Quick filters:
Placenta tissue Stock Photos and Images
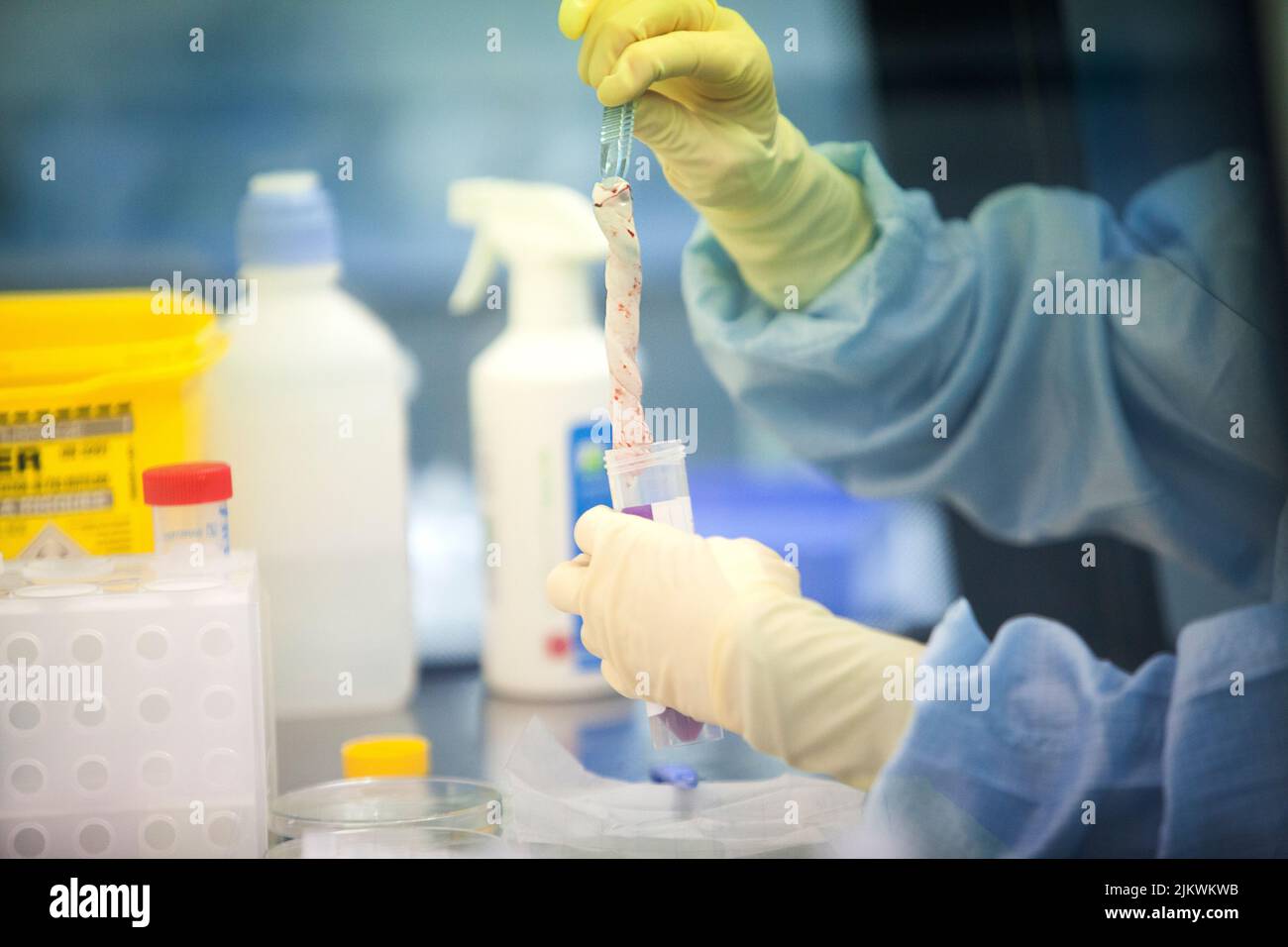 Biobank: umbilical cord tissue washed and stored before stem cell isolation. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-umbilical-cord-tissue-washed-and-stored-before-stem-cell-isolation-image476922807.html
Biobank: umbilical cord tissue washed and stored before stem cell isolation. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-umbilical-cord-tissue-washed-and-stored-before-stem-cell-isolation-image476922807.htmlRF2JKWKWB–Biobank: umbilical cord tissue washed and stored before stem cell isolation.
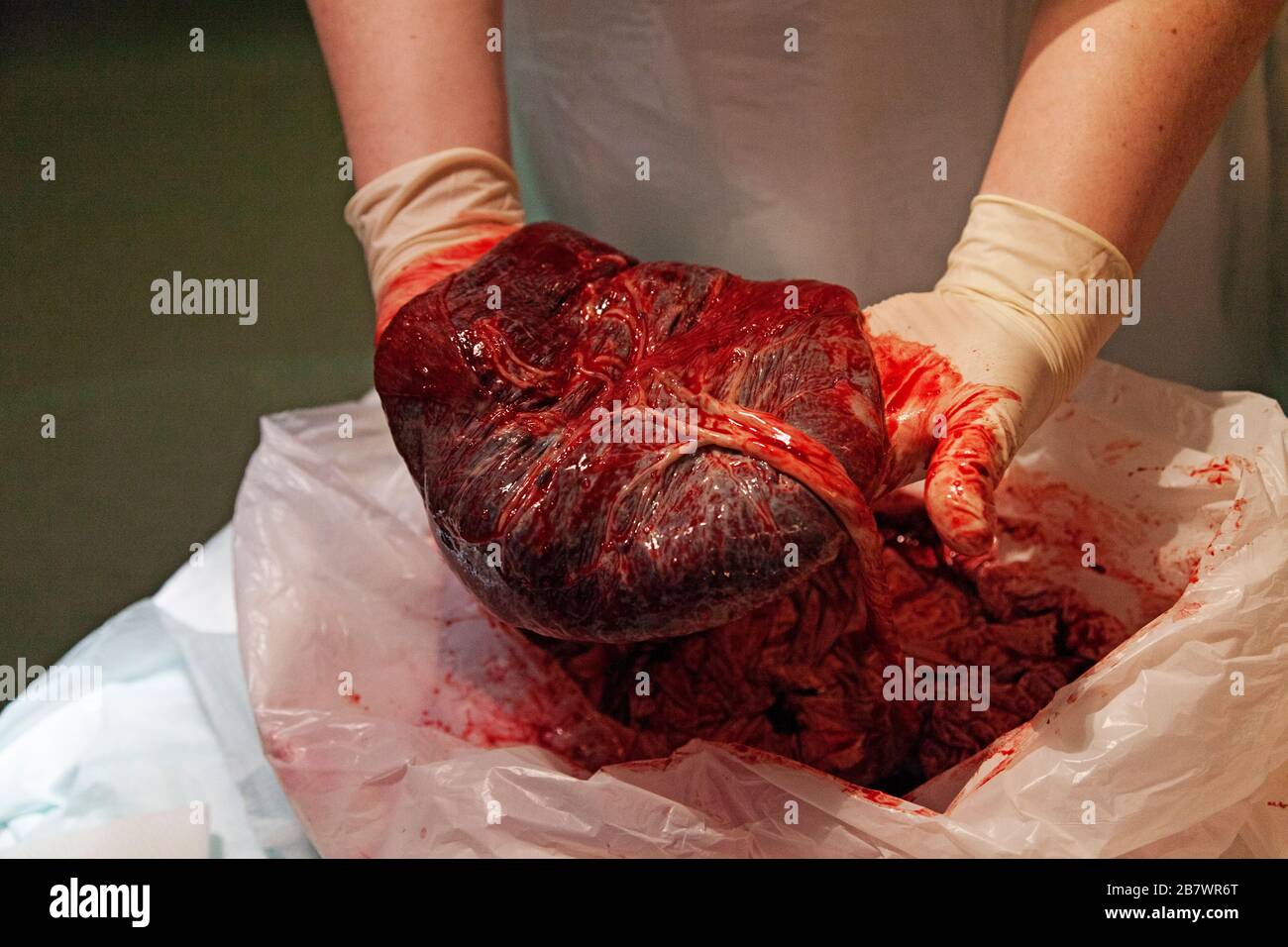
 Placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411564.html
Placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411564.htmlRMAN4PBW–Placenta immediately after birth
 placenta after giving birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-after-giving-birth-image68178917.html
placenta after giving birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-after-giving-birth-image68178917.htmlRFDXWPW9–placenta after giving birth
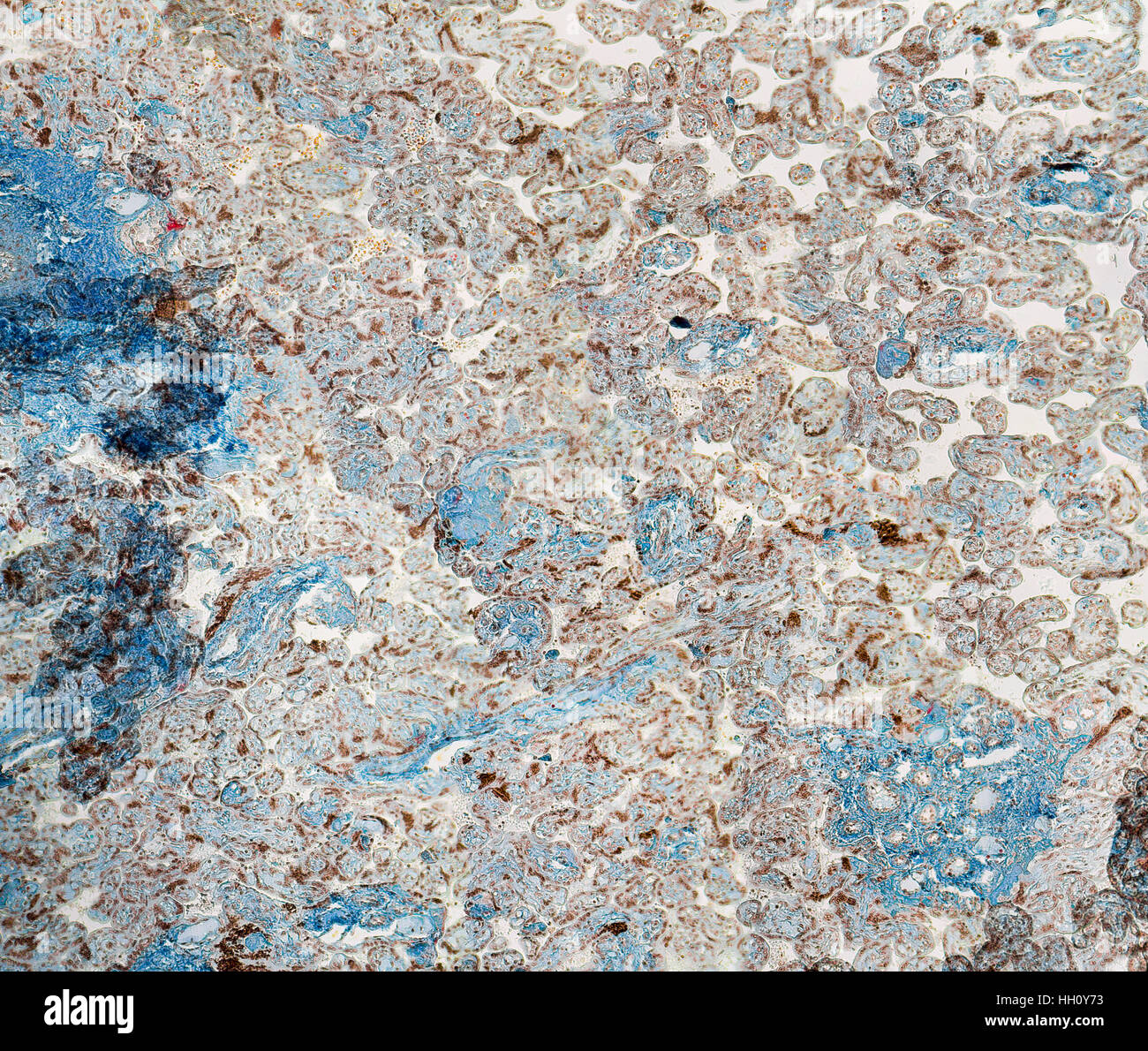 stained full frame human placenta micrography Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stained-full-frame-human-placenta-micrography-130943095.html
stained full frame human placenta micrography Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stained-full-frame-human-placenta-micrography-130943095.htmlRFHH0Y73–stained full frame human placenta micrography
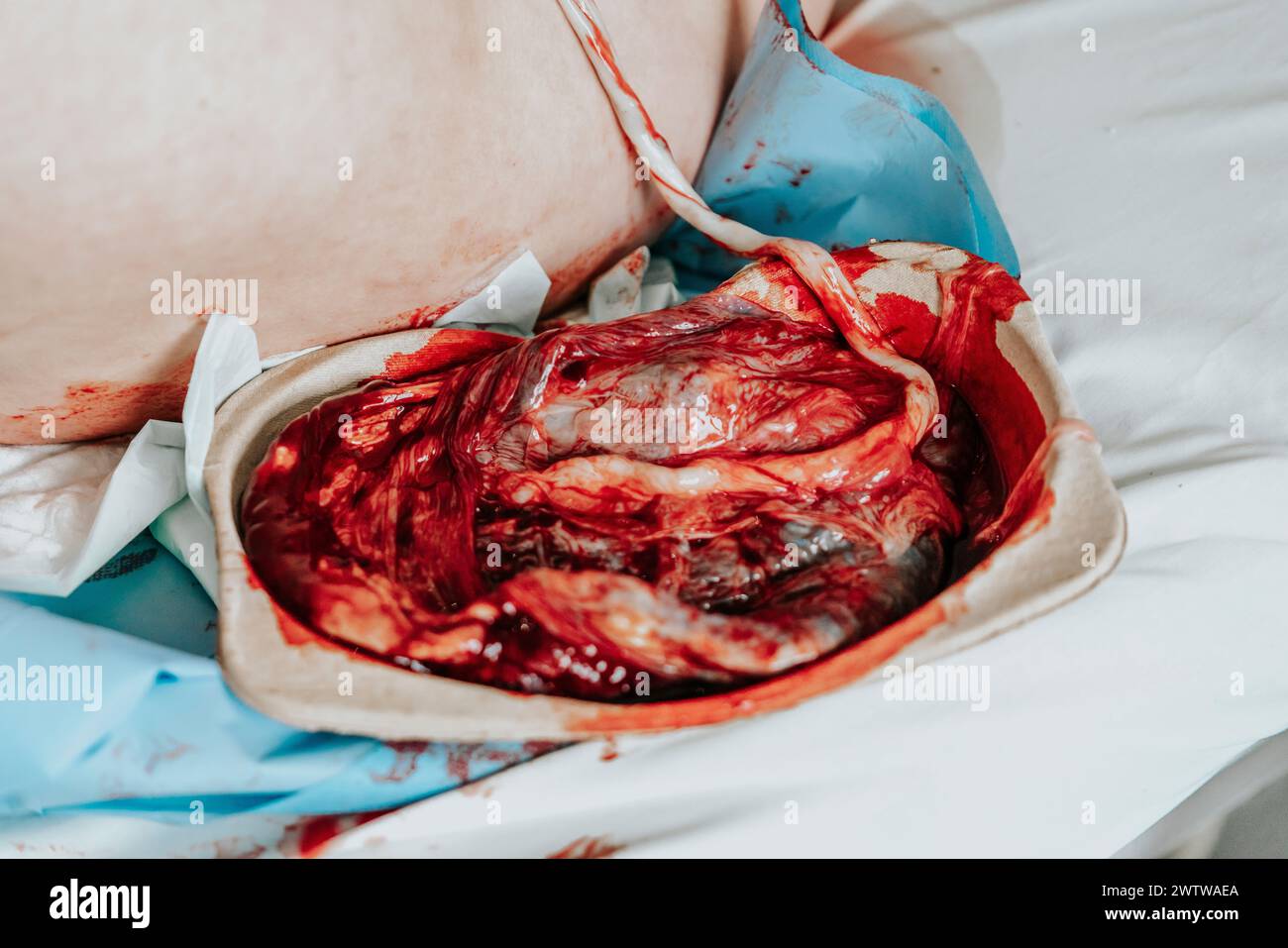 Human placenta moments after giving birth. Placenta still connected to the newborn baby, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-moments-after-giving-birth-placenta-still-connected-to-the-newborn-baby-image600461298.html
Human placenta moments after giving birth. Placenta still connected to the newborn baby, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-moments-after-giving-birth-placenta-still-connected-to-the-newborn-baby-image600461298.htmlRF2WTWAEA–Human placenta moments after giving birth. Placenta still connected to the newborn baby,
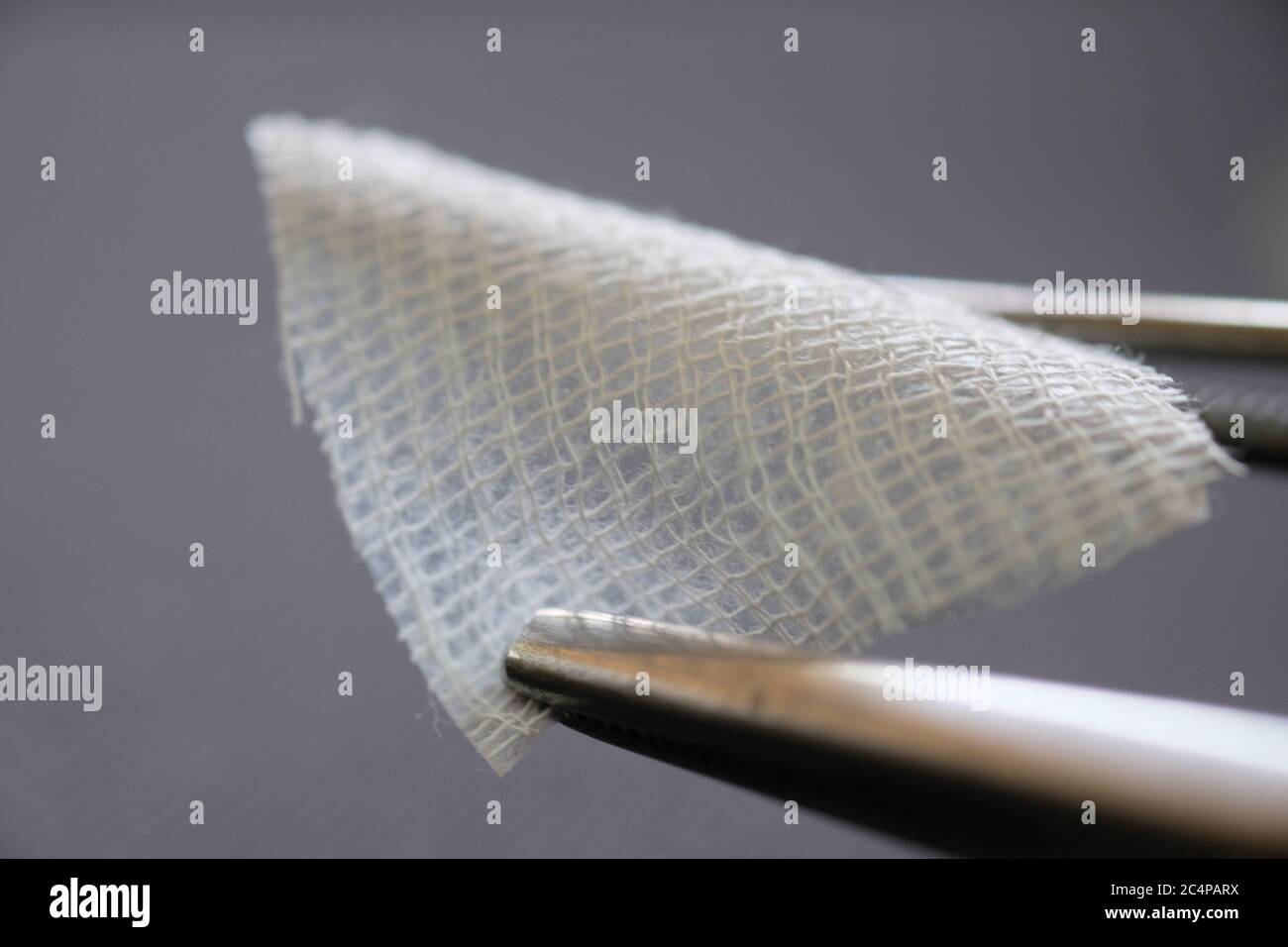 A close up photograph of human amniotic membrane for wound dressing Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-close-up-photograph-of-human-amniotic-membrane-for-wound-dressing-image364367806.html
A close up photograph of human amniotic membrane for wound dressing Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-close-up-photograph-of-human-amniotic-membrane-for-wound-dressing-image364367806.htmlRF2C4PARX–A close up photograph of human amniotic membrane for wound dressing
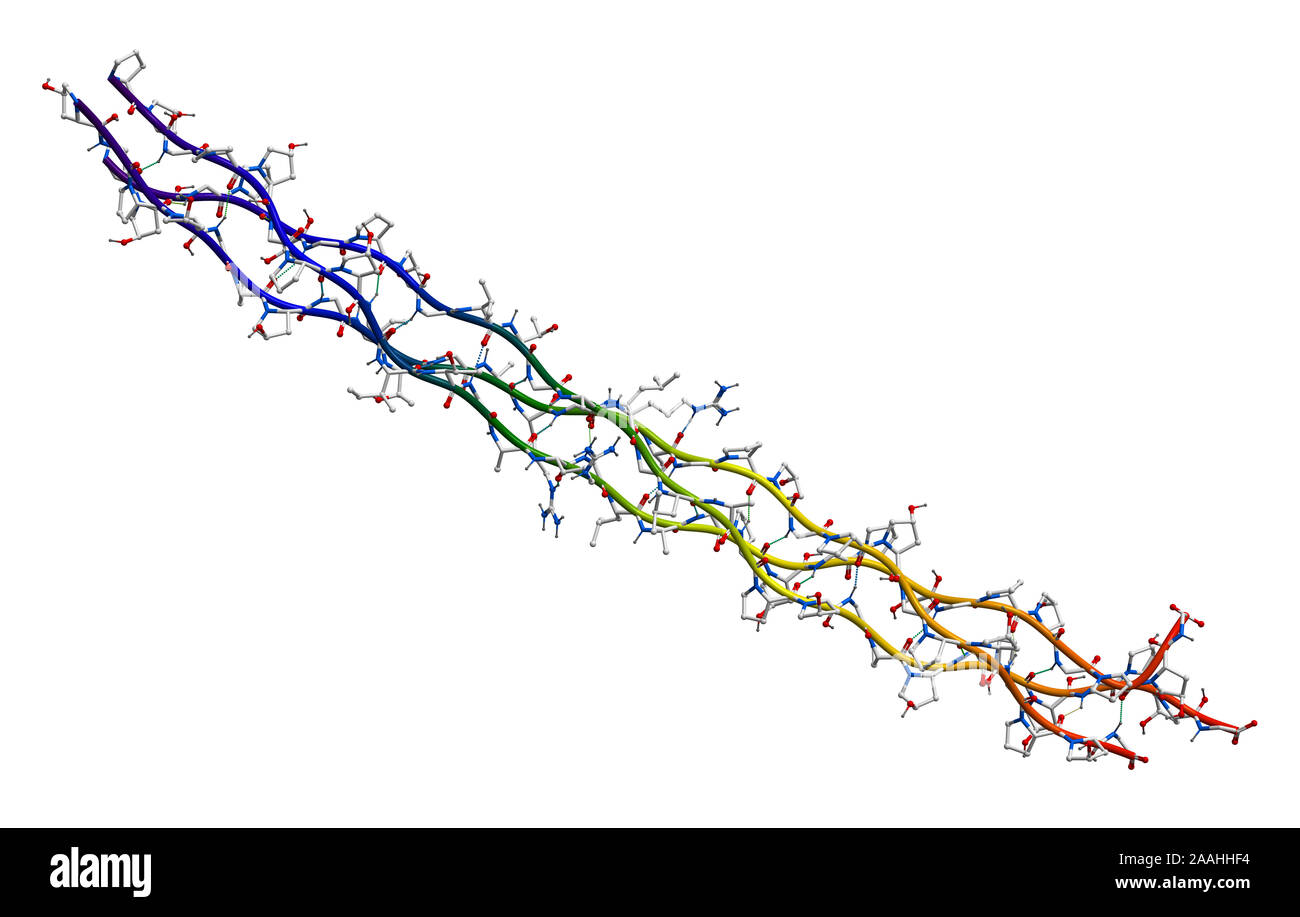 Human collagen molecule (segment) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-collagen-molecule-segment-image333530488.html
Human collagen molecule (segment) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-collagen-molecule-segment-image333530488.htmlRF2AAHHF4–Human collagen molecule (segment)
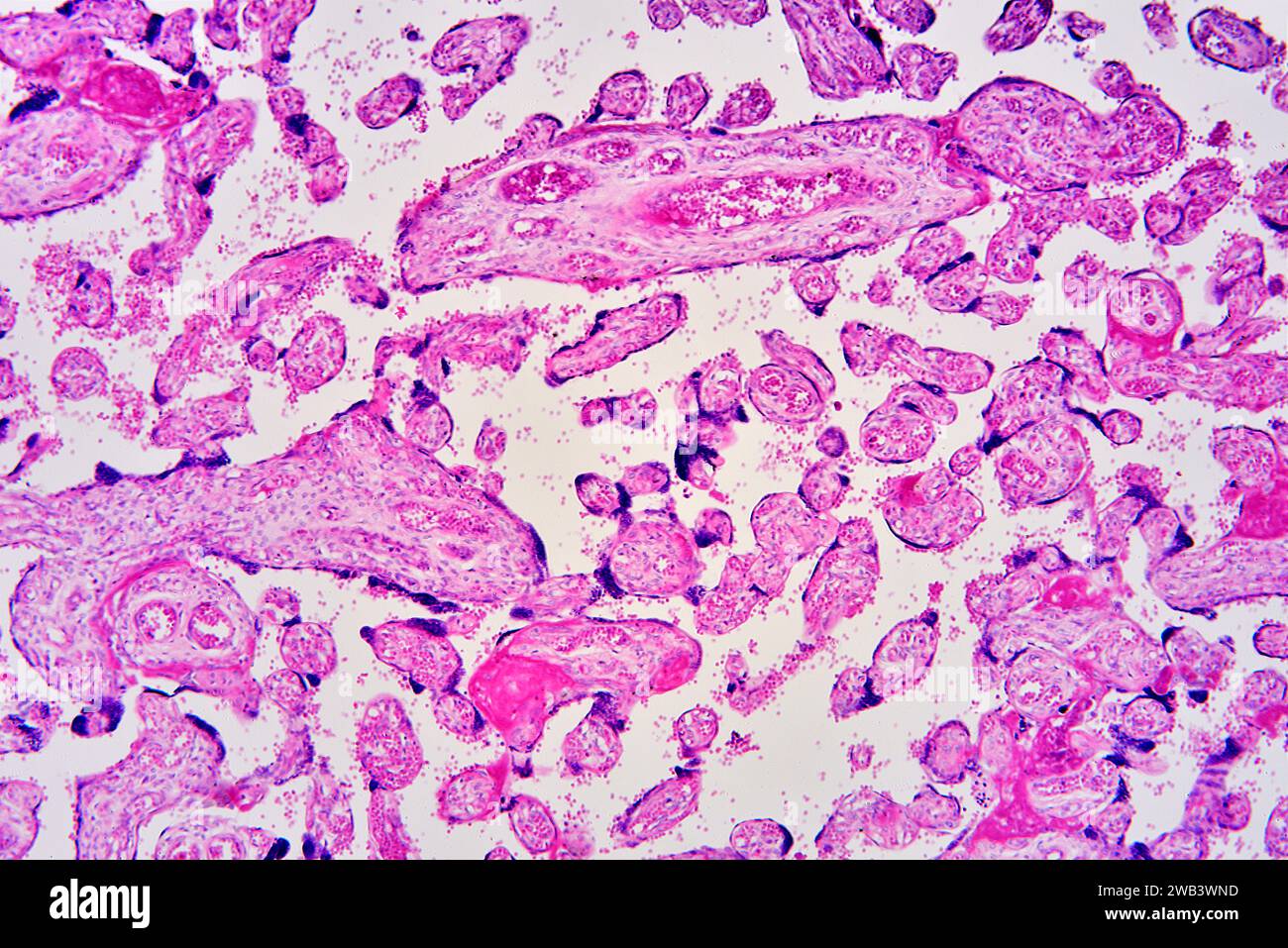
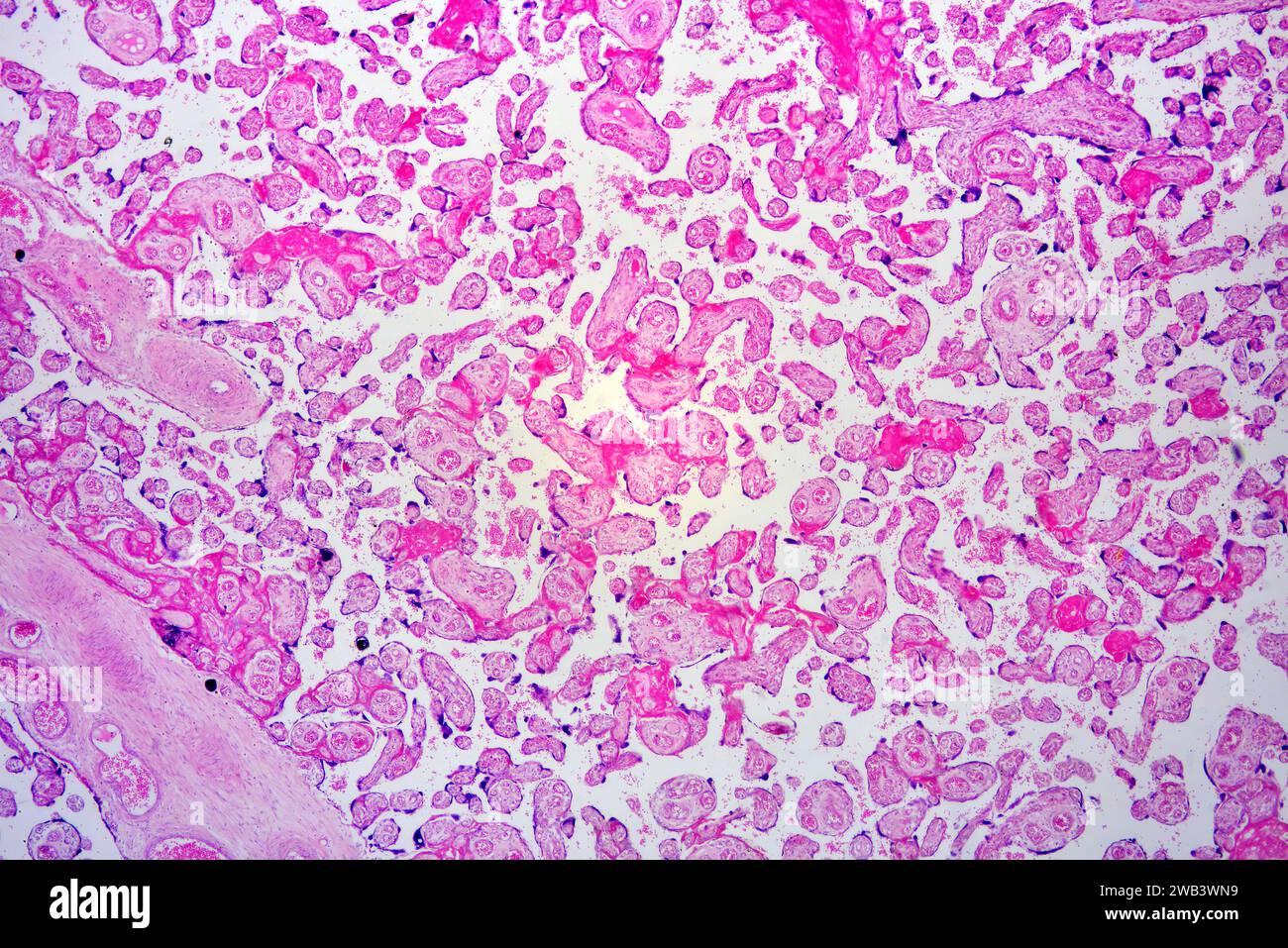 Human placenta with chorionic villi and blood vessels. X25 at 10 cm wide. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-with-chorionic-villi-and-blood-vessels-x25-at-10-cm-wide-image591999781.html
Human placenta with chorionic villi and blood vessels. X25 at 10 cm wide. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-with-chorionic-villi-and-blood-vessels-x25-at-10-cm-wide-image591999781.htmlRF2WB3WN9–Human placenta with chorionic villi and blood vessels. X25 at 10 cm wide.
