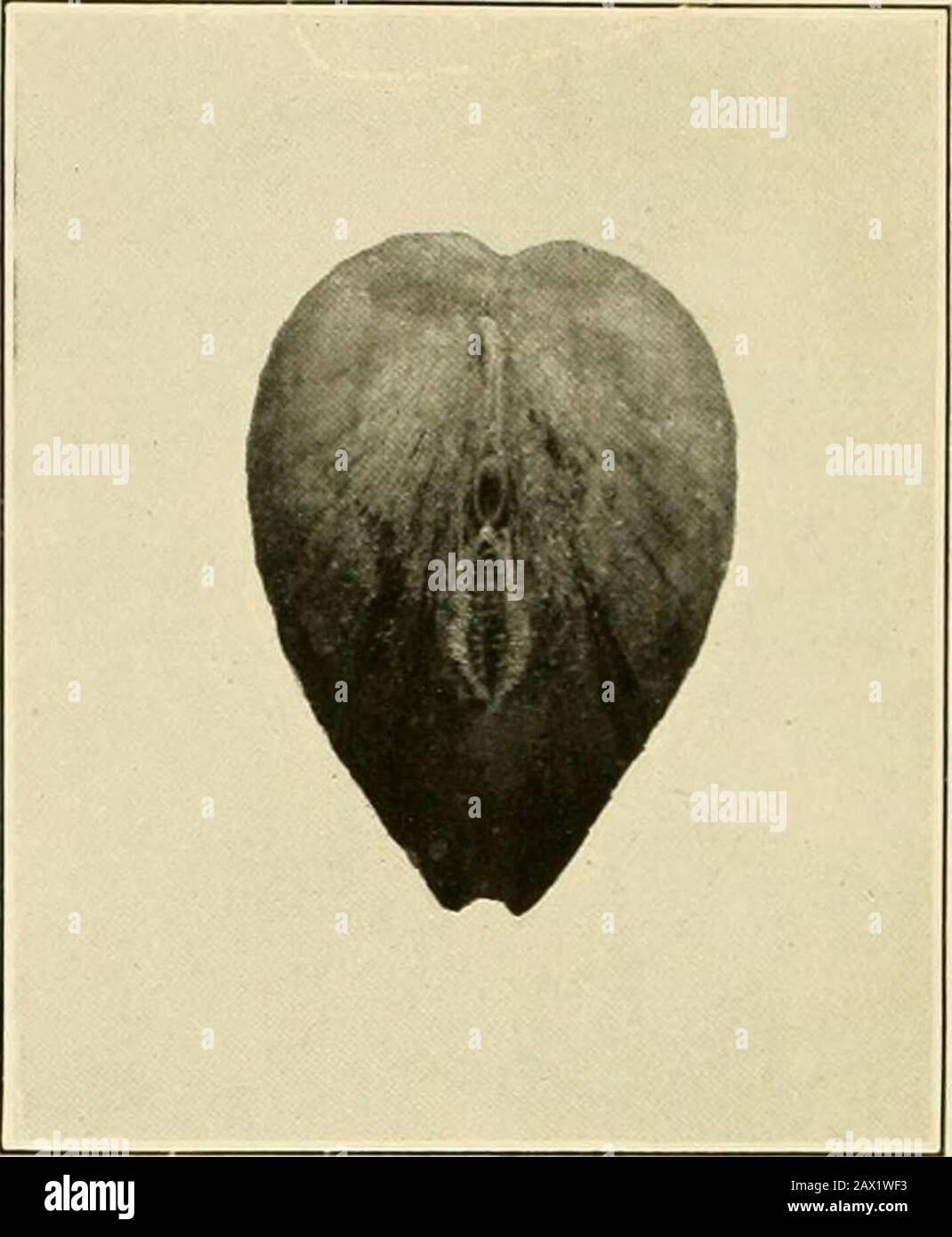 Natural history and propagation of fresh-water mussels . Fig. 1.—Rear view of yellow sand-shell in natural positionin bottom under water, showing the two siphonal open-ings, the gaping shell, and the apposed margins of themantle. Fig. 2.—Rear view of Anodonta corPulenta showingsiphonal openings. Note the very smooth margins ofthe upper exhalent opening and the fimbriae or feel-ers protecting the lower or inhalent opening. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/natural-history-and-propagation-of-fresh-water-mussels-fig-1rear-view-of-yellow-sand-shell-in-natural-positionin-bottom-under-water-showing-the-two-siphonal-open-ings-the-gaping-shell-and-the-apposed-margins-of-themantle-fig-2rear-view-of-anodonta-corpulenta-showingsiphonal-openings-note-the-very-smooth-margins-ofthe-upper-exhalent-opening-and-the-fimbriae-or-feel-ers-protecting-the-lower-or-inhalent-opening-image343020023.html
Natural history and propagation of fresh-water mussels . Fig. 1.—Rear view of yellow sand-shell in natural positionin bottom under water, showing the two siphonal open-ings, the gaping shell, and the apposed margins of themantle. Fig. 2.—Rear view of Anodonta corPulenta showingsiphonal openings. Note the very smooth margins ofthe upper exhalent opening and the fimbriae or feel-ers protecting the lower or inhalent opening. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/natural-history-and-propagation-of-fresh-water-mussels-fig-1rear-view-of-yellow-sand-shell-in-natural-positionin-bottom-under-water-showing-the-two-siphonal-open-ings-the-gaping-shell-and-the-apposed-margins-of-themantle-fig-2rear-view-of-anodonta-corpulenta-showingsiphonal-openings-note-the-very-smooth-margins-ofthe-upper-exhalent-opening-and-the-fimbriae-or-feel-ers-protecting-the-lower-or-inhalent-opening-image343020023.htmlRM2AX1WF3–Natural history and propagation of fresh-water mussels . Fig. 1.—Rear view of yellow sand-shell in natural positionin bottom under water, showing the two siphonal open-ings, the gaping shell, and the apposed margins of themantle. Fig. 2.—Rear view of Anodonta corPulenta showingsiphonal openings. Note the very smooth margins ofthe upper exhalent opening and the fimbriae or feel-ers protecting the lower or inhalent opening.
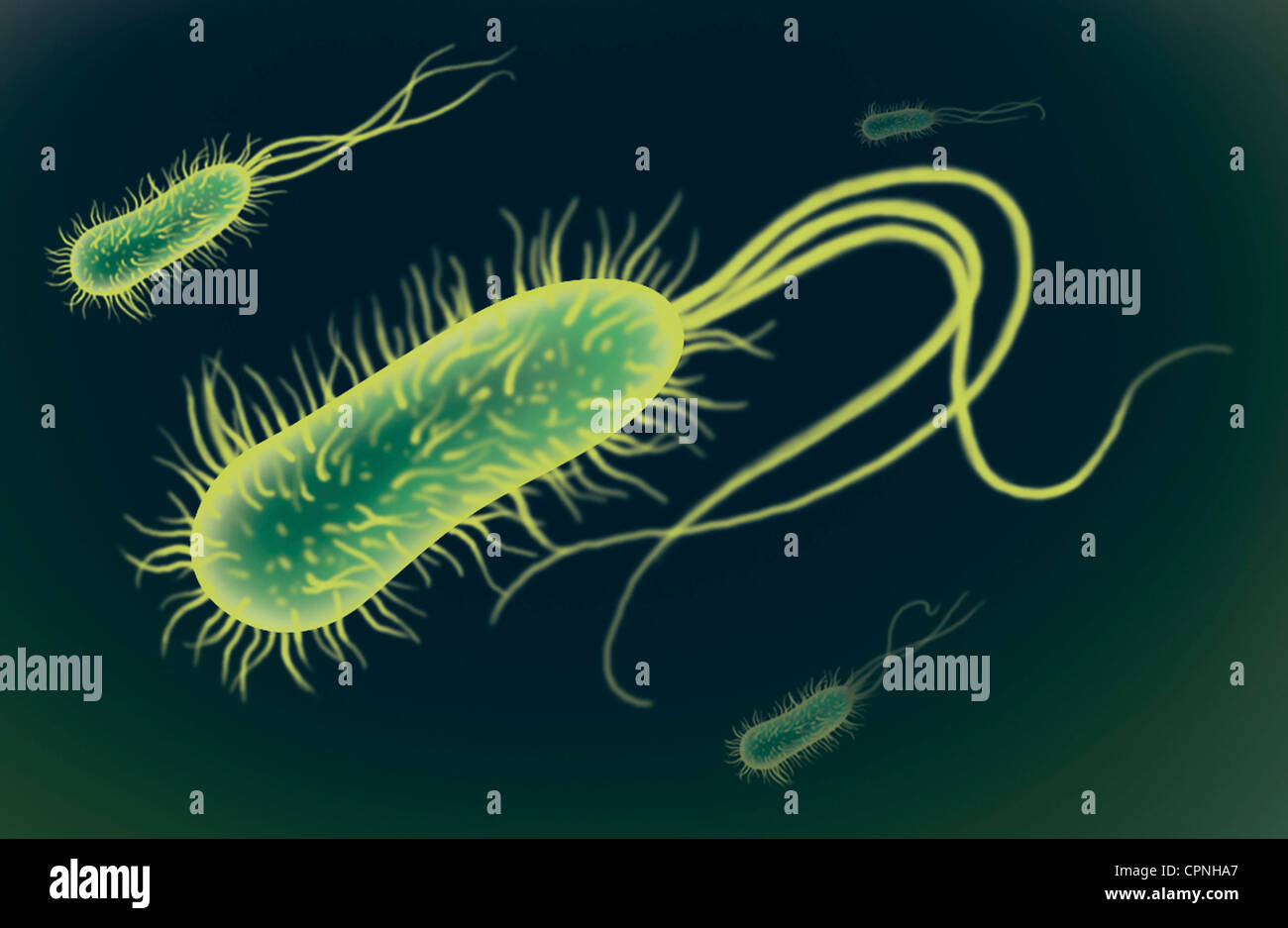 BACTERIUM, DRAWING Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacterium-drawing-48417775.html
BACTERIUM, DRAWING Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacterium-drawing-48417775.htmlRMCPNHA7–BACTERIUM, DRAWING
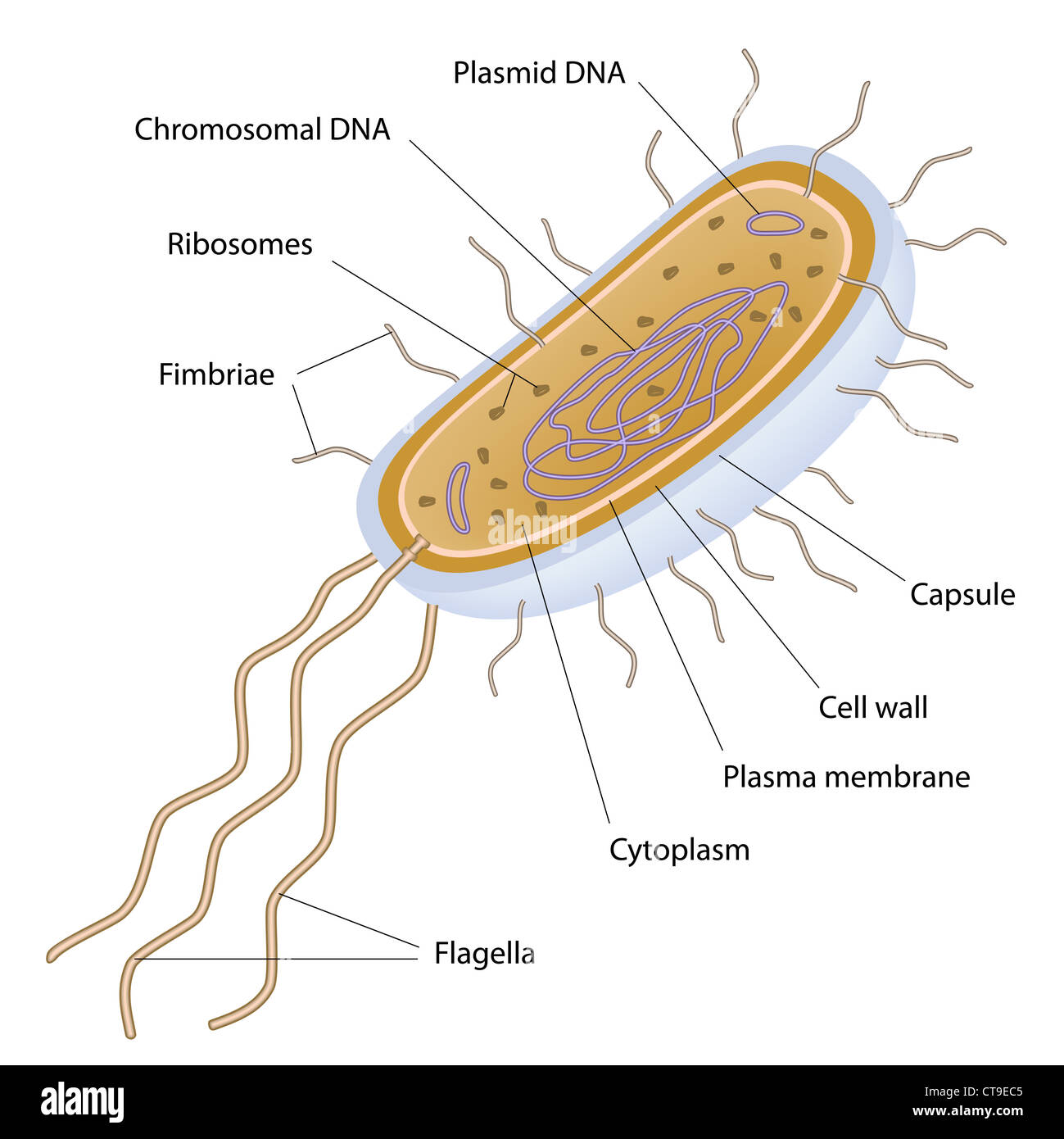 Structure of a bacterial cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-49381365.html
