Quick filters:
Sustentaculum tali Stock Photos and Images
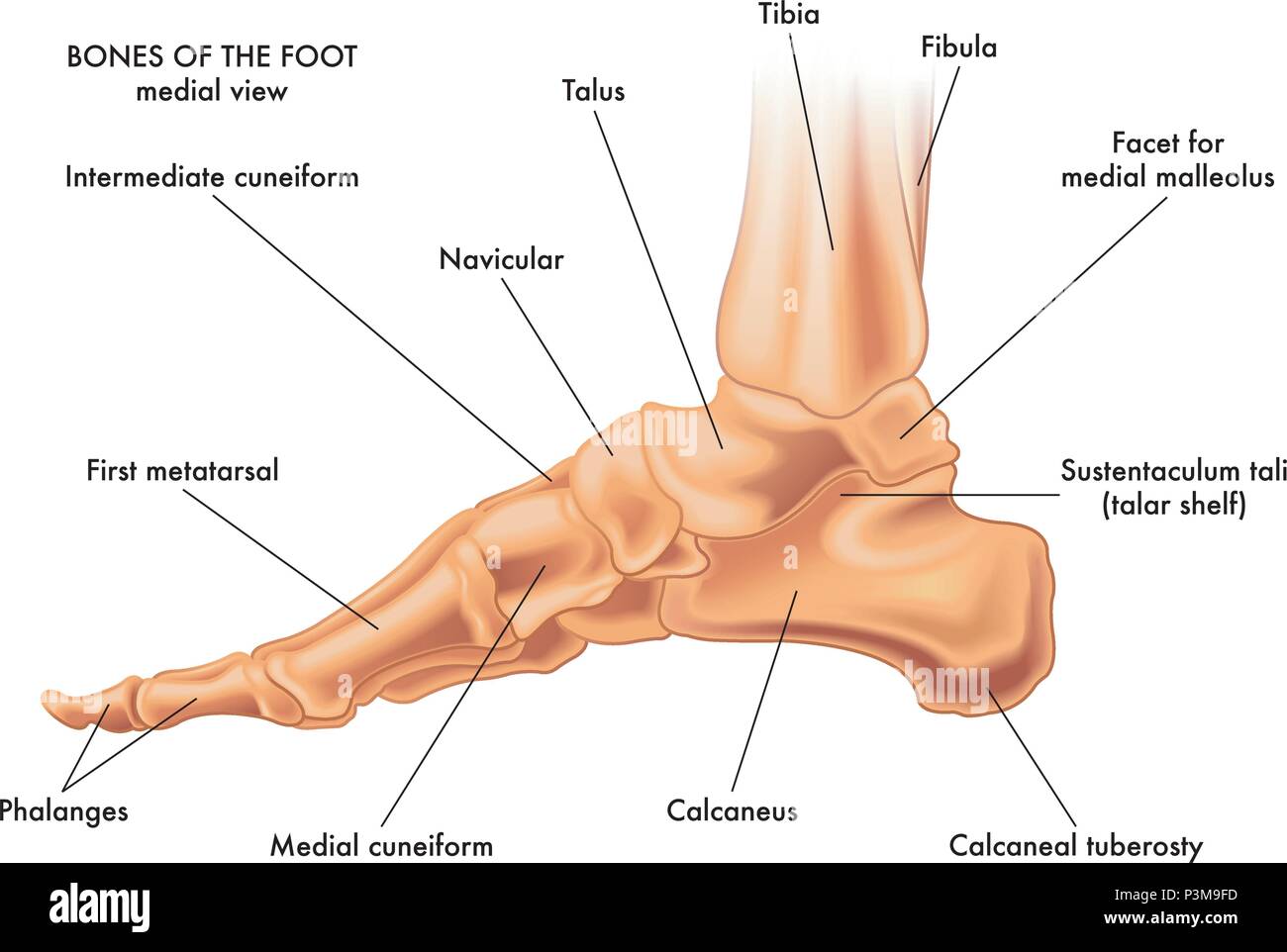 A medical vector illustration of the bones of a foot on a white background Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-medical-vector-illustration-of-the-bones-of-a-foot-on-a-white-background-image208814913.html
A medical vector illustration of the bones of a foot on a white background Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-medical-vector-illustration-of-the-bones-of-a-foot-on-a-white-background-image208814913.htmlRFP3M9FD–A medical vector illustration of the bones of a foot on a white background
 Superior view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superior-view-of-right-foot-image491876716.html
Superior view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superior-view-of-right-foot-image491876716.htmlRF2KG6WNG–Superior view of Right Foot
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE TALUS. 25> the dorsal surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Posteriorly the body is provided with two tubercles, separated by a groove; the lateral of these (processus posterior tali) is usually the larger, and is occasionally a separate ossicle (os trigonum). To it is attached the posterior talo-fibular ligament of the ankle- joint. The groove, which winds obliquely from above downwards and medially over the posterior surface of the bone, lodges the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The head, of oval form, is direct Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-talus-25gt-the-dorsal-surface-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-of-the-calcaneus-posteriorly-the-body-is-provided-with-two-tubercles-separated-by-a-groove-the-lateral-of-these-processus-posterior-tali-is-usually-the-larger-and-is-occasionally-a-separate-ossicle-os-trigonum-to-it-is-attached-the-posterior-talo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-the-groove-which-winds-obliquely-from-above-downwards-and-medially-over-the-posterior-surface-of-the-bone-lodges-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-hallucis-longus-muscle-the-head-of-oval-form-is-direct-image216341628.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE TALUS. 25> the dorsal surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Posteriorly the body is provided with two tubercles, separated by a groove; the lateral of these (processus posterior tali) is usually the larger, and is occasionally a separate ossicle (os trigonum). To it is attached the posterior talo-fibular ligament of the ankle- joint. The groove, which winds obliquely from above downwards and medially over the posterior surface of the bone, lodges the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The head, of oval form, is direct Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-talus-25gt-the-dorsal-surface-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-of-the-calcaneus-posteriorly-the-body-is-provided-with-two-tubercles-separated-by-a-groove-the-lateral-of-these-processus-posterior-tali-is-usually-the-larger-and-is-occasionally-a-separate-ossicle-os-trigonum-to-it-is-attached-the-posterior-talo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-the-groove-which-winds-obliquely-from-above-downwards-and-medially-over-the-posterior-surface-of-the-bone-lodges-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-hallucis-longus-muscle-the-head-of-oval-form-is-direct-image216341628.htmlRMPFY5XM–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE TALUS. 25> the dorsal surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Posteriorly the body is provided with two tubercles, separated by a groove; the lateral of these (processus posterior tali) is usually the larger, and is occasionally a separate ossicle (os trigonum). To it is attached the posterior talo-fibular ligament of the ankle- joint. The groove, which winds obliquely from above downwards and medially over the posterior surface of the bone, lodges the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The head, of oval form, is direct
 . Anatomy, descriptive and applied. Anatomy. Feroneal tubercle Groove for Feroneus longus tendo AchiUia External- tubercle B For posterim- facet of astragal:is For middle facet of astragalus For ntitei tor facet of astragalus. Internal tubercle Groove for Flexor longus hallucis Sustentaculum tali Groove for interosseous ligament Fig. 194.—The left calcaneus. A. Postero-external view. B. Antero-internal view. The posterior surface is rough, prominent, convex, and wider below than above. The posterior extremity is the projection of the heel. It is called the tuberosity (tuber calcanei). Its lowe Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-descriptive-and-applied-anatomy-feroneal-tubercle-groove-for-feroneus-longus-tendo-achiuia-external-tubercle-b-for-posterim-facet-of-astragalis-for-middle-facet-of-astragalus-for-ntitei-tor-facet-of-astragalus-internal-tubercle-groove-for-flexor-longus-hallucis-sustentaculum-tali-groove-for-interosseous-ligament-fig-194the-left-calcaneus-a-postero-external-view-b-antero-internal-view-the-posterior-surface-is-rough-prominent-convex-and-wider-below-than-above-the-posterior-extremity-is-the-projection-of-the-heel-it-is-called-the-tuberosity-tuber-calcanei-its-lowe-image236799966.html
. Anatomy, descriptive and applied. Anatomy. Feroneal tubercle Groove for Feroneus longus tendo AchiUia External- tubercle B For posterim- facet of astragal:is For middle facet of astragalus For ntitei tor facet of astragalus. Internal tubercle Groove for Flexor longus hallucis Sustentaculum tali Groove for interosseous ligament Fig. 194.—The left calcaneus. A. Postero-external view. B. Antero-internal view. The posterior surface is rough, prominent, convex, and wider below than above. The posterior extremity is the projection of the heel. It is called the tuberosity (tuber calcanei). Its lowe Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/anatomy-descriptive-and-applied-anatomy-feroneal-tubercle-groove-for-feroneus-longus-tendo-achiuia-external-tubercle-b-for-posterim-facet-of-astragalis-for-middle-facet-of-astragalus-for-ntitei-tor-facet-of-astragalus-internal-tubercle-groove-for-flexor-longus-hallucis-sustentaculum-tali-groove-for-interosseous-ligament-fig-194the-left-calcaneus-a-postero-external-view-b-antero-internal-view-the-posterior-surface-is-rough-prominent-convex-and-wider-below-than-above-the-posterior-extremity-is-the-projection-of-the-heel-it-is-called-the-tuberosity-tuber-calcanei-its-lowe-image236799966.htmlRMRN74NJ–. Anatomy, descriptive and applied. Anatomy. Feroneal tubercle Groove for Feroneus longus tendo AchiUia External- tubercle B For posterim- facet of astragal:is For middle facet of astragalus For ntitei tor facet of astragalus. Internal tubercle Groove for Flexor longus hallucis Sustentaculum tali Groove for interosseous ligament Fig. 194.—The left calcaneus. A. Postero-external view. B. Antero-internal view. The posterior surface is rough, prominent, convex, and wider below than above. The posterior extremity is the projection of the heel. It is called the tuberosity (tuber calcanei). Its lowe
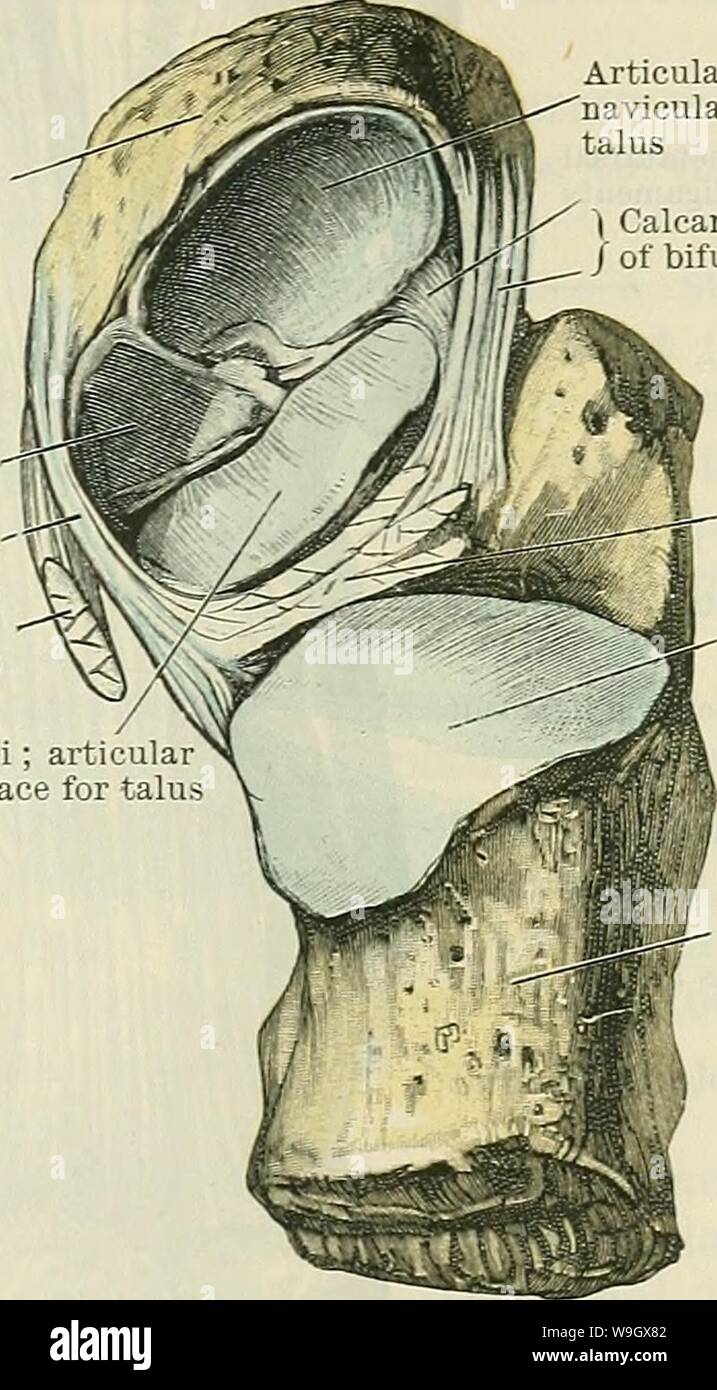 Archive image from page 388 of Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy (1914). Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy cunninghamstextb00cunn Year: 1914 ( INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibre Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-388-of-cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-1914-cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-cunninghamstextb00cunn-year-1914-inteetaesal-joints-355-navicular-bone-plantar-cal-c-caneo-navicular-j-ligament-tendon-of-tibialis-posterior-muscle-cut-sustentaculum-tali-articul-surface-for-talu-articular-surface-on-navicular-for-head-of-talus-calcaneonavicular-part-of-bifurcate-ligament-interosseous-talo-calcaneal-ligament-articular-surface-on-calcaneus-for-body-of-talus-a-deeper-plane-than-the-calcaneo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-it-con-sists-of-short-fibre-image264059266.html
Archive image from page 388 of Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy (1914). Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy cunninghamstextb00cunn Year: 1914 ( INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibre Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-388-of-cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-1914-cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-cunninghamstextb00cunn-year-1914-inteetaesal-joints-355-navicular-bone-plantar-cal-c-caneo-navicular-j-ligament-tendon-of-tibialis-posterior-muscle-cut-sustentaculum-tali-articul-surface-for-talu-articular-surface-on-navicular-for-head-of-talus-calcaneonavicular-part-of-bifurcate-ligament-interosseous-talo-calcaneal-ligament-articular-surface-on-calcaneus-for-body-of-talus-a-deeper-plane-than-the-calcaneo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-it-con-sists-of-short-fibre-image264059266.htmlRMW9GX82–Archive image from page 388 of Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy (1914). Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy cunninghamstextb00cunn Year: 1914 ( INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibre
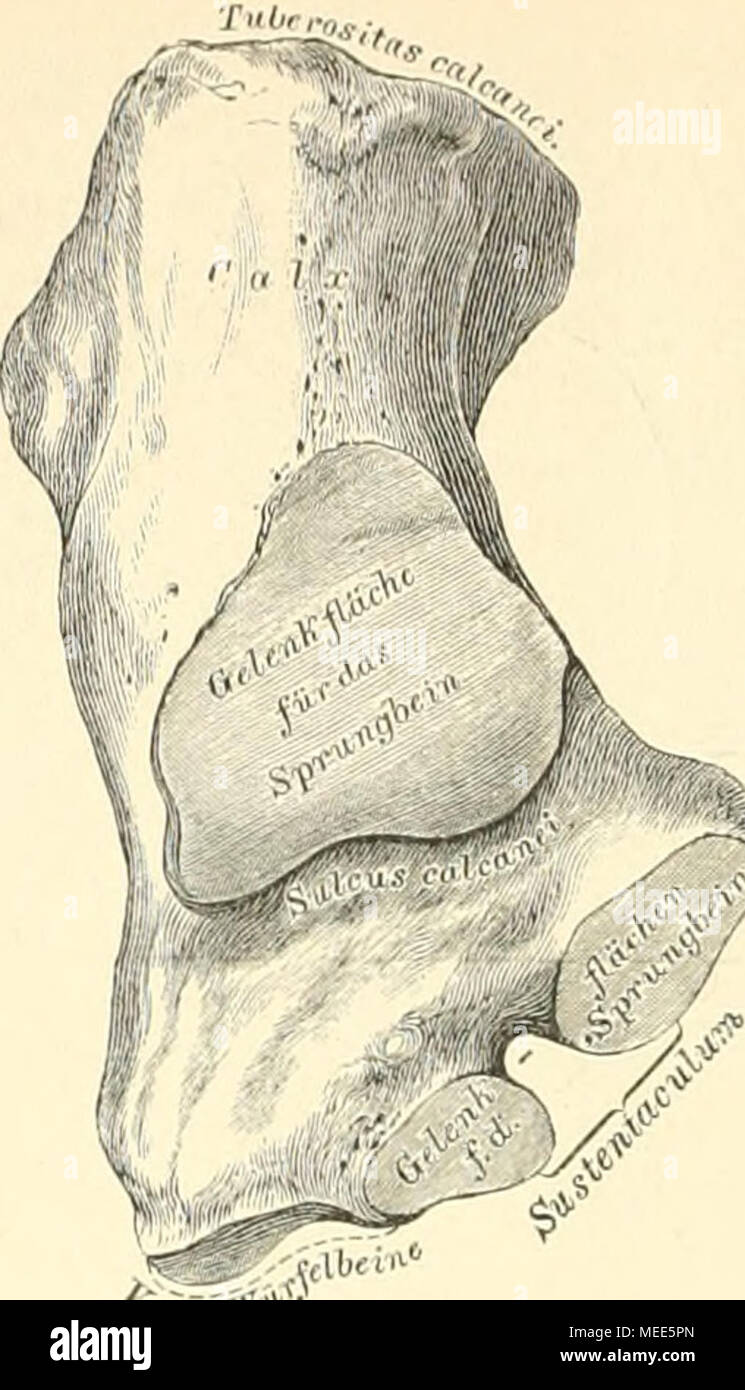 . Die descriptive und topographische Anatomie des Menschen . 232. Das rechte Fersenbein, Calcaneus, von oben. Das Fersenbein, unter dem Sprungbeine gelegen, verlängert sich nach hinten zur Hacke. Calx, welche mit dem Fersenhöcker, Tuberositas calcanei, endet. An der oberen Flache befindet sich die überknorpelte Stelle zur Ver- bindung mit dem Sprungbeinkörper, vor derselben verläuft der Sulcus calcanei, welcher mit dem entsprechenden Sulcus tali den Sinus tarsi erzeugt. Nach innen von der Gelenkfläche ragt ein an seiner oberen Fläche ebenfalls überknorpelter Fortsatz, das Sustentaculum vor, de Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/die-descriptive-und-topographische-anatomie-des-menschen-232-das-rechte-fersenbein-calcaneus-von-oben-das-fersenbein-unter-dem-sprungbeine-gelegen-verlngert-sich-nach-hinten-zur-hacke-calx-welche-mit-dem-fersenhcker-tuberositas-calcanei-endet-an-der-oberen-flache-befindet-sich-die-berknorpelte-stelle-zur-ver-bindung-mit-dem-sprungbeinkrper-vor-derselben-verluft-der-sulcus-calcanei-welcher-mit-dem-entsprechenden-sulcus-tali-den-sinus-tarsi-erzeugt-nach-innen-von-der-gelenkflche-ragt-ein-an-seiner-oberen-flche-ebenfalls-berknorpelter-fortsatz-das-sustentaculum-vor-de-image181020749.html
. Die descriptive und topographische Anatomie des Menschen . 232. Das rechte Fersenbein, Calcaneus, von oben. Das Fersenbein, unter dem Sprungbeine gelegen, verlängert sich nach hinten zur Hacke. Calx, welche mit dem Fersenhöcker, Tuberositas calcanei, endet. An der oberen Flache befindet sich die überknorpelte Stelle zur Ver- bindung mit dem Sprungbeinkörper, vor derselben verläuft der Sulcus calcanei, welcher mit dem entsprechenden Sulcus tali den Sinus tarsi erzeugt. Nach innen von der Gelenkfläche ragt ein an seiner oberen Fläche ebenfalls überknorpelter Fortsatz, das Sustentaculum vor, de Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/die-descriptive-und-topographische-anatomie-des-menschen-232-das-rechte-fersenbein-calcaneus-von-oben-das-fersenbein-unter-dem-sprungbeine-gelegen-verlngert-sich-nach-hinten-zur-hacke-calx-welche-mit-dem-fersenhcker-tuberositas-calcanei-endet-an-der-oberen-flache-befindet-sich-die-berknorpelte-stelle-zur-ver-bindung-mit-dem-sprungbeinkrper-vor-derselben-verluft-der-sulcus-calcanei-welcher-mit-dem-entsprechenden-sulcus-tali-den-sinus-tarsi-erzeugt-nach-innen-von-der-gelenkflche-ragt-ein-an-seiner-oberen-flche-ebenfalls-berknorpelter-fortsatz-das-sustentaculum-vor-de-image181020749.htmlRMMEE5PN–. Die descriptive und topographische Anatomie des Menschen . 232. Das rechte Fersenbein, Calcaneus, von oben. Das Fersenbein, unter dem Sprungbeine gelegen, verlängert sich nach hinten zur Hacke. Calx, welche mit dem Fersenhöcker, Tuberositas calcanei, endet. An der oberen Flache befindet sich die überknorpelte Stelle zur Ver- bindung mit dem Sprungbeinkörper, vor derselben verläuft der Sulcus calcanei, welcher mit dem entsprechenden Sulcus tali den Sinus tarsi erzeugt. Nach innen von der Gelenkfläche ragt ein an seiner oberen Fläche ebenfalls überknorpelter Fortsatz, das Sustentaculum vor, de