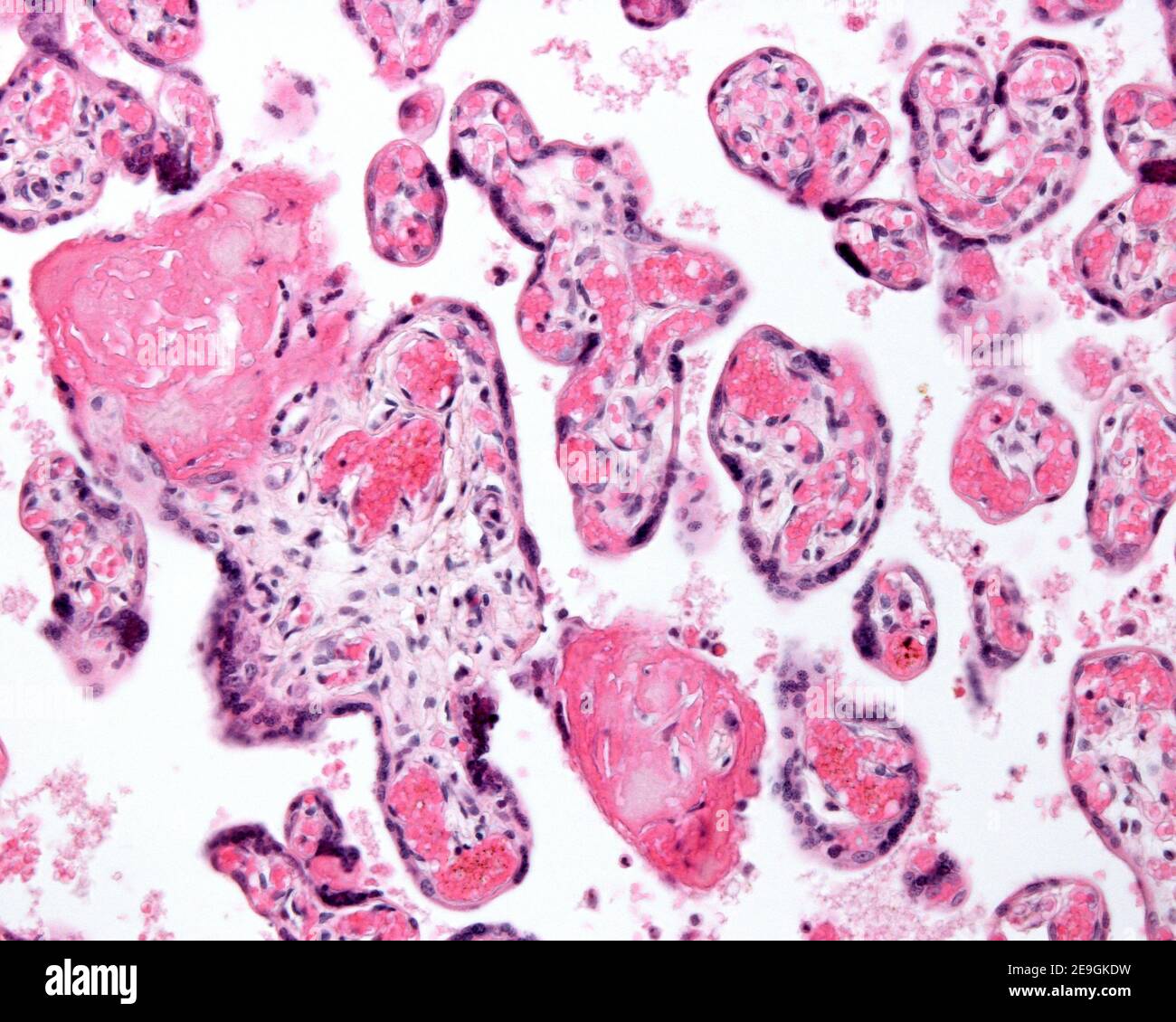
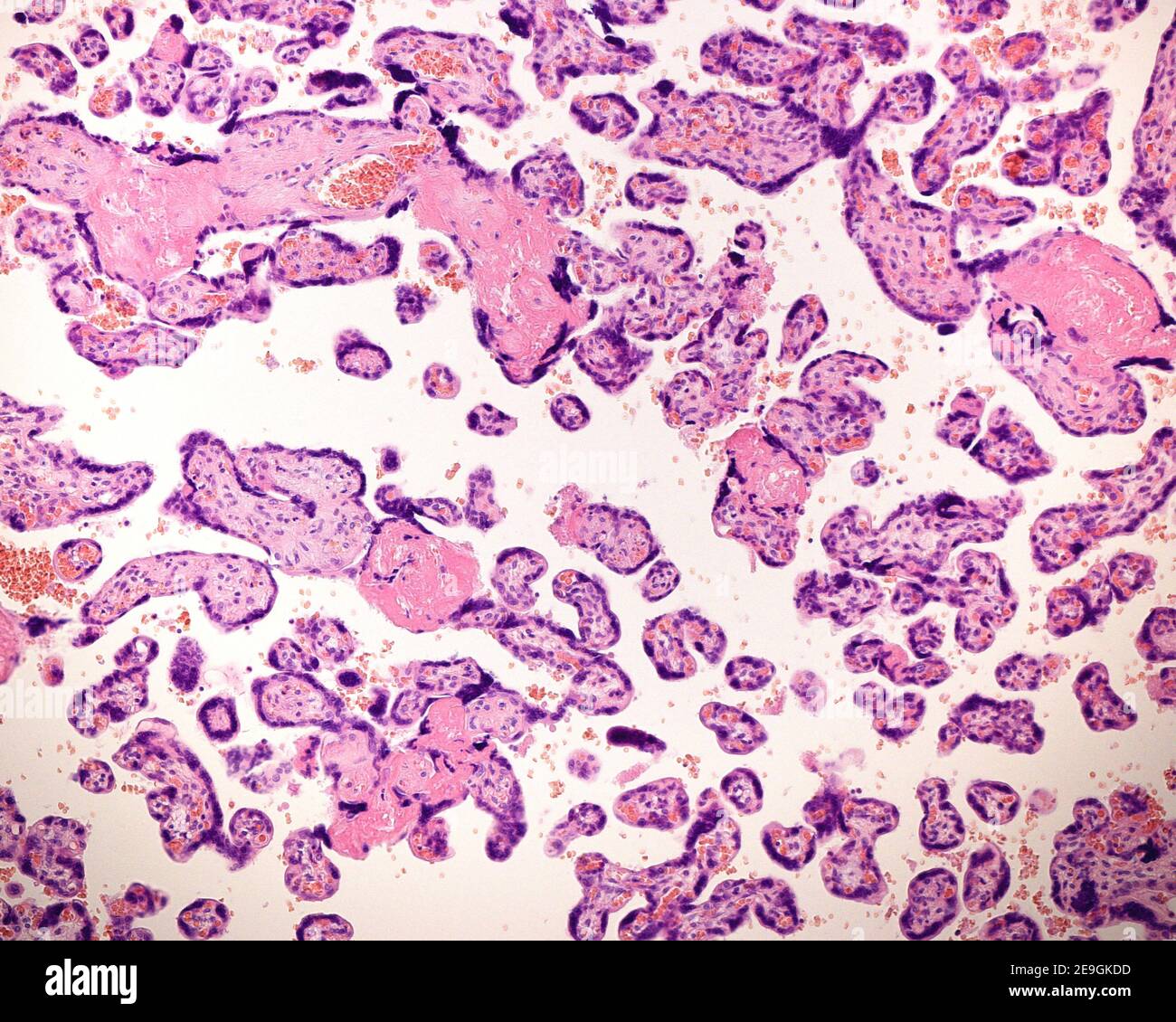 Chorionic villi of a at term placenta. The villi are small and show some syncytial knots and clumps of fibrin. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/chorionic-villi-of-a-at-term-placenta-the-villi-are-small-and-show-some-syncytial-knots-and-clumps-of-fibrin-image401736873.html
Chorionic villi of a at term placenta. The villi are small and show some syncytial knots and clumps of fibrin. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/chorionic-villi-of-a-at-term-placenta-the-villi-are-small-and-show-some-syncytial-knots-and-clumps-of-fibrin-image401736873.htmlRF2E9GKDD–Chorionic villi of a at term placenta. The villi are small and show some syncytial knots and clumps of fibrin.
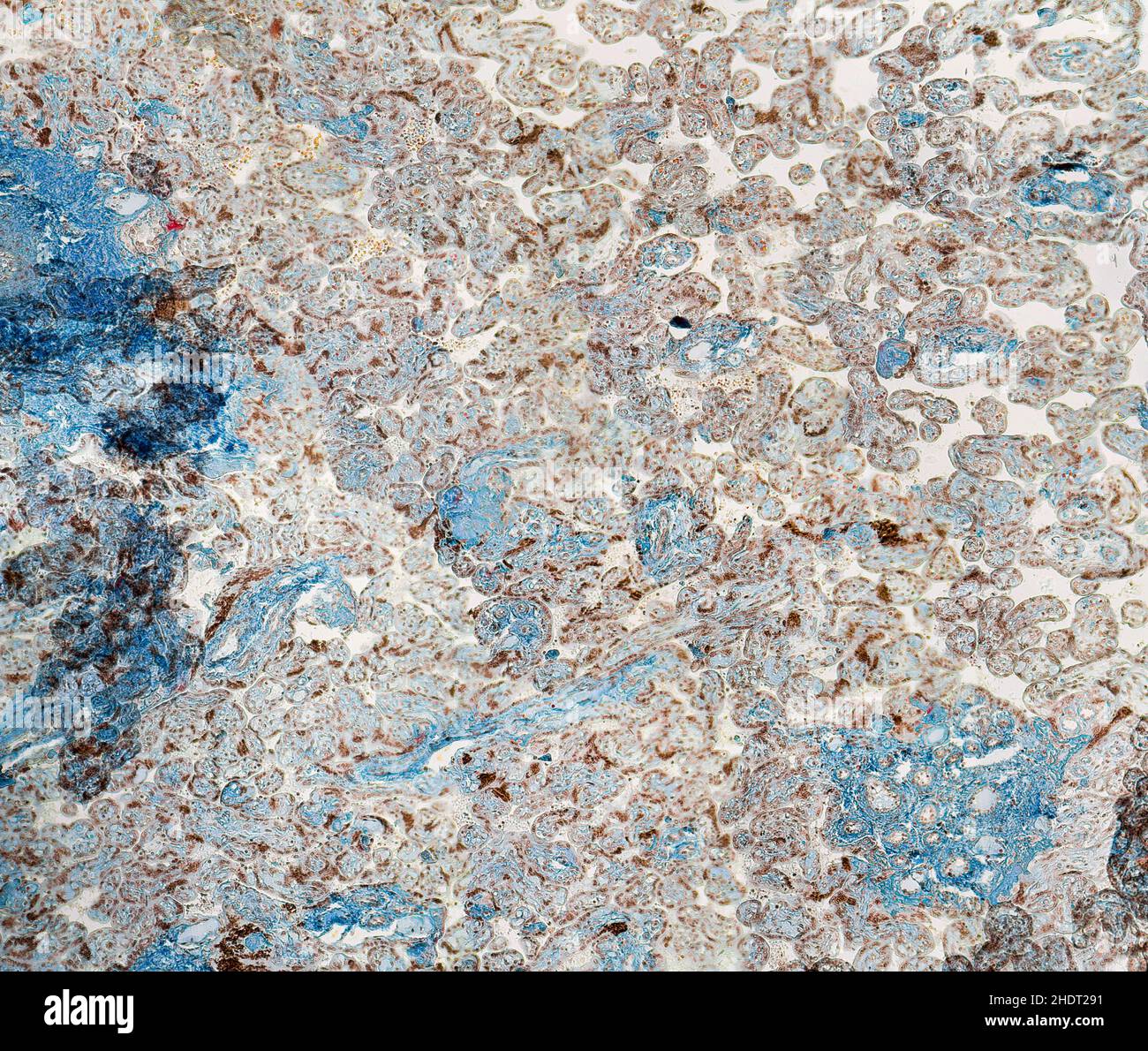 tissue, placenta, histology, tissues, placentas Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tissue-placenta-histology-tissues-placentas-image455988765.html
tissue, placenta, histology, tissues, placentas Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tissue-placenta-histology-tissues-placentas-image455988765.htmlRF2HDT291–tissue, placenta, histology, tissues, placentas
 a nurse shows what a placenta looks like, sometimes called the tree of life Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-nurse-shows-what-a-placenta-looks-like-sometimes-called-the-tree-of-life-image349076976.html
a nurse shows what a placenta looks like, sometimes called the tree of life Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-nurse-shows-what-a-placenta-looks-like-sometimes-called-the-tree-of-life-image349076976.htmlRF2B7WR6T–a nurse shows what a placenta looks like, sometimes called the tree of life
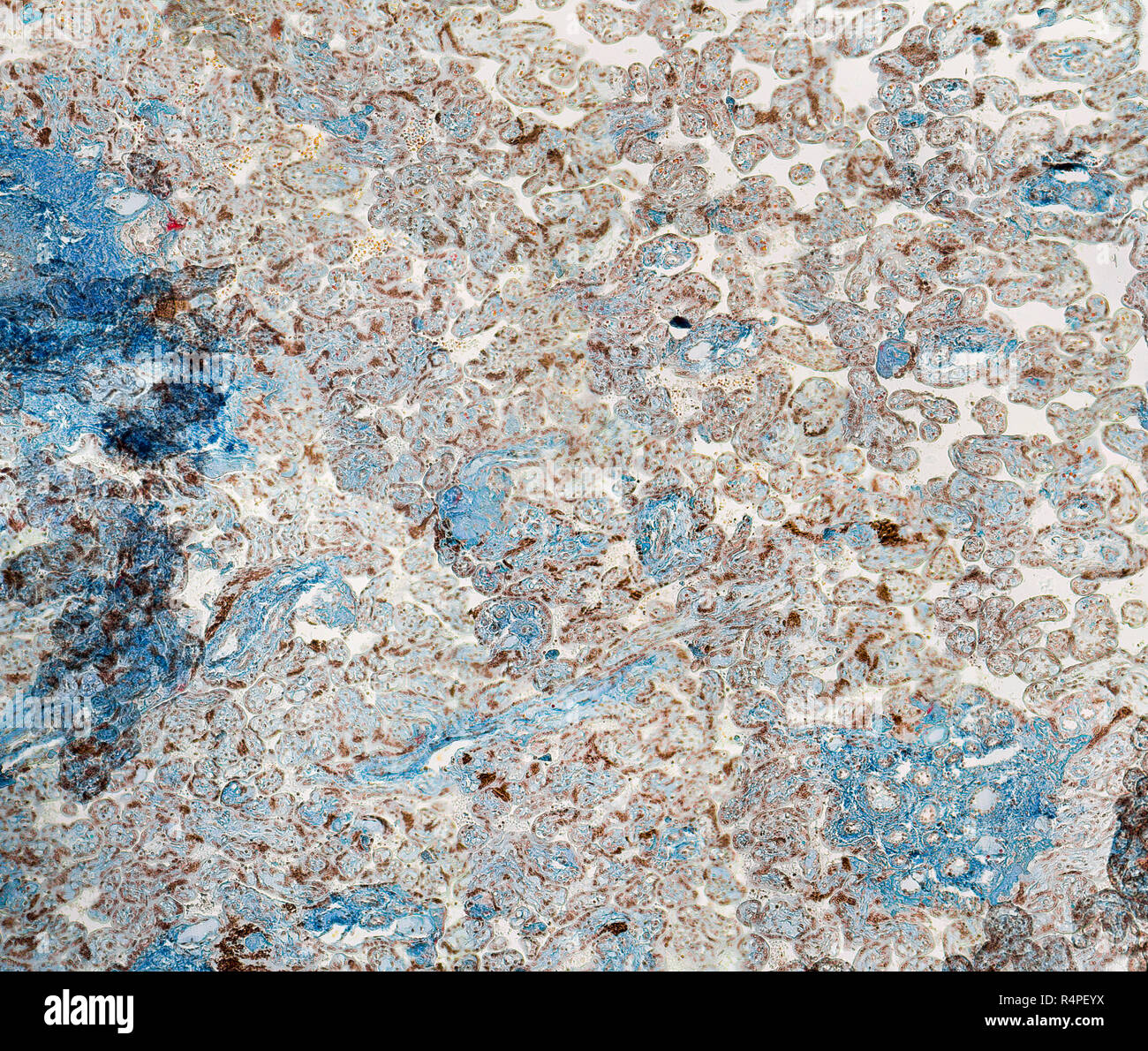 human placenta micrography Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-micrography-image226688110.html
human placenta micrography Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-micrography-image226688110.htmlRFR4PEYX–human placenta micrography
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073598.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073598.htmlRF2JGWD66–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth
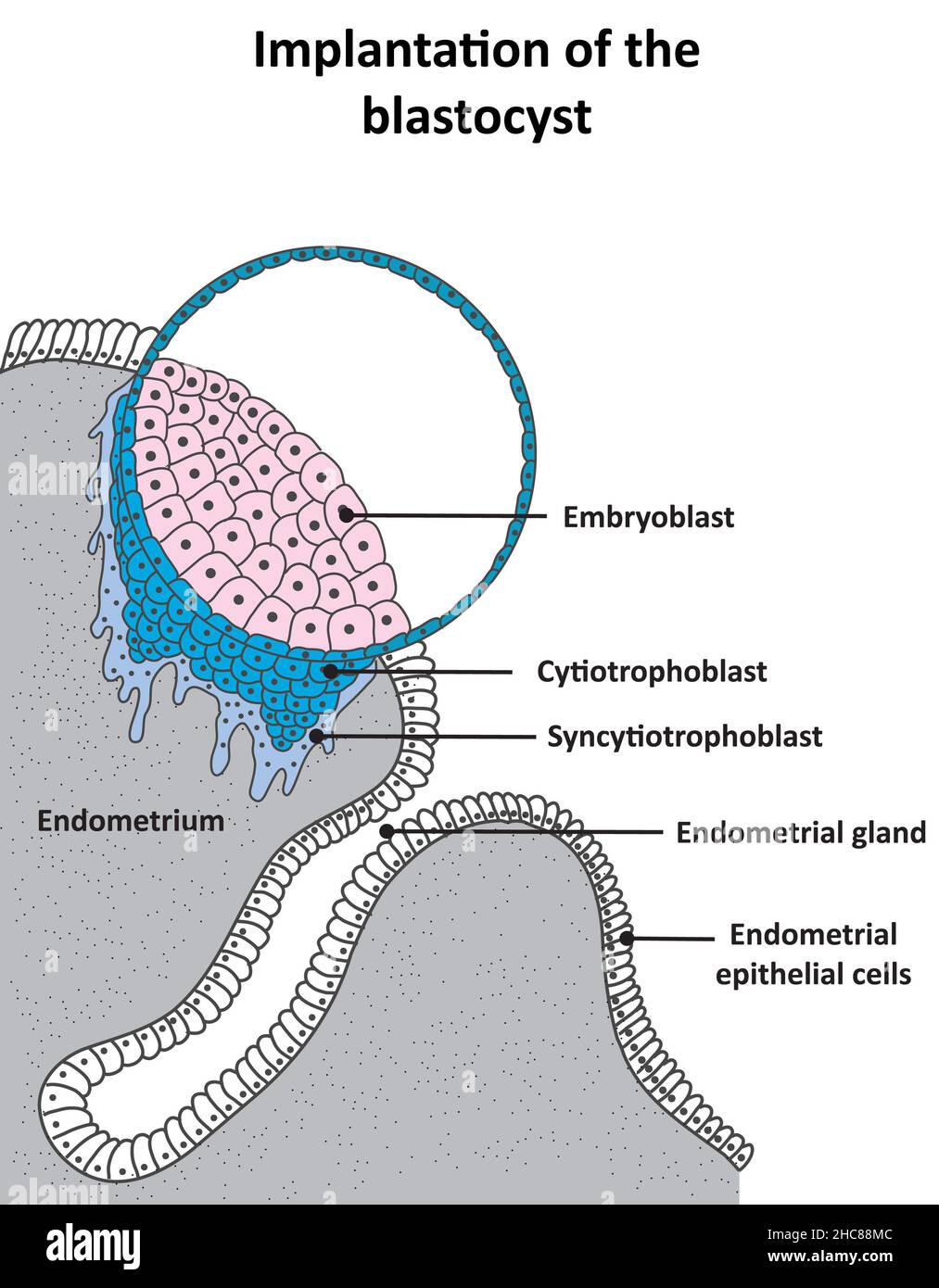 Implantation of the blastocyst and development of the cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/implantation-of-the-blastocyst-and-development-of-the-cytotrophoblast-and-syncytiotrophoblast-image455027900.html
Implantation of the blastocyst and development of the cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/implantation-of-the-blastocyst-and-development-of-the-cytotrophoblast-and-syncytiotrophoblast-image455027900.htmlRF2HC88MC–Implantation of the blastocyst and development of the cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast
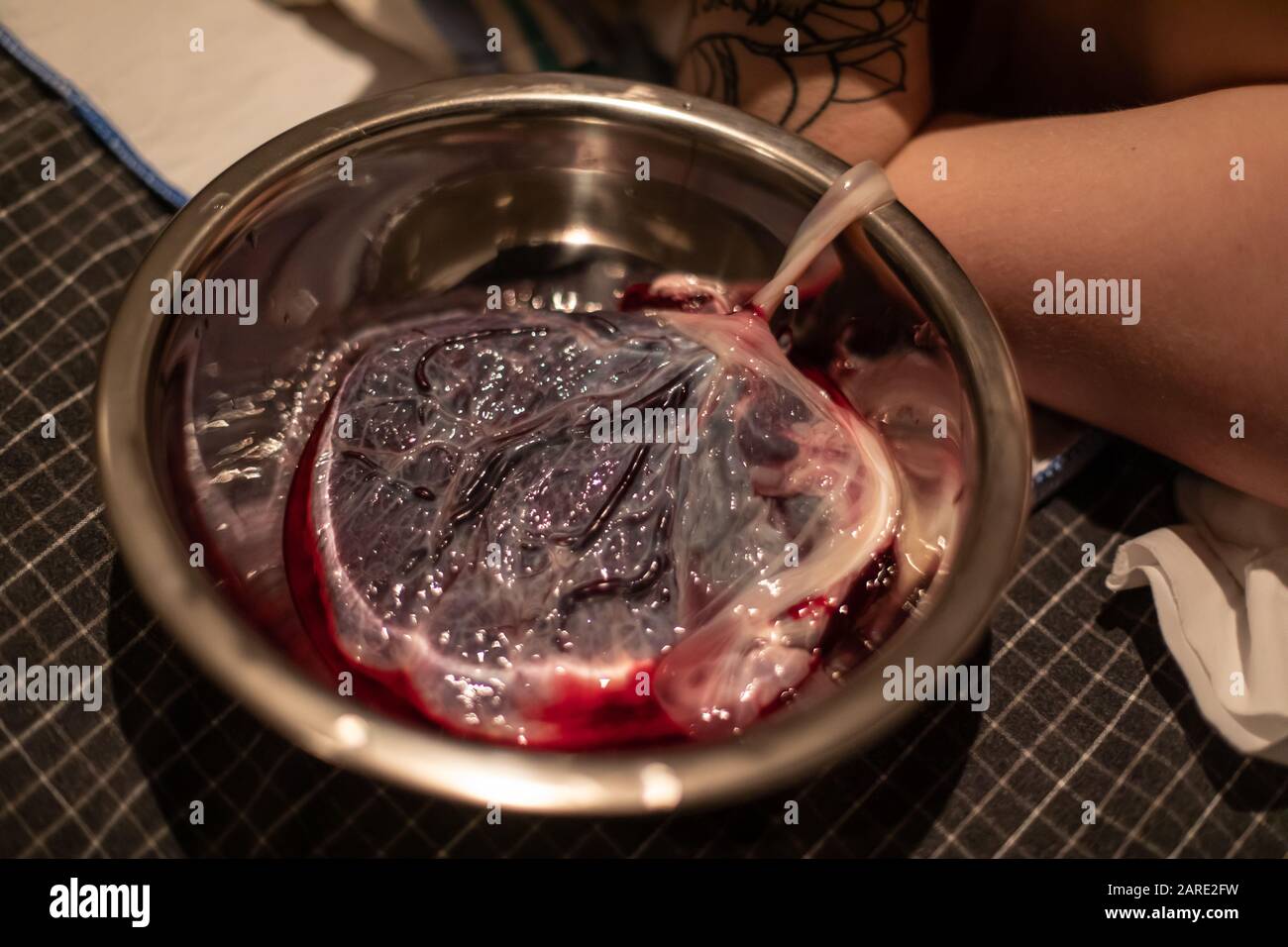 A close up detailed view of a bloody human placenta, maternal side, with intact umbilical cord in a sterile dish shortly after childbirth, copy space to sides Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-close-up-detailed-view-of-a-bloody-human-placenta-maternal-side-with-intact-umbilical-cord-in-a-sterile-dish-shortly-after-childbirth-copy-space-to-sides-image341443421.html
A close up detailed view of a bloody human placenta, maternal side, with intact umbilical cord in a sterile dish shortly after childbirth, copy space to sides Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-close-up-detailed-view-of-a-bloody-human-placenta-maternal-side-with-intact-umbilical-cord-in-a-sterile-dish-shortly-after-childbirth-copy-space-to-sides-image341443421.htmlRF2ARE2FW–A close up detailed view of a bloody human placenta, maternal side, with intact umbilical cord in a sterile dish shortly after childbirth, copy space to sides
 Dr Robert Newman demonstrates the process for creating a malaria blood film from placental tissue, a technique used to test for malaria following pregnancy, Burkina Faso, 2001. Image courtesy CDC/Dr. Robert Newman, EIS. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dr-robert-newman-demonstrates-the-process-for-creating-a-malaria-blood-170726574.html
Dr Robert Newman demonstrates the process for creating a malaria blood film from placental tissue, a technique used to test for malaria following pregnancy, Burkina Faso, 2001. Image courtesy CDC/Dr. Robert Newman, EIS. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dr-robert-newman-demonstrates-the-process-for-creating-a-malaria-blood-170726574.htmlRMKWN7DJ–Dr Robert Newman demonstrates the process for creating a malaria blood film from placental tissue, a technique used to test for malaria following pregnancy, Burkina Faso, 2001. Image courtesy CDC/Dr. Robert Newman, EIS. ()
 Cure for Preeclampsia, Pills Blister getting out from Red Box over White Background. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-cure-for-preeclampsia-pills-blister-getting-out-from-red-box-over-75982853.html
Cure for Preeclampsia, Pills Blister getting out from Red Box over White Background. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-cure-for-preeclampsia-pills-blister-getting-out-from-red-box-over-75982853.htmlRFEBH8W9–Cure for Preeclampsia, Pills Blister getting out from Red Box over White Background.
 A photomicrograph revealing cytoarchitectural changes seen in congenital syphilis of the placenta. The chorionic villi are enlarged, and contain dense laminated connective tissue, and the capillaries distributed throughout the villi are compressed by this connective tissue proliferation, HandE stain, magnification 450X, 1971. Image courtesy CDC/Susan Lindsley. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-a-photomicrograph-revealing-cytoarchitectural-changes-seen-in-congenital-169110851.html
A photomicrograph revealing cytoarchitectural changes seen in congenital syphilis of the placenta. The chorionic villi are enlarged, and contain dense laminated connective tissue, and the capillaries distributed throughout the villi are compressed by this connective tissue proliferation, HandE stain, magnification 450X, 1971. Image courtesy CDC/Susan Lindsley. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-a-photomicrograph-revealing-cytoarchitectural-changes-seen-in-congenital-169110851.htmlRMKR3JH7–A photomicrograph revealing cytoarchitectural changes seen in congenital syphilis of the placenta. The chorionic villi are enlarged, and contain dense laminated connective tissue, and the capillaries distributed throughout the villi are compressed by this connective tissue proliferation, HandE stain, magnification 450X, 1971. Image courtesy CDC/Susan Lindsley.
