Mouth bacteria sem Stock Photos and Images
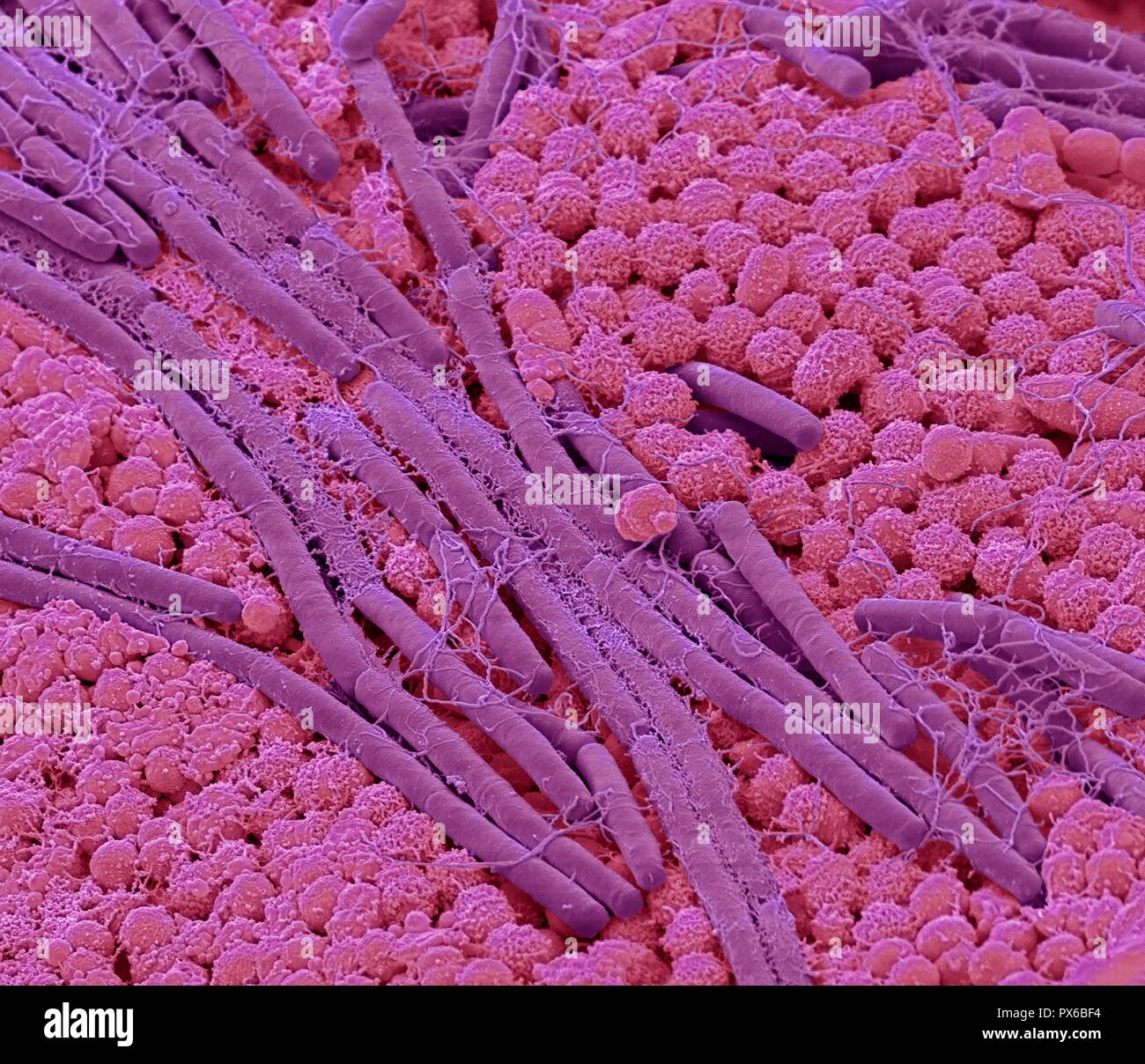 Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of bacteria can form a visible layer on the surface of the tongue. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Magnification: x10000 at 10cm wide. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-on-the-surface-of-a-human-tongue-large-numbers-of-bacteria-can-form-a-visible-layer-on-the-surface-of-the-tongue-the-mouth-contains-a-large-number-of-bacteria-most-of-which-are-harmless-or-even-beneficial-however-some-bacteria-can-cause-throat-infections-or-cause-the-formation-of-plaque-deposits-on-the-teeth-which-may-lead-to-decay-magnification-x10000-at-10cm-wide-image222646232.html
Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of bacteria can form a visible layer on the surface of the tongue. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Magnification: x10000 at 10cm wide. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-on-the-surface-of-a-human-tongue-large-numbers-of-bacteria-can-form-a-visible-layer-on-the-surface-of-the-tongue-the-mouth-contains-a-large-number-of-bacteria-most-of-which-are-harmless-or-even-beneficial-however-some-bacteria-can-cause-throat-infections-or-cause-the-formation-of-plaque-deposits-on-the-teeth-which-may-lead-to-decay-magnification-x10000-at-10cm-wide-image222646232.htmlRFPX6BF4–Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of bacteria can form a visible layer on the surface of the tongue. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Magnification: x10000 at 10cm wide.
 DENTAL CARE, ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-care-adolescent-49271055.html
DENTAL CARE, ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-care-adolescent-49271055.htmlRMCT4DMF–DENTAL CARE, ADOLESCENT
 Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-96296093.html
Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-96296093.htmlRFFGJJJ5–Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of
 SEM - Staphylococcus aureus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sem-staphylococcus-aureus-image4970064.html
SEM - Staphylococcus aureus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sem-staphylococcus-aureus-image4970064.htmlRMAMCP51–SEM - Staphylococcus aureus
 DENTAL CARE, ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-care-adolescent-49271060.html
DENTAL CARE, ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-care-adolescent-49271060.htmlRMCT4DMM–DENTAL CARE, ADOLESCENT
 Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-96296090.html
Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-96296090.htmlRFFGJJJ2–Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of
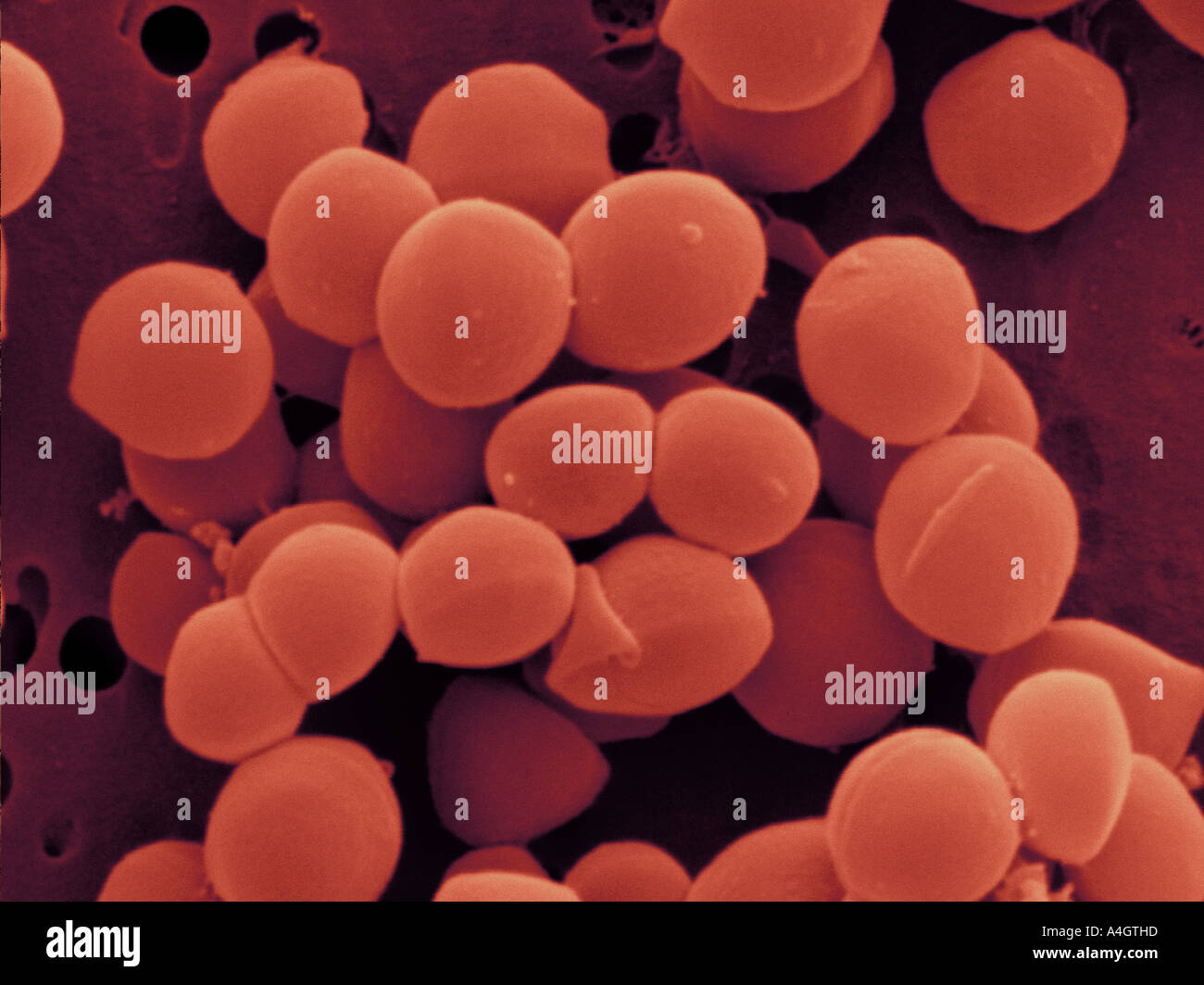 This is a colour enhanced scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-is-a-colour-enhanced-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-staphylococcus-image6312476.html
This is a colour enhanced scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-is-a-colour-enhanced-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-staphylococcus-image6312476.htmlRMA4GTHD–This is a colour enhanced scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus.
 PAINFUL TOOTH IN AN ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-painful-tooth-in-an-adolescent-49271086.html
PAINFUL TOOTH IN AN ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-painful-tooth-in-an-adolescent-49271086.htmlRMCT4DNJ–PAINFUL TOOTH IN AN ADOLESCENT
 Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-96296094.html
Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-96296094.htmlRFFGJJJ6–Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of
 This is a colour enhanced scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-is-a-colour-enhanced-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-staphylococcus-image6312478.html
This is a colour enhanced scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/this-is-a-colour-enhanced-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-staphylococcus-image6312478.htmlRMA4GTHF–This is a colour enhanced scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus.
