Quick filters:
Galaxies clusters Stock Photos and Images
 Galaxies and Star Clusters in Arp's Loop Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galaxies-and-star-clusters-in-arps-loop-52114624.html
Galaxies and Star Clusters in Arp's Loop Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galaxies-and-star-clusters-in-arps-loop-52114624.htmlRMD0P0MG–Galaxies and Star Clusters in Arp's Loop
 The Coma Cluster of galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-coma-cluster-of-galaxies-18696319.html
The Coma Cluster of galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-coma-cluster-of-galaxies-18696319.htmlRFB2BK9K–The Coma Cluster of galaxies.
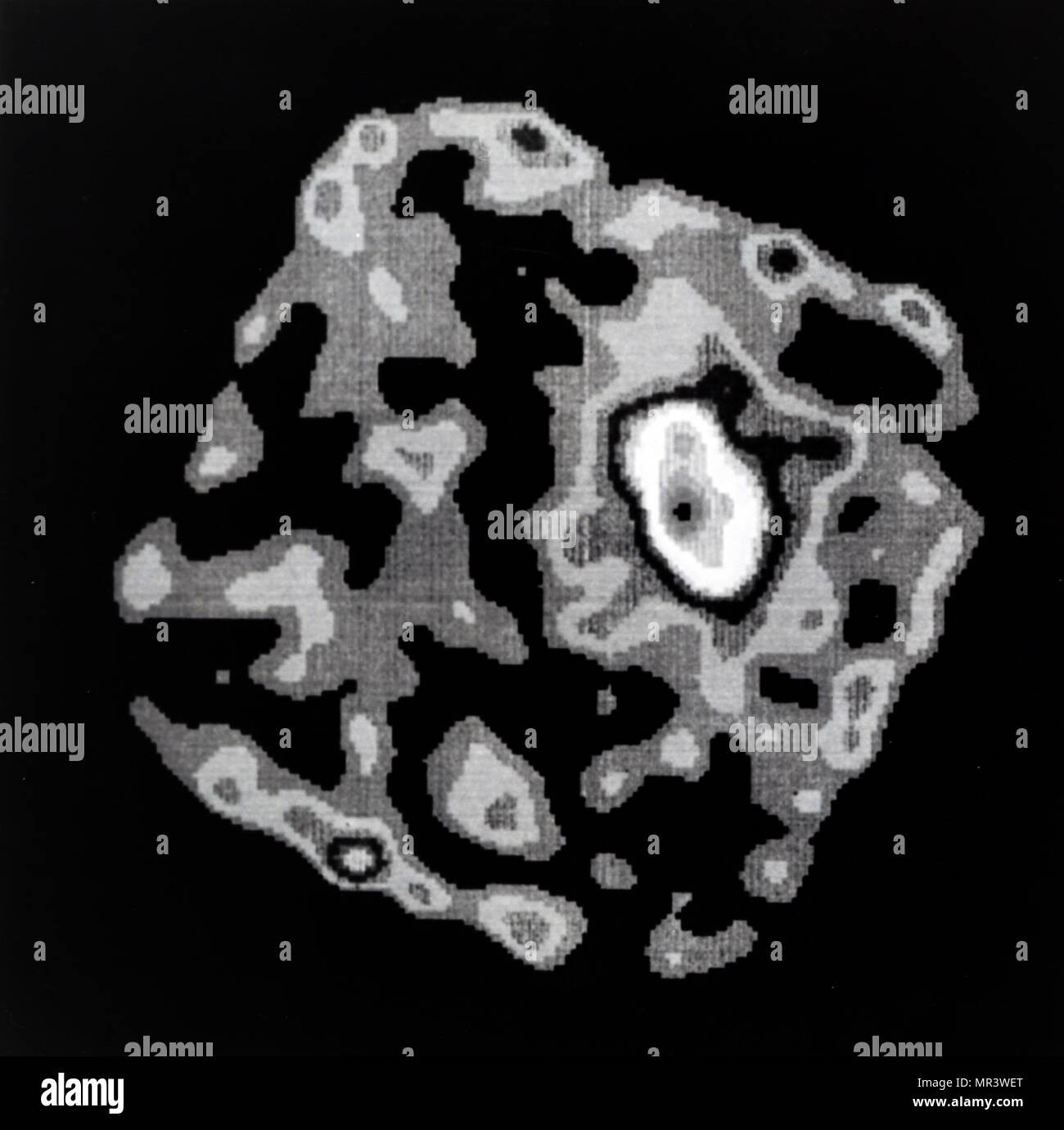 Cluster of galaxies known as Abell 2256. Galaxy clusters are traditionally strong x-ray emitters. The emission originates in the hot gas which is swept out of colliding galaxies and accumulates between galaxies. The gases are typically tens of millions degrees in temperature. The German Roentgen Satellite (ROAST) captured this 'first light' image as part of the satellite's orbital calibration and verification phase during June and July using NASA provided High Resolution Imager (HRI). ROAST is a joint international project involving Germany, the UK and the United States. Dated 20th century Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cluster-of-galaxies-known-as-abell-2256-galaxy-clusters-are-traditionally-strong-x-ray-emitters-the-emission-originates-in-the-hot-gas-which-is-swept-out-of-colliding-galaxies-and-accumulates-between-galaxies-the-gases-are-typically-tens-of-millions-degrees-in-temperature-the-german-roentgen-satellite-roast-captured-this-first-light-image-as-part-of-the-satellites-orbital-calibration-and-verification-phase-during-june-and-july-using-nasa-provided-high-resolution-imager-hri-roast-is-a-joint-international-project-involving-germany-the-uk-and-the-united-states-dated-20th-century-image186326640.html
Cluster of galaxies known as Abell 2256. Galaxy clusters are traditionally strong x-ray emitters. The emission originates in the hot gas which is swept out of colliding galaxies and accumulates between galaxies. The gases are typically tens of millions degrees in temperature. The German Roentgen Satellite (ROAST) captured this 'first light' image as part of the satellite's orbital calibration and verification phase during June and July using NASA provided High Resolution Imager (HRI). ROAST is a joint international project involving Germany, the UK and the United States. Dated 20th century Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cluster-of-galaxies-known-as-abell-2256-galaxy-clusters-are-traditionally-strong-x-ray-emitters-the-emission-originates-in-the-hot-gas-which-is-swept-out-of-colliding-galaxies-and-accumulates-between-galaxies-the-gases-are-typically-tens-of-millions-degrees-in-temperature-the-german-roentgen-satellite-roast-captured-this-first-light-image-as-part-of-the-satellites-orbital-calibration-and-verification-phase-during-june-and-july-using-nasa-provided-high-resolution-imager-hri-roast-is-a-joint-international-project-involving-germany-the-uk-and-the-united-states-dated-20th-century-image186326640.htmlRMMR3WET–Cluster of galaxies known as Abell 2256. Galaxy clusters are traditionally strong x-ray emitters. The emission originates in the hot gas which is swept out of colliding galaxies and accumulates between galaxies. The gases are typically tens of millions degrees in temperature. The German Roentgen Satellite (ROAST) captured this 'first light' image as part of the satellite's orbital calibration and verification phase during June and July using NASA provided High Resolution Imager (HRI). ROAST is a joint international project involving Germany, the UK and the United States. Dated 20th century
 Coma cluster of galaxies The Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) is a large cluster of galaxies that contains over 1,000 identified galaxies. Along with the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367) it is one of the two major clusters comprising the Coma Supercluster.. The cluster's mean distance from Earth is 99 Mpc (321 million light years). Its ten brightest spiral galaxies have apparent magnitudes of 12-14 that are observable with amateur telescopes larger than 20 cm. The central region is dominated by two giant elliptical galaxies: NGC 4874 and NGC 4889. The cluster is within a few degrees of the north galactic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/coma-cluster-of-galaxies-the-coma-cluster-abell-1656-is-a-large-cluster-of-galaxies-that-contains-over-1000-identified-galaxies-along-with-the-leo-cluster-abell-1367-it-is-one-of-the-two-major-clusters-comprising-the-coma-supercluster-the-clusters-mean-distance-from-earth-is-99-mpc-321-million-light-years-its-ten-brightest-spiral-galaxies-have-apparent-magnitudes-of-12-14-that-are-observable-with-amateur-telescopes-larger-than-20-cm-the-central-region-is-dominated-by-two-giant-elliptical-galaxies-ngc-4874-and-ngc-4889-the-cluster-is-within-a-few-degrees-of-the-north-galactic-image268850243.html
Coma cluster of galaxies The Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) is a large cluster of galaxies that contains over 1,000 identified galaxies. Along with the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367) it is one of the two major clusters comprising the Coma Supercluster.. The cluster's mean distance from Earth is 99 Mpc (321 million light years). Its ten brightest spiral galaxies have apparent magnitudes of 12-14 that are observable with amateur telescopes larger than 20 cm. The central region is dominated by two giant elliptical galaxies: NGC 4874 and NGC 4889. The cluster is within a few degrees of the north galactic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/coma-cluster-of-galaxies-the-coma-cluster-abell-1656-is-a-large-cluster-of-galaxies-that-contains-over-1000-identified-galaxies-along-with-the-leo-cluster-abell-1367-it-is-one-of-the-two-major-clusters-comprising-the-coma-supercluster-the-clusters-mean-distance-from-earth-is-99-mpc-321-million-light-years-its-ten-brightest-spiral-galaxies-have-apparent-magnitudes-of-12-14-that-are-observable-with-amateur-telescopes-larger-than-20-cm-the-central-region-is-dominated-by-two-giant-elliptical-galaxies-ngc-4874-and-ngc-4889-the-cluster-is-within-a-few-degrees-of-the-north-galactic-image268850243.htmlRMWHB56B–Coma cluster of galaxies The Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) is a large cluster of galaxies that contains over 1,000 identified galaxies. Along with the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367) it is one of the two major clusters comprising the Coma Supercluster.. The cluster's mean distance from Earth is 99 Mpc (321 million light years). Its ten brightest spiral galaxies have apparent magnitudes of 12-14 that are observable with amateur telescopes larger than 20 cm. The central region is dominated by two giant elliptical galaxies: NGC 4874 and NGC 4889. The cluster is within a few degrees of the north galactic
 Galaxies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/galaxies-image184212785.html
Galaxies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/galaxies-image184212785.htmlRMMKKH81–Galaxies
 Star Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-star-clusters-105292198.html
Star Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-star-clusters-105292198.htmlRMG38D7J–Star Clusters
 Galactic Center, Milky Way and Star Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galactic-center-milky-way-and-star-clusters-135021292.html
Galactic Center, Milky Way and Star Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galactic-center-milky-way-and-star-clusters-135021292.htmlRMHRJN10–Galactic Center, Milky Way and Star Clusters
 Star Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-clusters-image5547707.html
Star Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-clusters-image5547707.htmlRMAY4PBC–Star Clusters
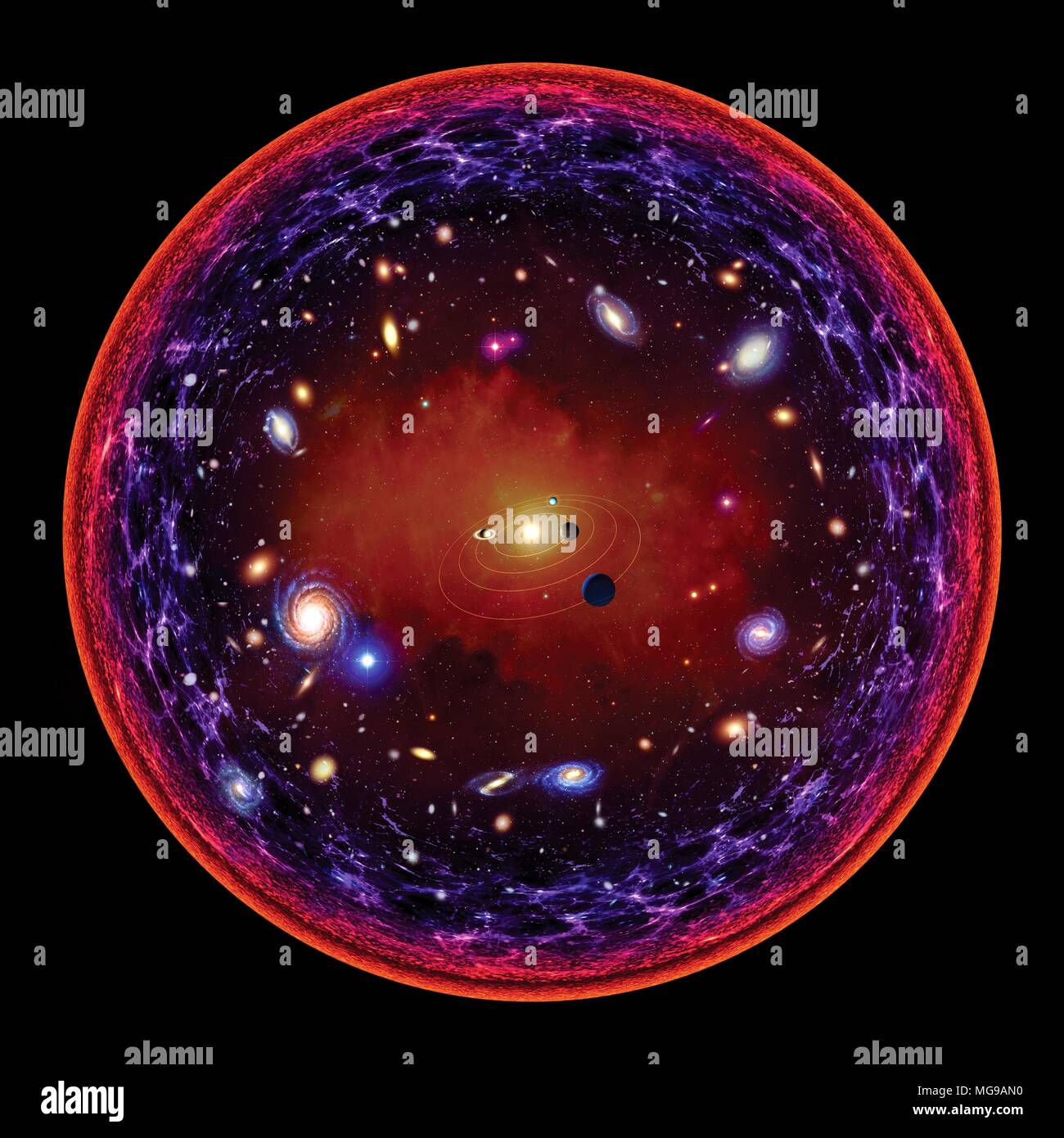 A conceptual illustration of the visible Universe. At the centre is the Solar System. As we move farther away, we encounter first stars, then galaxies. The farther into space we look, the deeper back in time we see, because of the finite speed of light. The furthest we can see is the point at which the universe became transparent - when the density of matter permitted photons to travel through the universe without absorption. This is depicted at the edge of the circle. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-conceptual-illustration-of-the-visible-universe-at-the-centre-is-the-solar-system-as-we-move-farther-away-we-encounter-first-stars-then-galaxies-the-farther-into-space-we-look-the-deeper-back-in-time-we-see-because-of-the-finite-speed-of-light-the-furthest-we-can-see-is-the-point-at-which-the-universe-became-transparent-when-the-density-of-matter-permitted-photons-to-travel-through-the-universe-without-absorption-this-is-depicted-at-the-edge-of-the-circle-image182144172.html
A conceptual illustration of the visible Universe. At the centre is the Solar System. As we move farther away, we encounter first stars, then galaxies. The farther into space we look, the deeper back in time we see, because of the finite speed of light. The furthest we can see is the point at which the universe became transparent - when the density of matter permitted photons to travel through the universe without absorption. This is depicted at the edge of the circle. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-conceptual-illustration-of-the-visible-universe-at-the-centre-is-the-solar-system-as-we-move-farther-away-we-encounter-first-stars-then-galaxies-the-farther-into-space-we-look-the-deeper-back-in-time-we-see-because-of-the-finite-speed-of-light-the-furthest-we-can-see-is-the-point-at-which-the-universe-became-transparent-when-the-density-of-matter-permitted-photons-to-travel-through-the-universe-without-absorption-this-is-depicted-at-the-edge-of-the-circle-image182144172.htmlRFMG9AN0–A conceptual illustration of the visible Universe. At the centre is the Solar System. As we move farther away, we encounter first stars, then galaxies. The farther into space we look, the deeper back in time we see, because of the finite speed of light. The furthest we can see is the point at which the universe became transparent - when the density of matter permitted photons to travel through the universe without absorption. This is depicted at the edge of the circle.
 Antennae galaxies in the process of colliding Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/antennae-galaxies-in-the-process-of-colliding-image66433237.html
Antennae galaxies in the process of colliding Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/antennae-galaxies-in-the-process-of-colliding-image66433237.htmlRMDT287H–Antennae galaxies in the process of colliding
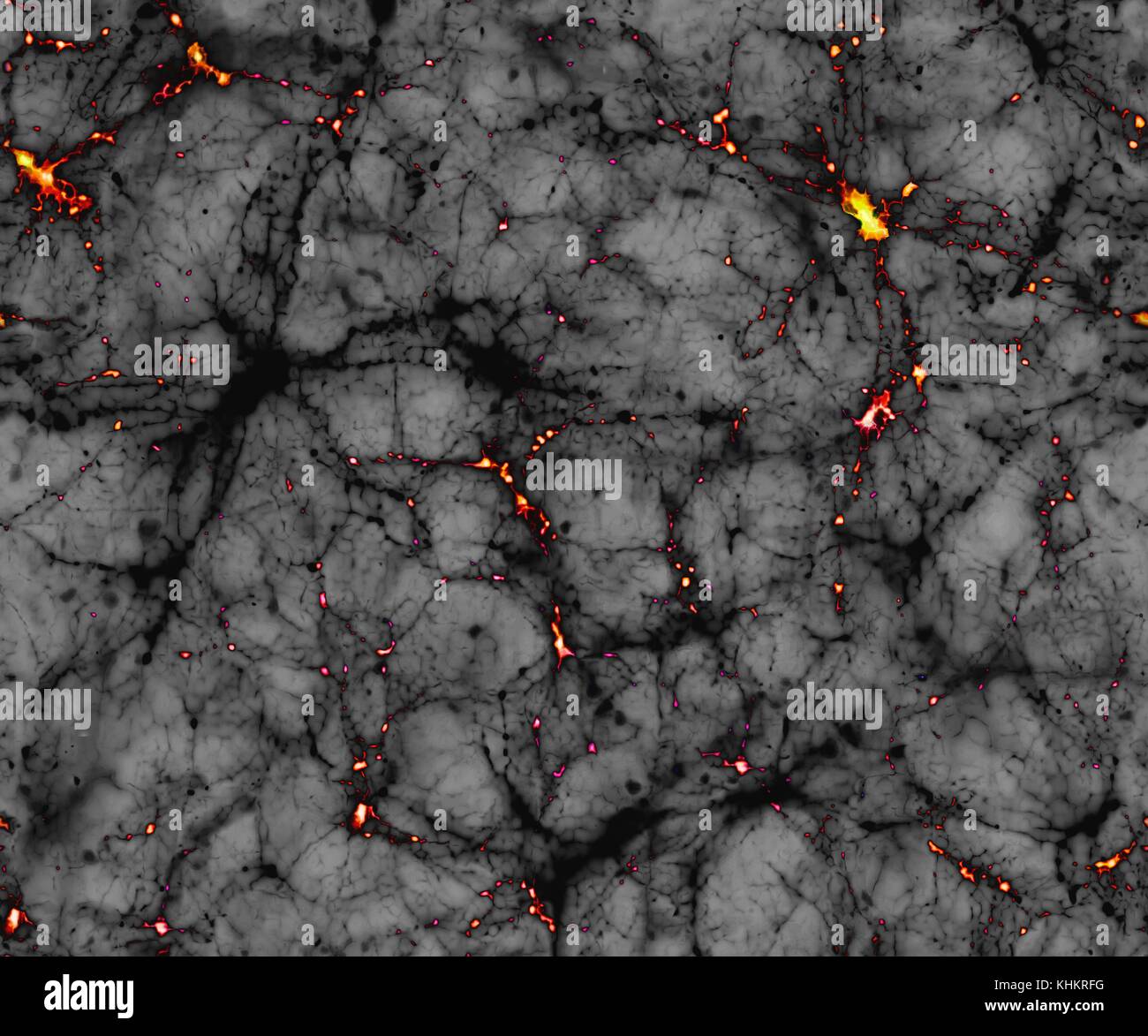 Dark matter, conceptual illustration. The image represents a region of space a few hundred megaparsecs across. Dark matter is a form of matter that cannot be detected by telescopes as it emits no radiation. It is thought that cold dark matter first formed after the Big Bang. This matter then collapsed under its own weight to form vast halos (bright yellow) which sucked in normal matter to form visible matter, such as galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-dark-matter-conceptual-illustration-the-image-represents-a-region-165778020.html
Dark matter, conceptual illustration. The image represents a region of space a few hundred megaparsecs across. Dark matter is a form of matter that cannot be detected by telescopes as it emits no radiation. It is thought that cold dark matter first formed after the Big Bang. This matter then collapsed under its own weight to form vast halos (bright yellow) which sucked in normal matter to form visible matter, such as galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-dark-matter-conceptual-illustration-the-image-represents-a-region-165778020.htmlRFKHKRFG–Dark matter, conceptual illustration. The image represents a region of space a few hundred megaparsecs across. Dark matter is a form of matter that cannot be detected by telescopes as it emits no radiation. It is thought that cold dark matter first formed after the Big Bang. This matter then collapsed under its own weight to form vast halos (bright yellow) which sucked in normal matter to form visible matter, such as galaxies.
