Meissner plexus Stock Photos and Images
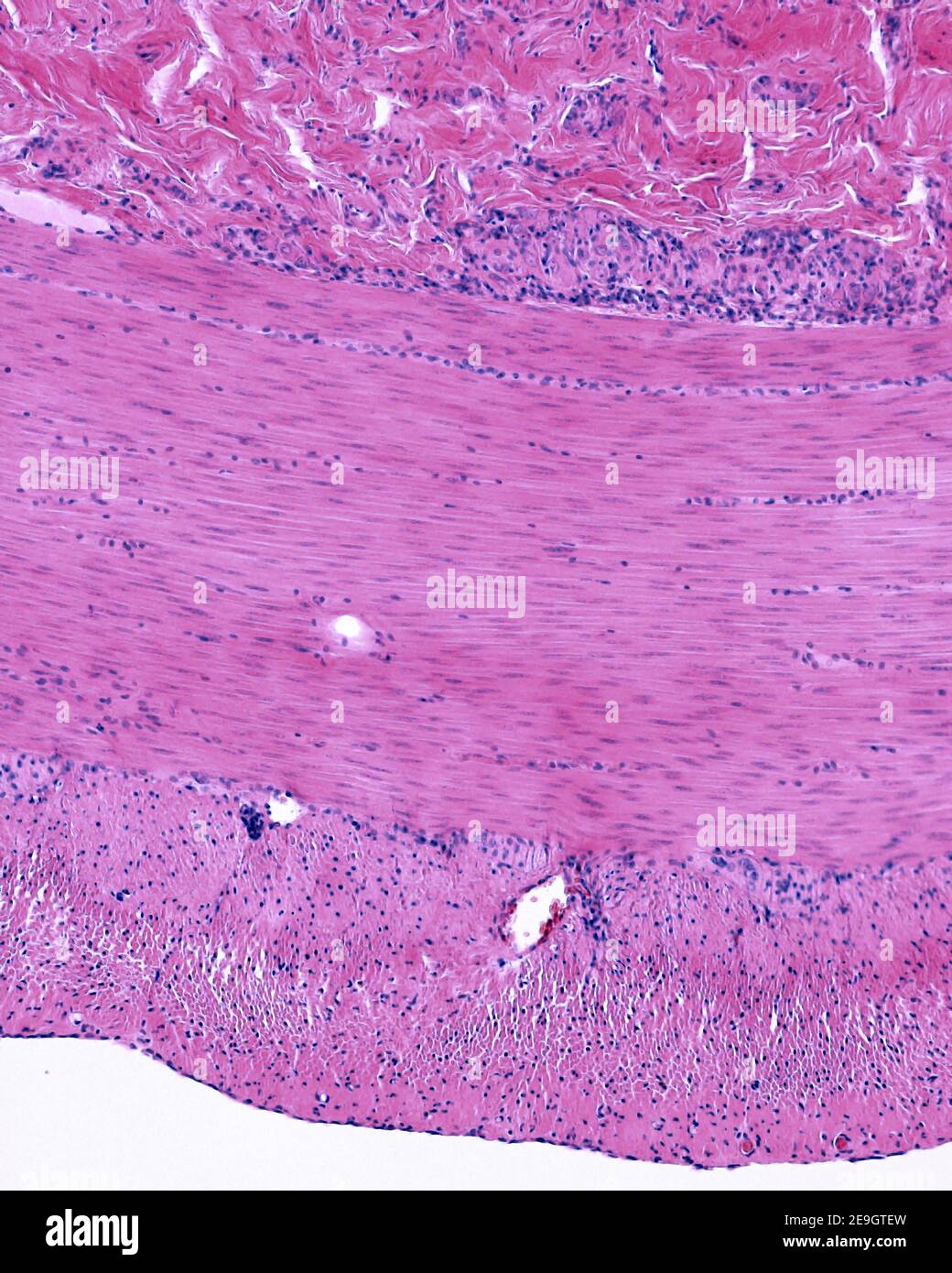 Muscular layer of small intestine showing the inner circular and the outer longitudinal layers. Above are neurons of the Meissner plexus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscular-layer-of-small-intestine-showing-the-inner-circular-and-the-outer-longitudinal-layers-above-are-neurons-of-the-meissner-plexus-image401740833.html
Muscular layer of small intestine showing the inner circular and the outer longitudinal layers. Above are neurons of the Meissner plexus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscular-layer-of-small-intestine-showing-the-inner-circular-and-the-outer-longitudinal-layers-above-are-neurons-of-the-meissner-plexus-image401740833.htmlRF2E9GTEW–Muscular layer of small intestine showing the inner circular and the outer longitudinal layers. Above are neurons of the Meissner plexus
 The laws and mechanics of circulation, with the principle involved in animal movement . Fig. 106.—Auerbachs Plexus of Small Intestine of Human Foetus, colored with gold.The plexus consists of fibrillated substance, and is made up of trabecular of variousthicknesses, which unite in large placoids. Nucleus-like elements (unformed gan-glion cells) and ganglion cells are embedded in the plexus, the whole of which isinclosed in a nucleated sheath. (Oc, 2 ; obj., 7.)—Klein. 272 NEBVJiS TO THE INTESTINES.A. r $ Fig. 107.—Nerves to the Intestines—partly ideal. 1, Ganglionic layer of Meissner ; 3,nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-laws-and-mechanics-of-circulation-with-the-principle-involved-in-animal-movement-fig-106auerbachs-plexus-of-small-intestine-of-human-foetus-colored-with-goldthe-plexus-consists-of-fibrillated-substance-and-is-made-up-of-trabecular-of-variousthicknesses-which-unite-in-large-placoids-nucleus-like-elements-unformed-gan-glion-cells-and-ganglion-cells-are-embedded-in-the-plexus-the-whole-of-which-isinclosed-in-a-nucleated-sheath-oc-2-obj-7klein-272-nebvjis-to-the-intestinesa-r-fig-107nerves-to-the-intestinespartly-ideal-1-ganglionic-layer-of-meissner-3nerve-image339955741.html