 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image636416221.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image636416221.htmlRF2YYB7AN–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across
 PAINFUL TOOTH IN AN ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-painful-tooth-in-an-adolescent-49271082.html
PAINFUL TOOTH IN AN ADOLESCENT Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-painful-tooth-in-an-adolescent-49271082.htmlRMCT4DNE–PAINFUL TOOTH IN AN ADOLESCENT
 PAINFUL TOOTH IN A WOMAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-painful-tooth-in-a-woman-49264522.html
PAINFUL TOOTH IN A WOMAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-painful-tooth-in-a-woman-49264522.htmlRMCT45B6–PAINFUL TOOTH IN A WOMAN
 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image636416244.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image636416244.htmlRF2YYB7BG–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across
 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image636416225.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image636416225.htmlRF2YYB7AW–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across
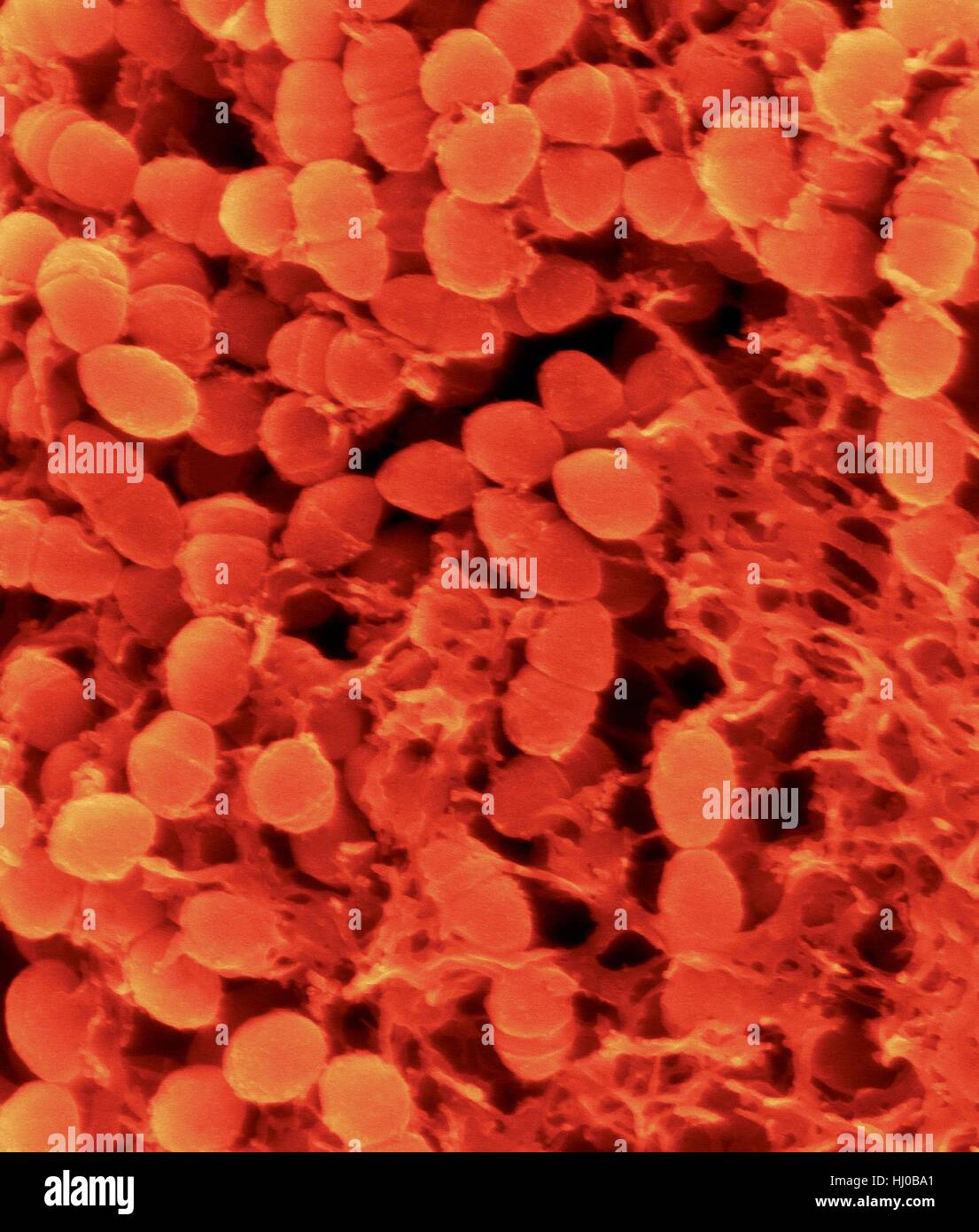 Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545289.html
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545289.htmlRFHJ0BA1–Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is
 Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545288.html
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545288.htmlRFHJ0BA0–Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is
 Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545290.html
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545290.htmlRFHJ0BA2–Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is
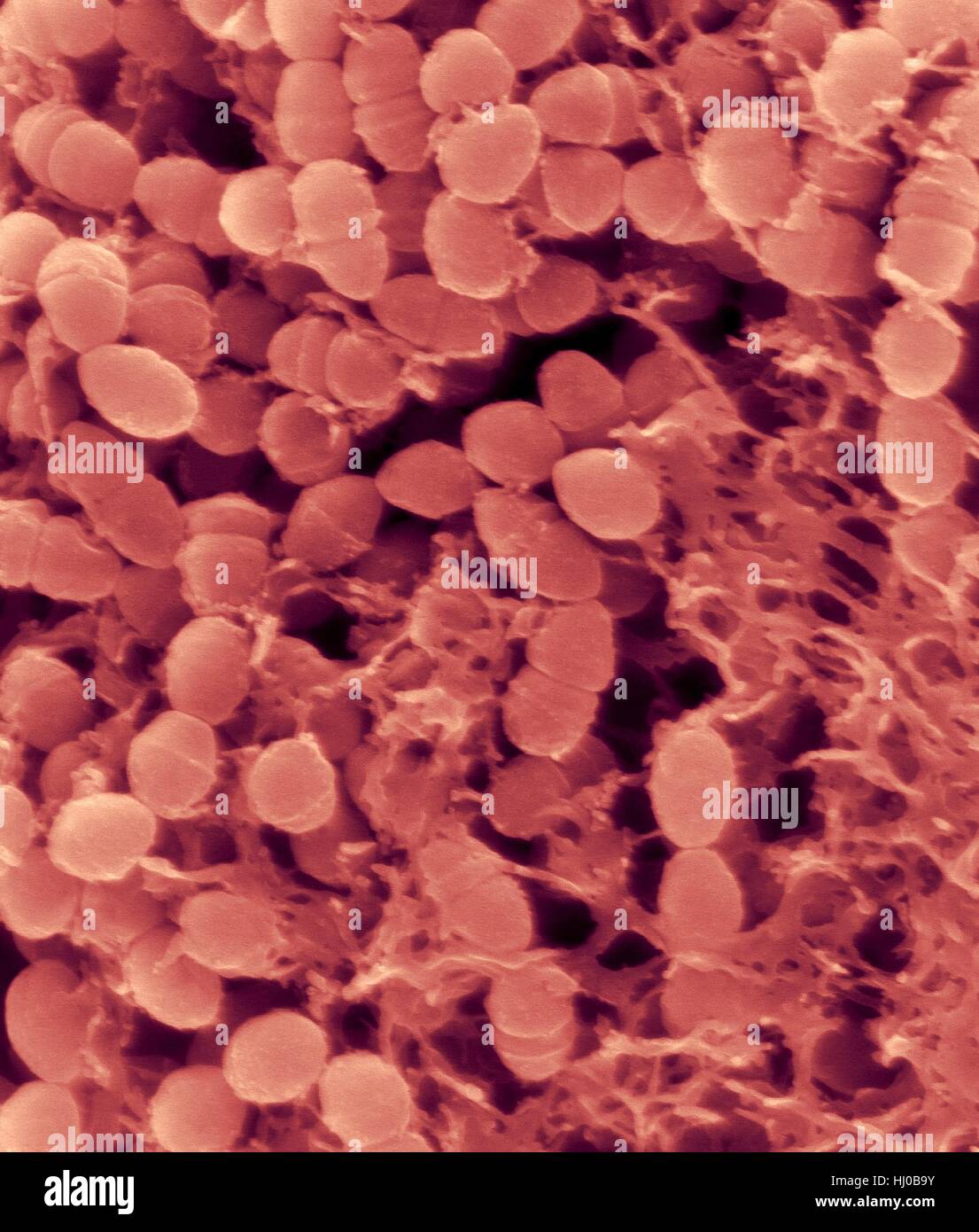 Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545287.html
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-oral-bacteriumstreptococcus-131545287.htmlRFHJ0B9Y–Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Oral bacterium,Streptococcus mutans surrounding dextran polysaccharide mucilage (glucan).S.mutans is coccoid shaped,Gram-positive,facultative anaerobic bacterium that is part of normal bacteria flora of mouth.It metabolizes sucrose to lactic acid is
 Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of bacteria can form a visible layer on the surface of the tongue. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Magnification: x10000 at 10cm wide.Tongue bacteria Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-on-the-surface-of-a-human-tongue-large-numbers-of-bacteria-can-form-a-visible-layer-on-the-surface-of-the-tongue-the-mouth-contains-a-large-number-of-bacteria-most-of-which-are-harmless-or-even-beneficial-however-some-bacteria-can-cause-throat-infections-or-cause-the-formation-of-plaque-deposits-on-the-teeth-which-may-lead-to-decay-magnification-x10000-at-10cm-widetongue-bacteria-image222646234.html
Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of bacteria can form a visible layer on the surface of the tongue. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Magnification: x10000 at 10cm wide.Tongue bacteria Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tongue-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacteria-on-the-surface-of-a-human-tongue-large-numbers-of-bacteria-can-form-a-visible-layer-on-the-surface-of-the-tongue-the-mouth-contains-a-large-number-of-bacteria-most-of-which-are-harmless-or-even-beneficial-however-some-bacteria-can-cause-throat-infections-or-cause-the-formation-of-plaque-deposits-on-the-teeth-which-may-lead-to-decay-magnification-x10000-at-10cm-widetongue-bacteria-image222646234.htmlRFPX6BF6–Tongue bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of bacteria on the surface of a human tongue. Large numbers of bacteria can form a visible layer on the surface of the tongue. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Magnification: x10000 at 10cm wide.Tongue bacteria
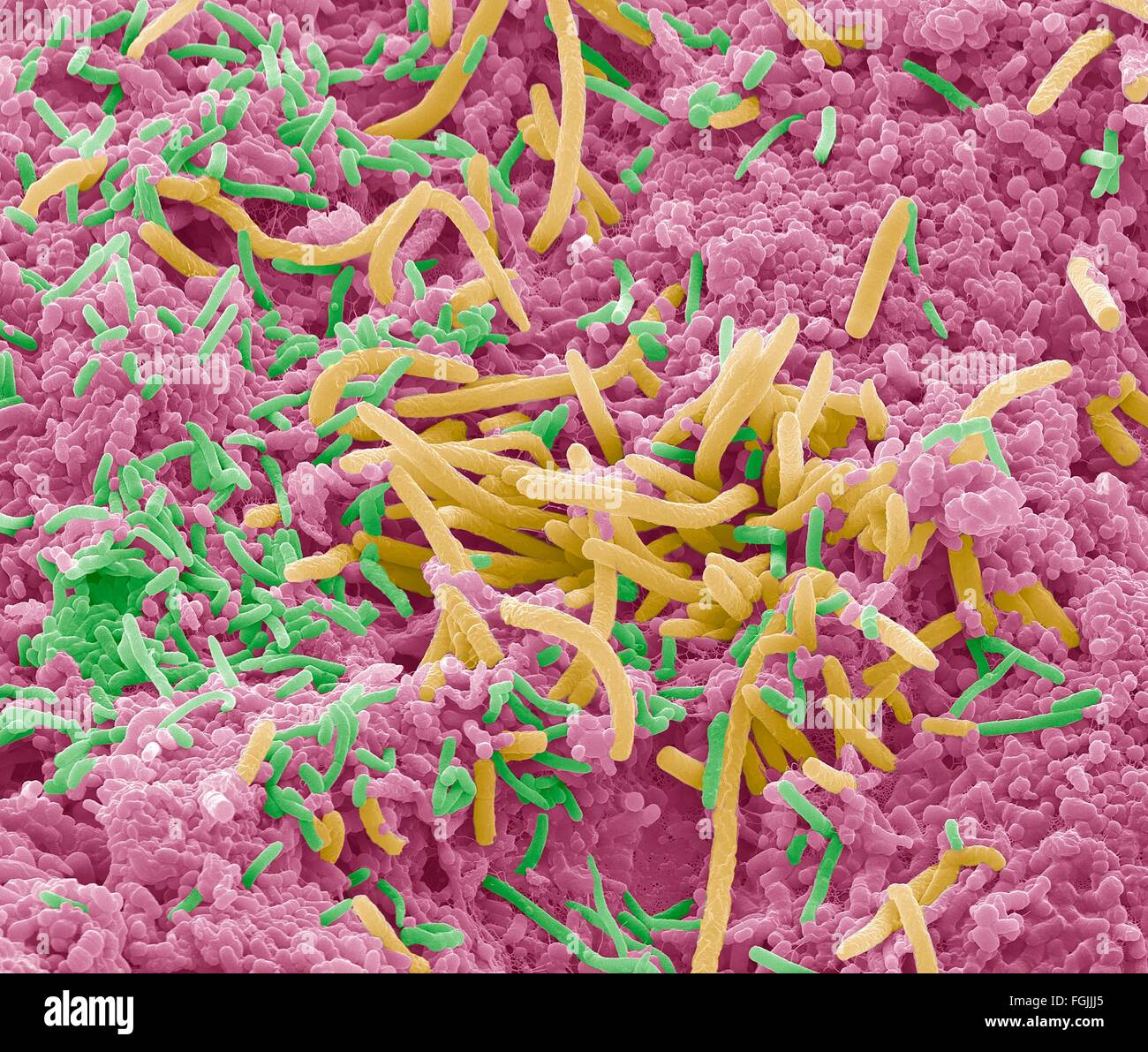
 Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Up to 700 species of oral bacteria exist with the average adult having between 30 and 70 different species of bacteria in their mouth. Magnification: x5000 at 10cm high. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-131545099.html
Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Up to 700 species of oral bacteria exist with the average adult having between 30 and 70 different species of bacteria in their mouth. Magnification: x5000 at 10cm high. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-131545099.htmlRFHJ0B37–Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Up to 700 species of oral bacteria exist with the average adult having between 30 and 70 different species of bacteria in their mouth. Magnification: x5000 at 10cm high.
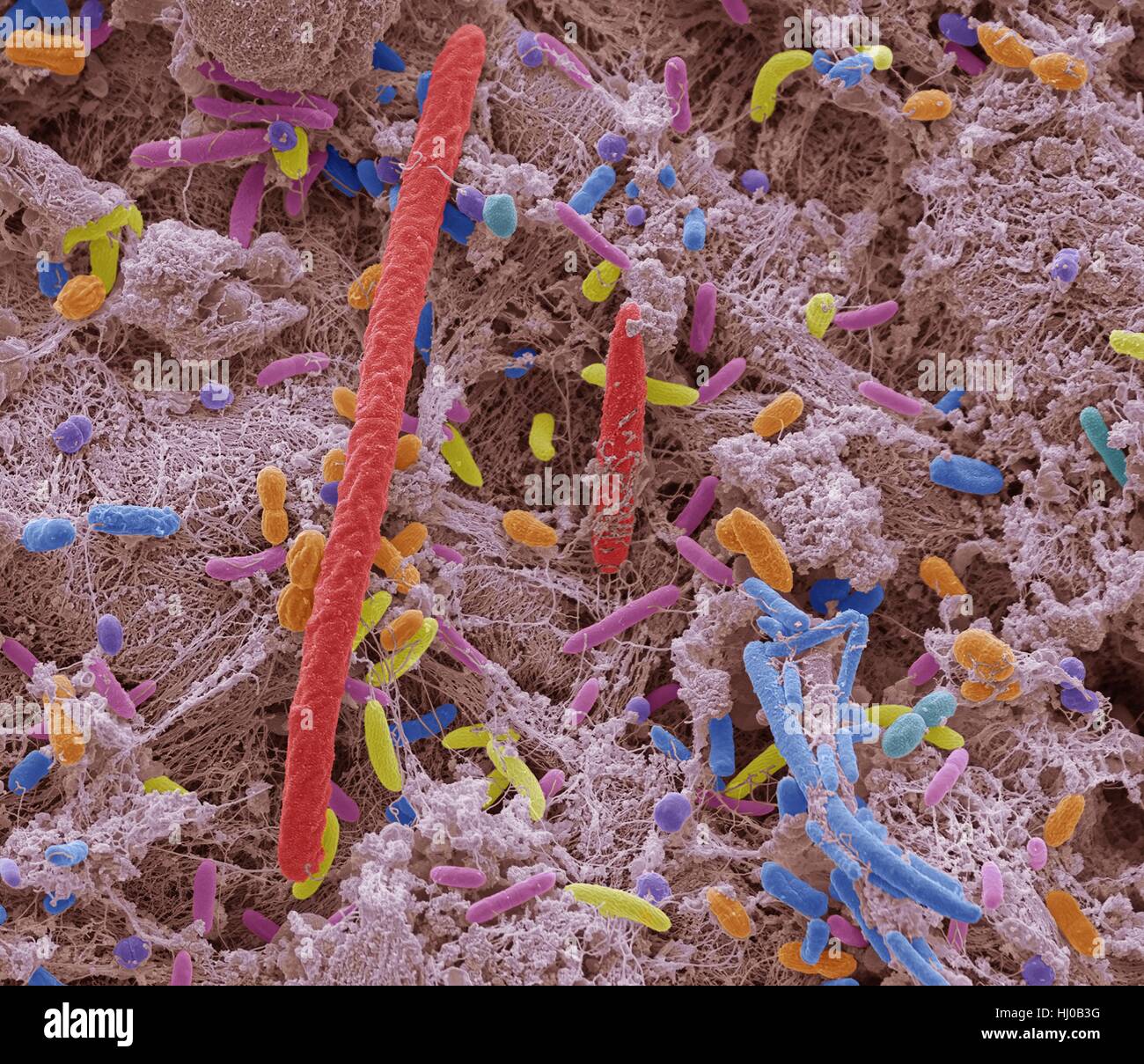 Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Up to 700 species of oral bacteria exist with the average adult having between 30 and 70 different species of bacteria in their mouth. Magnification: x5000 at 10cm high. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-131545108.html
Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Up to 700 species of oral bacteria exist with the average adult having between 30 and 70 different species of bacteria in their mouth. Magnification: x5000 at 10cm high. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-131545108.htmlRFHJ0B3G–Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria. The mouth contains a large number of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. However, some bacteria can cause throat infections or cause the formation of plaque deposits on the teeth, which may lead to decay. Up to 700 species of oral bacteria exist with the average adult having between 30 and 70 different species of bacteria in their mouth. Magnification: x5000 at 10cm high.