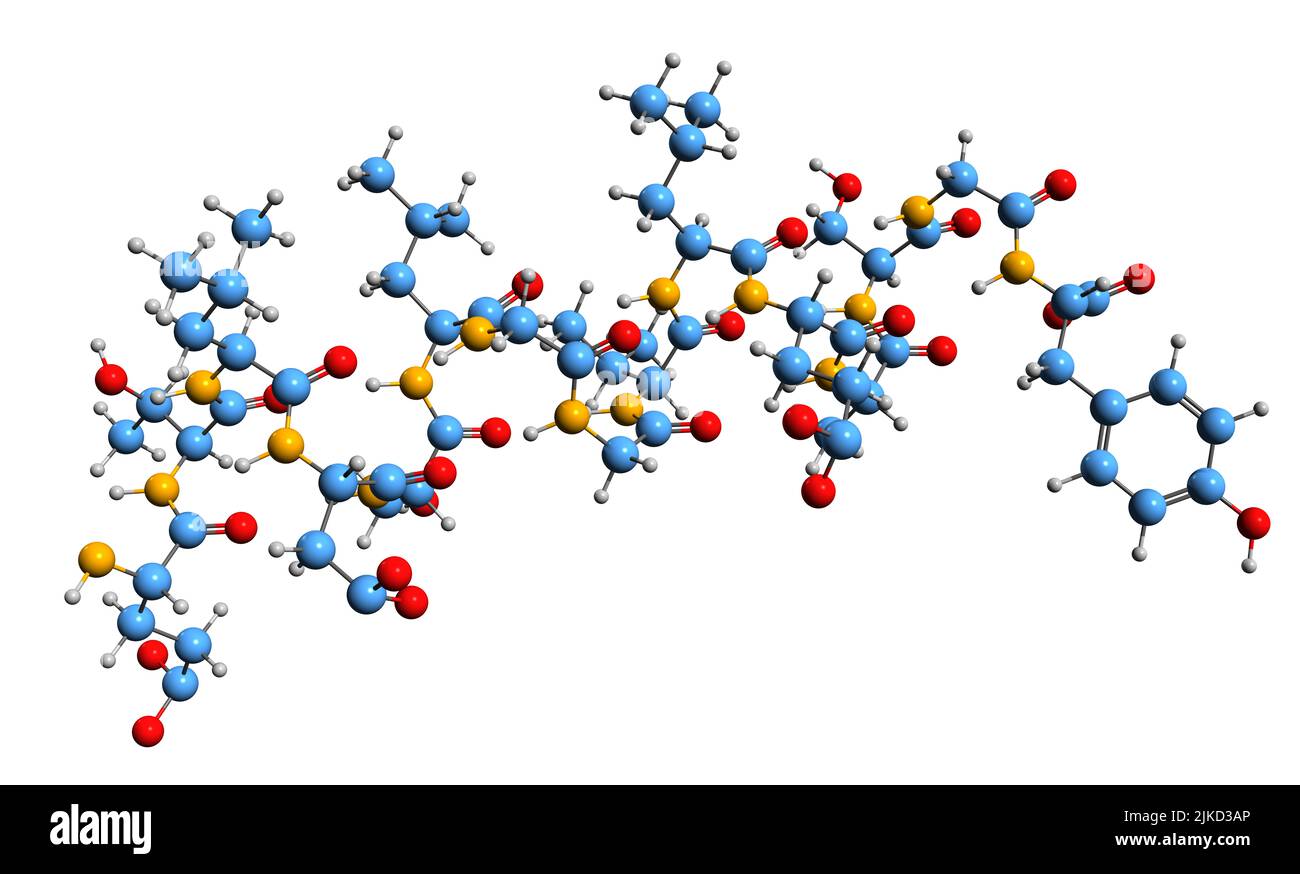 3D image of Leptin skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of adipose cells hormone isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-leptin-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-adipose-cells-hormone-isolated-on-white-background-image476646430.html
3D image of Leptin skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of adipose cells hormone isolated on white background Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-image-of-leptin-skeletal-formula-molecular-chemical-structure-of-adipose-cells-hormone-isolated-on-white-background-image476646430.htmlRF2JKD3AP–3D image of Leptin skeletal formula - molecular chemical structure of adipose cells hormone isolated on white background
 Biobank: umbilical cord tissue washed and stored before stem cell isolation. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-umbilical-cord-tissue-washed-and-stored-before-stem-cell-isolation-image476922814.html
Biobank: umbilical cord tissue washed and stored before stem cell isolation. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-umbilical-cord-tissue-washed-and-stored-before-stem-cell-isolation-image476922814.htmlRF2JKWKWJ–Biobank: umbilical cord tissue washed and stored before stem cell isolation.
 Placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411563.html
Placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411563.htmlRMAN4PBT–Placenta immediately after birth
 Veterinary obstetrics, including the diseases of breeding animals and of the new-born . layers of both the maternal and fetalcapillaries and an intervening layer of connective tissue. Thecapillaries of the allantois become greatly branched and grow outas villi which, sinking into the mucous membrane of the uterus,come into immediate contact with corresponding capillary loopsfrom the uterine ves.sels and become closely adherent with eachother with extremely thin walls, through which there is a free The Placenta 361 exchange of nutritive and waste products, but not of cellularelements. The separ Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/veterinary-obstetrics-including-the-diseases-of-breeding-animals-and-of-the-new-born-layers-of-both-the-maternal-and-fetalcapillaries-and-an-intervening-layer-of-connective-tissue-thecapillaries-of-the-allantois-become-greatly-branched-and-grow-outas-villi-which-sinking-into-the-mucous-membrane-of-the-uteruscome-into-immediate-contact-with-corresponding-capillary-loopsfrom-the-uterine-vessels-and-become-closely-adherent-with-eachother-with-extremely-thin-walls-through-which-there-is-a-free-the-placenta-361-exchange-of-nutritive-and-waste-products-but-not-of-cellularelements-the-separ-image340310122.html
Veterinary obstetrics, including the diseases of breeding animals and of the new-born . layers of both the maternal and fetalcapillaries and an intervening layer of connective tissue. Thecapillaries of the allantois become greatly branched and grow outas villi which, sinking into the mucous membrane of the uterus,come into immediate contact with corresponding capillary loopsfrom the uterine ves.sels and become closely adherent with eachother with extremely thin walls, through which there is a free The Placenta 361 exchange of nutritive and waste products, but not of cellularelements. The separ Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/veterinary-obstetrics-including-the-diseases-of-breeding-animals-and-of-the-new-born-layers-of-both-the-maternal-and-fetalcapillaries-and-an-intervening-layer-of-connective-tissue-thecapillaries-of-the-allantois-become-greatly-branched-and-grow-outas-villi-which-sinking-into-the-mucous-membrane-of-the-uteruscome-into-immediate-contact-with-corresponding-capillary-loopsfrom-the-uterine-vessels-and-become-closely-adherent-with-eachother-with-extremely-thin-walls-through-which-there-is-a-free-the-placenta-361-exchange-of-nutritive-and-waste-products-but-not-of-cellularelements-the-separ-image340310122.htmlRM2ANJD0X–Veterinary obstetrics, including the diseases of breeding animals and of the new-born . layers of both the maternal and fetalcapillaries and an intervening layer of connective tissue. Thecapillaries of the allantois become greatly branched and grow outas villi which, sinking into the mucous membrane of the uterus,come into immediate contact with corresponding capillary loopsfrom the uterine ves.sels and become closely adherent with eachother with extremely thin walls, through which there is a free The Placenta 361 exchange of nutritive and waste products, but not of cellularelements. The separ
 FDA Warns About Stem Cell Claims Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-fda-warns-about-stem-cell-claims-54562277.html
FDA Warns About Stem Cell Claims Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-fda-warns-about-stem-cell-claims-54562277.htmlRMD4NEMN–FDA Warns About Stem Cell Claims
 Human placenta with chorionic villi, blood vessels and red blood cells. X75 at 10 cm wide. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-with-chorionic-villi-blood-vessels-and-red-blood-cells-x75-at-10-cm-wide-image591999785.html
Human placenta with chorionic villi, blood vessels and red blood cells. X75 at 10 cm wide. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/human-placenta-with-chorionic-villi-blood-vessels-and-red-blood-cells-x75-at-10-cm-wide-image591999785.htmlRF2WB3WND–Human placenta with chorionic villi, blood vessels and red blood cells. X75 at 10 cm wide.
 Hypermature or aging placenta. The small chorionic villi show many foetal blood vessels, syncytial knots, and clumps of fibrin. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/hypermature-or-aging-placenta-the-small-chorionic-villi-show-many-foetal-blood-vessels-syncytial-knots-and-clumps-of-fibrin-image401736885.html
Hypermature or aging placenta. The small chorionic villi show many foetal blood vessels, syncytial knots, and clumps of fibrin. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/hypermature-or-aging-placenta-the-small-chorionic-villi-show-many-foetal-blood-vessels-syncytial-knots-and-clumps-of-fibrin-image401736885.htmlRF2E9GKDW–Hypermature or aging placenta. The small chorionic villi show many foetal blood vessels, syncytial knots, and clumps of fibrin.
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073541.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073541.htmlRF2JGWD45–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth
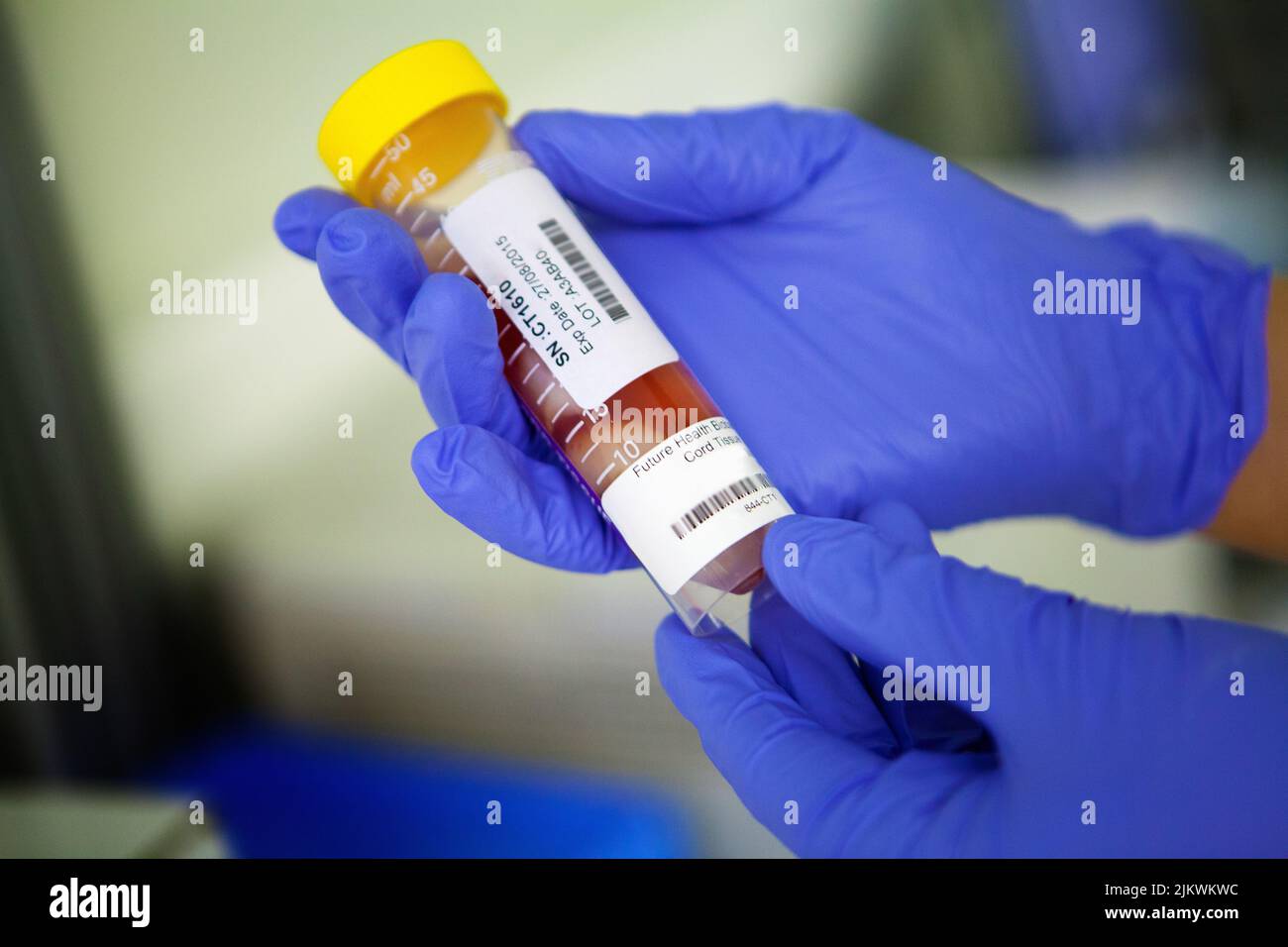 Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-storing-stem-cells-from-blood-and-cord-tissue-image476922808.html
Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-storing-stem-cells-from-blood-and-cord-tissue-image476922808.htmlRF2JKWKWC–Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue.
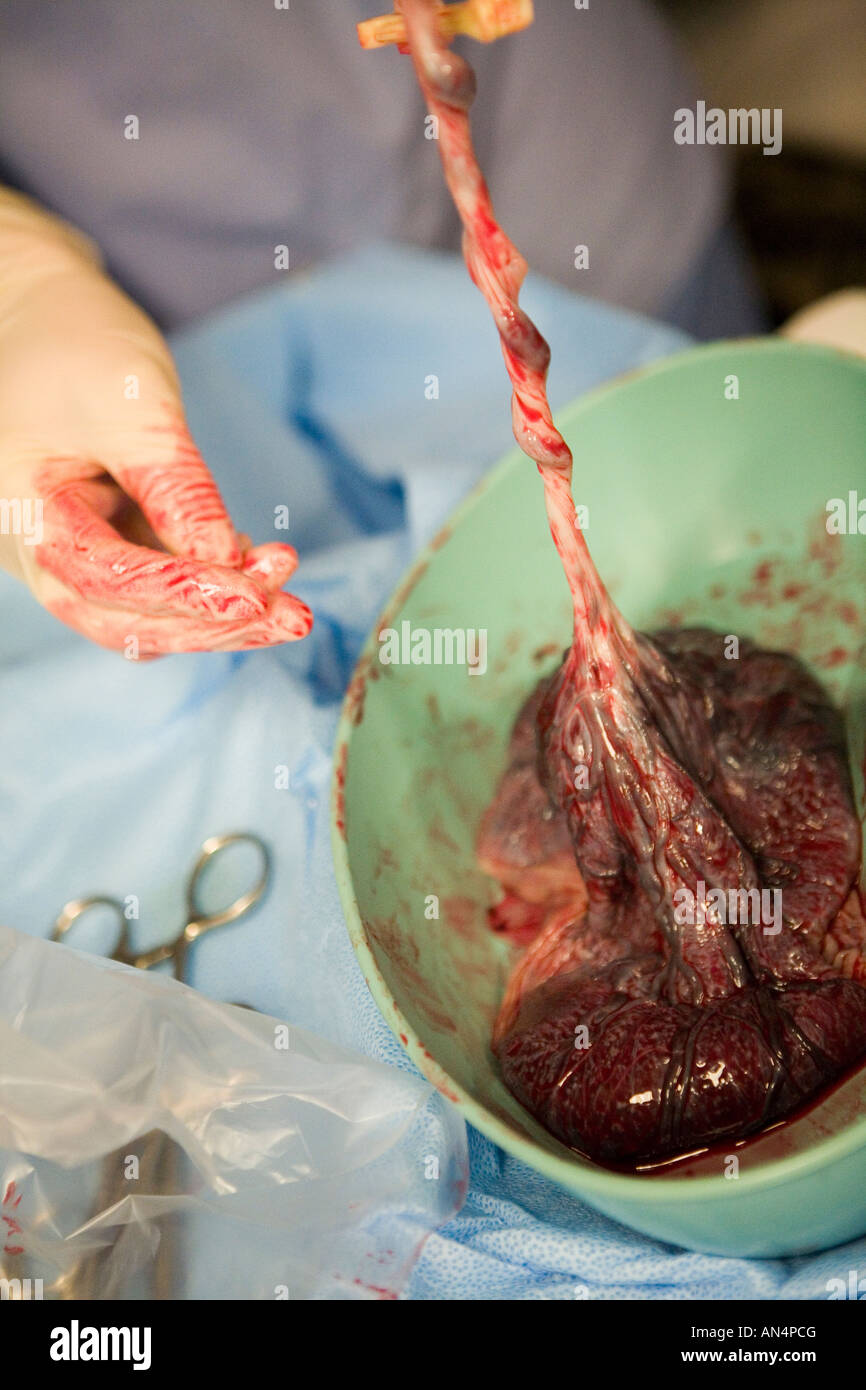 Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411567.html
Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411567.htmlRMAN4PCG–Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth
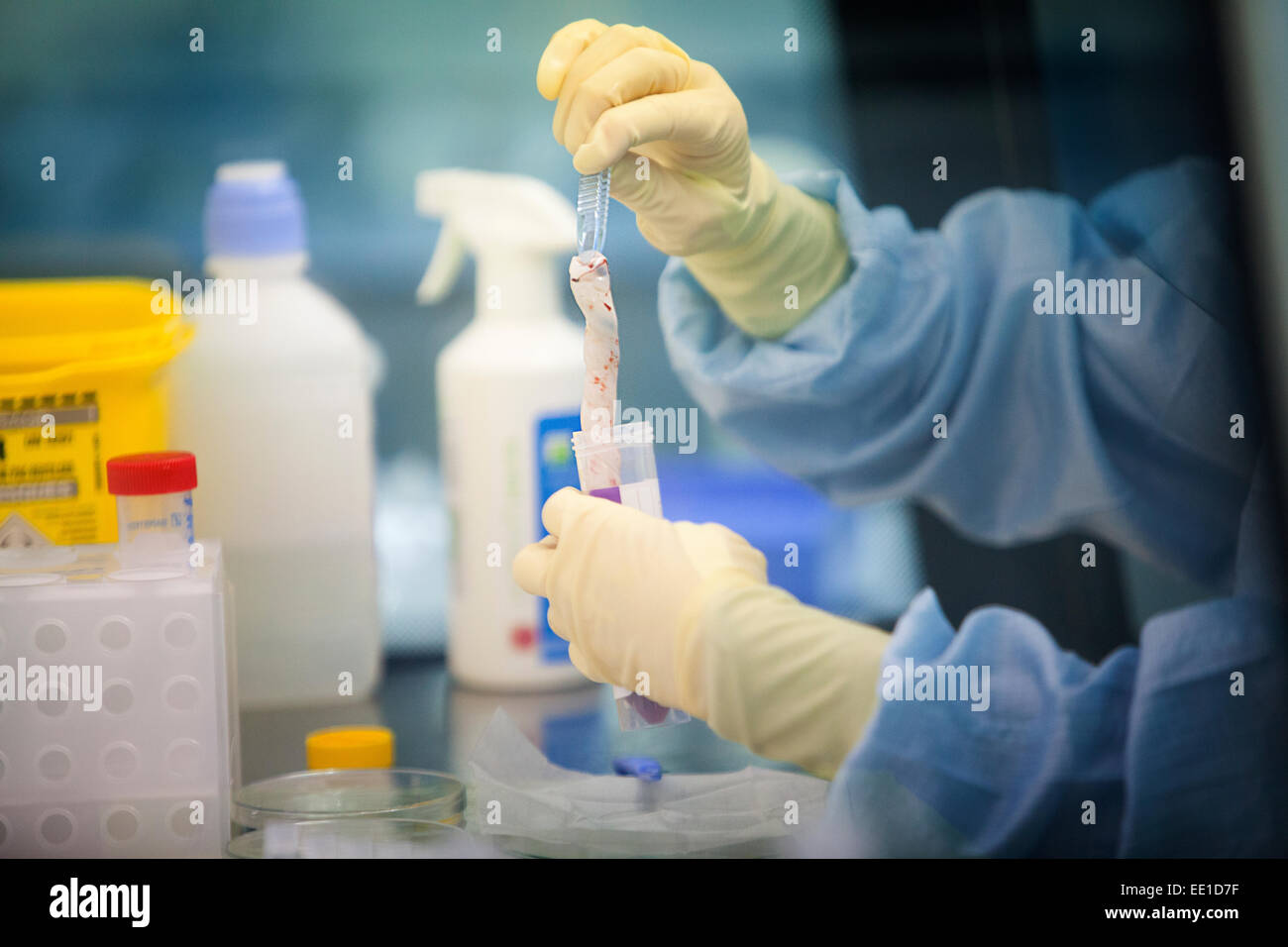 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479011.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479011.htmlRMEE1D7F–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 A treatise on the science and practice of midwifery . found the pus did not come fromthe placenta, but from an inflammation of the tissue of the uterine ves-sels and an accidental disposition in the tissue of the placenta. Theextravasations of blood here alluded to are of very common occurrence,and they are found in all parts of the organ—in its substance, on itsdecidual surface, or immediately below the amnion, where they serve aspoints of origin for the cysts that are there often observed. The fibrinthus deposited undergoes retrograde metamorphosis, as in other parts ofthe body; it becomes d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-the-science-and-practice-of-midwifery-found-the-pus-did-not-come-fromthe-placenta-but-from-an-inflammation-of-the-tissue-of-the-uterine-ves-sels-and-an-accidental-disposition-in-the-tissue-of-the-placenta-theextravasations-of-blood-here-alluded-to-are-of-very-common-occurrenceand-they-are-found-in-all-parts-of-the-organin-its-substance-on-itsdecidual-surface-or-immediately-below-the-amnion-where-they-serve-aspoints-of-origin-for-the-cysts-that-are-there-often-observed-the-fibrinthus-deposited-undergoes-retrograde-metamorphosis-as-in-other-parts-ofthe-body-it-becomes-d-image339127337.html
A treatise on the science and practice of midwifery . found the pus did not come fromthe placenta, but from an inflammation of the tissue of the uterine ves-sels and an accidental disposition in the tissue of the placenta. Theextravasations of blood here alluded to are of very common occurrence,and they are found in all parts of the organ—in its substance, on itsdecidual surface, or immediately below the amnion, where they serve aspoints of origin for the cysts that are there often observed. The fibrinthus deposited undergoes retrograde metamorphosis, as in other parts ofthe body; it becomes d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-the-science-and-practice-of-midwifery-found-the-pus-did-not-come-fromthe-placenta-but-from-an-inflammation-of-the-tissue-of-the-uterine-ves-sels-and-an-accidental-disposition-in-the-tissue-of-the-placenta-theextravasations-of-blood-here-alluded-to-are-of-very-common-occurrenceand-they-are-found-in-all-parts-of-the-organin-its-substance-on-itsdecidual-surface-or-immediately-below-the-amnion-where-they-serve-aspoints-of-origin-for-the-cysts-that-are-there-often-observed-the-fibrinthus-deposited-undergoes-retrograde-metamorphosis-as-in-other-parts-ofthe-body-it-becomes-d-image339127337.htmlRM2AKMGAH–A treatise on the science and practice of midwifery . found the pus did not come fromthe placenta, but from an inflammation of the tissue of the uterine ves-sels and an accidental disposition in the tissue of the placenta. Theextravasations of blood here alluded to are of very common occurrence,and they are found in all parts of the organ—in its substance, on itsdecidual surface, or immediately below the amnion, where they serve aspoints of origin for the cysts that are there often observed. The fibrinthus deposited undergoes retrograde metamorphosis, as in other parts ofthe body; it becomes d
 BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-biobank-102936099.html
BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-biobank-102936099.htmlRMFYD417–BIOBANK
 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Section showing the regional divisions of the uterus. ( Outlined ad Nat.) from which polypi, that are not cervical in their origin, most frequently arise; and it is very commonly the seat of those large hyper- trophic growths of the uterine tissue, which are usually termed fibrous tumours. The fundus is also the part to which the upper portion of the placenta is most frequently attached. The body is included between the line above indicated, and another, B B, drawn through the narrowest part of the organ, or that point a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-section-showing-the-regional-divisions-of-the-uterus-outlined-ad-nat-from-which-polypi-that-are-not-cervical-in-their-origin-most-frequently-arise-and-it-is-very-commonly-the-seat-of-those-large-hyper-trophic-growths-of-the-uterine-tissue-which-are-usually-termed-fibrous-tumours-the-fundus-is-also-the-part-to-which-the-upper-portion-of-the-placenta-is-most-frequently-attached-the-body-is-included-between-the-line-above-indicated-and-another-b-b-drawn-through-the-narrowest-part-of-the-organ-or-that-point-a-image216209023.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Section showing the regional divisions of the uterus. ( Outlined ad Nat.) from which polypi, that are not cervical in their origin, most frequently arise; and it is very commonly the seat of those large hyper- trophic growths of the uterine tissue, which are usually termed fibrous tumours. The fundus is also the part to which the upper portion of the placenta is most frequently attached. The body is included between the line above indicated, and another, B B, drawn through the narrowest part of the organ, or that point a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-section-showing-the-regional-divisions-of-the-uterus-outlined-ad-nat-from-which-polypi-that-are-not-cervical-in-their-origin-most-frequently-arise-and-it-is-very-commonly-the-seat-of-those-large-hyper-trophic-growths-of-the-uterine-tissue-which-are-usually-termed-fibrous-tumours-the-fundus-is-also-the-part-to-which-the-upper-portion-of-the-placenta-is-most-frequently-attached-the-body-is-included-between-the-line-above-indicated-and-another-b-b-drawn-through-the-narrowest-part-of-the-organ-or-that-point-a-image216209023.htmlRMPFN4PR–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Section showing the regional divisions of the uterus. ( Outlined ad Nat.) from which polypi, that are not cervical in their origin, most frequently arise; and it is very commonly the seat of those large hyper- trophic growths of the uterine tissue, which are usually termed fibrous tumours. The fundus is also the part to which the upper portion of the placenta is most frequently attached. The body is included between the line above indicated, and another, B B, drawn through the narrowest part of the organ, or that point a
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073596.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073596.htmlRF2JGWD64–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth
 Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411568.html
Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411568.htmlRMAN4PCH–Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth
 Cyclopædia of obstetrics and gynecology . ta. Here I could feel the abnormal partialthinning, as if the organ had been ruptured. The placenta was partlyimplanted upon the thinned area. It required injection of liq. ferri ses-quichlorati to stop the hemorrhage. There is not the slightest doubt that the thinned spot could not closethe mouths of the vessels on account of the deficiency in muscular tissue.And it is undoubtedly quite possible for such a spot to be the seat ofrupture. CHAPTER XXXVIl. SLIGHTER DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES OF THE UTERUS. I. OBLKiUITY OF THE UtEUUS. /^BLIQUITAS uteri quoad Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cyclopdia-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-ta-here-i-could-feel-the-abnormal-partialthinning-as-if-the-organ-had-been-ruptured-the-placenta-was-partlyimplanted-upon-the-thinned-area-it-required-injection-of-liq-ferri-ses-quichlorati-to-stop-the-hemorrhage-there-is-not-the-slightest-doubt-that-the-thinned-spot-could-not-closethe-mouths-of-the-vessels-on-account-of-the-deficiency-in-muscular-tissueand-it-is-undoubtedly-quite-possible-for-such-a-spot-to-be-the-seat-ofrupture-chapter-xxxvil-slighter-developmental-anomalies-of-the-uterus-i-oblkiuity-of-the-uteuus-bliquitas-uteri-quoad-image339244373.html
Cyclopædia of obstetrics and gynecology . ta. Here I could feel the abnormal partialthinning, as if the organ had been ruptured. The placenta was partlyimplanted upon the thinned area. It required injection of liq. ferri ses-quichlorati to stop the hemorrhage. There is not the slightest doubt that the thinned spot could not closethe mouths of the vessels on account of the deficiency in muscular tissue.And it is undoubtedly quite possible for such a spot to be the seat ofrupture. CHAPTER XXXVIl. SLIGHTER DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES OF THE UTERUS. I. OBLKiUITY OF THE UtEUUS. /^BLIQUITAS uteri quoad Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cyclopdia-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-ta-here-i-could-feel-the-abnormal-partialthinning-as-if-the-organ-had-been-ruptured-the-placenta-was-partlyimplanted-upon-the-thinned-area-it-required-injection-of-liq-ferri-ses-quichlorati-to-stop-the-hemorrhage-there-is-not-the-slightest-doubt-that-the-thinned-spot-could-not-closethe-mouths-of-the-vessels-on-account-of-the-deficiency-in-muscular-tissueand-it-is-undoubtedly-quite-possible-for-such-a-spot-to-be-the-seat-ofrupture-chapter-xxxvil-slighter-developmental-anomalies-of-the-uterus-i-oblkiuity-of-the-uteuus-bliquitas-uteri-quoad-image339244373.htmlRM2AKWWJD–Cyclopædia of obstetrics and gynecology . ta. Here I could feel the abnormal partialthinning, as if the organ had been ruptured. The placenta was partlyimplanted upon the thinned area. It required injection of liq. ferri ses-quichlorati to stop the hemorrhage. There is not the slightest doubt that the thinned spot could not closethe mouths of the vessels on account of the deficiency in muscular tissue.And it is undoubtedly quite possible for such a spot to be the seat ofrupture. CHAPTER XXXVIl. SLIGHTER DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES OF THE UTERUS. I. OBLKiUITY OF THE UtEUUS. /^BLIQUITAS uteri quoad
 BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-biobank-102936085.html
BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-biobank-102936085.htmlRMFYD40N–BIOBANK
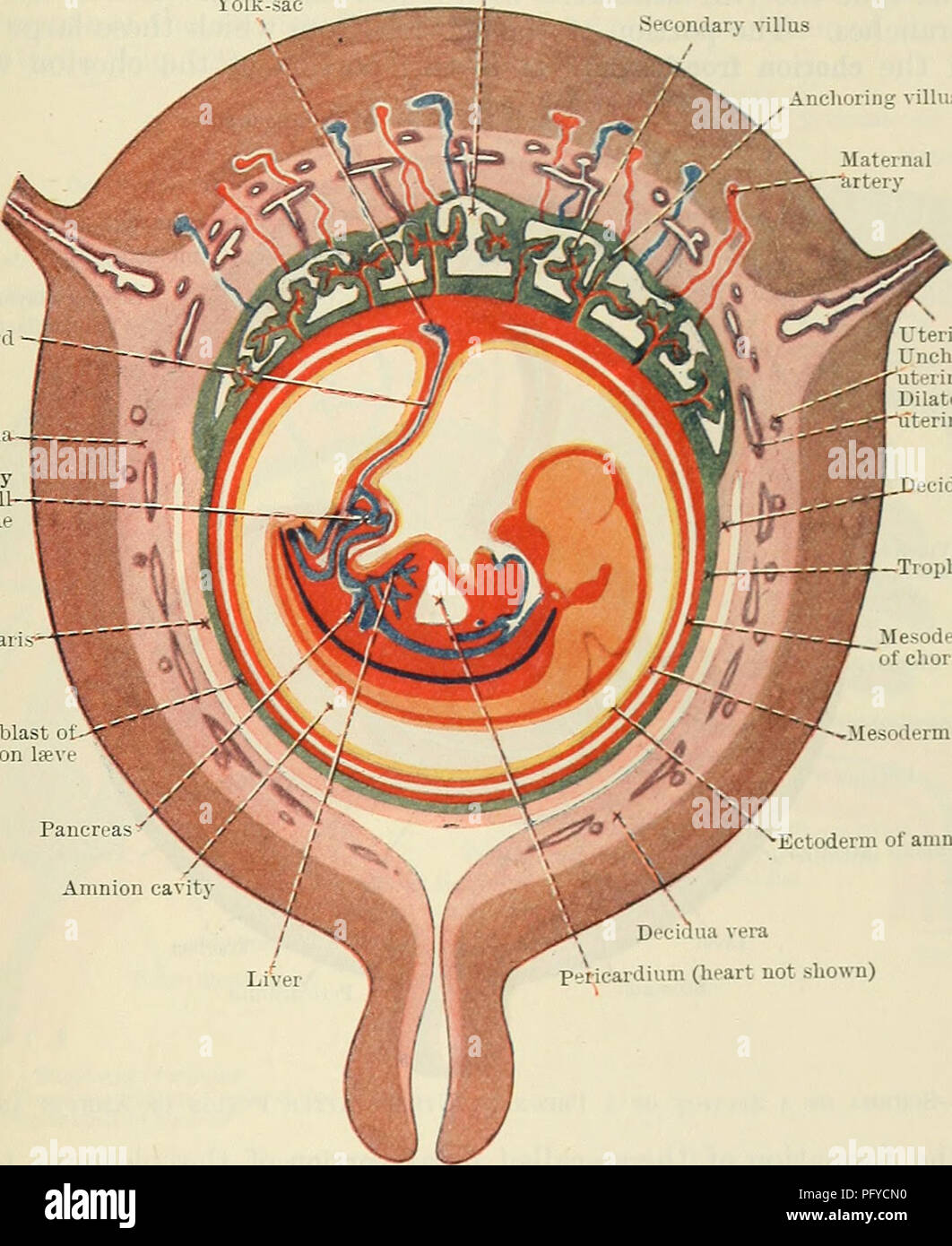 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 59 by a layer of cellular trophoblast, Langhan's layer, which lies next the mesoderm, and a layer of Plasmodium external to the cellular layer. The proximal end of .each villus is continuous with the chorion plate of the intervillous spaces, formed by the chorion, and the distal extremity is connected by the plasmodial basal layer of the trophoblast, which forms the outer boundary of the intervillous spaces and which is fused with the maternal decidual tissue. After a time branches are projected from the sides of the secondary villi i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-placenta-59-by-a-layer-of-cellular-trophoblast-langhans-layer-which-lies-next-the-mesoderm-and-a-layer-of-plasmodium-external-to-the-cellular-layer-the-proximal-end-of-each-villus-is-continuous-with-the-chorion-plate-of-the-intervillous-spaces-formed-by-the-chorion-and-the-distal-extremity-is-connected-by-the-plasmodial-basal-layer-of-the-trophoblast-which-forms-the-outer-boundary-of-the-intervillous-spaces-and-which-is-fused-with-the-maternal-decidual-tissue-after-a-time-branches-are-projected-from-the-sides-of-the-secondary-villi-i-image216346956.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 59 by a layer of cellular trophoblast, Langhan's layer, which lies next the mesoderm, and a layer of Plasmodium external to the cellular layer. The proximal end of .each villus is continuous with the chorion plate of the intervillous spaces, formed by the chorion, and the distal extremity is connected by the plasmodial basal layer of the trophoblast, which forms the outer boundary of the intervillous spaces and which is fused with the maternal decidual tissue. After a time branches are projected from the sides of the secondary villi i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-placenta-59-by-a-layer-of-cellular-trophoblast-langhans-layer-which-lies-next-the-mesoderm-and-a-layer-of-plasmodium-external-to-the-cellular-layer-the-proximal-end-of-each-villus-is-continuous-with-the-chorion-plate-of-the-intervillous-spaces-formed-by-the-chorion-and-the-distal-extremity-is-connected-by-the-plasmodial-basal-layer-of-the-trophoblast-which-forms-the-outer-boundary-of-the-intervillous-spaces-and-which-is-fused-with-the-maternal-decidual-tissue-after-a-time-branches-are-projected-from-the-sides-of-the-secondary-villi-i-image216346956.htmlRMPFYCN0–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 59 by a layer of cellular trophoblast, Langhan's layer, which lies next the mesoderm, and a layer of Plasmodium external to the cellular layer. The proximal end of .each villus is continuous with the chorion plate of the intervillous spaces, formed by the chorion, and the distal extremity is connected by the plasmodial basal layer of the trophoblast, which forms the outer boundary of the intervillous spaces and which is fused with the maternal decidual tissue. After a time branches are projected from the sides of the secondary villi i
 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77478955.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77478955.htmlRMEE1D5F–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073542.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073542.htmlRF2JGWD46–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth
 Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411551.html
Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411551.htmlRMAN4PAT–Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth
 Carpenter's principles of human physiology . elyentirely vanish. De Sinety§ shows that to the end of pregnancy, remains ofthe uterine glands lined with columnar epithelium may be found in certainparts of the cavity of the uterus ; after delivery, however, no epithelium canbe discovered, but in its place are a number of cells presenting embryonalcharacters, which infiltrate the whole tissue. That portion of the decidua verain which the chorionic tufts are embedded, and which afterwards forms thematernal portion of the placenta, is termed the Decidua Serotina; the greaterportion of it is deciduo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/carpenters-principles-of-human-physiology-elyentirely-vanish-de-sinety-shows-that-to-the-end-of-pregnancy-remains-ofthe-uterine-glands-lined-with-columnar-epithelium-may-be-found-in-certainparts-of-the-cavity-of-the-uterus-after-delivery-however-no-epithelium-canbe-discovered-but-in-its-place-are-a-number-of-cells-presenting-embryonalcharacters-which-infiltrate-the-whole-tissue-that-portion-of-the-decidua-verain-which-the-chorionic-tufts-are-embedded-and-which-afterwards-forms-thematernal-portion-of-the-placenta-is-termed-the-decidua-serotina-the-greaterportion-of-it-is-deciduo-image339984502.html
Carpenter's principles of human physiology . elyentirely vanish. De Sinety§ shows that to the end of pregnancy, remains ofthe uterine glands lined with columnar epithelium may be found in certainparts of the cavity of the uterus ; after delivery, however, no epithelium canbe discovered, but in its place are a number of cells presenting embryonalcharacters, which infiltrate the whole tissue. That portion of the decidua verain which the chorionic tufts are embedded, and which afterwards forms thematernal portion of the placenta, is termed the Decidua Serotina; the greaterportion of it is deciduo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/carpenters-principles-of-human-physiology-elyentirely-vanish-de-sinety-shows-that-to-the-end-of-pregnancy-remains-ofthe-uterine-glands-lined-with-columnar-epithelium-may-be-found-in-certainparts-of-the-cavity-of-the-uterus-after-delivery-however-no-epithelium-canbe-discovered-but-in-its-place-are-a-number-of-cells-presenting-embryonalcharacters-which-infiltrate-the-whole-tissue-that-portion-of-the-decidua-verain-which-the-chorionic-tufts-are-embedded-and-which-afterwards-forms-thematernal-portion-of-the-placenta-is-termed-the-decidua-serotina-the-greaterportion-of-it-is-deciduo-image339984502.htmlRM2AN3HKJ–Carpenter's principles of human physiology . elyentirely vanish. De Sinety§ shows that to the end of pregnancy, remains ofthe uterine glands lined with columnar epithelium may be found in certainparts of the cavity of the uterus ; after delivery, however, no epithelium canbe discovered, but in its place are a number of cells presenting embryonalcharacters, which infiltrate the whole tissue. That portion of the decidua verain which the chorionic tufts are embedded, and which afterwards forms thematernal portion of the placenta, is termed the Decidua Serotina; the greaterportion of it is deciduo