 astronomy, star clusters, omega fog, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-omega-fog-astronomies-image455934338.html
astronomy, star clusters, omega fog, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-omega-fog-astronomies-image455934338.htmlRF2HDNGW6–astronomy, star clusters, omega fog, astronomies
 A delicate tracery of dust and bright star clusters threads across this image from the James Webb Space Telescope. This view from the NIRCam instrument is studded by the galaxy's massive population of stars, most dense along its bright central bar, along with burning red clouds of gas illuminated by young stars within. These stars belong to the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068, located circa 17m light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo. This portrait of NGC 5068 is part of a campaign to create a repository of observations of star formation in nearby galaxies. Credit: NASA/ESA/CSA Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-delicate-tracery-of-dust-and-bright-star-clusters-threads-across-this-image-from-the-james-webb-space-telescope-this-view-from-the-nircam-instrument-is-studded-by-the-galaxys-massive-population-of-stars-most-dense-along-its-bright-central-bar-along-with-burning-red-clouds-of-gas-illuminated-by-young-stars-within-these-stars-belong-to-the-barred-spiral-galaxy-ngc-5068-located-circa-17m-light-years-from-earth-in-the-constellation-virgo-this-portrait-of-ngc-5068-is-part-of-a-campaign-to-create-a-repository-of-observations-of-star-formation-in-nearby-galaxies-credit-nasaesacsa-image601444227.html
A delicate tracery of dust and bright star clusters threads across this image from the James Webb Space Telescope. This view from the NIRCam instrument is studded by the galaxy's massive population of stars, most dense along its bright central bar, along with burning red clouds of gas illuminated by young stars within. These stars belong to the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068, located circa 17m light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo. This portrait of NGC 5068 is part of a campaign to create a repository of observations of star formation in nearby galaxies. Credit: NASA/ESA/CSA Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-delicate-tracery-of-dust-and-bright-star-clusters-threads-across-this-image-from-the-james-webb-space-telescope-this-view-from-the-nircam-instrument-is-studded-by-the-galaxys-massive-population-of-stars-most-dense-along-its-bright-central-bar-along-with-burning-red-clouds-of-gas-illuminated-by-young-stars-within-these-stars-belong-to-the-barred-spiral-galaxy-ngc-5068-located-circa-17m-light-years-from-earth-in-the-constellation-virgo-this-portrait-of-ngc-5068-is-part-of-a-campaign-to-create-a-repository-of-observations-of-star-formation-in-nearby-galaxies-credit-nasaesacsa-image601444227.htmlRM2WXE46Y–A delicate tracery of dust and bright star clusters threads across this image from the James Webb Space Telescope. This view from the NIRCam instrument is studded by the galaxy's massive population of stars, most dense along its bright central bar, along with burning red clouds of gas illuminated by young stars within. These stars belong to the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068, located circa 17m light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo. This portrait of NGC 5068 is part of a campaign to create a repository of observations of star formation in nearby galaxies. Credit: NASA/ESA/CSA
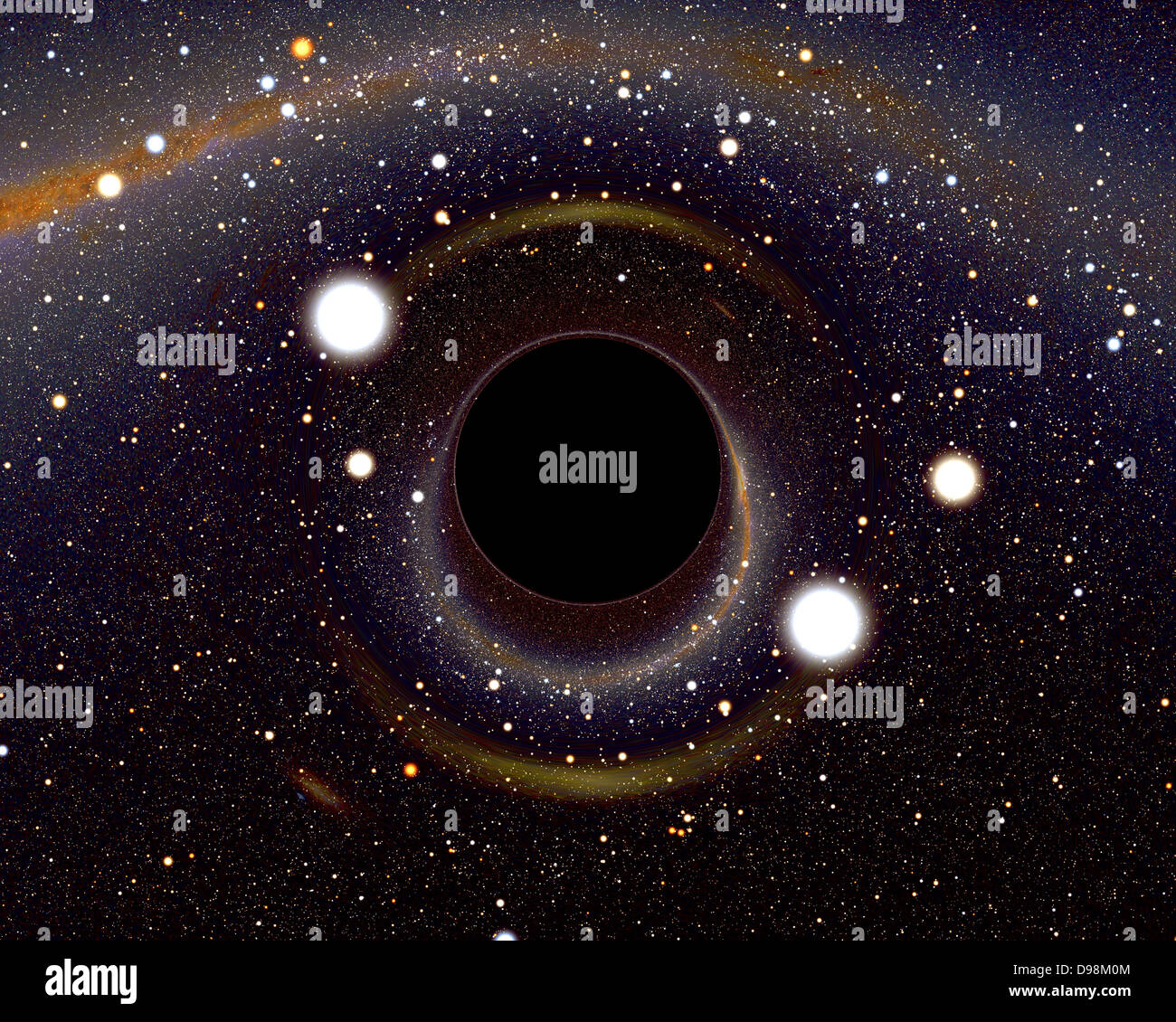 Computer image if a black hole light from every direction is bent around and comes back to you. The original background map was taken from the 2MASS infrared sky survey, with stars from the Henry Draper catalogue superposed. Black holes are thought to be the densest state of matter, and there is indirect evidence for their presence in stellar binary systems and the centres of globular clusters, galaxies, and quasars. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-computer-image-if-a-black-hole-light-from-every-direction-is-bent-57354324.html
Computer image if a black hole light from every direction is bent around and comes back to you. The original background map was taken from the 2MASS infrared sky survey, with stars from the Henry Draper catalogue superposed. Black holes are thought to be the densest state of matter, and there is indirect evidence for their presence in stellar binary systems and the centres of globular clusters, galaxies, and quasars. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-computer-image-if-a-black-hole-light-from-every-direction-is-bent-57354324.htmlRMD98M0M–Computer image if a black hole light from every direction is bent around and comes back to you. The original background map was taken from the 2MASS infrared sky survey, with stars from the Henry Draper catalogue superposed. Black holes are thought to be the densest state of matter, and there is indirect evidence for their presence in stellar binary systems and the centres of globular clusters, galaxies, and quasars.
 The visual grouping of five galaxies known as Stephans Quintet captured by the NASA Webb Telescope showing sparkling clusters of millions of young stars and starburst regions of fresh star being born, released from Goddard Space Flight Center July 12, 2022 in Greenbelt, Maryland. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-visual-grouping-of-five-galaxies-known-as-stephans-quintet-captured-by-the-nasa-webb-telescope-showing-sparkling-clusters-of-millions-of-young-stars-and-starburst-regions-of-fresh-star-being-born-released-from-goddard-space-flight-center-july-12-2022-in-greenbelt-maryland-image475561244.html
The visual grouping of five galaxies known as Stephans Quintet captured by the NASA Webb Telescope showing sparkling clusters of millions of young stars and starburst regions of fresh star being born, released from Goddard Space Flight Center July 12, 2022 in Greenbelt, Maryland. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-visual-grouping-of-five-galaxies-known-as-stephans-quintet-captured-by-the-nasa-webb-telescope-showing-sparkling-clusters-of-millions-of-young-stars-and-starburst-regions-of-fresh-star-being-born-released-from-goddard-space-flight-center-july-12-2022-in-greenbelt-maryland-image475561244.htmlRM2JHKK64–The visual grouping of five galaxies known as Stephans Quintet captured by the NASA Webb Telescope showing sparkling clusters of millions of young stars and starburst regions of fresh star being born, released from Goddard Space Flight Center July 12, 2022 in Greenbelt, Maryland.
 Jun. 06, 1984 - Kennedy Space Center, Fla.,--Technicians install the last major experiment called the ''Hard X-Ray Imaging of Clusters of Galaxies and Other Extended X-Ray Sources,'' on a Space lab 2 pallet in the Operations and Checkout train and will mark the first flight of the Igloo and Instrument Pointing System. The experiment, which consists of two identical X-ray telescopes will record images and spectra of extended X-ray sources which will be used to identify the sources and omission mechanisms Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/jun-06-1984-kennedy-space-center-fla-technicians-install-the-last-image69503043.html
Jun. 06, 1984 - Kennedy Space Center, Fla.,--Technicians install the last major experiment called the ''Hard X-Ray Imaging of Clusters of Galaxies and Other Extended X-Ray Sources,'' on a Space lab 2 pallet in the Operations and Checkout train and will mark the first flight of the Igloo and Instrument Pointing System. The experiment, which consists of two identical X-ray telescopes will record images and spectra of extended X-ray sources which will be used to identify the sources and omission mechanisms Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/jun-06-1984-kennedy-space-center-fla-technicians-install-the-last-image69503043.htmlRME123RF–Jun. 06, 1984 - Kennedy Space Center, Fla.,--Technicians install the last major experiment called the ''Hard X-Ray Imaging of Clusters of Galaxies and Other Extended X-Ray Sources,'' on a Space lab 2 pallet in the Operations and Checkout train and will mark the first flight of the Igloo and Instrument Pointing System. The experiment, which consists of two identical X-ray telescopes will record images and spectra of extended X-ray sources which will be used to identify the sources and omission mechanisms
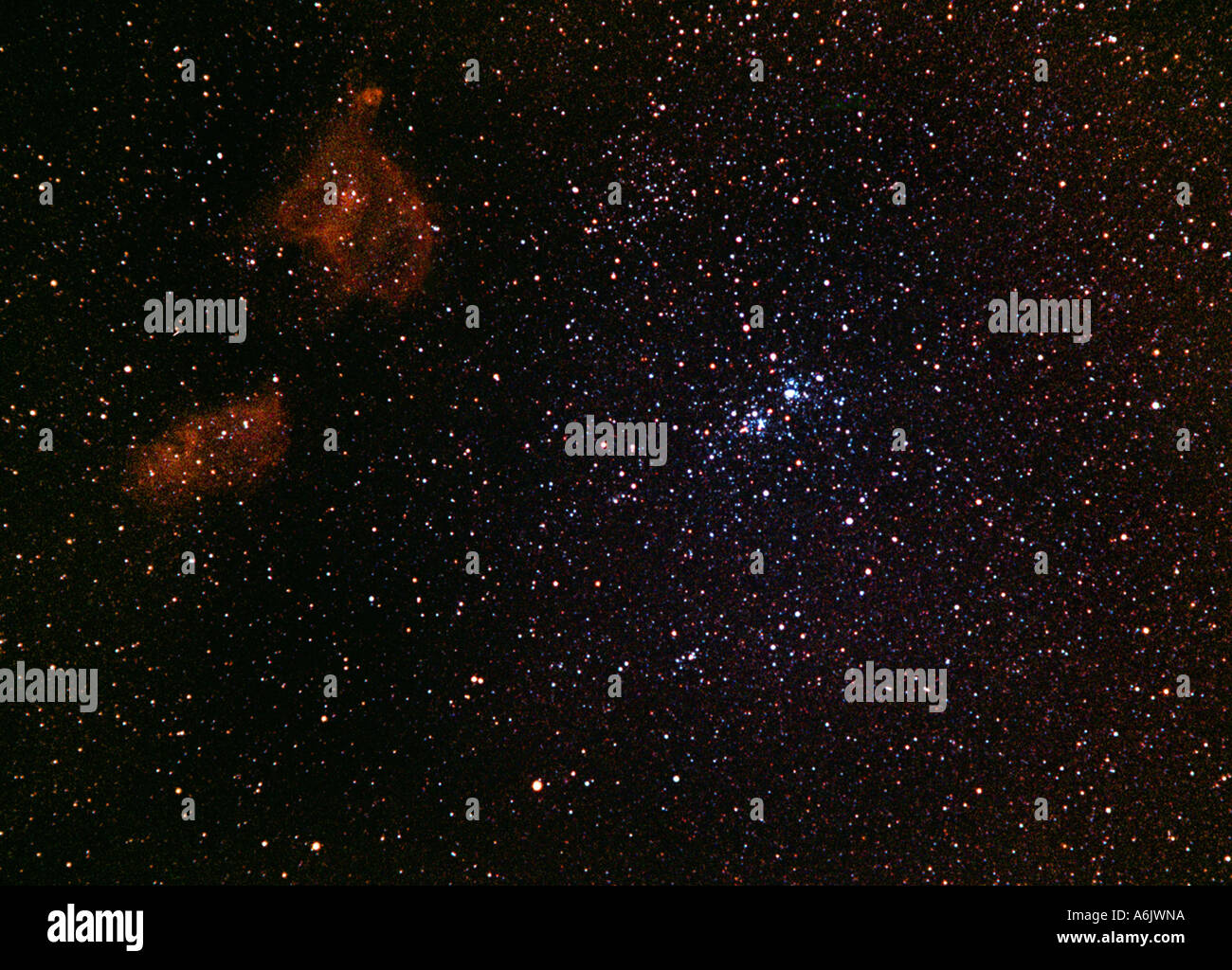 open clusters h and chi, NGC 869, NGC 884 in constellation Perseus, Germany, Baden-Wuerttemberg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-clusters-h-and-chi-ngc-869-ngc-884-in-constellation-perseus-germany-image6624537.html
open clusters h and chi, NGC 869, NGC 884 in constellation Perseus, Germany, Baden-Wuerttemberg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-clusters-h-and-chi-ngc-869-ngc-884-in-constellation-perseus-germany-image6624537.htmlRMA6JWNA–open clusters h and chi, NGC 869, NGC 884 in constellation Perseus, Germany, Baden-Wuerttemberg
 A spiral Galaxy in the Universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-spiral-galaxy-in-the-universe-image274164998.html
A spiral Galaxy in the Universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-spiral-galaxy-in-the-universe-image274164998.htmlRMWX1872–A spiral Galaxy in the Universe.
 1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-50539073.html
1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-50539073.htmlRMCX672W–1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae
 Messier 74, also called NGC 628, is a stunning example of a 'grand-design' spiral galaxy that is viewed by Earth observers nearly face-on. Its perfectly symmetrical spiral arms emanate from the central nucleus and are dotted with clusters of young blue stars and glowing pink regions of ionized hydrogen . Image source NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/messier-74-also-called-ngc-628-is-a-stunning-example-of-a-grand-design-spiral-galaxy-that-is-viewed-by-earth-observers-nearly-face-on-its-perfectly-symmetrical-spiral-arms-emanate-from-the-central-nucleus-and-are-dotted-with-clusters-of-young-blue-stars-and-glowing-pink-regions-of-ionized-hydrogen-image-source-nasaesa-hubble-space-telescope-image443555383.html
Messier 74, also called NGC 628, is a stunning example of a 'grand-design' spiral galaxy that is viewed by Earth observers nearly face-on. Its perfectly symmetrical spiral arms emanate from the central nucleus and are dotted with clusters of young blue stars and glowing pink regions of ionized hydrogen . Image source NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/messier-74-also-called-ngc-628-is-a-stunning-example-of-a-grand-design-spiral-galaxy-that-is-viewed-by-earth-observers-nearly-face-on-its-perfectly-symmetrical-spiral-arms-emanate-from-the-central-nucleus-and-are-dotted-with-clusters-of-young-blue-stars-and-glowing-pink-regions-of-ionized-hydrogen-image-source-nasaesa-hubble-space-telescope-image443555383.htmlRM2GNHKBK–Messier 74, also called NGC 628, is a stunning example of a 'grand-design' spiral galaxy that is viewed by Earth observers nearly face-on. Its perfectly symmetrical spiral arms emanate from the central nucleus and are dotted with clusters of young blue stars and glowing pink regions of ionized hydrogen . Image source NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope
 Description Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/description-image248510744.html
Description Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/description-image248510744.htmlRFTC8HYM–Description
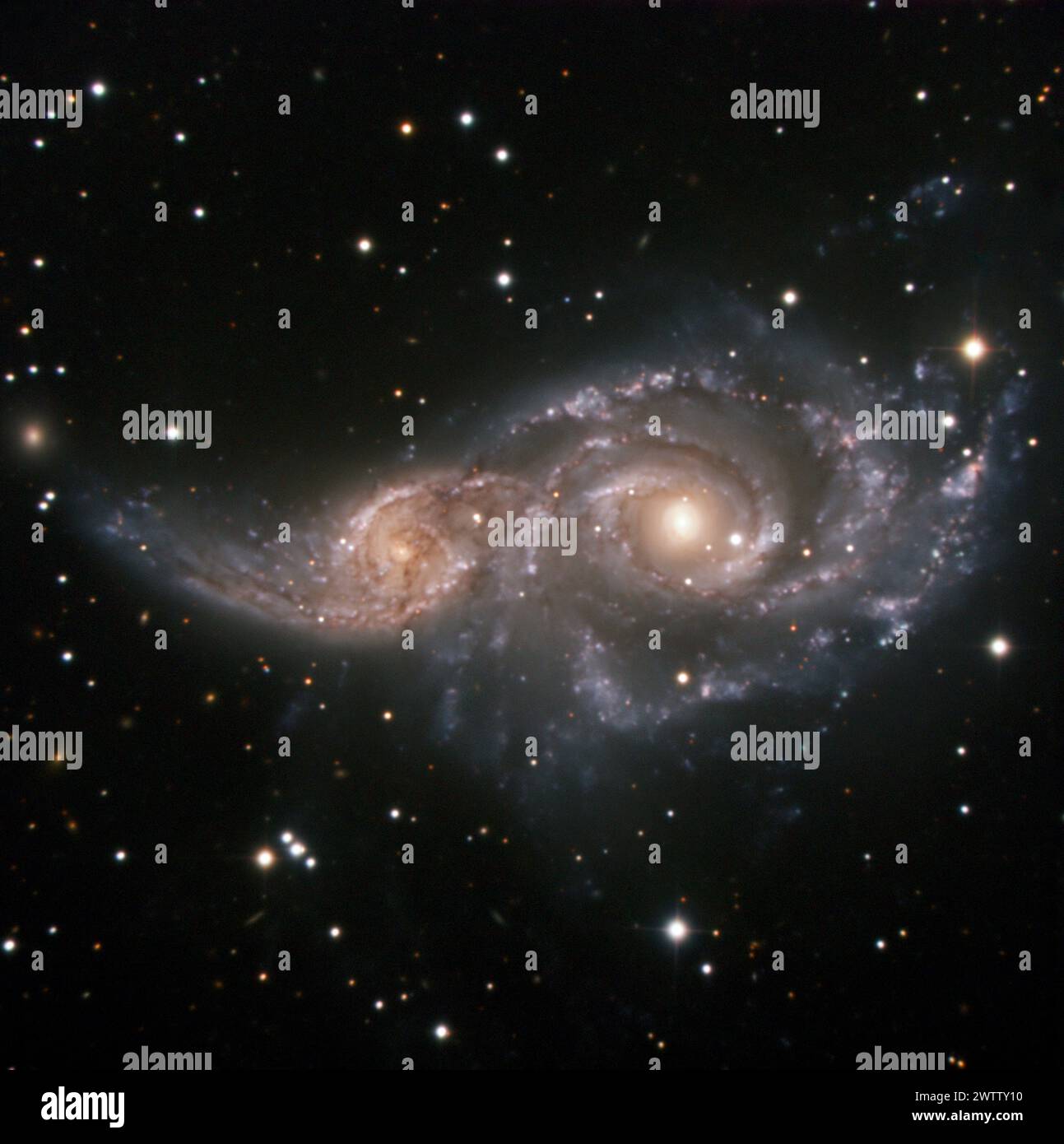 Interacting galaxies in space Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/interacting-galaxies-in-space-image600452300.html
Interacting galaxies in space Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/interacting-galaxies-in-space-image600452300.htmlRF2WTTY10–Interacting galaxies in space
 The Coma Berenices star cluster, with a smattering of galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-coma-berenices-star-cluster-with-a-smattering-of-galaxies-image431642717.html
The Coma Berenices star cluster, with a smattering of galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-coma-berenices-star-cluster-with-a-smattering-of-galaxies-image431642717.htmlRF2G270K9–The Coma Berenices star cluster, with a smattering of galaxies.
 1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-139468401.html
1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-139468401.htmlRMJ2W9A9–1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856
 The large star cluster in Coma Berenices called Mel 111, accompanied by several galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-large-star-cluster-in-coma-berenices-called-mel-111-accompanied-by-several-galaxies-image553196430.html
The large star cluster in Coma Berenices called Mel 111, accompanied by several galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-large-star-cluster-in-coma-berenices-called-mel-111-accompanied-by-several-galaxies-image553196430.htmlRF2R407KA–The large star cluster in Coma Berenices called Mel 111, accompanied by several galaxies.
