Quick filters:
Synaptic gap Stock Photos and Images
 3D Rendered Illustration, visualization of Neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualization-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image327746425.html
3D Rendered Illustration, visualization of Neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualization-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image327746425.htmlRF2A163WD–3D Rendered Illustration, visualization of Neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185384953.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185384953.htmlRFMNH0B5–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of the synaptic gap between neural cells with neurotransmitters exchanging Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-the-synaptic-gap-between-neural-cells-with-neurotransmitters-exchanging-image257033025.html
3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of the synaptic gap between neural cells with neurotransmitters exchanging Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-the-synaptic-gap-between-neural-cells-with-neurotransmitters-exchanging-image257033025.htmlRFTX4T6W–3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of the synaptic gap between neural cells with neurotransmitters exchanging
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470793376.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470793376.htmlRF2J9XDN4–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image244430422.html
3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image244430422.htmlRFT5JNDX–3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788035.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788035.htmlRF2J9X6XB–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image244427043.html
3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image244427043.htmlRFT5JH57–3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap
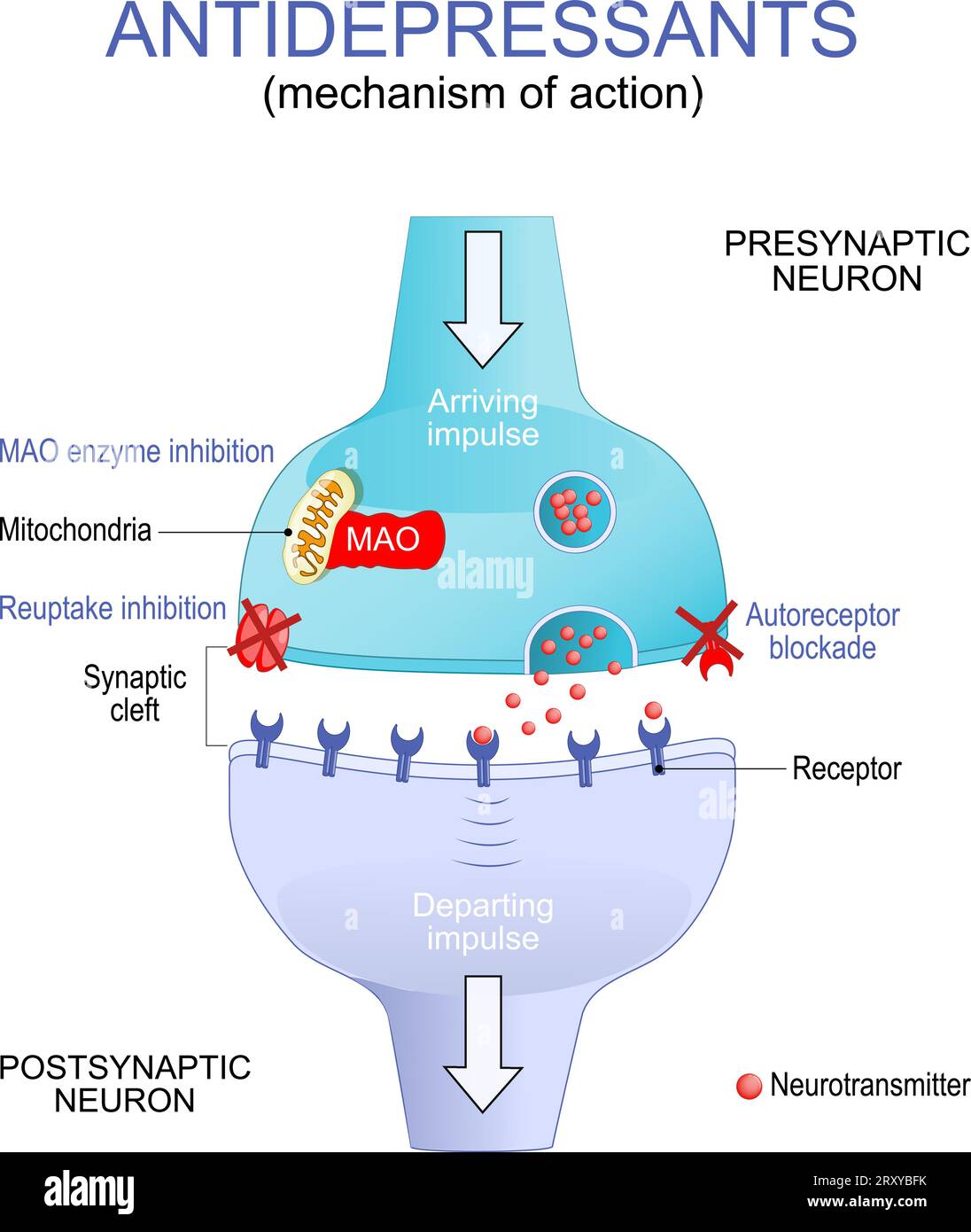 Antidepressant therapy for Depression treatment. Mechanism of action. Close-up of a Synaptic cleft. Neurons with Mitochondria, receptors and Neurotran Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/antidepressant-therapy-for-depression-treatment-mechanism-of-action-close-up-of-a-synaptic-cleft-neurons-with-mitochondria-receptors-and-neurotran-image567314599.html
Antidepressant therapy for Depression treatment. Mechanism of action. Close-up of a Synaptic cleft. Neurons with Mitochondria, receptors and Neurotran Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/antidepressant-therapy-for-depression-treatment-mechanism-of-action-close-up-of-a-synaptic-cleft-neurons-with-mitochondria-receptors-and-neurotran-image567314599.htmlRF2RXYBFK–Antidepressant therapy for Depression treatment. Mechanism of action. Close-up of a Synaptic cleft. Neurons with Mitochondria, receptors and Neurotran
 Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143416.html
Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143416.htmlRFHY3BR4–Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse.
 Synaptic transmission between nerve cells (neurons). The synapse is the gap between two neurons and is also called neuronal junction Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synaptic-transmission-between-nerve-cells-neurons-the-synapse-is-the-gap-between-two-neurons-and-is-also-called-neuronal-junction-image471640239.html
Synaptic transmission between nerve cells (neurons). The synapse is the gap between two neurons and is also called neuronal junction Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synaptic-transmission-between-nerve-cells-neurons-the-synapse-is-the-gap-between-two-neurons-and-is-also-called-neuronal-junction-image471640239.htmlRF2JB91X7–Synaptic transmission between nerve cells (neurons). The synapse is the gap between two neurons and is also called neuronal junction
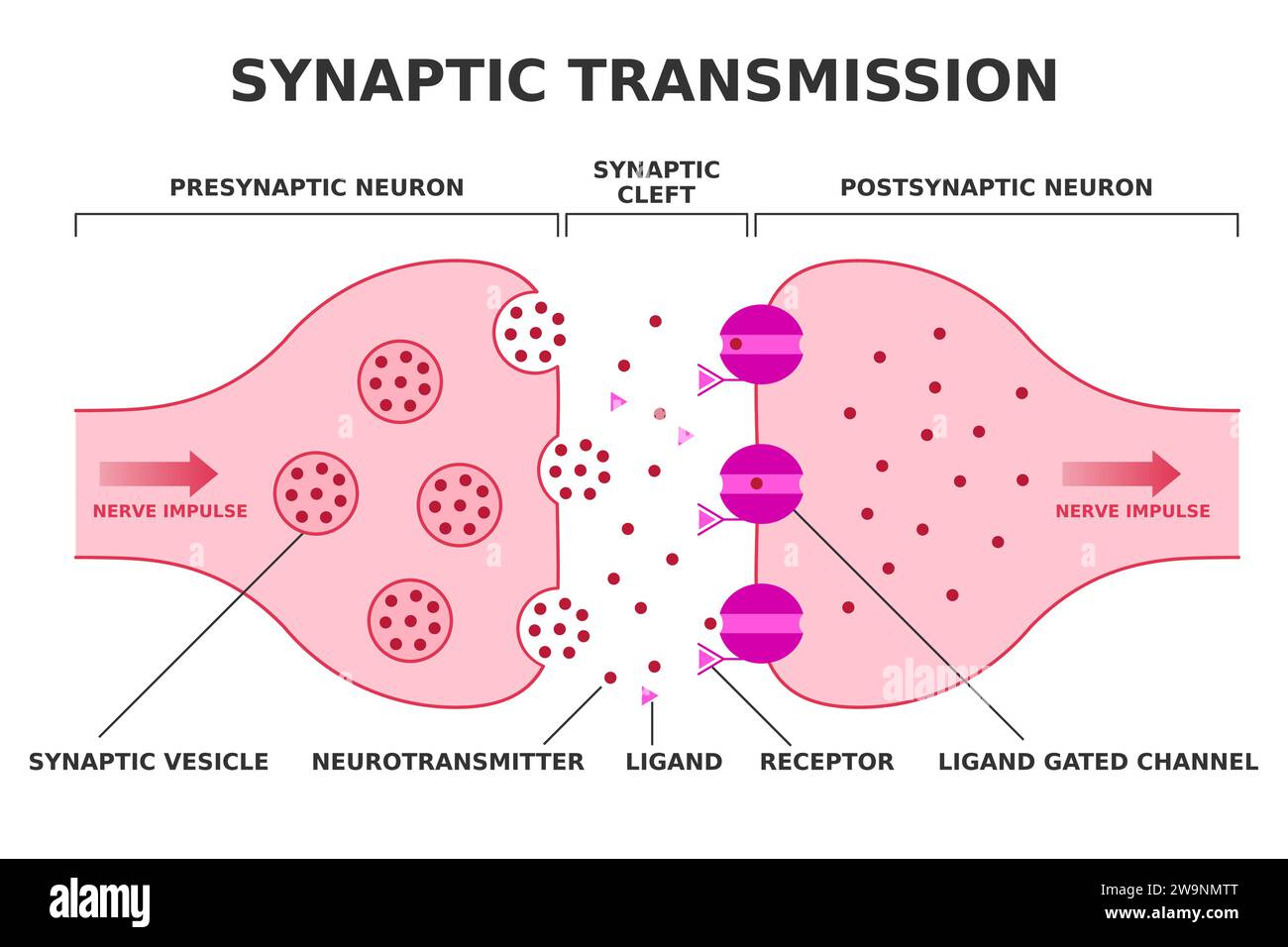 Synaptic transmission. Neurotransmission. Nerve impulse transition from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron. Neurotransmitter release. Vector Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synaptic-transmission-neurotransmission-nerve-impulse-transition-from-presynaptic-neuron-to-postsynaptic-neuron-neurotransmitter-release-vector-image591161784.html
Synaptic transmission. Neurotransmission. Nerve impulse transition from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron. Neurotransmitter release. Vector Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synaptic-transmission-neurotransmission-nerve-impulse-transition-from-presynaptic-neuron-to-postsynaptic-neuron-neurotransmitter-release-vector-image591161784.htmlRF2W9NMTT–Synaptic transmission. Neurotransmission. Nerve impulse transition from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron. Neurotransmitter release. Vector
 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482644769.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482644769.htmlRF2K16A95–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
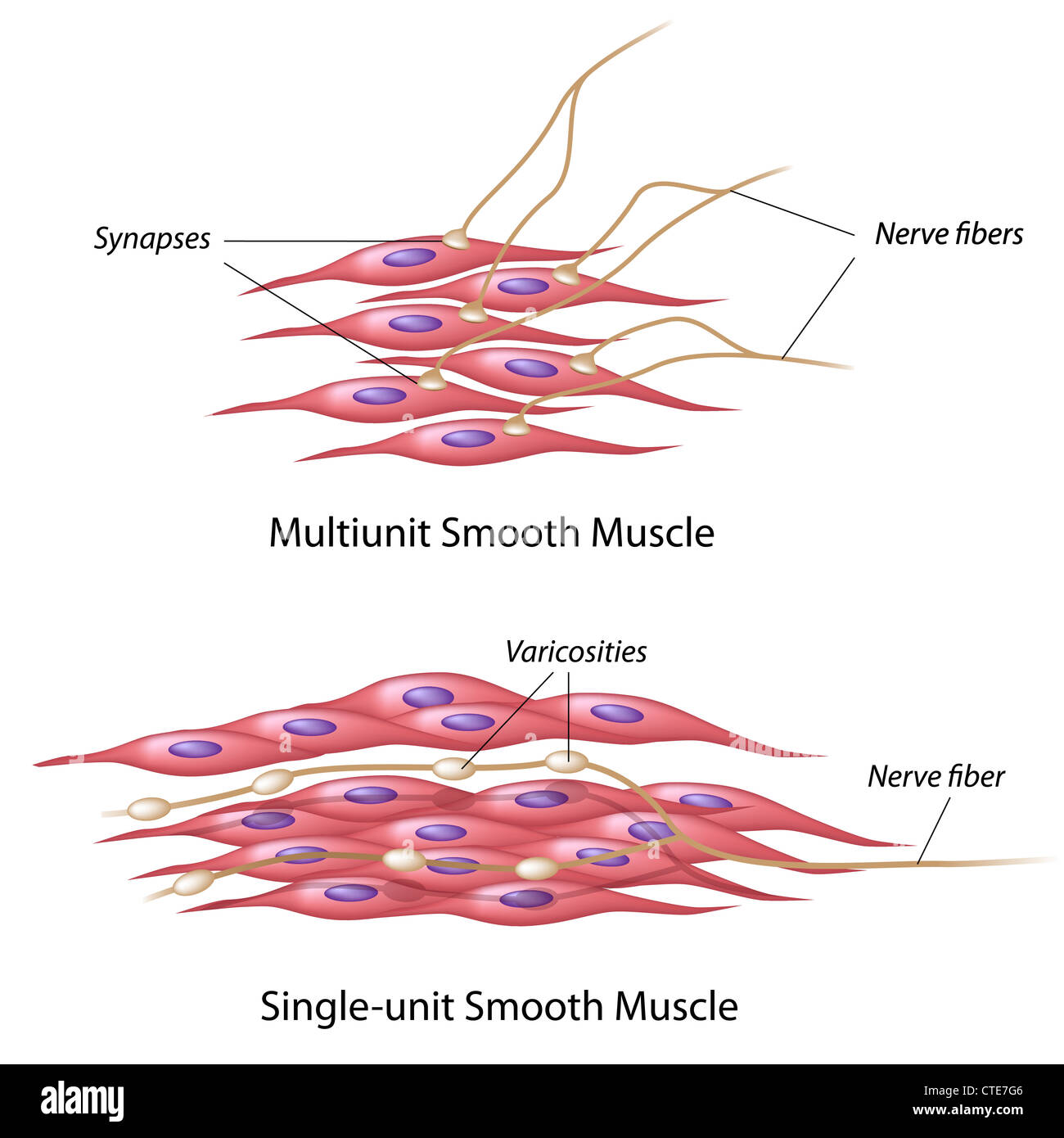 Smooth muscle innervation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-smooth-muscle-innervation-49485750.html
Smooth muscle innervation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-smooth-muscle-innervation-49485750.htmlRFCTE7G6–Smooth muscle innervation
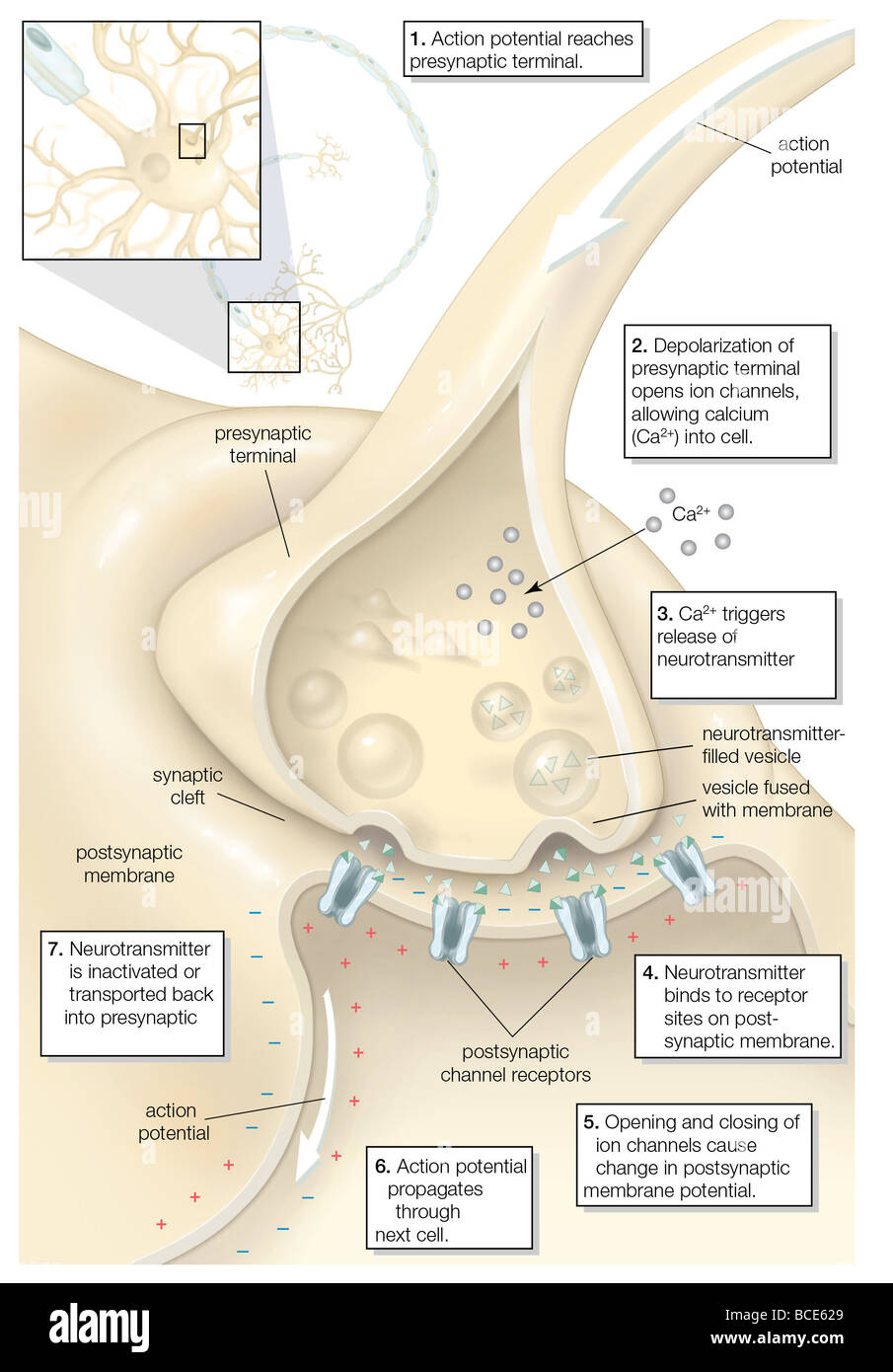 The chemical transmission of a nerve impulse at the synapse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-chemical-transmission-of-a-nerve-impulse-at-the-synapse-24898337.html
The chemical transmission of a nerve impulse at the synapse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-the-chemical-transmission-of-a-nerve-impulse-at-the-synapse-24898337.htmlRMBCE629–The chemical transmission of a nerve impulse at the synapse.