The laws and mechanics of circulation, with the principle involved in animal movement . Fig. 106.—Auerbachs Plexus of Small Intestine of Human Foetus, colored with gold.The plexus consists of fibrillated substance, and is made up of trabecular of variousthicknesses, which unite in large placoids. Nucleus-like elements (unformed gan-glion cells) and ganglion cells are embedded in the plexus, the whole of which isinclosed in a nucleated sheath. (Oc, 2 ; obj., 7.)—Klein. 272 NEBVJiS TO THE INTESTINES.A. r $ Fig. 107.—Nerves to the Intestines—partly ideal. 1, Ganglionic layer of Meissner ; 3,nerve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-laws-and-mechanics-of-circulation-with-the-principle-involved-in-animal-movement-fig-106auerbachs-plexus-of-small-intestine-of-human-foetus-colored-with-goldthe-plexus-consists-of-fibrillated-substance-and-is-made-up-of-trabecular-of-variousthicknesses-which-unite-in-large-placoids-nucleus-like-elements-unformed-gan-glion-cells-and-ganglion-cells-are-embedded-in-the-plexus-the-whole-of-which-isinclosed-in-a-nucleated-sheath-oc-2-obj-7klein-272-nebvjis-to-the-intestinesa-r-fig-107nerves-to-the-intestinespartly-ideal-1-ganglionic-layer-of-meissner-3nerve-image339955741.htmlRM2AN290D–The laws and mechanics of circulation, with the principle involved in animal movement . Fig. 106.—Auerbachs Plexus of Small Intestine of Human Foetus, colored with gold.The plexus consists of fibrillated substance, and is made up of trabecular of variousthicknesses, which unite in large placoids. Nucleus-like elements (unformed gan-glion cells) and ganglion cells are embedded in the plexus, the whole of which isinclosed in a nucleated sheath. (Oc, 2 ; obj., 7.)—Klein. 272 NEBVJiS TO THE INTESTINES.A. r $ Fig. 107.—Nerves to the Intestines—partly ideal. 1, Ganglionic layer of Meissner ; 3,nerve
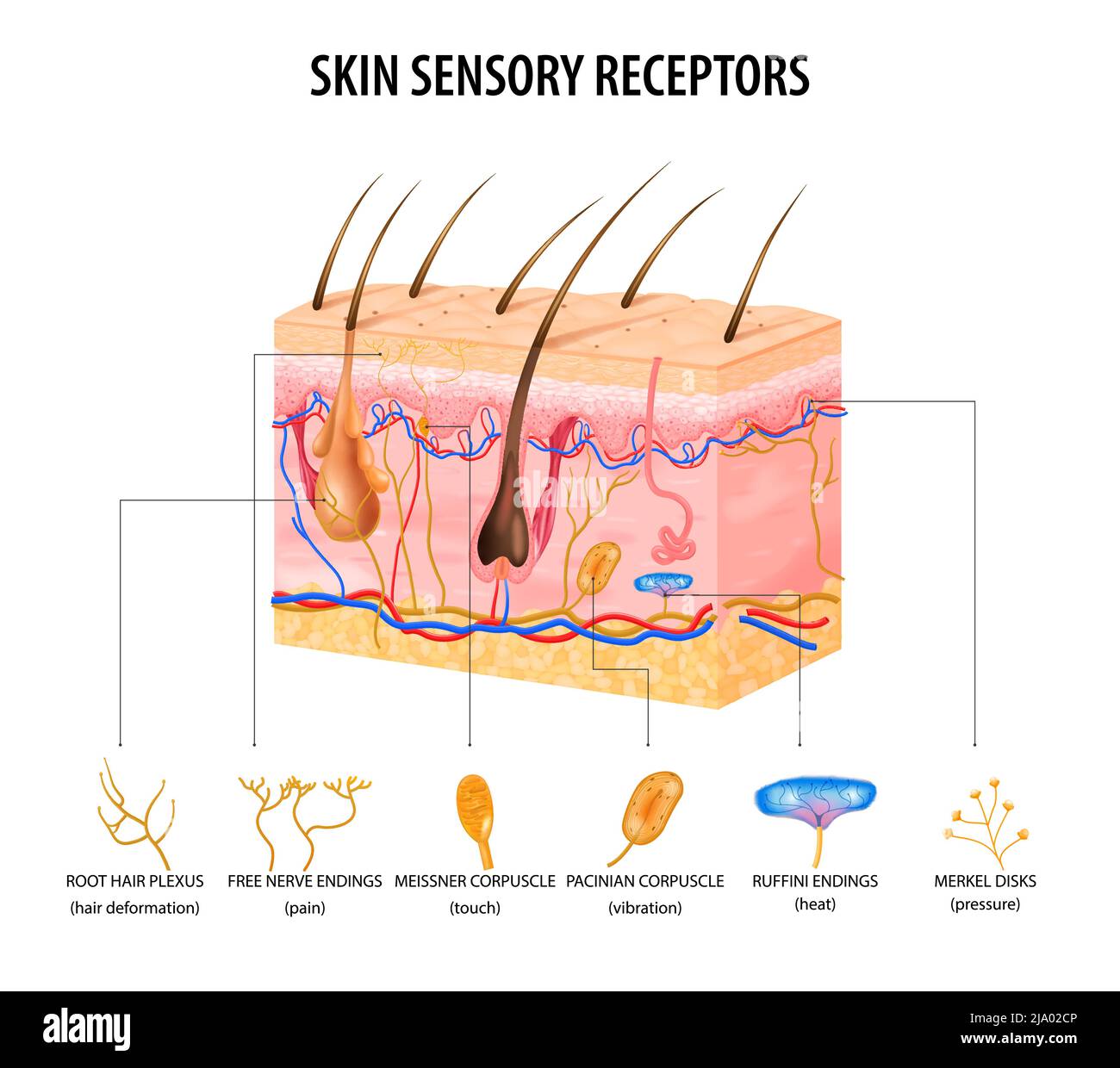 Skin sensory receptors concept with nerve and hair flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-nerve-and-hair-flat-vector-illustration-image470828422.html
Skin sensory receptors concept with nerve and hair flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-nerve-and-hair-flat-vector-illustration-image470828422.htmlRF2JA02CP–Skin sensory receptors concept with nerve and hair flat vector illustration