 Abell 520 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-abell-520-134988692.html
Abell 520 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-abell-520-134988692.htmlRMHRH7CM–Abell 520
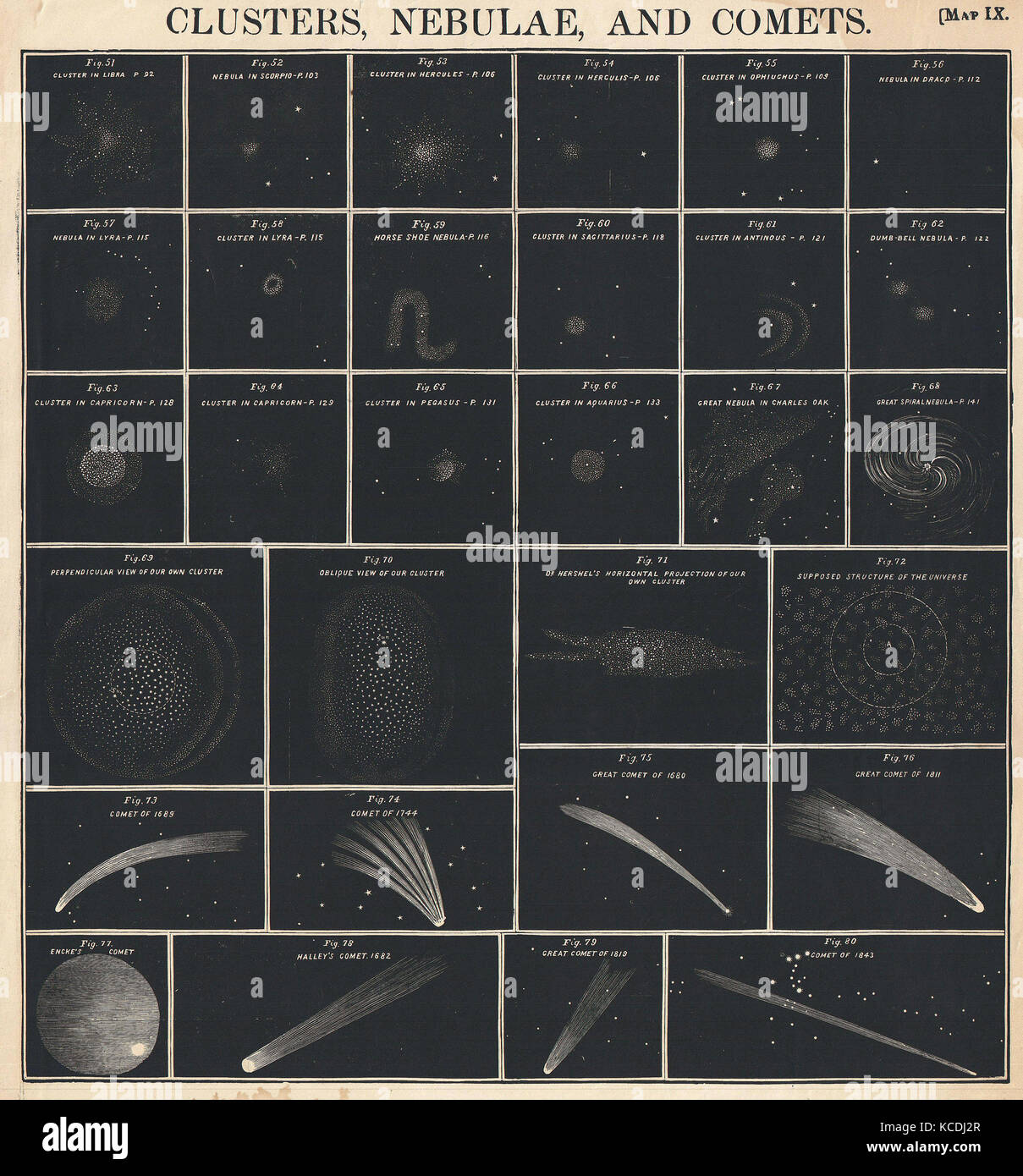 1856, Burritt, Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-162568751.html
1856, Burritt, Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-162568751.htmlRMKCDJ2R–1856, Burritt, Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae
 8 1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/8-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-nebulae-geographicus-comets2-burritt-1856-image214210426.html
8 1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/8-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-nebulae-geographicus-comets2-burritt-1856-image214210426.htmlRMPCE3GA–8 1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856
 Galaxy clusters mysteriously stream at a million miles per hour along a path centered aprox. on constellation Centaurus & Hydra Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galaxy-clusters-mysteriously-stream-at-a-million-miles-per-hour-along-34720723.html
Galaxy clusters mysteriously stream at a million miles per hour along a path centered aprox. on constellation Centaurus & Hydra Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galaxy-clusters-mysteriously-stream-at-a-million-miles-per-hour-along-34720723.htmlRMC0DJHR–Galaxy clusters mysteriously stream at a million miles per hour along a path centered aprox. on constellation Centaurus & Hydra
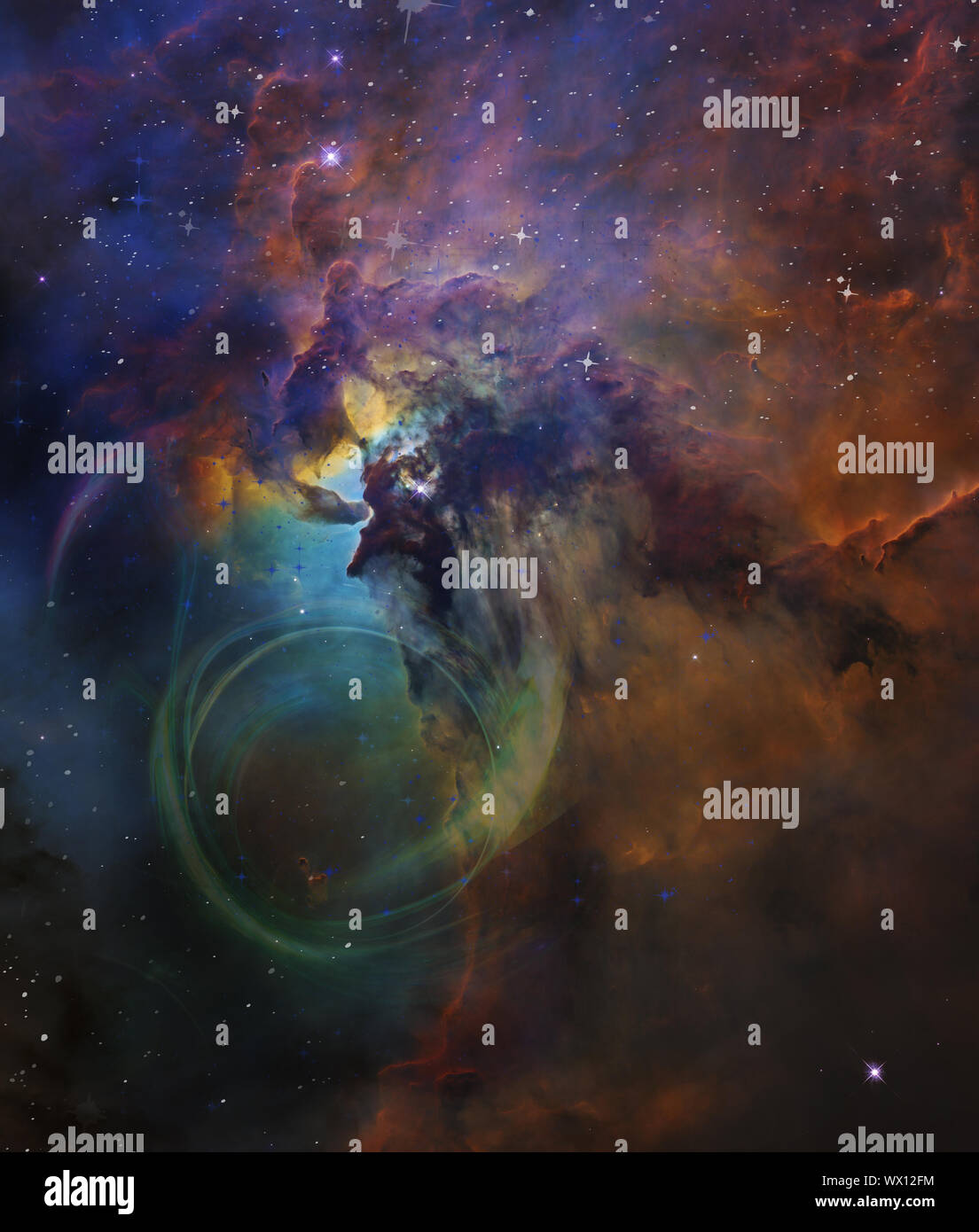 Star galaxies in the universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-galaxies-in-the-universe-image274160536.html
Star galaxies in the universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-galaxies-in-the-universe-image274160536.htmlRMWX12FM–Star galaxies in the universe.
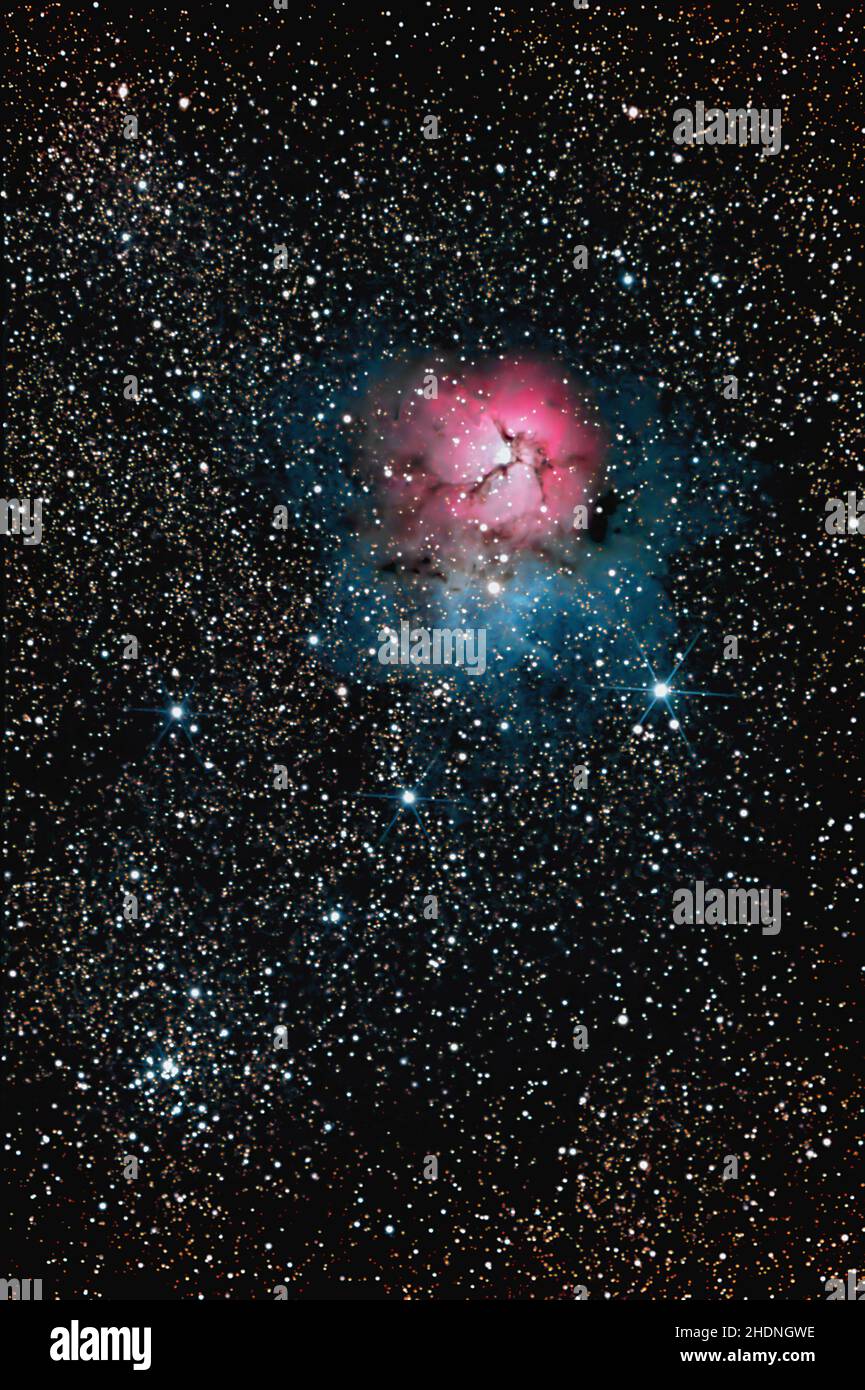 astronomy, star clusters, Trifid Nebula, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-trifid-nebula-astronomies-image455934346.html
astronomy, star clusters, Trifid Nebula, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-trifid-nebula-astronomies-image455934346.htmlRF2HDNGWE–astronomy, star clusters, Trifid Nebula, astronomies
 The Antennae galaxies, also known as NGC 4038/NGC 4039, are a pair of interacting galaxies in the constellation Corvus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-antennae-galaxies-also-known-as-ngc-4038ngc-4039-are-a-pair-of-image64844380.html
The Antennae galaxies, also known as NGC 4038/NGC 4039, are a pair of interacting galaxies in the constellation Corvus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-antennae-galaxies-also-known-as-ngc-4038ngc-4039-are-a-pair-of-image64844380.htmlRFDNDWJM–The Antennae galaxies, also known as NGC 4038/NGC 4039, are a pair of interacting galaxies in the constellation Corvus.
 These six images represent the potential for new images and discoveries housed in the Chandra Data Archive. To celebrate October as American Archive Month, these images - which include supernova remnants, pulsars, black holes, and clusters of galaxies - are being released. Each image represents data that are available to both the professional scientific community as well as the general public. 3c 295 cluster (or ClG J1411 5211) (Chandra - Hubble) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-these-six-images-represent-the-potential-for-new-images-and-discoveries-169456231.html
These six images represent the potential for new images and discoveries housed in the Chandra Data Archive. To celebrate October as American Archive Month, these images - which include supernova remnants, pulsars, black holes, and clusters of galaxies - are being released. Each image represents data that are available to both the professional scientific community as well as the general public. 3c 295 cluster (or ClG J1411 5211) (Chandra - Hubble) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-these-six-images-represent-the-potential-for-new-images-and-discoveries-169456231.htmlRMKRKB47–These six images represent the potential for new images and discoveries housed in the Chandra Data Archive. To celebrate October as American Archive Month, these images - which include supernova remnants, pulsars, black holes, and clusters of galaxies - are being released. Each image represents data that are available to both the professional scientific community as well as the general public. 3c 295 cluster (or ClG J1411 5211) (Chandra - Hubble)
 Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/swirling-galaxy-flame-fractal-art-image476488008.html
Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/swirling-galaxy-flame-fractal-art-image476488008.htmlRM2JK5W8T–Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art
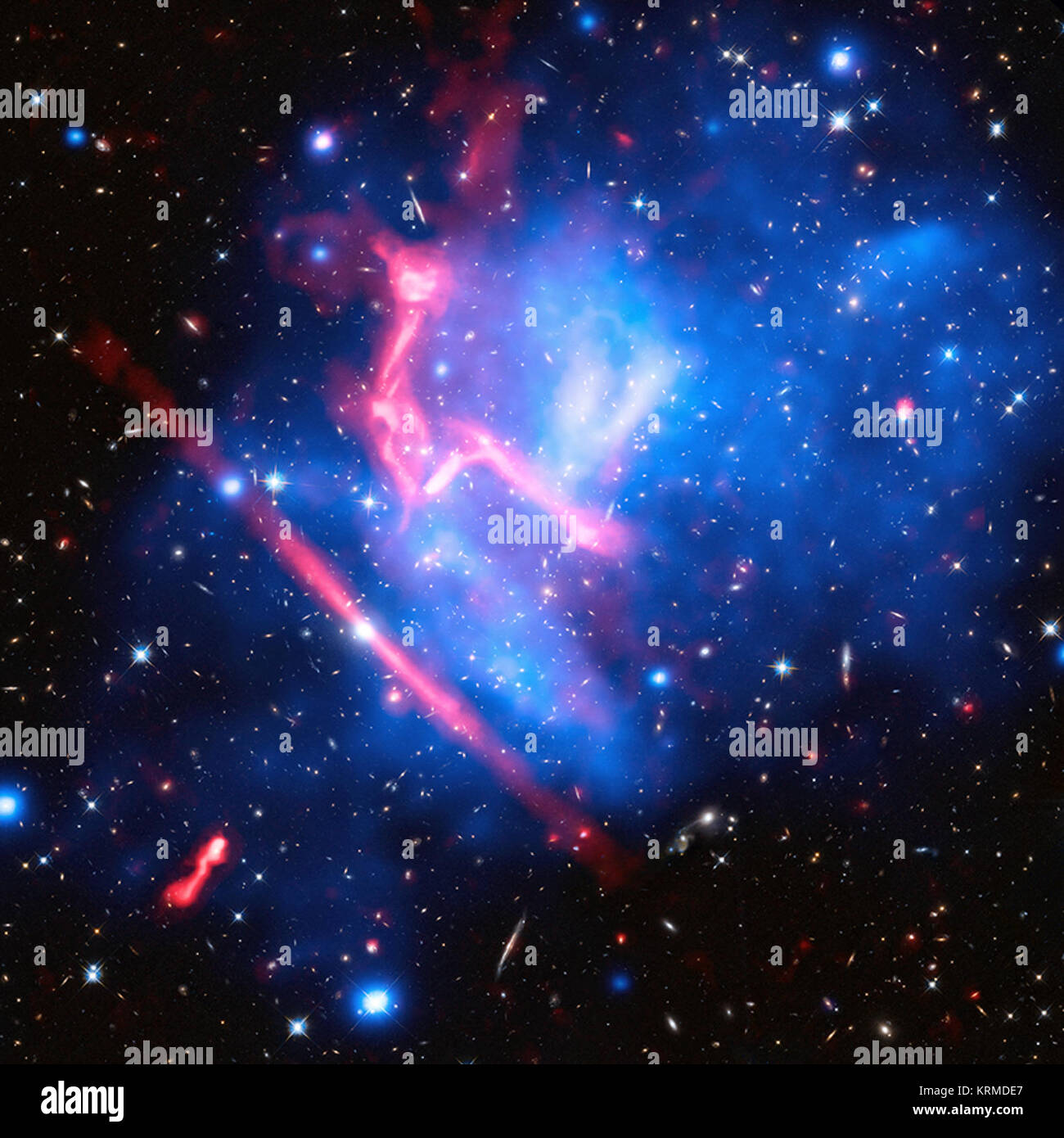 These two galaxy clusters are part of the 'Frontier Fields' project, which uses some of the world's most powerful telescopes to study these giant structures with long observations. Galaxy clusters are enormous collections of hundreds or thousands of galaxies and vast reservoirs of hot gas embedded in massive clouds of dark matter. These images contain X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical light from Hubble (red, green, and blue), and radio data from the Very Large Array (pink). MACS J0717.5 3745 (Chandra) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-these-two-galaxy-clusters-are-part-of-the-frontier-fields-project-169480031.html
These two galaxy clusters are part of the 'Frontier Fields' project, which uses some of the world's most powerful telescopes to study these giant structures with long observations. Galaxy clusters are enormous collections of hundreds or thousands of galaxies and vast reservoirs of hot gas embedded in massive clouds of dark matter. These images contain X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical light from Hubble (red, green, and blue), and radio data from the Very Large Array (pink). MACS J0717.5 3745 (Chandra) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-these-two-galaxy-clusters-are-part-of-the-frontier-fields-project-169480031.htmlRMKRMDE7–These two galaxy clusters are part of the 'Frontier Fields' project, which uses some of the world's most powerful telescopes to study these giant structures with long observations. Galaxy clusters are enormous collections of hundreds or thousands of galaxies and vast reservoirs of hot gas embedded in massive clouds of dark matter. These images contain X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical light from Hubble (red, green, and blue), and radio data from the Very Large Array (pink). MACS J0717.5 3745 (Chandra)
 open clusters h and chi, NGC 869, NGC 884 in constellation Perseus, Germany, Baden-Wuerttemberg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-clusters-h-and-chi-ngc-869-ngc-884-in-constellation-perseus-germany-image6624528.html
open clusters h and chi, NGC 869, NGC 884 in constellation Perseus, Germany, Baden-Wuerttemberg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/open-clusters-h-and-chi-ngc-869-ngc-884-in-constellation-perseus-germany-image6624528.htmlRMA6JWN1–open clusters h and chi, NGC 869, NGC 884 in constellation Perseus, Germany, Baden-Wuerttemberg
 Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/swirling-galaxy-flame-fractal-art-image476269530.html
Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/swirling-galaxy-flame-fractal-art-image476269530.htmlRM2JJRXJ2–Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art
 1856 Burritt Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Geographicus Comets2 burritt 1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-132409367.html
1856 Burritt Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Geographicus Comets2 burritt 1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-132409367.htmlRMHKBNDY–1856 Burritt Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Geographicus Comets2 burritt 1856
 This new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of the Antennae galaxies is the sharpest yet of this merging pair of galaxies. During the course of the collision, billions of stars will be formed. The brightest and most compact of these star birth regions are called super star clusters. The two spiral galaxies started to interact a few hundred million years ago, making the Antennae galaxies one of the nearest and youngest examples of a pair of colliding galaxies. Nearly half of the faint objects in the Antennae image are young clusters containing tens of thousands of stars. The orange blobs to th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-new-nasa-hubble-space-telescope-image-of-the-antennae-galaxies-is-the-sharpest-yet-of-this-merging-pair-of-galaxies-during-the-course-of-the-collision-billions-of-stars-will-be-formed-the-brightest-and-most-compact-of-these-star-birth-regions-are-called-super-star-clusters-the-two-spiral-galaxies-started-to-interact-a-few-hundred-million-years-ago-making-the-antennae-galaxies-one-of-the-nearest-and-youngest-examples-of-a-pair-of-colliding-galaxies-nearly-half-of-the-faint-objects-in-the-antennae-image-are-young-clusters-containing-tens-of-thousands-of-stars-the-orange-blobs-to-th-image335177743.html
This new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of the Antennae galaxies is the sharpest yet of this merging pair of galaxies. During the course of the collision, billions of stars will be formed. The brightest and most compact of these star birth regions are called super star clusters. The two spiral galaxies started to interact a few hundred million years ago, making the Antennae galaxies one of the nearest and youngest examples of a pair of colliding galaxies. Nearly half of the faint objects in the Antennae image are young clusters containing tens of thousands of stars. The orange blobs to th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-new-nasa-hubble-space-telescope-image-of-the-antennae-galaxies-is-the-sharpest-yet-of-this-merging-pair-of-galaxies-during-the-course-of-the-collision-billions-of-stars-will-be-formed-the-brightest-and-most-compact-of-these-star-birth-regions-are-called-super-star-clusters-the-two-spiral-galaxies-started-to-interact-a-few-hundred-million-years-ago-making-the-antennae-galaxies-one-of-the-nearest-and-youngest-examples-of-a-pair-of-colliding-galaxies-nearly-half-of-the-faint-objects-in-the-antennae-image-are-young-clusters-containing-tens-of-thousands-of-stars-the-orange-blobs-to-th-image335177743.htmlRF2AD8JHK–This new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of the Antennae galaxies is the sharpest yet of this merging pair of galaxies. During the course of the collision, billions of stars will be formed. The brightest and most compact of these star birth regions are called super star clusters. The two spiral galaxies started to interact a few hundred million years ago, making the Antennae galaxies one of the nearest and youngest examples of a pair of colliding galaxies. Nearly half of the faint objects in the Antennae image are young clusters containing tens of thousands of stars. The orange blobs to th
 Description Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/description-image248237242.html
Description Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/description-image248237242.htmlRFTBT53P–Description
 Starry night sky with galaxies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/starry-night-sky-with-galaxies-image567150091.html
Starry night sky with galaxies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/starry-night-sky-with-galaxies-image567150091.htmlRF2RXKWMB–Starry night sky with galaxies
