Quick filters:
Right common iliac Stock Photos and Images
 . Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. The abdominal aorta divides (bifurcates) at the lower border ofthe fourth lumbar vertebra into the right common iliac and the leftcommon iliac (Fig. 128). The two common iliac arteries diverge and v^^hen they reachthe sides (right and left) of the lumbo-sacral joint, each divides intohypogastric (or internal iliac) and external iliac (see Fig. 128). BRANCHES OF HYPOGASTRIC ARTERY. 179 The hypogastric artery passes into the pelvis and gives offbranches which supply the parts within and without the pelvicwall, including the perineum, and all of t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-the-abdominal-aorta-divides-bifurcates-at-the-lower-border-ofthe-fourth-lumbar-vertebra-into-the-right-common-iliac-and-the-leftcommon-iliac-fig-128-the-two-common-iliac-arteries-diverge-and-vhen-they-reachthe-sides-right-and-left-of-the-lumbo-sacral-joint-each-divides-intohypogastric-or-internal-iliac-and-external-iliac-see-fig-128-branches-of-hypogastric-artery-179-the-hypogastric-artery-passes-into-the-pelvis-and-gives-offbranches-which-supply-the-parts-within-and-without-the-pelvicwall-including-the-perineum-and-all-of-t-image370334981.html
. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. The abdominal aorta divides (bifurcates) at the lower border ofthe fourth lumbar vertebra into the right common iliac and the leftcommon iliac (Fig. 128). The two common iliac arteries diverge and v^^hen they reachthe sides (right and left) of the lumbo-sacral joint, each divides intohypogastric (or internal iliac) and external iliac (see Fig. 128). BRANCHES OF HYPOGASTRIC ARTERY. 179 The hypogastric artery passes into the pelvis and gives offbranches which supply the parts within and without the pelvicwall, including the perineum, and all of t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-the-abdominal-aorta-divides-bifurcates-at-the-lower-border-ofthe-fourth-lumbar-vertebra-into-the-right-common-iliac-and-the-leftcommon-iliac-fig-128-the-two-common-iliac-arteries-diverge-and-vhen-they-reachthe-sides-right-and-left-of-the-lumbo-sacral-joint-each-divides-intohypogastric-or-internal-iliac-and-external-iliac-see-fig-128-branches-of-hypogastric-artery-179-the-hypogastric-artery-passes-into-the-pelvis-and-gives-offbranches-which-supply-the-parts-within-and-without-the-pelvicwall-including-the-perineum-and-all-of-t-image370334981.htmlRM2CEE619–. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. The abdominal aorta divides (bifurcates) at the lower border ofthe fourth lumbar vertebra into the right common iliac and the leftcommon iliac (Fig. 128). The two common iliac arteries diverge and v^^hen they reachthe sides (right and left) of the lumbo-sacral joint, each divides intohypogastric (or internal iliac) and external iliac (see Fig. 128). BRANCHES OF HYPOGASTRIC ARTERY. 179 The hypogastric artery passes into the pelvis and gives offbranches which supply the parts within and without the pelvicwall, including the perineum, and all of t
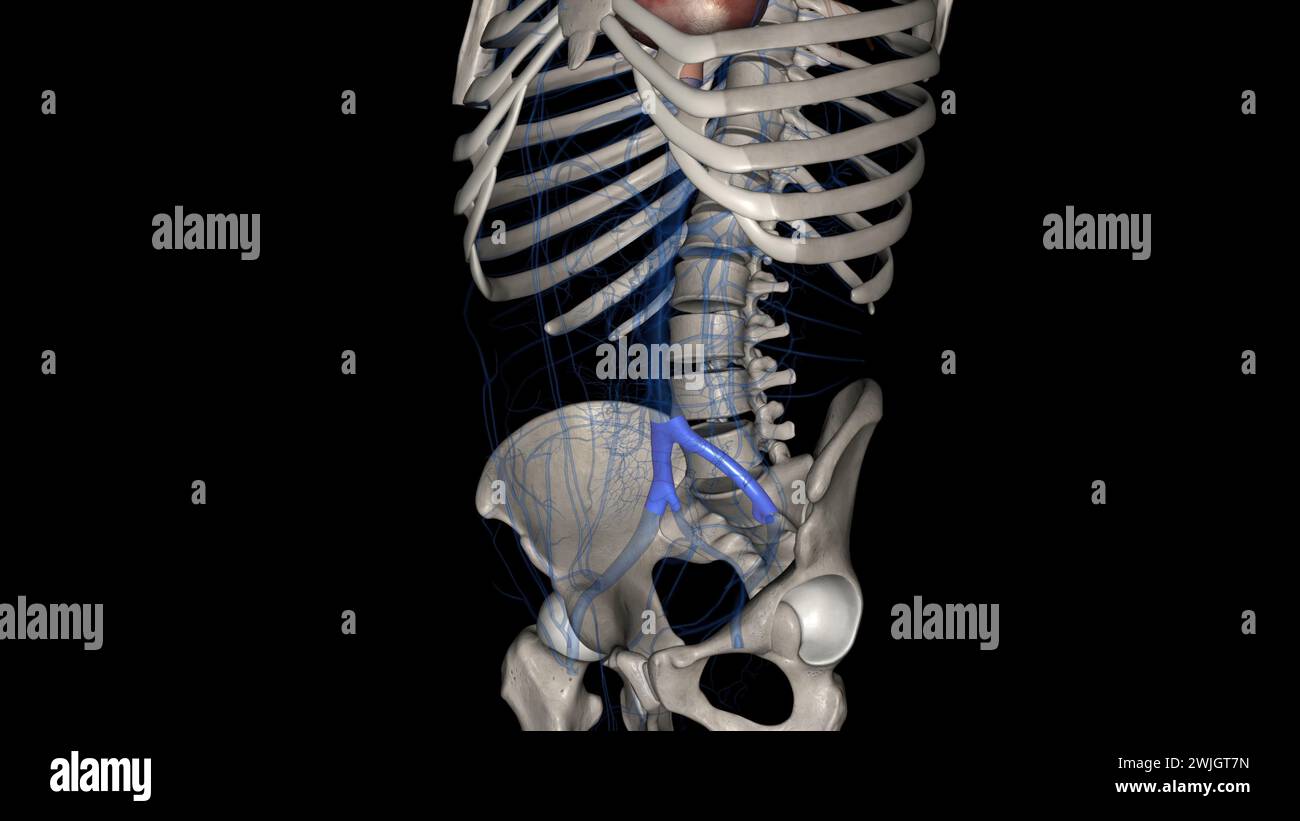 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596586585.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596586585.htmlRF2WJGT7N–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
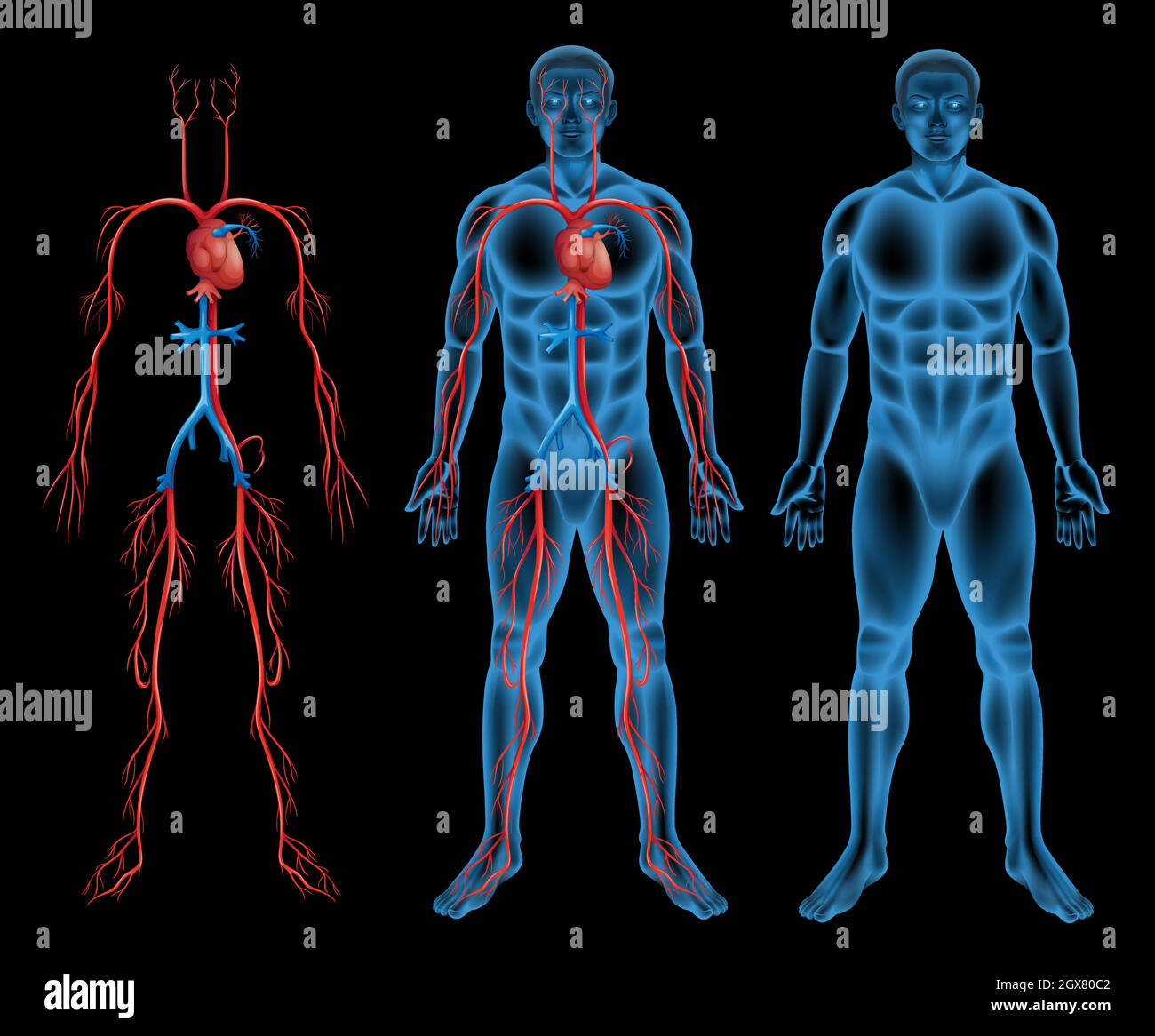 Male circulatory system Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/male-circulatory-system-image446416210.html
Male circulatory system Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/male-circulatory-system-image446416210.htmlRF2GX80C2–Male circulatory system
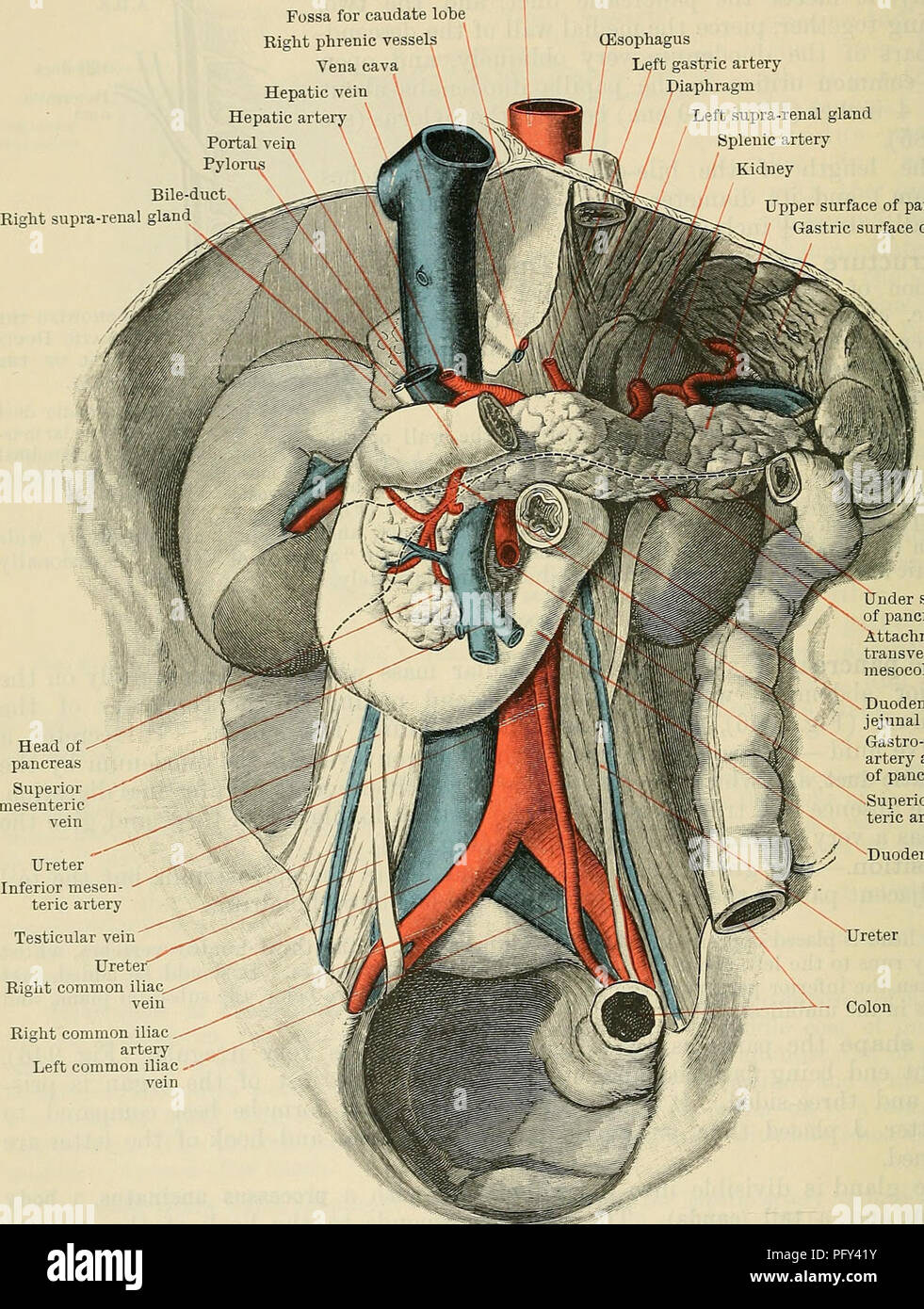 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1204 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. expressed as follows :-The head (Fig. 946) lies in the concavity of the duodenum, with the vena cava inferior and abdominal aorta behind it; the body crosses the Aorta Fossa for caudate lobe Right phrenic vessels Vena cava Hepatic vein Hepatic arte Portal vei Pylor Bile-duct Right supra-renal gland^ (Esophagus Left gastric artery diaphragm Left supra-renal gland Splenic artery Kidney Upper surface of pancreas / Gastric surface of spleen. Testicular vein Ureter" Right common iliac Right common iliac artery Left common Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1204-the-digestive-system-expressed-as-follows-the-head-fig-946-lies-in-the-concavity-of-the-duodenum-with-the-vena-cava-inferior-and-abdominal-aorta-behind-it-the-body-crosses-the-aorta-fossa-for-caudate-lobe-right-phrenic-vessels-vena-cava-hepatic-vein-hepatic-arte-portal-vei-pylor-bile-duct-right-supra-renal-gland-esophagus-left-gastric-artery-diaphragm-left-supra-renal-gland-splenic-artery-kidney-upper-surface-of-pancreas-gastric-surface-of-spleen-testicular-vein-ureterquot-right-common-iliac-right-common-iliac-artery-left-common-image216340151.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1204 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. expressed as follows :-The head (Fig. 946) lies in the concavity of the duodenum, with the vena cava inferior and abdominal aorta behind it; the body crosses the Aorta Fossa for caudate lobe Right phrenic vessels Vena cava Hepatic vein Hepatic arte Portal vei Pylor Bile-duct Right supra-renal gland^ (Esophagus Left gastric artery diaphragm Left supra-renal gland Splenic artery Kidney Upper surface of pancreas / Gastric surface of spleen. Testicular vein Ureter" Right common iliac Right common iliac artery Left common Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1204-the-digestive-system-expressed-as-follows-the-head-fig-946-lies-in-the-concavity-of-the-duodenum-with-the-vena-cava-inferior-and-abdominal-aorta-behind-it-the-body-crosses-the-aorta-fossa-for-caudate-lobe-right-phrenic-vessels-vena-cava-hepatic-vein-hepatic-arte-portal-vei-pylor-bile-duct-right-supra-renal-gland-esophagus-left-gastric-artery-diaphragm-left-supra-renal-gland-splenic-artery-kidney-upper-surface-of-pancreas-gastric-surface-of-spleen-testicular-vein-ureterquot-right-common-iliac-right-common-iliac-artery-left-common-image216340151.htmlRMPFY41Y–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1204 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. expressed as follows :-The head (Fig. 946) lies in the concavity of the duodenum, with the vena cava inferior and abdominal aorta behind it; the body crosses the Aorta Fossa for caudate lobe Right phrenic vessels Vena cava Hepatic vein Hepatic arte Portal vei Pylor Bile-duct Right supra-renal gland^ (Esophagus Left gastric artery diaphragm Left supra-renal gland Splenic artery Kidney Upper surface of pancreas / Gastric surface of spleen. Testicular vein Ureter" Right common iliac Right common iliac artery Left common
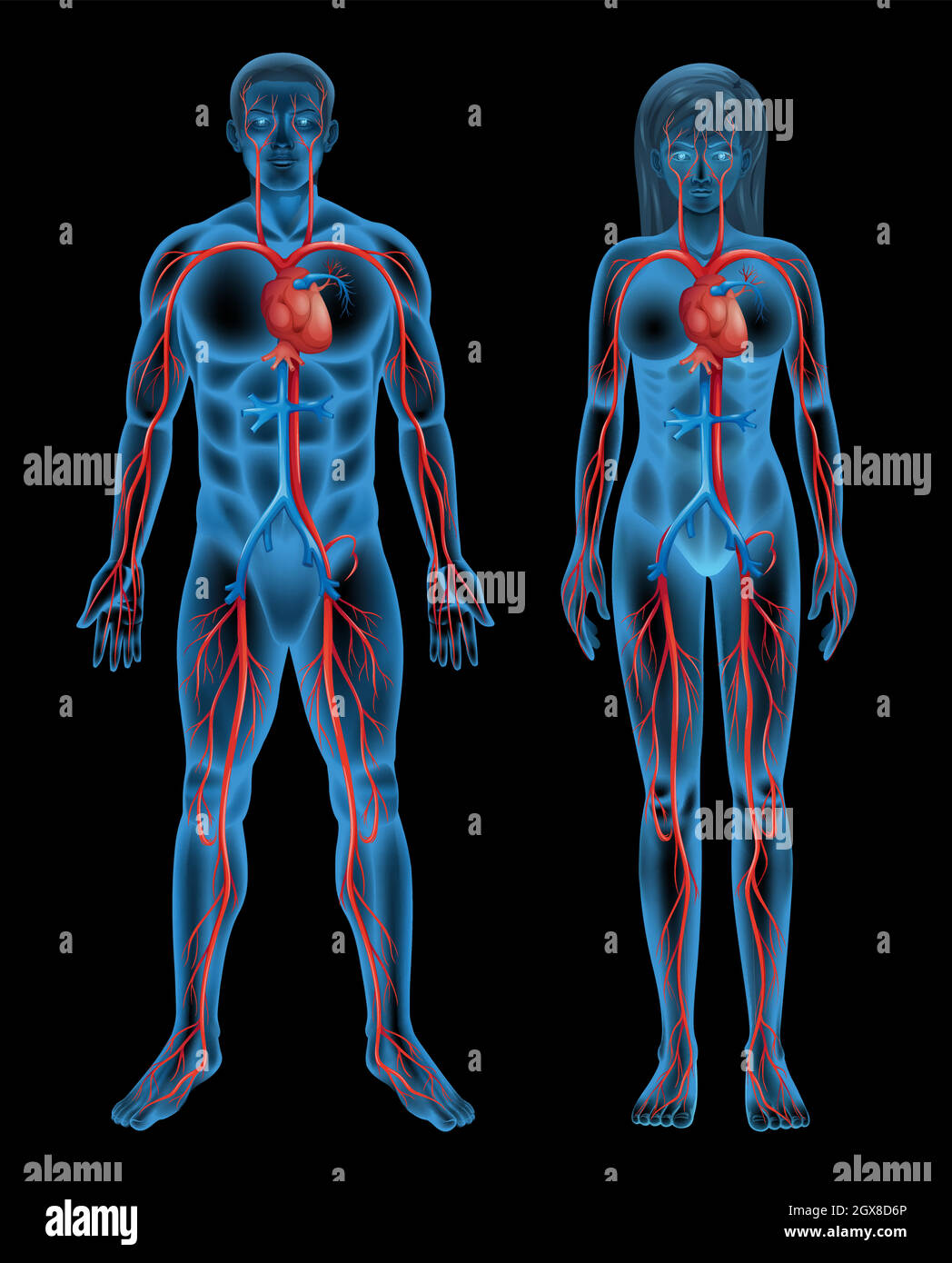 Circulatory system of a human Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/circulatory-system-of-a-human-image446426254.html
Circulatory system of a human Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/circulatory-system-of-a-human-image446426254.htmlRF2GX8D6P–Circulatory system of a human
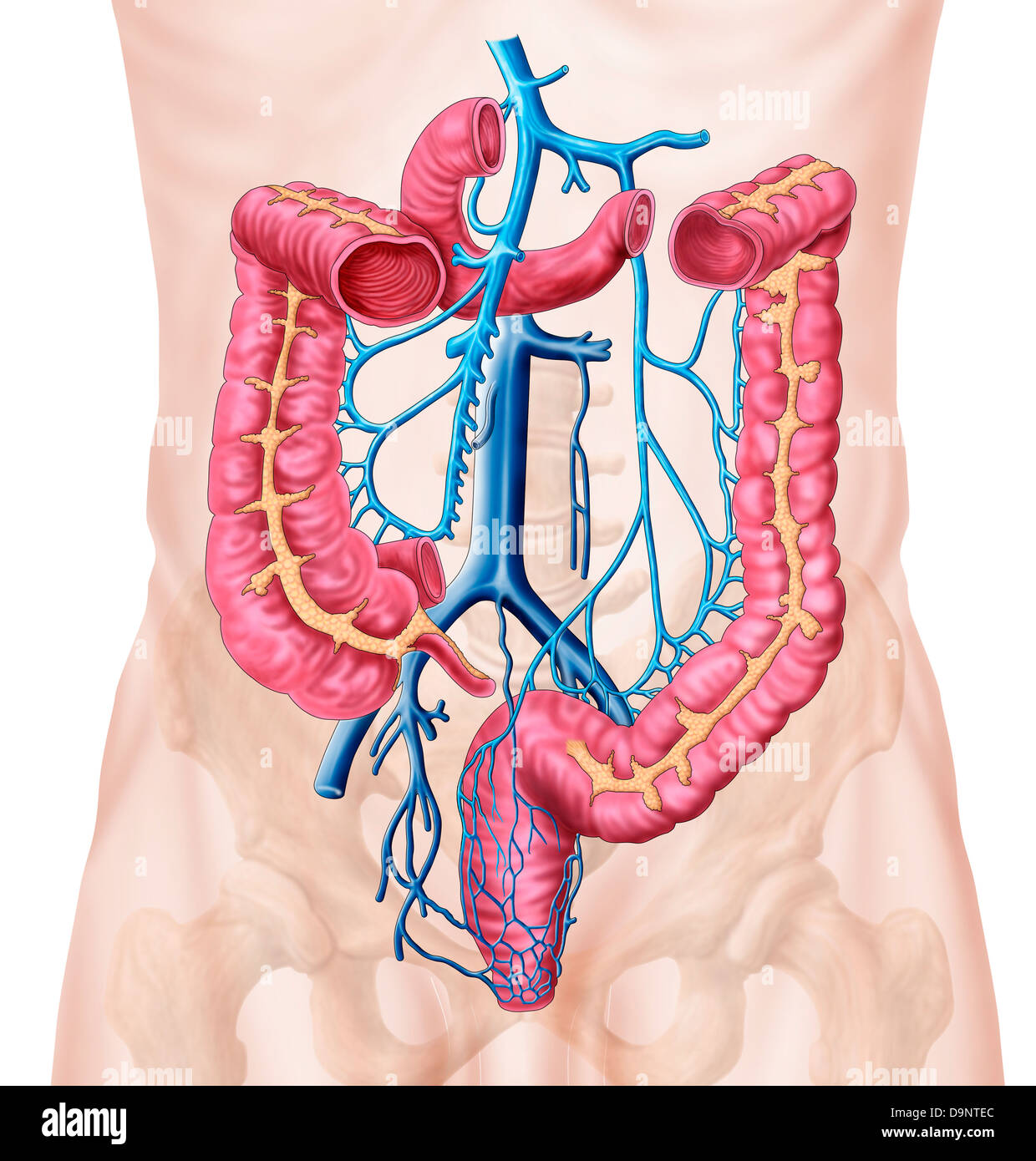 Anatomy of human abdominal vein system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomy-of-human-abdominal-vein-system-57643220.html
Anatomy of human abdominal vein system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomy-of-human-abdominal-vein-system-57643220.htmlRFD9NTEC–Anatomy of human abdominal vein system.