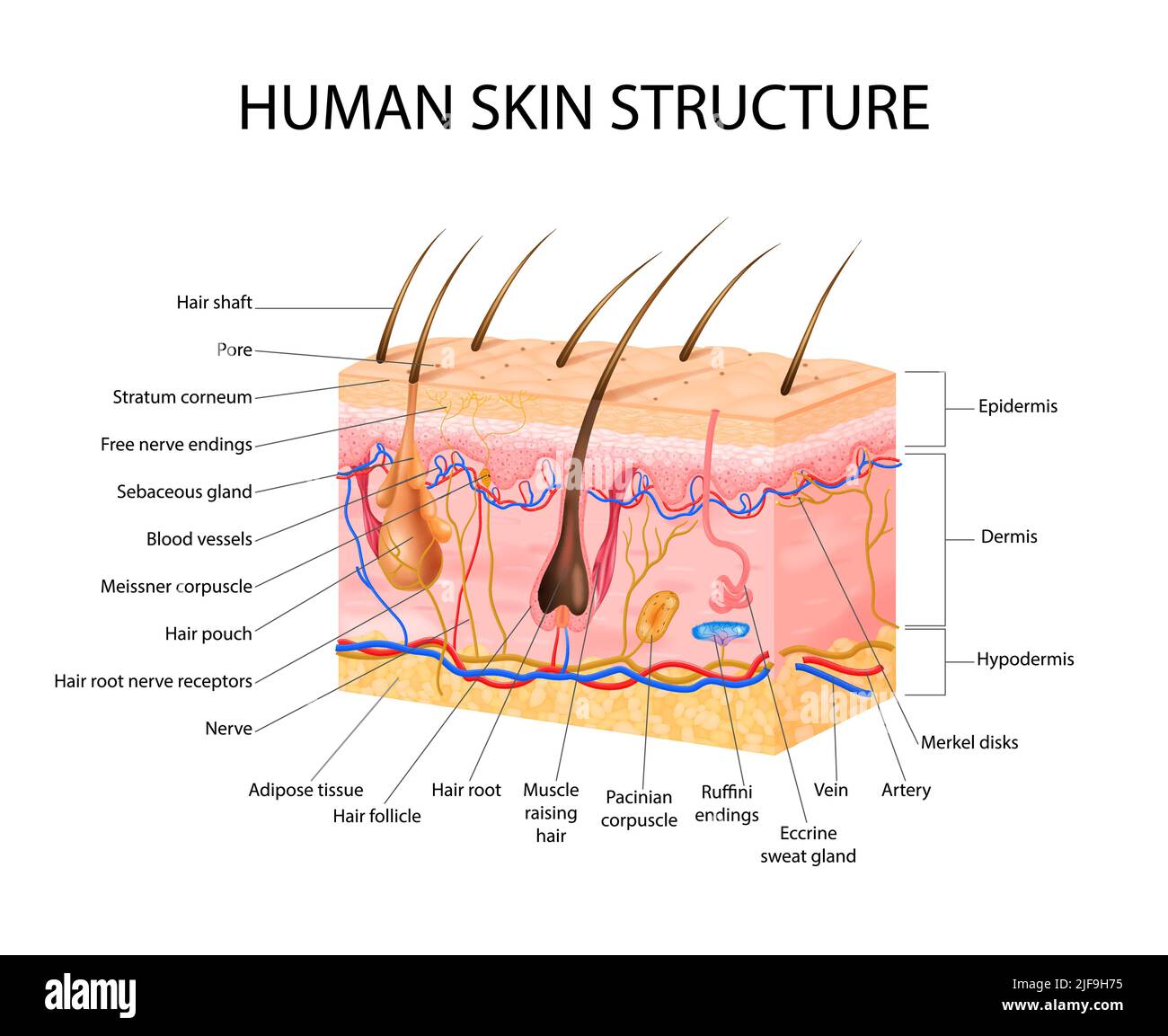 Skin sensory receptors concept with epidermis hair and dermis flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-epidermis-hair-and-dermis-flat-vector-illustration-image474110873.html
Skin sensory receptors concept with epidermis hair and dermis flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-epidermis-hair-and-dermis-flat-vector-illustration-image474110873.htmlRF2JF9H75–Skin sensory receptors concept with epidermis hair and dermis flat vector illustration
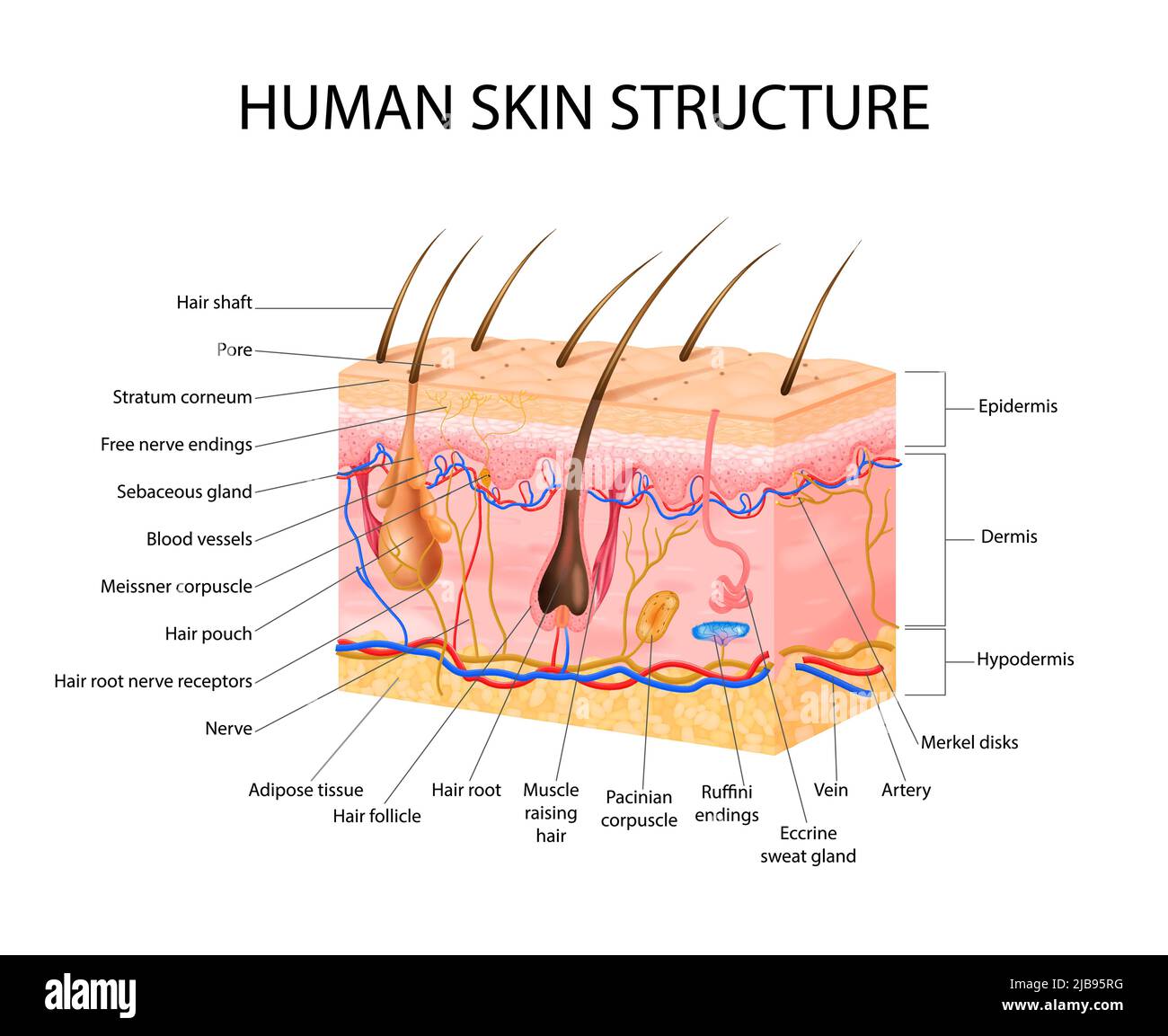 Skin sensory receptors concept with epidermis hair and dermis flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-epidermis-hair-and-dermis-flat-vector-illustration-image471643300.html
Skin sensory receptors concept with epidermis hair and dermis flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-epidermis-hair-and-dermis-flat-vector-illustration-image471643300.htmlRF2JB95RG–Skin sensory receptors concept with epidermis hair and dermis flat vector illustration
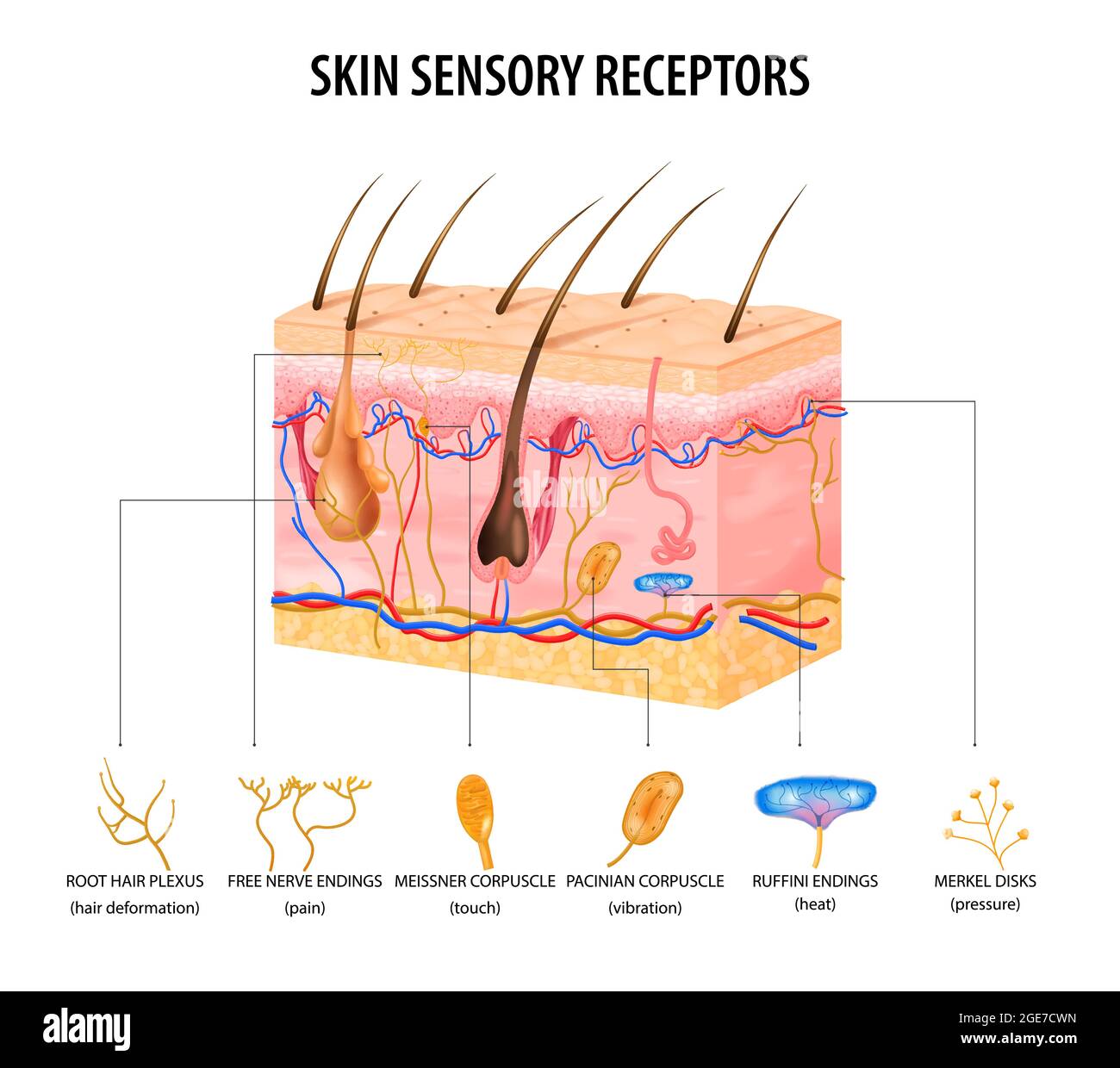 Skin sensory receptors concept with nerve and hair flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-nerve-and-hair-flat-vector-illustration-image439028177.html
Skin sensory receptors concept with nerve and hair flat vector illustration Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/skin-sensory-receptors-concept-with-nerve-and-hair-flat-vector-illustration-image439028177.htmlRF2GE7CWN–Skin sensory receptors concept with nerve and hair flat vector illustration
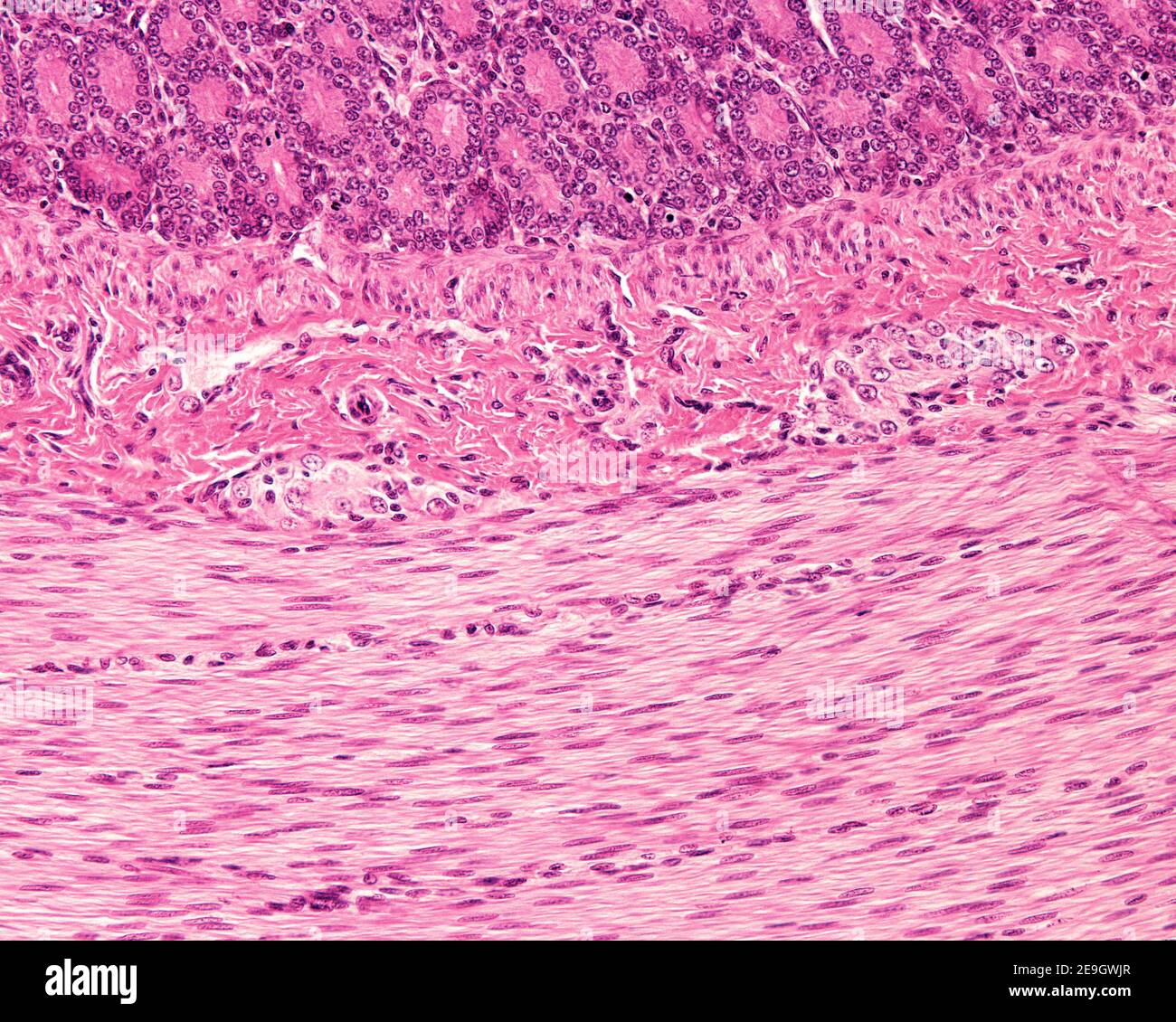 Meissner plexus in the submucosa of the digestive tract showing two small ganglia containing neuron cell bodies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/meissner-plexus-in-the-submucosa-of-the-digestive-tract-showing-two-small-ganglia-containing-neuron-cell-bodies-image401741727.html
Meissner plexus in the submucosa of the digestive tract showing two small ganglia containing neuron cell bodies. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/meissner-plexus-in-the-submucosa-of-the-digestive-tract-showing-two-small-ganglia-containing-neuron-cell-bodies-image401741727.htmlRF2E9GWJR–Meissner plexus in the submucosa of the digestive tract showing two small ganglia containing neuron cell bodies.