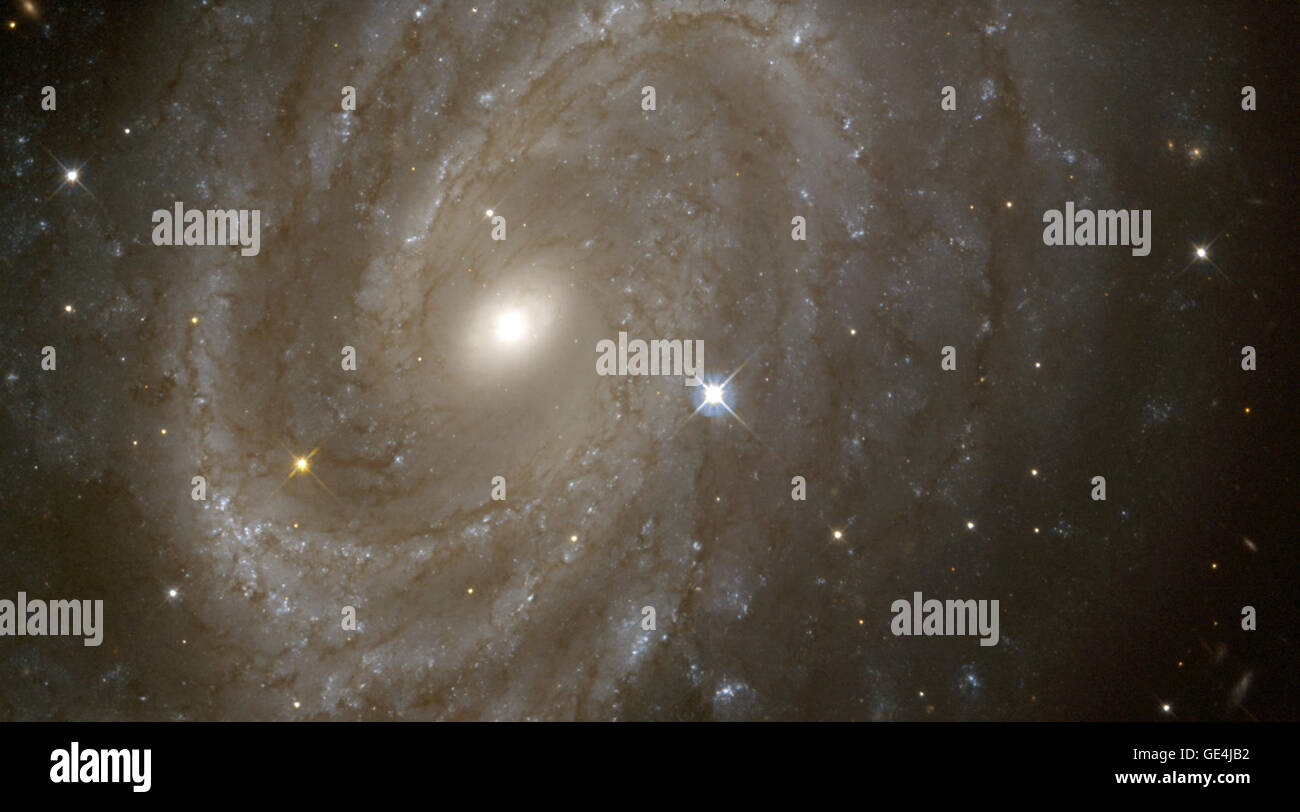 A NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) view of the magnificent spiral galaxy NGC 4603, the most distant galaxy in which a special class of pulsating stars called Cepheid variables have been found. It is associated with the Centaurus cluster, one of the most massive assemblages of galaxies in the nearby universe. The Local Group of galaxies, of which the Milky Way is a member, is moving in the direction of Centaurus at a speed of more than a million miles an hour under the influence of the gravitational pull of the matter in that direction. Clusters of young bright blue stars highlight the galaxy' Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-nasa-hubble-space-telescope-hst-view-of-the-magnificent-spiral-galaxy-111969622.html
A NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) view of the magnificent spiral galaxy NGC 4603, the most distant galaxy in which a special class of pulsating stars called Cepheid variables have been found. It is associated with the Centaurus cluster, one of the most massive assemblages of galaxies in the nearby universe. The Local Group of galaxies, of which the Milky Way is a member, is moving in the direction of Centaurus at a speed of more than a million miles an hour under the influence of the gravitational pull of the matter in that direction. Clusters of young bright blue stars highlight the galaxy' Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-nasa-hubble-space-telescope-hst-view-of-the-magnificent-spiral-galaxy-111969622.htmlRMGE4JB2–A NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) view of the magnificent spiral galaxy NGC 4603, the most distant galaxy in which a special class of pulsating stars called Cepheid variables have been found. It is associated with the Centaurus cluster, one of the most massive assemblages of galaxies in the nearby universe. The Local Group of galaxies, of which the Milky Way is a member, is moving in the direction of Centaurus at a speed of more than a million miles an hour under the influence of the gravitational pull of the matter in that direction. Clusters of young bright blue stars highlight the galaxy'
![Infographi learning to locate celestial objects, many people find the hobby very gratifying. With the aid of a star map, you can recognize galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, planets, and other objects. [6259x4015]. Stock Photo Infographi learning to locate celestial objects, many people find the hobby very gratifying. With the aid of a star map, you can recognize galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, planets, and other objects. [6259x4015]. Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2NEBXCP/infographi-learning-to-locate-celestial-objects-many-people-find-the-hobby-very-gratifying-with-the-aid-of-a-star-map-you-can-recognize-galaxies-nebulae-star-clusters-planets-and-other-objects-6259x4015-2NEBXCP.jpg) Infographi learning to locate celestial objects, many people find the hobby very gratifying. With the aid of a star map, you can recognize galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, planets, and other objects. [6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographi-learning-to-locate-celestial-objects-many-people-find-the-hobby-very-gratifying-with-the-aid-of-a-star-map-you-can-recognize-galaxies-nebulae-star-clusters-planets-and-other-objects-6259x4015-image525178438.html
Infographi learning to locate celestial objects, many people find the hobby very gratifying. With the aid of a star map, you can recognize galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, planets, and other objects. [6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographi-learning-to-locate-celestial-objects-many-people-find-the-hobby-very-gratifying-with-the-aid-of-a-star-map-you-can-recognize-galaxies-nebulae-star-clusters-planets-and-other-objects-6259x4015-image525178438.htmlRM2NEBXCP–Infographi learning to locate celestial objects, many people find the hobby very gratifying. With the aid of a star map, you can recognize galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, planets, and other objects. [6259x4015].
 1856 Burritt Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Geographicus Comets2 burritt 1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-136441846.html
1856 Burritt Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Geographicus Comets2 burritt 1856 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-136441846.htmlRMHWYCY2–1856 Burritt Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae Geographicus Comets2 burritt 1856
 Great Nebula in Orion Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-great-nebula-in-orion-134944536.html
Great Nebula in Orion Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-great-nebula-in-orion-134944536.htmlRMHRF73M–Great Nebula in Orion
 Jun. 06, 1984 - Technicians Install the last major experiment called the ''Hard X-Ray Imaging of Clusters of Galaxies and Other Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/jun-06-1984-technicians-install-the-last-major-experiment-called-the-image69503042.html
Jun. 06, 1984 - Technicians Install the last major experiment called the ''Hard X-Ray Imaging of Clusters of Galaxies and Other Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/jun-06-1984-technicians-install-the-last-major-experiment-called-the-image69503042.htmlRME123RE–Jun. 06, 1984 - Technicians Install the last major experiment called the ''Hard X-Ray Imaging of Clusters of Galaxies and Other
 Collision of a cluster of stars creating big glowing star and distant galaxies in background. Digitally enhanced. Elements of image furnished by NASA Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/collision-of-a-cluster-of-stars-creating-big-glowing-star-and-distant-galaxies-in-background-digitally-enhanced-elements-of-image-furnished-by-nasa-image499882514.html
Collision of a cluster of stars creating big glowing star and distant galaxies in background. Digitally enhanced. Elements of image furnished by NASA Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/collision-of-a-cluster-of-stars-creating-big-glowing-star-and-distant-galaxies-in-background-digitally-enhanced-elements-of-image-furnished-by-nasa-image499882514.htmlRF2M17H6X–Collision of a cluster of stars creating big glowing star and distant galaxies in background. Digitally enhanced. Elements of image furnished by NASA
 Hubble Frontier Field Abell 2744 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/hubble-frontier-field-abell-2744-image66261505.html
Hubble Frontier Field Abell 2744 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/hubble-frontier-field-abell-2744-image66261505.htmlRMDRPD69–Hubble Frontier Field Abell 2744
 Star galaxies in the universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-galaxies-in-the-universe-image274160530.html
Star galaxies in the universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-galaxies-in-the-universe-image274160530.htmlRMWX12FE–Star galaxies in the universe.
 astronomy, star clusters, omega fog, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-omega-fog-astronomies-image455934351.html
astronomy, star clusters, omega fog, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-omega-fog-astronomies-image455934351.htmlRF2HDNGWK–astronomy, star clusters, omega fog, astronomies
 Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This 'hefty' cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some 2 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is so massive that its enormous gravitational field deflects light rays passing through it, much as an optical lens bends light to form an image. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, magnifies, brightens, and distorts images from faraway objects. The cluster's magnify Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-scanning-the-heavens-for-the-first-time-since-the-successful-december-111966816.html
Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This 'hefty' cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some 2 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is so massive that its enormous gravitational field deflects light rays passing through it, much as an optical lens bends light to form an image. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, magnifies, brightens, and distorts images from faraway objects. The cluster's magnify Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-scanning-the-heavens-for-the-first-time-since-the-successful-december-111966816.htmlRMGE4EPT–Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This 'hefty' cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some 2 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is so massive that its enormous gravitational field deflects light rays passing through it, much as an optical lens bends light to form an image. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, magnifies, brightens, and distorts images from faraway objects. The cluster's magnify
 Clusters of stars in the night sky Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-clusters-of-stars-in-the-night-sky-162142545.html
Clusters of stars in the night sky Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-clusters-of-stars-in-the-night-sky-162142545.htmlRFKBP6D5–Clusters of stars in the night sky
 Whale and Hockey Stick Galaxies in Cosmic Harmony. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whale-and-hockey-stick-galaxies-in-cosmic-harmony-image565633003.html
Whale and Hockey Stick Galaxies in Cosmic Harmony. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/whale-and-hockey-stick-galaxies-in-cosmic-harmony-image565633003.htmlRF2RT6PJK–Whale and Hockey Stick Galaxies in Cosmic Harmony.
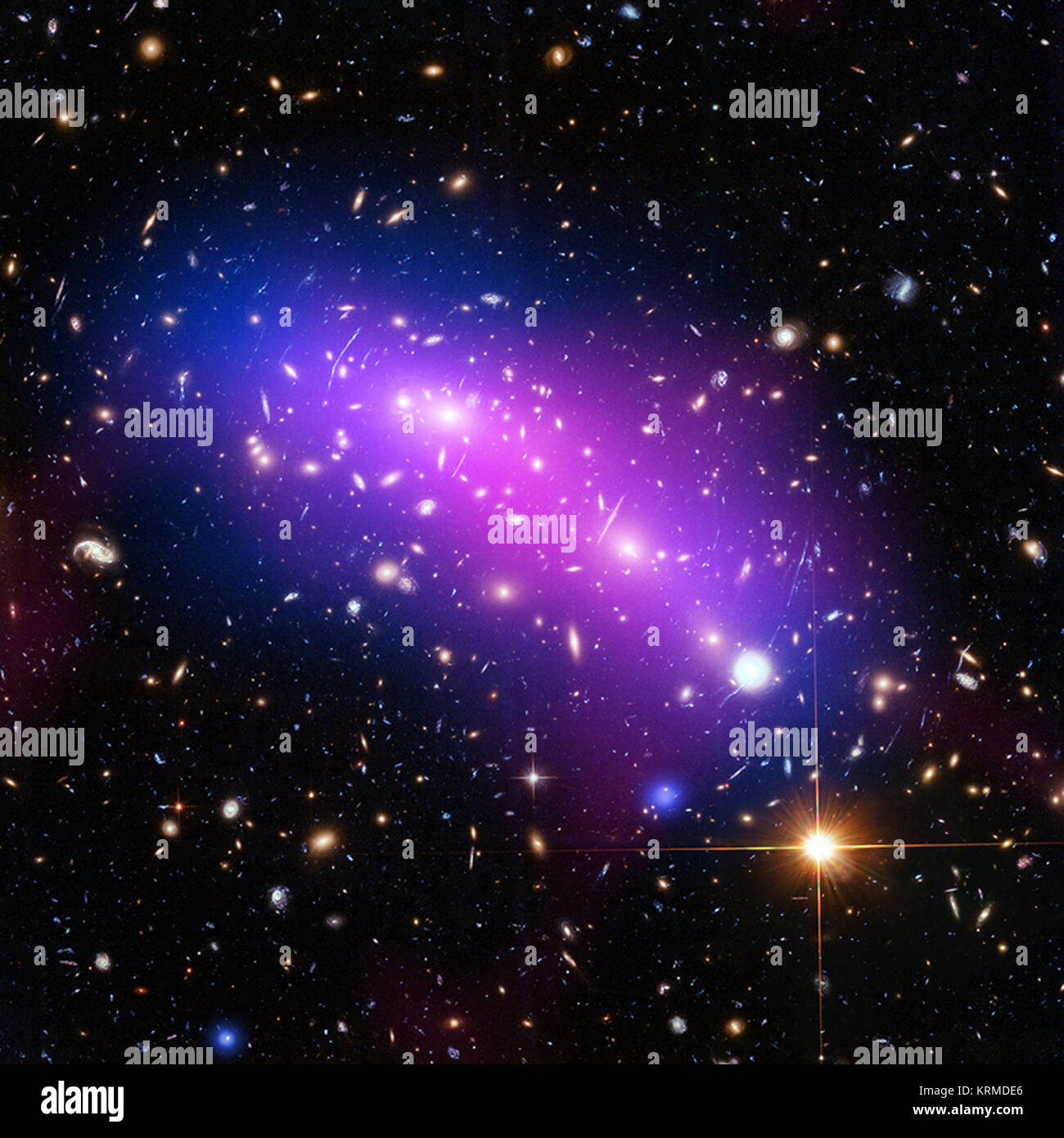 These two galaxy clusters are part of the 'Frontier Fields' project, which uses some of the world's most powerful telescopes to study these giant structures with long observations. Galaxy clusters are enormous collections of hundreds or thousands of galaxies and vast reservoirs of hot gas embedded in massive clouds of dark matter. These images contain X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical light from Hubble (red, green, and blue), and radio data from the Very Large Array (pink). MACS J0416.1-2403 (Chandra) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-these-two-galaxy-clusters-are-part-of-the-frontier-fields-project-169480030.html
These two galaxy clusters are part of the 'Frontier Fields' project, which uses some of the world's most powerful telescopes to study these giant structures with long observations. Galaxy clusters are enormous collections of hundreds or thousands of galaxies and vast reservoirs of hot gas embedded in massive clouds of dark matter. These images contain X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical light from Hubble (red, green, and blue), and radio data from the Very Large Array (pink). MACS J0416.1-2403 (Chandra) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-these-two-galaxy-clusters-are-part-of-the-frontier-fields-project-169480030.htmlRMKRMDE6–These two galaxy clusters are part of the 'Frontier Fields' project, which uses some of the world's most powerful telescopes to study these giant structures with long observations. Galaxy clusters are enormous collections of hundreds or thousands of galaxies and vast reservoirs of hot gas embedded in massive clouds of dark matter. These images contain X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical light from Hubble (red, green, and blue), and radio data from the Very Large Array (pink). MACS J0416.1-2403 (Chandra)
 Exploring the Leo Triplet: A Trio of Galaxies in Cosmic Harmony. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/exploring-the-leo-triplet-a-trio-of-galaxies-in-cosmic-harmony-image565632907.html
Exploring the Leo Triplet: A Trio of Galaxies in Cosmic Harmony. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/exploring-the-leo-triplet-a-trio-of-galaxies-in-cosmic-harmony-image565632907.htmlRF2RT6PF7–Exploring the Leo Triplet: A Trio of Galaxies in Cosmic Harmony.
