Guanosine diphosphate Stock Photos and Images
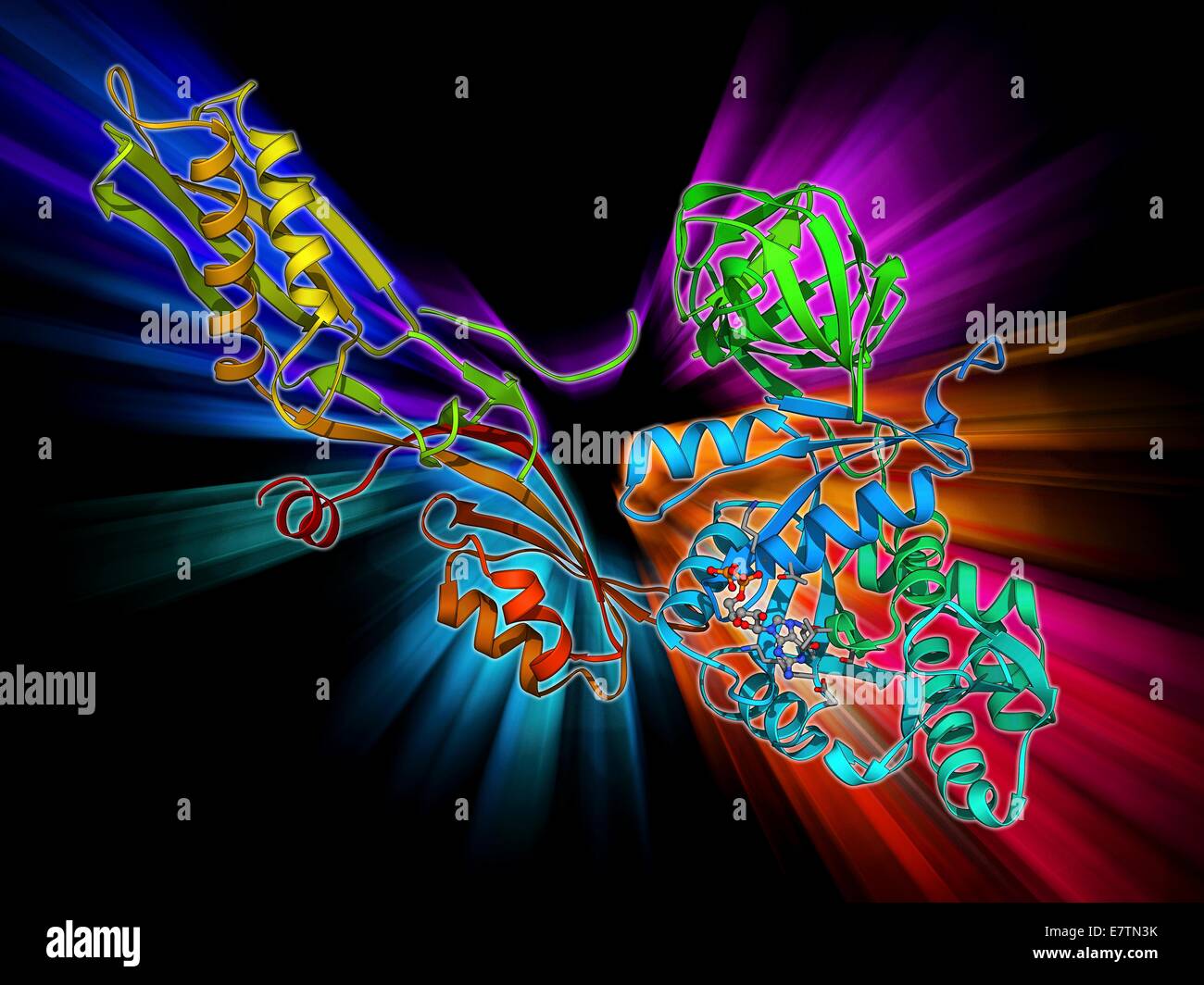 Elongation factor G. Molecular model of elongation factor G (EF-G) complexed with GDP (guanosine diphosphate). This enzyme is involved in the elongation of polypeptide chains during translation, the production of a protein from an mRNA (messenger ribonucl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-elongation-factor-g-molecular-model-of-elongation-factor-g-ef-g-complexed-73687479.html
Elongation factor G. Molecular model of elongation factor G (EF-G) complexed with GDP (guanosine diphosphate). This enzyme is involved in the elongation of polypeptide chains during translation, the production of a protein from an mRNA (messenger ribonucl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-elongation-factor-g-molecular-model-of-elongation-factor-g-ef-g-complexed-73687479.htmlRFE7TN3K–Elongation factor G. Molecular model of elongation factor G (EF-G) complexed with GDP (guanosine diphosphate). This enzyme is involved in the elongation of polypeptide chains during translation, the production of a protein from an mRNA (messenger ribonucl
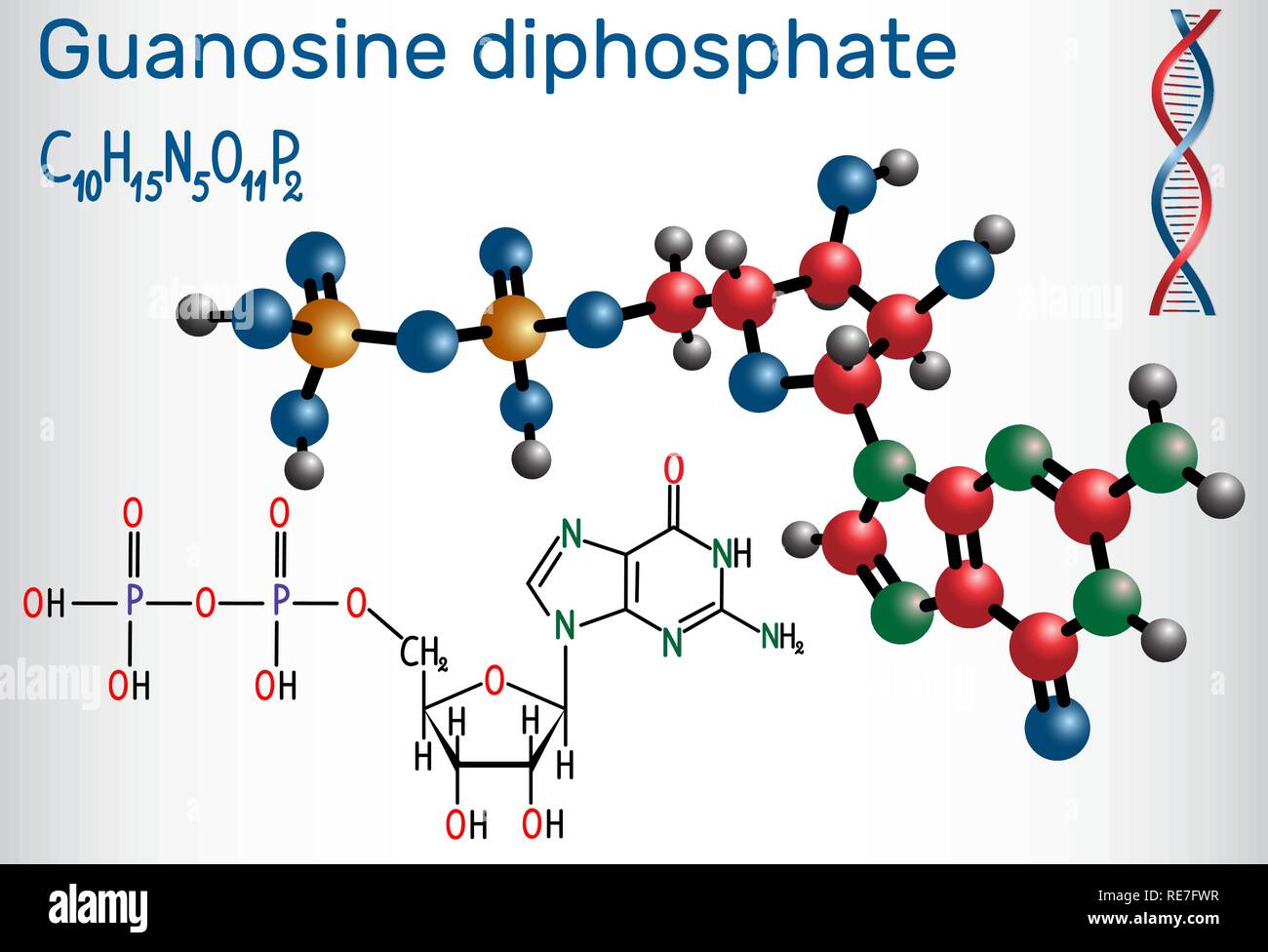 Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule. Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-diphosphate-gdp-molecule-structural-chemical-formula-and-molecule-model-vector-illustration-image232506115.html
Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule. Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-diphosphate-gdp-molecule-structural-chemical-formula-and-molecule-model-vector-illustration-image232506115.htmlRFRE7FWR–Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule. Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Vector illustration
 Inactive (left) and active (right) Ras proteins, illustration. Inactive Ras proteins have GDP (guanine diphosphate, orange) bound to their active site, while active Ras proteins have GTP (guanine triphosphate, orange) bound to their active site. Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells, turning on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing cells to subdivide without control, often leading to cancer. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-inactive-left-and-active-right-ras-proteins-illustration-inactive-177496932.html
