Posterior parietal cortex Stock Photos and Images
(27)See posterior parietal cortex stock video clipsQuick filters:
Posterior parietal cortex Stock Photos and Images
 Areas of the brain of the right hemisphere: cortex (visual, parietal, sensory, motor, premotor) and auditory area. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-of-the-right-hemisphere-cortex-visual-parietal-sensory-motor-premotor-and-auditory-area-image476925406.html
Areas of the brain of the right hemisphere: cortex (visual, parietal, sensory, motor, premotor) and auditory area. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-of-the-right-hemisphere-cortex-visual-parietal-sensory-motor-premotor-and-auditory-area-image476925406.htmlRF2JKWR66–Areas of the brain of the right hemisphere: cortex (visual, parietal, sensory, motor, premotor) and auditory area.
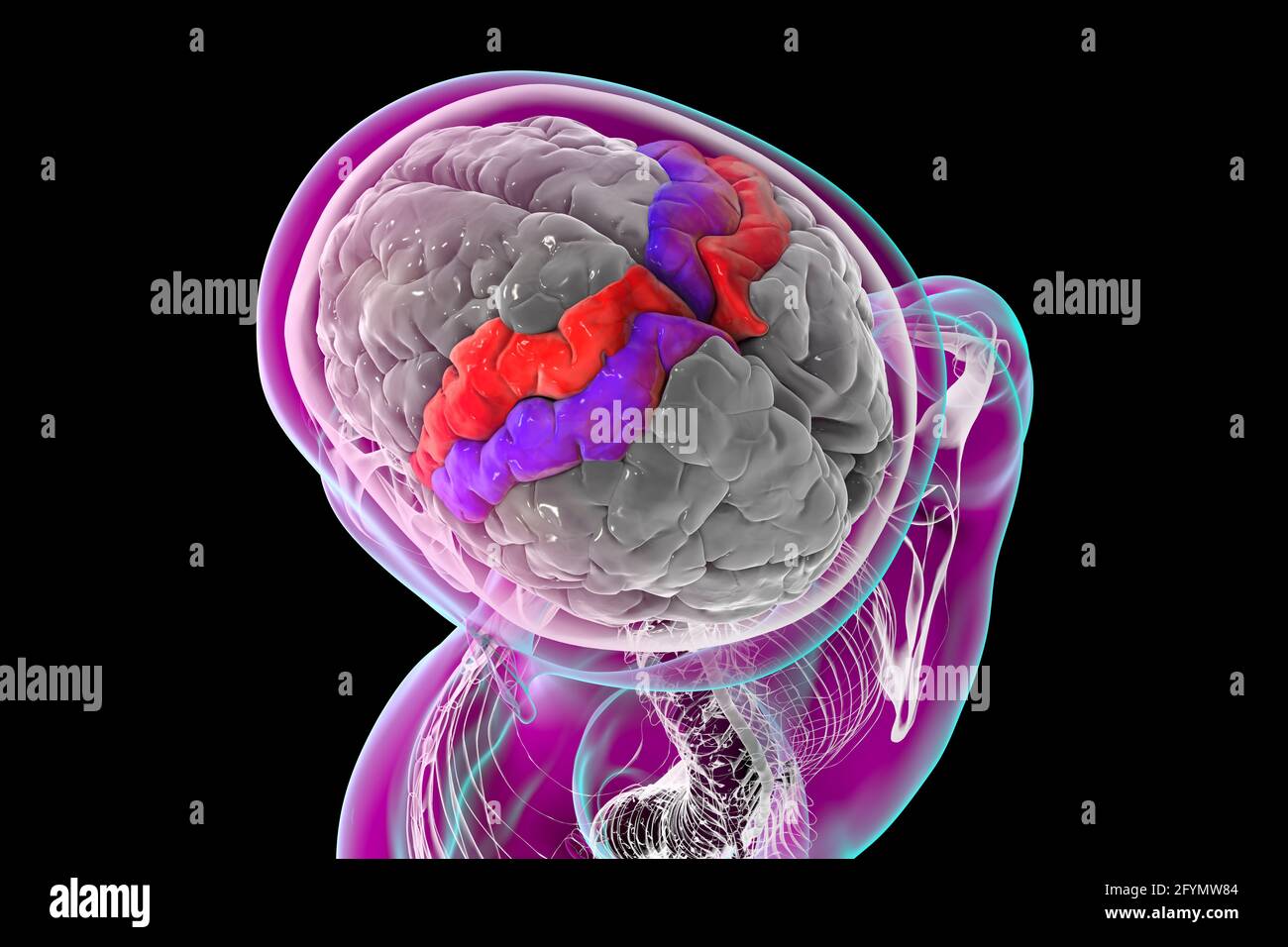 Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/precentral-and-postcentral-gyri-of-the-brain-illustration-image430103412.html
Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/precentral-and-postcentral-gyri-of-the-brain-illustration-image430103412.htmlRF2FYMW84–Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration
 The Journal of nervous and mental disease . radiating fibrespass out of the thalamus to become intermingled with thefibres of the internal capsule, and to be distributed to thecerebral cortex. Those from the front of the ganglion passto the frontal lobe; those from the middle are distributedto the posterior part of the frontal and to the parietal andtemporo-sphenoidal lobes ; those from the posterior partcan be traced to the temporo-sphenoidal and occipital lobes.From the region of the pulvinar, or posterior tubercle,fibres can be traced into the optic tract. 1 The Corpus Striatum, Journal of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-journal-of-nervous-and-mental-disease-radiating-fibrespass-out-of-the-thalamus-to-become-intermingled-with-thefibres-of-the-internal-capsule-and-to-be-distributed-to-thecerebral-cortex-those-from-the-front-of-the-ganglion-passto-the-frontal-lobe-those-from-the-middle-are-distributedto-the-posterior-part-of-the-frontal-and-to-the-parietal-andtemporo-sphenoidal-lobes-those-from-the-posterior-partcan-be-traced-to-the-temporo-sphenoidal-and-occipital-lobesfrom-the-region-of-the-pulvinar-or-posterior-tuberclefibres-can-be-traced-into-the-optic-tract-1-the-corpus-striatum-journal-of-image340073246.html
The Journal of nervous and mental disease . radiating fibrespass out of the thalamus to become intermingled with thefibres of the internal capsule, and to be distributed to thecerebral cortex. Those from the front of the ganglion passto the frontal lobe; those from the middle are distributedto the posterior part of the frontal and to the parietal andtemporo-sphenoidal lobes ; those from the posterior partcan be traced to the temporo-sphenoidal and occipital lobes.From the region of the pulvinar, or posterior tubercle,fibres can be traced into the optic tract. 1 The Corpus Striatum, Journal of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-journal-of-nervous-and-mental-disease-radiating-fibrespass-out-of-the-thalamus-to-become-intermingled-with-thefibres-of-the-internal-capsule-and-to-be-distributed-to-thecerebral-cortex-those-from-the-front-of-the-ganglion-passto-the-frontal-lobe-those-from-the-middle-are-distributedto-the-posterior-part-of-the-frontal-and-to-the-parietal-andtemporo-sphenoidal-lobes-those-from-the-posterior-partcan-be-traced-to-the-temporo-sphenoidal-and-occipital-lobesfrom-the-region-of-the-pulvinar-or-posterior-tuberclefibres-can-be-traced-into-the-optic-tract-1-the-corpus-striatum-journal-of-image340073246.htmlRM2AN7JW2–The Journal of nervous and mental disease . radiating fibrespass out of the thalamus to become intermingled with thefibres of the internal capsule, and to be distributed to thecerebral cortex. Those from the front of the ganglion passto the frontal lobe; those from the middle are distributedto the posterior part of the frontal and to the parietal andtemporo-sphenoidal lobes ; those from the posterior partcan be traced to the temporo-sphenoidal and occipital lobes.From the region of the pulvinar, or posterior tubercle,fibres can be traced into the optic tract. 1 The Corpus Striatum, Journal of
 Areas of the brain of the right hemisphere: cortex (visual, parietal, sensory, motor, premotor) and auditory area. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-of-the-right-hemisphere-cortex-visual-parietal-sensory-motor-premotor-and-auditory-area-image476925457.html
Areas of the brain of the right hemisphere: cortex (visual, parietal, sensory, motor, premotor) and auditory area. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-of-the-right-hemisphere-cortex-visual-parietal-sensory-motor-premotor-and-auditory-area-image476925457.htmlRF2JKWR81–Areas of the brain of the right hemisphere: cortex (visual, parietal, sensory, motor, premotor) and auditory area.
 Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/precentral-and-postcentral-gyri-of-the-brain-illustration-image430103405.html
Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/precentral-and-postcentral-gyri-of-the-brain-illustration-image430103405.htmlRF2FYMW7W–Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration
 Diseases of the nervous system .. . 61 research combined with the findings at autopsies, we know that the motorcerebral cortex is situated in the posterior and lower portion of the frontallobe, and in the anterior portion of the parietal Johe, especially in the anteriorand posterior ( ?) central com^olutions. Here also there are isolated fields forcertain motor regions. Thus, the center for the lower extremities is situated in the central con-volutions on both sides of the upper portion of the central furrow (Figs. Fig. 55.—Coxvkxity of the Brain from Above. (After Toldt.) 55-57); those for th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diseases-of-the-nervous-system-61-research-combined-with-the-findings-at-autopsies-we-know-that-the-motorcerebral-cortex-is-situated-in-the-posterior-and-lower-portion-of-the-frontallobe-and-in-the-anterior-portion-of-the-parietal-johe-especially-in-the-anteriorand-posterior-central-comolutions-here-also-there-are-isolated-fields-forcertain-motor-regions-thus-the-center-for-the-lower-extremities-is-situated-in-the-central-con-volutions-on-both-sides-of-the-upper-portion-of-the-central-furrow-figs-fig-55coxvkxity-of-the-brain-from-above-after-toldt-55-57-those-for-th-image342720332.html
Diseases of the nervous system .. . 61 research combined with the findings at autopsies, we know that the motorcerebral cortex is situated in the posterior and lower portion of the frontallobe, and in the anterior portion of the parietal Johe, especially in the anteriorand posterior ( ?) central com^olutions. Here also there are isolated fields forcertain motor regions. Thus, the center for the lower extremities is situated in the central con-volutions on both sides of the upper portion of the central furrow (Figs. Fig. 55.—Coxvkxity of the Brain from Above. (After Toldt.) 55-57); those for th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diseases-of-the-nervous-system-61-research-combined-with-the-findings-at-autopsies-we-know-that-the-motorcerebral-cortex-is-situated-in-the-posterior-and-lower-portion-of-the-frontallobe-and-in-the-anterior-portion-of-the-parietal-johe-especially-in-the-anteriorand-posterior-central-comolutions-here-also-there-are-isolated-fields-forcertain-motor-regions-thus-the-center-for-the-lower-extremities-is-situated-in-the-central-con-volutions-on-both-sides-of-the-upper-portion-of-the-central-furrow-figs-fig-55coxvkxity-of-the-brain-from-above-after-toldt-55-57-those-for-th-image342720332.htmlRM2AWG77T–Diseases of the nervous system .. . 61 research combined with the findings at autopsies, we know that the motorcerebral cortex is situated in the posterior and lower portion of the frontallobe, and in the anterior portion of the parietal Johe, especially in the anteriorand posterior ( ?) central com^olutions. Here also there are isolated fields forcertain motor regions. Thus, the center for the lower extremities is situated in the central con-volutions on both sides of the upper portion of the central furrow (Figs. Fig. 55.—Coxvkxity of the Brain from Above. (After Toldt.) 55-57); those for th
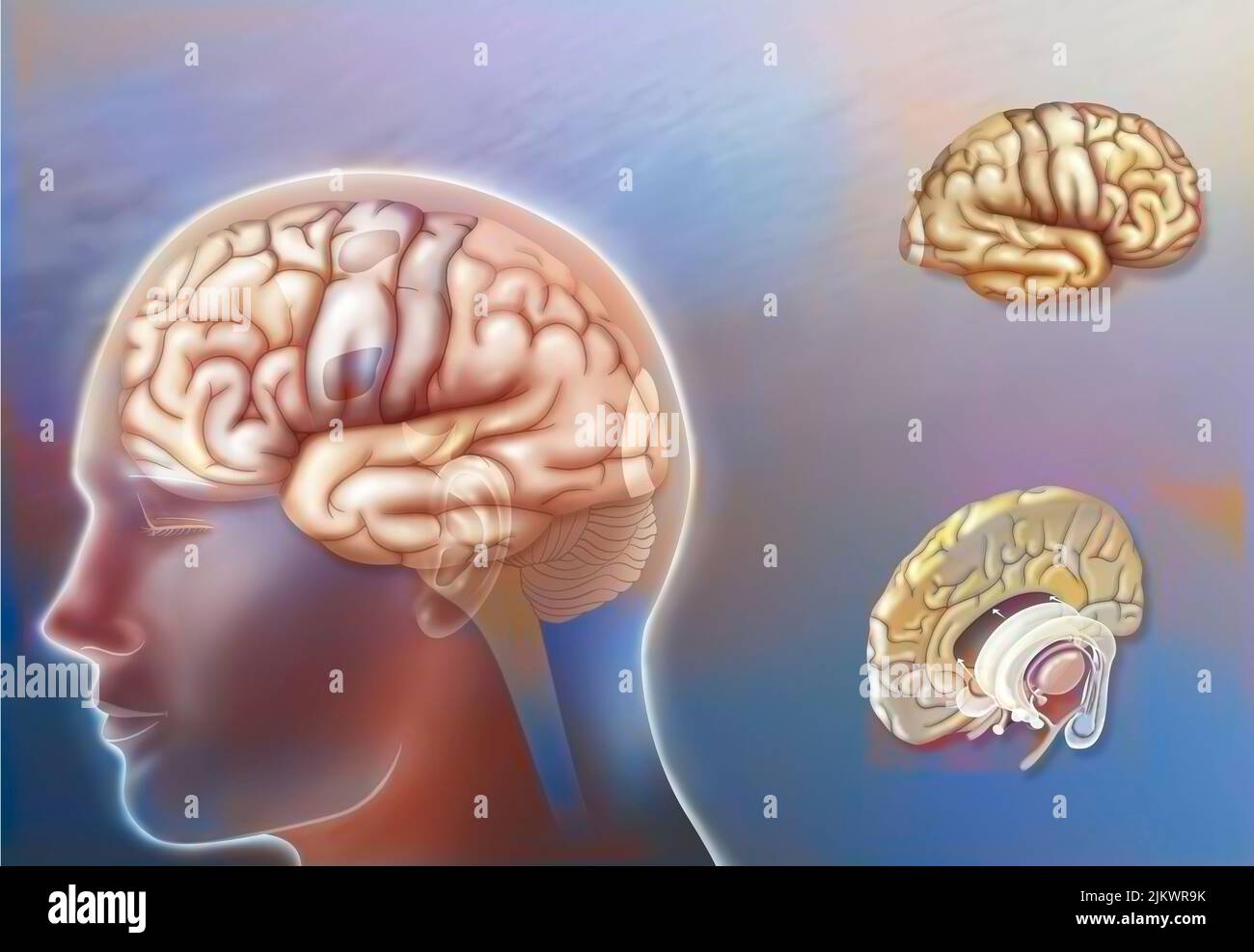 Left and right hemisphere brain areas and midline structures. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/left-and-right-hemisphere-brain-areas-and-midline-structures-image476925503.html
Left and right hemisphere brain areas and midline structures. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/left-and-right-hemisphere-brain-areas-and-midline-structures-image476925503.htmlRF2JKWR9K–Left and right hemisphere brain areas and midline structures.