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 61 of the uterus, until it is forced against the surrounding wall of the uterine cavity, where it fuses with the decidua vera, and thus the cavity of the uterus is obliterated. This fusion takes place towards the end of the second month, and as soon as it has occurred the discoid mass of placental tissue is continuous at its margin with the fused amnion, chorion, and decidua vera (Fig. 78). After the second month the fcetus lies in the amnion cavity, which is bounded by the fused chorion and uterine wall, except at the lower end of th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-placenta-61-of-the-uterus-until-it-is-forced-against-the-surrounding-wall-of-the-uterine-cavity-where-it-fuses-with-the-decidua-vera-and-thus-the-cavity-of-the-uterus-is-obliterated-this-fusion-takes-place-towards-the-end-of-the-second-month-and-as-soon-as-it-has-occurred-the-discoid-mass-of-placental-tissue-is-continuous-at-its-margin-with-the-fused-amnion-chorion-and-decidua-vera-fig-78-after-the-second-month-the-fcetus-lies-in-the-amnion-cavity-which-is-bounded-by-the-fused-chorion-and-uterine-wall-except-at-the-lower-end-of-th-image216346949.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 61 of the uterus, until it is forced against the surrounding wall of the uterine cavity, where it fuses with the decidua vera, and thus the cavity of the uterus is obliterated. This fusion takes place towards the end of the second month, and as soon as it has occurred the discoid mass of placental tissue is continuous at its margin with the fused amnion, chorion, and decidua vera (Fig. 78). After the second month the fcetus lies in the amnion cavity, which is bounded by the fused chorion and uterine wall, except at the lower end of th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-placenta-61-of-the-uterus-until-it-is-forced-against-the-surrounding-wall-of-the-uterine-cavity-where-it-fuses-with-the-decidua-vera-and-thus-the-cavity-of-the-uterus-is-obliterated-this-fusion-takes-place-towards-the-end-of-the-second-month-and-as-soon-as-it-has-occurred-the-discoid-mass-of-placental-tissue-is-continuous-at-its-margin-with-the-fused-amnion-chorion-and-decidua-vera-fig-78-after-the-second-month-the-fcetus-lies-in-the-amnion-cavity-which-is-bounded-by-the-fused-chorion-and-uterine-wall-except-at-the-lower-end-of-th-image216346949.htmlRMPFYCMN–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 61 of the uterus, until it is forced against the surrounding wall of the uterine cavity, where it fuses with the decidua vera, and thus the cavity of the uterus is obliterated. This fusion takes place towards the end of the second month, and as soon as it has occurred the discoid mass of placental tissue is continuous at its margin with the fused amnion, chorion, and decidua vera (Fig. 78). After the second month the fcetus lies in the amnion cavity, which is bounded by the fused chorion and uterine wall, except at the lower end of th
 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479012.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479012.htmlRMEE1D7G–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073532.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-childbirth-image475073532.htmlRF2JGWD3T–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after childbirth
 Placenta immediately after birth with surgical scissors Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-placenta-immediately-after-birth-with-surgical-scissors-15411557.html
Placenta immediately after birth with surgical scissors Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-placenta-immediately-after-birth-with-surgical-scissors-15411557.htmlRMAN4PBJ–Placenta immediately after birth with surgical scissors
 . Lessons with plants. Suggestions for seeing and interpreting some of the common forms of vegetation. there is a more or lessdistinct elevation or thickening of tissue at the THE PARTS OF THE PISTIL 143 place where the ovules are attached. This is em-phatically shown in the fruit of the May-apple ormandrake (shown incross-section in Fig.145). This point ofattachment is knownas the placenta (plu-ral, placentas), 158a. The placenta is de-fined with reference to its po-sition. It is evident thatthere are two general typesof placentse,—those which areborne upon the outward wallsof the ovary, and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lessons-with-plants-suggestions-for-seeing-and-interpreting-some-of-the-common-forms-of-vegetation-there-is-a-more-or-lessdistinct-elevation-or-thickening-of-tissue-at-the-the-parts-of-the-pistil-143-place-where-the-ovules-are-attached-this-is-em-phatically-shown-in-the-fruit-of-the-may-apple-ormandrake-shown-incross-section-in-fig145-this-point-ofattachment-is-knownas-the-placenta-plu-ral-placentas-158a-the-placenta-is-de-fined-with-reference-to-its-po-sition-it-is-evident-thatthere-are-two-general-typesof-placentsethose-which-areborne-upon-the-outward-wallsof-the-ovary-and-image336728500.html
. Lessons with plants. Suggestions for seeing and interpreting some of the common forms of vegetation. there is a more or lessdistinct elevation or thickening of tissue at the THE PARTS OF THE PISTIL 143 place where the ovules are attached. This is em-phatically shown in the fruit of the May-apple ormandrake (shown incross-section in Fig.145). This point ofattachment is knownas the placenta (plu-ral, placentas), 158a. The placenta is de-fined with reference to its po-sition. It is evident thatthere are two general typesof placentse,—those which areborne upon the outward wallsof the ovary, and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lessons-with-plants-suggestions-for-seeing-and-interpreting-some-of-the-common-forms-of-vegetation-there-is-a-more-or-lessdistinct-elevation-or-thickening-of-tissue-at-the-the-parts-of-the-pistil-143-place-where-the-ovules-are-attached-this-is-em-phatically-shown-in-the-fruit-of-the-may-apple-ormandrake-shown-incross-section-in-fig145-this-point-ofattachment-is-knownas-the-placenta-plu-ral-placentas-158a-the-placenta-is-de-fined-with-reference-to-its-po-sition-it-is-evident-thatthere-are-two-general-typesof-placentsethose-which-areborne-upon-the-outward-wallsof-the-ovary-and-image336728500.htmlRM2AFR8HT–. Lessons with plants. Suggestions for seeing and interpreting some of the common forms of vegetation. there is a more or lessdistinct elevation or thickening of tissue at the THE PARTS OF THE PISTIL 143 place where the ovules are attached. This is em-phatically shown in the fruit of the May-apple ormandrake (shown incross-section in Fig.145). This point ofattachment is knownas the placenta (plu-ral, placentas), 158a. The placenta is de-fined with reference to its po-sition. It is evident thatthere are two general typesof placentse,—those which areborne upon the outward wallsof the ovary, and
 . The origin of floral structures : through insect and other agencies. Plants; Flowers; Flowers. 296 THE STRUCTURE OF FLOWERS. Bcpchia diosmoefolia; * but as they grew on the interior of the wall and not on an axile placenta, as is the normal con- dition, in the Myrtacece, I expect that it was due to the staminal vascular cords branching off and coming out of the tissue within instead of at the summit of the hollow recepta- cnlar tube, the carpels being more or less arrested. A not t uncommon instance is to find the pistils of Willows with open ovaries and bearing one or more anthers on the ma Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-origin-of-floral-structures-through-insect-and-other-agencies-plants-flowers-flowers-296-the-structure-of-flowers-bcpchia-diosmoefolia-but-as-they-grew-on-the-interior-of-the-wall-and-not-on-an-axile-placenta-as-is-the-normal-con-dition-in-the-myrtacece-i-expect-that-it-was-due-to-the-staminal-vascular-cords-branching-off-and-coming-out-of-the-tissue-within-instead-of-at-the-summit-of-the-hollow-recepta-cnlar-tube-the-carpels-being-more-or-less-arrested-a-not-t-uncommon-instance-is-to-find-the-pistils-of-willows-with-open-ovaries-and-bearing-one-or-more-anthers-on-the-ma-image216438565.html
. The origin of floral structures : through insect and other agencies. Plants; Flowers; Flowers. 296 THE STRUCTURE OF FLOWERS. Bcpchia diosmoefolia; * but as they grew on the interior of the wall and not on an axile placenta, as is the normal con- dition, in the Myrtacece, I expect that it was due to the staminal vascular cords branching off and coming out of the tissue within instead of at the summit of the hollow recepta- cnlar tube, the carpels being more or less arrested. A not t uncommon instance is to find the pistils of Willows with open ovaries and bearing one or more anthers on the ma Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-origin-of-floral-structures-through-insect-and-other-agencies-plants-flowers-flowers-296-the-structure-of-flowers-bcpchia-diosmoefolia-but-as-they-grew-on-the-interior-of-the-wall-and-not-on-an-axile-placenta-as-is-the-normal-con-dition-in-the-myrtacece-i-expect-that-it-was-due-to-the-staminal-vascular-cords-branching-off-and-coming-out-of-the-tissue-within-instead-of-at-the-summit-of-the-hollow-recepta-cnlar-tube-the-carpels-being-more-or-less-arrested-a-not-t-uncommon-instance-is-to-find-the-pistils-of-willows-with-open-ovaries-and-bearing-one-or-more-anthers-on-the-ma-image216438565.htmlRMPG3HGN–. The origin of floral structures : through insect and other agencies. Plants; Flowers; Flowers. 296 THE STRUCTURE OF FLOWERS. Bcpchia diosmoefolia; * but as they grew on the interior of the wall and not on an axile placenta, as is the normal con- dition, in the Myrtacece, I expect that it was due to the staminal vascular cords branching off and coming out of the tissue within instead of at the summit of the hollow recepta- cnlar tube, the carpels being more or less arrested. A not t uncommon instance is to find the pistils of Willows with open ovaries and bearing one or more anthers on the ma
 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479013.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479013.htmlRMEE1D7H–STEM CELL BIOBANK
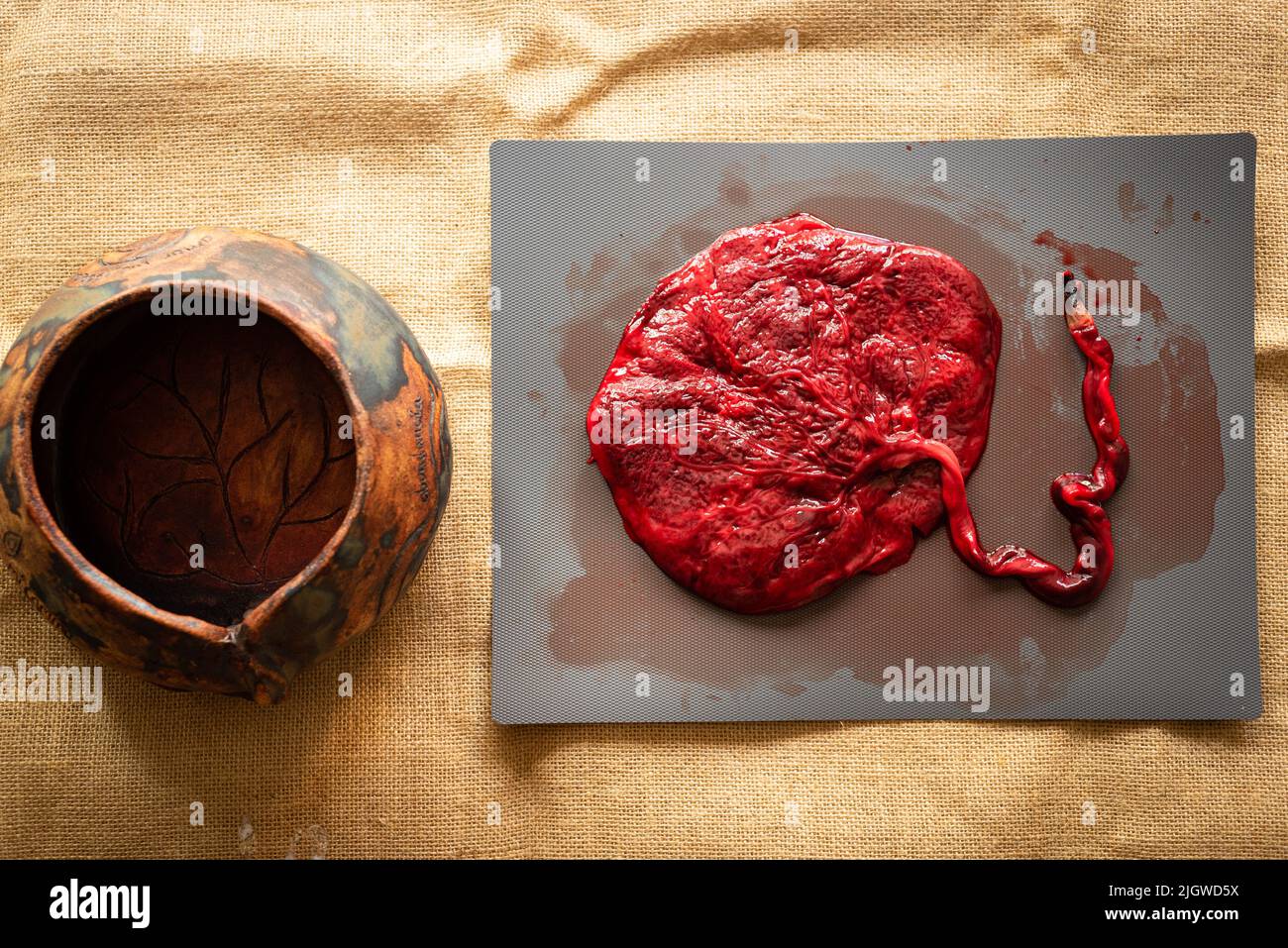 Top view of human placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/top-view-of-human-placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-with-a-ritual-pot-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-c-image475073590.html
Top view of human placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/top-view-of-human-placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-with-a-ritual-pot-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-c-image475073590.htmlRF2JGWD5X–Top view of human placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen c
 Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411561.html
Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-midwife-checking-placenta-immediately-after-birth-15411561.htmlRMAN4PBP–Midwife checking placenta immediately after birth
 A manual of obstetrics . h reversal of thedirection of rotation. Meclianism of the Third Stage of Labor.—There are variousviews advanced as to the manner in which the placenta be-comes detached from the uterine wall. The most probableone, and that which is now generally accepted, is that ofdiminution in the area of placental attachment. Accordingto this view the elastic placental tissue follows up the con-tracting uterus to a certain extent, probably to one-half ofits transverse diameter, and then, further condensation of itstissues becoming impossible, with the succeeding pain it is 156 A MAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-obstetrics-h-reversal-of-thedirection-of-rotation-meclianism-of-the-third-stage-of-laborthere-are-variousviews-advanced-as-to-the-manner-in-which-the-placenta-be-comes-detached-from-the-uterine-wall-the-most-probableone-and-that-which-is-now-generally-accepted-is-that-ofdiminution-in-the-area-of-placental-attachment-accordingto-this-view-the-elastic-placental-tissue-follows-up-the-con-tracting-uterus-to-a-certain-extent-probably-to-one-half-ofits-transverse-diameter-and-then-further-condensation-of-itstissues-becoming-impossible-with-the-succeeding-pain-it-is-156-a-man-image338183297.html
A manual of obstetrics . h reversal of thedirection of rotation. Meclianism of the Third Stage of Labor.—There are variousviews advanced as to the manner in which the placenta be-comes detached from the uterine wall. The most probableone, and that which is now generally accepted, is that ofdiminution in the area of placental attachment. Accordingto this view the elastic placental tissue follows up the con-tracting uterus to a certain extent, probably to one-half ofits transverse diameter, and then, further condensation of itstissues becoming impossible, with the succeeding pain it is 156 A MAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-obstetrics-h-reversal-of-thedirection-of-rotation-meclianism-of-the-third-stage-of-laborthere-are-variousviews-advanced-as-to-the-manner-in-which-the-placenta-be-comes-detached-from-the-uterine-wall-the-most-probableone-and-that-which-is-now-generally-accepted-is-that-ofdiminution-in-the-area-of-placental-attachment-accordingto-this-view-the-elastic-placental-tissue-follows-up-the-con-tracting-uterus-to-a-certain-extent-probably-to-one-half-ofits-transverse-diameter-and-then-further-condensation-of-itstissues-becoming-impossible-with-the-succeeding-pain-it-is-156-a-man-image338183297.htmlRM2AJ5G6W–A manual of obstetrics . h reversal of thedirection of rotation. Meclianism of the Third Stage of Labor.—There are variousviews advanced as to the manner in which the placenta be-comes detached from the uterine wall. The most probableone, and that which is now generally accepted, is that ofdiminution in the area of placental attachment. Accordingto this view the elastic placental tissue follows up the con-tracting uterus to a certain extent, probably to one-half ofits transverse diameter, and then, further condensation of itstissues becoming impossible, with the succeeding pain it is 156 A MAN
 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479031.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479031.htmlRMEE1D87–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-with-a-ritual-pot-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-a-image475709573.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-with-a-ritual-pot-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-a-image475709573.htmlRF2JHXCBH–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table a
 Pathology and treatment of diseases of women . tive tissue between the muscle fibres crammed withcocci which also migrate into the surrounding tissues, the latter showingthroughout a perivascular round cell infiltration. The smaller bloodvesselsbehave themselves much in the same way, a thrombophlebitic form, 204 DISEASES OF WOMEN especially near the site of the attachment of the placenta, is seen (seeFig. 109). The invading agents of infection may penetrate the entireuterine wall, the cocci may wander to the perimetrium and thus reachthe abdominal cavity. Here they cause either a general perit Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pathology-and-treatment-of-diseases-of-women-tive-tissue-between-the-muscle-fibres-crammed-withcocci-which-also-migrate-into-the-surrounding-tissues-the-latter-showingthroughout-a-perivascular-round-cell-infiltration-the-smaller-bloodvesselsbehave-themselves-much-in-the-same-way-a-thrombophlebitic-form-204-diseases-of-women-especially-near-the-site-of-the-attachment-of-the-placenta-is-seen-seefig-109-the-invading-agents-of-infection-may-penetrate-the-entireuterine-wall-the-cocci-may-wander-to-the-perimetrium-and-thus-reachthe-abdominal-cavity-here-they-cause-either-a-general-perit-image340005800.html
Pathology and treatment of diseases of women . tive tissue between the muscle fibres crammed withcocci which also migrate into the surrounding tissues, the latter showingthroughout a perivascular round cell infiltration. The smaller bloodvesselsbehave themselves much in the same way, a thrombophlebitic form, 204 DISEASES OF WOMEN especially near the site of the attachment of the placenta, is seen (seeFig. 109). The invading agents of infection may penetrate the entireuterine wall, the cocci may wander to the perimetrium and thus reachthe abdominal cavity. Here they cause either a general perit Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/pathology-and-treatment-of-diseases-of-women-tive-tissue-between-the-muscle-fibres-crammed-withcocci-which-also-migrate-into-the-surrounding-tissues-the-latter-showingthroughout-a-perivascular-round-cell-infiltration-the-smaller-bloodvesselsbehave-themselves-much-in-the-same-way-a-thrombophlebitic-form-204-diseases-of-women-especially-near-the-site-of-the-attachment-of-the-placenta-is-seen-seefig-109-the-invading-agents-of-infection-may-penetrate-the-entireuterine-wall-the-cocci-may-wander-to-the-perimetrium-and-thus-reachthe-abdominal-cavity-here-they-cause-either-a-general-perit-image340005800.htmlRM2AN4GT8–Pathology and treatment of diseases of women . tive tissue between the muscle fibres crammed withcocci which also migrate into the surrounding tissues, the latter showingthroughout a perivascular round cell infiltration. The smaller bloodvesselsbehave themselves much in the same way, a thrombophlebitic form, 204 DISEASES OF WOMEN especially near the site of the attachment of the placenta, is seen (seeFig. 109). The invading agents of infection may penetrate the entireuterine wall, the cocci may wander to the perimetrium and thus reachthe abdominal cavity. Here they cause either a general perit
 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479027.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77479027.htmlRMEE1D83–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 Top view of Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/top-view-of-placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-c-image475073534.html
Top view of Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/top-view-of-placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-after-c-image475073534.htmlRF2JGWD3X–Top view of Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table after c
 The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . e of thebleeding in placenta praevia during auterus forcing out from the organ blood which had already escaped during theinterval. In one way, up to a certain point, contractions do favor hemorrhageby detaching fresh portions of the placental tissue, but the actual loss of bloodcomes from the uterine sinuses during the interval and not during the contrac-tion. ;<,yi Course of Labor.—The first stage is liable to be delayed, since the pres-ence of the placenta interferes with the cervical dilatation; Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-e-of-thebleeding-in-placenta-praevia-during-auterus-forcing-out-from-the-organ-blood-which-had-already-escaped-during-theinterval-in-one-way-up-to-a-certain-point-contractions-do-favor-hemorrhageby-detaching-fresh-portions-of-the-placental-tissue-but-the-actual-loss-of-bloodcomes-from-the-uterine-sinuses-during-the-interval-and-not-during-the-contrac-tion-ltyi-course-of-laborthe-first-stage-is-liable-to-be-delayed-since-the-pres-ence-of-the-placenta-interferes-with-the-cervical-dilatation-image343310539.html
The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . e of thebleeding in placenta praevia during auterus forcing out from the organ blood which had already escaped during theinterval. In one way, up to a certain point, contractions do favor hemorrhageby detaching fresh portions of the placental tissue, but the actual loss of bloodcomes from the uterine sinuses during the interval and not during the contrac-tion. ;<,yi Course of Labor.—The first stage is liable to be delayed, since the pres-ence of the placenta interferes with the cervical dilatation; Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-e-of-thebleeding-in-placenta-praevia-during-auterus-forcing-out-from-the-organ-blood-which-had-already-escaped-during-theinterval-in-one-way-up-to-a-certain-point-contractions-do-favor-hemorrhageby-detaching-fresh-portions-of-the-placental-tissue-but-the-actual-loss-of-bloodcomes-from-the-uterine-sinuses-during-the-interval-and-not-during-the-contrac-tion-ltyi-course-of-laborthe-first-stage-is-liable-to-be-delayed-since-the-pres-ence-of-the-placenta-interferes-with-the-cervical-dilatation-image343310539.htmlRM2AXF42K–The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . e of thebleeding in placenta praevia during auterus forcing out from the organ blood which had already escaped during theinterval. In one way, up to a certain point, contractions do favor hemorrhageby detaching fresh portions of the placental tissue, but the actual loss of bloodcomes from the uterine sinuses during the interval and not during the contrac-tion. ;<,yi Course of Labor.—The first stage is liable to be delayed, since the pres-ence of the placenta interferes with the cervical dilatation;
 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77478954.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77478954.htmlRMEE1D5E–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-with-a-ritual-pot-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-a-image475073597.html
Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/placenta-and-umbilical-cord-of-newborn-baby-with-a-ritual-pot-are-seen-in-close-up-a-fresh-real-human-placenta-with-blood-is-seen-close-up-on-table-a-image475073597.htmlRF2JGWD65–Placenta and umbilical cord of newborn baby with a ritual pot are seen in close up. A fresh real human placenta with blood is seen close up on table a
 Treatise on gynæcology : medical and surgical . y preserve their normal volume anddiffer in that respect, and in the small amount of their protoplasm,from the cells of the placenta. In other words, we have to do (Fig.96) with an acute interstitial inflammation.10 Chronic Metritis.—The parenchymatous lesions of chronic metri-tis are particularly characterized by a hypertrophy of the connective 138 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE GYNECOLOGY. tissue, causing a general enlargement of the organ, which, however,does not exceed the size of a fist. This increase in volume may beabsent altogether, and then we h Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/treatise-on-gyncology-medical-and-surgical-y-preserve-their-normal-volume-anddiffer-in-that-respect-and-in-the-small-amount-of-their-protoplasmfrom-the-cells-of-the-placenta-in-other-words-we-have-to-do-fig96-with-an-acute-interstitial-inflammation10-chronic-metritisthe-parenchymatous-lesions-of-chronic-metri-tis-are-particularly-characterized-by-a-hypertrophy-of-the-connective-138-clinical-and-operative-gynecology-tissue-causing-a-general-enlargement-of-the-organ-which-howeverdoes-not-exceed-the-size-of-a-fist-this-increase-in-volume-may-beabsent-altogether-and-then-we-h-image342973274.html
Treatise on gynæcology : medical and surgical . y preserve their normal volume anddiffer in that respect, and in the small amount of their protoplasm,from the cells of the placenta. In other words, we have to do (Fig.96) with an acute interstitial inflammation.10 Chronic Metritis.—The parenchymatous lesions of chronic metri-tis are particularly characterized by a hypertrophy of the connective 138 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE GYNECOLOGY. tissue, causing a general enlargement of the organ, which, however,does not exceed the size of a fist. This increase in volume may beabsent altogether, and then we h Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/treatise-on-gyncology-medical-and-surgical-y-preserve-their-normal-volume-anddiffer-in-that-respect-and-in-the-small-amount-of-their-protoplasmfrom-the-cells-of-the-placenta-in-other-words-we-have-to-do-fig96-with-an-acute-interstitial-inflammation10-chronic-metritisthe-parenchymatous-lesions-of-chronic-metri-tis-are-particularly-characterized-by-a-hypertrophy-of-the-connective-138-clinical-and-operative-gynecology-tissue-causing-a-general-enlargement-of-the-organ-which-howeverdoes-not-exceed-the-size-of-a-fist-this-increase-in-volume-may-beabsent-altogether-and-then-we-h-image342973274.htmlRM2AWYNWE–Treatise on gynæcology : medical and surgical . y preserve their normal volume anddiffer in that respect, and in the small amount of their protoplasm,from the cells of the placenta. In other words, we have to do (Fig.96) with an acute interstitial inflammation.10 Chronic Metritis.—The parenchymatous lesions of chronic metri-tis are particularly characterized by a hypertrophy of the connective 138 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE GYNECOLOGY. tissue, causing a general enlargement of the organ, which, however,does not exceed the size of a fist. This increase in volume may beabsent altogether, and then we h
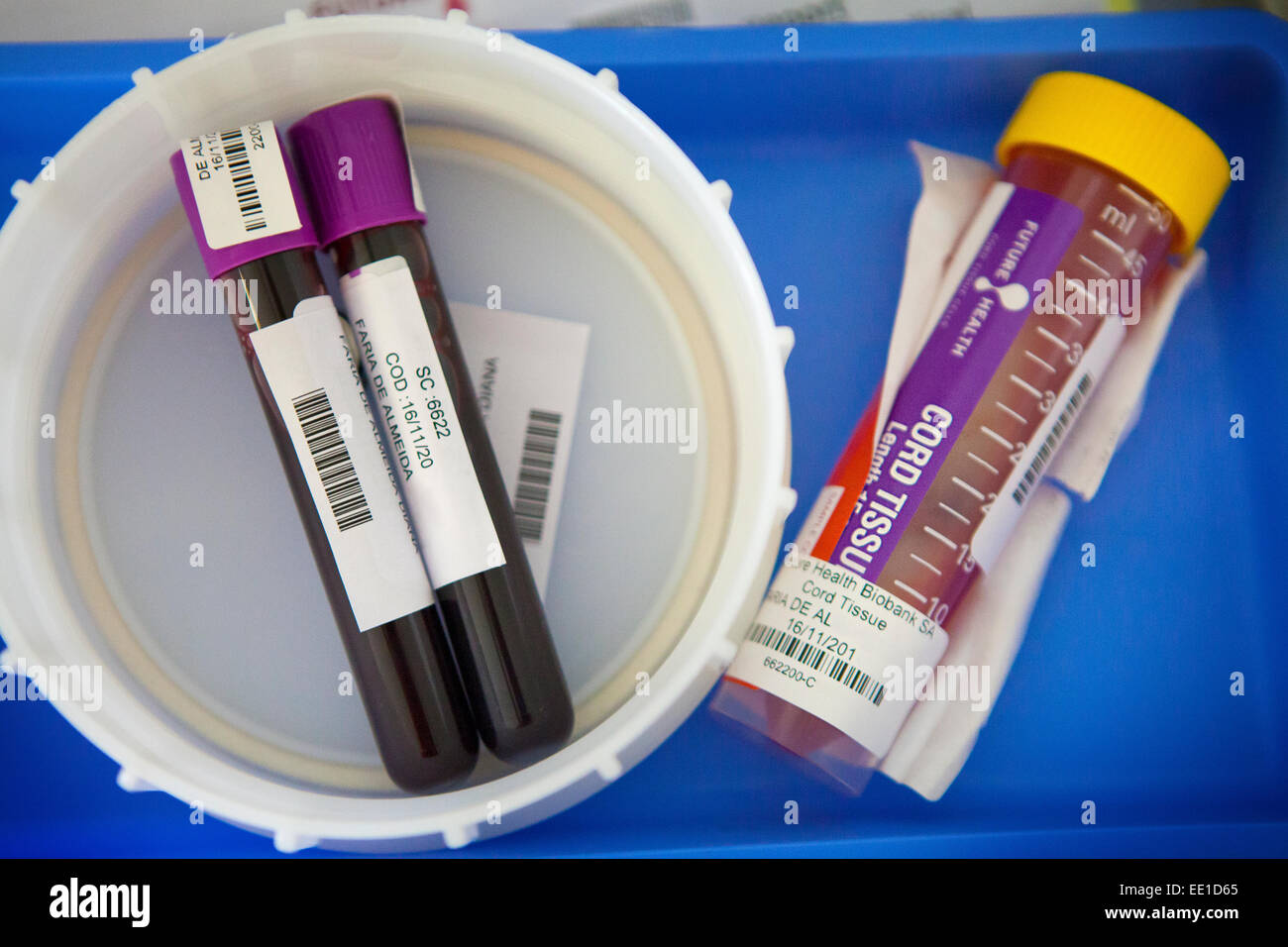 STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77478973.html
STEM CELL BIOBANK Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-stem-cell-biobank-77478973.htmlRMEE1D65–STEM CELL BIOBANK
 Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-storing-stem-cells-from-blood-and-cord-tissue-image476922792.html
Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-storing-stem-cells-from-blood-and-cord-tissue-image476922792.htmlRF2JKWKTT–Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue.
