Quick filters:
Neuromuscular junction Stock Photos and Images
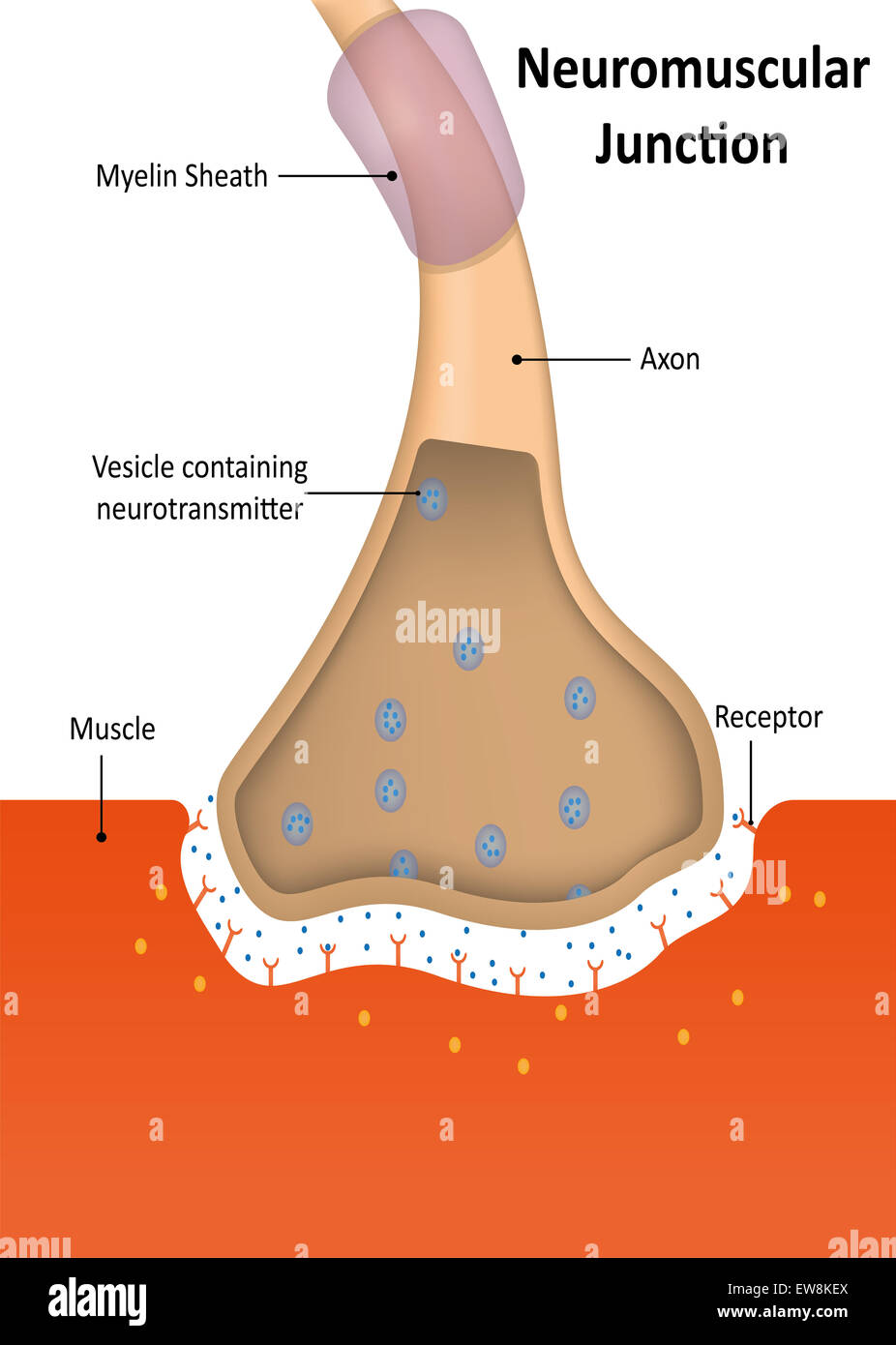 Neuromuscular Junction Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neuromuscular-junction-84398802.html
Neuromuscular Junction Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neuromuscular-junction-84398802.htmlRMEW8KEX–Neuromuscular Junction
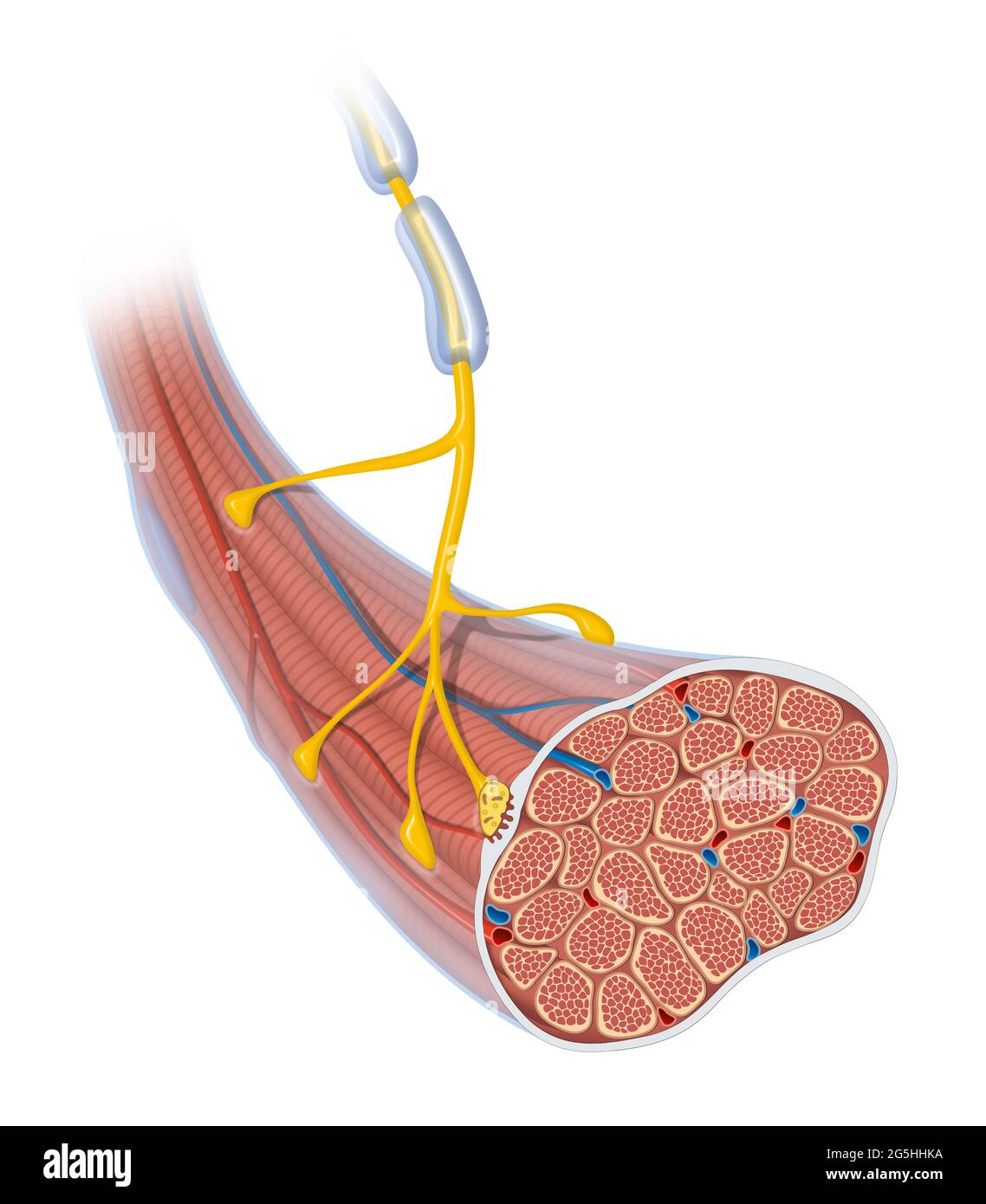 Neuromuscular junction. Skeletal muscle and motor neuron Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-junction-skeletal-muscle-and-motor-neuron-image433719534.html
Neuromuscular junction. Skeletal muscle and motor neuron Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-junction-skeletal-muscle-and-motor-neuron-image433719534.htmlRF2G5HHKA–Neuromuscular junction. Skeletal muscle and motor neuron
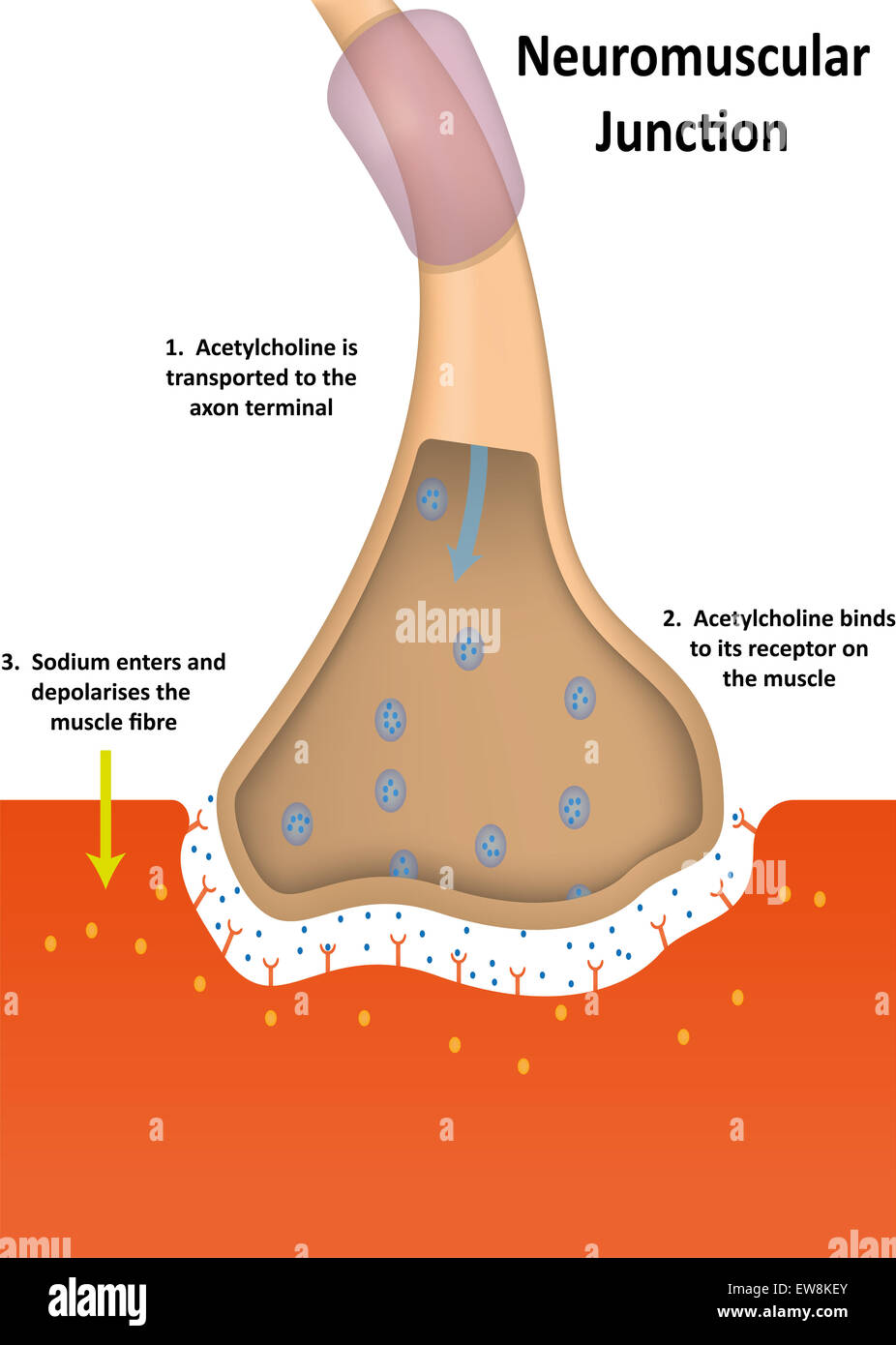 Neuromuscular Junction Physiology Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neuromuscular-junction-physiology-84398803.html
Neuromuscular Junction Physiology Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neuromuscular-junction-physiology-84398803.htmlRMEW8KEY–Neuromuscular Junction Physiology
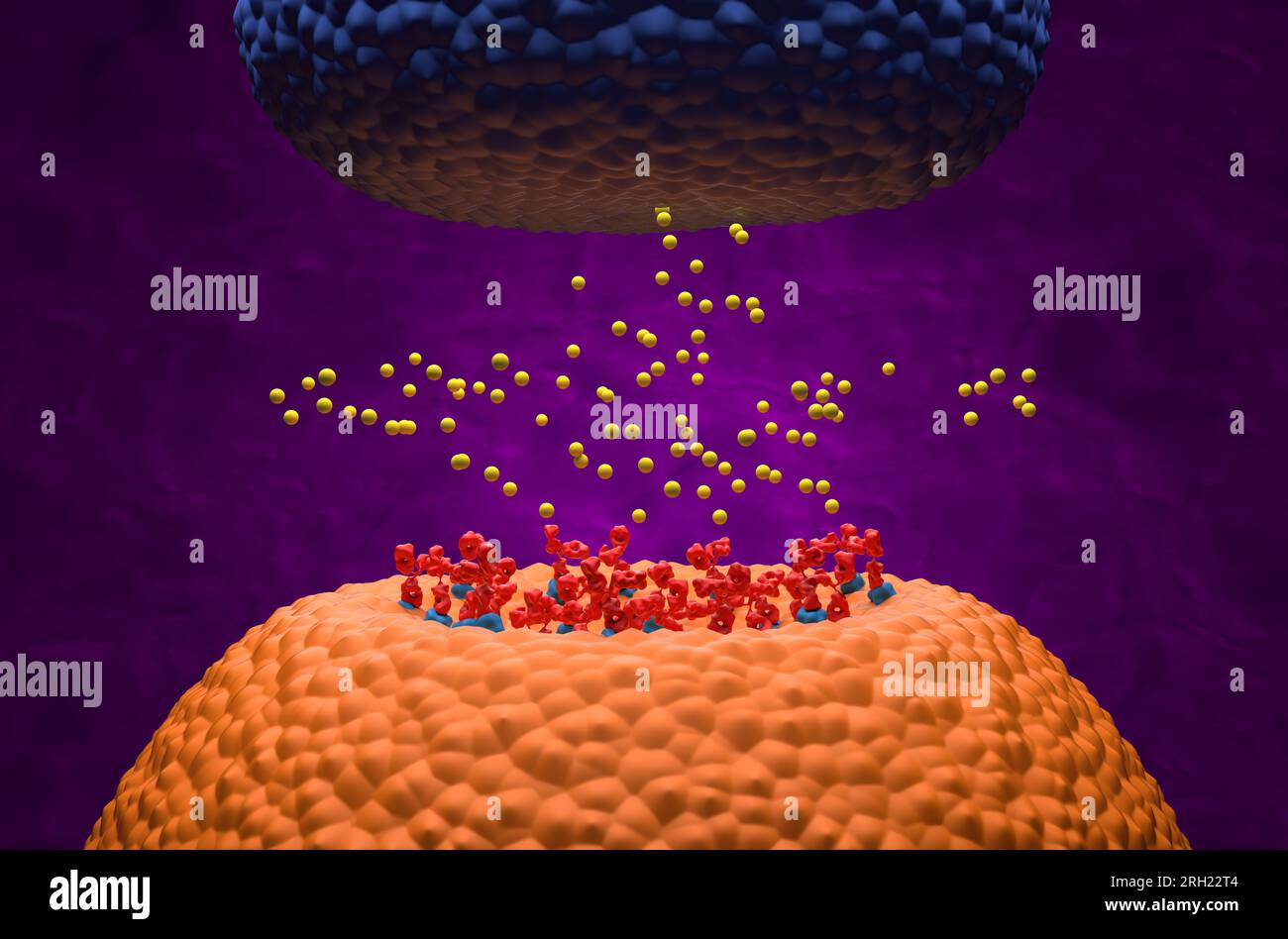 Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration isometric view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/autoantibodies-bond-to-receptor-achr-blocking-the-acetylcholine-transmitters-in-myasthenia-gravis-mg-3d-illustration-isometric-view-image561227076.html
Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration isometric view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/autoantibodies-bond-to-receptor-achr-blocking-the-acetylcholine-transmitters-in-myasthenia-gravis-mg-3d-illustration-isometric-view-image561227076.htmlRF2RH22T4–Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration isometric view
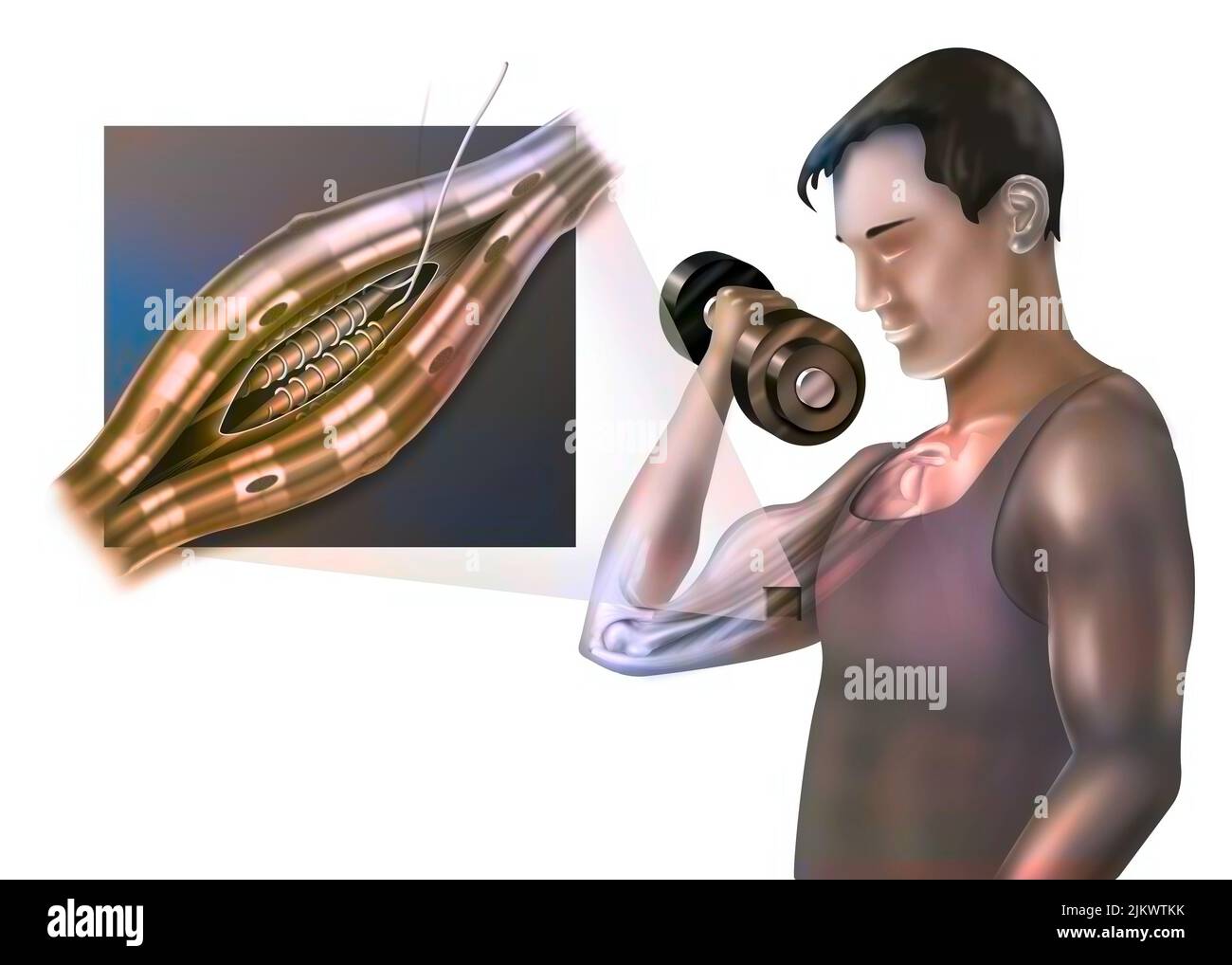 Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image476926567.html
Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image476926567.htmlRF2JKWTKK–Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body.
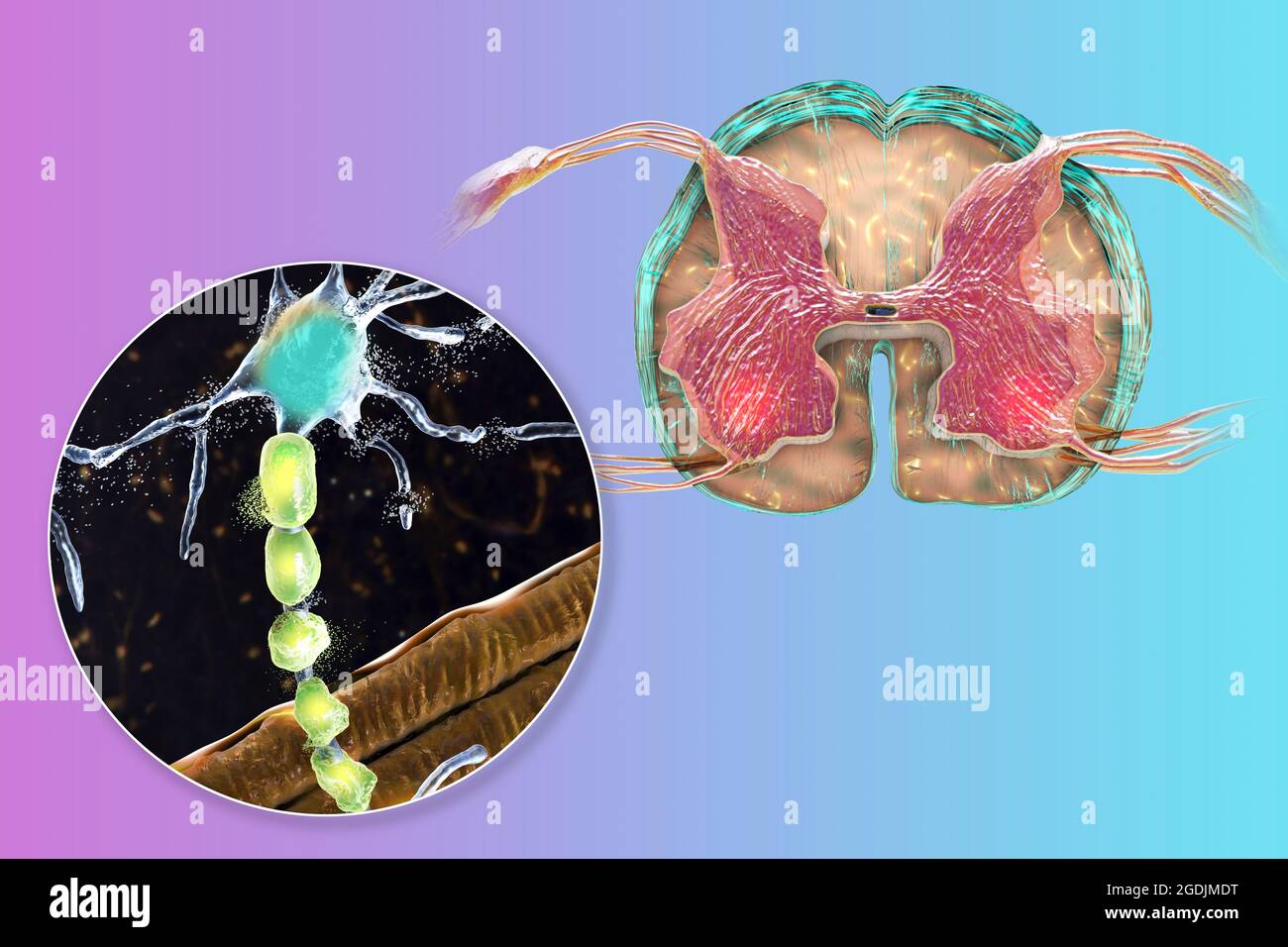 Motor neuron diseases, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-diseases-illustration-image438660932.html
Motor neuron diseases, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-diseases-illustration-image438660932.htmlRF2GDJMDT–Motor neuron diseases, illustration
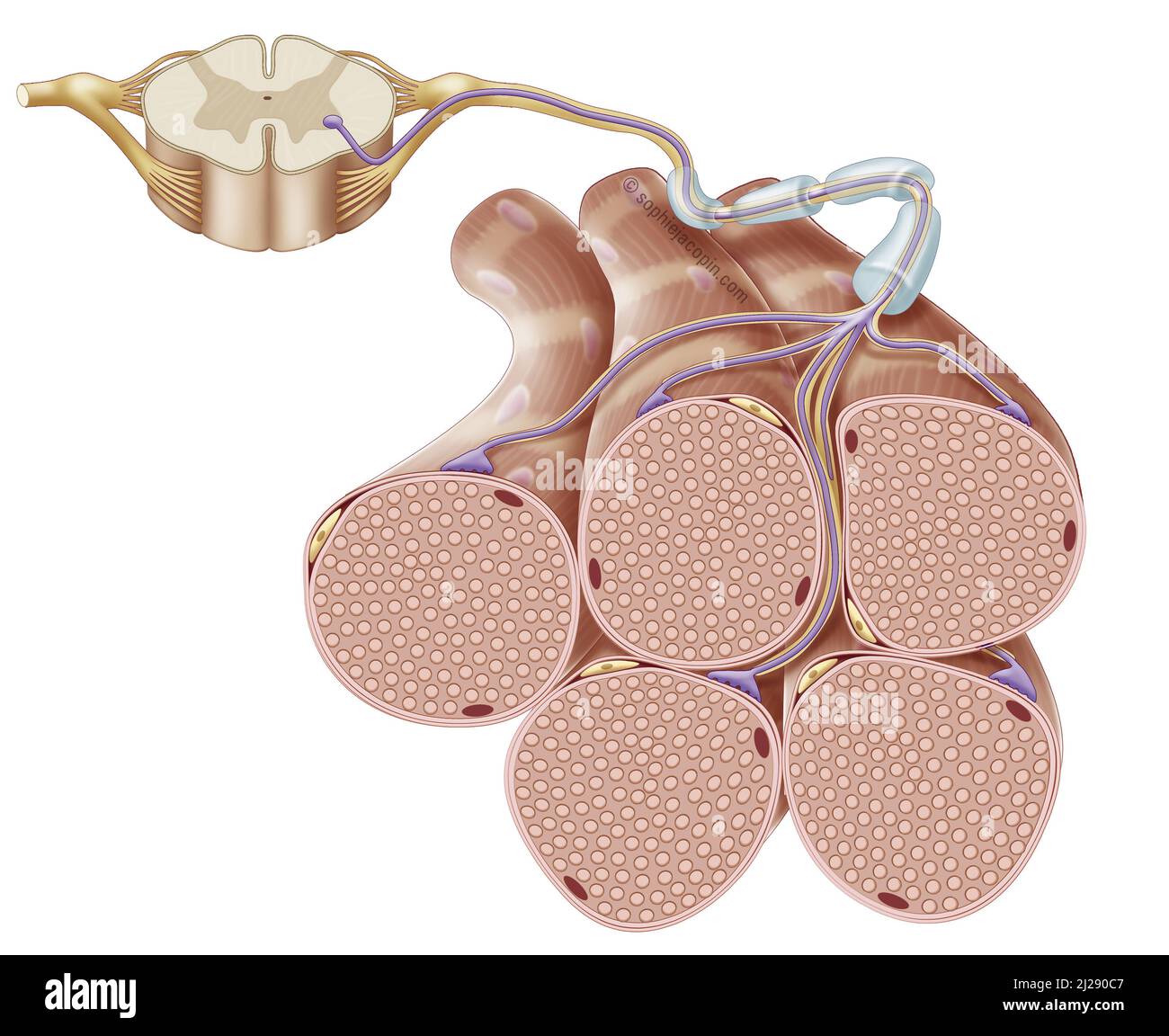 Motor neuron Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-image466107159.html
Motor neuron Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-image466107159.htmlRM2J290C7–Motor neuron
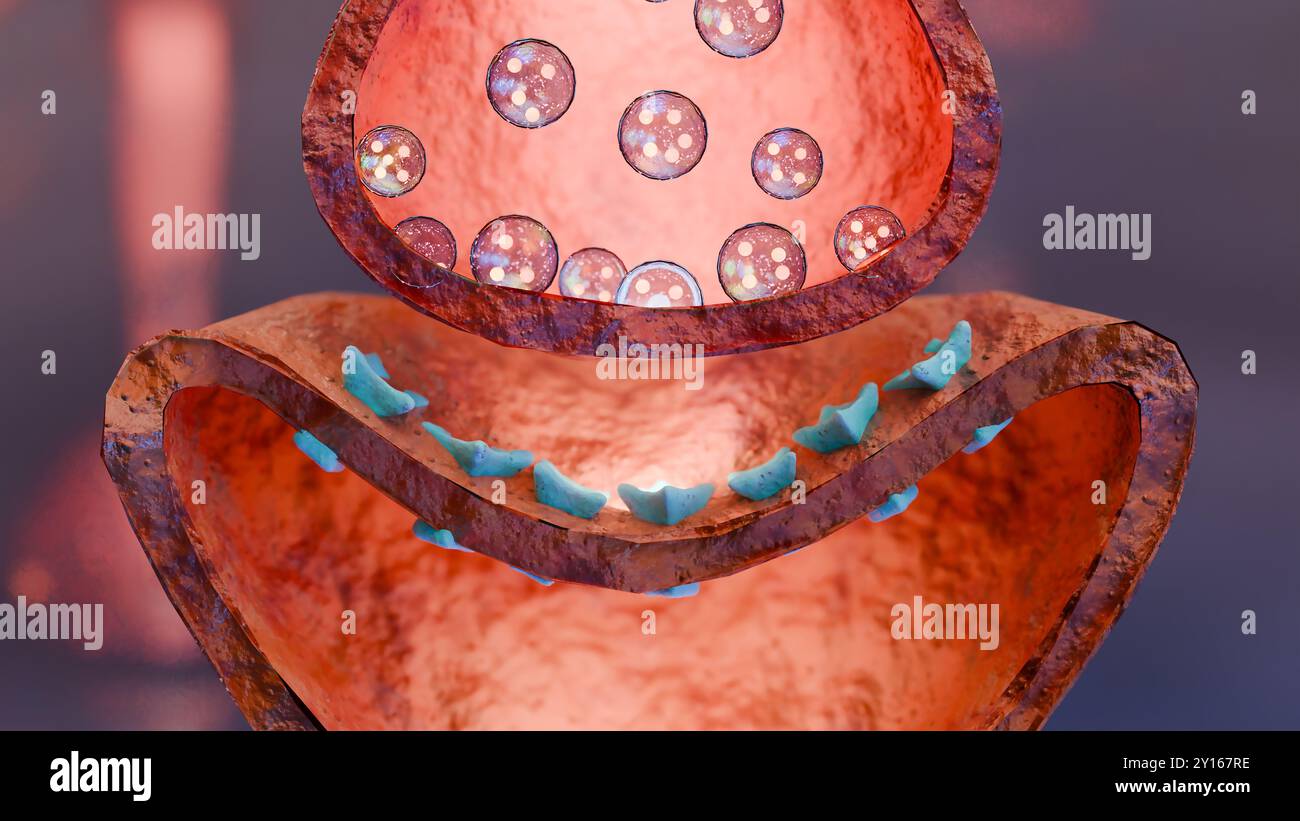 Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620325762.html
Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620325762.htmlRM2Y167RE–Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No
 Neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis - isometric view 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-junction-in-myasthenia-gravis-isometric-view-3d-illustration-image636278492.html
Neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis - isometric view 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-junction-in-myasthenia-gravis-isometric-view-3d-illustration-image636278492.htmlRF2YY4YKT–Neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis - isometric view 3d illustration
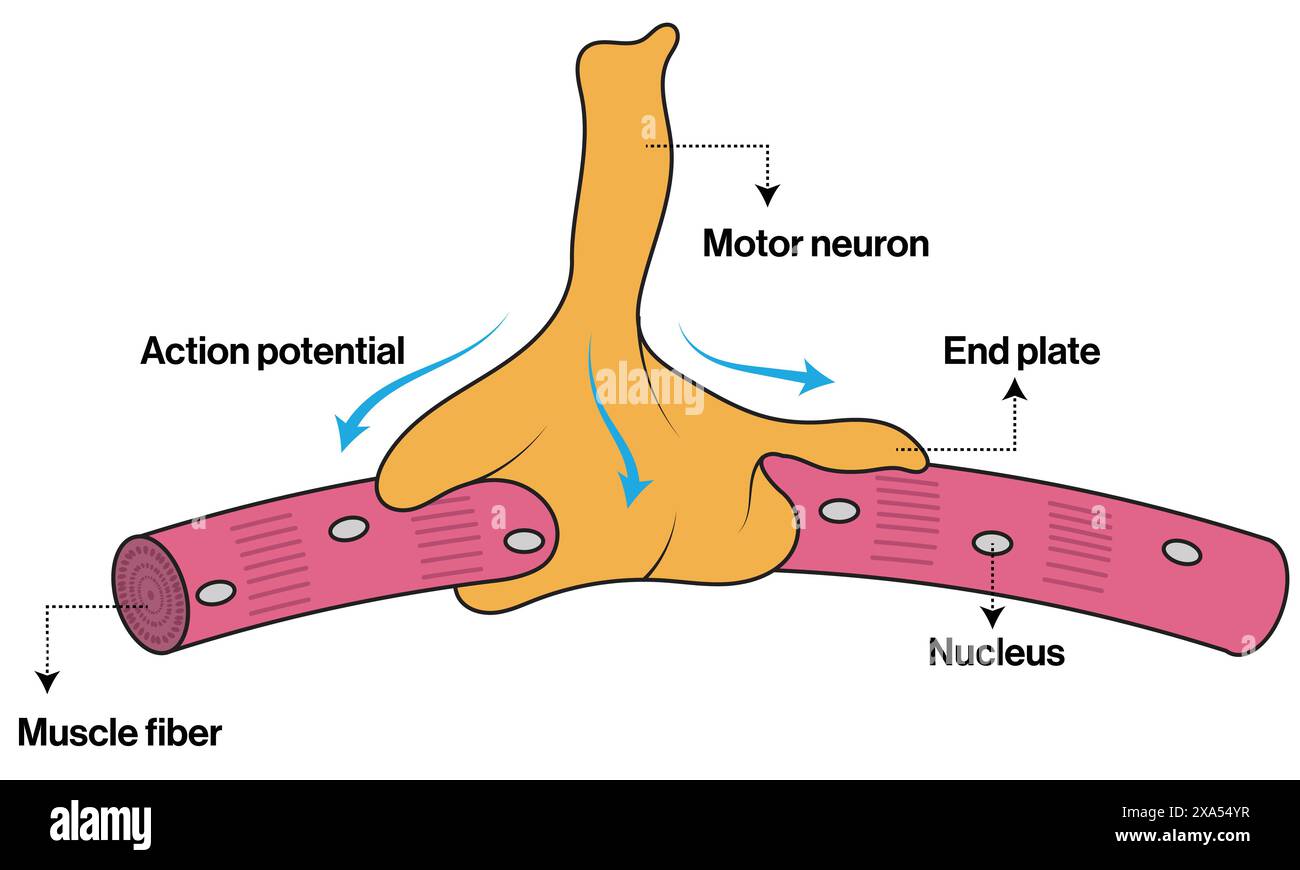 Detailed Vector Illustration of Neuromuscular Junction for Neuroscience, Anatomy, and Physiology Education on White Background. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/detailed-vector-illustration-of-neuromuscular-junction-for-neuroscience-anatomy-and-physiology-education-on-white-background-image608623115.html
Detailed Vector Illustration of Neuromuscular Junction for Neuroscience, Anatomy, and Physiology Education on White Background. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/detailed-vector-illustration-of-neuromuscular-junction-for-neuroscience-anatomy-and-physiology-education-on-white-background-image608623115.htmlRF2XA54YR–Detailed Vector Illustration of Neuromuscular Junction for Neuroscience, Anatomy, and Physiology Education on White Background.