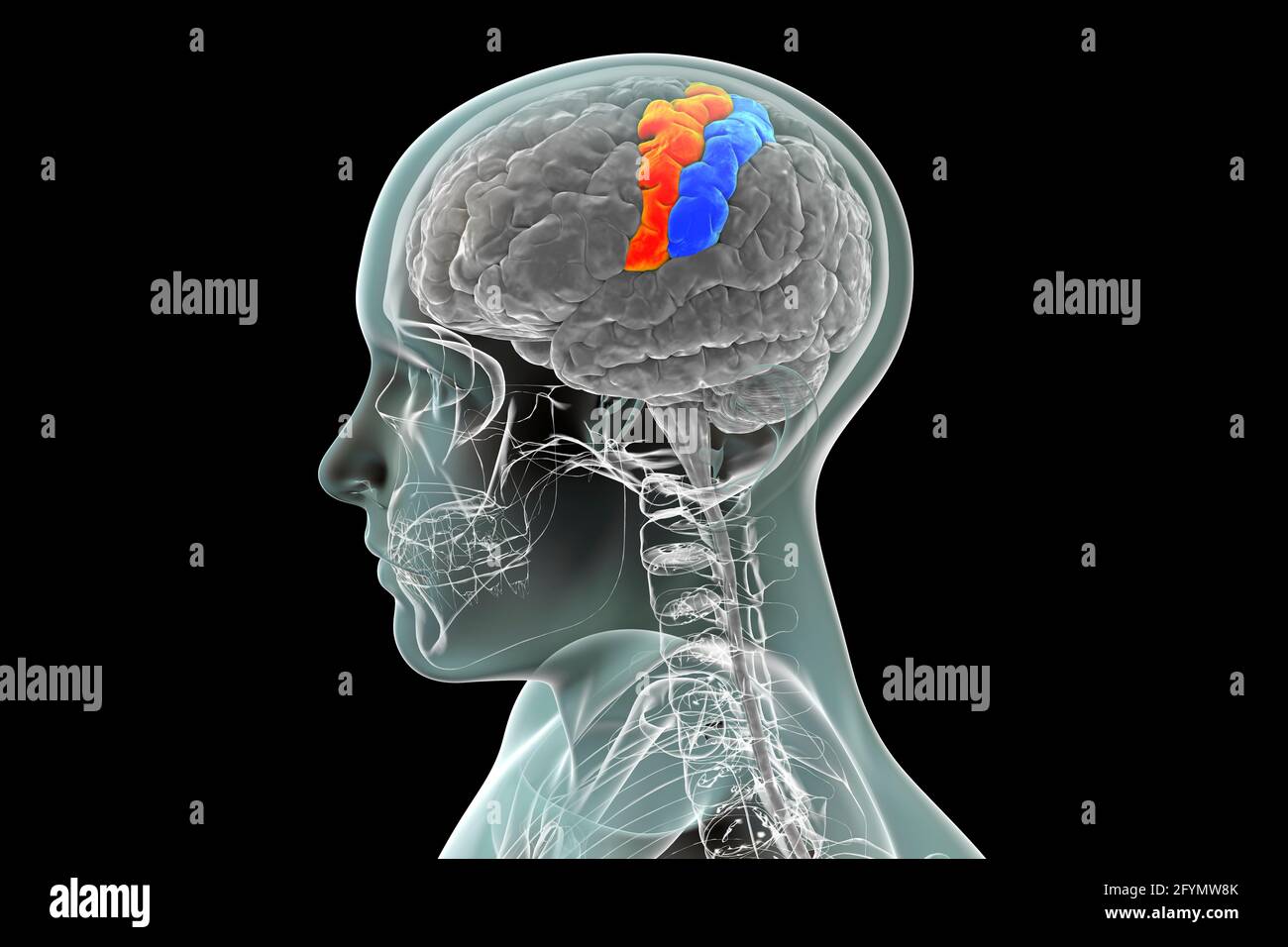 Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/precentral-and-postcentral-gyri-of-the-brain-illustration-image430103427.html
Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/precentral-and-postcentral-gyri-of-the-brain-illustration-image430103427.htmlRF2FYMW8K–Precentral and postcentral gyri of the brain, illustration
 Organic and functional nervous diseases; a text-book of neurology . Fia OTa The Vascular Supply of the Cerebral Cortex. (Dejerine.)The regions supplied by different arterial branches are shown in different colors The median surface.—Branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Fia. Anterior frontal. Fim.Middle frontal. Ftp. Posterior frontal. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery. OTa. Temporo-occipital anterior. OTm. Temporo-occipital median. K. Calcarine. The lateral surface.—Branches of the middle.cerebral artery. Fi. Inferior frontal. Fa. Ascend-inK frontal. Pa. Ai^cending parietal. Pi. I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/organic-and-functional-nervous-diseases-a-text-book-of-neurology-fia-ota-the-vascular-supply-of-the-cerebral-cortex-dejerinethe-regions-supplied-by-different-arterial-branches-are-shown-in-different-colors-the-median-surfacebranches-of-the-anterior-cerebral-artery-fia-anterior-frontal-fimmiddle-frontal-ftp-posterior-frontal-branches-of-the-posterior-cerebral-artery-ota-temporo-occipital-anterior-otm-temporo-occipital-median-k-calcarine-the-lateral-surfacebranches-of-the-middlecerebral-artery-fi-inferior-frontal-fa-ascend-ink-frontal-pa-aicending-parietal-pi-i-image339934212.html
Organic and functional nervous diseases; a text-book of neurology . Fia OTa The Vascular Supply of the Cerebral Cortex. (Dejerine.)The regions supplied by different arterial branches are shown in different colors The median surface.—Branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Fia. Anterior frontal. Fim.Middle frontal. Ftp. Posterior frontal. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery. OTa. Temporo-occipital anterior. OTm. Temporo-occipital median. K. Calcarine. The lateral surface.—Branches of the middle.cerebral artery. Fi. Inferior frontal. Fa. Ascend-inK frontal. Pa. Ai^cending parietal. Pi. I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/organic-and-functional-nervous-diseases-a-text-book-of-neurology-fia-ota-the-vascular-supply-of-the-cerebral-cortex-dejerinethe-regions-supplied-by-different-arterial-branches-are-shown-in-different-colors-the-median-surfacebranches-of-the-anterior-cerebral-artery-fia-anterior-frontal-fimmiddle-frontal-ftp-posterior-frontal-branches-of-the-posterior-cerebral-artery-ota-temporo-occipital-anterior-otm-temporo-occipital-median-k-calcarine-the-lateral-surfacebranches-of-the-middlecerebral-artery-fi-inferior-frontal-fa-ascend-ink-frontal-pa-aicending-parietal-pi-i-image339934212.htmlRM2AN19FG–Organic and functional nervous diseases; a text-book of neurology . Fia OTa The Vascular Supply of the Cerebral Cortex. (Dejerine.)The regions supplied by different arterial branches are shown in different colors The median surface.—Branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Fia. Anterior frontal. Fim.Middle frontal. Ftp. Posterior frontal. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery. OTa. Temporo-occipital anterior. OTm. Temporo-occipital median. K. Calcarine. The lateral surface.—Branches of the middle.cerebral artery. Fi. Inferior frontal. Fa. Ascend-inK frontal. Pa. Ai^cending parietal. Pi. I
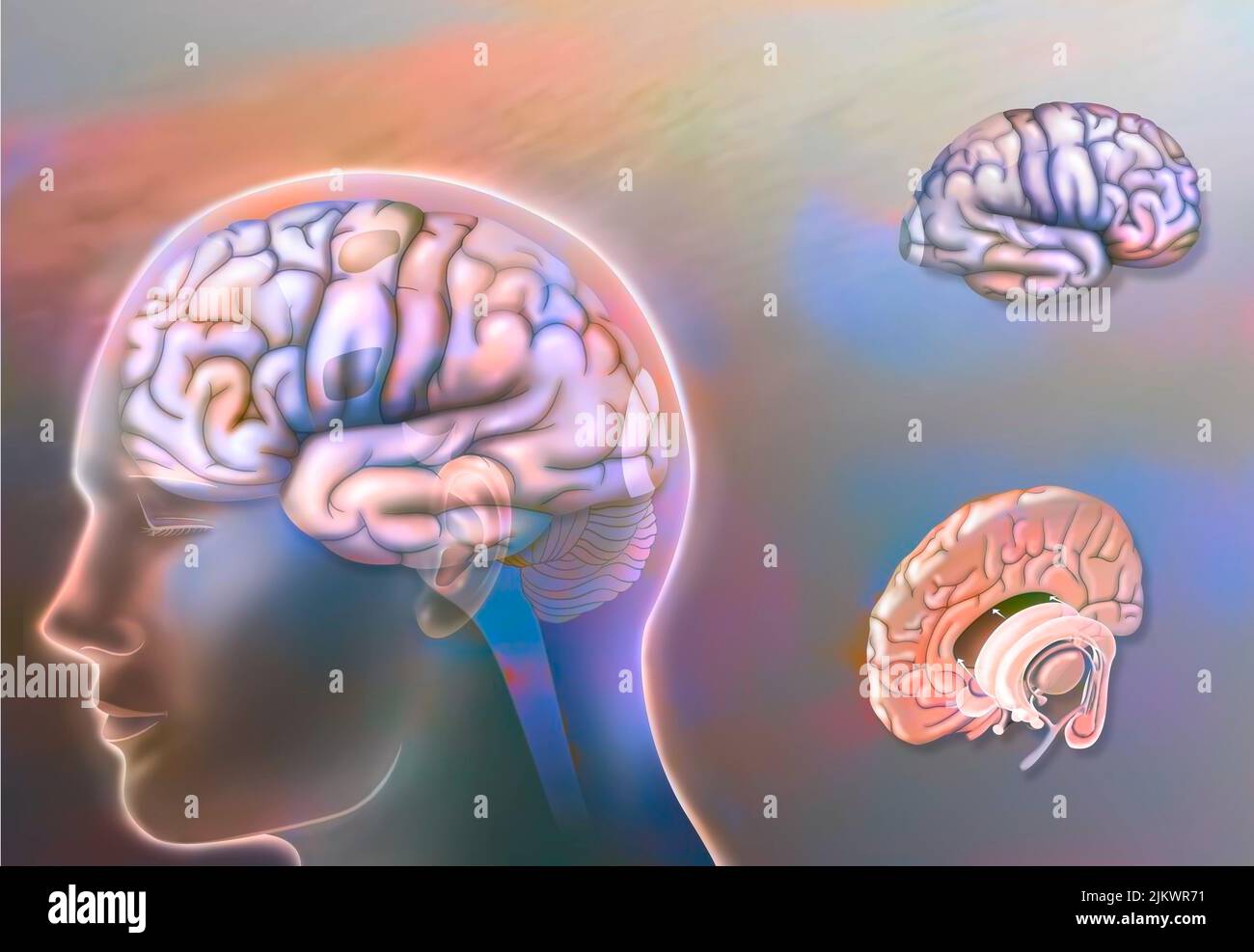 Left and right hemisphere brain areas and midline structures. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/left-and-right-hemisphere-brain-areas-and-midline-structures-image476925429.html
Left and right hemisphere brain areas and midline structures. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/left-and-right-hemisphere-brain-areas-and-midline-structures-image476925429.htmlRF2JKWR71–Left and right hemisphere brain areas and midline structures.