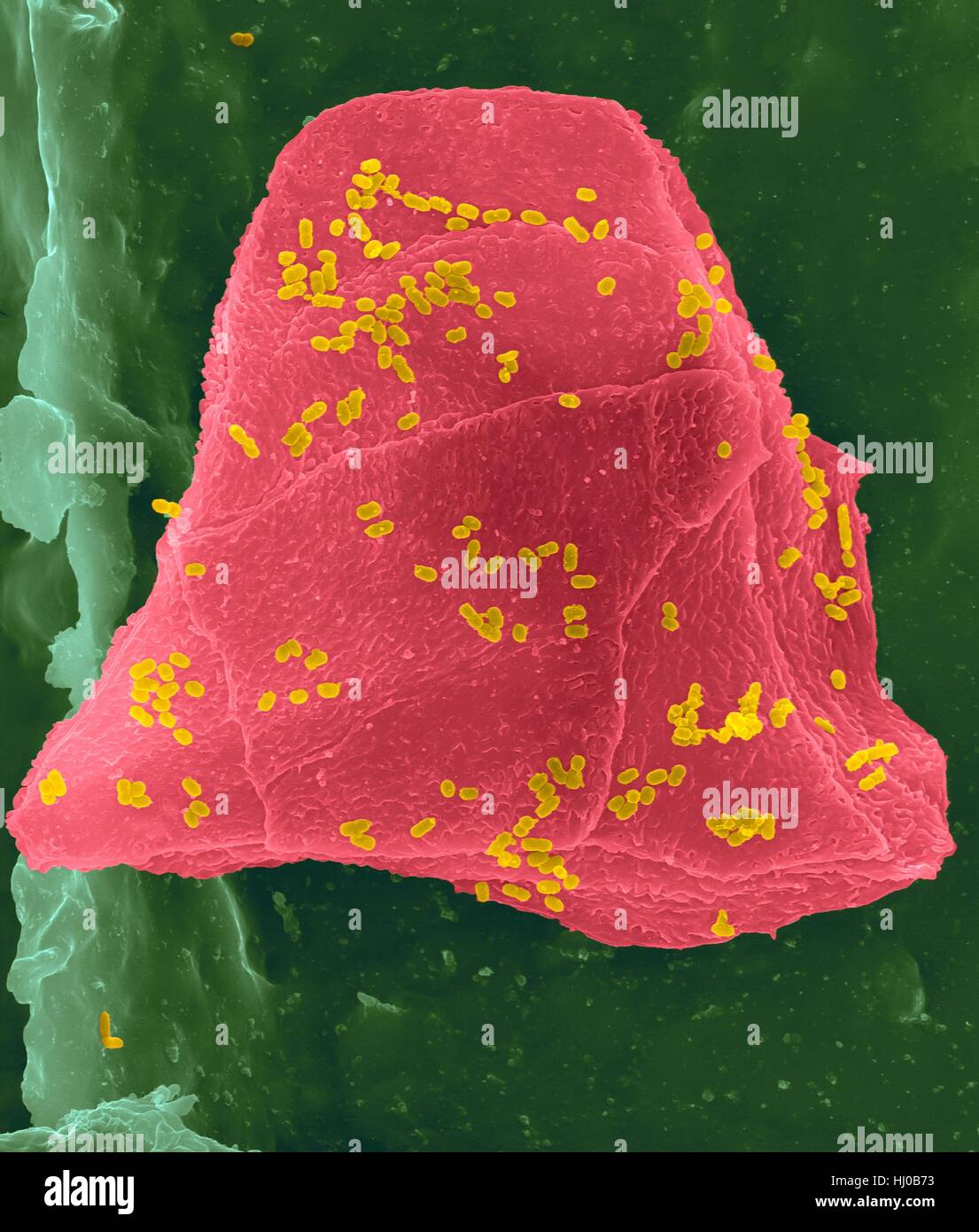 Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (pink) bacteria (yellow) on dental floss fibres (green),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-pink-bacteria-yellow-on-dental-131545207.html
Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (pink) bacteria (yellow) on dental floss fibres (green),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-pink-bacteria-yellow-on-dental-131545207.htmlRFHJ0B73–Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (pink) bacteria (yellow) on dental floss fibres (green),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque
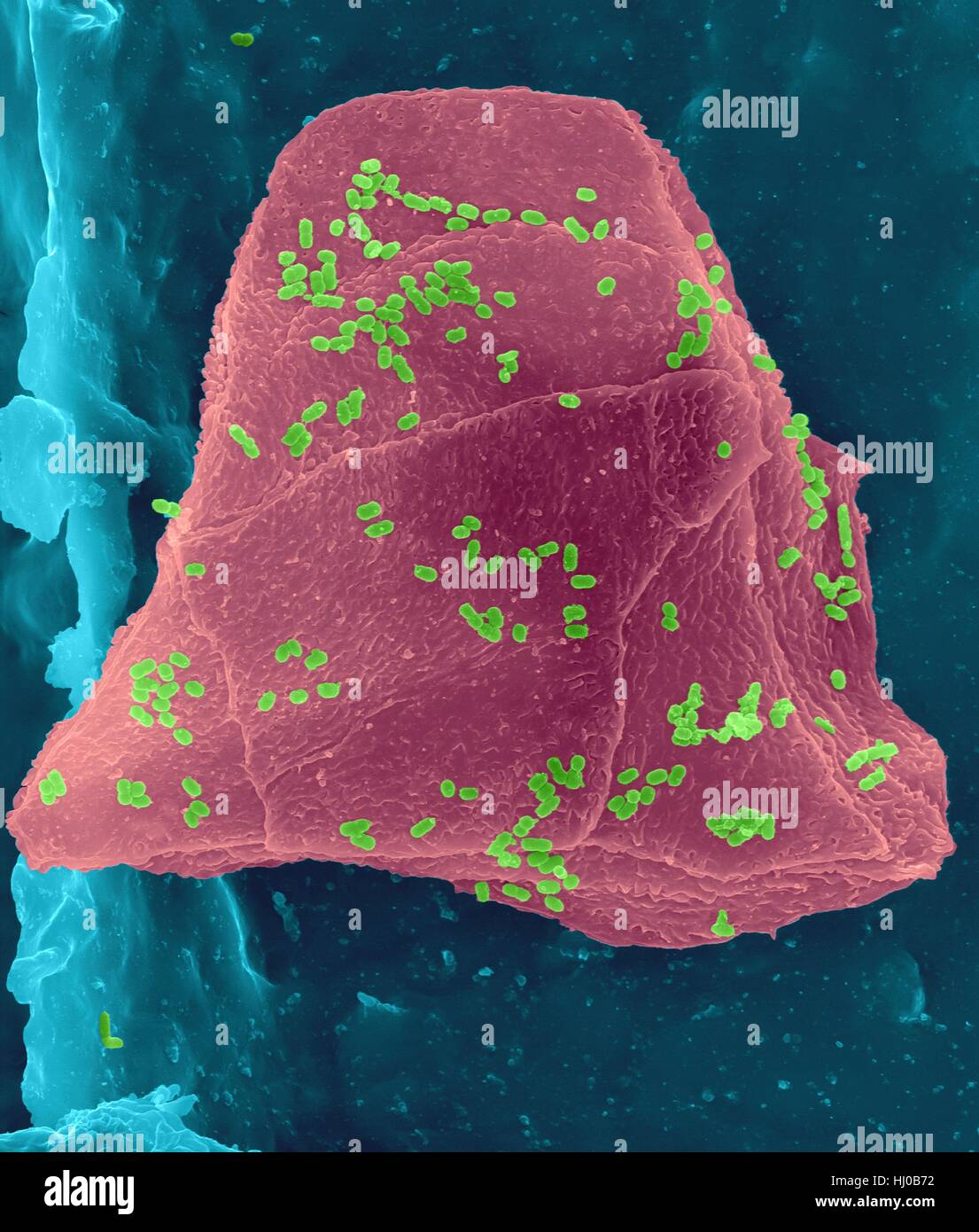
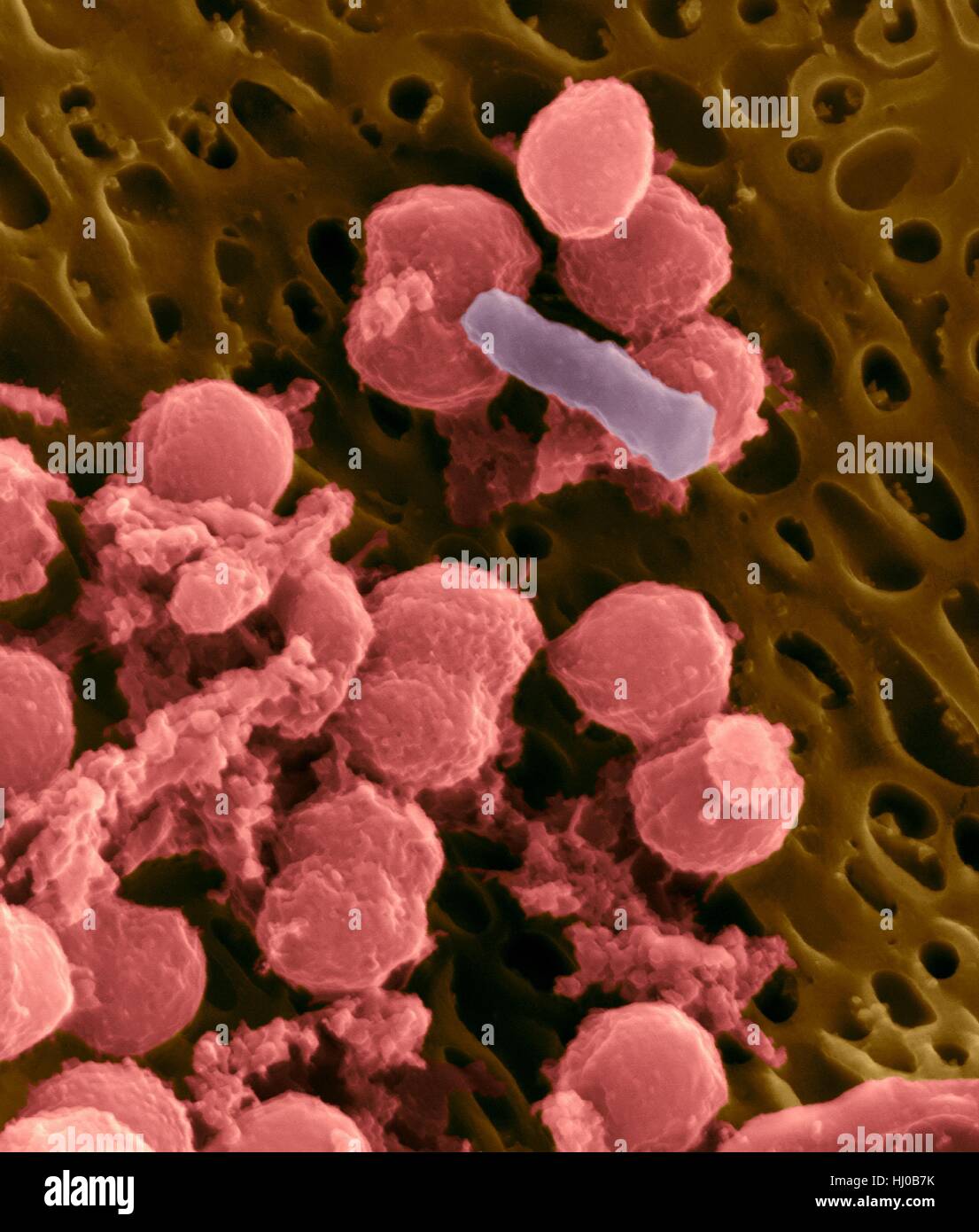 Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545223.html
Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545223.htmlRFHJ0B7K–Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
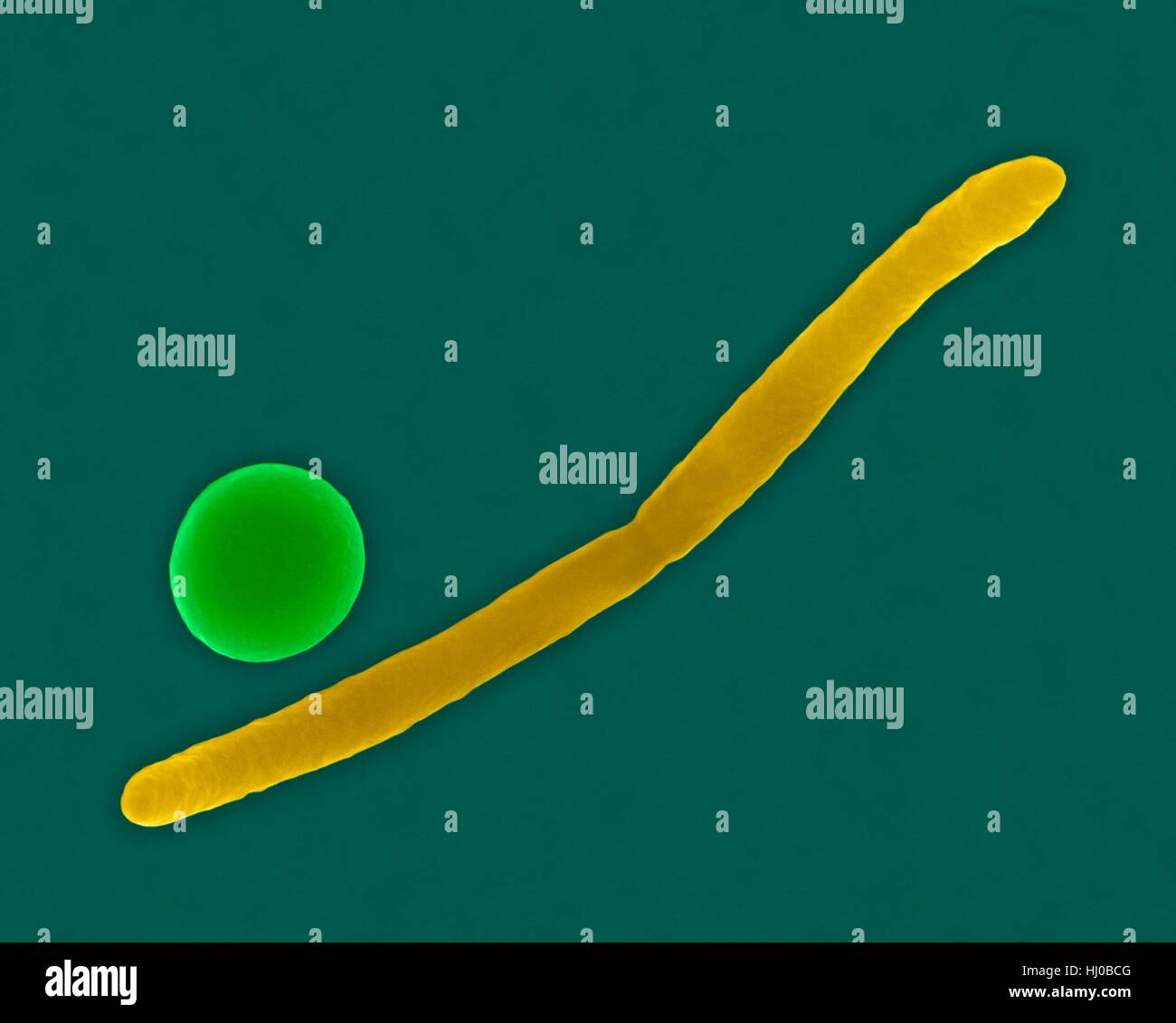 Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Bacillus versus Coccus bacteria morphology. Fusobacterium sp., Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-motile, bacillus prokaryote (characterized by a long, slender shape and pointed ends). Streptococcus sp.- Gram-positive coccus prokaryote. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacillus-versus-coccus-131545360.html
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Bacillus versus Coccus bacteria morphology. Fusobacterium sp., Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-motile, bacillus prokaryote (characterized by a long, slender shape and pointed ends). Streptococcus sp.- Gram-positive coccus prokaryote. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacillus-versus-coccus-131545360.htmlRFHJ0BCG–Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Bacillus versus Coccus bacteria morphology. Fusobacterium sp., Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-motile, bacillus prokaryote (characterized by a long, slender shape and pointed ends). Streptococcus sp.- Gram-positive coccus prokaryote. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
 Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Bacillus versus Coccus bacteria morphology. Fusobacterium sp., Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-motile, bacillus prokaryote (characterized by a long, slender shape and pointed ends). Streptococcus sp.- Gram-positive coccus prokaryote. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacillus-versus-coccus-131545361.html