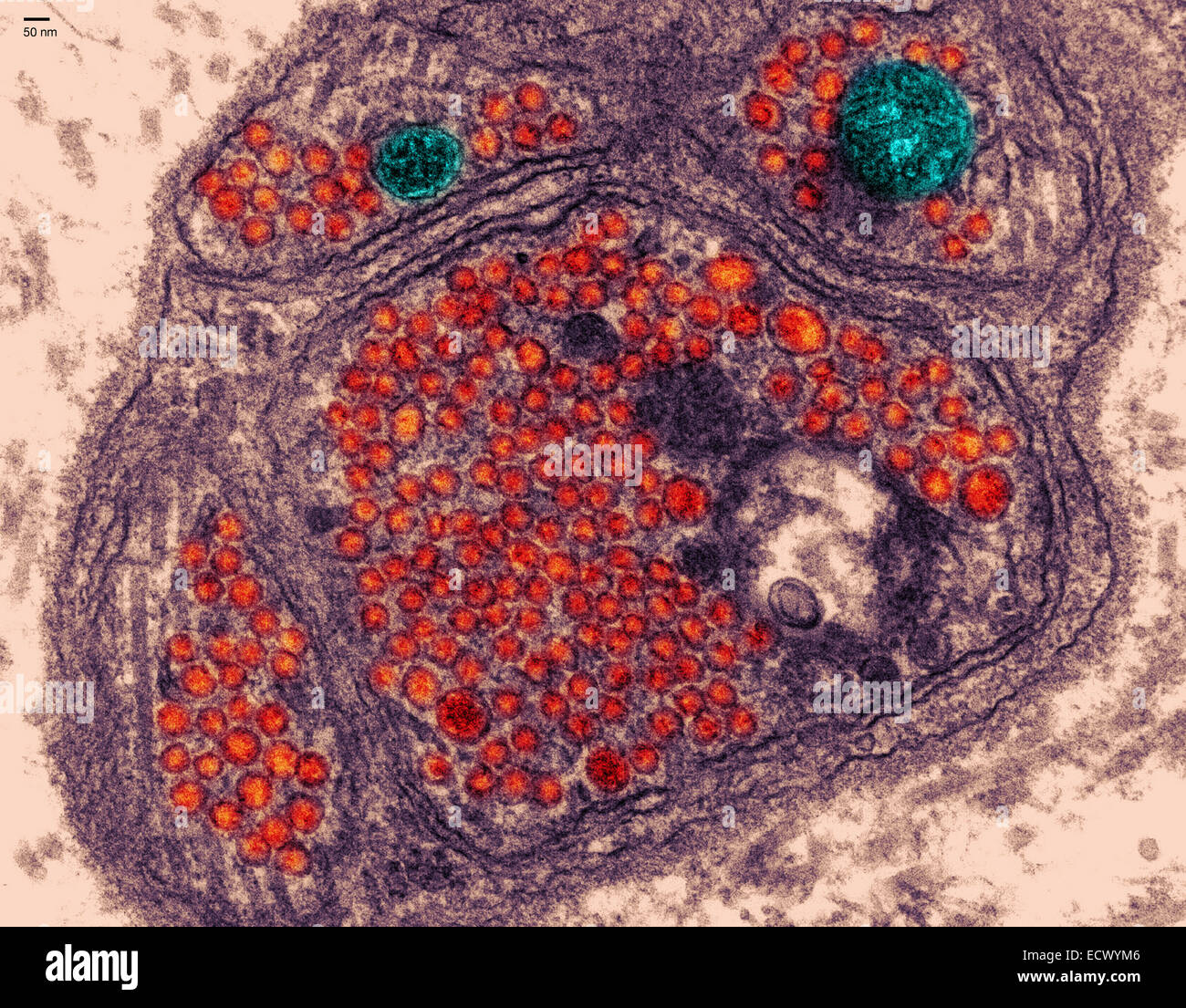 Electron micrograph of the neuromuscular junction. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-76787878.html
Electron micrograph of the neuromuscular junction. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-76787878.htmlRMECWYM6–Electron micrograph of the neuromuscular junction.
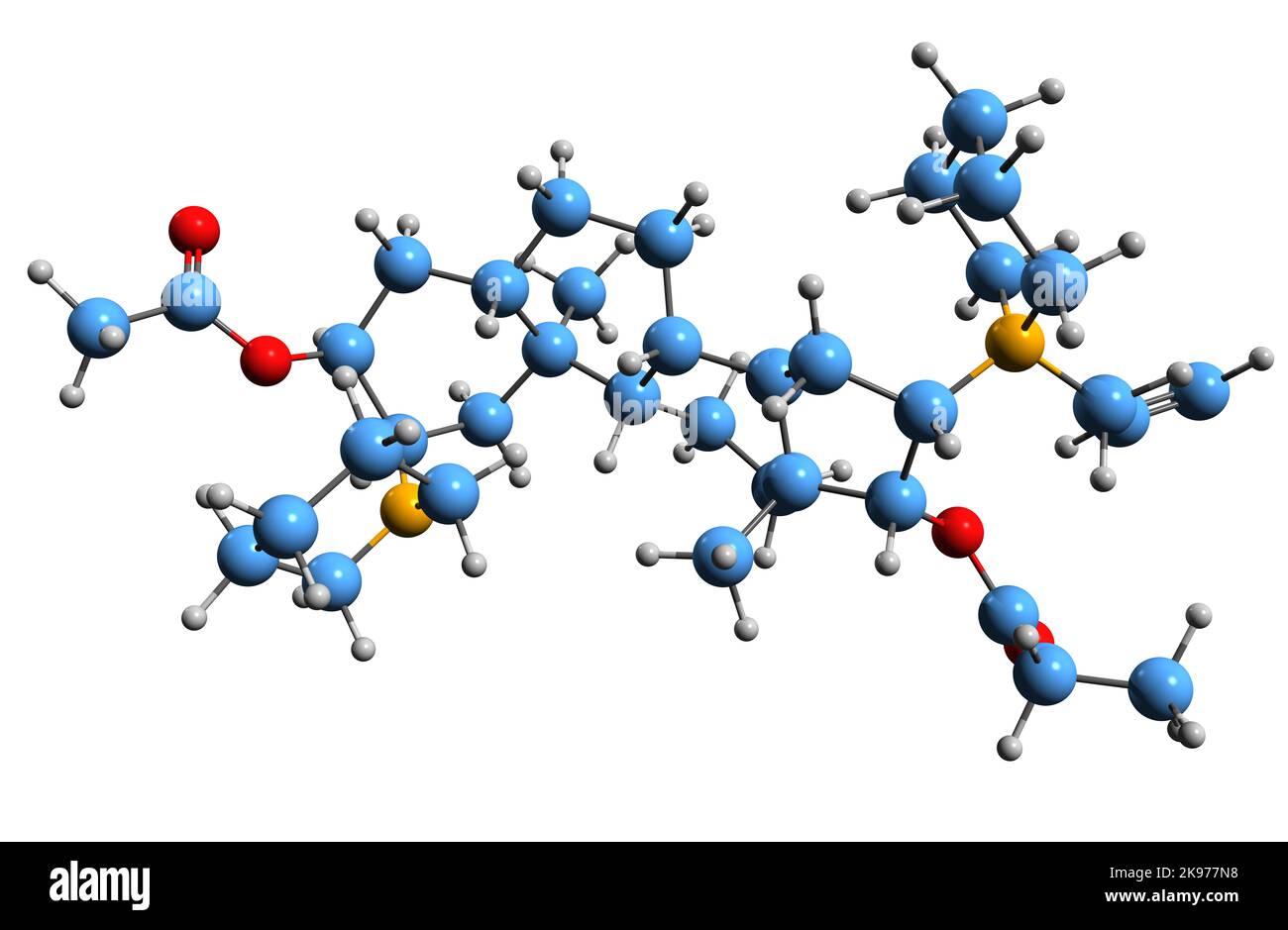 3D image of Rapacuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid neuromuscular blocker isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-rapacuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-neuromuscular-blocker-isolated-on-white-background-image487581956.html
3D image of Rapacuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid neuromuscular blocker isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-rapacuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-neuromuscular-blocker-isolated-on-white-background-image487581956.htmlRF2K977N8–3D image of Rapacuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid neuromuscular blocker isolated on white background
 Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration super closeup view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/autoantibodies-bond-to-receptor-achr-blocking-the-acetylcholine-transmitters-in-myasthenia-gravis-mg-3d-illustration-super-closeup-view-image562486565.html
Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration super closeup view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/autoantibodies-bond-to-receptor-achr-blocking-the-acetylcholine-transmitters-in-myasthenia-gravis-mg-3d-illustration-super-closeup-view-image562486565.htmlRF2RK3D9W–Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration super closeup view
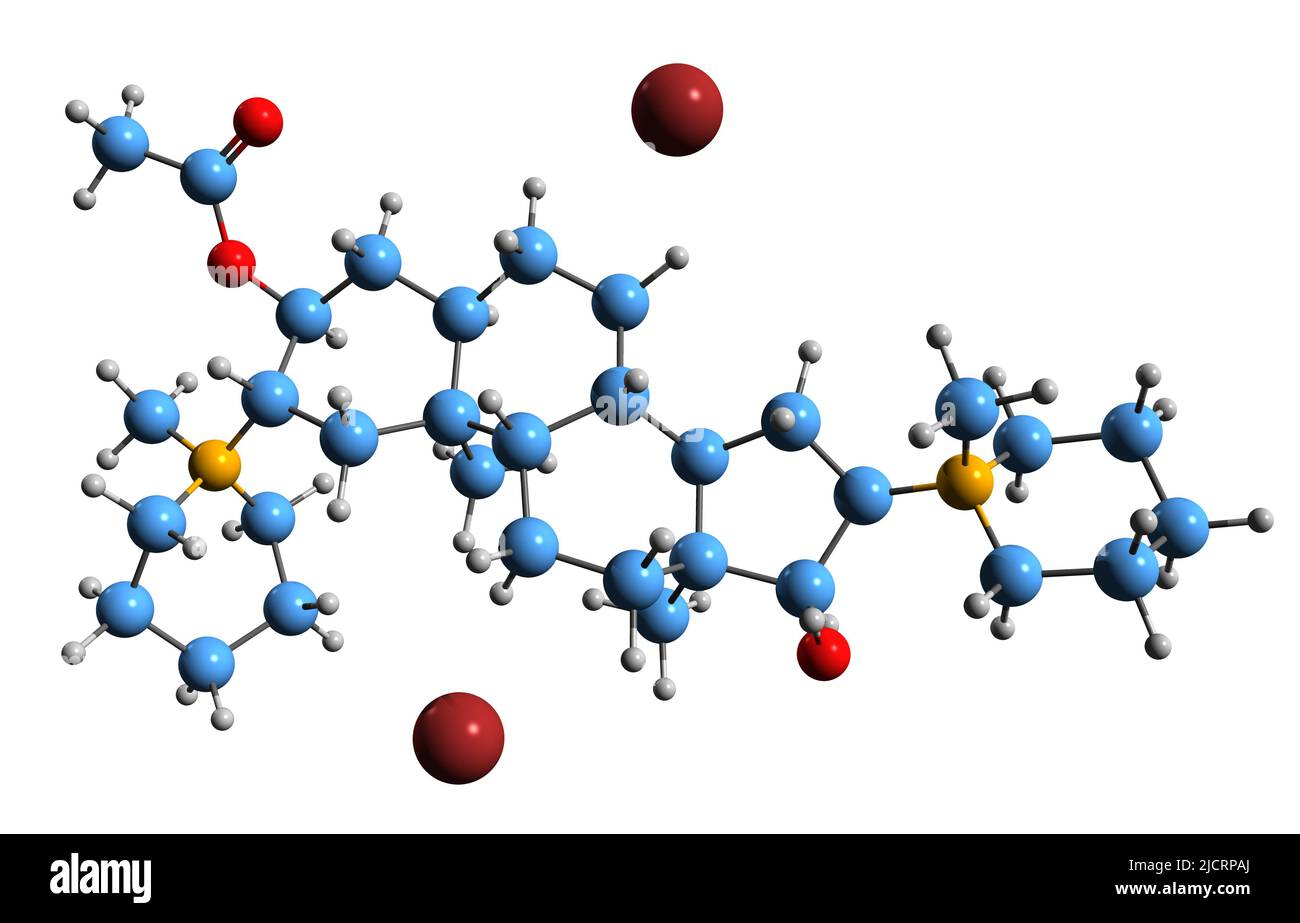 3D image of Dacuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-dacuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-isolated-on-white-background-image472578250.html
3D image of Dacuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-dacuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-isolated-on-white-background-image472578250.htmlRF2JCRPAJ–3D image of Dacuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background
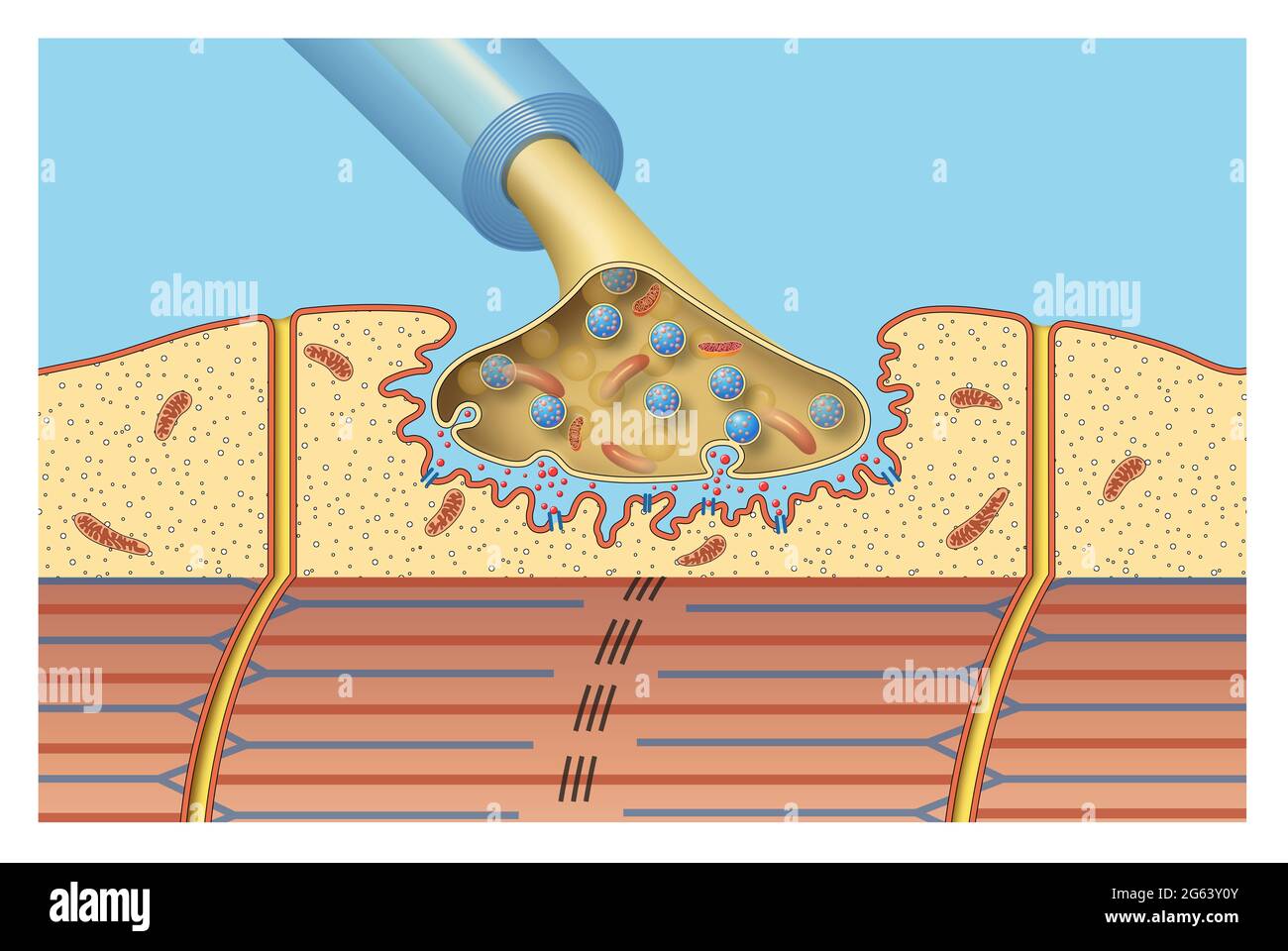 Synapse of the nervous system. Neuromuscular Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-of-the-nervous-system-neuromuscular-image434034187.html
Synapse of the nervous system. Neuromuscular Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-of-the-nervous-system-neuromuscular-image434034187.htmlRF2G63Y0Y–Synapse of the nervous system. Neuromuscular
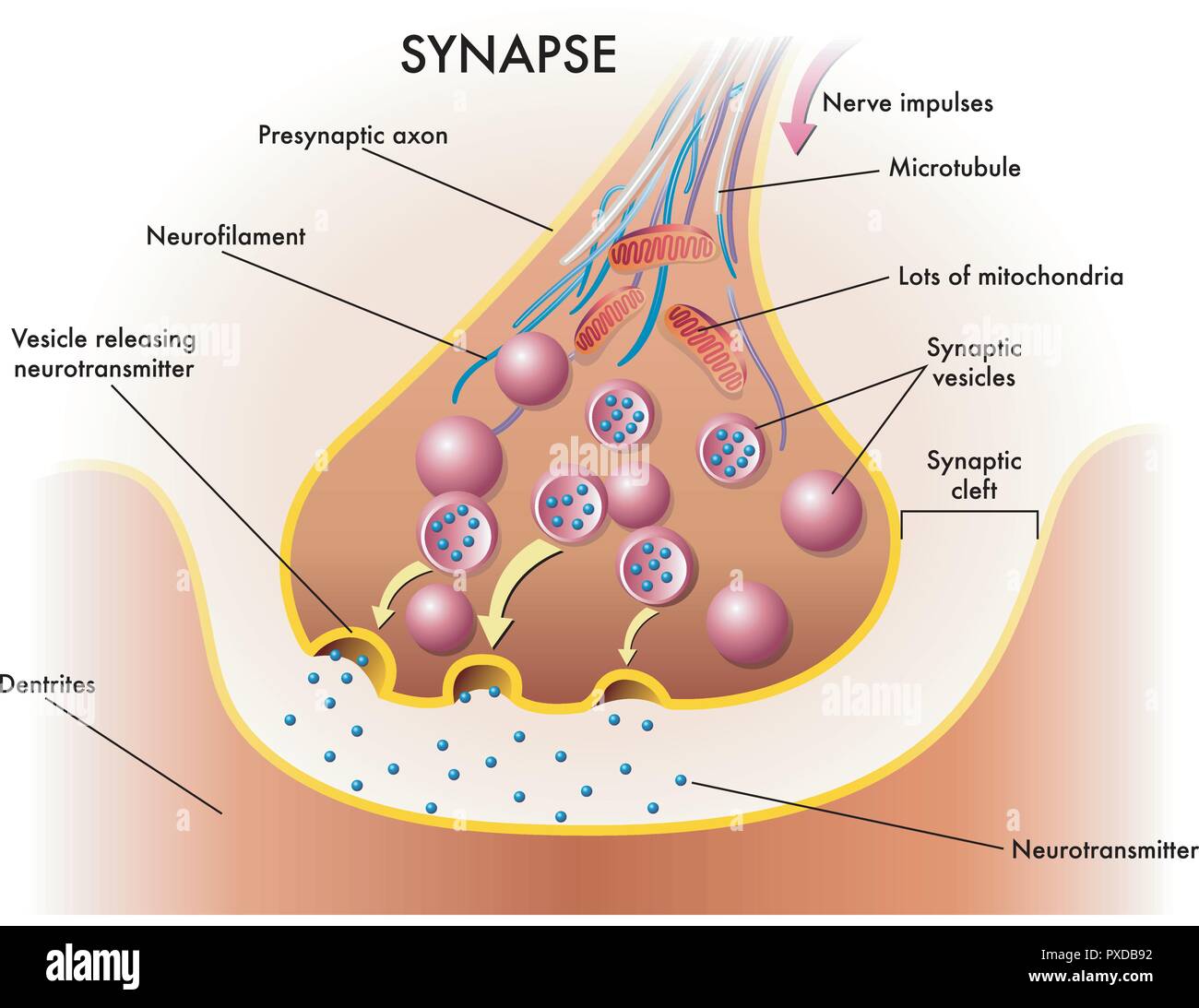 medical illustration of elements of synapse Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-elements-of-synapse-image222799726.html
medical illustration of elements of synapse Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-elements-of-synapse-image222799726.htmlRFPXDB92–medical illustration of elements of synapse
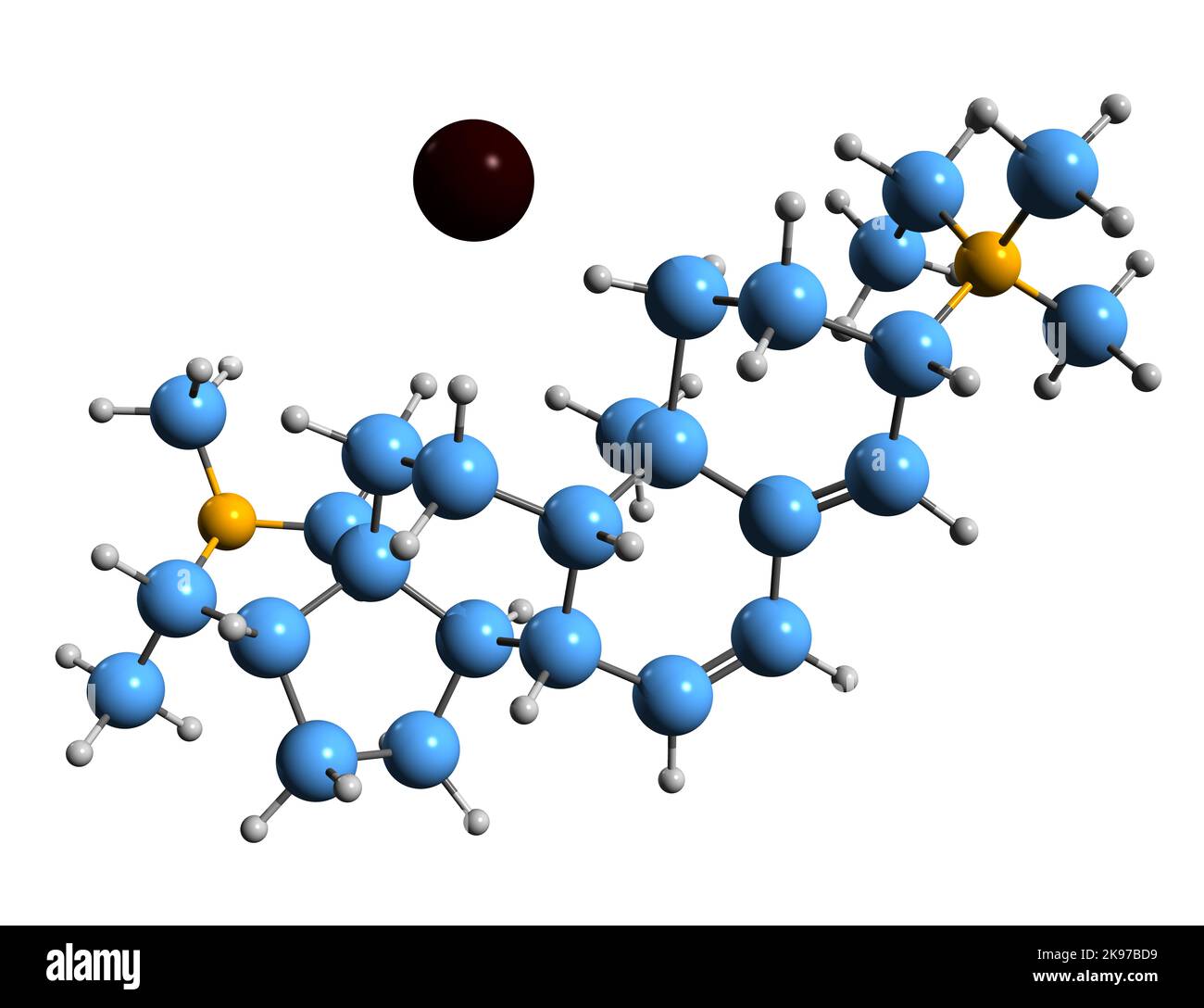 3D image of Stercuronium iodide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent isolated on white backg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-stercuronium-iodide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-neuromuscular-blocking-agent-isolated-on-white-backg-image487584869.html
3D image of Stercuronium iodide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent isolated on white backg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-stercuronium-iodide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-neuromuscular-blocking-agent-isolated-on-white-backg-image487584869.htmlRF2K97BD9–3D image of Stercuronium iodide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent isolated on white backg
 Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980841.html
Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980841.htmlRF2XFJ3PH–Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration.