Inactive (left) and active (right) Ras proteins, illustration. Inactive Ras proteins have GDP (guanine diphosphate, orange) bound to their active site, while active Ras proteins have GTP (guanine triphosphate, orange) bound to their active site. Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells, turning on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing cells to subdivide without control, often leading to cancer. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-inactive-left-and-active-right-ras-proteins-illustration-inactive-177496932.htmlRFM8NK44–Inactive (left) and active (right) Ras proteins, illustration. Inactive Ras proteins have GDP (guanine diphosphate, orange) bound to their active site, while active Ras proteins have GTP (guanine triphosphate, orange) bound to their active site. Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells, turning on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing cells to subdivide without control, often leading to cancer.
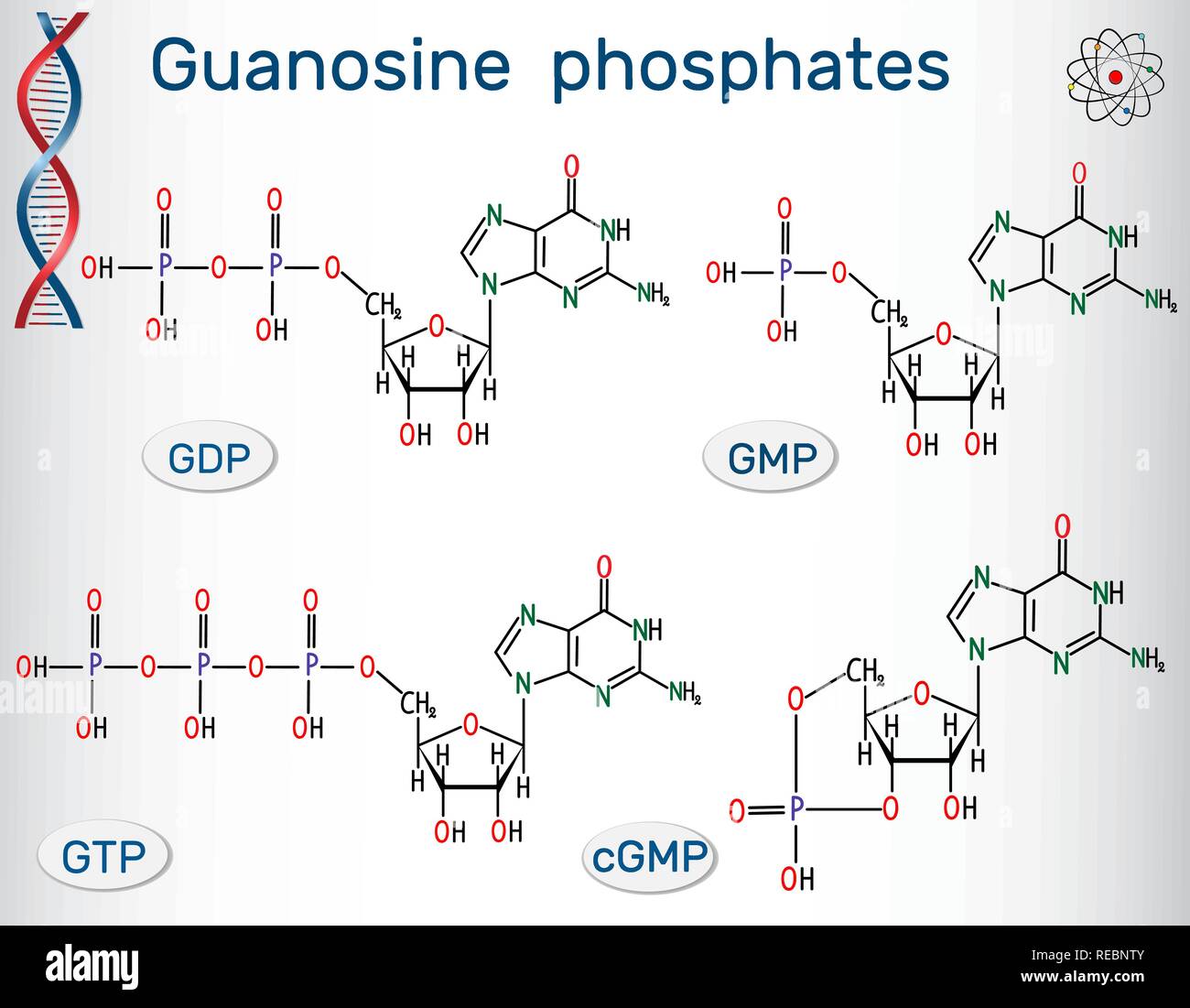 Guanosine phosphates (guanosine triphosphate, guanosine diphosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate). Structural chemical for Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-phosphates-guanosine-triphosphate-guanosine-diphosphate-guanosine-monophosphate-cyclic-guanosine-monophosphate-structural-chemical-for-image232598603.html
Guanosine phosphates (guanosine triphosphate, guanosine diphosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate). Structural chemical for Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-phosphates-guanosine-triphosphate-guanosine-diphosphate-guanosine-monophosphate-cyclic-guanosine-monophosphate-structural-chemical-for-image232598603.htmlRFREBNTY–Guanosine phosphates (guanosine triphosphate, guanosine diphosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate). Structural chemical for