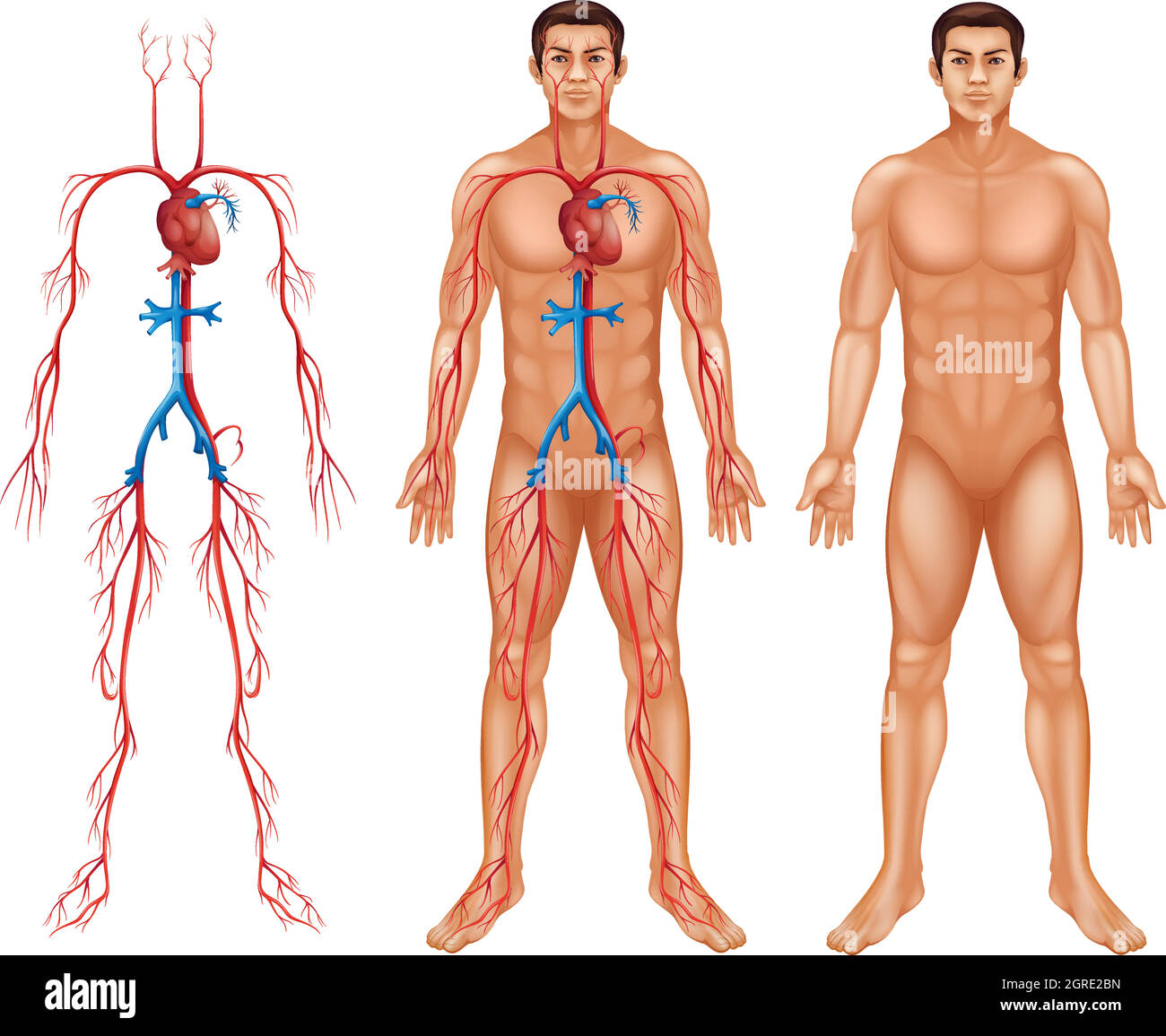 Male circulatory system Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/male-circulatory-system-image444705513.html
Male circulatory system Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/male-circulatory-system-image444705513.htmlRF2GRE2BN–Male circulatory system
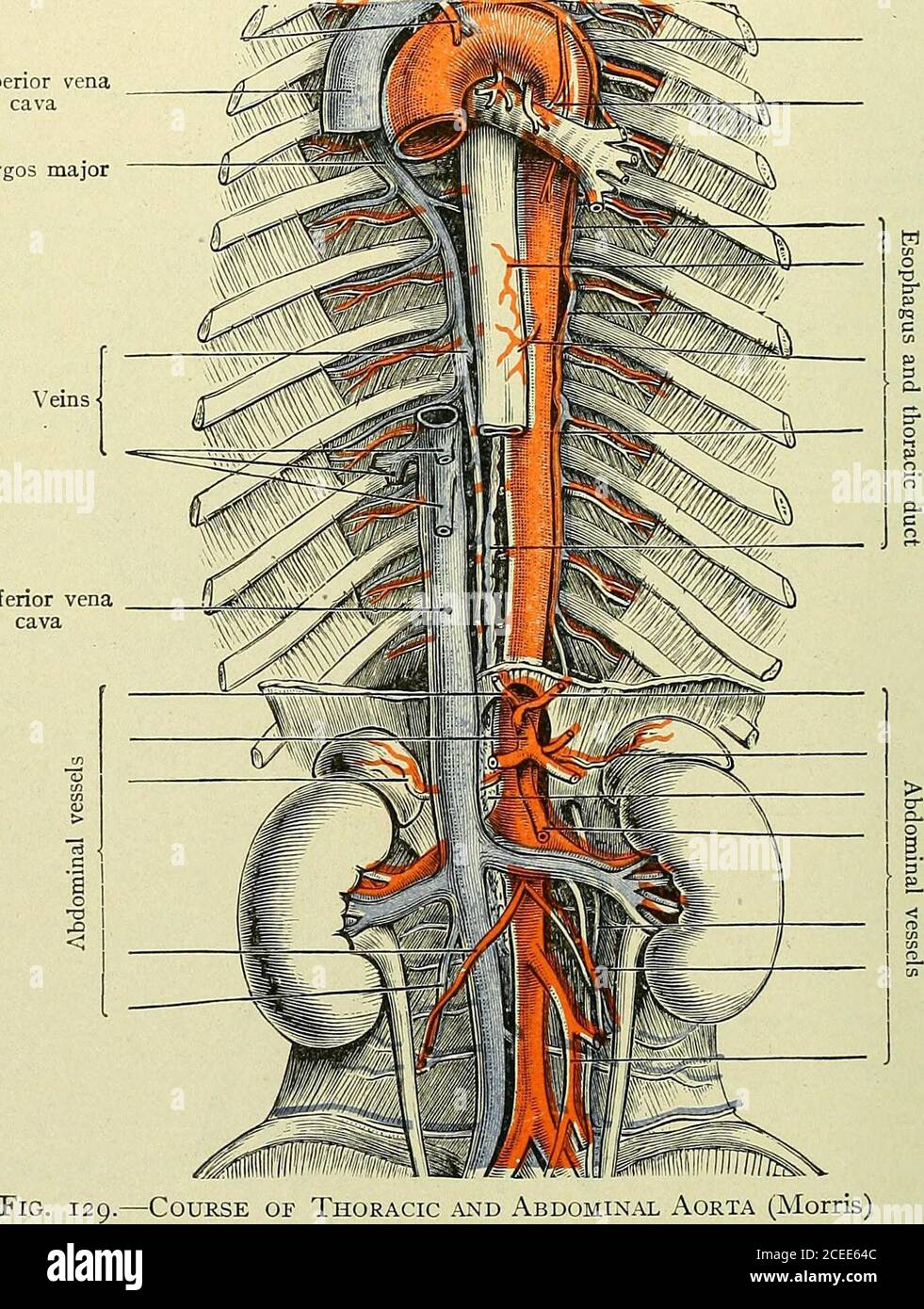 . Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. anch ofspermatic Ureteric branch ofcommon iliac Common iliac artery External iliac arteryInternal iliac artery Fig. 128.—Branches of the AnnoMiMAL Aorta (Morris).Note that the right common iliac is longer than the left. The spennatic artery runs downward and along the brim of thepelvis to pass out through the inguinal canal with the spermaticcord; it continues downward in the scrotum to supply the testes(Fig. 128). lyS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR NURSES. Special notes.—The superior mesenteric lies between the layers of themesentery. The inferior Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-anch-ofspermatic-ureteric-branch-ofcommon-iliac-common-iliac-artery-external-iliac-arteryinternal-iliac-artery-fig-128branches-of-the-annomimal-aorta-morrisnote-that-the-right-common-iliac-is-longer-than-the-left-the-spennatic-artery-runs-downward-and-along-the-brim-of-thepelvis-to-pass-out-through-the-inguinal-canal-with-the-spermaticcord-it-continues-downward-in-the-scrotum-to-supply-the-testesfig-128-lys-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-special-notesthe-superior-mesenteric-lies-between-the-layers-of-themesentery-the-inferior-image370335068.html
. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. anch ofspermatic Ureteric branch ofcommon iliac Common iliac artery External iliac arteryInternal iliac artery Fig. 128.—Branches of the AnnoMiMAL Aorta (Morris).Note that the right common iliac is longer than the left. The spennatic artery runs downward and along the brim of thepelvis to pass out through the inguinal canal with the spermaticcord; it continues downward in the scrotum to supply the testes(Fig. 128). lyS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR NURSES. Special notes.—The superior mesenteric lies between the layers of themesentery. The inferior Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-anch-ofspermatic-ureteric-branch-ofcommon-iliac-common-iliac-artery-external-iliac-arteryinternal-iliac-artery-fig-128branches-of-the-annomimal-aorta-morrisnote-that-the-right-common-iliac-is-longer-than-the-left-the-spennatic-artery-runs-downward-and-along-the-brim-of-thepelvis-to-pass-out-through-the-inguinal-canal-with-the-spermaticcord-it-continues-downward-in-the-scrotum-to-supply-the-testesfig-128-lys-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-special-notesthe-superior-mesenteric-lies-between-the-layers-of-themesentery-the-inferior-image370335068.htmlRM2CEE64C–. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. anch ofspermatic Ureteric branch ofcommon iliac Common iliac artery External iliac arteryInternal iliac artery Fig. 128.—Branches of the AnnoMiMAL Aorta (Morris).Note that the right common iliac is longer than the left. The spennatic artery runs downward and along the brim of thepelvis to pass out through the inguinal canal with the spermaticcord; it continues downward in the scrotum to supply the testes(Fig. 128). lyS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR NURSES. Special notes.—The superior mesenteric lies between the layers of themesentery. The inferior
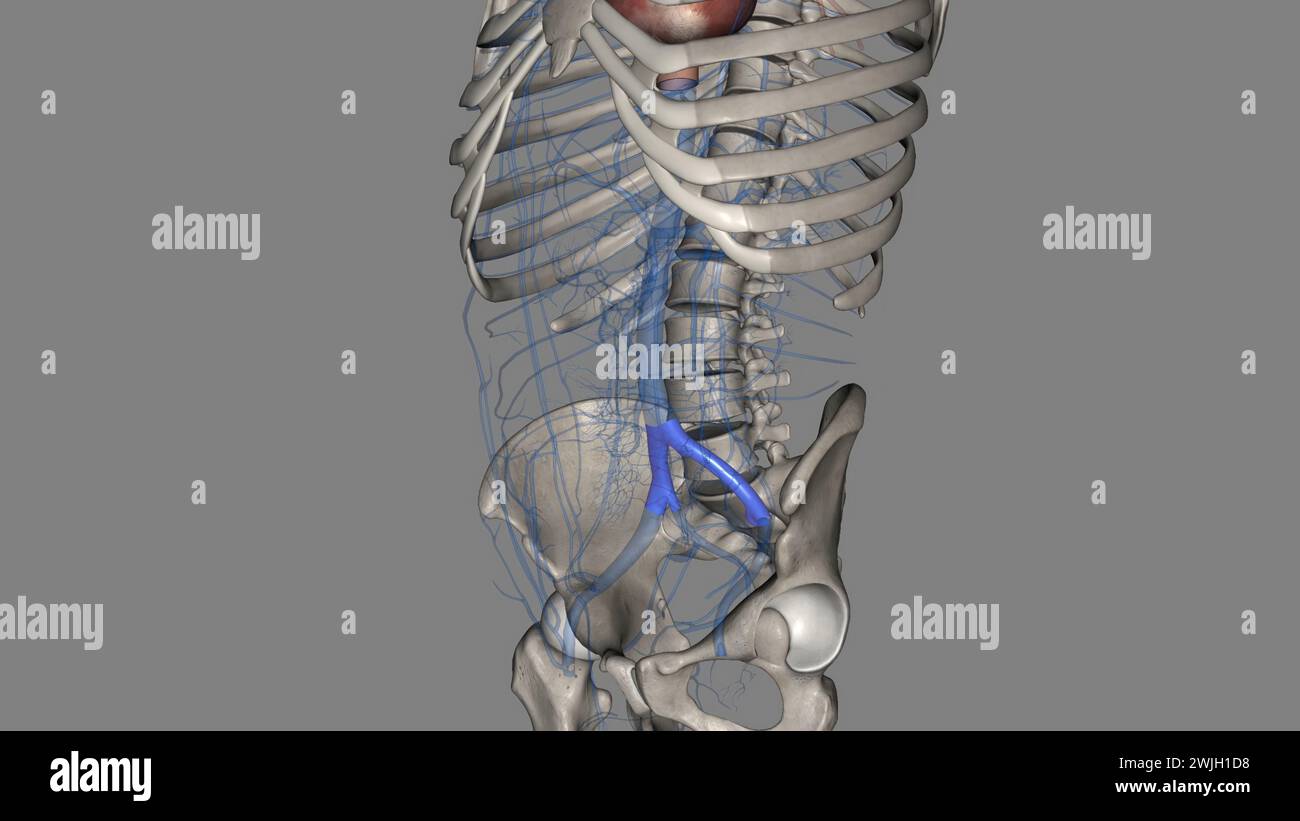 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596590660.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596590660.htmlRF2WJH1D8–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
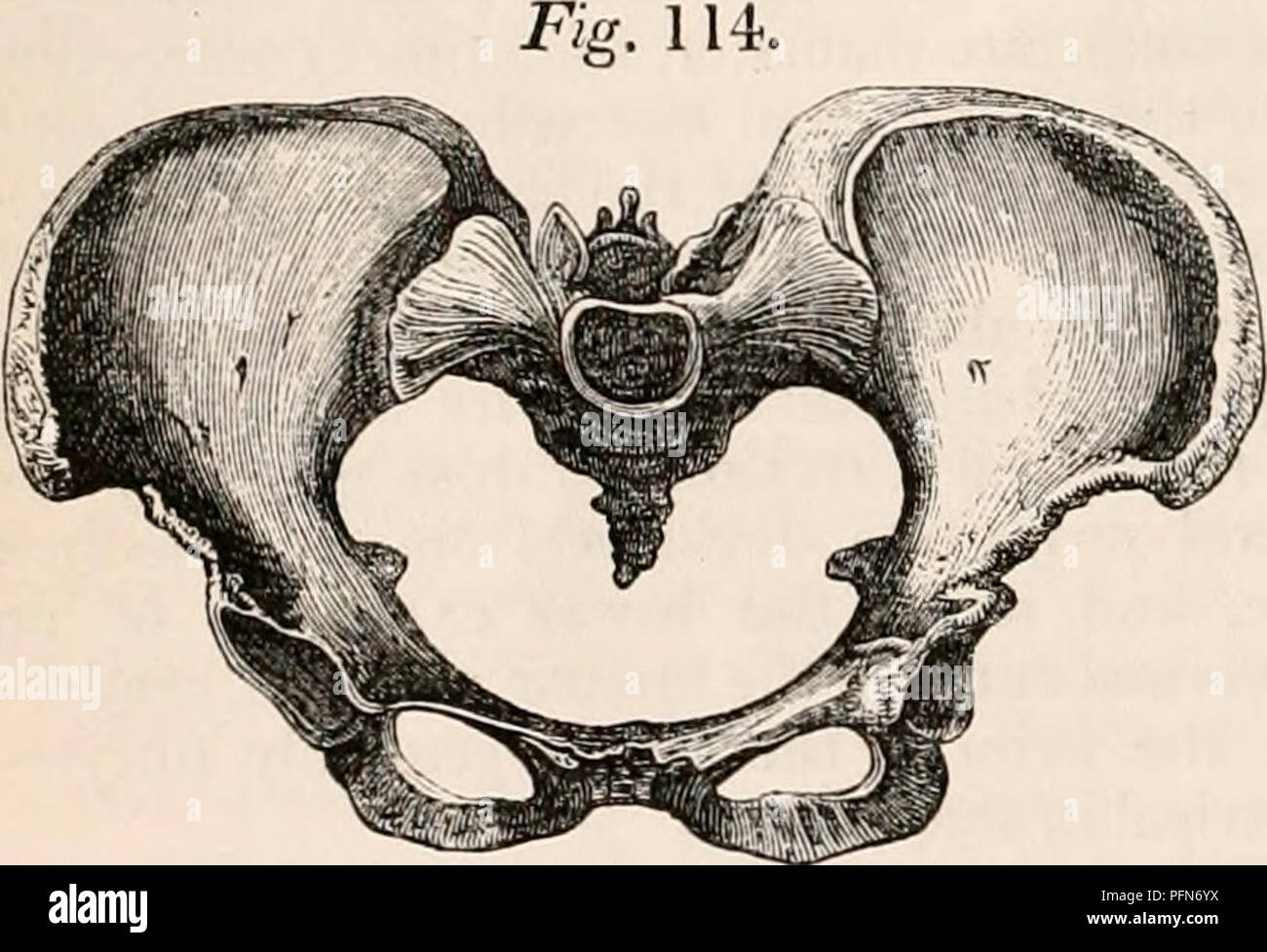 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. 182 PELVIS. line of thoracic vertebra to the right side, and is calculated to keep the line of the whole spinal column in equivalent relation to the di- rect and perpendicular line of gravity. It is an interesting question, how far this common ten- dency of the lumbar curve influences the po- sition of the fetal head, by affording more room for the sinciput at the right sacro-iliac joint, and determining its long axis in the left oblique diameter, which is generally allowed to be the most frequent presentation. In by Air Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-182-pelvis-line-of-thoracic-vertebra-to-the-right-side-and-is-calculated-to-keep-the-line-of-the-whole-spinal-column-in-equivalent-relation-to-the-di-rect-and-perpendicular-line-of-gravity-it-is-an-interesting-question-how-far-this-common-ten-dency-of-the-lumbar-curve-influences-the-po-sition-of-the-fetal-head-by-affording-more-room-for-the-sinciput-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-and-determining-its-long-axis-in-the-left-oblique-diameter-which-is-generally-allowed-to-be-the-most-frequent-presentation-in-by-air-image216210734.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. 182 PELVIS. line of thoracic vertebra to the right side, and is calculated to keep the line of the whole spinal column in equivalent relation to the di- rect and perpendicular line of gravity. It is an interesting question, how far this common ten- dency of the lumbar curve influences the po- sition of the fetal head, by affording more room for the sinciput at the right sacro-iliac joint, and determining its long axis in the left oblique diameter, which is generally allowed to be the most frequent presentation. In by Air Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-182-pelvis-line-of-thoracic-vertebra-to-the-right-side-and-is-calculated-to-keep-the-line-of-the-whole-spinal-column-in-equivalent-relation-to-the-di-rect-and-perpendicular-line-of-gravity-it-is-an-interesting-question-how-far-this-common-ten-dency-of-the-lumbar-curve-influences-the-po-sition-of-the-fetal-head-by-affording-more-room-for-the-sinciput-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-and-determining-its-long-axis-in-the-left-oblique-diameter-which-is-generally-allowed-to-be-the-most-frequent-presentation-in-by-air-image216210734.htmlRMPFN6YX–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. 182 PELVIS. line of thoracic vertebra to the right side, and is calculated to keep the line of the whole spinal column in equivalent relation to the di- rect and perpendicular line of gravity. It is an interesting question, how far this common ten- dency of the lumbar curve influences the po- sition of the fetal head, by affording more room for the sinciput at the right sacro-iliac joint, and determining its long axis in the left oblique diameter, which is generally allowed to be the most frequent presentation. In by Air
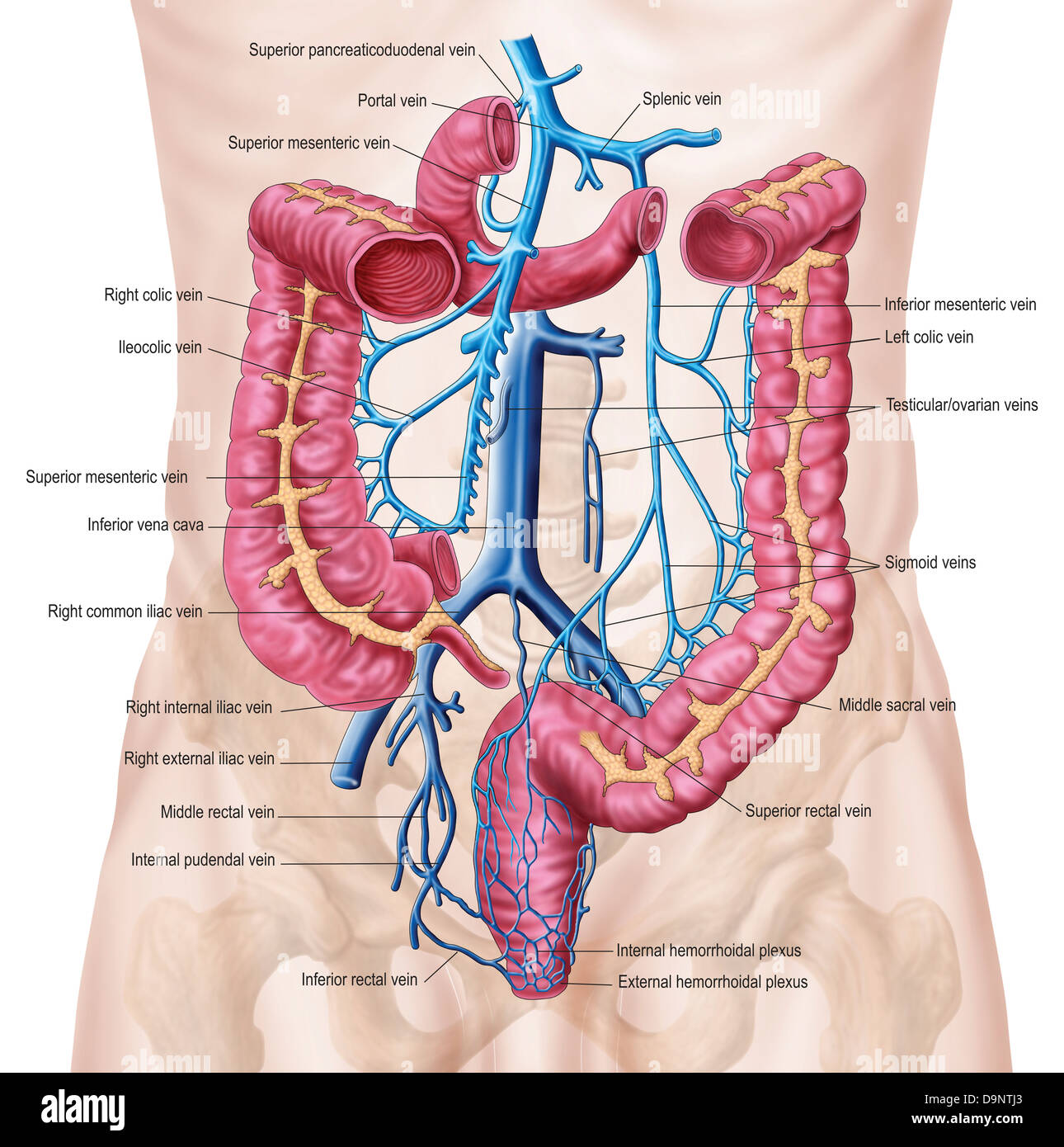 Anatomy of human abdominal vein system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomy-of-human-abdominal-vein-system-57643323.html
Anatomy of human abdominal vein system. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-anatomy-of-human-abdominal-vein-system-57643323.htmlRFD9NTJ3–Anatomy of human abdominal vein system.
 . The anatomical record. Anatomy; Anatomy. DUPLICATION OF INFERIOR VENA CAVA 477 left, inferior vena cava; 5 cm. inferior to the entrance of the large anterior renal vein (fig. 1). In the fall of 1911 a condition similar to the first was found in another subject (no. 401, Cornell series), a white male, aged fifty, who died of cirrhosis of the liver. On the right the external iliac vein is joined at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine by the internal iliac vein to form the AZYGOS ANASTOMOSING BRANCH RIGHT SUPRARENAL RENALS RIGHT SPERMATIC RIGHT INFERIOR VENA CAVA RIGHT COMMON ILIAC R Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomical-record-anatomy-anatomy-duplication-of-inferior-vena-cava-477-left-inferior-vena-cava-5-cm-inferior-to-the-entrance-of-the-large-anterior-renal-vein-fig-1-in-the-fall-of-1911-a-condition-similar-to-the-first-was-found-in-another-subject-no-401-cornell-series-a-white-male-aged-fifty-who-died-of-cirrhosis-of-the-liver-on-the-right-the-external-iliac-vein-is-joined-at-the-level-of-the-anterior-superior-iliac-spine-by-the-internal-iliac-vein-to-form-the-azygos-anastomosing-branch-right-suprarenal-renals-right-spermatic-right-inferior-vena-cava-right-common-iliac-r-image236863276.html
. The anatomical record. Anatomy; Anatomy. DUPLICATION OF INFERIOR VENA CAVA 477 left, inferior vena cava; 5 cm. inferior to the entrance of the large anterior renal vein (fig. 1). In the fall of 1911 a condition similar to the first was found in another subject (no. 401, Cornell series), a white male, aged fifty, who died of cirrhosis of the liver. On the right the external iliac vein is joined at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine by the internal iliac vein to form the AZYGOS ANASTOMOSING BRANCH RIGHT SUPRARENAL RENALS RIGHT SPERMATIC RIGHT INFERIOR VENA CAVA RIGHT COMMON ILIAC R Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomical-record-anatomy-anatomy-duplication-of-inferior-vena-cava-477-left-inferior-vena-cava-5-cm-inferior-to-the-entrance-of-the-large-anterior-renal-vein-fig-1-in-the-fall-of-1911-a-condition-similar-to-the-first-was-found-in-another-subject-no-401-cornell-series-a-white-male-aged-fifty-who-died-of-cirrhosis-of-the-liver-on-the-right-the-external-iliac-vein-is-joined-at-the-level-of-the-anterior-superior-iliac-spine-by-the-internal-iliac-vein-to-form-the-azygos-anastomosing-branch-right-suprarenal-renals-right-spermatic-right-inferior-vena-cava-right-common-iliac-r-image236863276.htmlRMRNA1EM–. The anatomical record. Anatomy; Anatomy. DUPLICATION OF INFERIOR VENA CAVA 477 left, inferior vena cava; 5 cm. inferior to the entrance of the large anterior renal vein (fig. 1). In the fall of 1911 a condition similar to the first was found in another subject (no. 401, Cornell series), a white male, aged fifty, who died of cirrhosis of the liver. On the right the external iliac vein is joined at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine by the internal iliac vein to form the AZYGOS ANASTOMOSING BRANCH RIGHT SUPRARENAL RENALS RIGHT SPERMATIC RIGHT INFERIOR VENA CAVA RIGHT COMMON ILIAC R
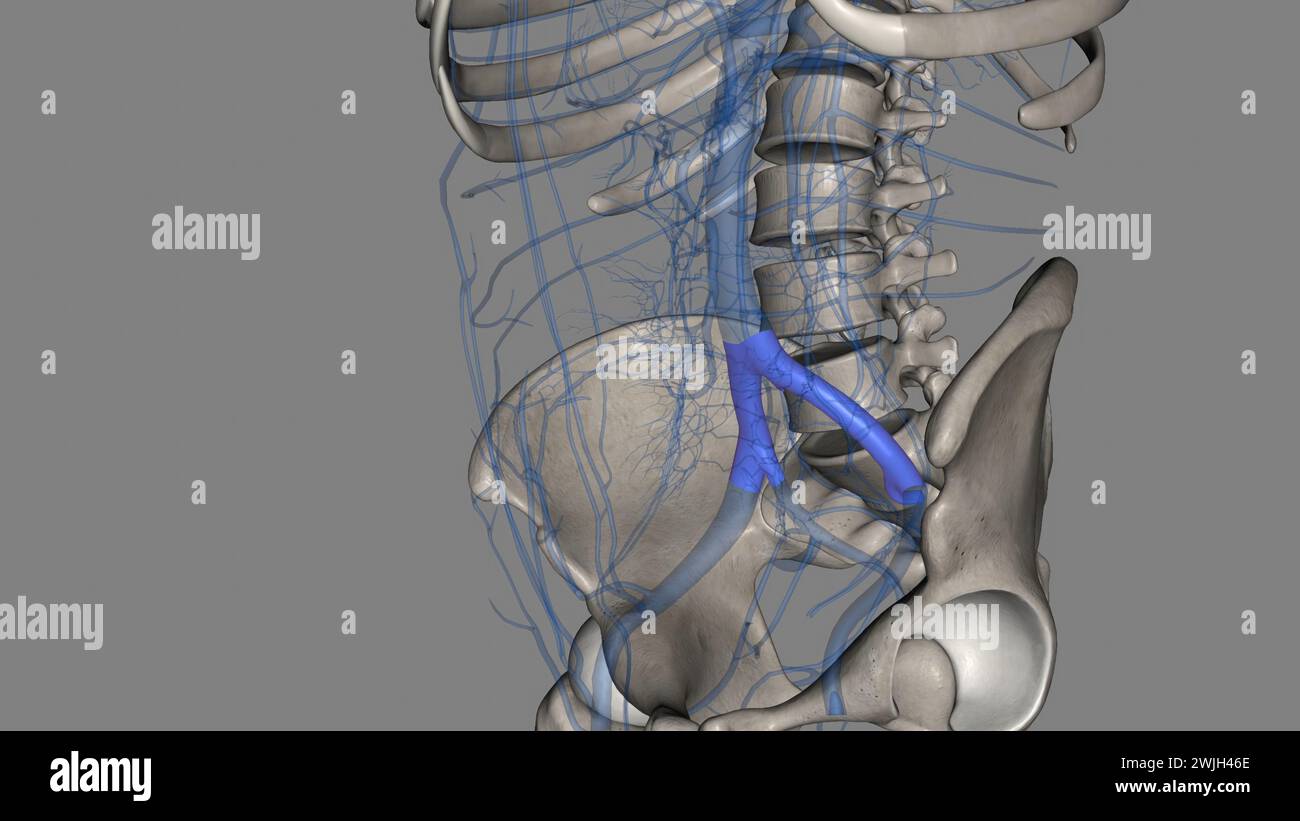 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596592822.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596592822.htmlRF2WJH46E–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
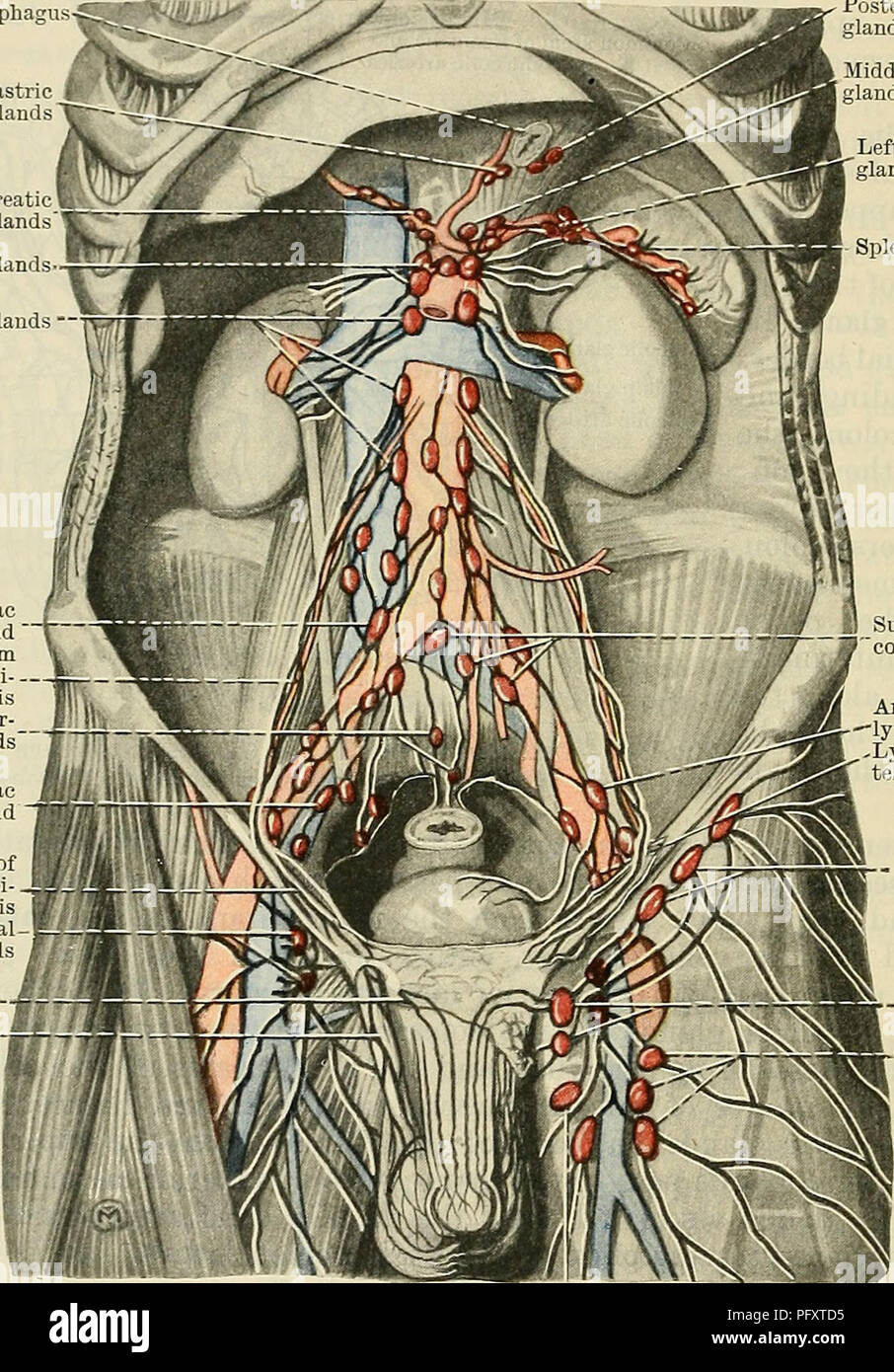 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1022 THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. iliac glands, (2) efferents from the sub-aortic glands, (3) efferents from the sacral glands, (4) some efferents from the hypogastric glands, (5) efferents from the main inferior mesenteric glands, (6) the lymph vessels from the testes and epididymides and their coverings in the male, and from the ovaries, the uterine tubes, and the upper part of the uterus in the female, (7) lymph vessels from the (Esophagus Posterior left gastric glands Right supra-pancreatic glands Main mesenteric glands- Lumhar glands —' A common iliac Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1022-the-vascular-system-iliac-glands-2-efferents-from-the-sub-aortic-glands-3-efferents-from-the-sacral-glands-4-some-efferents-from-the-hypogastric-glands-5-efferents-from-the-main-inferior-mesenteric-glands-6-the-lymph-vessels-from-the-testes-and-epididymides-and-their-coverings-in-the-male-and-from-the-ovaries-the-uterine-tubes-and-the-upper-part-of-the-uterus-in-the-female-7-lymph-vessels-from-the-esophagus-posterior-left-gastric-glands-right-supra-pancreatic-glands-main-mesenteric-glands-lumhar-glands-a-common-iliac-image216334193.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1022 THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. iliac glands, (2) efferents from the sub-aortic glands, (3) efferents from the sacral glands, (4) some efferents from the hypogastric glands, (5) efferents from the main inferior mesenteric glands, (6) the lymph vessels from the testes and epididymides and their coverings in the male, and from the ovaries, the uterine tubes, and the upper part of the uterus in the female, (7) lymph vessels from the (Esophagus Posterior left gastric glands Right supra-pancreatic glands Main mesenteric glands- Lumhar glands —' A common iliac Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1022-the-vascular-system-iliac-glands-2-efferents-from-the-sub-aortic-glands-3-efferents-from-the-sacral-glands-4-some-efferents-from-the-hypogastric-glands-5-efferents-from-the-main-inferior-mesenteric-glands-6-the-lymph-vessels-from-the-testes-and-epididymides-and-their-coverings-in-the-male-and-from-the-ovaries-the-uterine-tubes-and-the-upper-part-of-the-uterus-in-the-female-7-lymph-vessels-from-the-esophagus-posterior-left-gastric-glands-right-supra-pancreatic-glands-main-mesenteric-glands-lumhar-glands-a-common-iliac-image216334193.htmlRMPFXTD5–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1022 THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. iliac glands, (2) efferents from the sub-aortic glands, (3) efferents from the sacral glands, (4) some efferents from the hypogastric glands, (5) efferents from the main inferior mesenteric glands, (6) the lymph vessels from the testes and epididymides and their coverings in the male, and from the ovaries, the uterine tubes, and the upper part of the uterus in the female, (7) lymph vessels from the (Esophagus Posterior left gastric glands Right supra-pancreatic glands Main mesenteric glands- Lumhar glands —' A common iliac
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1204 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. expressed as follows :-The head (Fig. 946) lies in the concavity of the duodenum, with the vena cava inferior and abdominal aorta behind it; the body crosses the Aorta Fossa for caudate lobe Right phrenic vessels Vena cava Hepatic vein Hepatic arte Portal vei Pylor Bile-duct Right supra-renal gland^ (Esophagus Left gastric artery diaphragm Left supra-renal gland Splenic artery Kidney Upper surface of pancreas / Gastric surface of spleen. Testicular vein Ureter" Right common iliac Right common iliac artery Left common Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1204-the-digestive-system-expressed-as-follows-the-head-fig-946-lies-in-the-concavity-of-the-duodenum-with-the-vena-cava-inferior-and-abdominal-aorta-behind-it-the-body-crosses-the-aorta-fossa-for-caudate-lobe-right-phrenic-vessels-vena-cava-hepatic-vein-hepatic-arte-portal-vei-pylor-bile-duct-right-supra-renal-gland-esophagus-left-gastric-artery-diaphragm-left-supra-renal-gland-splenic-artery-kidney-upper-surface-of-pancreas-gastric-surface-of-spleen-testicular-vein-ureterquot-right-common-iliac-right-common-iliac-artery-left-common-image231849025.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1204 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. expressed as follows :-The head (Fig. 946) lies in the concavity of the duodenum, with the vena cava inferior and abdominal aorta behind it; the body crosses the Aorta Fossa for caudate lobe Right phrenic vessels Vena cava Hepatic vein Hepatic arte Portal vei Pylor Bile-duct Right supra-renal gland^ (Esophagus Left gastric artery diaphragm Left supra-renal gland Splenic artery Kidney Upper surface of pancreas / Gastric surface of spleen. Testicular vein Ureter" Right common iliac Right common iliac artery Left common Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1204-the-digestive-system-expressed-as-follows-the-head-fig-946-lies-in-the-concavity-of-the-duodenum-with-the-vena-cava-inferior-and-abdominal-aorta-behind-it-the-body-crosses-the-aorta-fossa-for-caudate-lobe-right-phrenic-vessels-vena-cava-hepatic-vein-hepatic-arte-portal-vei-pylor-bile-duct-right-supra-renal-gland-esophagus-left-gastric-artery-diaphragm-left-supra-renal-gland-splenic-artery-kidney-upper-surface-of-pancreas-gastric-surface-of-spleen-testicular-vein-ureterquot-right-common-iliac-right-common-iliac-artery-left-common-image231849025.htmlRMRD5HP9–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1204 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. expressed as follows :-The head (Fig. 946) lies in the concavity of the duodenum, with the vena cava inferior and abdominal aorta behind it; the body crosses the Aorta Fossa for caudate lobe Right phrenic vessels Vena cava Hepatic vein Hepatic arte Portal vei Pylor Bile-duct Right supra-renal gland^ (Esophagus Left gastric artery diaphragm Left supra-renal gland Splenic artery Kidney Upper surface of pancreas / Gastric surface of spleen. Testicular vein Ureter" Right common iliac Right common iliac artery Left common
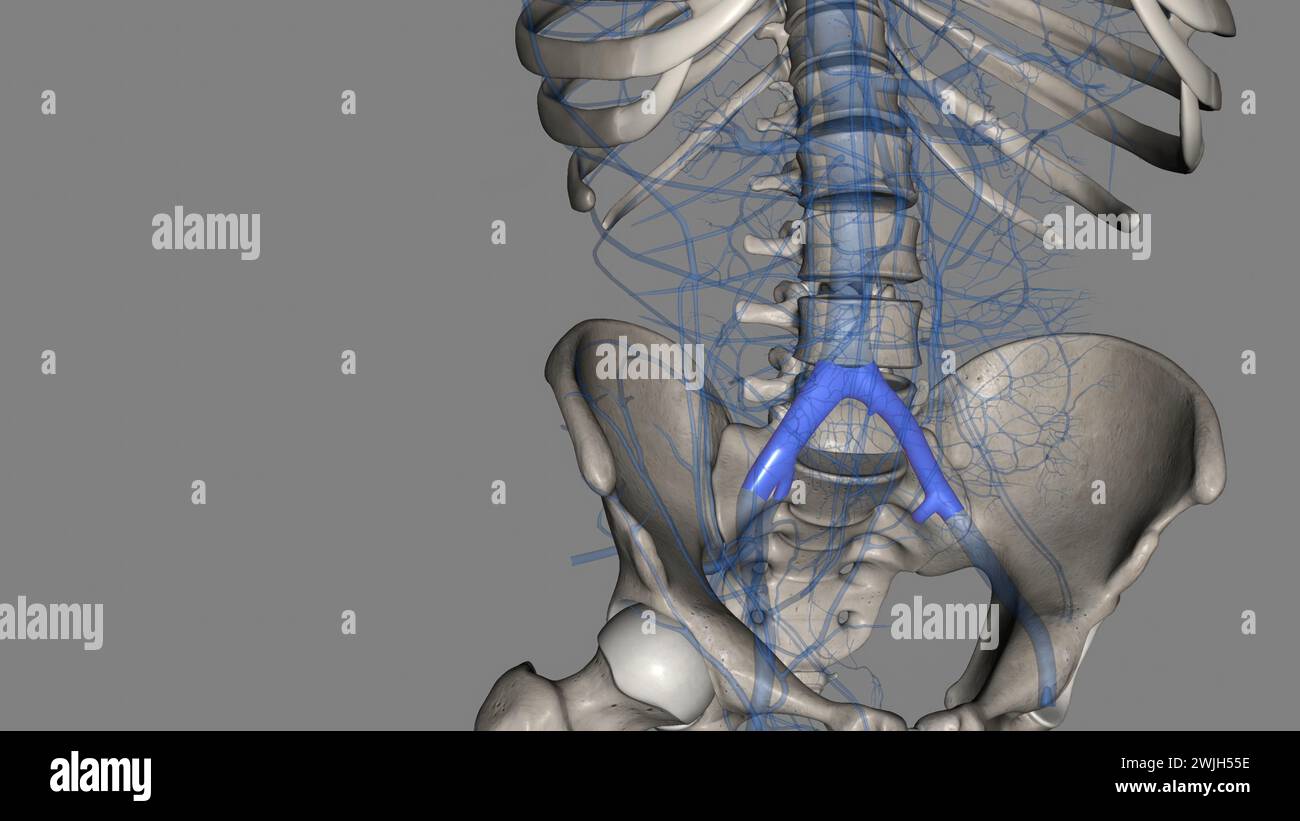 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596593578.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596593578.htmlRF2WJH55E–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
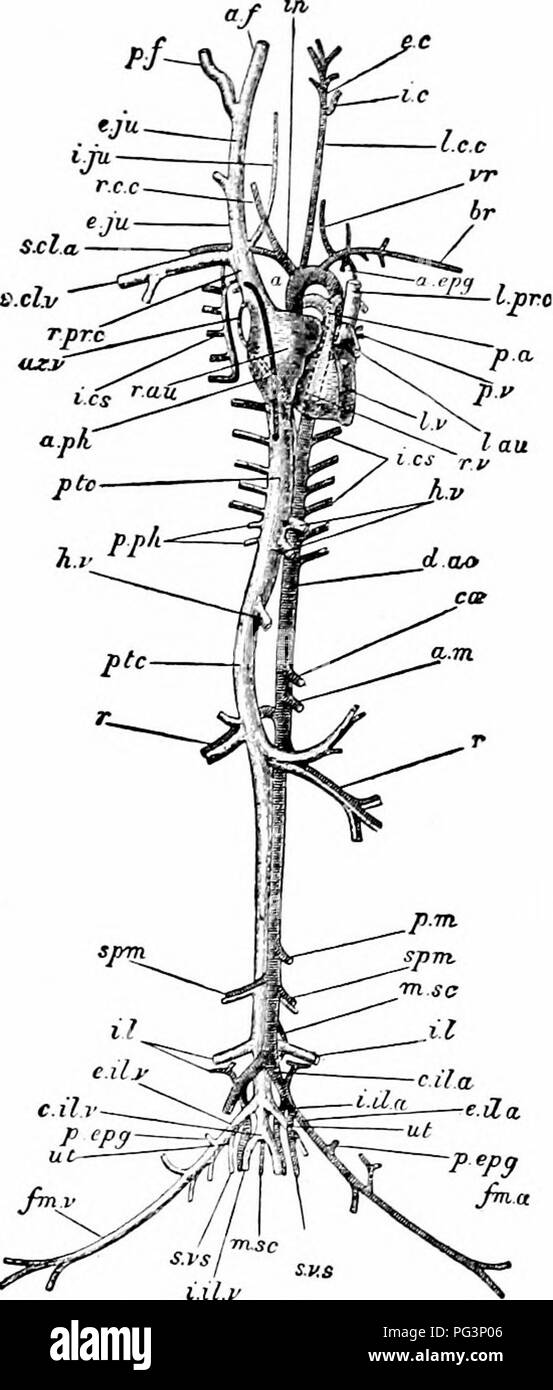 . A manual of zoology. . l.lt.t Fig. 307.—LepuS Cuniculus The vascular system. The heart is somewhat dis- placed towards the left of the subject: the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed a, arch of the aorta; a. epg, internal mammary artery; a. ft anterior facia! vein: a. m, anterior mesenteric artery; a. p/i, anterior phrenic vein; az. v, azygos vein; Br, branchial artery; c. il. a, common iliac artery; etc, cceliac artery ; d. no, dorsal aorta; e. e, external carotid artery; e. il. a, external iliac artery; e. il. v, external iliac vein: e. jn, ex Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-zoology-lltt-fig-307lepus-cuniculus-the-vascular-system-the-heart-is-somewhat-dis-placed-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-the-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-a-arch-of-the-aorta-a-epg-internal-mammary-artery-a-ft-anterior-facia!-vein-a-m-anterior-mesenteric-artery-a-pi-anterior-phrenic-vein-az-v-azygos-vein-br-branchial-artery-c-il-a-common-iliac-artery-etc-cceliac-artery-d-no-dorsal-aorta-e-e-external-carotid-artery-e-il-a-external-iliac-artery-e-il-v-external-iliac-vein-e-jn-ex-image216442022.html
. A manual of zoology. . l.lt.t Fig. 307.—LepuS Cuniculus The vascular system. The heart is somewhat dis- placed towards the left of the subject: the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed a, arch of the aorta; a. epg, internal mammary artery; a. ft anterior facia! vein: a. m, anterior mesenteric artery; a. p/i, anterior phrenic vein; az. v, azygos vein; Br, branchial artery; c. il. a, common iliac artery; etc, cceliac artery ; d. no, dorsal aorta; e. e, external carotid artery; e. il. a, external iliac artery; e. il. v, external iliac vein: e. jn, ex Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-zoology-lltt-fig-307lepus-cuniculus-the-vascular-system-the-heart-is-somewhat-dis-placed-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-the-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-a-arch-of-the-aorta-a-epg-internal-mammary-artery-a-ft-anterior-facia!-vein-a-m-anterior-mesenteric-artery-a-pi-anterior-phrenic-vein-az-v-azygos-vein-br-branchial-artery-c-il-a-common-iliac-artery-etc-cceliac-artery-d-no-dorsal-aorta-e-e-external-carotid-artery-e-il-a-external-iliac-artery-e-il-v-external-iliac-vein-e-jn-ex-image216442022.htmlRMPG3P06–. A manual of zoology. . l.lt.t Fig. 307.—LepuS Cuniculus The vascular system. The heart is somewhat dis- placed towards the left of the subject: the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed a, arch of the aorta; a. epg, internal mammary artery; a. ft anterior facia! vein: a. m, anterior mesenteric artery; a. p/i, anterior phrenic vein; az. v, azygos vein; Br, branchial artery; c. il. a, common iliac artery; etc, cceliac artery ; d. no, dorsal aorta; e. e, external carotid artery; e. il. a, external iliac artery; e. il. v, external iliac vein: e. jn, ex
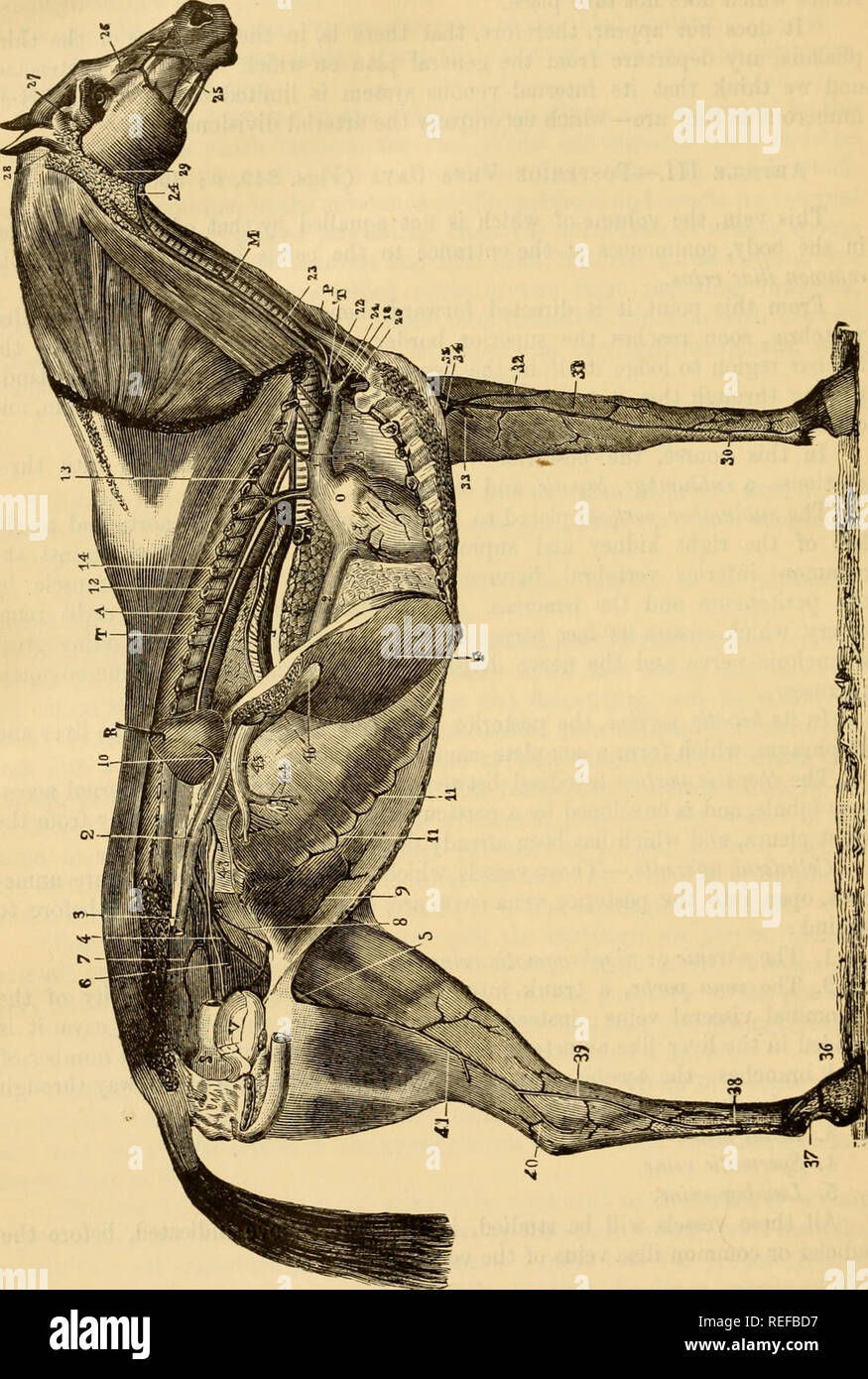 . The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Horses; Veterinary anatomy. 704 THE VEINS Fig 389.. GENERAL VIEW OF THE VEINS IN THE HORSE. 1. Anterior rena cava; 2, 2, posterior vena cava; 3, right common iliac vein, divided at the ilio- sacral articulation; 4, left common iliac rein; 5, femoral vein; 6, obturator vein; 7, subsacral vein; 8, left spermatic vein; 9, posterior abdominal vein; 10, renal vein: 11, 11, ascending branches of the asternal vein ; 12, vena azygos, with its intercostal branches, an,! m front the subdorsal venous branch, 13; 14, oesophageal vein; 15, dorsal or do Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-horses-veterinary-anatomy-704-the-veins-fig-389-general-view-of-the-veins-in-the-horse-1-anterior-rena-cava-2-2-posterior-vena-cava-3-right-common-iliac-vein-divided-at-the-ilio-sacral-articulation-4-left-common-iliac-rein-5-femoral-vein-6-obturator-vein-7-subsacral-vein-8-left-spermatic-vein-9-posterior-abdominal-vein-10-renal-vein-11-11-ascending-branches-of-the-asternal-vein-12-vena-azygos-with-its-intercostal-branches-an!-m-front-the-subdorsal-venous-branch-13-14-oesophageal-vein-15-dorsal-or-do-image232678243.html
. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Horses; Veterinary anatomy. 704 THE VEINS Fig 389.. GENERAL VIEW OF THE VEINS IN THE HORSE. 1. Anterior rena cava; 2, 2, posterior vena cava; 3, right common iliac vein, divided at the ilio- sacral articulation; 4, left common iliac rein; 5, femoral vein; 6, obturator vein; 7, subsacral vein; 8, left spermatic vein; 9, posterior abdominal vein; 10, renal vein: 11, 11, ascending branches of the asternal vein ; 12, vena azygos, with its intercostal branches, an,! m front the subdorsal venous branch, 13; 14, oesophageal vein; 15, dorsal or do Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-horses-veterinary-anatomy-704-the-veins-fig-389-general-view-of-the-veins-in-the-horse-1-anterior-rena-cava-2-2-posterior-vena-cava-3-right-common-iliac-vein-divided-at-the-ilio-sacral-articulation-4-left-common-iliac-rein-5-femoral-vein-6-obturator-vein-7-subsacral-vein-8-left-spermatic-vein-9-posterior-abdominal-vein-10-renal-vein-11-11-ascending-branches-of-the-asternal-vein-12-vena-azygos-with-its-intercostal-branches-an!-m-front-the-subdorsal-venous-branch-13-14-oesophageal-vein-15-dorsal-or-do-image232678243.htmlRMREFBD7–. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Horses; Veterinary anatomy. 704 THE VEINS Fig 389.. GENERAL VIEW OF THE VEINS IN THE HORSE. 1. Anterior rena cava; 2, 2, posterior vena cava; 3, right common iliac vein, divided at the ilio- sacral articulation; 4, left common iliac rein; 5, femoral vein; 6, obturator vein; 7, subsacral vein; 8, left spermatic vein; 9, posterior abdominal vein; 10, renal vein: 11, 11, ascending branches of the asternal vein ; 12, vena azygos, with its intercostal branches, an,! m front the subdorsal venous branch, 13; 14, oesophageal vein; 15, dorsal or do
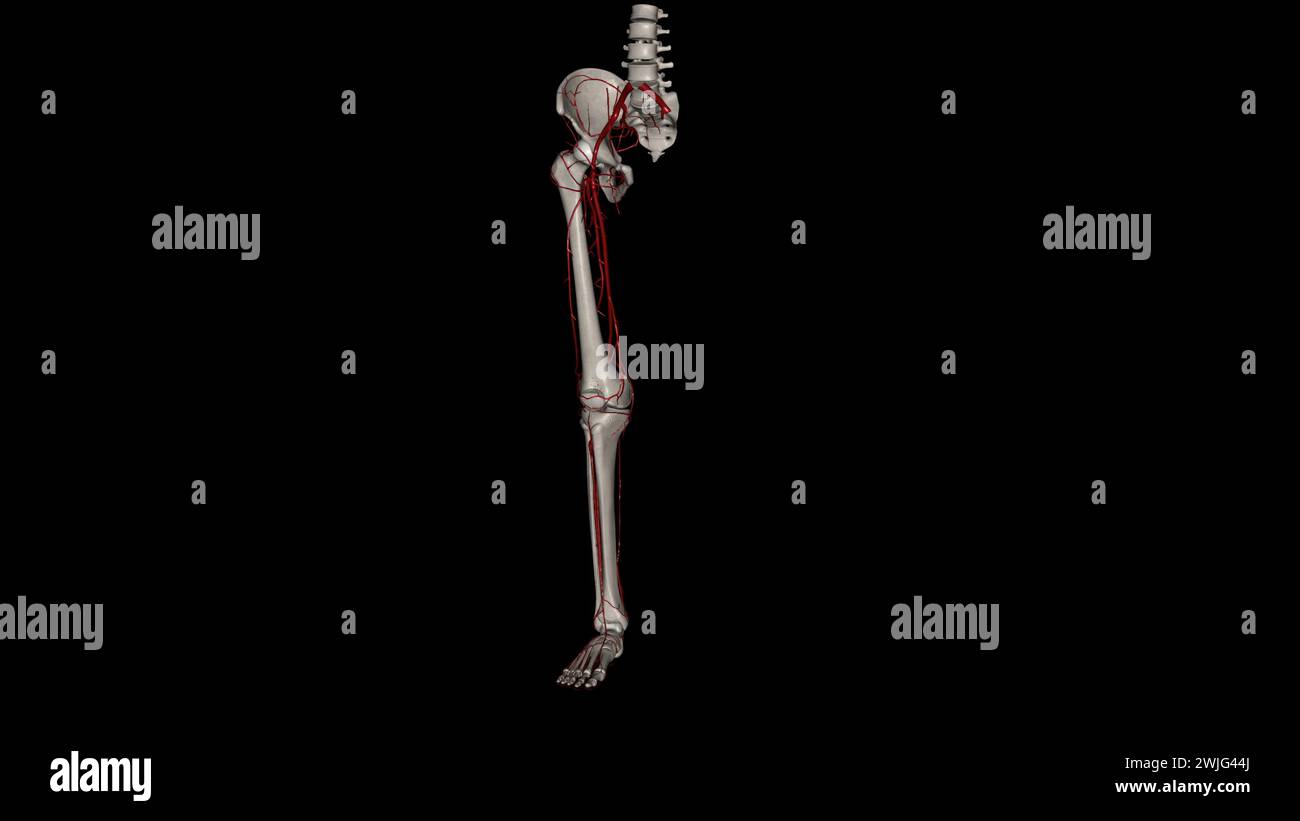 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570818.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570818.htmlRF2WJG44J–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
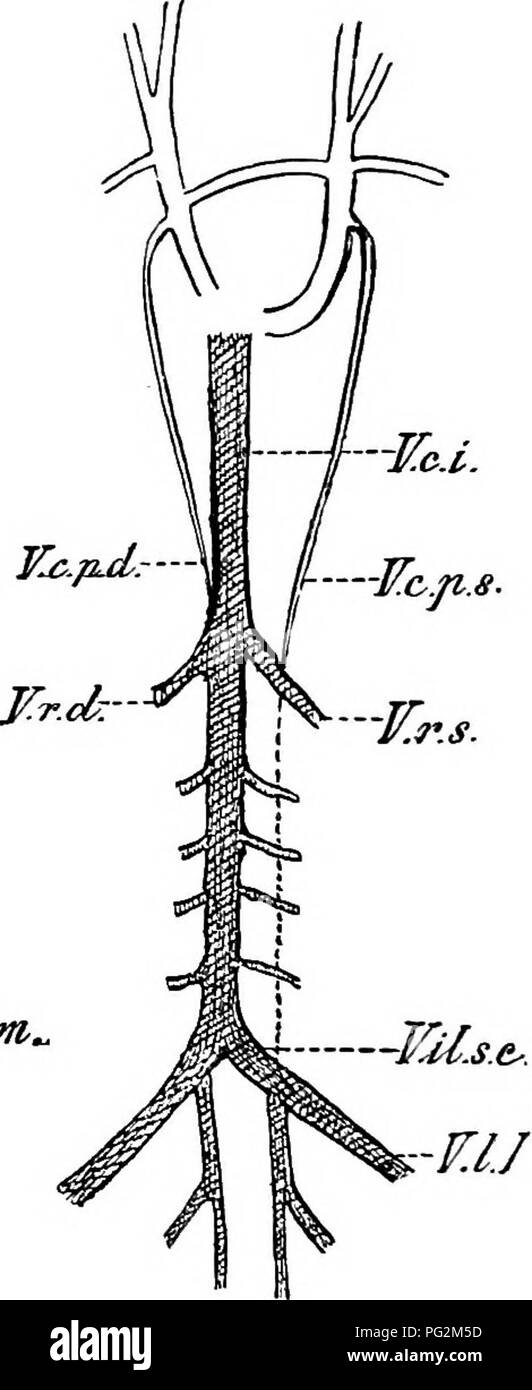 . Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. h-JCc, -TTrs.. 'VUM/tt.eomm, ¥.1.1. Pig. 269.—Diagram showing the Relations of the Posterior Cardinal AND Postcaval Veins in A, the Rabbit, and B, Man. (After Hooh- stetter). V.r.d, r.r..s, renal veins ; F.f?.s.e, common iliac vein; T7./, lumbar vein ; I^.c.r, postcaval; V.c.2^.d, F.c.p.s, right ancUeft posterior cardinals ; V.U.int.comm, conmion internal iliac vein. open into the precavals. In Eeptiles, Birds, Monotremes, and Marsupials, as well as in many Rodents, Insectivores, Bats, and Ungulates, both precavals per Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-the-comparative-anatomy-of-vertebrates-anatomy-comparative-h-jcc-ttrs-vumtteomm-11-pig-269diagram-showing-the-relations-of-the-posterior-cardinal-and-postcaval-veins-in-a-the-rabbit-and-b-man-after-hooh-stetter-vrd-rrs-renal-veins-ffse-common-iliac-vein-t7-lumbar-vein-icr-postcaval-vc2d-fcps-right-ancueft-posterior-cardinals-vuintcomm-conmion-internal-iliac-vein-open-into-the-precavals-in-eeptiles-birds-monotremes-and-marsupials-as-well-as-in-many-rodents-insectivores-bats-and-ungulates-both-precavals-per-image216418649.html
. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. h-JCc, -TTrs.. 'VUM/tt.eomm, ¥.1.1. Pig. 269.—Diagram showing the Relations of the Posterior Cardinal AND Postcaval Veins in A, the Rabbit, and B, Man. (After Hooh- stetter). V.r.d, r.r..s, renal veins ; F.f?.s.e, common iliac vein; T7./, lumbar vein ; I^.c.r, postcaval; V.c.2^.d, F.c.p.s, right ancUeft posterior cardinals ; V.U.int.comm, conmion internal iliac vein. open into the precavals. In Eeptiles, Birds, Monotremes, and Marsupials, as well as in many Rodents, Insectivores, Bats, and Ungulates, both precavals per Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-the-comparative-anatomy-of-vertebrates-anatomy-comparative-h-jcc-ttrs-vumtteomm-11-pig-269diagram-showing-the-relations-of-the-posterior-cardinal-and-postcaval-veins-in-a-the-rabbit-and-b-man-after-hooh-stetter-vrd-rrs-renal-veins-ffse-common-iliac-vein-t7-lumbar-vein-icr-postcaval-vc2d-fcps-right-ancueft-posterior-cardinals-vuintcomm-conmion-internal-iliac-vein-open-into-the-precavals-in-eeptiles-birds-monotremes-and-marsupials-as-well-as-in-many-rodents-insectivores-bats-and-ungulates-both-precavals-per-image216418649.htmlRMPG2M5D–. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. h-JCc, -TTrs.. 'VUM/tt.eomm, ¥.1.1. Pig. 269.—Diagram showing the Relations of the Posterior Cardinal AND Postcaval Veins in A, the Rabbit, and B, Man. (After Hooh- stetter). V.r.d, r.r..s, renal veins ; F.f?.s.e, common iliac vein; T7./, lumbar vein ; I^.c.r, postcaval; V.c.2^.d, F.c.p.s, right ancUeft posterior cardinals ; V.U.int.comm, conmion internal iliac vein. open into the precavals. In Eeptiles, Birds, Monotremes, and Marsupials, as well as in many Rodents, Insectivores, Bats, and Ungulates, both precavals per
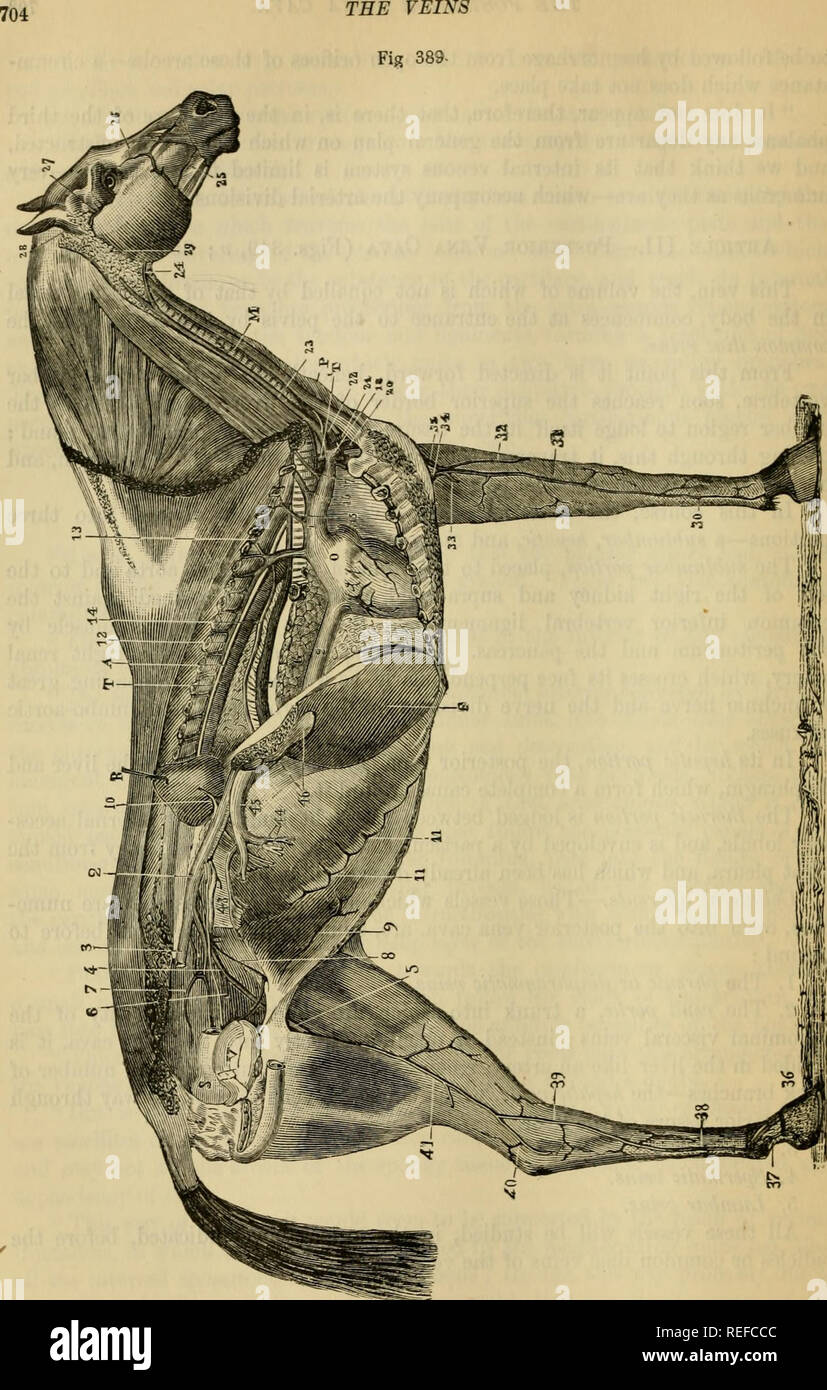 . The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Veterinary anatomy. GENERAL VIEW OF THE VEINS IN THE HORSE. 1, Anterior vena cava; 2, 2, posterior vena cava; 3. right common iliac vein, divided at the ilio- sacral articulation; 4, left common iliac vein; 5, femoral vein; 6, obturator vein; 7, subsacral vein; 8, left spermatic vein; 9, posterior abdominal vein; 10, renal vem: 11, 11, ascending branches of the asternal vein; 12, vena azvgos, with itsjntercostal tranche^, and in hjnt the subdorsal venous branch, 13; 14, oesophageal vein: " ' ' ' "â 15, dorsal or dorso-muscular ve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-veterinary-anatomy-general-view-of-the-veins-in-the-horse-1-anterior-vena-cava-2-2-posterior-vena-cava-3-right-common-iliac-vein-divided-at-the-ilio-sacral-articulation-4-left-common-iliac-vein-5-femoral-vein-6-obturator-vein-7-subsacral-vein-8-left-spermatic-vein-9-posterior-abdominal-vein-10-renal-vem-11-11-ascending-branches-of-the-asternal-vein-12-vena-azvgos-with-itsjntercostal-tranche-and-in-hjnt-the-subdorsal-venous-branch-13-14-oesophageal-vein-quot-quot-15-dorsal-or-dorso-muscular-ve-image232679004.html
. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Veterinary anatomy. GENERAL VIEW OF THE VEINS IN THE HORSE. 1, Anterior vena cava; 2, 2, posterior vena cava; 3. right common iliac vein, divided at the ilio- sacral articulation; 4, left common iliac vein; 5, femoral vein; 6, obturator vein; 7, subsacral vein; 8, left spermatic vein; 9, posterior abdominal vein; 10, renal vem: 11, 11, ascending branches of the asternal vein; 12, vena azvgos, with itsjntercostal tranche^, and in hjnt the subdorsal venous branch, 13; 14, oesophageal vein: " ' ' ' "â 15, dorsal or dorso-muscular ve Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-comparative-anatomy-of-the-domesticated-animals-veterinary-anatomy-general-view-of-the-veins-in-the-horse-1-anterior-vena-cava-2-2-posterior-vena-cava-3-right-common-iliac-vein-divided-at-the-ilio-sacral-articulation-4-left-common-iliac-vein-5-femoral-vein-6-obturator-vein-7-subsacral-vein-8-left-spermatic-vein-9-posterior-abdominal-vein-10-renal-vem-11-11-ascending-branches-of-the-asternal-vein-12-vena-azvgos-with-itsjntercostal-tranche-and-in-hjnt-the-subdorsal-venous-branch-13-14-oesophageal-vein-quot-quot-15-dorsal-or-dorso-muscular-ve-image232679004.htmlRMREFCCC–. The comparative anatomy of the domesticated animals. Veterinary anatomy. GENERAL VIEW OF THE VEINS IN THE HORSE. 1, Anterior vena cava; 2, 2, posterior vena cava; 3. right common iliac vein, divided at the ilio- sacral articulation; 4, left common iliac vein; 5, femoral vein; 6, obturator vein; 7, subsacral vein; 8, left spermatic vein; 9, posterior abdominal vein; 10, renal vem: 11, 11, ascending branches of the asternal vein; 12, vena azvgos, with itsjntercostal tranche^, and in hjnt the subdorsal venous branch, 13; 14, oesophageal vein: " ' ' ' "â 15, dorsal or dorso-muscular ve
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572247.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572247.htmlRF2WJG5YK–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
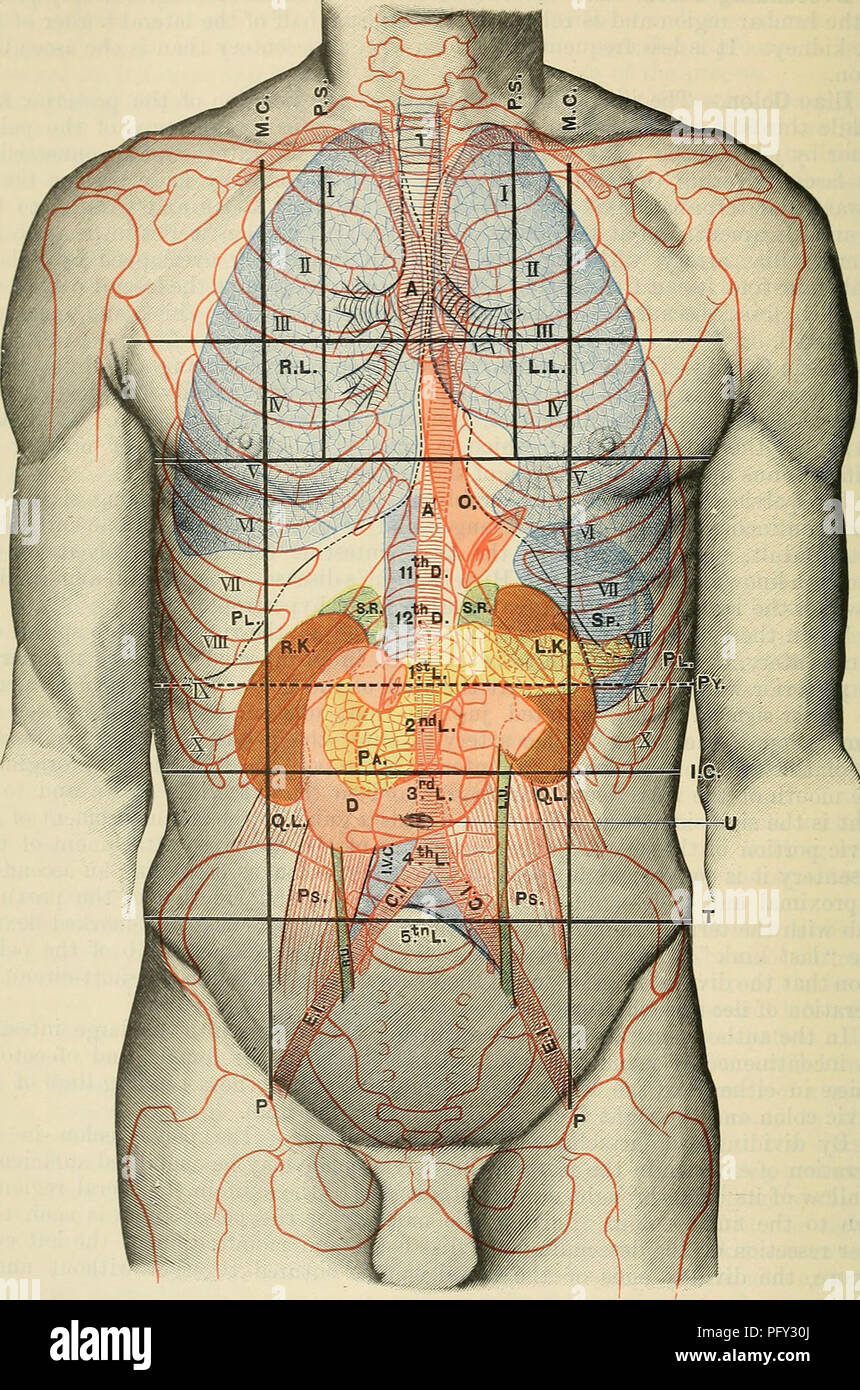 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. U24 SUEFACE AND SUEOICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1106.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-stemal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infra-costal line. T. Inter-tubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Paght lung. L.L. Left lung. Q.L. PI. Pleura. Ps. 0. (Esophagus. R.U. R.K. Right kidney. L.U. L.K. Left kidnev. C.I. Sp. Spleen. E.I. S.R. Suprarenal gland. I.V.( Pa. Pancreas. u. D. Duodenum. Quadratus lumborum. Psoas major. Right ureter. Left ureter. Common iliac ar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-u24-sueface-and-sueoical-anatomy-fig-1106anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-stemal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infra-costal-line-t-inter-tubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-paght-lung-ll-left-lung-ql-pi-pleura-ps-0-esophagus-ru-rk-right-kidney-lu-lk-left-kidnev-ci-sp-spleen-ei-sr-suprarenal-gland-iv-pa-pancreas-u-d-duodenum-quadratus-lumborum-psoas-major-right-ureter-left-ureter-common-iliac-ar-image216339330.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. U24 SUEFACE AND SUEOICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1106.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-stemal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infra-costal line. T. Inter-tubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Paght lung. L.L. Left lung. Q.L. PI. Pleura. Ps. 0. (Esophagus. R.U. R.K. Right kidney. L.U. L.K. Left kidnev. C.I. Sp. Spleen. E.I. S.R. Suprarenal gland. I.V.( Pa. Pancreas. u. D. Duodenum. Quadratus lumborum. Psoas major. Right ureter. Left ureter. Common iliac ar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-u24-sueface-and-sueoical-anatomy-fig-1106anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-stemal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infra-costal-line-t-inter-tubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-paght-lung-ll-left-lung-ql-pi-pleura-ps-0-esophagus-ru-rk-right-kidney-lu-lk-left-kidnev-ci-sp-spleen-ei-sr-suprarenal-gland-iv-pa-pancreas-u-d-duodenum-quadratus-lumborum-psoas-major-right-ureter-left-ureter-common-iliac-ar-image216339330.htmlRMPFY30J–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. U24 SUEFACE AND SUEOICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1106.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-stemal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infra-costal line. T. Inter-tubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Paght lung. L.L. Left lung. Q.L. PI. Pleura. Ps. 0. (Esophagus. R.U. R.K. Right kidney. L.U. L.K. Left kidnev. C.I. Sp. Spleen. E.I. S.R. Suprarenal gland. I.V.( Pa. Pancreas. u. D. Duodenum. Quadratus lumborum. Psoas major. Right ureter. Left ureter. Common iliac ar
 Health knowledge : a thorough and concise knowledge of the prevention, causes, and treatments of disease, simplified for home use . the head andneck, the upper limbs, and the chest wall. The inferior vena cava is formed, at the level of the fifth lum-bar vertebra, by the junction of the two common iliac veins, andascends through the abdomen on the right side of the vertebralcolumn, passes through the diaphragm, and ends in the lowerand back part of the right chamber. It returns the blood fromboth the lower limbs and from the walls and the contents of theabdomen and the pelvis. In addition to t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/health-knowledge-a-thorough-and-concise-knowledge-of-the-prevention-causes-and-treatments-of-disease-simplified-for-home-use-the-head-andneck-the-upper-limbs-and-the-chest-wall-the-inferior-vena-cava-is-formed-at-the-level-of-the-fifth-lum-bar-vertebra-by-the-junction-of-the-two-common-iliac-veins-andascends-through-the-abdomen-on-the-right-side-of-the-vertebralcolumn-passes-through-the-diaphragm-and-ends-in-the-lowerand-back-part-of-the-right-chamber-it-returns-the-blood-fromboth-the-lower-limbs-and-from-the-walls-and-the-contents-of-theabdomen-and-the-pelvis-in-addition-to-t-image339942891.html
Health knowledge : a thorough and concise knowledge of the prevention, causes, and treatments of disease, simplified for home use . the head andneck, the upper limbs, and the chest wall. The inferior vena cava is formed, at the level of the fifth lum-bar vertebra, by the junction of the two common iliac veins, andascends through the abdomen on the right side of the vertebralcolumn, passes through the diaphragm, and ends in the lowerand back part of the right chamber. It returns the blood fromboth the lower limbs and from the walls and the contents of theabdomen and the pelvis. In addition to t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/health-knowledge-a-thorough-and-concise-knowledge-of-the-prevention-causes-and-treatments-of-disease-simplified-for-home-use-the-head-andneck-the-upper-limbs-and-the-chest-wall-the-inferior-vena-cava-is-formed-at-the-level-of-the-fifth-lum-bar-vertebra-by-the-junction-of-the-two-common-iliac-veins-andascends-through-the-abdomen-on-the-right-side-of-the-vertebralcolumn-passes-through-the-diaphragm-and-ends-in-the-lowerand-back-part-of-the-right-chamber-it-returns-the-blood-fromboth-the-lower-limbs-and-from-the-walls-and-the-contents-of-theabdomen-and-the-pelvis-in-addition-to-t-image339942891.htmlRM2AN1MHF–Health knowledge : a thorough and concise knowledge of the prevention, causes, and treatments of disease, simplified for home use . the head andneck, the upper limbs, and the chest wall. The inferior vena cava is formed, at the level of the fifth lum-bar vertebra, by the junction of the two common iliac veins, andascends through the abdomen on the right side of the vertebralcolumn, passes through the diaphragm, and ends in the lowerand back part of the right chamber. It returns the blood fromboth the lower limbs and from the walls and the contents of theabdomen and the pelvis. In addition to t
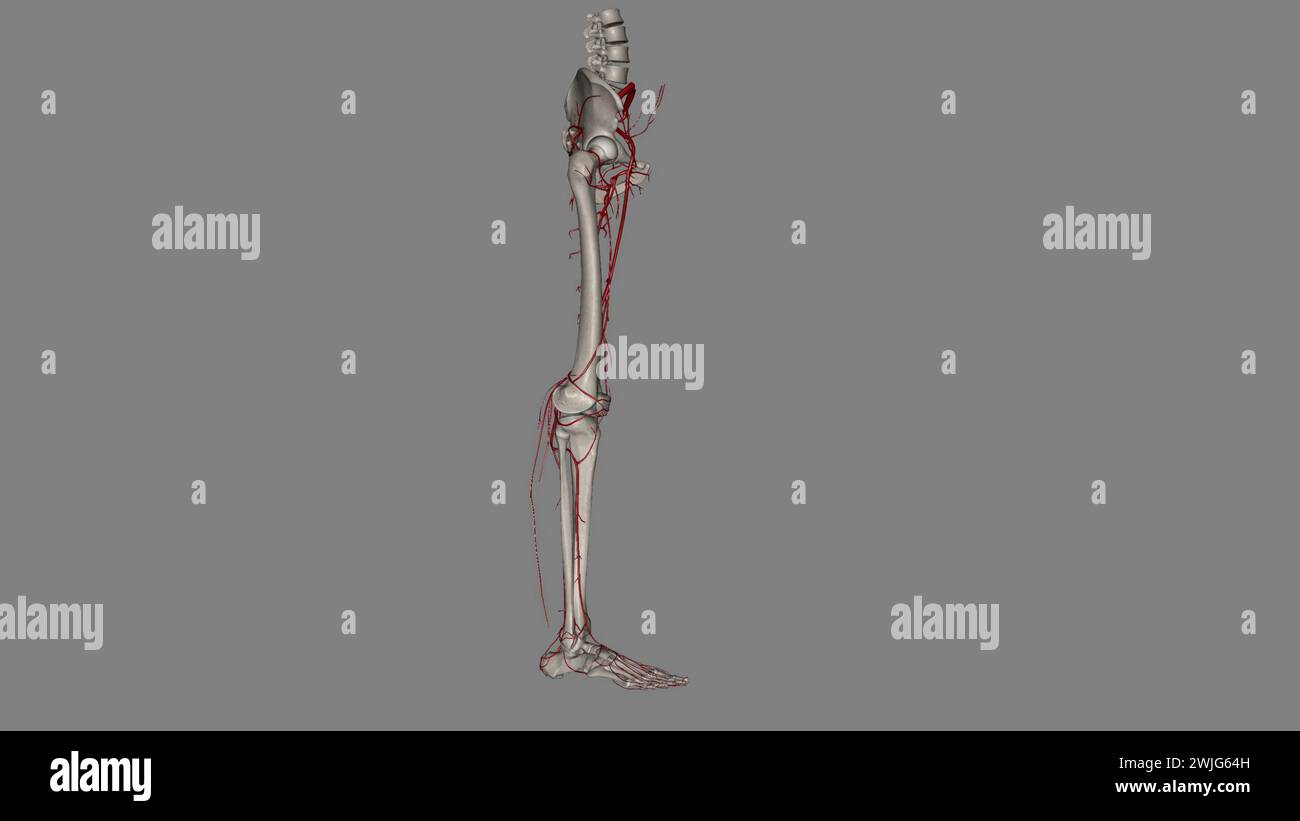 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572385.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572385.htmlRF2WJG64H–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE ABDOMINAL CAVITY. 1413. Fig. 1103.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left Lung. D.C. Descending colon. i.e. Infra-costal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.C. Pelvic colon. Py. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac artery H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I. Exte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-abdominal-cavity-1413-fig-1103anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-ie-infra-costal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-pc-pelvic-colon-py-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-artery-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-exte-image216339345.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE ABDOMINAL CAVITY. 1413. Fig. 1103.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left Lung. D.C. Descending colon. i.e. Infra-costal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.C. Pelvic colon. Py. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac artery H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I. Exte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-abdominal-cavity-1413-fig-1103anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-ie-infra-costal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-pc-pelvic-colon-py-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-artery-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-exte-image216339345.htmlRMPFY315–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE ABDOMINAL CAVITY. 1413. Fig. 1103.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left Lung. D.C. Descending colon. i.e. Infra-costal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.C. Pelvic colon. Py. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac artery H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I. Exte
 Manual of pathology : including bacteriology, the technic of postmortems, and methods of pathologic research . FiG. 146.—Termination of Aorta, the Common Iliac, External and Internal Illacs, Case of Thrombo-arteritis DUE to Para-uterine Inflammation and Extension to the Vessels from AdjacentTissues. A. Thrombus in common iliac artery secondary to and an extension from the primary thrombus in the right internaliliac. B. Point of initial thrombo-arteritis with partial organization of a peripheral gray thrombus; the centralmore recent thrombus was red. Note the great tliickening of the artery and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/manual-of-pathology-including-bacteriology-the-technic-of-postmortems-and-methods-of-pathologic-research-fig-146termination-of-aorta-the-common-iliac-external-and-internal-illacs-case-of-thrombo-arteritis-due-to-para-uterine-inflammation-and-extension-to-the-vessels-from-adjacenttissues-a-thrombus-in-common-iliac-artery-secondary-to-and-an-extension-from-the-primary-thrombus-in-the-right-internaliliac-b-point-of-initial-thrombo-arteritis-with-partial-organization-of-a-peripheral-gray-thrombus-the-centralmore-recent-thrombus-was-red-note-the-great-tliickening-of-the-artery-and-image338450481.html
Manual of pathology : including bacteriology, the technic of postmortems, and methods of pathologic research . FiG. 146.—Termination of Aorta, the Common Iliac, External and Internal Illacs, Case of Thrombo-arteritis DUE to Para-uterine Inflammation and Extension to the Vessels from AdjacentTissues. A. Thrombus in common iliac artery secondary to and an extension from the primary thrombus in the right internaliliac. B. Point of initial thrombo-arteritis with partial organization of a peripheral gray thrombus; the centralmore recent thrombus was red. Note the great tliickening of the artery and Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/manual-of-pathology-including-bacteriology-the-technic-of-postmortems-and-methods-of-pathologic-research-fig-146termination-of-aorta-the-common-iliac-external-and-internal-illacs-case-of-thrombo-arteritis-due-to-para-uterine-inflammation-and-extension-to-the-vessels-from-adjacenttissues-a-thrombus-in-common-iliac-artery-secondary-to-and-an-extension-from-the-primary-thrombus-in-the-right-internaliliac-b-point-of-initial-thrombo-arteritis-with-partial-organization-of-a-peripheral-gray-thrombus-the-centralmore-recent-thrombus-was-red-note-the-great-tliickening-of-the-artery-and-image338450481.htmlRM2AJHN15–Manual of pathology : including bacteriology, the technic of postmortems, and methods of pathologic research . FiG. 146.—Termination of Aorta, the Common Iliac, External and Internal Illacs, Case of Thrombo-arteritis DUE to Para-uterine Inflammation and Extension to the Vessels from AdjacentTissues. A. Thrombus in common iliac artery secondary to and an extension from the primary thrombus in the right internaliliac. B. Point of initial thrombo-arteritis with partial organization of a peripheral gray thrombus; the centralmore recent thrombus was red. Note the great tliickening of the artery and