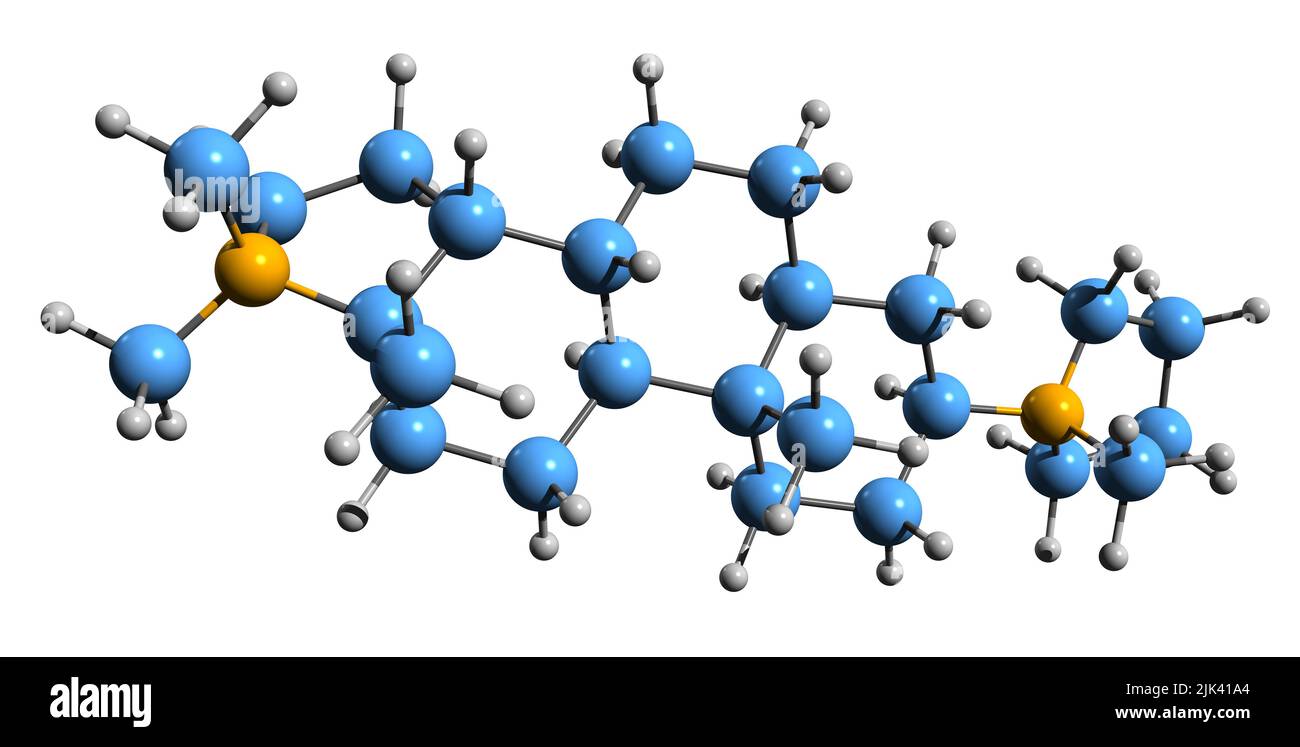 3D image of Dihydrochandonium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-dihydrochandonium-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-isolated-on-white-background-image476447276.html
3D image of Dihydrochandonium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-dihydrochandonium-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-isolated-on-white-background-image476447276.htmlRF2JK41A4–3D image of Dihydrochandonium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background
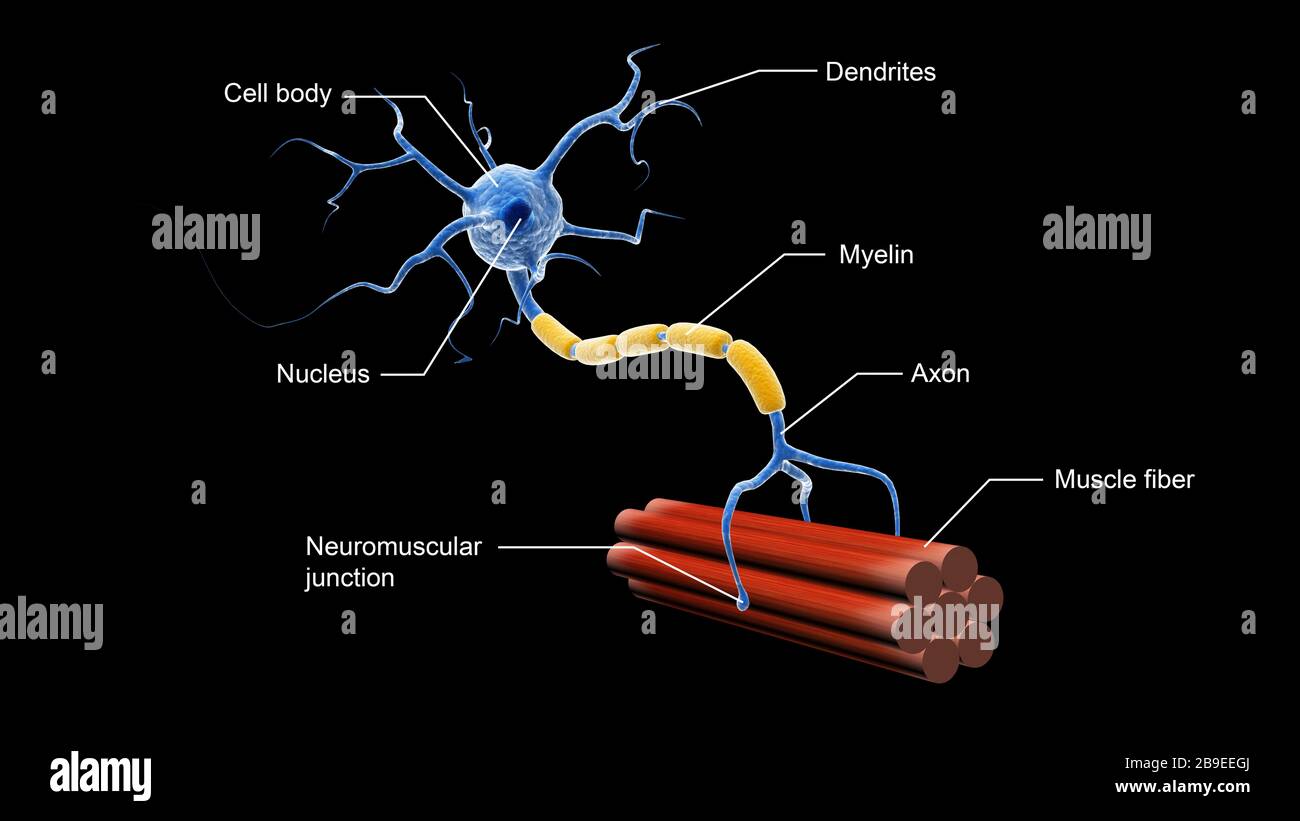 Medical illustration showing the structure of a motor neuron. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-showing-the-structure-of-a-motor-neuron-image350058034.html
Medical illustration showing the structure of a motor neuron. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-showing-the-structure-of-a-motor-neuron-image350058034.htmlRF2B9EEGJ–Medical illustration showing the structure of a motor neuron.
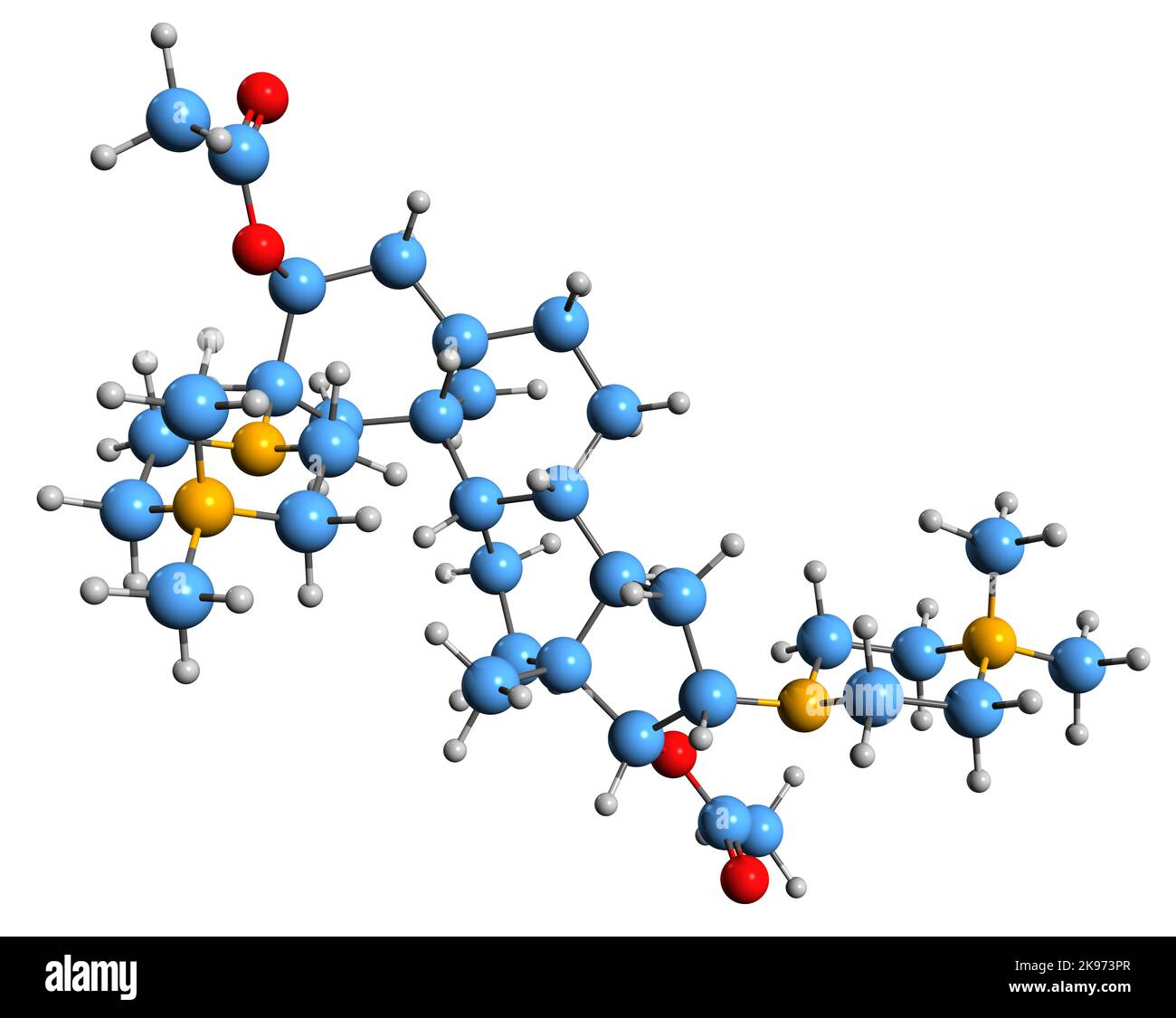 3D image of Pipecuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of bisquaternary aminosteroid muscle relaxant isolated on white back Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-pipecuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-bisquaternary-aminosteroid-muscle-relaxant-isolated-on-white-back-image487578863.html
3D image of Pipecuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of bisquaternary aminosteroid muscle relaxant isolated on white back Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-pipecuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-bisquaternary-aminosteroid-muscle-relaxant-isolated-on-white-back-image487578863.htmlRF2K973PR–3D image of Pipecuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of bisquaternary aminosteroid muscle relaxant isolated on white back
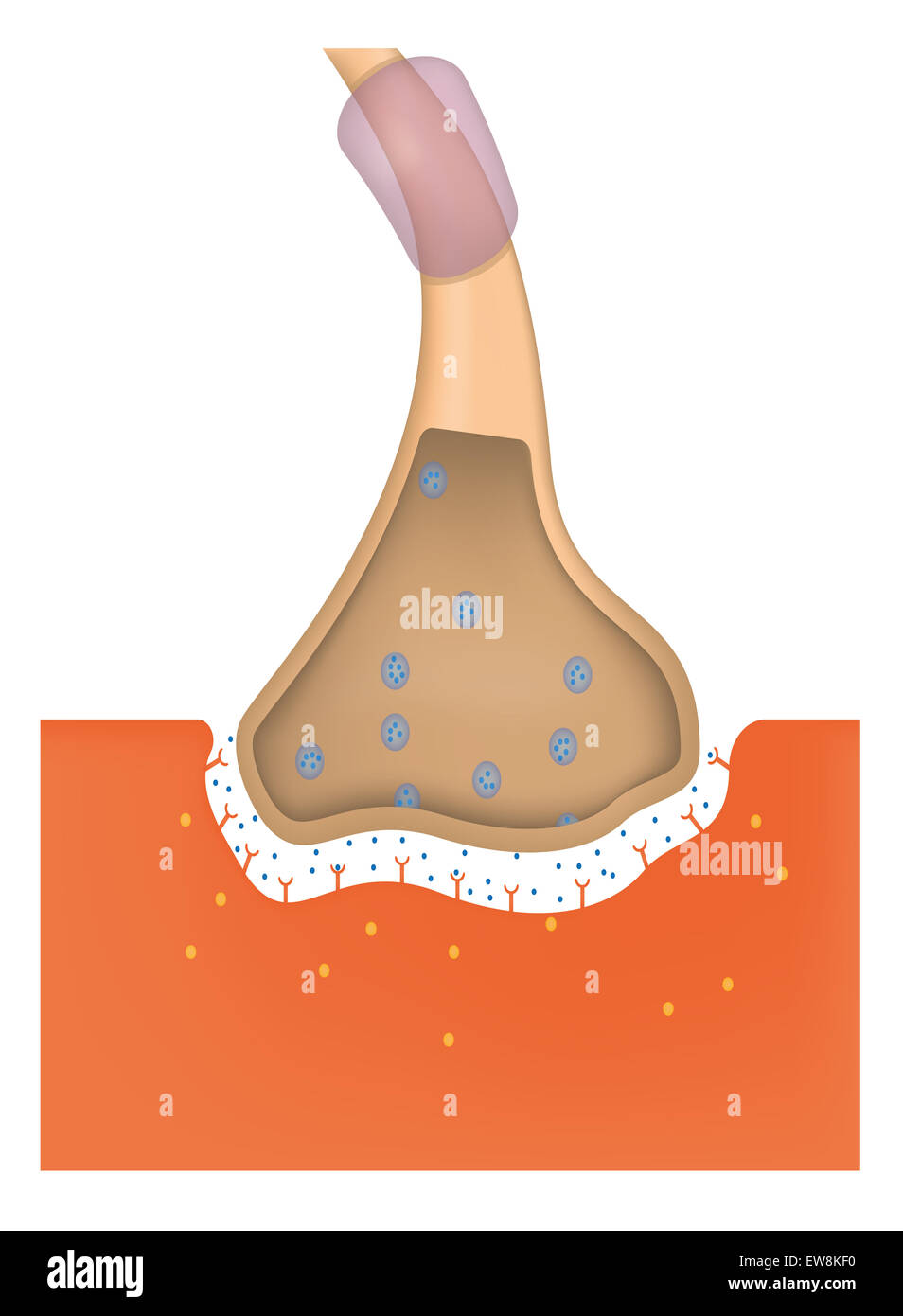 Neuromuscular Junction Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neuromuscular-junction-84398804.html
Neuromuscular Junction Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-neuromuscular-junction-84398804.htmlRMEW8KF0–Neuromuscular Junction
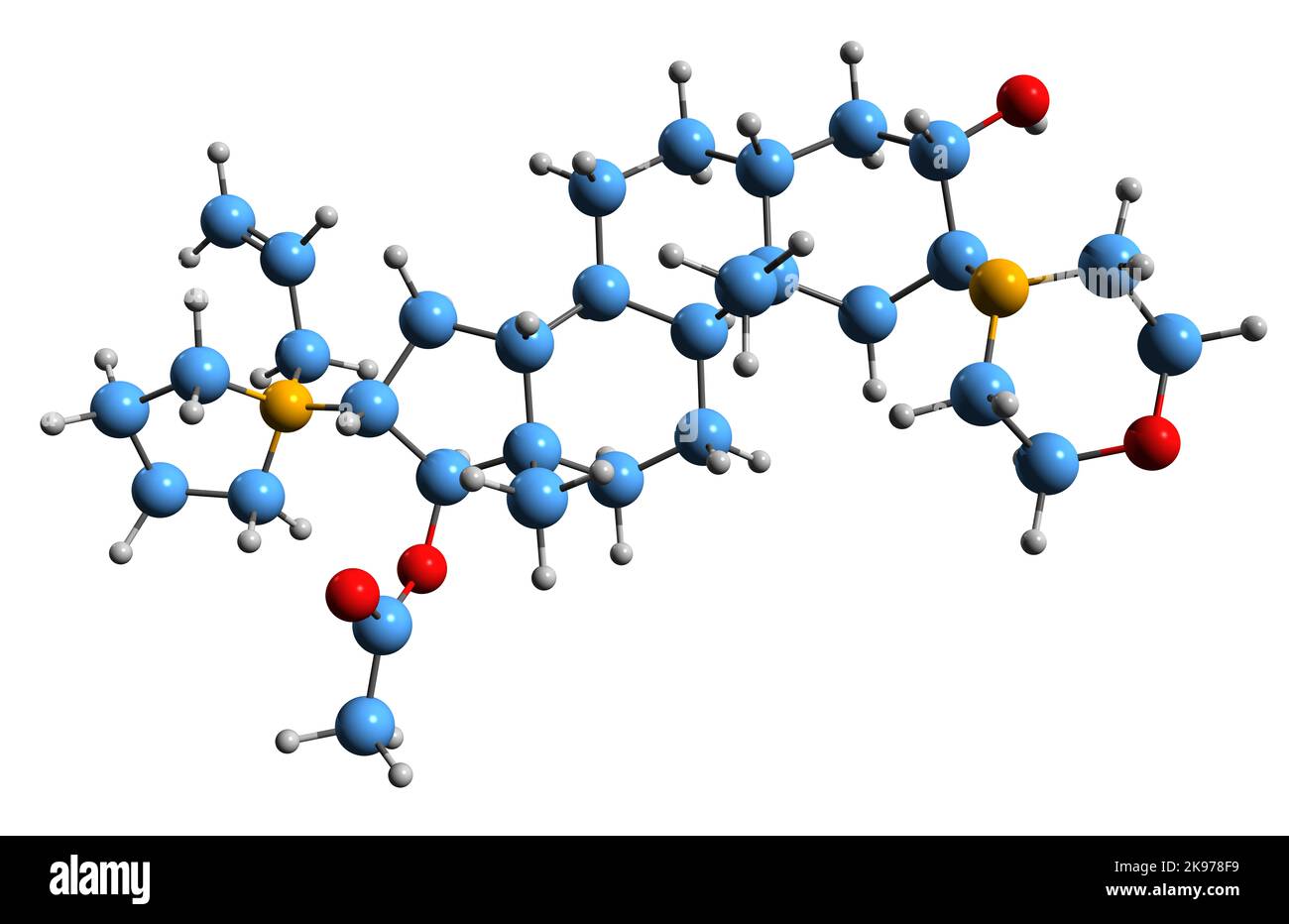 3D image of Rocuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker isolated on whi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-rocuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-non-depolarizing-neuromuscular-blocker-isolated-on-whi-image487582573.html
3D image of Rocuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker isolated on whi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-rocuronium-bromide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-non-depolarizing-neuromuscular-blocker-isolated-on-whi-image487582573.htmlRF2K978F9–3D image of Rocuronium bromide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker isolated on whi
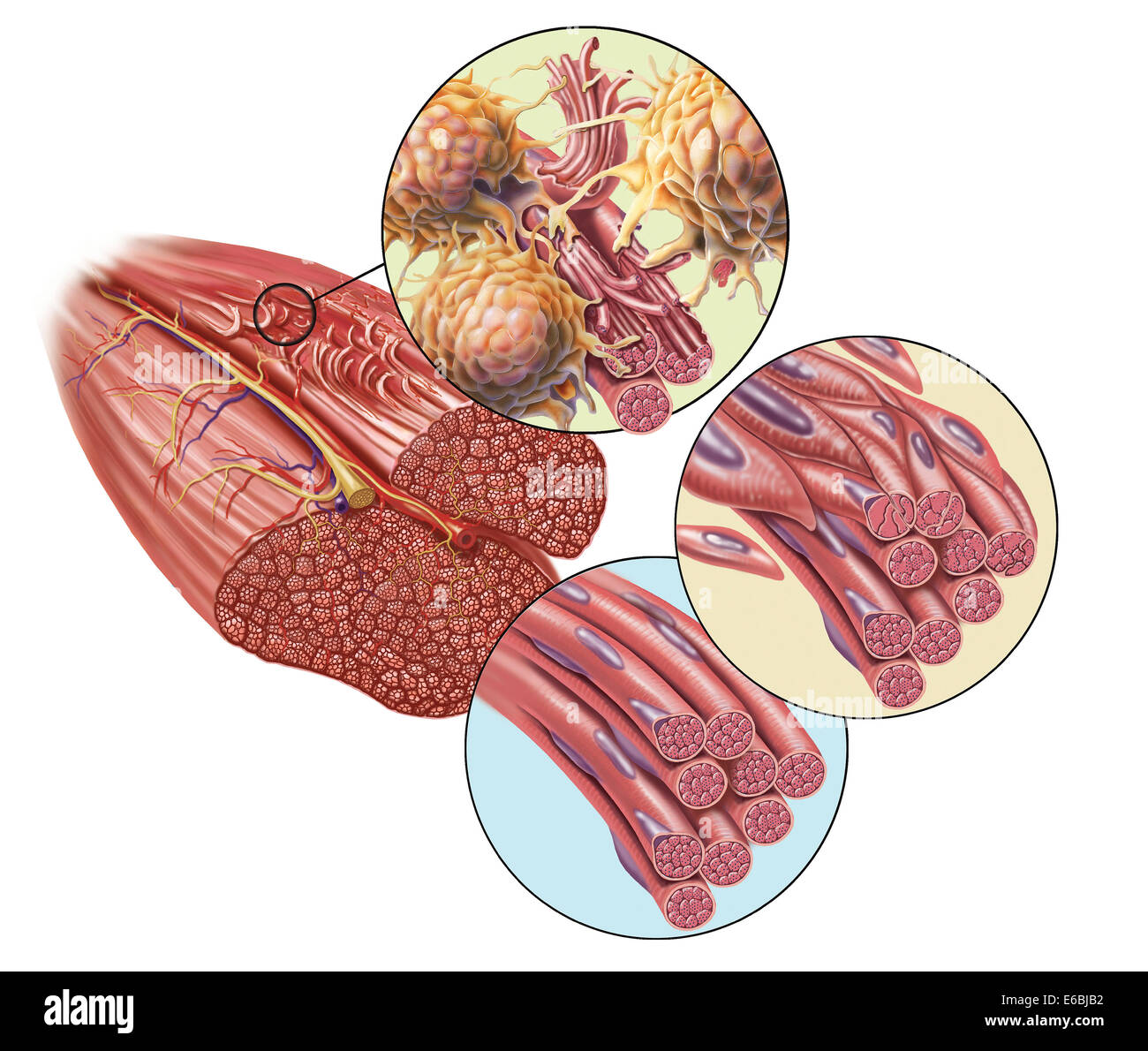 Torn muscle fibers with healing stages surrounding. 1. Macrophage clean-up. 2. New cells migrate to repair. 3. Cells differentia Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-torn-muscle-fibers-with-healing-stages-surrounding-1-macrophage-clean-72785302.html
Torn muscle fibers with healing stages surrounding. 1. Macrophage clean-up. 2. New cells migrate to repair. 3. Cells differentia Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-torn-muscle-fibers-with-healing-stages-surrounding-1-macrophage-clean-72785302.htmlRME6BJB2–Torn muscle fibers with healing stages surrounding. 1. Macrophage clean-up. 2. New cells migrate to repair. 3. Cells differentia
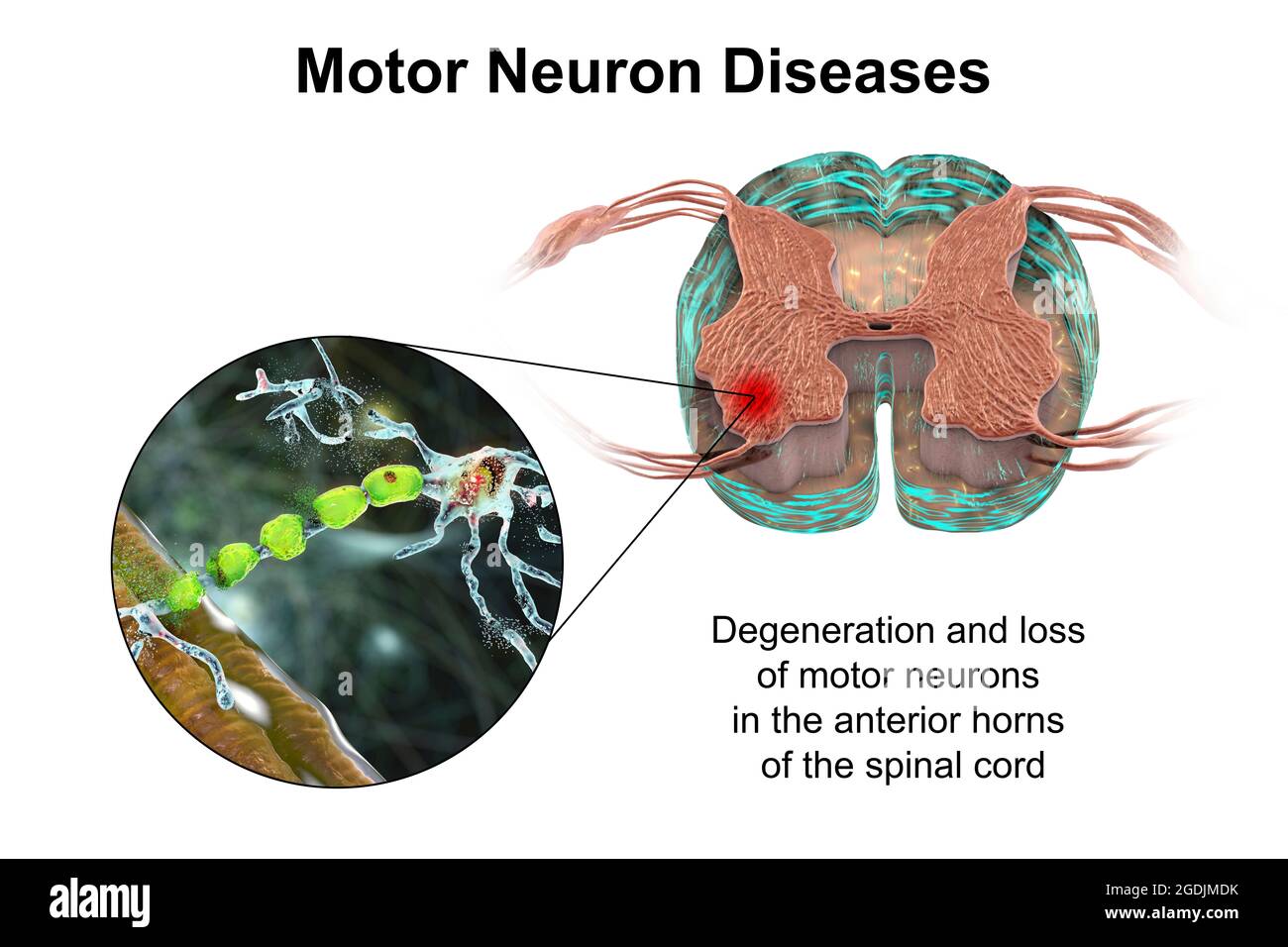 Motor neuron diseases, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-diseases-illustration-image438660927.html
Motor neuron diseases, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-diseases-illustration-image438660927.htmlRF2GDJMDK–Motor neuron diseases, illustration
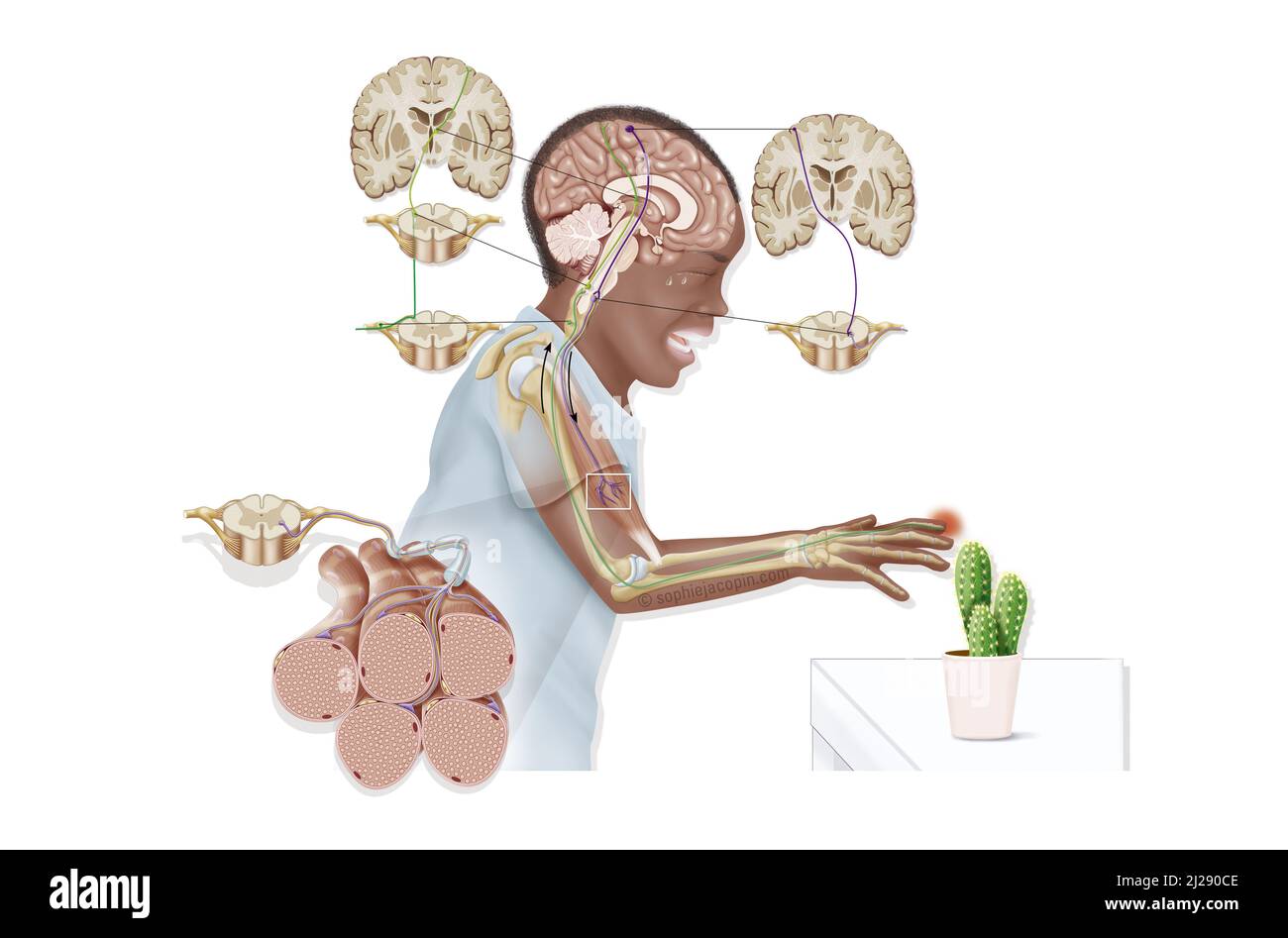 Reflex arc Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/reflex-arc-image466107166.html
Reflex arc Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/reflex-arc-image466107166.htmlRM2J290CE–Reflex arc
 Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620325610.html
Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620325610.htmlRM2Y167J2–Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No
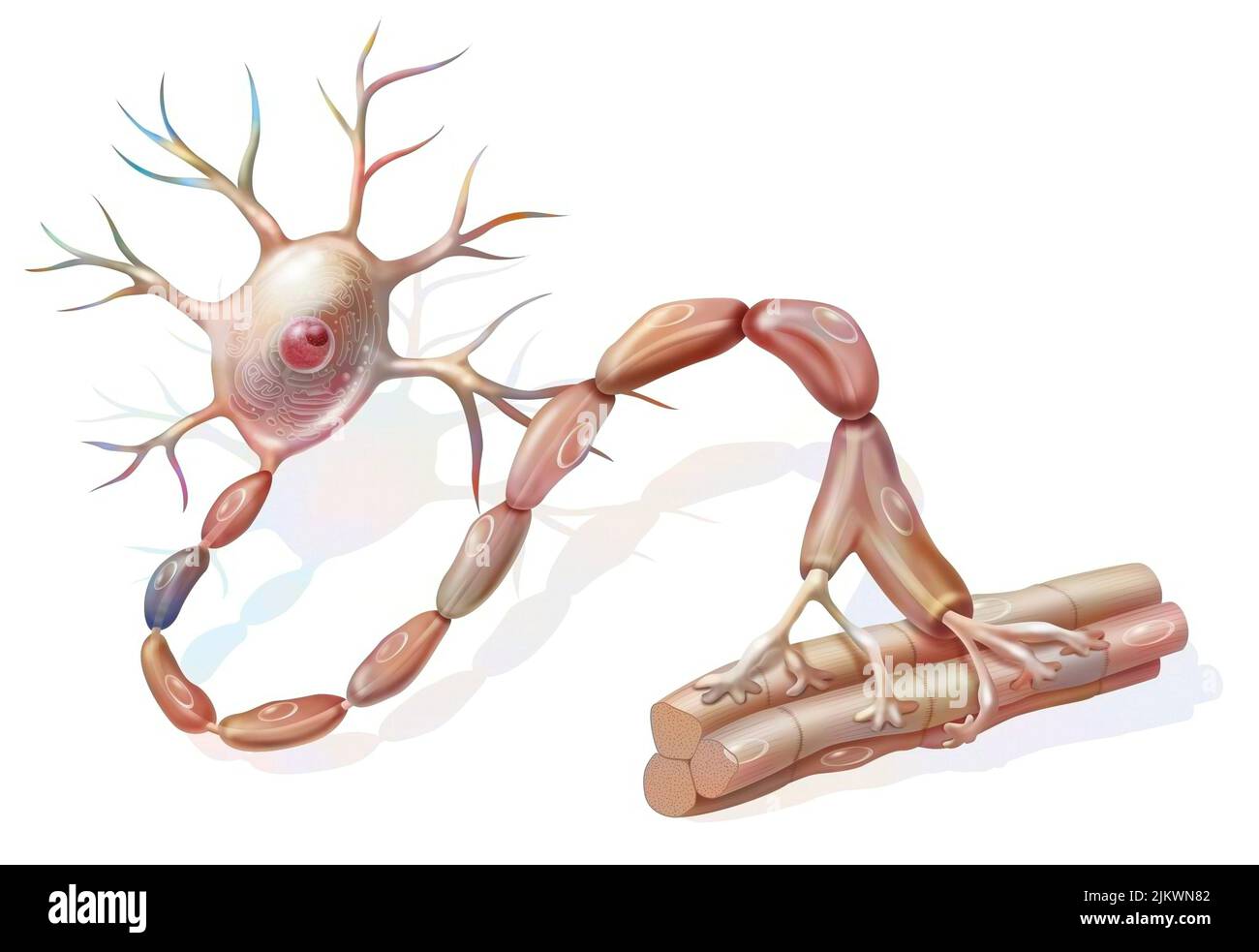 Motor neuron: neuron in contact with muscle fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-neuron-in-contact-with-muscle-fibers-image476923890.html
Motor neuron: neuron in contact with muscle fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-neuron-in-contact-with-muscle-fibers-image476923890.htmlRF2JKWN82–Motor neuron: neuron in contact with muscle fibers.