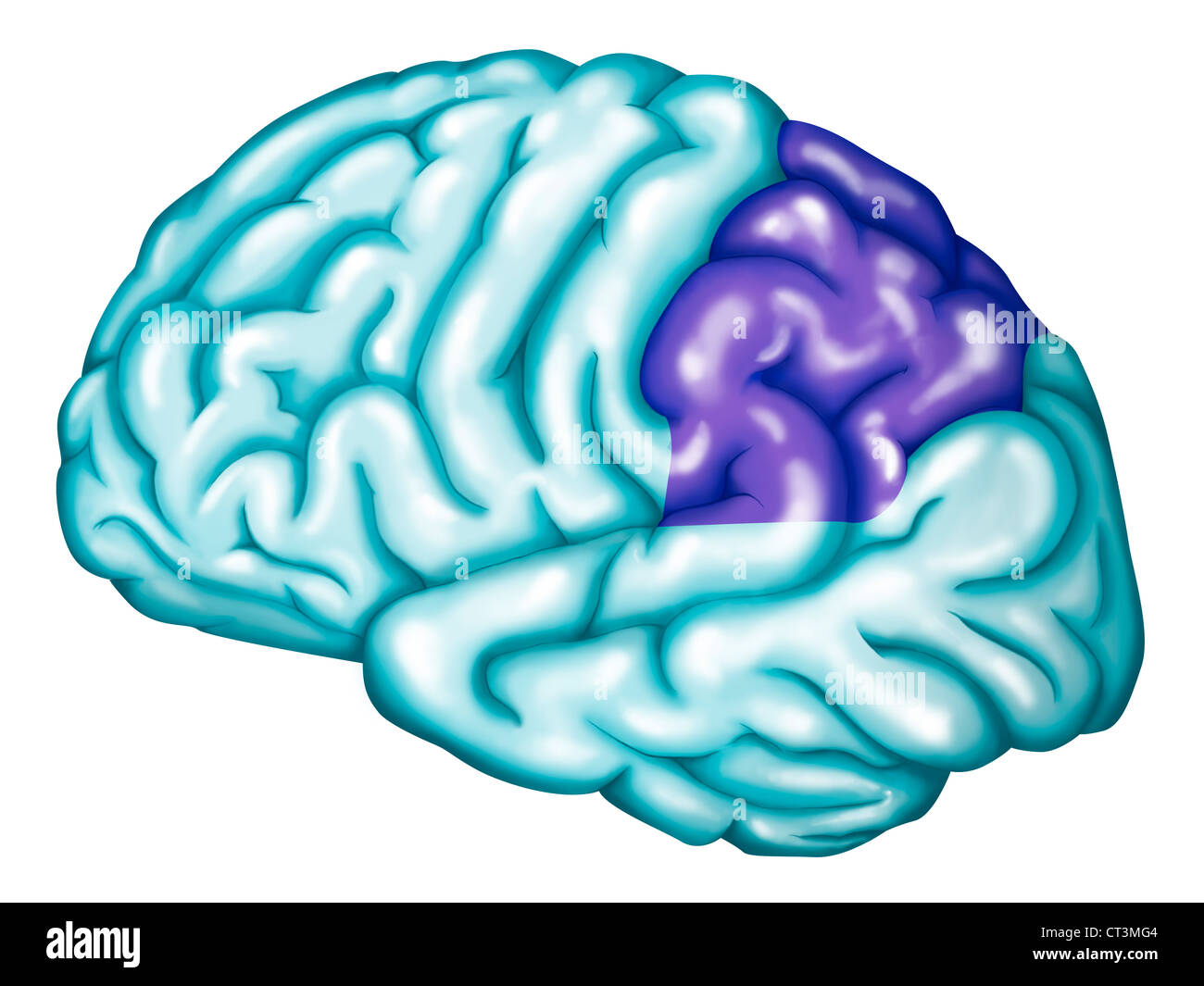 SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-somatosensory-cortex-49254468.html
SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-somatosensory-cortex-49254468.htmlRMCT3MG4–SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX
 Organic and functional nervous diseases; a text-book of neurology . Fia OTa The Vascular Supply of the Cerebral Cortex. (Dejerine.)The regions supplied by different arterial branches are shown in different colors The median surface.—Branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Fia. Anterior frontal. Fim.Middle frontal. Ftp. Posterior frontal. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery. OTa. Temporo-occipital anterior. OTm. Temporo-occipital median. K. Calcarine. The lateral surface.—Branches of the middle.cerebral artery. Fi. Inferior frontal. Fa. Ascend-inK frontal. Pa. Ai^cending parietal. Pi. I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/organic-and-functional-nervous-diseases-a-text-book-of-neurology-fia-ota-the-vascular-supply-of-the-cerebral-cortex-dejerinethe-regions-supplied-by-different-arterial-branches-are-shown-in-different-colors-the-median-surfacebranches-of-the-anterior-cerebral-artery-fia-anterior-frontal-fimmiddle-frontal-ftp-posterior-frontal-branches-of-the-posterior-cerebral-artery-ota-temporo-occipital-anterior-otm-temporo-occipital-median-k-calcarine-the-lateral-surfacebranches-of-the-middlecerebral-artery-fi-inferior-frontal-fa-ascend-ink-frontal-pa-aicending-parietal-pi-i-image339933862.html
Organic and functional nervous diseases; a text-book of neurology . Fia OTa The Vascular Supply of the Cerebral Cortex. (Dejerine.)The regions supplied by different arterial branches are shown in different colors The median surface.—Branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Fia. Anterior frontal. Fim.Middle frontal. Ftp. Posterior frontal. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery. OTa. Temporo-occipital anterior. OTm. Temporo-occipital median. K. Calcarine. The lateral surface.—Branches of the middle.cerebral artery. Fi. Inferior frontal. Fa. Ascend-inK frontal. Pa. Ai^cending parietal. Pi. I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/organic-and-functional-nervous-diseases-a-text-book-of-neurology-fia-ota-the-vascular-supply-of-the-cerebral-cortex-dejerinethe-regions-supplied-by-different-arterial-branches-are-shown-in-different-colors-the-median-surfacebranches-of-the-anterior-cerebral-artery-fia-anterior-frontal-fimmiddle-frontal-ftp-posterior-frontal-branches-of-the-posterior-cerebral-artery-ota-temporo-occipital-anterior-otm-temporo-occipital-median-k-calcarine-the-lateral-surfacebranches-of-the-middlecerebral-artery-fi-inferior-frontal-fa-ascend-ink-frontal-pa-aicending-parietal-pi-i-image339933862.htmlRM2AN1932–Organic and functional nervous diseases; a text-book of neurology . Fia OTa The Vascular Supply of the Cerebral Cortex. (Dejerine.)The regions supplied by different arterial branches are shown in different colors The median surface.—Branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Fia. Anterior frontal. Fim.Middle frontal. Ftp. Posterior frontal. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery. OTa. Temporo-occipital anterior. OTm. Temporo-occipital median. K. Calcarine. The lateral surface.—Branches of the middle.cerebral artery. Fi. Inferior frontal. Fa. Ascend-inK frontal. Pa. Ai^cending parietal. Pi. I
 SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-somatosensory-cortex-49254408.html
SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-somatosensory-cortex-49254408.htmlRMCT3ME0–SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX
