Quick filters:
Jellyfish pass Stock Photos and Images
 Sea anemones, A close relative of coral and jellyfish, anemones are stinging polyps that spend most of their time attached to rocks on the sea bottom or on coral reefs waiting for fish to pass close enough to get ensnared in their venom-filled tentacles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sea-anemones-a-close-relative-of-coral-and-jellyfish-anemones-are-stinging-polyps-that-spend-most-of-their-time-attached-to-rocks-on-the-sea-bottom-or-on-coral-reefs-waiting-for-fish-to-pass-close-enough-to-get-ensnared-in-their-venom-filled-tentacles-image573391645.html
Sea anemones, A close relative of coral and jellyfish, anemones are stinging polyps that spend most of their time attached to rocks on the sea bottom or on coral reefs waiting for fish to pass close enough to get ensnared in their venom-filled tentacles Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sea-anemones-a-close-relative-of-coral-and-jellyfish-anemones-are-stinging-polyps-that-spend-most-of-their-time-attached-to-rocks-on-the-sea-bottom-or-on-coral-reefs-waiting-for-fish-to-pass-close-enough-to-get-ensnared-in-their-venom-filled-tentacles-image573391645.htmlRM2T8T6W1–Sea anemones, A close relative of coral and jellyfish, anemones are stinging polyps that spend most of their time attached to rocks on the sea bottom or on coral reefs waiting for fish to pass close enough to get ensnared in their venom-filled tentacles
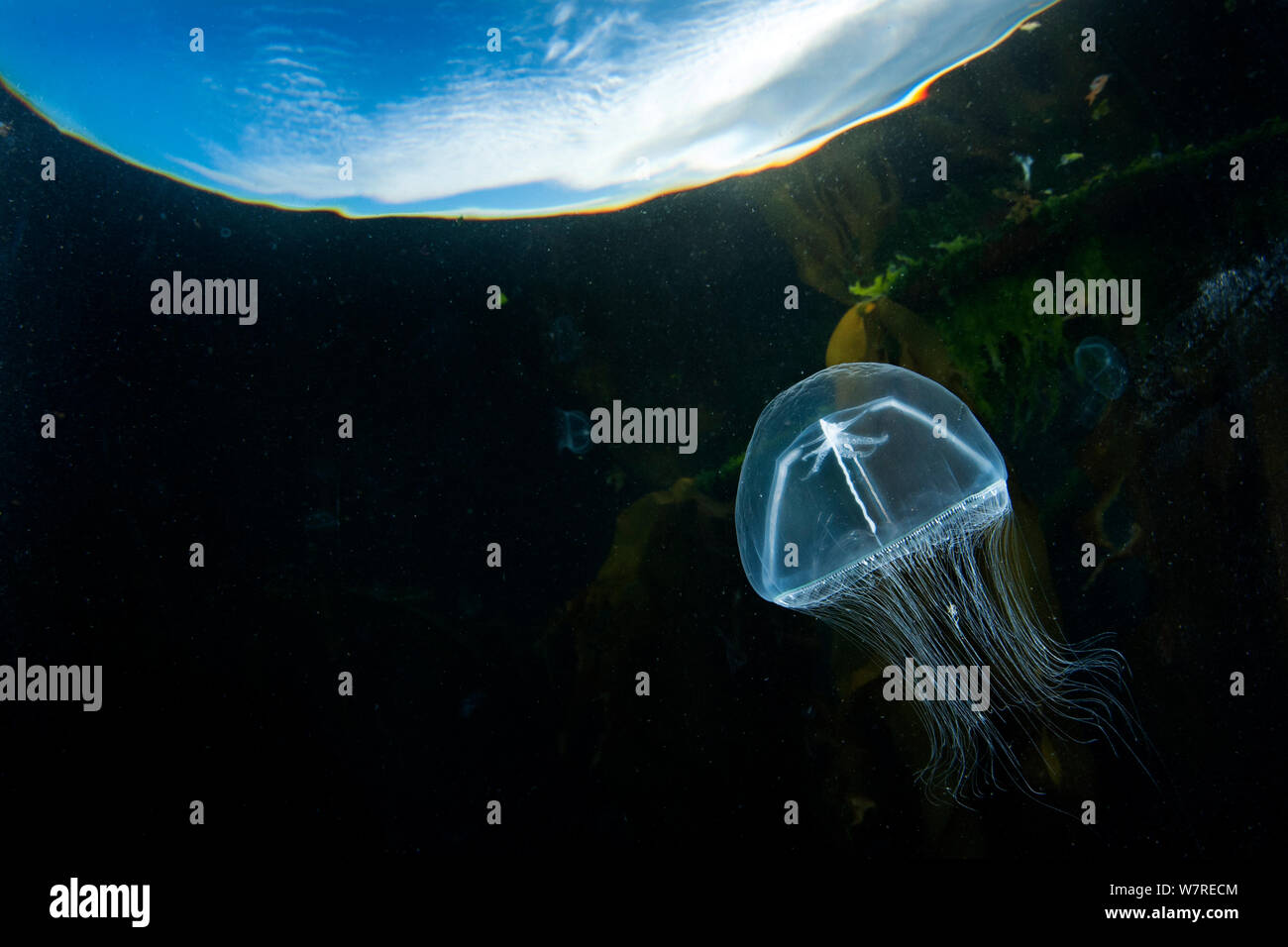 Cross jellyfish (Earleria cellularia) swims below the surface in the evening. Browning Pass, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. North East Pacific Ocean. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cross-jellyfish-earleria-cellularia-swims-below-the-surface-in-the-evening-browning-pass-vancouver-island-british-columbia-canada-north-east-pacific-ocean-image262974340.html
Cross jellyfish (Earleria cellularia) swims below the surface in the evening. Browning Pass, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. North East Pacific Ocean. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cross-jellyfish-earleria-cellularia-swims-below-the-surface-in-the-evening-browning-pass-vancouver-island-british-columbia-canada-north-east-pacific-ocean-image262974340.htmlRMW7RECM–Cross jellyfish (Earleria cellularia) swims below the surface in the evening. Browning Pass, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. North East Pacific Ocean.