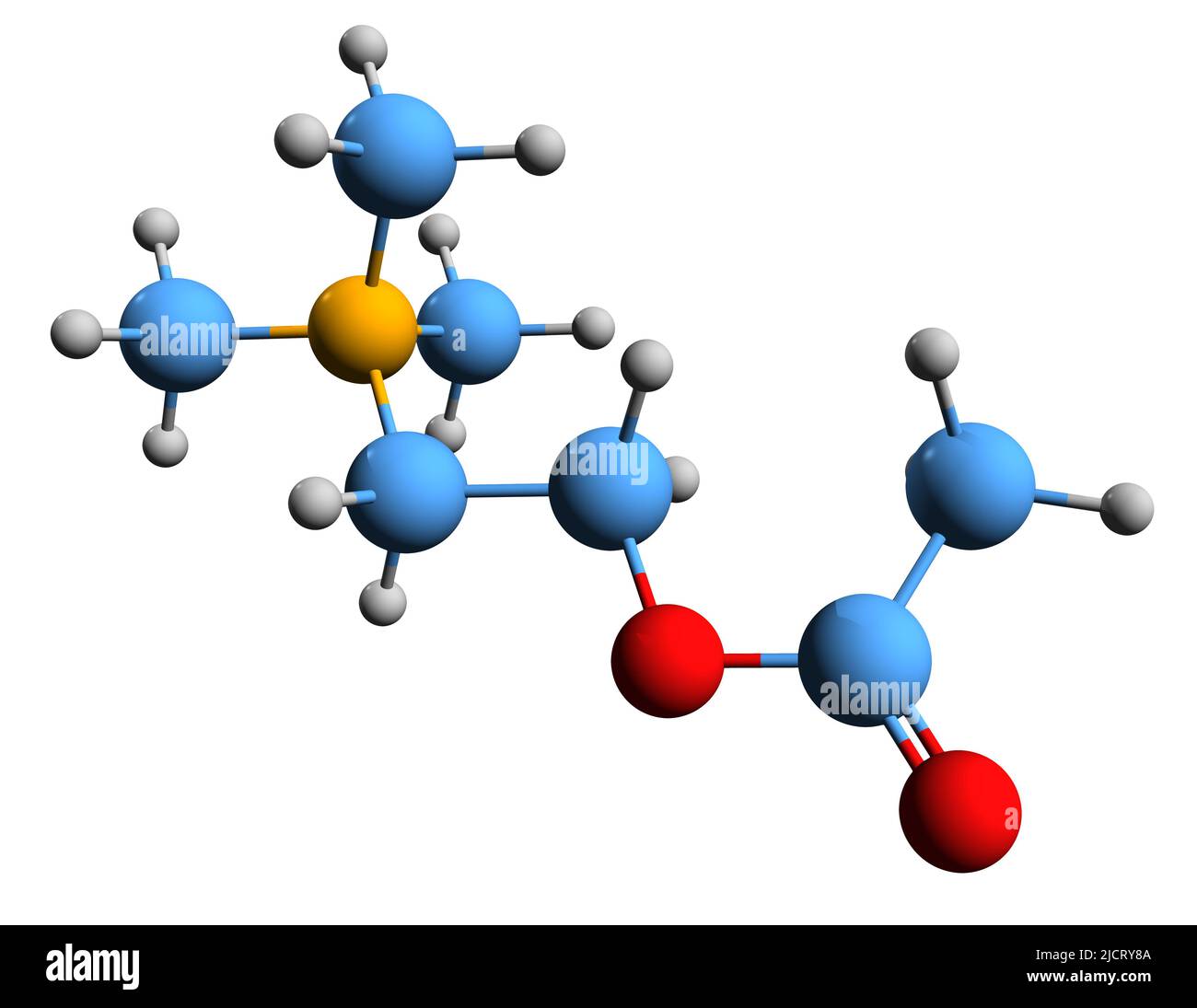 3D image of acetylcholine skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of neurotransmitter ACh isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-acetylcholine-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-neurotransmitter-ach-isolated-on-white-background-image472582106.html
3D image of acetylcholine skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of neurotransmitter ACh isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-acetylcholine-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-neurotransmitter-ach-isolated-on-white-background-image472582106.htmlRF2JCRY8A–3D image of acetylcholine skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of neurotransmitter ACh isolated on white background
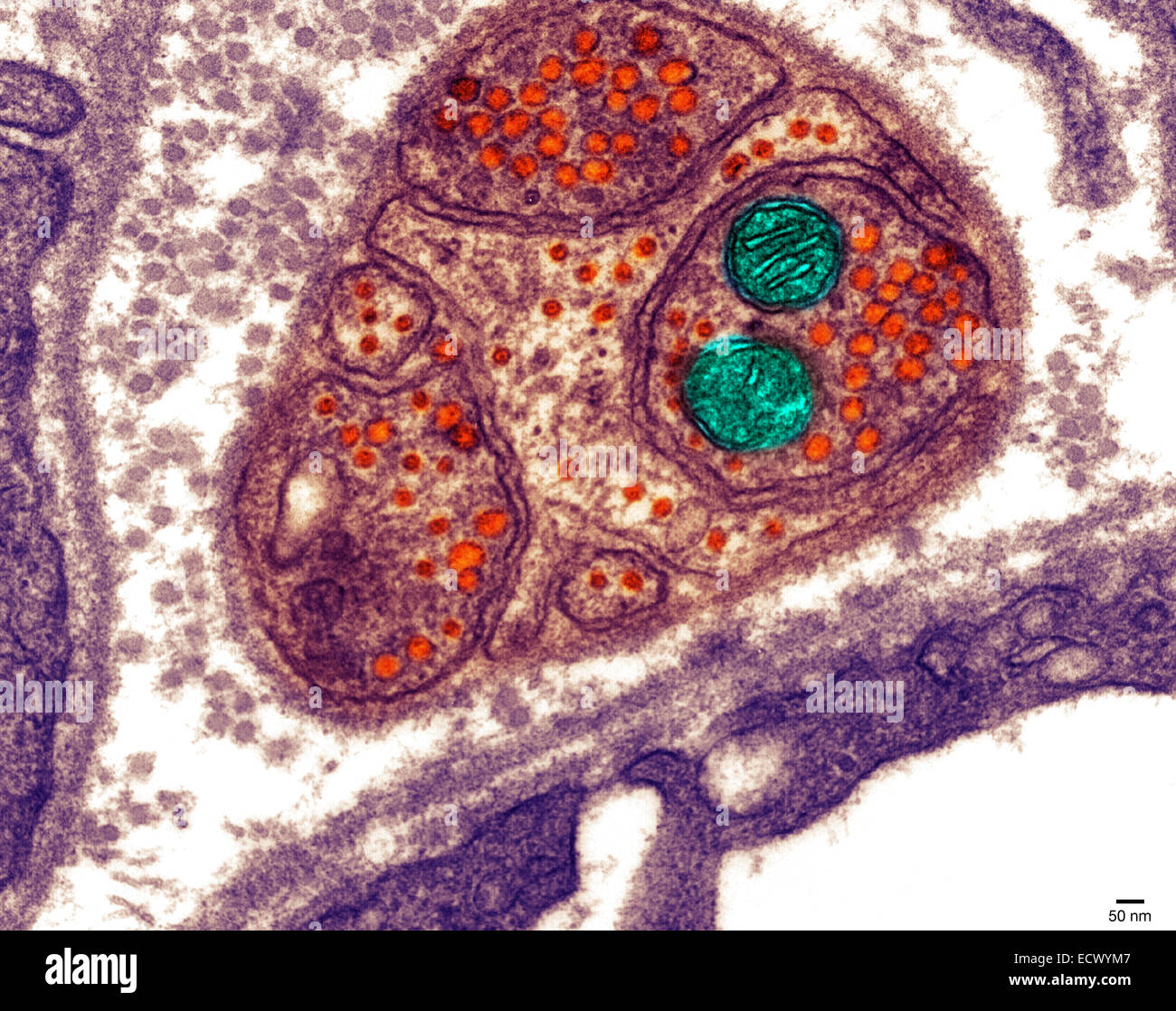 Electron micrograph of the neuromuscular junction. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-76787879.html
Electron micrograph of the neuromuscular junction. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-76787879.htmlRMECWYM7–Electron micrograph of the neuromuscular junction.
 Detail of deep back muscles with a close-up of sprain, strain and spasm. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-detail-of-deep-back-muscles-with-a-close-up-of-sprain-strain-and-spasm-72785329.html
Detail of deep back muscles with a close-up of sprain, strain and spasm. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-detail-of-deep-back-muscles-with-a-close-up-of-sprain-strain-and-spasm-72785329.htmlRME6BJC1–Detail of deep back muscles with a close-up of sprain, strain and spasm.
 Golgi Tendon Organ. It is a sensory organ that perceives tendon or muscle strength. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/golgi-tendon-organ-it-is-a-sensory-organ-that-perceives-tendon-or-muscle-strength-image626642104.html
Golgi Tendon Organ. It is a sensory organ that perceives tendon or muscle strength. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/golgi-tendon-organ-it-is-a-sensory-organ-that-perceives-tendon-or-muscle-strength-image626642104.htmlRF2YBE0B4–Golgi Tendon Organ. It is a sensory organ that perceives tendon or muscle strength.
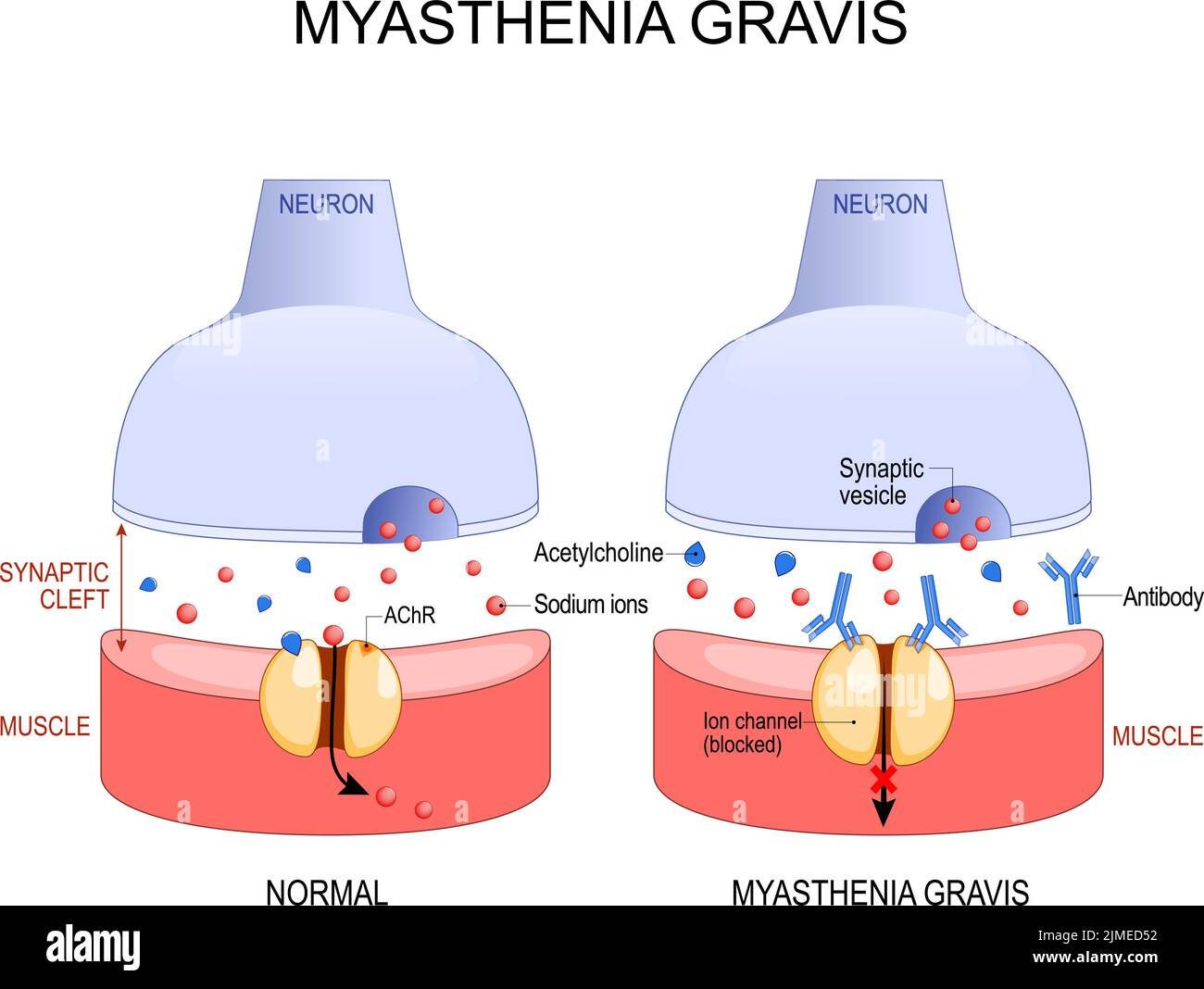 Myasthenia gravis. Autoimmune disease. space between neuron and muscle. In myasthenia gravis, abnormal antibodies prevent acetylcholine from binding, Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/myasthenia-gravis-autoimmune-disease-space-between-neuron-and-muscle-in-myasthenia-gravis-abnormal-antibodies-prevent-acetylcholine-from-binding-image477290718.html
Myasthenia gravis. Autoimmune disease. space between neuron and muscle. In myasthenia gravis, abnormal antibodies prevent acetylcholine from binding, Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/myasthenia-gravis-autoimmune-disease-space-between-neuron-and-muscle-in-myasthenia-gravis-abnormal-antibodies-prevent-acetylcholine-from-binding-image477290718.htmlRF2JMED52–Myasthenia gravis. Autoimmune disease. space between neuron and muscle. In myasthenia gravis, abnormal antibodies prevent acetylcholine from binding,
 MG on Warning Road Sign on Sunset Sky Background. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-mg-on-warning-road-sign-on-sunset-sky-background-75983546.html
MG on Warning Road Sign on Sunset Sky Background. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-mg-on-warning-road-sign-on-sunset-sky-background-75983546.htmlRFEBH9P2–MG on Warning Road Sign on Sunset Sky Background.
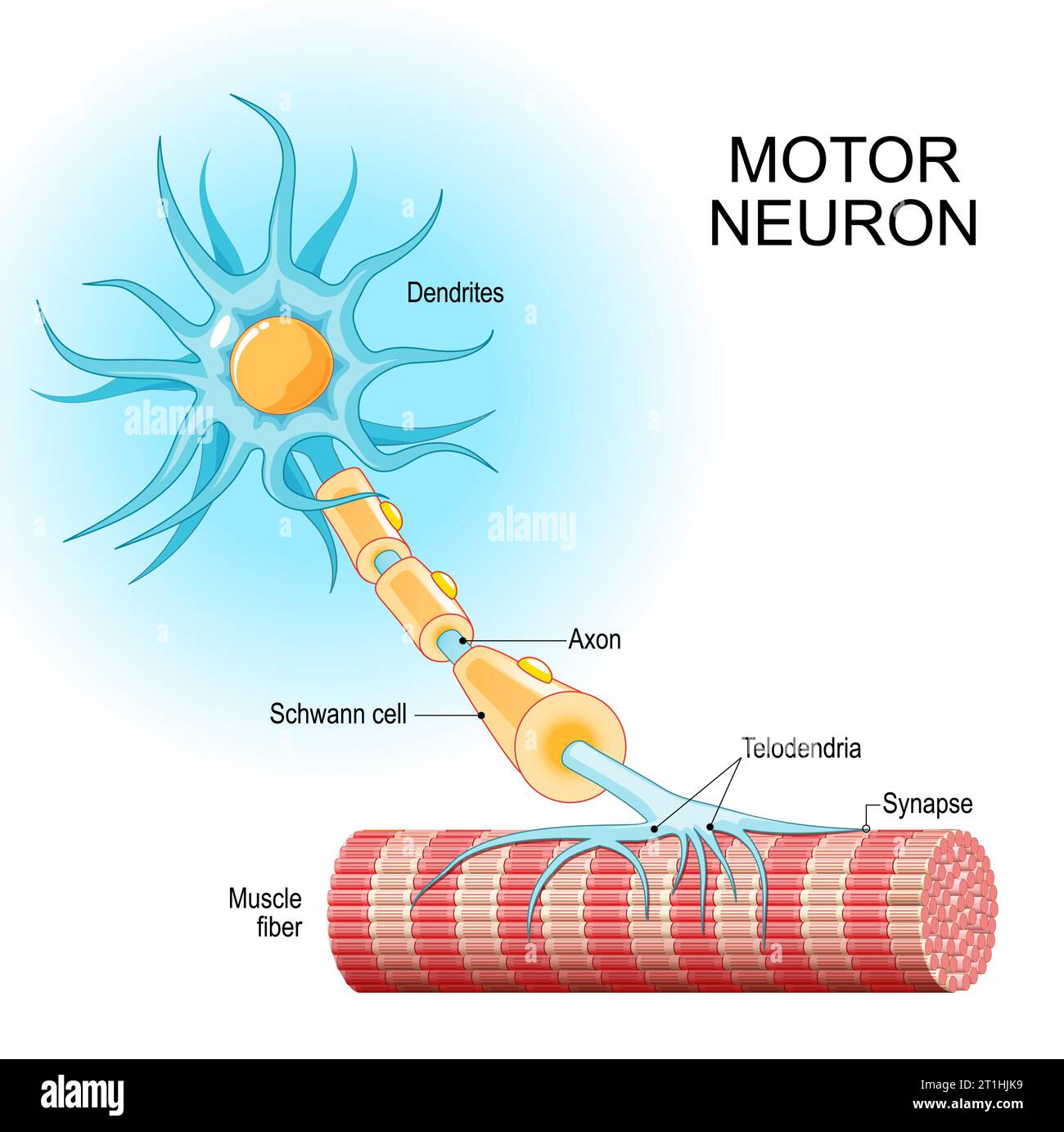 Motor neuron. Structure and anatomy of a efferent neuron. Close-up of a Muscle fiber, and motoneuron with Dendrites, Synapse, Telodendria, Axon, Schwa Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-structure-and-anatomy-of-a-efferent-neuron-close-up-of-a-muscle-fiber-and-motoneuron-with-dendrites-synapse-telodendria-axon-schwa-image568944637.html
Motor neuron. Structure and anatomy of a efferent neuron. Close-up of a Muscle fiber, and motoneuron with Dendrites, Synapse, Telodendria, Axon, Schwa Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-structure-and-anatomy-of-a-efferent-neuron-close-up-of-a-muscle-fiber-and-motoneuron-with-dendrites-synapse-telodendria-axon-schwa-image568944637.htmlRF2T1HJK9–Motor neuron. Structure and anatomy of a efferent neuron. Close-up of a Muscle fiber, and motoneuron with Dendrites, Synapse, Telodendria, Axon, Schwa
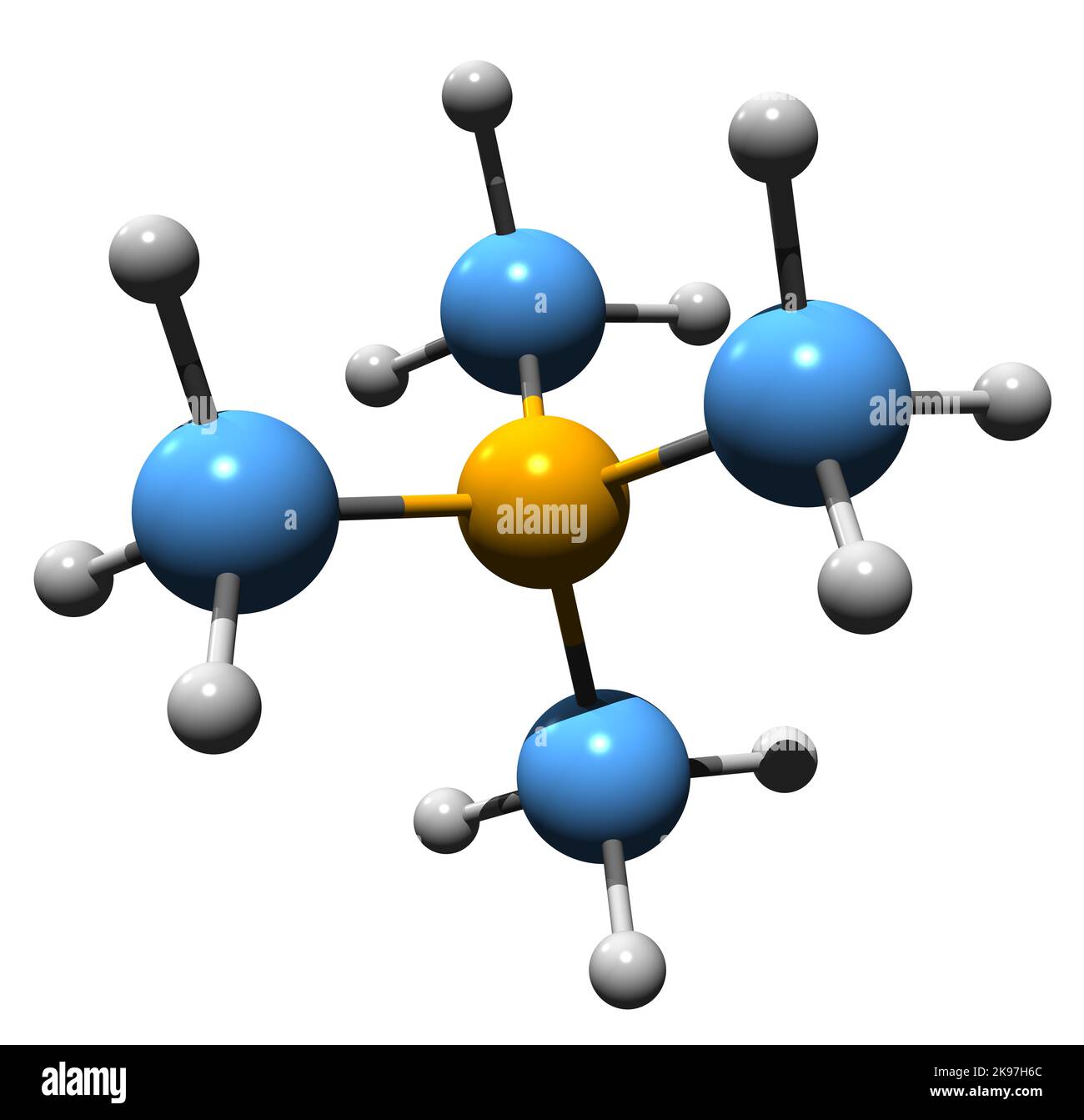 3D image of Tetramethylammonium hydroxide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of trimethylmethanaminium hydroxide TMAH isolated on white b Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-tetramethylammonium-hydroxide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-trimethylmethanaminium-hydroxide-tmah-isolated-on-white-b-image487589380.html
3D image of Tetramethylammonium hydroxide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of trimethylmethanaminium hydroxide TMAH isolated on white b Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-tetramethylammonium-hydroxide-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-trimethylmethanaminium-hydroxide-tmah-isolated-on-white-b-image487589380.htmlRF2K97H6C–3D image of Tetramethylammonium hydroxide skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of trimethylmethanaminium hydroxide TMAH isolated on white b
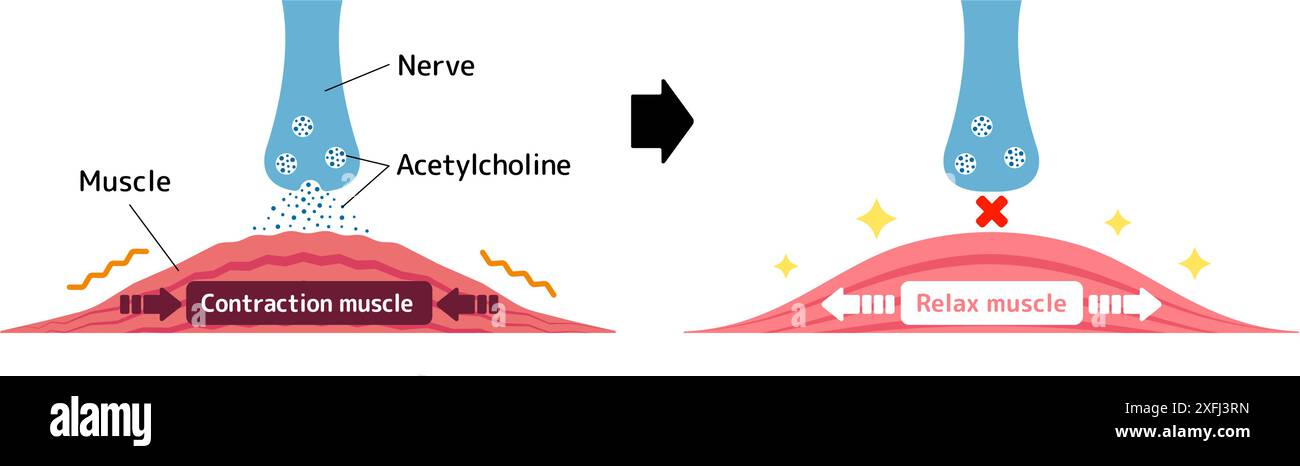 Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980873.html
Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980873.htmlRF2XFJ3RN–Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration.