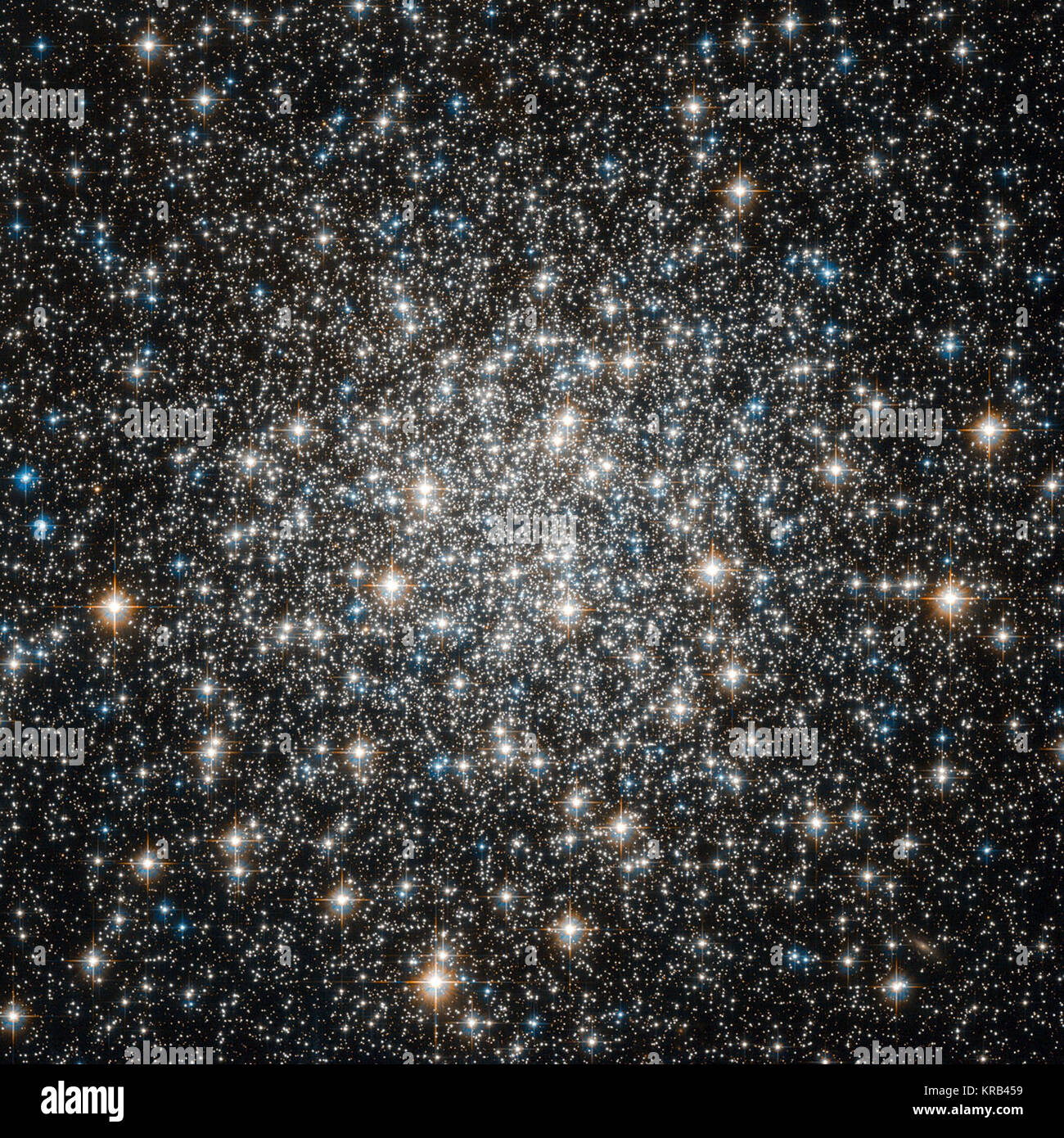 Like many of the most famous objects in the sky, globular cluster Messier 10 was of little interest to its discoverer: Charles Messier, the 18th century French astronomer, catalogued over 100 galaxies and clusters, but was primarily interested in comets. Through the telescopes available at the time, comets, nebulae, globular clusters and galaxies appeared just as faint, diffuse blobs and could easily be confused for one another. Only by carefully observing their motion — or lack of it — were astronomers able to distinguish them: comets move slowly relative to the stars in the background, while Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-like-many-of-the-most-famous-objects-in-the-sky-globular-cluster-messier-169275157.html
Like many of the most famous objects in the sky, globular cluster Messier 10 was of little interest to its discoverer: Charles Messier, the 18th century French astronomer, catalogued over 100 galaxies and clusters, but was primarily interested in comets. Through the telescopes available at the time, comets, nebulae, globular clusters and galaxies appeared just as faint, diffuse blobs and could easily be confused for one another. Only by carefully observing their motion — or lack of it — were astronomers able to distinguish them: comets move slowly relative to the stars in the background, while Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-like-many-of-the-most-famous-objects-in-the-sky-globular-cluster-messier-169275157.htmlRMKRB459–Like many of the most famous objects in the sky, globular cluster Messier 10 was of little interest to its discoverer: Charles Messier, the 18th century French astronomer, catalogued over 100 galaxies and clusters, but was primarily interested in comets. Through the telescopes available at the time, comets, nebulae, globular clusters and galaxies appeared just as faint, diffuse blobs and could easily be confused for one another. Only by carefully observing their motion — or lack of it — were astronomers able to distinguish them: comets move slowly relative to the stars in the background, while
 Dark Matter and Galaxies Part Ways in Collision between Hefty Galaxy Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/dark-matter-and-galaxies-part-ways-in-collision-between-hefty-galaxy-image68656634.html
Dark Matter and Galaxies Part Ways in Collision between Hefty Galaxy Clusters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/dark-matter-and-galaxies-part-ways-in-collision-between-hefty-galaxy-image68656634.htmlRMDYKG6J–Dark Matter and Galaxies Part Ways in Collision between Hefty Galaxy Clusters
 The giant cluster of elliptical galaxies in the center of this image contains so much dark matter mass that its gravity bends light. This means that for very distant galaxies in the background, the clusters gravitational field acts as a sort of magnifying glass, bending and concentrating the distant objects light towards Hubble. These gravitational lenses are one tool astronomers can use to extend Hubbles vision beyond what it would normally be capable of observing. Using Abell 383, a team of astronomers have identified and studied a galaxy so far away we see it as it was less than a billion Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-the-giant-cluster-of-elliptical-galaxies-in-the-center-of-this-image-169436239.html
The giant cluster of elliptical galaxies in the center of this image contains so much dark matter mass that its gravity bends light. This means that for very distant galaxies in the background, the clusters gravitational field acts as a sort of magnifying glass, bending and concentrating the distant objects light towards Hubble. These gravitational lenses are one tool astronomers can use to extend Hubbles vision beyond what it would normally be capable of observing. Using Abell 383, a team of astronomers have identified and studied a galaxy so far away we see it as it was less than a billion Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-the-giant-cluster-of-elliptical-galaxies-in-the-center-of-this-image-169436239.htmlRMKRJDJ7–The giant cluster of elliptical galaxies in the center of this image contains so much dark matter mass that its gravity bends light. This means that for very distant galaxies in the background, the clusters gravitational field acts as a sort of magnifying glass, bending and concentrating the distant objects light towards Hubble. These gravitational lenses are one tool astronomers can use to extend Hubbles vision beyond what it would normally be capable of observing. Using Abell 383, a team of astronomers have identified and studied a galaxy so far away we see it as it was less than a billion
 This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows the diverse collection of galaxies in the cluster Abell S0740 that is over 450 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation Centaurus. The giant elliptical ESO 325-G004 looms large at the cluster's center. The galaxy is as massive as 100 billion of our suns. Hubble resolves thousands of globular star clusters orbiting ESO 325-G004. Globular clusters are compact groups of hundreds of thousands of stars that are gravitationally bound together. At the galaxy's distance they appear as pinpoints of light contained within the di Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-image-from-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-shows-the-diverse-collection-of-galaxies-in-the-cluster-abell-s0740-that-is-over-450-million-light-years-away-in-the-direction-of-the-constellation-centaurus-the-giant-elliptical-eso-325-g004-looms-large-at-the-clusters-center-the-galaxy-is-as-massive-as-100-billion-of-our-suns-hubble-resolves-thousands-of-globular-star-clusters-orbiting-eso-325-g004-globular-clusters-are-compact-groups-of-hundreds-of-thousands-of-stars-that-are-gravitationally-bound-together-at-the-galaxys-distance-they-appear-as-pinpoints-of-light-contained-within-the-di-image335167161.html
This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows the diverse collection of galaxies in the cluster Abell S0740 that is over 450 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation Centaurus. The giant elliptical ESO 325-G004 looms large at the cluster's center. The galaxy is as massive as 100 billion of our suns. Hubble resolves thousands of globular star clusters orbiting ESO 325-G004. Globular clusters are compact groups of hundreds of thousands of stars that are gravitationally bound together. At the galaxy's distance they appear as pinpoints of light contained within the di Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-image-from-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-shows-the-diverse-collection-of-galaxies-in-the-cluster-abell-s0740-that-is-over-450-million-light-years-away-in-the-direction-of-the-constellation-centaurus-the-giant-elliptical-eso-325-g004-looms-large-at-the-clusters-center-the-galaxy-is-as-massive-as-100-billion-of-our-suns-hubble-resolves-thousands-of-globular-star-clusters-orbiting-eso-325-g004-globular-clusters-are-compact-groups-of-hundreds-of-thousands-of-stars-that-are-gravitationally-bound-together-at-the-galaxys-distance-they-appear-as-pinpoints-of-light-contained-within-the-di-image335167161.htmlRF2AD853N–This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows the diverse collection of galaxies in the cluster Abell S0740 that is over 450 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation Centaurus. The giant elliptical ESO 325-G004 looms large at the cluster's center. The galaxy is as massive as 100 billion of our suns. Hubble resolves thousands of globular star clusters orbiting ESO 325-G004. Globular clusters are compact groups of hundreds of thousands of stars that are gravitationally bound together. At the galaxy's distance they appear as pinpoints of light contained within the di
 Starry sky with galaxies and stars Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/starry-sky-with-galaxies-and-stars-image600452203.html
Starry sky with galaxies and stars Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/starry-sky-with-galaxies-and-stars-image600452203.htmlRF2WTTXWF–Starry sky with galaxies and stars
 Astronomers have found evidence for a 'radio phoenix' in the collision of two galaxy clusters, where vast clouds of high-energy particles have been regenerated. This composite image of Abell 1033 combines X-ray data from Chandra (pink) along with radio data (green) and optical data that reveals the density of the galaxies (blue). By tracing the history of mergers like the one found in Abell 1033, astronomers can better understand how galaxy clusters - the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity - evolve over time. Abell 1033 (Chandra) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-astronomers-have-found-evidence-for-a-radio-phoenix-in-the-collision-169416981.html
Astronomers have found evidence for a 'radio phoenix' in the collision of two galaxy clusters, where vast clouds of high-energy particles have been regenerated. This composite image of Abell 1033 combines X-ray data from Chandra (pink) along with radio data (green) and optical data that reveals the density of the galaxies (blue). By tracing the history of mergers like the one found in Abell 1033, astronomers can better understand how galaxy clusters - the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity - evolve over time. Abell 1033 (Chandra) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-astronomers-have-found-evidence-for-a-radio-phoenix-in-the-collision-169416981.htmlRMKRHH2D–Astronomers have found evidence for a 'radio phoenix' in the collision of two galaxy clusters, where vast clouds of high-energy particles have been regenerated. This composite image of Abell 1033 combines X-ray data from Chandra (pink) along with radio data (green) and optical data that reveals the density of the galaxies (blue). By tracing the history of mergers like the one found in Abell 1033, astronomers can better understand how galaxy clusters - the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity - evolve over time. Abell 1033 (Chandra)
 This Hubble Space Telescope composite image shows a ghostly 'ring' of dark matter in the galaxy cluster Cl 0024+17. The ring-like structure is evident in the blue map of the cluster's dark matter distribution. The map is superimposed on a Hubble image of the cluster. The ring is one of the strongest pieces of evidence to date for the existence of dark matter, an unknown substance that pervades the universe. The map was derived from Hubble observations of how the gravity of the cluster Cl 0024+17 distorts the light of more distant galaxies, an optical illusion called gravitational lensing. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-hubble-space-telescope-composite-image-shows-a-ghostly-ring-of-dark-matter-in-the-galaxy-cluster-cl-002417-the-ring-like-structure-is-evident-in-the-blue-map-of-the-clusters-dark-matter-distribution-the-map-is-superimposed-on-a-hubble-image-of-the-cluster-the-ring-is-one-of-the-strongest-pieces-of-evidence-to-date-for-the-existence-of-dark-matter-an-unknown-substance-that-pervades-the-universe-the-map-was-derived-from-hubble-observations-of-how-the-gravity-of-the-cluster-cl-002417-distorts-the-light-of-more-distant-galaxies-an-optical-illusion-called-gravitational-lensing-image335180837.html
This Hubble Space Telescope composite image shows a ghostly 'ring' of dark matter in the galaxy cluster Cl 0024+17. The ring-like structure is evident in the blue map of the cluster's dark matter distribution. The map is superimposed on a Hubble image of the cluster. The ring is one of the strongest pieces of evidence to date for the existence of dark matter, an unknown substance that pervades the universe. The map was derived from Hubble observations of how the gravity of the cluster Cl 0024+17 distorts the light of more distant galaxies, an optical illusion called gravitational lensing. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-hubble-space-telescope-composite-image-shows-a-ghostly-ring-of-dark-matter-in-the-galaxy-cluster-cl-002417-the-ring-like-structure-is-evident-in-the-blue-map-of-the-clusters-dark-matter-distribution-the-map-is-superimposed-on-a-hubble-image-of-the-cluster-the-ring-is-one-of-the-strongest-pieces-of-evidence-to-date-for-the-existence-of-dark-matter-an-unknown-substance-that-pervades-the-universe-the-map-was-derived-from-hubble-observations-of-how-the-gravity-of-the-cluster-cl-002417-distorts-the-light-of-more-distant-galaxies-an-optical-illusion-called-gravitational-lensing-image335180837.htmlRF2AD8PG5–This Hubble Space Telescope composite image shows a ghostly 'ring' of dark matter in the galaxy cluster Cl 0024+17. The ring-like structure is evident in the blue map of the cluster's dark matter distribution. The map is superimposed on a Hubble image of the cluster. The ring is one of the strongest pieces of evidence to date for the existence of dark matter, an unknown substance that pervades the universe. The map was derived from Hubble observations of how the gravity of the cluster Cl 0024+17 distorts the light of more distant galaxies, an optical illusion called gravitational lensing.
 In the centre of this image, taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, is the galaxy cluster SDSS J1038+4849 — and it seems to be smiling. You can make out its two orange eyes and white button nose. In the case of this “happy face”, the two eyes are very bright galaxies and the misleading smile lines are actually arcs caused by an effect known as strong gravitational lensing. Galaxy clusters are the most massive structures in the Universe and exert such a powerful gravitational pull that they warp the spacetime around them and act as cosmic lenses which can magnify, distort and bend the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-in-the-centre-of-this-image-taken-with-the-nasaesa-hubble-space-telescope-169412057.html
In the centre of this image, taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, is the galaxy cluster SDSS J1038+4849 — and it seems to be smiling. You can make out its two orange eyes and white button nose. In the case of this “happy face”, the two eyes are very bright galaxies and the misleading smile lines are actually arcs caused by an effect known as strong gravitational lensing. Galaxy clusters are the most massive structures in the Universe and exert such a powerful gravitational pull that they warp the spacetime around them and act as cosmic lenses which can magnify, distort and bend the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-in-the-centre-of-this-image-taken-with-the-nasaesa-hubble-space-telescope-169412057.htmlRMKRHAPH–In the centre of this image, taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, is the galaxy cluster SDSS J1038+4849 — and it seems to be smiling. You can make out its two orange eyes and white button nose. In the case of this “happy face”, the two eyes are very bright galaxies and the misleading smile lines are actually arcs caused by an effect known as strong gravitational lensing. Galaxy clusters are the most massive structures in the Universe and exert such a powerful gravitational pull that they warp the spacetime around them and act as cosmic lenses which can magnify, distort and bend the
 These images taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show the globular cluster systems of 100 galaxies observed within the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) Virgo Cluster Survey. Globular clusters, dense bunches of hundreds of thousands of stars, have some of the oldest surviving stars in the universe. Most of the star clusters in the Virgo survey are older than 5 billion years. The Hubble study found evidence that these globular clusters are more likely to form in dense areas where star birth occurs at a rapid rate, instead of uniformly from galaxy to galaxy. Comprised of over 2,000 galaxies a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/these-images-taken-by-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-show-the-globular-cluster-systems-of-100-galaxies-observed-within-the-advanced-camera-for-surveys-acs-virgo-cluster-survey-globular-clusters-dense-bunches-of-hundreds-of-thousands-of-stars-have-some-of-the-oldest-surviving-stars-in-the-universe-most-of-the-star-clusters-in-the-virgo-survey-are-older-than-5-billion-years-the-hubble-study-found-evidence-that-these-globular-clusters-are-more-likely-to-form-in-dense-areas-where-star-birth-occurs-at-a-rapid-rate-instead-of-uniformly-from-galaxy-to-galaxy-comprised-of-over-2000-galaxies-a-image335157671.html