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570778.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570778.htmlRF2WJG436–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1396 SUKFACE AND SUEGICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1090.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera M.C Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left lung. D.C. Descending colon. 1.0. Infracostal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.O. Pelvic colon. ±*y. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac arterj H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1396-sukface-and-suegical-anatomy-fig-1090anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-10-infracostal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-po-pelvic-colon-y-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-arterj-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-image216339431.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1396 SUKFACE AND SUEGICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1090.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera M.C Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left lung. D.C. Descending colon. 1.0. Infracostal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.O. Pelvic colon. ±*y. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac arterj H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1396-sukface-and-suegical-anatomy-fig-1090anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-10-infracostal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-po-pelvic-colon-y-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-arterj-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-image216339431.htmlRMPFY347–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1396 SUKFACE AND SUEGICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1090.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera M.C Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left lung. D.C. Descending colon. 1.0. Infracostal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.O. Pelvic colon. ±*y. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac arterj H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I
 Modern surgery, general and operative . is the inner border of the psoas magnus muscle. By its side anartery is felt. If the sacrovertebral prominence is above the vessel touched,the artery is the external iliac; othervise it is the common iliac. If the ex-ternal iliac is the vessel first exposed, follow it up to find the common trunk. 490 Diseases and Injuries of the Heart and Vessels When the common iliac is found, separate the fatty tissue about it and passthe ligature from the right toward the left in order to avoid the associated vem. Results: Jos. D. Bryant tells us that this vessel has Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/modern-surgery-general-and-operative-is-the-inner-border-of-the-psoas-magnus-muscle-by-its-side-anartery-is-felt-if-the-sacrovertebral-prominence-is-above-the-vessel-touchedthe-artery-is-the-external-iliac-othervise-it-is-the-common-iliac-if-the-ex-ternal-iliac-is-the-vessel-first-exposed-follow-it-up-to-find-the-common-trunk-490-diseases-and-injuries-of-the-heart-and-vessels-when-the-common-iliac-is-found-separate-the-fatty-tissue-about-it-and-passthe-ligature-from-the-right-toward-the-left-in-order-to-avoid-the-associated-vem-results-jos-d-bryant-tells-us-that-this-vessel-has-image339314671.html
Modern surgery, general and operative . is the inner border of the psoas magnus muscle. By its side anartery is felt. If the sacrovertebral prominence is above the vessel touched,the artery is the external iliac; othervise it is the common iliac. If the ex-ternal iliac is the vessel first exposed, follow it up to find the common trunk. 490 Diseases and Injuries of the Heart and Vessels When the common iliac is found, separate the fatty tissue about it and passthe ligature from the right toward the left in order to avoid the associated vem. Results: Jos. D. Bryant tells us that this vessel has Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/modern-surgery-general-and-operative-is-the-inner-border-of-the-psoas-magnus-muscle-by-its-side-anartery-is-felt-if-the-sacrovertebral-prominence-is-above-the-vessel-touchedthe-artery-is-the-external-iliac-othervise-it-is-the-common-iliac-if-the-ex-ternal-iliac-is-the-vessel-first-exposed-follow-it-up-to-find-the-common-trunk-490-diseases-and-injuries-of-the-heart-and-vessels-when-the-common-iliac-is-found-separate-the-fatty-tissue-about-it-and-passthe-ligature-from-the-right-toward-the-left-in-order-to-avoid-the-associated-vem-results-jos-d-bryant-tells-us-that-this-vessel-has-image339314671.htmlRM2AM1393–Modern surgery, general and operative . is the inner border of the psoas magnus muscle. By its side anartery is felt. If the sacrovertebral prominence is above the vessel touched,the artery is the external iliac; othervise it is the common iliac. If the ex-ternal iliac is the vessel first exposed, follow it up to find the common trunk. 490 Diseases and Injuries of the Heart and Vessels When the common iliac is found, separate the fatty tissue about it and passthe ligature from the right toward the left in order to avoid the associated vem. Results: Jos. D. Bryant tells us that this vessel has
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572143.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572143.htmlRF2WJG5RY–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1-100 SUEFACE AND SUEGIOAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1092.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-sternal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infracostal line. T. Intertubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Eight lung. L.L. Left lung. PI. Pleura. 0. (Esophagus. E.K. Right kidney. L.K. Left kidney. Sp. Spleen. S.R. Suprarenal gland. Pa. Pancreas. D. Duodenum. Q.L. Quadratus lumborum. P.S. Psoas major. , R.U. Right-ureter. L.U. Left ureter. C.I. Common iliac artery. E.I. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1-100-sueface-and-suegioal-anatomy-fig-1092anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-sternal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infracostal-line-t-intertubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-eight-lung-ll-left-lung-pi-pleura-0-esophagus-ek-right-kidney-lk-left-kidney-sp-spleen-sr-suprarenal-gland-pa-pancreas-d-duodenum-ql-quadratus-lumborum-ps-psoas-major-ru-right-ureter-lu-left-ureter-ci-common-iliac-artery-ei-image216339404.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1-100 SUEFACE AND SUEGIOAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1092.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-sternal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infracostal line. T. Intertubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Eight lung. L.L. Left lung. PI. Pleura. 0. (Esophagus. E.K. Right kidney. L.K. Left kidney. Sp. Spleen. S.R. Suprarenal gland. Pa. Pancreas. D. Duodenum. Q.L. Quadratus lumborum. P.S. Psoas major. , R.U. Right-ureter. L.U. Left ureter. C.I. Common iliac artery. E.I. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1-100-sueface-and-suegioal-anatomy-fig-1092anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-sternal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infracostal-line-t-intertubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-eight-lung-ll-left-lung-pi-pleura-0-esophagus-ek-right-kidney-lk-left-kidney-sp-spleen-sr-suprarenal-gland-pa-pancreas-d-duodenum-ql-quadratus-lumborum-ps-psoas-major-ru-right-ureter-lu-left-ureter-ci-common-iliac-artery-ei-image216339404.htmlRMPFY338–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1-100 SUEFACE AND SUEGIOAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1092.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-sternal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infracostal line. T. Intertubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Eight lung. L.L. Left lung. PI. Pleura. 0. (Esophagus. E.K. Right kidney. L.K. Left kidney. Sp. Spleen. S.R. Suprarenal gland. Pa. Pancreas. D. Duodenum. Q.L. Quadratus lumborum. P.S. Psoas major. , R.U. Right-ureter. L.U. Left ureter. C.I. Common iliac artery. E.I.
 The surgeon's handbook on the treatment of wounded in war : a prize essay . to the outer side the anterior cruralnerve covered by the iliac fascia; the genital branch of the genito-crural nerve crosses the artery obliquely. 56 Plate XV. Ligature of the femoral artery (common femoral) below Poupartsligament (right). 1. The cutaneous incision commences at a point midway betweenthe anterior superior spine of the ilium and the symphysis pubis,2mm above Pouparts ligament, and is carried downwards for 5cm. 2. The superficial fascia is divided. 3. The subcutaneous tissue is divided; the lymphatic gl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-surgeons-handbook-on-the-treatment-of-wounded-in-war-a-prize-essay-to-the-outer-side-the-anterior-cruralnerve-covered-by-the-iliac-fascia-the-genital-branch-of-the-genito-crural-nerve-crosses-the-artery-obliquely-56-plate-xv-ligature-of-the-femoral-artery-common-femoral-below-poupartsligament-right-1-the-cutaneous-incision-commences-at-a-point-midway-betweenthe-anterior-superior-spine-of-the-ilium-and-the-symphysis-pubis2mm-above-pouparts-ligament-and-is-carried-downwards-for-5cm-2-the-superficial-fascia-is-divided-3-the-subcutaneous-tissue-is-divided-the-lymphatic-gl-image343314348.html
The surgeon's handbook on the treatment of wounded in war : a prize essay . to the outer side the anterior cruralnerve covered by the iliac fascia; the genital branch of the genito-crural nerve crosses the artery obliquely. 56 Plate XV. Ligature of the femoral artery (common femoral) below Poupartsligament (right). 1. The cutaneous incision commences at a point midway betweenthe anterior superior spine of the ilium and the symphysis pubis,2mm above Pouparts ligament, and is carried downwards for 5cm. 2. The superficial fascia is divided. 3. The subcutaneous tissue is divided; the lymphatic gl Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-surgeons-handbook-on-the-treatment-of-wounded-in-war-a-prize-essay-to-the-outer-side-the-anterior-cruralnerve-covered-by-the-iliac-fascia-the-genital-branch-of-the-genito-crural-nerve-crosses-the-artery-obliquely-56-plate-xv-ligature-of-the-femoral-artery-common-femoral-below-poupartsligament-right-1-the-cutaneous-incision-commences-at-a-point-midway-betweenthe-anterior-superior-spine-of-the-ilium-and-the-symphysis-pubis2mm-above-pouparts-ligament-and-is-carried-downwards-for-5cm-2-the-superficial-fascia-is-divided-3-the-subcutaneous-tissue-is-divided-the-lymphatic-gl-image343314348.htmlRM2AXF8XM–The surgeon's handbook on the treatment of wounded in war : a prize essay . to the outer side the anterior cruralnerve covered by the iliac fascia; the genital branch of the genito-crural nerve crosses the artery obliquely. 56 Plate XV. Ligature of the femoral artery (common femoral) below Poupartsligament (right). 1. The cutaneous incision commences at a point midway betweenthe anterior superior spine of the ilium and the symphysis pubis,2mm above Pouparts ligament, and is carried downwards for 5cm. 2. The superficial fascia is divided. 3. The subcutaneous tissue is divided; the lymphatic gl
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570808.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570808.htmlRF2WJG448–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 A treatise on the science and practice of midwifery . the spine of the mother (Fig. 112). Each of these is sub-divided into two subsidiary classes, according as the head of thechild is placed in the right or left iliac fossa. Thus in dorso-anteriorpositions, if the head lie in the left iliac fossa, the right shoulder ofthe child presents; if in the right iliac fossa, the left. So in dorso-posterior positions, if the head lie in the left iliac fossa, the leftshoulder present; if in the right, the right. Of the two classes thedorso-anterior positions are more common, in the proportion, it issaid Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-the-science-and-practice-of-midwifery-the-spine-of-the-mother-fig-112-each-of-these-is-sub-divided-into-two-subsidiary-classes-according-as-the-head-of-thechild-is-placed-in-the-right-or-left-iliac-fossa-thus-in-dorso-anteriorpositions-if-the-head-lie-in-the-left-iliac-fossa-the-right-shoulder-ofthe-child-presents-if-in-the-right-iliac-fossa-the-left-so-in-dorso-posterior-positions-if-the-head-lie-in-the-left-iliac-fossa-the-leftshoulder-present-if-in-the-right-the-right-of-the-two-classes-thedorso-anterior-positions-are-more-common-in-the-proportion-it-issaid-image338405341.html
A treatise on the science and practice of midwifery . the spine of the mother (Fig. 112). Each of these is sub-divided into two subsidiary classes, according as the head of thechild is placed in the right or left iliac fossa. Thus in dorso-anteriorpositions, if the head lie in the left iliac fossa, the right shoulder ofthe child presents; if in the right iliac fossa, the left. So in dorso-posterior positions, if the head lie in the left iliac fossa, the leftshoulder present; if in the right, the right. Of the two classes thedorso-anterior positions are more common, in the proportion, it issaid Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-the-science-and-practice-of-midwifery-the-spine-of-the-mother-fig-112-each-of-these-is-sub-divided-into-two-subsidiary-classes-according-as-the-head-of-thechild-is-placed-in-the-right-or-left-iliac-fossa-thus-in-dorso-anteriorpositions-if-the-head-lie-in-the-left-iliac-fossa-the-right-shoulder-ofthe-child-presents-if-in-the-right-iliac-fossa-the-left-so-in-dorso-posterior-positions-if-the-head-lie-in-the-left-iliac-fossa-the-leftshoulder-present-if-in-the-right-the-right-of-the-two-classes-thedorso-anterior-positions-are-more-common-in-the-proportion-it-issaid-image338405341.htmlRM2AJFKD1–A treatise on the science and practice of midwifery . the spine of the mother (Fig. 112). Each of these is sub-divided into two subsidiary classes, according as the head of thechild is placed in the right or left iliac fossa. Thus in dorso-anteriorpositions, if the head lie in the left iliac fossa, the right shoulder ofthe child presents; if in the right iliac fossa, the left. So in dorso-posterior positions, if the head lie in the left iliac fossa, the leftshoulder present; if in the right, the right. Of the two classes thedorso-anterior positions are more common, in the proportion, it issaid
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570796.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570796.htmlRF2WJG43T–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 . Manual of operative surgery. /i inches (3 cm.) from the middle line and a trifle to theinner side of the pulsating artery, place the middle of a 2-inch incision throughthe peritoneum alone. By blunt dissection retract the outer lip of the peri-toneal wound and with it the ureter. Expose the common and the externaliliac arteries. A little downwards and inwards expose the internal iliac andligate it at a point a little more than ^^ inch below the bifurcation (Fig. 647).On the left side the ligation is not so easy as on the right, because the originof the meso-sigmoid hides the vessels. Two met Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/manual-of-operative-surgery-i-inches-3-cm-from-the-middle-line-and-a-trifle-to-theinner-side-of-the-pulsating-artery-place-the-middle-of-a-2-inch-incision-throughthe-peritoneum-alone-by-blunt-dissection-retract-the-outer-lip-of-the-peri-toneal-wound-and-with-it-the-ureter-expose-the-common-and-the-externaliliac-arteries-a-little-downwards-and-inwards-expose-the-internal-iliac-andligate-it-at-a-point-a-little-more-than-inch-below-the-bifurcation-fig-647on-the-left-side-the-ligation-is-not-so-easy-as-on-the-right-because-the-originof-the-meso-sigmoid-hides-the-vessels-two-met-image336875437.html
. Manual of operative surgery. /i inches (3 cm.) from the middle line and a trifle to theinner side of the pulsating artery, place the middle of a 2-inch incision throughthe peritoneum alone. By blunt dissection retract the outer lip of the peri-toneal wound and with it the ureter. Expose the common and the externaliliac arteries. A little downwards and inwards expose the internal iliac andligate it at a point a little more than ^^ inch below the bifurcation (Fig. 647).On the left side the ligation is not so easy as on the right, because the originof the meso-sigmoid hides the vessels. Two met Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/manual-of-operative-surgery-i-inches-3-cm-from-the-middle-line-and-a-trifle-to-theinner-side-of-the-pulsating-artery-place-the-middle-of-a-2-inch-incision-throughthe-peritoneum-alone-by-blunt-dissection-retract-the-outer-lip-of-the-peri-toneal-wound-and-with-it-the-ureter-expose-the-common-and-the-externaliliac-arteries-a-little-downwards-and-inwards-expose-the-internal-iliac-andligate-it-at-a-point-a-little-more-than-inch-below-the-bifurcation-fig-647on-the-left-side-the-ligation-is-not-so-easy-as-on-the-right-because-the-originof-the-meso-sigmoid-hides-the-vessels-two-met-image336875437.htmlRM2AG201H–. Manual of operative surgery. /i inches (3 cm.) from the middle line and a trifle to theinner side of the pulsating artery, place the middle of a 2-inch incision throughthe peritoneum alone. By blunt dissection retract the outer lip of the peri-toneal wound and with it the ureter. Expose the common and the externaliliac arteries. A little downwards and inwards expose the internal iliac andligate it at a point a little more than ^^ inch below the bifurcation (Fig. 647).On the left side the ligation is not so easy as on the right, because the originof the meso-sigmoid hides the vessels. Two met
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570807.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596570807.htmlRF2WJG447–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 The anatomist's vade mecum : a system of human anatomy . passing outwards to the right kidney.8. The lumbar arteries. 9. The superior mesenteric artery. 10. The twospermatic arteries. 11. The inferior mesenteric artery. 12. The sacramedia. 13. The common iliacs. 14. The internal iliac of the right side.15. The external iliac artery. 16. The epigastric artery, 17. The circum-flexa ilii artery. 18. The femoral artery. 334 SPLENIC ARTEEY. The Fancreatico-duodenalis curves along the fixed border of theduodenum, partly concealed by the attachment of the pancreas, andis distributed to the pancreas a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomists-vade-mecum-a-system-of-human-anatomy-passing-outwards-to-the-right-kidney8-the-lumbar-arteries-9-the-superior-mesenteric-artery-10-the-twospermatic-arteries-11-the-inferior-mesenteric-artery-12-the-sacramedia-13-the-common-iliacs-14-the-internal-iliac-of-the-right-side15-the-external-iliac-artery-16-the-epigastric-artery-17-the-circum-flexa-ilii-artery-18-the-femoral-artery-334-splenic-arteey-the-fancreatico-duodenalis-curves-along-the-fixed-border-of-theduodenum-partly-concealed-by-the-attachment-of-the-pancreas-andis-distributed-to-the-pancreas-a-image342746965.html
The anatomist's vade mecum : a system of human anatomy . passing outwards to the right kidney.8. The lumbar arteries. 9. The superior mesenteric artery. 10. The twospermatic arteries. 11. The inferior mesenteric artery. 12. The sacramedia. 13. The common iliacs. 14. The internal iliac of the right side.15. The external iliac artery. 16. The epigastric artery, 17. The circum-flexa ilii artery. 18. The femoral artery. 334 SPLENIC ARTEEY. The Fancreatico-duodenalis curves along the fixed border of theduodenum, partly concealed by the attachment of the pancreas, andis distributed to the pancreas a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomists-vade-mecum-a-system-of-human-anatomy-passing-outwards-to-the-right-kidney8-the-lumbar-arteries-9-the-superior-mesenteric-artery-10-the-twospermatic-arteries-11-the-inferior-mesenteric-artery-12-the-sacramedia-13-the-common-iliacs-14-the-internal-iliac-of-the-right-side15-the-external-iliac-artery-16-the-epigastric-artery-17-the-circum-flexa-ilii-artery-18-the-femoral-artery-334-splenic-arteey-the-fancreatico-duodenalis-curves-along-the-fixed-border-of-theduodenum-partly-concealed-by-the-attachment-of-the-pancreas-andis-distributed-to-the-pancreas-a-image342746965.htmlRM2AWHD71–The anatomist's vade mecum : a system of human anatomy . passing outwards to the right kidney.8. The lumbar arteries. 9. The superior mesenteric artery. 10. The twospermatic arteries. 11. The inferior mesenteric artery. 12. The sacramedia. 13. The common iliacs. 14. The internal iliac of the right side.15. The external iliac artery. 16. The epigastric artery, 17. The circum-flexa ilii artery. 18. The femoral artery. 334 SPLENIC ARTEEY. The Fancreatico-duodenalis curves along the fixed border of theduodenum, partly concealed by the attachment of the pancreas, andis distributed to the pancreas a
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572233.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572233.htmlRF2WJG5Y5–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