 A framing of the area in Gemini containing the large and bright star cluster Messier (M) 35 at right and the curving Jellyfish Nebula, aka IC 443, at Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-framing-of-the-area-in-gemini-containing-the-large-and-bright-star-cluster-messier-m-35-at-right-and-the-curving-jellyfish-nebula-aka-ic-443-at-image447290856.html
A framing of the area in Gemini containing the large and bright star cluster Messier (M) 35 at right and the curving Jellyfish Nebula, aka IC 443, at Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-framing-of-the-area-in-gemini-containing-the-large-and-bright-star-cluster-messier-m-35-at-right-and-the-curving-jellyfish-nebula-aka-ic-443-at-image447290856.htmlRM2GYKT1C–A framing of the area in Gemini containing the large and bright star cluster Messier (M) 35 at right and the curving Jellyfish Nebula, aka IC 443, at
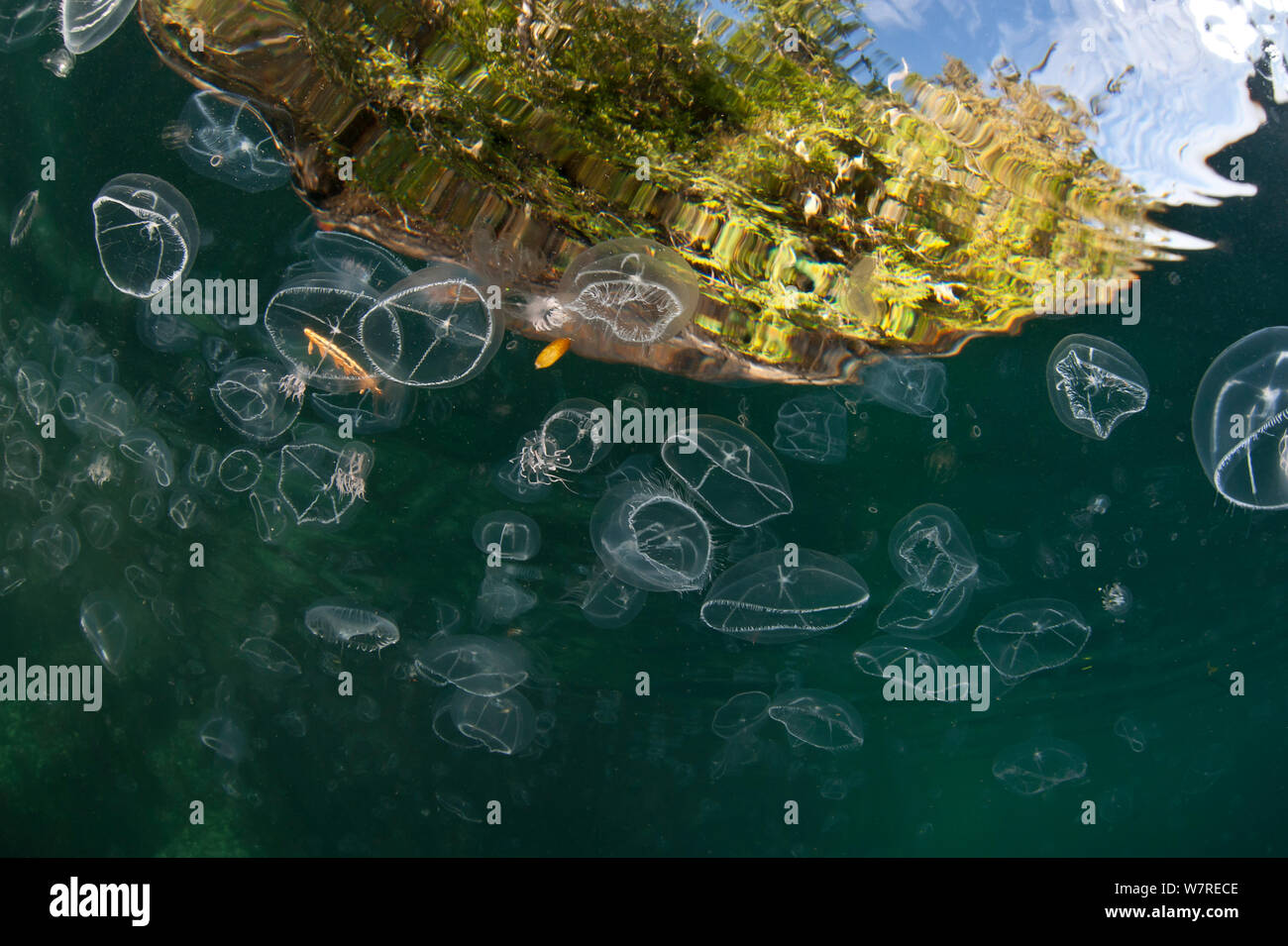 Mixed assemblage of jellyfish, mainly cross jellyfish (Earleria cellularia), at the surface. Browning Pass, Port Hardy, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. Pacific Ocean. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mixed-assemblage-of-jellyfish-mainly-cross-jellyfish-earleria-cellularia-at-the-surface-browning-pass-port-hardy-vancouver-island-british-columbia-canada-pacific-ocean-image262974334.html
Mixed assemblage of jellyfish, mainly cross jellyfish (Earleria cellularia), at the surface. Browning Pass, Port Hardy, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. Pacific Ocean. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mixed-assemblage-of-jellyfish-mainly-cross-jellyfish-earleria-cellularia-at-the-surface-browning-pass-port-hardy-vancouver-island-british-columbia-canada-pacific-ocean-image262974334.htmlRMW7RECE–Mixed assemblage of jellyfish, mainly cross jellyfish (Earleria cellularia), at the surface. Browning Pass, Port Hardy, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. Pacific Ocean.
 condominium beach ocean scenery Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-condominium-beach-ocean-scenery-139887584.html
condominium beach ocean scenery Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-condominium-beach-ocean-scenery-139887584.htmlRFJ3GC14–condominium beach ocean scenery
 Clinging jellyfish (Conionemus vertens) swimming in open water. The orange structures are reproductive organs. This species gets its name because it is able to cling to seagrass and algae. Browning Pass, Port Hardy, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. North East Pacific Ocean. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clinging-jellyfish-conionemus-vertens-swimming-in-open-water-the-orange-structures-are-reproductive-organs-this-species-gets-its-name-because-it-is-able-to-cling-to-seagrass-and-algae-browning-pass-port-hardy-vancouver-island-british-columbia-canada-north-east-pacific-ocean-image262974301.html
Clinging jellyfish (Conionemus vertens) swimming in open water. The orange structures are reproductive organs. This species gets its name because it is able to cling to seagrass and algae. Browning Pass, Port Hardy, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. North East Pacific Ocean. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/clinging-jellyfish-conionemus-vertens-swimming-in-open-water-the-orange-structures-are-reproductive-organs-this-species-gets-its-name-because-it-is-able-to-cling-to-seagrass-and-algae-browning-pass-port-hardy-vancouver-island-british-columbia-canada-north-east-pacific-ocean-image262974301.htmlRMW7REB9–Clinging jellyfish (Conionemus vertens) swimming in open water. The orange structures are reproductive organs. This species gets its name because it is able to cling to seagrass and algae. Browning Pass, Port Hardy, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. North East Pacific Ocean.
 Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402517105.html
Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402517105.htmlRF2EAT6JW–Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog
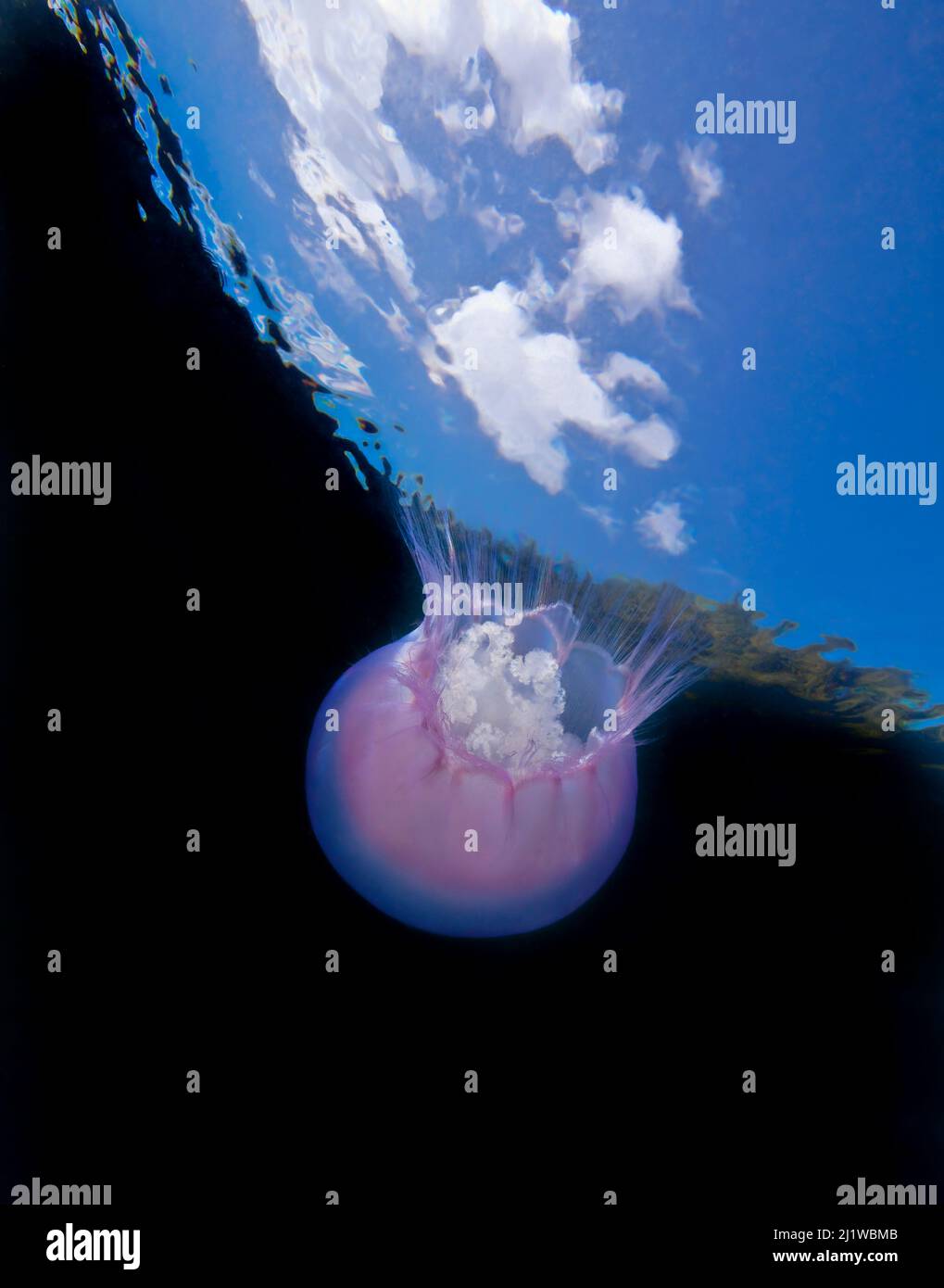 Moon jellyfish (Aurelia labiata) viewed from below, Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia, Canada. February. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moon-jellyfish-aurelia-labiata-viewed-from-below-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-strait-british-columbia-canada-february-image465852587.html
Moon jellyfish (Aurelia labiata) viewed from below, Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia, Canada. February. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moon-jellyfish-aurelia-labiata-viewed-from-below-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-strait-british-columbia-canada-february-image465852587.htmlRM2J1WBMB–Moon jellyfish (Aurelia labiata) viewed from below, Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia, Canada. February.