 . The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. FIGURE 8. A nerve ending containing a mixture of dense and clear synaptic vesicles. The glial cell (g) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-figure-7-the-initimate-juxtaposition-of-the-nerve-ending-and-muscle-cell-is-illustrated-here-a-sarcolemniic-tubule-is-also-clearly-pictured-arrow-scale-=10-micron-neuromuscular-junction-figs-7-8-9-the-muscle-cell-and-nerve-are-separated-by-a-gap-of-about-150-200-a-the-muscle-is-intimately-associated-with-the-nerve-ending-but-there-is-no-specialized-membrane-involution-in-the-junctional-area-such-r-ky-j-v-figure-8-a-nerve-ending-containing-a-mixture-of-dense-and-clear-synaptic-vesicles-the-glial-cell-g-image234649968.html
. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. FIGURE 8. A nerve ending containing a mixture of dense and clear synaptic vesicles. The glial cell (g) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-biological-bulletin-biology-zoology-biology-marine-biology-figure-7-the-initimate-juxtaposition-of-the-nerve-ending-and-muscle-cell-is-illustrated-here-a-sarcolemniic-tubule-is-also-clearly-pictured-arrow-scale-=10-micron-neuromuscular-junction-figs-7-8-9-the-muscle-cell-and-nerve-are-separated-by-a-gap-of-about-150-200-a-the-muscle-is-intimately-associated-with-the-nerve-ending-but-there-is-no-specialized-membrane-involution-in-the-junctional-area-such-r-ky-j-v-figure-8-a-nerve-ending-containing-a-mixture-of-dense-and-clear-synaptic-vesicles-the-glial-cell-g-image234649968.htmlRMRHN6C0–. The Biological bulletin. Biology; Zoology; Biology; Marine Biology. FIGURE 7. The initimate juxtaposition of the nerve ending and muscle cell is illustrated here. A sarcolemniic tubule is also clearly pictured (arrow) ; scale =1.0 micron. neuromuscular junction (Figs. 7, 8, 9). The muscle cell and nerve are separated by a gap of about 150-200 A. The muscle is intimately associated with the nerve ending but there is no specialized membrane involution in the junctional area such ,-r ky# J-v. FIGURE 8. A nerve ending containing a mixture of dense and clear synaptic vesicles. The glial cell (g)
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788024.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788024.htmlRF2J9X6X0–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image244429649.html
3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-image244429649.htmlRFT5JME9–3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap
 3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap, molecular biology Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-molecular-biology-image242197092.html
3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap, molecular biology Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/3d-rendered-illustration-visualisation-of-neurons-firing-neurotransmitters-in-the-synaptic-gap-molecular-biology-image242197092.htmlRFT210T4–3D Rendered Illustration, visualisation of neurons firing neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap, molecular biology