 . Diseases of infancy and childhood . Top View of tlio Fcvtal Skull, showiuo- tho :nitiMior fontnnollo and thefrontal, coronal, and sagittal suturos. ((^randin A: .larinan.) PLATE XXXVI. Posterior View of the Fcptal Skull, showing the posterior fontanelle and thelauibdoidal and sagittal sutures. (Grandin & Jarnian.) REFLEXES. 737 due to an increase in tlie thickness of the cortex and in the size of thecortical constituents. Difference Beiwe&n Infantile and Adult Brain.—The fissure of Sylviusin its relation to the spherio-parietal and squamous sutures occupies ahigher position in childhood than Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diseases-of-infancy-and-childhood-top-view-of-tlio-fcvtal-skull-showiuo-tho-nitimior-fontnnollo-and-thefrontal-coronal-and-sagittal-suturos-randin-a-larinan-plate-xxxvi-posterior-view-of-the-fcptal-skull-showing-the-posterior-fontanelle-and-thelauibdoidal-and-sagittal-sutures-grandin-jarnian-reflexes-737-due-to-an-increase-in-tlie-thickness-of-the-cortex-and-in-the-size-of-thecortical-constituents-difference-beiwen-infantile-and-adult-brainthe-fissure-of-sylviusin-its-relation-to-the-spherio-parietal-and-squamous-sutures-occupies-ahigher-position-in-childhood-than-image370082261.html
. Diseases of infancy and childhood . Top View of tlio Fcvtal Skull, showiuo- tho :nitiMior fontnnollo and thefrontal, coronal, and sagittal suturos. ((^randin A: .larinan.) PLATE XXXVI. Posterior View of the Fcptal Skull, showing the posterior fontanelle and thelauibdoidal and sagittal sutures. (Grandin & Jarnian.) REFLEXES. 737 due to an increase in tlie thickness of the cortex and in the size of thecortical constituents. Difference Beiwe&n Infantile and Adult Brain.—The fissure of Sylviusin its relation to the spherio-parietal and squamous sutures occupies ahigher position in childhood than Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diseases-of-infancy-and-childhood-top-view-of-tlio-fcvtal-skull-showiuo-tho-nitimior-fontnnollo-and-thefrontal-coronal-and-sagittal-suturos-randin-a-larinan-plate-xxxvi-posterior-view-of-the-fcptal-skull-showing-the-posterior-fontanelle-and-thelauibdoidal-and-sagittal-sutures-grandin-jarnian-reflexes-737-due-to-an-increase-in-tlie-thickness-of-the-cortex-and-in-the-size-of-thecortical-constituents-difference-beiwen-infantile-and-adult-brainthe-fissure-of-sylviusin-its-relation-to-the-spherio-parietal-and-squamous-sutures-occupies-ahigher-position-in-childhood-than-image370082261.htmlRM2CE2KKH–. Diseases of infancy and childhood . Top View of tlio Fcvtal Skull, showiuo- tho :nitiMior fontnnollo and thefrontal, coronal, and sagittal suturos. ((^randin A: .larinan.) PLATE XXXVI. Posterior View of the Fcptal Skull, showing the posterior fontanelle and thelauibdoidal and sagittal sutures. (Grandin & Jarnian.) REFLEXES. 737 due to an increase in tlie thickness of the cortex and in the size of thecortical constituents. Difference Beiwe&n Infantile and Adult Brain.—The fissure of Sylviusin its relation to the spherio-parietal and squamous sutures occupies ahigher position in childhood than
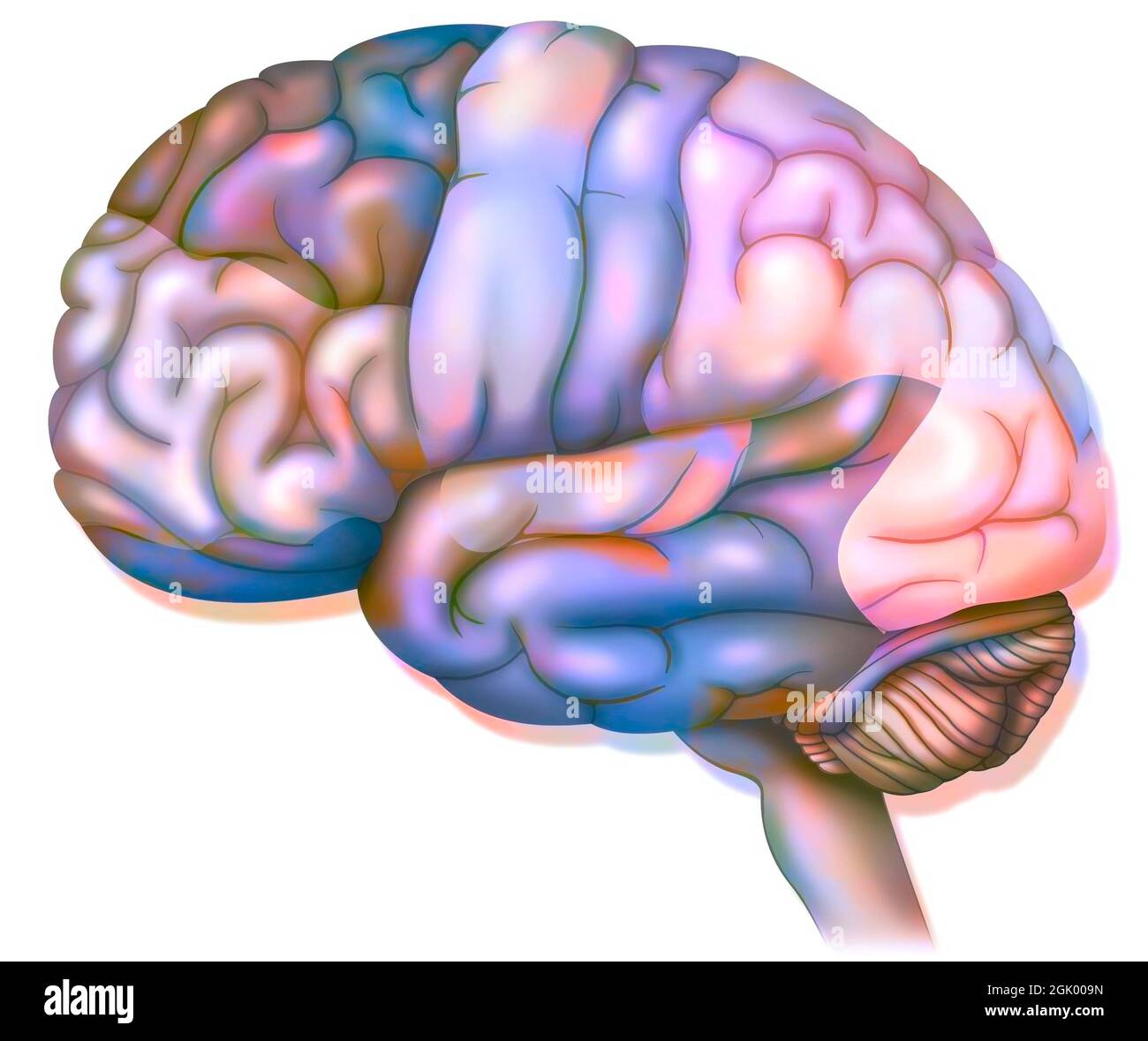 Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image441937937.html
Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image441937937.htmlRF2GK009N–Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. .
 Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image442065688.html
Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image442065688.htmlRF2GK5R88–Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. .
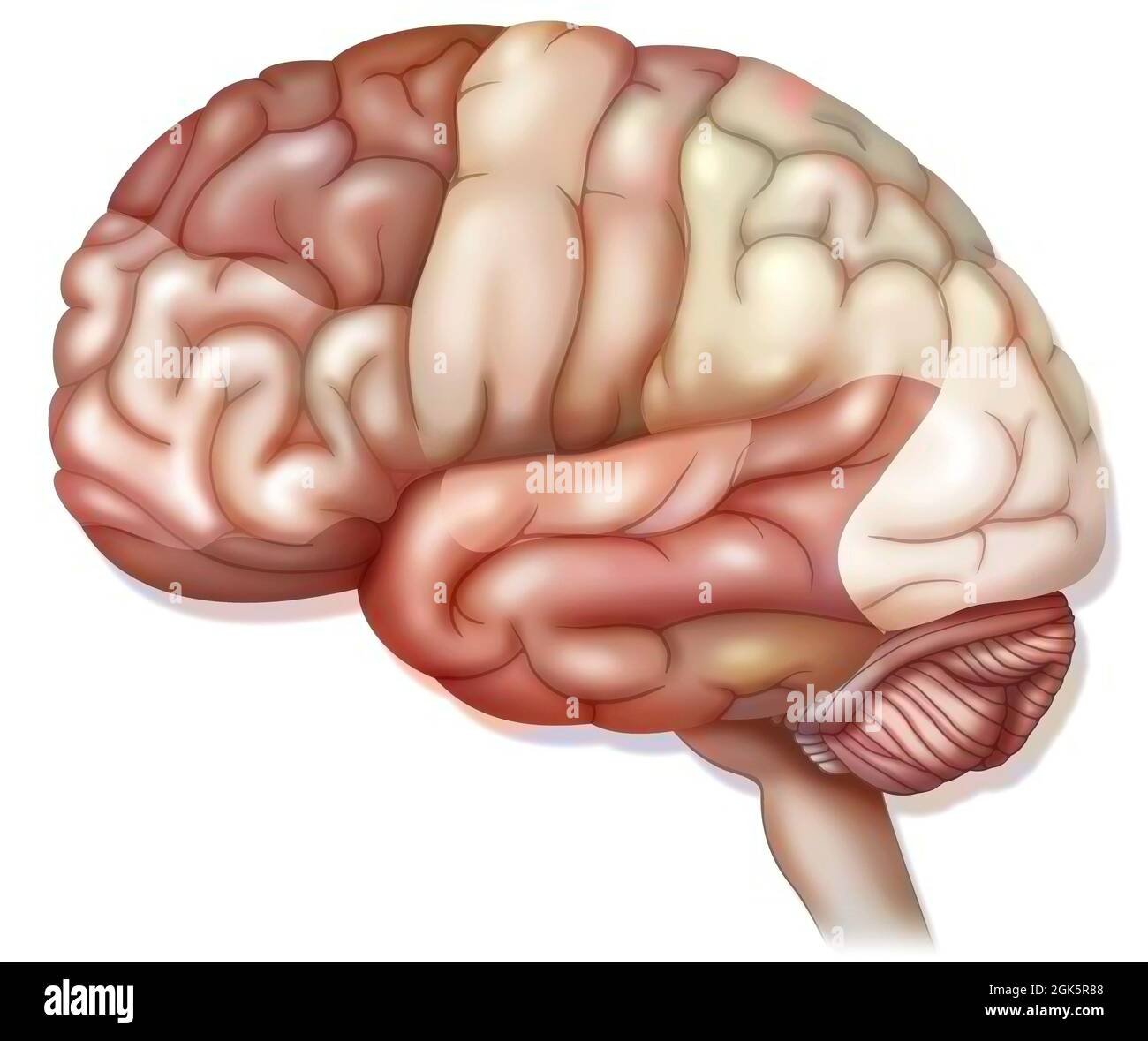
 Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image441937975.html
Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image441937975.htmlRF2GK00B3–Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. .