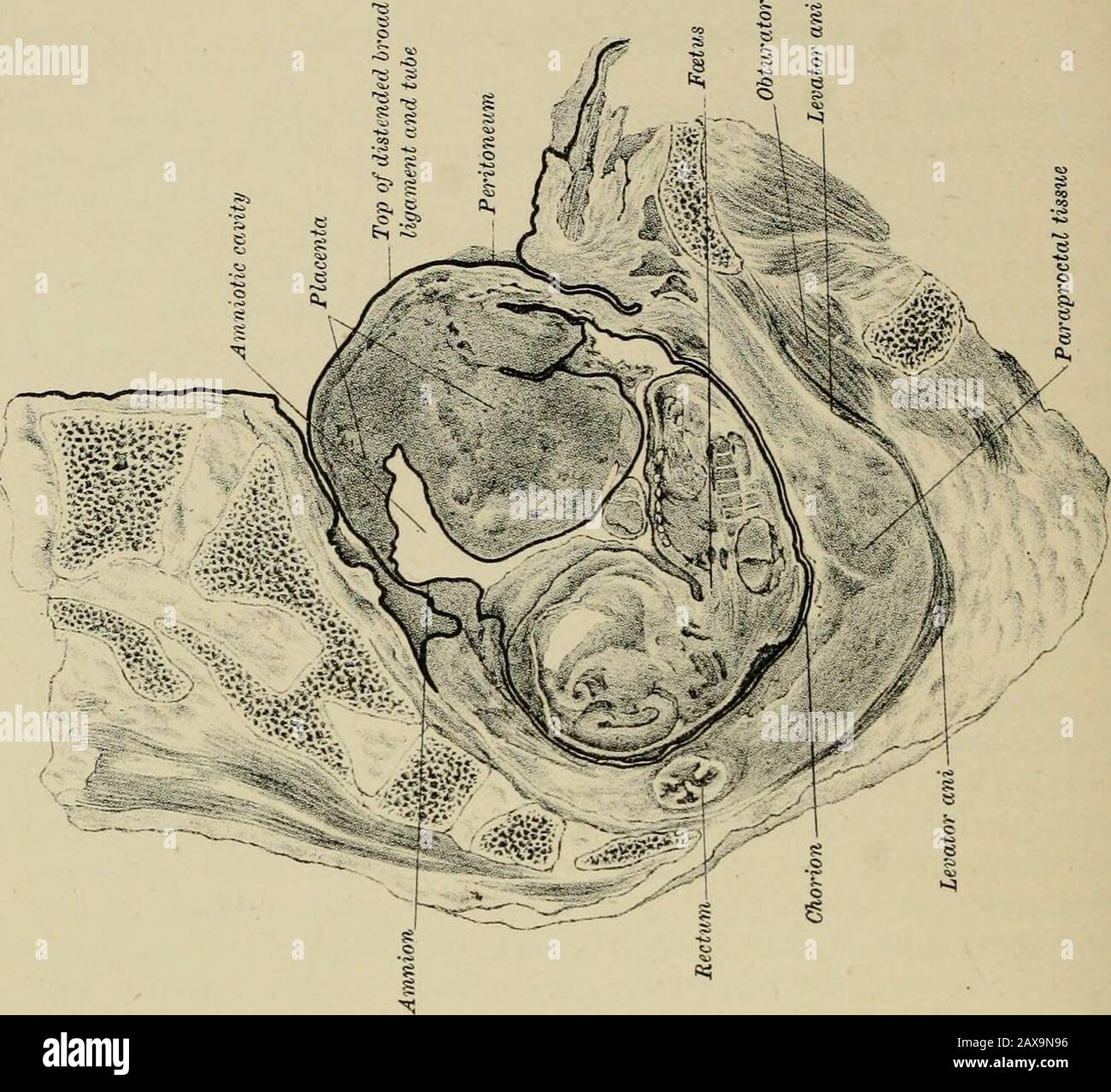 Lectures on ectopic pregnancy and pelvic haematocele . extra-peritoneal tissue, with its blood-vessels, is therefore not onlycapable of forming anastomoses in abdominal aneurism, as Turnerand Chiene have shown, but may attempt to carry on the functionsof the maternal portion of the placenta. We have here what may be termed slow displacement of tlieplacenta. At first it lay in the Fallopian tube, but the growingovum has slowly pushed it up (a process attended with bloodextravasation) from pelvis to abdominal cavity, until at last itsupper edge is about ten inches from its original site. Part of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lectures-on-ectopic-pregnancy-and-pelvic-haematocele-extra-peritoneal-tissue-with-its-blood-vessels-is-therefore-not-onlycapable-of-forming-anastomoses-in-abdominal-aneurism-as-turnerand-chiene-have-shown-but-may-attempt-to-carry-on-the-functionsof-the-maternal-portion-of-the-placenta-we-have-here-what-may-be-termed-slow-displacement-of-tlieplacenta-at-first-it-lay-in-the-fallopian-tube-but-the-growingovum-has-slowly-pushed-it-up-a-process-attended-with-bloodextravasation-from-pelvis-to-abdominal-cavity-until-at-last-itsupper-edge-is-about-ten-inches-from-its-original-site-part-of-image343192338.html
Lectures on ectopic pregnancy and pelvic haematocele . extra-peritoneal tissue, with its blood-vessels, is therefore not onlycapable of forming anastomoses in abdominal aneurism, as Turnerand Chiene have shown, but may attempt to carry on the functionsof the maternal portion of the placenta. We have here what may be termed slow displacement of tlieplacenta. At first it lay in the Fallopian tube, but the growingovum has slowly pushed it up (a process attended with bloodextravasation) from pelvis to abdominal cavity, until at last itsupper edge is about ten inches from its original site. Part of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lectures-on-ectopic-pregnancy-and-pelvic-haematocele-extra-peritoneal-tissue-with-its-blood-vessels-is-therefore-not-onlycapable-of-forming-anastomoses-in-abdominal-aneurism-as-turnerand-chiene-have-shown-but-may-attempt-to-carry-on-the-functionsof-the-maternal-portion-of-the-placenta-we-have-here-what-may-be-termed-slow-displacement-of-tlieplacenta-at-first-it-lay-in-the-fallopian-tube-but-the-growingovum-has-slowly-pushed-it-up-a-process-attended-with-bloodextravasation-from-pelvis-to-abdominal-cavity-until-at-last-itsupper-edge-is-about-ten-inches-from-its-original-site-part-of-image343192338.htmlRM2AX9N96–Lectures on ectopic pregnancy and pelvic haematocele . extra-peritoneal tissue, with its blood-vessels, is therefore not onlycapable of forming anastomoses in abdominal aneurism, as Turnerand Chiene have shown, but may attempt to carry on the functionsof the maternal portion of the placenta. We have here what may be termed slow displacement of tlieplacenta. At first it lay in the Fallopian tube, but the growingovum has slowly pushed it up (a process attended with bloodextravasation) from pelvis to abdominal cavity, until at last itsupper edge is about ten inches from its original site. Part of
 Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-storing-stem-cells-from-blood-and-cord-tissue-image476922798.html
Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/biobank-storing-stem-cells-from-blood-and-cord-tissue-image476922798.htmlRF2JKWKW2–Biobank storing stem cells from blood and cord tissue.
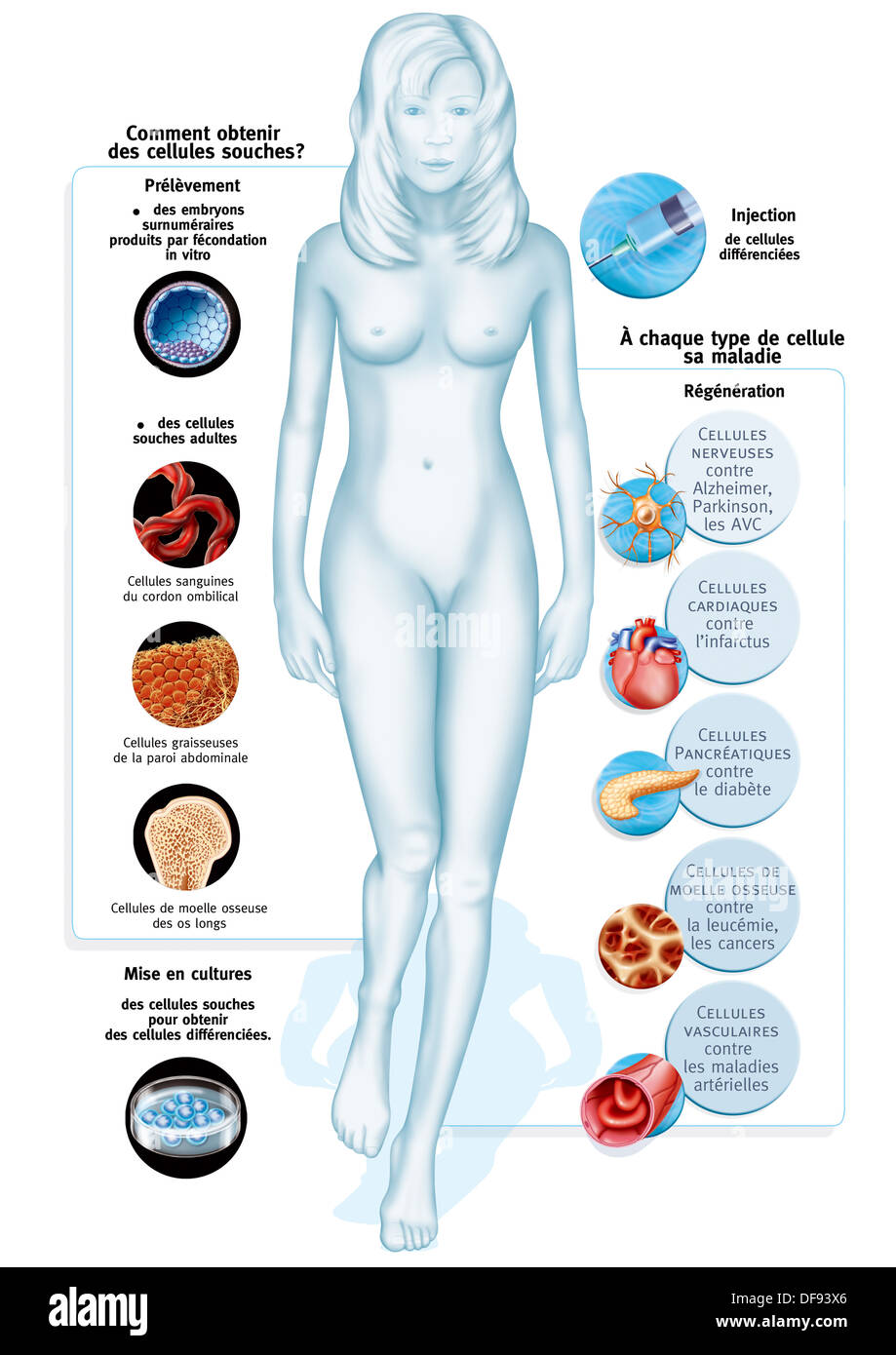 CELL THERAPY, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cell-therapy-illustration-image61051598.html
CELL THERAPY, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cell-therapy-illustration-image61051598.htmlRMDF93X6–CELL THERAPY, ILLUSTRATION
 A system of obstetrics . ituation of the placenta withinthe uterus may with equal frequency be found either upon the posterioror the anterior wall—occasionally, however, upon one of the lateralwalls, more frequently the right (Schroeder). A perpendicular section through the middle of a placenta which isstill attached to the uterine wall will reveal the most intimate connec-tion between the two. So close, indeed, is the connection between pla-centa and uterus that, as has been said, the line of separation when theplacenta is cast off is found in uterine tissue. This close adhesionbetween the fo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-obstetrics-ituation-of-the-placenta-withinthe-uterus-may-with-equal-frequency-be-found-either-upon-the-posterioror-the-anterior-walloccasionally-however-upon-one-of-the-lateralwalls-more-frequently-the-right-schroeder-a-perpendicular-section-through-the-middle-of-a-placenta-which-isstill-attached-to-the-uterine-wall-will-reveal-the-most-intimate-connec-tion-between-the-two-so-close-indeed-is-the-connection-between-pla-centa-and-uterus-that-as-has-been-said-the-line-of-separation-when-theplacenta-is-cast-off-is-found-in-uterine-tissue-this-close-adhesionbetween-the-fo-image342773706.html
A system of obstetrics . ituation of the placenta withinthe uterus may with equal frequency be found either upon the posterioror the anterior wall—occasionally, however, upon one of the lateralwalls, more frequently the right (Schroeder). A perpendicular section through the middle of a placenta which isstill attached to the uterine wall will reveal the most intimate connec-tion between the two. So close, indeed, is the connection between pla-centa and uterus that, as has been said, the line of separation when theplacenta is cast off is found in uterine tissue. This close adhesionbetween the fo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-obstetrics-ituation-of-the-placenta-withinthe-uterus-may-with-equal-frequency-be-found-either-upon-the-posterioror-the-anterior-walloccasionally-however-upon-one-of-the-lateralwalls-more-frequently-the-right-schroeder-a-perpendicular-section-through-the-middle-of-a-placenta-which-isstill-attached-to-the-uterine-wall-will-reveal-the-most-intimate-connec-tion-between-the-two-so-close-indeed-is-the-connection-between-pla-centa-and-uterus-that-as-has-been-said-the-line-of-separation-when-theplacenta-is-cast-off-is-found-in-uterine-tissue-this-close-adhesionbetween-the-fo-image342773706.htmlRM2AWJKA2–A system of obstetrics . ituation of the placenta withinthe uterus may with equal frequency be found either upon the posterioror the anterior wall—occasionally, however, upon one of the lateralwalls, more frequently the right (Schroeder). A perpendicular section through the middle of a placenta which isstill attached to the uterine wall will reveal the most intimate connec-tion between the two. So close, indeed, is the connection between pla-centa and uterus that, as has been said, the line of separation when theplacenta is cast off is found in uterine tissue. This close adhesionbetween the fo
 The causes and treatment of abortion . deposited either on the foetal or maternal surfaceof the placenta, or in its substance. In the latter case, therewill be induration. Wlien it occurs on the maternal surfacethere will be adhesions, and, if deposited on the foetal surface,there may be increase of the liquor amnii, and perhaps bands FCETAL CAUSES. 87 connecting it with sonic part of the fa3tal body. Bands of con-nective tissue have been found penetrating into tlie uterine tissues,thus rendering the separation of the placenta impossible. The inflammatory exudation in rare cases breaks down an Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-causes-and-treatment-of-abortion-deposited-either-on-the-foetal-or-maternal-surfaceof-the-placenta-or-in-its-substance-in-the-latter-case-therewill-be-induration-wlien-it-occurs-on-the-maternal-surfacethere-will-be-adhesions-and-if-deposited-on-the-foetal-surfacethere-may-be-increase-of-the-liquor-amnii-and-perhaps-bands-fcetal-causes-87-connecting-it-with-sonic-part-of-the-fa3tal-body-bands-of-con-nective-tissue-have-been-found-penetrating-into-tlie-uterine-tissuesthus-rendering-the-separation-of-the-placenta-impossible-the-inflammatory-exudation-in-rare-cases-breaks-down-an-image342719563.html
The causes and treatment of abortion . deposited either on the foetal or maternal surfaceof the placenta, or in its substance. In the latter case, therewill be induration. Wlien it occurs on the maternal surfacethere will be adhesions, and, if deposited on the foetal surface,there may be increase of the liquor amnii, and perhaps bands FCETAL CAUSES. 87 connecting it with sonic part of the fa3tal body. Bands of con-nective tissue have been found penetrating into tlie uterine tissues,thus rendering the separation of the placenta impossible. The inflammatory exudation in rare cases breaks down an Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-causes-and-treatment-of-abortion-deposited-either-on-the-foetal-or-maternal-surfaceof-the-placenta-or-in-its-substance-in-the-latter-case-therewill-be-induration-wlien-it-occurs-on-the-maternal-surfacethere-will-be-adhesions-and-if-deposited-on-the-foetal-surfacethere-may-be-increase-of-the-liquor-amnii-and-perhaps-bands-fcetal-causes-87-connecting-it-with-sonic-part-of-the-fa3tal-body-bands-of-con-nective-tissue-have-been-found-penetrating-into-tlie-uterine-tissuesthus-rendering-the-separation-of-the-placenta-impossible-the-inflammatory-exudation-in-rare-cases-breaks-down-an-image342719563.htmlRM2AWG68B–The causes and treatment of abortion . deposited either on the foetal or maternal surfaceof the placenta, or in its substance. In the latter case, therewill be induration. Wlien it occurs on the maternal surfacethere will be adhesions, and, if deposited on the foetal surface,there may be increase of the liquor amnii, and perhaps bands FCETAL CAUSES. 87 connecting it with sonic part of the fa3tal body. Bands of con-nective tissue have been found penetrating into tlie uterine tissues,thus rendering the separation of the placenta impossible. The inflammatory exudation in rare cases breaks down an
 The diseases of women : a handbook for students and practitioners . ate (Fig. 66). Some observers hold the opinion that sarcomata of thisvariety arising shortly after a labor or an abortion havetheir origin in retained fragments of decidua or placenta,but the evidence is not sufficient to support this hypothesis. 204 DISEASES OF WOMEN. It is well established that the histologic features of a sar-coma are largely modified by its environment, and as verylarge connective-tissue cells (decidual cells, Fig. 67) areabundant in the endometrium of a gravid uterus, it nat-urally follows that these cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-diseases-of-women-a-handbook-for-students-and-practitioners-ate-fig-66-some-observers-hold-the-opinion-that-sarcomata-of-thisvariety-arising-shortly-after-a-labor-or-an-abortion-havetheir-origin-in-retained-fragments-of-decidua-or-placentabut-the-evidence-is-not-sufficient-to-support-this-hypothesis-204-diseases-of-women-it-is-well-established-that-the-histologic-features-of-a-sar-coma-are-largely-modified-by-its-environment-and-as-verylarge-connective-tissue-cells-decidual-cells-fig-67-areabundant-in-the-endometrium-of-a-gravid-uterus-it-nat-urally-follows-that-these-cell-image342894800.html
The diseases of women : a handbook for students and practitioners . ate (Fig. 66). Some observers hold the opinion that sarcomata of thisvariety arising shortly after a labor or an abortion havetheir origin in retained fragments of decidua or placenta,but the evidence is not sufficient to support this hypothesis. 204 DISEASES OF WOMEN. It is well established that the histologic features of a sar-coma are largely modified by its environment, and as verylarge connective-tissue cells (decidual cells, Fig. 67) areabundant in the endometrium of a gravid uterus, it nat-urally follows that these cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-diseases-of-women-a-handbook-for-students-and-practitioners-ate-fig-66-some-observers-hold-the-opinion-that-sarcomata-of-thisvariety-arising-shortly-after-a-labor-or-an-abortion-havetheir-origin-in-retained-fragments-of-decidua-or-placentabut-the-evidence-is-not-sufficient-to-support-this-hypothesis-204-diseases-of-women-it-is-well-established-that-the-histologic-features-of-a-sar-coma-are-largely-modified-by-its-environment-and-as-verylarge-connective-tissue-cells-decidual-cells-fig-67-areabundant-in-the-endometrium-of-a-gravid-uterus-it-nat-urally-follows-that-these-cell-image342894800.htmlRM2AWT5PT–The diseases of women : a handbook for students and practitioners . ate (Fig. 66). Some observers hold the opinion that sarcomata of thisvariety arising shortly after a labor or an abortion havetheir origin in retained fragments of decidua or placenta,but the evidence is not sufficient to support this hypothesis. 204 DISEASES OF WOMEN. It is well established that the histologic features of a sar-coma are largely modified by its environment, and as verylarge connective-tissue cells (decidual cells, Fig. 67) areabundant in the endometrium of a gravid uterus, it nat-urally follows that these cell
 Gynecology . tremen-dously swollen, as may be seen if this is compared with the drawing of the placenta at full term. Thelayer of Langhans cells covered with syncytium are well shown on the surface of the villi. On thespace between the villi in the center are several fragments of syncytium. This space is normally filledwith blood in which these fragments lie. Moreover, a further difficulty in diagnosis exists in the fact that the tumorsexactly resemble the normal fetal tissue. Hitschmann and Cristofoletti came to the following conclusion: As a matter of fact, we are convinced that a histologic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynecology-tremen-dously-swollen-as-may-be-seen-if-this-is-compared-with-the-drawing-of-the-placenta-at-full-term-thelayer-of-langhans-cells-covered-with-syncytium-are-well-shown-on-the-surface-of-the-villi-on-thespace-between-the-villi-in-the-center-are-several-fragments-of-syncytium-this-space-is-normally-filledwith-blood-in-which-these-fragments-lie-moreover-a-further-difficulty-in-diagnosis-exists-in-the-fact-that-the-tumorsexactly-resemble-the-normal-fetal-tissue-hitschmann-and-cristofoletti-came-to-the-following-conclusion-as-a-matter-of-fact-we-are-convinced-that-a-histologic-image342733757.html
Gynecology . tremen-dously swollen, as may be seen if this is compared with the drawing of the placenta at full term. Thelayer of Langhans cells covered with syncytium are well shown on the surface of the villi. On thespace between the villi in the center are several fragments of syncytium. This space is normally filledwith blood in which these fragments lie. Moreover, a further difficulty in diagnosis exists in the fact that the tumorsexactly resemble the normal fetal tissue. Hitschmann and Cristofoletti came to the following conclusion: As a matter of fact, we are convinced that a histologic Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynecology-tremen-dously-swollen-as-may-be-seen-if-this-is-compared-with-the-drawing-of-the-placenta-at-full-term-thelayer-of-langhans-cells-covered-with-syncytium-are-well-shown-on-the-surface-of-the-villi-on-thespace-between-the-villi-in-the-center-are-several-fragments-of-syncytium-this-space-is-normally-filledwith-blood-in-which-these-fragments-lie-moreover-a-further-difficulty-in-diagnosis-exists-in-the-fact-that-the-tumorsexactly-resemble-the-normal-fetal-tissue-hitschmann-and-cristofoletti-came-to-the-following-conclusion-as-a-matter-of-fact-we-are-convinced-that-a-histologic-image342733757.htmlRM2AWGTB9–Gynecology . tremen-dously swollen, as may be seen if this is compared with the drawing of the placenta at full term. Thelayer of Langhans cells covered with syncytium are well shown on the surface of the villi. On thespace between the villi in the center are several fragments of syncytium. This space is normally filledwith blood in which these fragments lie. Moreover, a further difficulty in diagnosis exists in the fact that the tumorsexactly resemble the normal fetal tissue. Hitschmann and Cristofoletti came to the following conclusion: As a matter of fact, we are convinced that a histologic
 A nurse's handbook of obstetrics, for use in training-schools . nd unnatural one, andas the uterus is not prepared to cast off the placenta as it wouldat the normal end of pregnancy, some part of it is almost certainto be retained in the cavity of the womb. These retained frag-ments of placental tissue cause chronic inflammation of themembrane lining the uterus, even if they do not decompose andresult in blood poisoning, with the possible death of thepatient. In any event the outcome is bound to be serious unlessthe case is most carefully and intelligently treated, and even in CURETTAGE. 263 t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-nurses-handbook-of-obstetrics-for-use-in-training-schools-nd-unnatural-one-andas-the-uterus-is-not-prepared-to-cast-off-the-placenta-as-it-wouldat-the-normal-end-of-pregnancy-some-part-of-it-is-almost-certainto-be-retained-in-the-cavity-of-the-womb-these-retained-frag-ments-of-placental-tissue-cause-chronic-inflammation-of-themembrane-lining-the-uterus-even-if-they-do-not-decompose-andresult-in-blood-poisoning-with-the-possible-death-of-thepatient-in-any-event-the-outcome-is-bound-to-be-serious-unlessthe-case-is-most-carefully-and-intelligently-treated-and-even-in-curettage-263-t-image339057109.html
A nurse's handbook of obstetrics, for use in training-schools . nd unnatural one, andas the uterus is not prepared to cast off the placenta as it wouldat the normal end of pregnancy, some part of it is almost certainto be retained in the cavity of the womb. These retained frag-ments of placental tissue cause chronic inflammation of themembrane lining the uterus, even if they do not decompose andresult in blood poisoning, with the possible death of thepatient. In any event the outcome is bound to be serious unlessthe case is most carefully and intelligently treated, and even in CURETTAGE. 263 t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-nurses-handbook-of-obstetrics-for-use-in-training-schools-nd-unnatural-one-andas-the-uterus-is-not-prepared-to-cast-off-the-placenta-as-it-wouldat-the-normal-end-of-pregnancy-some-part-of-it-is-almost-certainto-be-retained-in-the-cavity-of-the-womb-these-retained-frag-ments-of-placental-tissue-cause-chronic-inflammation-of-themembrane-lining-the-uterus-even-if-they-do-not-decompose-andresult-in-blood-poisoning-with-the-possible-death-of-thepatient-in-any-event-the-outcome-is-bound-to-be-serious-unlessthe-case-is-most-carefully-and-intelligently-treated-and-even-in-curettage-263-t-image339057109.htmlRM2AKHAPD–A nurse's handbook of obstetrics, for use in training-schools . nd unnatural one, andas the uterus is not prepared to cast off the placenta as it wouldat the normal end of pregnancy, some part of it is almost certainto be retained in the cavity of the womb. These retained frag-ments of placental tissue cause chronic inflammation of themembrane lining the uterus, even if they do not decompose andresult in blood poisoning, with the possible death of thepatient. In any event the outcome is bound to be serious unlessthe case is most carefully and intelligently treated, and even in CURETTAGE. 263 t
 . Cyclopædia of obstetrics and gynecology. f placental tissue, and had taken itsorigin from a piece of retained placenta. The neoplasm grew throughthe walls of the uterus, producing by their perforation a fatal peri-uterinehematocele. ^ Kuchennieisters Zeitschrift fiirMedicin, etc., 1863. - Virchovvs Aichiv, vol. LXVII., p. 55. 3 Archiv fiir Gynak., vol. XVIH. ?* Virchows Archiv, vol. XCVI., p. 15. POLYPI AND ADENOMATA. 347 Clinical History and Symptoms. The symptoms produced by those erosions which have been describedas adenoma, do not differ from those of catarrh of the cervix and body ofthe Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cyclopdia-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-f-placental-tissue-and-had-taken-itsorigin-from-a-piece-of-retained-placenta-the-neoplasm-grew-throughthe-walls-of-the-uterus-producing-by-their-perforation-a-fatal-peri-uterinehematocele-kuchennieisters-zeitschrift-fiirmedicin-etc-1863-virchovvs-aichiv-vol-lxvii-p-55-3-archiv-fiir-gynak-vol-xvih-virchows-archiv-vol-xcvi-p-15-polypi-and-adenomata-347-clinical-history-and-symptoms-the-symptoms-produced-by-those-erosions-which-have-been-describedas-adenoma-do-not-differ-from-those-of-catarrh-of-the-cervix-and-body-ofthe-image336729541.html
. Cyclopædia of obstetrics and gynecology. f placental tissue, and had taken itsorigin from a piece of retained placenta. The neoplasm grew throughthe walls of the uterus, producing by their perforation a fatal peri-uterinehematocele. ^ Kuchennieisters Zeitschrift fiirMedicin, etc., 1863. - Virchovvs Aichiv, vol. LXVII., p. 55. 3 Archiv fiir Gynak., vol. XVIH. ?* Virchows Archiv, vol. XCVI., p. 15. POLYPI AND ADENOMATA. 347 Clinical History and Symptoms. The symptoms produced by those erosions which have been describedas adenoma, do not differ from those of catarrh of the cervix and body ofthe Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cyclopdia-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-f-placental-tissue-and-had-taken-itsorigin-from-a-piece-of-retained-placenta-the-neoplasm-grew-throughthe-walls-of-the-uterus-producing-by-their-perforation-a-fatal-peri-uterinehematocele-kuchennieisters-zeitschrift-fiirmedicin-etc-1863-virchovvs-aichiv-vol-lxvii-p-55-3-archiv-fiir-gynak-vol-xvih-virchows-archiv-vol-xcvi-p-15-polypi-and-adenomata-347-clinical-history-and-symptoms-the-symptoms-produced-by-those-erosions-which-have-been-describedas-adenoma-do-not-differ-from-those-of-catarrh-of-the-cervix-and-body-ofthe-image336729541.htmlRM2AFR9Y1–. Cyclopædia of obstetrics and gynecology. f placental tissue, and had taken itsorigin from a piece of retained placenta. The neoplasm grew throughthe walls of the uterus, producing by their perforation a fatal peri-uterinehematocele. ^ Kuchennieisters Zeitschrift fiirMedicin, etc., 1863. - Virchovvs Aichiv, vol. LXVII., p. 55. 3 Archiv fiir Gynak., vol. XVIH. ?* Virchows Archiv, vol. XCVI., p. 15. POLYPI AND ADENOMATA. 347 Clinical History and Symptoms. The symptoms produced by those erosions which have been describedas adenoma, do not differ from those of catarrh of the cervix and body ofthe
 The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . ^. Fig. 260.—Battledore Oval Placenta.{Auvard.) Fig. 261.—Placenta with VelamentgusCord Attachment.—(Ribemont-Lepage.) proliferation during the developm.ent of the placenta may divide the latterinto two or more segments, some of which may be small—mere single cotyledons, in fact. (2) Anovum may be implantedover a uterine angle, wherea complete placenta wouldnot form; as a result pla-cental tissue develops oneither side of the angle.This particular type isknown as the duplex or bi-partite placenta. Mul Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-fig-260battledore-oval-placentaauvard-fig-261placenta-with-velamentguscord-attachmentribemont-lepage-proliferation-during-the-development-of-the-placenta-may-divide-the-latterinto-two-or-more-segments-some-of-which-may-be-smallmere-single-cotyledons-in-fact-2-anovum-may-be-implantedover-a-uterine-angle-wherea-complete-placenta-wouldnot-form-as-a-result-pla-cental-tissue-develops-oneither-side-of-the-anglethis-particular-type-isknown-as-the-duplex-or-bi-partite-placenta-mul-image343311763.html
The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . ^. Fig. 260.—Battledore Oval Placenta.{Auvard.) Fig. 261.—Placenta with VelamentgusCord Attachment.—(Ribemont-Lepage.) proliferation during the developm.ent of the placenta may divide the latterinto two or more segments, some of which may be small—mere single cotyledons, in fact. (2) Anovum may be implantedover a uterine angle, wherea complete placenta wouldnot form; as a result pla-cental tissue develops oneither side of the angle.This particular type isknown as the duplex or bi-partite placenta. Mul Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-fig-260battledore-oval-placentaauvard-fig-261placenta-with-velamentguscord-attachmentribemont-lepage-proliferation-during-the-development-of-the-placenta-may-divide-the-latterinto-two-or-more-segments-some-of-which-may-be-smallmere-single-cotyledons-in-fact-2-anovum-may-be-implantedover-a-uterine-angle-wherea-complete-placenta-wouldnot-form-as-a-result-pla-cental-tissue-develops-oneither-side-of-the-anglethis-particular-type-isknown-as-the-duplex-or-bi-partite-placenta-mul-image343311763.htmlRM2AXF5JB–The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . ^. Fig. 260.—Battledore Oval Placenta.{Auvard.) Fig. 261.—Placenta with VelamentgusCord Attachment.—(Ribemont-Lepage.) proliferation during the developm.ent of the placenta may divide the latterinto two or more segments, some of which may be small—mere single cotyledons, in fact. (2) Anovum may be implantedover a uterine angle, wherea complete placenta wouldnot form; as a result pla-cental tissue develops oneither side of the angle.This particular type isknown as the duplex or bi-partite placenta. Mul
 Transactions of the American Association of Obstetricians, Gynecologists, and Abdominal Surgeons for the year ... . arly unruptured pregnancy, the ovumwas very small and separated from the tubal wall by a definite layerof blood. 118 JOHN 0. POLAK AND THURSTON S. WELTON The tubal and uterine placenta are identical in formation. Thepathologic changes which take place in tubal pregnancy are due tothe thin tube walls and the absence of a true decidua serotina, whichallows easy invasion by the trophoblast and syncytial cells; conse-quently there is no active connective tissue reaction set up by the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/transactions-of-the-american-association-of-obstetricians-gynecologists-and-abdominal-surgeons-for-the-year-arly-unruptured-pregnancy-the-ovumwas-very-small-and-separated-from-the-tubal-wall-by-a-definite-layerof-blood-118-john-0-polak-and-thurston-s-welton-the-tubal-and-uterine-placenta-are-identical-in-formation-thepathologic-changes-which-take-place-in-tubal-pregnancy-are-due-tothe-thin-tube-walls-and-the-absence-of-a-true-decidua-serotina-whichallows-easy-invasion-by-the-trophoblast-and-syncytial-cells-conse-quently-there-is-no-active-connective-tissue-reaction-set-up-by-the-image340165363.html