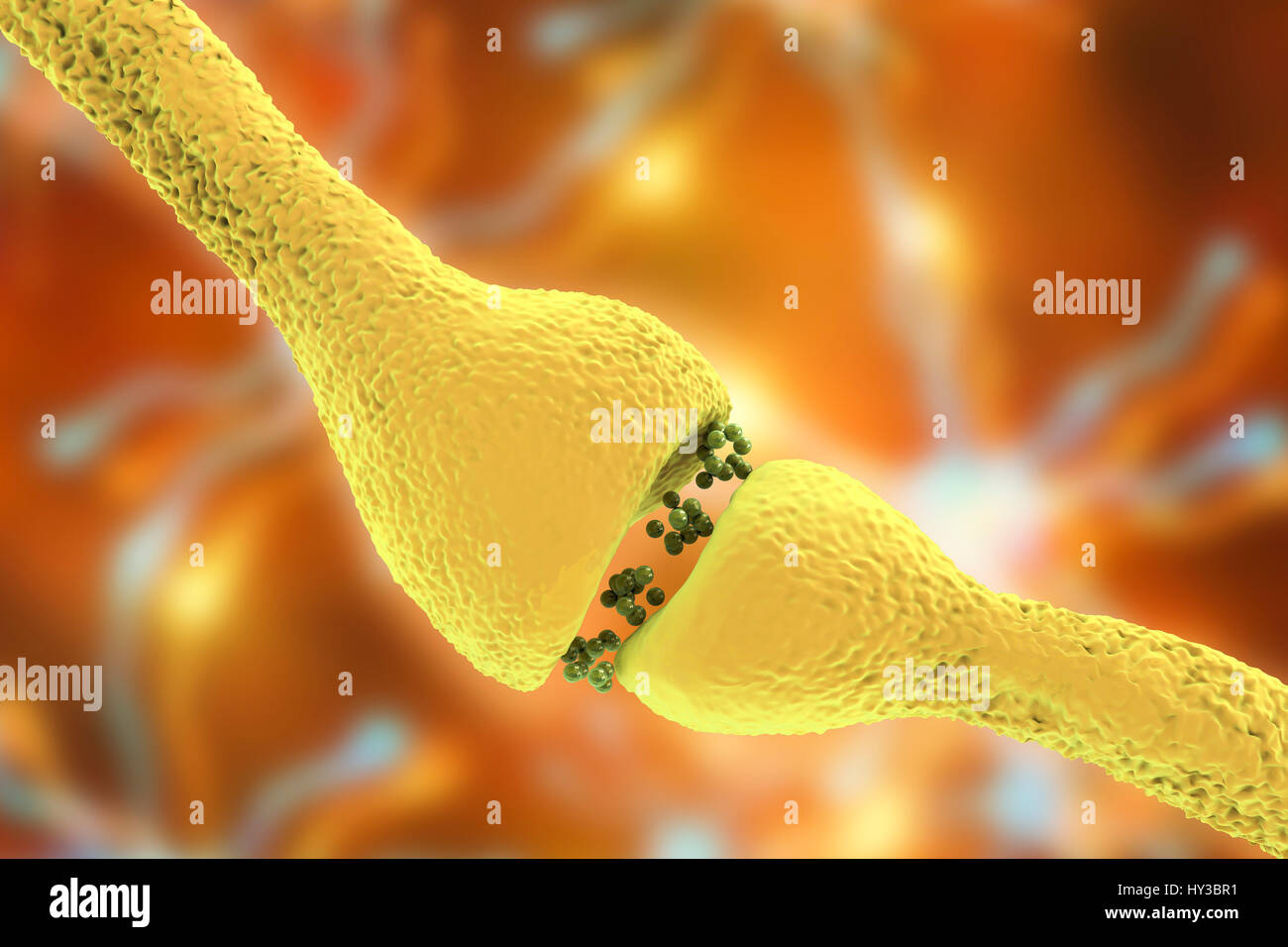 Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143413.html
Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143413.htmlRFHY3BR1–Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse.
 Illustration of synaptic gap between neural cells with neurotransmitters exchanging Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-of-synaptic-gap-between-neural-cells-with-neurotransmitters-exchanging-image333704846.html
Illustration of synaptic gap between neural cells with neurotransmitters exchanging Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/illustration-of-synaptic-gap-between-neural-cells-with-neurotransmitters-exchanging-image333704846.htmlRF2AAWFX6–Illustration of synaptic gap between neural cells with neurotransmitters exchanging
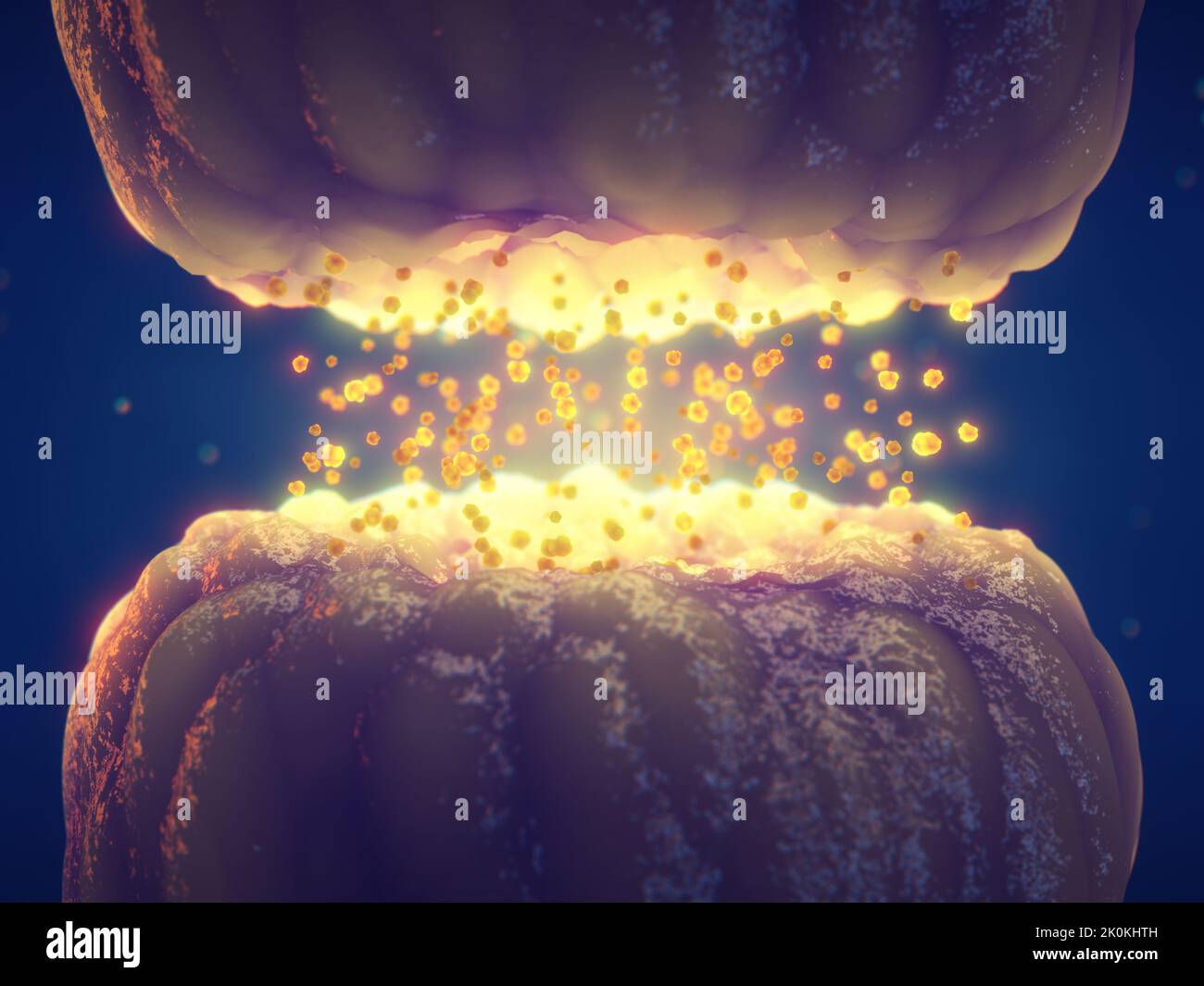 Synaptic transmission between nerve cells (Neurons). Synaptic transmission is the process in which one neurons communicate through neurotransmitters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synaptic-transmission-between-nerve-cells-neurons-synaptic-transmission-is-the-process-in-which-one-neurons-communicate-through-neurotransmitters-image482321409.html
Synaptic transmission between nerve cells (Neurons). Synaptic transmission is the process in which one neurons communicate through neurotransmitters Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synaptic-transmission-between-nerve-cells-neurons-synaptic-transmission-is-the-process-in-which-one-neurons-communicate-through-neurotransmitters-image482321409.htmlRF2K0KHTH–Synaptic transmission between nerve cells (Neurons). Synaptic transmission is the process in which one neurons communicate through neurotransmitters
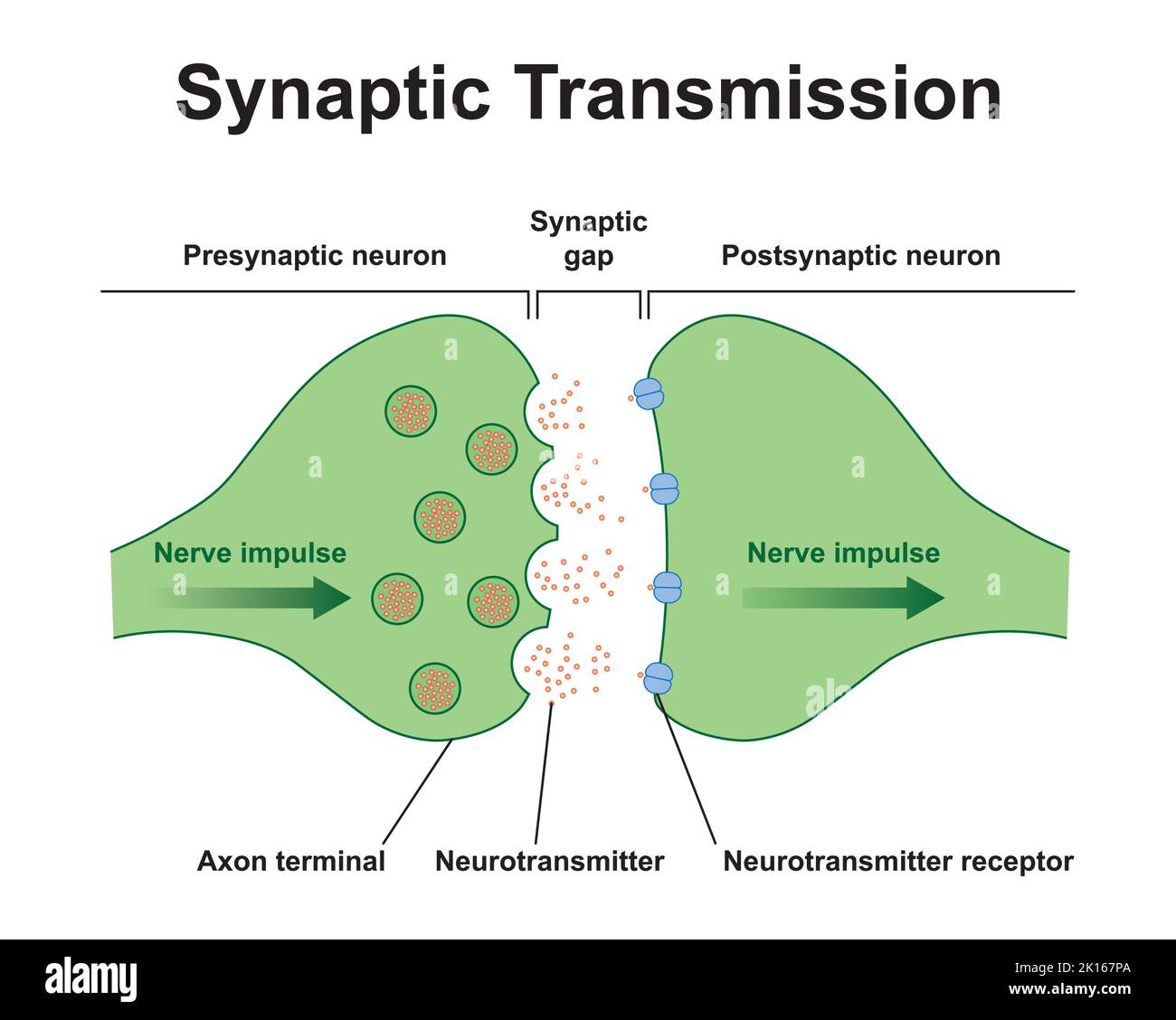 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482642786.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482642786.htmlRF2K167PA–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788026.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788026.htmlRF2J9X6X2–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
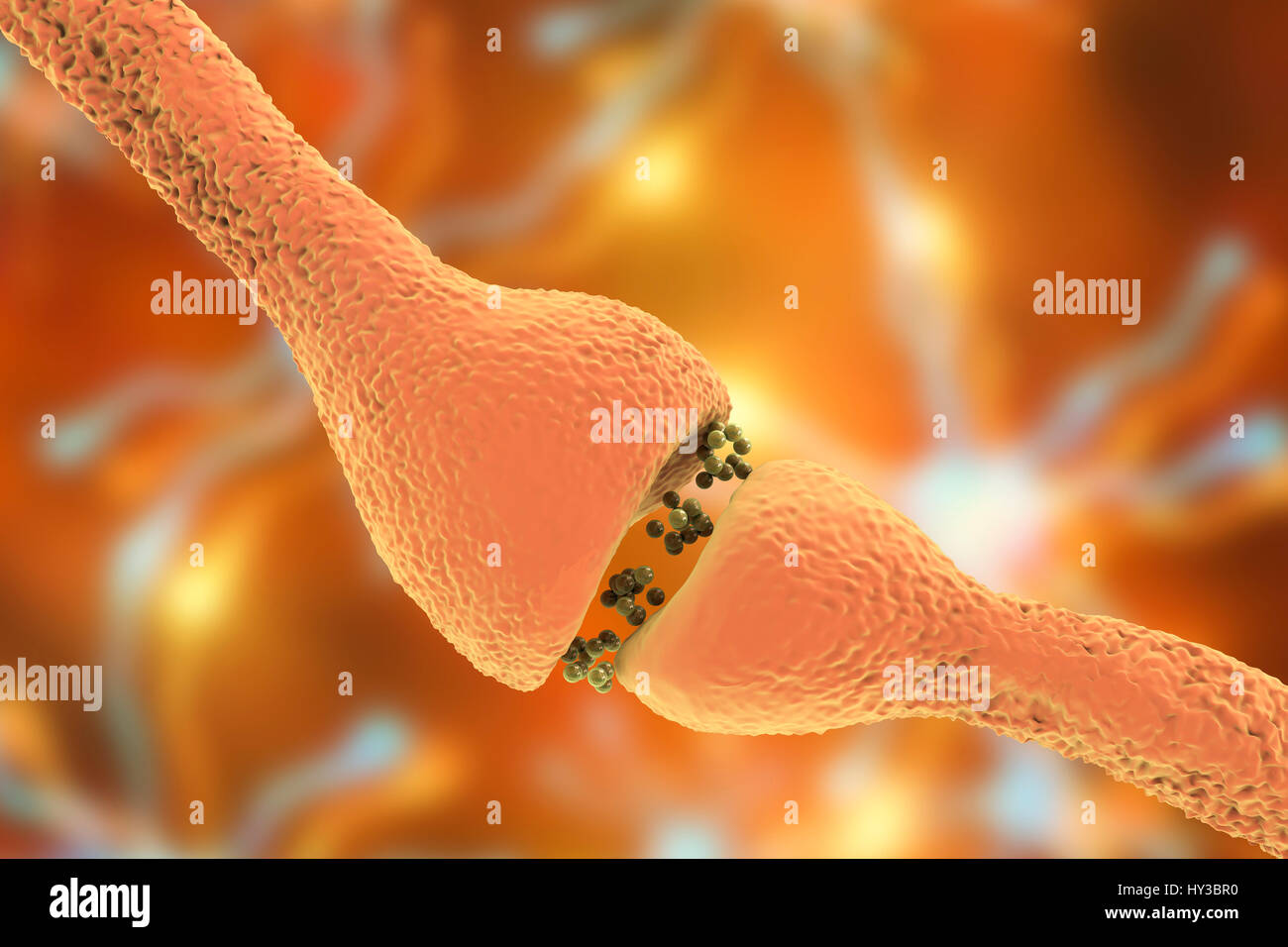 Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143412.html
Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143412.htmlRFHY3BR0–Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse.
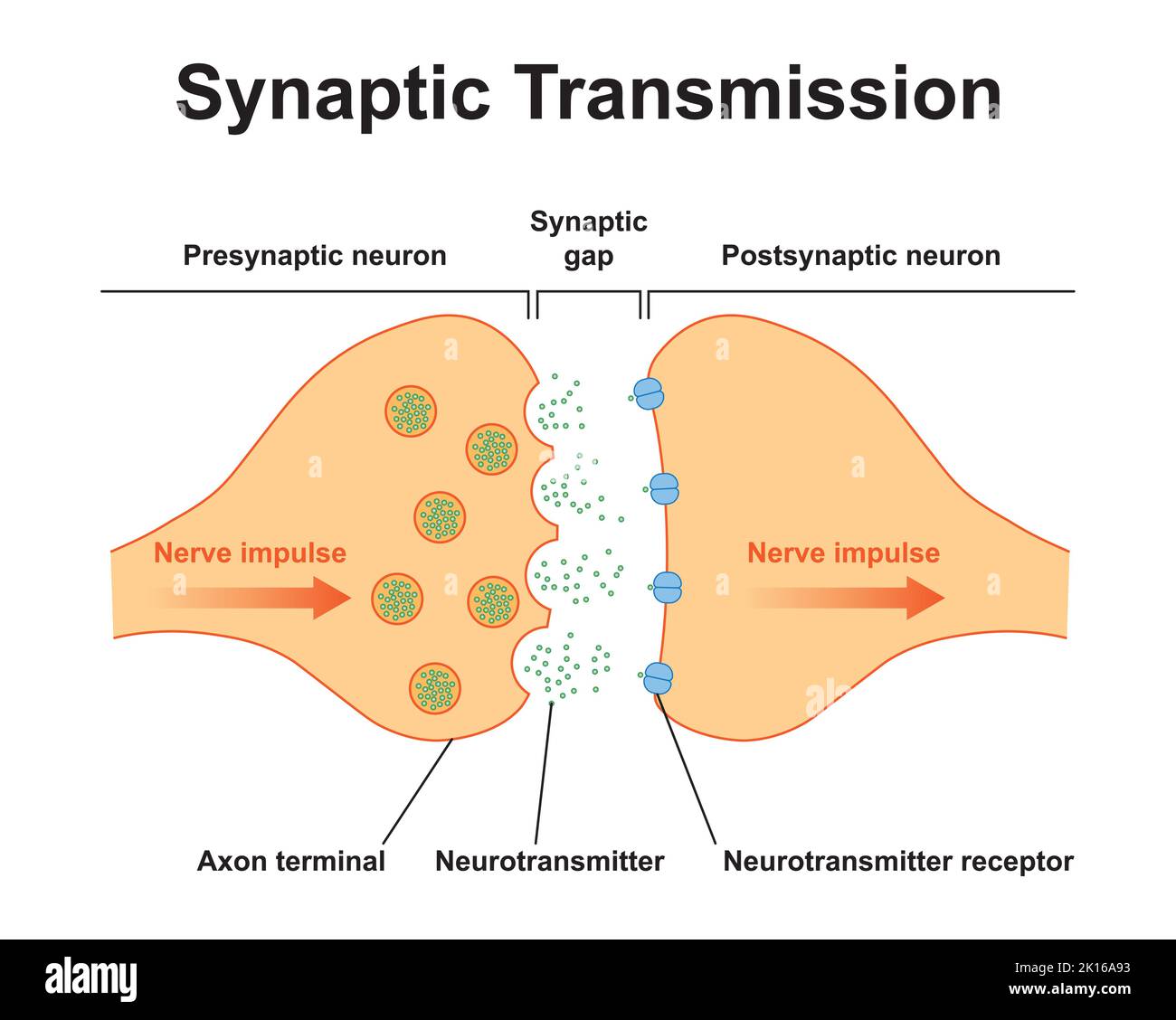 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482644767.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482644767.htmlRF2K16A93–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788018.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788018.htmlRF2J9X6WP–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
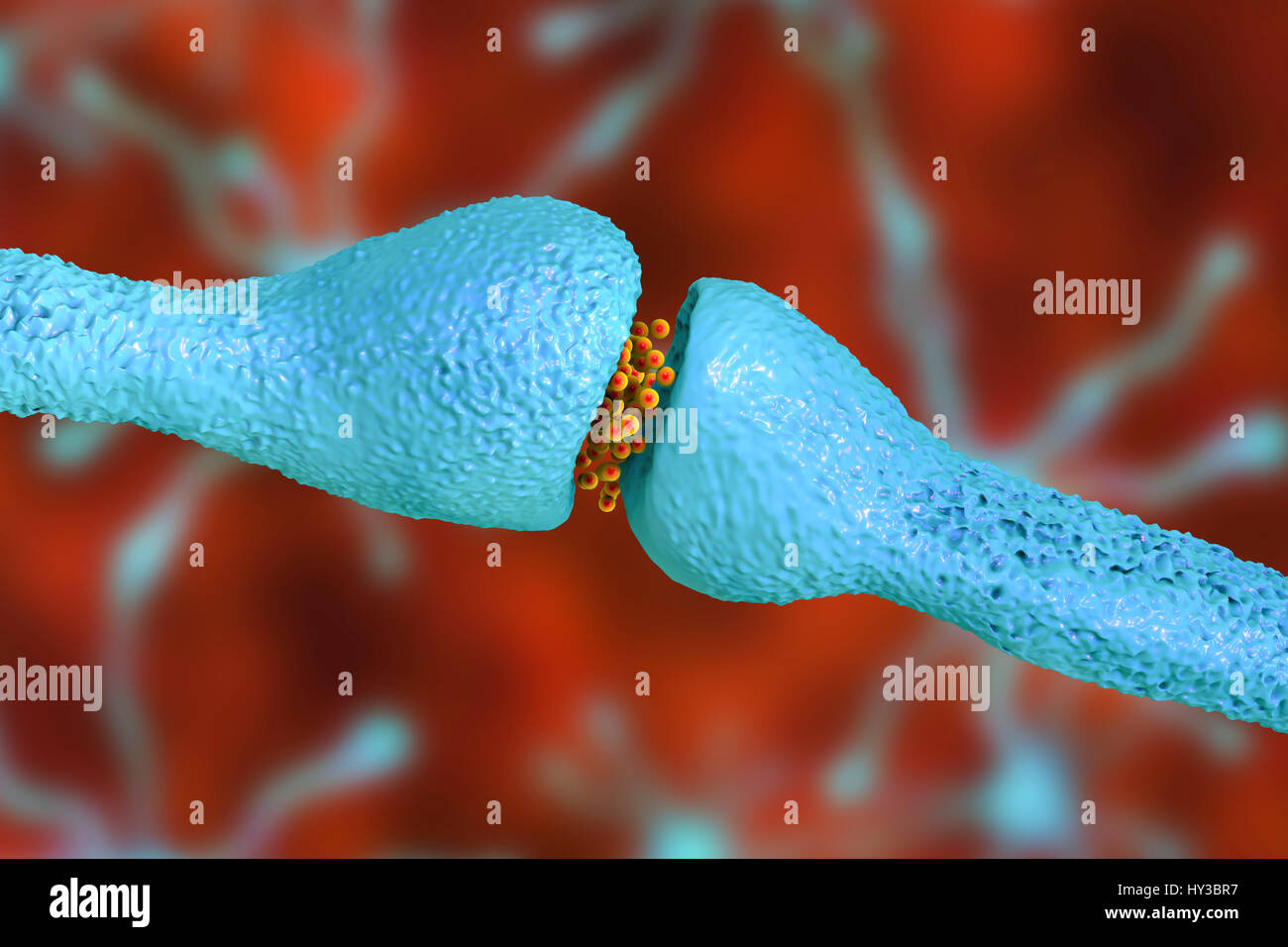 Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143419.html
Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143419.htmlRFHY3BR7–Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse.