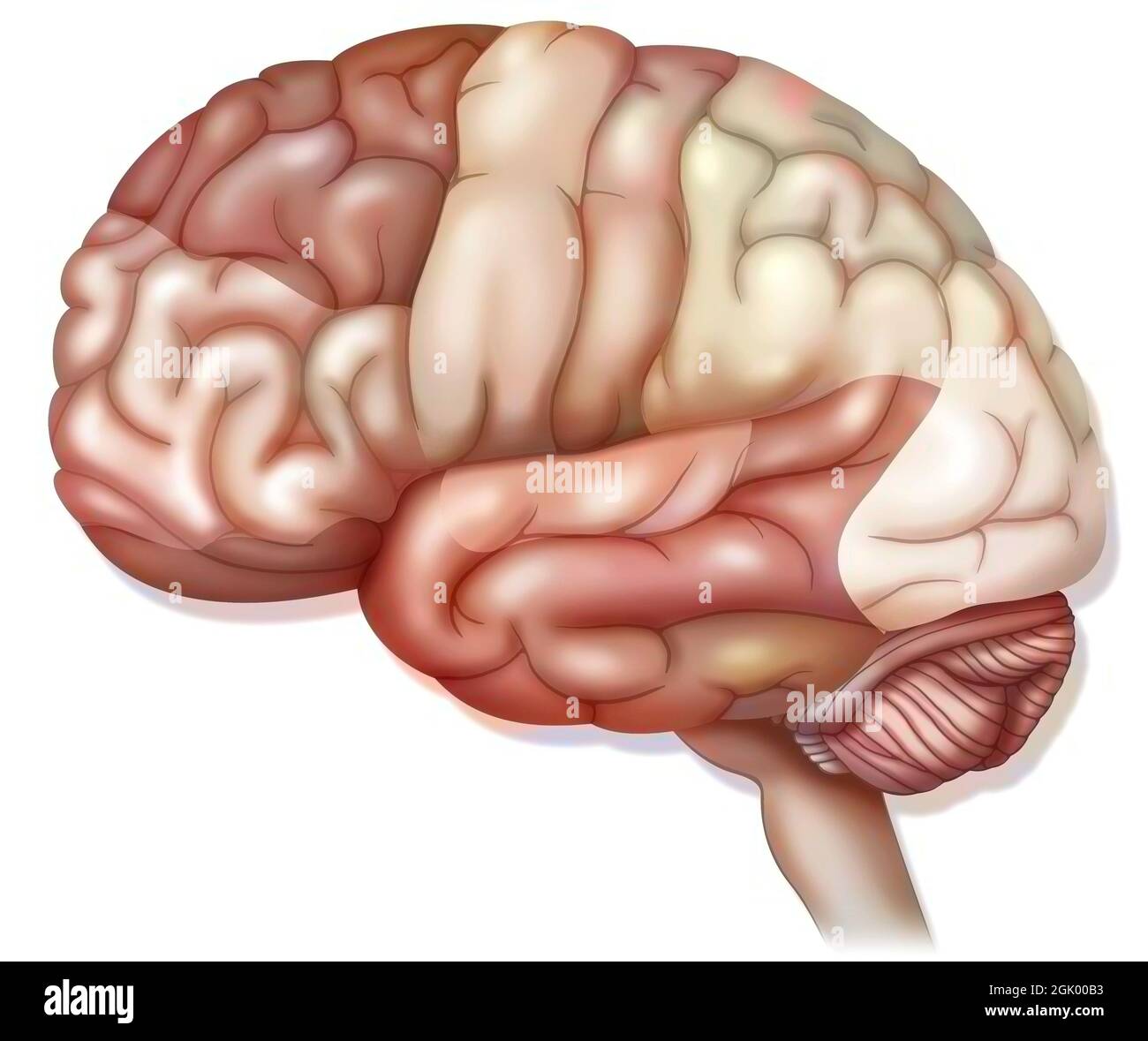
 Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image442065683.html
Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. . Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/areas-of-the-brain-prefrontal-cortex-premotor-cortex-and-oculomotor-cortex-image442065683.htmlRF2GK5R83–Areas of the brain: prefrontal cortex, premotor cortex and oculomotor cortex. .
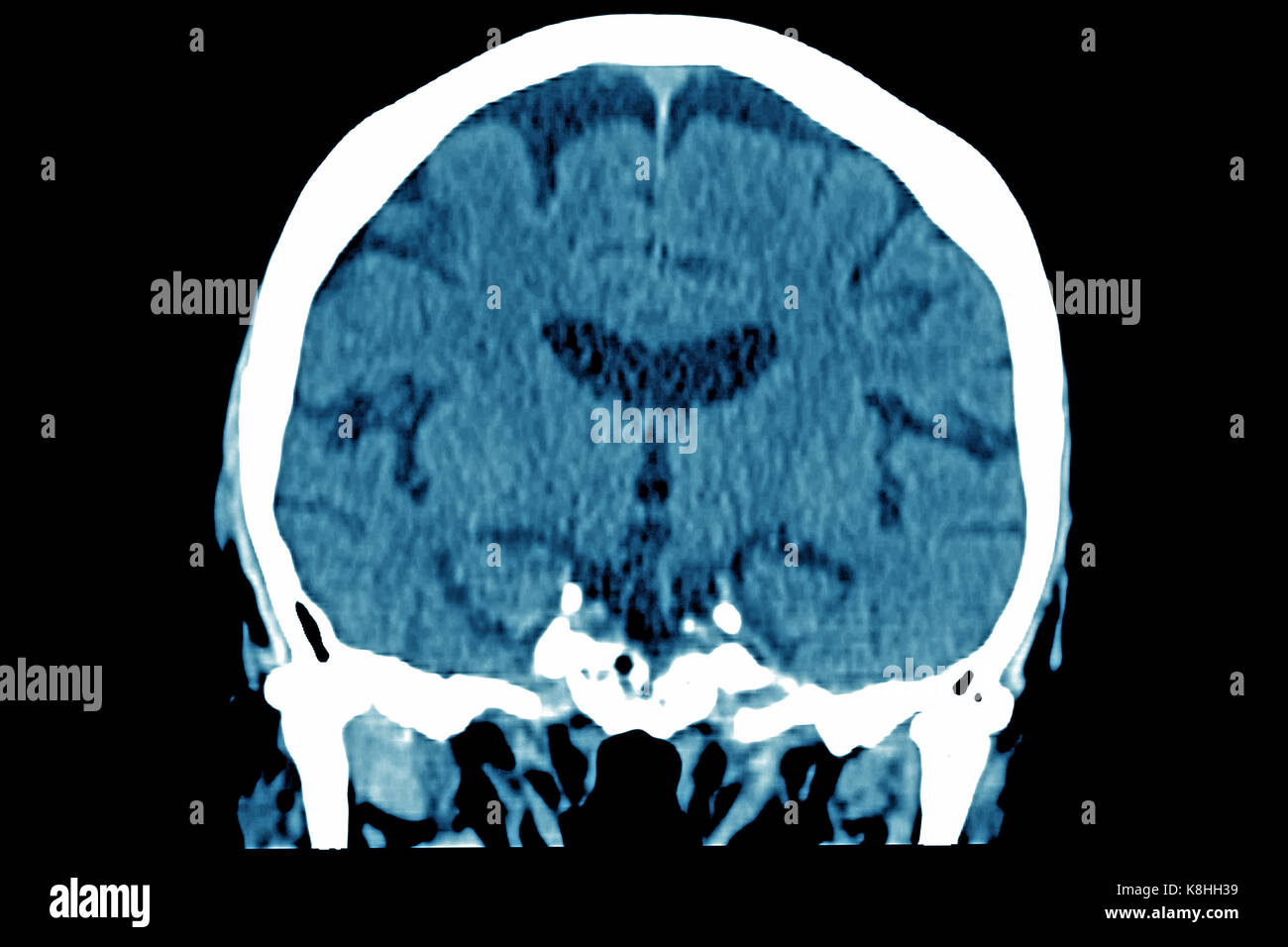
 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197172.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197172.htmlRMK8HH3G–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN
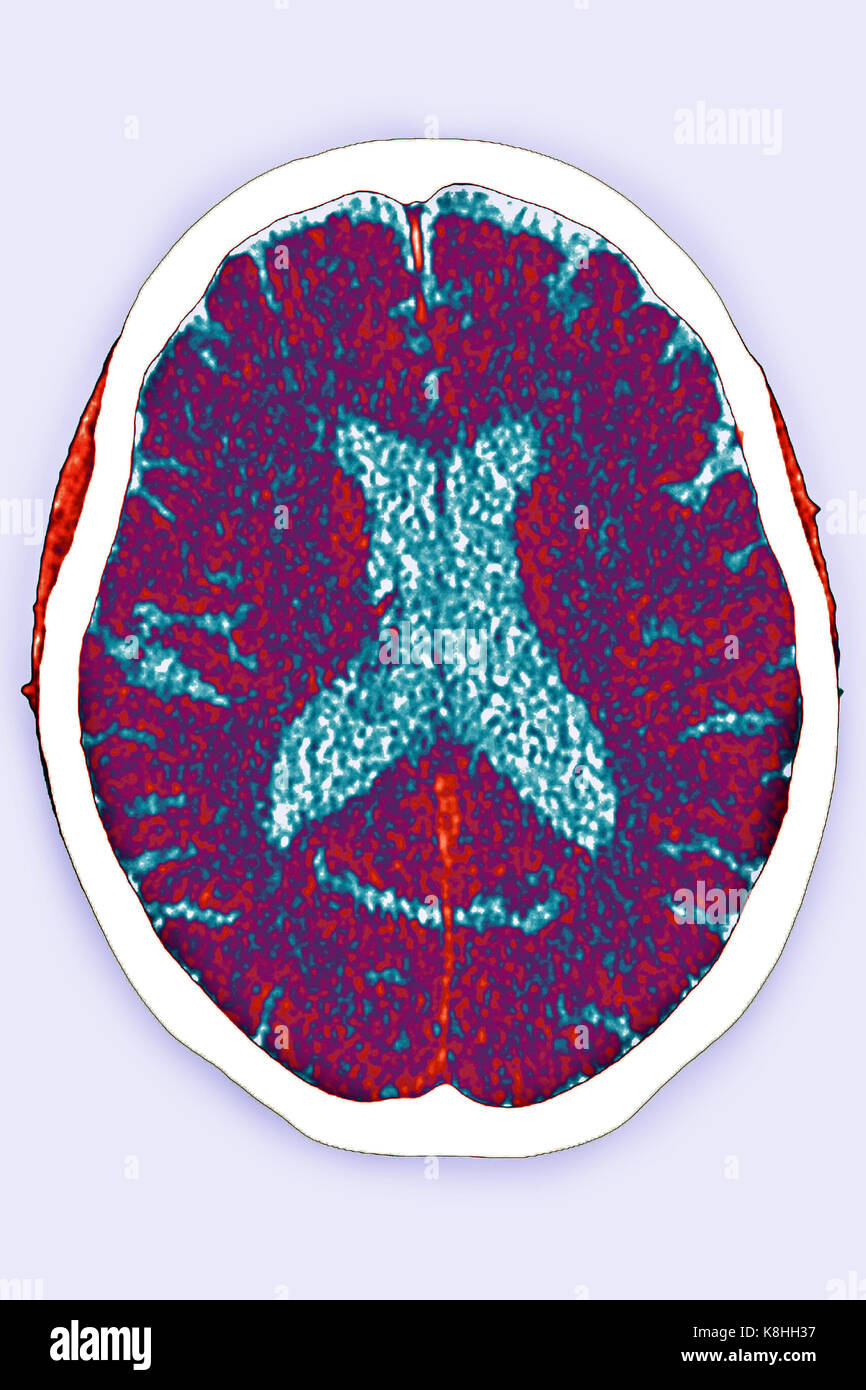 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197163.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197163.htmlRMK8HH37–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN
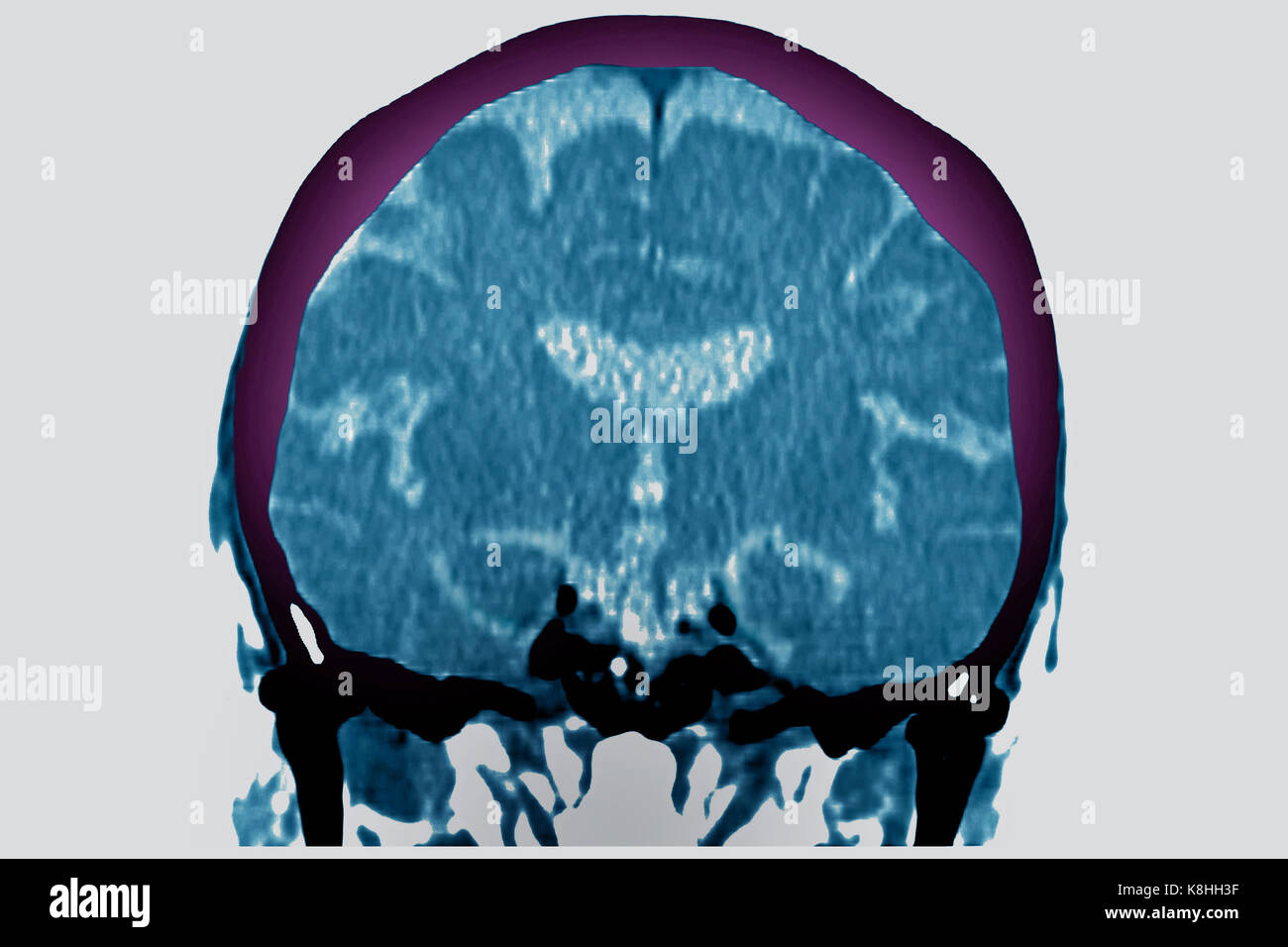 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197171.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197171.htmlRMK8HH3F–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN
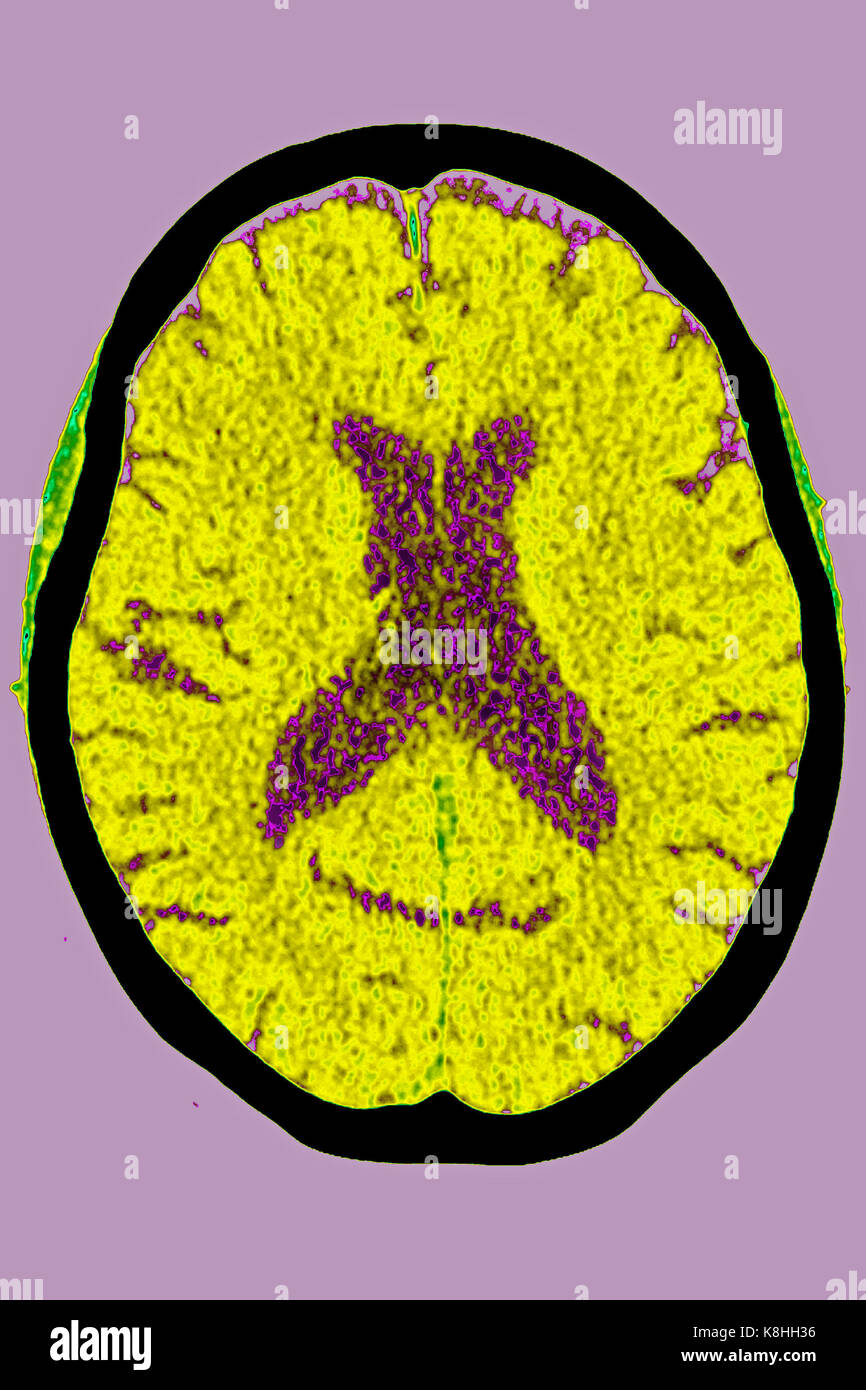 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197162.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197162.htmlRMK8HH36–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN
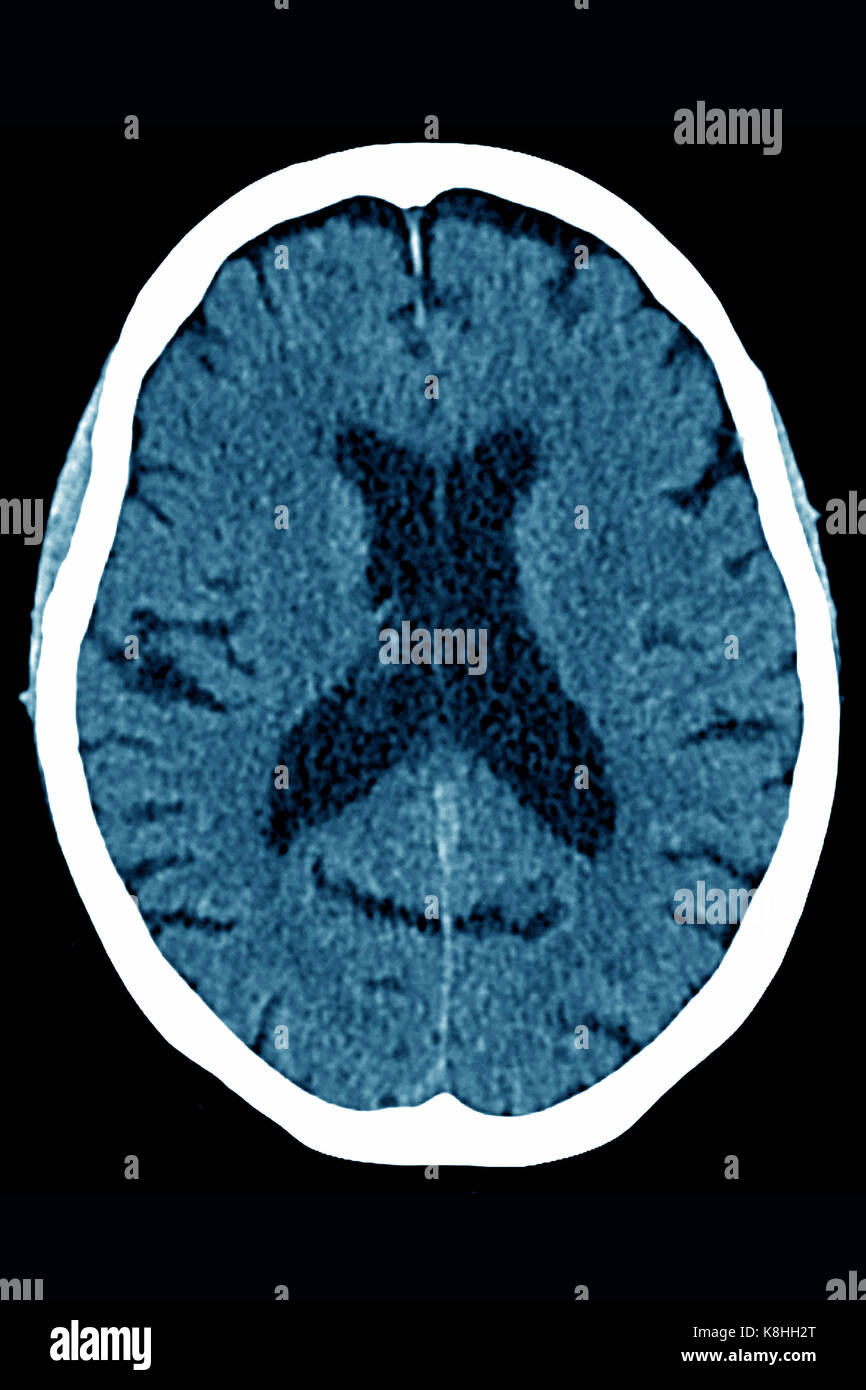 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197152.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197152.htmlRMK8HH2T–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN
 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197175.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197175.htmlRMK8HH3K–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN
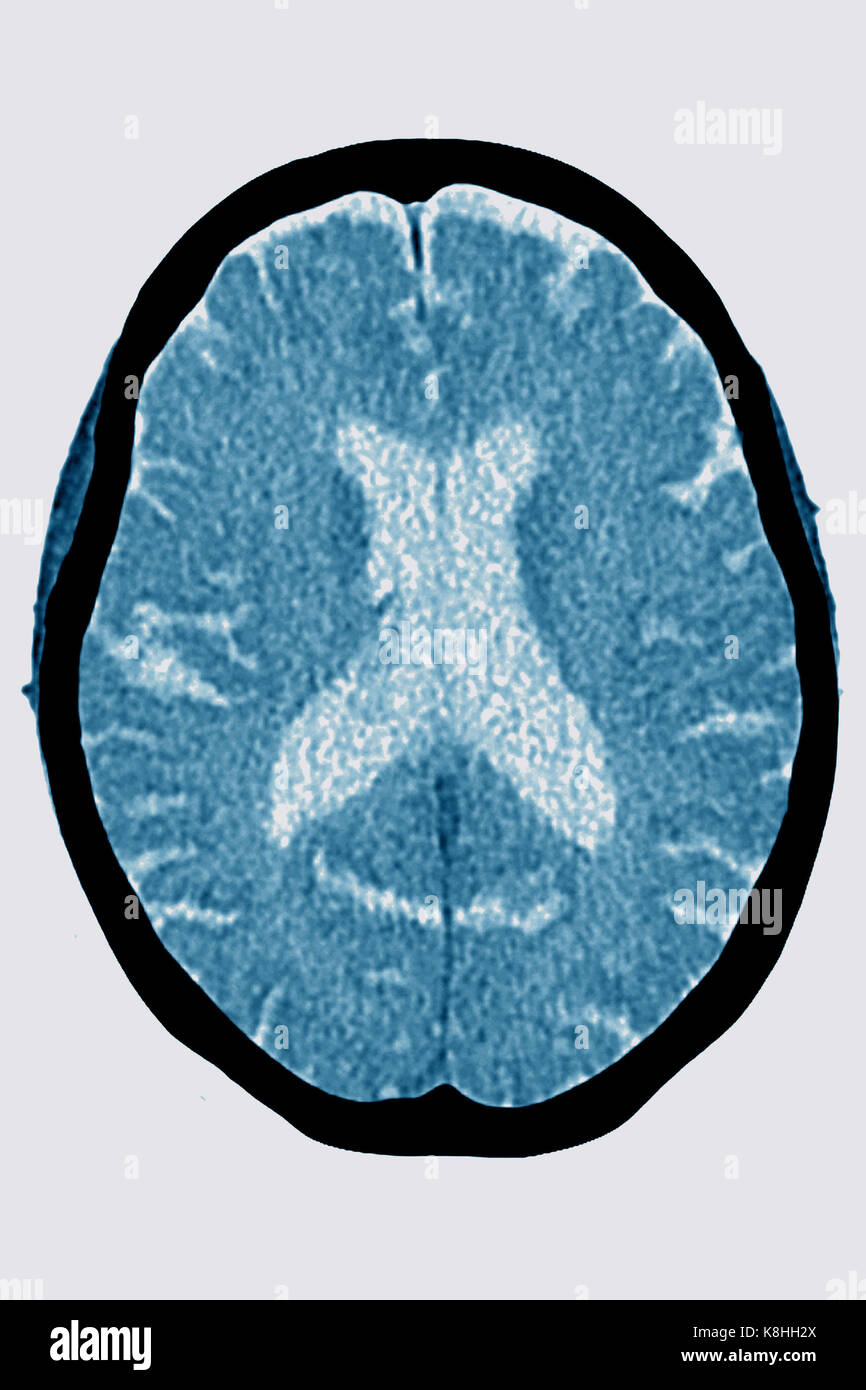 CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197154.html
CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-cerebral-atrophy-ct-scan-160197154.htmlRMK8HH2X–CEREBRAL ATROPHY, CT SCAN