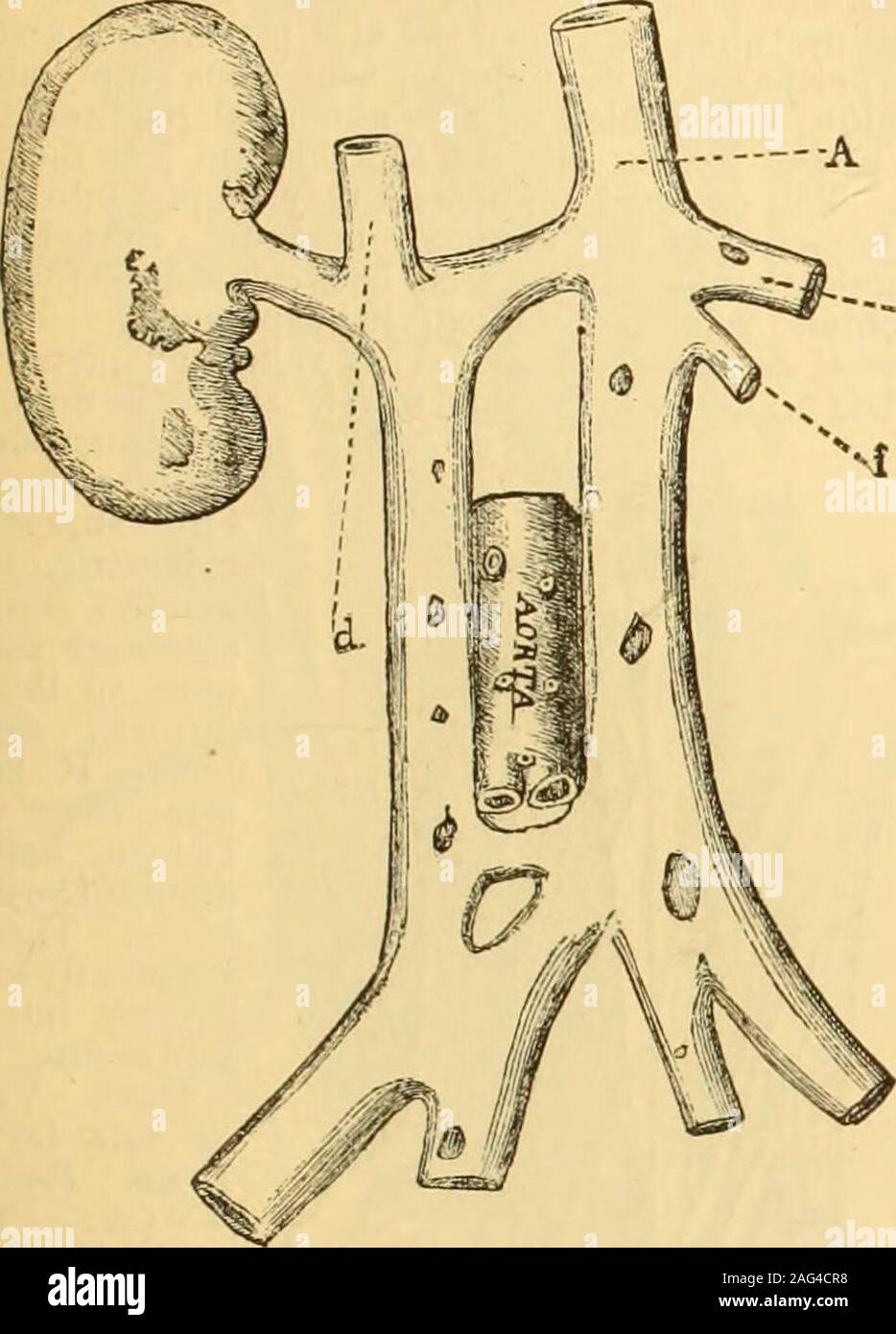 . A Reference handbook of the medical sciences : embracing the entire range of scientific and practical medicine and allied science. Fig. 4515.—The In-ferior Cava con- 608 REFERENCE HANDBOOK OF THE MEDICAL SCIENCES. Veins.Veins. vein has the usual mode of termination in the heart; (b)where it terminates in the superior vena cava. The common iliac veins may not join at the usualplace ; the left common iliac, after sending a branch acrossto join the right, may pass up on the left side of the aorta. —e Fio. 451G.—Case of Double Inferior Vena Cava, the two Common Iliacsbeing joineil by a Transvers Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-reference-handbook-of-the-medical-sciences-embracing-the-entire-range-of-scientific-and-practical-medicine-and-allied-science-fig-4515the-in-ferior-cava-con-608-reference-handbook-of-the-medical-sciences-veinsveins-vein-has-the-usual-mode-of-termination-in-the-heart-bwhere-it-terminates-in-the-superior-vena-cava-the-common-iliac-veins-may-not-join-at-the-usualplace-the-left-common-iliac-after-sending-a-branch-acrossto-join-the-right-may-pass-up-on-the-left-side-of-the-aorta-e-fio-451gcase-of-double-inferior-vena-cava-the-two-common-iliacsbeing-joineil-by-a-transvers-image336929356.html
. A Reference handbook of the medical sciences : embracing the entire range of scientific and practical medicine and allied science. Fig. 4515.—The In-ferior Cava con- 608 REFERENCE HANDBOOK OF THE MEDICAL SCIENCES. Veins.Veins. vein has the usual mode of termination in the heart; (b)where it terminates in the superior vena cava. The common iliac veins may not join at the usualplace ; the left common iliac, after sending a branch acrossto join the right, may pass up on the left side of the aorta. —e Fio. 451G.—Case of Double Inferior Vena Cava, the two Common Iliacsbeing joineil by a Transvers Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-reference-handbook-of-the-medical-sciences-embracing-the-entire-range-of-scientific-and-practical-medicine-and-allied-science-fig-4515the-in-ferior-cava-con-608-reference-handbook-of-the-medical-sciences-veinsveins-vein-has-the-usual-mode-of-termination-in-the-heart-bwhere-it-terminates-in-the-superior-vena-cava-the-common-iliac-veins-may-not-join-at-the-usualplace-the-left-common-iliac-after-sending-a-branch-acrossto-join-the-right-may-pass-up-on-the-left-side-of-the-aorta-e-fio-451gcase-of-double-inferior-vena-cava-the-two-common-iliacsbeing-joineil-by-a-transvers-image336929356.htmlRM2AG4CR8–. A Reference handbook of the medical sciences : embracing the entire range of scientific and practical medicine and allied science. Fig. 4515.—The In-ferior Cava con- 608 REFERENCE HANDBOOK OF THE MEDICAL SCIENCES. Veins.Veins. vein has the usual mode of termination in the heart; (b)where it terminates in the superior vena cava. The common iliac veins may not join at the usualplace ; the left common iliac, after sending a branch acrossto join the right, may pass up on the left side of the aorta. —e Fio. 451G.—Case of Double Inferior Vena Cava, the two Common Iliacsbeing joineil by a Transvers
 The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572127.html
The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-bony-pelvis-and-lower-limbs-receive-their-vascular-supply-from-the-distal-continuations-of-the-right-and-left-common-iliac-arteries-3d-illustratio-image596572127.htmlRF2WJG5RB–The bony pelvis and lower limbs receive their vascular supply from the distal continuations of the right and left common iliac arteries 3d illustratio
 . Outlines of zoology. Fig. 391.—Circulatory system ofthe rabbit. (a) Letters to right— e.c. External carotid.i.e. internal carotid.e.j. External jugular.scl.a. Subclavian artery.scl.v. Subclavian,vein.p.a. Pulmonary artery (cut short).p.v. Pulmonary vein,L.A. Left auricle.L. V. Left ventricle.d.ao. Dorsal aorta.h.v. Hepatic veins.c. Coeliac artery.a.Tn. Anterior mesenteric!s.r.b. Suprarenal body.Lr.a. Left renal artery.l.r.v. Left renal vein. K. Kidney.p,tH. Posterior mesenteric artery(inadvertently shown as ifpaired).spm. Spermatic arteries and veins.c.il.a. Common iliac artery.(/) Letters t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/outlines-of-zoology-fig-391circulatory-system-ofthe-rabbit-a-letters-to-right-ec-external-carotidie-internal-carotidej-external-jugularscla-subclavian-arterysclv-subclavianveinpa-pulmonary-artery-cut-shortpv-pulmonary-veinla-left-auriclel-v-left-ventricledao-dorsal-aortahv-hepatic-veinsc-coeliac-arteryatn-anterior-mesenteric!srb-suprarenal-bodylra-left-renal-arterylrv-left-renal-vein-k-kidneypth-posterior-mesenteric-arteryinadvertently-shown-as-ifpairedspm-spermatic-arteries-and-veinscila-common-iliac-artery-letters-t-image337088097.html
. Outlines of zoology. Fig. 391.—Circulatory system ofthe rabbit. (a) Letters to right— e.c. External carotid.i.e. internal carotid.e.j. External jugular.scl.a. Subclavian artery.scl.v. Subclavian,vein.p.a. Pulmonary artery (cut short).p.v. Pulmonary vein,L.A. Left auricle.L. V. Left ventricle.d.ao. Dorsal aorta.h.v. Hepatic veins.c. Coeliac artery.a.Tn. Anterior mesenteric!s.r.b. Suprarenal body.Lr.a. Left renal artery.l.r.v. Left renal vein. K. Kidney.p,tH. Posterior mesenteric artery(inadvertently shown as ifpaired).spm. Spermatic arteries and veins.c.il.a. Common iliac artery.(/) Letters t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/outlines-of-zoology-fig-391circulatory-system-ofthe-rabbit-a-letters-to-right-ec-external-carotidie-internal-carotidej-external-jugularscla-subclavian-arterysclv-subclavianveinpa-pulmonary-artery-cut-shortpv-pulmonary-veinla-left-auriclel-v-left-ventricledao-dorsal-aortahv-hepatic-veinsc-coeliac-arteryatn-anterior-mesenteric!srb-suprarenal-bodylra-left-renal-arterylrv-left-renal-vein-k-kidneypth-posterior-mesenteric-arteryinadvertently-shown-as-ifpairedspm-spermatic-arteries-and-veinscila-common-iliac-artery-letters-t-image337088097.htmlRM2AGBK8H–. Outlines of zoology. Fig. 391.—Circulatory system ofthe rabbit. (a) Letters to right— e.c. External carotid.i.e. internal carotid.e.j. External jugular.scl.a. Subclavian artery.scl.v. Subclavian,vein.p.a. Pulmonary artery (cut short).p.v. Pulmonary vein,L.A. Left auricle.L. V. Left ventricle.d.ao. Dorsal aorta.h.v. Hepatic veins.c. Coeliac artery.a.Tn. Anterior mesenteric!s.r.b. Suprarenal body.Lr.a. Left renal artery.l.r.v. Left renal vein. K. Kidney.p,tH. Posterior mesenteric artery(inadvertently shown as ifpaired).spm. Spermatic arteries and veins.c.il.a. Common iliac artery.(/) Letters t
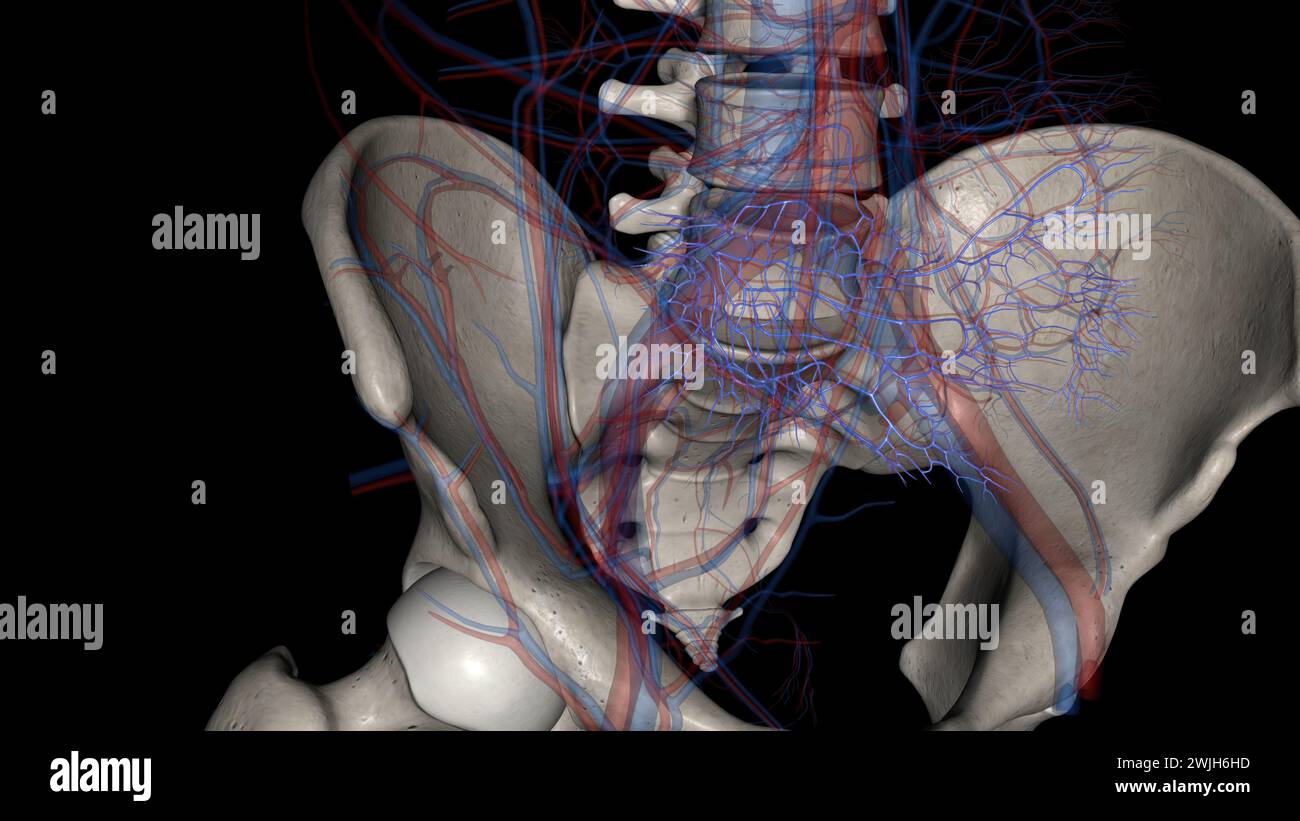 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596594697.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596594697.htmlRF2WJH6HD–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . American practice of surgery ; a complete system of the science and art of surgery . Fig. 55. — Intramuscular Vertical Incisiontlirough the Right Rectus Muscle above theUmbilicus. The fibres of the muscle are sepa-rated and held apart by retractors. 126 AMERICAN PRACTICE OF SURGERY. gall-ducts, kidney, and spleen; the oblique ventral incision is used for exploringthe csecuni and sigmoid, and for ligating the common iliac artery: the oljliqueinguinal cut may be made above or below Pouparts ligament, and is employedin herniotomy, in operations upon the cord, round ligaments, etc.; the obliquel Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/american-practice-of-surgery-a-complete-system-of-the-science-and-art-of-surgery-fig-55-intramuscular-vertical-incisiontlirough-the-right-rectus-muscle-above-theumbilicus-the-fibres-of-the-muscle-are-sepa-rated-and-held-apart-by-retractors-126-american-practice-of-surgery-gall-ducts-kidney-and-spleen-the-oblique-ventral-incision-is-used-for-exploringthe-csecuni-and-sigmoid-and-for-ligating-the-common-iliac-artery-the-oljliqueinguinal-cut-may-be-made-above-or-below-pouparts-ligament-and-is-employedin-herniotomy-in-operations-upon-the-cord-round-ligaments-etc-the-obliquel-image372598071.html
. American practice of surgery ; a complete system of the science and art of surgery . Fig. 55. — Intramuscular Vertical Incisiontlirough the Right Rectus Muscle above theUmbilicus. The fibres of the muscle are sepa-rated and held apart by retractors. 126 AMERICAN PRACTICE OF SURGERY. gall-ducts, kidney, and spleen; the oblique ventral incision is used for exploringthe csecuni and sigmoid, and for ligating the common iliac artery: the oljliqueinguinal cut may be made above or below Pouparts ligament, and is employedin herniotomy, in operations upon the cord, round ligaments, etc.; the obliquel Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/american-practice-of-surgery-a-complete-system-of-the-science-and-art-of-surgery-fig-55-intramuscular-vertical-incisiontlirough-the-right-rectus-muscle-above-theumbilicus-the-fibres-of-the-muscle-are-sepa-rated-and-held-apart-by-retractors-126-american-practice-of-surgery-gall-ducts-kidney-and-spleen-the-oblique-ventral-incision-is-used-for-exploringthe-csecuni-and-sigmoid-and-for-ligating-the-common-iliac-artery-the-oljliqueinguinal-cut-may-be-made-above-or-below-pouparts-ligament-and-is-employedin-herniotomy-in-operations-upon-the-cord-round-ligaments-etc-the-obliquel-image372598071.htmlRM2CJ58HY–. American practice of surgery ; a complete system of the science and art of surgery . Fig. 55. — Intramuscular Vertical Incisiontlirough the Right Rectus Muscle above theUmbilicus. The fibres of the muscle are sepa-rated and held apart by retractors. 126 AMERICAN PRACTICE OF SURGERY. gall-ducts, kidney, and spleen; the oblique ventral incision is used for exploringthe csecuni and sigmoid, and for ligating the common iliac artery: the oljliqueinguinal cut may be made above or below Pouparts ligament, and is employedin herniotomy, in operations upon the cord, round ligaments, etc.; the obliquel
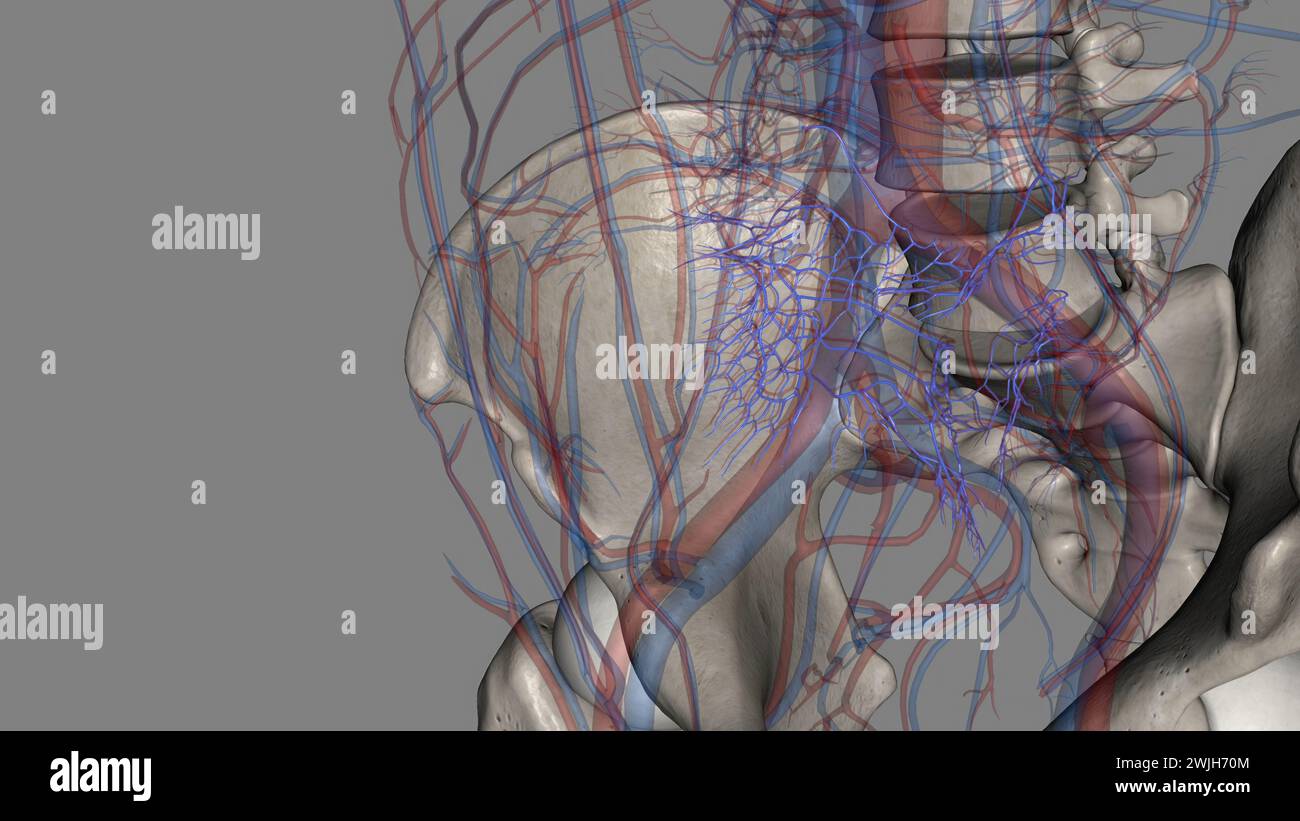 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596595012.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596595012.htmlRF2WJH70M–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . Brow presentation.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) Face presentation. Descent of the fetus.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) forehead is directed toward the mothers left side, the back of the childbeing also on the left. These are termed frouto-anterior and first posi-tions in face presentations, the most common of these being left fronto-anterior. In these positions the chin is upon the right side of thepelvis and obliquely behind, at the right sacro-iliac joint. FACE PRESENTATIONS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. 213 Others prefer to take as a cardinal point t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-obstetrics-for-students-and-practitioners-brow-presentationfaraboeuf-and-varnier-face-presentation-descent-of-the-fetusfaraboeuf-and-varnier-forehead-is-directed-toward-the-mothers-left-side-the-back-of-the-childbeing-also-on-the-left-these-are-termed-frouto-anterior-and-first-posi-tions-in-face-presentations-the-most-common-of-these-being-left-fronto-anterior-in-these-positions-the-chin-is-upon-the-right-side-of-thepelvis-and-obliquely-behind-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-face-presentations-and-their-management-213-others-prefer-to-take-as-a-cardinal-point-t-image376049223.html
. A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . Brow presentation.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) Face presentation. Descent of the fetus.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) forehead is directed toward the mothers left side, the back of the childbeing also on the left. These are termed frouto-anterior and first posi-tions in face presentations, the most common of these being left fronto-anterior. In these positions the chin is upon the right side of thepelvis and obliquely behind, at the right sacro-iliac joint. FACE PRESENTATIONS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. 213 Others prefer to take as a cardinal point t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-obstetrics-for-students-and-practitioners-brow-presentationfaraboeuf-and-varnier-face-presentation-descent-of-the-fetusfaraboeuf-and-varnier-forehead-is-directed-toward-the-mothers-left-side-the-back-of-the-childbeing-also-on-the-left-these-are-termed-frouto-anterior-and-first-posi-tions-in-face-presentations-the-most-common-of-these-being-left-fronto-anterior-in-these-positions-the-chin-is-upon-the-right-side-of-thepelvis-and-obliquely-behind-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-face-presentations-and-their-management-213-others-prefer-to-take-as-a-cardinal-point-t-image376049223.htmlRM2CRPEHB–. A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . Brow presentation.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) Face presentation. Descent of the fetus.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) forehead is directed toward the mothers left side, the back of the childbeing also on the left. These are termed frouto-anterior and first posi-tions in face presentations, the most common of these being left fronto-anterior. In these positions the chin is upon the right side of thepelvis and obliquely behind, at the right sacro-iliac joint. FACE PRESENTATIONS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. 213 Others prefer to take as a cardinal point t
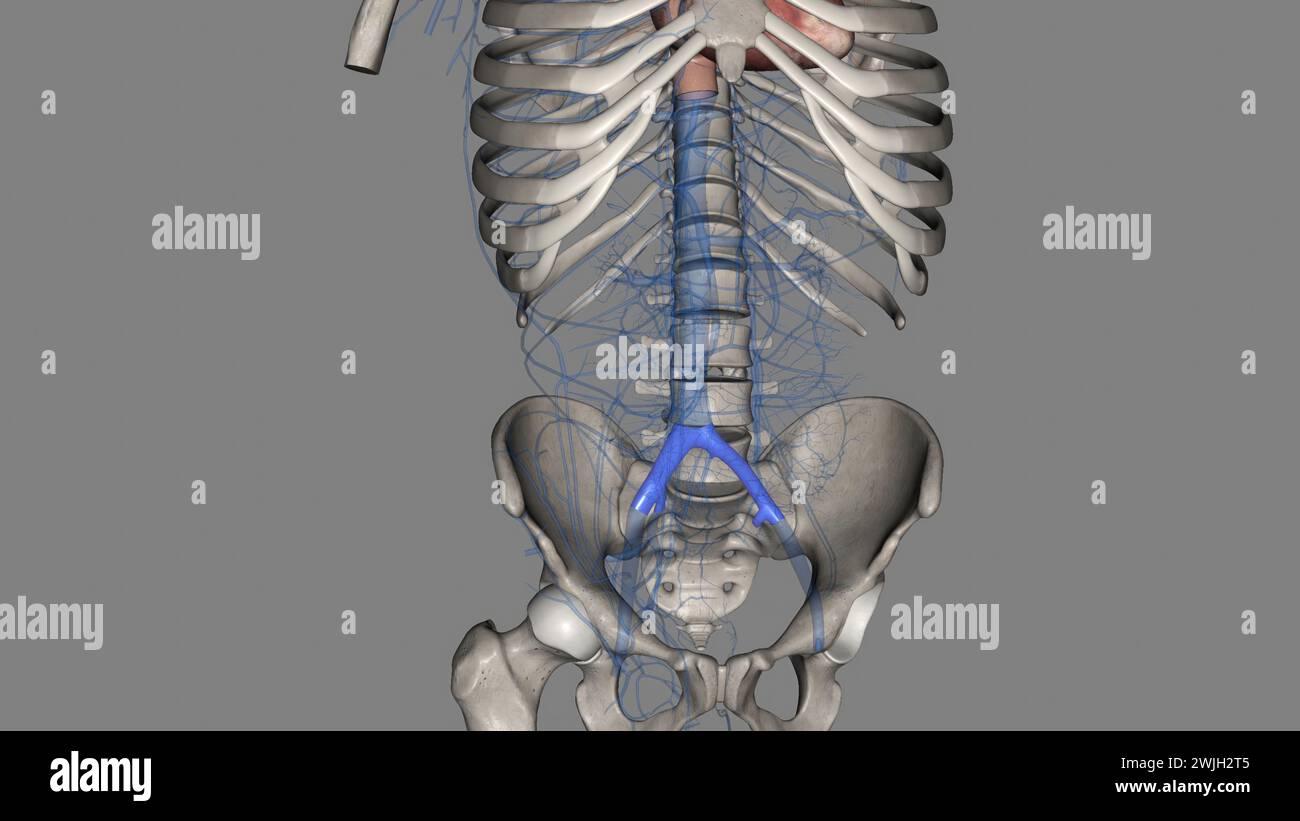 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596591749.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596591749.htmlRF2WJH2T5–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . A practical treatise on medical diagnosis for students and physicians . ac and iliac regions, and reach beyond the middle linetoward the right groin. Sometimes a venous hum can be heard over it.As the result of this enlargement the diaphragm is pushed upward,,increasing the dyspnoea already caused by anaemia, and sometimes in-ducing palpitation. The gastric functions are disturbed from pressure;vomiting and other symptoms of dyspepsia are common. A rise in temperature is a very common symptom. The fever is ofirregular type, usually with nocturnal exacerbations, the temperature notoften risin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-practical-treatise-on-medical-diagnosis-for-students-and-physicians-ac-and-iliac-regions-and-reach-beyond-the-middle-linetoward-the-right-groin-sometimes-a-venous-hum-can-be-heard-over-itas-the-result-of-this-enlargement-the-diaphragm-is-pushed-upwardincreasing-the-dyspnoea-already-caused-by-anaemia-and-sometimes-in-ducing-palpitation-the-gastric-functions-are-disturbed-from-pressurevomiting-and-other-symptoms-of-dyspepsia-are-common-a-rise-in-temperature-is-a-very-common-symptom-the-fever-is-ofirregular-type-usually-with-nocturnal-exacerbations-the-temperature-notoften-risin-image375951893.html
. A practical treatise on medical diagnosis for students and physicians . ac and iliac regions, and reach beyond the middle linetoward the right groin. Sometimes a venous hum can be heard over it.As the result of this enlargement the diaphragm is pushed upward,,increasing the dyspnoea already caused by anaemia, and sometimes in-ducing palpitation. The gastric functions are disturbed from pressure;vomiting and other symptoms of dyspepsia are common. A rise in temperature is a very common symptom. The fever is ofirregular type, usually with nocturnal exacerbations, the temperature notoften risin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-practical-treatise-on-medical-diagnosis-for-students-and-physicians-ac-and-iliac-regions-and-reach-beyond-the-middle-linetoward-the-right-groin-sometimes-a-venous-hum-can-be-heard-over-itas-the-result-of-this-enlargement-the-diaphragm-is-pushed-upwardincreasing-the-dyspnoea-already-caused-by-anaemia-and-sometimes-in-ducing-palpitation-the-gastric-functions-are-disturbed-from-pressurevomiting-and-other-symptoms-of-dyspepsia-are-common-a-rise-in-temperature-is-a-very-common-symptom-the-fever-is-ofirregular-type-usually-with-nocturnal-exacerbations-the-temperature-notoften-risin-image375951893.htmlRM2CRJ2D9–. A practical treatise on medical diagnosis for students and physicians . ac and iliac regions, and reach beyond the middle linetoward the right groin. Sometimes a venous hum can be heard over it.As the result of this enlargement the diaphragm is pushed upward,,increasing the dyspnoea already caused by anaemia, and sometimes in-ducing palpitation. The gastric functions are disturbed from pressure;vomiting and other symptoms of dyspepsia are common. A rise in temperature is a very common symptom. The fever is ofirregular type, usually with nocturnal exacerbations, the temperature notoften risin
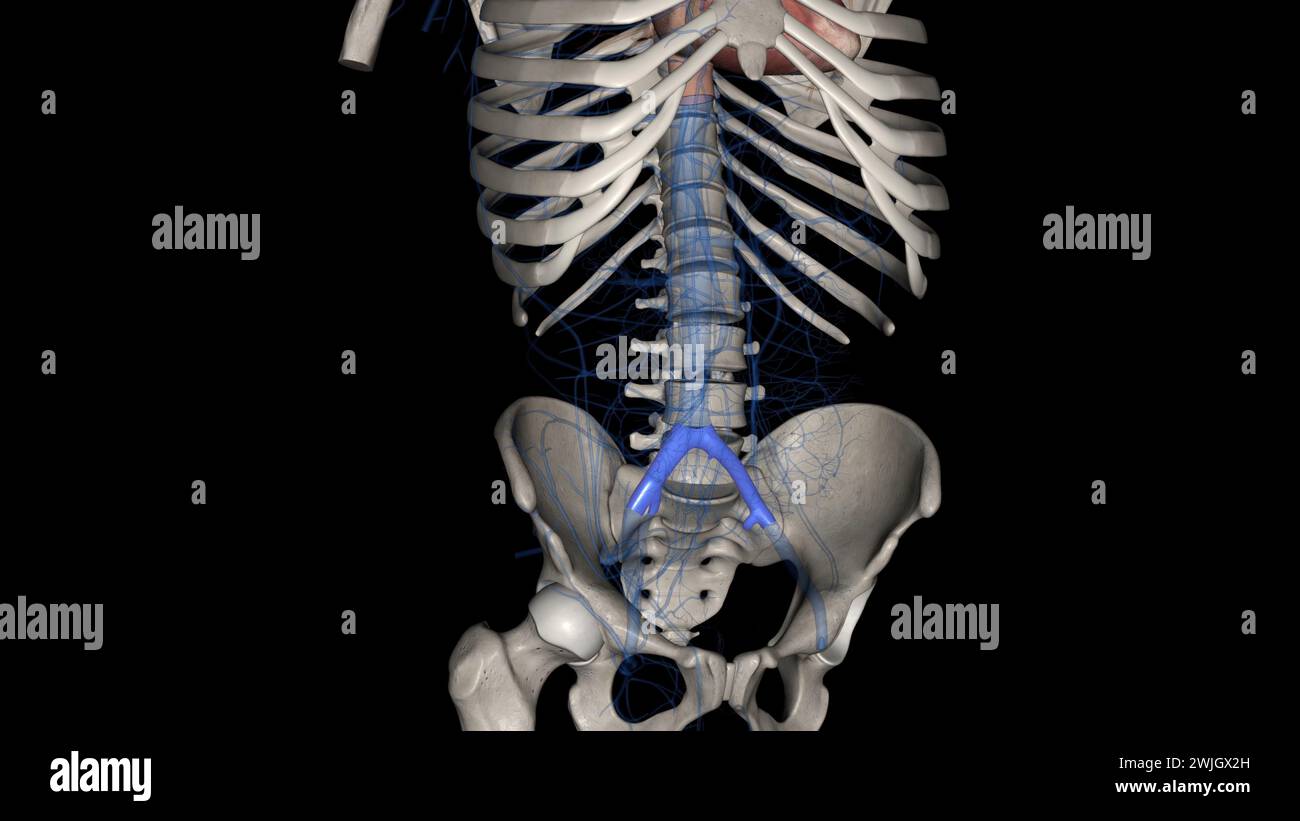 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596588009.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596588009.htmlRF2WJGX2H–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . Brow presentation.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) Face presentation. Descent of the fetus.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) forehead is directed toward the mothers left side, the back of the childbeing also on the left. These are termed frouto-anterior and first posi-tions in face presentations, the most common of these being left fronto-anterior. In these positions the chin is upon the right side of thepelvis and obliquely behind, at the right sacro-iliac joint. FACE PRESENTATIONS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. 213 Others prefer to take as a cardinal point t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-obstetrics-for-students-and-practitioners-brow-presentationfaraboeuf-and-varnier-face-presentation-descent-of-the-fetusfaraboeuf-and-varnier-forehead-is-directed-toward-the-mothers-left-side-the-back-of-the-childbeing-also-on-the-left-these-are-termed-frouto-anterior-and-first-posi-tions-in-face-presentations-the-most-common-of-these-being-left-fronto-anterior-in-these-positions-the-chin-is-upon-the-right-side-of-thepelvis-and-obliquely-behind-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-face-presentations-and-their-management-213-others-prefer-to-take-as-a-cardinal-point-t-image376049216.html
. A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . Brow presentation.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) Face presentation. Descent of the fetus.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) forehead is directed toward the mothers left side, the back of the childbeing also on the left. These are termed frouto-anterior and first posi-tions in face presentations, the most common of these being left fronto-anterior. In these positions the chin is upon the right side of thepelvis and obliquely behind, at the right sacro-iliac joint. FACE PRESENTATIONS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. 213 Others prefer to take as a cardinal point t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-treatise-on-obstetrics-for-students-and-practitioners-brow-presentationfaraboeuf-and-varnier-face-presentation-descent-of-the-fetusfaraboeuf-and-varnier-forehead-is-directed-toward-the-mothers-left-side-the-back-of-the-childbeing-also-on-the-left-these-are-termed-frouto-anterior-and-first-posi-tions-in-face-presentations-the-most-common-of-these-being-left-fronto-anterior-in-these-positions-the-chin-is-upon-the-right-side-of-thepelvis-and-obliquely-behind-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-face-presentations-and-their-management-213-others-prefer-to-take-as-a-cardinal-point-t-image376049216.htmlRM2CRPEH4–. A treatise on obstetrics for students and practitioners . Brow presentation.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) Face presentation. Descent of the fetus.(Faraboeuf and Varnier.) forehead is directed toward the mothers left side, the back of the childbeing also on the left. These are termed frouto-anterior and first posi-tions in face presentations, the most common of these being left fronto-anterior. In these positions the chin is upon the right side of thepelvis and obliquely behind, at the right sacro-iliac joint. FACE PRESENTATIONS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. 213 Others prefer to take as a cardinal point t
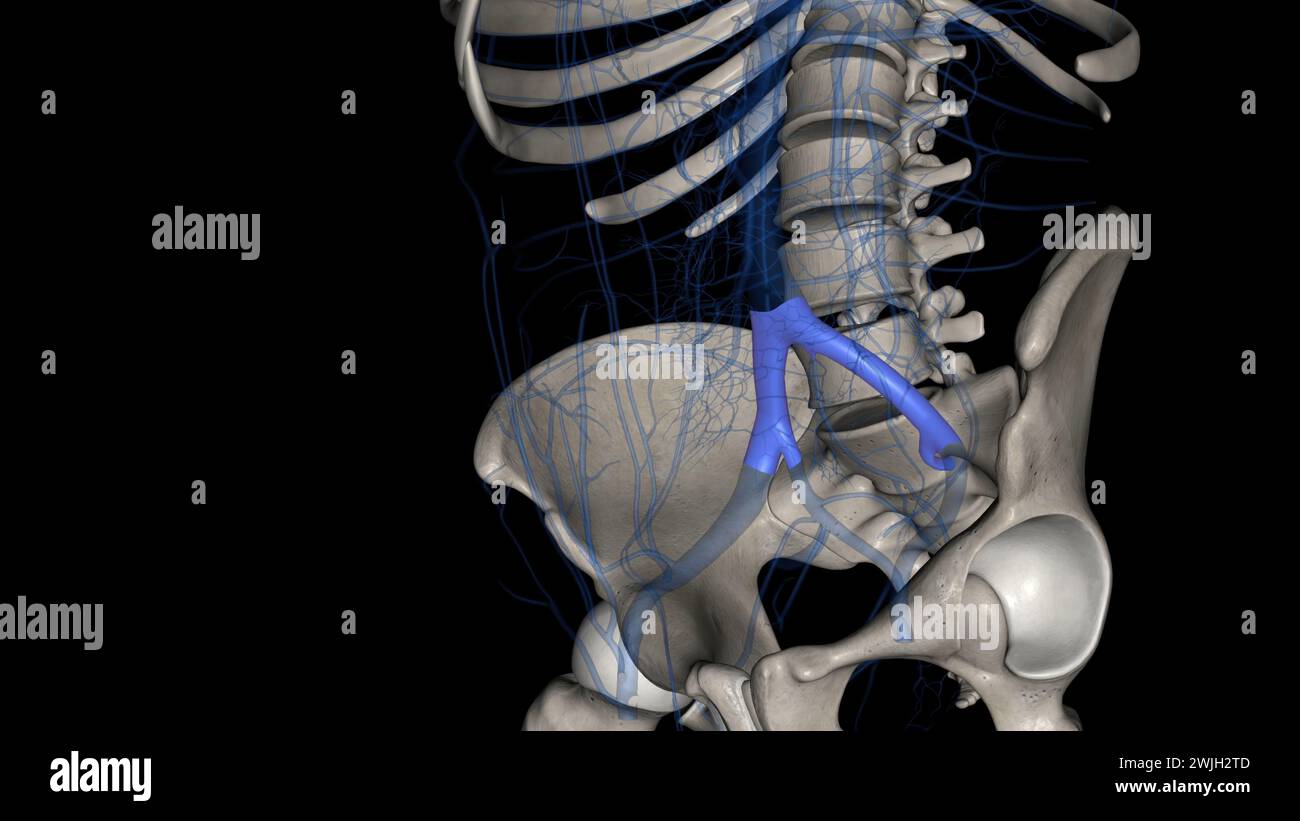 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596591757.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596591757.htmlRF2WJH2TD–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . A text-book of comparative physiology for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine . Cuvieri (precaval veins); E,external iliac arteries; H. G,posterior cardinal vein; Ic,common iliac arteries; If. L.Kill clefts ; R. A, right andleft, rootn of the aorta; S. S,branchial collecting trunksor veins ; ,S7>. subclavian ar-tery ; 8b, subclavian vein;Si, sinus venosus; V, ventri-cle ; VC, anterior cardinalvein; Vm, vitelline veins. left side the nature of the extension of partsalready marked out rather than theformation of entirely new ones. Thefollowing are the principal c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-cuvieri-precaval-veins-eexternal-iliac-arteries-h-gposterior-cardinal-vein-iccommon-iliac-arteries-if-lkill-clefts-r-a-right-andleft-rootn-of-the-aorta-s-sbranchial-collecting-trunksor-veins-s7gt-subclavian-ar-tery-8b-subclavian-veinsi-sinus-venosus-v-ventri-cle-vc-anterior-cardinalvein-vm-vitelline-veins-left-side-the-nature-of-the-extension-of-partsalready-marked-out-rather-than-theformation-of-entirely-new-ones-thefollowing-are-the-principal-c-image372578155.html