 A manual of human physiology, including histology and microscopical anatomy, with special reference to the requirements of practical medicine . Fig. 131. Plexus of Auerbach, prepared from the small intestine of a dog, by the action ofgold chloride. The nerve-cells are shown at the nodes, while the fibrils pro-ceeding from the ganglia, and the anastomosing fibres, lie between themuscular bundles.. Fig. 132. Plexus of Meissner—a, ganglia; b, anastomosing fibres; r, artery; d, vaso-motor nerve-fibres accompanying c. 2. When blood containing the normal amount of blood-gases passesthroiigh the inte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-human-physiology-including-histology-and-microscopical-anatomy-with-special-reference-to-the-requirements-of-practical-medicine-fig-131-plexus-of-auerbach-prepared-from-the-small-intestine-of-a-dog-by-the-action-ofgold-chloride-the-nerve-cells-are-shown-at-the-nodes-while-the-fibrils-pro-ceeding-from-the-ganglia-and-the-anastomosing-fibres-lie-between-themuscular-bundles-fig-132-plexus-of-meissnera-ganglia-b-anastomosing-fibres-r-artery-d-vaso-motor-nerve-fibres-accompanying-c-2-when-blood-containing-the-normal-amount-of-blood-gases-passesthroiigh-the-inte-image340027663.html
A manual of human physiology, including histology and microscopical anatomy, with special reference to the requirements of practical medicine . Fig. 131. Plexus of Auerbach, prepared from the small intestine of a dog, by the action ofgold chloride. The nerve-cells are shown at the nodes, while the fibrils pro-ceeding from the ganglia, and the anastomosing fibres, lie between themuscular bundles.. Fig. 132. Plexus of Meissner—a, ganglia; b, anastomosing fibres; r, artery; d, vaso-motor nerve-fibres accompanying c. 2. When blood containing the normal amount of blood-gases passesthroiigh the inte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-human-physiology-including-histology-and-microscopical-anatomy-with-special-reference-to-the-requirements-of-practical-medicine-fig-131-plexus-of-auerbach-prepared-from-the-small-intestine-of-a-dog-by-the-action-ofgold-chloride-the-nerve-cells-are-shown-at-the-nodes-while-the-fibrils-pro-ceeding-from-the-ganglia-and-the-anastomosing-fibres-lie-between-themuscular-bundles-fig-132-plexus-of-meissnera-ganglia-b-anastomosing-fibres-r-artery-d-vaso-motor-nerve-fibres-accompanying-c-2-when-blood-containing-the-normal-amount-of-blood-gases-passesthroiigh-the-inte-image340027663.htmlRM2AN5GN3–A manual of human physiology, including histology and microscopical anatomy, with special reference to the requirements of practical medicine . Fig. 131. Plexus of Auerbach, prepared from the small intestine of a dog, by the action ofgold chloride. The nerve-cells are shown at the nodes, while the fibrils pro-ceeding from the ganglia, and the anastomosing fibres, lie between themuscular bundles.. Fig. 132. Plexus of Meissner—a, ganglia; b, anastomosing fibres; r, artery; d, vaso-motor nerve-fibres accompanying c. 2. When blood containing the normal amount of blood-gases passesthroiigh the inte
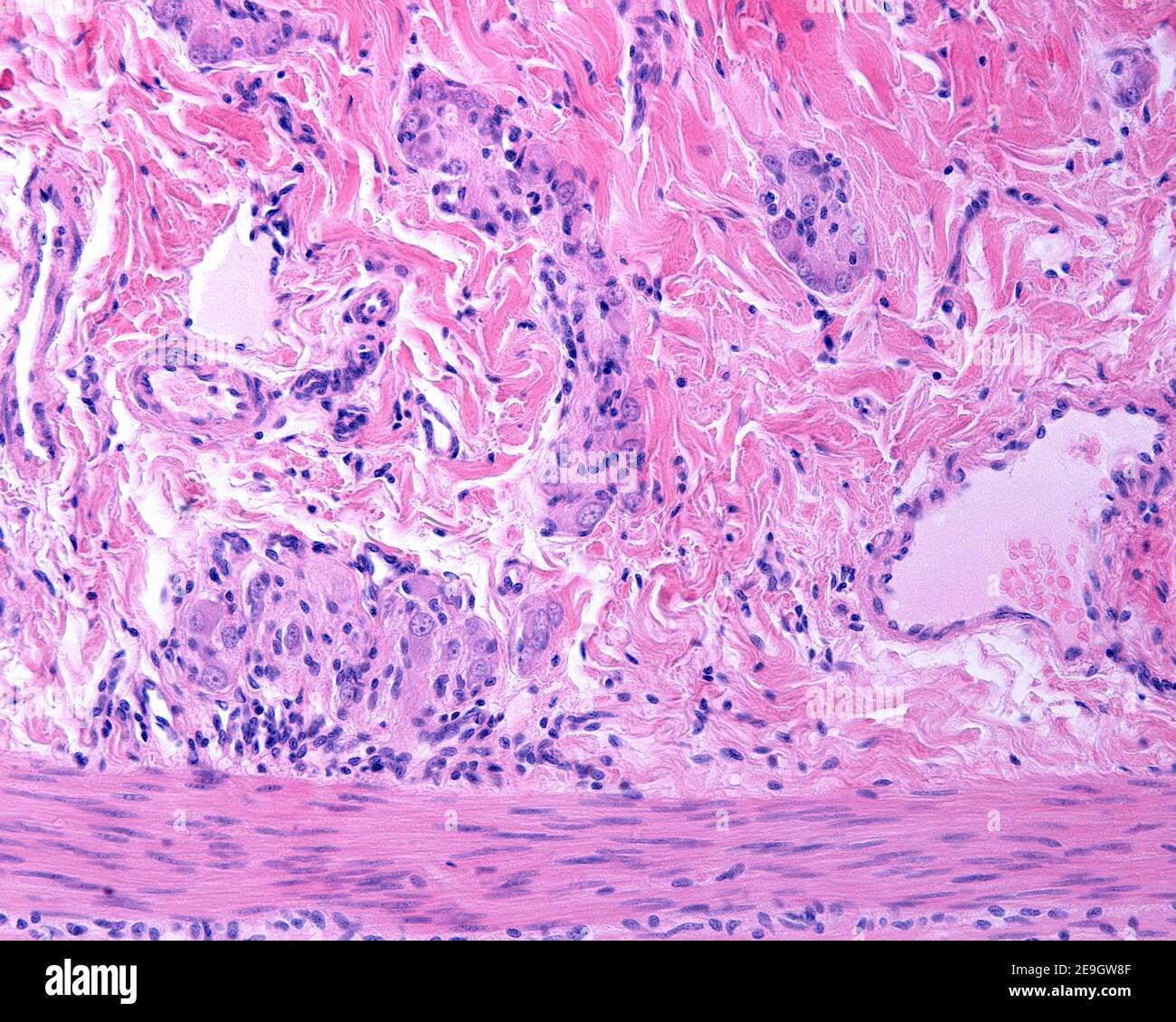 Meissner plexus in the submucosa of the digestive tract showing several ganglia containing neuron cell bodies and nerve fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/meissner-plexus-in-the-submucosa-of-the-digestive-tract-showing-several-ganglia-containing-neuron-cell-bodies-and-nerve-fibers-image401741439.html
Meissner plexus in the submucosa of the digestive tract showing several ganglia containing neuron cell bodies and nerve fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/meissner-plexus-in-the-submucosa-of-the-digestive-tract-showing-several-ganglia-containing-neuron-cell-bodies-and-nerve-fibers-image401741439.htmlRF2E9GW8F–Meissner plexus in the submucosa of the digestive tract showing several ganglia containing neuron cell bodies and nerve fibers.