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Bacillus versus Coccus bacteria morphology. Fusobacterium sp., Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-motile, bacillus prokaryote (characterized by a long, slender shape and pointed ends). Streptococcus sp.- Gram-positive coccus prokaryote. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-of-bacillus-versus-coccus-131545361.htmlRFHJ0BCH–Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Bacillus versus Coccus bacteria morphology. Fusobacterium sp., Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-motile, bacillus prokaryote (characterized by a long, slender shape and pointed ends). Streptococcus sp.- Gram-positive coccus prokaryote. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
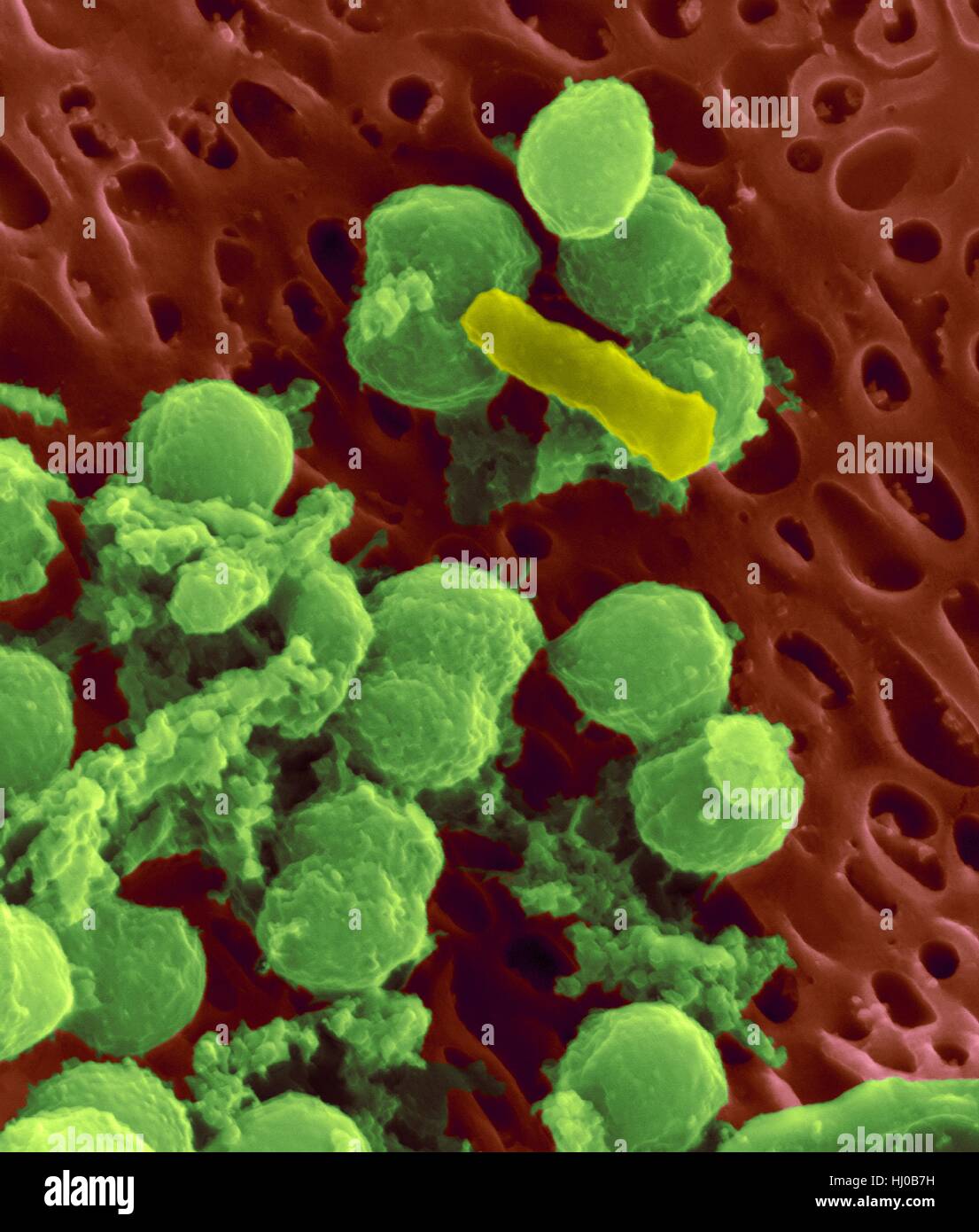 Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545221.html
Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545221.htmlRFHJ0B7H–Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
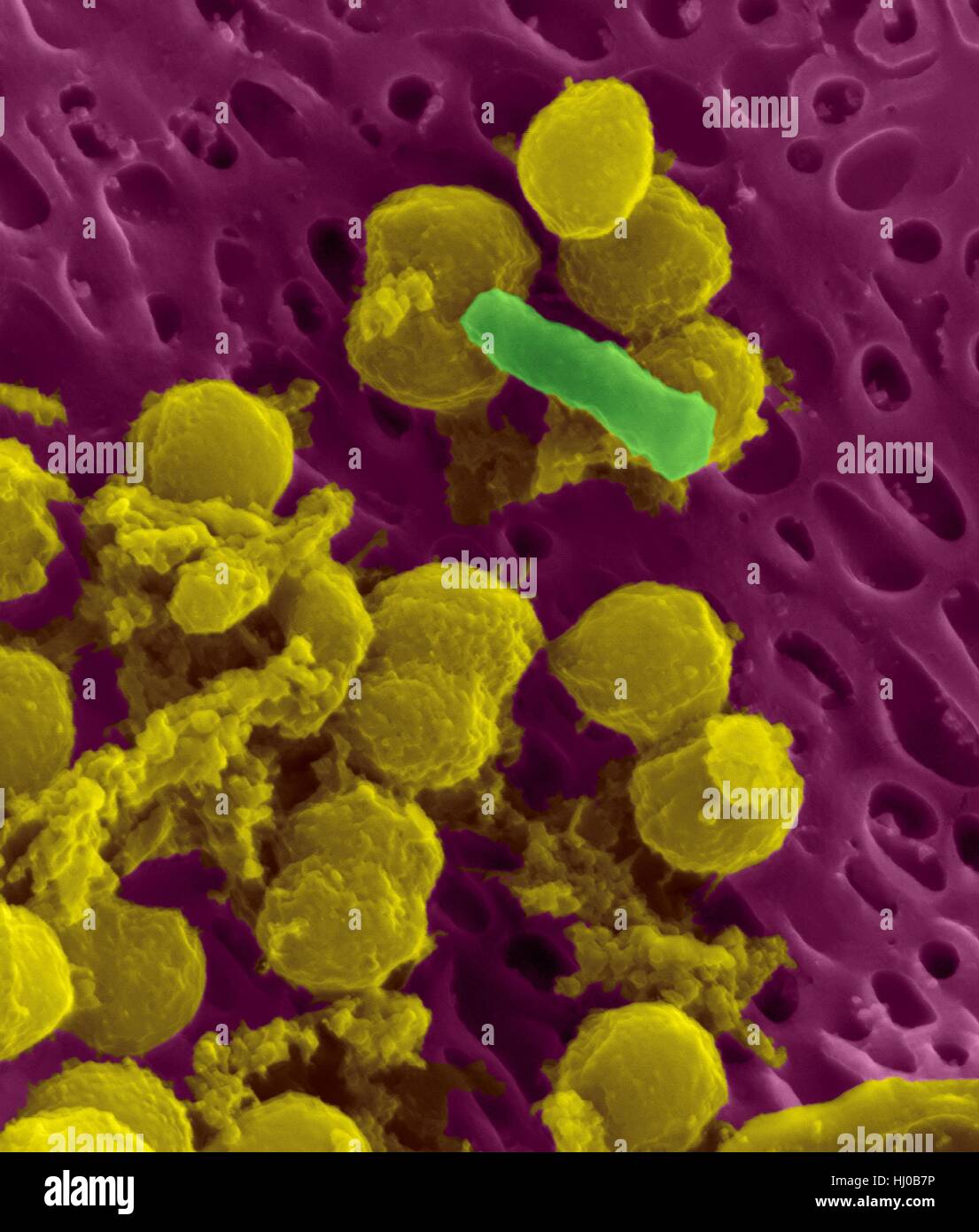 Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545226.html
Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545226.htmlRFHJ0B7P–Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
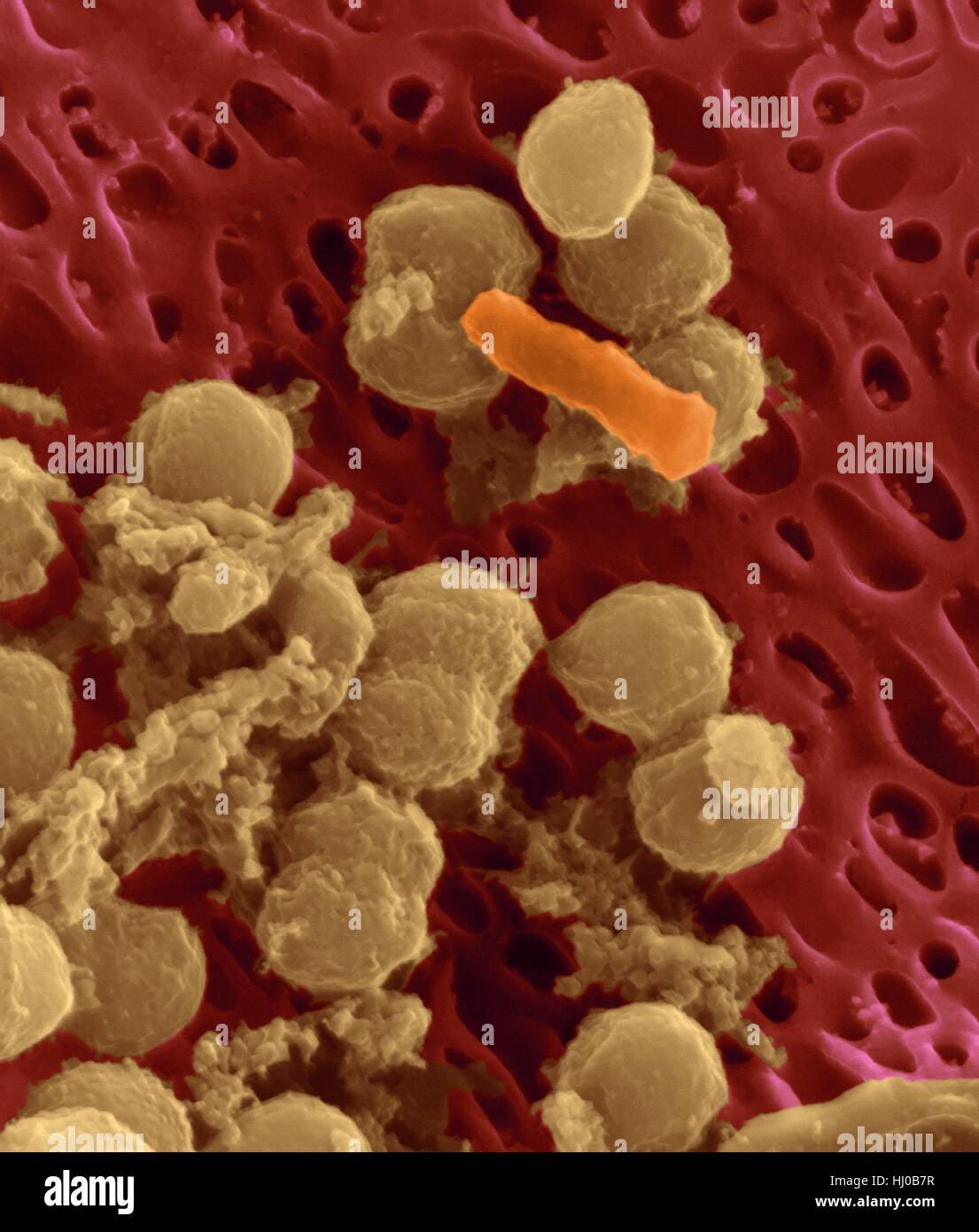 Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545227.html
Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteria-on-an-epithelial-cell-from-the-human-tongue-filiform-papilla-131545227.htmlRFHJ0B7R–Bacteria on an epithelial cell from the human tongue filiform papilla, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Coccoid bacteria (likely Streptococcus mutans due to the fibrous glucan matrix that surrounds the cells) and one rod bacterium are seen on the epithelial surface. Most bacteria on the human tongue are harmless or even beneficial. However some bacteria can cause throat infections and form plaque deposits on teeth. Plaque will also lead to tooth decay and periodontal disease. Magnification: x5, 000 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
 Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electr micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria attached to a buccal cell (pink) from the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electr-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-100016087.html
Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electr micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria attached to a buccal cell (pink) from the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electr-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-100016087.htmlRFFPM3F3–Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electr micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria attached to a buccal cell (pink) from the
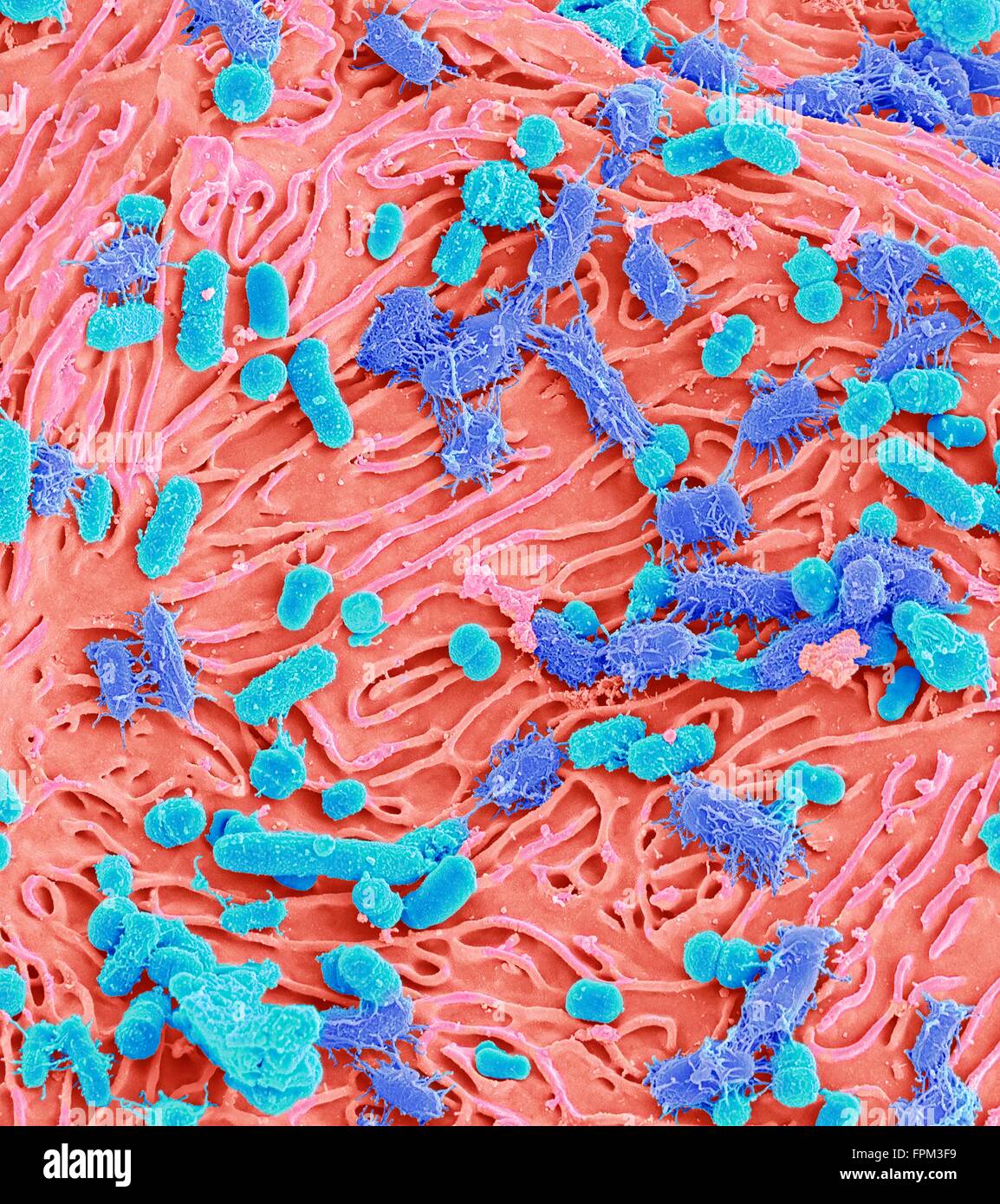 Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electr micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria attached to a buccal cell (pink) from the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electr-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-100016093.html
Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electr micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria attached to a buccal cell (pink) from the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-oral-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electr-micrograph-sem-of-mixed-oral-100016093.htmlRFFPM3F9–Oral bacteria. Coloured scanning electr micrograph (SEM) of mixed oral bacteria attached to a buccal cell (pink) from the
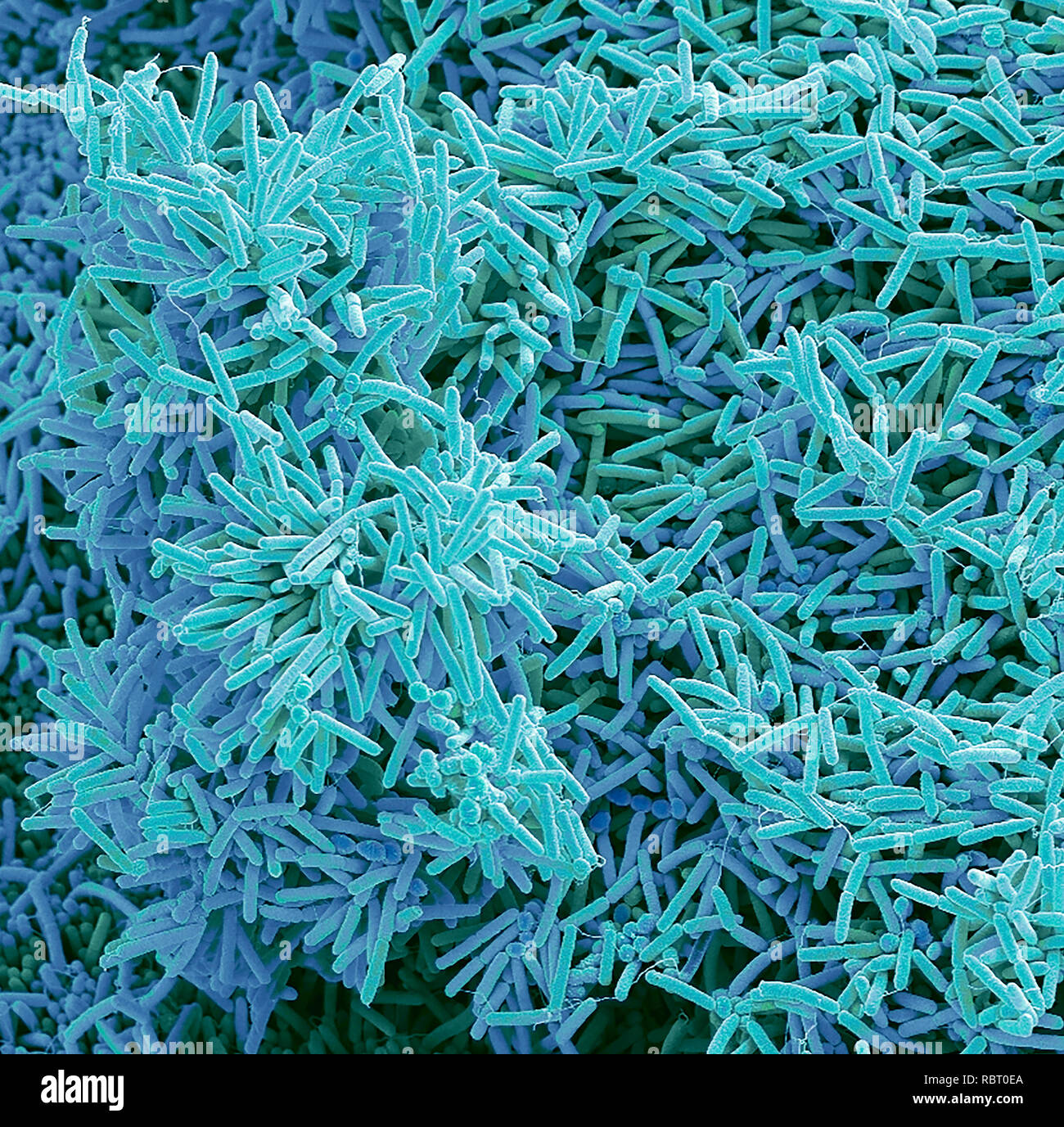 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x3000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x3000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image231023250.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x3000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x3000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image231023250.htmlRFRBT0EA–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x3000 when printed at 10 centimetres across
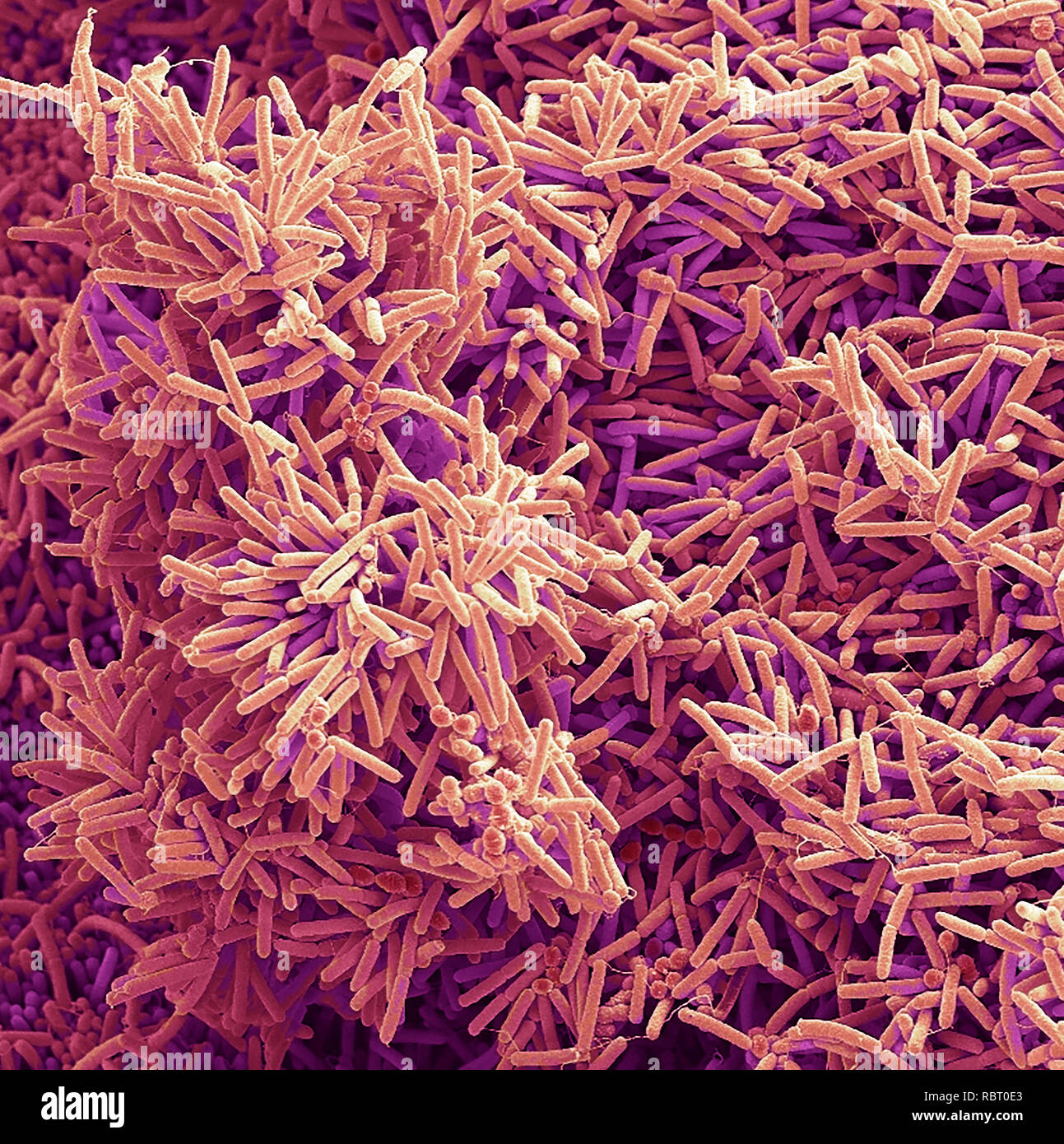 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image231023243.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanning-electron-micrograph-sem-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-embedded-in-a-glycoprotein-matrix-the-matrix-is-formed-from-bacterial-secretions-and-saliva-plaque-is-the-main-cause-of-tooth-decay-the-bacteria-feed-on-sugars-in-food-producing-acid-as-a-waste-product-this-acid-corrodes-the-teeths-enamel-coating-resulting-in-dental-caries-a-build-up-of-dental-plaque-can-also-lead-to-inflamed-and-infected-gums-severe-gum-disease-can-lead-to-teeth-falling-out-magnification-x2000-when-printed-at-10-centimetres-across-image231023243.htmlRFRBT0E3–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions and saliva. Plaque is the main cause of tooth decay. The bacteria feed on sugars in food, producing acid as a waste product. This acid corrodes the teeth's enamel coating, resulting in dental caries. A build-up of dental plaque can also lead to inflamed and infected gums. Severe gum disease can lead to teeth falling out. Magnification: x2000 when printed at 10 centimetres across
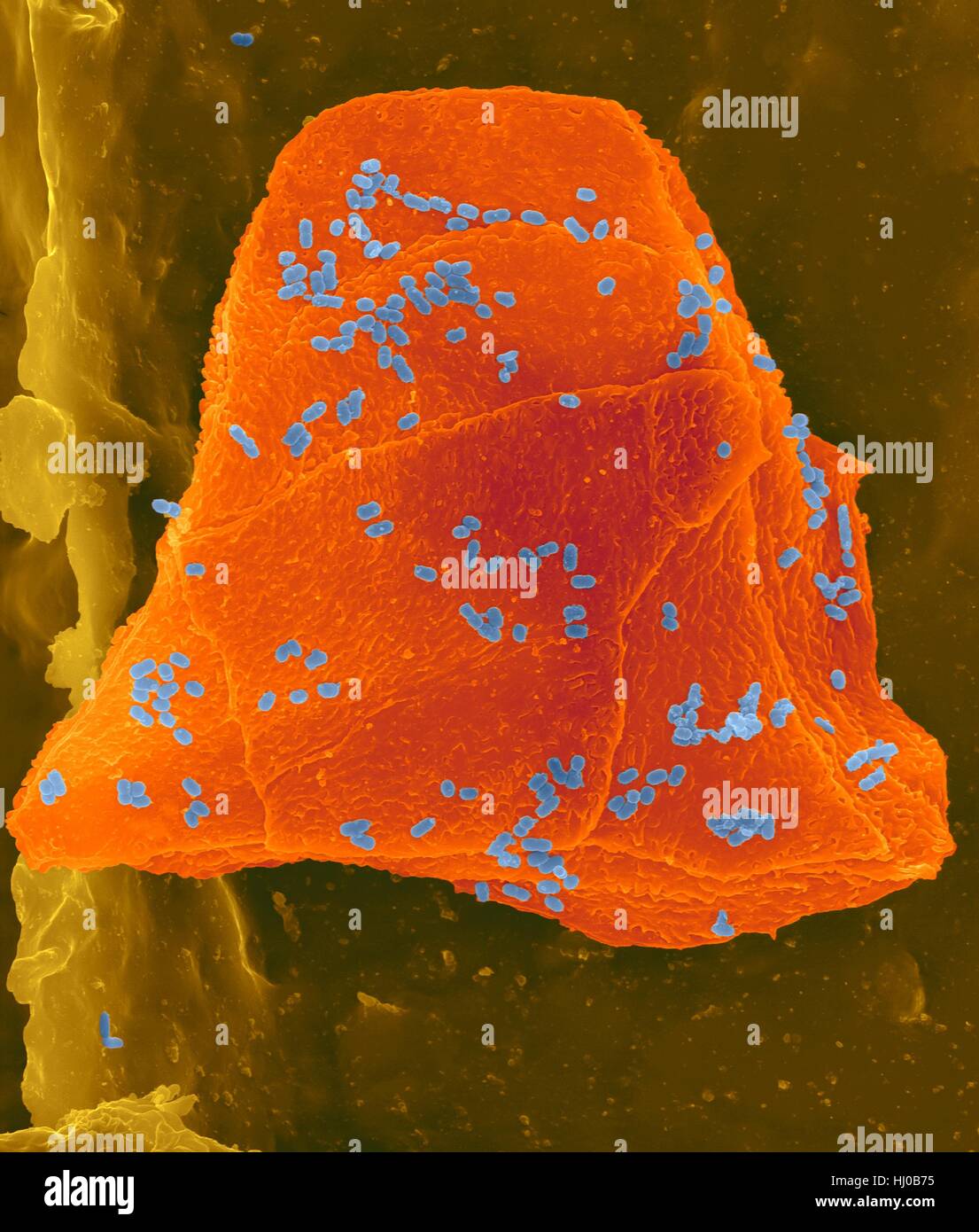 Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (orange) bacteria (blue) on dental floss fibres (brown),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-orange-bacteria-blue-on-dental-131545209.html
Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (orange) bacteria (blue) on dental floss fibres (brown),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-orange-bacteria-blue-on-dental-131545209.htmlRFHJ0B75–Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (orange) bacteria (blue) on dental floss fibres (brown),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque
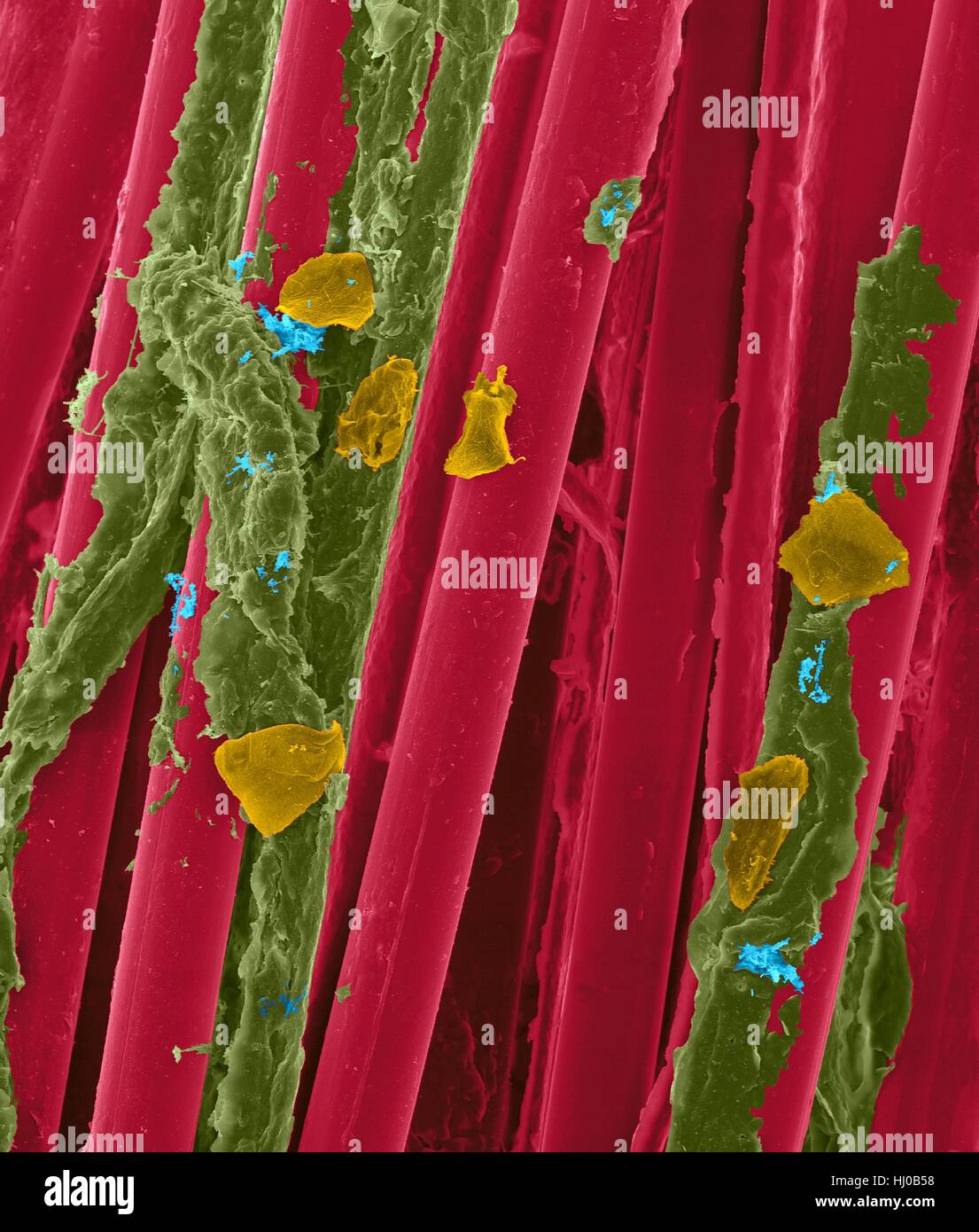
 Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (purple) bacteria (green) on dental floss fibres (blue),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-purple-bacteria-green-on-dental-131545206.html
Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (purple) bacteria (green) on dental floss fibres (blue),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-purple-bacteria-green-on-dental-131545206.htmlRFHJ0B72–Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (purple) bacteria (green) on dental floss fibres (blue),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque
 Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (yellow) bacteria (green) on dental floss fibres (pink),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-yellow-bacteria-green-on-dental-131545208.html
Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (yellow) bacteria (green) on dental floss fibres (pink),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-cheek-cells-yellow-bacteria-green-on-dental-131545208.htmlRFHJ0B74–Used wax dental floss with cheek cells (yellow) bacteria (green) on dental floss fibres (pink),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Cheek cells often get scraped from inside of your mouth when flossing your teeth.Numerous bacteria are present as part of normal mouth flora.Bacterial plaque
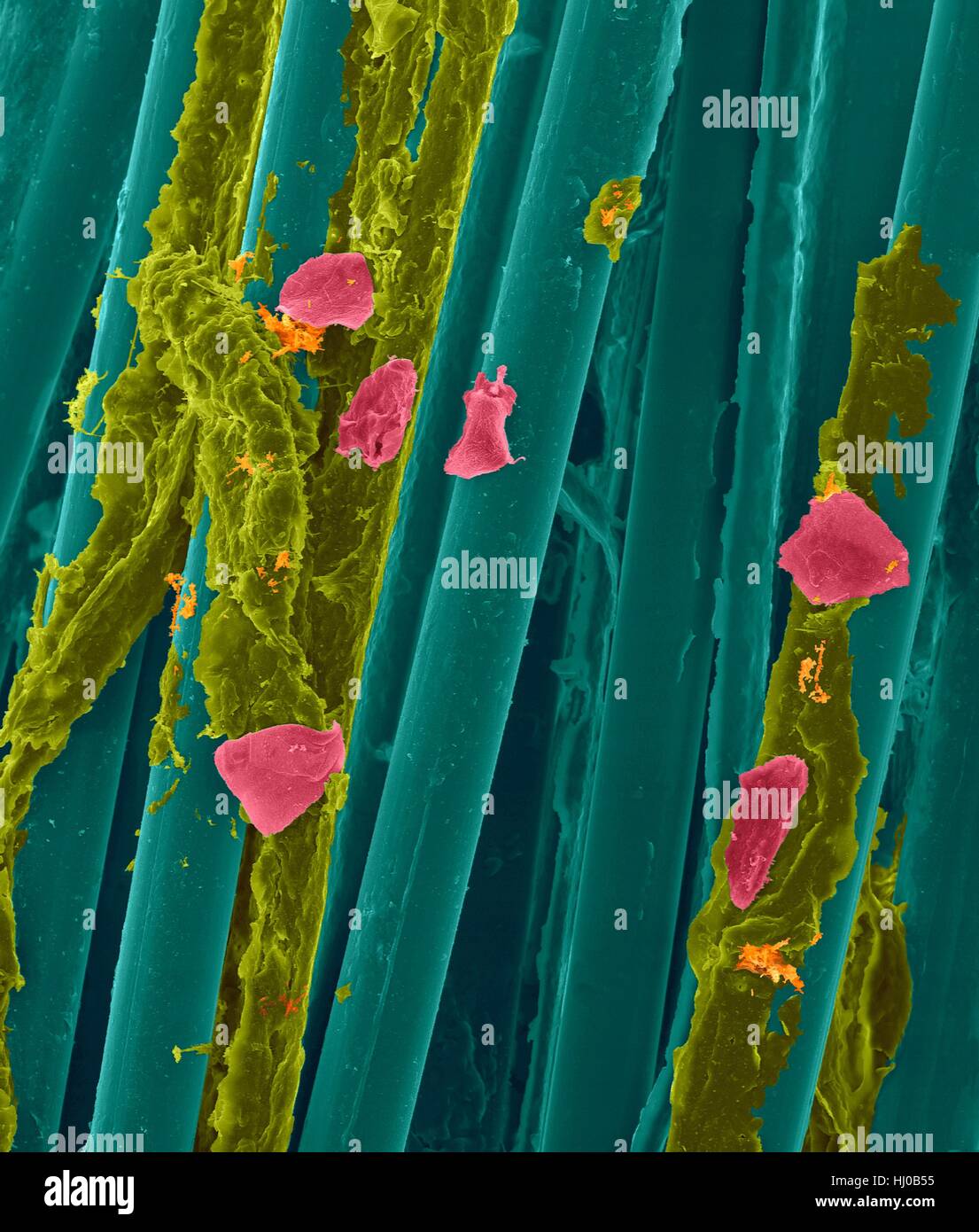
 Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (brown),bacteria (blue) cheek cells (orange) on dental floss fibres (red),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-brownbacteria-blue-cheek-131545156.html
Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (brown),bacteria (blue) cheek cells (orange) on dental floss fibres (red),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-brownbacteria-blue-cheek-131545156.htmlRFHJ0B58–Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (brown),bacteria (blue) cheek cells (orange) on dental floss fibres (red),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The
 Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (yellow),bacteria (orange) cheek cells (pink) on dental floss fibres (blue),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-yellowbacteria-orange-cheek-131545153.html
Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (yellow),bacteria (orange) cheek cells (pink) on dental floss fibres (blue),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-yellowbacteria-orange-cheek-131545153.htmlRFHJ0B55–Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (yellow),bacteria (orange) cheek cells (pink) on dental floss fibres (blue),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The
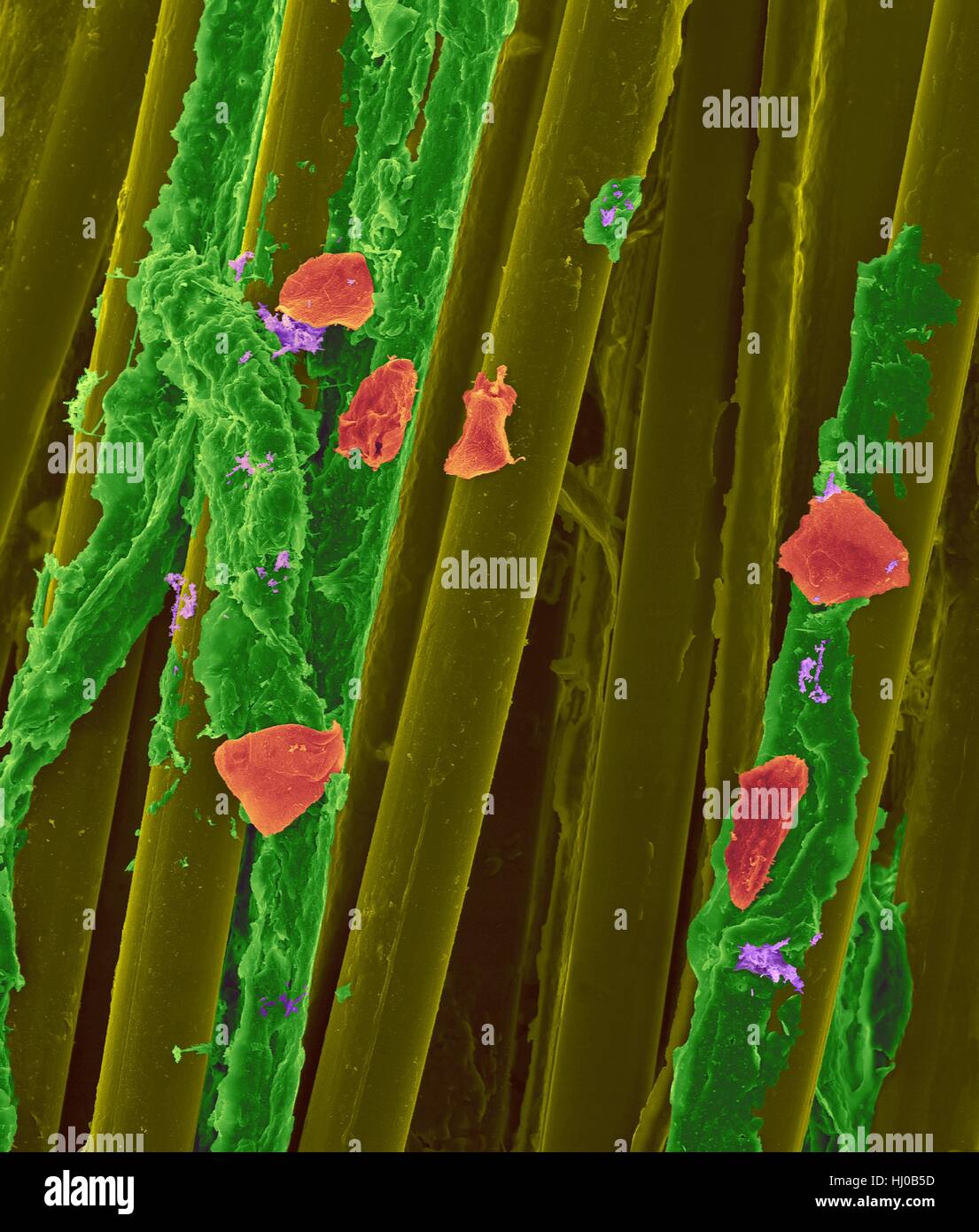 Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (green),bacteria (purple) cheek cells (red) on dental floss fibres (yellow),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-greenbacteria-purple-cheek-131545161.html
Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (green),bacteria (purple) cheek cells (red) on dental floss fibres (yellow),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-greenbacteria-purple-cheek-131545161.htmlRFHJ0B5D–Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (green),bacteria (purple) cheek cells (red) on dental floss fibres (yellow),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The
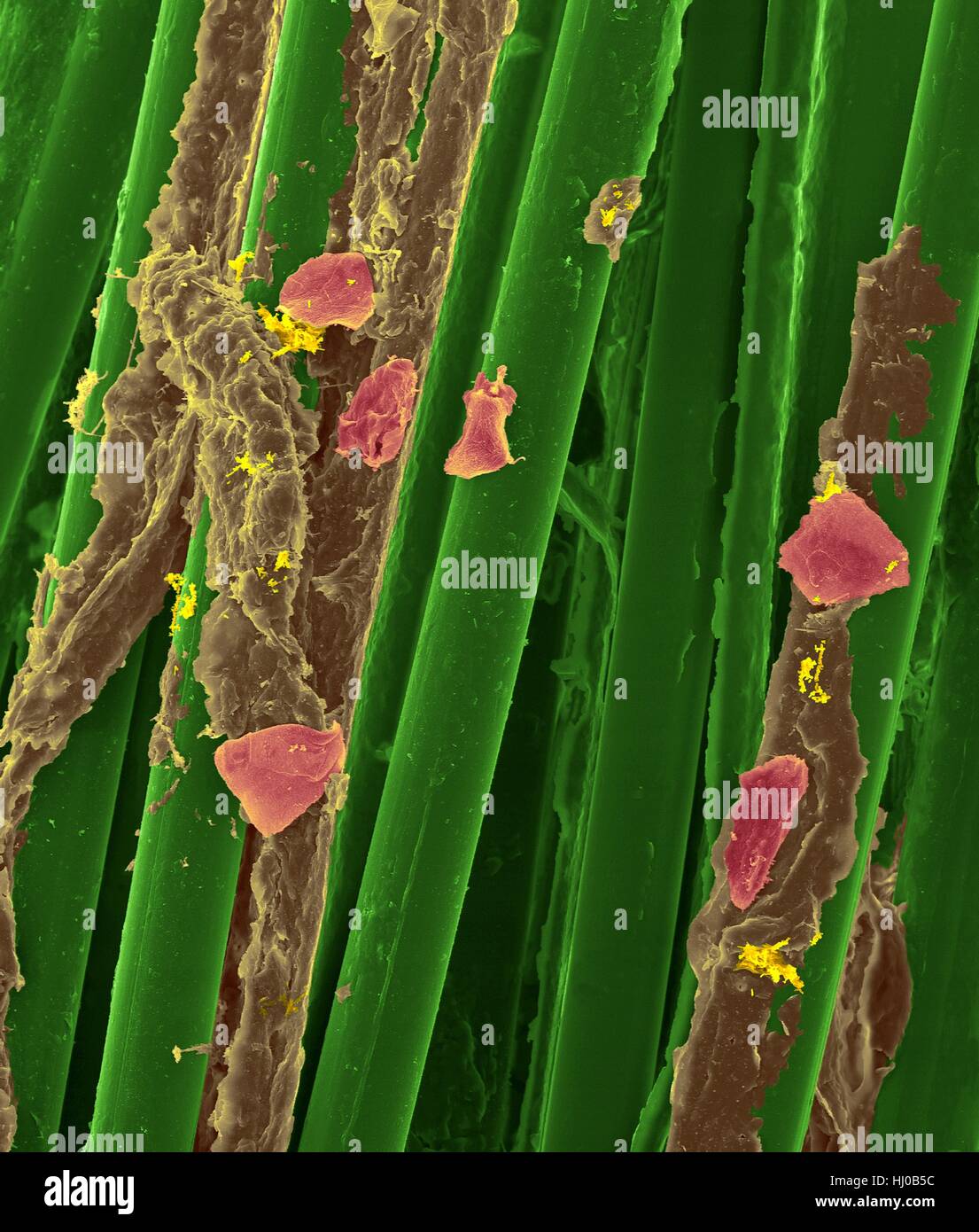 Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (brown),bacteria (yellow) cheek cells (purple) on dental floss fibres (green),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-brownbacteria-yellow-cheek-131545160.html
Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (brown),bacteria (yellow) cheek cells (purple) on dental floss fibres (green),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-used-wax-dental-floss-with-dental-plaque-brownbacteria-yellow-cheek-131545160.htmlRFHJ0B5C–Used wax dental floss with dental plaque (brown),bacteria (yellow) cheek cells (purple) on dental floss fibres (green),coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM).Plaque consists of biofilm of bacteria embedded in glycoprotein matrix.The matrix is formed from bacterial secretions saliva.The
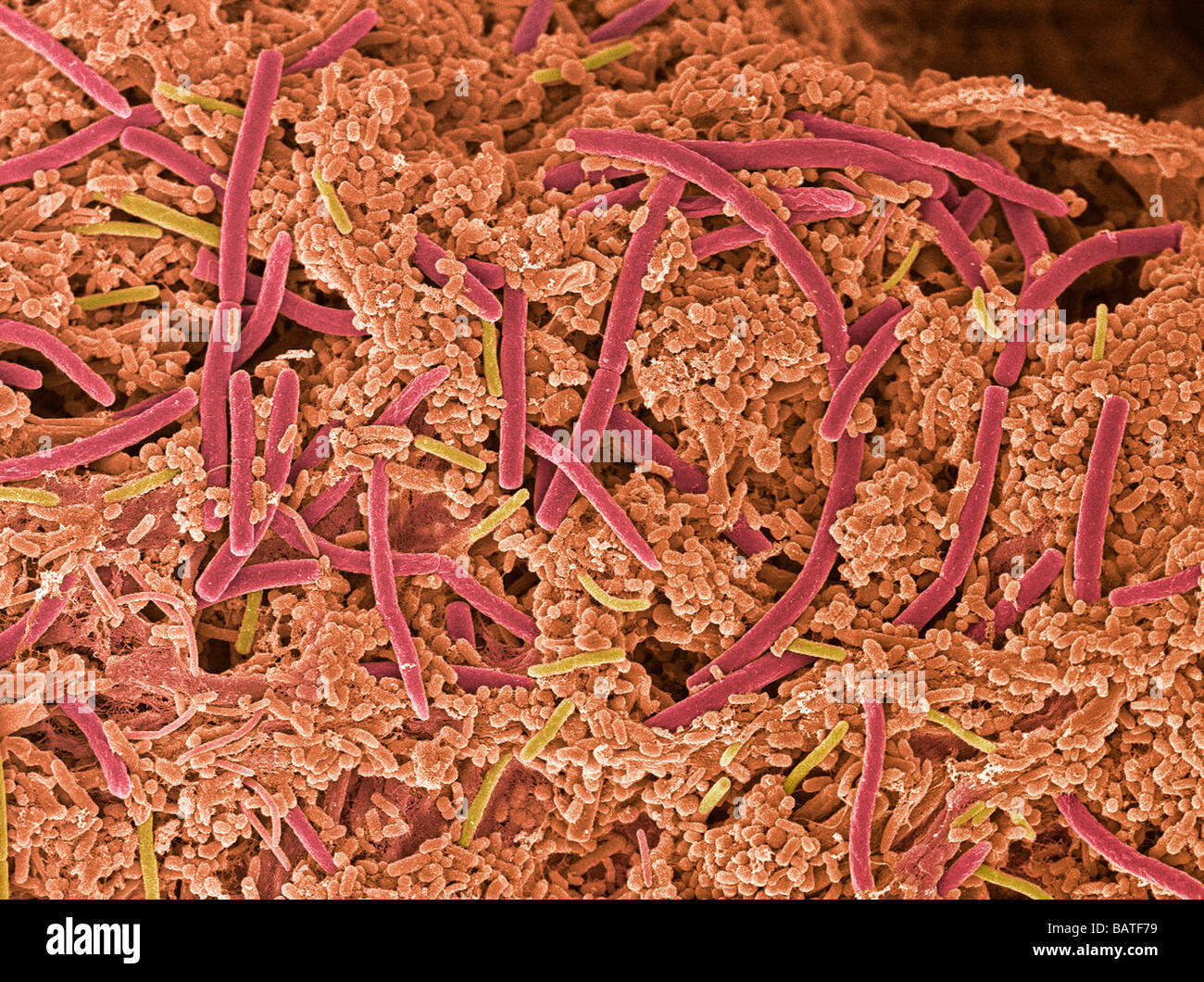 Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-scanning-electronmicrograph-sem-plaque-consists-23895741.html
Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-scanning-electronmicrograph-sem-plaque-consists-23895741.htmlRFBATF79–Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix.
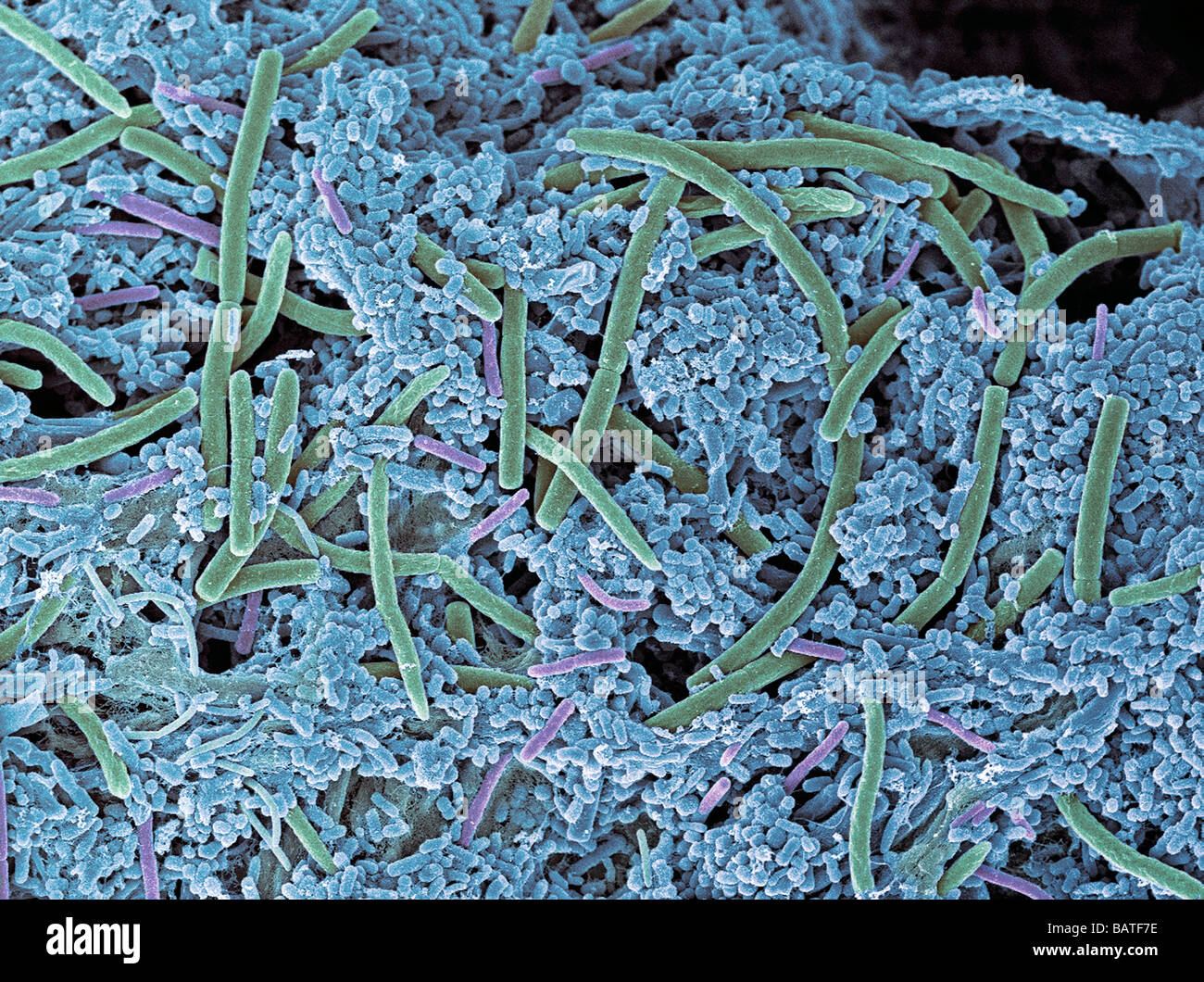 Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-scanning-electronmicrograph-sem-plaque-consists-23895746.html
Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-scanning-electronmicrograph-sem-plaque-consists-23895746.htmlRFBATF7E–Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix.
 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph(SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrographsem-dental-23895160.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph(SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrographsem-dental-23895160.htmlRFBATEEG–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph(SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth.
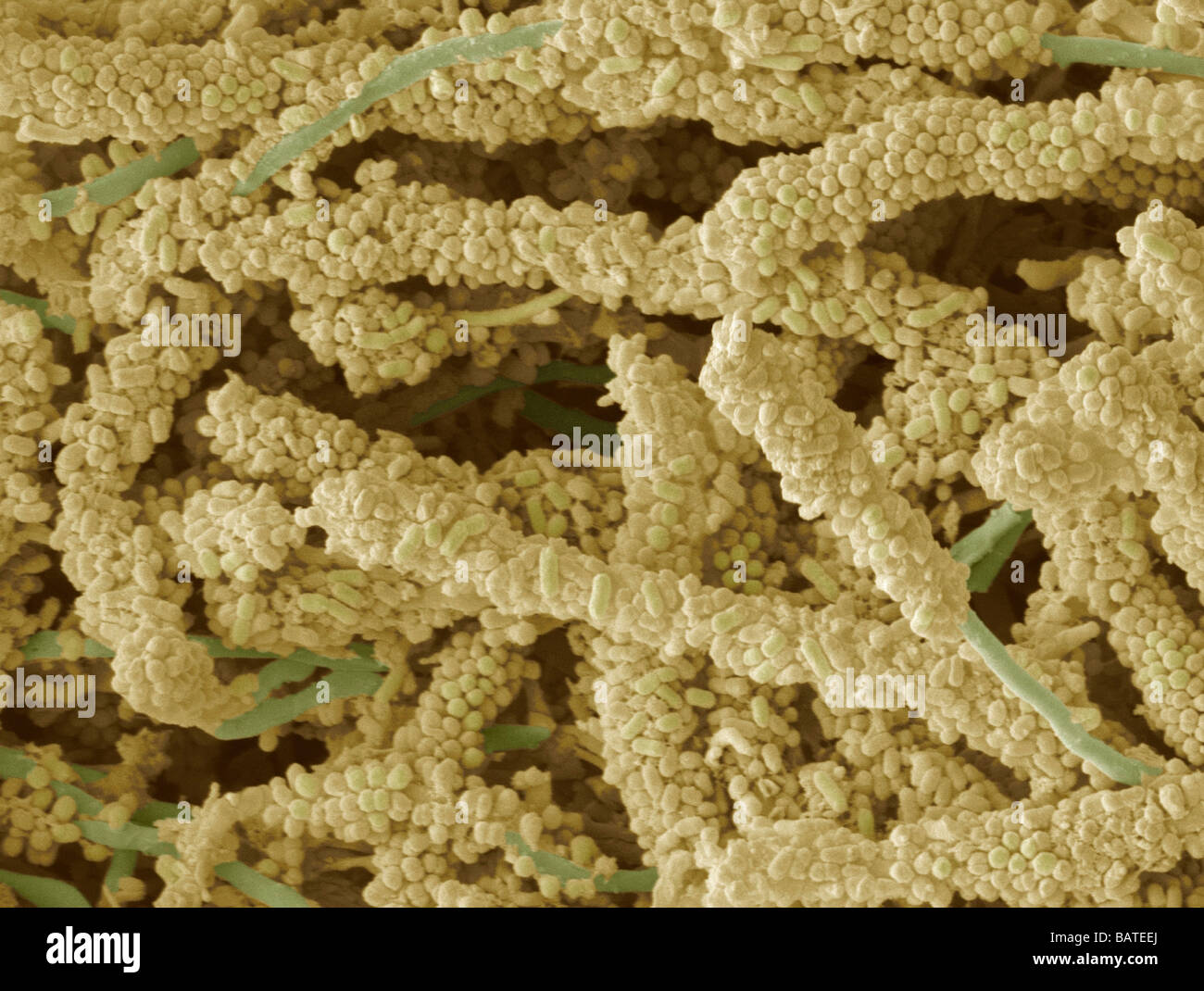 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph(SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrographsem-dental-23895162.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph(SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrographsem-dental-23895162.htmlRFBATEEJ–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph(SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth.