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517050.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517050.htmlRF2EAT6GX–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
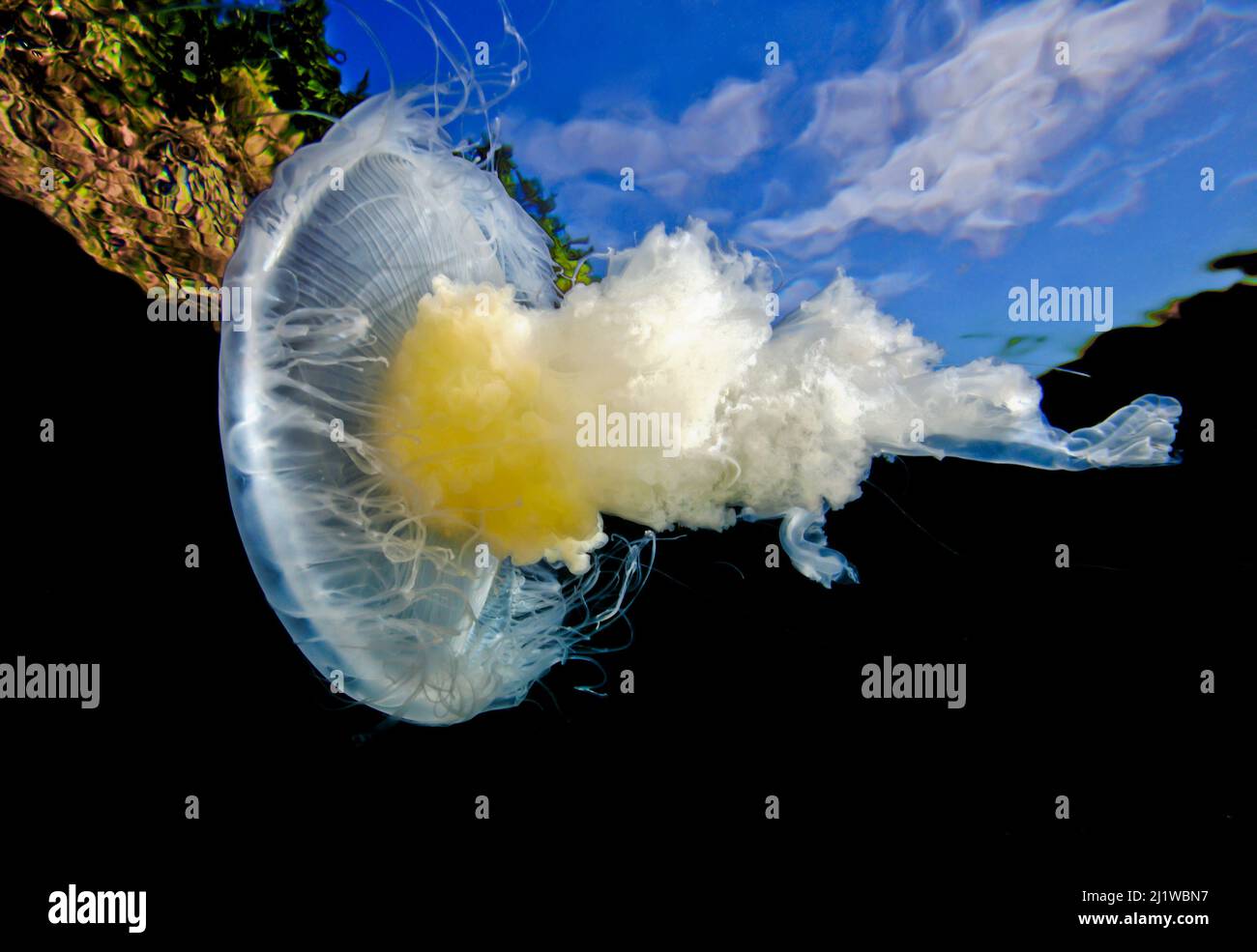 Fried egg jellyfish (Phacellophora camtschatica) viewed from below; Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia, Canada. September. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fried-egg-jellyfish-phacellophora-camtschatica-viewed-from-below-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-strait-british-columbia-canada-september-image465852611.html
Fried egg jellyfish (Phacellophora camtschatica) viewed from below; Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia, Canada. September. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fried-egg-jellyfish-phacellophora-camtschatica-viewed-from-below-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-strait-british-columbia-canada-september-image465852611.htmlRM2J1WBN7–Fried egg jellyfish (Phacellophora camtschatica) viewed from below; Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia, Canada. September.
![. The Canadian field-naturalist. October, 1930] The Canadian Field-Naturalist 155 occurred where the spoons were worked close to the surface, between Ship Island and Satellite Pass. Deeper down than 5 fathoms the action did not occur. There were large numbers of big, brown jellyfish in the water and these fouled the lines. It was suspected that some fluid from the jellyfish caused the pitting of the hooks, which could be detected after a few hours in the sea. VELELLA Velella, (Fig. 5), popularly known as Fortu- guese-Man-o'-War, was extremely abundant dur- ing the summer of 1926 off Barkley So Stock Photo . The Canadian field-naturalist. October, 1930] The Canadian Field-Naturalist 155 occurred where the spoons were worked close to the surface, between Ship Island and Satellite Pass. Deeper down than 5 fathoms the action did not occur. There were large numbers of big, brown jellyfish in the water and these fouled the lines. It was suspected that some fluid from the jellyfish caused the pitting of the hooks, which could be detected after a few hours in the sea. VELELLA Velella, (Fig. 5), popularly known as Fortu- guese-Man-o'-War, was extremely abundant dur- ing the summer of 1926 off Barkley So Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/RG3AD3/the-canadian-field-naturalist-october-1930-the-canadian-field-naturalist-155-occurred-where-the-spoons-were-worked-close-to-the-surface-between-ship-island-and-satellite-pass-deeper-down-than-5-fathoms-the-action-did-not-occur-there-were-large-numbers-of-big-brown-jellyfish-in-the-water-and-these-fouled-the-lines-it-was-suspected-that-some-fluid-from-the-jellyfish-caused-the-pitting-of-the-hooks-which-could-be-detected-after-a-few-hours-in-the-sea-velella-velella-fig-5-popularly-known-as-fortu-guese-man-o-war-was-extremely-abundant-dur-ing-the-summer-of-1926-off-barkley-so-RG3AD3.jpg) . The Canadian field-naturalist. October, 1930] The Canadian Field-Naturalist 155 occurred where the spoons were worked close to the surface, between Ship Island and Satellite Pass. Deeper down than 5 fathoms the action did not occur. There were large numbers of big, brown jellyfish in the water and these fouled the lines. It was suspected that some fluid from the jellyfish caused the pitting of the hooks, which could be detected after a few hours in the sea. VELELLA Velella, (Fig. 5), popularly known as Fortu- guese-Man-o'-War, was extremely abundant dur- ing the summer of 1926 off Barkley So Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-canadian-field-naturalist-october-1930-the-canadian-field-naturalist-155-occurred-where-the-spoons-were-worked-close-to-the-surface-between-ship-island-and-satellite-pass-deeper-down-than-5-fathoms-the-action-did-not-occur-there-were-large-numbers-of-big-brown-jellyfish-in-the-water-and-these-fouled-the-lines-it-was-suspected-that-some-fluid-from-the-jellyfish-caused-the-pitting-of-the-hooks-which-could-be-detected-after-a-few-hours-in-the-sea-velella-velella-fig-5-popularly-known-as-fortu-guese-man-o-war-was-extremely-abundant-dur-ing-the-summer-of-1926-off-barkley-so-image233643343.html