 3D image of Curare skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of alkaloid arrow poison isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-curare-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-alkaloid-arrow-poison-isolated-on-white-background-image491509174.html
3D image of Curare skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of alkaloid arrow poison isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-curare-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-alkaloid-arrow-poison-isolated-on-white-background-image491509174.htmlRF2KFJ4Y2–3D image of Curare skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of alkaloid arrow poison isolated on white background
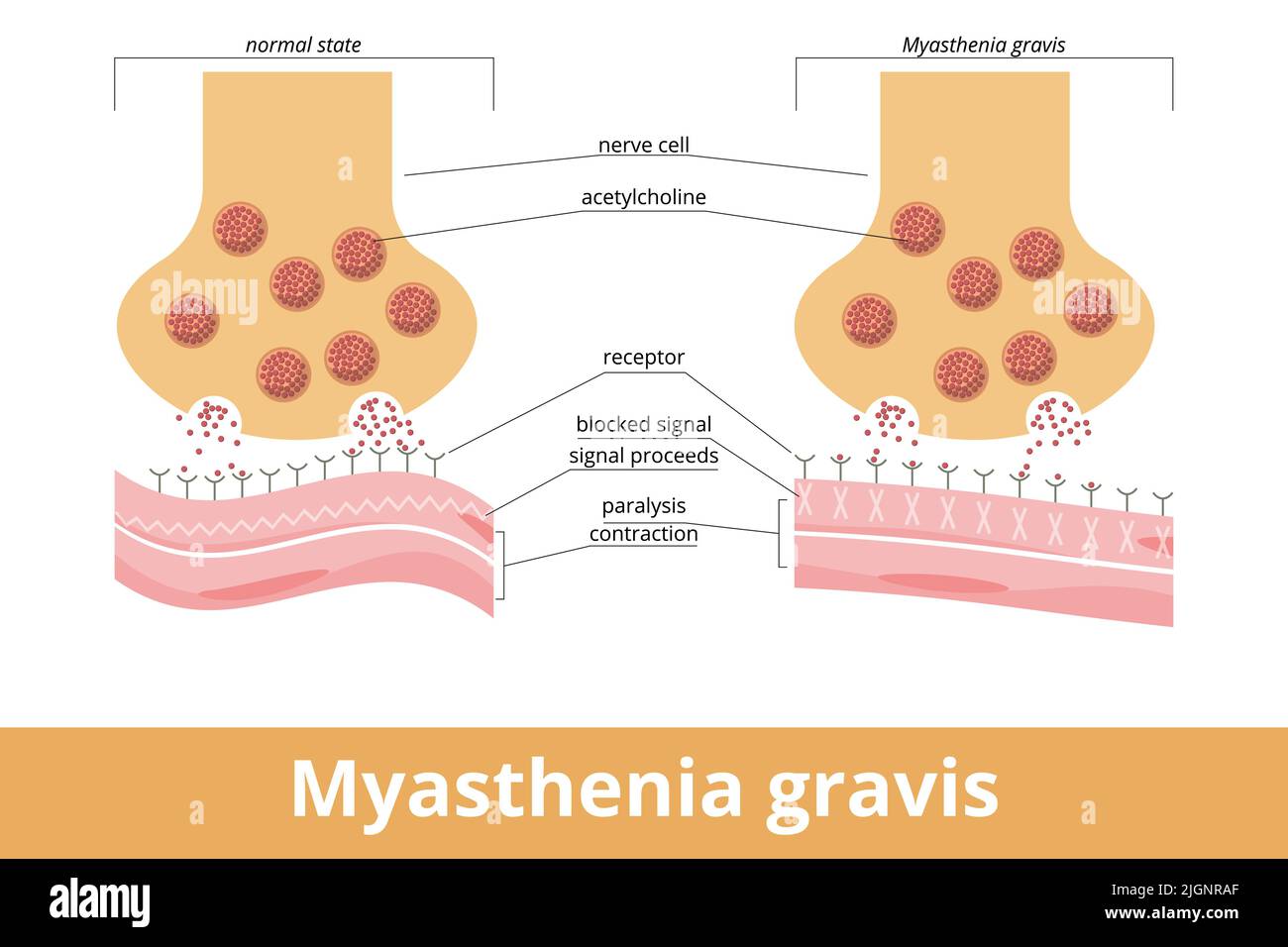 Myasthenia gravis. An autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction when antibodies block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/myasthenia-gravis-an-autoimmune-disease-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-when-antibodies-block-or-destroy-nicotinic-acetylcholine-receptors-achr-image474993751.html
Myasthenia gravis. An autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction when antibodies block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/myasthenia-gravis-an-autoimmune-disease-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-when-antibodies-block-or-destroy-nicotinic-acetylcholine-receptors-achr-image474993751.htmlRF2JGNRAF–Myasthenia gravis. An autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction when antibodies block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR)
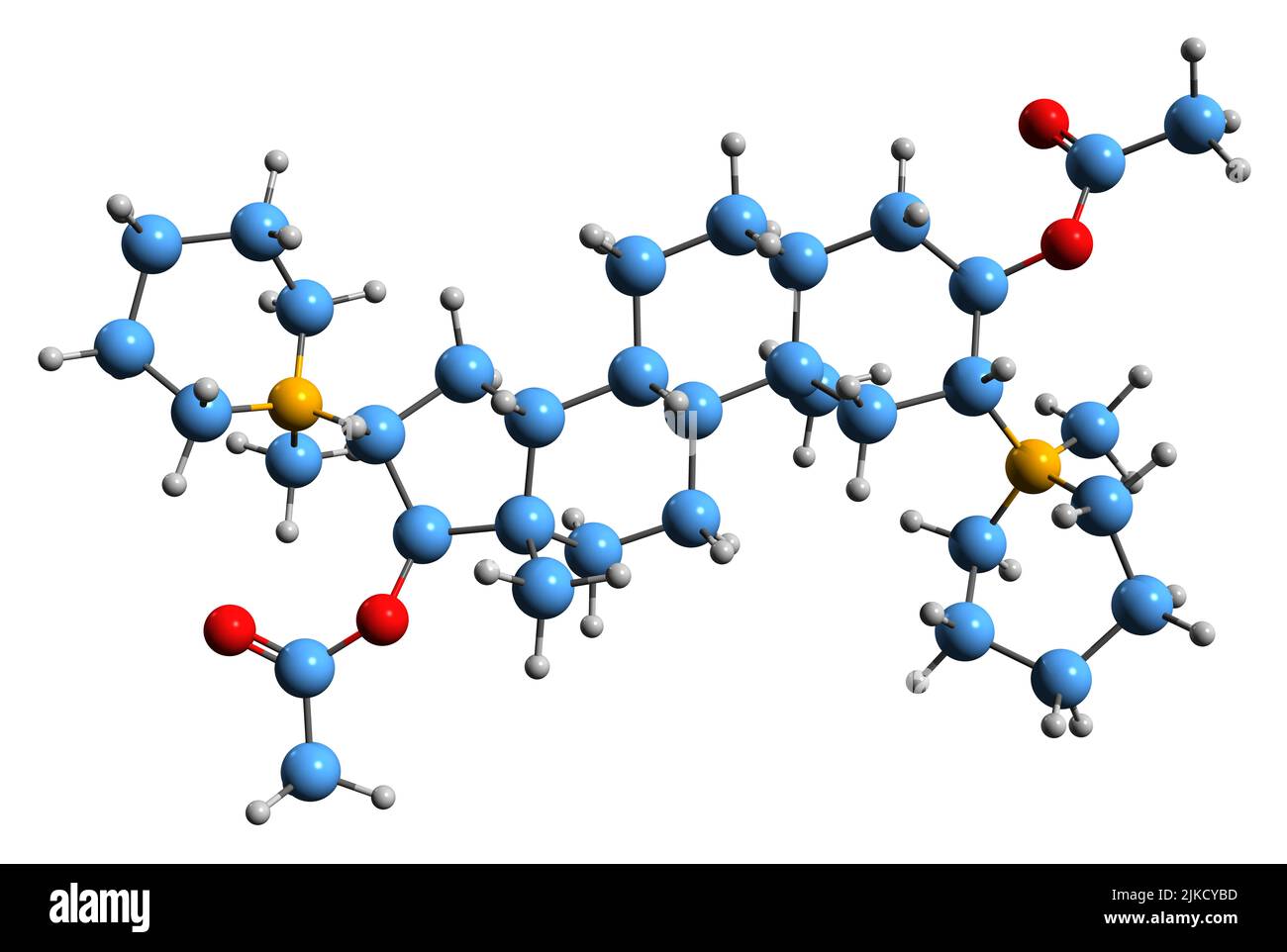 3D image of Pancuronium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid muscle relaxant isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-pancuronium-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-muscle-relaxant-isolated-on-white-background-image476643313.html
3D image of Pancuronium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid muscle relaxant isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-pancuronium-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-muscle-relaxant-isolated-on-white-background-image476643313.htmlRF2JKCYBD–3D image of Pancuronium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid muscle relaxant isolated on white background
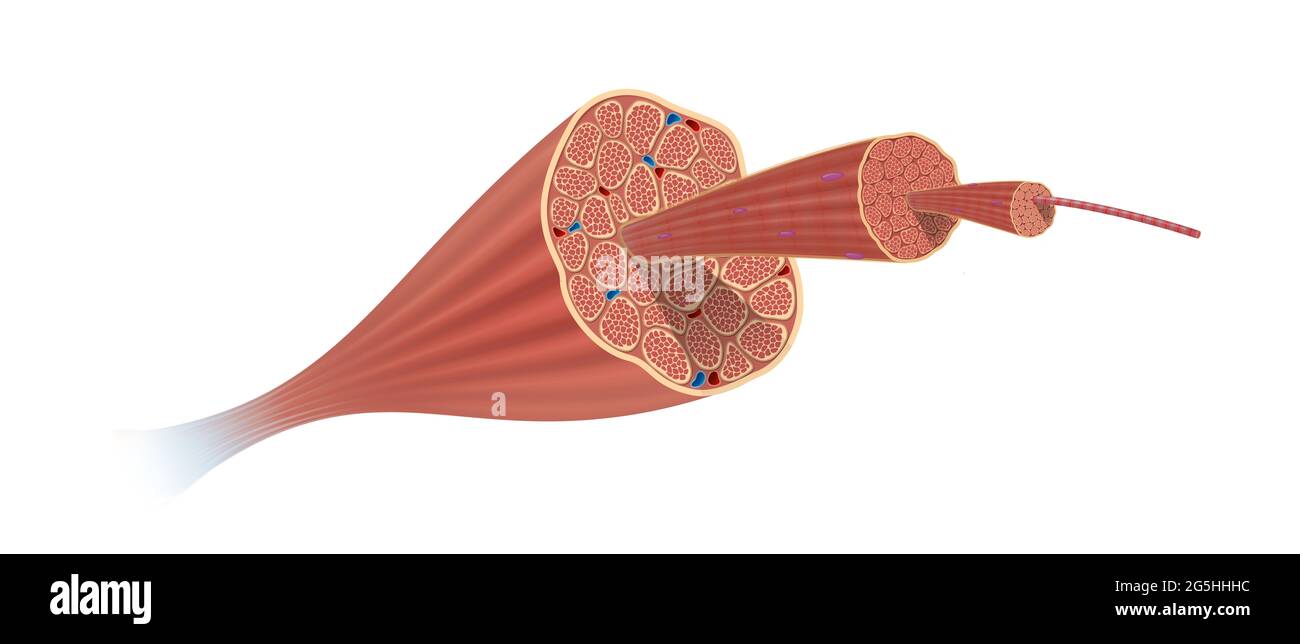 Structure Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-skeletal-muscle-anatomy-image433719480.html
Structure Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/structure-skeletal-muscle-anatomy-image433719480.htmlRF2G5HHHC–Structure Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
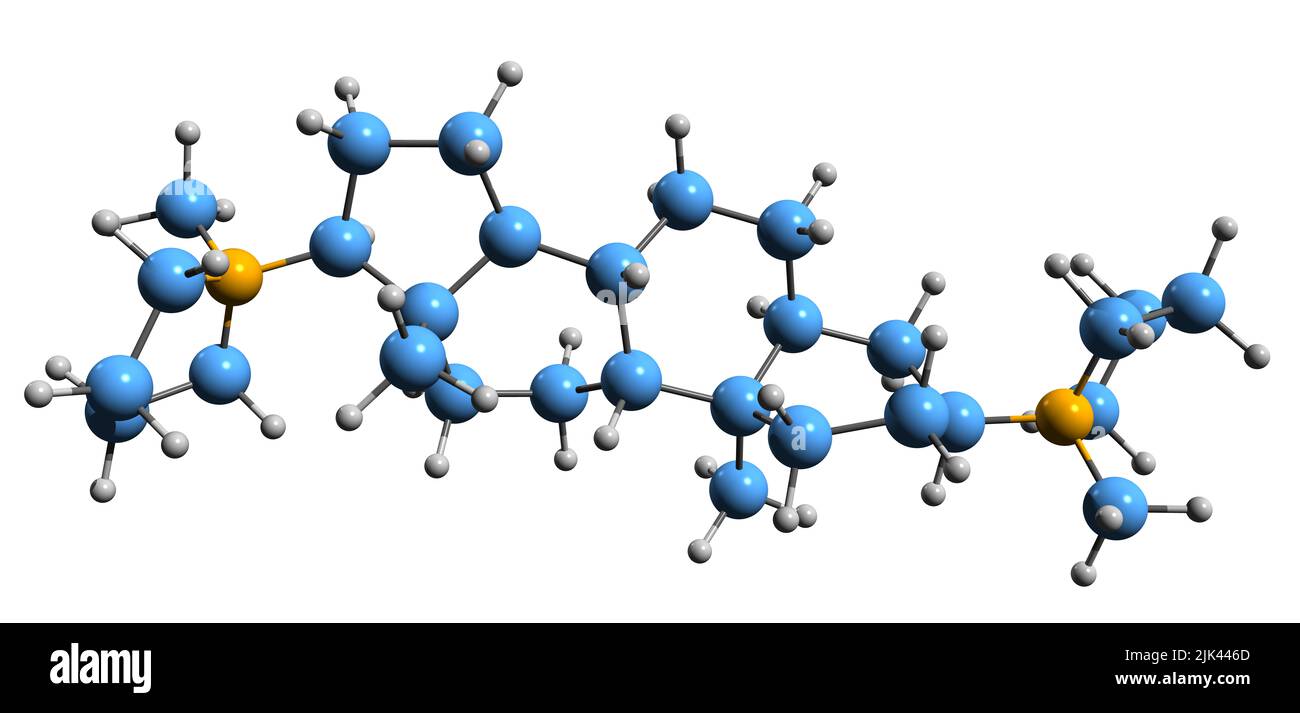 3D image of Dipyrandium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-dipyrandium-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-isolated-on-white-background-image476449525.html
3D image of Dipyrandium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-dipyrandium-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-aminosteroid-isolated-on-white-background-image476449525.htmlRF2JK446D–3D image of Dipyrandium skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of aminosteroid isolated on white background
 An infographic template related to the neuromuscular junction, nerves, muscles, cells, and ions of the body with a dark red and yellow color scheme. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-infographic-template-related-to-the-neuromuscular-junction-nerves-muscles-cells-and-ions-of-the-body-with-a-dark-red-and-yellow-color-scheme-image429972727.html
An infographic template related to the neuromuscular junction, nerves, muscles, cells, and ions of the body with a dark red and yellow color scheme. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-infographic-template-related-to-the-neuromuscular-junction-nerves-muscles-cells-and-ions-of-the-body-with-a-dark-red-and-yellow-color-scheme-image429972727.htmlRF2FYEXGR–An infographic template related to the neuromuscular junction, nerves, muscles, cells, and ions of the body with a dark red and yellow color scheme.
 Concept of Myasthenia Gravis write on sticky notes isolated on Wooden Table. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/concept-of-myasthenia-gravis-write-on-sticky-notes-isolated-on-wooden-table-image551040291.html
Concept of Myasthenia Gravis write on sticky notes isolated on Wooden Table. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/concept-of-myasthenia-gravis-write-on-sticky-notes-isolated-on-wooden-table-image551040291.htmlRF2R0E1EB–Concept of Myasthenia Gravis write on sticky notes isolated on Wooden Table.
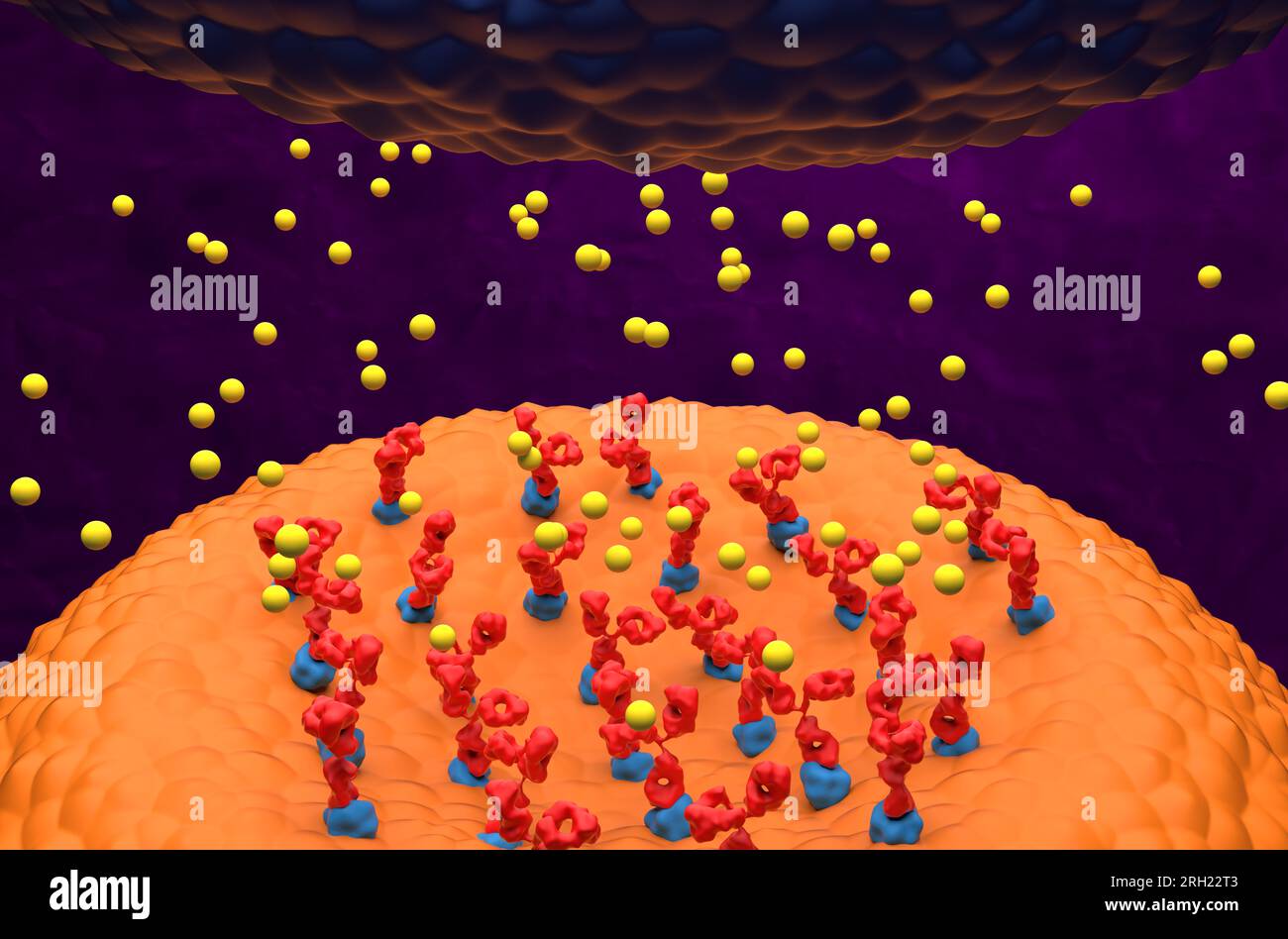 Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration closeup view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/autoantibodies-bond-to-receptor-achr-blocking-the-acetylcholine-transmitters-in-myasthenia-gravis-mg-3d-illustration-closeup-view-image561227075.html
Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration closeup view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/autoantibodies-bond-to-receptor-achr-blocking-the-acetylcholine-transmitters-in-myasthenia-gravis-mg-3d-illustration-closeup-view-image561227075.htmlRF2RH22T3–Autoantibodies bond to receptor (achr) blocking the acetylcholine transmitters in Myasthenia gravis (MG) - 3d illustration closeup view
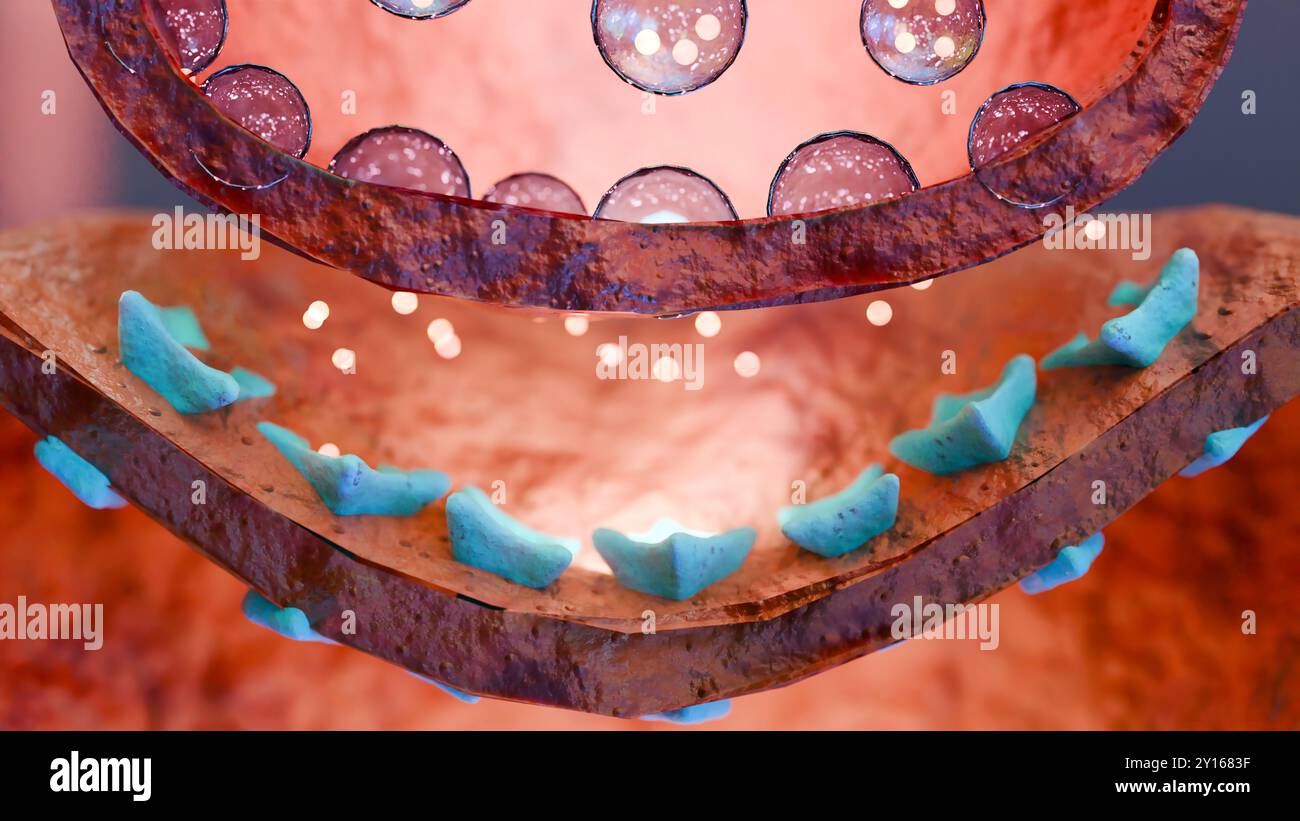 Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620325987.html
Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620325987.htmlRM2Y1683F–Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No
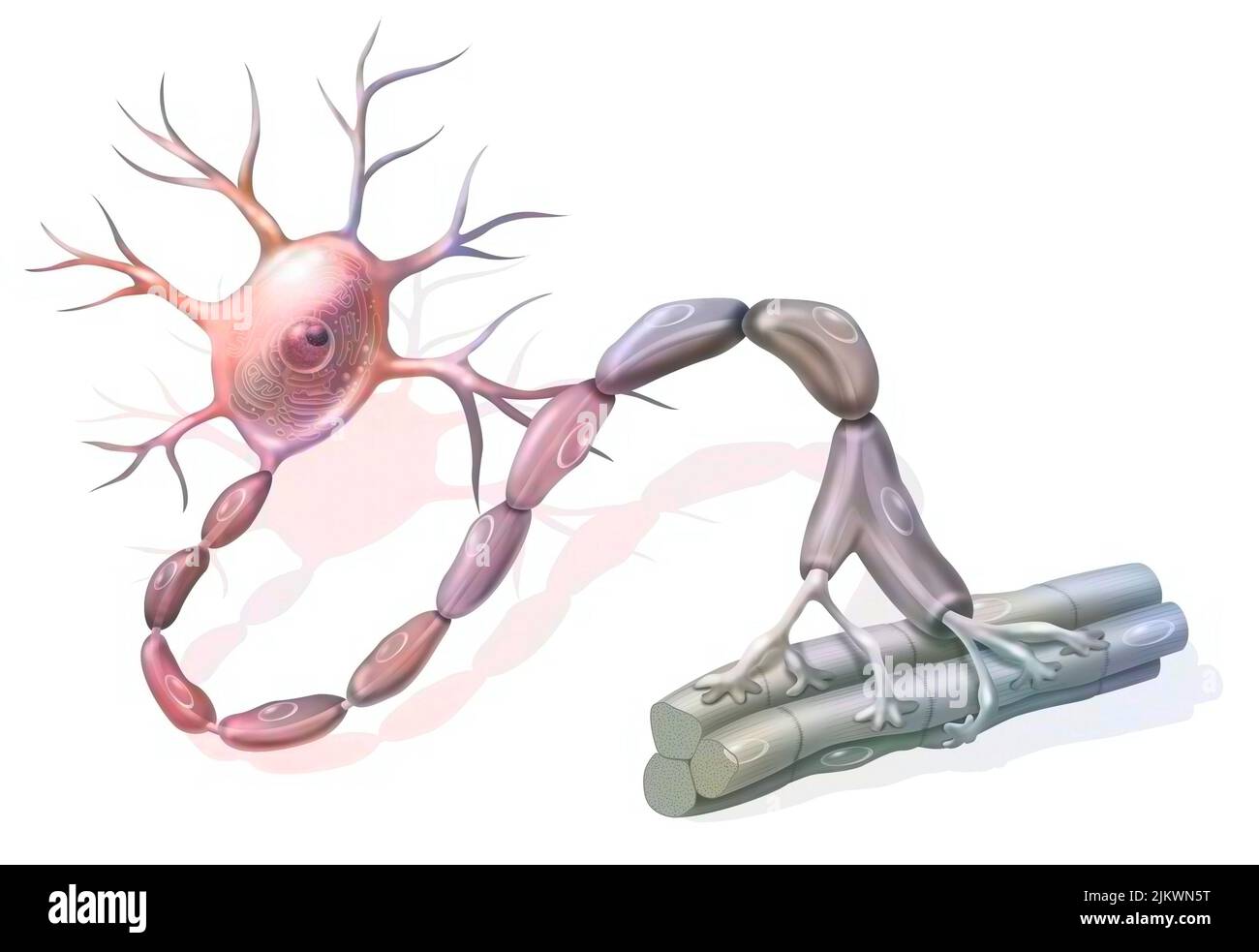 Motor neuron: neuron in contact with muscle fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-neuron-in-contact-with-muscle-fibers-image476923828.html
Motor neuron: neuron in contact with muscle fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-neuron-in-contact-with-muscle-fibers-image476923828.htmlRF2JKWN5T–Motor neuron: neuron in contact with muscle fibers.