Structure of a bacterial cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-structure-of-a-bacterial-cell-49381365.htmlRFCT9EC5–Structure of a bacterial cell
 Old blank book on a textile background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/old-blank-book-on-a-textile-background-image369145568.html
Old blank book on a textile background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/old-blank-book-on-a-textile-background-image369145568.htmlRF2CCG0X8–Old blank book on a textile background
 Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387298430.html
Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387298430.htmlRF2DE2Y2P–Aksolotl
 Note 'Be my Valentine' on checked fabric Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/note-be-my-valentine-on-checked-fabric-image414691121.html
Note 'Be my Valentine' on checked fabric Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/note-be-my-valentine-on-checked-fabric-image414691121.htmlRF2F2JPN5–Note 'Be my Valentine' on checked fabric
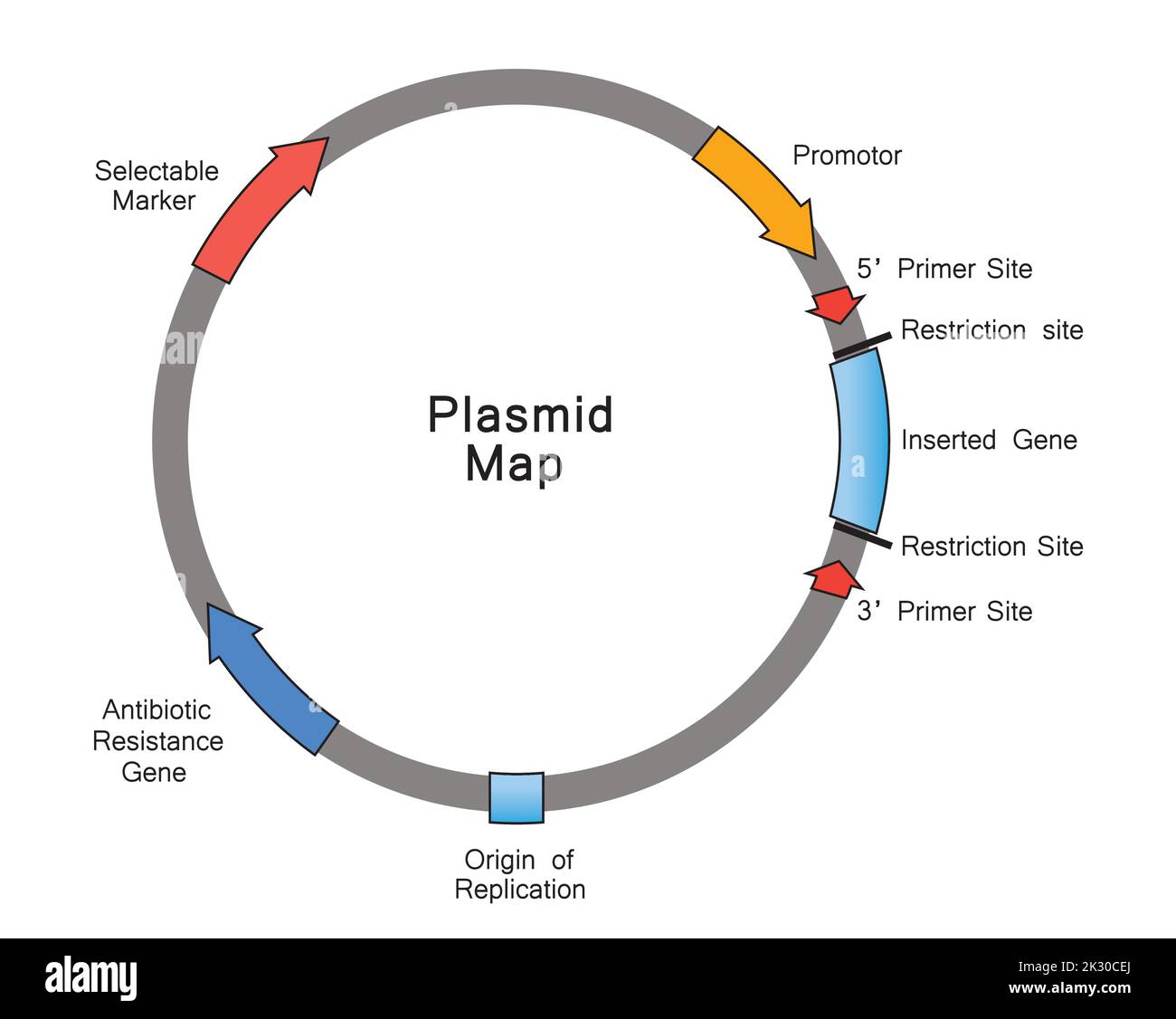 Simple Illustration of Plasmid Map. Colorful Symbols. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/simple-illustration-of-plasmid-map-colorful-symbols-vector-illustration-image483744090.html
Simple Illustration of Plasmid Map. Colorful Symbols. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/simple-illustration-of-plasmid-map-colorful-symbols-vector-illustration-image483744090.htmlRF2K30CEJ–Simple Illustration of Plasmid Map. Colorful Symbols. Vector Illustration.
 Reproductive system vector linear Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/reproductive-system-vector-linear-image601403744.html
Reproductive system vector linear Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/reproductive-system-vector-linear-image601403744.htmlRF2WXC8H4–Reproductive system vector linear
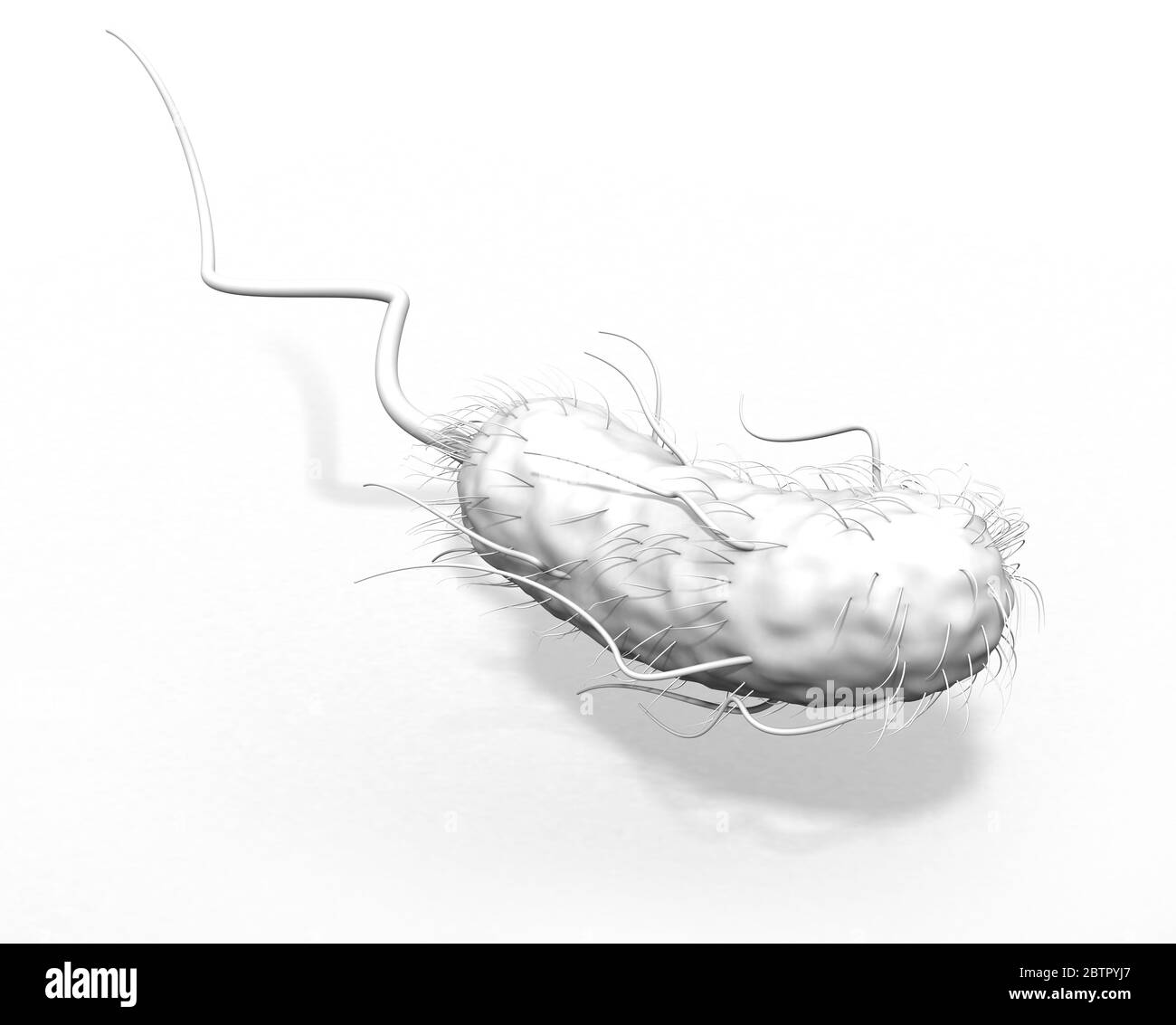 3D Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with flagellum and fimbriae on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-flagellum-and-fimbriae-on-white-background-image359463727.html
3D Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with flagellum and fimbriae on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-flagellum-and-fimbriae-on-white-background-image359463727.htmlRF2BTPYJ7–3D Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with flagellum and fimbriae on white background
 Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image629862016.html
Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image629862016.htmlRF2YGMKC0–Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock.