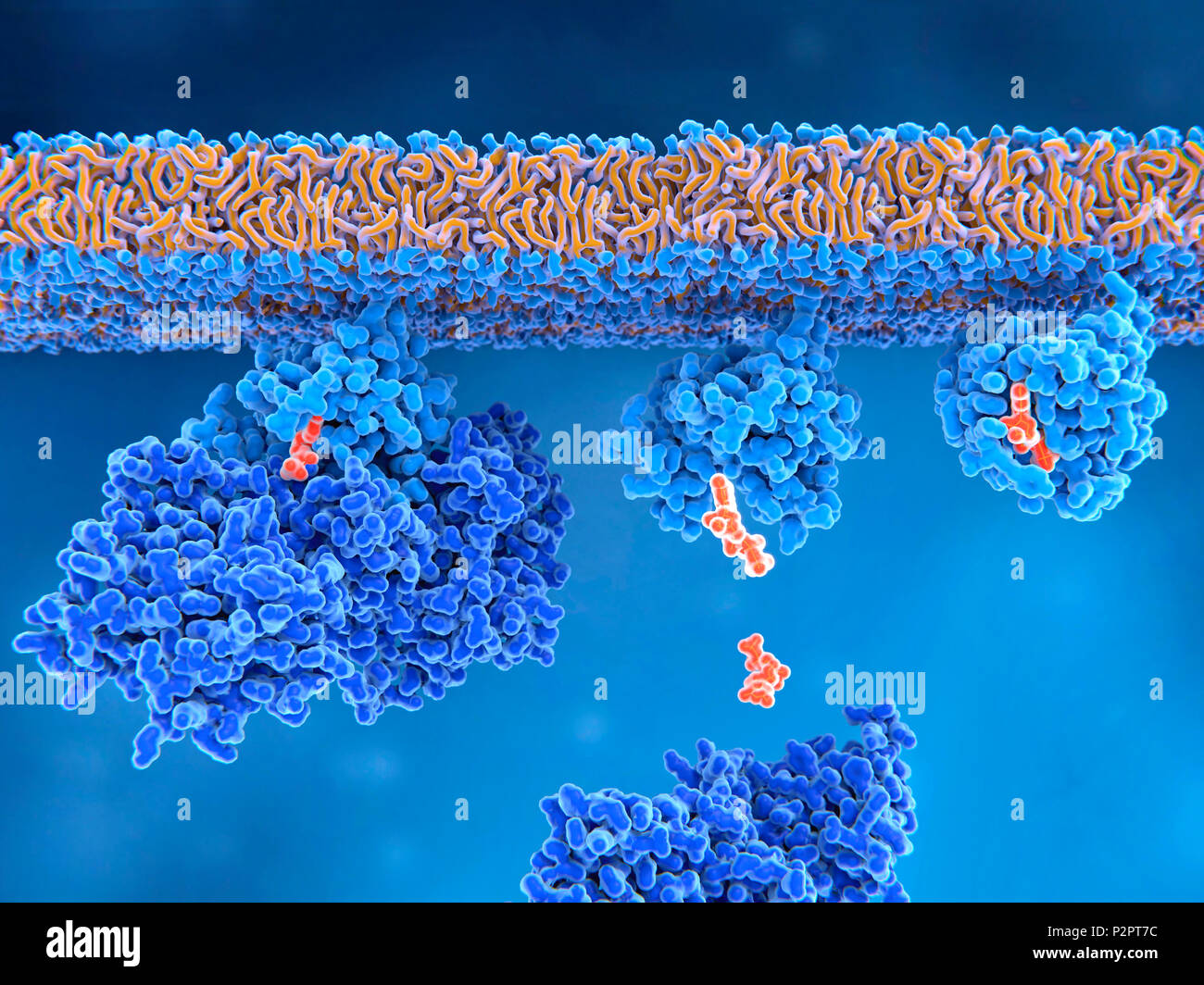 Activation of ras protein, illustration. An inactive ras protein (light blue, upper left) has a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor, dark blue) protein bound to it. GEF stimulates the release of GDP (guanine diphosphate, orange) from ras's binding site (centre). This allows a GTP molecule (guanine triphosphate, orange) to bind to ras, changing it into the active form (upper right). Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells, turning on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/activation-of-ras-protein-illustration-an-inactive-ras-protein-light-blue-upper-left-has-a-gef-guanine-nucleotide-exchange-factor-dark-blue-protein-bound-to-it-gef-stimulates-the-release-of-gdp-guanine-diphosphate-orange-from-rass-binding-site-centre-this-allows-a-gtp-molecule-guanine-triphosphate-orange-to-bind-to-ras-changing-it-into-the-active-form-upper-right-ras-proteins-are-involved-in-transmitting-signals-within-cells-turning-on-genes-involved-in-cell-growth-differentiation-and-survival-mutations-in-ras-genes-can-lead-to-permanently-activated-proteins-causing-image208255696.html
Activation of ras protein, illustration. An inactive ras protein (light blue, upper left) has a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor, dark blue) protein bound to it. GEF stimulates the release of GDP (guanine diphosphate, orange) from ras's binding site (centre). This allows a GTP molecule (guanine triphosphate, orange) to bind to ras, changing it into the active form (upper right). Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells, turning on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/activation-of-ras-protein-illustration-an-inactive-ras-protein-light-blue-upper-left-has-a-gef-guanine-nucleotide-exchange-factor-dark-blue-protein-bound-to-it-gef-stimulates-the-release-of-gdp-guanine-diphosphate-orange-from-rass-binding-site-centre-this-allows-a-gtp-molecule-guanine-triphosphate-orange-to-bind-to-ras-changing-it-into-the-active-form-upper-right-ras-proteins-are-involved-in-transmitting-signals-within-cells-turning-on-genes-involved-in-cell-growth-differentiation-and-survival-mutations-in-ras-genes-can-lead-to-permanently-activated-proteins-causing-image208255696.htmlRFP2PT7C–Activation