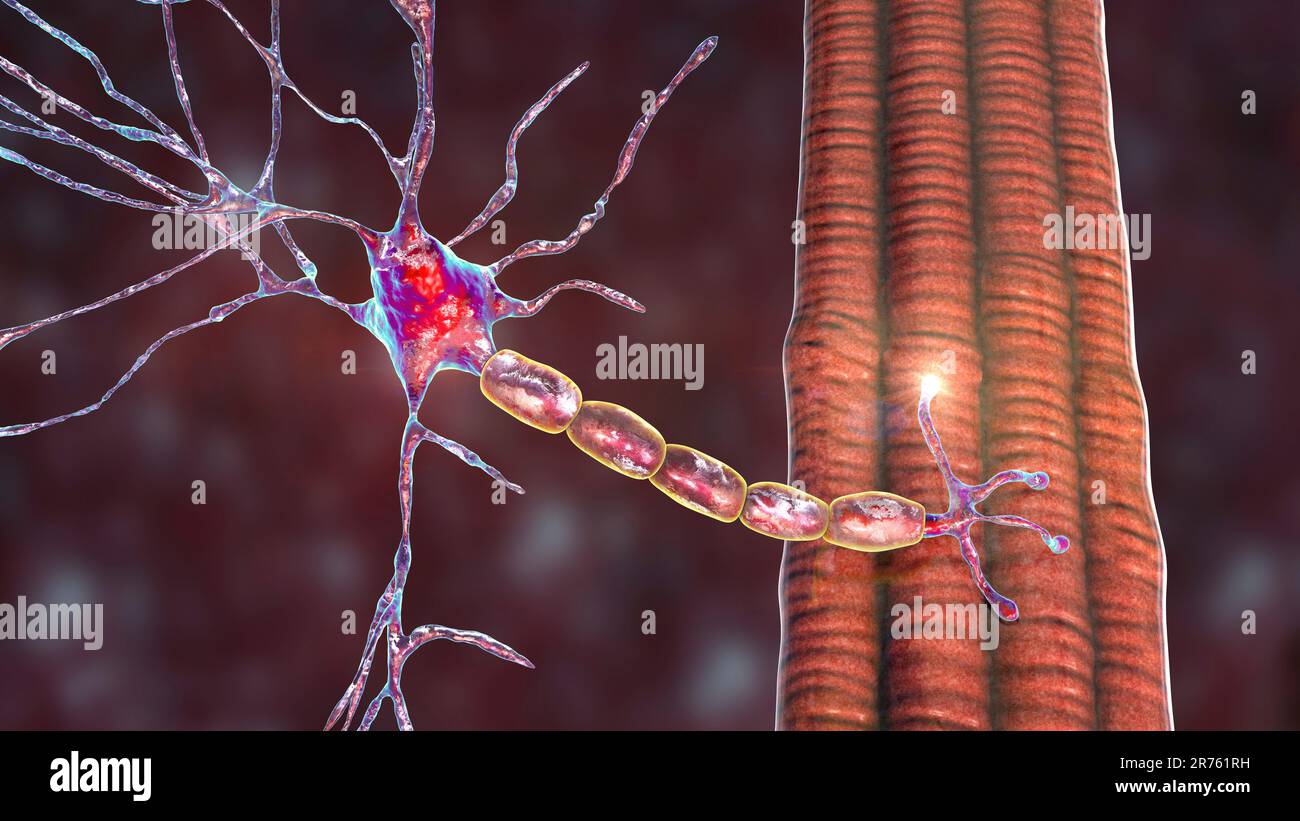 Motor neuron connecting to a muscle fiber, computer illustration. A neuromuscular junction allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-connecting-to-a-muscle-fiber-computer-illustration-a-neuromuscular-junction-allows-the-motor-neuron-to-transmit-a-signal-to-the-muscle-image555167525.html
Motor neuron connecting to a muscle fiber, computer illustration. A neuromuscular junction allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/motor-neuron-connecting-to-a-muscle-fiber-computer-illustration-a-neuromuscular-junction-allows-the-motor-neuron-to-transmit-a-signal-to-the-muscle-image555167525.htmlRF2R761RH–Motor neuron connecting to a muscle fiber, computer illustration. A neuromuscular junction allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle
 SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sensorimotor-system-image62636550.html
SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/sensorimotor-system-image62636550.htmlRMDHW9FJ–SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM
 Microelectrode array (MEA) with cell guide. The NMJ model is established on a MEA surface to enable spatially localized detection of neuromuscular signals resulting from the firing of the synapse. The cell guide mounted on the array is part of the process of growing the muscle and nerve cells with the right anatomical organization. (DTRA image) Multiwell system with LED: The NMJ is established in culture dishes like this to start development of a high throughput NMJ model system. For this prototype, a custom-made array of LED lights allows multiple NMJ setups to simultaneously be stimulated w Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/microelectrode-array-mea-with-cell-guide-the-nmj-model-is-established-on-a-mea-surface-to-enable-spatially-localized-detection-of-neuromuscular-signals-resulting-from-the-firing-of-the-synapse-the-cell-guide-mounted-on-the-array-is-part-of-the-process-of-growing-the-muscle-and-nerve-cells-with-the-right-anatomical-organization-dtra-image-multiwell-system-with-led-the-nmj-is-established-in-culture-dishes-like-this-to-start-development-of-a-high-throughput-nmj-model-system-for-this-prototype-a-custom-made-array-of-led-lights-allows-multiple-nmj-setups-to-simultaneously-be-stimulated-w-image442543912.html
Microelectrode array (MEA) with cell guide. The NMJ model is established on a MEA surface to enable spatially localized detection of neuromuscular signals resulting from the firing of the synapse. The cell guide mounted on the array is part of the process of growing the muscle and nerve cells with the right anatomical organization. (DTRA image) Multiwell system with LED: The NMJ is established in culture dishes like this to start development of a high throughput NMJ model system. For this prototype, a custom-made array of LED lights allows multiple NMJ setups to simultaneously be stimulated w Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/microelectrode-array-mea-with-cell-guide-the-nmj-model-is-established-on-a-mea-surface-to-enable-spatially-localized-detection-of-neuromuscular-signals-resulting-from-the-firing-of-the-synapse-the-cell-guide-mounted-on-the-array-is-part-of-the-process-of-growing-the-muscle-and-nerve-cells-with-the-right-anatomical-organization-dtra-image-multiwell-system-with-led-the-nmj-is-established-in-culture-dishes-like-this-to-start-development-of-a-high-throughput-nmj-model-system-for-this-prototype-a-custom-made-array-of-led-lights-allows-multiple-nmj-setups-to-simultaneously-be-stimulated-w-image442543912.htmlRM2GKYH7M–Microelectrode array (MEA) with cell guide. The NMJ model is established on a MEA surface to enable spatially localized detection of neuromuscular signals resulting from the firing of the synapse. The cell guide mounted on the array is part of the process of growing the muscle and nerve cells with the right anatomical organization. (DTRA image) Multiwell system with LED: The NMJ is established in culture dishes like this to start development of a high throughput NMJ model system. For this prototype, a custom-made array of LED lights allows multiple NMJ setups to simultaneously be stimulated w
 Pompe disease is a rare hereditary disease characterized by the deficiency of an enzyme called acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA). One of the main features of Pompe disease is the progressive breakdown of communications between nerve and muscle cells. This image is of a leg muscle (tibialis anterior) from an adult mouse model of Pompe disease. Nerve cells (green) and cellular nerve-muscle communication sites, called neuromuscular junctions, (red) are fluorescently labeled to observe the continued deterioration of neuromuscular junctions. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pompe-disease-is-a-rare-hereditary-disease-characterized-by-the-deficiency-of-an-enzyme-called-acid-alpha-glucosidase-gaa-one-of-the-main-features-of-pompe-disease-is-the-progressive-breakdown-of-communications-between-nerve-and-muscle-cells-this-image-is-of-a-leg-muscle-tibialis-anterior-from-an-adult-mouse-model-of-pompe-disease-nerve-cells-green-and-cellular-nerve-muscle-communication-sites-called-neuromuscular-junctions-red-are-fluorescently-labeled-to-observe-the-continued-deterioration-of-neuromuscular-junctions-image476706896.html
Pompe disease is a rare hereditary disease characterized by the deficiency of an enzyme called acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA). One of the main features of Pompe disease is the progressive breakdown of communications between nerve and muscle cells. This image is of a leg muscle (tibialis anterior) from an adult mouse model of Pompe disease. Nerve cells (green) and cellular nerve-muscle communication sites, called neuromuscular junctions, (red) are fluorescently labeled to observe the continued deterioration of neuromuscular junctions. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pompe-disease-is-a-rare-hereditary-disease-characterized-by-the-deficiency-of-an-enzyme-called-acid-alpha-glucosidase-gaa-one-of-the-main-features-of-pompe-disease-is-the-progressive-breakdown-of-communications-between-nerve-and-muscle-cells-this-image-is-of-a-leg-muscle-tibialis-anterior-from-an-adult-mouse-model-of-pompe-disease-nerve-cells-green-and-cellular-nerve-muscle-communication-sites-called-neuromuscular-junctions-red-are-fluorescently-labeled-to-observe-the-continued-deterioration-of-neuromuscular-junctions-image476706896.htmlRM2JKFTE8–Pompe disease is a rare hereditary disease characterized by the deficiency of an enzyme called acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA). One of the main features of Pompe disease is the progressive breakdown of communications between nerve and muscle cells. This image is of a leg muscle (tibialis anterior) from an adult mouse model of Pompe disease. Nerve cells (green) and cellular nerve-muscle communication sites, called neuromuscular junctions, (red) are fluorescently labeled to observe the continued deterioration of neuromuscular junctions.
 Golgi Tendon Organ. It is a sensory organ that perceives tendon or muscle strength. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/golgi-tendon-organ-it-is-a-sensory-organ-that-perceives-tendon-or-muscle-strength-image626642117.html
Golgi Tendon Organ. It is a sensory organ that perceives tendon or muscle strength. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/golgi-tendon-organ-it-is-a-sensory-organ-that-perceives-tendon-or-muscle-strength-image626642117.htmlRF2YBE0BH–Golgi Tendon Organ. It is a sensory organ that perceives tendon or muscle strength.
 Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image442065608.html
Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image442065608.htmlRF2GK5R5C–Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body.
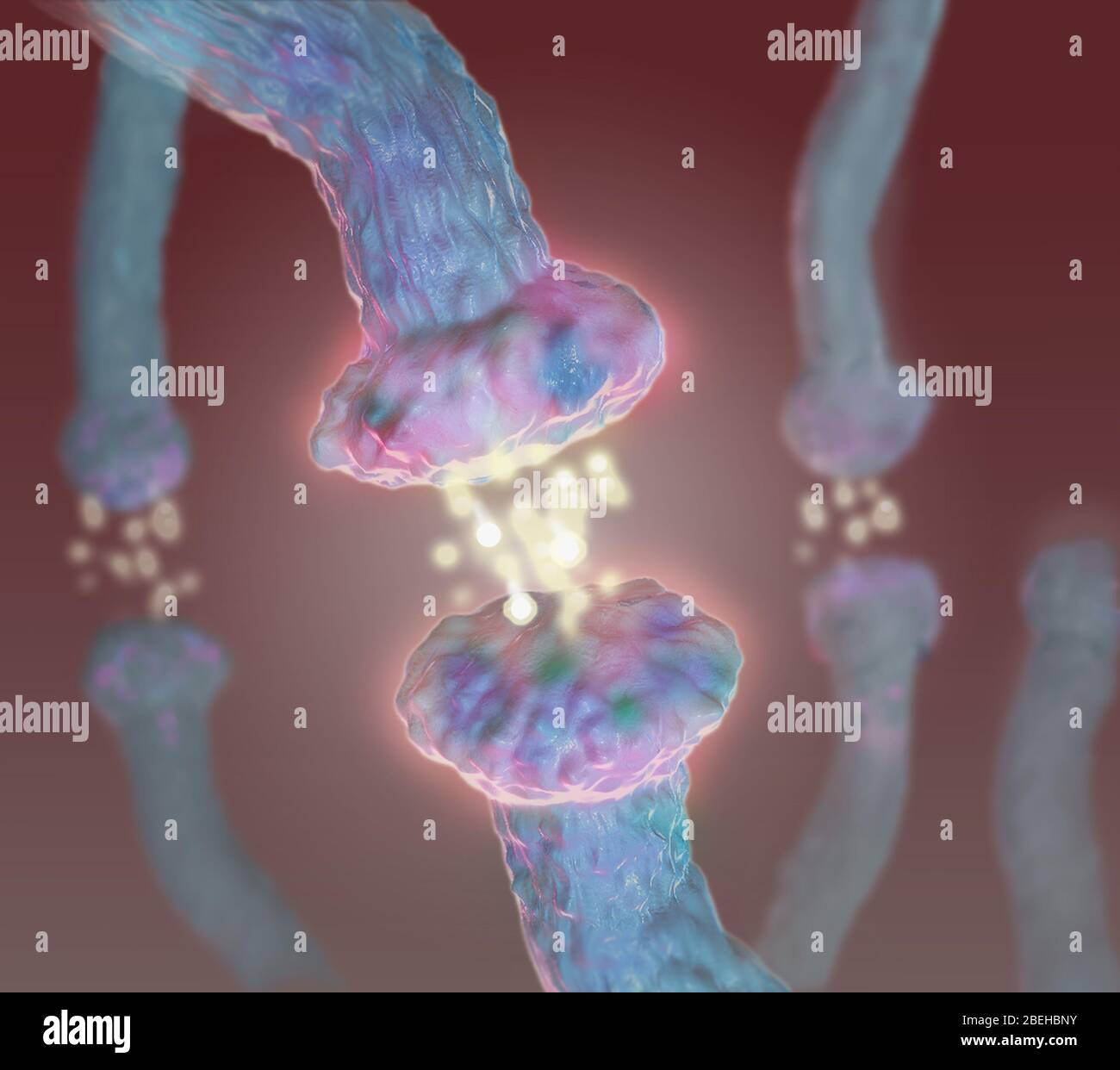 Neurotransmitters, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neurotransmitters-illustration-image353194967.html
Neurotransmitters, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neurotransmitters-illustration-image353194967.htmlRM2BEHBNY–Neurotransmitters, Illustration
RF2H5R7N3–Neuromuscular linear icon
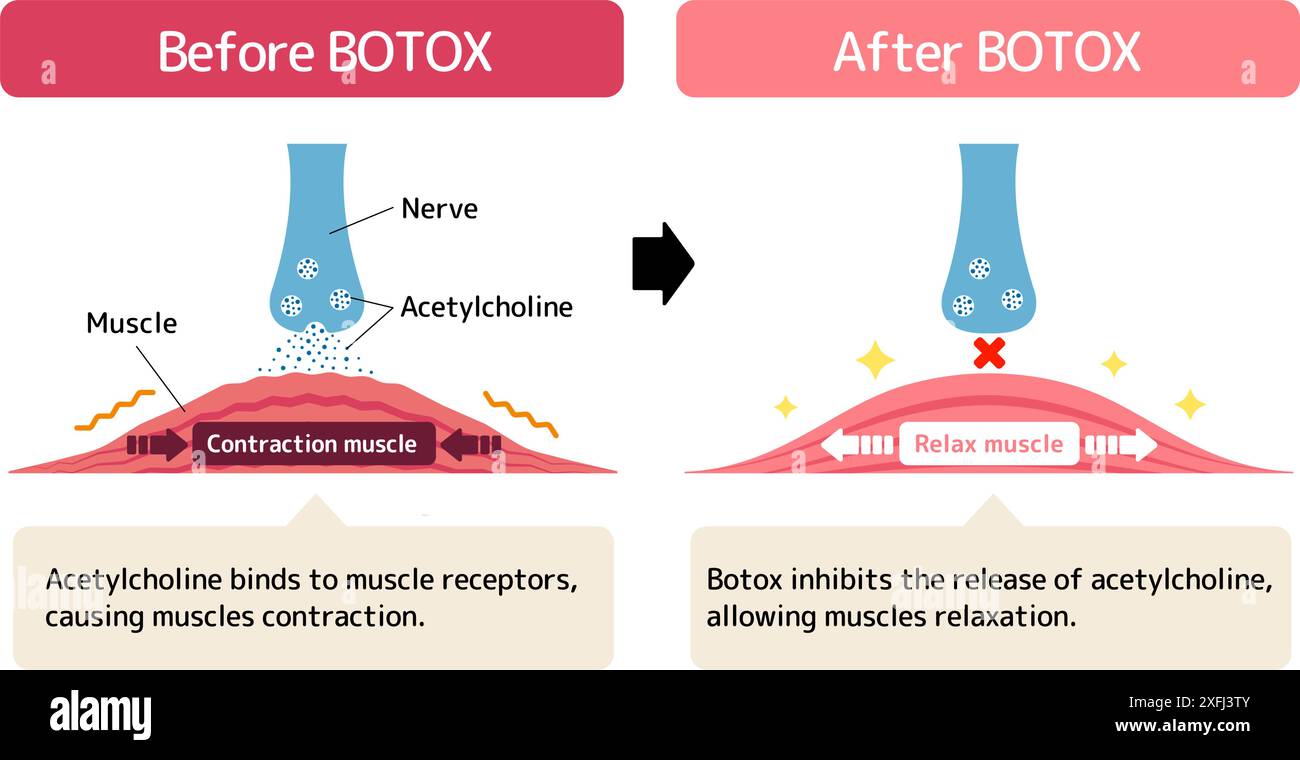 Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980907.html
Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980907.htmlRF2XFJ3TY–Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration.
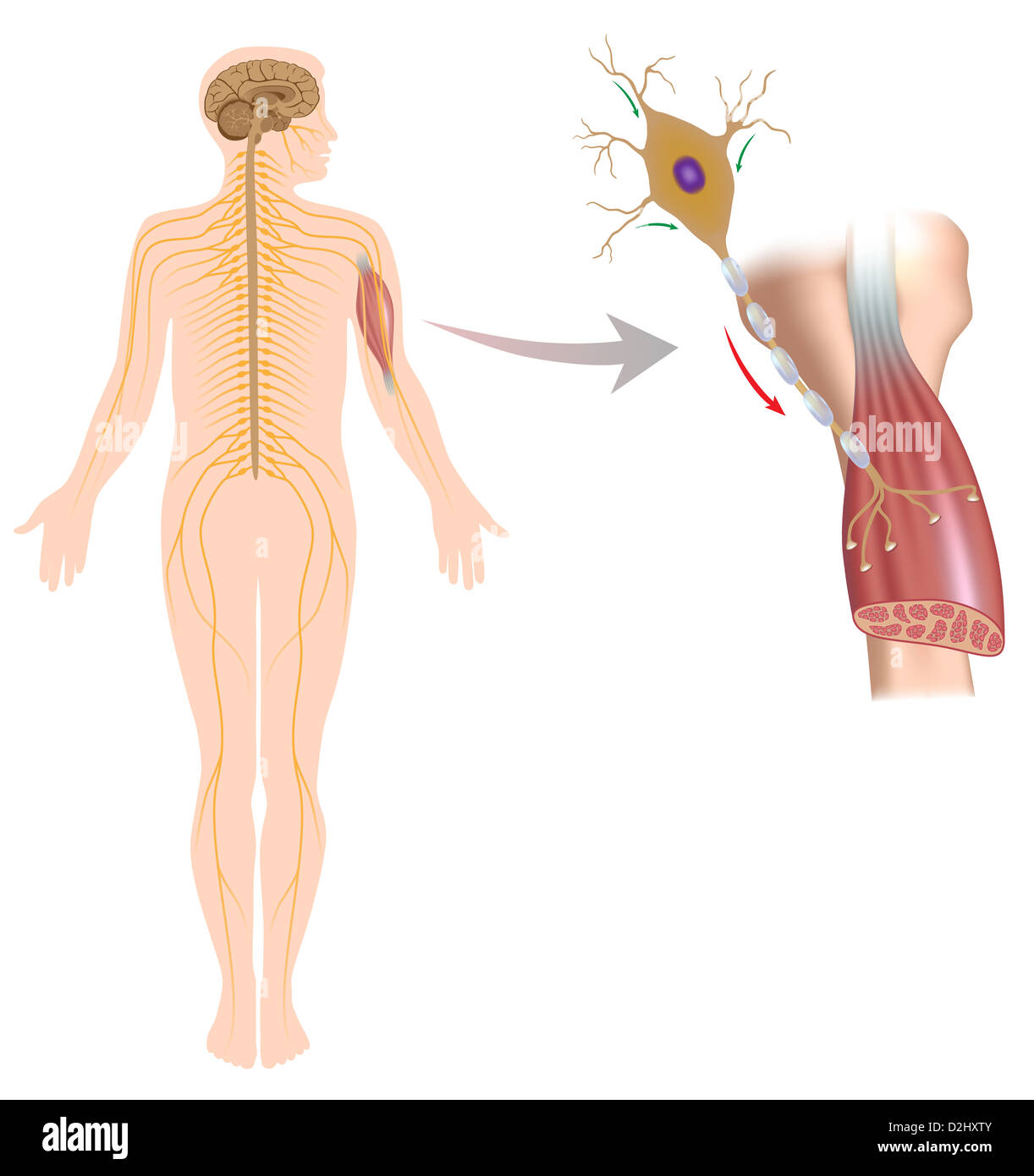 Motor neuron controls muscle movement Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-motor-neuron-controls-muscle-movement-53254683.html
Motor neuron controls muscle movement Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-motor-neuron-controls-muscle-movement-53254683.htmlRFD2HXTY–Motor neuron controls muscle movement
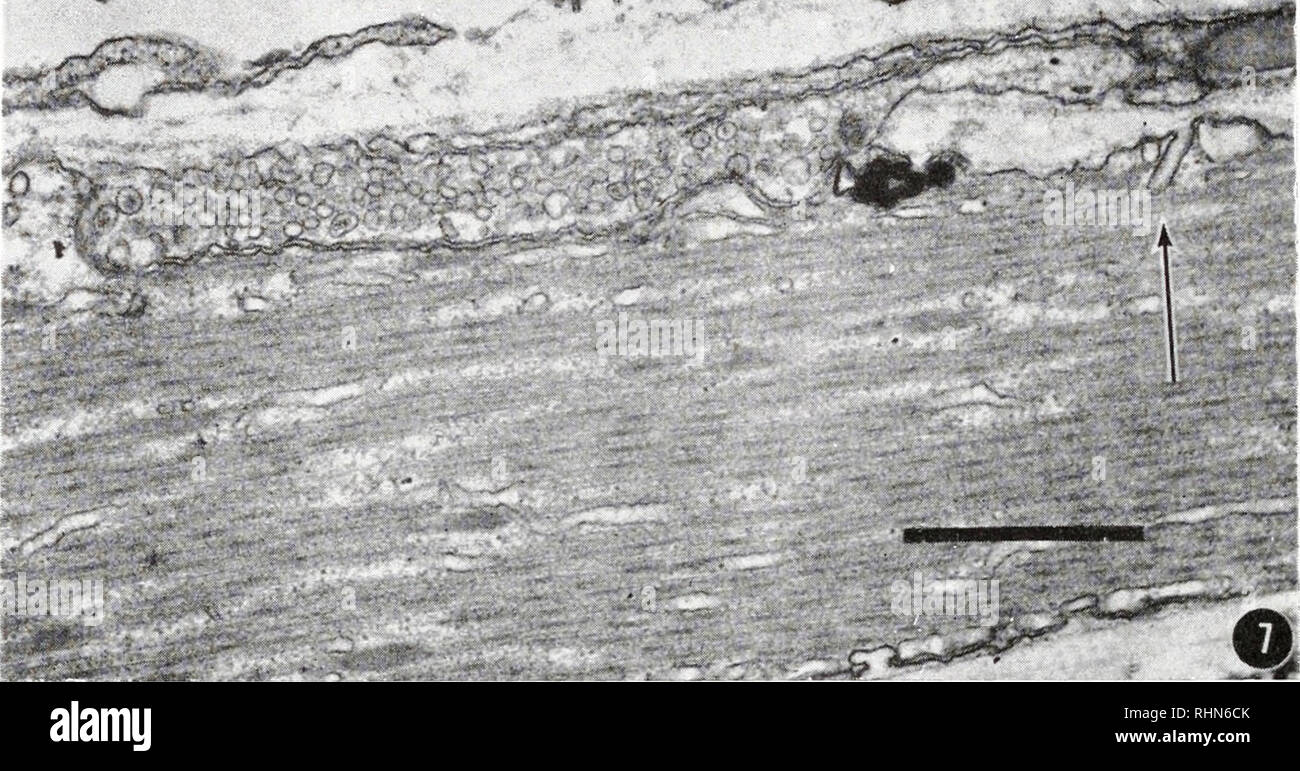 . The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. R. B. HILL AND J. W. SANGER . •«•» •.' ,." -^. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. Please note that these images are extracted from sc Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-r-b-hill-and-j-w-sanger-quot-figure-7-the-initimate-juxtaposition-of-the-nerve-ending-and-muscle-cell-is-illustrated-here-a-sarcolemniic-tubule-is-also-clearly-pictured-arrow-scale-=10-micron-neuromuscular-junction-figs-7-8-9-the-muscle-cell-and-nerve-are-separated-by-a-gap-of-about-150-200-a-the-muscle-is-intimately-associated-with-the-nerve-ending-but-there-is-no-specialized-membrane-involution-in-the-junctional-area-such-r-ky-j-v-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-sc-image234649987.html
. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. R. B. HILL AND J. W. SANGER . •«•» •.' ,." -^. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. Please note that these images are extracted from sc Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-r-b-hill-and-j-w-sanger-quot-figure-7-the-initimate-juxtaposition-of-the-nerve-ending-and-muscle-cell-is-illustrated-here-a-sarcolemniic-tubule-is-also-clearly-pictured-arrow-scale-=10-micron-neuromuscular-junction-figs-7-8-9-the-muscle-cell-and-nerve-are-separated-by-a-gap-of-about-150-200-a-the-muscle-is-intimately-associated-with-the-nerve-ending-but-there-is-no-specialized-membrane-involution-in-the-junctional-area-such-r-ky-j-v-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-sc-image234649987.htmlRMRHN6CK–. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. R. B. HILL AND J. W. SANGER . •«•» •.' ,." -^. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. Please note that these images are extracted from sc
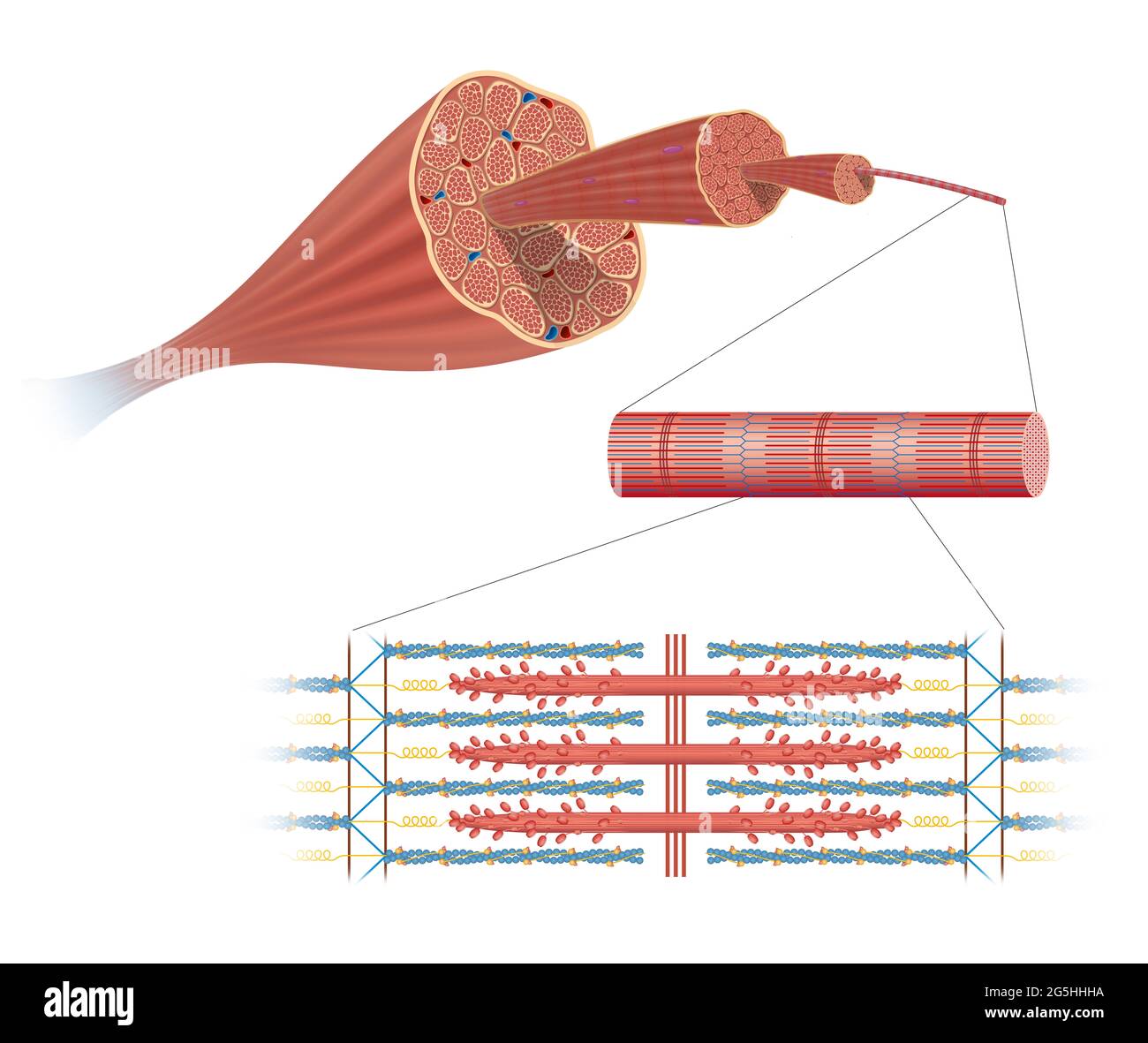 Illustration of Structure Skeletal Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-of-structure-skeletal-muscle-image433719478.html
Illustration of Structure Skeletal Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-of-structure-skeletal-muscle-image433719478.htmlRF2G5HHHA–Illustration of Structure Skeletal Muscle
 Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620326380.html
Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620326380.htmlRM2Y168HG–Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No
 Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image441937890.html
Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image441937890.htmlRF2GK0082–Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body.