These images taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show the globular cluster systems of 100 galaxies observed within the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) Virgo Cluster Survey. Globular clusters, dense bunches of hundreds of thousands of stars, have some of the oldest surviving stars in the universe. Most of the star clusters in the Virgo survey are older than 5 billion years. The Hubble study found evidence that these globular clusters are more likely to form in dense areas where star birth occurs at a rapid rate, instead of uniformly from galaxy to galaxy. Comprised of over 2,000 galaxies a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/these-images-taken-by-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-show-the-globular-cluster-systems-of-100-galaxies-observed-within-the-advanced-camera-for-surveys-acs-virgo-cluster-survey-globular-clusters-dense-bunches-of-hundreds-of-thousands-of-stars-have-some-of-the-oldest-surviving-stars-in-the-universe-most-of-the-star-clusters-in-the-virgo-survey-are-older-than-5-billion-years-the-hubble-study-found-evidence-that-these-globular-clusters-are-more-likely-to-form-in-dense-areas-where-star-birth-occurs-at-a-rapid-rate-instead-of-uniformly-from-galaxy-to-galaxy-comprised-of-over-2000-galaxies-a-image335157671.htmlRF2AD7N0R–These images taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope show the globular cluster systems of 100 galaxies observed within the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) Virgo Cluster Survey. Globular clusters, dense bunches of hundreds of thousands of stars, have some of the oldest surviving stars in the universe. Most of the star clusters in the Virgo survey are older than 5 billion years. The Hubble study found evidence that these globular clusters are more likely to form in dense areas where star birth occurs at a rapid rate, instead of uniformly from galaxy to galaxy. Comprised of over 2,000 galaxies a
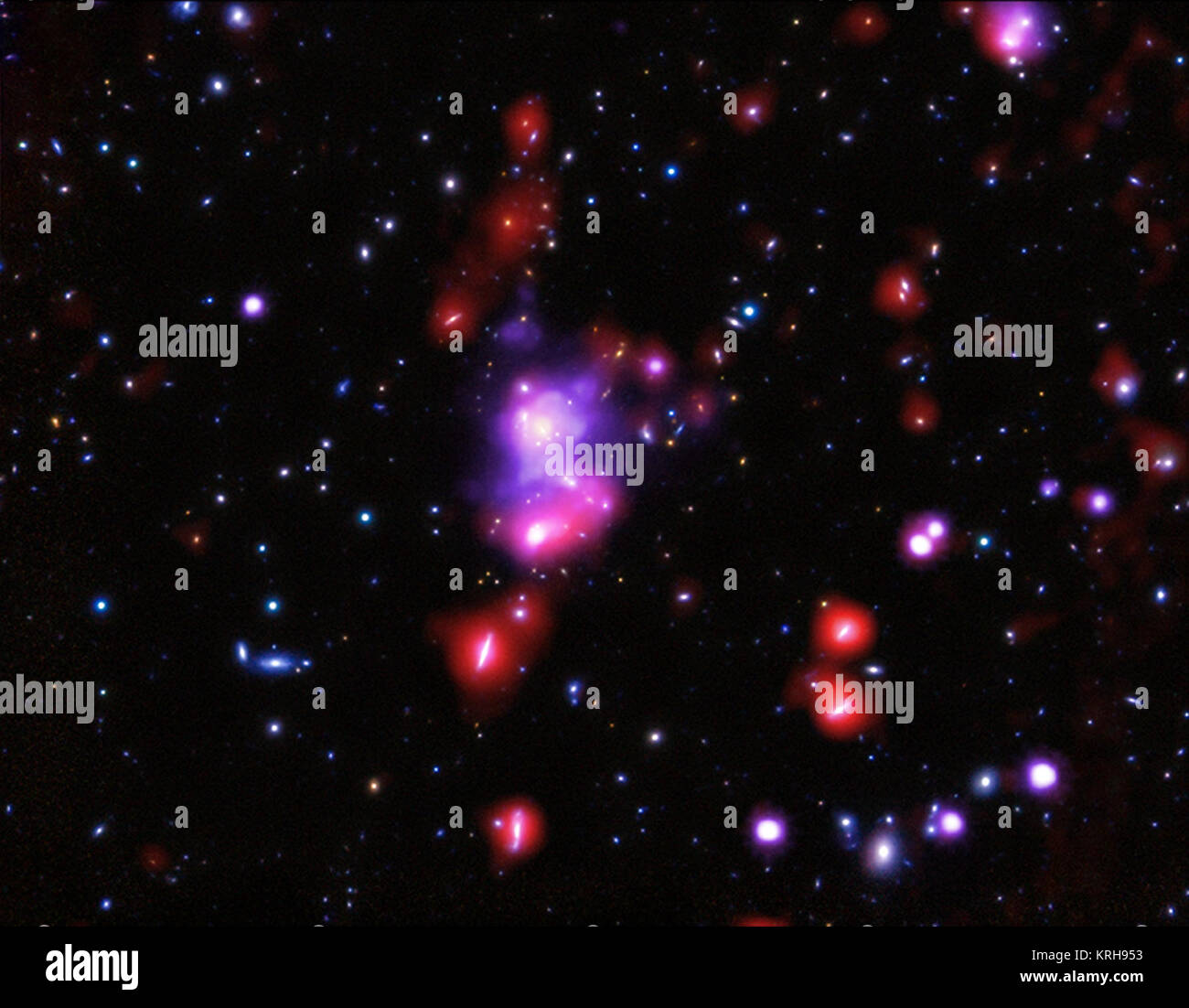 The most massive cluster of galaxies with an age of 800 million years or younger has been discovered and studied. X-ray data from Chandra allowed astronomers to accurately determine the mass and other properties of this cluster, nicknamed the 'Gioiello' (Italian for 'Jewel') cluster. This composite image of the Gioiello Cluster contains X-rays from Chandra (purple), infrared data from Herschel (red), and an optical image from Subaru (red, green, and blue). Results like this help astronomers better understand how galaxy clusters, the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-the-most-massive-cluster-of-galaxies-with-an-age-of-800-million-years-169410783.html
The most massive cluster of galaxies with an age of 800 million years or younger has been discovered and studied. X-ray data from Chandra allowed astronomers to accurately determine the mass and other properties of this cluster, nicknamed the 'Gioiello' (Italian for 'Jewel') cluster. This composite image of the Gioiello Cluster contains X-rays from Chandra (purple), infrared data from Herschel (red), and an optical image from Subaru (red, green, and blue). Results like this help astronomers better understand how galaxy clusters, the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-the-most-massive-cluster-of-galaxies-with-an-age-of-800-million-years-169410783.htmlRMKRH953–The most massive cluster of galaxies with an age of 800 million years or younger has been discovered and studied. X-ray data from Chandra allowed astronomers to accurately determine the mass and other properties of this cluster, nicknamed the 'Gioiello' (Italian for 'Jewel') cluster. This composite image of the Gioiello Cluster contains X-rays from Chandra (purple), infrared data from Herschel (red), and an optical image from Subaru (red, green, and blue). Results like this help astronomers better understand how galaxy clusters, the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity,
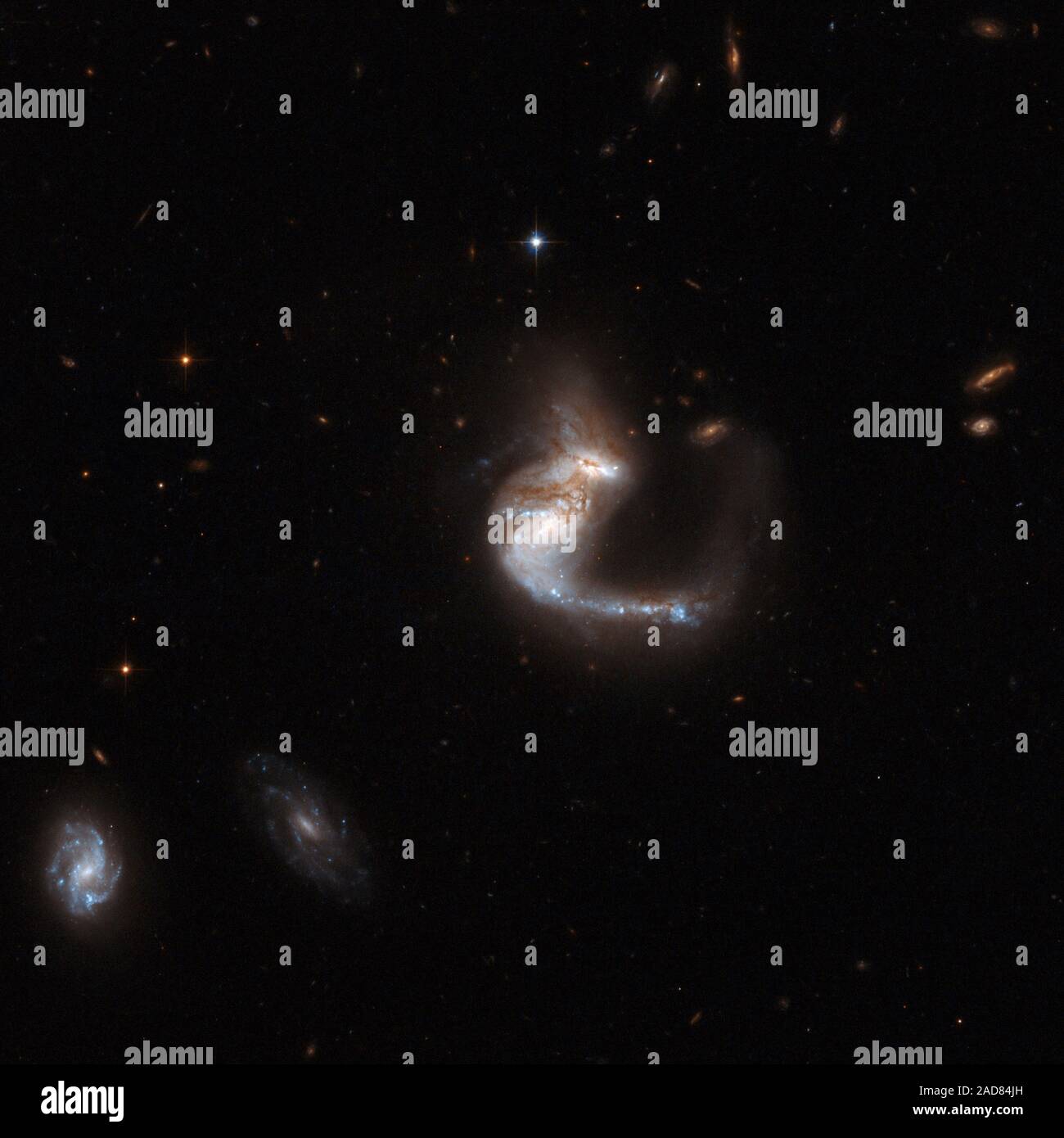 UGC 4881, known as the 'The Grasshopper,' is a stunning system consisting of two colliding galaxies. It has a bright curly tail containing a remarkable number of star clusters. The galaxies are thought to be halfway through a merger the cores of the parent galaxies are still clearly separated, but their disks are overlapping. A supernova exploded in this system in 1999 and astronomers believe that a vigorous burst of star formation may have just started. This notable object is located in the constellation of Lynx, some 500 million light-years away from Earth. UGC 4881 is the 55th galaxy in Arp Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/ugc-4881-known-as-the-the-grasshopper-is-a-stunning-system-consisting-of-two-colliding-galaxies-it-has-a-bright-curly-tail-containing-a-remarkable-number-of-star-clusters-the-galaxies-are-thought-to-be-halfway-through-a-merger-the-cores-of-the-parent-galaxies-are-still-clearly-separated-but-their-disks-are-overlapping-a-supernova-exploded-in-this-system-in-1999-and-astronomers-believe-that-a-vigorous-burst-of-star-formation-may-have-just-started-this-notable-object-is-located-in-the-constellation-of-lynx-some-500-million-light-years-away-from-earth-ugc-4881-is-the-55th-galaxy-in-arp-image335166793.html
UGC 4881, known as the 'The Grasshopper,' is a stunning system consisting of two colliding galaxies. It has a bright curly tail containing a remarkable number of star clusters. The galaxies are thought to be halfway through a merger the cores of the parent galaxies are still clearly separated, but their disks are overlapping. A supernova exploded in this system in 1999 and astronomers believe that a vigorous burst of star formation may have just started. This notable object is located in the constellation of Lynx, some 500 million light-years away from Earth. UGC 4881 is the 55th galaxy in Arp Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/ugc-4881-known-as-the-the-grasshopper-is-a-stunning-system-consisting-of-two-colliding-galaxies-it-has-a-bright-curly-tail-containing-a-remarkable-number-of-star-clusters-the-galaxies-are-thought-to-be-halfway-through-a-merger-the-cores-of-the-parent-galaxies-are-still-clearly-separated-but-their-disks-are-overlapping-a-supernova-exploded-in-this-system-in-1999-and-astronomers-believe-that-a-vigorous-burst-of-star-formation-may-have-just-started-this-notable-object-is-located-in-the-constellation-of-lynx-some-500-million-light-years-away-from-earth-ugc-4881-is-the-55th-galaxy-in-arp-image335166793.htmlRF2AD84JH–UGC 4881, known as the 'The Grasshopper,' is a stunning system consisting of two colliding galaxies. It has a bright curly tail containing a remarkable number of star clusters. The galaxies are thought to be halfway through a merger the cores of the parent galaxies are still clearly separated, but their disks are overlapping. A supernova exploded in this system in 1999 and astronomers believe that a vigorous burst of star formation may have just started. This notable object is located in the constellation of Lynx, some 500 million light-years away from Earth. UGC 4881 is the 55th galaxy in Arp
 Tadpole Galaxy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tadpole-galaxy-image66261795.html
Tadpole Galaxy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tadpole-galaxy-image66261795.htmlRMDRPDGK–Tadpole Galaxy
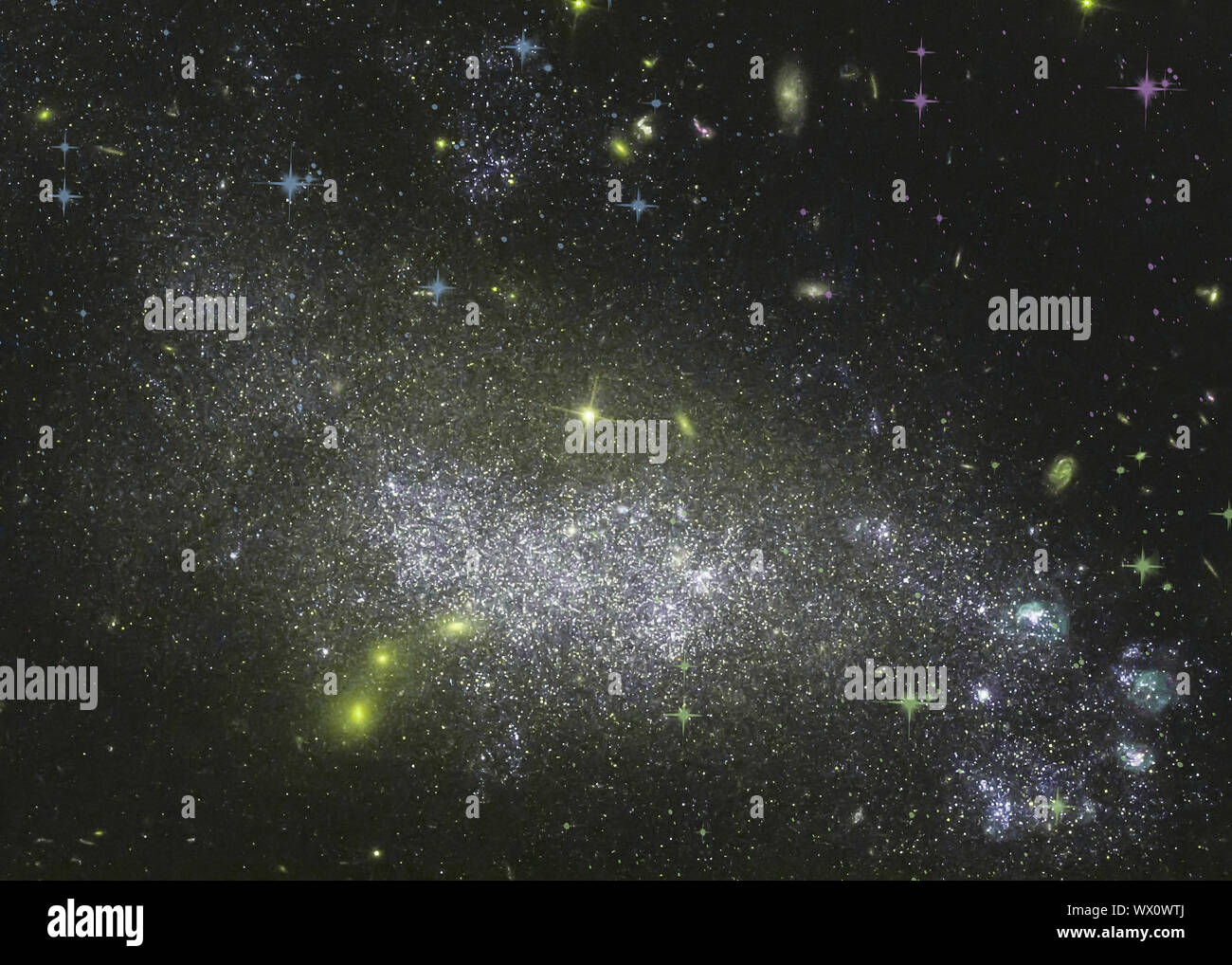 Star galaxies in the universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-galaxies-in-the-universe-image274156866.html
Star galaxies in the universe. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-galaxies-in-the-universe-image274156866.htmlRMWX0WTJ–Star galaxies in the universe.
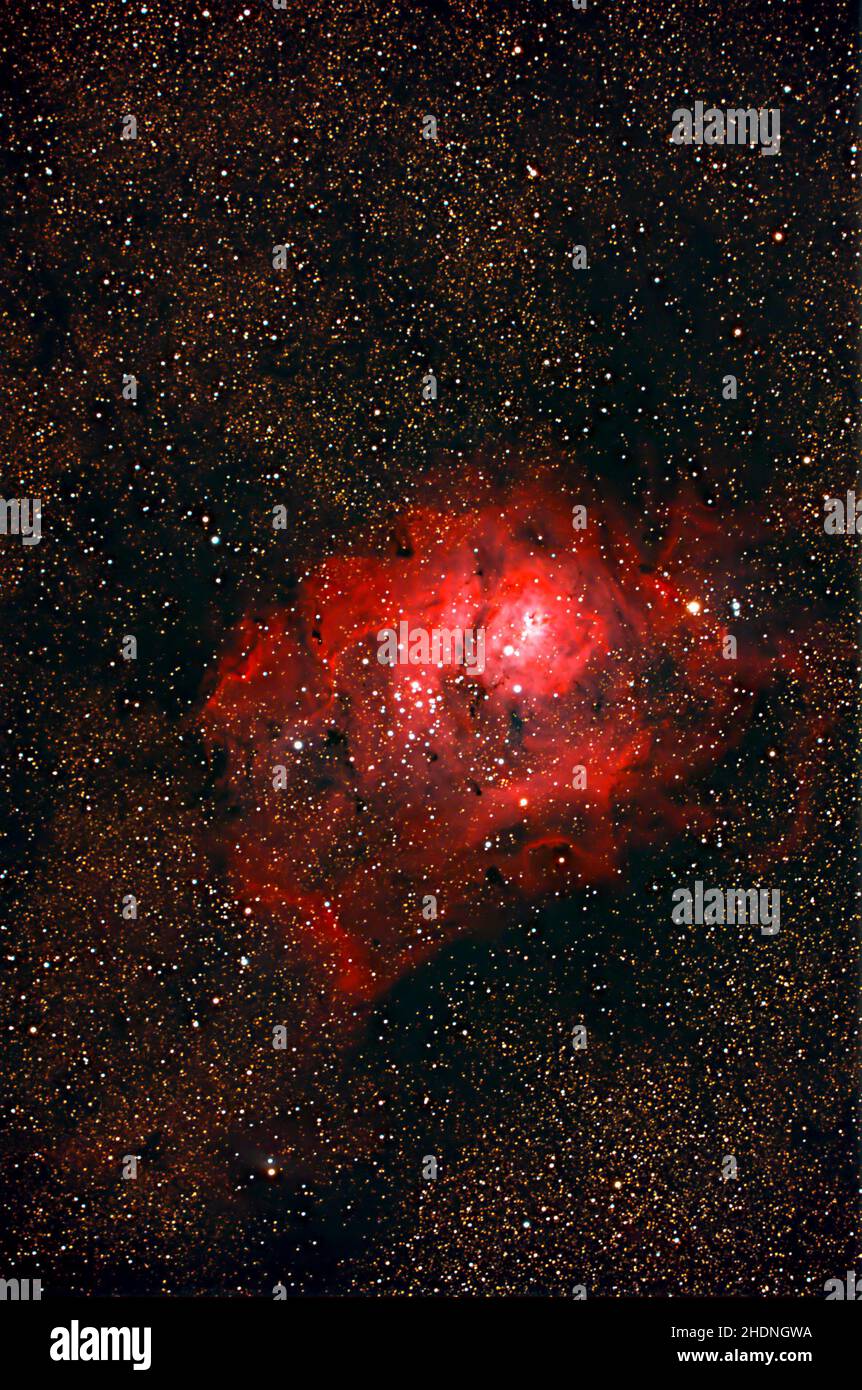 astronomy, star clusters, lagoon nebula, hourglass fog, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-lagoon-nebula-hourglass-fog-astronomies-image455934342.html
astronomy, star clusters, lagoon nebula, hourglass fog, astronomies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/astronomy-star-clusters-lagoon-nebula-hourglass-fog-astronomies-image455934342.htmlRF2HDNGWA–astronomy, star clusters, lagoon nebula, hourglass fog, astronomies
 An infinite universe with planets and Galaxies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-infinite-universe-with-planets-and-galaxies-image389222864.html
An infinite universe with planets and Galaxies Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-infinite-universe-with-planets-and-galaxies-image389222864.htmlRF2DH6HMG–An infinite universe with planets and Galaxies
 Galaxy clusters are some of the most massive structures that can be found in the Universe — large groups of galaxies bound together by gravity. This image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope reveals one of these clusters, known as MACS J0454.1-0300. Each of the bright spots seen here is a galaxy, and each is home to many millions, or even billions, of stars. Astronomers have determined the mass of MACS J0454.1-0300 to be around 180 trillion times the mass of the Sun. Clusters like this are so massive that their gravity can even change the behaviour of space around them, bending the path o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-galaxy-clusters-are-some-of-the-most-massive-structures-that-can-be-169395823.html
Galaxy clusters are some of the most massive structures that can be found in the Universe — large groups of galaxies bound together by gravity. This image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope reveals one of these clusters, known as MACS J0454.1-0300. Each of the bright spots seen here is a galaxy, and each is home to many millions, or even billions, of stars. Astronomers have determined the mass of MACS J0454.1-0300 to be around 180 trillion times the mass of the Sun. Clusters like this are so massive that their gravity can even change the behaviour of space around them, bending the path o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-galaxy-clusters-are-some-of-the-most-massive-structures-that-can-be-169395823.htmlRMKRGJ2R–Galaxy clusters are some of the most massive structures that can be found in the Universe — large groups of galaxies bound together by gravity. This image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope reveals one of these clusters, known as MACS J0454.1-0300. Each of the bright spots seen here is a galaxy, and each is home to many millions, or even billions, of stars. Astronomers have determined the mass of MACS J0454.1-0300 to be around 180 trillion times the mass of the Sun. Clusters like this are so massive that their gravity can even change the behaviour of space around them, bending the path o
 Star clusters, nebula and galaxies. Deep space background in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-clusters-nebula-and-galaxies-deep-space-background-in-high-resolution-image187871119.html
Star clusters, nebula and galaxies. Deep space background in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-clusters-nebula-and-galaxies-deep-space-background-in-high-resolution-image187871119.htmlRFMWJ7ER–Star clusters, nebula and galaxies. Deep space background in high resolution.
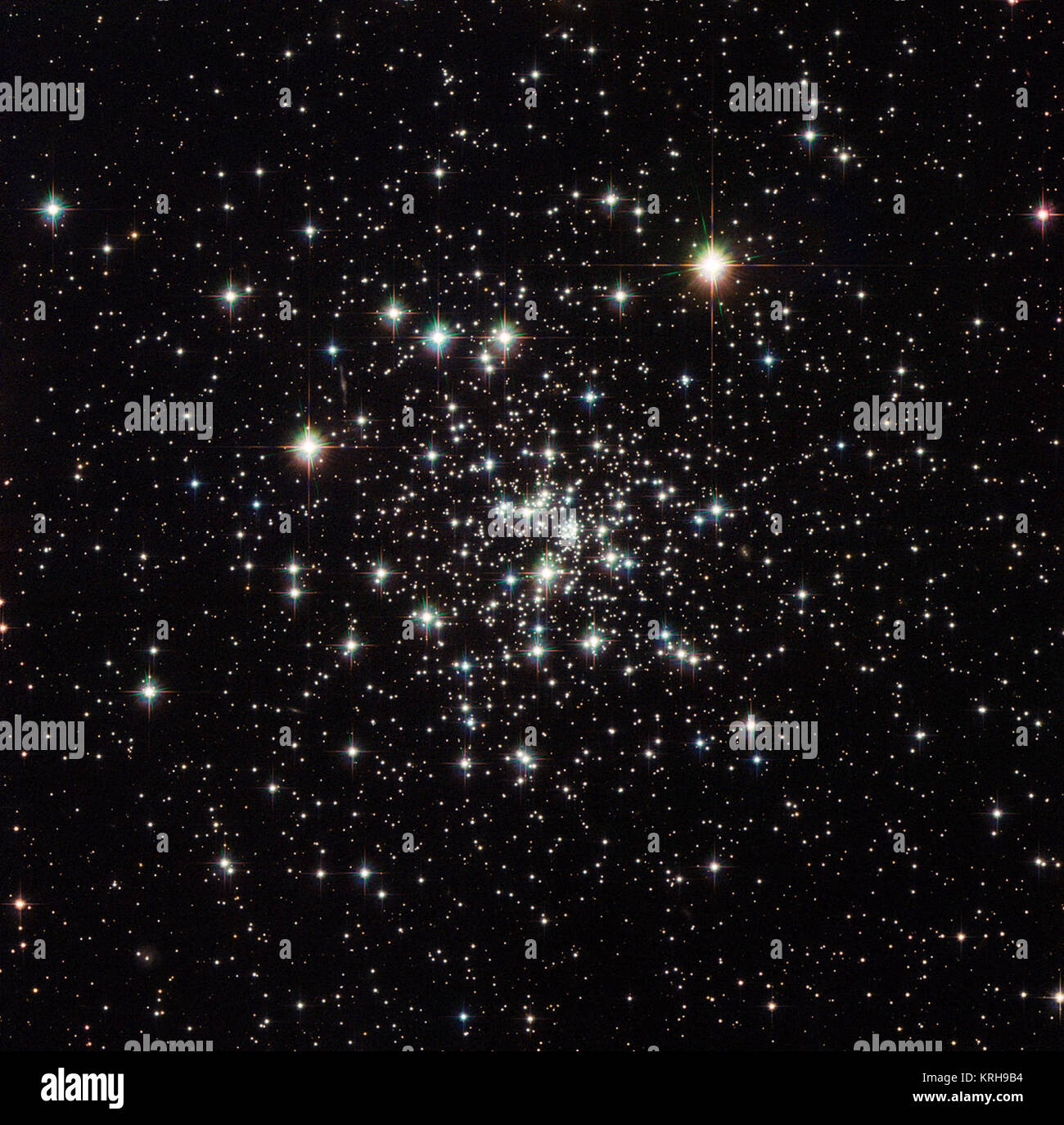 This image captures the stunning NGC 6535, a globular cluster 22 000 light-years away in the constellation of Serpens (The Serpent) that measures one light-year across. Globular clusters are tightly bound groups of stars which orbit galaxies. The large mass in the rich stellar centre of the globular cluster pulls the stars inward to form a ball of stars. The word globulus, from which these clusters take their name, is Latin for small sphere. Globular clusters are generally very ancient objects formed around the same time as their host galaxy. To date, no new star formations have been observed Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-this-image-captures-the-stunning-ngc-6535-a-globular-cluster-22-000-169410952.html
This image captures the stunning NGC 6535, a globular cluster 22 000 light-years away in the constellation of Serpens (The Serpent) that measures one light-year across. Globular clusters are tightly bound groups of stars which orbit galaxies. The large mass in the rich stellar centre of the globular cluster pulls the stars inward to form a ball of stars. The word globulus, from which these clusters take their name, is Latin for small sphere. Globular clusters are generally very ancient objects formed around the same time as their host galaxy. To date, no new star formations have been observed Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-this-image-captures-the-stunning-ngc-6535-a-globular-cluster-22-000-169410952.htmlRMKRH9B4–This image captures the stunning NGC 6535, a globular cluster 22 000 light-years away in the constellation of Serpens (The Serpent) that measures one light-year across. Globular clusters are tightly bound groups of stars which orbit galaxies. The large mass in the rich stellar centre of the globular cluster pulls the stars inward to form a ball of stars. The word globulus, from which these clusters take their name, is Latin for small sphere. Globular clusters are generally very ancient objects formed around the same time as their host galaxy. To date, no new star formations have been observed
 Star clusters, nebula and galaxies. Deep space background in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-clusters-nebula-and-galaxies-deep-space-background-in-high-resolution-image207353828.html
Star clusters, nebula and galaxies. Deep space background in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/star-clusters-nebula-and-galaxies-deep-space-background-in-high-resolution-image207353828.htmlRFP19NWT–Star clusters, nebula and galaxies. Deep space background in high resolution.
 ZwCl 1358+62 is located 3.7 billion light-years from Earth (z=0.33) and is made up of at least 150 individual galaxies. This image depicts multiple blue, red and orange arcs scattered across the image, which represent amplified and stretched images of the galaxies behind the cluster's core. The colours displayed by the various lensed galaxies vary according to their distance and galaxy types. The natural gravitational lensing effect in combination with Hubble's potent mirrors provide astronomers with a powerful set of tools to gather information on the nature of distant galaxies and the workin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-zwcl-135862-is-located-37-billion-light-years-from-earth-z=033-and-169396677.html
ZwCl 1358+62 is located 3.7 billion light-years from Earth (z=0.33) and is made up of at least 150 individual galaxies. This image depicts multiple blue, red and orange arcs scattered across the image, which represent amplified and stretched images of the galaxies behind the cluster's core. The colours displayed by the various lensed galaxies vary according to their distance and galaxy types. The natural gravitational lensing effect in combination with Hubble's potent mirrors provide astronomers with a powerful set of tools to gather information on the nature of distant galaxies and the workin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-zwcl-135862-is-located-37-billion-light-years-from-earth-z=033-and-169396677.htmlRMKRGK59–ZwCl 1358+62 is located 3.7 billion light-years from Earth (z=0.33) and is made up of at least 150 individual galaxies. This image depicts multiple blue, red and orange arcs scattered across the image, which represent amplified and stretched images of the galaxies behind the cluster's core. The colours displayed by the various lensed galaxies vary according to their distance and galaxy types. The natural gravitational lensing effect in combination with Hubble's potent mirrors provide astronomers with a powerful set of tools to gather information on the nature of distant galaxies and the workin
 Deep space full of star clusters and galaxies. Infinite universe in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/deep-space-full-of-star-clusters-and-galaxies-infinite-universe-in-high-resolution-image207353827.html
Deep space full of star clusters and galaxies. Infinite universe in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/deep-space-full-of-star-clusters-and-galaxies-infinite-universe-in-high-resolution-image207353827.htmlRFP19NWR–Deep space full of star clusters and galaxies. Infinite universe in high resolution.