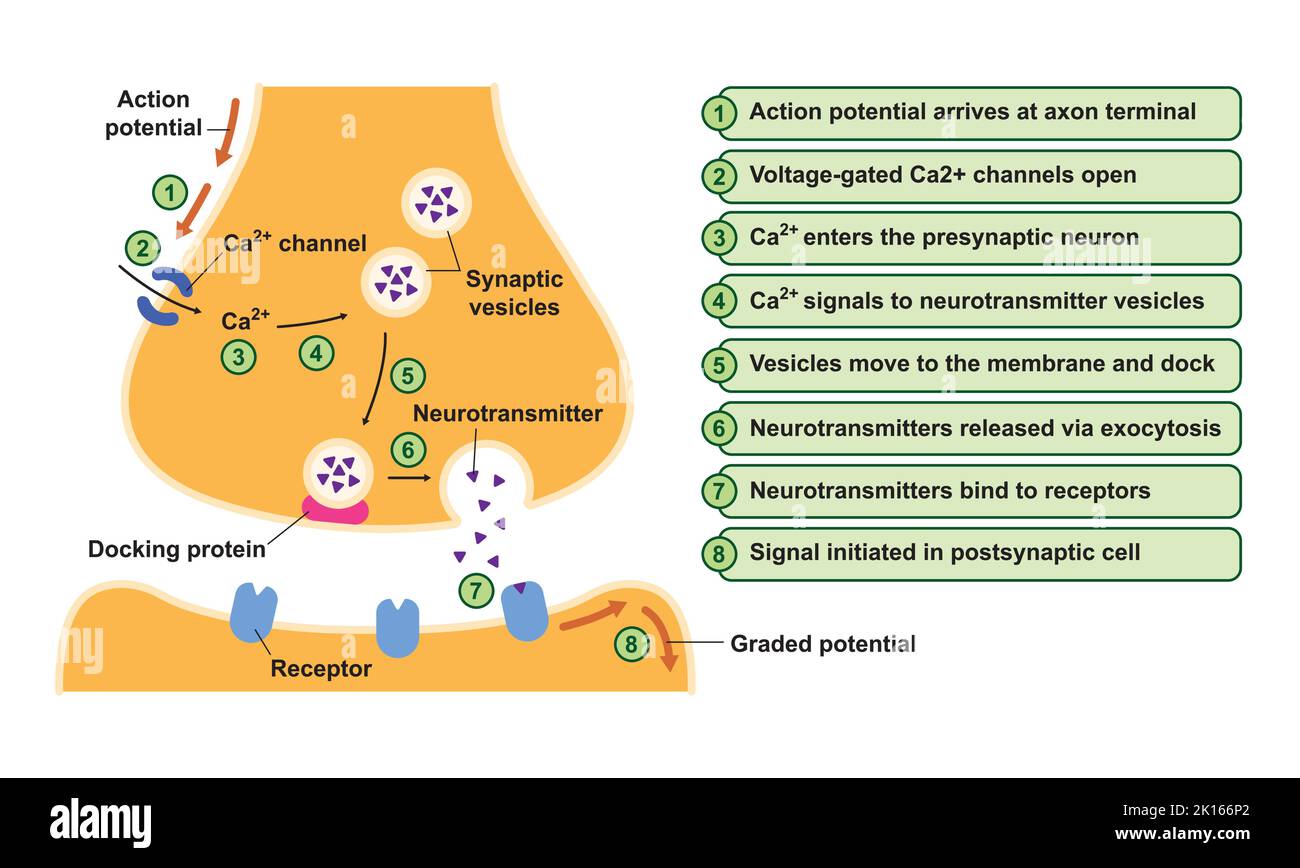 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482641994.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482641994.htmlRF2K166P2–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
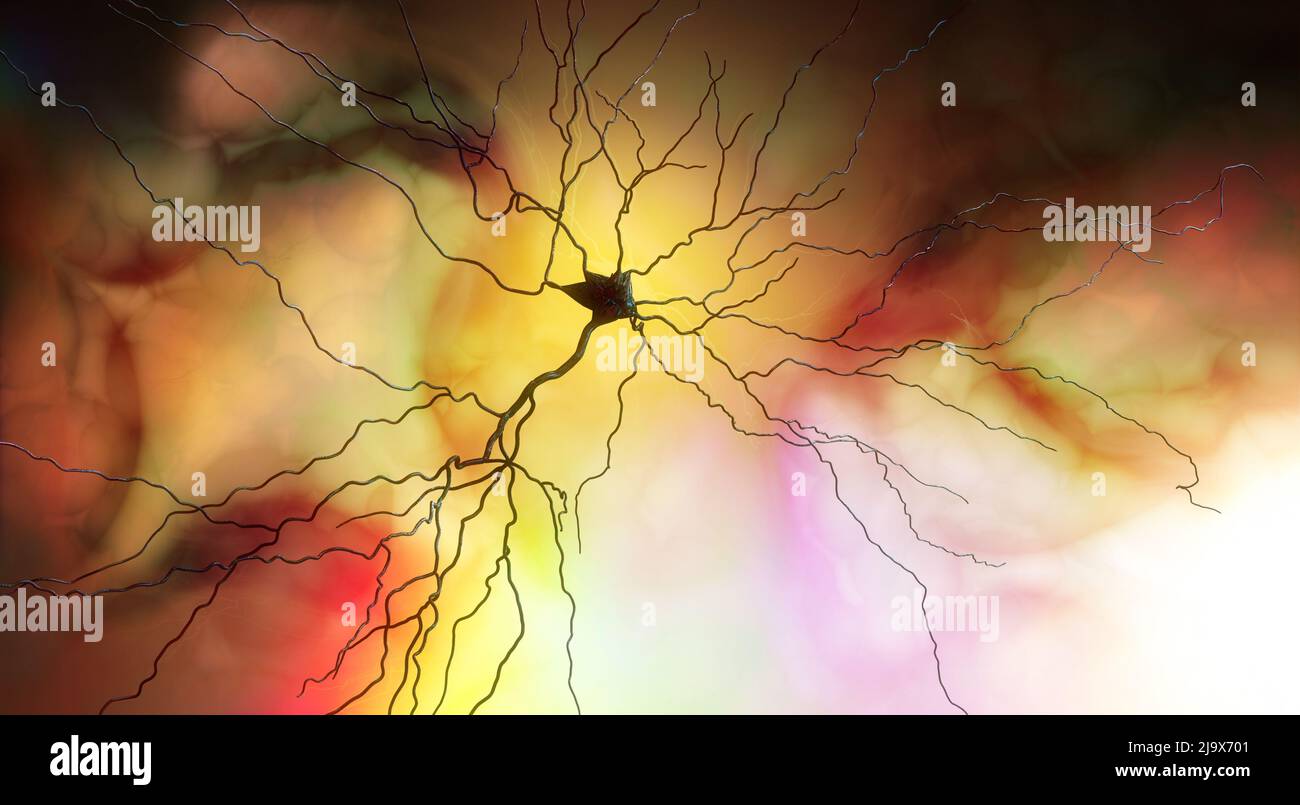 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788081.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788081.htmlRF2J9X701–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143420.html
Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-junction-or-synapse-between-137143420.htmlRFHY3BR8–Nerve synapse. Computer illustration of a junction, or synapse, between two nerve cells (neurons). As the electrical signal reaches the presynaptic end of a neuron it triggers the release of neurotransmitters across the gap, or synaptic cleft, between the two cells. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, changing the membrane's excitability and triggering an electrical impulse.
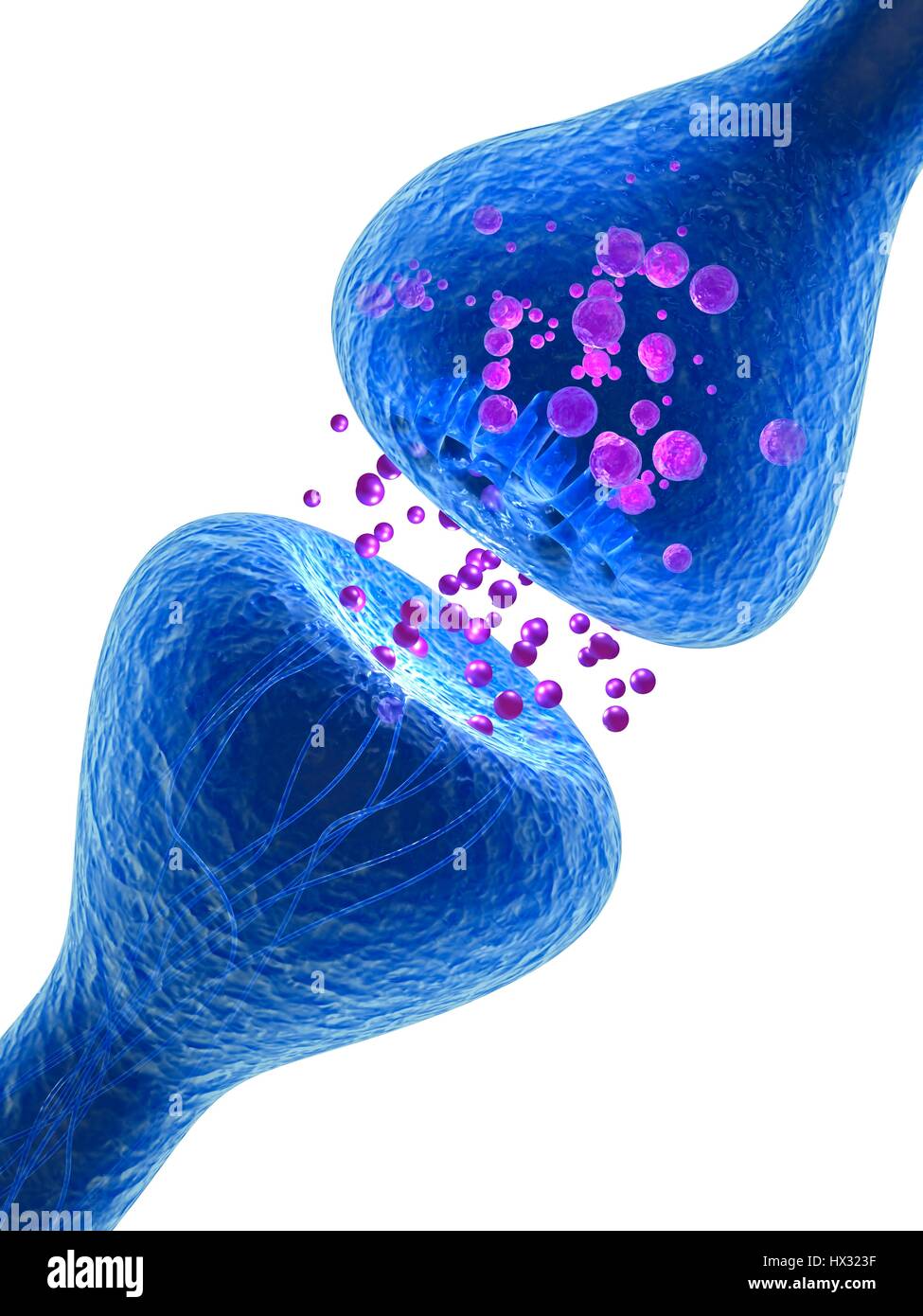 Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521155.html
Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521155.htmlRFHX323F–Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse.
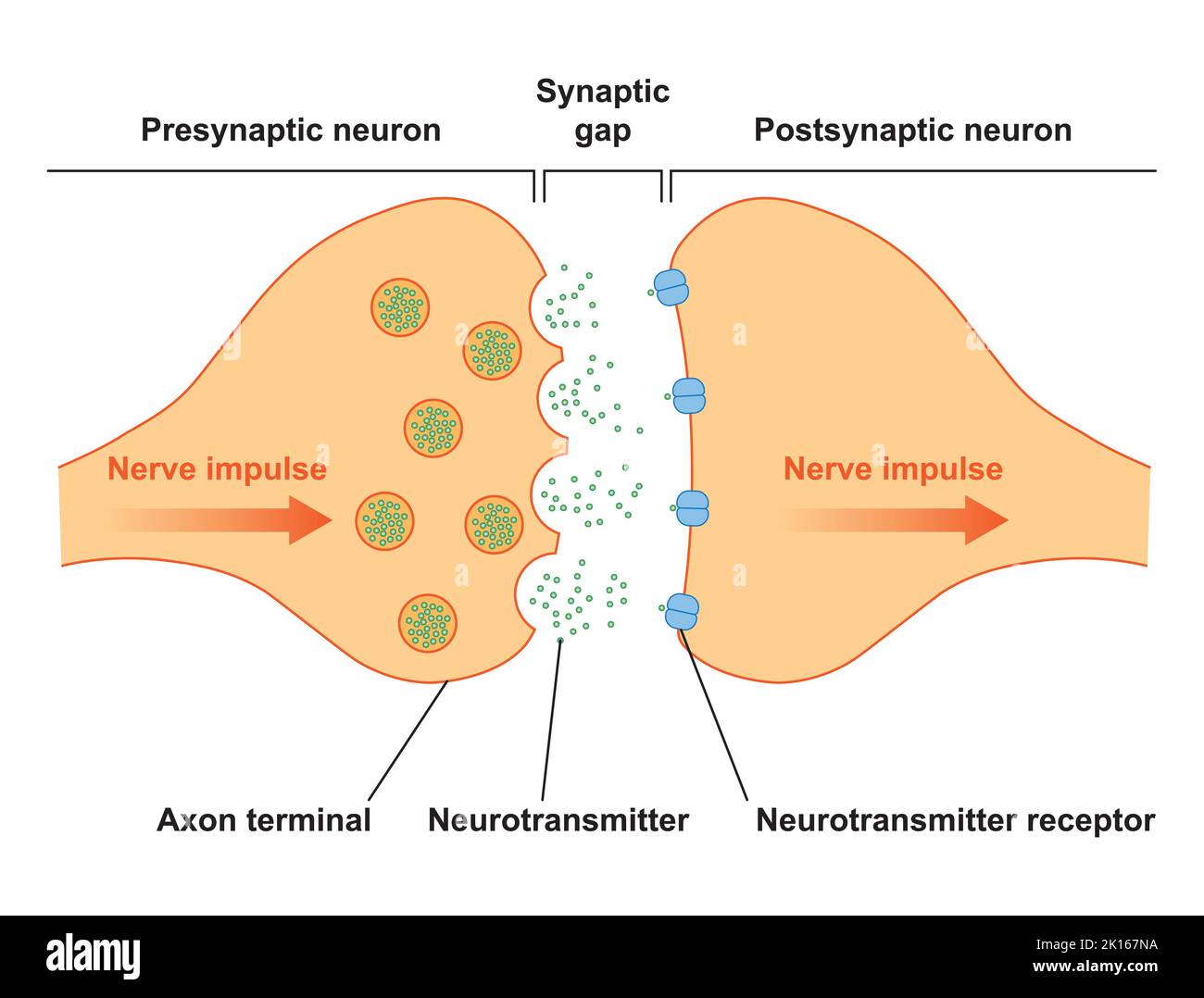 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482642758.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482642758.htmlRF2K167NA–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
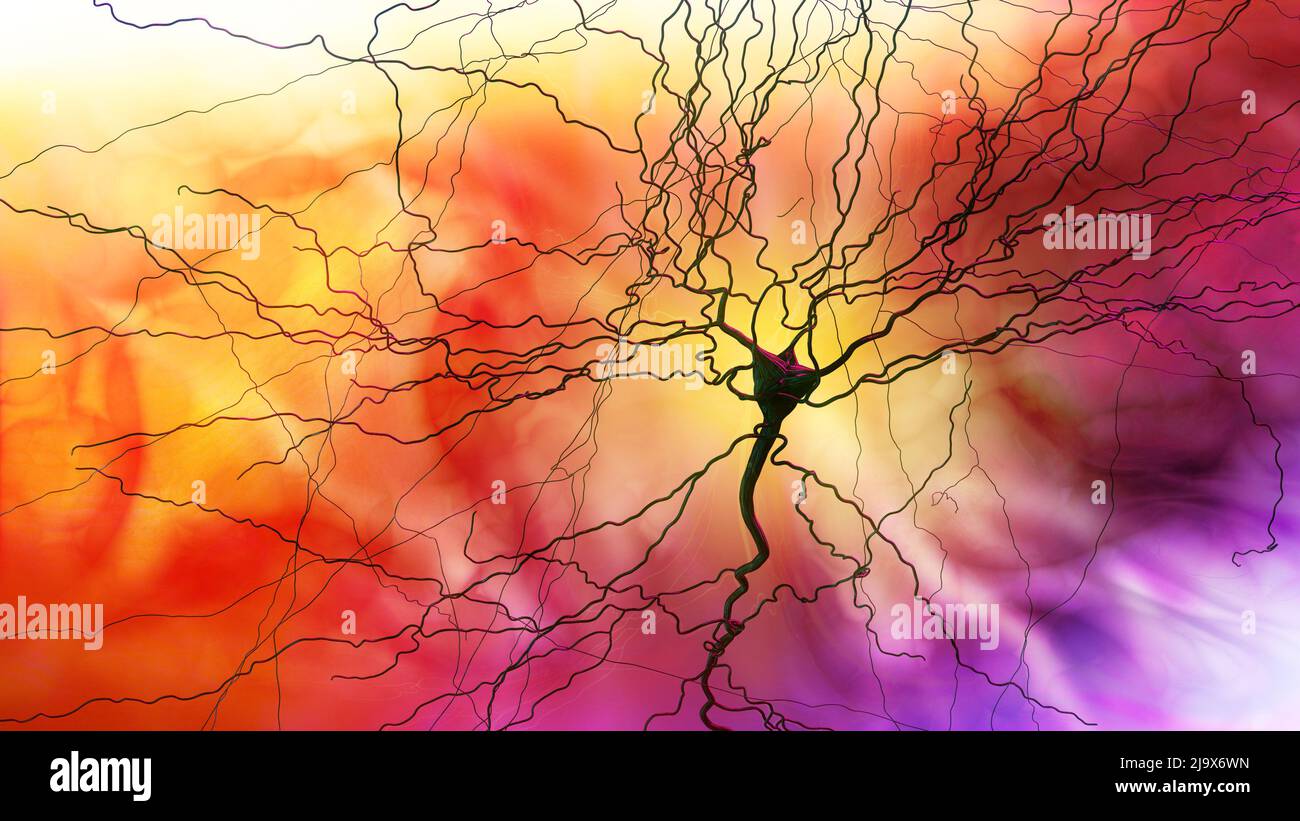 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788017.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788017.htmlRF2J9X6WN–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