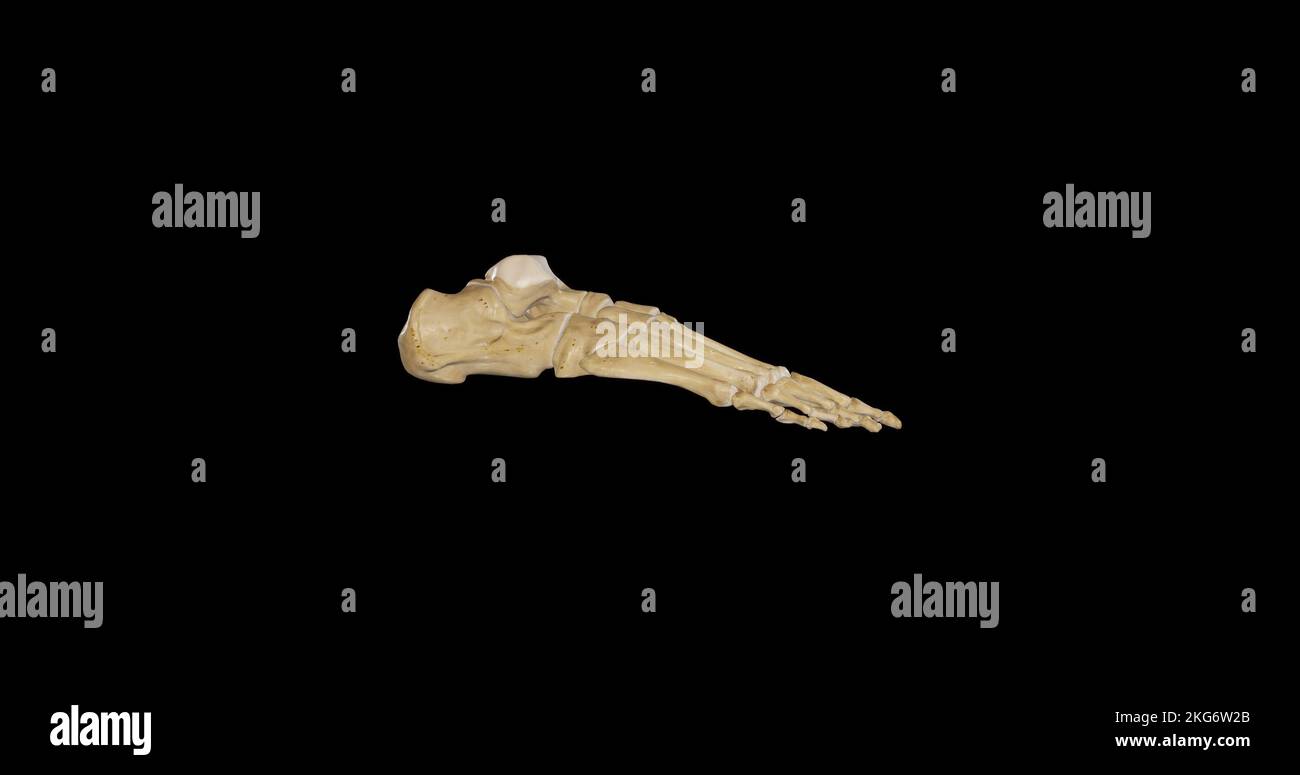 Lateral view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lateral-view-of-right-foot-image491876179.html
Lateral view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/lateral-view-of-right-foot-image491876179.htmlRF2KG6W2B–Lateral view of Right Foot
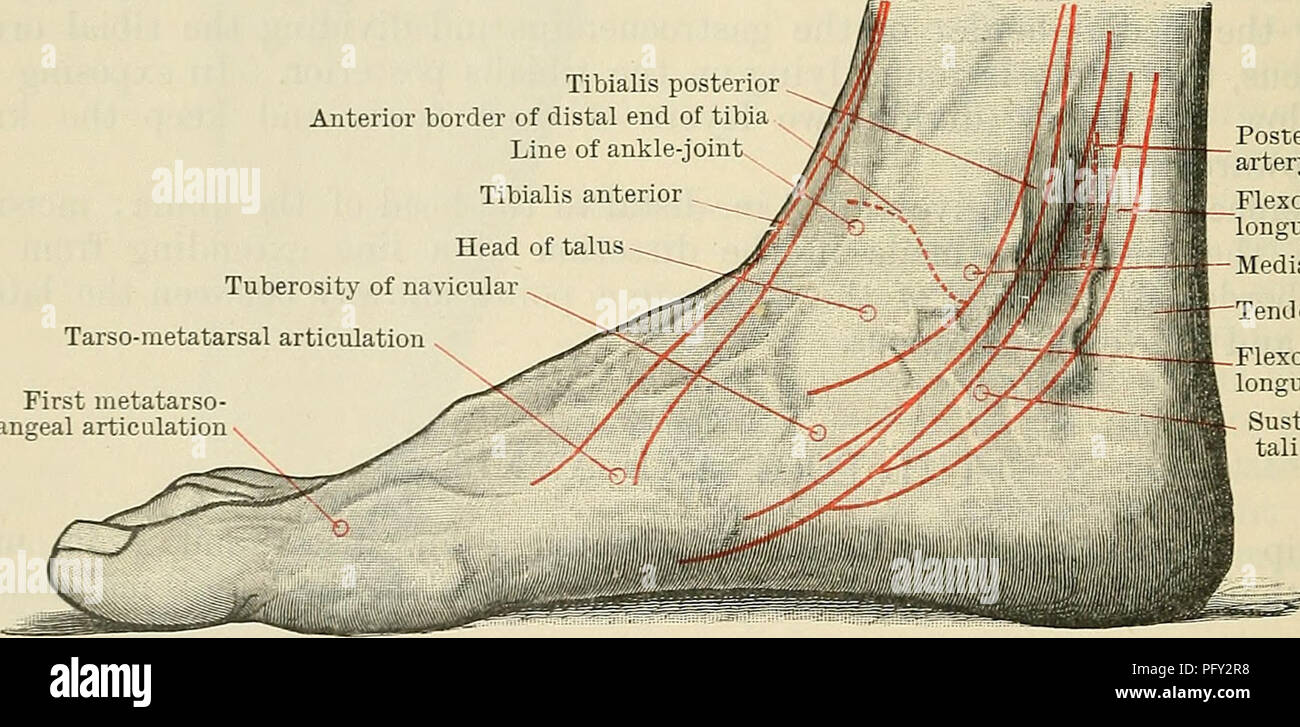 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 146-1 SUKFACE AND SUKGICAL ANATOMY. of the tibia. The small posterior surface of the talus is felt distal and posterior to the medial malleolus, at the anterior part of the hollow between it and the heel. In effusions into the ankle-joint the hollows in front and behind the malleoli are obliterated, and the extensor tendons are raised from the front of the joint. A finder's breadth distal to the tip of the medial malleolus is the sustentaculum tali; 1 in. in front of the sustentaculum, and midway between the dorsal and plantar margins of the media Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-146-1-sukface-and-sukgical-anatomy-of-the-tibia-the-small-posterior-surface-of-the-talus-is-felt-distal-and-posterior-to-the-medial-malleolus-at-the-anterior-part-of-the-hollow-between-it-and-the-heel-in-effusions-into-the-ankle-joint-the-hollows-in-front-and-behind-the-malleoli-are-obliterated-and-the-extensor-tendons-are-raised-from-the-front-of-the-joint-a-finders-breadth-distal-to-the-tip-of-the-medial-malleolus-is-the-sustentaculum-tali-1-in-in-front-of-the-sustentaculum-and-midway-between-the-dorsal-and-plantar-margins-of-the-media-image216339180.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 146-1 SUKFACE AND SUKGICAL ANATOMY. of the tibia. The small posterior surface of the talus is felt distal and posterior to the medial malleolus, at the anterior part of the hollow between it and the heel. In effusions into the ankle-joint the hollows in front and behind the malleoli are obliterated, and the extensor tendons are raised from the front of the joint. A finder's breadth distal to the tip of the medial malleolus is the sustentaculum tali; 1 in. in front of the sustentaculum, and midway between the dorsal and plantar margins of the media Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-146-1-sukface-and-sukgical-anatomy-of-the-tibia-the-small-posterior-surface-of-the-talus-is-felt-distal-and-posterior-to-the-medial-malleolus-at-the-anterior-part-of-the-hollow-between-it-and-the-heel-in-effusions-into-the-ankle-joint-the-hollows-in-front-and-behind-the-malleoli-are-obliterated-and-the-extensor-tendons-are-raised-from-the-front-of-the-joint-a-finders-breadth-distal-to-the-tip-of-the-medial-malleolus-is-the-sustentaculum-tali-1-in-in-front-of-the-sustentaculum-and-midway-between-the-dorsal-and-plantar-margins-of-the-media-image216339180.htmlRMPFY2R8–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 146-1 SUKFACE AND SUKGICAL ANATOMY. of the tibia. The small posterior surface of the talus is felt distal and posterior to the medial malleolus, at the anterior part of the hollow between it and the heel. In effusions into the ankle-joint the hollows in front and behind the malleoli are obliterated, and the extensor tendons are raised from the front of the joint. A finder's breadth distal to the tip of the medial malleolus is the sustentaculum tali; 1 in. in front of the sustentaculum, and midway between the dorsal and plantar margins of the media
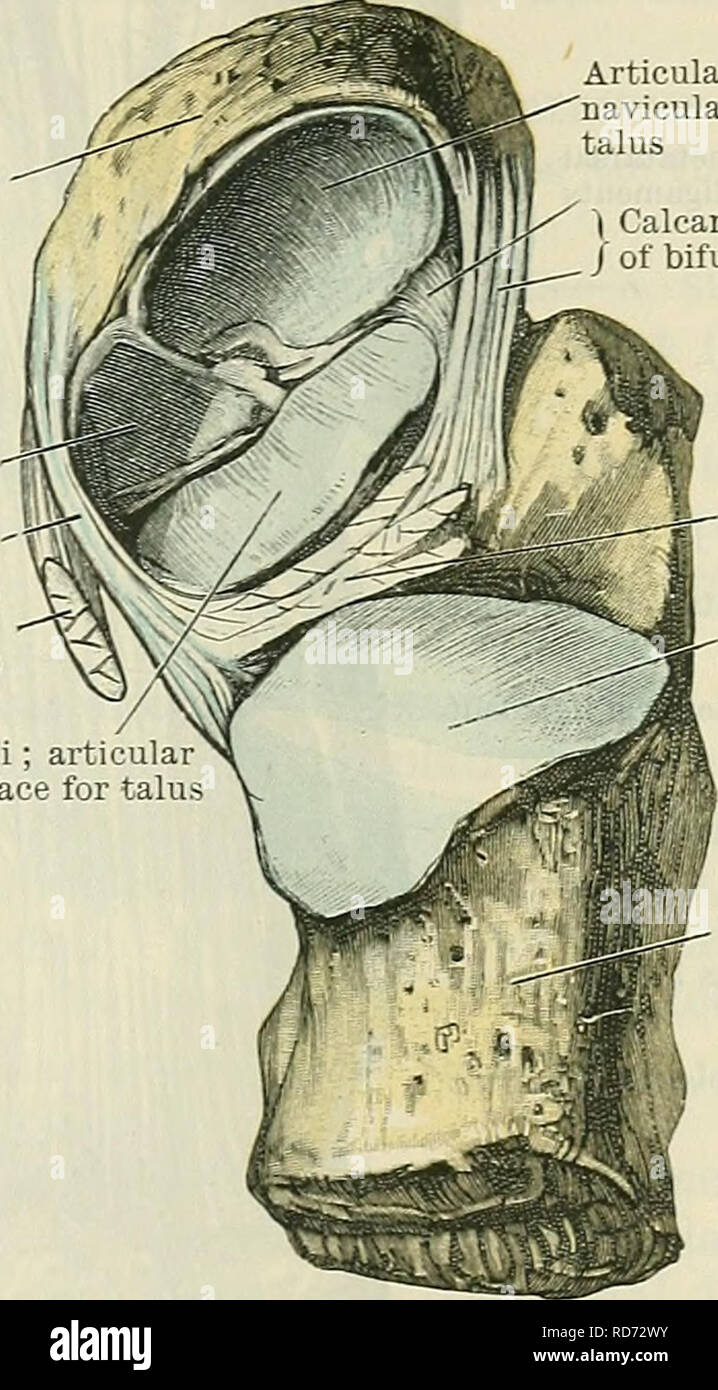 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibres passing between the adjacent rough lateral margins of the two bones. The ligamentum talocalcaneu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-inteetaesal-joints-355-navicular-bone-plantar-cal-c-caneo-navicular-j-ligament-tendon-of-tibialis-posterior-muscle-cut-sustentaculum-tali-articul-surface-for-talu-articular-surface-on-navicular-for-head-of-talus-calcaneonavicular-part-of-bifurcate-ligament-interosseous-talo-calcaneal-ligament-articular-surface-on-calcaneus-for-body-of-talus-a-deeper-plane-than-the-calcaneo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-it-con-sists-of-short-fibres-passing-between-the-adjacent-rough-lateral-margins-of-the-two-bones-the-ligamentum-talocalcaneu-image231881271.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibres passing between the adjacent rough lateral margins of the two bones. The ligamentum talocalcaneu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-inteetaesal-joints-355-navicular-bone-plantar-cal-c-caneo-navicular-j-ligament-tendon-of-tibialis-posterior-muscle-cut-sustentaculum-tali-articul-surface-for-talu-articular-surface-on-navicular-for-head-of-talus-calcaneonavicular-part-of-bifurcate-ligament-interosseous-talo-calcaneal-ligament-articular-surface-on-calcaneus-for-body-of-talus-a-deeper-plane-than-the-calcaneo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-it-con-sists-of-short-fibres-passing-between-the-adjacent-rough-lateral-margins-of-the-two-bones-the-ligamentum-talocalcaneu-image231881271.htmlRMRD72WY–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibres passing between the adjacent rough lateral margins of the two bones. The ligamentum talocalcaneu
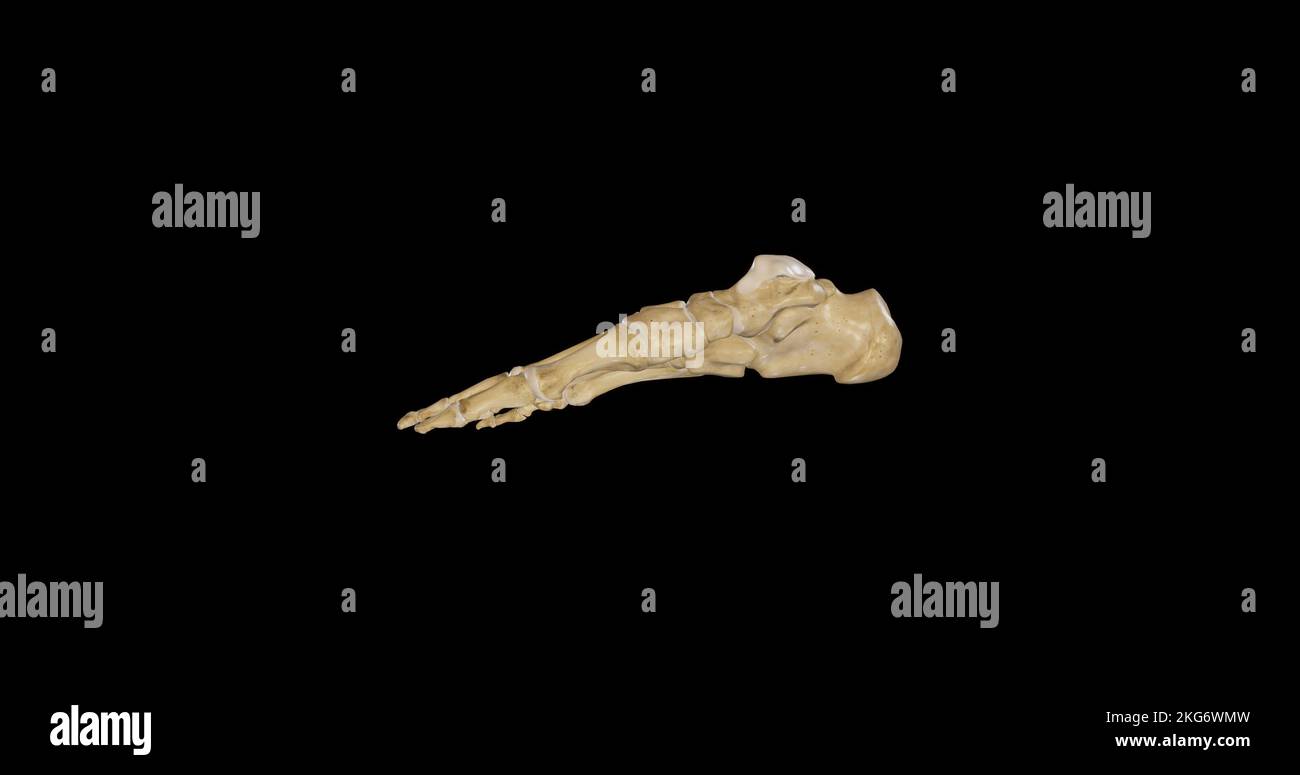 Medial view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medial-view-of-right-foot-image491876697.html
Medial view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medial-view-of-right-foot-image491876697.htmlRF2KG6WMW–Medial view of Right Foot
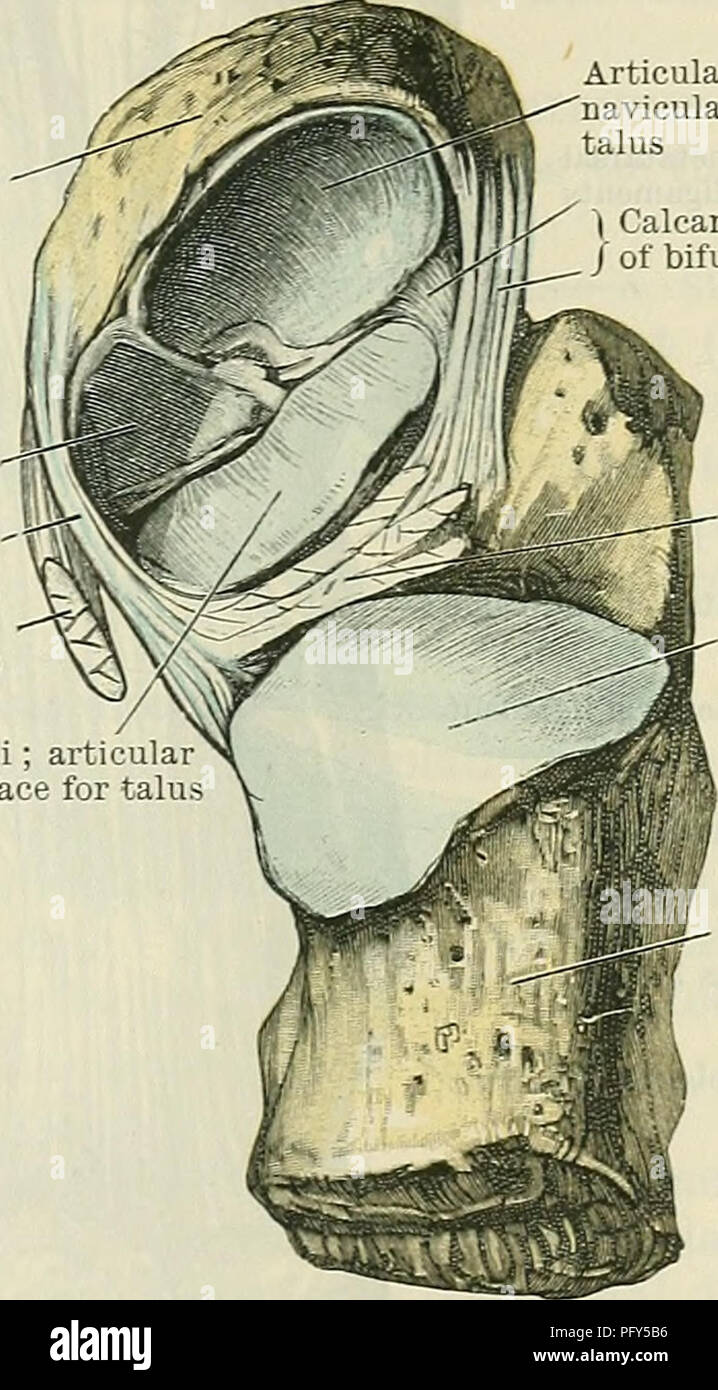 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibres passing between the adjacent rough lateral margins of the two bones. The ligamentum talocalcaneu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-inteetaesal-joints-355-navicular-bone-plantar-cal-c-caneo-navicular-j-ligament-tendon-of-tibialis-posterior-muscle-cut-sustentaculum-tali-articul-surface-for-talu-articular-surface-on-navicular-for-head-of-talus-calcaneonavicular-part-of-bifurcate-ligament-interosseous-talo-calcaneal-ligament-articular-surface-on-calcaneus-for-body-of-talus-a-deeper-plane-than-the-calcaneo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-it-con-sists-of-short-fibres-passing-between-the-adjacent-rough-lateral-margins-of-the-two-bones-the-ligamentum-talocalcaneu-image216341194.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibres passing between the adjacent rough lateral margins of the two bones. The ligamentum talocalcaneu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-inteetaesal-joints-355-navicular-bone-plantar-cal-c-caneo-navicular-j-ligament-tendon-of-tibialis-posterior-muscle-cut-sustentaculum-tali-articul-surface-for-talu-articular-surface-on-navicular-for-head-of-talus-calcaneonavicular-part-of-bifurcate-ligament-interosseous-talo-calcaneal-ligament-articular-surface-on-calcaneus-for-body-of-talus-a-deeper-plane-than-the-calcaneo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-it-con-sists-of-short-fibres-passing-between-the-adjacent-rough-lateral-margins-of-the-two-bones-the-ligamentum-talocalcaneu-image216341194.htmlRMPFY5B6–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. INTEETAESAL JOINTS. 355 Navicular bone Plantar cal- C caneo-navicular-j ligament (. Tendon of tibialis posterior muscle (cut) Sustentaculum tali; articul; surface for talu Articular surface on navicular for head of talus | Calcaneonavicular part / of bifurcate ligament Interosseous talo- calcaneal ligament Articular surface on calcaneus for body of talus a deeper plane than, the calcaneo-fibular ligament of the ankle-joint. It con- sists of short fibres passing between the adjacent rough lateral margins of the two bones. The ligamentum talocalcaneu
 Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . of the astragalus thus brought into view.The joint between the head of the astragalus and the scaphoid isopened (tuberosity of the scaphoid is the guide), and also the jointbetween the astragalus and the os calcis (sustentaculum tali) ; afterthis the astragalus is seized with a bone-forceps, and, twisting andat the same time cutting close to the bone, it is removed. In re-secting the ankle-joint for tuberculosis, if the astragalus is diseased,it is well to remove this bone entire. AMPUTATIONS, RESECTIONS, ETC. 80 AxKLE-JOiXT (Koexig).—Tliis i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/operative-surgery-for-students-and-practitioners-of-the-astragalus-thus-brought-into-viewthe-joint-between-the-head-of-the-astragalus-and-the-scaphoid-isopened-tuberosity-of-the-scaphoid-is-the-guide-and-also-the-jointbetween-the-astragalus-and-the-os-calcis-sustentaculum-tali-afterthis-the-astragalus-is-seized-with-a-bone-forceps-and-twisting-andat-the-same-time-cutting-close-to-the-bone-it-is-removed-in-re-secting-the-ankle-joint-for-tuberculosis-if-the-astragalus-is-diseasedit-is-well-to-remove-this-bone-entire-amputations-resections-etc-80-axkle-joixt-koexigtliis-i-image340302671.html
Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . of the astragalus thus brought into view.The joint between the head of the astragalus and the scaphoid isopened (tuberosity of the scaphoid is the guide), and also the jointbetween the astragalus and the os calcis (sustentaculum tali) ; afterthis the astragalus is seized with a bone-forceps, and, twisting andat the same time cutting close to the bone, it is removed. In re-secting the ankle-joint for tuberculosis, if the astragalus is diseased,it is well to remove this bone entire. AMPUTATIONS, RESECTIONS, ETC. 80 AxKLE-JOiXT (Koexig).—Tliis i Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/operative-surgery-for-students-and-practitioners-of-the-astragalus-thus-brought-into-viewthe-joint-between-the-head-of-the-astragalus-and-the-scaphoid-isopened-tuberosity-of-the-scaphoid-is-the-guide-and-also-the-jointbetween-the-astragalus-and-the-os-calcis-sustentaculum-tali-afterthis-the-astragalus-is-seized-with-a-bone-forceps-and-twisting-andat-the-same-time-cutting-close-to-the-bone-it-is-removed-in-re-secting-the-ankle-joint-for-tuberculosis-if-the-astragalus-is-diseasedit-is-well-to-remove-this-bone-entire-amputations-resections-etc-80-axkle-joixt-koexigtliis-i-image340302671.htmlRM2ANJ3ER–Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . of the astragalus thus brought into view.The joint between the head of the astragalus and the scaphoid isopened (tuberosity of the scaphoid is the guide), and also the jointbetween the astragalus and the os calcis (sustentaculum tali) ; afterthis the astragalus is seized with a bone-forceps, and, twisting andat the same time cutting close to the bone, it is removed. In re-secting the ankle-joint for tuberculosis, if the astragalus is diseased,it is well to remove this bone entire. AMPUTATIONS, RESECTIONS, ETC. 80 AxKLE-JOiXT (Koexig).—Tliis i
 Inferior view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-right-foot-image491876164.html
Inferior view of Right Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/inferior-view-of-right-foot-image491876164.htmlRF2KG6W1T–Inferior view of Right Foot