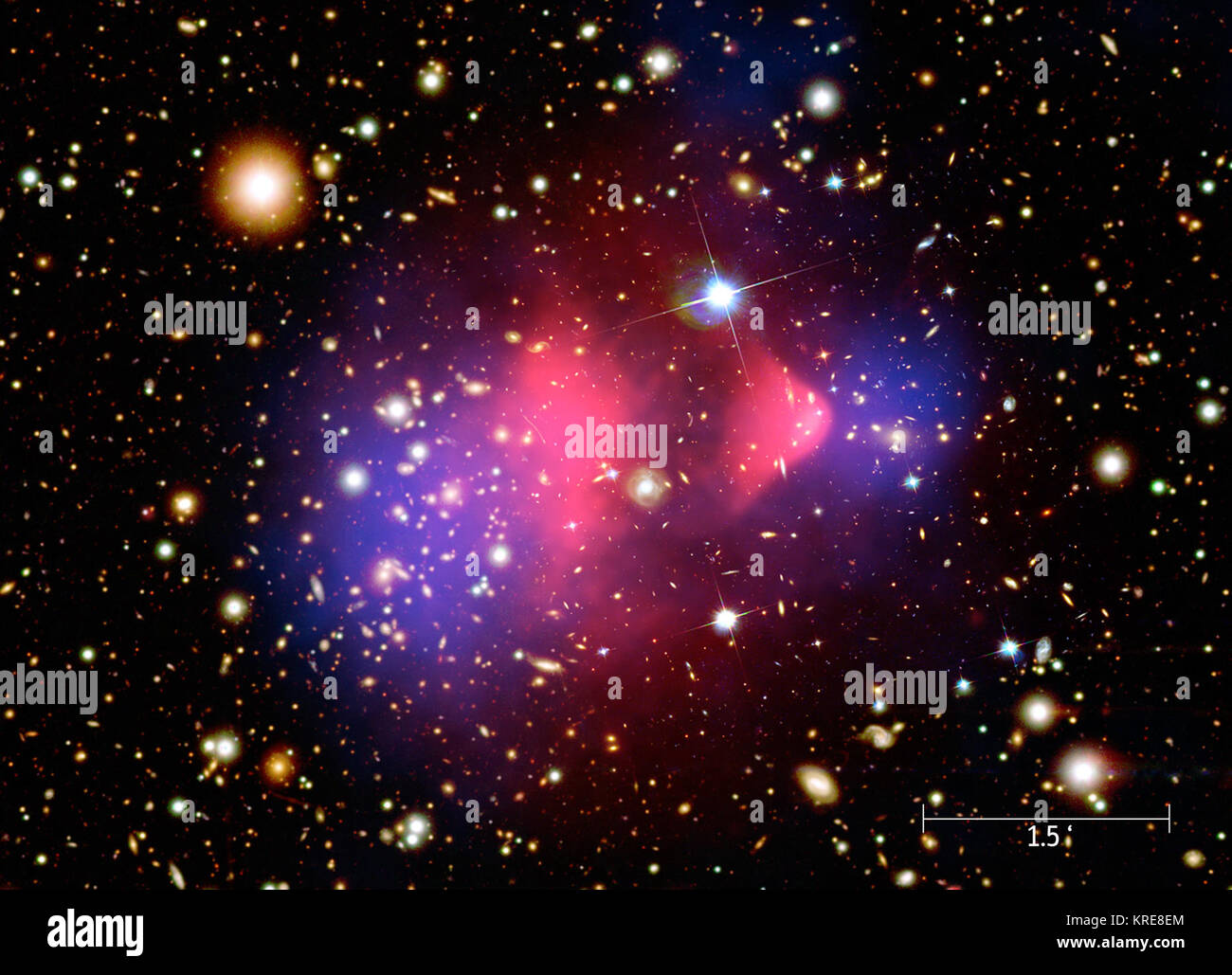 This composite image shows the galaxy cluster 1E 0657-56, also known as the 'bullet cluster', formed after the collision of two large clusters of galaxies. Hot gas detected by Chandra is seen as two pink clumps in the image and contains most of the 'normal' matter in the two clusters. An optical image from Magellan and the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies in orange and white. The blue clumps show where most of the mass in the clusters is found, using a technique known as gravitational lensing. Most of the matter in the clusters (blue) is clearly separate from the normal matter (pink), Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-this-composite-image-shows-the-galaxy-cluster-1e-0657-56-also-known-169344412.html
This composite image shows the galaxy cluster 1E 0657-56, also known as the 'bullet cluster', formed after the collision of two large clusters of galaxies. Hot gas detected by Chandra is seen as two pink clumps in the image and contains most of the 'normal' matter in the two clusters. An optical image from Magellan and the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies in orange and white. The blue clumps show where most of the mass in the clusters is found, using a technique known as gravitational lensing. Most of the matter in the clusters (blue) is clearly separate from the normal matter (pink), Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-this-composite-image-shows-the-galaxy-cluster-1e-0657-56-also-known-169344412.htmlRMKRE8EM–This composite image shows the galaxy cluster 1E 0657-56, also known as the 'bullet cluster', formed after the collision of two large clusters of galaxies. Hot gas detected by Chandra is seen as two pink clumps in the image and contains most of the 'normal' matter in the two clusters. An optical image from Magellan and the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies in orange and white. The blue clumps show where most of the mass in the clusters is found, using a technique known as gravitational lensing. Most of the matter in the clusters (blue) is clearly separate from the normal matter (pink),
 Star Clusters Born Among the Interacting Galaxies of Stephans Quintet from the Hubble Space Telescope Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-star-clusters-born-among-the-interacting-galaxies-of-stephans-quintet-12367358.html
Star Clusters Born Among the Interacting Galaxies of Stephans Quintet from the Hubble Space Telescope Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-star-clusters-born-among-the-interacting-galaxies-of-stephans-quintet-12367358.htmlRMA9H67Y–Star Clusters Born Among the Interacting Galaxies of Stephans Quintet from the Hubble Space Telescope
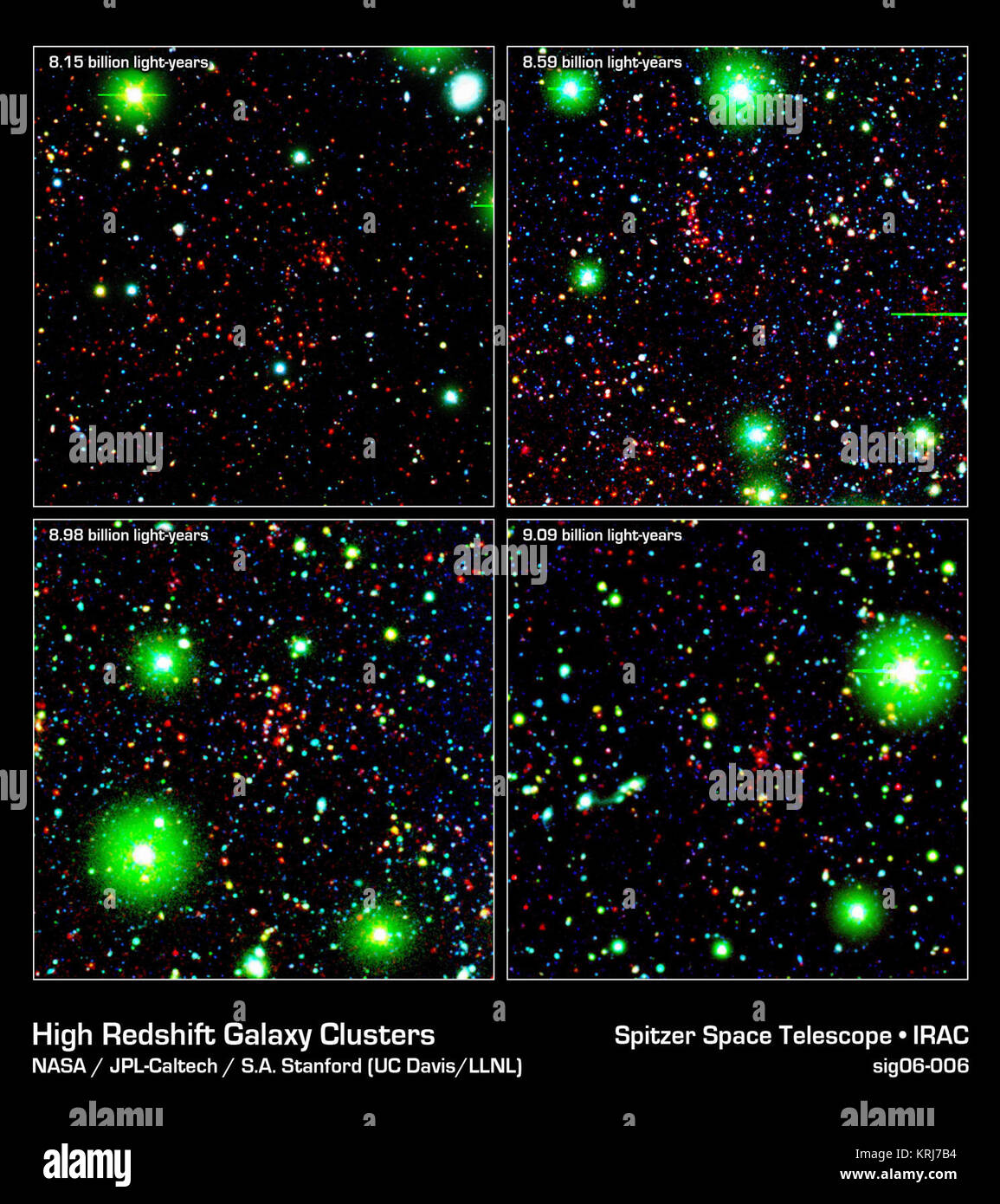 Like great friends, galaxies stick together. Astronomers using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope have spotted a handful of great galactic pals bonding back when the universe was a mere 4.6 billion years old. The universe is believed to be 13.7 billion years old. Collectively, these great galactic buddies are called galaxy clusters. A typical galaxy cluster can contain hundreds of galaxies and trillions of stars. In this false-color composite, some of the oldest galaxy clusters in the universe pose for Spitzer's Infrared Array Camera. The individual galaxies that make up the distant clusters are Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-like-great-friends-galaxies-stick-together-astronomers-using-nasas-169431336.html
Like great friends, galaxies stick together. Astronomers using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope have spotted a handful of great galactic pals bonding back when the universe was a mere 4.6 billion years old. The universe is believed to be 13.7 billion years old. Collectively, these great galactic buddies are called galaxy clusters. A typical galaxy cluster can contain hundreds of galaxies and trillions of stars. In this false-color composite, some of the oldest galaxy clusters in the universe pose for Spitzer's Infrared Array Camera. The individual galaxies that make up the distant clusters are Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-like-great-friends-galaxies-stick-together-astronomers-using-nasas-169431336.htmlRMKRJ7B4–Like great friends, galaxies stick together. Astronomers using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope have spotted a handful of great galactic pals bonding back when the universe was a mere 4.6 billion years old. The universe is believed to be 13.7 billion years old. Collectively, these great galactic buddies are called galaxy clusters. A typical galaxy cluster can contain hundreds of galaxies and trillions of stars. In this false-color composite, some of the oldest galaxy clusters in the universe pose for Spitzer's Infrared Array Camera. The individual galaxies that make up the distant clusters are
 Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/swirling-galaxy-flame-fractal-art-image476269533.html
Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/swirling-galaxy-flame-fractal-art-image476269533.htmlRM2JJRXJ5–Swirling Galaxy - Flame Fractal Art
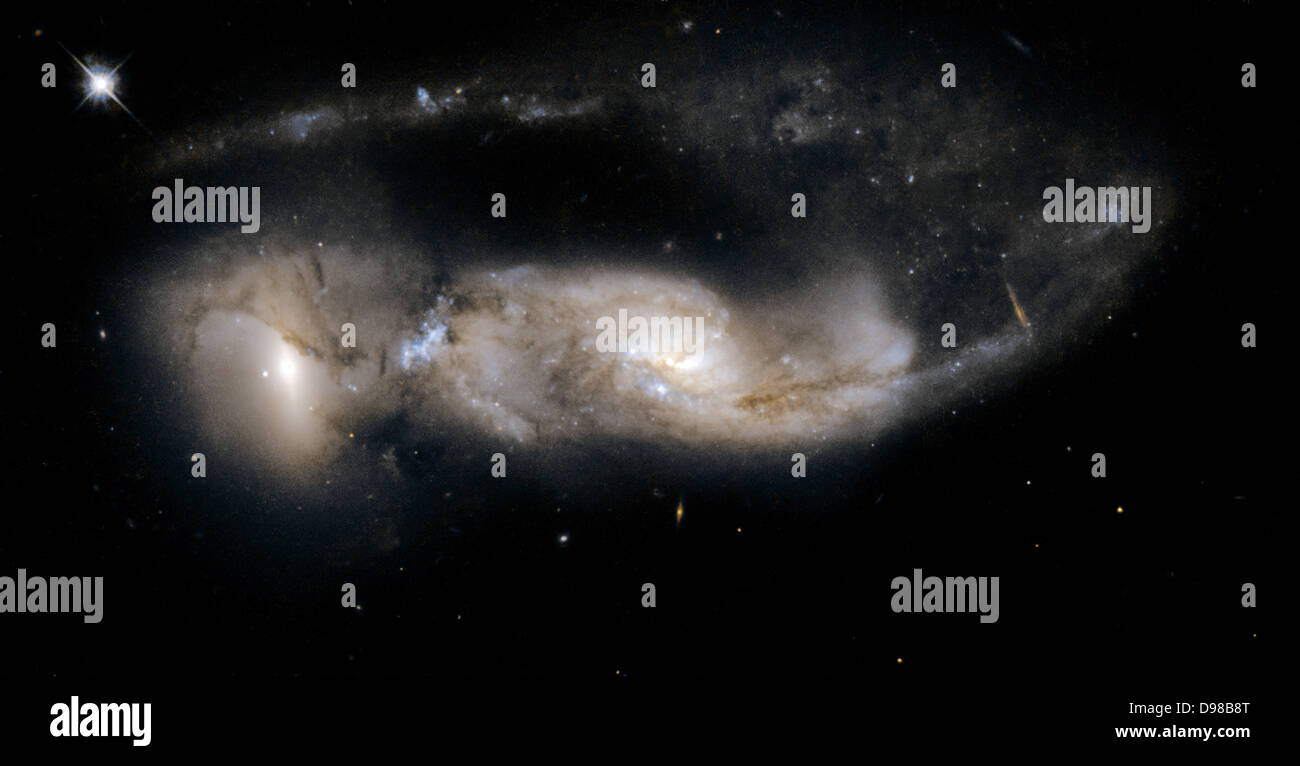 NGC 6621/2 (VV 247, Arp 81) is a strongly interacting pair of galaxies, seen about 100 million years after their closest Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-ngc-66212-vv-247-arp-81-is-a-strongly-interacting-pair-of-galaxies-57347496.html
NGC 6621/2 (VV 247, Arp 81) is a strongly interacting pair of galaxies, seen about 100 million years after their closest Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-ngc-66212-vv-247-arp-81-is-a-strongly-interacting-pair-of-galaxies-57347496.htmlRMD98B8T–NGC 6621/2 (VV 247, Arp 81) is a strongly interacting pair of galaxies, seen about 100 million years after their closest
 Widefield view of the constellations Virgo and Coma Berenices, showing thousands of galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/widefield-view-of-the-constellations-virgo-and-coma-berenices-showing-image61419885.html
Widefield view of the constellations Virgo and Coma Berenices, showing thousands of galaxies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/widefield-view-of-the-constellations-virgo-and-coma-berenices-showing-image61419885.htmlRFDFWWK9–Widefield view of the constellations Virgo and Coma Berenices, showing thousands of galaxies.
 1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-nebulae-geographicus-comets2-burritt-1856-image210071382.html
1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/1856-burritt-huntington-chart-of-comets-star-clusters-galaxies-and-nebulae-geographicus-comets2-burritt-1856-image210071382.htmlRMP5NG5A–1856 Burritt - Huntington Chart of Comets, Star Clusters, Galaxies, and Nebulae - Geographicus - Comets2-burritt-1856.
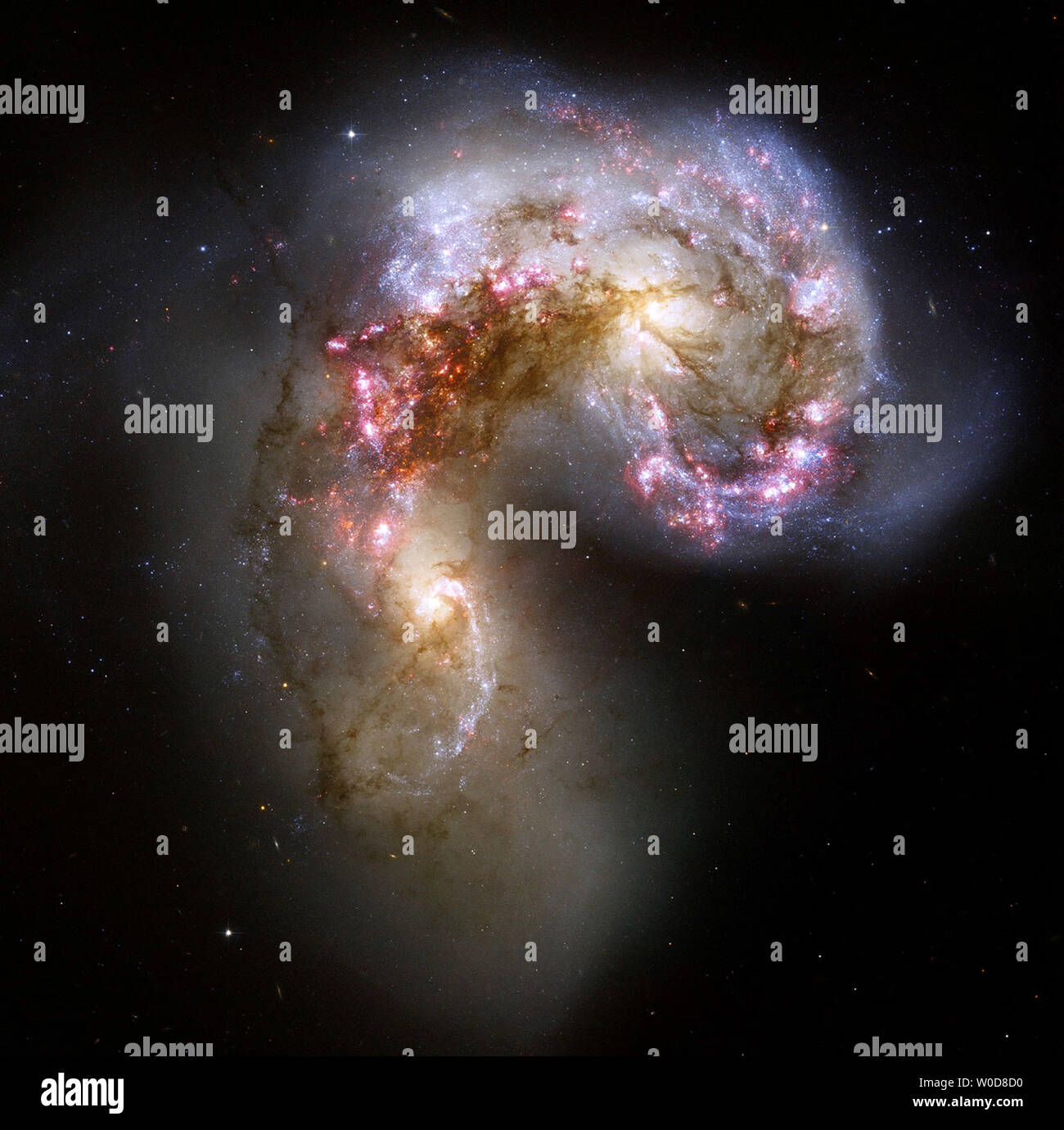 A new Hubble image of the Antennae galaxies is the sharpest yet of this merging pair of galaxies. As the two galaxies smash together, billions of stars are born, mostly in groups and clusters of stars. The brightest and most compact of these are called super star clusters. (UPI Photo/NASA) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-new-hubble-image-of-the-antennae-galaxies-is-the-sharpest-yet-of-this-merging-pair-of-galaxies-as-the-two-galaxies-smash-together-billions-of-stars-are-born-mostly-in-groups-and-clusters-of-stars-the-brightest-and-most-compact-of-these-are-called-super-star-clusters-upi-photonasa-image258447532.html
A new Hubble image of the Antennae galaxies is the sharpest yet of this merging pair of galaxies. As the two galaxies smash together, billions of stars are born, mostly in groups and clusters of stars. The brightest and most compact of these are called super star clusters. (UPI Photo/NASA) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-new-hubble-image-of-the-antennae-galaxies-is-the-sharpest-yet-of-this-merging-pair-of-galaxies-as-the-two-galaxies-smash-together-billions-of-stars-are-born-mostly-in-groups-and-clusters-of-stars-the-brightest-and-most-compact-of-these-are-called-super-star-clusters-upi-photonasa-image258447532.htmlRMW0D8D0–A new Hubble image of the Antennae galaxies is the sharpest yet of this merging pair of galaxies. As the two galaxies smash together, billions of stars are born, mostly in groups and clusters of stars. The brightest and most compact of these are called super star clusters. (UPI Photo/NASA)
 IC 883 displays a very disturbed, complex central region with two tidal tails of approximately the same length emerging at nearly right angles: one diagonally to the top right of the frame and the other to the bottom right. The twin tidal tails suggest that IC 883 is the remnant of the merger of two gas-rich disk galaxies. The collision appears to have triggered a burst of star formation, indicated by a number of bright star clusters in the central region. IC 883 is 300 million light-years away toward the constellation of Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs. It is Number 193 in Arp's Atlas of Pec Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/ic-883-displays-a-very-disturbed-complex-central-region-with-two-tidal-tails-of-approximately-the-same-length-emerging-at-nearly-right-angles-one-diagonally-to-the-top-right-of-the-frame-and-the-other-to-the-bottom-right-the-twin-tidal-tails-suggest-that-ic-883-is-the-remnant-of-the-merger-of-two-gas-rich-disk-galaxies-the-collision-appears-to-have-triggered-a-burst-of-star-formation-indicated-by-a-number-of-bright-star-clusters-in-the-central-region-ic-883-is-300-million-light-years-away-toward-the-constellation-of-canes-venatici-the-hunting-dogs-it-is-number-193-in-arps-atlas-of-pec-image335178666.html
IC 883 displays a very disturbed, complex central region with two tidal tails of approximately the same length emerging at nearly right angles: one diagonally to the top right of the frame and the other to the bottom right. The twin tidal tails suggest that IC 883 is the remnant of the merger of two gas-rich disk galaxies. The collision appears to have triggered a burst of star formation, indicated by a number of bright star clusters in the central region. IC 883 is 300 million light-years away toward the constellation of Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs. It is Number 193 in Arp's Atlas of Pec Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/ic-883-displays-a-very-disturbed-complex-central-region-with-two-tidal-tails-of-approximately-the-same-length-emerging-at-nearly-right-angles-one-diagonally-to-the-top-right-of-the-frame-and-the-other-to-the-bottom-right-the-twin-tidal-tails-suggest-that-ic-883-is-the-remnant-of-the-merger-of-two-gas-rich-disk-galaxies-the-collision-appears-to-have-triggered-a-burst-of-star-formation-indicated-by-a-number-of-bright-star-clusters-in-the-central-region-ic-883-is-300-million-light-years-away-toward-the-constellation-of-canes-venatici-the-hunting-dogs-it-is-number-193-in-arps-atlas-of-pec-image335178666.htmlRF2AD8KPJ–IC 883 displays a very disturbed, complex central region with two tidal tails of approximately the same length emerging at nearly right angles: one diagonally to the top right of the frame and the other to the bottom right. The twin tidal tails suggest that IC 883 is the remnant of the merger of two gas-rich disk galaxies. The collision appears to have triggered a burst of star formation, indicated by a number of bright star clusters in the central region. IC 883 is 300 million light-years away toward the constellation of Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs. It is Number 193 in Arp's Atlas of Pec
 Galaxy Cluster Abell 1689 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/galaxy-cluster-abell-1689-image66433262.html
Galaxy Cluster Abell 1689 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/galaxy-cluster-abell-1689-image66433262.htmlRMDT288E–Galaxy Cluster Abell 1689
 The elliptical galaxy NGC 1132 reveals the final result of what may have been a group of galaxies that merged together in the recent past. Another possibility is that the galaxy formed in isolation as a 'lone wolf' in a universe ablaze with galaxy groups and clusters. NGC 1132 is dubbed a 'fossil group' because it contains enormous concentrations of dark matter, comparable to the dark matter found in an entire group of galaxies. NGC 1132 also has a strong X-ray glow from an abundant amount of hot gas that is normally only found in galaxy groups. In visible light, however, it appears as a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elliptical-galaxy-ngc-1132-reveals-the-final-result-of-what-may-have-been-a-group-of-galaxies-that-merged-together-in-the-recent-past-another-possibility-is-that-the-galaxy-formed-in-isolation-as-a-lone-wolf-in-a-universe-ablaze-with-galaxy-groups-and-clusters-ngc-1132-is-dubbed-a-fossil-group-because-it-contains-enormous-concentrations-of-dark-matter-comparable-to-the-dark-matter-found-in-an-entire-group-of-galaxies-ngc-1132-also-has-a-strong-x-ray-glow-from-an-abundant-amount-of-hot-gas-that-is-normally-only-found-in-galaxy-groups-in-visible-light-however-it-appears-as-a-image335177781.html
The elliptical galaxy NGC 1132 reveals the final result of what may have been a group of galaxies that merged together in the recent past. Another possibility is that the galaxy formed in isolation as a 'lone wolf' in a universe ablaze with galaxy groups and clusters. NGC 1132 is dubbed a 'fossil group' because it contains enormous concentrations of dark matter, comparable to the dark matter found in an entire group of galaxies. NGC 1132 also has a strong X-ray glow from an abundant amount of hot gas that is normally only found in galaxy groups. In visible light, however, it appears as a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-elliptical-galaxy-ngc-1132-reveals-the-final-result-of-what-may-have-been-a-group-of-galaxies-that-merged-together-in-the-recent-past-another-possibility-is-that-the-galaxy-formed-in-isolation-as-a-lone-wolf-in-a-universe-ablaze-with-galaxy-groups-and-clusters-ngc-1132-is-dubbed-a-fossil-group-because-it-contains-enormous-concentrations-of-dark-matter-comparable-to-the-dark-matter-found-in-an-entire-group-of-galaxies-ngc-1132-also-has-a-strong-x-ray-glow-from-an-abundant-amount-of-hot-gas-that-is-normally-only-found-in-galaxy-groups-in-visible-light-however-it-appears-as-a-image335177781.htmlRF2AD8JK1–The elliptical galaxy NGC 1132 reveals the final result of what may have been a group of galaxies that merged together in the recent past. Another possibility is that the galaxy formed in isolation as a 'lone wolf' in a universe ablaze with galaxy groups and clusters. NGC 1132 is dubbed a 'fossil group' because it contains enormous concentrations of dark matter, comparable to the dark matter found in an entire group of galaxies. NGC 1132 also has a strong X-ray glow from an abundant amount of hot gas that is normally only found in galaxy groups. In visible light, however, it appears as a
 universe,galaxy,orion fog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-universegalaxyorion-fog-72791267.html
universe,galaxy,orion fog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-universegalaxyorion-fog-72791267.htmlRFE6BX03–universe,galaxy,orion fog
 A massive cluster of yellowish galaxies, seemingly caught in a red and blue spider web of eerily distorted background galaxies, makes for a spellbinding picture from the new Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. To make this unprecedented image of the cosmos, Hubble peered straight through the center of one of the most massive galaxy clusters known, called Abell 1689. The gravity of the cluster's trillion stars -- plus dark matter -- acts as a 2-million-light-year-wide 'lens' in space. This 'gravitational lens' bends and magnifies the light of the galaxies located f Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-massive-cluster-of-yellowish-galaxies-seemingly-caught-in-a-red-and-blue-spider-web-of-eerily-distorted-background-galaxies-makes-for-a-spellbinding-picture-from-the-new-advanced-camera-for-surveys-aboard-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-to-make-this-unprecedented-image-of-the-cosmos-hubble-peered-straight-through-the-center-of-one-of-the-most-massive-galaxy-clusters-known-called-abell-1689-the-gravity-of-the-clusters-trillion-stars-plus-dark-matter-acts-as-a-2-million-light-year-wide-lens-in-space-this-gravitational-lens-bends-and-magnifies-the-light-of-the-galaxies-located-f-image335177234.html