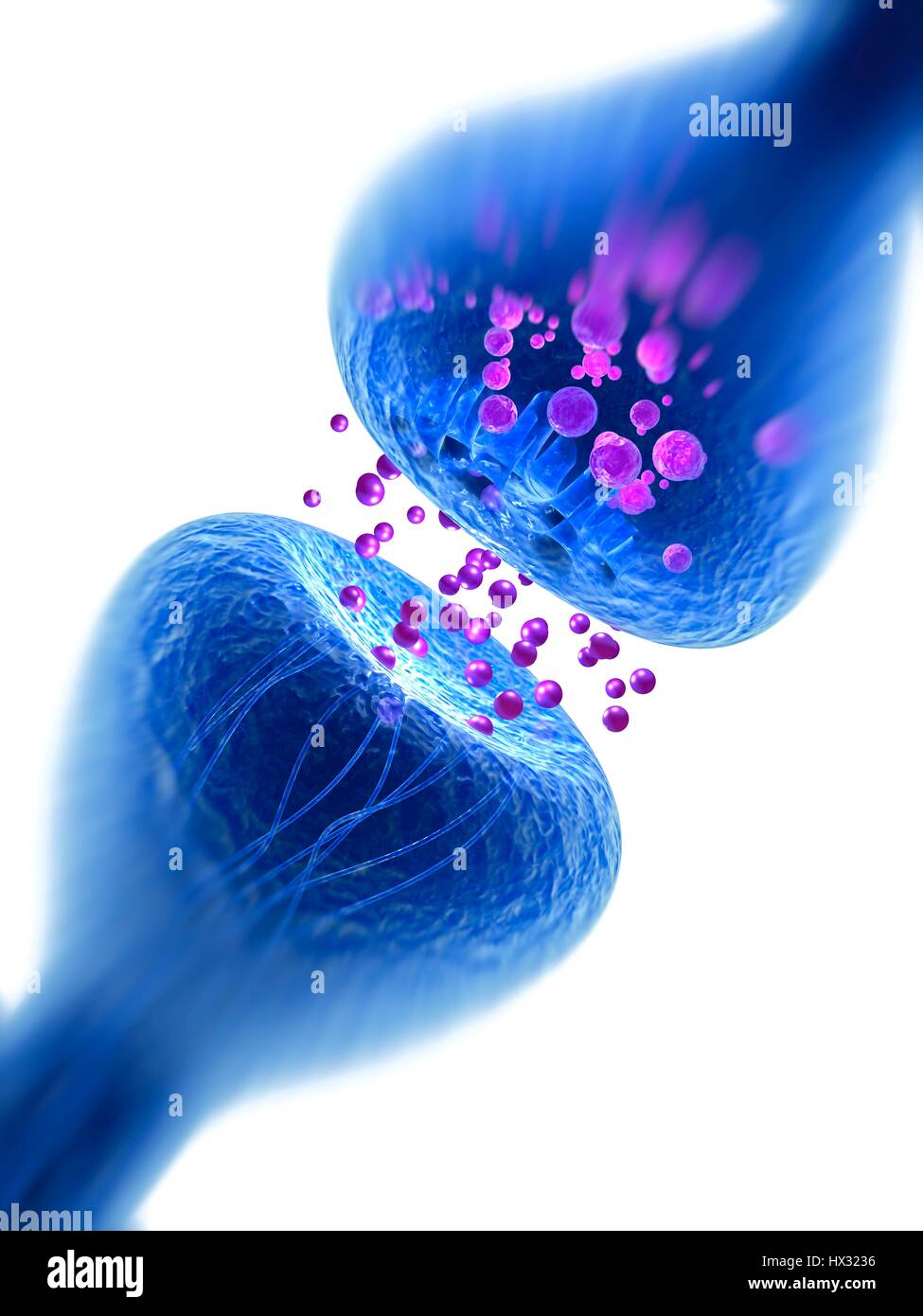 Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521146.html
Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521146.htmlRFHX3236–Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse.
 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482642871.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482642871.htmlRF2K167WB–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788042.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788042.htmlRF2J9X6XJ–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575631.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575631.htmlRF2J7Y0E7–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
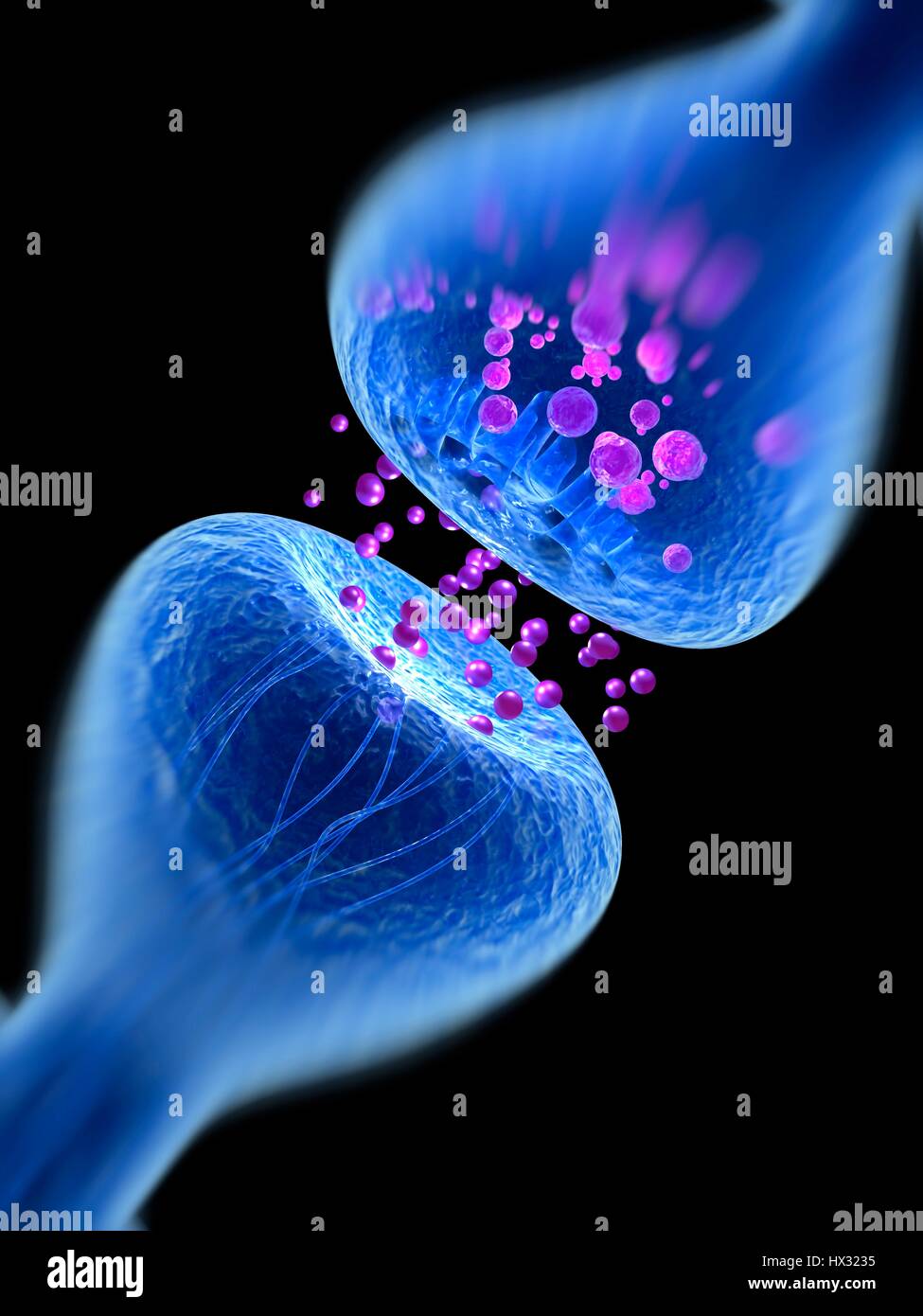 Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521145.html
Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521145.htmlRFHX3235–Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse.
 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482644768.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482644768.htmlRF2K16A94–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575621.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575621.htmlRF2J7Y0DW–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
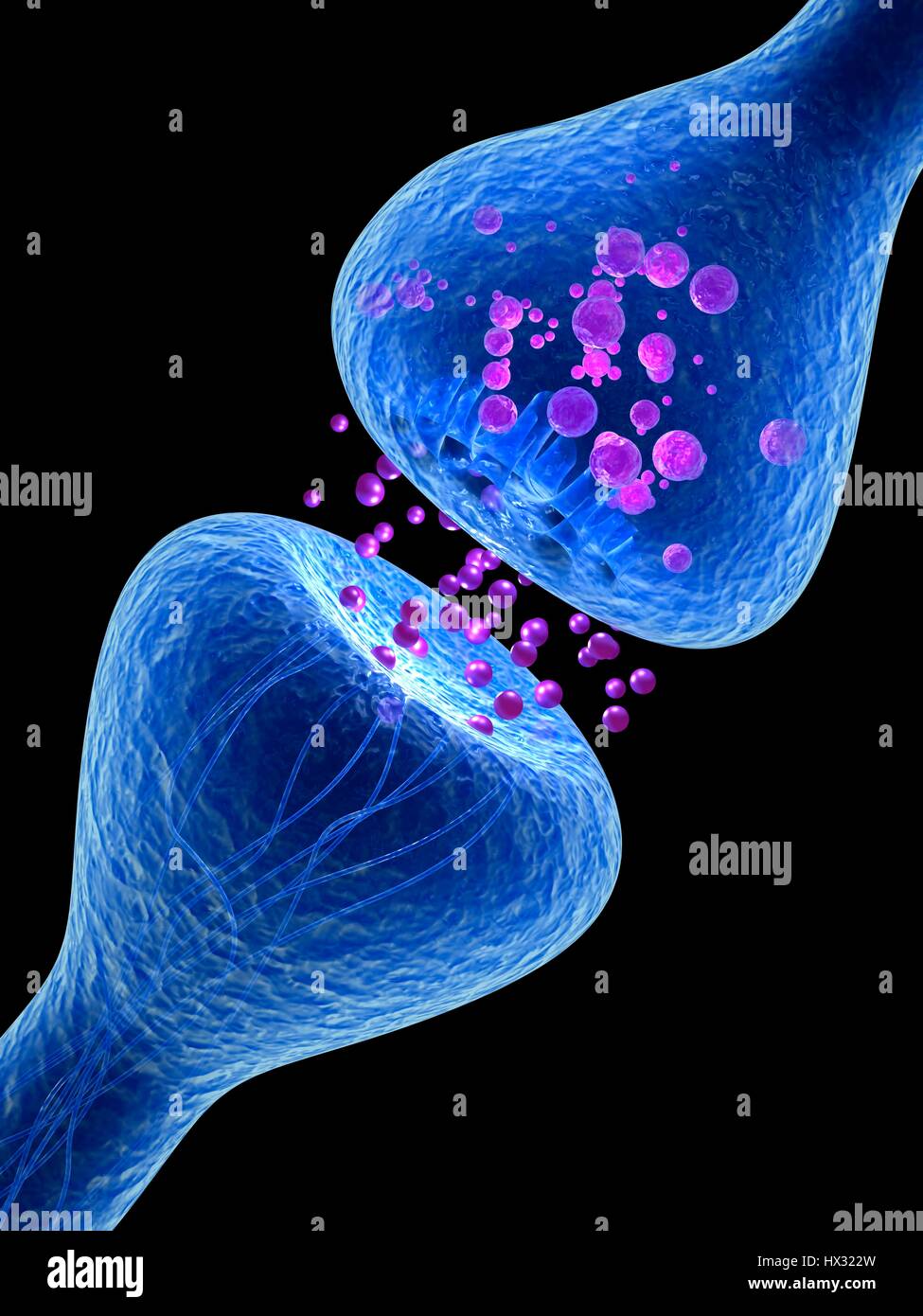 Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521137.html
Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-synapse-computer-illustration-of-a-synapse-the-junction-between-two-136521137.htmlRFHX322W–Synapse. Computer illustration of a synapse, the junction between two neurons. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass through channels into the receptor nerve cell (top), where they trigger an electrical impulse.