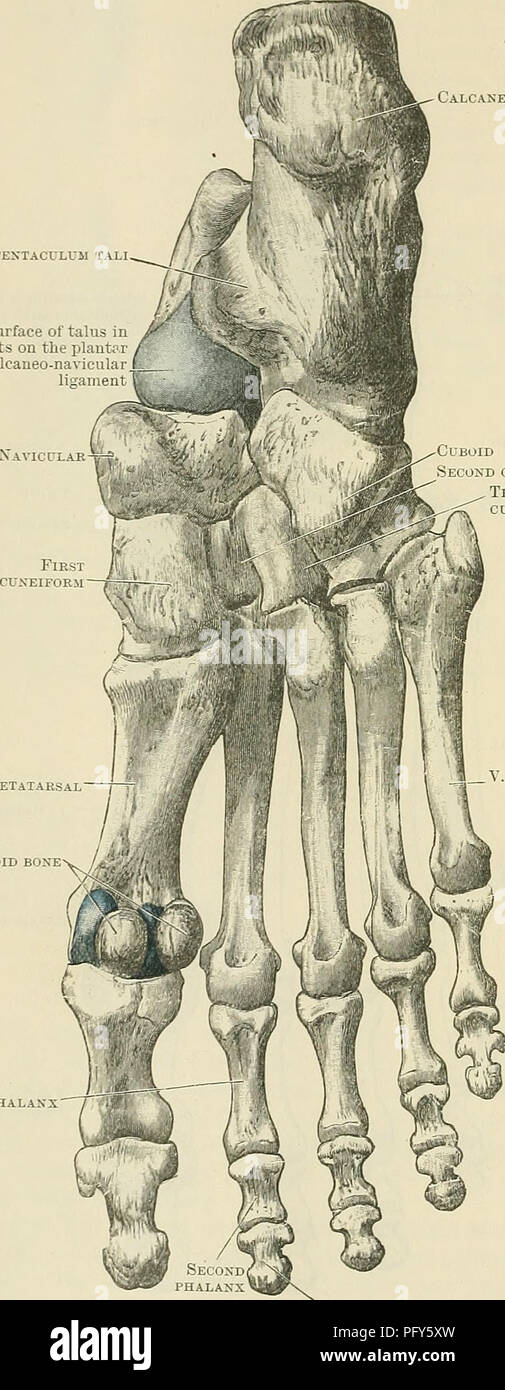 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 256 OSTEOLOGY. placed obliquely from behind forwards and laterally ; this, rests upon a corre- sponding surface on the dorsal aspect of the calcaneus. In front of this, and crossing the bone from the medial side laterally and forwards, is a deep furrow (sulcus tali), Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Surface of talus in blue tests on the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament Navicular-^ First phalanx. Cuboid Second cuneiform Third cuneiform I. Metatarsal Sesamoid bone V. Metatarsal Third or terminal phalanx Fig. 255.—Plantar Surface of the Bones of the Rig Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-256-osteology-placed-obliquely-from-behind-forwards-and-laterally-this-rests-upon-a-corre-sponding-surface-on-the-dorsal-aspect-of-the-calcaneus-in-front-of-this-and-crossing-the-bone-from-the-medial-side-laterally-and-forwards-is-a-deep-furrow-sulcus-tali-calcaneus-sustentaculum-tali-surface-of-talus-in-blue-tests-on-the-plantar-calcaneonavicular-ligament-navicular-first-phalanx-cuboid-second-cuneiform-third-cuneiform-i-metatarsal-sesamoid-bone-v-metatarsal-third-or-terminal-phalanx-fig-255plantar-surface-of-the-bones-of-the-rig-image216341633.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 256 OSTEOLOGY. placed obliquely from behind forwards and laterally ; this, rests upon a corre- sponding surface on the dorsal aspect of the calcaneus. In front of this, and crossing the bone from the medial side laterally and forwards, is a deep furrow (sulcus tali), Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Surface of talus in blue tests on the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament Navicular-^ First phalanx. Cuboid Second cuneiform Third cuneiform I. Metatarsal Sesamoid bone V. Metatarsal Third or terminal phalanx Fig. 255.—Plantar Surface of the Bones of the Rig Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-256-osteology-placed-obliquely-from-behind-forwards-and-laterally-this-rests-upon-a-corre-sponding-surface-on-the-dorsal-aspect-of-the-calcaneus-in-front-of-this-and-crossing-the-bone-from-the-medial-side-laterally-and-forwards-is-a-deep-furrow-sulcus-tali-calcaneus-sustentaculum-tali-surface-of-talus-in-blue-tests-on-the-plantar-calcaneonavicular-ligament-navicular-first-phalanx-cuboid-second-cuneiform-third-cuneiform-i-metatarsal-sesamoid-bone-v-metatarsal-third-or-terminal-phalanx-fig-255plantar-surface-of-the-bones-of-the-rig-image216341633.htmlRMPFY5XW–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 256 OSTEOLOGY. placed obliquely from behind forwards and laterally ; this, rests upon a corre- sponding surface on the dorsal aspect of the calcaneus. In front of this, and crossing the bone from the medial side laterally and forwards, is a deep furrow (sulcus tali), Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Surface of talus in blue tests on the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament Navicular-^ First phalanx. Cuboid Second cuneiform Third cuneiform I. Metatarsal Sesamoid bone V. Metatarsal Third or terminal phalanx Fig. 255.—Plantar Surface of the Bones of the Rig
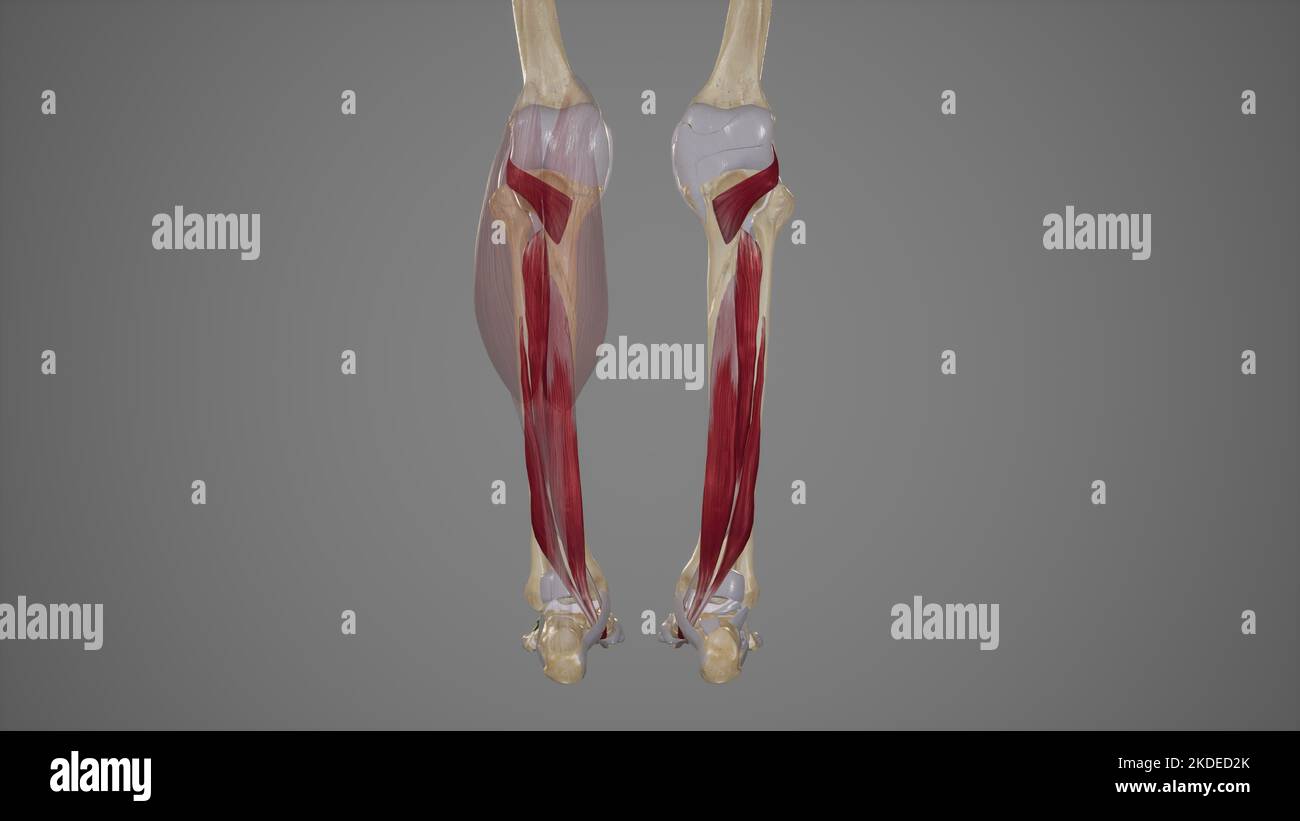 Deep Posterior Muscles of Lower Leg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/deep-posterior-muscles-of-lower-leg-image490198427.html
Deep Posterior Muscles of Lower Leg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/deep-posterior-muscles-of-lower-leg-image490198427.htmlRF2KDED2K–Deep Posterior Muscles of Lower Leg
 A system of human anatomy, general and special . s, adductor pollicis and transversus pedis; to thefourth, two dorsal and one plantar interosseous, adductor pollicis andtransversus pedis; to the fifth, one dorsal and one plantar interosseous, » The sole of the left foot. 1. The inner tuberosity of the os calcis. 2. The outertuberosity, x. Its posterior tuberosity. 3. The groove for the tendon of the flexor longusdigitorura ; this figure indicates also the sustentaculum tali. 4. The rounded head of theastragalus. 5. The scaphoid bone. 6. Its tuberosity. 7. The internal cuneiform bone;its broad Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-human-anatomy-general-and-special-s-adductor-pollicis-and-transversus-pedis-to-thefourth-two-dorsal-and-one-plantar-interosseous-adductor-pollicis-andtransversus-pedis-to-the-fifth-one-dorsal-and-one-plantar-interosseous-the-sole-of-the-left-foot-1-the-inner-tuberosity-of-the-os-calcis-2-the-outertuberosity-x-its-posterior-tuberosity-3-the-groove-for-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longusdigitorura-this-figure-indicates-also-the-sustentaculum-tali-4-the-rounded-head-of-theastragalus-5-the-scaphoid-bone-6-its-tuberosity-7-the-internal-cuneiform-boneits-broad-image342749053.html
A system of human anatomy, general and special . s, adductor pollicis and transversus pedis; to thefourth, two dorsal and one plantar interosseous, adductor pollicis andtransversus pedis; to the fifth, one dorsal and one plantar interosseous, » The sole of the left foot. 1. The inner tuberosity of the os calcis. 2. The outertuberosity, x. Its posterior tuberosity. 3. The groove for the tendon of the flexor longusdigitorura ; this figure indicates also the sustentaculum tali. 4. The rounded head of theastragalus. 5. The scaphoid bone. 6. Its tuberosity. 7. The internal cuneiform bone;its broad Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-system-of-human-anatomy-general-and-special-s-adductor-pollicis-and-transversus-pedis-to-thefourth-two-dorsal-and-one-plantar-interosseous-adductor-pollicis-andtransversus-pedis-to-the-fifth-one-dorsal-and-one-plantar-interosseous-the-sole-of-the-left-foot-1-the-inner-tuberosity-of-the-os-calcis-2-the-outertuberosity-x-its-posterior-tuberosity-3-the-groove-for-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longusdigitorura-this-figure-indicates-also-the-sustentaculum-tali-4-the-rounded-head-of-theastragalus-5-the-scaphoid-bone-6-its-tuberosity-7-the-internal-cuneiform-boneits-broad-image342749053.htmlRM2AWHFWH–A system of human anatomy, general and special . s, adductor pollicis and transversus pedis; to thefourth, two dorsal and one plantar interosseous, adductor pollicis andtransversus pedis; to the fifth, one dorsal and one plantar interosseous, » The sole of the left foot. 1. The inner tuberosity of the os calcis. 2. The outertuberosity, x. Its posterior tuberosity. 3. The groove for the tendon of the flexor longusdigitorura ; this figure indicates also the sustentaculum tali. 4. The rounded head of theastragalus. 5. The scaphoid bone. 6. Its tuberosity. 7. The internal cuneiform bone;its broad
 . Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte und Morphologie des Hand- und Fussskelets der Marsupialier. 375 durch schmale Zonen vom Bildungsgewebe getrennt; der Sinus tarsi verläuft schief, weil der Talus, von der Planta betrachtet, von dem aus dem Calcaneum sich entwickelnden Sustentaculum tali theilweise überlagert wird (Fig. 25—28); die Tuberositas calcanei ist in Continuität mit dem Rest des Fersenbeins verknorpelt. Zwischen Talus und den Unterschenkelbeinen, aber in näherer Beziehung zur Tibia als zur Fibula erscheint Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/denkschriften-der-medicinisch-naturwissenschaftlichen-gesellschaft-zu-jena-beitrge-zur-entwickelungsgeschichte-und-morphologie-des-hand-und-fussskelets-der-marsupialier-375-durch-schmale-zonen-vom-bildungsgewebe-getrennt-der-sinus-tarsi-verluft-schief-weil-der-talus-von-der-planta-betrachtet-von-dem-aus-dem-calcaneum-sich-entwickelnden-sustentaculum-tali-theilweise-berlagert-wird-fig-2528-die-tuberositas-calcanei-ist-in-continuitt-mit-dem-rest-des-fersenbeins-verknorpelt-zwischen-talus-und-den-unterschenkelbeinen-aber-in-nherer-beziehung-zur-tibia-als-zur-fibula-erscheint-image216168922.html
. Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte und Morphologie des Hand- und Fussskelets der Marsupialier. 375 durch schmale Zonen vom Bildungsgewebe getrennt; der Sinus tarsi verläuft schief, weil der Talus, von der Planta betrachtet, von dem aus dem Calcaneum sich entwickelnden Sustentaculum tali theilweise überlagert wird (Fig. 25—28); die Tuberositas calcanei ist in Continuität mit dem Rest des Fersenbeins verknorpelt. Zwischen Talus und den Unterschenkelbeinen, aber in näherer Beziehung zur Tibia als zur Fibula erscheint Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/denkschriften-der-medicinisch-naturwissenschaftlichen-gesellschaft-zu-jena-beitrge-zur-entwickelungsgeschichte-und-morphologie-des-hand-und-fussskelets-der-marsupialier-375-durch-schmale-zonen-vom-bildungsgewebe-getrennt-der-sinus-tarsi-verluft-schief-weil-der-talus-von-der-planta-betrachtet-von-dem-aus-dem-calcaneum-sich-entwickelnden-sustentaculum-tali-theilweise-berlagert-wird-fig-2528-die-tuberositas-calcanei-ist-in-continuitt-mit-dem-rest-des-fersenbeins-verknorpelt-zwischen-talus-und-den-unterschenkelbeinen-aber-in-nherer-beziehung-zur-tibia-als-zur-fibula-erscheint-image216168922.htmlRMPFK9JJ–. Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte und Morphologie des Hand- und Fussskelets der Marsupialier. 375 durch schmale Zonen vom Bildungsgewebe getrennt; der Sinus tarsi verläuft schief, weil der Talus, von der Planta betrachtet, von dem aus dem Calcaneum sich entwickelnden Sustentaculum tali theilweise überlagert wird (Fig. 25—28); die Tuberositas calcanei ist in Continuität mit dem Rest des Fersenbeins verknorpelt. Zwischen Talus und den Unterschenkelbeinen, aber in näherer Beziehung zur Tibia als zur Fibula erscheint
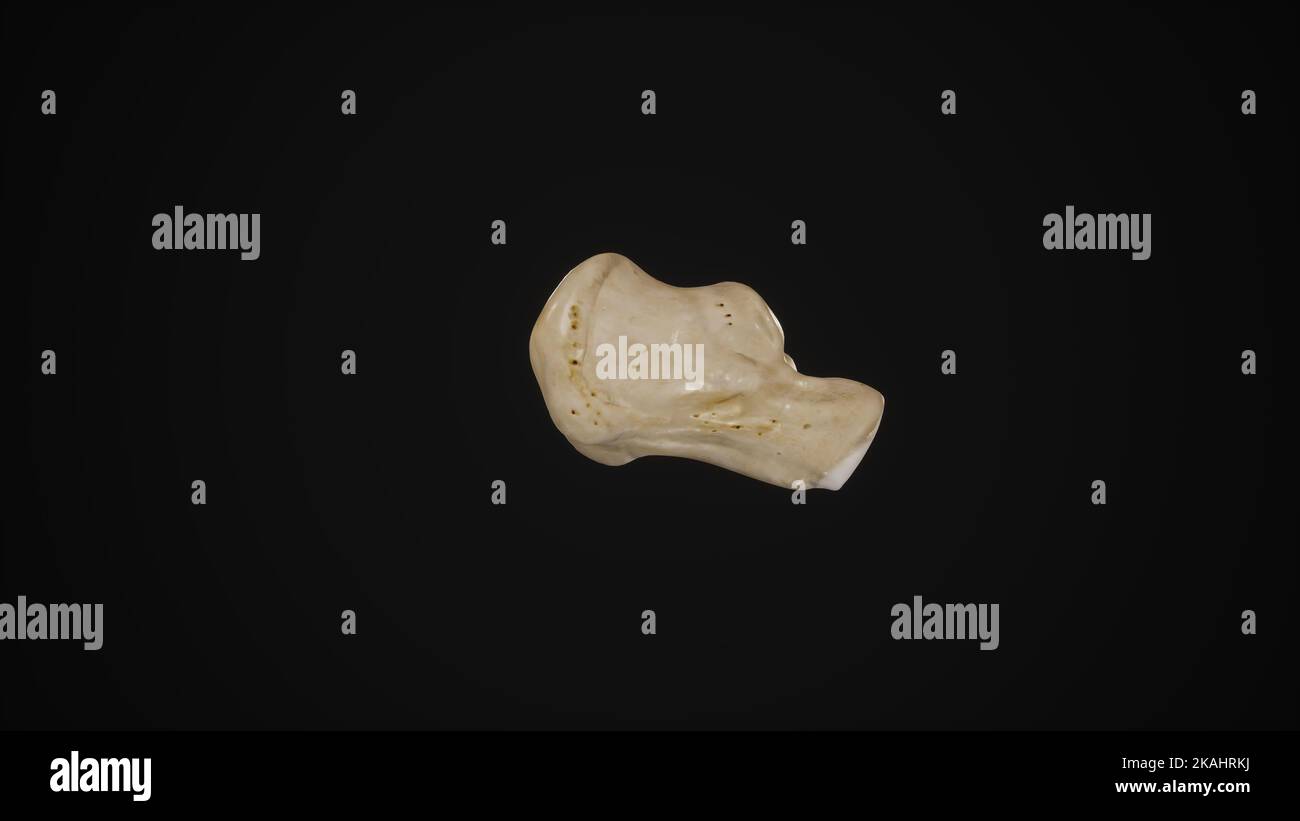 medically accurate illustration of the calcaneus bone-Lateral View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medically-accurate-illustration-of-the-calcaneus-bone-lateral-view-image488428630.html
medically accurate illustration of the calcaneus bone-Lateral View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medically-accurate-illustration-of-the-calcaneus-bone-lateral-view-image488428630.htmlRF2KAHRKJ–medically accurate illustration of the calcaneus bone-Lateral View
![. A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupon his left foot. I saw him on the followin Stock Photo . A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupon his left foot. I saw him on the followin Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2AFP0BM/a-practical-treatise-on-fractures-and-dislocations-frutui-with-the-result-of-rhhicino-iractuiv-of-the-tiliila-as-deseriheil-on-gtaue452-or-rupture-of-the-trnal-hiteral-lioauumit-or-avulsion-oi-a-seale-462-fractures-of-bone-from-the-side-of-the-calcaneum-where-the-ligament-is-insertedor-fracture-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-with-the-first-of-these-we-have-not-here-to-deal-a-case-of-avulsionof-a-scale-of-bone-came-under-my-observation-at-the-presbyterian-hos-pital-in-1880-the-patient-had-fallen-from-a-height-of-ten-feet-strikingupon-his-left-foot-i-saw-him-on-the-followin-2AFP0BM.jpg) . A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupon his left foot. I saw him on the followin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-practical-treatise-on-fractures-and-dislocations-frutui-with-the-result-of-rhhicino-iractuiv-of-the-tiliila-as-deseriheil-on-gtaue452-or-rupture-of-the-trnal-hiteral-lioauumit-or-avulsion-oi-a-seale-462-fractures-of-bone-from-the-side-of-the-calcaneum-where-the-ligament-is-insertedor-fracture-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-with-the-first-of-these-we-have-not-here-to-deal-a-case-of-avulsionof-a-scale-of-bone-came-under-my-observation-at-the-presbyterian-hos-pital-in-1880-the-patient-had-fallen-from-a-height-of-ten-feet-strikingupon-his-left-foot-i-saw-him-on-the-followin-image336700104.html
. A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupon his left foot. I saw him on the followin Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-practical-treatise-on-fractures-and-dislocations-frutui-with-the-result-of-rhhicino-iractuiv-of-the-tiliila-as-deseriheil-on-gtaue452-or-rupture-of-the-trnal-hiteral-lioauumit-or-avulsion-oi-a-seale-462-fractures-of-bone-from-the-side-of-the-calcaneum-where-the-ligament-is-insertedor-fracture-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-with-the-first-of-these-we-have-not-here-to-deal-a-case-of-avulsionof-a-scale-of-bone-came-under-my-observation-at-the-presbyterian-hos-pital-in-1880-the-patient-had-fallen-from-a-height-of-ten-feet-strikingupon-his-left-foot-i-saw-him-on-the-followin-image336700104.htmlRM2AFP0BM–. A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupon his left foot. I saw him on the followin