A massive cluster of yellowish galaxies, seemingly caught in a red and blue spider web of eerily distorted background galaxies, makes for a spellbinding picture from the new Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. To make this unprecedented image of the cosmos, Hubble peered straight through the center of one of the most massive galaxy clusters known, called Abell 1689. The gravity of the cluster's trillion stars -- plus dark matter -- acts as a 2-million-light-year-wide 'lens' in space. This 'gravitational lens' bends and magnifies the light of the galaxies located f Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-massive-cluster-of-yellowish-galaxies-seemingly-caught-in-a-red-and-blue-spider-web-of-eerily-distorted-background-galaxies-makes-for-a-spellbinding-picture-from-the-new-advanced-camera-for-surveys-aboard-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-to-make-this-unprecedented-image-of-the-cosmos-hubble-peered-straight-through-the-center-of-one-of-the-most-massive-galaxy-clusters-known-called-abell-1689-the-gravity-of-the-clusters-trillion-stars-plus-dark-matter-acts-as-a-2-million-light-year-wide-lens-in-space-this-gravitational-lens-bends-and-magnifies-the-light-of-the-galaxies-located-f-image335177234.htmlRF2AD8HYE–A massive cluster of yellowish galaxies, seemingly caught in a red and blue spider web of eerily distorted background galaxies, makes for a spellbinding picture from the new Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. To make this unprecedented image of the cosmos, Hubble peered straight through the center of one of the most massive galaxy clusters known, called Abell 1689. The gravity of the cluster's trillion stars -- plus dark matter -- acts as a 2-million-light-year-wide 'lens' in space. This 'gravitational lens' bends and magnifies the light of the galaxies located f
 This August, 5 2008 NASA image captured by the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxy NGC 4458 in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. NGC 4458 is one of the recently identified 5 billion year-old globular clusters in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. (UPI Photo/NASA) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-august-5-2008-nasa-image-captured-by-the-hubble-space-telescope-shows-galaxy-ngc-4458-in-the-virgo-cluster-of-galaxies-ngc-4458-is-one-of-the-recently-identified-5-billion-year-old-globular-clusters-in-the-virgo-cluster-of-galaxies-upi-photonasa-image258604653.html
This August, 5 2008 NASA image captured by the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxy NGC 4458 in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. NGC 4458 is one of the recently identified 5 billion year-old globular clusters in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. (UPI Photo/NASA) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-august-5-2008-nasa-image-captured-by-the-hubble-space-telescope-shows-galaxy-ngc-4458-in-the-virgo-cluster-of-galaxies-ngc-4458-is-one-of-the-recently-identified-5-billion-year-old-globular-clusters-in-the-virgo-cluster-of-galaxies-upi-photonasa-image258604653.htmlRMW0MCTD–This August, 5 2008 NASA image captured by the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxy NGC 4458 in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. NGC 4458 is one of the recently identified 5 billion year-old globular clusters in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. (UPI Photo/NASA)
![Infographic about stars and galaxies near and more distant from Earth. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photo Infographic about stars and galaxies near and more distant from Earth. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2NEBRX2/infographic-about-stars-and-galaxies-near-and-more-distant-from-earth-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-2NEBRX2.jpg) Infographic about stars and galaxies near and more distant from Earth. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-about-stars-and-galaxies-near-and-more-distant-from-earth-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-image525176458.html
Infographic about stars and galaxies near and more distant from Earth. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015]. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/infographic-about-stars-and-galaxies-near-and-more-distant-from-earth-quarkxpress-qxp-6259x4015-image525176458.htmlRM2NEBRX2–Infographic about stars and galaxies near and more distant from Earth. [QuarkXPress (.qxp); 6259x4015].
 Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This 'hefty' cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some 2 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is so massive that its enormous gravitational field deflects light rays passing through it, much as an optical lens bends light to form an image. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, magnifies, brightens, and distorts images from faraway objects. The cluster's magnify Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scanning-the-heavens-for-the-first-time-since-the-successful-december-1999-servicing-mission-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-imaged-a-giant-cosmic-magnifying-glass-a-massive-cluster-of-galaxies-called-abell-2218-this-hefty-cluster-resides-in-the-constellation-draco-some-2-billion-light-years-from-earth-the-cluster-is-so-massive-that-its-enormous-gravitational-field-deflects-light-rays-passing-through-it-much-as-an-optical-lens-bends-light-to-form-an-image-this-phenomenon-called-gravitational-lensing-magnifies-brightens-and-distorts-images-from-faraway-objects-the-clusters-magnify-image547776499.html
Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This 'hefty' cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some 2 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is so massive that its enormous gravitational field deflects light rays passing through it, much as an optical lens bends light to form an image. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, magnifies, brightens, and distorts images from faraway objects. The cluster's magnify Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scanning-the-heavens-for-the-first-time-since-the-successful-december-1999-servicing-mission-nasas-hubble-space-telescope-imaged-a-giant-cosmic-magnifying-glass-a-massive-cluster-of-galaxies-called-abell-2218-this-hefty-cluster-resides-in-the-constellation-draco-some-2-billion-light-years-from-earth-the-cluster-is-so-massive-that-its-enormous-gravitational-field-deflects-light-rays-passing-through-it-much-as-an-optical-lens-bends-light-to-form-an-image-this-phenomenon-called-gravitational-lensing-magnifies-brightens-and-distorts-images-from-faraway-objects-the-clusters-magnify-image547776499.htmlRM2PR5AEB–Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This 'hefty' cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some 2 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is so massive that its enormous gravitational field deflects light rays passing through it, much as an optical lens bends light to form an image. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, magnifies, brightens, and distorts images from faraway objects. The cluster's magnify
 Most galaxies are clumped together in groups or clusters. A neighboring galaxy is never far away. But this galaxy, known as NGC 6503, has found itself in a lonely position, at the edge of a strangely empty patch of space called the Local Void. The Local Void is a huge stretch of space that is at least 150 million light-years across. It seems completely empty of stars or galaxies. The galaxy’s odd location on the edge of this never-land led stargazer Stephen James O’Meara to dub it the “Lost-In-Space galaxy” in his 2007 book, Hidden Treasures. NGC 6503 is 18 million light-years away from us i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-most-galaxies-are-clumped-together-in-groups-or-clusters-a-neighboring-86475048.html
Most galaxies are clumped together in groups or clusters. A neighboring galaxy is never far away. But this galaxy, known as NGC 6503, has found itself in a lonely position, at the edge of a strangely empty patch of space called the Local Void. The Local Void is a huge stretch of space that is at least 150 million light-years across. It seems completely empty of stars or galaxies. The galaxy’s odd location on the edge of this never-land led stargazer Stephen James O’Meara to dub it the “Lost-In-Space galaxy” in his 2007 book, Hidden Treasures. NGC 6503 is 18 million light-years away from us i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-most-galaxies-are-clumped-together-in-groups-or-clusters-a-neighboring-86475048.htmlRMF0K7PG–Most galaxies are clumped together in groups or clusters. A neighboring galaxy is never far away. But this galaxy, known as NGC 6503, has found itself in a lonely position, at the edge of a strangely empty patch of space called the Local Void. The Local Void is a huge stretch of space that is at least 150 million light-years across. It seems completely empty of stars or galaxies. The galaxy’s odd location on the edge of this never-land led stargazer Stephen James O’Meara to dub it the “Lost-In-Space galaxy” in his 2007 book, Hidden Treasures. NGC 6503 is 18 million light-years away from us i
 Abstract black hole star and galaxy clusters spiral inward Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-abstract-black-hole-star-and-galaxy-clusters-spiral-inward-90291287.html
Abstract black hole star and galaxy clusters spiral inward Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-abstract-black-hole-star-and-galaxy-clusters-spiral-inward-90291287.htmlRFF6W3CR–Abstract black hole star and galaxy clusters spiral inward
 Deep space full of star clusters and galaxies. Infinite universe in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-deep-space-full-of-star-clusters-and-galaxies-infinite-universe-in-175967160.html
Deep space full of star clusters and galaxies. Infinite universe in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-deep-space-full-of-star-clusters-and-galaxies-infinite-universe-in-175967160.htmlRFM67YWC–Deep space full of star clusters and galaxies. Infinite universe in high resolution.
 Hubble Catches Galaxies Swarmed by Star Clusters 37361692672 o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-hubble-catches-galaxies-swarmed-by-star-clusters-37361692672-o-171963978.html
Hubble Catches Galaxies Swarmed by Star Clusters 37361692672 o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-hubble-catches-galaxies-swarmed-by-star-clusters-37361692672-o-171963978.htmlRMKYNHPJ–Hubble Catches Galaxies Swarmed by Star Clusters 37361692672 o
 Galaxies, star clusters and nebula in deep space. Universe background in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galaxies-star-clusters-and-nebula-in-deep-space-universe-background-176896917.html
Galaxies, star clusters and nebula in deep space. Universe background in high resolution. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-galaxies-star-clusters-and-nebula-in-deep-space-universe-background-176896917.htmlRFM7P9R1–Galaxies, star clusters and nebula in deep space. Universe background in high resolution.
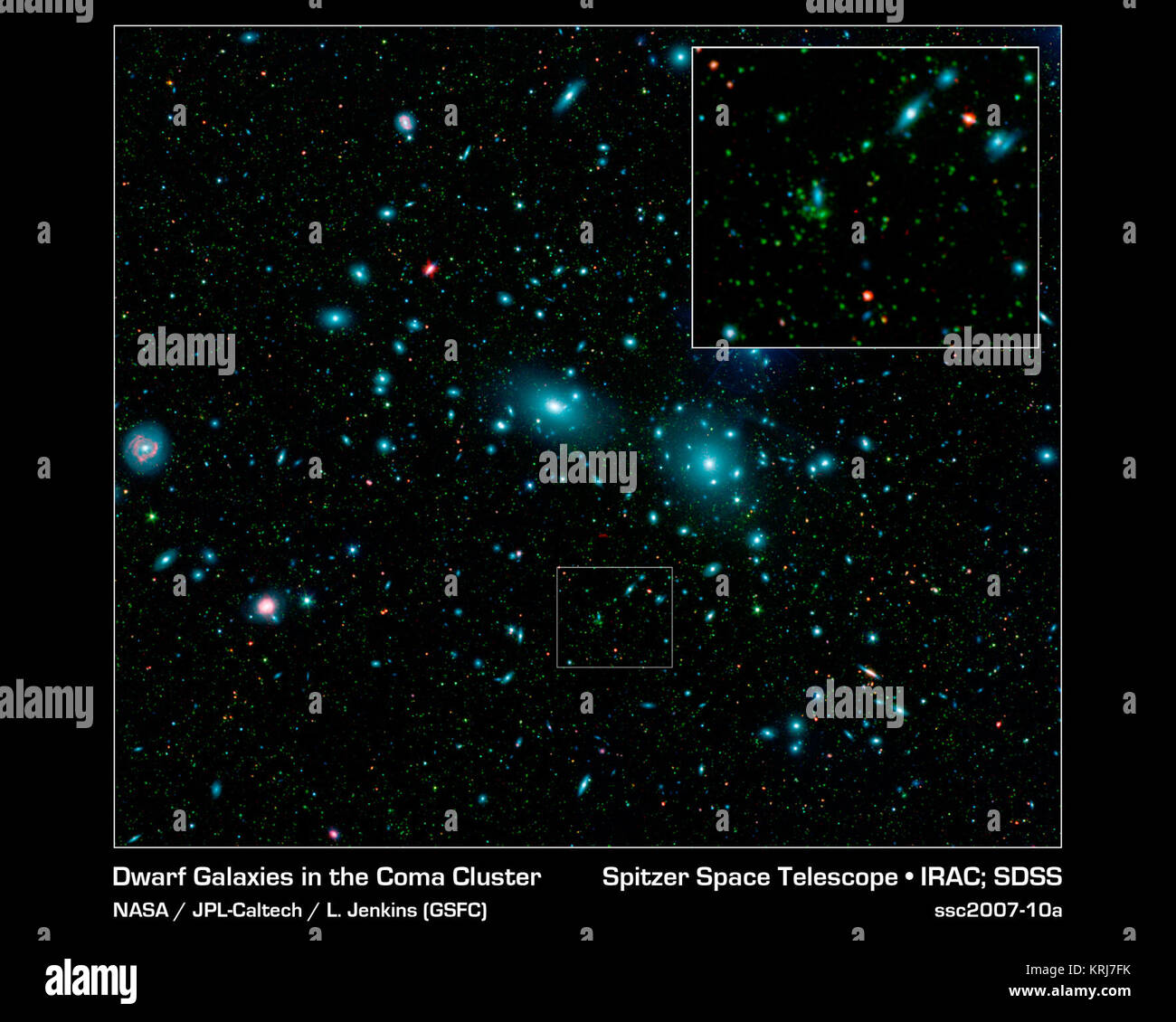 This false-color mosaic of the central region of the Coma cluster combines infrared and visible-light images to reveal thousands of faint objects (green). Follow-up observations showed that many of these objects, which appear here as faint green smudges, are dwarf galaxies belonging to the cluster. Two large elliptical galaxies, NGC 4889 and NGC 4874, dominate the cluster's center. The mosaic combines visible-light data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (color coded blue) with long- and short-wavelength infrared views (red and green, respectively) from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Dwarf Gal Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-this-false-color-mosaic-of-the-central-region-of-the-coma-cluster-169431463.html
This false-color mosaic of the central region of the Coma cluster combines infrared and visible-light images to reveal thousands of faint objects (green). Follow-up observations showed that many of these objects, which appear here as faint green smudges, are dwarf galaxies belonging to the cluster. Two large elliptical galaxies, NGC 4889 and NGC 4874, dominate the cluster's center. The mosaic combines visible-light data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (color coded blue) with long- and short-wavelength infrared views (red and green, respectively) from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Dwarf Gal Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-this-false-color-mosaic-of-the-central-region-of-the-coma-cluster-169431463.htmlRMKRJ7FK–This false-color mosaic of the central region of the Coma cluster combines infrared and visible-light images to reveal thousands of faint objects (green). Follow-up observations showed that many of these objects, which appear here as faint green smudges, are dwarf galaxies belonging to the cluster. Two large elliptical galaxies, NGC 4889 and NGC 4874, dominate the cluster's center. The mosaic combines visible-light data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (color coded blue) with long- and short-wavelength infrared views (red and green, respectively) from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Dwarf Gal
 Planet Earth in outer space with star clusters, constellations and galaxies far away behind - Elements of this illustration furnished by NASA. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/planet-earth-in-outer-space-with-star-clusters-constellations-and-galaxies-far-away-behind-elements-of-this-illustration-furnished-by-nasa-image221002650.html
Planet Earth in outer space with star clusters, constellations and galaxies far away behind - Elements of this illustration furnished by NASA. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/planet-earth-in-outer-space-with-star-clusters-constellations-and-galaxies-far-away-behind-elements-of-this-illustration-furnished-by-nasa-image221002650.htmlRFPRFF3P–Planet Earth in outer space with star clusters, constellations and galaxies far away behind - Elements of this illustration furnished by NASA.
 The collection of red dots seen near the center of this image show one of several very distant galaxy clusters discovered by combining ground-based optical data from the National Optical Astronomy Observatory's Kitt Peak National Observatory with infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. This galaxy cluster, named ISCS J1434.7+3519, is located about 9 billion light-years from Earth. The large white and yellow dots in this picture are stars in our galaxy, while the rest of the smaller dots are distant galaxies. The cluster, comprised of red dots near the center, includes more than 10 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-the-collection-of-red-dots-seen-near-the-center-of-this-image-show-169394539.html
The collection of red dots seen near the center of this image show one of several very distant galaxy clusters discovered by combining ground-based optical data from the National Optical Astronomy Observatory's Kitt Peak National Observatory with infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. This galaxy cluster, named ISCS J1434.7+3519, is located about 9 billion light-years from Earth. The large white and yellow dots in this picture are stars in our galaxy, while the rest of the smaller dots are distant galaxies. The cluster, comprised of red dots near the center, includes more than 10 Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-the-collection-of-red-dots-seen-near-the-center-of-this-image-show-169394539.htmlRMKRGGCY–The collection of red dots seen near the center of this image show one of several very distant galaxy clusters discovered by combining ground-based optical data from the National Optical Astronomy Observatory's Kitt Peak National Observatory with infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. This galaxy cluster, named ISCS J1434.7+3519, is located about 9 billion light-years from Earth. The large white and yellow dots in this picture are stars in our galaxy, while the rest of the smaller dots are distant galaxies. The cluster, comprised of red dots near the center, includes more than 10