 The laws and mechanics of circulation, with the principle involved in animal movement . r $ Fig. 107.—Nerves to the Intestines—partly ideal. 1, Ganglionic layer of Meissner ; 3,nerves from the same to the villi and columnar epithelium ; 3, nerves connecting samewith the ganglionic layer of Auerbach ; 4, ganglionic layer of Auerbach ; 5, 5, 5,nerves connecting the intestinal apparatus with the solar plexus. A, A, villi ; B,summit of a lymphoid follicle ; d, muscularis mucosae ; E, circular muscles ; /, longi-tudinal muscles ; g, peritoneum ; v, v, arterial capillaries; h, submucosa. NERVES TO T Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-laws-and-mechanics-of-circulation-with-the-principle-involved-in-animal-movement-r-fig-107nerves-to-the-intestinespartly-ideal-1-ganglionic-layer-of-meissner-3nerves-from-the-same-to-the-villi-and-columnar-epithelium-3-nerves-connecting-samewith-the-ganglionic-layer-of-auerbach-4-ganglionic-layer-of-auerbach-5-5-5nerves-connecting-the-intestinal-apparatus-with-the-solar-plexus-a-a-villi-bsummit-of-a-lymphoid-follicle-d-muscularis-mucosae-e-circular-muscles-longi-tudinal-muscles-g-peritoneum-v-v-arterial-capillaries-h-submucosa-nerves-to-t-image339954937.html
The laws and mechanics of circulation, with the principle involved in animal movement . r $ Fig. 107.—Nerves to the Intestines—partly ideal. 1, Ganglionic layer of Meissner ; 3,nerves from the same to the villi and columnar epithelium ; 3, nerves connecting samewith the ganglionic layer of Auerbach ; 4, ganglionic layer of Auerbach ; 5, 5, 5,nerves connecting the intestinal apparatus with the solar plexus. A, A, villi ; B,summit of a lymphoid follicle ; d, muscularis mucosae ; E, circular muscles ; /, longi-tudinal muscles ; g, peritoneum ; v, v, arterial capillaries; h, submucosa. NERVES TO T Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-laws-and-mechanics-of-circulation-with-the-principle-involved-in-animal-movement-r-fig-107nerves-to-the-intestinespartly-ideal-1-ganglionic-layer-of-meissner-3nerves-from-the-same-to-the-villi-and-columnar-epithelium-3-nerves-connecting-samewith-the-ganglionic-layer-of-auerbach-4-ganglionic-layer-of-auerbach-5-5-5nerves-connecting-the-intestinal-apparatus-with-the-solar-plexus-a-a-villi-bsummit-of-a-lymphoid-follicle-d-muscularis-mucosae-e-circular-muscles-longi-tudinal-muscles-g-peritoneum-v-v-arterial-capillaries-h-submucosa-nerves-to-t-image339954937.htmlRM2AN27YN–The laws and mechanics of circulation, with the principle involved in animal movement . r $ Fig. 107.—Nerves to the Intestines—partly ideal. 1, Ganglionic layer of Meissner ; 3,nerves from the same to the villi and columnar epithelium ; 3, nerves connecting samewith the ganglionic layer of Auerbach ; 4, ganglionic layer of Auerbach ; 5, 5, 5,nerves connecting the intestinal apparatus with the solar plexus. A, A, villi ; B,summit of a lymphoid follicle ; d, muscularis mucosae ; E, circular muscles ; /, longi-tudinal muscles ; g, peritoneum ; v, v, arterial capillaries; h, submucosa. NERVES TO T
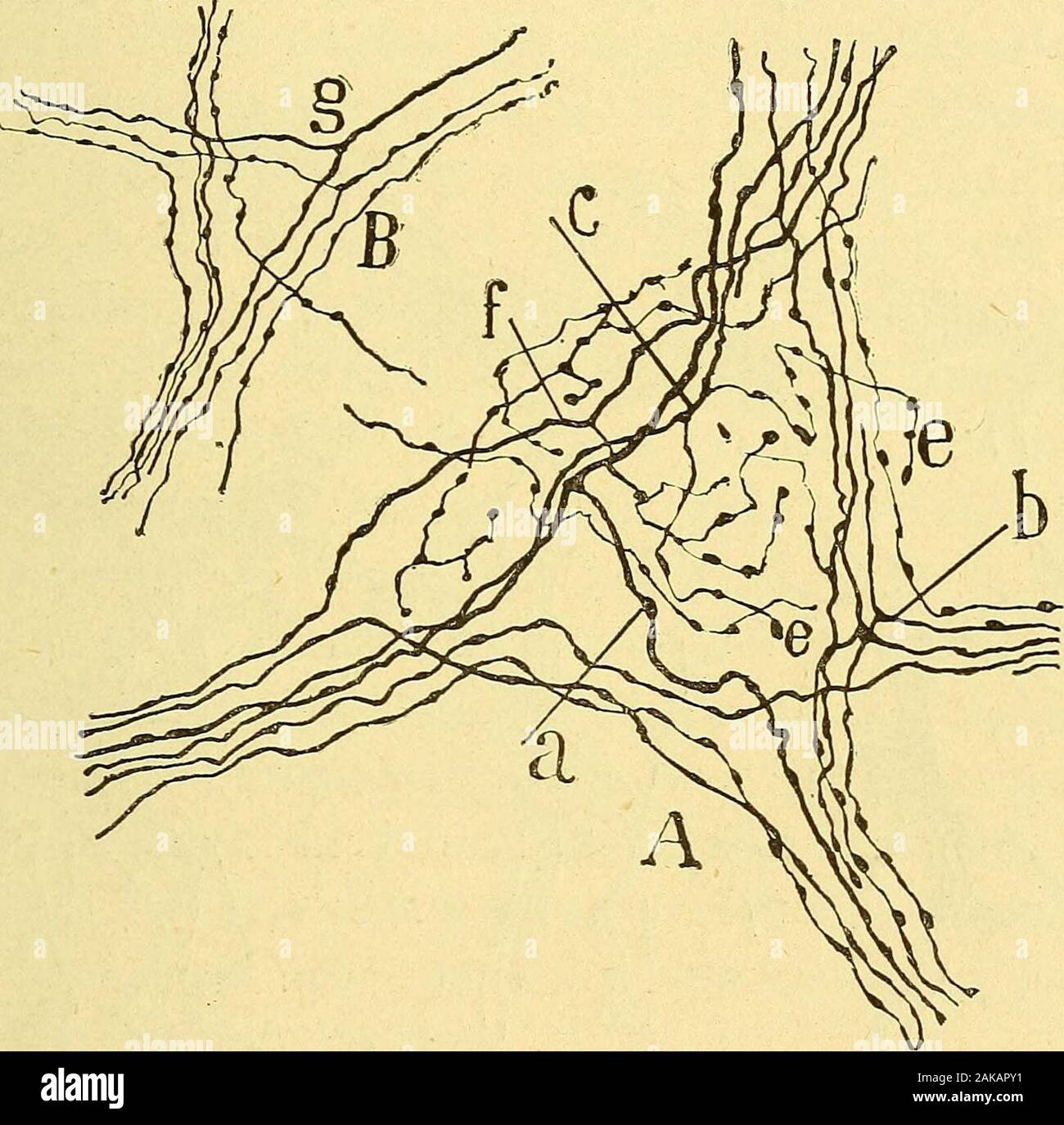 Les nouvelles idées sur la structure du système nerveux : chez l'homme et chez les vertébrés . stin grcle du cobaye. — Figure demi-schématiquedestinée à montrer la totalité des plexus et des ganglions de lintestin. /l couche des fibres musculaires longitudinales; B couche des libres musculairescirculaires; C tissu conjonctif sous-muqueux, avec le plexus et les ganglions deMeissner; D couche des glandes de Lieberkuhn ; E villosités; — a plexus dAuer-bach ; g ganglion dAuerbach ; b plexus musculaire profond coupe en travers ;c fascicules du plexus de Meissner: e faisceaux du plexus périglandulai Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/les-nouvelles-ides-sur-la-structure-du-systme-nerveux-chez-lhomme-et-chez-les-vertbrs-stin-grcle-du-cobaye-figure-demi-schmatiquedestine-montrer-la-totalit-des-plexus-et-des-ganglions-de-lintestin-l-couche-des-fibres-musculaires-longitudinales-b-couche-des-libres-musculairescirculaires-c-tissu-conjonctif-sous-muqueux-avec-le-plexus-et-les-ganglions-demeissner-d-couche-des-glandes-de-lieberkuhn-e-villosits-a-plexus-dauer-bach-g-ganglion-dauerbach-b-plexus-musculaire-profond-coupe-en-travers-c-fascicules-du-plexus-de-meissner-e-faisceaux-du-plexus-priglandulai-image338912981.html
Les nouvelles idées sur la structure du système nerveux : chez l'homme et chez les vertébrés . stin grcle du cobaye. — Figure demi-schématiquedestinée à montrer la totalité des plexus et des ganglions de lintestin. /l couche des fibres musculaires longitudinales; B couche des libres musculairescirculaires; C tissu conjonctif sous-muqueux, avec le plexus et les ganglions deMeissner; D couche des glandes de Lieberkuhn ; E villosités; — a plexus dAuer-bach ; g ganglion dAuerbach ; b plexus musculaire profond coupe en travers ;c fascicules du plexus de Meissner: e faisceaux du plexus périglandulai Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/les-nouvelles-ides-sur-la-structure-du-systme-nerveux-chez-lhomme-et-chez-les-vertbrs-stin-grcle-du-cobaye-figure-demi-schmatiquedestine-montrer-la-totalit-des-plexus-et-des-ganglions-de-lintestin-l-couche-des-fibres-musculaires-longitudinales-b-couche-des-libres-musculairescirculaires-c-tissu-conjonctif-sous-muqueux-avec-le-plexus-et-les-ganglions-demeissner-d-couche-des-glandes-de-lieberkuhn-e-villosits-a-plexus-dauer-bach-g-ganglion-dauerbach-b-plexus-musculaire-profond-coupe-en-travers-c-fascicules-du-plexus-de-meissner-e-faisceaux-du-plexus-priglandulai-image338912981.htmlRM2AKAPY1–Les nouvelles idées sur la structure du système nerveux : chez l'homme et chez les vertébrés . stin grcle du cobaye. — Figure demi-schématiquedestinée à montrer la totalité des plexus et des ganglions de lintestin. /l couche des fibres musculaires longitudinales; B couche des libres musculairescirculaires; C tissu conjonctif sous-muqueux, avec le plexus et les ganglions deMeissner; D couche des glandes de Lieberkuhn ; E villosités; — a plexus dAuer-bach ; g ganglion dAuerbach ; b plexus musculaire profond coupe en travers ;c fascicules du plexus de Meissner: e faisceaux du plexus périglandulai