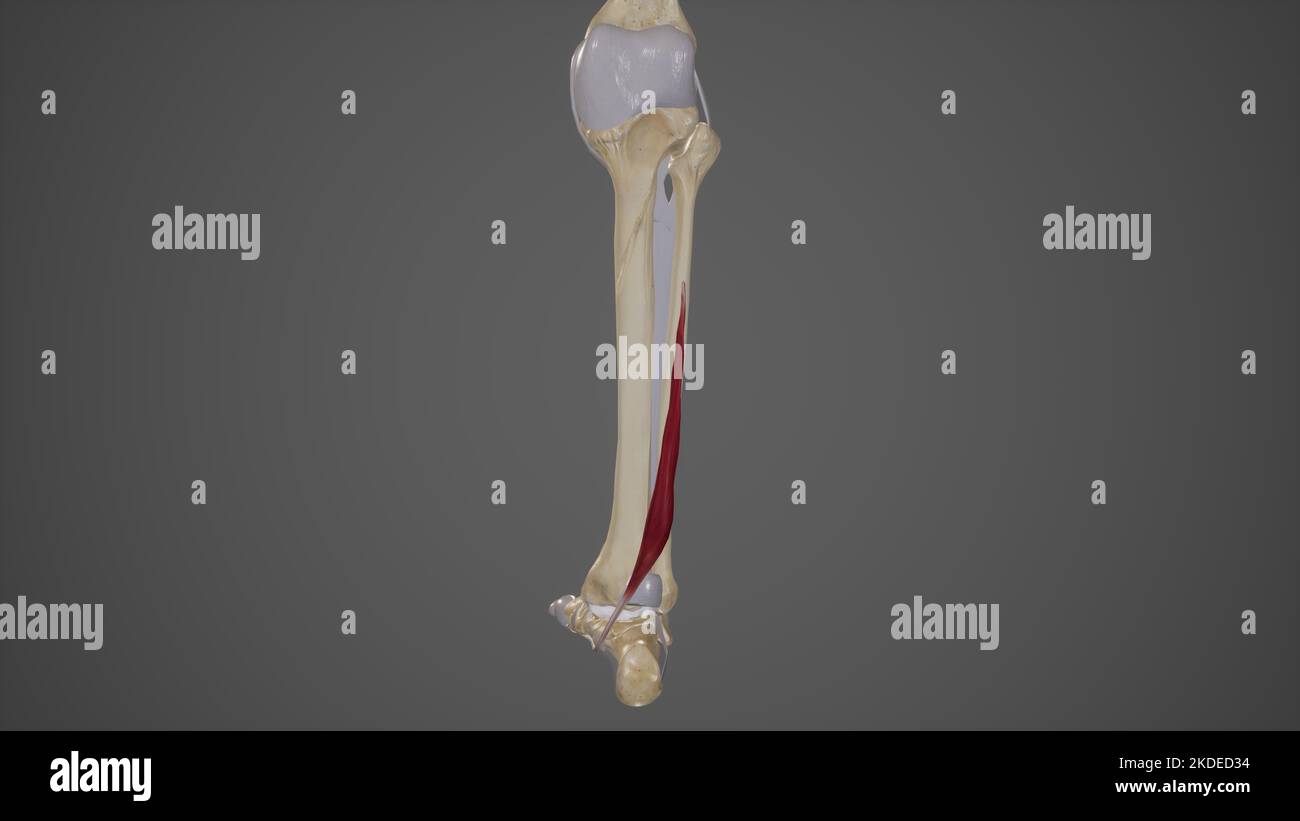 Medical Illustration of Flexor Hallucis Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-flexor-hallucis-longus-image490198440.html
Medical Illustration of Flexor Hallucis Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-flexor-hallucis-longus-image490198440.htmlRF2KDED34–Medical Illustration of Flexor Hallucis Longus
![. A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fracture of os calcis. (Cabot.)Fig. 341.. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupo Stock Photo . A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fracture of os calcis. (Cabot.)Fig. 341.. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupo Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2AFP0TH/a-practical-treatise-on-fractures-and-dislocations-fracture-of-os-calcis-cabotfig-341-frutui-with-the-result-of-rhhicino-iractuiv-of-the-tiliila-as-deseriheil-on-gtaue452-or-rupture-of-the-trnal-hiteral-lioauumit-or-avulsion-oi-a-seale-462-fractures-of-bone-from-the-side-of-the-calcaneum-where-the-ligament-is-insertedor-fracture-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-with-the-first-of-these-we-have-not-here-to-deal-a-case-of-avulsionof-a-scale-of-bone-came-under-my-observation-at-the-presbyterian-hos-pital-in-1880-the-patient-had-fallen-from-a-height-of-ten-feet-strikingupo-2AFP0TH.jpg) . A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fracture of os calcis. (Cabot.)Fig. 341.. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-practical-treatise-on-fractures-and-dislocations-fracture-of-os-calcis-cabotfig-341-frutui-with-the-result-of-rhhicino-iractuiv-of-the-tiliila-as-deseriheil-on-gtaue452-or-rupture-of-the-trnal-hiteral-lioauumit-or-avulsion-oi-a-seale-462-fractures-of-bone-from-the-side-of-the-calcaneum-where-the-ligament-is-insertedor-fracture-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-with-the-first-of-these-we-have-not-here-to-deal-a-case-of-avulsionof-a-scale-of-bone-came-under-my-observation-at-the-presbyterian-hos-pital-in-1880-the-patient-had-fallen-from-a-height-of-ten-feet-strikingupo-image336700465.html
. A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fracture of os calcis. (Cabot.)Fig. 341.. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-practical-treatise-on-fractures-and-dislocations-fracture-of-os-calcis-cabotfig-341-frutui-with-the-result-of-rhhicino-iractuiv-of-the-tiliila-as-deseriheil-on-gtaue452-or-rupture-of-the-trnal-hiteral-lioauumit-or-avulsion-oi-a-seale-462-fractures-of-bone-from-the-side-of-the-calcaneum-where-the-ligament-is-insertedor-fracture-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-with-the-first-of-these-we-have-not-here-to-deal-a-case-of-avulsionof-a-scale-of-bone-came-under-my-observation-at-the-presbyterian-hos-pital-in-1880-the-patient-had-fallen-from-a-height-of-ten-feet-strikingupo-image336700465.htmlRM2AFP0TH–. A practical treatise on fractures and dislocations. Fracture of os calcis. (Cabot.)Fig. 341.. Fr;Utui with the result of ])r(Hhicino iractuiv of the til)iila, as deseriheil on ]>aue452, or rupture of the (t(^rnal hiteral lioauuMit, or avulsion oi a seale 462 FRACTURES. of bone from the side of the calcaneum where the ligament is inserted,or fracture of the sustentaculum tali. With the first of these we have not here to deal. A case of avulsionof a scale of bone came under my observation at the Presbyterian Hos-pital in 1880; the patient had fallen from a height of ten feet, strikingupo
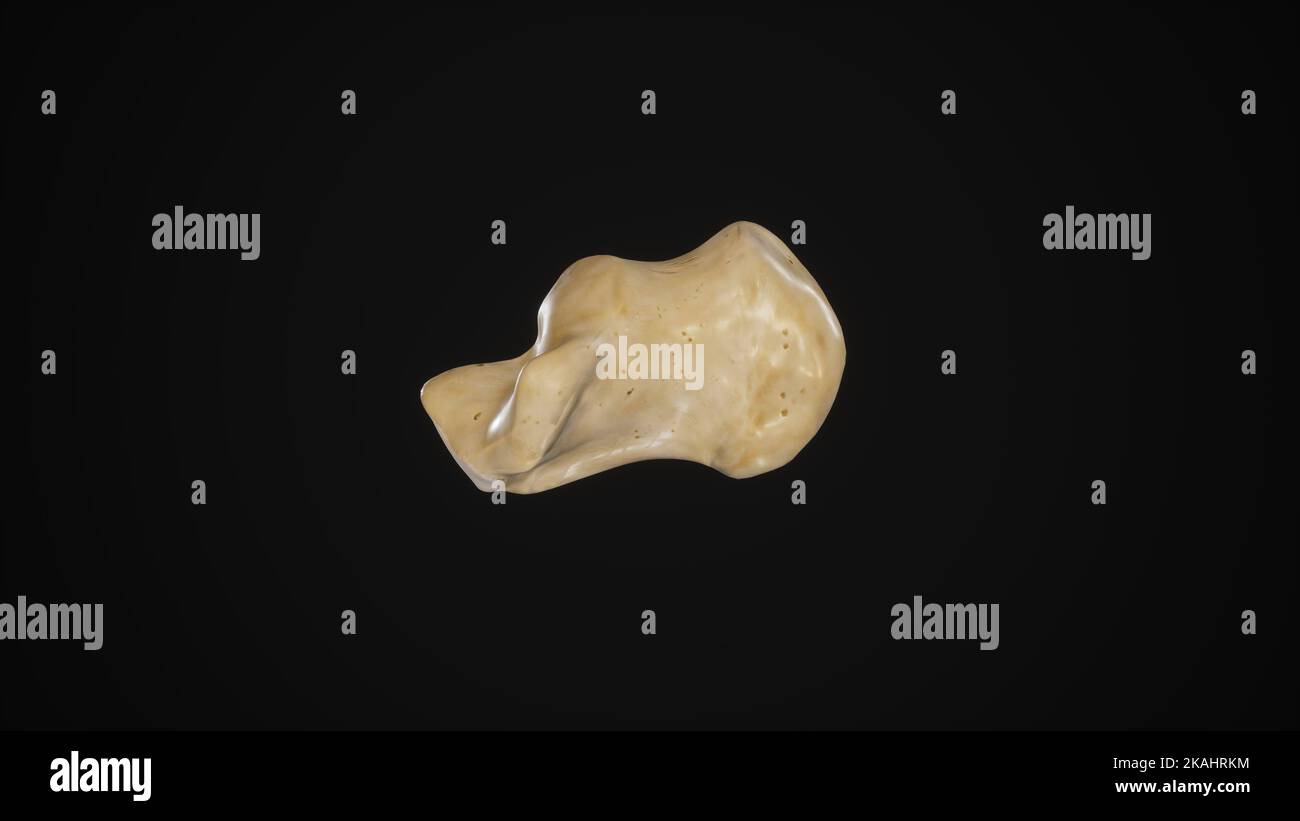 medically accurate illustration of the calcaneus bone-Medial View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medically-accurate-illustration-of-the-calcaneus-bone-medial-view-image488428632.html
medically accurate illustration of the calcaneus bone-Medial View Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medically-accurate-illustration-of-the-calcaneus-bone-medial-view-image488428632.htmlRF2KAHRKM–medically accurate illustration of the calcaneus bone-Medial View
 . Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . of the astragalus thus brought into view.The joint between the head of the astragalus and the scaphoid isopened (tuberosity of the scaphoid is the guide), and also the jointbetween the astragalus and the os calcis (sustentaculum tali); afterthis the astragalus is seized with a bone forceps, and, twisting andat the same time cutting close to the bone, it is removed. In re-secting the ankle-joint for tuberculosis, if the astragalus is diseased,it is well to remove this bone entire. AMPUTATIONS, RESECTIONS, ETC. 601 Ankle-joint (Koenig).—This Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/operative-surgery-for-students-and-practitioners-of-the-astragalus-thus-brought-into-viewthe-joint-between-the-head-of-the-astragalus-and-the-scaphoid-isopened-tuberosity-of-the-scaphoid-is-the-guide-and-also-the-jointbetween-the-astragalus-and-the-os-calcis-sustentaculum-tali-afterthis-the-astragalus-is-seized-with-a-bone-forceps-and-twisting-andat-the-same-time-cutting-close-to-the-bone-it-is-removed-in-re-secting-the-ankle-joint-for-tuberculosis-if-the-astragalus-is-diseasedit-is-well-to-remove-this-bone-entire-amputations-resections-etc-601-ankle-joint-koenigthis-image370094411.html
. Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . of the astragalus thus brought into view.The joint between the head of the astragalus and the scaphoid isopened (tuberosity of the scaphoid is the guide), and also the jointbetween the astragalus and the os calcis (sustentaculum tali); afterthis the astragalus is seized with a bone forceps, and, twisting andat the same time cutting close to the bone, it is removed. In re-secting the ankle-joint for tuberculosis, if the astragalus is diseased,it is well to remove this bone entire. AMPUTATIONS, RESECTIONS, ETC. 601 Ankle-joint (Koenig).—This Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/operative-surgery-for-students-and-practitioners-of-the-astragalus-thus-brought-into-viewthe-joint-between-the-head-of-the-astragalus-and-the-scaphoid-isopened-tuberosity-of-the-scaphoid-is-the-guide-and-also-the-jointbetween-the-astragalus-and-the-os-calcis-sustentaculum-tali-afterthis-the-astragalus-is-seized-with-a-bone-forceps-and-twisting-andat-the-same-time-cutting-close-to-the-bone-it-is-removed-in-re-secting-the-ankle-joint-for-tuberculosis-if-the-astragalus-is-diseasedit-is-well-to-remove-this-bone-entire-amputations-resections-etc-601-ankle-joint-koenigthis-image370094411.htmlRM2CE375F–. Operative surgery, for students and practitioners . of the astragalus thus brought into view.The joint between the head of the astragalus and the scaphoid isopened (tuberosity of the scaphoid is the guide), and also the jointbetween the astragalus and the os calcis (sustentaculum tali); afterthis the astragalus is seized with a bone forceps, and, twisting andat the same time cutting close to the bone, it is removed. In re-secting the ankle-joint for tuberculosis, if the astragalus is diseased,it is well to remove this bone entire. AMPUTATIONS, RESECTIONS, ETC. 601 Ankle-joint (Koenig).—This
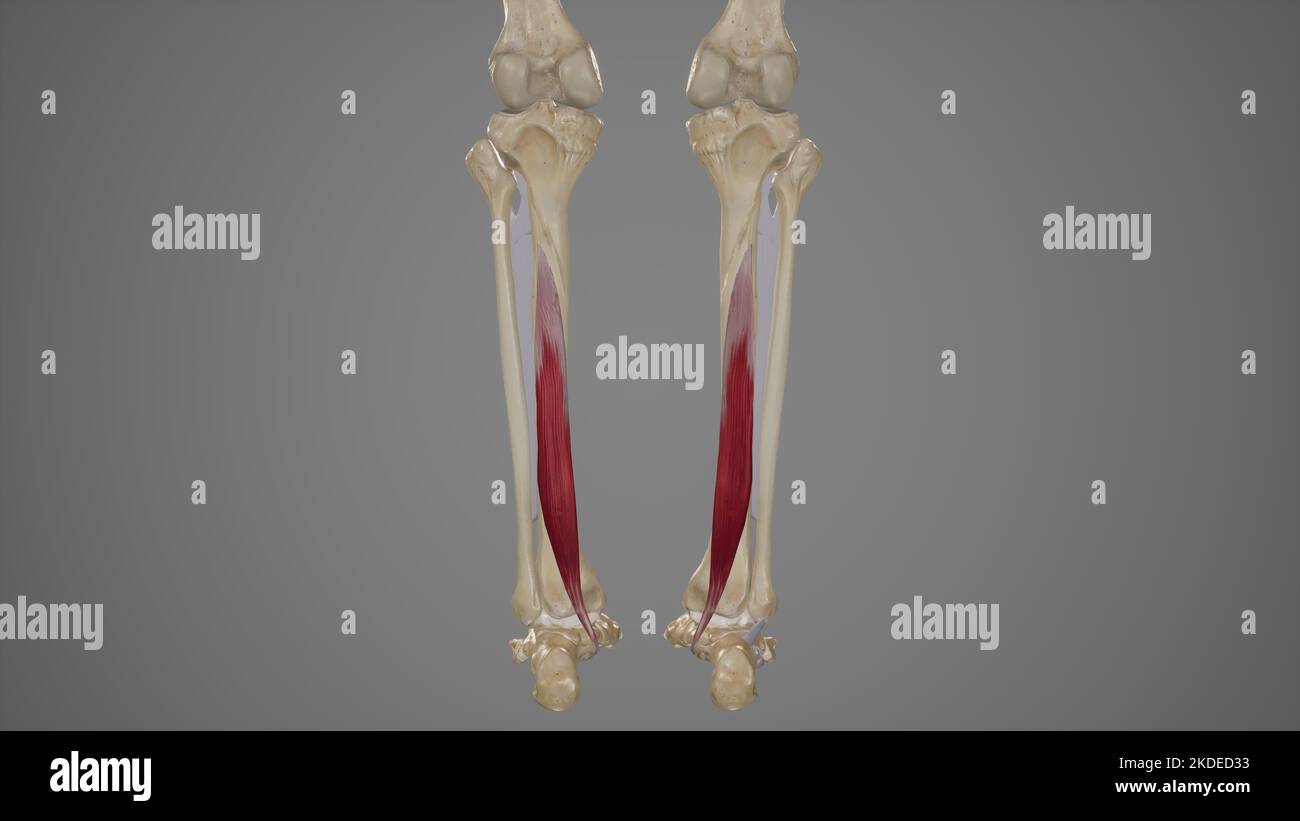 Medical Illustration of Flexor Digitorum Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-flexor-digitorum-longus-image490198439.html
Medical Illustration of Flexor Digitorum Longus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-flexor-digitorum-longus-image490198439.htmlRF2KDED33–Medical Illustration of Flexor Digitorum Longus
 . Text-book of operative surgery . its outer and under surfaces,and lastly from its inner and posterior surfaces. The greatest difficulty is met with atthe inner side in Clearing the projecting sustentaculum tali. If the soft parts are insufficient, the projecting head of the astragalus may be sawnofi*. The astragalus fits well into the heel cap. The stump bears weight excellently. 45. Subastragaloid Osteoplastic Amputation. This Operation, introduced byHancock, consists in sawing off the tuberosity of the os calcis, and applying it to the ^ Deulsche raed, Wochenschr., January 1899. AMPUTATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-operative-surgery-its-outer-and-under-surfacesand-lastly-from-its-inner-and-posterior-surfaces-the-greatest-difficulty-is-met-with-atthe-inner-side-in-clearing-the-projecting-sustentaculum-tali-if-the-soft-parts-are-insufficient-the-projecting-head-of-the-astragalus-may-be-sawnofi-the-astragalus-fits-well-into-the-heel-cap-the-stump-bears-weight-excellently-45-subastragaloid-osteoplastic-amputation-this-operation-introduced-byhancock-consists-in-sawing-off-the-tuberosity-of-the-os-calcis-and-applying-it-to-the-deulsche-raed-wochenschr-january-1899-amputation-image372046493.html
. Text-book of operative surgery . its outer and under surfaces,and lastly from its inner and posterior surfaces. The greatest difficulty is met with atthe inner side in Clearing the projecting sustentaculum tali. If the soft parts are insufficient, the projecting head of the astragalus may be sawnofi*. The astragalus fits well into the heel cap. The stump bears weight excellently. 45. Subastragaloid Osteoplastic Amputation. This Operation, introduced byHancock, consists in sawing off the tuberosity of the os calcis, and applying it to the ^ Deulsche raed, Wochenschr., January 1899. AMPUTATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-operative-surgery-its-outer-and-under-surfacesand-lastly-from-its-inner-and-posterior-surfaces-the-greatest-difficulty-is-met-with-atthe-inner-side-in-clearing-the-projecting-sustentaculum-tali-if-the-soft-parts-are-insufficient-the-projecting-head-of-the-astragalus-may-be-sawnofi-the-astragalus-fits-well-into-the-heel-cap-the-stump-bears-weight-excellently-45-subastragaloid-osteoplastic-amputation-this-operation-introduced-byhancock-consists-in-sawing-off-the-tuberosity-of-the-os-calcis-and-applying-it-to-the-deulsche-raed-wochenschr-january-1899-amputation-image372046493.htmlRM2CH852N–. Text-book of operative surgery . its outer and under surfaces,and lastly from its inner and posterior surfaces. The greatest difficulty is met with atthe inner side in Clearing the projecting sustentaculum tali. If the soft parts are insufficient, the projecting head of the astragalus may be sawnofi*. The astragalus fits well into the heel cap. The stump bears weight excellently. 45. Subastragaloid Osteoplastic Amputation. This Operation, introduced byHancock, consists in sawing off the tuberosity of the os calcis, and applying it to the ^ Deulsche raed, Wochenschr., January 1899. AMPUTATION
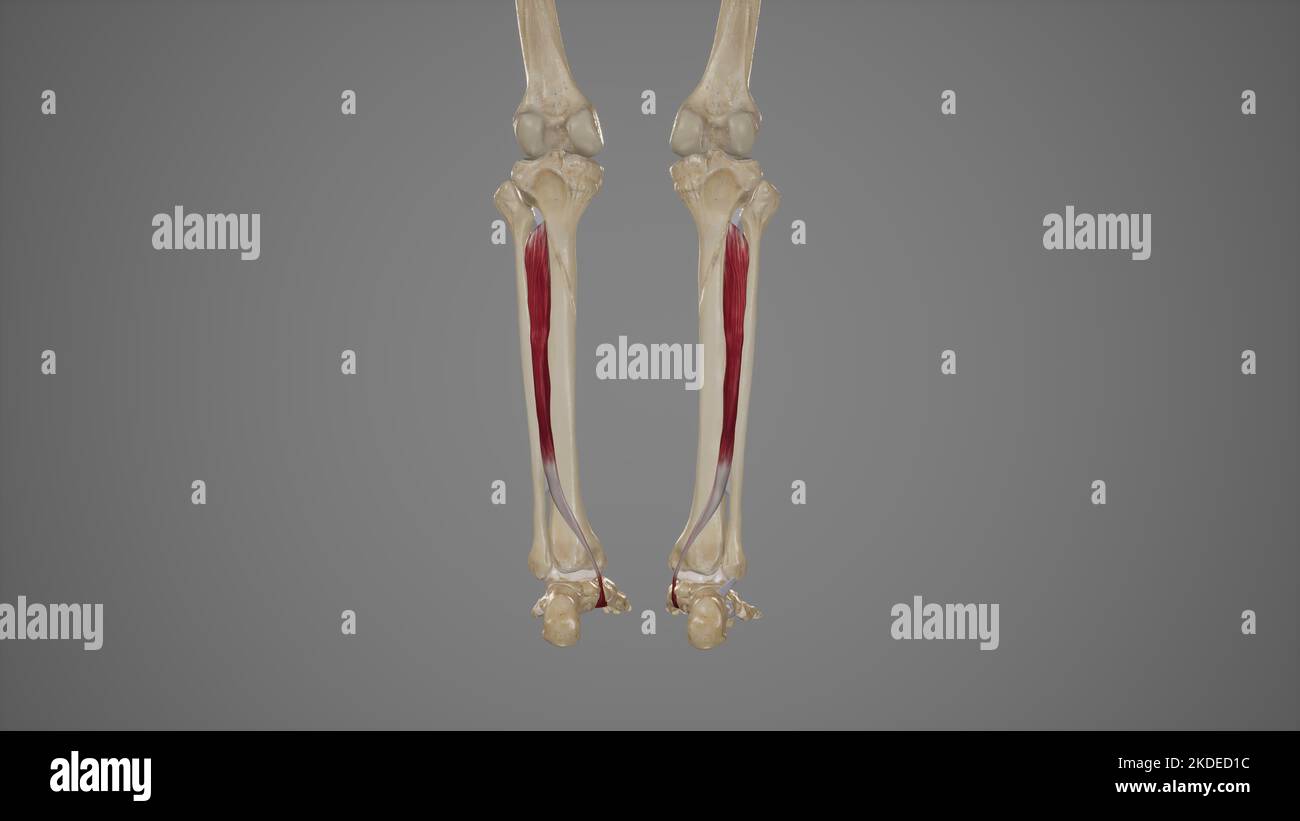 Medical Illustration of Tibialis Posterior Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-tibialis-posterior-image490198392.html
Medical Illustration of Tibialis Posterior Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-tibialis-posterior-image490198392.htmlRF2KDED1C–Medical Illustration of Tibialis Posterior
 . Text-book of operative surgery . Fig. 147.—Excisiou of os calcis. OPERATIVE SURGERY. Fig. 148. -Resection of the posterior tarsus(Kocher). sustentaculum tali. Lastly, the os calcis is seized with a streng pair of forceps, andthe internal lateral ligament of the ankle-joint, the subjacent calcaneo-astragaloidcapsule, and (anteriorly) the ligaments connectmg the tibia with the scaphoid andos calcis are detached. Landerer recommends a mesial longitudinal incision extending from the tendoAchillis over the heel into the sole of the foot. By this incision he removes not onlythe OS calcis, but, if Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-operative-surgery-fig-147excisiou-of-os-calcis-operative-surgery-fig-148-resection-of-the-posterior-tarsuskocher-sustentaculum-tali-lastly-the-os-calcis-is-seized-with-a-streng-pair-of-forceps-andthe-internal-lateral-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-the-subjacent-calcaneo-astragaloidcapsule-and-anteriorly-the-ligaments-connectmg-the-tibia-with-the-scaphoid-andos-calcis-are-detached-landerer-recommends-a-mesial-longitudinal-incision-extending-from-the-tendoachillis-over-the-heel-into-the-sole-of-the-foot-by-this-incision-he-removes-not-onlythe-os-calcis-but-if-image372127498.html