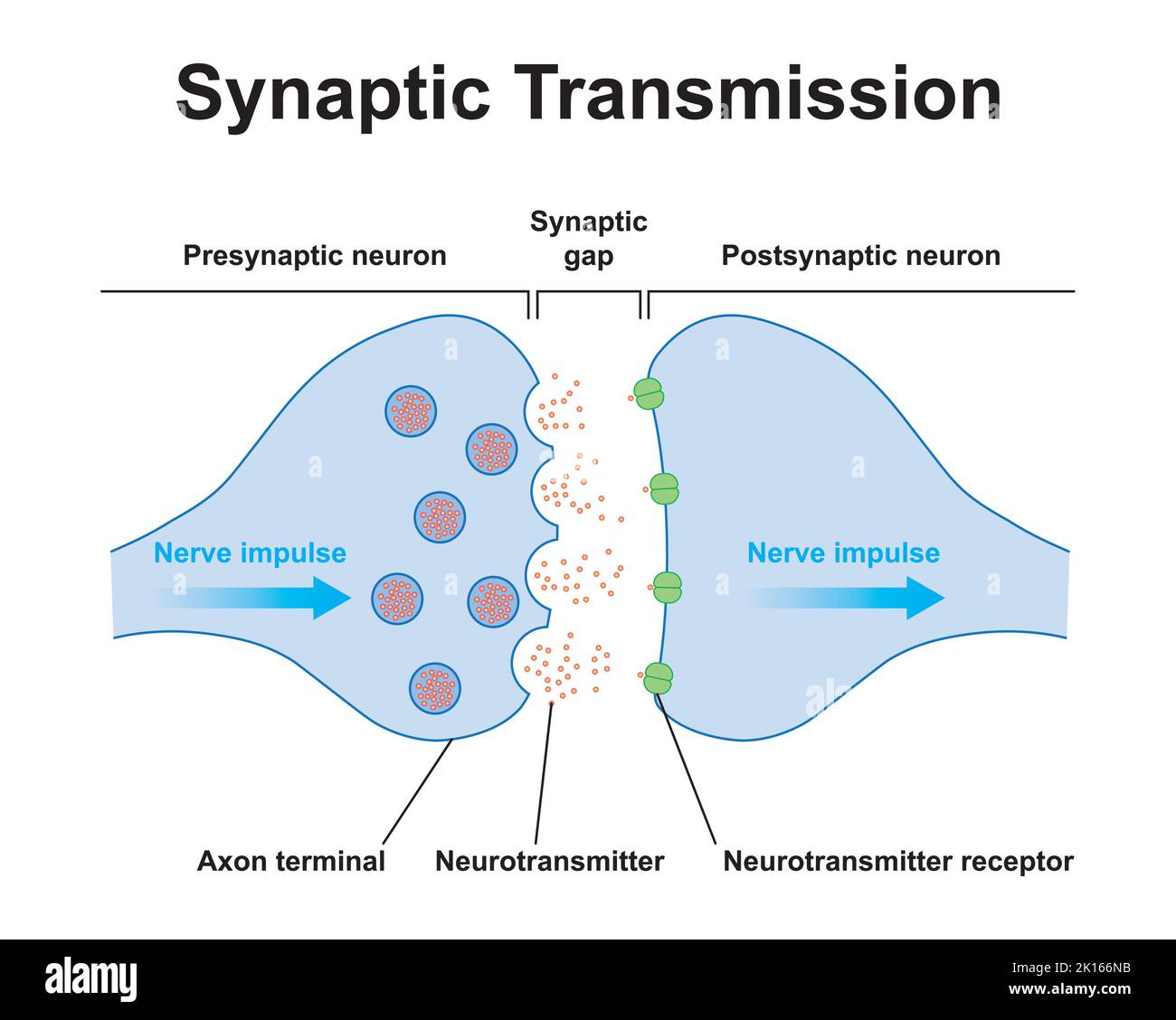 Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482641975.html
Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/scientific-designing-of-synapse-structure-the-synaptic-transmission-isolated-on-black-background-vector-illustration-image482641975.htmlRF2K166NB–Scientific Designing of Synapse Structure. The Synaptic Transmission. Isolated on Black Background. Vector Illustration.
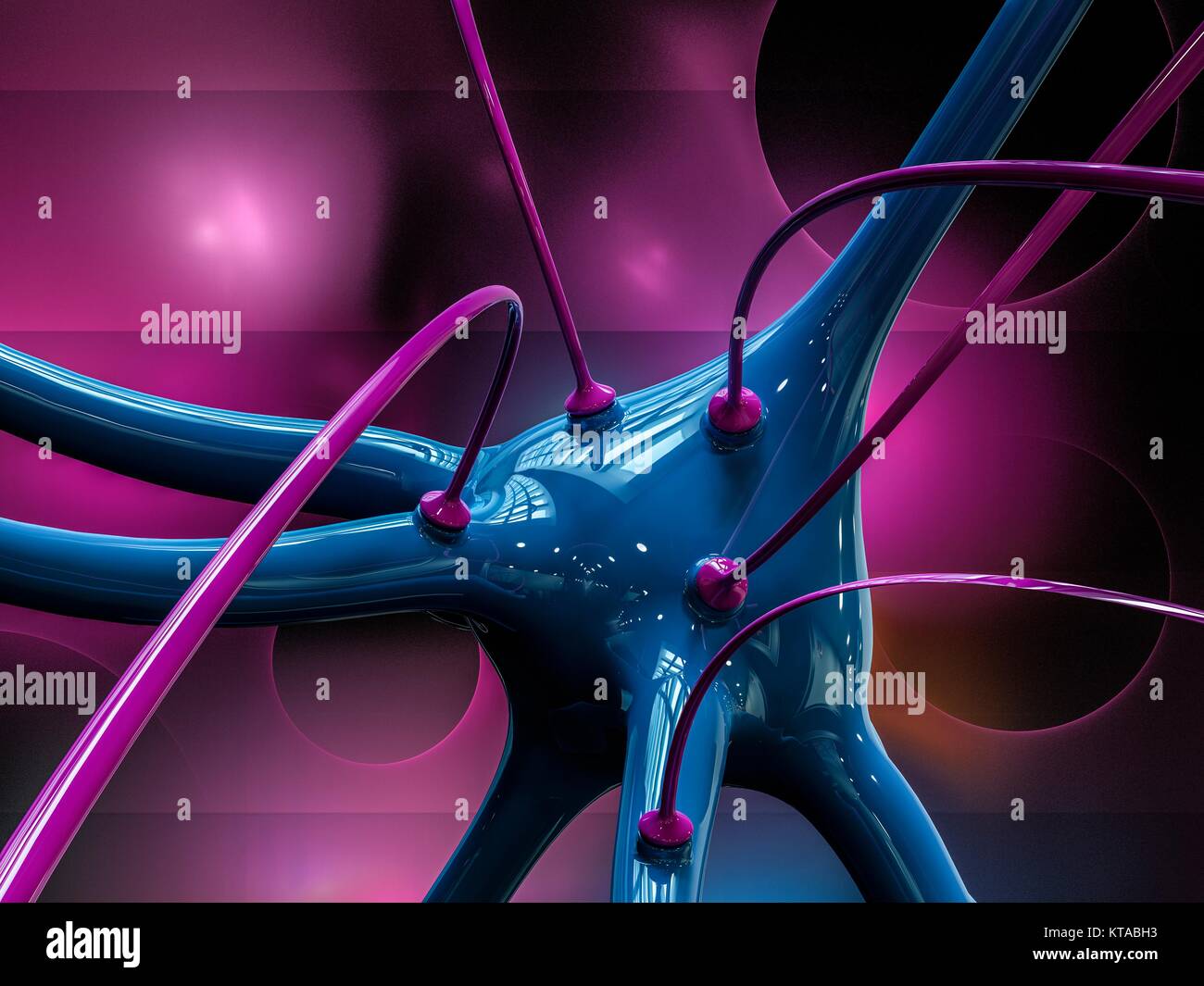 Nerve cell and synapses, computer illustration. Nerve cells, or neurons, relay information around the central nervous system (CNS) and from the CNS to the rest of the body. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the terminal swelling of the presynaptic cell. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass into the receptor nerve cell, where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-nerve-cell-and-synapses-computer-illustration-nerve-cells-or-neurons-169873679.html
Nerve cell and synapses, computer illustration. Nerve cells, or neurons, relay information around the central nervous system (CNS) and from the CNS to the rest of the body. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the terminal swelling of the presynaptic cell. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass into the receptor nerve cell, where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-nerve-cell-and-synapses-computer-illustration-nerve-cells-or-neurons-169873679.htmlRFKTABH3–Nerve cell and synapses, computer illustration. Nerve cells, or neurons, relay information around the central nervous system (CNS) and from the CNS to the rest of the body. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the terminal swelling of the presynaptic cell. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass into the receptor nerve cell, where they trigger an electrical impulse.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575635.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575635.htmlRF2J7Y0EB–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image248373992.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image248373992.htmlRFTC2BFM–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575627.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image469575627.htmlRF2J7Y0E3–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185420049.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185420049.htmlRFMNJH4H–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Nerve cell and synapses, computer illustration. Nerve cells, or neurons, relay information around the central nervous system (CNS) and from the CNS to the rest of the body. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the terminal swelling of the presynaptic cell. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass into the receptor nerve cell, where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-nerve-cell-and-synapses-computer-illustration-nerve-cells-or-neurons-169873680.html