. A text-book of comparative physiology for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine . Cuvieri (precaval veins); E,external iliac arteries; H. G,posterior cardinal vein; Ic,common iliac arteries; If. L.Kill clefts ; R. A, right andleft, rootn of the aorta; S. S,branchial collecting trunksor veins ; ,S7>. subclavian ar-tery ; 8b, subclavian vein;Si, sinus venosus; V, ventri-cle ; VC, anterior cardinalvein; Vm, vitelline veins. left side the nature of the extension of partsalready marked out rather than theformation of entirely new ones. Thefollowing are the principal c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-comparative-physiology-for-students-and-practitioners-of-comparative-veterinary-medicine-cuvieri-precaval-veins-eexternal-iliac-arteries-h-gposterior-cardinal-vein-iccommon-iliac-arteries-if-lkill-clefts-r-a-right-andleft-rootn-of-the-aorta-s-sbranchial-collecting-trunksor-veins-s7gt-subclavian-ar-tery-8b-subclavian-veinsi-sinus-venosus-v-ventri-cle-vc-anterior-cardinalvein-vm-vitelline-veins-left-side-the-nature-of-the-extension-of-partsalready-marked-out-rather-than-theformation-of-entirely-new-ones-thefollowing-are-the-principal-c-image372578155.htmlRM2CJ4B6K–. A text-book of comparative physiology for students and practitioners of comparative (veterinary) medicine . Cuvieri (precaval veins); E,external iliac arteries; H. G,posterior cardinal vein; Ic,common iliac arteries; If. L.Kill clefts ; R. A, right andleft, rootn of the aorta; S. S,branchial collecting trunksor veins ; ,S7>. subclavian ar-tery ; 8b, subclavian vein;Si, sinus venosus; V, ventri-cle ; VC, anterior cardinalvein; Vm, vitelline veins. left side the nature of the extension of partsalready marked out rather than theformation of entirely new ones. Thefollowing are the principal c
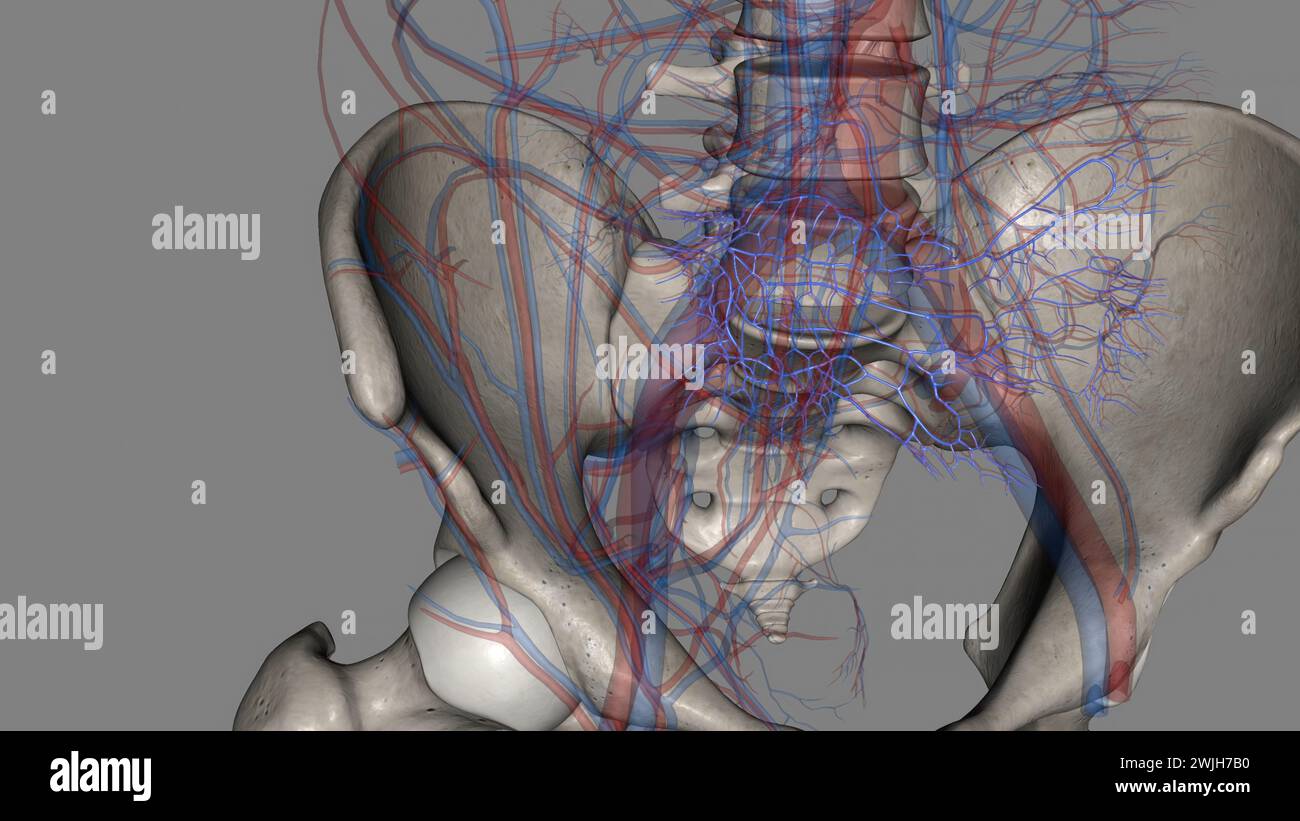 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596595300.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596595300.htmlRF2WJH7B0–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. Fig. 139.—Showing Forma-tion OF THE Large Veins.I, Superior vena cava, 2,3,innominate veins; 4, right sub-clavian; 5,6, int. and ext. jugu-lar veins; 8, inferior vena cava;14, common iliac veins. (Re-maining references not given.)(Holden.) This is formed by the union of thetwo common iliac veins at the right sideof the bifurcation of the adbominal aorta (at the level of thelower border of the fourth lumbar vertebra). It runs upwardthrough the abdomen, on the right side of the aorta, close to thespinal column, to pass through the diaphragm and e Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-fig-139showing-forma-tion-of-the-large-veinsi-superior-vena-cava-23innominate-veins-4-right-sub-clavian-56-int-and-ext-jugu-lar-veins-8-inferior-vena-cava14-common-iliac-veins-re-maining-references-not-givenholden-this-is-formed-by-the-union-of-thetwo-common-iliac-veins-at-the-right-sideof-the-bifurcation-of-the-adbominal-aorta-at-the-level-of-thelower-border-of-the-fourth-lumbar-vertebra-it-runs-upwardthrough-the-abdomen-on-the-right-side-of-the-aorta-close-to-thespinal-column-to-pass-through-the-diaphragm-and-e-image370334417.html
. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. Fig. 139.—Showing Forma-tion OF THE Large Veins.I, Superior vena cava, 2,3,innominate veins; 4, right sub-clavian; 5,6, int. and ext. jugu-lar veins; 8, inferior vena cava;14, common iliac veins. (Re-maining references not given.)(Holden.) This is formed by the union of thetwo common iliac veins at the right sideof the bifurcation of the adbominal aorta (at the level of thelower border of the fourth lumbar vertebra). It runs upwardthrough the abdomen, on the right side of the aorta, close to thespinal column, to pass through the diaphragm and e Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-anatomy-and-physiology-for-nurses-fig-139showing-forma-tion-of-the-large-veinsi-superior-vena-cava-23innominate-veins-4-right-sub-clavian-56-int-and-ext-jugu-lar-veins-8-inferior-vena-cava14-common-iliac-veins-re-maining-references-not-givenholden-this-is-formed-by-the-union-of-thetwo-common-iliac-veins-at-the-right-sideof-the-bifurcation-of-the-adbominal-aorta-at-the-level-of-thelower-border-of-the-fourth-lumbar-vertebra-it-runs-upwardthrough-the-abdomen-on-the-right-side-of-the-aorta-close-to-thespinal-column-to-pass-through-the-diaphragm-and-e-image370334417.htmlRM2CEE595–. Text-book of anatomy and physiology for nurses. Fig. 139.—Showing Forma-tion OF THE Large Veins.I, Superior vena cava, 2,3,innominate veins; 4, right sub-clavian; 5,6, int. and ext. jugu-lar veins; 8, inferior vena cava;14, common iliac veins. (Re-maining references not given.)(Holden.) This is formed by the union of thetwo common iliac veins at the right sideof the bifurcation of the adbominal aorta (at the level of thelower border of the fourth lumbar vertebra). It runs upwardthrough the abdomen, on the right side of the aorta, close to thespinal column, to pass through the diaphragm and e
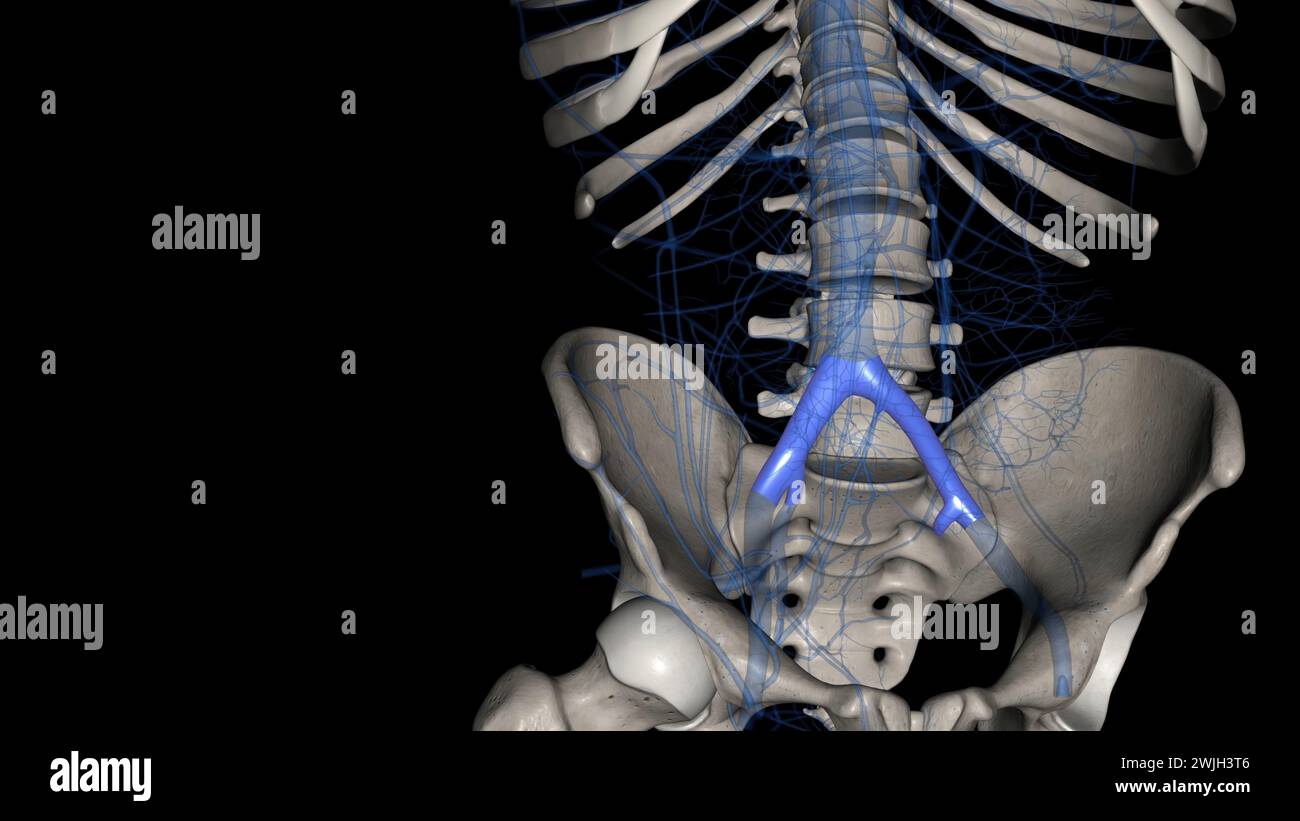 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596592534.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596592534.htmlRF2WJH3T6–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. 182 PELVIS. line of thoracic vertebra to the right side, and is calculated to keep the line of the whole spinal column in equivalent relation to the di- rect and perpendicular line of gravity. It is an interesting question, how far this common ten- dency of the lumbar curve influences the po- sition of the fetal head, by affording more room for the sinciput at the right sacro-iliac joint, and determining its long axis in the left oblique diameter, which is generally allowed to be the most frequent presentation. In by Air Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-182-pelvis-line-of-thoracic-vertebra-to-the-right-side-and-is-calculated-to-keep-the-line-of-the-whole-spinal-column-in-equivalent-relation-to-the-di-rect-and-perpendicular-line-of-gravity-it-is-an-interesting-question-how-far-this-common-ten-dency-of-the-lumbar-curve-influences-the-po-sition-of-the-fetal-head-by-affording-more-room-for-the-sinciput-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-and-determining-its-long-axis-in-the-left-oblique-diameter-which-is-generally-allowed-to-be-the-most-frequent-presentation-in-by-air-image231851471.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. 182 PELVIS. line of thoracic vertebra to the right side, and is calculated to keep the line of the whole spinal column in equivalent relation to the di- rect and perpendicular line of gravity. It is an interesting question, how far this common ten- dency of the lumbar curve influences the po- sition of the fetal head, by affording more room for the sinciput at the right sacro-iliac joint, and determining its long axis in the left oblique diameter, which is generally allowed to be the most frequent presentation. In by Air Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-182-pelvis-line-of-thoracic-vertebra-to-the-right-side-and-is-calculated-to-keep-the-line-of-the-whole-spinal-column-in-equivalent-relation-to-the-di-rect-and-perpendicular-line-of-gravity-it-is-an-interesting-question-how-far-this-common-ten-dency-of-the-lumbar-curve-influences-the-po-sition-of-the-fetal-head-by-affording-more-room-for-the-sinciput-at-the-right-sacro-iliac-joint-and-determining-its-long-axis-in-the-left-oblique-diameter-which-is-generally-allowed-to-be-the-most-frequent-presentation-in-by-air-image231851471.htmlRMRD5MWK–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. 182 PELVIS. line of thoracic vertebra to the right side, and is calculated to keep the line of the whole spinal column in equivalent relation to the di- rect and perpendicular line of gravity. It is an interesting question, how far this common ten- dency of the lumbar curve influences the po- sition of the fetal head, by affording more room for the sinciput at the right sacro-iliac joint, and determining its long axis in the left oblique diameter, which is generally allowed to be the most frequent presentation. In by Air
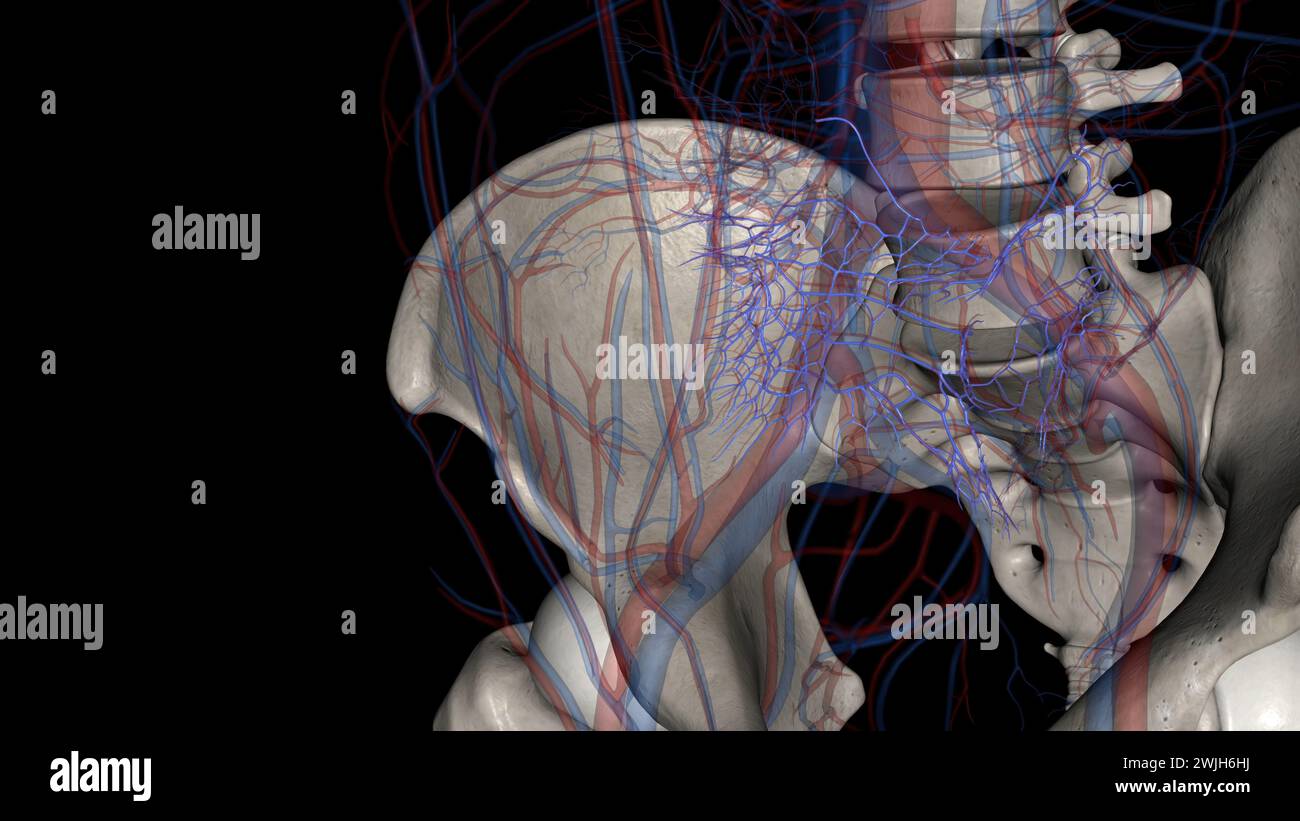 The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596594702.html
The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-common-iliac-vein-is-formed-by-the-unification-of-the-internal-and-external-iliac-veins-3d-illustration-image596594702.htmlRF2WJH6HJ–The common iliac vein is formed by the unification of the internal and external iliac veins 3d illustration
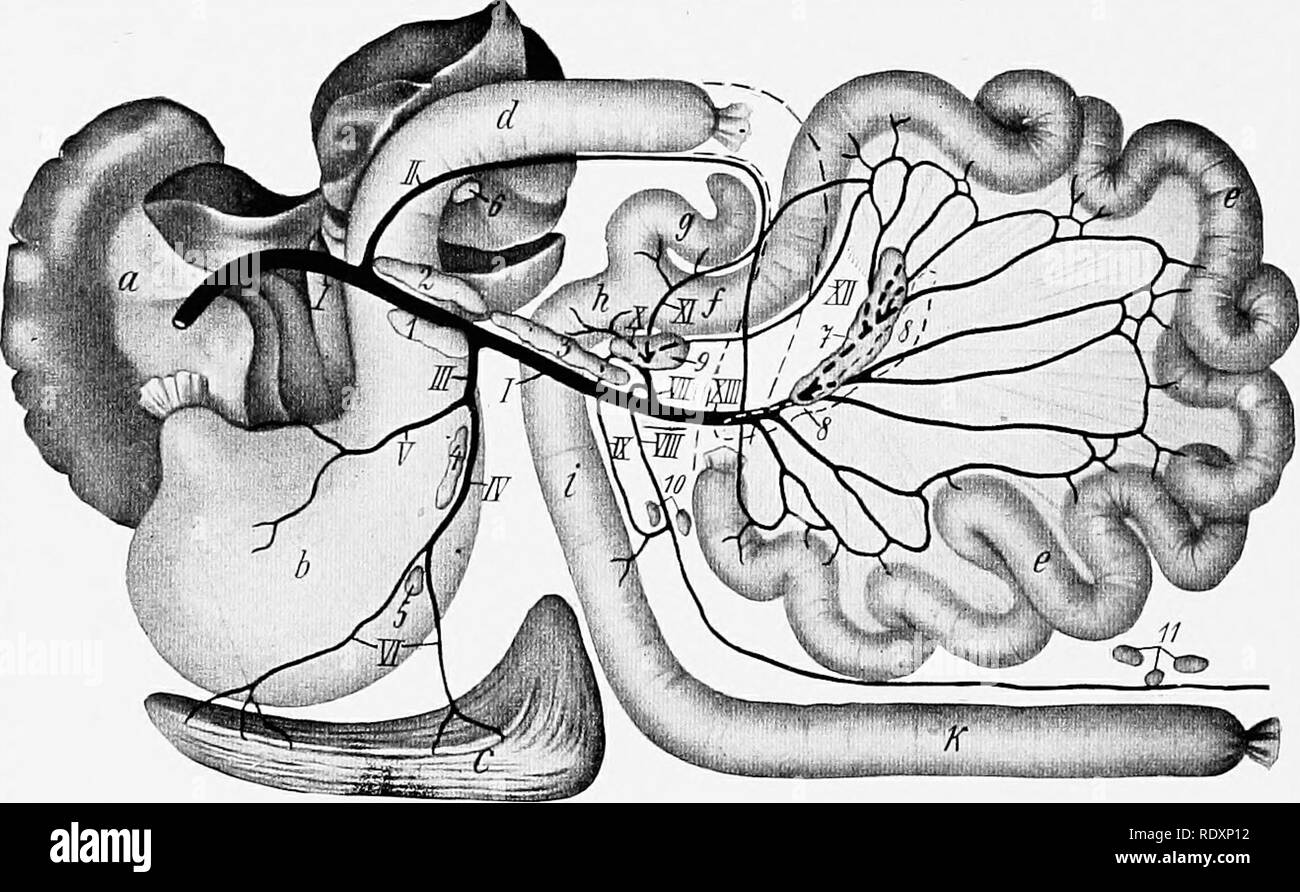 . The anatomy of the domestic animals . Veterinary anatomy. 758 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OF THE DOG The liombar lymph glands are situated in the sublumbar region around and between the aorta and posterior vena cava. Most of them are very small and are difficult to find in the fat in which they are usually embedded. Their number is very variable; as many as fifteen have been counted. Usually two large internal iliac lymph glands are present. The right one lies along the posterior part of the posterior vena cava and the common iliac vein; the left one is similarly placed in relation to the aorta and l Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-domestic-animals-veterinary-anatomy-758-circulatory-system-of-the-dog-the-liombar-lymph-glands-are-situated-in-the-sublumbar-region-around-and-between-the-aorta-and-posterior-vena-cava-most-of-them-are-very-small-and-are-difficult-to-find-in-the-fat-in-which-they-are-usually-embedded-their-number-is-very-variable-as-many-as-fifteen-have-been-counted-usually-two-large-internal-iliac-lymph-glands-are-present-the-right-one-lies-along-the-posterior-part-of-the-posterior-vena-cava-and-the-common-iliac-vein-the-left-one-is-similarly-placed-in-relation-to-the-aorta-and-l-image232313342.html
. The anatomy of the domestic animals . Veterinary anatomy. 758 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OF THE DOG The liombar lymph glands are situated in the sublumbar region around and between the aorta and posterior vena cava. Most of them are very small and are difficult to find in the fat in which they are usually embedded. Their number is very variable; as many as fifteen have been counted. Usually two large internal iliac lymph glands are present. The right one lies along the posterior part of the posterior vena cava and the common iliac vein; the left one is similarly placed in relation to the aorta and l Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-domestic-animals-veterinary-anatomy-758-circulatory-system-of-the-dog-the-liombar-lymph-glands-are-situated-in-the-sublumbar-region-around-and-between-the-aorta-and-posterior-vena-cava-most-of-them-are-very-small-and-are-difficult-to-find-in-the-fat-in-which-they-are-usually-embedded-their-number-is-very-variable-as-many-as-fifteen-have-been-counted-usually-two-large-internal-iliac-lymph-glands-are-present-the-right-one-lies-along-the-posterior-part-of-the-posterior-vena-cava-and-the-common-iliac-vein-the-left-one-is-similarly-placed-in-relation-to-the-aorta-and-l-image232313342.htmlRMRDXP12–. The anatomy of the domestic animals . Veterinary anatomy. 758 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OF THE DOG The liombar lymph glands are situated in the sublumbar region around and between the aorta and posterior vena cava. Most of them are very small and are difficult to find in the fat in which they are usually embedded. Their number is very variable; as many as fifteen have been counted. Usually two large internal iliac lymph glands are present. The right one lies along the posterior part of the posterior vena cava and the common iliac vein; the left one is similarly placed in relation to the aorta and l
 . The anatomy of the human body. Human anatomy; Anatomy. THE INTERNAT. ILIAC ARTERY. 553 is entirely wanting ; the aorta dividing into three branches, two on the right, viz., the in- ternal and external iliacs, and one on the left, viz., the common iliac, which is distributed in the usual manner. In this case the descending aorta resembled, to a certain extent, the ascending aprta, and, like it, gave off three trunks Relations.—They are covered by, and loosely connected with, the peritoneum; they are crossed by the ureters and the spermatic vessels, besides which, the left common il- iac is cr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-human-body-human-anatomy-anatomy-the-internat-iliac-artery-553-is-entirely-wanting-the-aorta-dividing-into-three-branches-two-on-the-right-viz-the-in-ternal-and-external-iliacs-and-one-on-the-left-viz-the-common-iliac-which-is-distributed-in-the-usual-manner-in-this-case-the-descending-aorta-resembled-to-a-certain-extent-the-ascending-aprta-and-like-it-gave-off-three-trunks-relationsthey-are-covered-by-and-loosely-connected-with-the-peritoneum-they-are-crossed-by-the-ureters-and-the-spermatic-vessels-besides-which-the-left-common-il-iac-is-cr-image236759535.html
. The anatomy of the human body. Human anatomy; Anatomy. THE INTERNAT. ILIAC ARTERY. 553 is entirely wanting ; the aorta dividing into three branches, two on the right, viz., the in- ternal and external iliacs, and one on the left, viz., the common iliac, which is distributed in the usual manner. In this case the descending aorta resembled, to a certain extent, the ascending aprta, and, like it, gave off three trunks Relations.—They are covered by, and loosely connected with, the peritoneum; they are crossed by the ureters and the spermatic vessels, besides which, the left common il- iac is cr Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-human-body-human-anatomy-anatomy-the-internat-iliac-artery-553-is-entirely-wanting-the-aorta-dividing-into-three-branches-two-on-the-right-viz-the-in-ternal-and-external-iliacs-and-one-on-the-left-viz-the-common-iliac-which-is-distributed-in-the-usual-manner-in-this-case-the-descending-aorta-resembled-to-a-certain-extent-the-ascending-aprta-and-like-it-gave-off-three-trunks-relationsthey-are-covered-by-and-loosely-connected-with-the-peritoneum-they-are-crossed-by-the-ureters-and-the-spermatic-vessels-besides-which-the-left-common-il-iac-is-cr-image236759535.htmlRMRN595K–. The anatomy of the human body. Human anatomy; Anatomy. THE INTERNAT. ILIAC ARTERY. 553 is entirely wanting ; the aorta dividing into three branches, two on the right, viz., the in- ternal and external iliacs, and one on the left, viz., the common iliac, which is distributed in the usual manner. In this case the descending aorta resembled, to a certain extent, the ascending aprta, and, like it, gave off three trunks Relations.—They are covered by, and loosely connected with, the peritoneum; they are crossed by the ureters and the spermatic vessels, besides which, the left common il- iac is cr
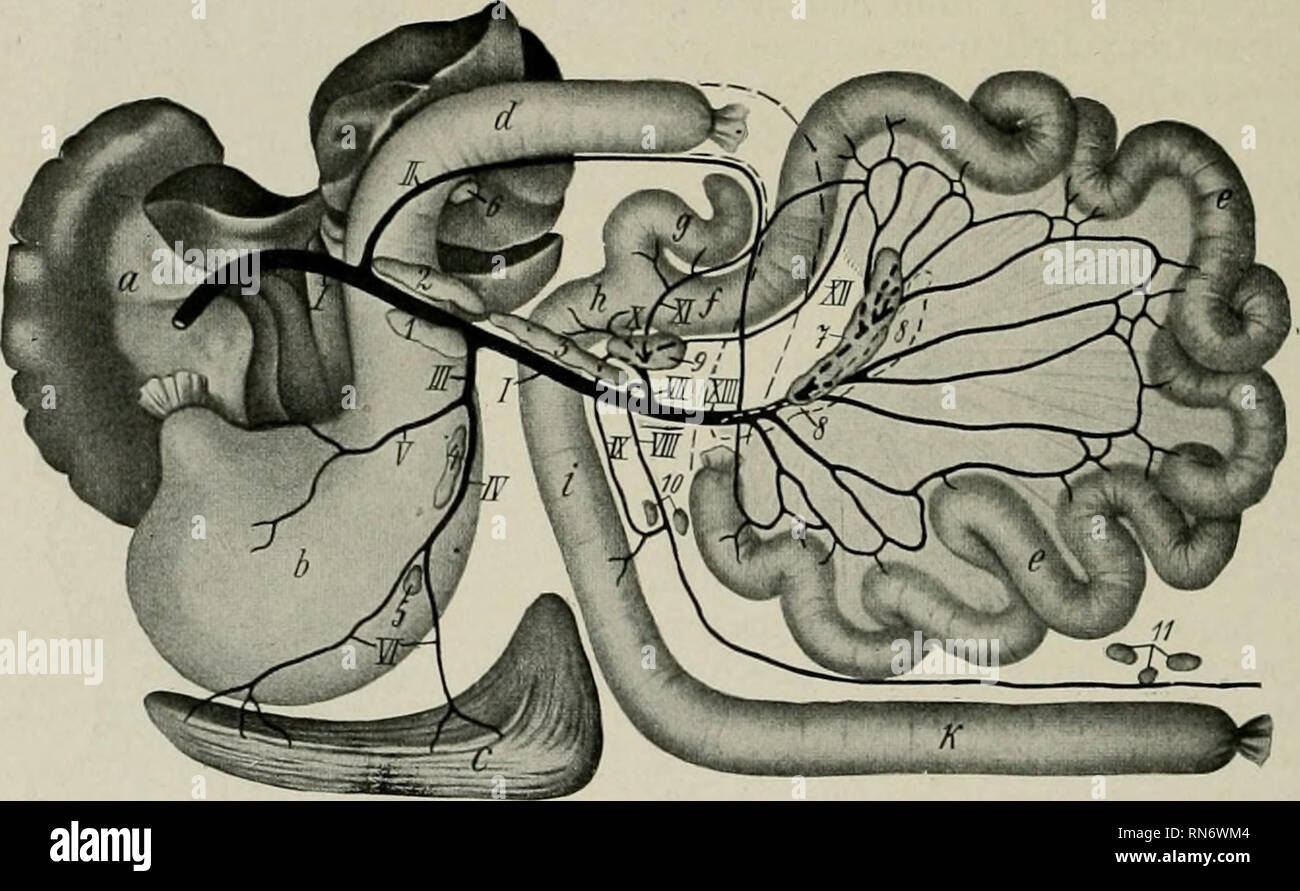 . The anatomy of the domestic animals. Veterinary anatomy. 758 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OP THE DOG The lumbar lymph glands are situated in the sublumbar region around and between the aorta and posterior vena cava. Most of them are very small and are difficult to find in the fat in which they are usually embedded. Their number is very variable; as many as fifteen have been counted. Usually two large internal iliac lymph glands are present. The right one lies along the posterior part of the posterior vena cava and the common iliac vein; the left one is similarly placed in relation to the aorta and lef Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-domestic-animals-veterinary-anatomy-758-circulatory-system-op-the-dog-the-lumbar-lymph-glands-are-situated-in-the-sublumbar-region-around-and-between-the-aorta-and-posterior-vena-cava-most-of-them-are-very-small-and-are-difficult-to-find-in-the-fat-in-which-they-are-usually-embedded-their-number-is-very-variable-as-many-as-fifteen-have-been-counted-usually-two-large-internal-iliac-lymph-glands-are-present-the-right-one-lies-along-the-posterior-part-of-the-posterior-vena-cava-and-the-common-iliac-vein-the-left-one-is-similarly-placed-in-relation-to-the-aorta-and-lef-image236794436.html
. The anatomy of the domestic animals. Veterinary anatomy. 758 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OP THE DOG The lumbar lymph glands are situated in the sublumbar region around and between the aorta and posterior vena cava. Most of them are very small and are difficult to find in the fat in which they are usually embedded. Their number is very variable; as many as fifteen have been counted. Usually two large internal iliac lymph glands are present. The right one lies along the posterior part of the posterior vena cava and the common iliac vein; the left one is similarly placed in relation to the aorta and lef Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-anatomy-of-the-domestic-animals-veterinary-anatomy-758-circulatory-system-op-the-dog-the-lumbar-lymph-glands-are-situated-in-the-sublumbar-region-around-and-between-the-aorta-and-posterior-vena-cava-most-of-them-are-very-small-and-are-difficult-to-find-in-the-fat-in-which-they-are-usually-embedded-their-number-is-very-variable-as-many-as-fifteen-have-been-counted-usually-two-large-internal-iliac-lymph-glands-are-present-the-right-one-lies-along-the-posterior-part-of-the-posterior-vena-cava-and-the-common-iliac-vein-the-left-one-is-similarly-placed-in-relation-to-the-aorta-and-lef-image236794436.htmlRMRN6WM4–. The anatomy of the domestic animals. Veterinary anatomy. 758 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OP THE DOG The lumbar lymph glands are situated in the sublumbar region around and between the aorta and posterior vena cava. Most of them are very small and are difficult to find in the fat in which they are usually embedded. Their number is very variable; as many as fifteen have been counted. Usually two large internal iliac lymph glands are present. The right one lies along the posterior part of the posterior vena cava and the common iliac vein; the left one is similarly placed in relation to the aorta and lef
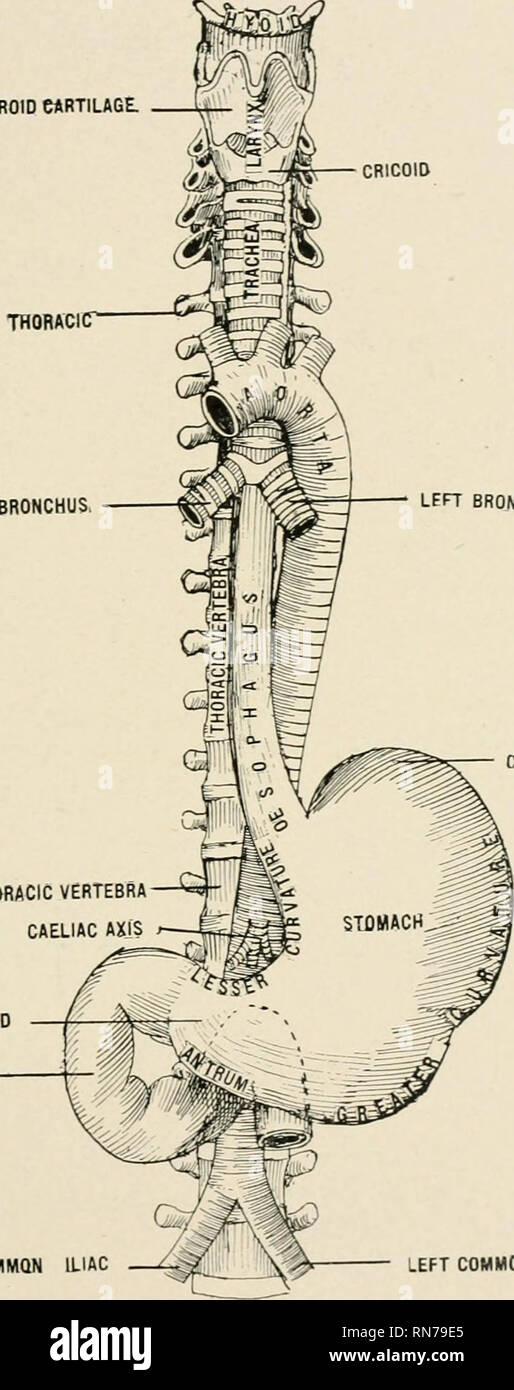 . Anatomy in a nutshell : a treatise on human anatomy in its relation to osteopathy. Human anatomy; Osteopathic medicine; Osteopathic Medicine; Anatomy. ANATOMY IN A NUTSHELL. 325 closed because they are surrounded by the capsule of Glisson while the hepatic veins gape open, being adherent to the liver substance. The gall-bladder retains the bile and is situated between the right and PLATE CXLVI. THYROID CARTILAGE. CRICOID FIRST THORACICT RIGHT BRONCHUS LFFT BRONCHUS. CASuiAC END TflflFTH THORACIC VERTEBRA CAELIAC AXIS PYLORIC END DUODENUM 1IGHT COMMON ILIAC LEFT COMMON ILIAC The (Esophagus an Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-in-a-nutshell-a-treatise-on-human-anatomy-in-its-relation-to-osteopathy-human-anatomy-osteopathic-medicine-osteopathic-medicine-anatomy-anatomy-in-a-nutshell-325-closed-because-they-are-surrounded-by-the-capsule-of-glisson-while-the-hepatic-veins-gape-open-being-adherent-to-the-liver-substance-the-gall-bladder-retains-the-bile-and-is-situated-between-the-right-and-plate-cxlvi-thyroid-cartilage-cricoid-first-thoracict-right-bronchus-lfft-bronchus-casuiac-end-tflflfth-thoracic-vertebra-caeliac-axis-pyloric-end-duodenum-1ight-common-iliac-left-common-iliac-the-esophagus-an-image236803677.html