Transactions of the American Association of Obstetricians, Gynecologists, and Abdominal Surgeons for the year ... . arly unruptured pregnancy, the ovumwas very small and separated from the tubal wall by a definite layerof blood. 118 JOHN 0. POLAK AND THURSTON S. WELTON The tubal and uterine placenta are identical in formation. Thepathologic changes which take place in tubal pregnancy are due tothe thin tube walls and the absence of a true decidua serotina, whichallows easy invasion by the trophoblast and syncytial cells; conse-quently there is no active connective tissue reaction set up by the Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/transactions-of-the-american-association-of-obstetricians-gynecologists-and-abdominal-surgeons-for-the-year-arly-unruptured-pregnancy-the-ovumwas-very-small-and-separated-from-the-tubal-wall-by-a-definite-layerof-blood-118-john-0-polak-and-thurston-s-welton-the-tubal-and-uterine-placenta-are-identical-in-formation-thepathologic-changes-which-take-place-in-tubal-pregnancy-are-due-tothe-thin-tube-walls-and-the-absence-of-a-true-decidua-serotina-whichallows-easy-invasion-by-the-trophoblast-and-syncytial-cells-conse-quently-there-is-no-active-connective-tissue-reaction-set-up-by-the-image340165363.htmlRM2ANBTAY–Transactions of the American Association of Obstetricians, Gynecologists, and Abdominal Surgeons for the year ... . arly unruptured pregnancy, the ovumwas very small and separated from the tubal wall by a definite layerof blood. 118 JOHN 0. POLAK AND THURSTON S. WELTON The tubal and uterine placenta are identical in formation. Thepathologic changes which take place in tubal pregnancy are due tothe thin tube walls and the absence of a true decidua serotina, whichallows easy invasion by the trophoblast and syncytial cells; conse-quently there is no active connective tissue reaction set up by the
 A nurse's handbook of obstetrics, for use in training-schools . nd unnatural one, andas the uterus is not prepared to cast off the placenta as it wouldat the normal end of pregnancy, some part of it is almost certainto be retained in the cavity of the womb. These retained frag-ments of placental tissue cause chronic inflammation of themembrane lining the uterus, even if they do not decompose andresult in blood poisoning, with the possible death of thepatient. In any event the outcome is bound to be serious unlessthe case is most carefully and intelligently treated, and even in Curettage. 263 t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-nurses-handbook-of-obstetrics-for-use-in-training-schools-nd-unnatural-one-andas-the-uterus-is-not-prepared-to-cast-off-the-placenta-as-it-wouldat-the-normal-end-of-pregnancy-some-part-of-it-is-almost-certainto-be-retained-in-the-cavity-of-the-womb-these-retained-frag-ments-of-placental-tissue-cause-chronic-inflammation-of-themembrane-lining-the-uterus-even-if-they-do-not-decompose-andresult-in-blood-poisoning-with-the-possible-death-of-thepatient-in-any-event-the-outcome-is-bound-to-be-serious-unlessthe-case-is-most-carefully-and-intelligently-treated-and-even-in-curettage-263-t-image342704712.html
A nurse's handbook of obstetrics, for use in training-schools . nd unnatural one, andas the uterus is not prepared to cast off the placenta as it wouldat the normal end of pregnancy, some part of it is almost certainto be retained in the cavity of the womb. These retained frag-ments of placental tissue cause chronic inflammation of themembrane lining the uterus, even if they do not decompose andresult in blood poisoning, with the possible death of thepatient. In any event the outcome is bound to be serious unlessthe case is most carefully and intelligently treated, and even in Curettage. 263 t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-nurses-handbook-of-obstetrics-for-use-in-training-schools-nd-unnatural-one-andas-the-uterus-is-not-prepared-to-cast-off-the-placenta-as-it-wouldat-the-normal-end-of-pregnancy-some-part-of-it-is-almost-certainto-be-retained-in-the-cavity-of-the-womb-these-retained-frag-ments-of-placental-tissue-cause-chronic-inflammation-of-themembrane-lining-the-uterus-even-if-they-do-not-decompose-andresult-in-blood-poisoning-with-the-possible-death-of-thepatient-in-any-event-the-outcome-is-bound-to-be-serious-unlessthe-case-is-most-carefully-and-intelligently-treated-and-even-in-curettage-263-t-image342704712.htmlRM2AWFFA0–A nurse's handbook of obstetrics, for use in training-schools . nd unnatural one, andas the uterus is not prepared to cast off the placenta as it wouldat the normal end of pregnancy, some part of it is almost certainto be retained in the cavity of the womb. These retained frag-ments of placental tissue cause chronic inflammation of themembrane lining the uterus, even if they do not decompose andresult in blood poisoning, with the possible death of thepatient. In any event the outcome is bound to be serious unlessthe case is most carefully and intelligently treated, and even in Curettage. 263 t
 The diseases of women : a handbook for students and practitioners . Fig. 51.—Retained fragment of placenta (Museum R. C. Surgeons). uterine wall, both after full-time delivery and after abortion.It is most frequent in the latter case. The principal symp- 66 DISEASES OF WOMEN.. Fig. 53.—Microscopic appearance of placental tissue long retained in the uterus (A. E. G). DISEASES OF THE UTERUS. 167 torn is irregular hemorrhage, continued in some instancesfor many months. The other symptoms and the physicalsigns closely resemble those just described as resultingfrom subinvolution. The diagnosis gene Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-diseases-of-women-a-handbook-for-students-and-practitioners-fig-51retained-fragment-of-placenta-museum-r-c-surgeons-uterine-wall-both-after-full-time-delivery-and-after-abortionit-is-most-frequent-in-the-latter-case-the-principal-symp-66-diseases-of-women-fig-53microscopic-appearance-of-placental-tissue-long-retained-in-the-uterus-a-e-g-diseases-of-the-uterus-167-torn-is-irregular-hemorrhage-continued-in-some-instancesfor-many-months-the-other-symptoms-and-the-physicalsigns-closely-resemble-those-just-described-as-resultingfrom-subinvolution-the-diagnosis-gene-image342899324.html
The diseases of women : a handbook for students and practitioners . Fig. 51.—Retained fragment of placenta (Museum R. C. Surgeons). uterine wall, both after full-time delivery and after abortion.It is most frequent in the latter case. The principal symp- 66 DISEASES OF WOMEN.. Fig. 53.—Microscopic appearance of placental tissue long retained in the uterus (A. E. G). DISEASES OF THE UTERUS. 167 torn is irregular hemorrhage, continued in some instancesfor many months. The other symptoms and the physicalsigns closely resemble those just described as resultingfrom subinvolution. The diagnosis gene Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-diseases-of-women-a-handbook-for-students-and-practitioners-fig-51retained-fragment-of-placenta-museum-r-c-surgeons-uterine-wall-both-after-full-time-delivery-and-after-abortionit-is-most-frequent-in-the-latter-case-the-principal-symp-66-diseases-of-women-fig-53microscopic-appearance-of-placental-tissue-long-retained-in-the-uterus-a-e-g-diseases-of-the-uterus-167-torn-is-irregular-hemorrhage-continued-in-some-instancesfor-many-months-the-other-symptoms-and-the-physicalsigns-closely-resemble-those-just-described-as-resultingfrom-subinvolution-the-diagnosis-gene-image342899324.htmlRM2AWTBGC–The diseases of women : a handbook for students and practitioners . Fig. 51.—Retained fragment of placenta (Museum R. C. Surgeons). uterine wall, both after full-time delivery and after abortion.It is most frequent in the latter case. The principal symp- 66 DISEASES OF WOMEN.. Fig. 53.—Microscopic appearance of placental tissue long retained in the uterus (A. E. G). DISEASES OF THE UTERUS. 167 torn is irregular hemorrhage, continued in some instancesfor many months. The other symptoms and the physicalsigns closely resemble those just described as resultingfrom subinvolution. The diagnosis gene
 The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . divide the latterinto two or more segments, some of which may be small—mere single cotyledons, in fact. (2) Anovum may be implantedover a uterine angle, wherea complete placenta wouldnot form; as a result pla-cental tissue develops oneither side of the angle.This particular type isknown as the duplex or bi-partite placenta. Multipleplacenta as a class are saidto occur in one labor out ofabout 352 (Ribemont-Des-saignes). The most commontype of multiple placenta isthe placenta duplex, or bi-lobed placent Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-divide-the-latterinto-two-or-more-segments-some-of-which-may-be-smallmere-single-cotyledons-in-fact-2-anovum-may-be-implantedover-a-uterine-angle-wherea-complete-placenta-wouldnot-form-as-a-result-pla-cental-tissue-develops-oneither-side-of-the-anglethis-particular-type-isknown-as-the-duplex-or-bi-partite-placenta-multipleplacenta-as-a-class-are-saidto-occur-in-one-labor-out-ofabout-352-ribemont-des-saignes-the-most-commontype-of-multiple-placenta-isthe-placenta-duplex-or-bi-lobed-placent-image343311659.html
The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . divide the latterinto two or more segments, some of which may be small—mere single cotyledons, in fact. (2) Anovum may be implantedover a uterine angle, wherea complete placenta wouldnot form; as a result pla-cental tissue develops oneither side of the angle.This particular type isknown as the duplex or bi-partite placenta. Multipleplacenta as a class are saidto occur in one labor out ofabout 352 (Ribemont-Des-saignes). The most commontype of multiple placenta isthe placenta duplex, or bi-lobed placent Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-divide-the-latterinto-two-or-more-segments-some-of-which-may-be-smallmere-single-cotyledons-in-fact-2-anovum-may-be-implantedover-a-uterine-angle-wherea-complete-placenta-wouldnot-form-as-a-result-pla-cental-tissue-develops-oneither-side-of-the-anglethis-particular-type-isknown-as-the-duplex-or-bi-partite-placenta-multipleplacenta-as-a-class-are-saidto-occur-in-one-labor-out-ofabout-352-ribemont-des-saignes-the-most-commontype-of-multiple-placenta-isthe-placenta-duplex-or-bi-lobed-placent-image343311659.htmlRM2AXF5EK–The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . divide the latterinto two or more segments, some of which may be small—mere single cotyledons, in fact. (2) Anovum may be implantedover a uterine angle, wherea complete placenta wouldnot form; as a result pla-cental tissue develops oneither side of the angle.This particular type isknown as the duplex or bi-partite placenta. Multipleplacenta as a class are saidto occur in one labor out ofabout 352 (Ribemont-Des-saignes). The most commontype of multiple placenta isthe placenta duplex, or bi-lobed placent
 The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . Fig. III.—Section of Human PlacentaOF Seven Months in situ. Am., Am-nion; Cho., chorion; Vi, trunk of villus;vi, sections of villi in the substance ofthe placenta; D, decidua basalis; Mc,muscularis; D,compact layer of decidua;Ve., uterine artery opening into theplacenta. The fetal blood-vessels aredrawn black; the maternal blood-spacesare left white; the chorionic tissue isstippled except the canalized fibrin,which is shaded by lines; the remnantsof the gland-cavities in D^^ are stippledblack.—{Minot.) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-fig-iiisection-of-human-placentaof-seven-months-in-situ-am-am-nion-cho-chorion-vi-trunk-of-villusvi-sections-of-villi-in-the-substance-ofthe-placenta-d-decidua-basalis-mcmuscularis-dcompact-layer-of-deciduave-uterine-artery-opening-into-theplacenta-the-fetal-blood-vessels-aredrawn-black-the-maternal-blood-spacesare-left-white-the-chorionic-tissue-isstippled-except-the-canalized-fibrinwhich-is-shaded-by-lines-the-remnantsof-the-gland-cavities-in-d-are-stippledblackminot-image343350944.html
The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . Fig. III.—Section of Human PlacentaOF Seven Months in situ. Am., Am-nion; Cho., chorion; Vi, trunk of villus;vi, sections of villi in the substance ofthe placenta; D, decidua basalis; Mc,muscularis; D,compact layer of decidua;Ve., uterine artery opening into theplacenta. The fetal blood-vessels aredrawn black; the maternal blood-spacesare left white; the chorionic tissue isstippled except the canalized fibrin,which is shaded by lines; the remnantsof the gland-cavities in D^^ are stippledblack.—{Minot.) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-fig-iiisection-of-human-placentaof-seven-months-in-situ-am-am-nion-cho-chorion-vi-trunk-of-villusvi-sections-of-villi-in-the-substance-ofthe-placenta-d-decidua-basalis-mcmuscularis-dcompact-layer-of-deciduave-uterine-artery-opening-into-theplacenta-the-fetal-blood-vessels-aredrawn-black-the-maternal-blood-spacesare-left-white-the-chorionic-tissue-isstippled-except-the-canalized-fibrinwhich-is-shaded-by-lines-the-remnantsof-the-gland-cavities-in-d-are-stippledblackminot-image343350944.htmlRM2AXGYHM–The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . Fig. III.—Section of Human PlacentaOF Seven Months in situ. Am., Am-nion; Cho., chorion; Vi, trunk of villus;vi, sections of villi in the substance ofthe placenta; D, decidua basalis; Mc,muscularis; D,compact layer of decidua;Ve., uterine artery opening into theplacenta. The fetal blood-vessels aredrawn black; the maternal blood-spacesare left white; the chorionic tissue isstippled except the canalized fibrin,which is shaded by lines; the remnantsof the gland-cavities in D^^ are stippledblack.—{Minot.)
 The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . Fig. III.—Section of Human PlacentaOF Seven Months in situ. Am., Am-nion; Cho., chorion; Vi, trunk of villus;vi, sections of villi in the substance ofthe placenta; D, decidua basalis; Mc,muscularis; D,compact layer of decidua;Ve., uterine artery opening into theplacenta. The fetal blood-vessels aredrawn black; the maternal blood-spacesare left white; the chorionic tissue isstippled except the canalized fibrin,which is shaded by lines; the remnantsof the gland-cavities in D^^ are stippledblack.—{Minot.) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-fig-iiisection-of-human-placentaof-seven-months-in-situ-am-am-nion-cho-chorion-vi-trunk-of-villusvi-sections-of-villi-in-the-substance-ofthe-placenta-d-decidua-basalis-mcmuscularis-dcompact-layer-of-deciduave-uterine-artery-opening-into-theplacenta-the-fetal-blood-vessels-aredrawn-black-the-maternal-blood-spacesare-left-white-the-chorionic-tissue-isstippled-except-the-canalized-fibrinwhich-is-shaded-by-lines-the-remnantsof-the-gland-cavities-in-d-are-stippledblackminot-image343350743.html
The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . Fig. III.—Section of Human PlacentaOF Seven Months in situ. Am., Am-nion; Cho., chorion; Vi, trunk of villus;vi, sections of villi in the substance ofthe placenta; D, decidua basalis; Mc,muscularis; D,compact layer of decidua;Ve., uterine artery opening into theplacenta. The fetal blood-vessels aredrawn black; the maternal blood-spacesare left white; the chorionic tissue isstippled except the canalized fibrin,which is shaded by lines; the remnantsof the gland-cavities in D^^ are stippledblack.—{Minot.) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-practice-of-obstetrics-designed-for-the-use-of-students-and-practitioners-of-medicine-fig-iiisection-of-human-placentaof-seven-months-in-situ-am-am-nion-cho-chorion-vi-trunk-of-villusvi-sections-of-villi-in-the-substance-ofthe-placenta-d-decidua-basalis-mcmuscularis-dcompact-layer-of-deciduave-uterine-artery-opening-into-theplacenta-the-fetal-blood-vessels-aredrawn-black-the-maternal-blood-spacesare-left-white-the-chorionic-tissue-isstippled-except-the-canalized-fibrinwhich-is-shaded-by-lines-the-remnantsof-the-gland-cavities-in-d-are-stippledblackminot-image343350743.htmlRM2AXGYAF–The practice of obstetrics, designed for the use of students and practitioners of medicine . Fig. III.—Section of Human PlacentaOF Seven Months in situ. Am., Am-nion; Cho., chorion; Vi, trunk of villus;vi, sections of villi in the substance ofthe placenta; D, decidua basalis; Mc,muscularis; D,compact layer of decidua;Ve., uterine artery opening into theplacenta. The fetal blood-vessels aredrawn black; the maternal blood-spacesare left white; the chorionic tissue isstippled except the canalized fibrin,which is shaded by lines; the remnantsof the gland-cavities in D^^ are stippledblack.—{Minot.)
 Gynecology . /,: /*-rv ^. >*% Kj£> <tV;j ?% *:. aft 4r - V s! ? V3 s. *£- ^a&N fea& ^v* V*» s^-^t* H##*l Fig. 113.—Placenta at Full Term.Low power. On the right is an area of decidua consisting of greatly enlarged cells derived fromthe stroma of the endometrium. The enlargement takes place mostly in the protoplasm of the cell,the nucleus enlarging proportionately little. On the left are chorionic villi cut in various planes.They consist of a loose connective tissue containing comparatively large blood-vessels, covered by alayer of Langhans cells and syncytium. The intervillous space Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynecology-rv-gt-kjgt-lttvj-aft-4r-v-s!-v3-s-an-fea-v-v-s-t-hl-fig-113placenta-at-full-termlow-power-on-the-right-is-an-area-of-decidua-consisting-of-greatly-enlarged-cells-derived-fromthe-stroma-of-the-endometrium-the-enlargement-takes-place-mostly-in-the-protoplasm-of-the-cellthe-nucleus-enlarging-proportionately-little-on-the-left-are-chorionic-villi-cut-in-various-planesthey-consist-of-a-loose-connective-tissue-containing-comparatively-large-blood-vessels-covered-by-alayer-of-langhans-cells-and-syncytium-the-intervillous-space-image342734543.html
Gynecology . /,: /*-rv ^. >*% Kj£> <tV;j ?% *:. aft 4r - V s! ? V3 s. *£- ^a&N fea& ^v* V*» s^-^t* H##*l Fig. 113.—Placenta at Full Term.Low power. On the right is an area of decidua consisting of greatly enlarged cells derived fromthe stroma of the endometrium. The enlargement takes place mostly in the protoplasm of the cell,the nucleus enlarging proportionately little. On the left are chorionic villi cut in various planes.They consist of a loose connective tissue containing comparatively large blood-vessels, covered by alayer of Langhans cells and syncytium. The intervillous space Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynecology-rv-gt-kjgt-lttvj-aft-4r-v-s!-v3-s-an-fea-v-v-s-t-hl-fig-113placenta-at-full-termlow-power-on-the-right-is-an-area-of-decidua-consisting-of-greatly-enlarged-cells-derived-fromthe-stroma-of-the-endometrium-the-enlargement-takes-place-mostly-in-the-protoplasm-of-the-cellthe-nucleus-enlarging-proportionately-little-on-the-left-are-chorionic-villi-cut-in-various-planesthey-consist-of-a-loose-connective-tissue-containing-comparatively-large-blood-vessels-covered-by-alayer-of-langhans-cells-and-syncytium-the-intervillous-space-image342734543.htmlRM2AWGWBB–Gynecology . /,: /*-rv ^. >*% Kj£> <tV;j ?% *:. aft 4r - V s! ? V3 s. *£- ^a&N fea& ^v* V*» s^-^t* H##*l Fig. 113.—Placenta at Full Term.Low power. On the right is an area of decidua consisting of greatly enlarged cells derived fromthe stroma of the endometrium. The enlargement takes place mostly in the protoplasm of the cell,the nucleus enlarging proportionately little. On the left are chorionic villi cut in various planes.They consist of a loose connective tissue containing comparatively large blood-vessels, covered by alayer of Langhans cells and syncytium. The intervillous space
 . A system of obstetrics . esem-bling the placenta in appearance. It consists of connective tissue inaddition to the vessels. It is the representative of the cerebral men-inges, and is continuous below with the spinal meninges. Its smoothsurface is the analogue of the arachnoid. The sensation which isimparted to the finger of the accoucheur pressed upon it is very sim-ilar to that produced by a placenta. In some specimens small por-tions of cerebral matter are found among the vessels of this tumor?but they are so disconnected and isolated that they do not perform inany way the functions of a b Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-obstetrics-esem-bling-the-placenta-in-appearance-it-consists-of-connective-tissue-inaddition-to-the-vessels-it-is-the-representative-of-the-cerebral-men-inges-and-is-continuous-below-with-the-spinal-meninges-its-smoothsurface-is-the-analogue-of-the-arachnoid-the-sensation-which-isimparted-to-the-finger-of-the-accoucheur-pressed-upon-it-is-very-sim-ilar-to-that-produced-by-a-placenta-in-some-specimens-small-por-tions-of-cerebral-matter-are-found-among-the-vessels-of-this-tumorbut-they-are-so-disconnected-and-isolated-that-they-do-not-perform-inany-way-the-functions-of-a-b-image370118548.html
. A system of obstetrics . esem-bling the placenta in appearance. It consists of connective tissue inaddition to the vessels. It is the representative of the cerebral men-inges, and is continuous below with the spinal meninges. Its smoothsurface is the analogue of the arachnoid. The sensation which isimparted to the finger of the accoucheur pressed upon it is very sim-ilar to that produced by a placenta. In some specimens small por-tions of cerebral matter are found among the vessels of this tumor?but they are so disconnected and isolated that they do not perform inany way the functions of a b Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-obstetrics-esem-bling-the-placenta-in-appearance-it-consists-of-connective-tissue-inaddition-to-the-vessels-it-is-the-representative-of-the-cerebral-men-inges-and-is-continuous-below-with-the-spinal-meninges-its-smoothsurface-is-the-analogue-of-the-arachnoid-the-sensation-which-isimparted-to-the-finger-of-the-accoucheur-pressed-upon-it-is-very-sim-ilar-to-that-produced-by-a-placenta-in-some-specimens-small-por-tions-of-cerebral-matter-are-found-among-the-vessels-of-this-tumorbut-they-are-so-disconnected-and-isolated-that-they-do-not-perform-inany-way-the-functions-of-a-b-image370118548.htmlRM2CE49YG–. A system of obstetrics . esem-bling the placenta in appearance. It consists of connective tissue inaddition to the vessels. It is the representative of the cerebral men-inges, and is continuous below with the spinal meninges. Its smoothsurface is the analogue of the arachnoid. The sensation which isimparted to the finger of the accoucheur pressed upon it is very sim-ilar to that produced by a placenta. In some specimens small por-tions of cerebral matter are found among the vessels of this tumor?but they are so disconnected and isolated that they do not perform inany way the functions of a b
 . The science and art of midwifery . omplete amputation of the head. Codingsof the cord around the fotus Occurring at birth are of little impor-tance unless they he numerous. In that ease they lead to a shorten-ing of the cord, and produce anomalous positions, premature separa-tion of the placenta, retarded second stage of labor, and even death of the foetus from interference of the umbilical circulation. DISEASES OF THE OVUM. 29 V. Cysts.—Cysts of the umbilical cord within the amniotic sheathare either produced by liquefaction of mucoid tissue, or by accumula-tion of serum between the epithel Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-science-and-art-of-midwifery-omplete-amputation-of-the-head-codingsof-the-cord-around-the-fotus-occurring-at-birth-are-of-little-impor-tance-unless-they-he-numerous-in-that-ease-they-lead-to-a-shorten-ing-of-the-cord-and-produce-anomalous-positions-premature-separa-tion-of-the-placenta-retarded-second-stage-of-labor-and-even-death-of-the-foetus-from-interference-of-the-umbilical-circulation-diseases-of-the-ovum-29-v-cystscysts-of-the-umbilical-cord-within-the-amniotic-sheathare-either-produced-by-liquefaction-of-mucoid-tissue-or-by-accumula-tion-of-serum-between-the-epithel-image372489786.html
. The science and art of midwifery . omplete amputation of the head. Codingsof the cord around the fotus Occurring at birth are of little impor-tance unless they he numerous. In that ease they lead to a shorten-ing of the cord, and produce anomalous positions, premature separa-tion of the placenta, retarded second stage of labor, and even death of the foetus from interference of the umbilical circulation. DISEASES OF THE OVUM. 29 V. Cysts.—Cysts of the umbilical cord within the amniotic sheathare either produced by liquefaction of mucoid tissue, or by accumula-tion of serum between the epithel Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-science-and-art-of-midwifery-omplete-amputation-of-the-head-codingsof-the-cord-around-the-fotus-occurring-at-birth-are-of-little-impor-tance-unless-they-he-numerous-in-that-ease-they-lead-to-a-shorten-ing-of-the-cord-and-produce-anomalous-positions-premature-separa-tion-of-the-placenta-retarded-second-stage-of-labor-and-even-death-of-the-foetus-from-interference-of-the-umbilical-circulation-diseases-of-the-ovum-29-v-cystscysts-of-the-umbilical-cord-within-the-amniotic-sheathare-either-produced-by-liquefaction-of-mucoid-tissue-or-by-accumula-tion-of-serum-between-the-epithel-image372489786.htmlRM2CJ0AEJ–. The science and art of midwifery . omplete amputation of the head. Codingsof the cord around the fotus Occurring at birth are of little impor-tance unless they he numerous. In that ease they lead to a shorten-ing of the cord, and produce anomalous positions, premature separa-tion of the placenta, retarded second stage of labor, and even death of the foetus from interference of the umbilical circulation. DISEASES OF THE OVUM. 29 V. Cysts.—Cysts of the umbilical cord within the amniotic sheathare either produced by liquefaction of mucoid tissue, or by accumula-tion of serum between the epithel
 . The science and art of midwifery . local.They attack dead tissue only (clots, bits of placenta, shreds of mem-brane, portions of decidua). They do not themselves invade the tis-sues. The products of putrefaction contain certain poisons termedptomaines, which when they enter the circulat ion, cause a general in-toxication. When the offending substances are removed from theuterine cavity, the systemic symptoms disappear. The instinct which prompts the employment of the disinfectantdouche in cases where there is a stinking lochia! discharge is a soundone, but it is a common clinical observation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-science-and-art-of-midwifery-localthey-attack-dead-tissue-only-clots-bits-of-placenta-shreds-of-mem-brane-portions-of-decidua-they-do-not-themselves-invade-the-tis-sues-the-products-of-putrefaction-contain-certain-poisons-termedptomaines-which-when-they-enter-the-circulat-ion-cause-a-general-in-toxication-when-the-offending-substances-are-removed-from-theuterine-cavity-the-systemic-symptoms-disappear-the-instinct-which-prompts-the-employment-of-the-disinfectantdouche-in-cases-where-there-is-a-stinking-lochia!-discharge-is-a-soundone-but-it-is-a-common-clinical-observation-image372358970.html
. The science and art of midwifery . local.They attack dead tissue only (clots, bits of placenta, shreds of mem-brane, portions of decidua). They do not themselves invade the tis-sues. The products of putrefaction contain certain poisons termedptomaines, which when they enter the circulat ion, cause a general in-toxication. When the offending substances are removed from theuterine cavity, the systemic symptoms disappear. The instinct which prompts the employment of the disinfectantdouche in cases where there is a stinking lochia! discharge is a soundone, but it is a common clinical observation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-science-and-art-of-midwifery-localthey-attack-dead-tissue-only-clots-bits-of-placenta-shreds-of-mem-brane-portions-of-decidua-they-do-not-themselves-invade-the-tis-sues-the-products-of-putrefaction-contain-certain-poisons-termedptomaines-which-when-they-enter-the-circulat-ion-cause-a-general-in-toxication-when-the-offending-substances-are-removed-from-theuterine-cavity-the-systemic-symptoms-disappear-the-instinct-which-prompts-the-employment-of-the-disinfectantdouche-in-cases-where-there-is-a-stinking-lochia!-discharge-is-a-soundone-but-it-is-a-common-clinical-observation-image372358970.htmlRM2CHPBJJ–. The science and art of midwifery . local.They attack dead tissue only (clots, bits of placenta, shreds of mem-brane, portions of decidua). They do not themselves invade the tis-sues. The products of putrefaction contain certain poisons termedptomaines, which when they enter the circulat ion, cause a general in-toxication. When the offending substances are removed from theuterine cavity, the systemic symptoms disappear. The instinct which prompts the employment of the disinfectantdouche in cases where there is a stinking lochia! discharge is a soundone, but it is a common clinical observation