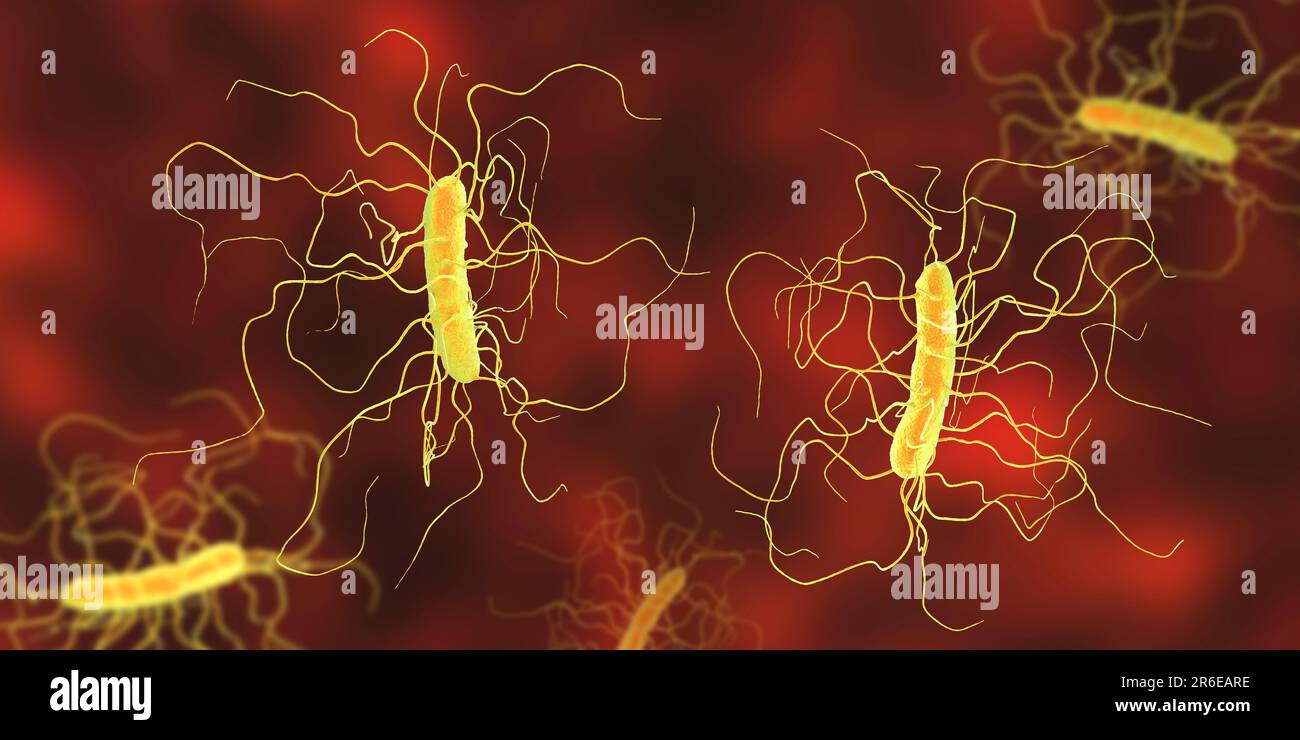 Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritricous-flagella-computer-illustration-c-difficile-is-gram-positive-anaerobic-spore-forming-rod-shaped-image554735538.html
Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritricous-flagella-computer-illustration-c-difficile-is-gram-positive-anaerobic-spore-forming-rod-shaped-image554735538.htmlRF2R6EARE–Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped
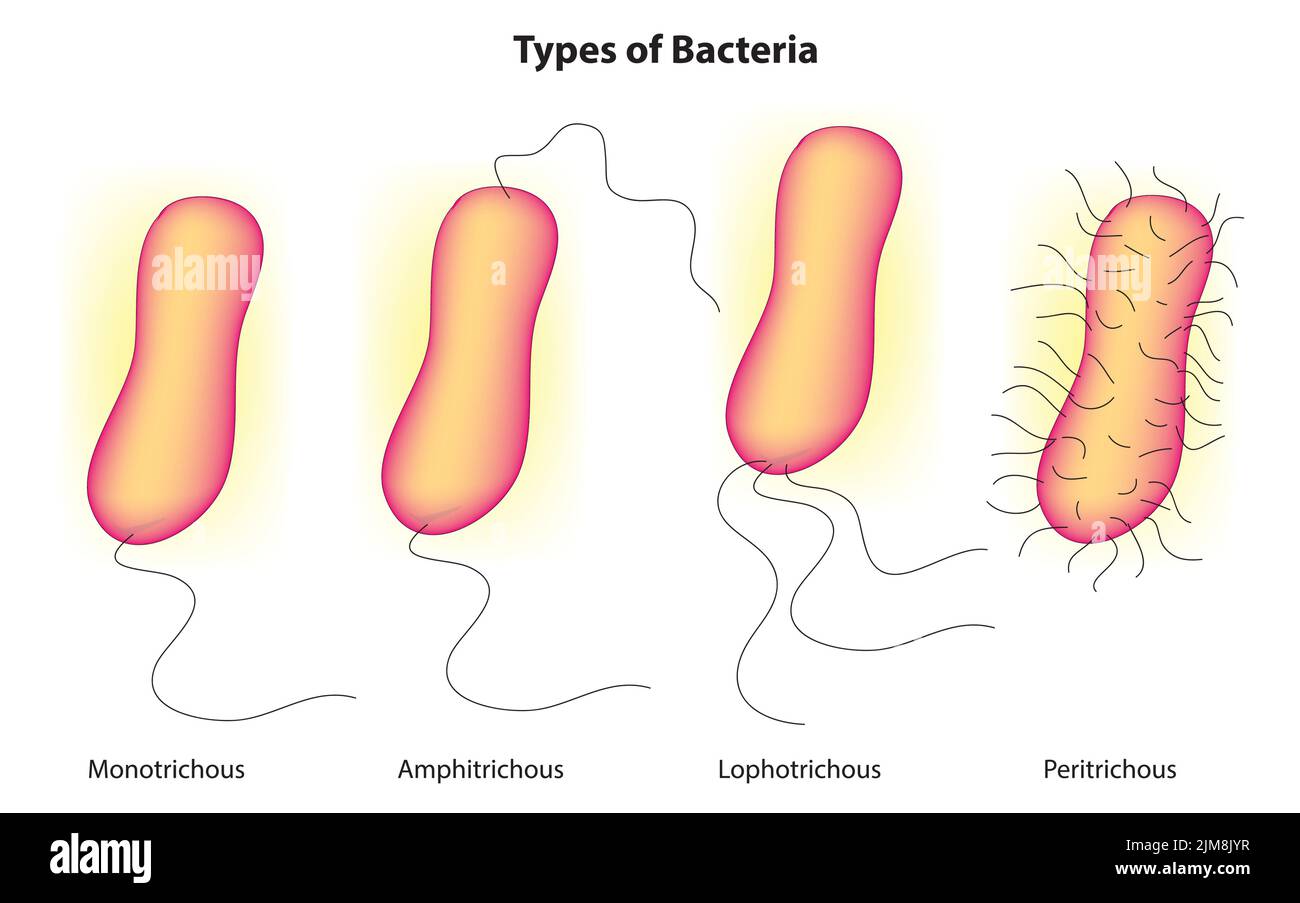 Types of bacteria Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/types-of-bacteria-image477163563.html
Types of bacteria Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/types-of-bacteria-image477163563.htmlRF2JM8JYR–Types of bacteria
 E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119761.html
E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119761.htmlRF2C7J5DN–E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis.
 ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-escherichia-coli-tem-49180018.html
ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-escherichia-coli-tem-49180018.htmlRMCT09H6–ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM
RF2HX9Y7C–Focal Adenomyosis Human anatomy Female reproductive Sick system vs versus normal. Compared educational healthy and abnormal anatomy organs uterus icon flat cartoon vector illustration isolated
 An illustrated posterior view of the uterus, ovaries and uterine tubes. Included are the ureters leading into the bladder as well as the round ligaments of the uterus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-an-illustrated-posterior-view-of-the-uterus-ovaries-and-uterine-tubes-103991357.html
An illustrated posterior view of the uterus, ovaries and uterine tubes. Included are the ureters leading into the bladder as well as the round ligaments of the uterus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-an-illustrated-posterior-view-of-the-uterus-ovaries-and-uterine-tubes-103991357.htmlRMG15611–An illustrated posterior view of the uterus, ovaries and uterine tubes. Included are the ureters leading into the bladder as well as the round ligaments of the uterus.
 . The anatomy of the domestic fowl . Domestic animals; Veterinary medicine; Poultry. i84 ANATOMY OF THE DOMESTIC FOWL ridges (Fig. 60, A). The fimbriae are continuous with the dorsal and the ventral ligament of the oviduct; and from this point, where the ridges of the mucous membrane are almost nil, they gradually increase in height as they extend down the tube. These ridges are continued in those of the second, or albumin-secreting portion (Fig. 60, D). At this point they increase in height very rapidly. Here the bundles of muscular fibers of the middle coat are thin and distributed among bun Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-domestic-fowl-domestic-animals-veterinary-medicine-poultry-i84-anatomy-of-the-domestic-fowl-ridges-fig-60-a-the-fimbriae-are-continuous-with-the-dorsal-and-the-ventral-ligament-of-the-oviduct-and-from-this-point-where-the-ridges-of-the-mucous-membrane-are-almost-nil-they-gradually-increase-in-height-as-they-extend-down-the-tube-these-ridges-are-continued-in-those-of-the-second-or-albumin-secreting-portion-fig-60-d-at-this-point-they-increase-in-height-very-rapidly-here-the-bundles-of-muscular-fibers-of-the-middle-coat-are-thin-and-distributed-among-bun-image216389148.html
. The anatomy of the domestic fowl . Domestic animals; Veterinary medicine; Poultry. i84 ANATOMY OF THE DOMESTIC FOWL ridges (Fig. 60, A). The fimbriae are continuous with the dorsal and the ventral ligament of the oviduct; and from this point, where the ridges of the mucous membrane are almost nil, they gradually increase in height as they extend down the tube. These ridges are continued in those of the second, or albumin-secreting portion (Fig. 60, D). At this point they increase in height very rapidly. Here the bundles of muscular fibers of the middle coat are thin and distributed among bun Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-domestic-fowl-domestic-animals-veterinary-medicine-poultry-i84-anatomy-of-the-domestic-fowl-ridges-fig-60-a-the-fimbriae-are-continuous-with-the-dorsal-and-the-ventral-ligament-of-the-oviduct-and-from-this-point-where-the-ridges-of-the-mucous-membrane-are-almost-nil-they-gradually-increase-in-height-as-they-extend-down-the-tube-these-ridges-are-continued-in-those-of-the-second-or-albumin-secreting-portion-fig-60-d-at-this-point-they-increase-in-height-very-rapidly-here-the-bundles-of-muscular-fibers-of-the-middle-coat-are-thin-and-distributed-among-bun-image216389148.htmlRMPG1AFT–. The anatomy of the domestic fowl . Domestic animals; Veterinary medicine; Poultry. i84 ANATOMY OF THE DOMESTIC FOWL ridges (Fig. 60, A). The fimbriae are continuous with the dorsal and the ventral ligament of the oviduct; and from this point, where the ridges of the mucous membrane are almost nil, they gradually increase in height as they extend down the tube. These ridges are continued in those of the second, or albumin-secreting portion (Fig. 60, D). At this point they increase in height very rapidly. Here the bundles of muscular fibers of the middle coat are thin and distributed among bun
![Infography about viruses and bacteria. [Adobe InDesign (.indd); 3543x4842]. Stock Photo Infography about viruses and bacteria. [Adobe InDesign (.indd); 3543x4842]. Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2NEBF3H/infography-about-viruses-and-bacteria-adobe-indesign-indd-3543x4842-2NEBF3H.jpg) Infography about viruses and bacteria. [Adobe InDesign (.indd); 3543x4842]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infography-about-viruses-and-bacteria-adobe-indesign-indd-3543x4842-image525169557.html
Infography about viruses and bacteria. [Adobe InDesign (.indd); 3543x4842]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infography-about-viruses-and-bacteria-adobe-indesign-indd-3543x4842-image525169557.htmlRM2NEBF3H–Infography about viruses and bacteria. [Adobe InDesign (.indd); 3543x4842].