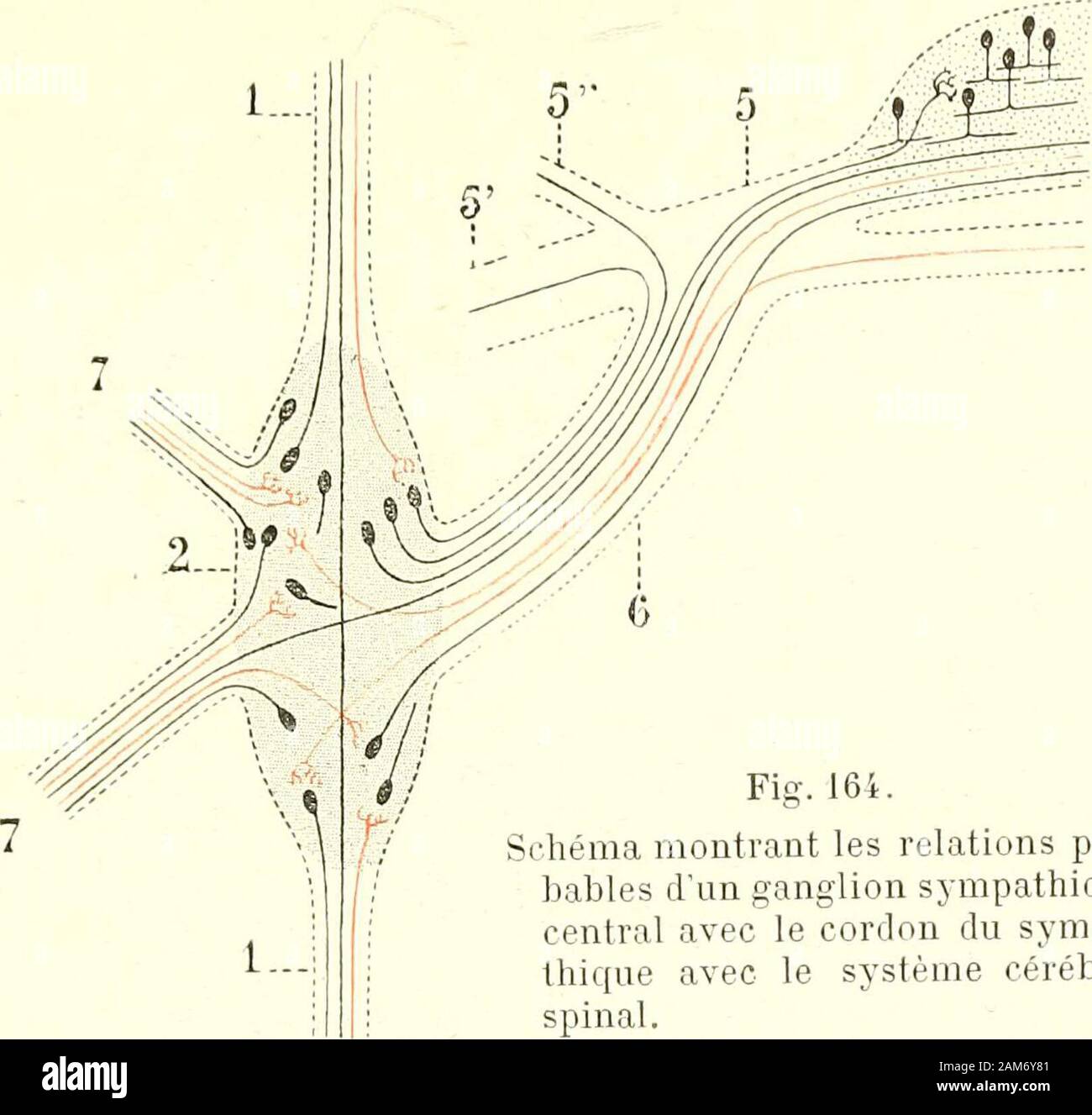 Traité d'anatomie humaine . ériphériques, par opposition aux ganglions centraux,qui sont situés sur le tronc même du grand sympathique. Les ganglions nerveuxpériphériques sont, à leur tour, très variables dans leur volume : les uns sontvisibles à Tœil nu, comme les ganglions du plexus solaire; les autres, et cesont incontestablement les plus nombreux, ne sont visibles quà laide du micros-cope, comme les ganglions du tube intestinal, suspendus çà et là aux mailles duplexus dAuerbach et du plexus de Meissner. Le grand sympattiique tient sous sa dépendance un ordre particulier de mouvements quiso Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/trait-danatomie-humaine-riphriques-par-opposition-aux-ganglions-centrauxqui-sont-situs-sur-le-tronc-mme-du-grand-sympathique-les-ganglions-nerveuxpriphriques-sont-leur-tour-trs-variables-dans-leur-volume-les-uns-sontvisibles-til-nu-comme-les-ganglions-du-plexus-solaire-les-autres-et-cesont-incontestablement-les-plus-nombreux-ne-sont-visibles-qu-laide-du-micros-cope-comme-les-ganglions-du-tube-intestinal-suspendus-et-l-aux-mailles-duplexus-dauerbach-et-du-plexus-de-meissner-le-grand-sympattiique-tient-sous-sa-dpendance-un-ordre-particulier-de-mouvements-quiso-image339443217.html
Traité d'anatomie humaine . ériphériques, par opposition aux ganglions centraux,qui sont situés sur le tronc même du grand sympathique. Les ganglions nerveuxpériphériques sont, à leur tour, très variables dans leur volume : les uns sontvisibles à Tœil nu, comme les ganglions du plexus solaire; les autres, et cesont incontestablement les plus nombreux, ne sont visibles quà laide du micros-cope, comme les ganglions du tube intestinal, suspendus çà et là aux mailles duplexus dAuerbach et du plexus de Meissner. Le grand sympattiique tient sous sa dépendance un ordre particulier de mouvements quiso Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/trait-danatomie-humaine-riphriques-par-opposition-aux-ganglions-centrauxqui-sont-situs-sur-le-tronc-mme-du-grand-sympathique-les-ganglions-nerveuxpriphriques-sont-leur-tour-trs-variables-dans-leur-volume-les-uns-sontvisibles-til-nu-comme-les-ganglions-du-plexus-solaire-les-autres-et-cesont-incontestablement-les-plus-nombreux-ne-sont-visibles-qu-laide-du-micros-cope-comme-les-ganglions-du-tube-intestinal-suspendus-et-l-aux-mailles-duplexus-dauerbach-et-du-plexus-de-meissner-le-grand-sympattiique-tient-sous-sa-dpendance-un-ordre-particulier-de-mouvements-quiso-image339443217.htmlRM2AM6Y81–Traité d'anatomie humaine . ériphériques, par opposition aux ganglions centraux,qui sont situés sur le tronc même du grand sympathique. Les ganglions nerveuxpériphériques sont, à leur tour, très variables dans leur volume : les uns sontvisibles à Tœil nu, comme les ganglions du plexus solaire; les autres, et cesont incontestablement les plus nombreux, ne sont visibles quà laide du micros-cope, comme les ganglions du tube intestinal, suspendus çà et là aux mailles duplexus dAuerbach et du plexus de Meissner. Le grand sympattiique tient sous sa dépendance un ordre particulier de mouvements quiso
 . Anatomie des centres nerveux. Fig. S6. — Cellules et groupes de fibres duganglion spinal dun embryon humain dequatre semaines et demie. (DaprèsW. His.) Plexus ganglion-naires dAuerbach et Meissner. Ganglioblastes cé-rébro-rachidiens. Fibres en T deRanvier. Unipolarisation des.ganglioblastes desvertébrés supérieurs. Fibres centralesdes ganglioblastes. Cordon postérieurprimitif. 148 A.NATO.MIE DES CENTRES NERVEUX. coupes transversales de la moelle embryonnaire ce cordon, situé à la péri-phérie, présente une surface de section plus ou moins arrondie qui lui avalu le nom de faisceau ovalaire (Hi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomie-des-centres-nerveux-fig-s6-cellules-et-groupes-de-fibres-duganglion-spinal-dun-embryon-humain-dequatre-semaines-et-demie-daprsw-his-plexus-ganglion-naires-dauerbach-et-meissner-ganglioblastes-c-rbro-rachidiens-fibres-en-t-deranvier-unipolarisation-desganglioblastes-desvertbrs-suprieurs-fibres-centralesdes-ganglioblastes-cordon-postrieurprimitif-148-anatomie-des-centres-nerveux-coupes-transversales-de-la-moelle-embryonnaire-ce-cordon-situ-la-pri-phrie-prsente-une-surface-de-section-plus-ou-moins-arrondie-qui-lui-avalu-le-nom-de-faisceau-ovalaire-hi-image370557696.html