of ras protein, illustration. An inactive ras protein (light blue, upper left) has a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor, dark blue) protein bound to it. GEF stimulates the release of GDP (guanine diphosphate, orange) from ras's binding site (centre). This allows a GTP molecule (guanine triphosphate, orange) to bind to ras, changing it into the active form (upper right). Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells, turning on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing
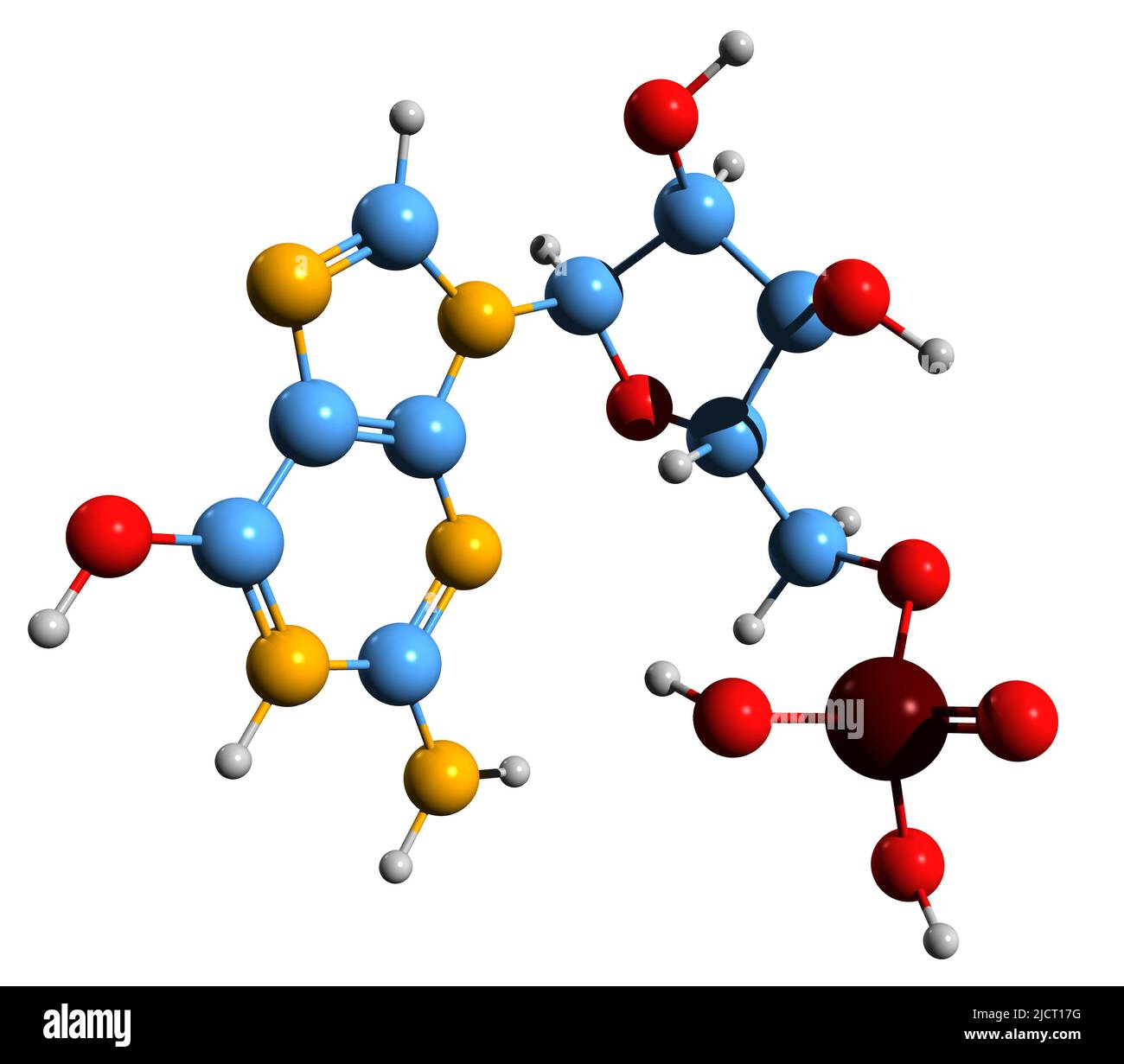 3D image of guanylic acid skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of Guanosine monophosphate E626 isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-guanylic-acid-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-guanosine-monophosphate-e626-isolated-on-white-background-image472583652.html
3D image of guanylic acid skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of Guanosine monophosphate E626 isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-guanylic-acid-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-guanosine-monophosphate-e626-isolated-on-white-background-image472583652.htmlRF2JCT17G–3D image of guanylic acid skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of Guanosine monophosphate E626 isolated on white background
 Activation of Ras protein,illustration. An inactive Ras protein (left) has a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) protein bound.GEF stimulates the release of GDP (guanine diphosphate,orange) from Ras's binding site. This allows a GTP molecule (guanine triphosphate, orange) to bind to RAS changing it into the active form (right).Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells turning on genes involved in cell growth differentiation and survival.Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing cells to subdivide without control often leading to cancer. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-activation-of-ras-proteinillustration-an-inactive-ras-protein-left-177496931.html