 Archive image from page 222 of Die Anatomie des Kaninschens in. Die Anatomie des Kaninschens in topographischer und operativer Rücksicht . dieanatomiedeska00krau Year: 1884 Mundhöhle. 201 Die Länge der Fimbriae linguae beträgt 5—6 mm, die Breite 2,5—3,5 mm, die Anzahl der Querfurchen nur 10—14 (625). Die Anzahl der Geschmacks- knospen, von denen jedesmal 4 übereinander zu sitzen pflegen, in Summa 7440 jederseits (625). Die Länge der Geschmacksknospen beträgt 0,0575 mm (657). Nerven der Zunge. An den Ästen der Nn. glossopharyngeus, lingualis und hypoglossus innerhalb der Zunge kommen mikroskop Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-222-of-die-anatomie-des-kaninschens-in-die-anatomie-des-kaninschens-in-topographischer-und-operativer-rcksicht-dieanatomiedeska00krau-year-1884-mundhhle-201-die-lnge-der-fimbriae-linguae-betrgt-56-mm-die-breite-2535-mm-die-anzahl-der-querfurchen-nur-1014-625-die-anzahl-der-geschmacks-knospen-von-denen-jedesmal-4-bereinander-zu-sitzen-pflegen-in-summa-7440-jederseits-625-die-lnge-der-geschmacksknospen-betrgt-00575-mm-657-nerven-der-zunge-an-den-sten-der-nn-glossopharyngeus-lingualis-und-hypoglossus-innerhalb-der-zunge-kommen-mikroskop-image258907350.html
Archive image from page 222 of Die Anatomie des Kaninschens in. Die Anatomie des Kaninschens in topographischer und operativer Rücksicht . dieanatomiedeska00krau Year: 1884 Mundhöhle. 201 Die Länge der Fimbriae linguae beträgt 5—6 mm, die Breite 2,5—3,5 mm, die Anzahl der Querfurchen nur 10—14 (625). Die Anzahl der Geschmacks- knospen, von denen jedesmal 4 übereinander zu sitzen pflegen, in Summa 7440 jederseits (625). Die Länge der Geschmacksknospen beträgt 0,0575 mm (657). Nerven der Zunge. An den Ästen der Nn. glossopharyngeus, lingualis und hypoglossus innerhalb der Zunge kommen mikroskop Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-222-of-die-anatomie-des-kaninschens-in-die-anatomie-des-kaninschens-in-topographischer-und-operativer-rcksicht-dieanatomiedeska00krau-year-1884-mundhhle-201-die-lnge-der-fimbriae-linguae-betrgt-56-mm-die-breite-2535-mm-die-anzahl-der-querfurchen-nur-1014-625-die-anzahl-der-geschmacks-knospen-von-denen-jedesmal-4-bereinander-zu-sitzen-pflegen-in-summa-7440-jederseits-625-die-lnge-der-geschmacksknospen-betrgt-00575-mm-657-nerven-der-zunge-an-den-sten-der-nn-glossopharyngeus-lingualis-und-hypoglossus-innerhalb-der-zunge-kommen-mikroskop-image258907350.htmlRMW166Y2–Archive image from page 222 of Die Anatomie des Kaninschens in. Die Anatomie des Kaninschens in topographischer und operativer Rücksicht . dieanatomiedeska00krau Year: 1884 Mundhöhle. 201 Die Länge der Fimbriae linguae beträgt 5—6 mm, die Breite 2,5—3,5 mm, die Anzahl der Querfurchen nur 10—14 (625). Die Anzahl der Geschmacks- knospen, von denen jedesmal 4 übereinander zu sitzen pflegen, in Summa 7440 jederseits (625). Die Länge der Geschmacksknospen beträgt 0,0575 mm (657). Nerven der Zunge. An den Ästen der Nn. glossopharyngeus, lingualis und hypoglossus innerhalb der Zunge kommen mikroskop
 A System of midwifery : including the diseases of pregnancy and the puerperal state . ch it is about to escape bydehiscence is firmly grasped by the fimbriae ( morms diabolx), and the ovum is received int.. the oviduct, and by it conducted to the uterus, where it i- retained and de eloped, or hence it is discharged, accordingto circumstances. Leading from the inner extremity of the ovary an organ to behereafter described isa dense cord, composed mainly of fibro-areolartissue, hut containing also muscular fibres. This is the ligament of tinovary, which is also, like the round ligament an I the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-midwifery-including-the-diseases-of-pregnancy-and-the-puerperal-state-ch-it-is-about-to-escape-bydehiscence-is-firmly-grasped-by-the-fimbriae-morms-diabolx-and-the-ovum-is-received-int-the-oviduct-and-by-it-conducted-to-the-uterus-where-it-i-retained-and-de-eloped-or-hence-it-is-discharged-accordingto-circumstances-leading-from-the-inner-extremity-of-the-ovary-an-organ-to-behereafter-described-isa-dense-cord-composed-mainly-of-fibro-areolartissue-hut-containing-also-muscular-fibres-this-is-the-ligament-of-tinovary-which-is-also-like-the-round-ligament-an-i-the-image339035505.html
A System of midwifery : including the diseases of pregnancy and the puerperal state . ch it is about to escape bydehiscence is firmly grasped by the fimbriae ( morms diabolx), and the ovum is received int.. the oviduct, and by it conducted to the uterus, where it i- retained and de eloped, or hence it is discharged, accordingto circumstances. Leading from the inner extremity of the ovary an organ to behereafter described isa dense cord, composed mainly of fibro-areolartissue, hut containing also muscular fibres. This is the ligament of tinovary, which is also, like the round ligament an I the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-midwifery-including-the-diseases-of-pregnancy-and-the-puerperal-state-ch-it-is-about-to-escape-bydehiscence-is-firmly-grasped-by-the-fimbriae-morms-diabolx-and-the-ovum-is-received-int-the-oviduct-and-by-it-conducted-to-the-uterus-where-it-i-retained-and-de-eloped-or-hence-it-is-discharged-accordingto-circumstances-leading-from-the-inner-extremity-of-the-ovary-an-organ-to-behereafter-described-isa-dense-cord-composed-mainly-of-fibro-areolartissue-hut-containing-also-muscular-fibres-this-is-the-ligament-of-tinovary-which-is-also-like-the-round-ligament-an-i-the-image339035505.htmlRM2AKGB6W–A System of midwifery : including the diseases of pregnancy and the puerperal state . ch it is about to escape bydehiscence is firmly grasped by the fimbriae ( morms diabolx), and the ovum is received int.. the oviduct, and by it conducted to the uterus, where it i- retained and de eloped, or hence it is discharged, accordingto circumstances. Leading from the inner extremity of the ovary an organ to behereafter described isa dense cord, composed mainly of fibro-areolartissue, hut containing also muscular fibres. This is the ligament of tinovary, which is also, like the round ligament an I the
RFWXPY9W–Cell bacteria icon. Flat illustration of cell bacteria vector icon for web design
 entertaining Clown salmonella caricature character design style Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/entertaining-clown-salmonella-caricature-character-design-style-image357337439.html