. Anatomie des centres nerveux. Fig. S6. — Cellules et groupes de fibres duganglion spinal dun embryon humain dequatre semaines et demie. (DaprèsW. His.) Plexus ganglion-naires dAuerbach et Meissner. Ganglioblastes cé-rébro-rachidiens. Fibres en T deRanvier. Unipolarisation des.ganglioblastes desvertébrés supérieurs. Fibres centralesdes ganglioblastes. Cordon postérieurprimitif. 148 A.NATO.MIE DES CENTRES NERVEUX. coupes transversales de la moelle embryonnaire ce cordon, situé à la péri-phérie, présente une surface de section plus ou moins arrondie qui lui avalu le nom de faisceau ovalaire (Hi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomie-des-centres-nerveux-fig-s6-cellules-et-groupes-de-fibres-duganglion-spinal-dun-embryon-humain-dequatre-semaines-et-demie-daprsw-his-plexus-ganglion-naires-dauerbach-et-meissner-ganglioblastes-c-rbro-rachidiens-fibres-en-t-deranvier-unipolarisation-desganglioblastes-desvertbrs-suprieurs-fibres-centralesdes-ganglioblastes-cordon-postrieurprimitif-148-anatomie-des-centres-nerveux-coupes-transversales-de-la-moelle-embryonnaire-ce-cordon-situ-la-pri-phrie-prsente-une-surface-de-section-plus-ou-moins-arrondie-qui-lui-avalu-le-nom-de-faisceau-ovalaire-hi-image370557696.htmlRM2CETA3C–. Anatomie des centres nerveux. Fig. S6. — Cellules et groupes de fibres duganglion spinal dun embryon humain dequatre semaines et demie. (DaprèsW. His.) Plexus ganglion-naires dAuerbach et Meissner. Ganglioblastes cé-rébro-rachidiens. Fibres en T deRanvier. Unipolarisation des.ganglioblastes desvertébrés supérieurs. Fibres centralesdes ganglioblastes. Cordon postérieurprimitif. 148 A.NATO.MIE DES CENTRES NERVEUX. coupes transversales de la moelle embryonnaire ce cordon, situé à la péri-phérie, présente une surface de section plus ou moins arrondie qui lui avalu le nom de faisceau ovalaire (Hi
 . The chordates. Chordata. 174 Basic Structure of Vertebrates PLEXUS OF AUERBACH>-0 PLEXUS OF MEISSNER* SYMPATHETIC. -PERITONEUM Fig. 154. Stereogram of a portion of the small intestine, showing the arrange- ment of sympathetic neurons in the plexuses of Meissner and Auerbach. Motor cells are shown in black, sensory cells with white nuclei. (After Kahn. Courtesy, Neal and Rand: "Chordate Anatomy," Philadelphia, The Blakiston Company.) environment continues to pulsate, but in this case it is difficult to as- certain that the fragment is quite devoid of nervous elements. When a shor Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-chordates-chordata-174-basic-structure-of-vertebrates-plexus-of-auerbachgt-0-plexus-of-meissner-sympathetic-peritoneum-fig-154-stereogram-of-a-portion-of-the-small-intestine-showing-the-arrange-ment-of-sympathetic-neurons-in-the-plexuses-of-meissner-and-auerbach-motor-cells-are-shown-in-black-sensory-cells-with-white-nuclei-after-kahn-courtesy-neal-and-rand-quotchordate-anatomyquot-philadelphia-the-blakiston-company-environment-continues-to-pulsate-but-in-this-case-it-is-difficult-to-as-certain-that-the-fragment-is-quite-devoid-of-nervous-elements-when-a-shor-image234909166.html
. The chordates. Chordata. 174 Basic Structure of Vertebrates PLEXUS OF AUERBACH>-0 PLEXUS OF MEISSNER* SYMPATHETIC. -PERITONEUM Fig. 154. Stereogram of a portion of the small intestine, showing the arrange- ment of sympathetic neurons in the plexuses of Meissner and Auerbach. Motor cells are shown in black, sensory cells with white nuclei. (After Kahn. Courtesy, Neal and Rand: "Chordate Anatomy," Philadelphia, The Blakiston Company.) environment continues to pulsate, but in this case it is difficult to as- certain that the fragment is quite devoid of nervous elements. When a shor Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-chordates-chordata-174-basic-structure-of-vertebrates-plexus-of-auerbachgt-0-plexus-of-meissner-sympathetic-peritoneum-fig-154-stereogram-of-a-portion-of-the-small-intestine-showing-the-arrange-ment-of-sympathetic-neurons-in-the-plexuses-of-meissner-and-auerbach-motor-cells-are-shown-in-black-sensory-cells-with-white-nuclei-after-kahn-courtesy-neal-and-rand-quotchordate-anatomyquot-philadelphia-the-blakiston-company-environment-continues-to-pulsate-but-in-this-case-it-is-difficult-to-as-certain-that-the-fragment-is-quite-devoid-of-nervous-elements-when-a-shor-image234909166.htmlRMRJ5112–. The chordates. Chordata. 174 Basic Structure of Vertebrates PLEXUS OF AUERBACH>-0 PLEXUS OF MEISSNER* SYMPATHETIC. -PERITONEUM Fig. 154. Stereogram of a portion of the small intestine, showing the arrange- ment of sympathetic neurons in the plexuses of Meissner and Auerbach. Motor cells are shown in black, sensory cells with white nuclei. (After Kahn. Courtesy, Neal and Rand: "Chordate Anatomy," Philadelphia, The Blakiston Company.) environment continues to pulsate, but in this case it is difficult to as- certain that the fragment is quite devoid of nervous elements. When a shor
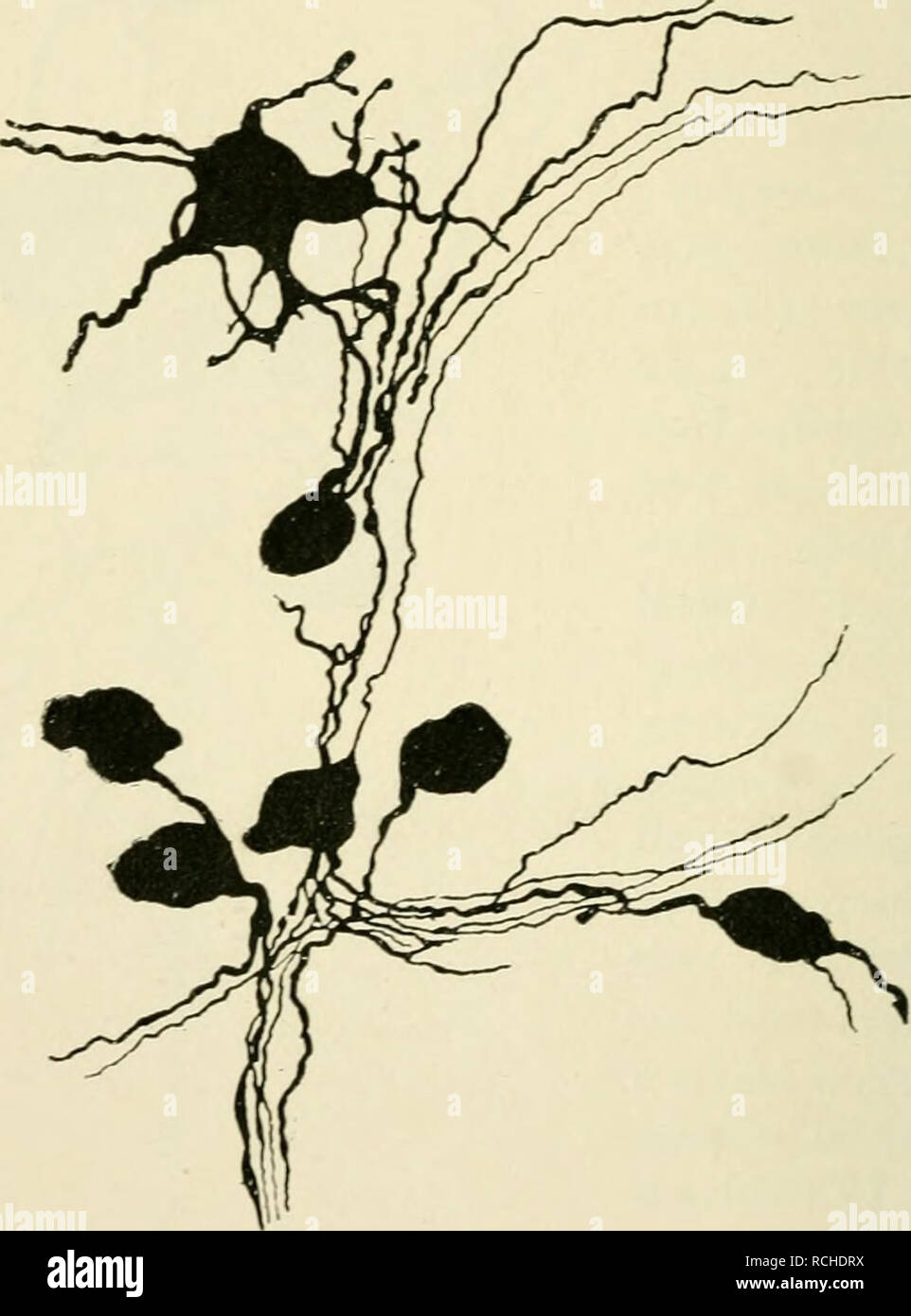 . Elements of histology. Histology. 266 Elements of Histology. the ganglion cell. This straight process is entwined by a thin spiral fibre which, farther away from the body of the irancvlion cell, is a medullated fibre ; it ramifies on the substance of the ganglion cell (Fig. 174).. Fig. 172.—Group of Ganglion Cells from the Plexus of Meissner of a Puppy ; amongst them a Multipolar and several Unipolar Cells. (Kolliker, II.) Arnold, then Ehrlich and further Retzius (the last two by ibjection of methylene blue into the blood- vessels of the living frog) have shown this spiral fibre (stained blu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-histology-histology-266-elements-of-histology-the-ganglion-cell-this-straight-process-is-entwined-by-a-thin-spiral-fibre-which-farther-away-from-the-body-of-the-irancvlion-cell-is-a-medullated-fibre-it-ramifies-on-the-substance-of-the-ganglion-cell-fig-174-fig-172group-of-ganglion-cells-from-the-plexus-of-meissner-of-a-puppy-amongst-them-a-multipolar-and-several-unipolar-cells-kolliker-ii-arnold-then-ehrlich-and-further-retzius-the-last-two-by-ibjection-of-methylene-blue-into-the-blood-vessels-of-the-living-frog-have-shown-this-spiral-fibre-stained-blu-image231494702.html