. Text-book of operative surgery . Fig. 147.—Excisiou of os calcis. OPERATIVE SURGERY. Fig. 148. -Resection of the posterior tarsus(Kocher). sustentaculum tali. Lastly, the os calcis is seized with a streng pair of forceps, andthe internal lateral ligament of the ankle-joint, the subjacent calcaneo-astragaloidcapsule, and (anteriorly) the ligaments connectmg the tibia with the scaphoid andos calcis are detached. Landerer recommends a mesial longitudinal incision extending from the tendoAchillis over the heel into the sole of the foot. By this incision he removes not onlythe OS calcis, but, if Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/text-book-of-operative-surgery-fig-147excisiou-of-os-calcis-operative-surgery-fig-148-resection-of-the-posterior-tarsuskocher-sustentaculum-tali-lastly-the-os-calcis-is-seized-with-a-streng-pair-of-forceps-andthe-internal-lateral-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-the-subjacent-calcaneo-astragaloidcapsule-and-anteriorly-the-ligaments-connectmg-the-tibia-with-the-scaphoid-andos-calcis-are-detached-landerer-recommends-a-mesial-longitudinal-incision-extending-from-the-tendoachillis-over-the-heel-into-the-sole-of-the-foot-by-this-incision-he-removes-not-onlythe-os-calcis-but-if-image372127498.htmlRM2CHBTBP–. Text-book of operative surgery . Fig. 147.—Excisiou of os calcis. OPERATIVE SURGERY. Fig. 148. -Resection of the posterior tarsus(Kocher). sustentaculum tali. Lastly, the os calcis is seized with a streng pair of forceps, andthe internal lateral ligament of the ankle-joint, the subjacent calcaneo-astragaloidcapsule, and (anteriorly) the ligaments connectmg the tibia with the scaphoid andos calcis are detached. Landerer recommends a mesial longitudinal incision extending from the tendoAchillis over the heel into the sole of the foot. By this incision he removes not onlythe OS calcis, but, if
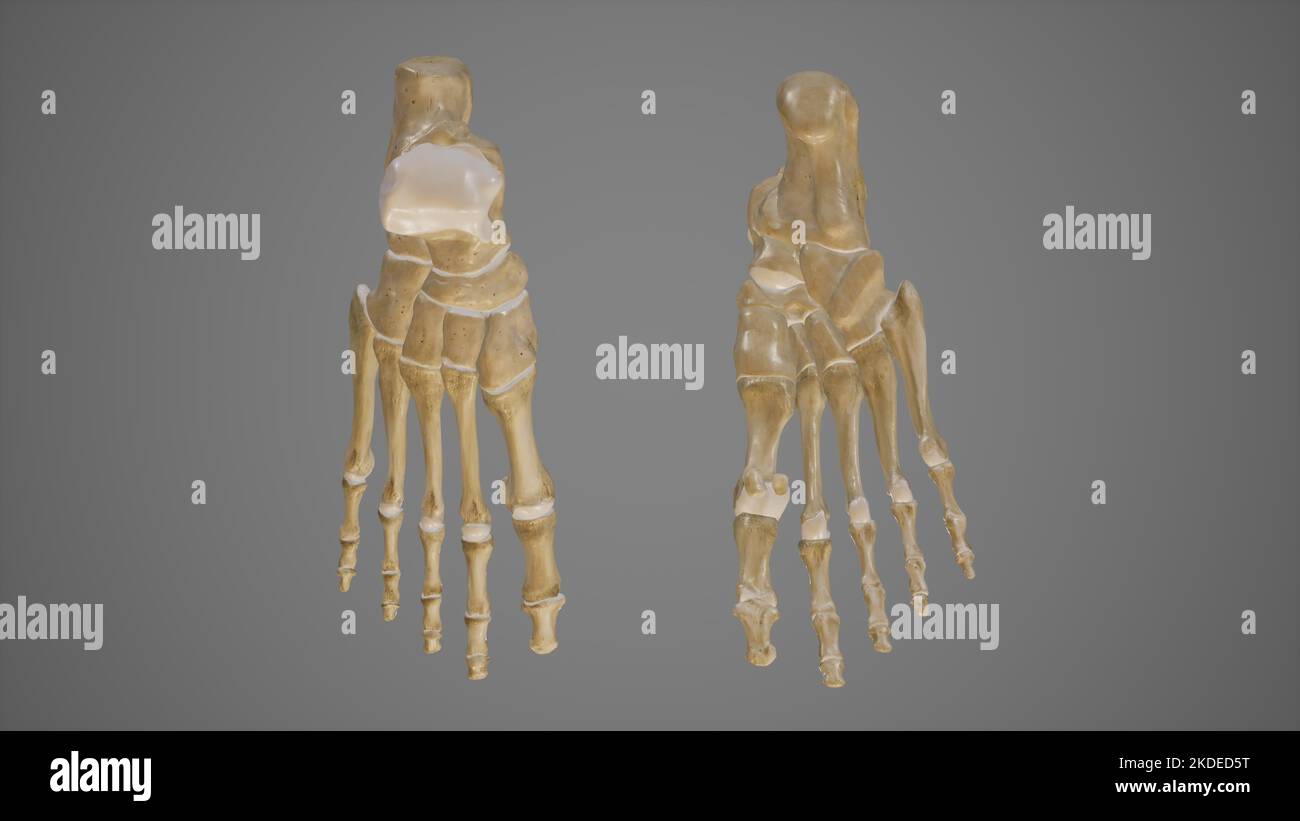 Dorsal and Plantar View of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/dorsal-and-plantar-view-of-foot-image490198516.html
Dorsal and Plantar View of Foot Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/dorsal-and-plantar-view-of-foot-image490198516.htmlRF2KDED5T–Dorsal and Plantar View of Foot
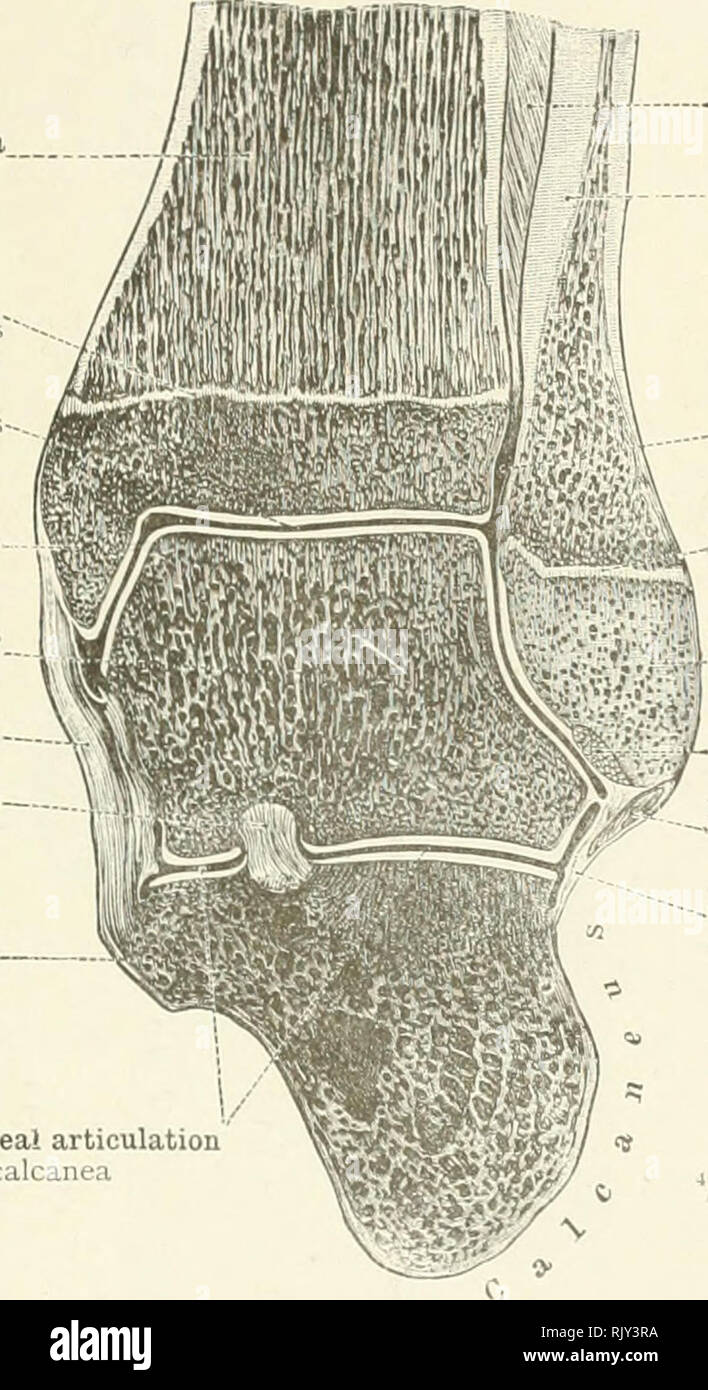 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB 239 Shaft (diaphysis) of the tibia Diaphysis tibia? Epiphysial disc Synchondrosis epiphyseos' The ankle-joint Articulatio talocrurali Internal malleolus Malleolus medialis Body of the astragalus Trochlea tali Calcaneotibial portion of the internal lateral, or deltoid, ligament of the ankle-joint Lig. calcaneotibiale Interosseous astragalocalcaneal ligament Lig. talocalcaneum interosseum Sustentaculum tal Sustentaculum tali Astragalocalcaneal articulation Articulatio talocalcanea. Interosseous Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-articulations-of-the-lower-limb-239-shaft-diaphysis-of-the-tibia-diaphysis-tibia-epiphysial-disc-synchondrosis-epiphyseos-the-ankle-joint-articulatio-talocrurali-internal-malleolus-malleolus-medialis-body-of-the-astragalus-trochlea-tali-calcaneotibial-portion-of-the-internal-lateral-or-deltoid-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-lig-calcaneotibiale-interosseous-astragalocalcaneal-ligament-lig-talocalcaneum-interosseum-sustentaculum-tal-sustentaculum-tali-astragalocalcaneal-articulation-articulatio-talocalcanea-interosseous-image235394302.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB 239 Shaft (diaphysis) of the tibia Diaphysis tibia? Epiphysial disc Synchondrosis epiphyseos' The ankle-joint Articulatio talocrurali Internal malleolus Malleolus medialis Body of the astragalus Trochlea tali Calcaneotibial portion of the internal lateral, or deltoid, ligament of the ankle-joint Lig. calcaneotibiale Interosseous astragalocalcaneal ligament Lig. talocalcaneum interosseum Sustentaculum tal Sustentaculum tali Astragalocalcaneal articulation Articulatio talocalcanea. Interosseous Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-articulations-of-the-lower-limb-239-shaft-diaphysis-of-the-tibia-diaphysis-tibia-epiphysial-disc-synchondrosis-epiphyseos-the-ankle-joint-articulatio-talocrurali-internal-malleolus-malleolus-medialis-body-of-the-astragalus-trochlea-tali-calcaneotibial-portion-of-the-internal-lateral-or-deltoid-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-lig-calcaneotibiale-interosseous-astragalocalcaneal-ligament-lig-talocalcaneum-interosseum-sustentaculum-tal-sustentaculum-tali-astragalocalcaneal-articulation-articulatio-talocalcanea-interosseous-image235394302.htmlRMRJY3RA–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB 239 Shaft (diaphysis) of the tibia Diaphysis tibia? Epiphysial disc Synchondrosis epiphyseos' The ankle-joint Articulatio talocrurali Internal malleolus Malleolus medialis Body of the astragalus Trochlea tali Calcaneotibial portion of the internal lateral, or deltoid, ligament of the ankle-joint Lig. calcaneotibiale Interosseous astragalocalcaneal ligament Lig. talocalcaneum interosseum Sustentaculum tal Sustentaculum tali Astragalocalcaneal articulation Articulatio talocalcanea. Interosseous
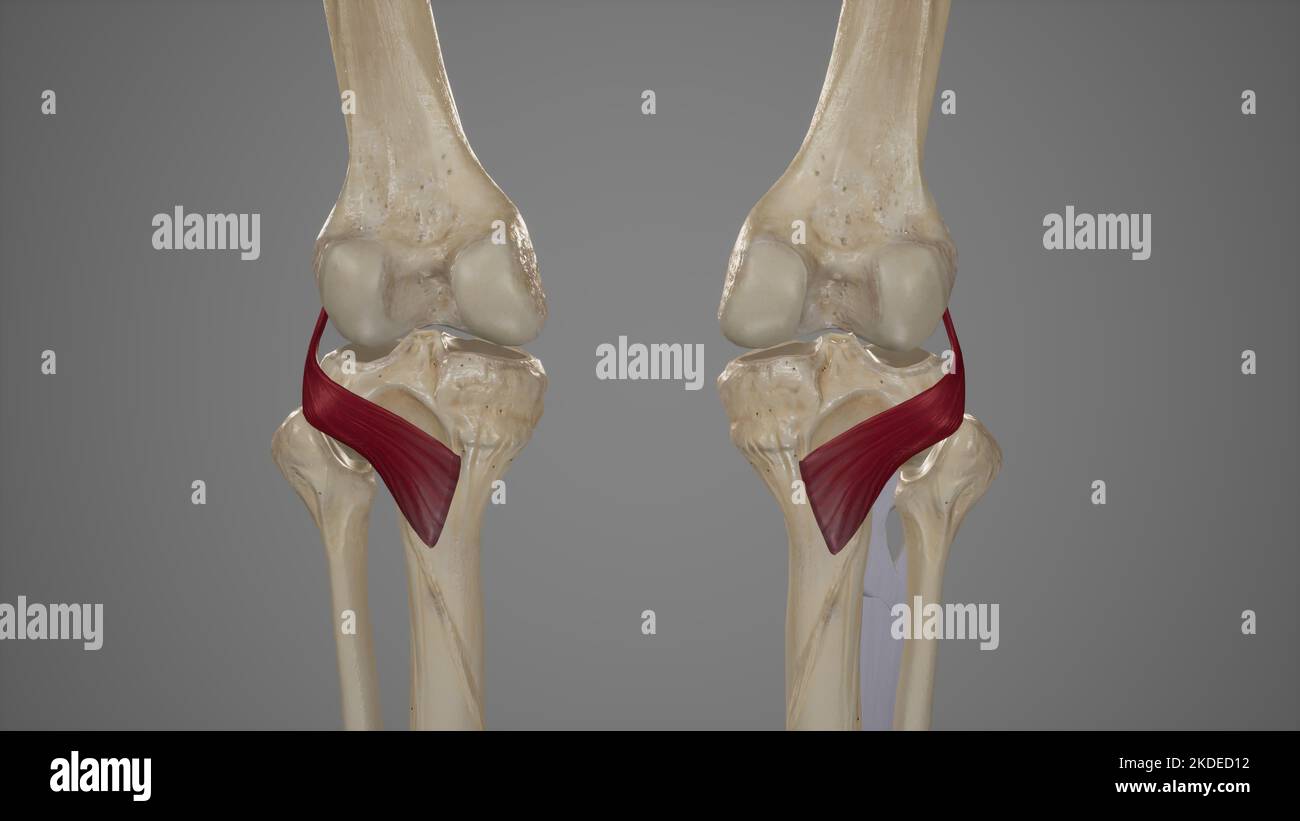 Medical Illustration of Popliteus Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-popliteus-muscle-image490198382.html
Medical Illustration of Popliteus Muscle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-popliteus-muscle-image490198382.htmlRF2KDED12–Medical Illustration of Popliteus Muscle
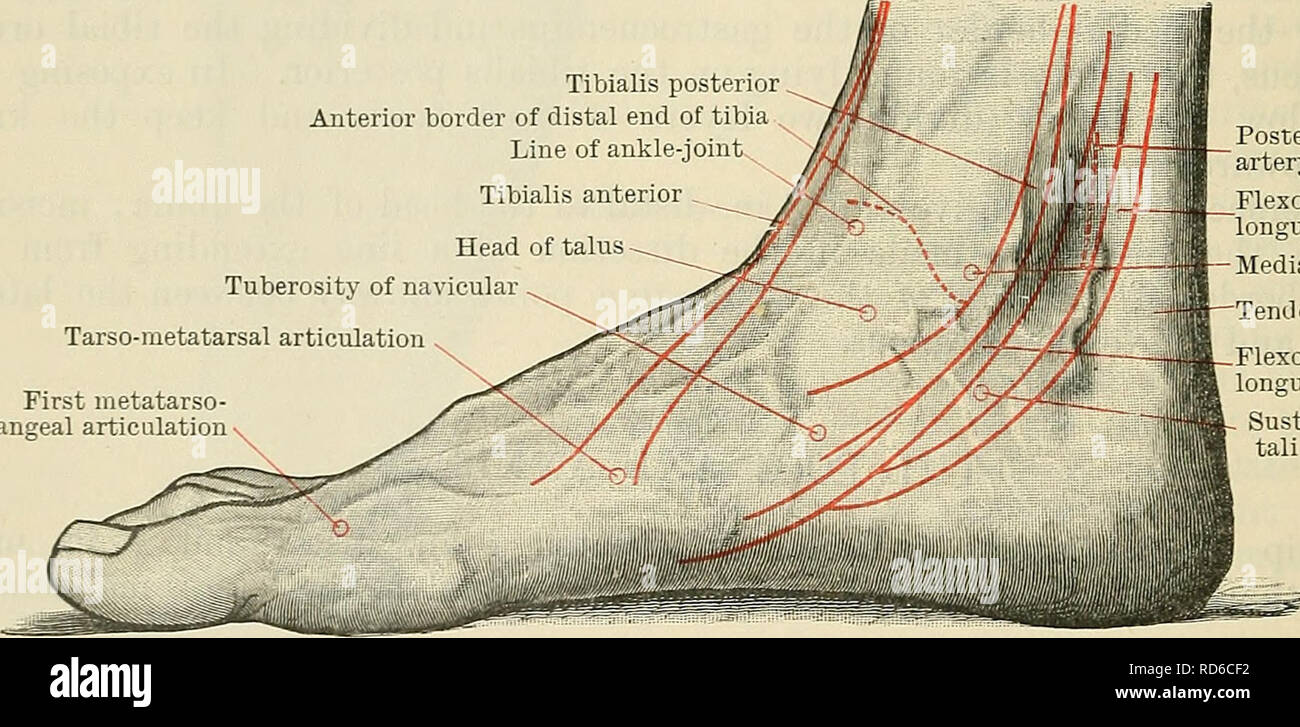 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 146-1 SUKFACE AND SUKGICAL ANATOMY. of the tibia. The small posterior surface of the talus is felt distal and posterior to the medial malleolus, at the anterior part of the hollow between it and the heel. In effusions into the ankle-joint the hollows in front and behind the malleoli are obliterated, and the extensor tendons are raised from the front of the joint. A finder's breadth distal to the tip of the medial malleolus is the sustentaculum tali; 1 in. in front of the sustentaculum, and midway between the dorsal and plantar margins of the media Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-146-1-sukface-and-sukgical-anatomy-of-the-tibia-the-small-posterior-surface-of-the-talus-is-felt-distal-and-posterior-to-the-medial-malleolus-at-the-anterior-part-of-the-hollow-between-it-and-the-heel-in-effusions-into-the-ankle-joint-the-hollows-in-front-and-behind-the-malleoli-are-obliterated-and-the-extensor-tendons-are-raised-from-the-front-of-the-joint-a-finders-breadth-distal-to-the-tip-of-the-medial-malleolus-is-the-sustentaculum-tali-1-in-in-front-of-the-sustentaculum-and-midway-between-the-dorsal-and-plantar-margins-of-the-media-image231866854.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 146-1 SUKFACE AND SUKGICAL ANATOMY. of the tibia. The small posterior surface of the talus is felt distal and posterior to the medial malleolus, at the anterior part of the hollow between it and the heel. In effusions into the ankle-joint the hollows in front and behind the malleoli are obliterated, and the extensor tendons are raised from the front of the joint. A finder's breadth distal to the tip of the medial malleolus is the sustentaculum tali; 1 in. in front of the sustentaculum, and midway between the dorsal and plantar margins of the media Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-146-1-sukface-and-sukgical-anatomy-of-the-tibia-the-small-posterior-surface-of-the-talus-is-felt-distal-and-posterior-to-the-medial-malleolus-at-the-anterior-part-of-the-hollow-between-it-and-the-heel-in-effusions-into-the-ankle-joint-the-hollows-in-front-and-behind-the-malleoli-are-obliterated-and-the-extensor-tendons-are-raised-from-the-front-of-the-joint-a-finders-breadth-distal-to-the-tip-of-the-medial-malleolus-is-the-sustentaculum-tali-1-in-in-front-of-the-sustentaculum-and-midway-between-the-dorsal-and-plantar-margins-of-the-media-image231866854.htmlRMRD6CF2–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 146-1 SUKFACE AND SUKGICAL ANATOMY. of the tibia. The small posterior surface of the talus is felt distal and posterior to the medial malleolus, at the anterior part of the hollow between it and the heel. In effusions into the ankle-joint the hollows in front and behind the malleoli are obliterated, and the extensor tendons are raised from the front of the joint. A finder's breadth distal to the tip of the medial malleolus is the sustentaculum tali; 1 in. in front of the sustentaculum, and midway between the dorsal and plantar margins of the media
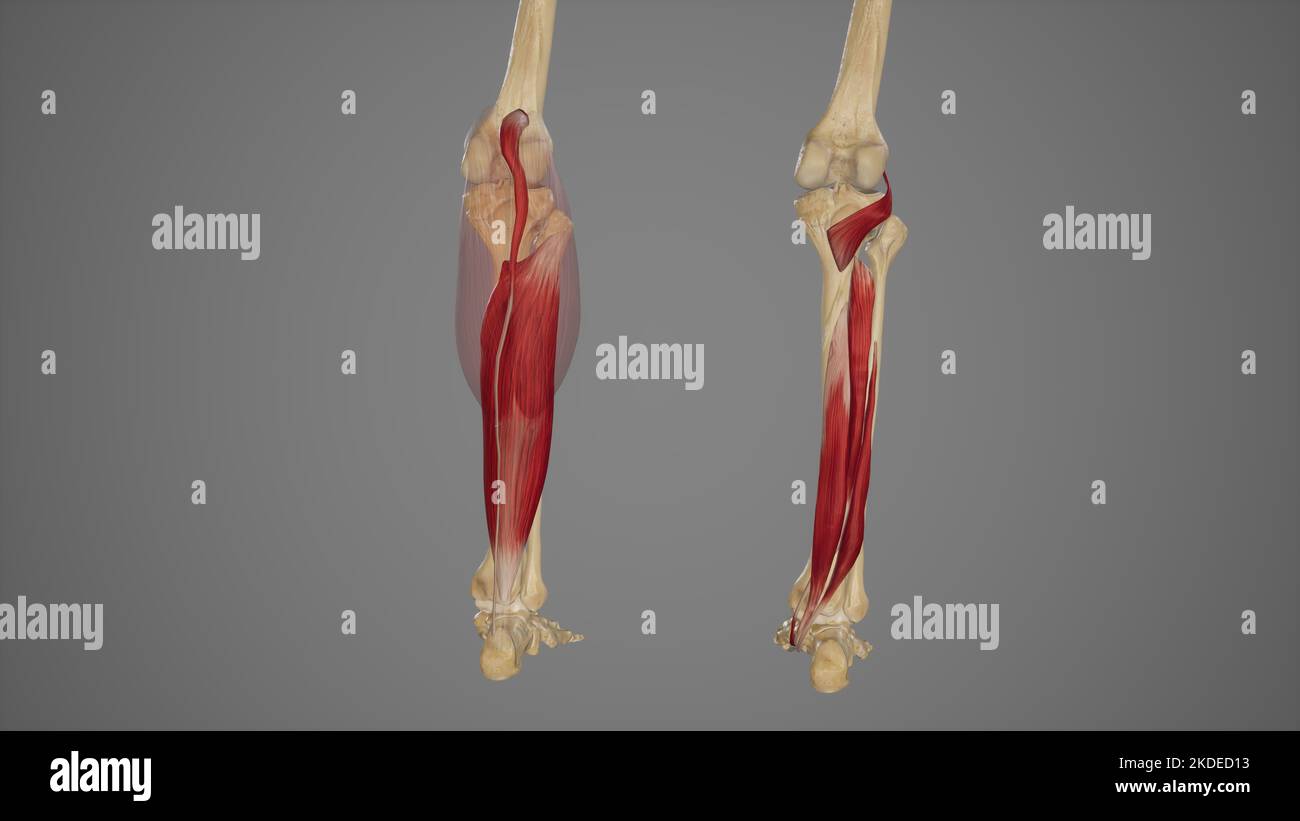 Superficial and Deep Muscles of Posterior Leg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superficial-and-deep-muscles-of-posterior-leg-image490198383.html
Superficial and Deep Muscles of Posterior Leg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/superficial-and-deep-muscles-of-posterior-leg-image490198383.htmlRF2KDED13–Superficial and Deep Muscles of Posterior Leg
 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE TALUS. 25> the dorsal surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Posteriorly the body is provided with two tubercles, separated by a groove; the lateral of these (processus posterior tali) is usually the larger, and is occasionally a separate ossicle (os trigonum). To it is attached the posterior talo-fibular ligament of the ankle- joint. The groove, which winds obliquely from above downwards and medially over the posterior surface of the bone, lodges the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The head, of oval form, is direct Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-talus-25gt-the-dorsal-surface-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-of-the-calcaneus-posteriorly-the-body-is-provided-with-two-tubercles-separated-by-a-groove-the-lateral-of-these-processus-posterior-tali-is-usually-the-larger-and-is-occasionally-a-separate-ossicle-os-trigonum-to-it-is-attached-the-posterior-talo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-the-groove-which-winds-obliquely-from-above-downwards-and-medially-over-the-posterior-surface-of-the-bone-lodges-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-hallucis-longus-muscle-the-head-of-oval-form-is-direct-image231881938.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE TALUS. 25> the dorsal surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Posteriorly the body is provided with two tubercles, separated by a groove; the lateral of these (processus posterior tali) is usually the larger, and is occasionally a separate ossicle (os trigonum). To it is attached the posterior talo-fibular ligament of the ankle- joint. The groove, which winds obliquely from above downwards and medially over the posterior surface of the bone, lodges the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The head, of oval form, is direct Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-the-talus-25gt-the-dorsal-surface-of-the-sustentaculum-tali-of-the-calcaneus-posteriorly-the-body-is-provided-with-two-tubercles-separated-by-a-groove-the-lateral-of-these-processus-posterior-tali-is-usually-the-larger-and-is-occasionally-a-separate-ossicle-os-trigonum-to-it-is-attached-the-posterior-talo-fibular-ligament-of-the-ankle-joint-the-groove-which-winds-obliquely-from-above-downwards-and-medially-over-the-posterior-surface-of-the-bone-lodges-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-hallucis-longus-muscle-the-head-of-oval-form-is-direct-image231881938.htmlRMRD73NP–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE TALUS. 25> the dorsal surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Posteriorly the body is provided with two tubercles, separated by a groove; the lateral of these (processus posterior tali) is usually the larger, and is occasionally a separate ossicle (os trigonum). To it is attached the posterior talo-fibular ligament of the ankle- joint. The groove, which winds obliquely from above downwards and medially over the posterior surface of the bone, lodges the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The head, of oval form, is direct