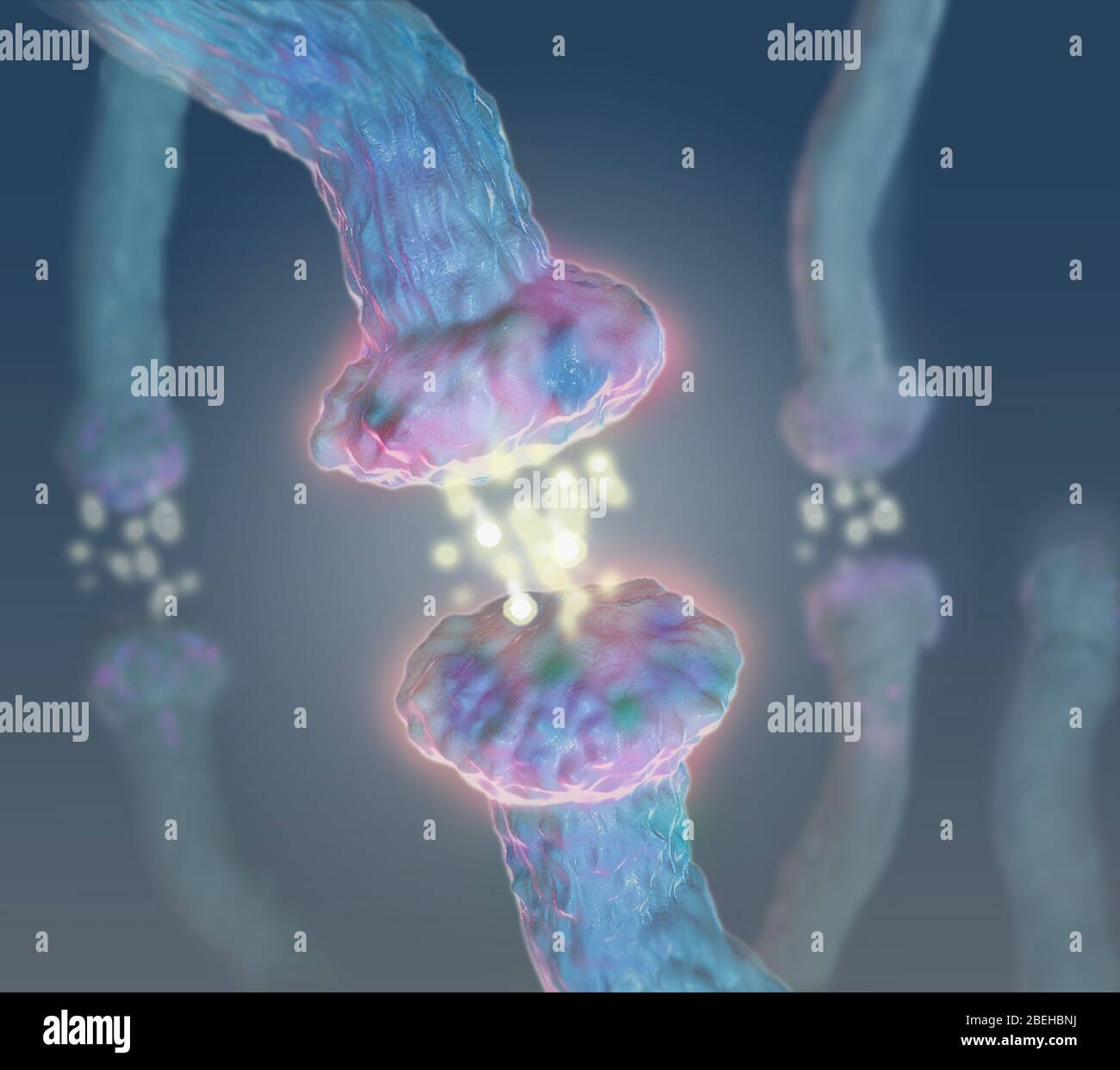 Neurotransmitters, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neurotransmitters-illustration-image353194958.html
Neurotransmitters, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neurotransmitters-illustration-image353194958.htmlRM2BEHBNJ–Neurotransmitters, Illustration
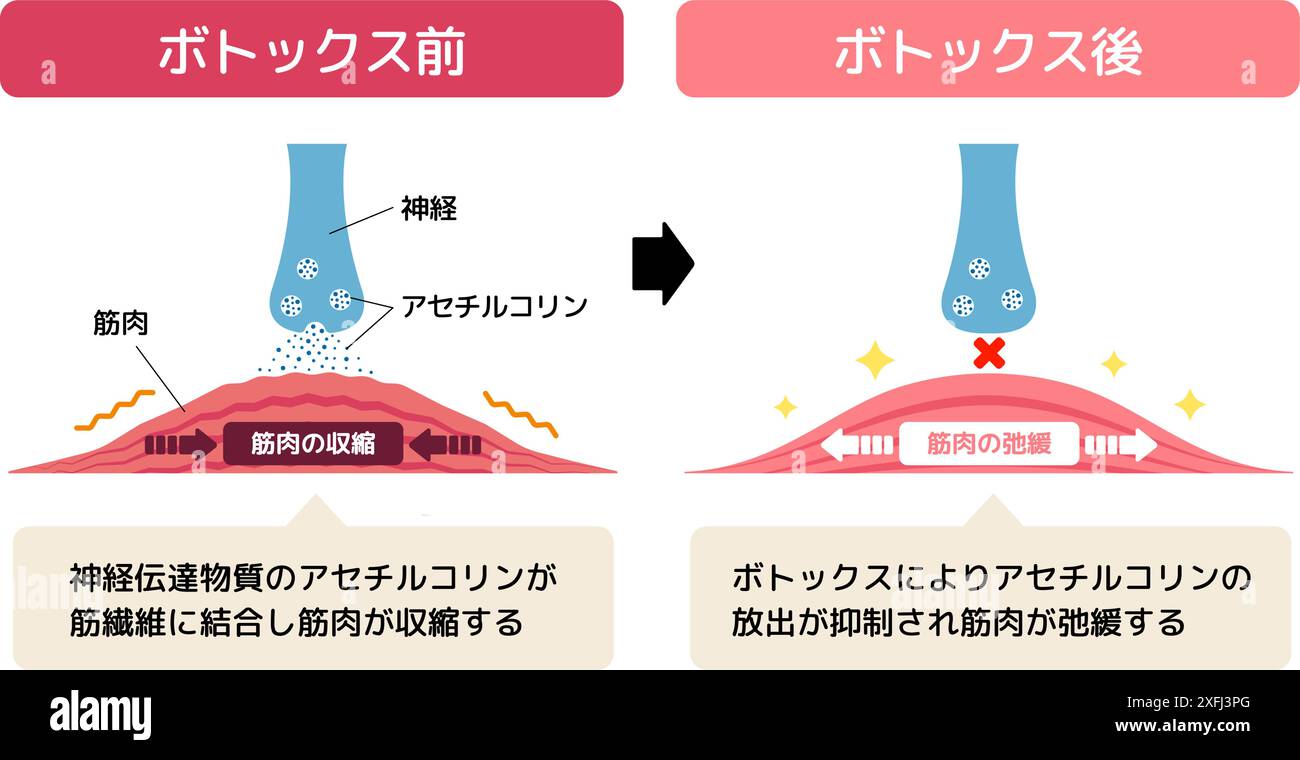 Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980840.html
Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980840.htmlRF2XFJ3PG–Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration.
 Skeletal muscle innervation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-skeletal-muscle-innervation-49341588.html
Skeletal muscle innervation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-skeletal-muscle-innervation-49341588.htmlRFCT7KKG–Skeletal muscle innervation
 . The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. Mongolia: velum stained with methylene blue: A., whole lobe; B., an enlarged area near the margin, ne represents nerve process; scales, 50 ^ in A, 10 /JL in B.. FIGURE 8. Mongolia: section of velar margin in the region of the marginal muscle band (see Fig. 10). Abbreviations are am, process of amoebocyte; ne, nerve process; mm, marginal muscle fiber; rm, radial muscle fiber. Arrow shows a neuromuscular junction; scale, 1.0 M-. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-figure-7-mongolia-velum-stained-with-methylene-blue-a-whole-lobe-b-an-enlarged-area-near-the-margin-ne-represents-nerve-process-scales-50-in-a-10-jl-in-b-figure-8-mongolia-section-of-velar-margin-in-the-region-of-the-marginal-muscle-band-see-fig-10-abbreviations-are-am-process-of-amoebocyte-ne-nerve-process-mm-marginal-muscle-fiber-rm-radial-muscle-fiber-arrow-shows-a-neuromuscular-junction-scale-10-m-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-d-image234637596.html
. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. Mongolia: velum stained with methylene blue: A., whole lobe; B., an enlarged area near the margin, ne represents nerve process; scales, 50 ^ in A, 10 /JL in B.. FIGURE 8. Mongolia: section of velar margin in the region of the marginal muscle band (see Fig. 10). Abbreviations are am, process of amoebocyte; ne, nerve process; mm, marginal muscle fiber; rm, radial muscle fiber. Arrow shows a neuromuscular junction; scale, 1.0 M-. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-figure-7-mongolia-velum-stained-with-methylene-blue-a-whole-lobe-b-an-enlarged-area-near-the-margin-ne-represents-nerve-process-scales-50-in-a-10-jl-in-b-figure-8-mongolia-section-of-velar-margin-in-the-region-of-the-marginal-muscle-band-see-fig-10-abbreviations-are-am-process-of-amoebocyte-ne-nerve-process-mm-marginal-muscle-fiber-rm-radial-muscle-fiber-arrow-shows-a-neuromuscular-junction-scale-10-m-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-d-image234637596.htmlRMRHMJJ4–. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. Mongolia: velum stained with methylene blue: A., whole lobe; B., an enlarged area near the margin, ne represents nerve process; scales, 50 ^ in A, 10 /JL in B.. FIGURE 8. Mongolia: section of velar margin in the region of the marginal muscle band (see Fig. 10). Abbreviations are am, process of amoebocyte; ne, nerve process; mm, marginal muscle fiber; rm, radial muscle fiber. Arrow shows a neuromuscular junction; scale, 1.0 M-. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been d
 Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620326246.html
Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620326246.htmlRM2Y168CP–Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No
 Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image441937963.html
Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image441937963.htmlRF2GK00AK–Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body.
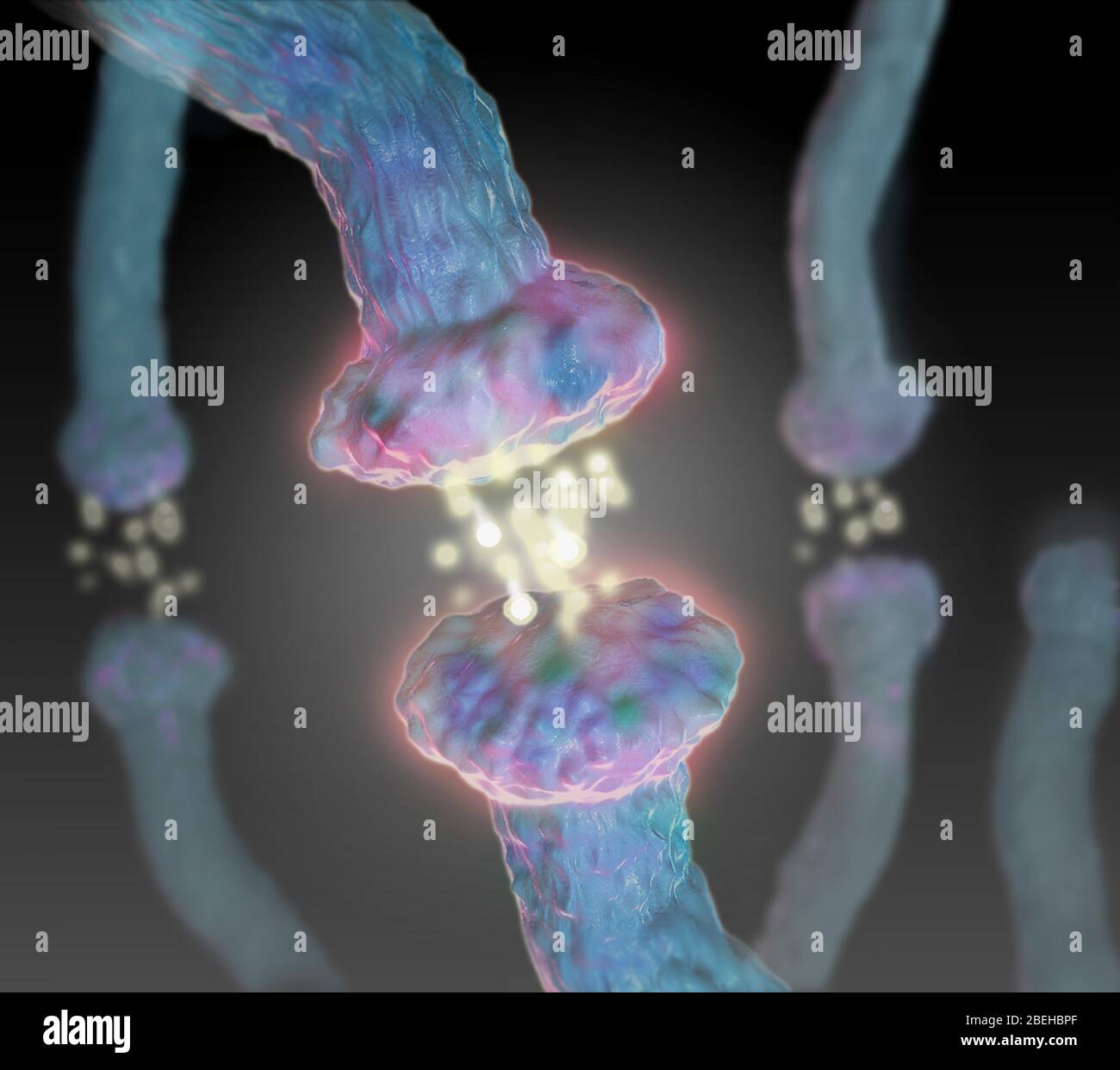 Neurotransmitters, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neurotransmitters-illustration-image353194983.html
Neurotransmitters, Illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neurotransmitters-illustration-image353194983.htmlRM2BEHBPF–Neurotransmitters, Illustration
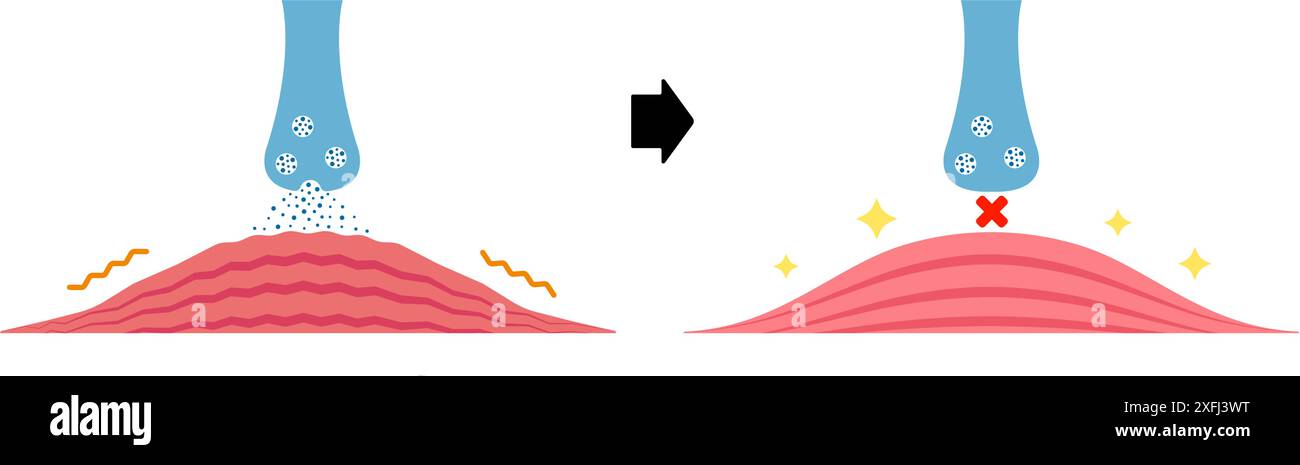 Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980932.html
Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/mechanism-of-muscle-relaxation-by-botox-vector-illustration-image611980932.htmlRF2XFJ3WT–Mechanism of muscle relaxation by Botox. Vector illustration.
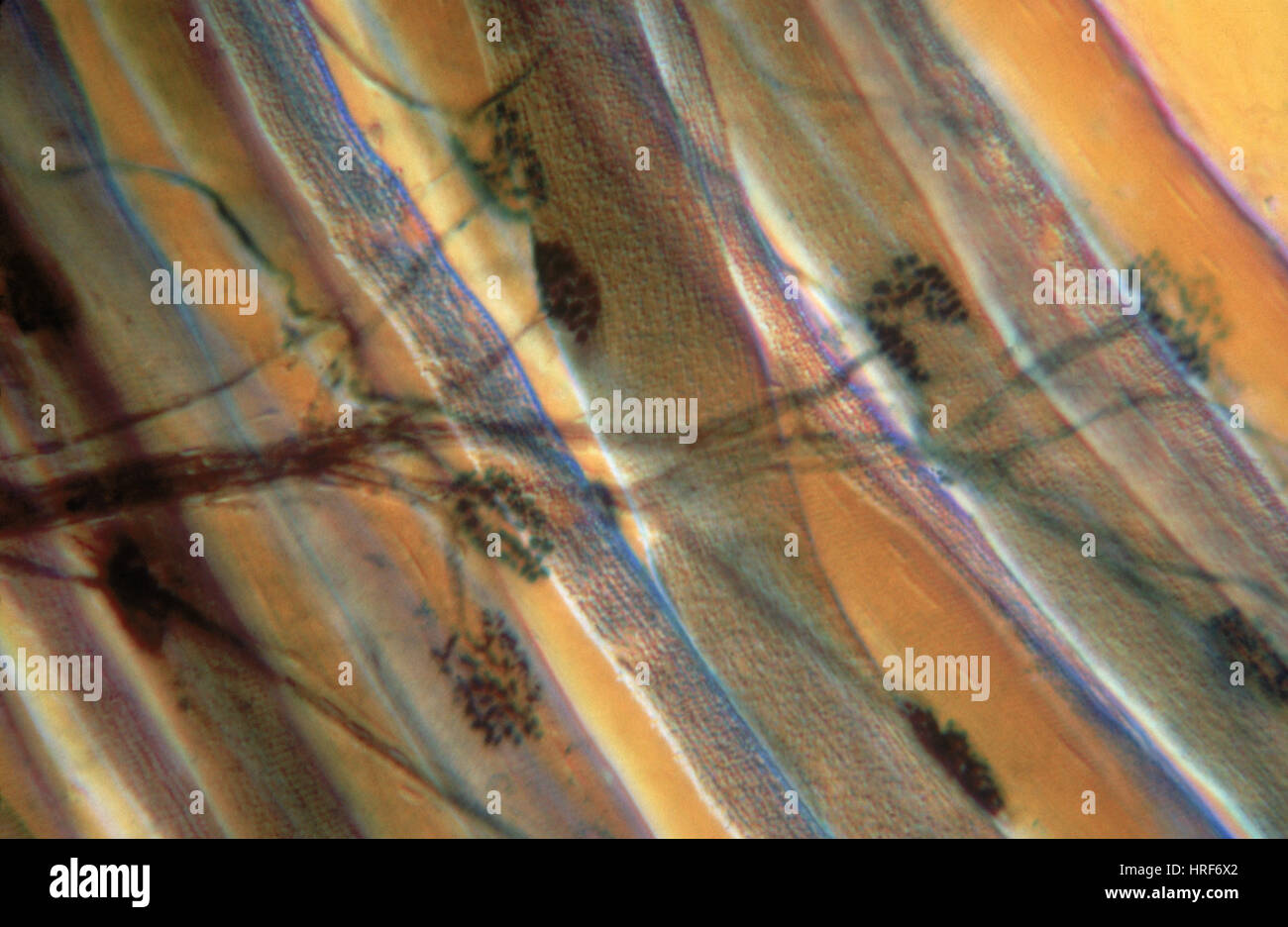 Motor End Plate Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-motor-end-plate-134944378.html
Motor End Plate Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-motor-end-plate-134944378.htmlRMHRF6X2–Motor End Plate
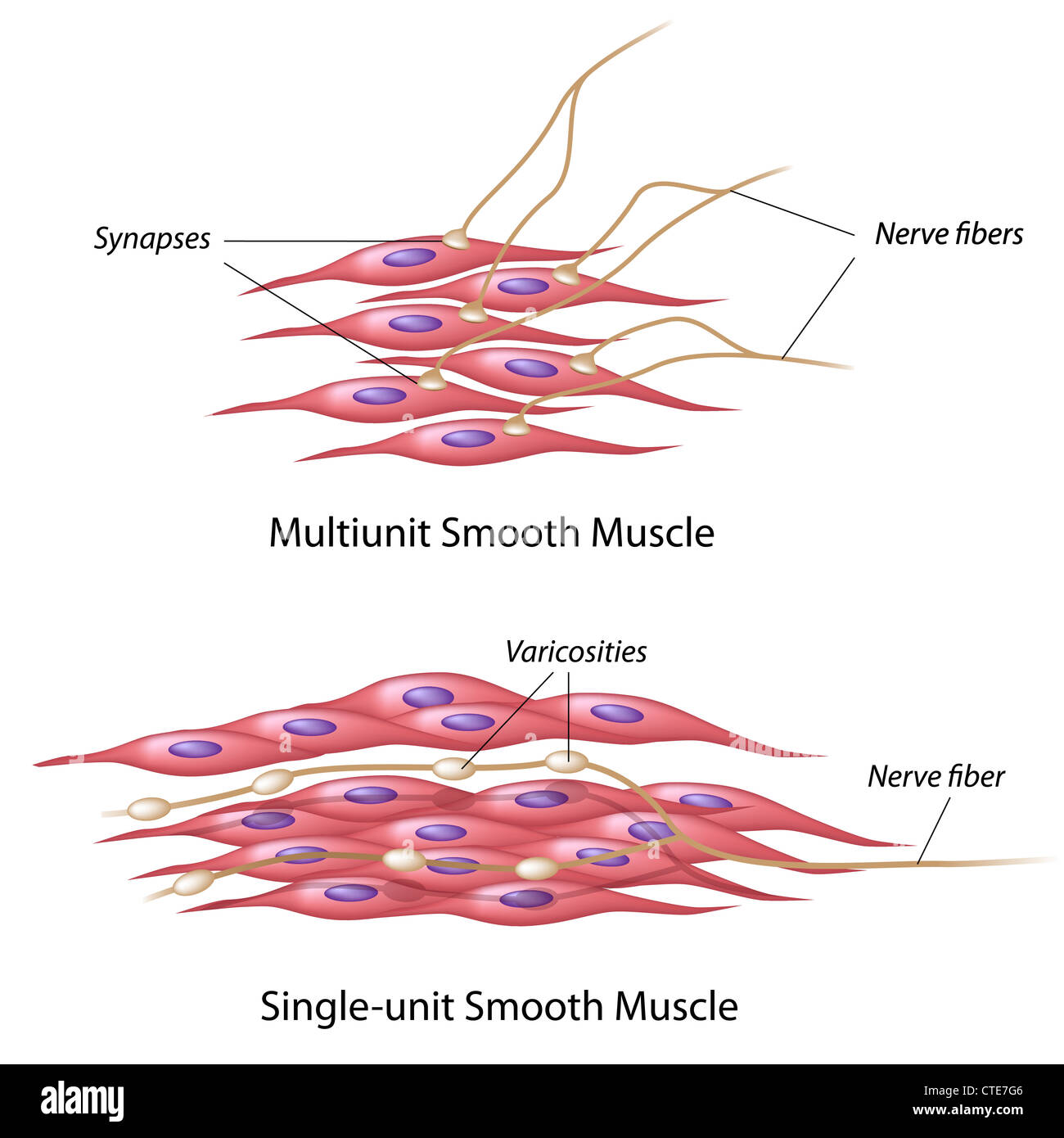 Smooth muscle innervation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-smooth-muscle-innervation-49485750.html
Smooth muscle innervation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-smooth-muscle-innervation-49485750.htmlRFCTE7G6–Smooth muscle innervation
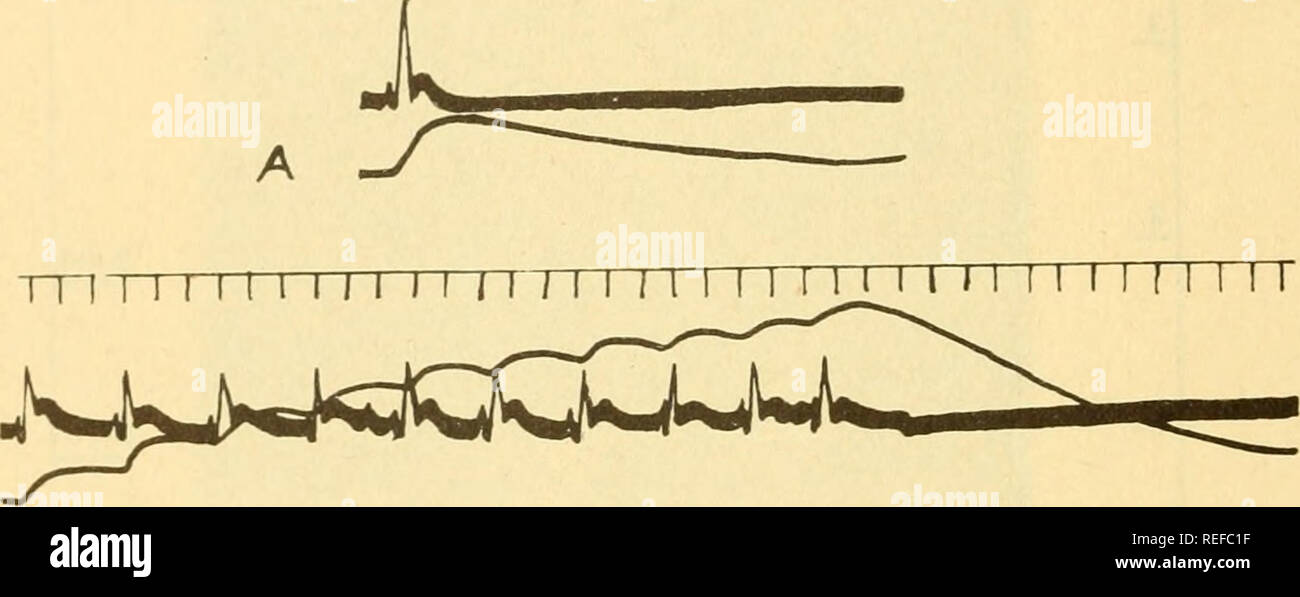 . Comparative animal physiology. Physiology, Comparative; Physiology, Comparative. cgQ Comparative Animal Physiology In Crustacea the graded potentials of the neuromuscular junction con- tribute largely to the total action potential of the muscle. Their role in con- traction will be discussed below. In long-fibered smooth muscles, such as the anterior retractor of the byssus in Mytilns, impulses appear to be propagated at a rate of 13-20 cm./sec. with a simple action potential of duration 2-3 sec.^o^- 10.5 when the muscle is stimulated repetitively the action potentials increase in height (sta Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/comparative-animal-physiology-physiology-comparative-physiology-comparative-cgq-comparative-animal-physiology-in-crustacea-the-graded-potentials-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-con-tribute-largely-to-the-total-action-potential-of-the-muscle-their-role-in-con-traction-will-be-discussed-below-in-long-fibered-smooth-muscles-such-as-the-anterior-retractor-of-the-byssus-in-mytilns-impulses-appear-to-be-propagated-at-a-rate-of-13-20-cmsec-with-a-simple-action-potential-of-duration-2-3-seco-105-when-the-muscle-is-stimulated-repetitively-the-action-potentials-increase-in-height-sta-image232678699.html
. Comparative animal physiology. Physiology, Comparative; Physiology, Comparative. cgQ Comparative Animal Physiology In Crustacea the graded potentials of the neuromuscular junction con- tribute largely to the total action potential of the muscle. Their role in con- traction will be discussed below. In long-fibered smooth muscles, such as the anterior retractor of the byssus in Mytilns, impulses appear to be propagated at a rate of 13-20 cm./sec. with a simple action potential of duration 2-3 sec.^o^- 10.5 when the muscle is stimulated repetitively the action potentials increase in height (sta Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/comparative-animal-physiology-physiology-comparative-physiology-comparative-cgq-comparative-animal-physiology-in-crustacea-the-graded-potentials-of-the-neuromuscular-junction-con-tribute-largely-to-the-total-action-potential-of-the-muscle-their-role-in-con-traction-will-be-discussed-below-in-long-fibered-smooth-muscles-such-as-the-anterior-retractor-of-the-byssus-in-mytilns-impulses-appear-to-be-propagated-at-a-rate-of-13-20-cmsec-with-a-simple-action-potential-of-duration-2-3-seco-105-when-the-muscle-is-stimulated-repetitively-the-action-potentials-increase-in-height-sta-image232678699.htmlRMREFC1F–. Comparative animal physiology. Physiology, Comparative; Physiology, Comparative. cgQ Comparative Animal Physiology In Crustacea the graded potentials of the neuromuscular junction con- tribute largely to the total action potential of the muscle. Their role in con- traction will be discussed below. In long-fibered smooth muscles, such as the anterior retractor of the byssus in Mytilns, impulses appear to be propagated at a rate of 13-20 cm./sec. with a simple action potential of duration 2-3 sec.^o^- 10.5 when the muscle is stimulated repetitively the action potentials increase in height (sta
 Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620326630.html
Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/muscarinic-acetylcholine-receptors-muscle-fiber-sarcolemma-neurotransmitter-or-neuromuscular-junction-cycle-of-ach-release-in-myasthenia-gravis-no-image620326630.htmlRM2Y168XE–Muscarinic Acetylcholine receptors, muscle fiber sarcolemma, neurotransmitter or neuromuscular junction, cycle of ACH release in Myasthenia gravis, No
 Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image442065594.html
Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/neuromuscular-spindle-and-proprioception-perception-of-the-position-of-parts-of-the-body-image442065594.htmlRF2GK5R4X–Neuromuscular spindle and proprioception: perception of the position of parts of the body.