. Anatomy in a nutshell : a treatise on human anatomy in its relation to osteopathy. Human anatomy; Osteopathic medicine; Osteopathic Medicine; Anatomy. ANATOMY IN A NUTSHELL. 325 closed because they are surrounded by the capsule of Glisson while the hepatic veins gape open, being adherent to the liver substance. The gall-bladder retains the bile and is situated between the right and PLATE CXLVI. THYROID CARTILAGE. CRICOID FIRST THORACICT RIGHT BRONCHUS LFFT BRONCHUS. CASuiAC END TflflFTH THORACIC VERTEBRA CAELIAC AXIS PYLORIC END DUODENUM 1IGHT COMMON ILIAC LEFT COMMON ILIAC The (Esophagus an Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-in-a-nutshell-a-treatise-on-human-anatomy-in-its-relation-to-osteopathy-human-anatomy-osteopathic-medicine-osteopathic-medicine-anatomy-anatomy-in-a-nutshell-325-closed-because-they-are-surrounded-by-the-capsule-of-glisson-while-the-hepatic-veins-gape-open-being-adherent-to-the-liver-substance-the-gall-bladder-retains-the-bile-and-is-situated-between-the-right-and-plate-cxlvi-thyroid-cartilage-cricoid-first-thoracict-right-bronchus-lfft-bronchus-casuiac-end-tflflfth-thoracic-vertebra-caeliac-axis-pyloric-end-duodenum-1ight-common-iliac-left-common-iliac-the-esophagus-an-image236803677.htmlRMRN79E5–. Anatomy in a nutshell : a treatise on human anatomy in its relation to osteopathy. Human anatomy; Osteopathic medicine; Osteopathic Medicine; Anatomy. ANATOMY IN A NUTSHELL. 325 closed because they are surrounded by the capsule of Glisson while the hepatic veins gape open, being adherent to the liver substance. The gall-bladder retains the bile and is situated between the right and PLATE CXLVI. THYROID CARTILAGE. CRICOID FIRST THORACICT RIGHT BRONCHUS LFFT BRONCHUS. CASuiAC END TflflFTH THORACIC VERTEBRA CAELIAC AXIS PYLORIC END DUODENUM 1IGHT COMMON ILIAC LEFT COMMON ILIAC The (Esophagus an
 . Chordate anatomy. Chordata; Anatomy, Comparative. 286 CHORDATE ANATOMY. SUPERFICIAL VOLAR ARCH DEEP VOLAR ARCH VOLAR INTEROSSEOUS ULNAR COM. INTEROSSEOUS RADIAL RECURRENT SUPERIOR ULNAR COLLATERAL DEEP BRACHIAL THORACODORSAL! S SUBSCAPULAR LATERAL THORAC IC INNOMINATE VENA CAVA RIGHT AURICLE RIGHT GASTRIC GASTRODUODENAL HEPATIC COELIAC RIGHT COLIC INTESTINALS INFERIOR MESENTERIC ILIOLUMBAR COMMON ILIAC MIDDLE SACRAL HYPOGASTRIC EXTERNAL ILIAC SUPERIOR GLUTEAL CIRCUMFLEX lUUM PROF INFERIOR VESICALIS HEMORRHOIDAL INTERNAL PUDENDAL RAM. FRONTAL TEMPORAL TRANSVERSE FACIAL OCCIPITAL INFERIOR ALVE Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/chordate-anatomy-chordata-anatomy-comparative-286-chordate-anatomy-superficial-volar-arch-deep-volar-arch-volar-interosseous-ulnar-com-interosseous-radial-recurrent-superior-ulnar-collateral-deep-brachial-thoracodorsal!-s-subscapular-lateral-thorac-ic-innominate-vena-cava-right-auricle-right-gastric-gastroduodenal-hepatic-coeliac-right-colic-intestinals-inferior-mesenteric-iliolumbar-common-iliac-middle-sacral-hypogastric-external-iliac-superior-gluteal-circumflex-luum-prof-inferior-vesicalis-hemorrhoidal-internal-pudendal-ram-frontal-temporal-transverse-facial-occipital-inferior-alve-image234902638.html
. Chordate anatomy. Chordata; Anatomy, Comparative. 286 CHORDATE ANATOMY. SUPERFICIAL VOLAR ARCH DEEP VOLAR ARCH VOLAR INTEROSSEOUS ULNAR COM. INTEROSSEOUS RADIAL RECURRENT SUPERIOR ULNAR COLLATERAL DEEP BRACHIAL THORACODORSAL! S SUBSCAPULAR LATERAL THORAC IC INNOMINATE VENA CAVA RIGHT AURICLE RIGHT GASTRIC GASTRODUODENAL HEPATIC COELIAC RIGHT COLIC INTESTINALS INFERIOR MESENTERIC ILIOLUMBAR COMMON ILIAC MIDDLE SACRAL HYPOGASTRIC EXTERNAL ILIAC SUPERIOR GLUTEAL CIRCUMFLEX lUUM PROF INFERIOR VESICALIS HEMORRHOIDAL INTERNAL PUDENDAL RAM. FRONTAL TEMPORAL TRANSVERSE FACIAL OCCIPITAL INFERIOR ALVE Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/chordate-anatomy-chordata-anatomy-comparative-286-chordate-anatomy-superficial-volar-arch-deep-volar-arch-volar-interosseous-ulnar-com-interosseous-radial-recurrent-superior-ulnar-collateral-deep-brachial-thoracodorsal!-s-subscapular-lateral-thorac-ic-innominate-vena-cava-right-auricle-right-gastric-gastroduodenal-hepatic-coeliac-right-colic-intestinals-inferior-mesenteric-iliolumbar-common-iliac-middle-sacral-hypogastric-external-iliac-superior-gluteal-circumflex-luum-prof-inferior-vesicalis-hemorrhoidal-internal-pudendal-ram-frontal-temporal-transverse-facial-occipital-inferior-alve-image234902638.htmlRMRJ4MKX–. Chordate anatomy. Chordata; Anatomy, Comparative. 286 CHORDATE ANATOMY. SUPERFICIAL VOLAR ARCH DEEP VOLAR ARCH VOLAR INTEROSSEOUS ULNAR COM. INTEROSSEOUS RADIAL RECURRENT SUPERIOR ULNAR COLLATERAL DEEP BRACHIAL THORACODORSAL! S SUBSCAPULAR LATERAL THORAC IC INNOMINATE VENA CAVA RIGHT AURICLE RIGHT GASTRIC GASTRODUODENAL HEPATIC COELIAC RIGHT COLIC INTESTINALS INFERIOR MESENTERIC ILIOLUMBAR COMMON ILIAC MIDDLE SACRAL HYPOGASTRIC EXTERNAL ILIAC SUPERIOR GLUTEAL CIRCUMFLEX lUUM PROF INFERIOR VESICALIS HEMORRHOIDAL INTERNAL PUDENDAL RAM. FRONTAL TEMPORAL TRANSVERSE FACIAL OCCIPITAL INFERIOR ALVE
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1022 THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. iliac glands, (2) efferents from the sub-aortic glands, (3) efferents from the sacral glands, (4) some efferents from the hypogastric glands, (5) efferents from the main inferior mesenteric glands, (6) the lymph vessels from the testes and epididymides and their coverings in the male, and from the ovaries, the uterine tubes, and the upper part of the uterus in the female, (7) lymph vessels from the (Esophagus Posterior left gastric glands Right supra-pancreatic glands Main mesenteric glands- Lumhar glands —' A common iliac Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1022-the-vascular-system-iliac-glands-2-efferents-from-the-sub-aortic-glands-3-efferents-from-the-sacral-glands-4-some-efferents-from-the-hypogastric-glands-5-efferents-from-the-main-inferior-mesenteric-glands-6-the-lymph-vessels-from-the-testes-and-epididymides-and-their-coverings-in-the-male-and-from-the-ovaries-the-uterine-tubes-and-the-upper-part-of-the-uterus-in-the-female-7-lymph-vessels-from-the-esophagus-posterior-left-gastric-glands-right-supra-pancreatic-glands-main-mesenteric-glands-lumhar-glands-a-common-iliac-image231855069.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1022 THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. iliac glands, (2) efferents from the sub-aortic glands, (3) efferents from the sacral glands, (4) some efferents from the hypogastric glands, (5) efferents from the main inferior mesenteric glands, (6) the lymph vessels from the testes and epididymides and their coverings in the male, and from the ovaries, the uterine tubes, and the upper part of the uterus in the female, (7) lymph vessels from the (Esophagus Posterior left gastric glands Right supra-pancreatic glands Main mesenteric glands- Lumhar glands —' A common iliac Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1022-the-vascular-system-iliac-glands-2-efferents-from-the-sub-aortic-glands-3-efferents-from-the-sacral-glands-4-some-efferents-from-the-hypogastric-glands-5-efferents-from-the-main-inferior-mesenteric-glands-6-the-lymph-vessels-from-the-testes-and-epididymides-and-their-coverings-in-the-male-and-from-the-ovaries-the-uterine-tubes-and-the-upper-part-of-the-uterus-in-the-female-7-lymph-vessels-from-the-esophagus-posterior-left-gastric-glands-right-supra-pancreatic-glands-main-mesenteric-glands-lumhar-glands-a-common-iliac-image231855069.htmlRMRD5WE5–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1022 THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. iliac glands, (2) efferents from the sub-aortic glands, (3) efferents from the sacral glands, (4) some efferents from the hypogastric glands, (5) efferents from the main inferior mesenteric glands, (6) the lymph vessels from the testes and epididymides and their coverings in the male, and from the ovaries, the uterine tubes, and the upper part of the uterus in the female, (7) lymph vessels from the (Esophagus Posterior left gastric glands Right supra-pancreatic glands Main mesenteric glands- Lumhar glands —' A common iliac
 . The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. CAVITIES OF HEART 67 has remained. This fact, therefore, shows that the mammal cannot have been derived from a bird-like ancestor, but that. Fig. 43.âLrpn.^ cuniciilus. Ven- tral view of the vascular .sys- tem. The heart is somewhat displaced towards the left of the subject; tlie arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed, a.cpg, internal mam- mary artery; a.f, anterior facial vein ; a.m, anterior mesenteric artery ; a.ph, anterior phrenic vein ; az.ii^ azygos vein ; ir^ lirachial artery ; cil.a, common iliac arte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cambridge-natural-history-zoology-cavities-of-heart-67-has-remained-this-fact-therefore-shows-that-the-mammal-cannot-have-been-derived-from-a-bird-like-ancestor-but-that-fig-43lrpn-cuniciilus-ven-tral-view-of-the-vascular-sys-tem-the-heart-is-somewhat-displaced-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-tlie-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-acpg-internal-mam-mary-artery-af-anterior-facial-vein-am-anterior-mesenteric-artery-aph-anterior-phrenic-vein-azii-azygos-vein-ir-lirachial-artery-cila-common-iliac-arte-image232173075.html
. The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. CAVITIES OF HEART 67 has remained. This fact, therefore, shows that the mammal cannot have been derived from a bird-like ancestor, but that. Fig. 43.âLrpn.^ cuniciilus. Ven- tral view of the vascular .sys- tem. The heart is somewhat displaced towards the left of the subject; tlie arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed, a.cpg, internal mam- mary artery; a.f, anterior facial vein ; a.m, anterior mesenteric artery ; a.ph, anterior phrenic vein ; az.ii^ azygos vein ; ir^ lirachial artery ; cil.a, common iliac arte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cambridge-natural-history-zoology-cavities-of-heart-67-has-remained-this-fact-therefore-shows-that-the-mammal-cannot-have-been-derived-from-a-bird-like-ancestor-but-that-fig-43lrpn-cuniciilus-ven-tral-view-of-the-vascular-sys-tem-the-heart-is-somewhat-displaced-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-tlie-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-acpg-internal-mam-mary-artery-af-anterior-facial-vein-am-anterior-mesenteric-artery-aph-anterior-phrenic-vein-azii-azygos-vein-ir-lirachial-artery-cila-common-iliac-arte-image232173075.htmlRMRDMB3F–. The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. CAVITIES OF HEART 67 has remained. This fact, therefore, shows that the mammal cannot have been derived from a bird-like ancestor, but that. Fig. 43.âLrpn.^ cuniciilus. Ven- tral view of the vascular .sys- tem. The heart is somewhat displaced towards the left of the subject; tlie arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed, a.cpg, internal mam- mary artery; a.f, anterior facial vein ; a.m, anterior mesenteric artery ; a.ph, anterior phrenic vein ; az.ii^ azygos vein ; ir^ lirachial artery ; cil.a, common iliac arte
 . The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. CAVITIES OF HEART 67 has remained. This fact, therefore, shows that the mammal cannot have been derived from a bird-like ancestor, but that. Fig. 43.âLepus cunicuhis. Veu- tral view of the vascular sys- tem. The heart is somewhat displaced towards the left of the subject; the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed, a-cpy, internal mam- mary artery; a.f, anterior facial vein ; a.m, anterior mesenteric artery ; a.ph, anterior phrenic vein ; az.% azygos vein ; hr, brachial artery; c.il.a, common iliac artery ; c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cambridge-natural-history-zoology-cavities-of-heart-67-has-remained-this-fact-therefore-shows-that-the-mammal-cannot-have-been-derived-from-a-bird-like-ancestor-but-that-fig-43lepus-cunicuhis-veu-tral-view-of-the-vascular-sys-tem-the-heart-is-somewhat-displaced-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-the-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-a-cpy-internal-mam-mary-artery-af-anterior-facial-vein-am-anterior-mesenteric-artery-aph-anterior-phrenic-vein-az-azygos-vein-hr-brachial-artery-cila-common-iliac-artery-c-image233655297.html
. The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. CAVITIES OF HEART 67 has remained. This fact, therefore, shows that the mammal cannot have been derived from a bird-like ancestor, but that. Fig. 43.âLepus cunicuhis. Veu- tral view of the vascular sys- tem. The heart is somewhat displaced towards the left of the subject; the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed, a-cpy, internal mam- mary artery; a.f, anterior facial vein ; a.m, anterior mesenteric artery ; a.ph, anterior phrenic vein ; az.% azygos vein ; hr, brachial artery; c.il.a, common iliac artery ; c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cambridge-natural-history-zoology-cavities-of-heart-67-has-remained-this-fact-therefore-shows-that-the-mammal-cannot-have-been-derived-from-a-bird-like-ancestor-but-that-fig-43lepus-cunicuhis-veu-tral-view-of-the-vascular-sys-tem-the-heart-is-somewhat-displaced-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-the-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-a-cpy-internal-mam-mary-artery-af-anterior-facial-vein-am-anterior-mesenteric-artery-aph-anterior-phrenic-vein-az-azygos-vein-hr-brachial-artery-cila-common-iliac-artery-c-image233655297.htmlRMRG3WM1–. The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. CAVITIES OF HEART 67 has remained. This fact, therefore, shows that the mammal cannot have been derived from a bird-like ancestor, but that. Fig. 43.âLepus cunicuhis. Veu- tral view of the vascular sys- tem. The heart is somewhat displaced towards the left of the subject; the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed, a-cpy, internal mam- mary artery; a.f, anterior facial vein ; a.m, anterior mesenteric artery ; a.ph, anterior phrenic vein ; az.% azygos vein ; hr, brachial artery; c.il.a, common iliac artery ; c
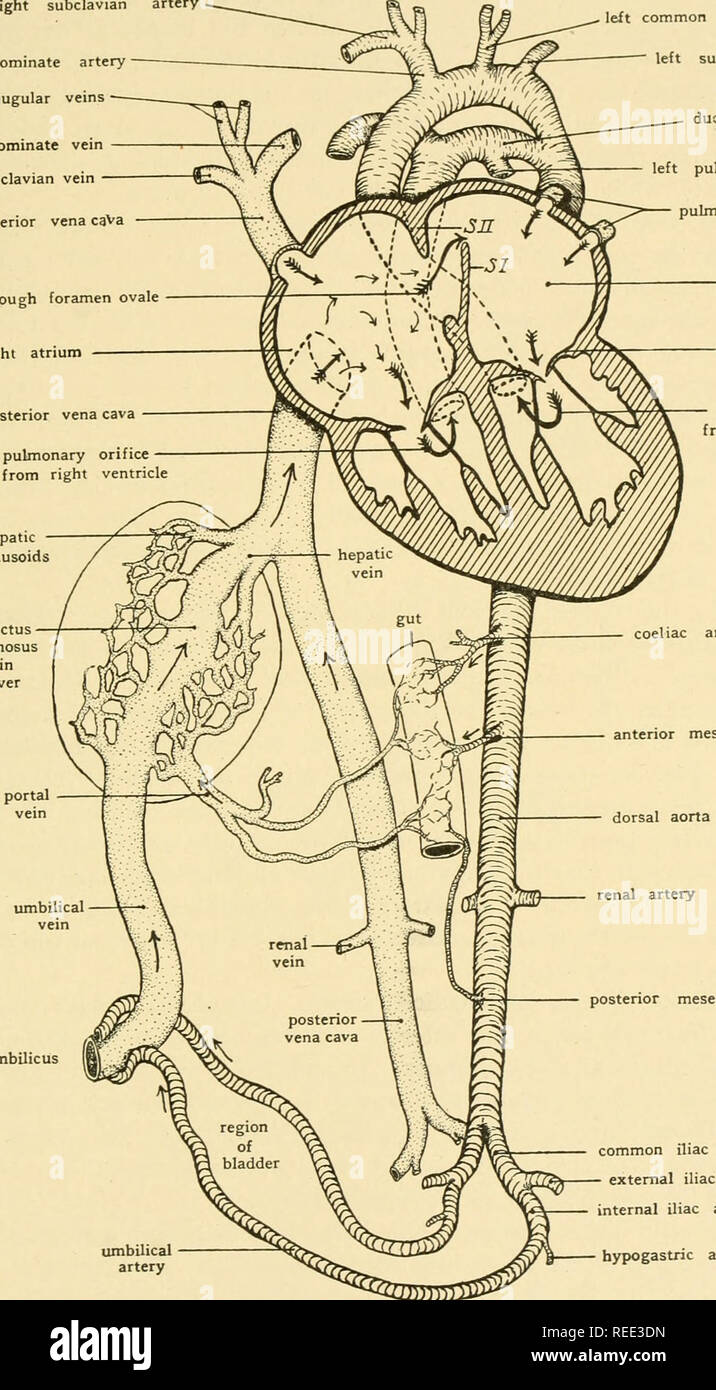 . Comparative anatomy. Anatomy, Comparative. THE VASCULAR SYSTEM 383 right subclavian artery innominate artery jugular veins innominate vein subclavian vein anterior vena caVa through foramen ovale right atrium posterior vena cava to pulmonary orifice from hepatic sinusoids umbilicus umbilical artery coeliac artery. left common carotid artery left subclavian artery ductus arteriosus left pulmonary artery pulmonary veins left atrium mitral valve to aortic orifice from left ventricle anterior mesenteric a. dorsal aorta posterior mesenteric a. common iliac artery external iliac artery internal il Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/comparative-anatomy-anatomy-comparative-the-vascular-system-383-right-subclavian-artery-innominate-artery-jugular-veins-innominate-vein-subclavian-vein-anterior-vena-cava-through-foramen-ovale-right-atrium-posterior-vena-cava-to-pulmonary-orifice-from-hepatic-sinusoids-umbilicus-umbilical-artery-coeliac-artery-left-common-carotid-artery-left-subclavian-artery-ductus-arteriosus-left-pulmonary-artery-pulmonary-veins-left-atrium-mitral-valve-to-aortic-orifice-from-left-ventricle-anterior-mesenteric-a-dorsal-aorta-posterior-mesenteric-a-common-iliac-artery-external-iliac-artery-internal-il-image232650033.html
. Comparative anatomy. Anatomy, Comparative. THE VASCULAR SYSTEM 383 right subclavian artery innominate artery jugular veins innominate vein subclavian vein anterior vena caVa through foramen ovale right atrium posterior vena cava to pulmonary orifice from hepatic sinusoids umbilicus umbilical artery coeliac artery. left common carotid artery left subclavian artery ductus arteriosus left pulmonary artery pulmonary veins left atrium mitral valve to aortic orifice from left ventricle anterior mesenteric a. dorsal aorta posterior mesenteric a. common iliac artery external iliac artery internal il Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/comparative-anatomy-anatomy-comparative-the-vascular-system-383-right-subclavian-artery-innominate-artery-jugular-veins-innominate-vein-subclavian-vein-anterior-vena-cava-through-foramen-ovale-right-atrium-posterior-vena-cava-to-pulmonary-orifice-from-hepatic-sinusoids-umbilicus-umbilical-artery-coeliac-artery-left-common-carotid-artery-left-subclavian-artery-ductus-arteriosus-left-pulmonary-artery-pulmonary-veins-left-atrium-mitral-valve-to-aortic-orifice-from-left-ventricle-anterior-mesenteric-a-dorsal-aorta-posterior-mesenteric-a-common-iliac-artery-external-iliac-artery-internal-il-image232650033.htmlRMREE3DN–. Comparative anatomy. Anatomy, Comparative. THE VASCULAR SYSTEM 383 right subclavian artery innominate artery jugular veins innominate vein subclavian vein anterior vena caVa through foramen ovale right atrium posterior vena cava to pulmonary orifice from hepatic sinusoids umbilicus umbilical artery coeliac artery. left common carotid artery left subclavian artery ductus arteriosus left pulmonary artery pulmonary veins left atrium mitral valve to aortic orifice from left ventricle anterior mesenteric a. dorsal aorta posterior mesenteric a. common iliac artery external iliac artery internal il
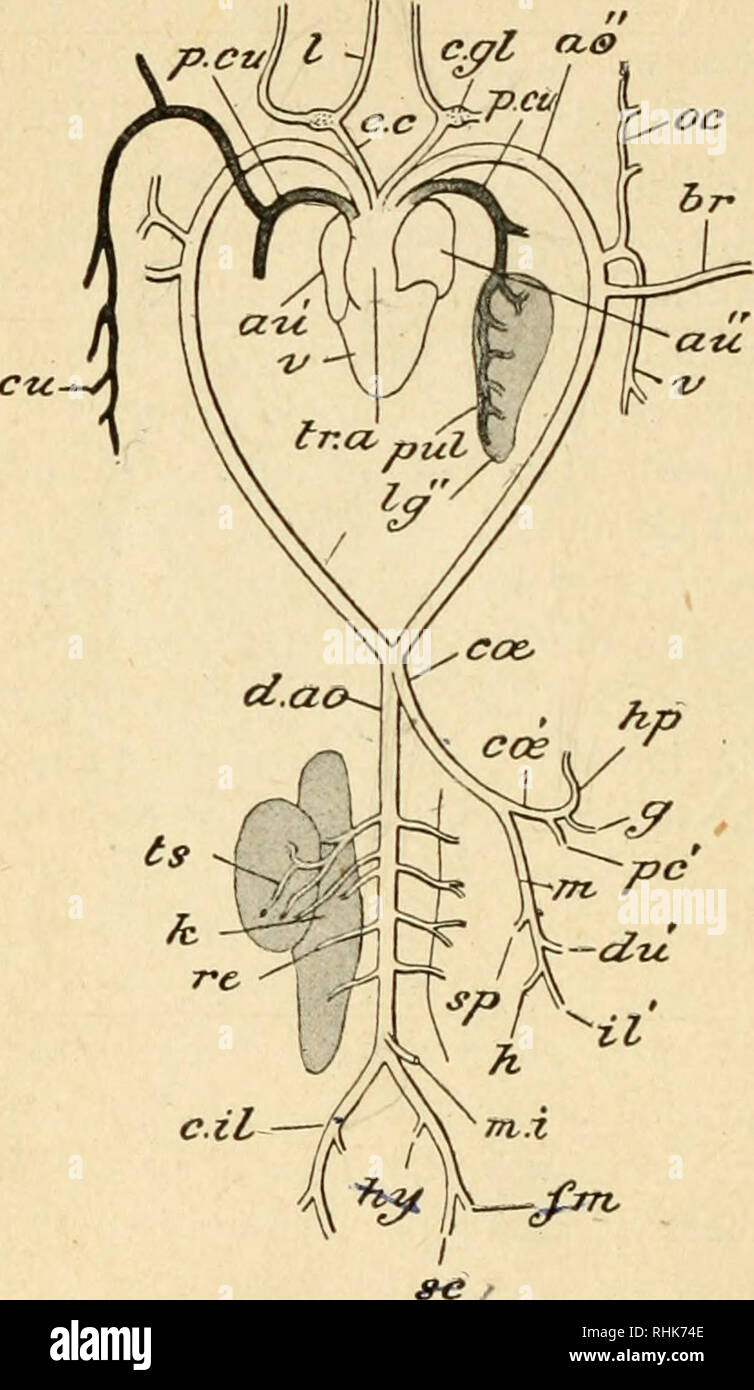 . The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG. ^ ^ )j^—,A^ Fig. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the frog, seen from the ventral side, ao", aortic arch; au', right auricle ; a«", left auricle ; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; cce, coeliaco-mes- enteric; ccb', coeliac; ai,. cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; //«,'femoral; g, gastric; //, hasmorrhoidal; hp, hepatic; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; /^", left lung; VI, anterior mesenteric; m.i, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; /c', pancreatic; p.c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biology-of-the-frog-frogs-268-the-biology-of-the-frog-ja-fig-74-diagram-of-the-arterial-system-of-the-frog-seen-from-the-ventral-side-aoquot-aortic-arch-au-right-auricle-aquot-left-auricle-br-brachial-artery-cc-carotid-cgl-carotid-gland-cil-common-iliac-cce-coeliaco-mes-enteric-ccb-coeliac-ai-cutaneous-dao-dorsal-aorta-femoral-g-gastric-hasmorrhoidal-hp-hepatic-hy-epigastrico-vesical-k-kidney-lingual-quot-left-lung-vi-anterior-mesenteric-mi-posterior-mesen-teric-oc-occipital-c-pancreatic-pc-image234606638.html
. The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG. ^ ^ )j^—,A^ Fig. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the frog, seen from the ventral side, ao", aortic arch; au', right auricle ; a«", left auricle ; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; cce, coeliaco-mes- enteric; ccb', coeliac; ai,. cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; //«,'femoral; g, gastric; //, hasmorrhoidal; hp, hepatic; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; /^", left lung; VI, anterior mesenteric; m.i, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; /c', pancreatic; p.c Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biology-of-the-frog-frogs-268-the-biology-of-the-frog-ja-fig-74-diagram-of-the-arterial-system-of-the-frog-seen-from-the-ventral-side-aoquot-aortic-arch-au-right-auricle-aquot-left-auricle-br-brachial-artery-cc-carotid-cgl-carotid-gland-cil-common-iliac-cce-coeliaco-mes-enteric-ccb-coeliac-ai-cutaneous-dao-dorsal-aorta-femoral-g-gastric-hasmorrhoidal-hp-hepatic-hy-epigastrico-vesical-k-kidney-lingual-quot-left-lung-vi-anterior-mesenteric-mi-posterior-mesen-teric-oc-occipital-c-pancreatic-pc-image234606638.htmlRMRHK74E–. The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG. ^ ^ )j^—,A^ Fig. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the frog, seen from the ventral side, ao", aortic arch; au', right auricle ; a«", left auricle ; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; cce, coeliaco-mes- enteric; ccb', coeliac; ai,. cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; //«,'femoral; g, gastric; //, hasmorrhoidal; hp, hepatic; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; /^", left lung; VI, anterior mesenteric; m.i, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; /c', pancreatic; p.c
 . The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG CHAP.. Fig. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the fiog, seen trom the vential side, ao", aortic arch; an', right auricle ; ati", left auricle ; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; ccs, cceliaco-mes- enteric; c(£', coeliac; cu, cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; fin, femoral; g, gastric; h, hsemorrhoidal; hp, hepatic; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; /^", left lung; m, anterior mesenteric; w./, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; /t', pancreatic; p.cu, pulmo- Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biology-of-the-frog-frogs-268-the-biology-of-the-frog-chap-fig-74-diagram-of-the-arterial-system-of-the-fiog-seen-trom-the-vential-side-aoquot-aortic-arch-an-right-auricle-atiquot-left-auricle-br-brachial-artery-cc-carotid-cgl-carotid-gland-cil-common-iliac-ccs-cceliaco-mes-enteric-c-coeliac-cu-cutaneous-dao-dorsal-aorta-fin-femoral-g-gastric-h-hsemorrhoidal-hp-hepatic-hy-epigastrico-vesical-k-kidney-lingual-quot-left-lung-m-anterior-mesenteric-w-posterior-mesen-teric-oc-occipital-t-pancreatic-pcu-pulmo-image234606361.html