 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph (SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrograph-sem-dental-23895095.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph (SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrograph-sem-dental-23895095.htmlRFBATEC7–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph (SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth.
 Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph (SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrograph-sem-dental-23895097.html
Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph (SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plaque-forming-bacteria-coloured-scanningelectron-micrograph-sem-dental-23895097.htmlRFBATEC9–Plaque-forming bacteria, coloured scanningelectron micrograph (SEM). Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms on teeth.
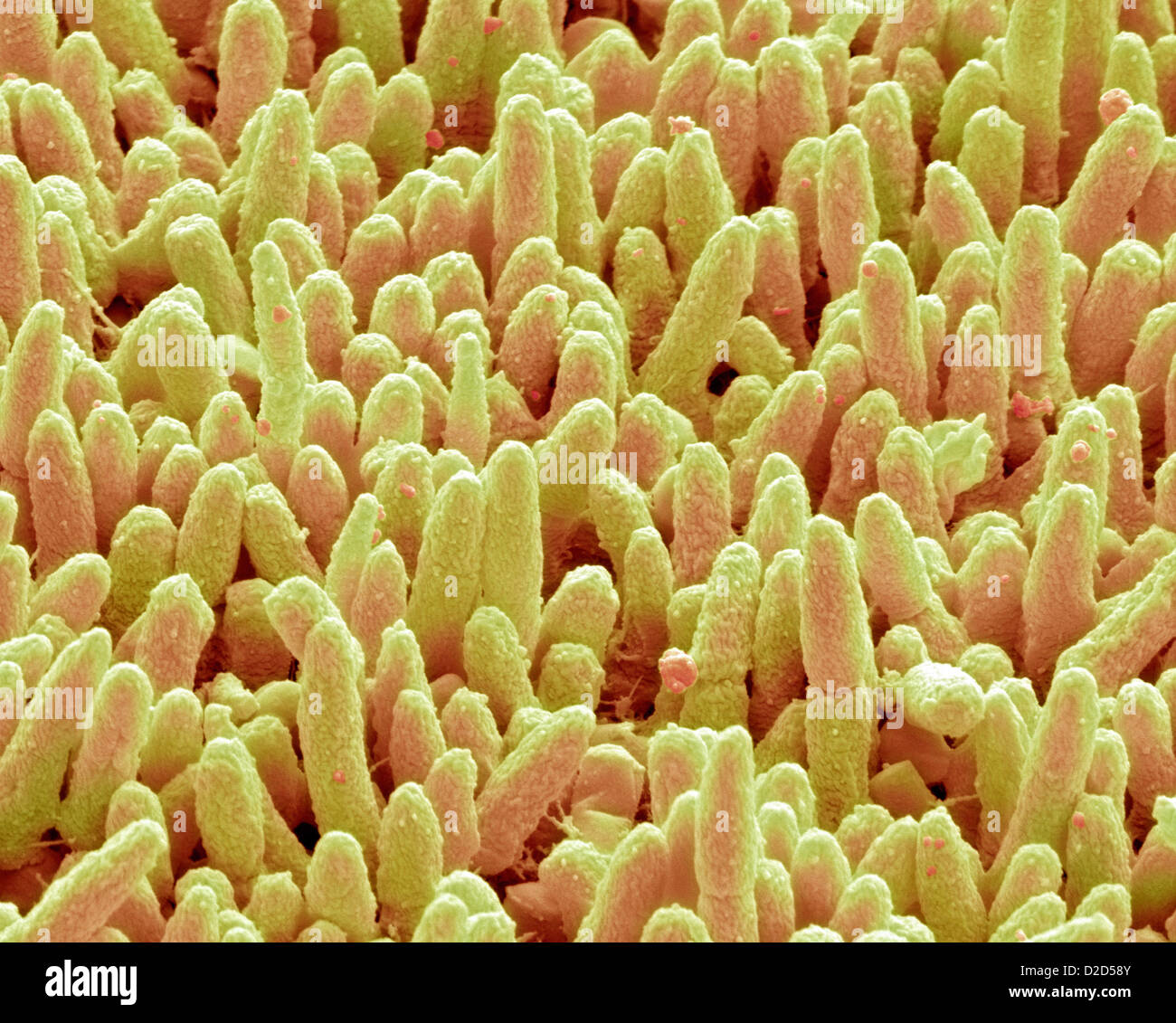 Dental plaque SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-sem-of-dental-plaque-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-53149963.html
Dental plaque SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-sem-of-dental-plaque-plaque-consists-of-a-film-of-bacteria-53149963.htmlRFD2D58Y–Dental plaque SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix
 Dental plaque Coloured SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-sem-of-dental-plaque-plaque-consists-of-a-film-53149968.html
Dental plaque Coloured SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-sem-of-dental-plaque-plaque-consists-of-a-film-53149968.htmlRFD2D594–Dental plaque Coloured SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix
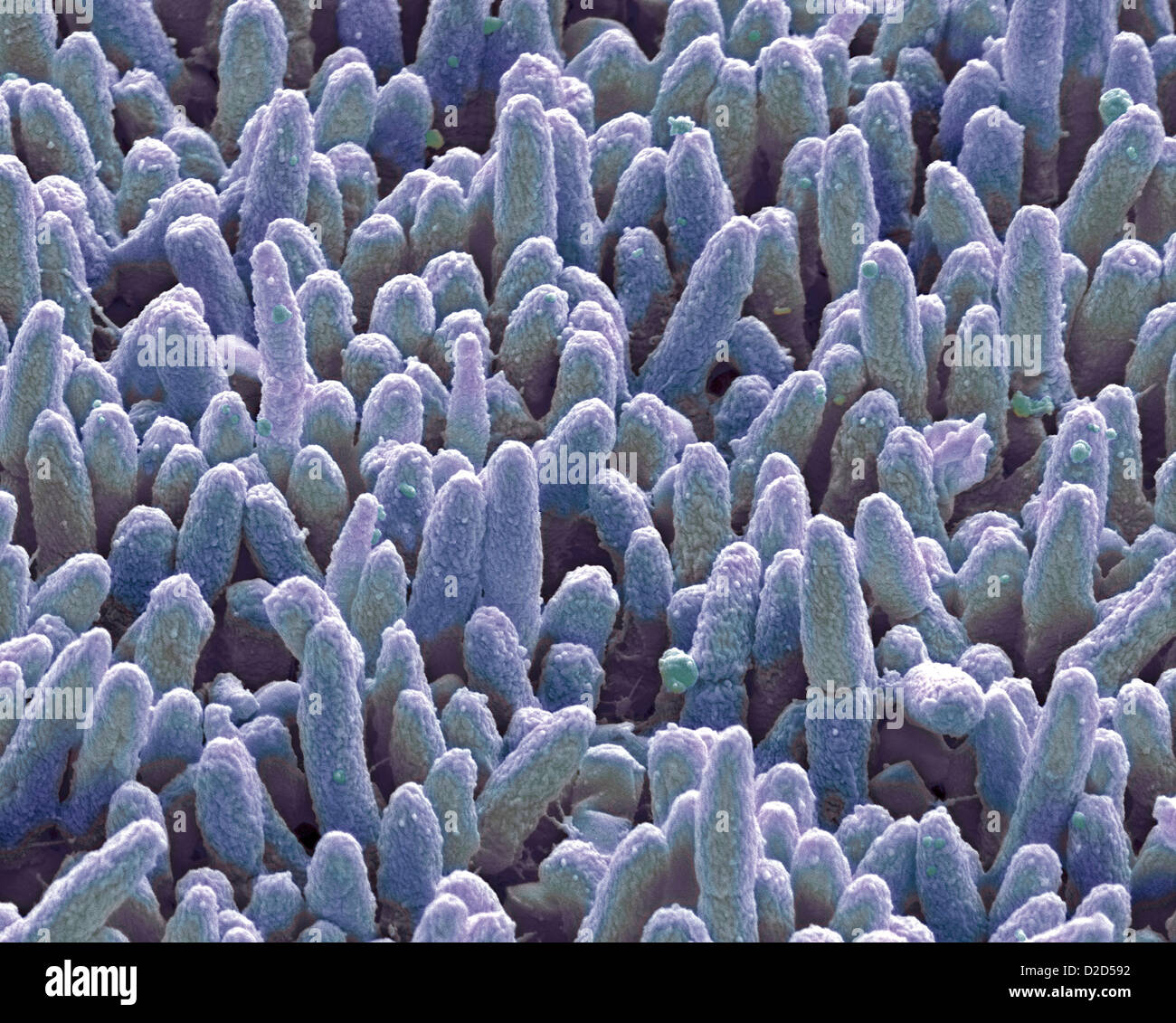 Dental plaque Coloured SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-sem-of-dental-plaque-plaque-consists-of-a-film-53149966.html
Dental plaque Coloured SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-sem-of-dental-plaque-plaque-consists-of-a-film-53149966.htmlRFD2D592–Dental plaque Coloured SEM of dental plaque Plaque consists of a film of bacteria embedded in a glycoprotein matrix
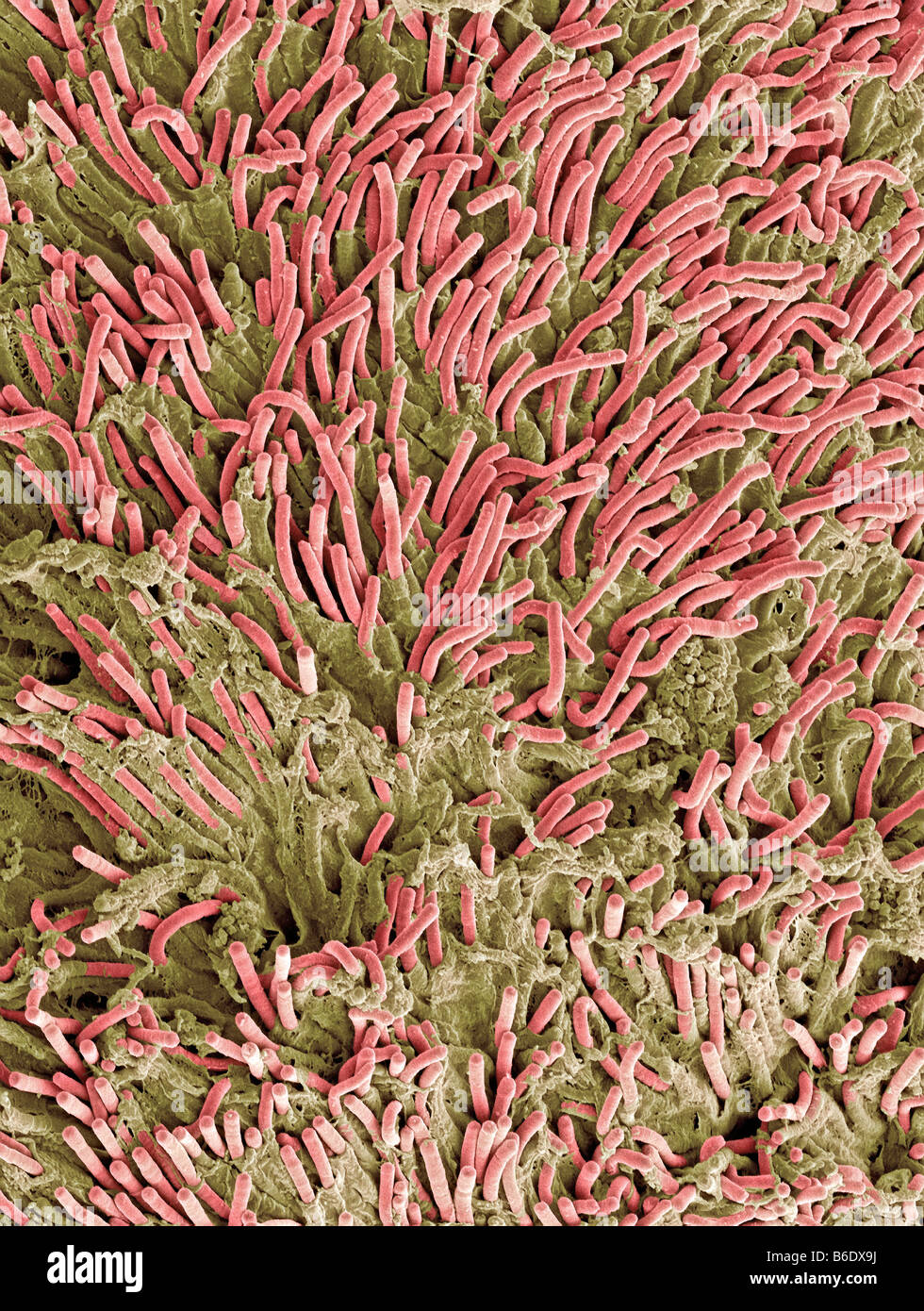 Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film ofbacteria. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-scanning-electronmicrograph-sem-plaque-consists-21204334.html
Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film ofbacteria. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dental-plaque-coloured-scanning-electronmicrograph-sem-plaque-consists-21204334.htmlRFB6DX9J–Dental plaque, coloured scanning electronmicrograph (SEM). Plaque consists of a film ofbacteria.