Nerve cell and synapses, computer illustration. Nerve cells, or neurons, relay information around the central nervous system (CNS) and from the CNS to the rest of the body. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the terminal swelling of the presynaptic cell. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass into the receptor nerve cell, where they trigger an electrical impulse. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-image-nerve-cell-and-synapses-computer-illustration-nerve-cells-or-neurons-169873680.htmlRFKTABH4–Nerve cell and synapses, computer illustration. Nerve cells, or neurons, relay information around the central nervous system (CNS) and from the CNS to the rest of the body. Synapses transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to the next. When the signal reaches the synapse it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the terminal swelling of the presynaptic cell. The neurotransmitters cross a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft and pass into the receptor nerve cell, where they trigger an electrical impulse.
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image223497824.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image223497824.htmlRFPYH5N4–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
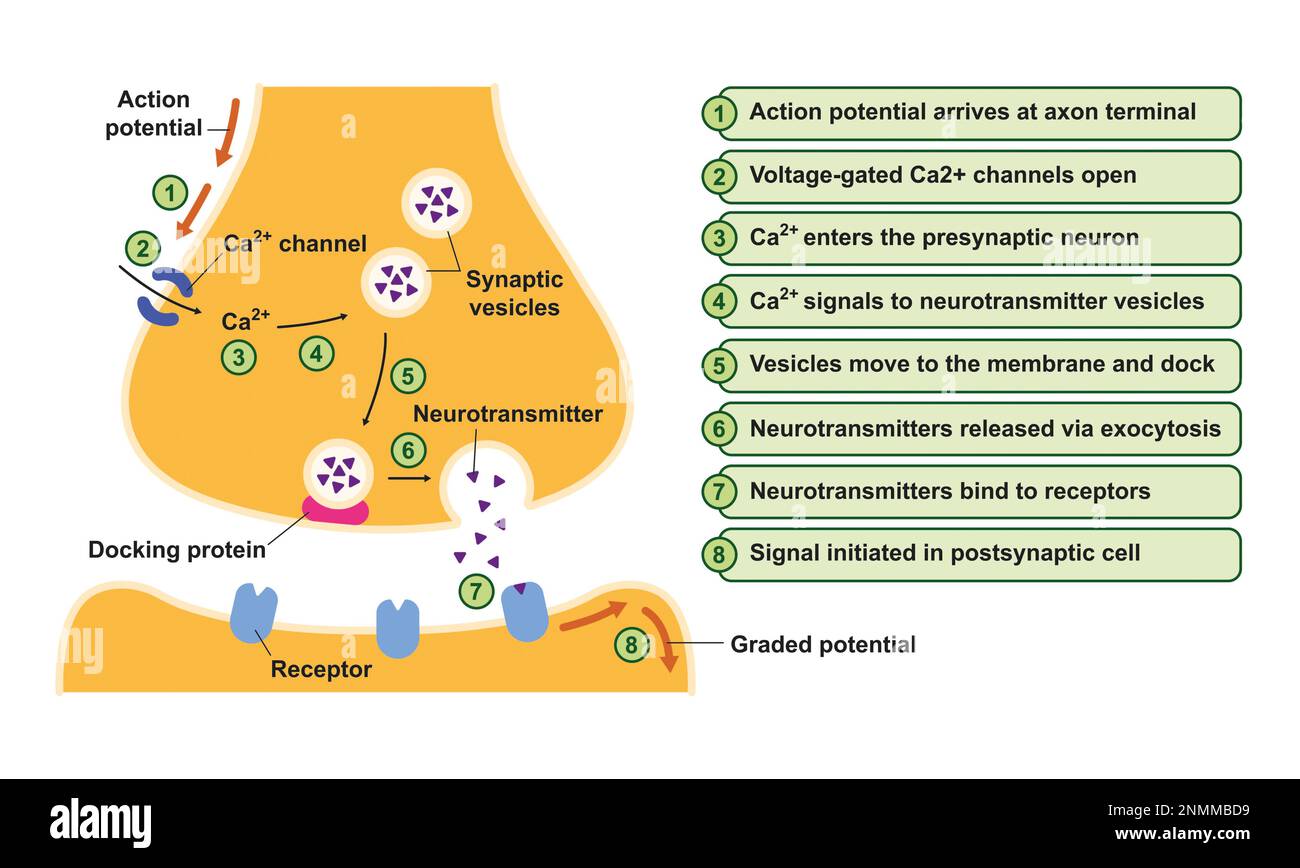 Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052197.html
Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052197.htmlRF2NMMBD9–Synapse structure, illustration
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-image419189913.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-image419189913.htmlRF2F9YN09–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain
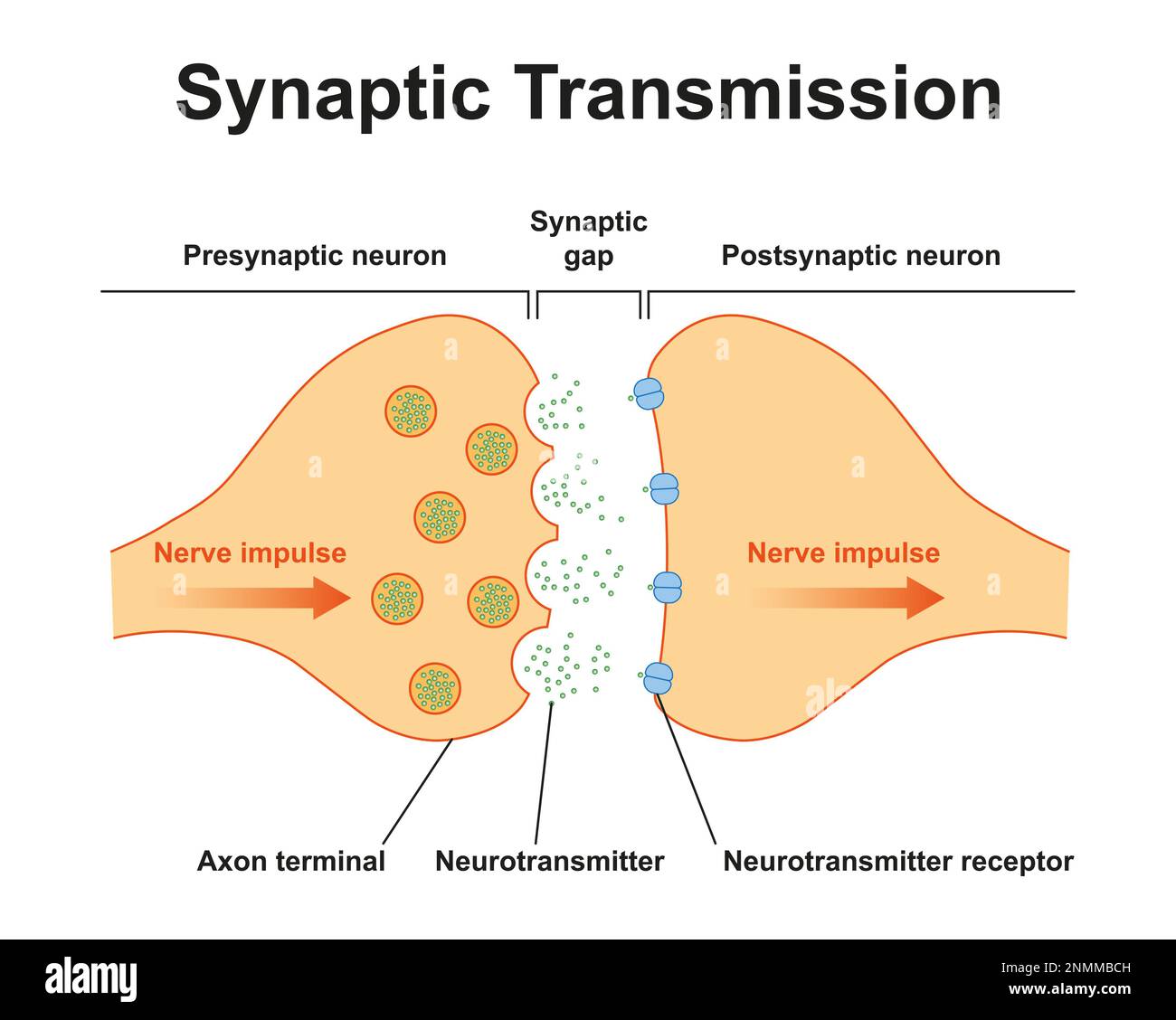 Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052177.html
Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052177.htmlRF2NMMBCH–Synapse structure, illustration
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-image419195968.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-image419195968.htmlRF2FA00MG–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213504916.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213504916.htmlRFPB9YKG–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