Activation of Ras protein,illustration. An inactive Ras protein (left) has a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) protein bound.GEF stimulates the release of GDP (guanine diphosphate,orange) from Ras's binding site. This allows a GTP molecule (guanine triphosphate, orange) to bind to RAS changing it into the active form (right).Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells turning on genes involved in cell growth differentiation and survival.Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing cells to subdivide without control often leading to cancer. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-activation-of-ras-proteinillustration-an-inactive-ras-protein-left-177496931.htmlRFM8NK43–Activation of Ras protein,illustration. An inactive Ras protein (left) has a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) protein bound.GEF stimulates the release of GDP (guanine diphosphate,orange) from Ras's binding site. This allows a GTP molecule (guanine triphosphate, orange) to bind to RAS changing it into the active form (right).Ras proteins are involved in transmitting signals within cells turning on genes involved in cell growth differentiation and survival.Mutations in ras genes can lead to permanently activated proteins causing cells to subdivide without control often leading to cancer.
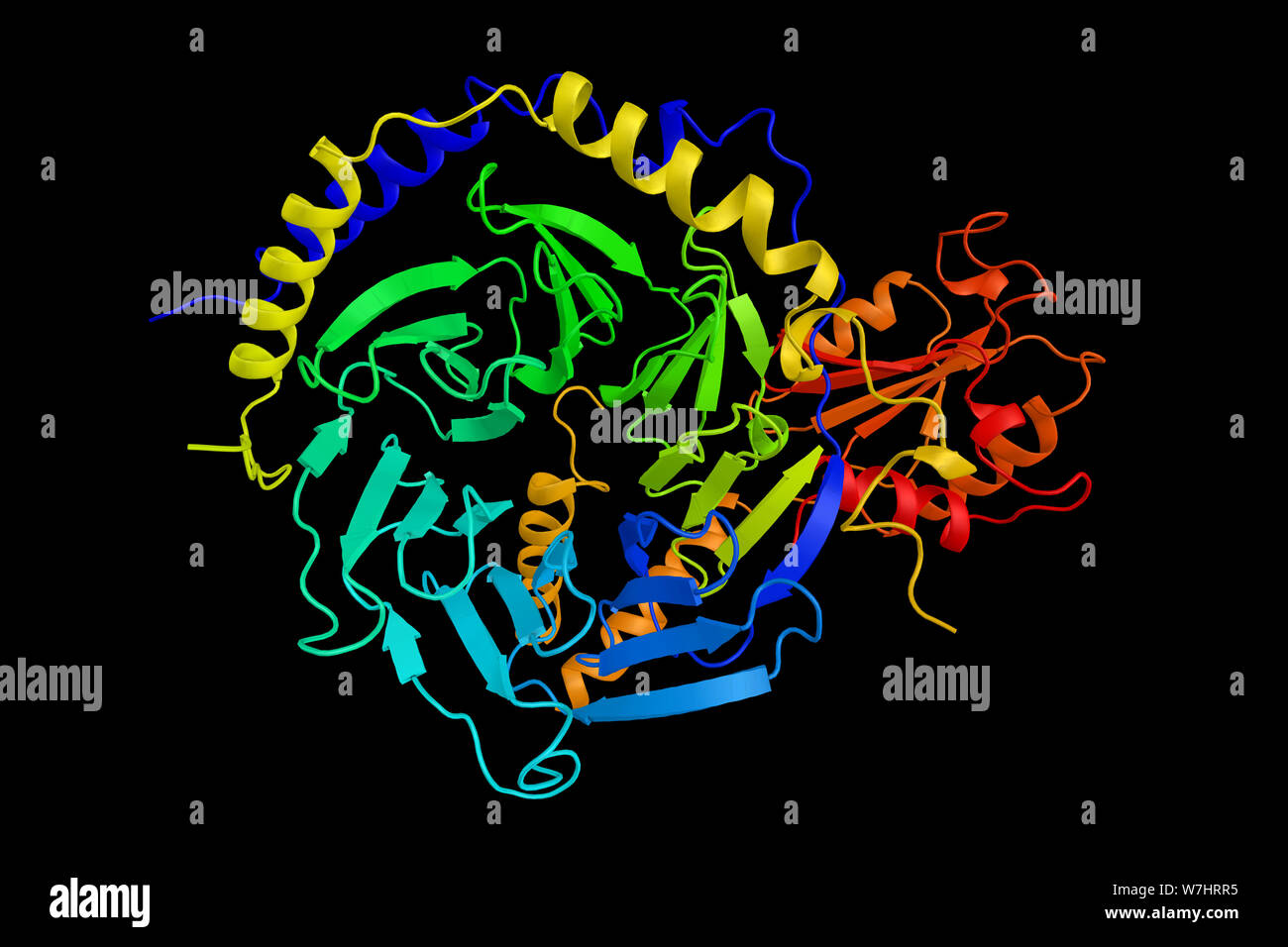 Phosducin-transducin beta-gamma complex, a part of the G protein family. These proteins are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/phosducin-transducin-beta-gamma-complex-a-part-of-the-g-protein-family-these-proteins-are-involved-in-transmitting-signals-from-a-variety-of-stimuli-image262849977.html