. The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG CHAP.. Fig. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the fiog, seen trom the vential side, ao", aortic arch; an', right auricle ; ati", left auricle ; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; ccs, cceliaco-mes- enteric; c(£', coeliac; cu, cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; fin, femoral; g, gastric; h, hsemorrhoidal; hp, hepatic; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; /^", left lung; m, anterior mesenteric; w./, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; /t', pancreatic; p.cu, pulmo- Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biology-of-the-frog-frogs-268-the-biology-of-the-frog-chap-fig-74-diagram-of-the-arterial-system-of-the-fiog-seen-trom-the-vential-side-aoquot-aortic-arch-an-right-auricle-atiquot-left-auricle-br-brachial-artery-cc-carotid-cgl-carotid-gland-cil-common-iliac-ccs-cceliaco-mes-enteric-c-coeliac-cu-cutaneous-dao-dorsal-aorta-fin-femoral-g-gastric-h-hsemorrhoidal-hp-hepatic-hy-epigastrico-vesical-k-kidney-lingual-quot-left-lung-m-anterior-mesenteric-w-posterior-mesen-teric-oc-occipital-t-pancreatic-pcu-pulmo-image234606361.htmlRMRHK6PH–. The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG CHAP.. Fig. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the fiog, seen trom the vential side, ao", aortic arch; an', right auricle ; ati", left auricle ; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; ccs, cceliaco-mes- enteric; c(£', coeliac; cu, cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; fin, femoral; g, gastric; h, hsemorrhoidal; hp, hepatic; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; /^", left lung; m, anterior mesenteric; w./, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; /t', pancreatic; p.cu, pulmo-
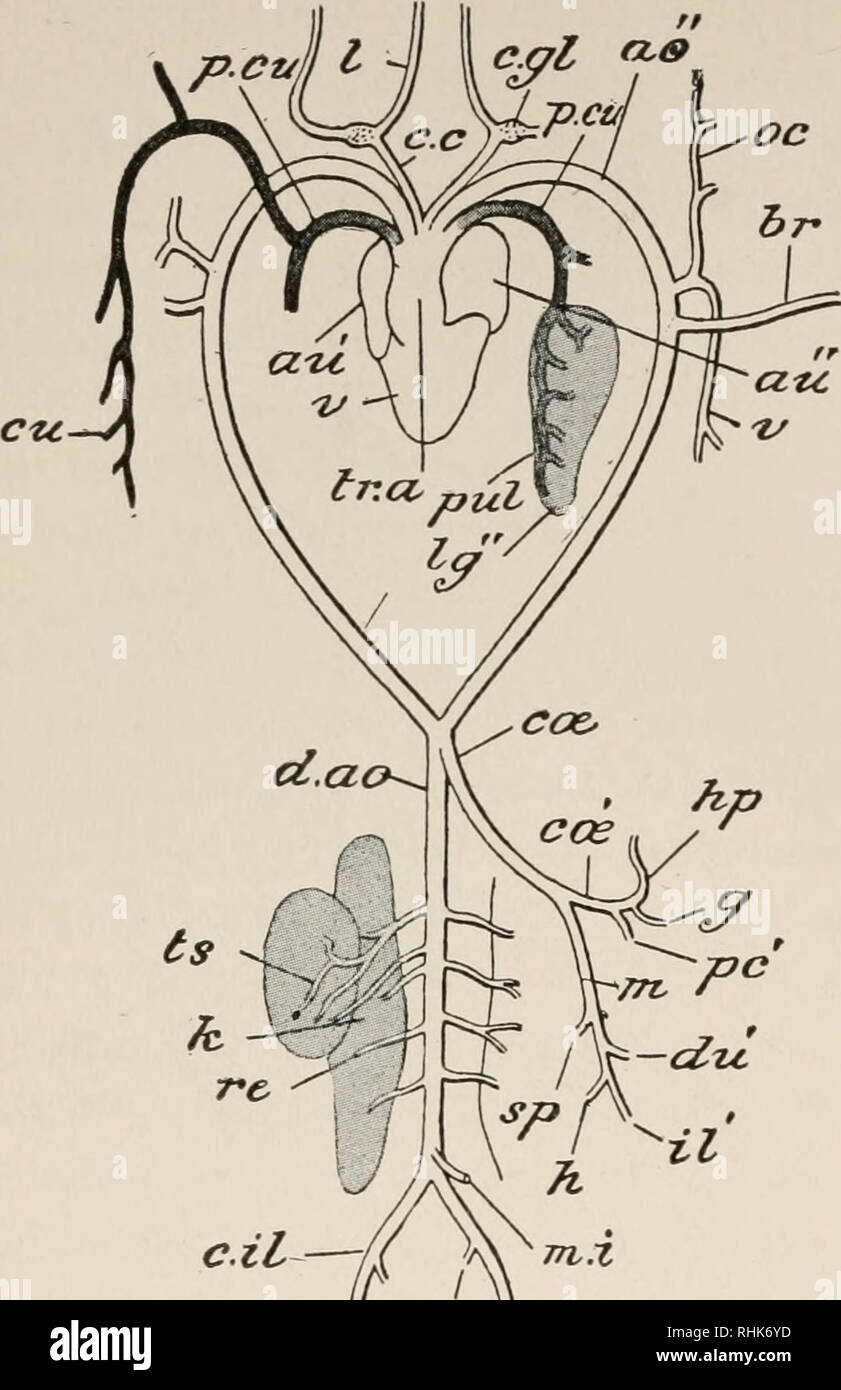 . The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG CHAP.. c.il—-i 4 *•* f- sc FlG. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the frog, seen from the ventral side, ao", aortic arch; au'', right auricle; au", left auricle; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; c&, cceliaco-mes- enteric; cos', coeliac; cti, cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; /m, femoral; gt gastric; //, haemorrhoidal; hp, hepatic ; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; Ig", left lung; in, anterior mesenteric ; tn.i, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; pc' Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biology-of-the-frog-frogs-268-the-biology-of-the-frog-chap-cil-i-4-f-sc-flg-74-diagram-of-the-arterial-system-of-the-frog-seen-from-the-ventral-side-aoquot-aortic-arch-au-right-auricle-auquot-left-auricle-br-brachial-artery-cc-carotid-cgl-carotid-gland-cil-common-iliac-camp-cceliaco-mes-enteric-cos-coeliac-cti-cutaneous-dao-dorsal-aorta-m-femoral-gt-gastric-haemorrhoidal-hp-hepatic-hy-epigastrico-vesical-k-kidney-lingual-igquot-left-lung-in-anterior-mesenteric-tni-posterior-mesen-teric-oc-occipital-pc-image234606497.html
. The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG CHAP.. c.il—-i 4 *•* f- sc FlG. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the frog, seen from the ventral side, ao", aortic arch; au'', right auricle; au", left auricle; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; c&, cceliaco-mes- enteric; cos', coeliac; cti, cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; /m, femoral; gt gastric; //, haemorrhoidal; hp, hepatic ; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; Ig", left lung; in, anterior mesenteric ; tn.i, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; pc' Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biology-of-the-frog-frogs-268-the-biology-of-the-frog-chap-cil-i-4-f-sc-flg-74-diagram-of-the-arterial-system-of-the-frog-seen-from-the-ventral-side-aoquot-aortic-arch-au-right-auricle-auquot-left-auricle-br-brachial-artery-cc-carotid-cgl-carotid-gland-cil-common-iliac-camp-cceliaco-mes-enteric-cos-coeliac-cti-cutaneous-dao-dorsal-aorta-m-femoral-gt-gastric-haemorrhoidal-hp-hepatic-hy-epigastrico-vesical-k-kidney-lingual-igquot-left-lung-in-anterior-mesenteric-tni-posterior-mesen-teric-oc-occipital-pc-image234606497.htmlRMRHK6YD–. The biology of the frog. Frogs. 268 THE BIOLOGY OF THE FROG CHAP.. c.il—-i 4 *•* f- sc FlG. 74. — Diagram of the arterial system of the frog, seen from the ventral side, ao", aortic arch; au'', right auricle; au", left auricle; br, brachial artery; c.c, carotid; c.gl, carotid gland; c.il, common iliac; c&, cceliaco-mes- enteric; cos', coeliac; cti, cutaneous; d.ao, dorsal aorta; /m, femoral; gt gastric; //, haemorrhoidal; hp, hepatic ; hy, epigastrico- vesical; k, kidney; /, lingual; Ig", left lung; in, anterior mesenteric ; tn.i, posterior mesen- teric; oc, occipital; pc'
 . A manual of zoology. . l.lt.t Fig. 307.—LepuS Cuniculus The vascular system. The heart is somewhat dis- placed towards the left of the subject: the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed a, arch of the aorta; a. epg, internal mammary artery; a. ft anterior facia! vein: a. m, anterior mesenteric artery; a. p/i, anterior phrenic vein; az. v, azygos vein; Br, branchial artery; c. il. a, common iliac artery; etc, cceliac artery ; d. no, dorsal aorta; e. e, external carotid artery; e. il. a, external iliac artery; e. il. v, external iliac vein: e. jn, ex Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-zoology-lltt-fig-307lepus-cuniculus-the-vascular-system-the-heart-is-somewhat-dis-placed-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-the-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-a-arch-of-the-aorta-a-epg-internal-mammary-artery-a-ft-anterior-facia!-vein-a-m-anterior-mesenteric-artery-a-pi-anterior-phrenic-vein-az-v-azygos-vein-br-branchial-artery-c-il-a-common-iliac-artery-etc-cceliac-artery-d-no-dorsal-aorta-e-e-external-carotid-artery-e-il-a-external-iliac-artery-e-il-v-external-iliac-vein-e-jn-ex-image232125398.html
. A manual of zoology. . l.lt.t Fig. 307.—LepuS Cuniculus The vascular system. The heart is somewhat dis- placed towards the left of the subject: the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed a, arch of the aorta; a. epg, internal mammary artery; a. ft anterior facia! vein: a. m, anterior mesenteric artery; a. p/i, anterior phrenic vein; az. v, azygos vein; Br, branchial artery; c. il. a, common iliac artery; etc, cceliac artery ; d. no, dorsal aorta; e. e, external carotid artery; e. il. a, external iliac artery; e. il. v, external iliac vein: e. jn, ex Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-manual-of-zoology-lltt-fig-307lepus-cuniculus-the-vascular-system-the-heart-is-somewhat-dis-placed-towards-the-left-of-the-subject-the-arteries-of-the-right-and-the-veins-of-the-left-side-are-in-great-measure-removed-a-arch-of-the-aorta-a-epg-internal-mammary-artery-a-ft-anterior-facia!-vein-a-m-anterior-mesenteric-artery-a-pi-anterior-phrenic-vein-az-v-azygos-vein-br-branchial-artery-c-il-a-common-iliac-artery-etc-cceliac-artery-d-no-dorsal-aorta-e-e-external-carotid-artery-e-il-a-external-iliac-artery-e-il-v-external-iliac-vein-e-jn-ex-image232125398.htmlRMRDJ68P–. A manual of zoology. . l.lt.t Fig. 307.—LepuS Cuniculus The vascular system. The heart is somewhat dis- placed towards the left of the subject: the arteries of the right and the veins of the left side are in great measure removed a, arch of the aorta; a. epg, internal mammary artery; a. ft anterior facia! vein: a. m, anterior mesenteric artery; a. p/i, anterior phrenic vein; az. v, azygos vein; Br, branchial artery; c. il. a, common iliac artery; etc, cceliac artery ; d. no, dorsal aorta; e. e, external carotid artery; e. il. a, external iliac artery; e. il. v, external iliac vein: e. jn, ex
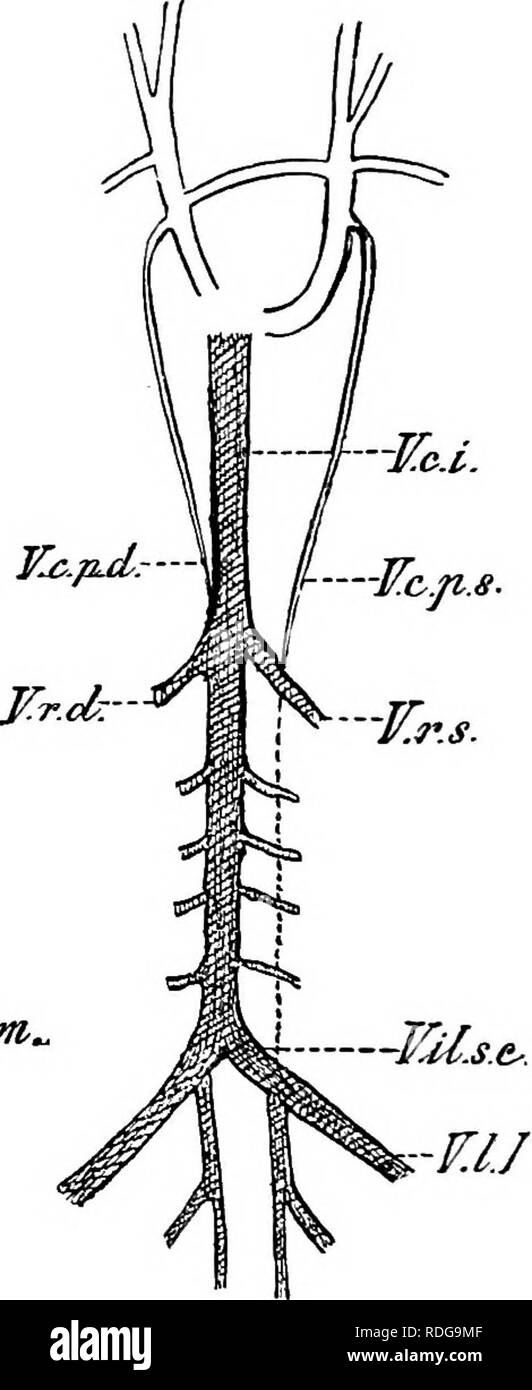 . Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. h-JCc, -TTrs.. 'VUM/tt.eomm, ¥.1.1. Pig. 269.—Diagram showing the Relations of the Posterior Cardinal AND Postcaval Veins in A, the Rabbit, and B, Man. (After Hooh- stetter). V.r.d, r.r..s, renal veins ; F.f?.s.e, common iliac vein; T7./, lumbar vein ; I^.c.r, postcaval; V.c.2^.d, F.c.p.s, right ancUeft posterior cardinals ; V.U.int.comm, conmion internal iliac vein. open into the precavals. In Eeptiles, Birds, Monotremes, and Marsupials, as well as in many Rodents, Insectivores, Bats, and Ungulates, both precavals per Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-the-comparative-anatomy-of-vertebrates-anatomy-comparative-h-jcc-ttrs-vumtteomm-11-pig-269diagram-showing-the-relations-of-the-posterior-cardinal-and-postcaval-veins-in-a-the-rabbit-and-b-man-after-hooh-stetter-vrd-rrs-renal-veins-ffse-common-iliac-vein-t7-lumbar-vein-icr-postcaval-vc2d-fcps-right-ancueft-posterior-cardinals-vuintcomm-conmion-internal-iliac-vein-open-into-the-precavals-in-eeptiles-birds-monotremes-and-marsupials-as-well-as-in-many-rodents-insectivores-bats-and-ungulates-both-precavals-per-image232084175.html
. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. h-JCc, -TTrs.. 'VUM/tt.eomm, ¥.1.1. Pig. 269.—Diagram showing the Relations of the Posterior Cardinal AND Postcaval Veins in A, the Rabbit, and B, Man. (After Hooh- stetter). V.r.d, r.r..s, renal veins ; F.f?.s.e, common iliac vein; T7./, lumbar vein ; I^.c.r, postcaval; V.c.2^.d, F.c.p.s, right ancUeft posterior cardinals ; V.U.int.comm, conmion internal iliac vein. open into the precavals. In Eeptiles, Birds, Monotremes, and Marsupials, as well as in many Rodents, Insectivores, Bats, and Ungulates, both precavals per Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elements-of-the-comparative-anatomy-of-vertebrates-anatomy-comparative-h-jcc-ttrs-vumtteomm-11-pig-269diagram-showing-the-relations-of-the-posterior-cardinal-and-postcaval-veins-in-a-the-rabbit-and-b-man-after-hooh-stetter-vrd-rrs-renal-veins-ffse-common-iliac-vein-t7-lumbar-vein-icr-postcaval-vc2d-fcps-right-ancueft-posterior-cardinals-vuintcomm-conmion-internal-iliac-vein-open-into-the-precavals-in-eeptiles-birds-monotremes-and-marsupials-as-well-as-in-many-rodents-insectivores-bats-and-ungulates-both-precavals-per-image232084175.htmlRMRDG9MF–. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. h-JCc, -TTrs.. 'VUM/tt.eomm, ¥.1.1. Pig. 269.—Diagram showing the Relations of the Posterior Cardinal AND Postcaval Veins in A, the Rabbit, and B, Man. (After Hooh- stetter). V.r.d, r.r..s, renal veins ; F.f?.s.e, common iliac vein; T7./, lumbar vein ; I^.c.r, postcaval; V.c.2^.d, F.c.p.s, right ancUeft posterior cardinals ; V.U.int.comm, conmion internal iliac vein. open into the precavals. In Eeptiles, Birds, Monotremes, and Marsupials, as well as in many Rodents, Insectivores, Bats, and Ungulates, both precavals per
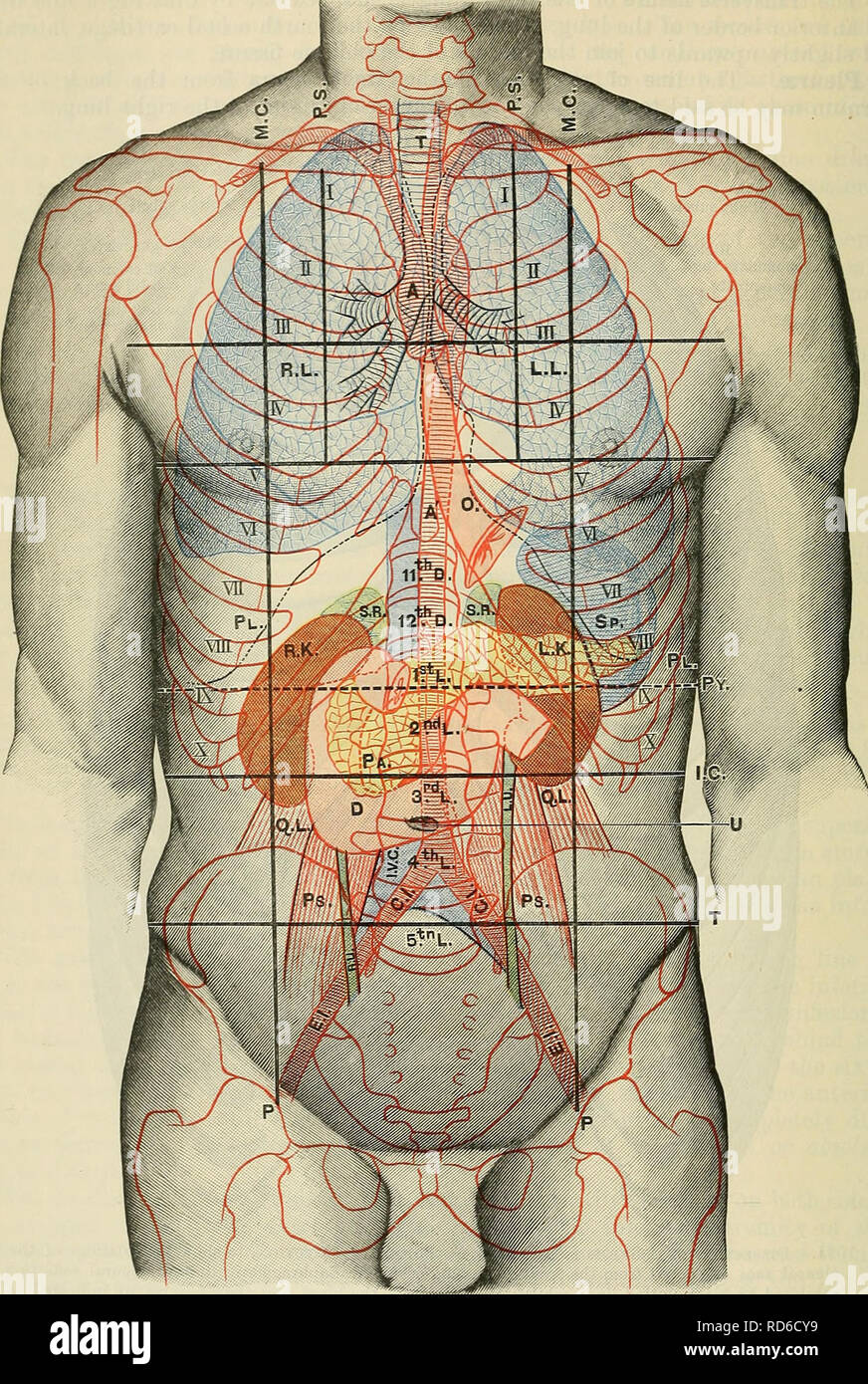 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1-100 SUEFACE AND SUEGIOAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1092.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-sternal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infracostal line. T. Intertubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Eight lung. L.L. Left lung. PI. Pleura. 0. (Esophagus. E.K. Right kidney. L.K. Left kidney. Sp. Spleen. S.R. Suprarenal gland. Pa. Pancreas. D. Duodenum. Q.L. Quadratus lumborum. P.S. Psoas major. , R.U. Right-ureter. L.U. Left ureter. C.I. Common iliac artery. E.I. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1-100-sueface-and-suegioal-anatomy-fig-1092anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-sternal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infracostal-line-t-intertubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-eight-lung-ll-left-lung-pi-pleura-0-esophagus-ek-right-kidney-lk-left-kidney-sp-spleen-sr-suprarenal-gland-pa-pancreas-d-duodenum-ql-quadratus-lumborum-ps-psoas-major-ru-right-ureter-lu-left-ureter-ci-common-iliac-artery-ei-image231867197.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1-100 SUEFACE AND SUEGIOAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1092.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-sternal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infracostal line. T. Intertubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Eight lung. L.L. Left lung. PI. Pleura. 0. (Esophagus. E.K. Right kidney. L.K. Left kidney. Sp. Spleen. S.R. Suprarenal gland. Pa. Pancreas. D. Duodenum. Q.L. Quadratus lumborum. P.S. Psoas major. , R.U. Right-ureter. L.U. Left ureter. C.I. Common iliac artery. E.I. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1-100-sueface-and-suegioal-anatomy-fig-1092anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-sternal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infracostal-line-t-intertubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-eight-lung-ll-left-lung-pi-pleura-0-esophagus-ek-right-kidney-lk-left-kidney-sp-spleen-sr-suprarenal-gland-pa-pancreas-d-duodenum-ql-quadratus-lumborum-ps-psoas-major-ru-right-ureter-lu-left-ureter-ci-common-iliac-artery-ei-image231867197.htmlRMRD6CY9–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1-100 SUEFACE AND SUEGIOAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1092.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-sternal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infracostal line. T. Intertubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Eight lung. L.L. Left lung. PI. Pleura. 0. (Esophagus. E.K. Right kidney. L.K. Left kidney. Sp. Spleen. S.R. Suprarenal gland. Pa. Pancreas. D. Duodenum. Q.L. Quadratus lumborum. P.S. Psoas major. , R.U. Right-ureter. L.U. Left ureter. C.I. Common iliac artery. E.I.
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. U24 SUEFACE AND SUEOICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1106.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-stemal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infra-costal line. T. Inter-tubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Paght lung. L.L. Left lung. Q.L. PI. Pleura. Ps. 0. (Esophagus. R.U. R.K. Right kidney. L.U. L.K. Left kidnev. C.I. Sp. Spleen. E.I. S.R. Suprarenal gland. I.V.( Pa. Pancreas. u. D. Duodenum. Quadratus lumborum. Psoas major. Right ureter. Left ureter. Common iliac ar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-u24-sueface-and-sueoical-anatomy-fig-1106anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-stemal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infra-costal-line-t-inter-tubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-paght-lung-ll-left-lung-ql-pi-pleura-ps-0-esophagus-ru-rk-right-kidney-lu-lk-left-kidnev-ci-sp-spleen-ei-sr-suprarenal-gland-iv-pa-pancreas-u-d-duodenum-quadratus-lumborum-psoas-major-right-ureter-left-ureter-common-iliac-ar-image231867070.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. U24 SUEFACE AND SUEOICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1106.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-stemal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infra-costal line. T. Inter-tubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Paght lung. L.L. Left lung. Q.L. PI. Pleura. Ps. 0. (Esophagus. R.U. R.K. Right kidney. L.U. L.K. Left kidnev. C.I. Sp. Spleen. E.I. S.R. Suprarenal gland. I.V.( Pa. Pancreas. u. D. Duodenum. Quadratus lumborum. Psoas major. Right ureter. Left ureter. Common iliac ar Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-u24-sueface-and-sueoical-anatomy-fig-1106anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-ps-para-stemal-line-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ic-infra-costal-line-t-inter-tubercular-line-py-transpyloric-line-t-trachea-a-aorta-rl-paght-lung-ll-left-lung-ql-pi-pleura-ps-0-esophagus-ru-rk-right-kidney-lu-lk-left-kidnev-ci-sp-spleen-ei-sr-suprarenal-gland-iv-pa-pancreas-u-d-duodenum-quadratus-lumborum-psoas-major-right-ureter-left-ureter-common-iliac-ar-image231867070.htmlRMRD6CPP–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. U24 SUEFACE AND SUEOICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1106.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. P.S. Para-stemal line. P. Inguinal vertical line. I.C. Infra-costal line. T. Inter-tubercular line. Py. Transpyloric line. T. Trachea. A. Aorta. R.L. Paght lung. L.L. Left lung. Q.L. PI. Pleura. Ps. 0. (Esophagus. R.U. R.K. Right kidney. L.U. L.K. Left kidnev. C.I. Sp. Spleen. E.I. S.R. Suprarenal gland. I.V.( Pa. Pancreas. u. D. Duodenum. Quadratus lumborum. Psoas major. Right ureter. Left ureter. Common iliac ar
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1396 SUKFACE AND SUEGICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1090.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera M.C Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left lung. D.C. Descending colon. 1.0. Infracostal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.O. Pelvic colon. ±*y. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac arterj H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1396-sukface-and-suegical-anatomy-fig-1090anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-10-infracostal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-po-pelvic-colon-y-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-arterj-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-image231867226.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1396 SUKFACE AND SUEGICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1090.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera M.C Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left lung. D.C. Descending colon. 1.0. Infracostal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.O. Pelvic colon. ±*y. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac arterj H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-1396-sukface-and-suegical-anatomy-fig-1090anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-10-infracostal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-po-pelvic-colon-y-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-arterj-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-image231867226.htmlRMRD6D0A–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 1396 SUKFACE AND SUEGICAL ANATOMY.. Fig. 1090.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera M.C Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left lung. D.C. Descending colon. 1.0. Infracostal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.O. Pelvic colon. ±*y. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac arterj H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I
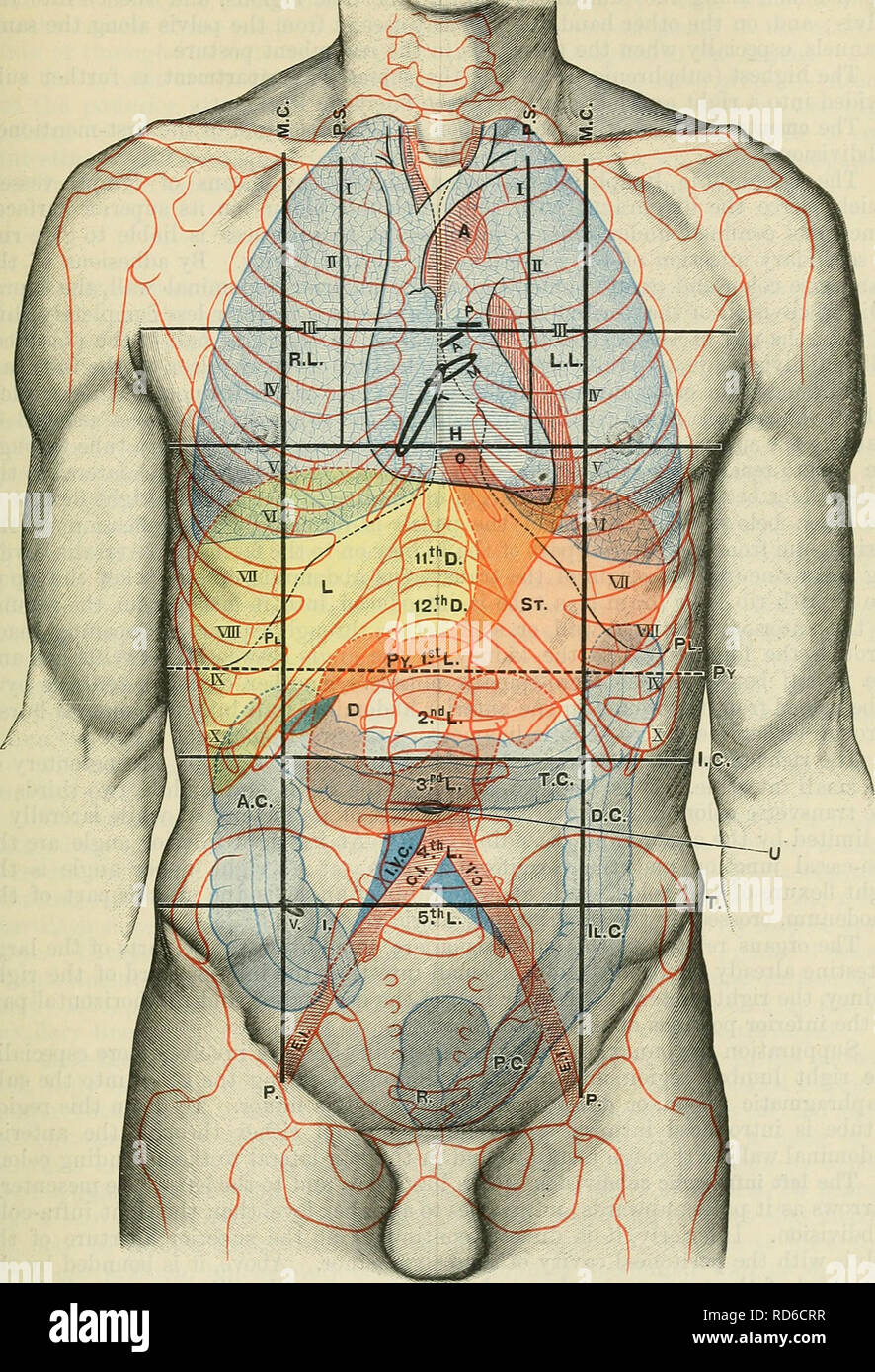 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE ABDOMINAL CAVITY. 1413. Fig. 1103.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left Lung. D.C. Descending colon. i.e. Infra-costal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.C. Pelvic colon. Py. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac artery H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I. Exte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-abdominal-cavity-1413-fig-1103anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-ie-infra-costal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-pc-pelvic-colon-py-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-artery-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-exte-image231867099.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE ABDOMINAL CAVITY. 1413. Fig. 1103.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left Lung. D.C. Descending colon. i.e. Infra-costal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.C. Pelvic colon. Py. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac artery H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I. Exte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-abdominal-cavity-1413-fig-1103anterior-aspect-of-trunk-showing-surface-topography-of-viscera-mc-mid-clavicular-line-t-tricuspid-orifice-ac-ascending-colon-ps-para-sternal-line-rl-right-lung-tc-transverse-colon-p-inguinal-vertical-line-ll-left-lung-dc-descending-colon-ie-infra-costal-line-pi-pleura-11-c-iliac-colon-t-intertubercular-line-l-liver-pc-pelvic-colon-py-transpyloric-line-of-addison-0-esophagus-r-rectum-a-aorta-st-stomach-ci-common-iliac-artery-h-heart-py-pylorus-ei-exte-image231867099.htmlRMRD6CRR–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE ABDOMINAL CAVITY. 1413. Fig. 1103.—Anterior Aspect of Trunk, showing Surface Topography of Viscera. M.C. Mid-clavicular line. T. Tricuspid orifice. A.C. Ascending colon. P.S. Para-sternal line. R.L. Right lung. T.C. Transverse colon. P. Inguinal vertical line. L.L. Left Lung. D.C. Descending colon. i.e. Infra-costal line. PI. Pleura. 11. C. Iliac colon. T. Intertubercular line. L. Liver. P.C. Pelvic colon. Py. Transpyloric line of Addison. 0. (Esophagus. R. Rectum. A. Aorta. St. Stomach. C.I. Common iliac artery H. Heart. Py. Pylorus. E.I. Exte