entertaining Clown salmonella caricature character design style Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/entertaining-clown-salmonella-caricature-character-design-style-image357337439.htmlRF2BNA3FB–entertaining Clown salmonella caricature character design style
 . Murie (1873) in Globicephala melaena found that the broad ligament and the fimbriae form "a delicate arched covering or pavilion which overarches the ovary". Turner (1870 b), describing the conditions in Ora'mts, wrote: " Immediately on the uterine side of this mouth" (of the Fallopian tube) "was an elongated deep pouch-like recess formed by a folding on that part of the broad ligament which extended between the Fallopian tube and the root of the ovary ". A comparable deepening of the ligamentum latum occurs in man and the Ruminants, and there is a similar enlar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/murie-1873-in-globicephala-melaena-found-that-the-broad-ligament-and-the-fimbriae-form-quota-delicate-arched-covering-or-pavilion-which-overarches-the-ovaryquot-turner-1870-b-describing-the-conditions-in-oramts-wrote-quot-immediately-on-the-uterine-side-of-this-mouthquot-of-the-fallopian-tube-quotwas-an-elongated-deep-pouch-like-recess-formed-by-a-folding-on-that-part-of-the-broad-ligament-which-extended-between-the-fallopian-tube-and-the-root-of-the-ovary-quot-a-comparable-deepening-of-the-ligamentum-latum-occurs-in-man-and-the-ruminants-and-there-is-a-similar-enlar-image180025718.html
. Murie (1873) in Globicephala melaena found that the broad ligament and the fimbriae form "a delicate arched covering or pavilion which overarches the ovary". Turner (1870 b), describing the conditions in Ora'mts, wrote: " Immediately on the uterine side of this mouth" (of the Fallopian tube) "was an elongated deep pouch-like recess formed by a folding on that part of the broad ligament which extended between the Fallopian tube and the root of the ovary ". A comparable deepening of the ligamentum latum occurs in man and the Ruminants, and there is a similar enlar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/murie-1873-in-globicephala-melaena-found-that-the-broad-ligament-and-the-fimbriae-form-quota-delicate-arched-covering-or-pavilion-which-overarches-the-ovaryquot-turner-1870-b-describing-the-conditions-in-oramts-wrote-quot-immediately-on-the-uterine-side-of-this-mouthquot-of-the-fallopian-tube-quotwas-an-elongated-deep-pouch-like-recess-formed-by-a-folding-on-that-part-of-the-broad-ligament-which-extended-between-the-fallopian-tube-and-the-root-of-the-ovary-quot-a-comparable-deepening-of-the-ligamentum-latum-occurs-in-man-and-the-ruminants-and-there-is-a-similar-enlar-image180025718.htmlRMMCTTHX–. Murie (1873) in Globicephala melaena found that the broad ligament and the fimbriae form "a delicate arched covering or pavilion which overarches the ovary". Turner (1870 b), describing the conditions in Ora'mts, wrote: " Immediately on the uterine side of this mouth" (of the Fallopian tube) "was an elongated deep pouch-like recess formed by a folding on that part of the broad ligament which extended between the Fallopian tube and the root of the ovary ". A comparable deepening of the ligamentum latum occurs in man and the Ruminants, and there is a similar enlar
 Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387299420.html
Aksolotl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/aksolotl-image387299420.htmlRF2DE30A4–Aksolotl
 Checkered fabric heart for Valentine's Day Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/checkered-fabric-heart-for-valentines-day-image414690633.html
Checkered fabric heart for Valentine's Day Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/checkered-fabric-heart-for-valentines-day-image414690633.htmlRF2F2JP3N–Checkered fabric heart for Valentine's Day
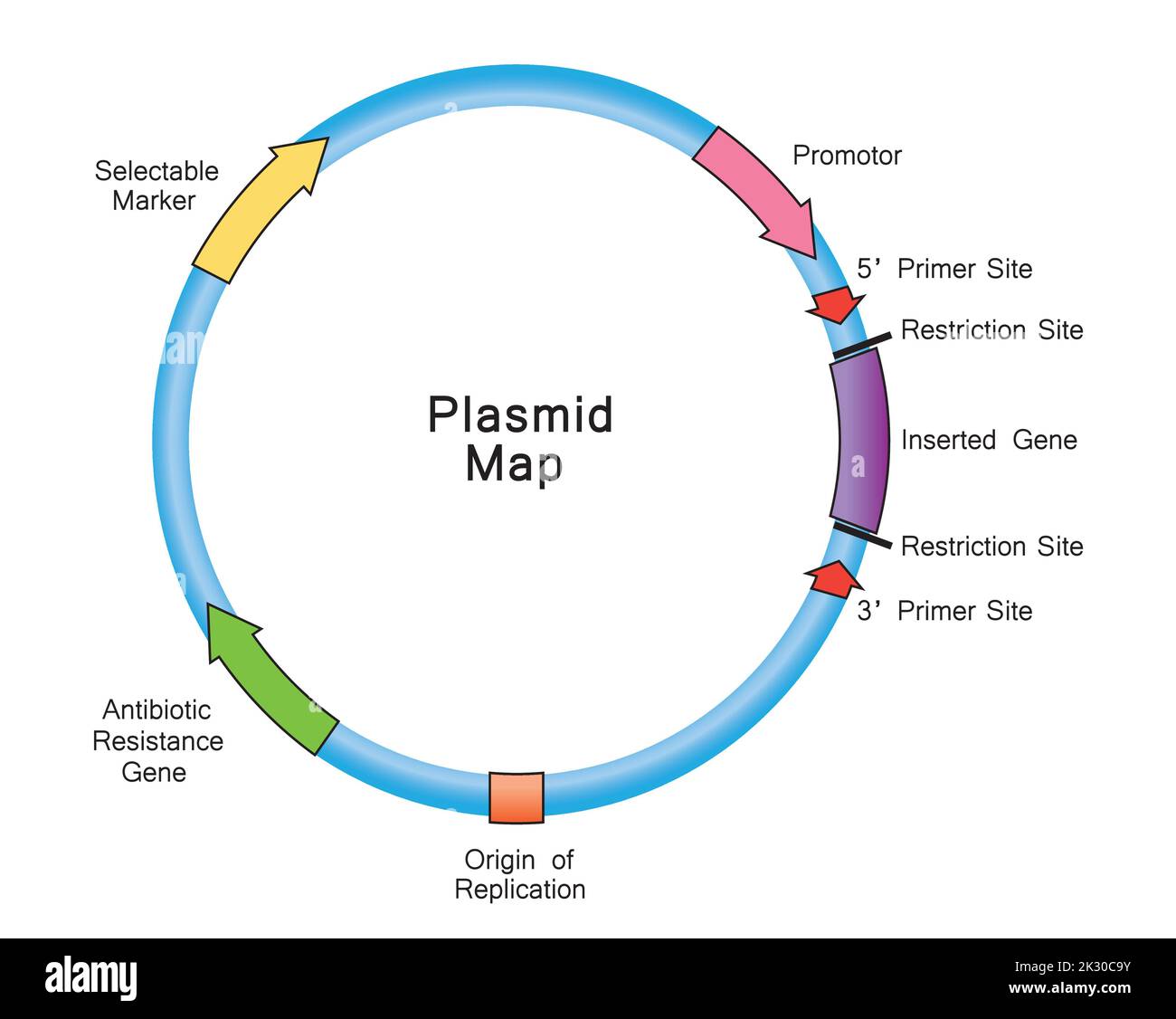 Simple Illustration of Plasmid Map. Colorful Symbols. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/simple-illustration-of-plasmid-map-colorful-symbols-vector-illustration-image483743959.html
Simple Illustration of Plasmid Map. Colorful Symbols. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/simple-illustration-of-plasmid-map-colorful-symbols-vector-illustration-image483743959.htmlRF2K30C9Y–Simple Illustration of Plasmid Map. Colorful Symbols. Vector Illustration.
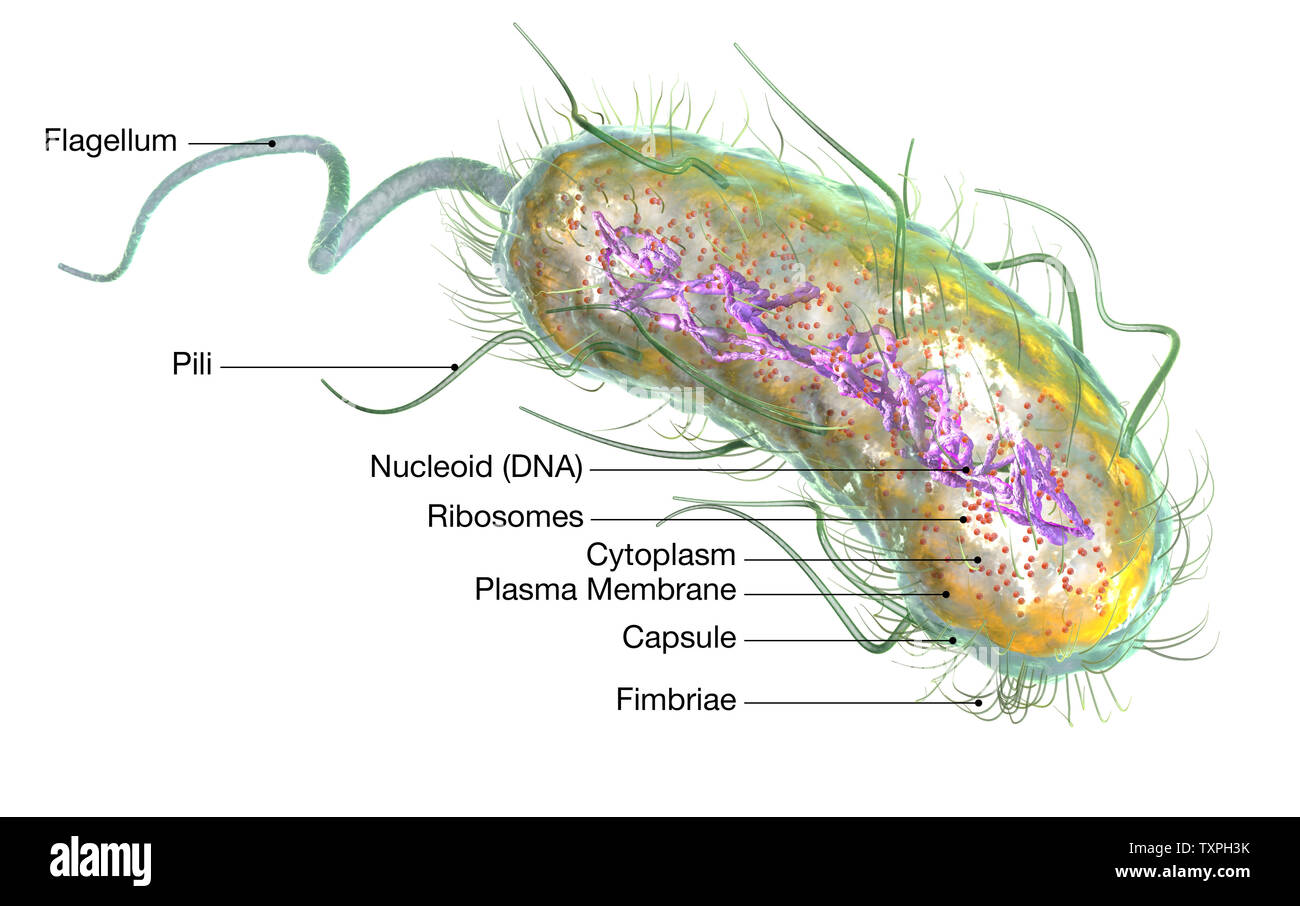 Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257422583.html
Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257422583.htmlRFTXPH3K–Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae
 Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image614825217.html
Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image614825217.htmlRF2XM7KRD–Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock.
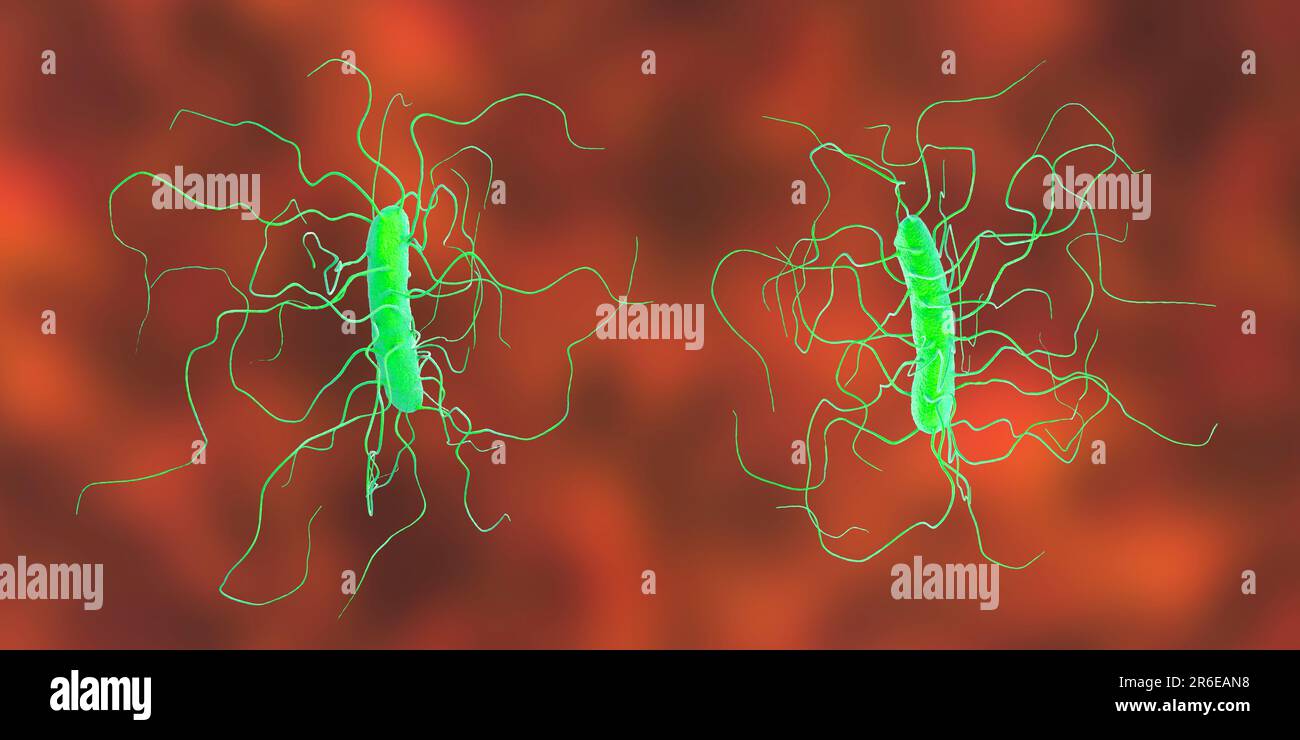 Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritricous-flagella-computer-illustration-c-difficile-is-gram-positive-anaerobic-spore-forming-rod-shaped-image554735476.html
Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritricous-flagella-computer-illustration-c-difficile-is-gram-positive-anaerobic-spore-forming-rod-shaped-image554735476.htmlRF2R6EAN8–Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped
 E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119743.html
E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/e-coli-bacteria-illustration-escherichia-coli-is-a-rod-shaped-bacterium-bacillus-its-cell-membrane-is-covered-in-fine-filaments-called-pili-or-fimbriae-hair-like-structures-called-flagella-at-the-rear-of-each-bacterium-provide-propulsion-to-make-it-move-e-coli-is-a-normal-component-of-the-intestinal-bacterial-flora-but-under-certain-conditions-some-strains-can-cause-severe-infections-such-as-gastroenteritis-image366119743.htmlRF2C7J5D3–E. coli bacteria, illustration. Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped bacterium (bacillus). Its cell membrane is covered in fine filaments called pili or fimbriae. Hair-like structures called flagella at the rear of each bacterium provide propulsion to make it move. E. coli is a normal component of the intestinal bacterial flora, but under certain conditions some strains can cause severe infections such as gastroenteritis.
 ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-escherichia-coli-tem-49180003.html
ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-escherichia-coli-tem-49180003.htmlRMCT09GK–ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM
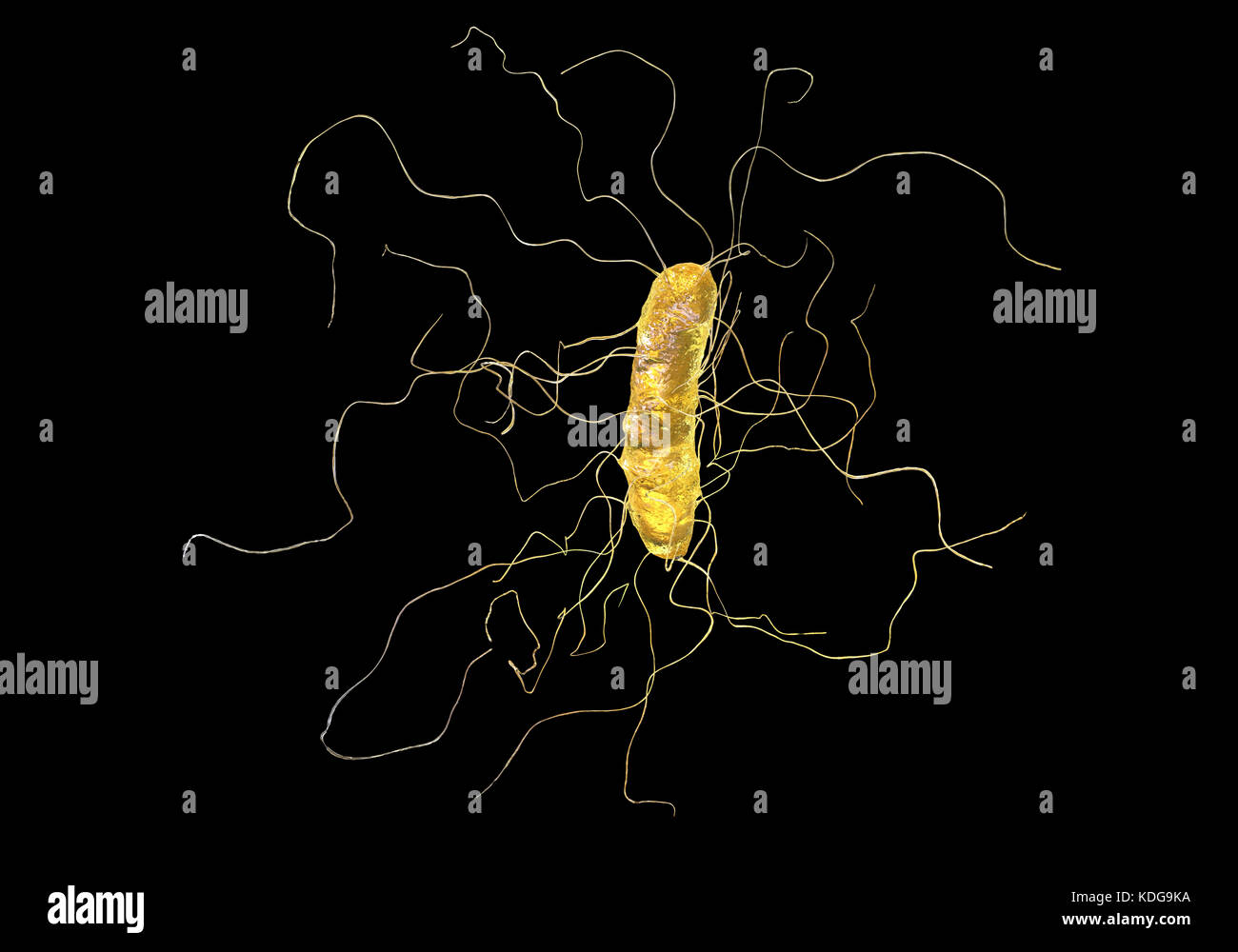 Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intestinal flora, especially in young children. C. difficile is the major cause of pseudomembranous colitis and antibiotic produced diarrhoea. It is now becoming resistant to most antibiotics. Treatment is by discontinuing antibiotics and starting specific anticlostridial antibiotics, such as metronidazole. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritrichous-flagella-computer-163242670.html
Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intestinal flora, especially in young children. C. difficile is the major cause of pseudomembranous colitis and antibiotic produced diarrhoea. It is now becoming resistant to most antibiotics. Treatment is by discontinuing antibiotics and starting specific anticlostridial antibiotics, such as metronidazole. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritrichous-flagella-computer-163242670.htmlRFKDG9KA–Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intestinal flora, especially in young children. C. difficile is the major cause of pseudomembranous colitis and antibiotic produced diarrhoea. It is now becoming resistant to most antibiotics. Treatment is by discontinuing antibiotics and starting specific anticlostridial antibiotics, such as metronidazole.
RF2HXMX6Y–Focal Adenomyosis Human anatomy Female Sick and normal reproductive system organs. Location scheme Cross section uterus, cervix, ovary, fallopian tube icon. Vector illustration isolated on white
 Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intes Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritrichous-flagella-computer-139311314.html
Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intes Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritrichous-flagella-computer-139311314.htmlRFJ2J502–Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intes
![Infographic of the parts of a bacteria, their classification and functions. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photo Infographic of the parts of a bacteria, their classification and functions. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2NEC7RH/infographic-of-the-parts-of-a-bacteria-their-classification-and-functions-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-2NEC7RH.jpg) Infographic of the parts of a bacteria, their classification and functions. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-of-the-parts-of-a-bacteria-their-classification-and-functions-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-image525185797.html
Infographic of the parts of a bacteria, their classification and functions. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-of-the-parts-of-a-bacteria-their-classification-and-functions-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-image525185797.htmlRM2NEC7RH–Infographic of the parts of a bacteria, their classification and functions. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015].
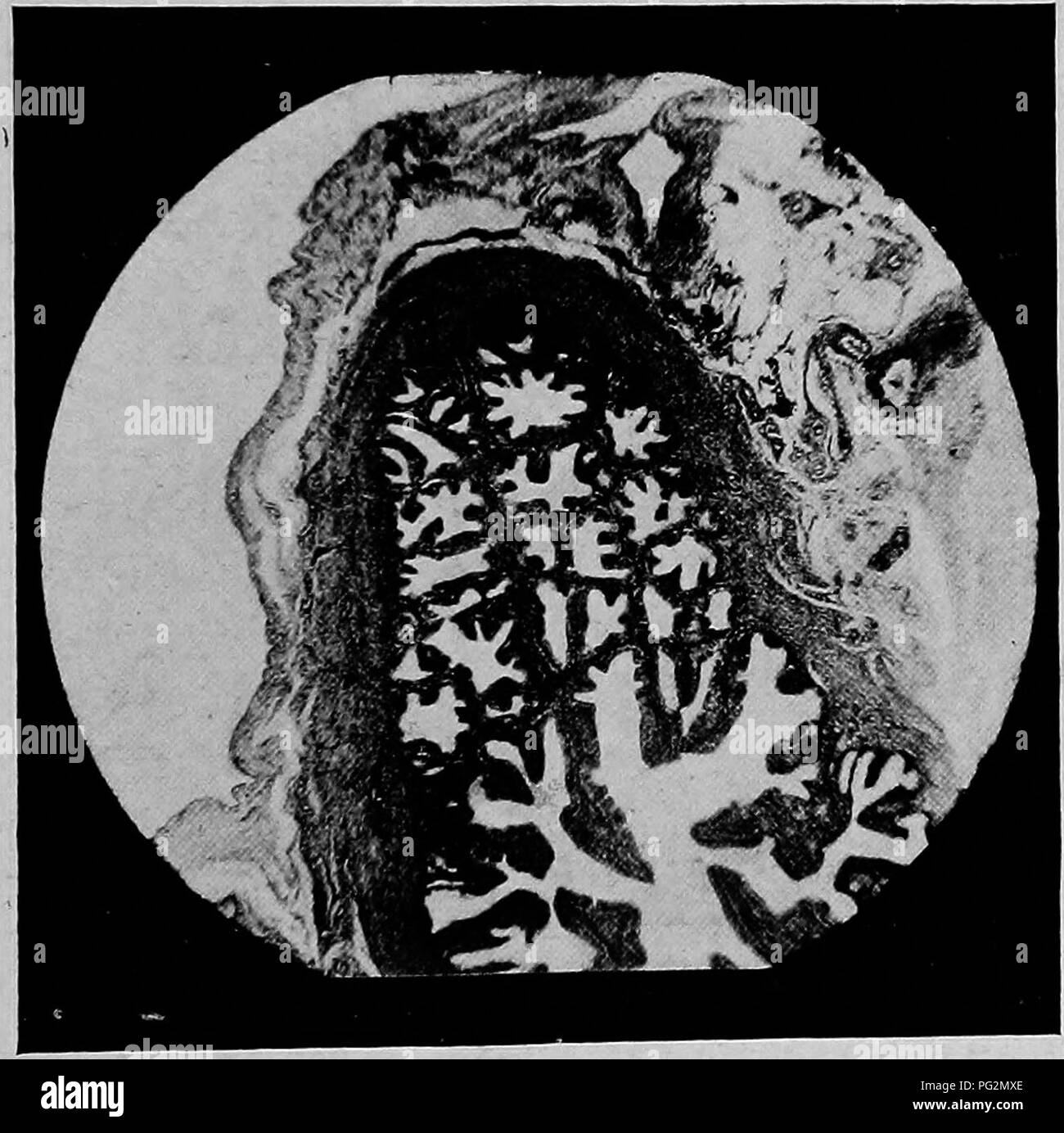 . The diseases of the genital organs of domestic animals. Veterinary medicine. Salpingitis 433 the ampulla, however, they increase in number and height, with the formation of numerous secondary folds, so that at the ampulla the otherwise broad lumen becomes almost oc- cluded. At the fimbriated end, the folds widen and are con- tinued out on the free ends of the fimbriae, forming ridges which branch freely, giving the pavilion a more or less honeycombed appearance. Not infrequently one finds the folds ramifying elaborately, particularly at their bases, forming cavities lined by a sort of flatte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-diseases-of-the-genital-organs-of-domestic-animals-veterinary-medicine-salpingitis-433-the-ampulla-however-they-increase-in-number-and-height-with-the-formation-of-numerous-secondary-folds-so-that-at-the-ampulla-the-otherwise-broad-lumen-becomes-almost-oc-cluded-at-the-fimbriated-end-the-folds-widen-and-are-con-tinued-out-on-the-free-ends-of-the-fimbriae-forming-ridges-which-branch-freely-giving-the-pavilion-a-more-or-less-honeycombed-appearance-not-infrequently-one-finds-the-folds-ramifying-elaborately-particularly-at-their-bases-forming-cavities-lined-by-a-sort-of-flatte-image216419238.html
. The diseases of the genital organs of domestic animals. Veterinary medicine. Salpingitis 433 the ampulla, however, they increase in number and height, with the formation of numerous secondary folds, so that at the ampulla the otherwise broad lumen becomes almost oc- cluded. At the fimbriated end, the folds widen and are con- tinued out on the free ends of the fimbriae, forming ridges which branch freely, giving the pavilion a more or less honeycombed appearance. Not infrequently one finds the folds ramifying elaborately, particularly at their bases, forming cavities lined by a sort of flatte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-diseases-of-the-genital-organs-of-domestic-animals-veterinary-medicine-salpingitis-433-the-ampulla-however-they-increase-in-number-and-height-with-the-formation-of-numerous-secondary-folds-so-that-at-the-ampulla-the-otherwise-broad-lumen-becomes-almost-oc-cluded-at-the-fimbriated-end-the-folds-widen-and-are-con-tinued-out-on-the-free-ends-of-the-fimbriae-forming-ridges-which-branch-freely-giving-the-pavilion-a-more-or-less-honeycombed-appearance-not-infrequently-one-finds-the-folds-ramifying-elaborately-particularly-at-their-bases-forming-cavities-lined-by-a-sort-of-flatte-image216419238.htmlRMPG2MXE–. The diseases of the genital organs of domestic animals. Veterinary medicine. Salpingitis 433 the ampulla, however, they increase in number and height, with the formation of numerous secondary folds, so that at the ampulla the otherwise broad lumen becomes almost oc- cluded. At the fimbriated end, the folds widen and are con- tinued out on the free ends of the fimbriae, forming ridges which branch freely, giving the pavilion a more or less honeycombed appearance. Not infrequently one finds the folds ramifying elaborately, particularly at their bases, forming cavities lined by a sort of flatte