. Elements of histology. Histology. 266 Elements of Histology. the ganglion cell. This straight process is entwined by a thin spiral fibre which, farther away from the body of the irancvlion cell, is a medullated fibre ; it ramifies on the substance of the ganglion cell (Fig. 174).. Fig. 172.—Group of Ganglion Cells from the Plexus of Meissner of a Puppy ; amongst them a Multipolar and several Unipolar Cells. (Kolliker, II.) Arnold, then Ehrlich and further Retzius (the last two by ibjection of methylene blue into the blood- vessels of the living frog) have shown this spiral fibre (stained blu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-histology-histology-266-elements-of-histology-the-ganglion-cell-this-straight-process-is-entwined-by-a-thin-spiral-fibre-which-farther-away-from-the-body-of-the-irancvlion-cell-is-a-medullated-fibre-it-ramifies-on-the-substance-of-the-ganglion-cell-fig-174-fig-172group-of-ganglion-cells-from-the-plexus-of-meissner-of-a-puppy-amongst-them-a-multipolar-and-several-unipolar-cells-kolliker-ii-arnold-then-ehrlich-and-further-retzius-the-last-two-by-ibjection-of-methylene-blue-into-the-blood-vessels-of-the-living-frog-have-shown-this-spiral-fibre-stained-blu-image231494702.htmlRMRCHDRX–. Elements of histology. Histology. 266 Elements of Histology. the ganglion cell. This straight process is entwined by a thin spiral fibre which, farther away from the body of the irancvlion cell, is a medullated fibre ; it ramifies on the substance of the ganglion cell (Fig. 174).. Fig. 172.—Group of Ganglion Cells from the Plexus of Meissner of a Puppy ; amongst them a Multipolar and several Unipolar Cells. (Kolliker, II.) Arnold, then Ehrlich and further Retzius (the last two by ibjection of methylene blue into the blood- vessels of the living frog) have shown this spiral fibre (stained blu
 . Elements of histology. Histology. 170 Elements of Histology. [Chap. xx. of the external muscular coat in the alimentary canal, known as the plexus myentericus of Auerbach, the ganglia in the plexus of nerve branches of the sub-. Fig. 101.—Plexus of fine Sympathetic Nerve-fibres, with Ganglionic Enlargements in the Nodal Points. From the Plexus of Meissner in the Submucous Tissue of the Intestine. a, Fine nerve-fibres; 6, groups of ganglion cells interposed between the nerve-fibres. mucous tissue in the alimentary canal, and known as Meissner's plexus (Fig. 101), the ganglia in the plexuses o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-histology-histology-170-elements-of-histology-chap-xx-of-the-external-muscular-coat-in-the-alimentary-canal-known-as-the-plexus-myentericus-of-auerbach-the-ganglia-in-the-plexus-of-nerve-branches-of-the-sub-fig-101plexus-of-fine-sympathetic-nerve-fibres-with-ganglionic-enlargements-in-the-nodal-points-from-the-plexus-of-meissner-in-the-submucous-tissue-of-the-intestine-a-fine-nerve-fibres-6-groups-of-ganglion-cells-interposed-between-the-nerve-fibres-mucous-tissue-in-the-alimentary-canal-and-known-as-meissners-plexus-fig-101-the-ganglia-in-the-plexuses-o-image231472157.html
. Elements of histology. Histology. 170 Elements of Histology. [Chap. xx. of the external muscular coat in the alimentary canal, known as the plexus myentericus of Auerbach, the ganglia in the plexus of nerve branches of the sub-. Fig. 101.—Plexus of fine Sympathetic Nerve-fibres, with Ganglionic Enlargements in the Nodal Points. From the Plexus of Meissner in the Submucous Tissue of the Intestine. a, Fine nerve-fibres; 6, groups of ganglion cells interposed between the nerve-fibres. mucous tissue in the alimentary canal, and known as Meissner's plexus (Fig. 101), the ganglia in the plexuses o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-histology-histology-170-elements-of-histology-chap-xx-of-the-external-muscular-coat-in-the-alimentary-canal-known-as-the-plexus-myentericus-of-auerbach-the-ganglia-in-the-plexus-of-nerve-branches-of-the-sub-fig-101plexus-of-fine-sympathetic-nerve-fibres-with-ganglionic-enlargements-in-the-nodal-points-from-the-plexus-of-meissner-in-the-submucous-tissue-of-the-intestine-a-fine-nerve-fibres-6-groups-of-ganglion-cells-interposed-between-the-nerve-fibres-mucous-tissue-in-the-alimentary-canal-and-known-as-meissners-plexus-fig-101-the-ganglia-in-the-plexuses-o-image231472157.htmlRMRCGD2N–. Elements of histology. Histology. 170 Elements of Histology. [Chap. xx. of the external muscular coat in the alimentary canal, known as the plexus myentericus of Auerbach, the ganglia in the plexus of nerve branches of the sub-. Fig. 101.—Plexus of fine Sympathetic Nerve-fibres, with Ganglionic Enlargements in the Nodal Points. From the Plexus of Meissner in the Submucous Tissue of the Intestine. a, Fine nerve-fibres; 6, groups of ganglion cells interposed between the nerve-fibres. mucous tissue in the alimentary canal, and known as Meissner's plexus (Fig. 101), the ganglia in the plexuses o