. The Canadian field-naturalist. October, 1930] The Canadian Field-Naturalist 155 occurred where the spoons were worked close to the surface, between Ship Island and Satellite Pass. Deeper down than 5 fathoms the action did not occur. There were large numbers of big, brown jellyfish in the water and these fouled the lines. It was suspected that some fluid from the jellyfish caused the pitting of the hooks, which could be detected after a few hours in the sea. VELELLA Velella, (Fig. 5), popularly known as Fortu- guese-Man-o'-War, was extremely abundant dur- ing the summer of 1926 off Barkley So Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-canadian-field-naturalist-october-1930-the-canadian-field-naturalist-155-occurred-where-the-spoons-were-worked-close-to-the-surface-between-ship-island-and-satellite-pass-deeper-down-than-5-fathoms-the-action-did-not-occur-there-were-large-numbers-of-big-brown-jellyfish-in-the-water-and-these-fouled-the-lines-it-was-suspected-that-some-fluid-from-the-jellyfish-caused-the-pitting-of-the-hooks-which-could-be-detected-after-a-few-hours-in-the-sea-velella-velella-fig-5-popularly-known-as-fortu-guese-man-o-war-was-extremely-abundant-dur-ing-the-summer-of-1926-off-barkley-so-image233643343.htmlRMRG3AD3–. The Canadian field-naturalist. October, 1930] The Canadian Field-Naturalist 155 occurred where the spoons were worked close to the surface, between Ship Island and Satellite Pass. Deeper down than 5 fathoms the action did not occur. There were large numbers of big, brown jellyfish in the water and these fouled the lines. It was suspected that some fluid from the jellyfish caused the pitting of the hooks, which could be detected after a few hours in the sea. VELELLA Velella, (Fig. 5), popularly known as Fortu- guese-Man-o'-War, was extremely abundant dur- ing the summer of 1926 off Barkley So
 Split level of a Lion's mane Jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) and Feather-boa kelp (Egregia menziesii), Seven-tree Island, Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/split-level-of-a-lions-mane-jellyfish-cyanea-capillata-and-feather-boa-kelp-egregia-menziesii-seven-tree-island-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-image465852593.html
Split level of a Lion's mane Jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) and Feather-boa kelp (Egregia menziesii), Seven-tree Island, Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/split-level-of-a-lions-mane-jellyfish-cyanea-capillata-and-feather-boa-kelp-egregia-menziesii-seven-tree-island-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-image465852593.htmlRM2J1WBMH–Split level of a Lion's mane Jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) and Feather-boa kelp (Egregia menziesii), Seven-tree Island, Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte
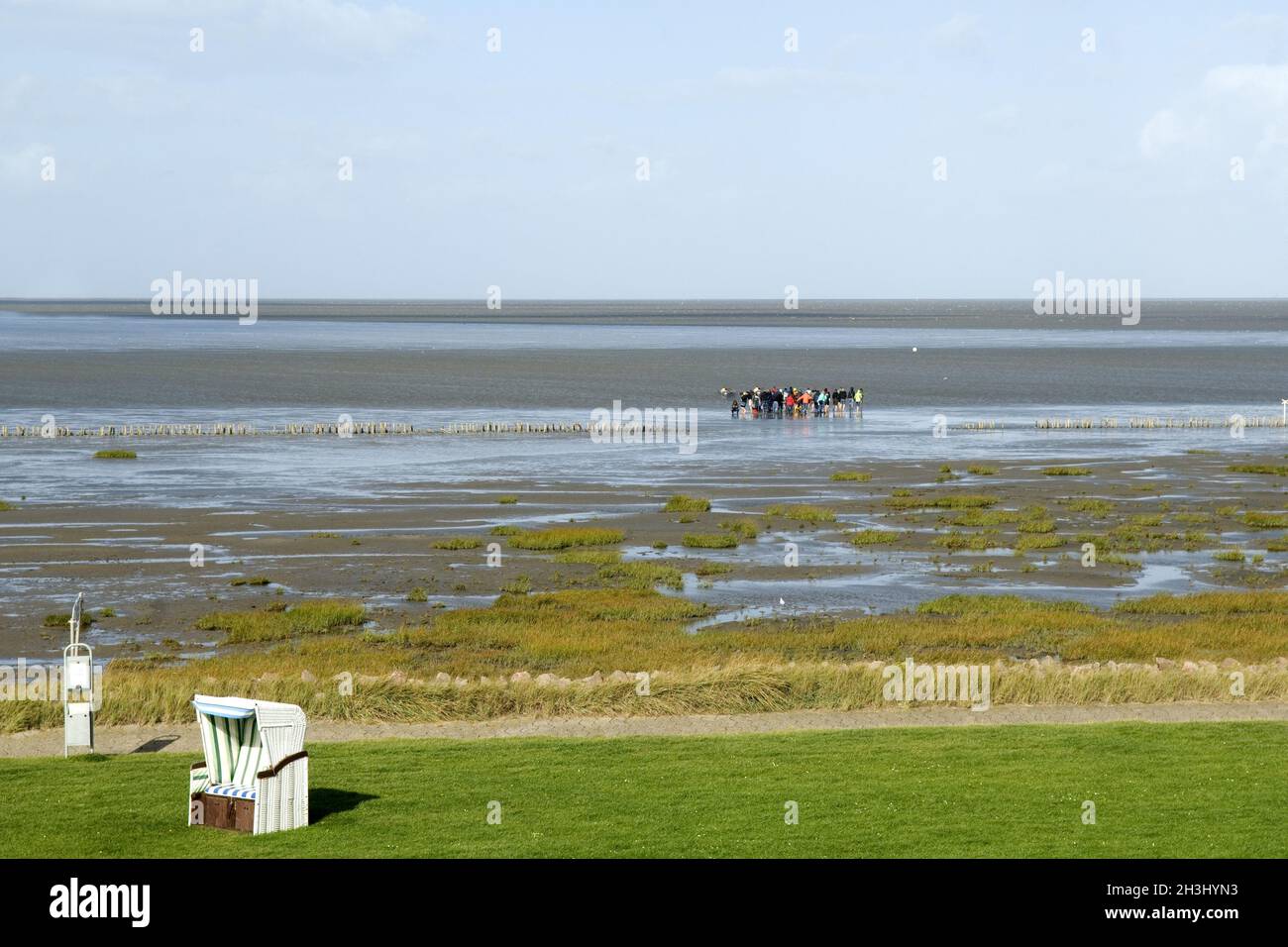
 Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-image449708624.html
Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-image449708624.htmlRM2H3HYX8–Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast,
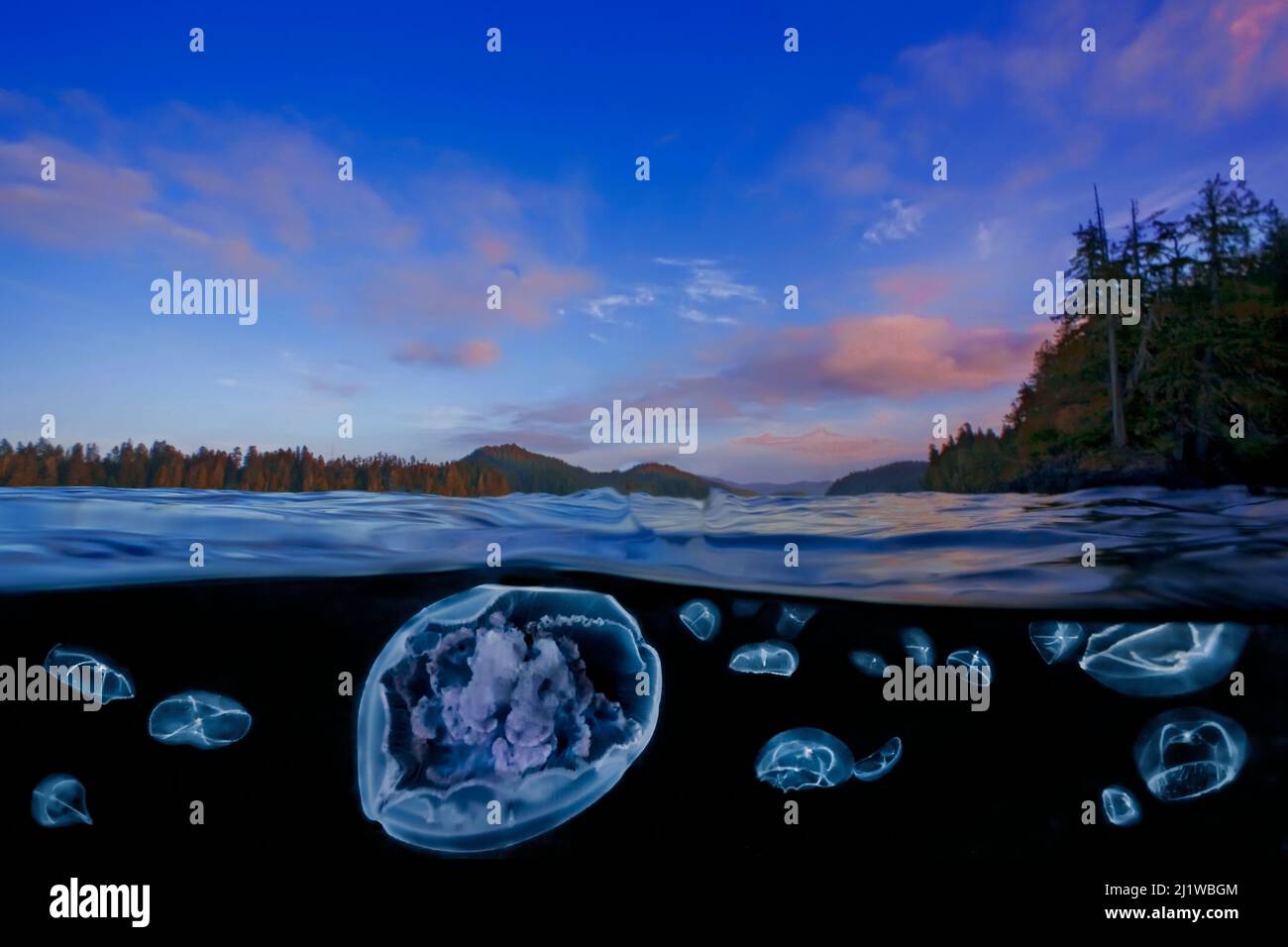 Moon jelly (Aurelia labiata) and Cross jellies (Mitrocoma cellularia) split level view in Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia. O Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moon-jelly-aurelia-labiata-and-cross-jellies-mitrocoma-cellularia-split-level-view-in-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-strait-british-columbia-o-image465852484.html