 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB 247 Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus Tuberculum mediale processus posterioris tali Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus hallucis Sulcus m tlexoris hallucis longi — Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus digitorum pedis—Sulcus m. rlexons digitorum longi Middle fibrocartilaginous portion of the internal calcaneonavicular ligament (Groove of the tendoi. of the tibialis posticus muscle) Inferior portion of the internal calcaneo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-articulations-of-the-lower-limb-247-inner-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-tuberculum-mediale-processus-posterioris-tali-sustentaculum-tali-sustentaculum-tali-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-sulcus-m-tlexoris-hallucis-longi-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-digitorum-pedissulcus-m-rlexons-digitorum-longi-middle-fibrocartilaginous-portion-of-the-internal-calcaneonavicular-ligament-groove-of-the-tendoi-of-the-tibialis-posticus-muscle-inferior-portion-of-the-internal-calcaneo-image235388463.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB 247 Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus Tuberculum mediale processus posterioris tali Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus hallucis Sulcus m tlexoris hallucis longi — Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus digitorum pedis—Sulcus m. rlexons digitorum longi Middle fibrocartilaginous portion of the internal calcaneonavicular ligament (Groove of the tendoi. of the tibialis posticus muscle) Inferior portion of the internal calcaneo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-articulations-of-the-lower-limb-247-inner-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-tuberculum-mediale-processus-posterioris-tali-sustentaculum-tali-sustentaculum-tali-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-sulcus-m-tlexoris-hallucis-longi-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-digitorum-pedissulcus-m-rlexons-digitorum-longi-middle-fibrocartilaginous-portion-of-the-internal-calcaneonavicular-ligament-groove-of-the-tendoi-of-the-tibialis-posticus-muscle-inferior-portion-of-the-internal-calcaneo-image235388463.htmlRMRJXTAR–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB 247 Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus Tuberculum mediale processus posterioris tali Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus hallucis Sulcus m tlexoris hallucis longi — Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus digitorum pedis—Sulcus m. rlexons digitorum longi Middle fibrocartilaginous portion of the internal calcaneonavicular ligament (Groove of the tendoi. of the tibialis posticus muscle) Inferior portion of the internal calcaneo
 . The topographical anatomy of the limbs of the horse. Horses; Physiology. -Tibia. - Groove for tendon of in. peronajus longus. oUaterale flbulare (deep), bone (talus). coUaterale flbulare (superficial). Central tarsal bone (scaphoid). Third tarsal bone (cuneiform). ... — Third metatarsal bone. Fig. 113.—Lateral Aspect of the Tarsal Articulations. third metatarsal bones. The short ligament divides into two portions; one of which ends on the talus, while the other, somewhat longer, is attached to the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Lig. collaterale flbulare (deep). : Lig. collaterale flbu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-topographical-anatomy-of-the-limbs-of-the-horse-horses-physiology-tibia-groove-for-tendon-of-in-peronajus-longus-ouaterale-flbulare-deep-bone-talus-couaterale-flbulare-superficial-central-tarsal-bone-scaphoid-third-tarsal-bone-cuneiform-third-metatarsal-bone-fig-113lateral-aspect-of-the-tarsal-articulations-third-metatarsal-bones-the-short-ligament-divides-into-two-portions-one-of-which-ends-on-the-talus-while-the-other-somewhat-longer-is-attached-to-the-sustentaculum-tali-of-the-calcaneus-lig-collaterale-flbulare-deep-lig-collaterale-flbu-image232425114.html
. The topographical anatomy of the limbs of the horse. Horses; Physiology. -Tibia. - Groove for tendon of in. peronajus longus. oUaterale flbulare (deep), bone (talus). coUaterale flbulare (superficial). Central tarsal bone (scaphoid). Third tarsal bone (cuneiform). ... — Third metatarsal bone. Fig. 113.—Lateral Aspect of the Tarsal Articulations. third metatarsal bones. The short ligament divides into two portions; one of which ends on the talus, while the other, somewhat longer, is attached to the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Lig. collaterale flbulare (deep). : Lig. collaterale flbu Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-topographical-anatomy-of-the-limbs-of-the-horse-horses-physiology-tibia-groove-for-tendon-of-in-peronajus-longus-ouaterale-flbulare-deep-bone-talus-couaterale-flbulare-superficial-central-tarsal-bone-scaphoid-third-tarsal-bone-cuneiform-third-metatarsal-bone-fig-113lateral-aspect-of-the-tarsal-articulations-third-metatarsal-bones-the-short-ligament-divides-into-two-portions-one-of-which-ends-on-the-talus-while-the-other-somewhat-longer-is-attached-to-the-sustentaculum-tali-of-the-calcaneus-lig-collaterale-flbulare-deep-lig-collaterale-flbu-image232425114.htmlRMRE3TGX–. The topographical anatomy of the limbs of the horse. Horses; Physiology. -Tibia. - Groove for tendon of in. peronajus longus. oUaterale flbulare (deep), bone (talus). coUaterale flbulare (superficial). Central tarsal bone (scaphoid). Third tarsal bone (cuneiform). ... — Third metatarsal bone. Fig. 113.—Lateral Aspect of the Tarsal Articulations. third metatarsal bones. The short ligament divides into two portions; one of which ends on the talus, while the other, somewhat longer, is attached to the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. Lig. collaterale flbulare (deep). : Lig. collaterale flbu
 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. Epiphysial disc Synchondrosis epiphyseos Internal malleolus ^.Malleolus medialis Deltoid ligament, or internal lateral ligament of ankle-joint Calcaneotibial portion of the internal lateral, or deltoid, liga- ' ment of the ankle-joint (4) Outer tubercle of the posterior . process of the astragalus (5) ' Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus (6) Groove of the tendon of the — flexor longus hallucis (7) Sv 1 Posterior astragalo- v*§t ' calcaneal ligament (3). Calcaneum, 01 os calcis ' Sustentaculum tali-Sustent Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-epiphysial-disc-synchondrosis-epiphyseos-internal-malleolus-malleolus-medialis-deltoid-ligament-or-internal-lateral-ligament-of-ankle-joint-calcaneotibial-portion-of-the-internal-lateral-or-deltoid-liga-ment-of-the-ankle-joint-4-outer-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-5-inner-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-6-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-7-sv-1-posterior-astragalo-vt-calcaneal-ligament-3-calcaneum-01-os-calcis-sustentaculum-tali-sustent-image235394192.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. Epiphysial disc Synchondrosis epiphyseos Internal malleolus ^.Malleolus medialis Deltoid ligament, or internal lateral ligament of ankle-joint Calcaneotibial portion of the internal lateral, or deltoid, liga- ' ment of the ankle-joint (4) Outer tubercle of the posterior . process of the astragalus (5) ' Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus (6) Groove of the tendon of the — flexor longus hallucis (7) Sv 1 Posterior astragalo- v*§t ' calcaneal ligament (3). Calcaneum, 01 os calcis ' Sustentaculum tali-Sustent Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-epiphysial-disc-synchondrosis-epiphyseos-internal-malleolus-malleolus-medialis-deltoid-ligament-or-internal-lateral-ligament-of-ankle-joint-calcaneotibial-portion-of-the-internal-lateral-or-deltoid-liga-ment-of-the-ankle-joint-4-outer-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-5-inner-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-6-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-7-sv-1-posterior-astragalo-vt-calcaneal-ligament-3-calcaneum-01-os-calcis-sustentaculum-tali-sustent-image235394192.htmlRMRJY3KC–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. Epiphysial disc Synchondrosis epiphyseos Internal malleolus ^.Malleolus medialis Deltoid ligament, or internal lateral ligament of ankle-joint Calcaneotibial portion of the internal lateral, or deltoid, liga- ' ment of the ankle-joint (4) Outer tubercle of the posterior . process of the astragalus (5) ' Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus (6) Groove of the tendon of the — flexor longus hallucis (7) Sv 1 Posterior astragalo- v*§t ' calcaneal ligament (3). Calcaneum, 01 os calcis ' Sustentaculum tali-Sustent
 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. 24 K THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus Tuben alum mediale -., â¡ issus posterioris tali Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Tendon of the tibialis posticus muscle Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus hallucis muscle Sulcus m. flexoris hallucis longi Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus digitorum pedis muscle Sulcus m. flexoris digitorum longi Inferior portion of the internal calcaneonavicular ligament (i) Deep portion of the interior calcaneocu- boid ligamen Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-24-k-the-articulations-of-the-lower-limb-inner-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-tuben-alum-mediale-issus-posterioris-tali-sustentaculum-tali-sustentaculum-tali-tendon-of-the-tibialis-posticus-muscle-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-muscle-sulcus-m-flexoris-hallucis-longi-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-digitorum-pedis-muscle-sulcus-m-flexoris-digitorum-longi-inferior-portion-of-the-internal-calcaneonavicular-ligament-i-deep-portion-of-the-interior-calcaneocu-boid-ligamen-image235388485.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. 24 K THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus Tuben alum mediale -., â¡ issus posterioris tali Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Tendon of the tibialis posticus muscle Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus hallucis muscle Sulcus m. flexoris hallucis longi Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus digitorum pedis muscle Sulcus m. flexoris digitorum longi Inferior portion of the internal calcaneonavicular ligament (i) Deep portion of the interior calcaneocu- boid ligamen Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-24-k-the-articulations-of-the-lower-limb-inner-tubercle-of-the-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-tuben-alum-mediale-issus-posterioris-tali-sustentaculum-tali-sustentaculum-tali-tendon-of-the-tibialis-posticus-muscle-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-muscle-sulcus-m-flexoris-hallucis-longi-groove-of-the-tendon-of-the-flexor-longus-digitorum-pedis-muscle-sulcus-m-flexoris-digitorum-longi-inferior-portion-of-the-internal-calcaneonavicular-ligament-i-deep-portion-of-the-interior-calcaneocu-boid-ligamen-image235388485.htmlRMRJXTBH–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. 24 K THE ARTICULATIONS OF THE LOWER LIMB Inner tubercle of the posterior process of the astragalus Tuben alum mediale -., â¡ issus posterioris tali Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Tendon of the tibialis posticus muscle Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus hallucis muscle Sulcus m. flexoris hallucis longi Groove of the tendon of the flexor longus digitorum pedis muscle Sulcus m. flexoris digitorum longi Inferior portion of the internal calcaneonavicular ligament (i) Deep portion of the interior calcaneocu- boid ligamen