 . Gynecology : . remen-dously swollen, as may be seen if this is compared with the drawing of the placenta at full term. Thelayer of Langhans cells covered with syncytium .are well shown on the surface of the villi. On thespace between the villi in the center are several fragments of syncytium. This space is normally filledwith blood in which these fragments lie. Moreover, a further difficulty in diagnosis exists in the fact that the tumorsexactly resemble the normal fetal tissue. Hitschmann and Cristofoletti came to the following conclusion: As a matter of fact, we are convinced that a histol Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynecology-remen-dously-swollen-as-may-be-seen-if-this-is-compared-with-the-drawing-of-the-placenta-at-full-term-thelayer-of-langhans-cells-covered-with-syncytium-are-well-shown-on-the-surface-of-the-villi-on-thespace-between-the-villi-in-the-center-are-several-fragments-of-syncytium-this-space-is-normally-filledwith-blood-in-which-these-fragments-lie-moreover-a-further-difficulty-in-diagnosis-exists-in-the-fact-that-the-tumorsexactly-resemble-the-normal-fetal-tissue-hitschmann-and-cristofoletti-came-to-the-following-conclusion-as-a-matter-of-fact-we-are-convinced-that-a-histol-image369837158.html
. Gynecology : . remen-dously swollen, as may be seen if this is compared with the drawing of the placenta at full term. Thelayer of Langhans cells covered with syncytium .are well shown on the surface of the villi. On thespace between the villi in the center are several fragments of syncytium. This space is normally filledwith blood in which these fragments lie. Moreover, a further difficulty in diagnosis exists in the fact that the tumorsexactly resemble the normal fetal tissue. Hitschmann and Cristofoletti came to the following conclusion: As a matter of fact, we are convinced that a histol Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/gynecology-remen-dously-swollen-as-may-be-seen-if-this-is-compared-with-the-drawing-of-the-placenta-at-full-term-thelayer-of-langhans-cells-covered-with-syncytium-are-well-shown-on-the-surface-of-the-villi-on-thespace-between-the-villi-in-the-center-are-several-fragments-of-syncytium-this-space-is-normally-filledwith-blood-in-which-these-fragments-lie-moreover-a-further-difficulty-in-diagnosis-exists-in-the-fact-that-the-tumorsexactly-resemble-the-normal-fetal-tissue-hitschmann-and-cristofoletti-came-to-the-following-conclusion-as-a-matter-of-fact-we-are-convinced-that-a-histol-image369837158.htmlRM2CDKF1X–. Gynecology : . remen-dously swollen, as may be seen if this is compared with the drawing of the placenta at full term. Thelayer of Langhans cells covered with syncytium .are well shown on the surface of the villi. On thespace between the villi in the center are several fragments of syncytium. This space is normally filledwith blood in which these fragments lie. Moreover, a further difficulty in diagnosis exists in the fact that the tumorsexactly resemble the normal fetal tissue. Hitschmann and Cristofoletti came to the following conclusion: As a matter of fact, we are convinced that a histol
 . A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . ailure of strength and deathcomplete the picture. The appendages of the syphilitic fcetus giveample evidence of the pathological process. The maternal surface ofthe placenta is dark in color and contains abundant areas of grayish-yellow tissue, which is composed of infarcts at various stages of fattydegeneration. The membranes are grayish-yellow in many cases, theamniotic liquid is turbid, and the chorion especially is darker in colorand more friable than in normal cases. The degree of syphilitic infection and its course will depend n Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-obstetrics-for-students-and-practitioners-ailure-of-strength-and-deathcomplete-the-picture-the-appendages-of-the-syphilitic-fcetus-giveample-evidence-of-the-pathological-process-the-maternal-surface-ofthe-placenta-is-dark-in-color-and-contains-abundant-areas-of-grayish-yellow-tissue-which-is-composed-of-infarcts-at-various-stages-of-fattydegeneration-the-membranes-are-grayish-yellow-in-many-cases-theamniotic-liquid-is-turbid-and-the-chorion-especially-is-darker-in-colorand-more-friable-than-in-normal-cases-the-degree-of-syphilitic-infection-and-its-course-will-depend-n-image376043453.html
. A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . ailure of strength and deathcomplete the picture. The appendages of the syphilitic fcetus giveample evidence of the pathological process. The maternal surface ofthe placenta is dark in color and contains abundant areas of grayish-yellow tissue, which is composed of infarcts at various stages of fattydegeneration. The membranes are grayish-yellow in many cases, theamniotic liquid is turbid, and the chorion especially is darker in colorand more friable than in normal cases. The degree of syphilitic infection and its course will depend n Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-obstetrics-for-students-and-practitioners-ailure-of-strength-and-deathcomplete-the-picture-the-appendages-of-the-syphilitic-fcetus-giveample-evidence-of-the-pathological-process-the-maternal-surface-ofthe-placenta-is-dark-in-color-and-contains-abundant-areas-of-grayish-yellow-tissue-which-is-composed-of-infarcts-at-various-stages-of-fattydegeneration-the-membranes-are-grayish-yellow-in-many-cases-theamniotic-liquid-is-turbid-and-the-chorion-especially-is-darker-in-colorand-more-friable-than-in-normal-cases-the-degree-of-syphilitic-infection-and-its-course-will-depend-n-image376043453.htmlRM2CRP779–. A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . ailure of strength and deathcomplete the picture. The appendages of the syphilitic fcetus giveample evidence of the pathological process. The maternal surface ofthe placenta is dark in color and contains abundant areas of grayish-yellow tissue, which is composed of infarcts at various stages of fattydegeneration. The membranes are grayish-yellow in many cases, theamniotic liquid is turbid, and the chorion especially is darker in colorand more friable than in normal cases. The degree of syphilitic infection and its course will depend n
 . American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. n. Sarway, in Doderleins Uandhuch (1915), states that these infarcts are fre-quently found in placental tissue as changes with fibrin formation which resultfrom coagulation necrosis. These areas are bright yellow or white, round or oval,sometimes several centimeters in diameter. They may be more or less indurated.There may be flattened or nodular areas, sometimes wedge shaped, located oneither the fetal or the maternal surface of the placenta, usually not lying deeplyin the placental tissue. Islands may occur in the middle of the placenta whichh Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/american-journal-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-n-sarway-in-doderleins-uandhuch-1915-states-that-these-infarcts-are-fre-quently-found-in-placental-tissue-as-changes-with-fibrin-formation-which-resultfrom-coagulation-necrosis-these-areas-are-bright-yellow-or-white-round-or-ovalsometimes-several-centimeters-in-diameter-they-may-be-more-or-less-induratedthere-may-be-flattened-or-nodular-areas-sometimes-wedge-shaped-located-oneither-the-fetal-or-the-maternal-surface-of-the-placenta-usually-not-lying-deeplyin-the-placental-tissue-islands-may-occur-in-the-middle-of-the-placenta-whichh-image370560225.html
. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. n. Sarway, in Doderleins Uandhuch (1915), states that these infarcts are fre-quently found in placental tissue as changes with fibrin formation which resultfrom coagulation necrosis. These areas are bright yellow or white, round or oval,sometimes several centimeters in diameter. They may be more or less indurated.There may be flattened or nodular areas, sometimes wedge shaped, located oneither the fetal or the maternal surface of the placenta, usually not lying deeplyin the placental tissue. Islands may occur in the middle of the placenta whichh Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/american-journal-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-n-sarway-in-doderleins-uandhuch-1915-states-that-these-infarcts-are-fre-quently-found-in-placental-tissue-as-changes-with-fibrin-formation-which-resultfrom-coagulation-necrosis-these-areas-are-bright-yellow-or-white-round-or-ovalsometimes-several-centimeters-in-diameter-they-may-be-more-or-less-induratedthere-may-be-flattened-or-nodular-areas-sometimes-wedge-shaped-located-oneither-the-fetal-or-the-maternal-surface-of-the-placenta-usually-not-lying-deeplyin-the-placental-tissue-islands-may-occur-in-the-middle-of-the-placenta-whichh-image370560225.htmlRM2CETD9N–. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. n. Sarway, in Doderleins Uandhuch (1915), states that these infarcts are fre-quently found in placental tissue as changes with fibrin formation which resultfrom coagulation necrosis. These areas are bright yellow or white, round or oval,sometimes several centimeters in diameter. They may be more or less indurated.There may be flattened or nodular areas, sometimes wedge shaped, located oneither the fetal or the maternal surface of the placenta, usually not lying deeplyin the placental tissue. Islands may occur in the middle of the placenta whichh
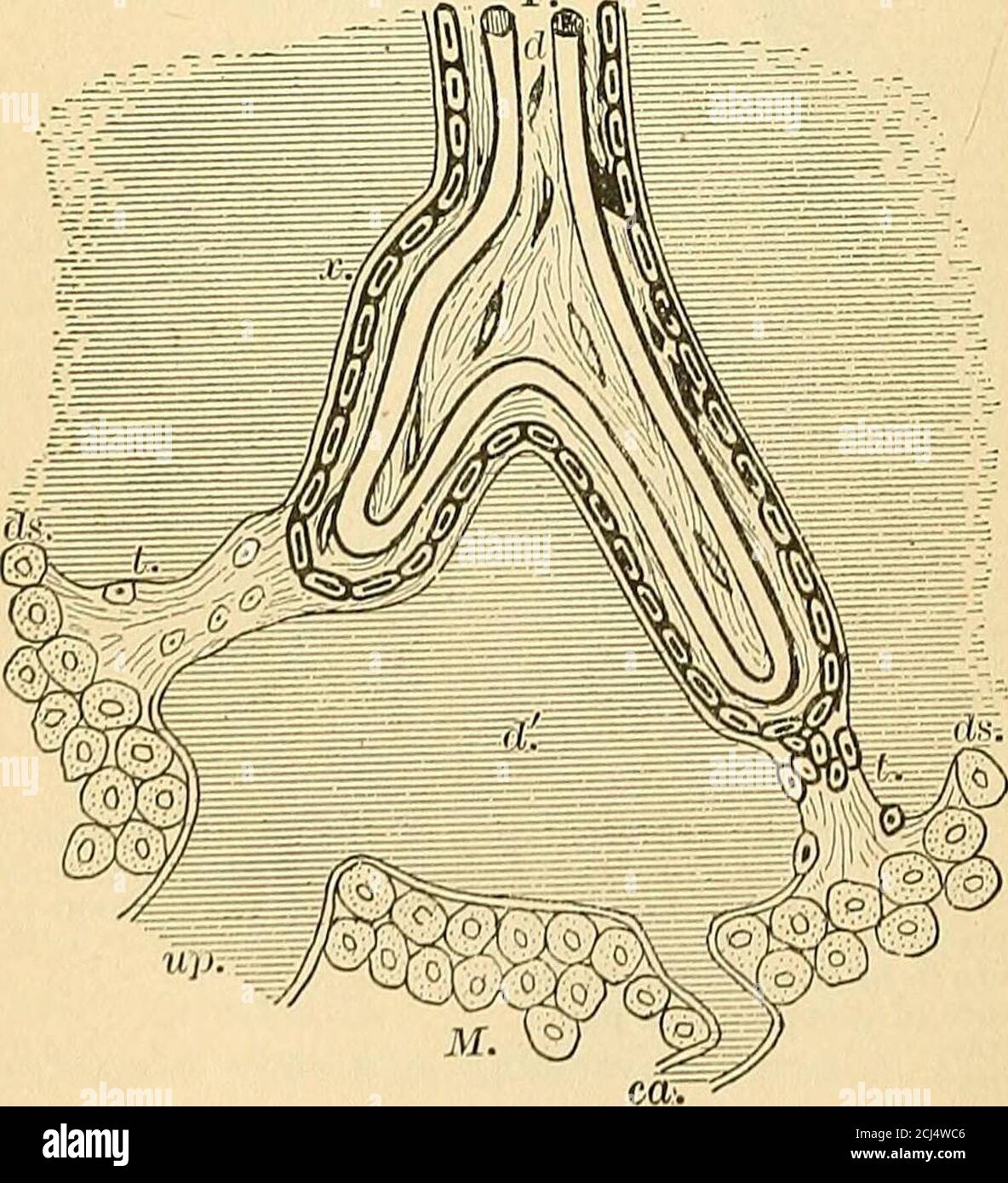 . A text-book of comparative physiology for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine . e-F.. Fig 97.—Structure of human placenta; ds, decidua serotina; L trabecnlae of serotinapassing to f«lal villi; ca, curling artery; up, utero-placental vein; a;, prolongationof maternal tissue on exterior of villus, outside cellular layer e, which may repre-sent either endothelium of maternal blood-vessels or delicate connective tissue ofthe serotina or both; e, maternal cells of the serotina. REPRODUCTION. 93 cance of this general arrangement will be explained in thechapter on the ph Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-e-f-fig-97structure-of-human-placenta-ds-decidua-serotina-l-trabecnlae-of-serotinapassing-to-flal-villi-ca-curling-artery-up-utero-placental-vein-a-prolongationof-maternal-tissue-on-exterior-of-villus-outside-cellular-layer-e-which-may-repre-sent-either-endothelium-of-maternal-blood-vessels-or-delicate-connective-tissue-ofthe-serotina-or-both-e-maternal-cells-of-the-serotina-reproduction-93-cance-of-this-general-arrangement-will-be-explained-in-thechapter-on-the-ph-image372589286.html
. A text-book of comparative physiology for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine . e-F.. Fig 97.—Structure of human placenta; ds, decidua serotina; L trabecnlae of serotinapassing to f«lal villi; ca, curling artery; up, utero-placental vein; a;, prolongationof maternal tissue on exterior of villus, outside cellular layer e, which may repre-sent either endothelium of maternal blood-vessels or delicate connective tissue ofthe serotina or both; e, maternal cells of the serotina. REPRODUCTION. 93 cance of this general arrangement will be explained in thechapter on the ph Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-e-f-fig-97structure-of-human-placenta-ds-decidua-serotina-l-trabecnlae-of-serotinapassing-to-flal-villi-ca-curling-artery-up-utero-placental-vein-a-prolongationof-maternal-tissue-on-exterior-of-villus-outside-cellular-layer-e-which-may-repre-sent-either-endothelium-of-maternal-blood-vessels-or-delicate-connective-tissue-ofthe-serotina-or-both-e-maternal-cells-of-the-serotina-reproduction-93-cance-of-this-general-arrangement-will-be-explained-in-thechapter-on-the-ph-image372589286.htmlRM2CJ4WC6–. A text-book of comparative physiology for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine . e-F.. Fig 97.—Structure of human placenta; ds, decidua serotina; L trabecnlae of serotinapassing to f«lal villi; ca, curling artery; up, utero-placental vein; a;, prolongationof maternal tissue on exterior of villus, outside cellular layer e, which may repre-sent either endothelium of maternal blood-vessels or delicate connective tissue ofthe serotina or both; e, maternal cells of the serotina. REPRODUCTION. 93 cance of this general arrangement will be explained in thechapter on the ph
 . American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. i.Hrarjg*- -^fc«*:;^-f^- jjvi/^.-it^^T^ y Pig. 6-B. Pig. 6.—Normal pregnancy with no signs of toxemia. Placenta showed marked?evidence of degeneration. There was a rather large necrotic area surrounded byfibrous tissue. A, Photomicrograph from markedly degenerated area showing theblood vessels. B, Photomicrograph showing vessels from normal area in this placenta. more frequent in toxic cases, they still do not seem to l)e limitedto cases presenting a true eclamptic toxemia. (3) It is difficult to 562 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECO Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/american-journal-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-ihrarjg-fc-f-jjvi-itt-y-pig-6-b-pig-6normal-pregnancy-with-no-signs-of-toxemia-placenta-showed-markedevidence-of-degeneration-there-was-a-rather-large-necrotic-area-surrounded-byfibrous-tissue-a-photomicrograph-from-markedly-degenerated-area-showing-theblood-vessels-b-photomicrograph-showing-vessels-from-normal-area-in-this-placenta-more-frequent-in-toxic-cases-they-still-do-not-seem-to-le-limitedto-cases-presenting-a-true-eclamptic-toxemia-3-it-is-difficult-to-562-the-american-journal-of-obstetrics-and-gyneco-image370559024.html
. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. i.Hrarjg*- -^fc«*:;^-f^- jjvi/^.-it^^T^ y Pig. 6-B. Pig. 6.—Normal pregnancy with no signs of toxemia. Placenta showed marked?evidence of degeneration. There was a rather large necrotic area surrounded byfibrous tissue. A, Photomicrograph from markedly degenerated area showing theblood vessels. B, Photomicrograph showing vessels from normal area in this placenta. more frequent in toxic cases, they still do not seem to l)e limitedto cases presenting a true eclamptic toxemia. (3) It is difficult to 562 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECO Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/american-journal-of-obstetrics-and-gynecology-ihrarjg-fc-f-jjvi-itt-y-pig-6-b-pig-6normal-pregnancy-with-no-signs-of-toxemia-placenta-showed-markedevidence-of-degeneration-there-was-a-rather-large-necrotic-area-surrounded-byfibrous-tissue-a-photomicrograph-from-markedly-degenerated-area-showing-theblood-vessels-b-photomicrograph-showing-vessels-from-normal-area-in-this-placenta-more-frequent-in-toxic-cases-they-still-do-not-seem-to-le-limitedto-cases-presenting-a-true-eclamptic-toxemia-3-it-is-difficult-to-562-the-american-journal-of-obstetrics-and-gyneco-image370559024.htmlRM2CETBPT–. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. i.Hrarjg*- -^fc«*:;^-f^- jjvi/^.-it^^T^ y Pig. 6-B. Pig. 6.—Normal pregnancy with no signs of toxemia. Placenta showed marked?evidence of degeneration. There was a rather large necrotic area surrounded byfibrous tissue. A, Photomicrograph from markedly degenerated area showing theblood vessels. B, Photomicrograph showing vessels from normal area in this placenta. more frequent in toxic cases, they still do not seem to l)e limitedto cases presenting a true eclamptic toxemia. (3) It is difficult to 562 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECO
 . An American text-book of obstetrics. For practitioners and students. Fig. 81—Section through placenta of seven months in sifa(Minot): Am, amnion; Cho, chorion; 17,root of a villus; vi, sections of ramifications of the villi among the maternal blood-spaces; D, deep layerof the decidua, showing remains of enlarged glands of stratum spongiosum; Ve, uterine blood-vesselconnected with placental sinus; Mc, muscular wall of uterus. up of a stroma of embryonal connective tissue containing large branched cells 92 AMERICAN TEXT-BOOK OF OBSTETRICS. and blood-vessels; these latter consist of the larger Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-american-text-book-of-obstetrics-for-practitioners-and-students-fig-81section-through-placenta-of-seven-months-in-sifaminot-am-amnion-cho-chorion-17root-of-a-villus-vi-sections-of-ramifications-of-the-villi-among-the-maternal-blood-spaces-d-deep-layerof-the-decidua-showing-remains-of-enlarged-glands-of-stratum-spongiosum-ve-uterine-blood-vesselconnected-with-placental-sinus-mc-muscular-wall-of-uterus-up-of-a-stroma-of-embryonal-connective-tissue-containing-large-branched-cells-92-american-text-book-of-obstetrics-and-blood-vessels-these-latter-consist-of-the-larger-image370596991.html
. An American text-book of obstetrics. For practitioners and students. Fig. 81—Section through placenta of seven months in sifa(Minot): Am, amnion; Cho, chorion; 17,root of a villus; vi, sections of ramifications of the villi among the maternal blood-spaces; D, deep layerof the decidua, showing remains of enlarged glands of stratum spongiosum; Ve, uterine blood-vesselconnected with placental sinus; Mc, muscular wall of uterus. up of a stroma of embryonal connective tissue containing large branched cells 92 AMERICAN TEXT-BOOK OF OBSTETRICS. and blood-vessels; these latter consist of the larger Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-american-text-book-of-obstetrics-for-practitioners-and-students-fig-81section-through-placenta-of-seven-months-in-sifaminot-am-amnion-cho-chorion-17root-of-a-villus-vi-sections-of-ramifications-of-the-villi-among-the-maternal-blood-spaces-d-deep-layerof-the-decidua-showing-remains-of-enlarged-glands-of-stratum-spongiosum-ve-uterine-blood-vesselconnected-with-placental-sinus-mc-muscular-wall-of-uterus-up-of-a-stroma-of-embryonal-connective-tissue-containing-large-branched-cells-92-american-text-book-of-obstetrics-and-blood-vessels-these-latter-consist-of-the-larger-image370596991.htmlRM2CEX46R–. An American text-book of obstetrics. For practitioners and students. Fig. 81—Section through placenta of seven months in sifa(Minot): Am, amnion; Cho, chorion; 17,root of a villus; vi, sections of ramifications of the villi among the maternal blood-spaces; D, deep layerof the decidua, showing remains of enlarged glands of stratum spongiosum; Ve, uterine blood-vesselconnected with placental sinus; Mc, muscular wall of uterus. up of a stroma of embryonal connective tissue containing large branched cells 92 AMERICAN TEXT-BOOK OF OBSTETRICS. and blood-vessels; these latter consist of the larger
 . Morphology of angiosperms (Morphology of spermatophytes. Part II). Angiosperms; Plant morphology. THE EMBRYO 195 Corallorhiza multiflora, in which it consists of two very long- cells and embeds its tip into the placenta; of Habenaria tri- dentata, and of II. blephariglottis, in which each of the six or seven cells of the snspensor usually sends out a branch, some of them short and reaching the integument, others elongated and passing parallel with the suspensor into the tissue at the base of the funiculus. These four types of monocotyledonous embryos, which for convenience may be spoken of a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-angiosperms-morphology-of-spermatophytes-part-ii-angiosperms-plant-morphology-the-embryo-195-corallorhiza-multiflora-in-which-it-consists-of-two-very-long-cells-and-embeds-its-tip-into-the-placenta-of-habenaria-tri-dentata-and-of-ii-blephariglottis-in-which-each-of-the-six-or-seven-cells-of-the-snspensor-usually-sends-out-a-branch-some-of-them-short-and-reaching-the-integument-others-elongated-and-passing-parallel-with-the-suspensor-into-the-tissue-at-the-base-of-the-funiculus-these-four-types-of-monocotyledonous-embryos-which-for-convenience-may-be-spoken-of-a-image232331954.html
. Morphology of angiosperms (Morphology of spermatophytes. Part II). Angiosperms; Plant morphology. THE EMBRYO 195 Corallorhiza multiflora, in which it consists of two very long- cells and embeds its tip into the placenta; of Habenaria tri- dentata, and of II. blephariglottis, in which each of the six or seven cells of the snspensor usually sends out a branch, some of them short and reaching the integument, others elongated and passing parallel with the suspensor into the tissue at the base of the funiculus. These four types of monocotyledonous embryos, which for convenience may be spoken of a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-angiosperms-morphology-of-spermatophytes-part-ii-angiosperms-plant-morphology-the-embryo-195-corallorhiza-multiflora-in-which-it-consists-of-two-very-long-cells-and-embeds-its-tip-into-the-placenta-of-habenaria-tri-dentata-and-of-ii-blephariglottis-in-which-each-of-the-six-or-seven-cells-of-the-snspensor-usually-sends-out-a-branch-some-of-them-short-and-reaching-the-integument-others-elongated-and-passing-parallel-with-the-suspensor-into-the-tissue-at-the-base-of-the-funiculus-these-four-types-of-monocotyledonous-embryos-which-for-convenience-may-be-spoken-of-a-image232331954.htmlRMRDYHNP–. Morphology of angiosperms (Morphology of spermatophytes. Part II). Angiosperms; Plant morphology. THE EMBRYO 195 Corallorhiza multiflora, in which it consists of two very long- cells and embeds its tip into the placenta; of Habenaria tri- dentata, and of II. blephariglottis, in which each of the six or seven cells of the snspensor usually sends out a branch, some of them short and reaching the integument, others elongated and passing parallel with the suspensor into the tissue at the base of the funiculus. These four types of monocotyledonous embryos, which for convenience may be spoken of a
 . The physiology of reproduction. Reproduction. FCETAL NUTRITION: THE PLACENTA 445 as in the mouse, an inversion of the germinal layers, but in the guinea-pig the amnio-embryonic vesicle is closed and separates the thickened trophoblast from the embryonic ectoderm (Fig. 108). With the growth of the blastodermic vesicle, the roof of the implantation cavity projects into the lumen of the uterus, and in time obhterates it by coming in contact and fusing, at the tenth day, with the mesometrial mucosa (Fig. 109). Here also the cellular tissue has developed at the expense of the glands, and the surf Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-physiology-of-reproduction-reproduction-fcetal-nutrition-the-placenta-445-as-in-the-mouse-an-inversion-of-the-germinal-layers-but-in-the-guinea-pig-the-amnio-embryonic-vesicle-is-closed-and-separates-the-thickened-trophoblast-from-the-embryonic-ectoderm-fig-108-with-the-growth-of-the-blastodermic-vesicle-the-roof-of-the-implantation-cavity-projects-into-the-lumen-of-the-uterus-and-in-time-obhterates-it-by-coming-in-contact-and-fusing-at-the-tenth-day-with-the-mesometrial-mucosa-fig-109-here-also-the-cellular-tissue-has-developed-at-the-expense-of-the-glands-and-the-surf-image232371884.html
. The physiology of reproduction. Reproduction. FCETAL NUTRITION: THE PLACENTA 445 as in the mouse, an inversion of the germinal layers, but in the guinea-pig the amnio-embryonic vesicle is closed and separates the thickened trophoblast from the embryonic ectoderm (Fig. 108). With the growth of the blastodermic vesicle, the roof of the implantation cavity projects into the lumen of the uterus, and in time obhterates it by coming in contact and fusing, at the tenth day, with the mesometrial mucosa (Fig. 109). Here also the cellular tissue has developed at the expense of the glands, and the surf Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-physiology-of-reproduction-reproduction-fcetal-nutrition-the-placenta-445-as-in-the-mouse-an-inversion-of-the-germinal-layers-but-in-the-guinea-pig-the-amnio-embryonic-vesicle-is-closed-and-separates-the-thickened-trophoblast-from-the-embryonic-ectoderm-fig-108-with-the-growth-of-the-blastodermic-vesicle-the-roof-of-the-implantation-cavity-projects-into-the-lumen-of-the-uterus-and-in-time-obhterates-it-by-coming-in-contact-and-fusing-at-the-tenth-day-with-the-mesometrial-mucosa-fig-109-here-also-the-cellular-tissue-has-developed-at-the-expense-of-the-glands-and-the-surf-image232371884.htmlRMRE1CKT–. The physiology of reproduction. Reproduction. FCETAL NUTRITION: THE PLACENTA 445 as in the mouse, an inversion of the germinal layers, but in the guinea-pig the amnio-embryonic vesicle is closed and separates the thickened trophoblast from the embryonic ectoderm (Fig. 108). With the growth of the blastodermic vesicle, the roof of the implantation cavity projects into the lumen of the uterus, and in time obhterates it by coming in contact and fusing, at the tenth day, with the mesometrial mucosa (Fig. 109). Here also the cellular tissue has developed at the expense of the glands, and the surf
 . A Manual of botany : being an introduction to the study of the structure, physiology, and classification of plants . Botany. ESSENTIAL OEGANS—THE OVULE. 255 ments are united at the base of the ovule by a cellulo-vascular process called the chalaza (fig. 458 ch). This is often coloured, of a denser texture than the surrounding tissue, and is traversed by fibro- vasoular bundles, which come from the placenta, to nourish the ovule. When the ovule is so developed that the union between the primine, seoundine, and nucleus, with the chalaza, is at the hilum or base (next the placenta), and the for Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-botany-being-an-introduction-to-the-study-of-the-structure-physiology-and-classification-of-plants-botany-essential-oegansthe-ovule-255-ments-are-united-at-the-base-of-the-ovule-by-a-cellulo-vascular-process-called-the-chalaza-fig-458-ch-this-is-often-coloured-of-a-denser-texture-than-the-surrounding-tissue-and-is-traversed-by-fibro-vasoular-bundles-which-come-from-the-placenta-to-nourish-the-ovule-when-the-ovule-is-so-developed-that-the-union-between-the-primine-seoundine-and-nucleus-with-the-chalaza-is-at-the-hilum-or-base-next-the-placenta-and-the-for-image232090663.html