Phosducin-transducin beta-gamma complex, a part of the G protein family. These proteins are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/phosducin-transducin-beta-gamma-complex-a-part-of-the-g-protein-family-these-proteins-are-involved-in-transmitting-signals-from-a-variety-of-stimuli-image262849977.htmlRFW7HRR5–Phosducin-transducin beta-gamma complex, a part of the G protein family. These proteins are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli
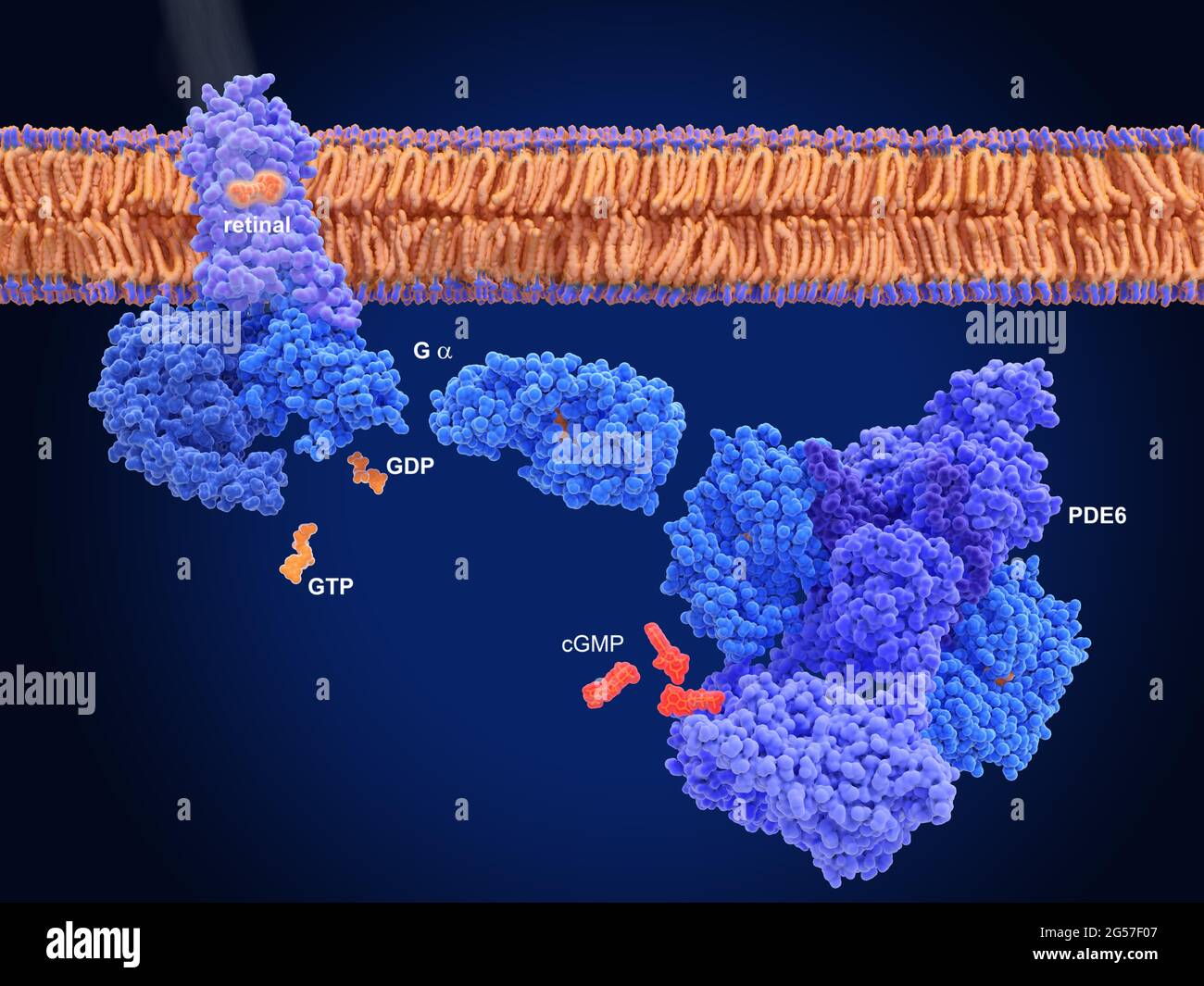
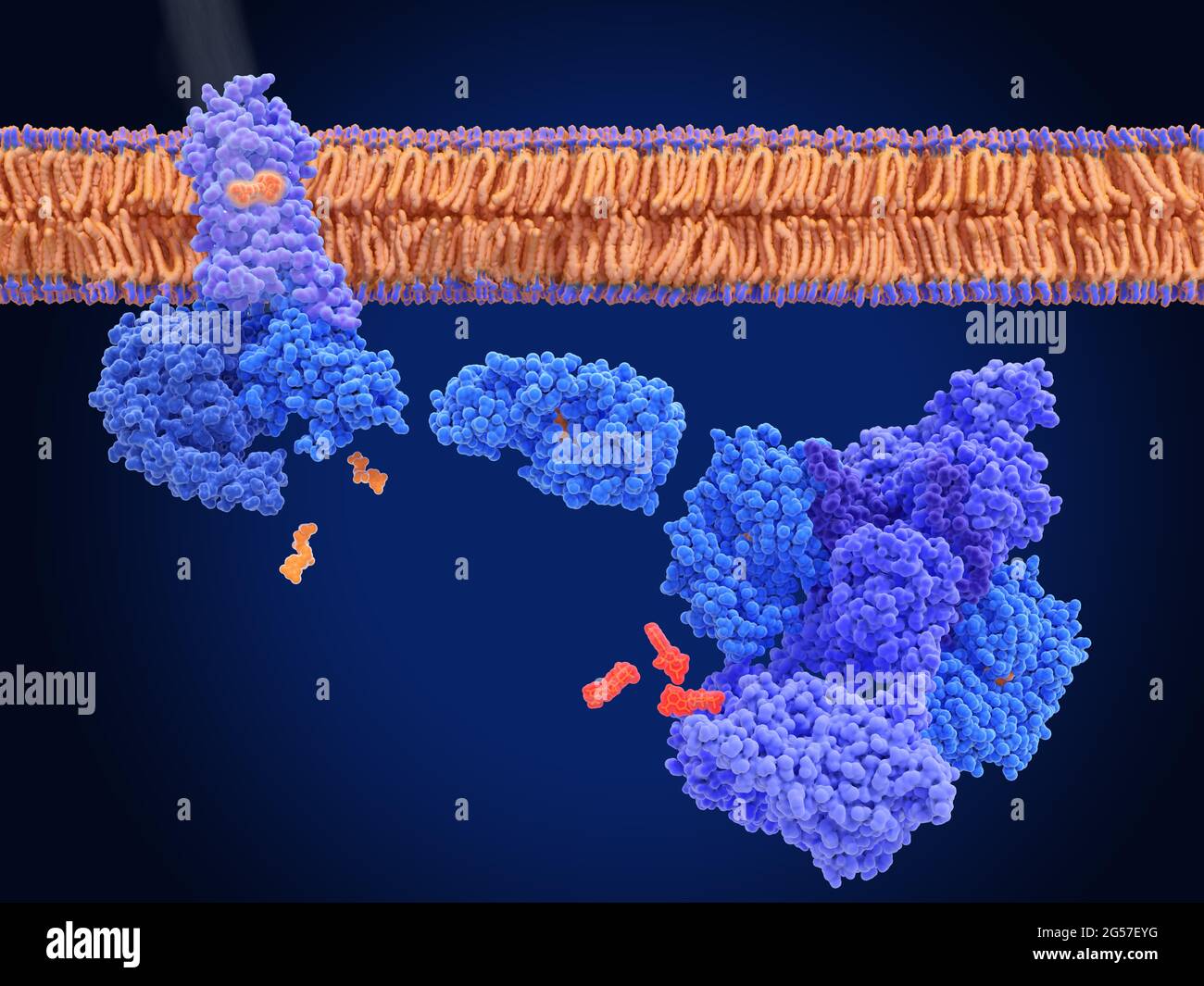 Activation of rhodopsin by light, molecular model Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/activation-of-rhodopsin-by-light-molecular-model-image433497892.html
Activation of rhodopsin by light, molecular model Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/activation-of-rhodopsin-by-light-molecular-model-image433497892.htmlRF2G57EYG–Activation of rhodopsin by light, molecular model
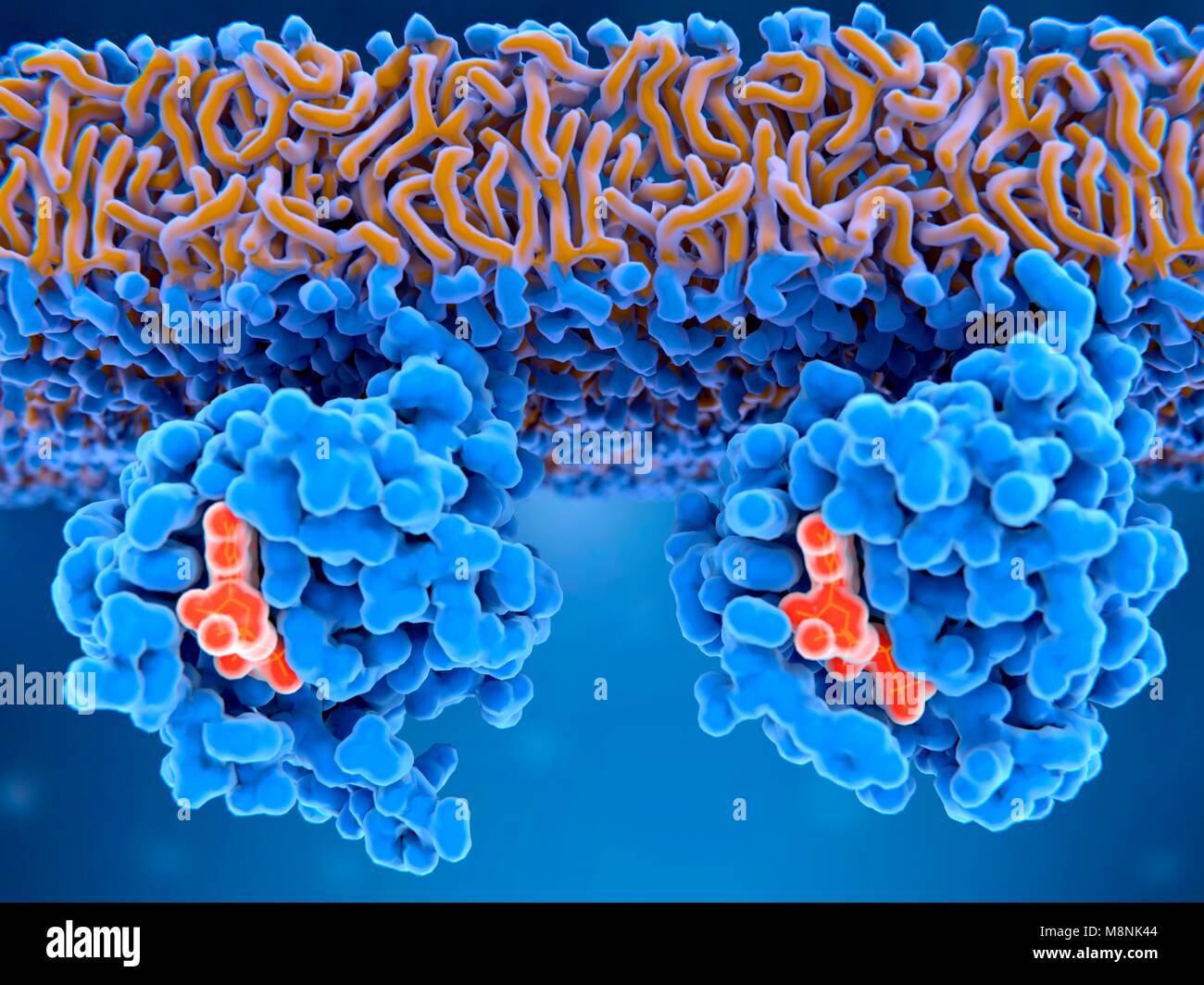
 Structure of KRAS4B-GDP homodimer on a lipid bilayer nanodisc, 3D cartoon model isolated, white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-kras4b-gdp-homodimer-on-a-lipid-bilayer-nanodisc-3d-cartoon-model-isolated-white-background-image416315506.html
Structure of KRAS4B-GDP homodimer on a lipid bilayer nanodisc, 3D cartoon model isolated, white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-of-kras4b-gdp-homodimer-on-a-lipid-bilayer-nanodisc-3d-cartoon-model-isolated-white-background-image416315506.htmlRF2F58PJX–Structure of KRAS4B-GDP homodimer on a lipid bilayer nanodisc, 3D cartoon model isolated, white background
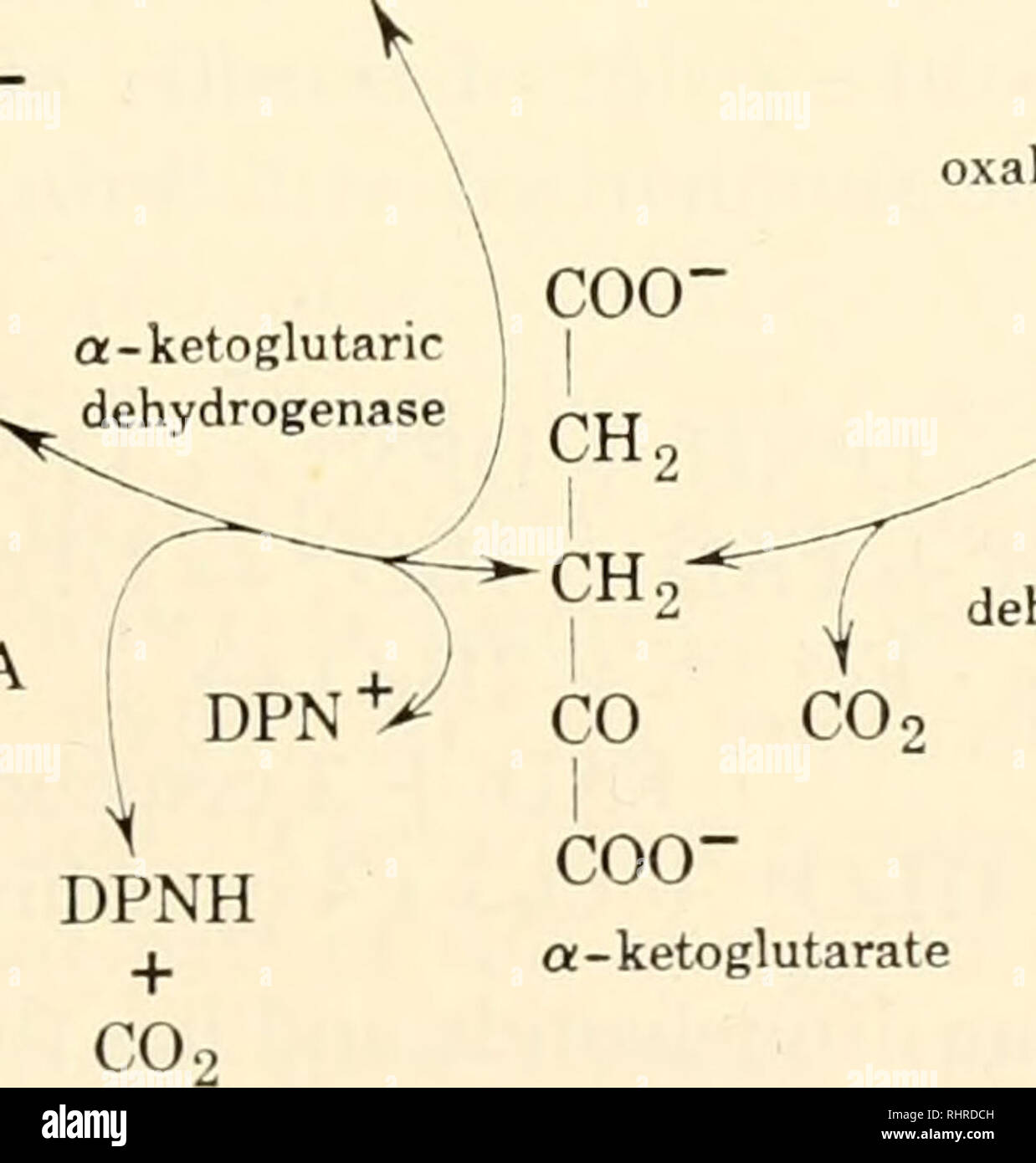 . Biochemistry of plants and animals, an introduction. Biochemistry. isocitru' dehydrogenase TPP Mg++COO- succinyl CoA transphosphorylase y^ pir HPOf + GDP SCoA succinyl CoA. TPNH oxalosuccinatc CH9COO" CHCOOH COCOO" . + + Mu- isocitric dehydrogenase COO- a-ketoglutarate FIGURE 7-2. The Krebs tricarboxylic acid cycle as written in 1959. GTP and GDP represent guanosine triphosphate and guanosine diphosphate, respectively, com- pounds similar to ATP and ADP l)ut containing guanine instead of adenine. TPP represents thiamine pyrophosphate (page 330), known also as cocarboxylase, and