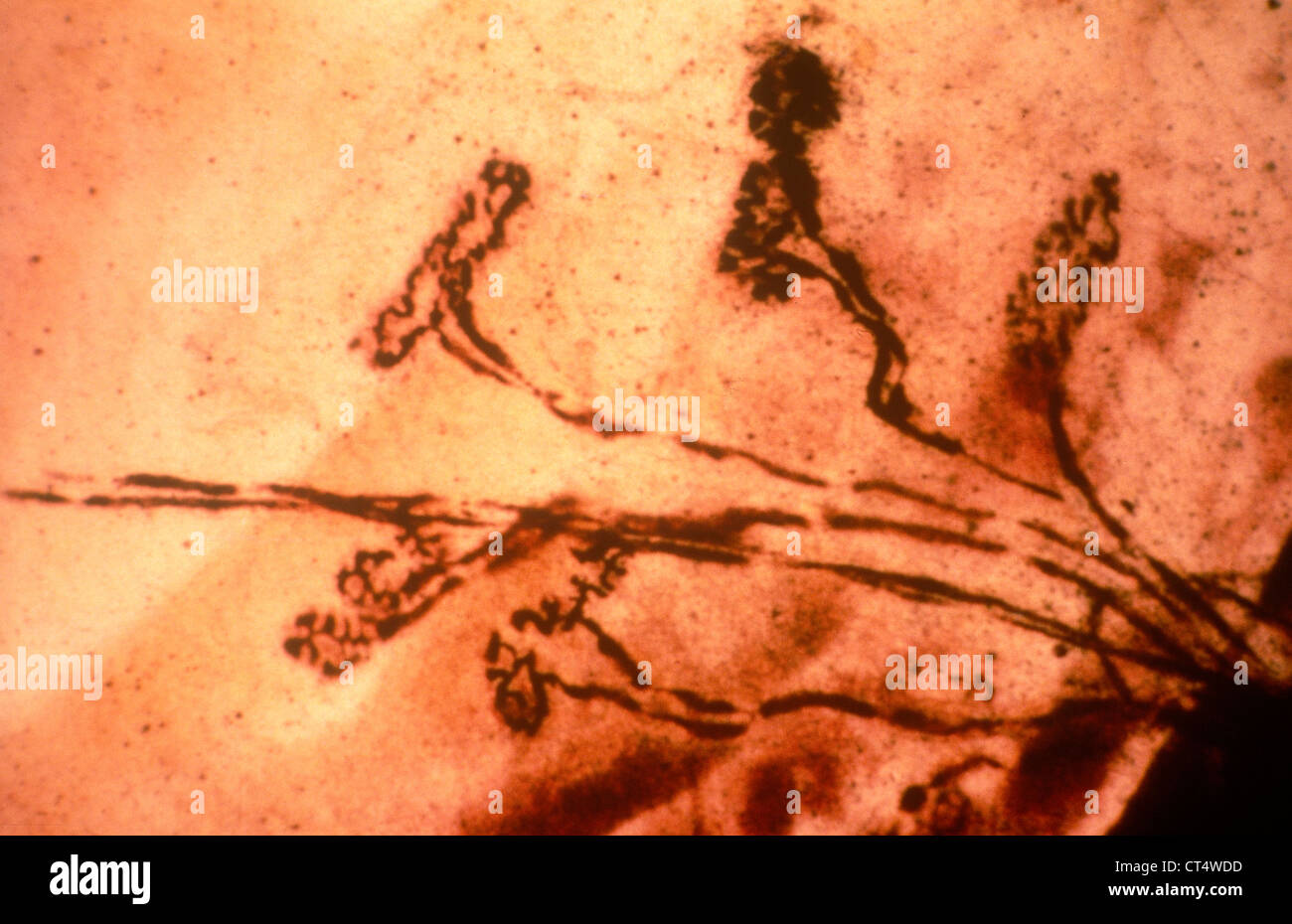 MYONEURAL JUNCTION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-myoneural-junction-49280265.html
MYONEURAL JUNCTION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-myoneural-junction-49280265.htmlRMCT4WDD–MYONEURAL JUNCTION
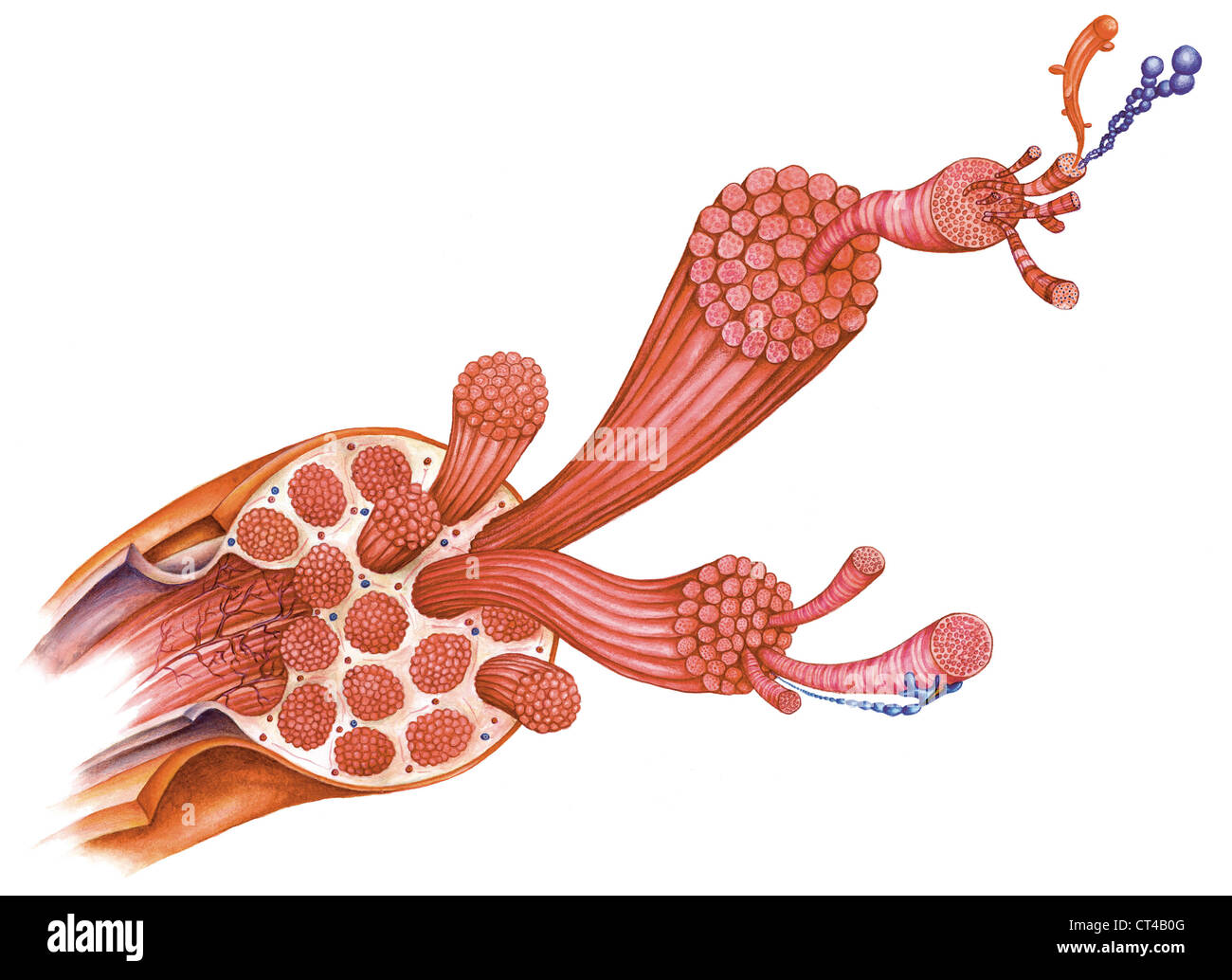 SKELETAL MUSCLE, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-skeletal-muscle-illustration-49268928.html
SKELETAL MUSCLE, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-skeletal-muscle-illustration-49268928.htmlRMCT4B0G–SKELETAL MUSCLE, ILLUSTRATION
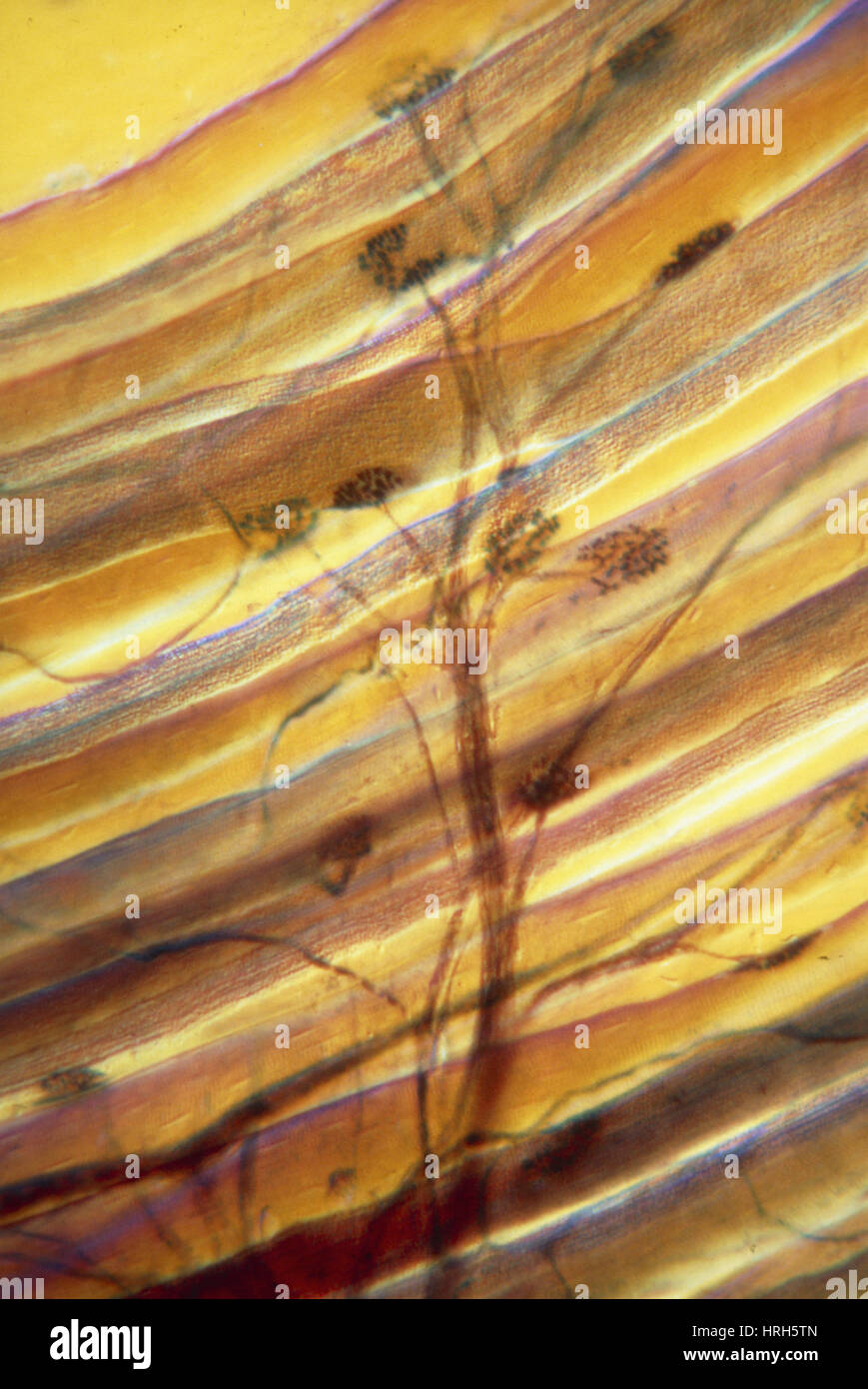 LM: synapses between motor neuron & muscle cells Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-lm-synapses-between-motor-neuron-muscle-cells-134987461.html
LM: synapses between motor neuron & muscle cells Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-lm-synapses-between-motor-neuron-muscle-cells-134987461.htmlRMHRH5TN–LM: synapses between motor neuron & muscle cells
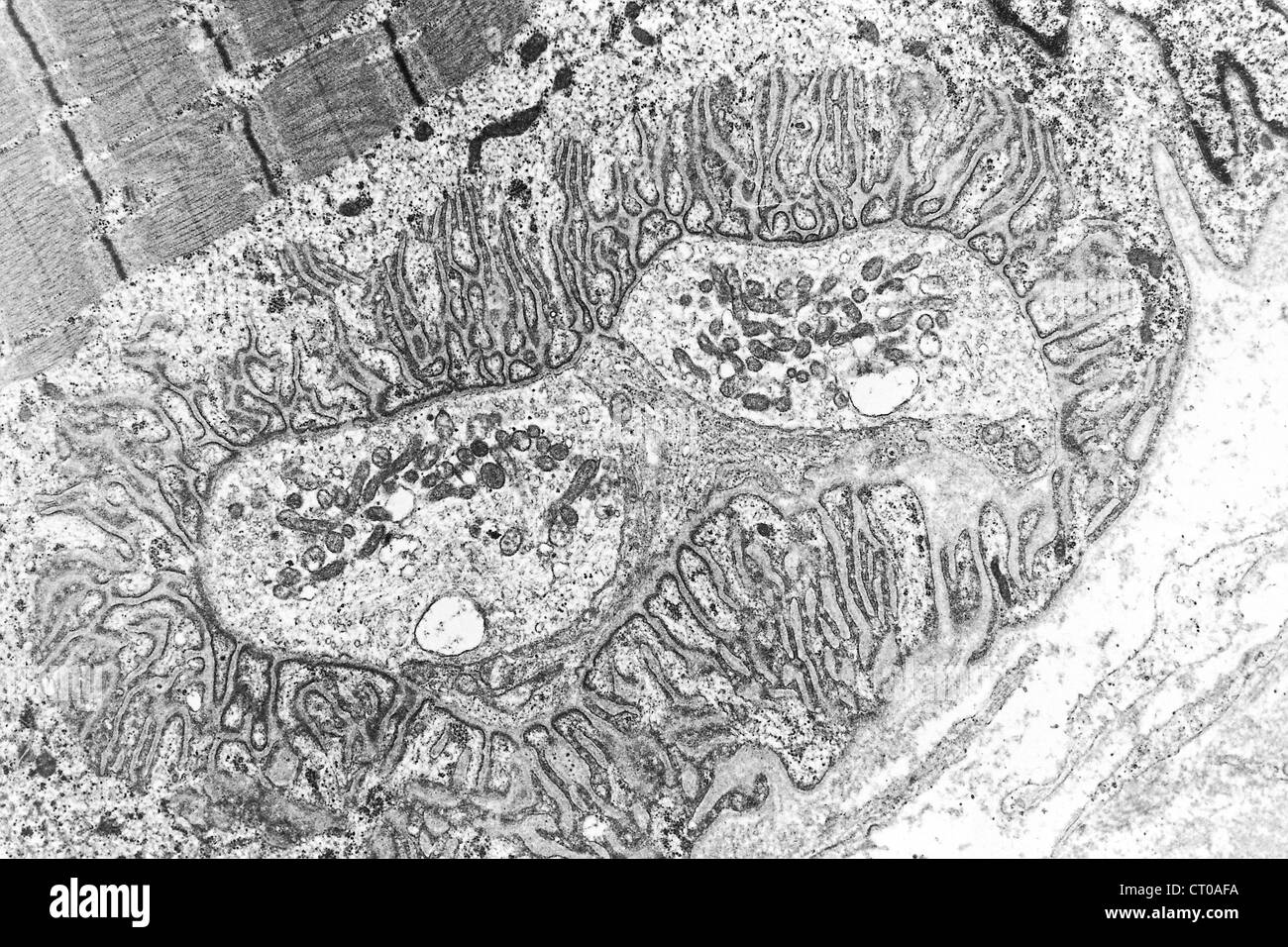 MYONEURAL JUNCTION, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-myoneural-junction-tem-49180750.html
MYONEURAL JUNCTION, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-myoneural-junction-tem-49180750.htmlRMCT0AFA–MYONEURAL JUNCTION, TEM
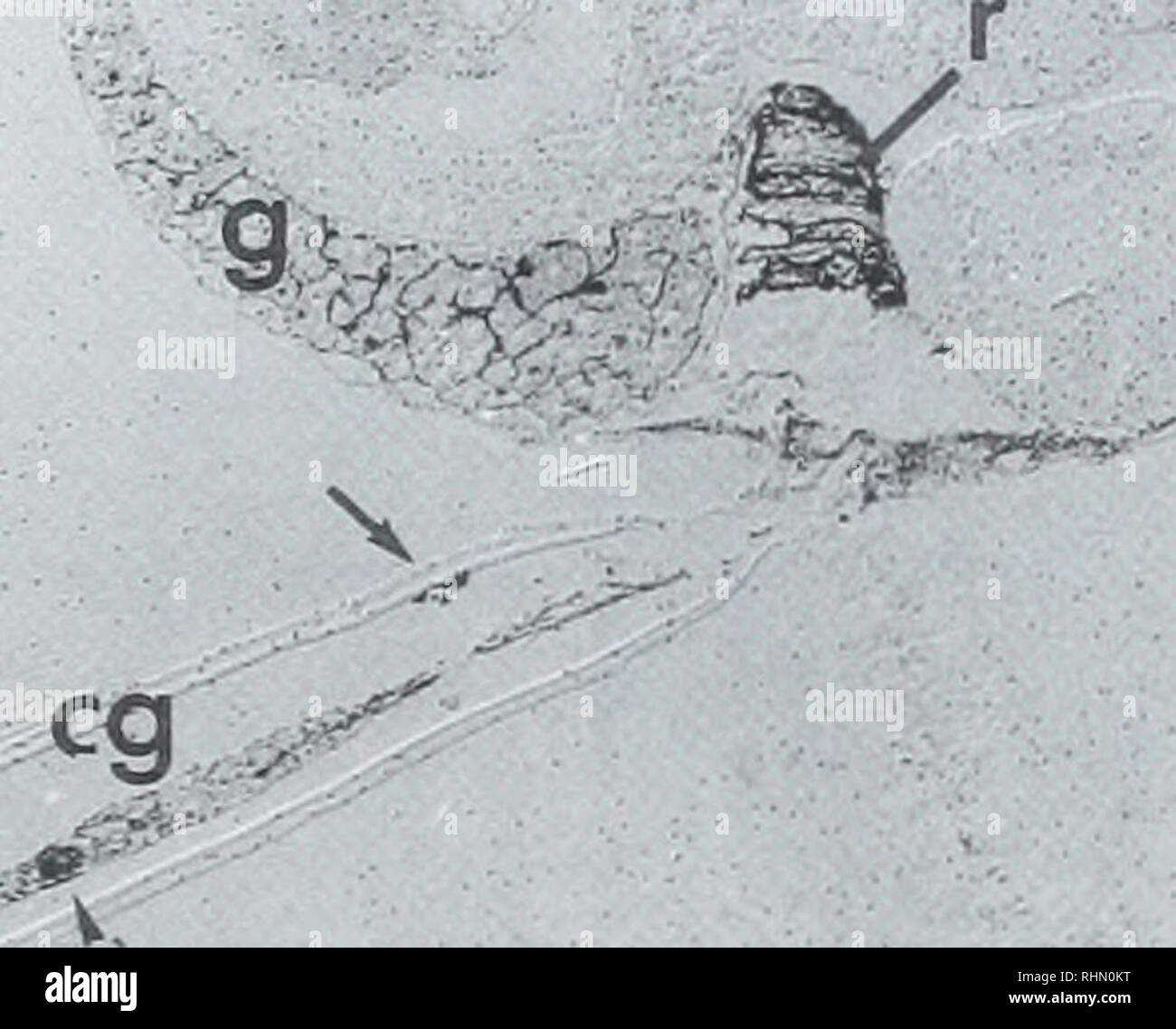 . The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. GABA IN OIKOPLKL'RA NERVOUS SYSTEM 121 •<^ IL br. Y|Ai-4Q*ij ' ,'•'• Figure 2. Sagittal section through the whole animal showing the localization and GABA-like immu- noreactivity (arrowheads) of the brain (br), one of the anterior bulbs (ab). the nerve cord (n), the caudal ganglion (eg) and in a neuromuscular junction of the tail (arrow). Staining can also be seen in the gonads (g), at the apical surface of some of the intestinal cells (i). and in the rectum (r). No staining could be seen in an adjacent section treated wi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-gaba-in-oikoplklra-nervous-system-121-lt-il-br-yai-4qij-figure-2-sagittal-section-through-the-whole-animal-showing-the-localization-and-gaba-like-immu-noreactivity-arrowheads-of-the-brain-br-one-of-the-anterior-bulbs-ab-the-nerve-cord-n-the-caudal-ganglion-eg-and-in-a-neuromuscular-junction-of-the-tail-arrow-staining-can-also-be-seen-in-the-gonads-g-at-the-apical-surface-of-some-of-the-intestinal-cells-i-and-in-the-rectum-r-no-staining-could-be-seen-in-an-adjacent-section-treated-wi-image234645484.html
. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. GABA IN OIKOPLKL'RA NERVOUS SYSTEM 121 •<^ IL br. Y|Ai-4Q*ij ' ,'•'• Figure 2. Sagittal section through the whole animal showing the localization and GABA-like immu- noreactivity (arrowheads) of the brain (br), one of the anterior bulbs (ab). the nerve cord (n), the caudal ganglion (eg) and in a neuromuscular junction of the tail (arrow). Staining can also be seen in the gonads (g), at the apical surface of some of the intestinal cells (i). and in the rectum (r). No staining could be seen in an adjacent section treated wi Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-gaba-in-oikoplklra-nervous-system-121-lt-il-br-yai-4qij-figure-2-sagittal-section-through-the-whole-animal-showing-the-localization-and-gaba-like-immu-noreactivity-arrowheads-of-the-brain-br-one-of-the-anterior-bulbs-ab-the-nerve-cord-n-the-caudal-ganglion-eg-and-in-a-neuromuscular-junction-of-the-tail-arrow-staining-can-also-be-seen-in-the-gonads-g-at-the-apical-surface-of-some-of-the-intestinal-cells-i-and-in-the-rectum-r-no-staining-could-be-seen-in-an-adjacent-section-treated-wi-image234645484.htmlRMRHN0KT–. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. GABA IN OIKOPLKL'RA NERVOUS SYSTEM 121 •<^ IL br. Y|Ai-4Q*ij ' ,'•'• Figure 2. Sagittal section through the whole animal showing the localization and GABA-like immu- noreactivity (arrowheads) of the brain (br), one of the anterior bulbs (ab). the nerve cord (n), the caudal ganglion (eg) and in a neuromuscular junction of the tail (arrow). Staining can also be seen in the gonads (g), at the apical surface of some of the intestinal cells (i). and in the rectum (r). No staining could be seen in an adjacent section treated wi
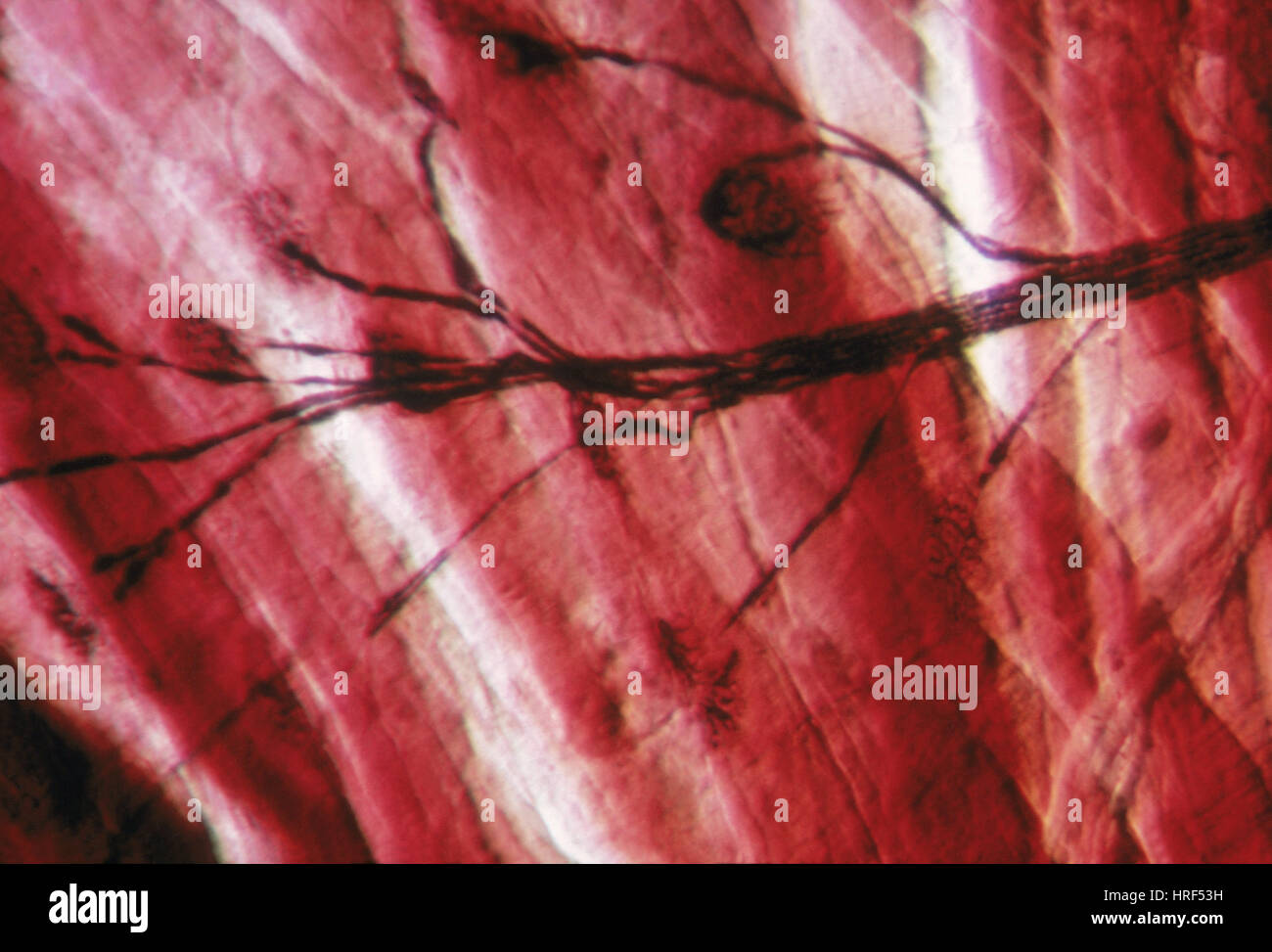 Motor End Plate Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-motor-end-plate-134942965.html
Motor End Plate Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-motor-end-plate-134942965.htmlRMHRF53H–Motor End Plate
 . The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. $ ' -:.-•• ' L^ ^;^i|if^,. Figure 4. Transmission electron micrographs of synaptic profiles contacting circular mantle muscle fibers (juvenile: 8 weeks old). (A and B) Longitudinal mantle section (circular fibers in cross section). A nerve process (NP) runs within the central muscle layer and forms putative synaptic contacts (arrows) onto several CMP fibers. Note the relatively large dimensions of the synaptic profiles in relation to the size of the muscle fiber. (C) Neuromuscular junction onto a CMP fiber. The synaptic prof Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-l-iif-figure-4-transmission-electron-micrographs-of-synaptic-profiles-contacting-circular-mantle-muscle-fibers-juvenile-8-weeks-old-a-and-b-longitudinal-mantle-section-circular-fibers-in-cross-section-a-nerve-process-np-runs-within-the-central-muscle-layer-and-forms-putative-synaptic-contacts-arrows-onto-several-cmp-fibers-note-the-relatively-large-dimensions-of-the-synaptic-profiles-in-relation-to-the-size-of-the-muscle-fiber-c-neuromuscular-junction-onto-a-cmp-fiber-the-synaptic-prof-image234633592.html
. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. $ ' -:.-•• ' L^ ^;^i|if^,. Figure 4. Transmission electron micrographs of synaptic profiles contacting circular mantle muscle fibers (juvenile: 8 weeks old). (A and B) Longitudinal mantle section (circular fibers in cross section). A nerve process (NP) runs within the central muscle layer and forms putative synaptic contacts (arrows) onto several CMP fibers. Note the relatively large dimensions of the synaptic profiles in relation to the size of the muscle fiber. (C) Neuromuscular junction onto a CMP fiber. The synaptic prof Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-l-iif-figure-4-transmission-electron-micrographs-of-synaptic-profiles-contacting-circular-mantle-muscle-fibers-juvenile-8-weeks-old-a-and-b-longitudinal-mantle-section-circular-fibers-in-cross-section-a-nerve-process-np-runs-within-the-central-muscle-layer-and-forms-putative-synaptic-contacts-arrows-onto-several-cmp-fibers-note-the-relatively-large-dimensions-of-the-synaptic-profiles-in-relation-to-the-size-of-the-muscle-fiber-c-neuromuscular-junction-onto-a-cmp-fiber-the-synaptic-prof-image234633592.htmlRMRHMDF4–. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. $ ' -:.-•• ' L^ ^;^i|if^,. Figure 4. Transmission electron micrographs of synaptic profiles contacting circular mantle muscle fibers (juvenile: 8 weeks old). (A and B) Longitudinal mantle section (circular fibers in cross section). A nerve process (NP) runs within the central muscle layer and forms putative synaptic contacts (arrows) onto several CMP fibers. Note the relatively large dimensions of the synaptic profiles in relation to the size of the muscle fiber. (C) Neuromuscular junction onto a CMP fiber. The synaptic prof
 . The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. FIGURE 8. A nerve ending containing a mixture of dense and clear synaptic vesicles. The glial cell (g) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-figure-7-the-initimate-juxtaposition-of-the-nerve-ending-and-muscle-cell-is-illustrated-here-a-sarcolemniic-tubule-is-also-clearly-pictured-arrow-scale-=10-micron-neuromuscular-junction-figs-7-8-9-the-muscle-cell-and-nerve-are-separated-by-a-gap-of-about-150-200-a-the-muscle-is-intimately-associated-with-the-nerve-ending-but-there-is-no-specialized-membrane-involution-in-the-junctional-area-such-r-ky-j-v-figure-8-a-nerve-ending-containing-a-mixture-of-dense-and-clear-synaptic-vesicles-the-glial-cell-g-image234649968.html
. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. FIGURE 8. A nerve ending containing a mixture of dense and clear synaptic vesicles. The glial cell (g) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-figure-7-the-initimate-juxtaposition-of-the-nerve-ending-and-muscle-cell-is-illustrated-here-a-sarcolemniic-tubule-is-also-clearly-pictured-arrow-scale-=10-micron-neuromuscular-junction-figs-7-8-9-the-muscle-cell-and-nerve-are-separated-by-a-gap-of-about-150-200-a-the-muscle-is-intimately-associated-with-the-nerve-ending-but-there-is-no-specialized-membrane-involution-in-the-junctional-area-such-r-ky-j-v-figure-8-a-nerve-ending-containing-a-mixture-of-dense-and-clear-synaptic-vesicles-the-glial-cell-g-image234649968.htmlRMRHN6C0–. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. FIGURE 8. A nerve ending containing a mixture of dense and clear synaptic vesicles. The glial cell (g)