. A Manual of botany : being an introduction to the study of the structure, physiology, and classification of plants . Botany. ESSENTIAL OEGANS—THE OVULE. 255 ments are united at the base of the ovule by a cellulo-vascular process called the chalaza (fig. 458 ch). This is often coloured, of a denser texture than the surrounding tissue, and is traversed by fibro- vasoular bundles, which come from the placenta, to nourish the ovule. When the ovule is so developed that the union between the primine, seoundine, and nucleus, with the chalaza, is at the hilum or base (next the placenta), and the for Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-botany-being-an-introduction-to-the-study-of-the-structure-physiology-and-classification-of-plants-botany-essential-oegansthe-ovule-255-ments-are-united-at-the-base-of-the-ovule-by-a-cellulo-vascular-process-called-the-chalaza-fig-458-ch-this-is-often-coloured-of-a-denser-texture-than-the-surrounding-tissue-and-is-traversed-by-fibro-vasoular-bundles-which-come-from-the-placenta-to-nourish-the-ovule-when-the-ovule-is-so-developed-that-the-union-between-the-primine-seoundine-and-nucleus-with-the-chalaza-is-at-the-hilum-or-base-next-the-placenta-and-the-for-image232090663.htmlRMRDGJ07–. A Manual of botany : being an introduction to the study of the structure, physiology, and classification of plants . Botany. ESSENTIAL OEGANS—THE OVULE. 255 ments are united at the base of the ovule by a cellulo-vascular process called the chalaza (fig. 458 ch). This is often coloured, of a denser texture than the surrounding tissue, and is traversed by fibro- vasoular bundles, which come from the placenta, to nourish the ovule. When the ovule is so developed that the union between the primine, seoundine, and nucleus, with the chalaza, is at the hilum or base (next the placenta), and the for
 . Text-book of botany, morphological and physiological. Botany. 55* PHANEROGAMS. consist of one or more closed chambers in which the ovules are formed ; the lower, hollow, swollen part of. each separate seed-chamber which encloses the ovules is called the Ovary; the place or the mass of tissue from which the ovules spring directly into the ovary is a Placenta. Above the ovary the seed-vessel narrows into one or more thin stalk-like structures or Styles, which bear the Stigmas ; these are glandular swellings or expansions of various forms which retain the pollen that is carried to them, and by Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-botany-morphological-and-physiological-botany-55-phanerogams-consist-of-one-or-more-closed-chambers-in-which-the-ovules-are-formed-the-lower-hollow-swollen-part-of-each-separate-seed-chamber-which-encloses-the-ovules-is-called-the-ovary-the-place-or-the-mass-of-tissue-from-which-the-ovules-spring-directly-into-the-ovary-is-a-placenta-above-the-ovary-the-seed-vessel-narrows-into-one-or-more-thin-stalk-like-structures-or-styles-which-bear-the-stigmas-these-are-glandular-swellings-or-expansions-of-various-forms-which-retain-the-pollen-that-is-carried-to-them-and-by-image237841278.html
. Text-book of botany, morphological and physiological. Botany. 55* PHANEROGAMS. consist of one or more closed chambers in which the ovules are formed ; the lower, hollow, swollen part of. each separate seed-chamber which encloses the ovules is called the Ovary; the place or the mass of tissue from which the ovules spring directly into the ovary is a Placenta. Above the ovary the seed-vessel narrows into one or more thin stalk-like structures or Styles, which bear the Stigmas ; these are glandular swellings or expansions of various forms which retain the pollen that is carried to them, and by Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-botany-morphological-and-physiological-botany-55-phanerogams-consist-of-one-or-more-closed-chambers-in-which-the-ovules-are-formed-the-lower-hollow-swollen-part-of-each-separate-seed-chamber-which-encloses-the-ovules-is-called-the-ovary-the-place-or-the-mass-of-tissue-from-which-the-ovules-spring-directly-into-the-ovary-is-a-placenta-above-the-ovary-the-seed-vessel-narrows-into-one-or-more-thin-stalk-like-structures-or-styles-which-bear-the-stigmas-these-are-glandular-swellings-or-expansions-of-various-forms-which-retain-the-pollen-that-is-carried-to-them-and-by-image237841278.htmlRMRPXGYA–. Text-book of botany, morphological and physiological. Botany. 55* PHANEROGAMS. consist of one or more closed chambers in which the ovules are formed ; the lower, hollow, swollen part of. each separate seed-chamber which encloses the ovules is called the Ovary; the place or the mass of tissue from which the ovules spring directly into the ovary is a Placenta. Above the ovary the seed-vessel narrows into one or more thin stalk-like structures or Styles, which bear the Stigmas ; these are glandular swellings or expansions of various forms which retain the pollen that is carried to them, and by
![. A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photo . A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/REW118/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-microform-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-physiology-comparative-veterinary-physiology-physiologie-compare-physiologie-vtrinaire-m-comparativb-physiology-in-the-placenta-of-the-apes-and-of-the-human-sub-ject-the-most-marked-depart-ure-from-simplicity-is-found-the-maternal-vessels-are-said-to-constitute-large-intercom-municating-sinuses-the-villi-may-hang-freely-suspended-in-these-sinuses-or-be-anchored-to-their-walls-by-strands-of-tissue-there-is-believed-to-be-only-one-layer-of-epithe-lial-cells-REW118.jpg) . A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-microform-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-physiology-comparative-veterinary-physiology-physiologie-compare-physiologie-vtrinaire-m-comparativb-physiology-in-the-placenta-of-the-apes-and-of-the-human-sub-ject-the-most-marked-depart-ure-from-simplicity-is-found-the-maternal-vessels-are-said-to-constitute-large-intercom-municating-sinuses-the-villi-may-hang-freely-suspended-in-these-sinuses-or-be-anchored-to-their-walls-by-strands-of-tissue-there-is-believed-to-be-only-one-layer-of-epithe-lial-cells-image232889588.html
. A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-microform-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-physiology-comparative-veterinary-physiology-physiologie-compare-physiologie-vtrinaire-m-comparativb-physiology-in-the-placenta-of-the-apes-and-of-the-human-sub-ject-the-most-marked-depart-ure-from-simplicity-is-found-the-maternal-vessels-are-said-to-constitute-large-intercom-municating-sinuses-the-villi-may-hang-freely-suspended-in-these-sinuses-or-be-anchored-to-their-walls-by-strands-of-tissue-there-is-believed-to-be-only-one-layer-of-epithe-lial-cells-image232889588.htmlRMREW118–. A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells
 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Section showing the regional divisions of the uterus. ( Outlined ad Nat.) from which polypi, that are not cervical in their origin, most frequently arise; and it is very commonly the seat of those large hyper- trophic growths of the uterine tissue, which are usually termed fibrous tumours. The fundus is also the part to which the upper portion of the placenta is most frequently attached. The body is included between the line above indicated, and another, B B, drawn through the narrowest part of the organ, or that point a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-section-showing-the-regional-divisions-of-the-uterus-outlined-ad-nat-from-which-polypi-that-are-not-cervical-in-their-origin-most-frequently-arise-and-it-is-very-commonly-the-seat-of-those-large-hyper-trophic-growths-of-the-uterine-tissue-which-are-usually-termed-fibrous-tumours-the-fundus-is-also-the-part-to-which-the-upper-portion-of-the-placenta-is-most-frequently-attached-the-body-is-included-between-the-line-above-indicated-and-another-b-b-drawn-through-the-narrowest-part-of-the-organ-or-that-point-a-image231797595.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Section showing the regional divisions of the uterus. ( Outlined ad Nat.) from which polypi, that are not cervical in their origin, most frequently arise; and it is very commonly the seat of those large hyper- trophic growths of the uterine tissue, which are usually termed fibrous tumours. The fundus is also the part to which the upper portion of the placenta is most frequently attached. The body is included between the line above indicated, and another, B B, drawn through the narrowest part of the organ, or that point a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-section-showing-the-regional-divisions-of-the-uterus-outlined-ad-nat-from-which-polypi-that-are-not-cervical-in-their-origin-most-frequently-arise-and-it-is-very-commonly-the-seat-of-those-large-hyper-trophic-growths-of-the-uterine-tissue-which-are-usually-termed-fibrous-tumours-the-fundus-is-also-the-part-to-which-the-upper-portion-of-the-placenta-is-most-frequently-attached-the-body-is-included-between-the-line-above-indicated-and-another-b-b-drawn-through-the-narrowest-part-of-the-organ-or-that-point-a-image231797595.htmlRMRD385F–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. Section showing the regional divisions of the uterus. ( Outlined ad Nat.) from which polypi, that are not cervical in their origin, most frequently arise; and it is very commonly the seat of those large hyper- trophic growths of the uterine tissue, which are usually termed fibrous tumours. The fundus is also the part to which the upper portion of the placenta is most frequently attached. The body is included between the line above indicated, and another, B B, drawn through the narrowest part of the organ, or that point a
![. A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photo . A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/RHXRF5/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-microform-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-physiology-comparative-veterinary-physiology-physiologie-compare-physiologie-vtrinaire-m-comparativb-physiology-in-the-placenta-of-the-apes-and-of-the-human-sub-ject-the-most-marked-depart-ure-from-simplicity-is-found-the-maternal-vessels-are-said-to-constitute-large-intercom-municating-sinuses-the-villi-may-hang-freely-suspended-in-these-sinuses-or-be-anchored-to-their-walls-by-strands-of-tissue-there-is-believed-to-be-only-one-layer-of-epithe-lial-cells-RHXRF5.jpg) . A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-microform-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-physiology-comparative-veterinary-physiology-physiologie-compare-physiologie-vtrinaire-m-comparativb-physiology-in-the-placenta-of-the-apes-and-of-the-human-sub-ject-the-most-marked-depart-ure-from-simplicity-is-found-the-maternal-vessels-are-said-to-constitute-large-intercom-municating-sinuses-the-villi-may-hang-freely-suspended-in-these-sinuses-or-be-anchored-to-their-walls-by-strands-of-tissue-there-is-believed-to-be-only-one-layer-of-epithe-lial-cells-image234773145.html
. A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-microform-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-physiology-comparative-veterinary-physiology-physiologie-compare-physiologie-vtrinaire-m-comparativb-physiology-in-the-placenta-of-the-apes-and-of-the-human-sub-ject-the-most-marked-depart-ure-from-simplicity-is-found-the-maternal-vessels-are-said-to-constitute-large-intercom-municating-sinuses-the-villi-may-hang-freely-suspended-in-these-sinuses-or-be-anchored-to-their-walls-by-strands-of-tissue-there-is-believed-to-be-only-one-layer-of-epithe-lial-cells-image234773145.htmlRMRHXRF5–. A text-book of comparative physiology [microform] : for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine. Physiology, Comparative; Veterinary physiology; Physiologie comparée; Physiologie vétérinaire. M COMPARATIVB PHYSIOLOGY. In the placenta of the apes and of the human sub- ject the most marked depart- ure from simplicity is found. The maternal vessels are said to constitute' large intercom- municating sinuses; the villi may hang freely suspended in these sinuses, or be anchored to their walls by strands of tissue. There is believed to be only one layer of epithe- lial cells
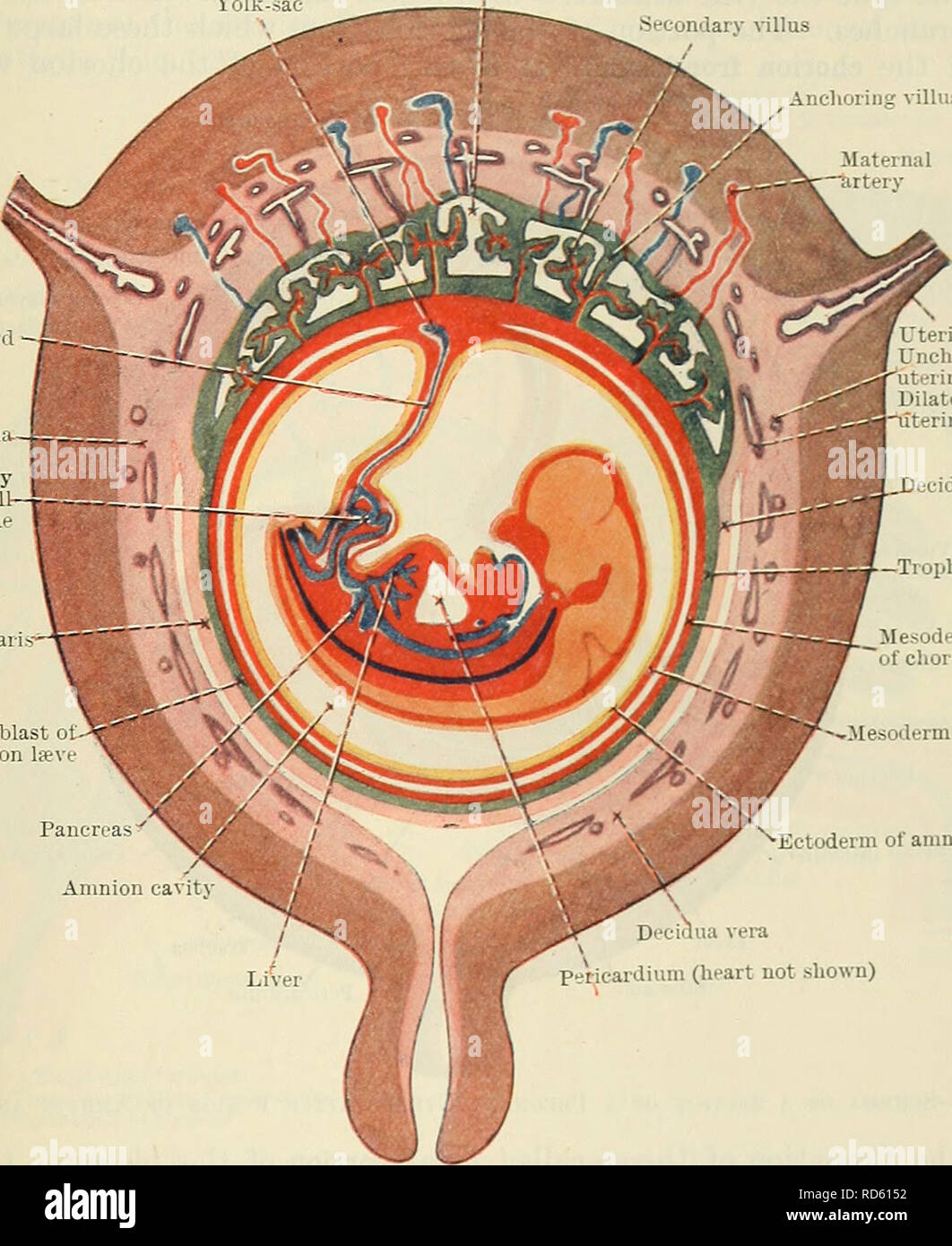 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 59 by a layer of cellular trophoblast, Langhan's layer, which lies next the mesoderm, and a layer of Plasmodium external to the cellular layer. The proximal end of .each villus is continuous with the chorion plate of the intervillous spaces, formed by the chorion, and the distal extremity is connected by the plasmodial basal layer of the trophoblast, which forms the outer boundary of the intervillous spaces and which is fused with the maternal decidual tissue. After a time branches are projected from the sides of the secondary villi i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-placenta-59-by-a-layer-of-cellular-trophoblast-langhans-layer-which-lies-next-the-mesoderm-and-a-layer-of-plasmodium-external-to-the-cellular-layer-the-proximal-end-of-each-villus-is-continuous-with-the-chorion-plate-of-the-intervillous-spaces-formed-by-the-chorion-and-the-distal-extremity-is-connected-by-the-plasmodial-basal-layer-of-the-trophoblast-which-forms-the-outer-boundary-of-the-intervillous-spaces-and-which-is-fused-with-the-maternal-decidual-tissue-after-a-time-branches-are-projected-from-the-sides-of-the-secondary-villi-i-image231857950.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 59 by a layer of cellular trophoblast, Langhan's layer, which lies next the mesoderm, and a layer of Plasmodium external to the cellular layer. The proximal end of .each villus is continuous with the chorion plate of the intervillous spaces, formed by the chorion, and the distal extremity is connected by the plasmodial basal layer of the trophoblast, which forms the outer boundary of the intervillous spaces and which is fused with the maternal decidual tissue. After a time branches are projected from the sides of the secondary villi i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-placenta-59-by-a-layer-of-cellular-trophoblast-langhans-layer-which-lies-next-the-mesoderm-and-a-layer-of-plasmodium-external-to-the-cellular-layer-the-proximal-end-of-each-villus-is-continuous-with-the-chorion-plate-of-the-intervillous-spaces-formed-by-the-chorion-and-the-distal-extremity-is-connected-by-the-plasmodial-basal-layer-of-the-trophoblast-which-forms-the-outer-boundary-of-the-intervillous-spaces-and-which-is-fused-with-the-maternal-decidual-tissue-after-a-time-branches-are-projected-from-the-sides-of-the-secondary-villi-i-image231857950.htmlRMRD6152–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE PLACENTA. 59 by a layer of cellular trophoblast, Langhan's layer, which lies next the mesoderm, and a layer of Plasmodium external to the cellular layer. The proximal end of .each villus is continuous with the chorion plate of the intervillous spaces, formed by the chorion, and the distal extremity is connected by the plasmodial basal layer of the trophoblast, which forms the outer boundary of the intervillous spaces and which is fused with the maternal decidual tissue. After a time branches are projected from the sides of the secondary villi i
 . The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Veterinary anatomy. TEE FCETUS. 1029 2. Pig.—The placenta is formed by an expansion of the villous tubercles, as in Solipeds. The chorion is not entirely covered by these tubercles, but here and there it shows bright little patches, where its tissue is merely covered by an epithelial layer; it is also glabrous at those points wliere it is in cont:ict with the chorion of neighbouring foetuses. The chorion has not a body and two coruua, but is merely an elongated sac, the two extremities of which are in relation with the adjacent foetuses. T Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-veterinary-anatomy-tee-fcetus-1029-2-pigthe-placenta-is-formed-by-an-expansion-of-the-villous-tubercles-as-in-solipeds-the-chorion-is-not-entirely-covered-by-these-tubercles-but-here-and-there-it-shows-bright-little-patches-where-its-tissue-is-merely-covered-by-an-epithelial-layer-it-is-also-glabrous-at-those-points-wliere-it-is-in-contict-with-the-chorion-of-neighbouring-foetuses-the-chorion-has-not-a-body-and-two-coruua-but-is-merely-an-elongated-sac-the-two-extremities-of-which-are-in-relation-with-the-adjacent-foetuses-t-image232676981.html
. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Veterinary anatomy. TEE FCETUS. 1029 2. Pig.—The placenta is formed by an expansion of the villous tubercles, as in Solipeds. The chorion is not entirely covered by these tubercles, but here and there it shows bright little patches, where its tissue is merely covered by an epithelial layer; it is also glabrous at those points wliere it is in cont:ict with the chorion of neighbouring foetuses. The chorion has not a body and two coruua, but is merely an elongated sac, the two extremities of which are in relation with the adjacent foetuses. T Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-veterinary-anatomy-tee-fcetus-1029-2-pigthe-placenta-is-formed-by-an-expansion-of-the-villous-tubercles-as-in-solipeds-the-chorion-is-not-entirely-covered-by-these-tubercles-but-here-and-there-it-shows-bright-little-patches-where-its-tissue-is-merely-covered-by-an-epithelial-layer-it-is-also-glabrous-at-those-points-wliere-it-is-in-contict-with-the-chorion-of-neighbouring-foetuses-the-chorion-has-not-a-body-and-two-coruua-but-is-merely-an-elongated-sac-the-two-extremities-of-which-are-in-relation-with-the-adjacent-foetuses-t-image232676981.htmlRMREF9T5–. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Veterinary anatomy. TEE FCETUS. 1029 2. Pig.—The placenta is formed by an expansion of the villous tubercles, as in Solipeds. The chorion is not entirely covered by these tubercles, but here and there it shows bright little patches, where its tissue is merely covered by an epithelial layer; it is also glabrous at those points wliere it is in cont:ict with the chorion of neighbouring foetuses. The chorion has not a body and two coruua, but is merely an elongated sac, the two extremities of which are in relation with the adjacent foetuses. T
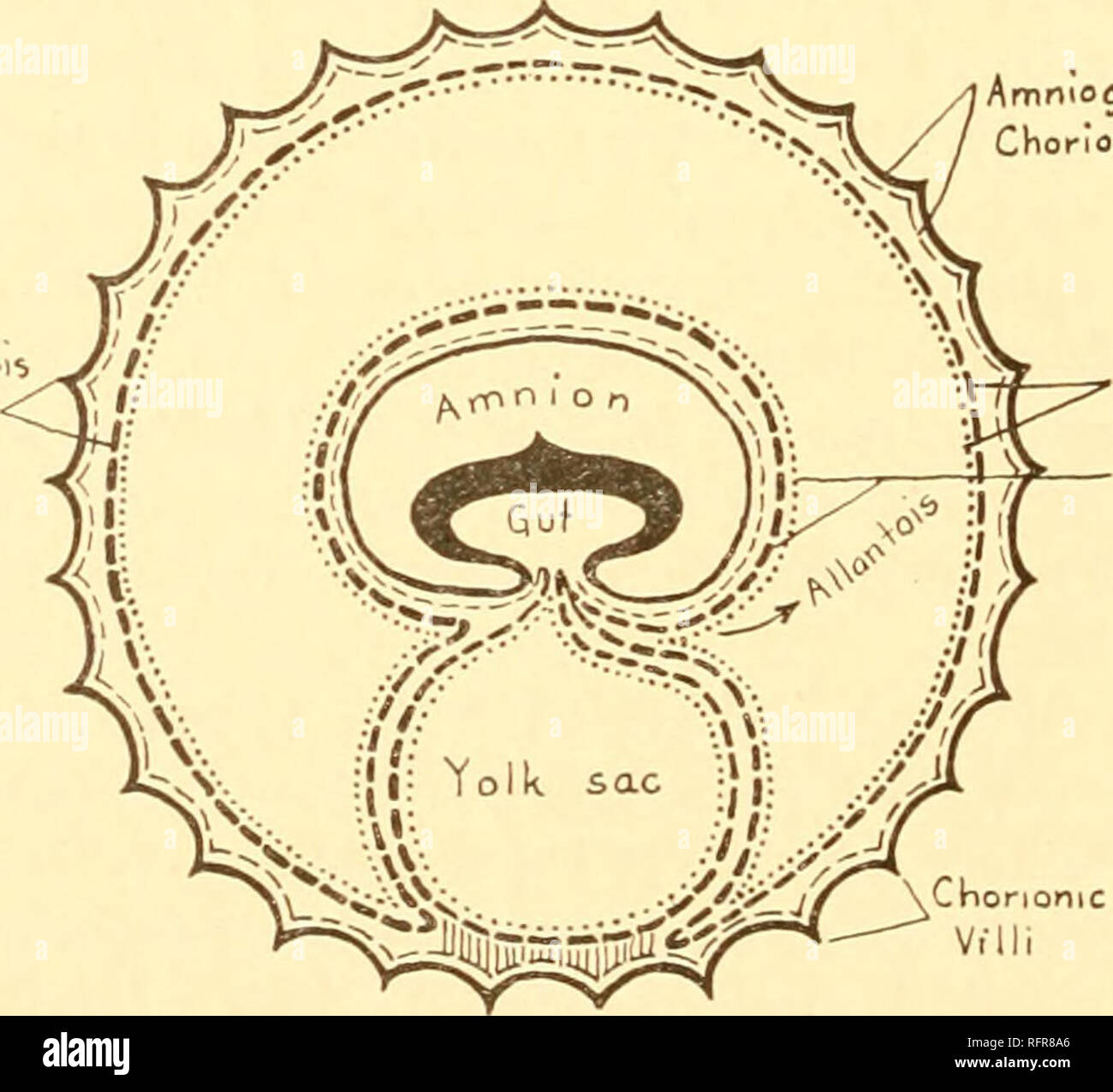 . Carnegie Institution of Washington publication. 52 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON FETAL ABSORPTION. comes in contact with the maternal tissue of the uterine wall. Goldmann showed that in the mouse this layer of cells plays an important role, similar to that of chorionic epithelium, in the transmission of nutritive material from mother to fetus. The endodermal cells have an enormous capacity for storing colloidal material. They, as well as the chorionic epithelium of the placenta, are responsible for the failure of foreign colloids, injected into the maternal blood-stream, to enter the fetus (figs. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/carnegie-institution-of-washington-publication-52-experimental-studies-on-fetal-absorption-comes-in-contact-with-the-maternal-tissue-of-the-uterine-wall-goldmann-showed-that-in-the-mouse-this-layer-of-cells-plays-an-important-role-similar-to-that-of-chorionic-epithelium-in-the-transmission-of-nutritive-material-from-mother-to-fetus-the-endodermal-cells-have-an-enormous-capacity-for-storing-colloidal-material-they-as-well-as-the-chorionic-epithelium-of-the-placenta-are-responsible-for-the-failure-of-foreign-colloids-injected-into-the-maternal-blood-stream-to-enter-the-fetus-figs-image233466078.html
. Carnegie Institution of Washington publication. 52 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON FETAL ABSORPTION. comes in contact with the maternal tissue of the uterine wall. Goldmann showed that in the mouse this layer of cells plays an important role, similar to that of chorionic epithelium, in the transmission of nutritive material from mother to fetus. The endodermal cells have an enormous capacity for storing colloidal material. They, as well as the chorionic epithelium of the placenta, are responsible for the failure of foreign colloids, injected into the maternal blood-stream, to enter the fetus (figs. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/carnegie-institution-of-washington-publication-52-experimental-studies-on-fetal-absorption-comes-in-contact-with-the-maternal-tissue-of-the-uterine-wall-goldmann-showed-that-in-the-mouse-this-layer-of-cells-plays-an-important-role-similar-to-that-of-chorionic-epithelium-in-the-transmission-of-nutritive-material-from-mother-to-fetus-the-endodermal-cells-have-an-enormous-capacity-for-storing-colloidal-material-they-as-well-as-the-chorionic-epithelium-of-the-placenta-are-responsible-for-the-failure-of-foreign-colloids-injected-into-the-maternal-blood-stream-to-enter-the-fetus-figs-image233466078.htmlRMRFR8A6–. Carnegie Institution of Washington publication. 52 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON FETAL ABSORPTION. comes in contact with the maternal tissue of the uterine wall. Goldmann showed that in the mouse this layer of cells plays an important role, similar to that of chorionic epithelium, in the transmission of nutritive material from mother to fetus. The endodermal cells have an enormous capacity for storing colloidal material. They, as well as the chorionic epithelium of the placenta, are responsible for the failure of foreign colloids, injected into the maternal blood-stream, to enter the fetus (figs.
 . The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Horses; Veterinary anatomy. TEE FCETUS. 1029 2. Pig.—The placenta is formed by an expansion of the villous tubercles, aa in Solipeds. The ciiorion is not entirely covereil by tliese tubercles, but here and there it shows briglit little patches, where its tissue is menly covered by an epitiitlial layer; it is also glabrous at those points where it is in contict with the chorion of neighbouring foetuses. The chorion lias not a body and two coruua, but is merely an elongated sac, the two extremities of whicli are in relation witli the adjacen Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-horses-veterinary-anatomy-tee-fcetus-1029-2-pigthe-placenta-is-formed-by-an-expansion-of-the-villous-tubercles-aa-in-solipeds-the-ciiorion-is-not-entirely-covereil-by-tliese-tubercles-but-here-and-there-it-shows-briglit-little-patches-where-its-tissue-is-menly-covered-by-an-epitiitlial-layer-it-is-also-glabrous-at-those-points-where-it-is-in-contict-with-the-chorion-of-neighbouring-foetuses-the-chorion-lias-not-a-body-and-two-coruua-but-is-merely-an-elongated-sac-the-two-extremities-of-whicli-are-in-relation-witli-the-adjacen-image232650686.html
. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Horses; Veterinary anatomy. TEE FCETUS. 1029 2. Pig.—The placenta is formed by an expansion of the villous tubercles, aa in Solipeds. The ciiorion is not entirely covereil by tliese tubercles, but here and there it shows briglit little patches, where its tissue is menly covered by an epitiitlial layer; it is also glabrous at those points where it is in contict with the chorion of neighbouring foetuses. The chorion lias not a body and two coruua, but is merely an elongated sac, the two extremities of whicli are in relation witli the adjacen Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-horses-veterinary-anatomy-tee-fcetus-1029-2-pigthe-placenta-is-formed-by-an-expansion-of-the-villous-tubercles-aa-in-solipeds-the-ciiorion-is-not-entirely-covereil-by-tliese-tubercles-but-here-and-there-it-shows-briglit-little-patches-where-its-tissue-is-menly-covered-by-an-epitiitlial-layer-it-is-also-glabrous-at-those-points-where-it-is-in-contict-with-the-chorion-of-neighbouring-foetuses-the-chorion-lias-not-a-body-and-two-coruua-but-is-merely-an-elongated-sac-the-two-extremities-of-whicli-are-in-relation-witli-the-adjacen-image232650686.htmlRMREE492–. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Horses; Veterinary anatomy. TEE FCETUS. 1029 2. Pig.—The placenta is formed by an expansion of the villous tubercles, aa in Solipeds. The ciiorion is not entirely covereil by tliese tubercles, but here and there it shows briglit little patches, where its tissue is menly covered by an epitiitlial layer; it is also glabrous at those points where it is in contict with the chorion of neighbouring foetuses. The chorion lias not a body and two coruua, but is merely an elongated sac, the two extremities of whicli are in relation witli the adjacen
 . Chemical embryology. Embryology. 30 10 gms. weight, embryos Fig. 371. The normal data are here represented by continuous lines; the phloridzin data by points not joined together. per cent, is by no means the maximum capacity of the embryonic liver, for by means of phloridzin the amount was raised to as much as 30-49 per cent, (wet weight). These experiments showed that phloridzin must pass the placenta, and make it highly probable that the physiological fatty infiltration is not derived from the tissue fat but some other source. Perhaps this other source is that postulated by Wesson in his e Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/chemical-embryology-embryology-30-10-gms-weight-embryos-fig-371-the-normal-data-are-here-represented-by-continuous-lines-the-phloridzin-data-by-points-not-joined-together-per-cent-is-by-no-means-the-maximum-capacity-of-the-embryonic-liver-for-by-means-of-phloridzin-the-amount-was-raised-to-as-much-as-30-49-per-cent-wet-weight-these-experiments-showed-that-phloridzin-must-pass-the-placenta-and-make-it-highly-probable-that-the-physiological-fatty-infiltration-is-not-derived-from-the-tissue-fat-but-some-other-source-perhaps-this-other-source-is-that-postulated-by-wesson-in-his-e-image234963287.html
. Chemical embryology. Embryology. 30 10 gms. weight, embryos Fig. 371. The normal data are here represented by continuous lines; the phloridzin data by points not joined together. per cent, is by no means the maximum capacity of the embryonic liver, for by means of phloridzin the amount was raised to as much as 30-49 per cent, (wet weight). These experiments showed that phloridzin must pass the placenta, and make it highly probable that the physiological fatty infiltration is not derived from the tissue fat but some other source. Perhaps this other source is that postulated by Wesson in his e Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/chemical-embryology-embryology-30-10-gms-weight-embryos-fig-371-the-normal-data-are-here-represented-by-continuous-lines-the-phloridzin-data-by-points-not-joined-together-per-cent-is-by-no-means-the-maximum-capacity-of-the-embryonic-liver-for-by-means-of-phloridzin-the-amount-was-raised-to-as-much-as-30-49-per-cent-wet-weight-these-experiments-showed-that-phloridzin-must-pass-the-placenta-and-make-it-highly-probable-that-the-physiological-fatty-infiltration-is-not-derived-from-the-tissue-fat-but-some-other-source-perhaps-this-other-source-is-that-postulated-by-wesson-in-his-e-image234963287.htmlRMRJ7E1Y–. Chemical embryology. Embryology. 30 10 gms. weight, embryos Fig. 371. The normal data are here represented by continuous lines; the phloridzin data by points not joined together. per cent, is by no means the maximum capacity of the embryonic liver, for by means of phloridzin the amount was raised to as much as 30-49 per cent, (wet weight). These experiments showed that phloridzin must pass the placenta, and make it highly probable that the physiological fatty infiltration is not derived from the tissue fat but some other source. Perhaps this other source is that postulated by Wesson in his e