pr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biochemistry-of-plants-and-animals-an-introduction-biochemistry-isocitru-dehydrogenase-tpp-mgcoo-succinyl-coa-transphosphorylase-y-pir-hpof-gdp-scoa-succinyl-coa-tpnh-oxalosuccinatc-ch9cooquot-chcooh-cocooquot-mu-isocitric-dehydrogenase-coo-a-ketoglutarate-figure-7-2-the-krebs-tricarboxylic-acid-cycle-as-written-in-1959-gtp-and-gdp-represent-guanosine-triphosphate-and-guanosine-diphosphate-respectively-com-pounds-similar-to-atp-and-adp-lut-containing-guanine-instead-of-adenine-tpp-represents-thiamine-pyrophosphate-page-330-known-also-as-cocarboxylase-and-pr-image234699377.html
. Biochemistry of plants and animals, an introduction. Biochemistry. isocitru' dehydrogenase TPP Mg++COO- succinyl CoA transphosphorylase y^ pir HPOf + GDP SCoA succinyl CoA. TPNH oxalosuccinatc CH9COO" CHCOOH COCOO" . + + Mu- isocitric dehydrogenase COO- a-ketoglutarate FIGURE 7-2. The Krebs tricarboxylic acid cycle as written in 1959. GTP and GDP represent guanosine triphosphate and guanosine diphosphate, respectively, com- pounds similar to ATP and ADP l)ut containing guanine instead of adenine. TPP represents thiamine pyrophosphate (page 330), known also as cocarboxylase, and pr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biochemistry-of-plants-and-animals-an-introduction-biochemistry-isocitru-dehydrogenase-tpp-mgcoo-succinyl-coa-transphosphorylase-y-pir-hpof-gdp-scoa-succinyl-coa-tpnh-oxalosuccinatc-ch9cooquot-chcooh-cocooquot-mu-isocitric-dehydrogenase-coo-a-ketoglutarate-figure-7-2-the-krebs-tricarboxylic-acid-cycle-as-written-in-1959-gtp-and-gdp-represent-guanosine-triphosphate-and-guanosine-diphosphate-respectively-com-pounds-similar-to-atp-and-adp-lut-containing-guanine-instead-of-adenine-tpp-represents-thiamine-pyrophosphate-page-330-known-also-as-cocarboxylase-and-pr-image234699377.htmlRMRHRDCH–. Biochemistry of plants and animals, an introduction. Biochemistry. isocitru' dehydrogenase TPP Mg++COO- succinyl CoA transphosphorylase y^ pir HPOf + GDP SCoA succinyl CoA. TPNH oxalosuccinatc CH9COO" CHCOOH COCOO" . + + Mu- isocitric dehydrogenase