 Gynaecology for students and practitioners . fusion of the fimbriae owing to destruction ofthe surface-epithelium. Closure is often effected by the formationof an external pseudomembrane, or through the fusion of theabdominal ostium to neighbouring organs. In such cases, after theseparation of the adhesions the abdominal ostium may be found tobe still open, and the plicae still visible, so that indrawing of the plicaeis not so essential to the formation of a pyosalpinx as it is to the 618 GYNECOLOGY formation of a hydrosalpinx. In fact, retention of pus may occurthrough the swelling of the muc Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynaecology-for-students-and-practitioners-fusion-of-the-fimbriae-owing-to-destruction-ofthe-surface-epithelium-closure-is-often-effected-by-the-formationof-an-external-pseudomembrane-or-through-the-fusion-of-theabdominal-ostium-to-neighbouring-organs-in-such-cases-after-theseparation-of-the-adhesions-the-abdominal-ostium-may-be-found-tobe-still-open-and-the-plicae-still-visible-so-that-indrawing-of-the-plicaeis-not-so-essential-to-the-formation-of-a-pyosalpinx-as-it-is-to-the-618-gynecology-formation-of-a-hydrosalpinx-in-fact-retention-of-pus-may-occurthrough-the-swelling-of-the-muc-image339959312.html
Gynaecology for students and practitioners . fusion of the fimbriae owing to destruction ofthe surface-epithelium. Closure is often effected by the formationof an external pseudomembrane, or through the fusion of theabdominal ostium to neighbouring organs. In such cases, after theseparation of the adhesions the abdominal ostium may be found tobe still open, and the plicae still visible, so that indrawing of the plicaeis not so essential to the formation of a pyosalpinx as it is to the 618 GYNECOLOGY formation of a hydrosalpinx. In fact, retention of pus may occurthrough the swelling of the muc Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynaecology-for-students-and-practitioners-fusion-of-the-fimbriae-owing-to-destruction-ofthe-surface-epithelium-closure-is-often-effected-by-the-formationof-an-external-pseudomembrane-or-through-the-fusion-of-theabdominal-ostium-to-neighbouring-organs-in-such-cases-after-theseparation-of-the-adhesions-the-abdominal-ostium-may-be-found-tobe-still-open-and-the-plicae-still-visible-so-that-indrawing-of-the-plicaeis-not-so-essential-to-the-formation-of-a-pyosalpinx-as-it-is-to-the-618-gynecology-formation-of-a-hydrosalpinx-in-fact-retention-of-pus-may-occurthrough-the-swelling-of-the-muc-image339959312.htmlRM2AN2DG0–Gynaecology for students and practitioners . fusion of the fimbriae owing to destruction ofthe surface-epithelium. Closure is often effected by the formationof an external pseudomembrane, or through the fusion of theabdominal ostium to neighbouring organs. In such cases, after theseparation of the adhesions the abdominal ostium may be found tobe still open, and the plicae still visible, so that indrawing of the plicaeis not so essential to the formation of a pyosalpinx as it is to the 618 GYNECOLOGY formation of a hydrosalpinx. In fact, retention of pus may occurthrough the swelling of the muc
RF2A2TM54–Cell bacteria icon. Simple illustration of cell bacteria vector icon for web design isolated on white background
 mascot design concept of salmonella with confuse gesture Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mascot-design-concept-of-salmonella-with-confuse-gesture-image357337005.html
mascot design concept of salmonella with confuse gesture Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mascot-design-concept-of-salmonella-with-confuse-gesture-image357337005.htmlRF2BNA2YW–mascot design concept of salmonella with confuse gesture
 Archive image from page 419 of Discovery reports (1932) Discovery reports discoveryreports05inst Year: 1932 Murie (1873) in Globicephala melaena found that the broad ligament and the fimbriae form 'a delicate arched covering or pavilion which overarches the ovary'. Turner (1870 b), describing the conditions in Ora'mts, wrote: ' Immediately on the uterine side of this mouth' (of the Fallopian tube) 'was an elongated deep pouch-like recess formed by a folding on that part of the broad ligament which extended between the Fallopian tube and the root of the ovary '. A comparable deepening of the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-419-of-discovery-reports-1932-discovery-reports-discoveryreports05inst-year-1932-murie-1873-in-globicephala-melaena-found-that-the-broad-ligament-and-the-fimbriae-form-a-delicate-arched-covering-or-pavilion-which-overarches-the-ovary-turner-1870-b-describing-the-conditions-in-oramts-wrote-immediately-on-the-uterine-side-of-this-mouth-of-the-fallopian-tube-was-an-elongated-deep-pouch-like-recess-formed-by-a-folding-on-that-part-of-the-broad-ligament-which-extended-between-the-fallopian-tube-and-the-root-of-the-ovary-a-comparable-deepening-of-the-image242269511.html
Archive image from page 419 of Discovery reports (1932) Discovery reports discoveryreports05inst Year: 1932 Murie (1873) in Globicephala melaena found that the broad ligament and the fimbriae form 'a delicate arched covering or pavilion which overarches the ovary'. Turner (1870 b), describing the conditions in Ora'mts, wrote: ' Immediately on the uterine side of this mouth' (of the Fallopian tube) 'was an elongated deep pouch-like recess formed by a folding on that part of the broad ligament which extended between the Fallopian tube and the root of the ovary '. A comparable deepening of the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-419-of-discovery-reports-1932-discovery-reports-discoveryreports05inst-year-1932-murie-1873-in-globicephala-melaena-found-that-the-broad-ligament-and-the-fimbriae-form-a-delicate-arched-covering-or-pavilion-which-overarches-the-ovary-turner-1870-b-describing-the-conditions-in-oramts-wrote-immediately-on-the-uterine-side-of-this-mouth-of-the-fallopian-tube-was-an-elongated-deep-pouch-like-recess-formed-by-a-folding-on-that-part-of-the-broad-ligament-which-extended-between-the-fallopian-tube-and-the-root-of-the-ovary-a-comparable-deepening-of-the-image242269511.htmlRMT2496F–Archive image from page 419 of Discovery reports (1932) Discovery reports discoveryreports05inst Year: 1932 Murie (1873) in Globicephala melaena found that the broad ligament and the fimbriae form 'a delicate arched covering or pavilion which overarches the ovary'. Turner (1870 b), describing the conditions in Ora'mts, wrote: ' Immediately on the uterine side of this mouth' (of the Fallopian tube) 'was an elongated deep pouch-like recess formed by a folding on that part of the broad ligament which extended between the Fallopian tube and the root of the ovary '. A comparable deepening of the
 Checkered fabric heart for Valentine's Day Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/checkered-fabric-heart-for-valentines-day-image414691132.html
Checkered fabric heart for Valentine's Day Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/checkered-fabric-heart-for-valentines-day-image414691132.htmlRF2F2JPNG–Checkered fabric heart for Valentine's Day
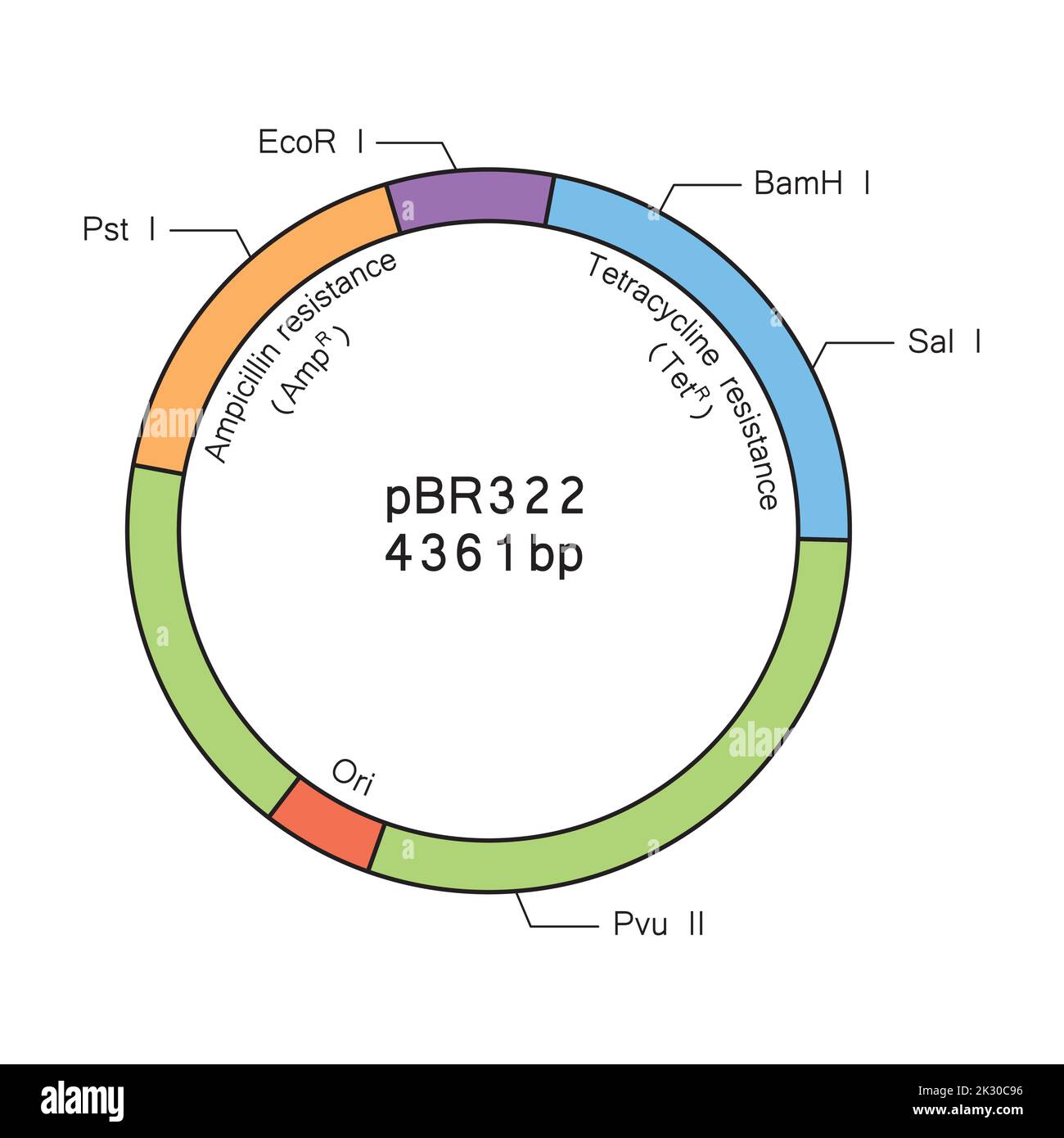 Colorful Deseigning of Plasmid pBR322 Structure. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/colorful-deseigning-of-plasmid-pbr322-structure-vector-illustration-image483743938.html
Colorful Deseigning of Plasmid pBR322 Structure. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/colorful-deseigning-of-plasmid-pbr322-structure-vector-illustration-image483743938.htmlRF2K30C96–Colorful Deseigning of Plasmid pBR322 Structure. Vector Illustration.