 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE SKELETON OE THE LOWER EXTREMITY 14! Inner tubercle of the tuberosity of the calcaneum Processus medialis tuberis calcanei Posterior process of the astragalus â (internal tubercle) I'rocessus posterior tali Groove of tendon of flexor longus hallucis Sulcus ra. flexoris hallucis longi Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Tuberosity of the navicular bone Tuberositas ossis navicularis Internal cuneiform bon Os cuneiforme I. Tuberosity of the first metatarsal bone. Tuberositas ossis metatarsalis I. Sesamoid bones Ossa sesamoide Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-skeleton-oe-the-lower-extremity-14!-inner-tubercle-of-the-tuberosity-of-the-calcaneum-processus-medialis-tuberis-calcanei-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-internal-tubercle-irocessus-posterior-tali-groove-of-tendon-of-flexor-longus-hallucis-sulcus-ra-flexoris-hallucis-longi-sustentaculum-tali-sustentaculum-tali-tuberosity-of-the-navicular-bone-tuberositas-ossis-navicularis-internal-cuneiform-bon-os-cuneiforme-i-tuberosity-of-the-first-metatarsal-bone-tuberositas-ossis-metatarsalis-i-sesamoid-bones-ossa-sesamoide-image235397318.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE SKELETON OE THE LOWER EXTREMITY 14! Inner tubercle of the tuberosity of the calcaneum Processus medialis tuberis calcanei Posterior process of the astragalus â (internal tubercle) I'rocessus posterior tali Groove of tendon of flexor longus hallucis Sulcus ra. flexoris hallucis longi Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Tuberosity of the navicular bone Tuberositas ossis navicularis Internal cuneiform bon Os cuneiforme I. Tuberosity of the first metatarsal bone. Tuberositas ossis metatarsalis I. Sesamoid bones Ossa sesamoide Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-skeleton-oe-the-lower-extremity-14!-inner-tubercle-of-the-tuberosity-of-the-calcaneum-processus-medialis-tuberis-calcanei-posterior-process-of-the-astragalus-internal-tubercle-irocessus-posterior-tali-groove-of-tendon-of-flexor-longus-hallucis-sulcus-ra-flexoris-hallucis-longi-sustentaculum-tali-sustentaculum-tali-tuberosity-of-the-navicular-bone-tuberositas-ossis-navicularis-internal-cuneiform-bon-os-cuneiforme-i-tuberosity-of-the-first-metatarsal-bone-tuberositas-ossis-metatarsalis-i-sesamoid-bones-ossa-sesamoide-image235397318.htmlRMRJY7K2–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE SKELETON OE THE LOWER EXTREMITY 14! Inner tubercle of the tuberosity of the calcaneum Processus medialis tuberis calcanei Posterior process of the astragalus â (internal tubercle) I'rocessus posterior tali Groove of tendon of flexor longus hallucis Sulcus ra. flexoris hallucis longi Sustentaculum tali Sustentaculum tali Tuberosity of the navicular bone Tuberositas ossis navicularis Internal cuneiform bon Os cuneiforme I. Tuberosity of the first metatarsal bone. Tuberositas ossis metatarsalis I. Sesamoid bones Ossa sesamoide
 . Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College. Zoology. -caf. Figure 24. Stereophotographs of dorsal view of A) nearly complete right pes, and B) left calcaneum of lEucosmodon sp. (AMNH 16325). Missing from the right pes are the mesocuneiform and parts of metatarsals and phalanges of digits l-IV. Phalanges from both pedes were used to reconstruct the foot skeleton shown; their relative positions are uncertain. - 1.0. Abbreviations: caf, proximal calcaneoastragalar facet; cut, cuboid facet; pt, peroneal tubercle; st, sustentaculum tali. Other Material—IsoViied ossicles (MCZ Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-museum-of-comparative-zoology-at-harvard-college-zoology-caf-figure-24-stereophotographs-of-dorsal-view-of-a-nearly-complete-right-pes-and-b-left-calcaneum-of-leucosmodon-sp-amnh-16325-missing-from-the-right-pes-are-the-mesocuneiform-and-parts-of-metatarsals-and-phalanges-of-digits-l-iv-phalanges-from-both-pedes-were-used-to-reconstruct-the-foot-skeleton-shown-their-relative-positions-are-uncertain-10-abbreviations-caf-proximal-calcaneoastragalar-facet-cut-cuboid-facet-pt-peroneal-tubercle-st-sustentaculum-tali-other-materialisoviied-ossicles-mcz-image233861068.html
. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College. Zoology. -caf. Figure 24. Stereophotographs of dorsal view of A) nearly complete right pes, and B) left calcaneum of lEucosmodon sp. (AMNH 16325). Missing from the right pes are the mesocuneiform and parts of metatarsals and phalanges of digits l-IV. Phalanges from both pedes were used to reconstruct the foot skeleton shown; their relative positions are uncertain. - 1.0. Abbreviations: caf, proximal calcaneoastragalar facet; cut, cuboid facet; pt, peroneal tubercle; st, sustentaculum tali. Other Material—IsoViied ossicles (MCZ Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/bulletin-of-the-museum-of-comparative-zoology-at-harvard-college-zoology-caf-figure-24-stereophotographs-of-dorsal-view-of-a-nearly-complete-right-pes-and-b-left-calcaneum-of-leucosmodon-sp-amnh-16325-missing-from-the-right-pes-are-the-mesocuneiform-and-parts-of-metatarsals-and-phalanges-of-digits-l-iv-phalanges-from-both-pedes-were-used-to-reconstruct-the-foot-skeleton-shown-their-relative-positions-are-uncertain-10-abbreviations-caf-proximal-calcaneoastragalar-facet-cut-cuboid-facet-pt-peroneal-tubercle-st-sustentaculum-tali-other-materialisoviied-ossicles-mcz-image233861068.htmlRMRGD850–. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College. Zoology. -caf. Figure 24. Stereophotographs of dorsal view of A) nearly complete right pes, and B) left calcaneum of lEucosmodon sp. (AMNH 16325). Missing from the right pes are the mesocuneiform and parts of metatarsals and phalanges of digits l-IV. Phalanges from both pedes were used to reconstruct the foot skeleton shown; their relative positions are uncertain. - 1.0. Abbreviations: caf, proximal calcaneoastragalar facet; cut, cuboid facet; pt, peroneal tubercle; st, sustentaculum tali. Other Material—IsoViied ossicles (MCZ
 . Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. Posterior articular facet A liifdie articular facet Anterior articular f-tri-t Articular facet for cuboid. Sustentaculum tali A nterior articular facet Middle articular facet Articular facK ^ for cul^oid. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta, Johannes, 1869-1945; McMurrich, J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939. Philadelphia, Saunders Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-posterior-articular-facet-a-liifdie-articular-facet-anterior-articular-f-tri-t-articular-facet-for-cuboid-sustentaculum-tali-a-nterior-articular-facet-middle-articular-facet-articular-fack-for-culoid-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-work-sobotta-johannes-1869-1945-mcmurrich-j-playfair-james-playfair-1859-1939-philadelphia-saunders-image235396638.html
. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. Posterior articular facet A liifdie articular facet Anterior articular f-tri-t Articular facet for cuboid. Sustentaculum tali A nterior articular facet Middle articular facet Articular facK ^ for cul^oid. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta, Johannes, 1869-1945; McMurrich, J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939. Philadelphia, Saunders Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-posterior-articular-facet-a-liifdie-articular-facet-anterior-articular-f-tri-t-articular-facet-for-cuboid-sustentaculum-tali-a-nterior-articular-facet-middle-articular-facet-articular-fack-for-culoid-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-perfectly-resemble-the-original-work-sobotta-johannes-1869-1945-mcmurrich-j-playfair-james-playfair-1859-1939-philadelphia-saunders-image235396638.htmlRMRJY6PP–. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. Posterior articular facet A liifdie articular facet Anterior articular f-tri-t Articular facet for cuboid. Sustentaculum tali A nterior articular facet Middle articular facet Articular facK ^ for cul^oid. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Sobotta, Johannes, 1869-1945; McMurrich, J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939. Philadelphia, Saunders
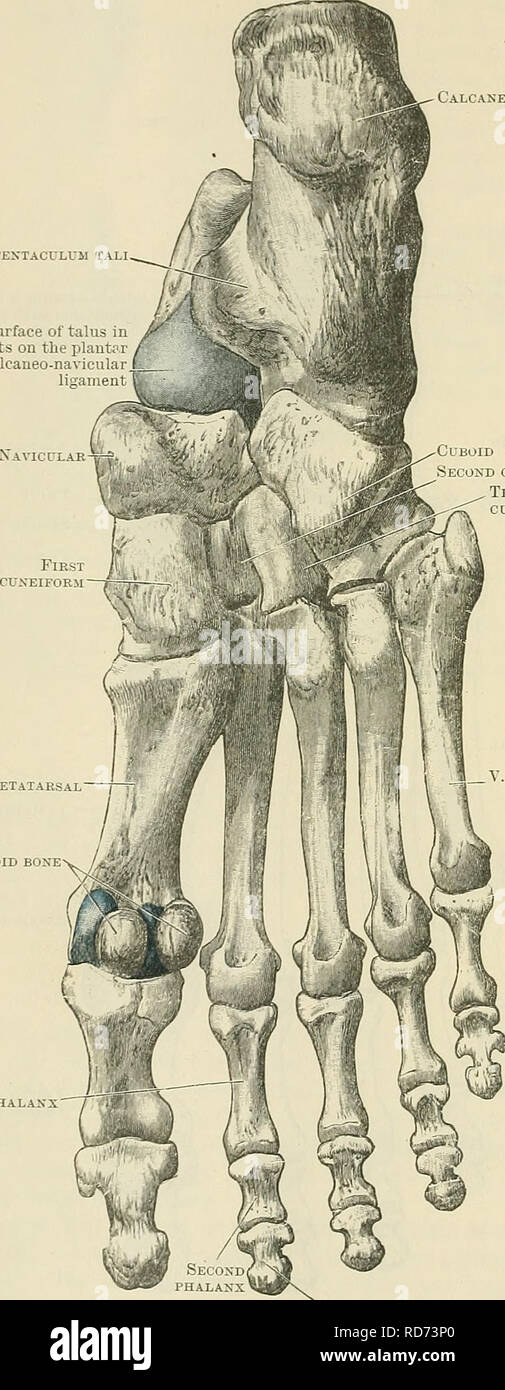 . Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 256 OSTEOLOGY. placed obliquely from behind forwards and laterally ; this, rests upon a corre- sponding surface on the dorsal aspect of the calcaneus. In front of this, and crossing the bone from the medial side laterally and forwards, is a deep furrow (sulcus tali), Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Surface of talus in blue tests on the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament Navicular-^ First phalanx. Cuboid Second cuneiform Third cuneiform I. Metatarsal Sesamoid bone V. Metatarsal Third or terminal phalanx Fig. 255.—Plantar Surface of the Bones of the Rig Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-256-osteology-placed-obliquely-from-behind-forwards-and-laterally-this-rests-upon-a-corre-sponding-surface-on-the-dorsal-aspect-of-the-calcaneus-in-front-of-this-and-crossing-the-bone-from-the-medial-side-laterally-and-forwards-is-a-deep-furrow-sulcus-tali-calcaneus-sustentaculum-tali-surface-of-talus-in-blue-tests-on-the-plantar-calcaneonavicular-ligament-navicular-first-phalanx-cuboid-second-cuneiform-third-cuneiform-i-metatarsal-sesamoid-bone-v-metatarsal-third-or-terminal-phalanx-fig-255plantar-surface-of-the-bones-of-the-rig-image231881944.html
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 256 OSTEOLOGY. placed obliquely from behind forwards and laterally ; this, rests upon a corre- sponding surface on the dorsal aspect of the calcaneus. In front of this, and crossing the bone from the medial side laterally and forwards, is a deep furrow (sulcus tali), Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Surface of talus in blue tests on the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament Navicular-^ First phalanx. Cuboid Second cuneiform Third cuneiform I. Metatarsal Sesamoid bone V. Metatarsal Third or terminal phalanx Fig. 255.—Plantar Surface of the Bones of the Rig Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cunninghams-text-book-of-anatomy-anatomy-256-osteology-placed-obliquely-from-behind-forwards-and-laterally-this-rests-upon-a-corre-sponding-surface-on-the-dorsal-aspect-of-the-calcaneus-in-front-of-this-and-crossing-the-bone-from-the-medial-side-laterally-and-forwards-is-a-deep-furrow-sulcus-tali-calcaneus-sustentaculum-tali-surface-of-talus-in-blue-tests-on-the-plantar-calcaneonavicular-ligament-navicular-first-phalanx-cuboid-second-cuneiform-third-cuneiform-i-metatarsal-sesamoid-bone-v-metatarsal-third-or-terminal-phalanx-fig-255plantar-surface-of-the-bones-of-the-rig-image231881944.htmlRMRD73P0–. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. 256 OSTEOLOGY. placed obliquely from behind forwards and laterally ; this, rests upon a corre- sponding surface on the dorsal aspect of the calcaneus. In front of this, and crossing the bone from the medial side laterally and forwards, is a deep furrow (sulcus tali), Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Surface of talus in blue tests on the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament Navicular-^ First phalanx. Cuboid Second cuneiform Third cuneiform I. Metatarsal Sesamoid bone V. Metatarsal Third or terminal phalanx Fig. 255.—Plantar Surface of the Bones of the Rig
 . Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. Sustentaculum tali A nterior articular facet Middle articular facet Articular facK ^ for cul^oid. Fiir. 15S. Groove for tendon of flexor hallucis lon^us Posterior articular facet Tuberosity Inner process of tuberosity Sulcus calcanci 't i Tuberosity Outer process Trochlear process of tuberosity f^/ar^ J^Q^ Articular facet (mid. cuneiform bone) Hir. 162.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-sustentaculum-tali-a-nterior-articular-facet-middle-articular-facet-articular-fack-for-culoid-fiir-15s-groove-for-tendon-of-flexor-hallucis-lonus-posterior-articular-facet-tuberosity-inner-process-of-tuberosity-sulcus-calcanci-t-i-tuberosity-outer-process-trochlear-process-of-tuberosity-far-jq-articular-facet-mid-cuneiform-bone-hir-162-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-image235396613.html
. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. Sustentaculum tali A nterior articular facet Middle articular facet Articular facK ^ for cul^oid. Fiir. 15S. Groove for tendon of flexor hallucis lon^us Posterior articular facet Tuberosity Inner process of tuberosity Sulcus calcanci 't i Tuberosity Outer process Trochlear process of tuberosity f^/ar^ J^Q^ Articular facet (mid. cuneiform bone) Hir. 162.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atlas-and-text-book-of-human-anatomy-anatomy-atlases-sustentaculum-tali-a-nterior-articular-facet-middle-articular-facet-articular-fack-for-culoid-fiir-15s-groove-for-tendon-of-flexor-hallucis-lonus-posterior-articular-facet-tuberosity-inner-process-of-tuberosity-sulcus-calcanci-t-i-tuberosity-outer-process-trochlear-process-of-tuberosity-far-jq-articular-facet-mid-cuneiform-bone-hir-162-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-page-images-that-may-have-been-digitally-enhanced-for-readability-coloration-and-appearance-of-these-illustrations-may-not-image235396613.htmlRMRJY6NW–. Atlas and text-book of human anatomy. Anatomy -- Atlases. Sustentaculum tali A nterior articular facet Middle articular facet Articular facK ^ for cul^oid. Fiir. 15S. Groove for tendon of flexor hallucis lon^us Posterior articular facet Tuberosity Inner process of tuberosity Sulcus calcanci 't i Tuberosity Outer process Trochlear process of tuberosity f^/ar^ J^Q^ Articular facet (mid. cuneiform bone) Hir. 162.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not
 . Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte und Morphologie des Hand- und Fussskelets der Marsupialier. 375 durch schmale Zonen vom Bildungsgewebe getrennt; der Sinus tarsi verläuft schief, weil der Talus, von der Planta betrachtet, von dem aus dem Calcaneum sich entwickelnden Sustentaculum tali theilweise überlagert wird (Fig. 25—28); die Tuberositas calcanei ist in Continuität mit dem Rest des Fersenbeins verknorpelt. Zwischen Talus und den Unterschenkelbeinen, aber in näherer Beziehung zur Tibia als zur Fibula erscheint Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/denkschriften-der-medicinisch-naturwissenschaftlichen-gesellschaft-zu-jena-beitrge-zur-entwickelungsgeschichte-und-morphologie-des-hand-und-fussskelets-der-marsupialier-375-durch-schmale-zonen-vom-bildungsgewebe-getrennt-der-sinus-tarsi-verluft-schief-weil-der-talus-von-der-planta-betrachtet-von-dem-aus-dem-calcaneum-sich-entwickelnden-sustentaculum-tali-theilweise-berlagert-wird-fig-2528-die-tuberositas-calcanei-ist-in-continuitt-mit-dem-rest-des-fersenbeins-verknorpelt-zwischen-talus-und-den-unterschenkelbeinen-aber-in-nherer-beziehung-zur-tibia-als-zur-fibula-erscheint-image231780962.html
. Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte und Morphologie des Hand- und Fussskelets der Marsupialier. 375 durch schmale Zonen vom Bildungsgewebe getrennt; der Sinus tarsi verläuft schief, weil der Talus, von der Planta betrachtet, von dem aus dem Calcaneum sich entwickelnden Sustentaculum tali theilweise überlagert wird (Fig. 25—28); die Tuberositas calcanei ist in Continuität mit dem Rest des Fersenbeins verknorpelt. Zwischen Talus und den Unterschenkelbeinen, aber in näherer Beziehung zur Tibia als zur Fibula erscheint Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/denkschriften-der-medicinisch-naturwissenschaftlichen-gesellschaft-zu-jena-beitrge-zur-entwickelungsgeschichte-und-morphologie-des-hand-und-fussskelets-der-marsupialier-375-durch-schmale-zonen-vom-bildungsgewebe-getrennt-der-sinus-tarsi-verluft-schief-weil-der-talus-von-der-planta-betrachtet-von-dem-aus-dem-calcaneum-sich-entwickelnden-sustentaculum-tali-theilweise-berlagert-wird-fig-2528-die-tuberositas-calcanei-ist-in-continuitt-mit-dem-rest-des-fersenbeins-verknorpelt-zwischen-talus-und-den-unterschenkelbeinen-aber-in-nherer-beziehung-zur-tibia-als-zur-fibula-erscheint-image231780962.htmlRMRD2EYE–. Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte und Morphologie des Hand- und Fussskelets der Marsupialier. 375 durch schmale Zonen vom Bildungsgewebe getrennt; der Sinus tarsi verläuft schief, weil der Talus, von der Planta betrachtet, von dem aus dem Calcaneum sich entwickelnden Sustentaculum tali theilweise überlagert wird (Fig. 25—28); die Tuberositas calcanei ist in Continuität mit dem Rest des Fersenbeins verknorpelt. Zwischen Talus und den Unterschenkelbeinen, aber in näherer Beziehung zur Tibia als zur Fibula erscheint
 . An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE SKELETON OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY U3 Posterior articular facet Facies articularis posted Anterior articular facet Facies articularis anterior Interosseous groove Sulcus calcanei Internal articular facet â Facies articularis media /Sustentaculum taliâSustentaculum tali Tuberosity of the calcaneum Tuber calcanei Articular facet for the cuboid bone Facies articularis cuboide Groove of the tendon ot the / flexor longus hallucis ' Sulcus m. flexoris hallucis longi External tubercle of the tuberosity of the calcaneum Processus later Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-skeleton-of-the-lower-extremity-u3-posterior-articular-facet-facies-articularis-posted-anterior-articular-facet-facies-articularis-anterior-interosseous-groove-sulcus-calcanei-internal-articular-facet-facies-articularis-media-sustentaculum-talisustentaculum-tali-tuberosity-of-the-calcaneum-tuber-calcanei-articular-facet-for-the-cuboid-bone-facies-articularis-cuboide-groove-of-the-tendon-ot-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-sulcus-m-flexoris-hallucis-longi-external-tubercle-of-the-tuberosity-of-the-calcaneum-processus-later-image235397267.html
. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE SKELETON OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY U3 Posterior articular facet Facies articularis posted Anterior articular facet Facies articularis anterior Interosseous groove Sulcus calcanei Internal articular facet â Facies articularis media /Sustentaculum taliâSustentaculum tali Tuberosity of the calcaneum Tuber calcanei Articular facet for the cuboid bone Facies articularis cuboide Groove of the tendon ot the / flexor longus hallucis ' Sulcus m. flexoris hallucis longi External tubercle of the tuberosity of the calcaneum Processus later Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/an-atlas-of-human-anatomy-for-students-and-physicians-anatomy-the-skeleton-of-the-lower-extremity-u3-posterior-articular-facet-facies-articularis-posted-anterior-articular-facet-facies-articularis-anterior-interosseous-groove-sulcus-calcanei-internal-articular-facet-facies-articularis-media-sustentaculum-talisustentaculum-tali-tuberosity-of-the-calcaneum-tuber-calcanei-articular-facet-for-the-cuboid-bone-facies-articularis-cuboide-groove-of-the-tendon-ot-the-flexor-longus-hallucis-sulcus-m-flexoris-hallucis-longi-external-tubercle-of-the-tuberosity-of-the-calcaneum-processus-later-image235397267.htmlRMRJY7H7–. An atlas of human anatomy for students and physicians. Anatomy. THE SKELETON OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY U3 Posterior articular facet Facies articularis posted Anterior articular facet Facies articularis anterior Interosseous groove Sulcus calcanei Internal articular facet â Facies articularis media /Sustentaculum taliâSustentaculum tali Tuberosity of the calcaneum Tuber calcanei Articular facet for the cuboid bone Facies articularis cuboide Groove of the tendon ot the / flexor longus hallucis ' Sulcus m. flexoris hallucis longi External tubercle of the tuberosity of the calcaneum Processus later
 . Die descriptive und topographische Anatomie des Menschen. Anatomy. 232. Das rechte Fersenbein, Calcaneus, von oben. Das Fersenbein, unter dem Sprungbeine gelegen, verlängert sich nach hinten zur Hacke. Calx, welche mit dem Fersenhöcker, Tuberositas calcanei, endet. An der oberen Flache befindet sich die überknorpelte Stelle zur Ver- bindung mit dem Sprungbeinkörper, vor derselben verläuft der Sulcus calcanei, welcher mit dem entsprechenden Sulcus tali den Sinus tarsi erzeugt. Nach innen von der Gelenkfläche ragt ein an seiner oberen Fläche ebenfalls überknorpelter Fortsatz, das Sustentaculum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/die-descriptive-und-topographische-anatomie-des-menschen-anatomy-232-das-rechte-fersenbein-calcaneus-von-oben-das-fersenbein-unter-dem-sprungbeine-gelegen-verlngert-sich-nach-hinten-zur-hacke-calx-welche-mit-dem-fersenhcker-tuberositas-calcanei-endet-an-der-oberen-flache-befindet-sich-die-berknorpelte-stelle-zur-ver-bindung-mit-dem-sprungbeinkrper-vor-derselben-verluft-der-sulcus-calcanei-welcher-mit-dem-entsprechenden-sulcus-tali-den-sinus-tarsi-erzeugt-nach-innen-von-der-gelenkflche-ragt-ein-an-seiner-oberen-flche-ebenfalls-berknorpelter-fortsatz-das-sustentaculum-image231568127.html
. Die descriptive und topographische Anatomie des Menschen. Anatomy. 232. Das rechte Fersenbein, Calcaneus, von oben. Das Fersenbein, unter dem Sprungbeine gelegen, verlängert sich nach hinten zur Hacke. Calx, welche mit dem Fersenhöcker, Tuberositas calcanei, endet. An der oberen Flache befindet sich die überknorpelte Stelle zur Ver- bindung mit dem Sprungbeinkörper, vor derselben verläuft der Sulcus calcanei, welcher mit dem entsprechenden Sulcus tali den Sinus tarsi erzeugt. Nach innen von der Gelenkfläche ragt ein an seiner oberen Fläche ebenfalls überknorpelter Fortsatz, das Sustentaculum Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/die-descriptive-und-topographische-anatomie-des-menschen-anatomy-232-das-rechte-fersenbein-calcaneus-von-oben-das-fersenbein-unter-dem-sprungbeine-gelegen-verlngert-sich-nach-hinten-zur-hacke-calx-welche-mit-dem-fersenhcker-tuberositas-calcanei-endet-an-der-oberen-flache-befindet-sich-die-berknorpelte-stelle-zur-ver-bindung-mit-dem-sprungbeinkrper-vor-derselben-verluft-der-sulcus-calcanei-welcher-mit-dem-entsprechenden-sulcus-tali-den-sinus-tarsi-erzeugt-nach-innen-von-der-gelenkflche-ragt-ein-an-seiner-oberen-flche-ebenfalls-berknorpelter-fortsatz-das-sustentaculum-image231568127.htmlRMRCMRE7–. Die descriptive und topographische Anatomie des Menschen. Anatomy. 232. Das rechte Fersenbein, Calcaneus, von oben. Das Fersenbein, unter dem Sprungbeine gelegen, verlängert sich nach hinten zur Hacke. Calx, welche mit dem Fersenhöcker, Tuberositas calcanei, endet. An der oberen Flache befindet sich die überknorpelte Stelle zur Ver- bindung mit dem Sprungbeinkörper, vor derselben verläuft der Sulcus calcanei, welcher mit dem entsprechenden Sulcus tali den Sinus tarsi erzeugt. Nach innen von der Gelenkfläche ragt ein an seiner oberen Fläche ebenfalls überknorpelter Fortsatz, das Sustentaculum