Moon jelly (Aurelia labiata) and Cross jellies (Mitrocoma cellularia) split level view in Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia. O Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/moon-jelly-aurelia-labiata-and-cross-jellies-mitrocoma-cellularia-split-level-view-in-browning-pass-queen-charlotte-strait-british-columbia-o-image465852484.htmlRM2J1WBGM–Moon jelly (Aurelia labiata) and Cross jellies (Mitrocoma cellularia) split level view in Browning Pass, Queen Charlotte Strait, British Columbia. O
 Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402517038.html
Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402517038.htmlRF2EAT6GE–Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog
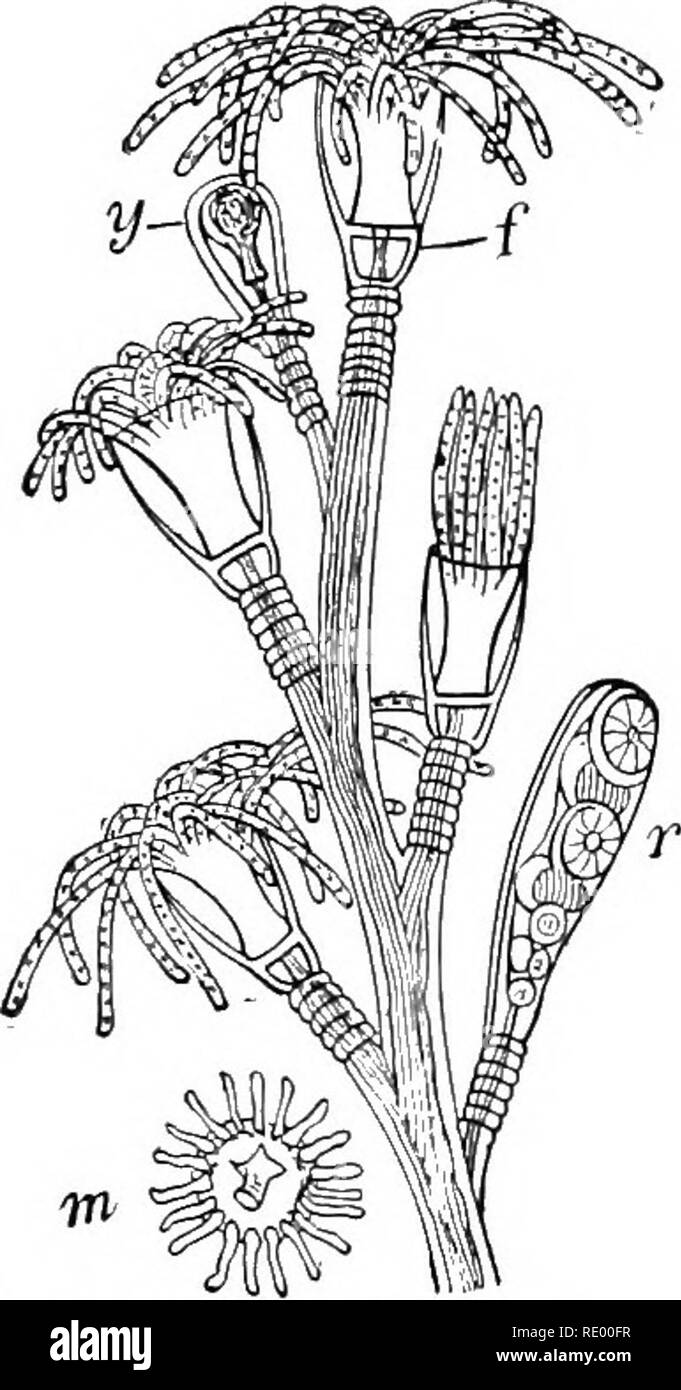 . Essentials of biology presented in problems. Biology. 208 THE METAZOA—DIVISION OF LABOR. Medusa. — Among the most interesting of all the coelenterates inhabit- ing the salt water are the jellyflshes or medusse. These animals vary greatly in size from a tiny umbrella-shaped animal little larger than the head of a pin to huge jellyfish several feet in diameter. Development. — Many species of medusas pass through another stage of hfe. As medusae they reproduce by eggs and sperms, that is, sexually. The egg of the medusa segments, forming ultim.ately a ball of cells (the blastula) which swims ar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/essentials-of-biology-presented-in-problems-biology-208-the-metazoadivision-of-labor-medusa-among-the-most-interesting-of-all-the-coelenterates-inhabit-ing-the-salt-water-are-the-jellyflshes-or-medusse-these-animals-vary-greatly-in-size-from-a-tiny-umbrella-shaped-animal-little-larger-than-the-head-of-a-pin-to-huge-jellyfish-several-feet-in-diameter-development-many-species-of-medusas-pass-through-another-stage-of-hfe-as-medusae-they-reproduce-by-eggs-and-sperms-that-is-sexually-the-egg-of-the-medusa-segments-forming-ultimately-a-ball-of-cells-the-blastula-which-swims-ar-image232340411.html
. Essentials of biology presented in problems. Biology. 208 THE METAZOA—DIVISION OF LABOR. Medusa. — Among the most interesting of all the coelenterates inhabit- ing the salt water are the jellyflshes or medusse. These animals vary greatly in size from a tiny umbrella-shaped animal little larger than the head of a pin to huge jellyfish several feet in diameter. Development. — Many species of medusas pass through another stage of hfe. As medusae they reproduce by eggs and sperms, that is, sexually. The egg of the medusa segments, forming ultim.ately a ball of cells (the blastula) which swims ar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/essentials-of-biology-presented-in-problems-biology-208-the-metazoadivision-of-labor-medusa-among-the-most-interesting-of-all-the-coelenterates-inhabit-ing-the-salt-water-are-the-jellyflshes-or-medusse-these-animals-vary-greatly-in-size-from-a-tiny-umbrella-shaped-animal-little-larger-than-the-head-of-a-pin-to-huge-jellyfish-several-feet-in-diameter-development-many-species-of-medusas-pass-through-another-stage-of-hfe-as-medusae-they-reproduce-by-eggs-and-sperms-that-is-sexually-the-egg-of-the-medusa-segments-forming-ultimately-a-ball-of-cells-the-blastula-which-swims-ar-image232340411.htmlRMRE00FR–. Essentials of biology presented in problems. Biology. 208 THE METAZOA—DIVISION OF LABOR. Medusa. — Among the most interesting of all the coelenterates inhabit- ing the salt water are the jellyflshes or medusse. These animals vary greatly in size from a tiny umbrella-shaped animal little larger than the head of a pin to huge jellyfish several feet in diameter. Development. — Many species of medusas pass through another stage of hfe. As medusae they reproduce by eggs and sperms, that is, sexually. The egg of the medusa segments, forming ultim.ately a ball of cells (the blastula) which swims ar
 Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708634.html
Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708634.htmlRM2H3HYXJ–Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402516919.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402516919.htmlRF2EAT6C7–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
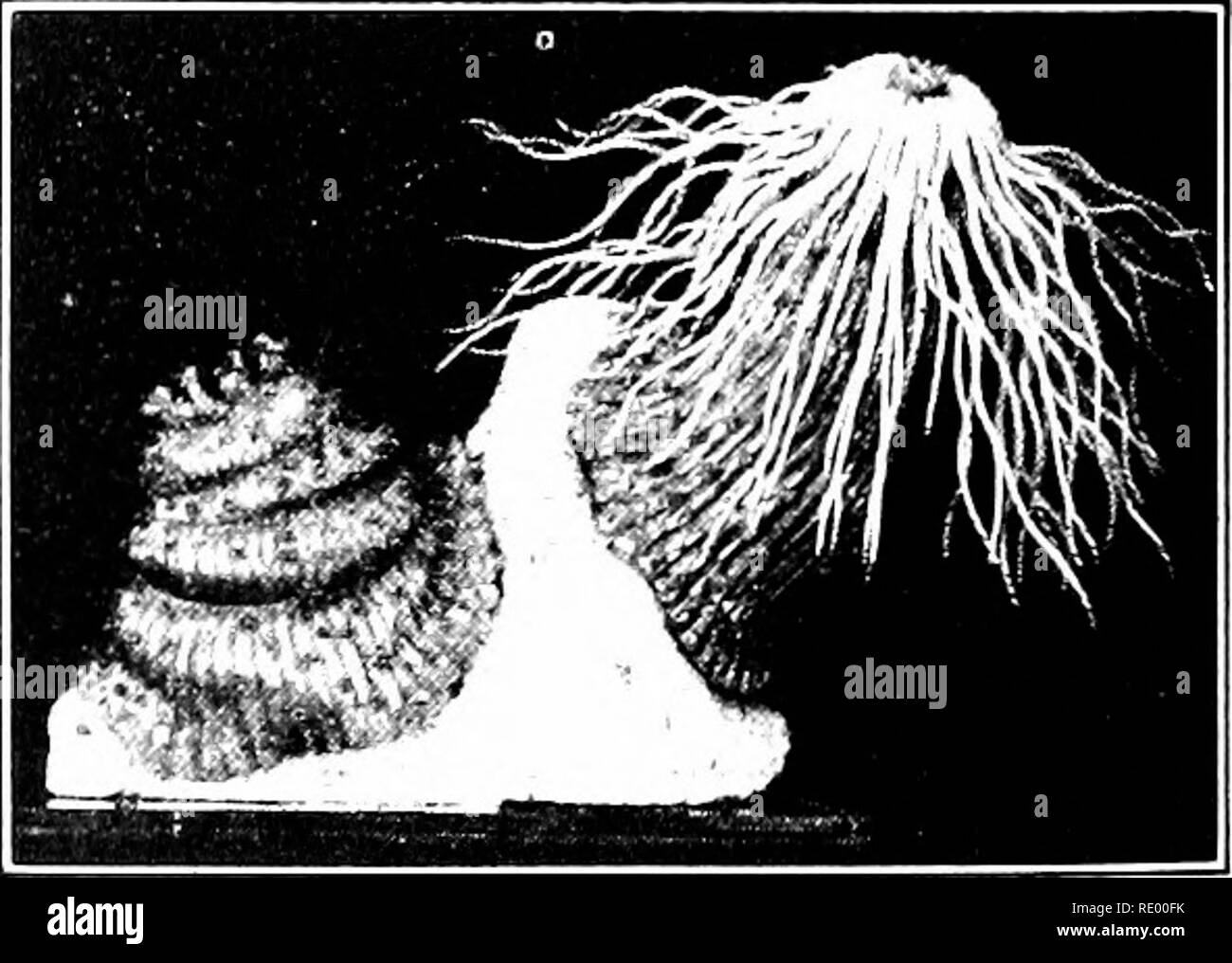 . Essentials of biology presented in problems. Biology. Medusa. — Among the most interesting of all the coelenterates inhabit- ing the salt water are the jellyflshes or medusse. These animals vary greatly in size from a tiny umbrella-shaped animal little larger than the head of a pin to huge jellyfish several feet in diameter. Development. — Many species of medusas pass through another stage of hfe. As medusae they reproduce by eggs and sperms, that is, sexually. The egg of the medusa segments, forming ultim.ately a ball of cells (the blastula) which swims around by means of cOia. Ulti- mately Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/essentials-of-biology-presented-in-problems-biology-medusa-among-the-most-interesting-of-all-the-coelenterates-inhabit-ing-the-salt-water-are-the-jellyflshes-or-medusse-these-animals-vary-greatly-in-size-from-a-tiny-umbrella-shaped-animal-little-larger-than-the-head-of-a-pin-to-huge-jellyfish-several-feet-in-diameter-development-many-species-of-medusas-pass-through-another-stage-of-hfe-as-medusae-they-reproduce-by-eggs-and-sperms-that-is-sexually-the-egg-of-the-medusa-segments-forming-ultimately-a-ball-of-cells-the-blastula-which-swims-around-by-means-of-coia-ulti-mately-image232340407.html
. Essentials of biology presented in problems. Biology. Medusa. — Among the most interesting of all the coelenterates inhabit- ing the salt water are the jellyflshes or medusse. These animals vary greatly in size from a tiny umbrella-shaped animal little larger than the head of a pin to huge jellyfish several feet in diameter. Development. — Many species of medusas pass through another stage of hfe. As medusae they reproduce by eggs and sperms, that is, sexually. The egg of the medusa segments, forming ultim.ately a ball of cells (the blastula) which swims around by means of cOia. Ulti- mately Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/essentials-of-biology-presented-in-problems-biology-medusa-among-the-most-interesting-of-all-the-coelenterates-inhabit-ing-the-salt-water-are-the-jellyflshes-or-medusse-these-animals-vary-greatly-in-size-from-a-tiny-umbrella-shaped-animal-little-larger-than-the-head-of-a-pin-to-huge-jellyfish-several-feet-in-diameter-development-many-species-of-medusas-pass-through-another-stage-of-hfe-as-medusae-they-reproduce-by-eggs-and-sperms-that-is-sexually-the-egg-of-the-medusa-segments-forming-ultimately-a-ball-of-cells-the-blastula-which-swims-around-by-means-of-coia-ulti-mately-image232340407.htmlRMRE00FK–. Essentials of biology presented in problems. Biology. Medusa. — Among the most interesting of all the coelenterates inhabit- ing the salt water are the jellyflshes or medusse. These animals vary greatly in size from a tiny umbrella-shaped animal little larger than the head of a pin to huge jellyfish several feet in diameter. Development. — Many species of medusas pass through another stage of hfe. As medusae they reproduce by eggs and sperms, that is, sexually. The egg of the medusa segments, forming ultim.ately a ball of cells (the blastula) which swims around by means of cOia. Ulti- mately
 Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708619.html
Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708619.htmlRM2H3HYX3–Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708464.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708464.htmlRM2H3HYMG–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402516911.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402516911.htmlRF2EAT6BY–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708466.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708466.htmlRM2H3HYMJ–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog
 Wattwanderung, Wattenmeer, Nordseekueste, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-wattenmeer-nordseekueste-image402517111.html
Wattwanderung, Wattenmeer, Nordseekueste, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-wattenmeer-nordseekueste-image402517111.htmlRF2EAT6K3–Wattwanderung, Wattenmeer, Nordseekueste,
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708463.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708463.htmlRM2H3HYMF–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog
 Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708660.html
Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708660.htmlRM2H3HYYG–Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517072.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517072.htmlRF2EAT6HM–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
 Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708620.html
Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-landscape-friedrichskoog-image449708620.htmlRM2H3HYX4–Wadden Sea; North Sea coast, landscape, Friedrichskoog
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517078.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517078.htmlRF2EAT6HX–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-image449708630.html
Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-image449708630.htmlRM2H3HYXE–Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast,
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517091.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517091.htmlRF2EAT6JB–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-image449708622.html
Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-wadden-sea-north-sea-coast-image449708622.htmlRM2H3HYX6–Mudflat walk, Wadden Sea, North Sea coast,
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708469.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708469.htmlRM2H3HYMN–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog
 Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517094.html
Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattwanderung-friedrichskoog-image402517094.htmlRF2EAT6JE–Wattwanderung, Friedrichskoog
 Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402516985.html
Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402516985.htmlRF2EAT6EH–Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708462.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708462.htmlRM2H3HYME–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog
 Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402516994.html
Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402516994.htmlRF2EAT6EX–Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog
 Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402517034.html
Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/wattenmeer-nordseekueste-landschaft-friedrichskoog-image402517034.htmlRF2EAT6GA–Wattenmeer; Nordseekueste, Landschaft, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708465.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708465.htmlRM2H3HYMH–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog
 Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708407.html
Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mudflat-walk-friedrichskoog-image449708407.htmlRM2H3HYJF–Mudflat walk, Friedrichskoog