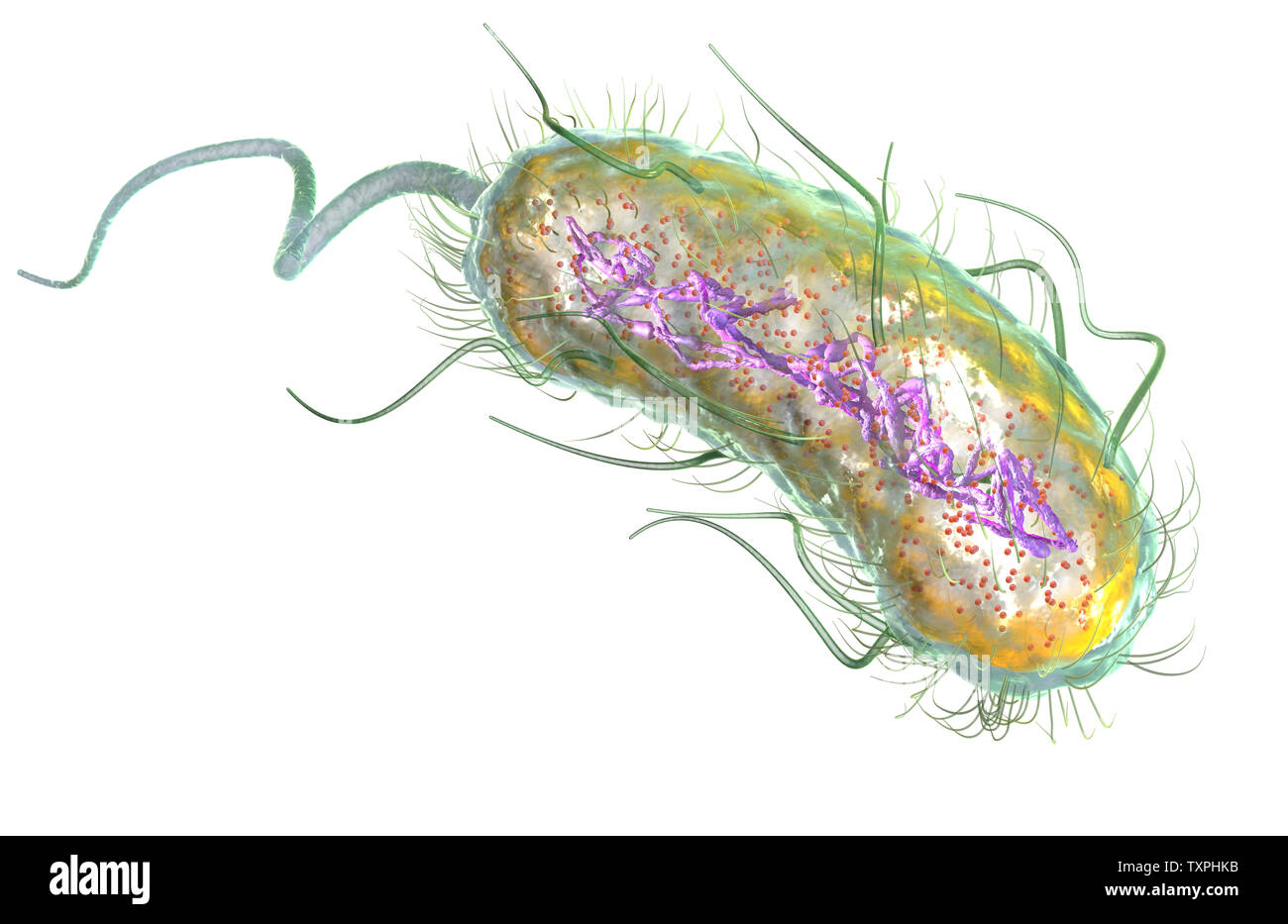 Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257423023.html
Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-showing-escherichia-coli-bacteria-e-coli-with-nucleoid-dna-ribosomes-cytoplasm-flagellum-and-fimbriae-image257423023.htmlRFTXPHKB–Illustration showing Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli) with Nucleoid (DNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Flagellum and Fimbriae
 Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image604289610.html
Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/close-up-of-the-trumpet-lichen-cladonia-fimbriata-between-stone-flowers-and-moss-on-a-rock-image604289610.htmlRF2X33NFP–Close up of the trumpet lichen Cladonia fimbriata between stone flowers and moss on a rock.
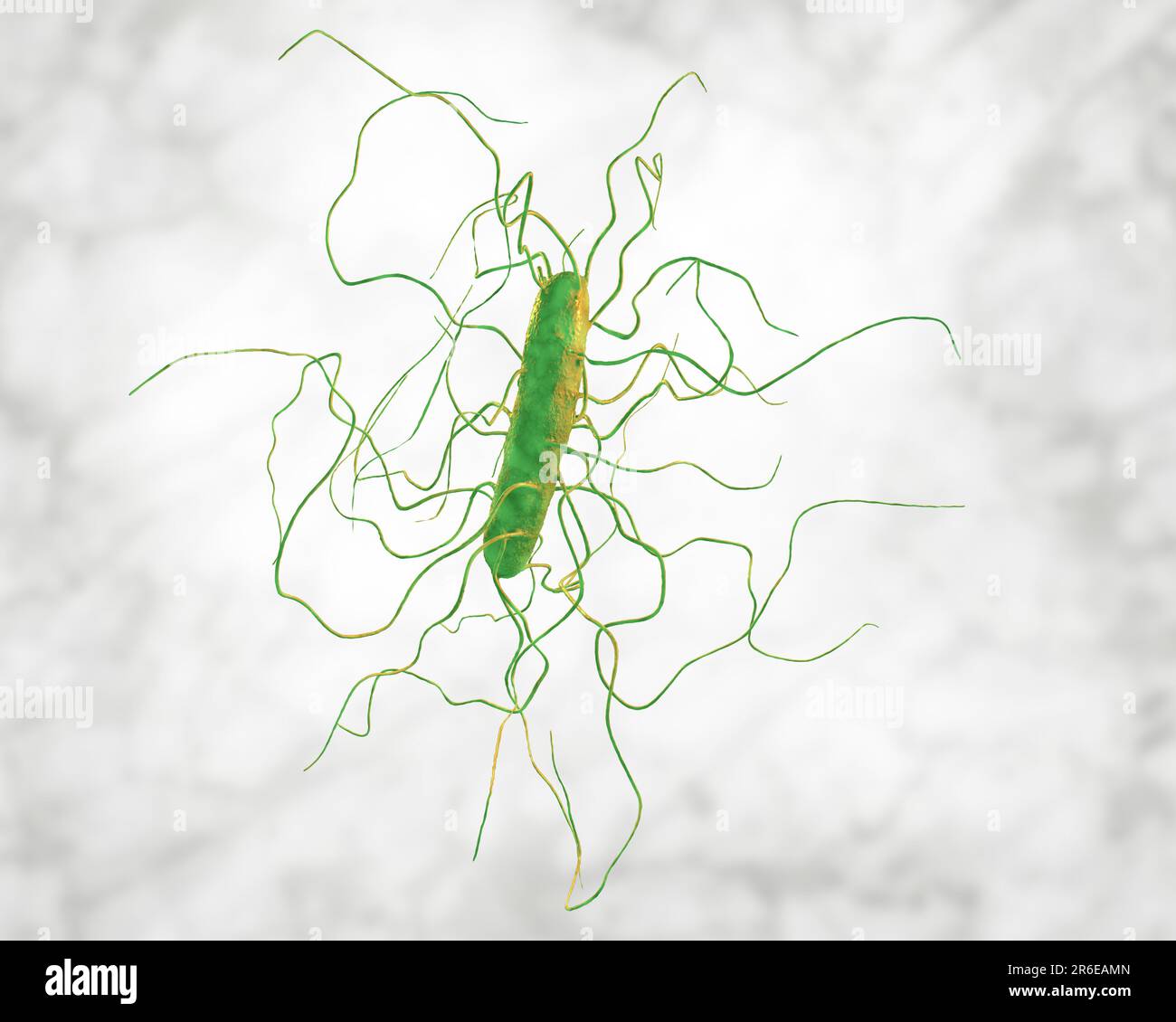 Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritricous-flagella-computer-illustration-c-difficile-is-gram-positive-anaerobic-spore-forming-rod-shaped-image554735461.html
Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritricous-flagella-computer-illustration-c-difficile-is-gram-positive-anaerobic-spore-forming-rod-shaped-image554735461.htmlRF2R6EAMN–Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritricous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped
 ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-escherichia-coli-tem-49180015.html
ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-escherichia-coli-tem-49180015.htmlRMCT09H3–ESCHERICHIA COLI, TEM
RF2J3N9KF–Diffuse Adenomyosis Human anatomy Female reproductive Sick system vs versus normal. Compared educational healthy and abnormal anatomy organs uterus icon flat cartoon vector illustration isolated
 Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intes Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritrichous-flagella-computer-139311315.html
Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intes Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-clostridium-difficile-bacterium-with-peritrichous-flagella-computer-139311315.htmlRFJ2J503–Clostridium difficile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, computer illustration. C. difficile is Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore forming, rod-shaped prokaryote with peritrichous flagella. It is a spore-forming bacteria that is a normal part of the intes