COO- a-ketoglutarate FIGURE 7-2. The Krebs tricarboxylic acid cycle as written in 1959. GTP and GDP represent guanosine triphosphate and guanosine diphosphate, respectively, com- pounds similar to ATP and ADP l)ut containing guanine instead of adenine. TPP represents thiamine pyrophosphate (page 330), known also as cocarboxylase, and pr
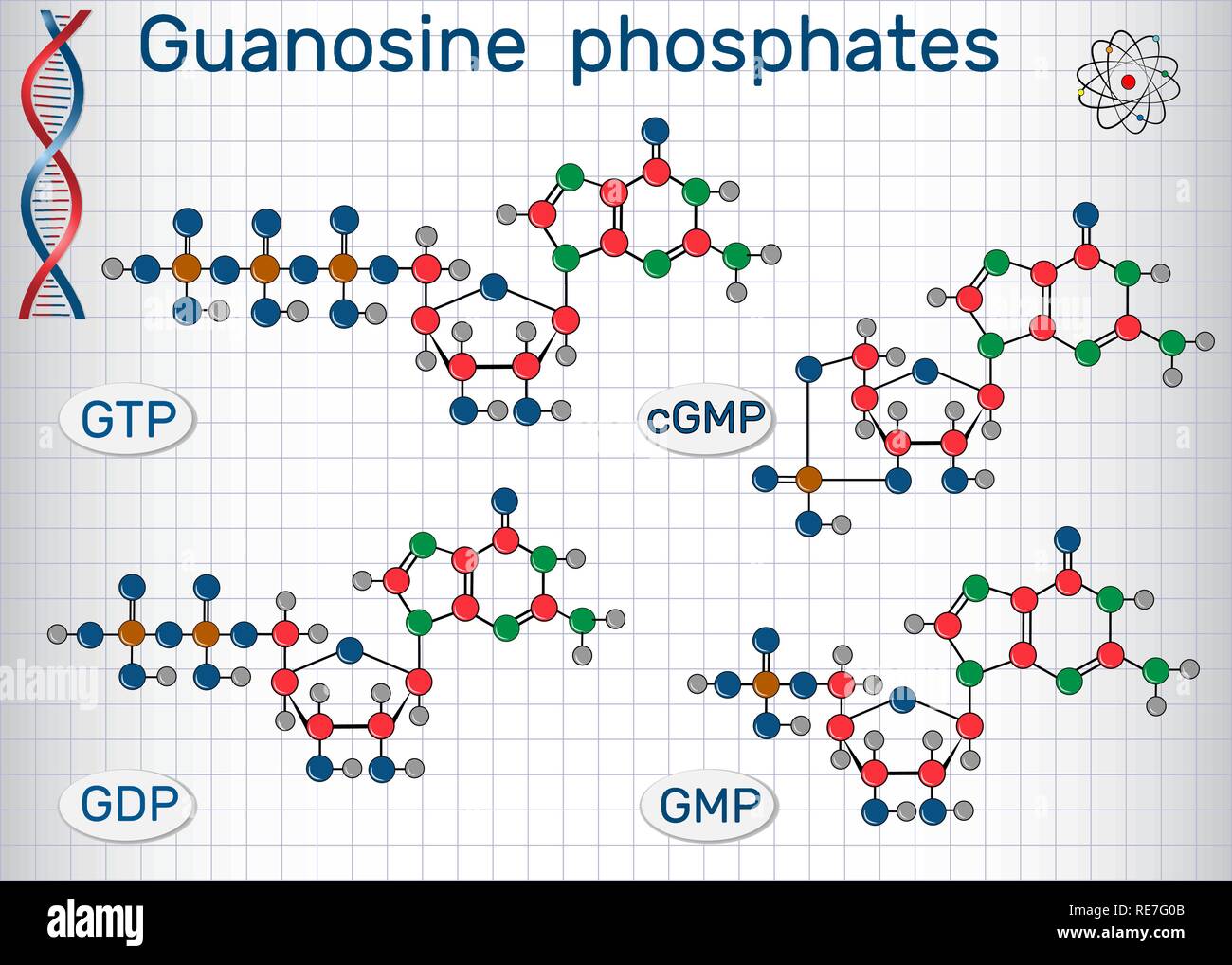 Guanosine phosphates (guanosine triphosphate, guanosine diphosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate). Sheet of paper in a cag Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-phosphates-guanosine-triphosphate-guanosine-diphosphate-guanosine-monophosphate-cyclic-guanosine-monophosphate-sheet-of-paper-in-a-cag-image232506187.html
Guanosine phosphates (guanosine triphosphate, guanosine diphosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate). Sheet of paper in a cag Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-phosphates-guanosine-triphosphate-guanosine-diphosphate-guanosine-monophosphate-cyclic-guanosine-monophosphate-sheet-of-paper-in-a-cag-image232506187.htmlRFRE7G0B–Guanosine phosphates (guanosine triphosphate, guanosine diphosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate). Sheet of paper in a cag
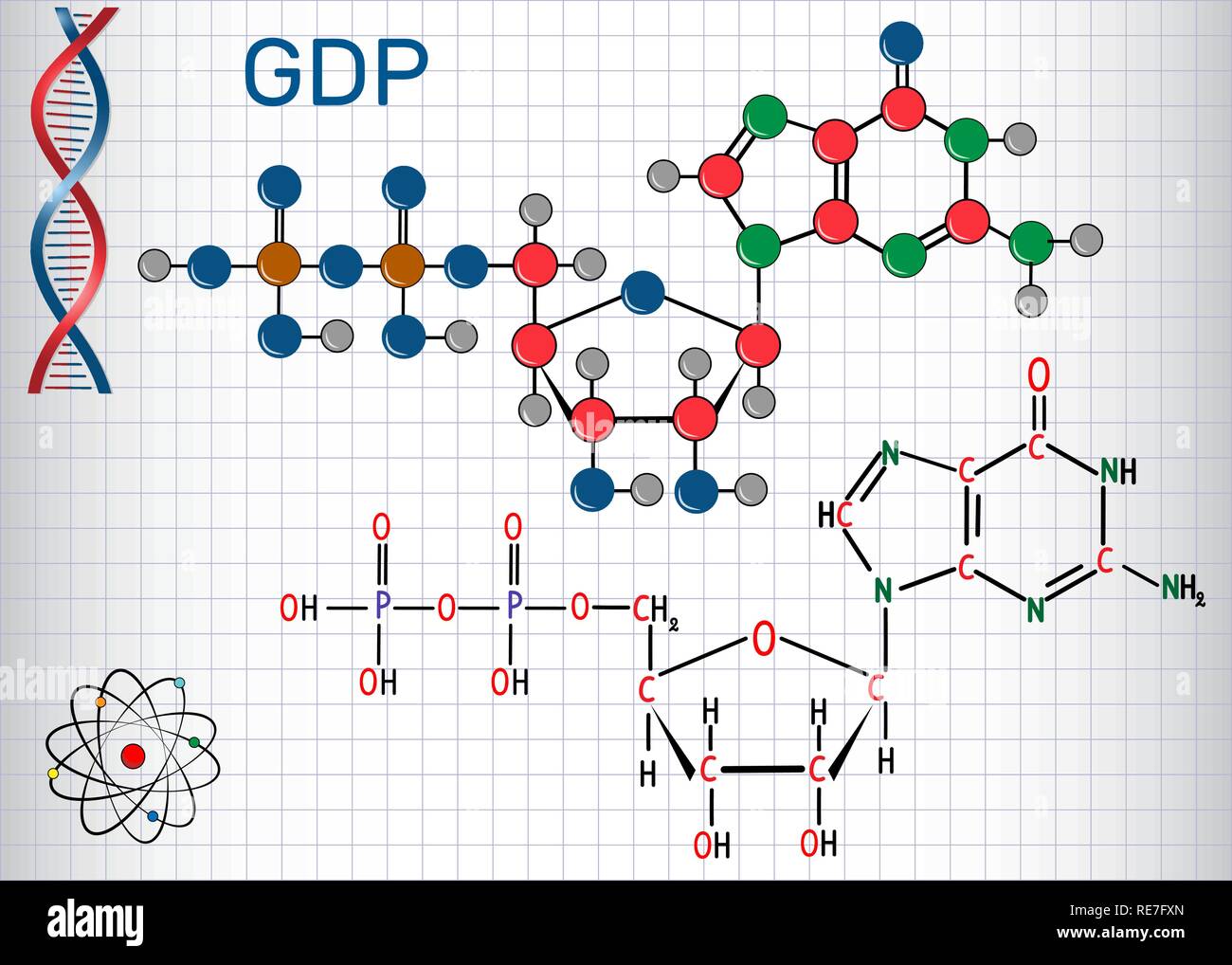 Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule. Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Sheet of paper in a cage. Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-diphosphate-gdp-molecule-structural-chemical-formula-and-molecule-model-sheet-of-paper-in-a-cage-vector-illustration-image232506141.html
Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule. Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Sheet of paper in a cage. Vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/guanosine-diphosphate-gdp-molecule-structural-chemical-formula-and-molecule-model-sheet-of-paper-in-a-cage-vector-illustration-image232506141.htmlRFRE7FXN–Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule. Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Sheet of paper in a cage. Vector illustration