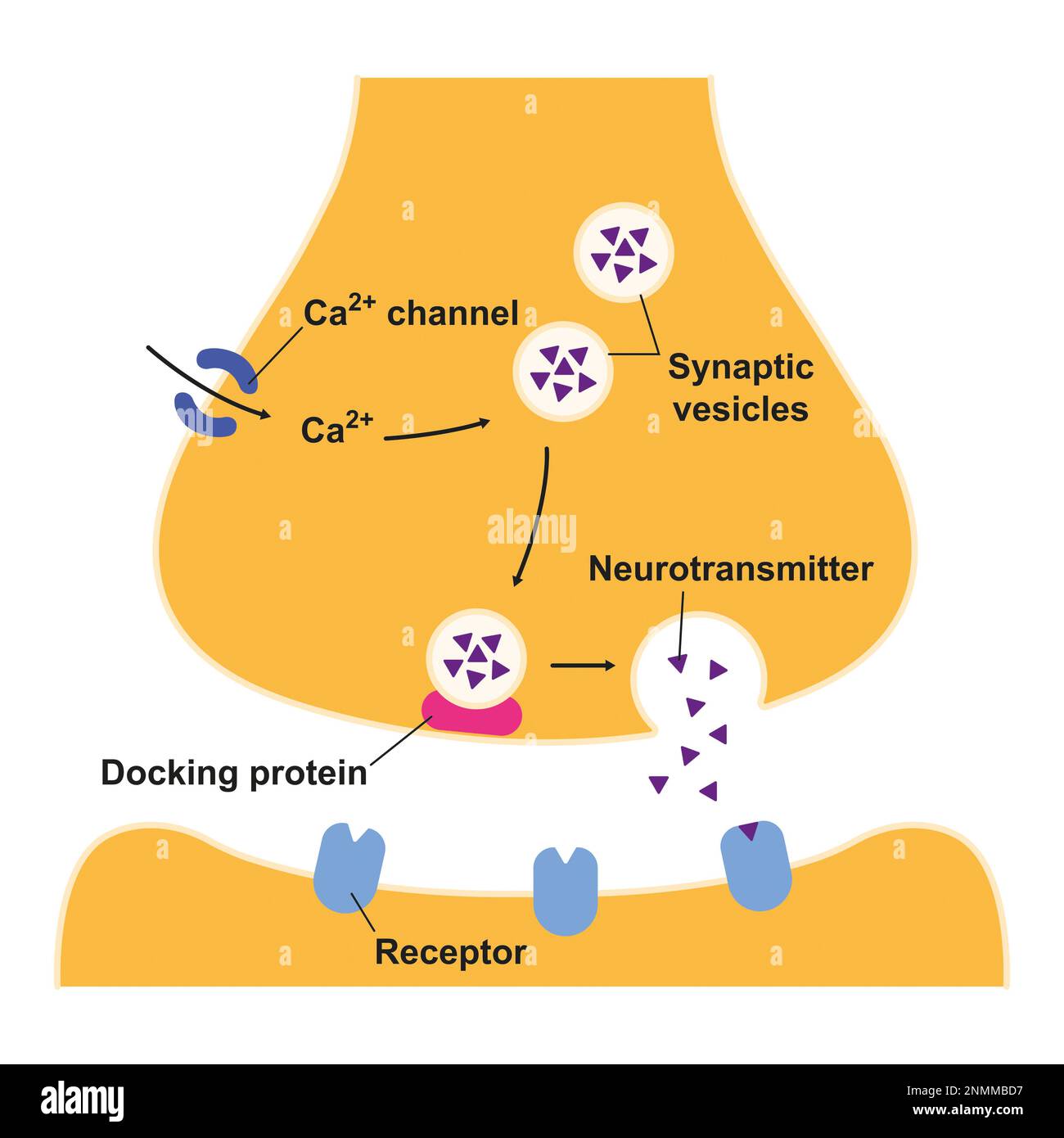 Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052195.html
Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052195.htmlRF2NMMBD7–Synapse structure, illustration
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213506714.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213506714.htmlRFPBA1YP–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
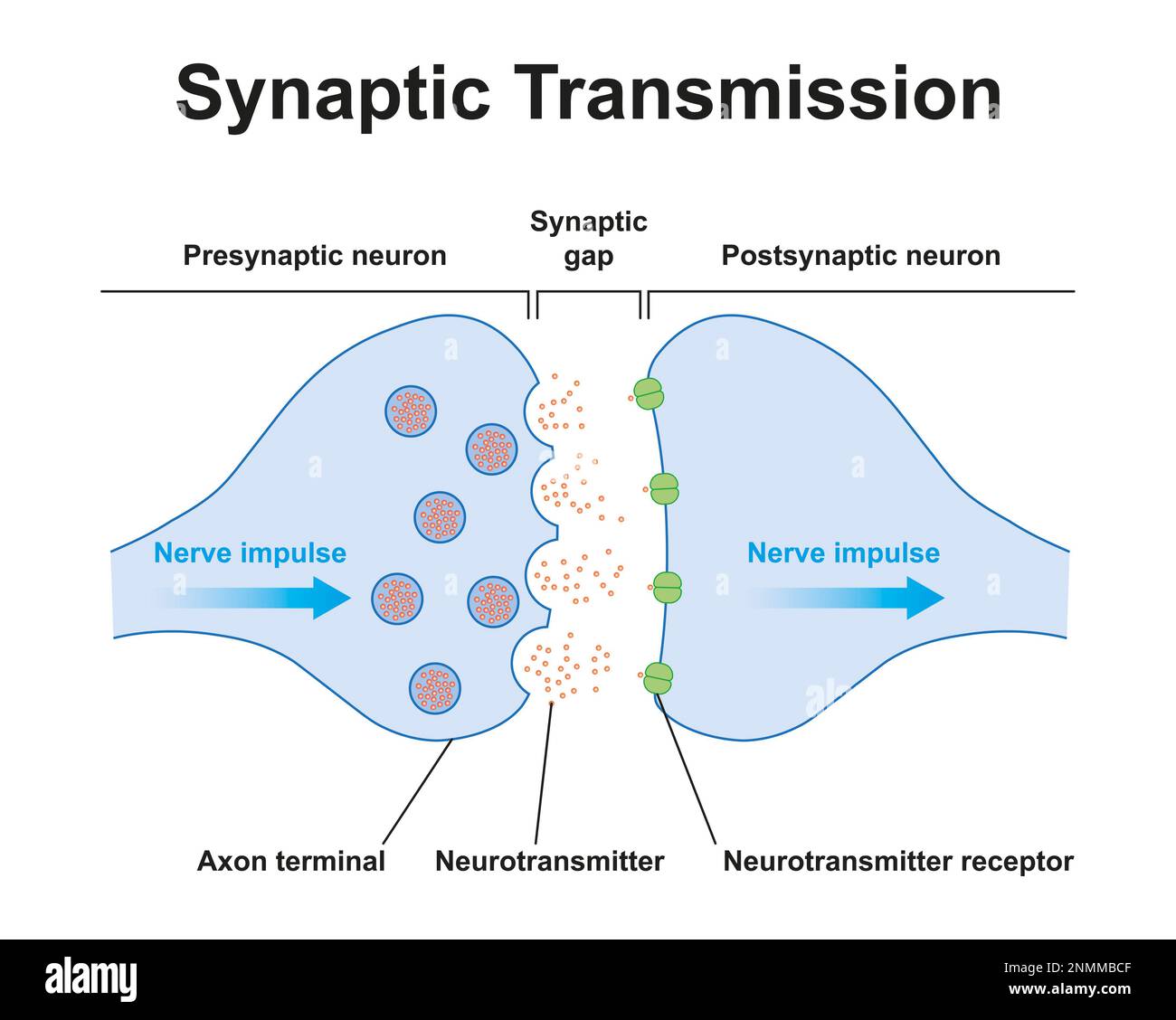 Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052175.html
Synapse structure, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-structure-illustration-image529052175.htmlRF2NMMBCF–Synapse structure, illustration
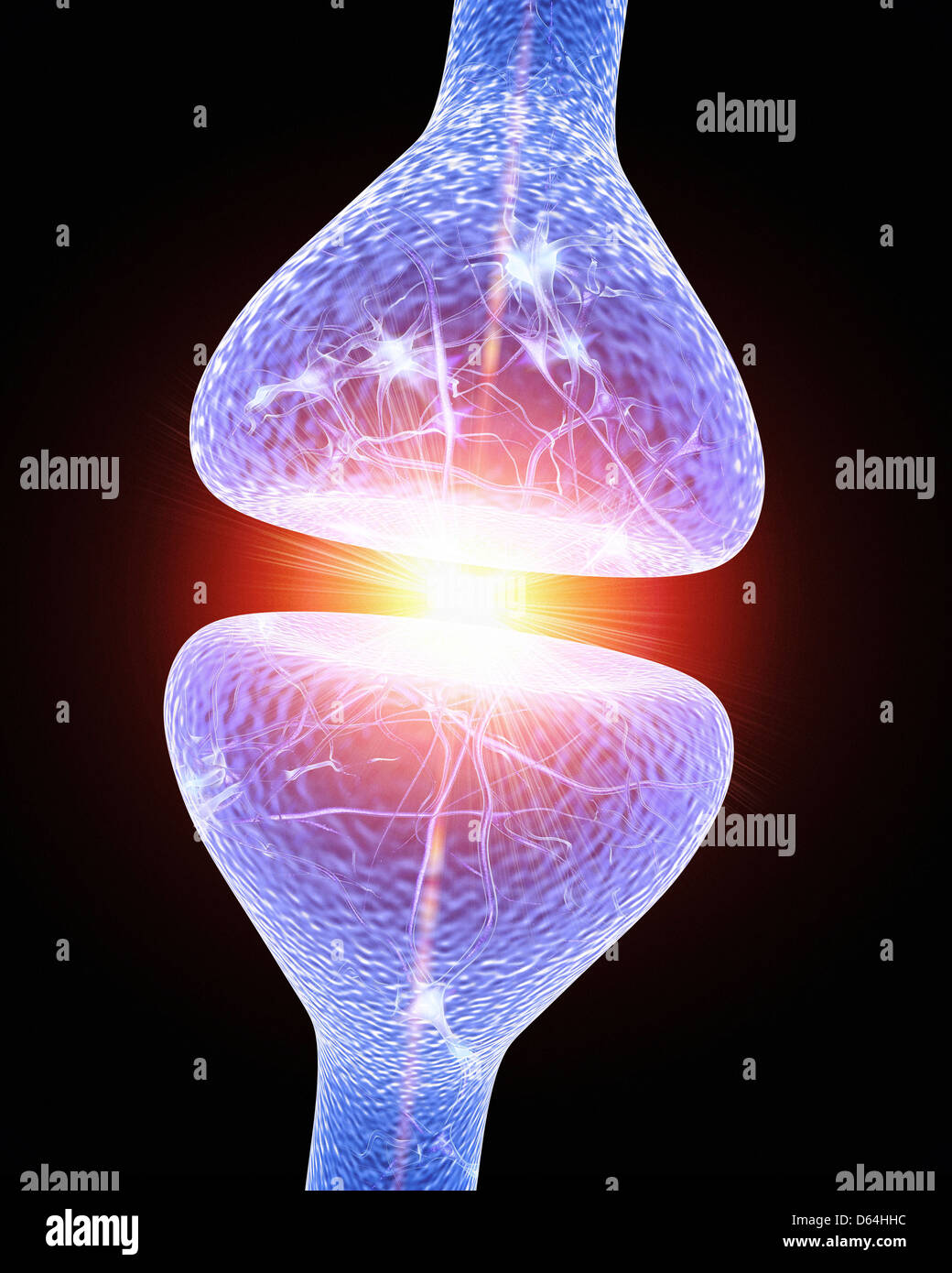 Nerve synapse, artwork Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-artwork-55420664.html
Nerve synapse, artwork Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-artwork-55420664.htmlRFD64HHC–Nerve synapse, artwork
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213505018.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213505018.htmlRFPB9YR6–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
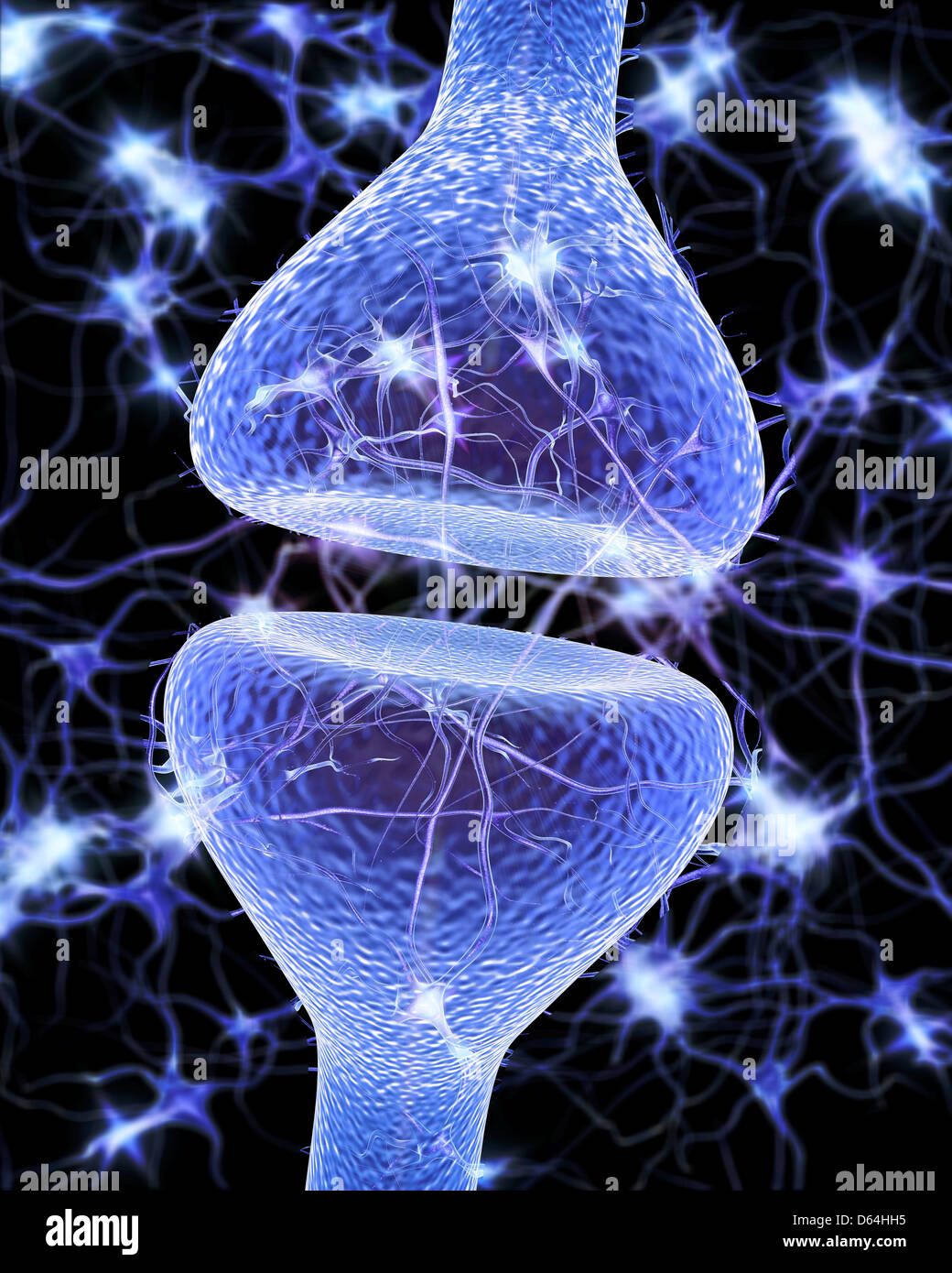 Nerve synapse, artwork Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-artwork-55420657.html
Nerve synapse, artwork Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-artwork-55420657.htmlRFD64HH5–Nerve synapse, artwork
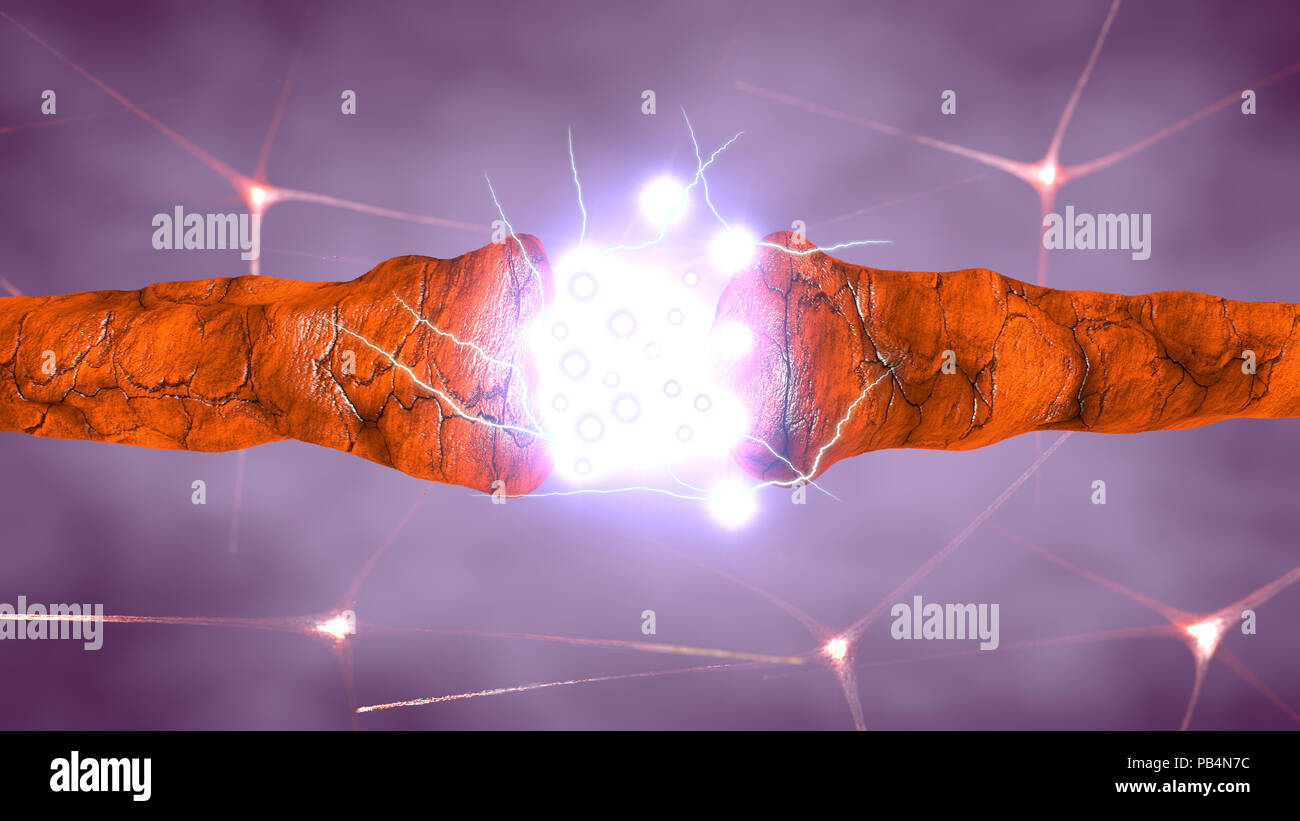 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213390112.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image213390112.htmlRFPB4N7C–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632135.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632135.htmlRF2J9K42F–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
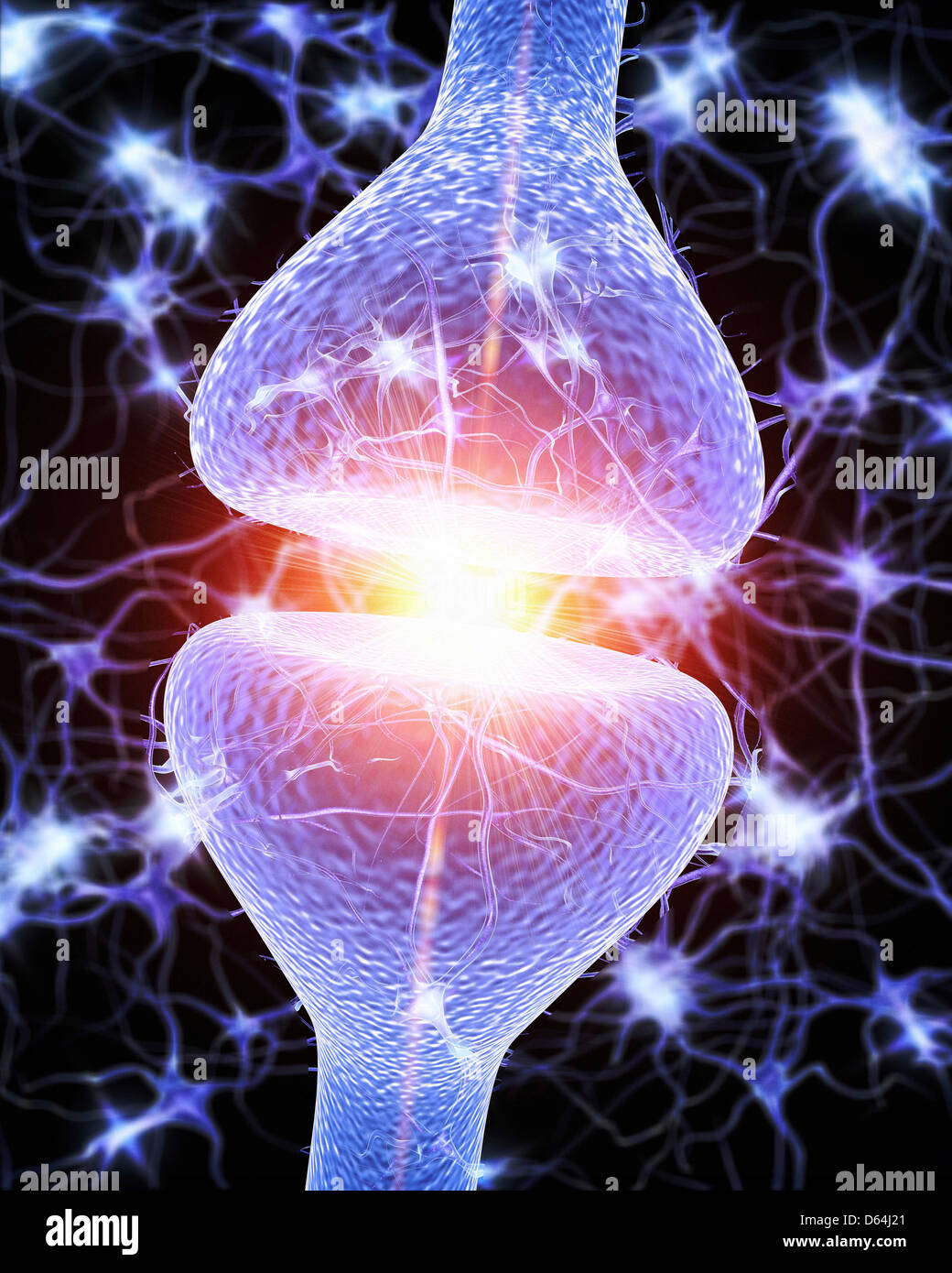 Nerve synapse, artwork Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-artwork-55421017.html
Nerve synapse, artwork Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nerve-synapse-artwork-55421017.htmlRFD64J21–Nerve synapse, artwork
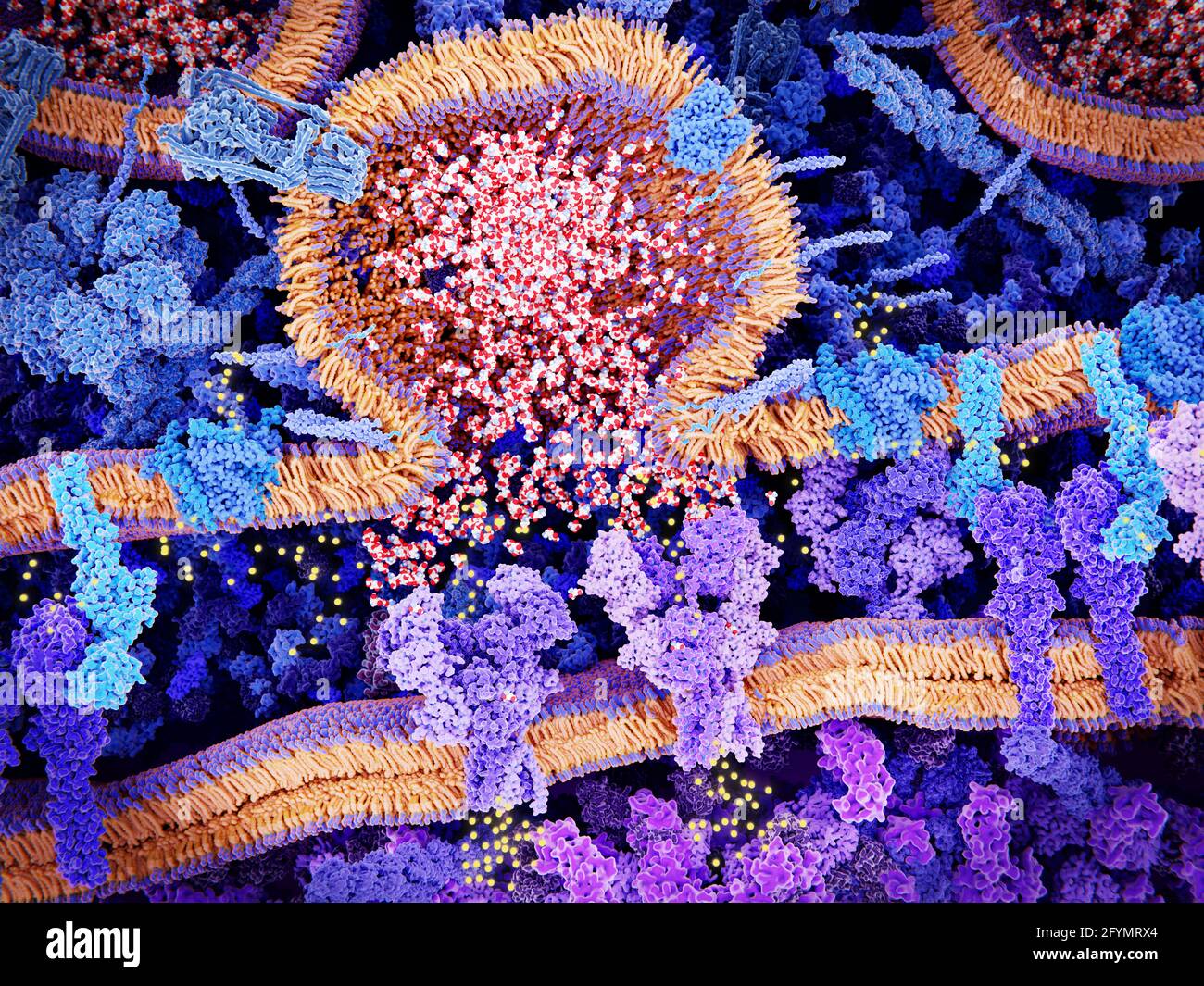 Excitatory synapse, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/excitatory-synapse-illustration-image430102348.html
Excitatory synapse, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/excitatory-synapse-illustration-image430102348.htmlRF2FYMRX4–Excitatory synapse, illustration
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632136.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632136.htmlRF2J9K42G–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
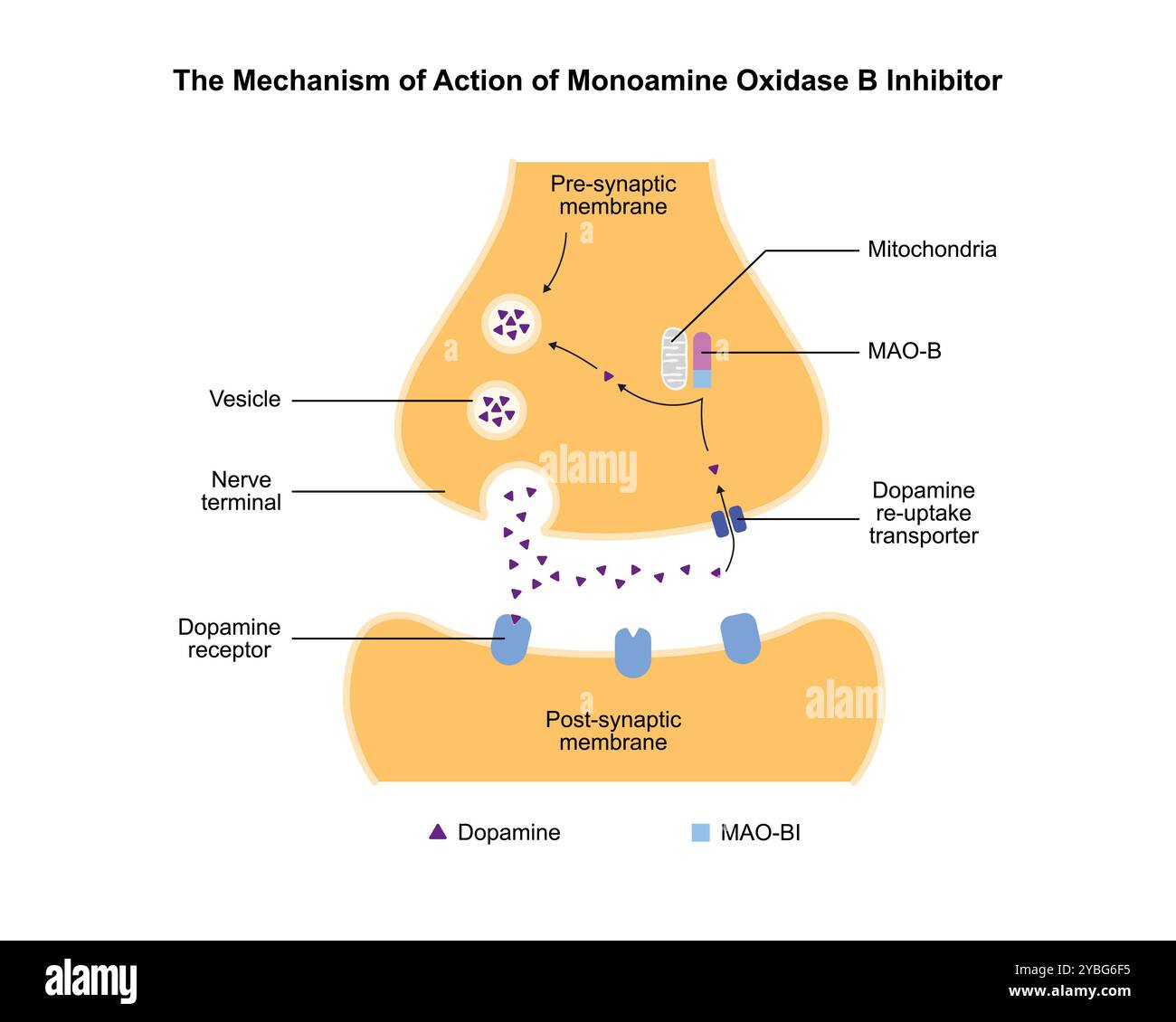 Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor-illustration-image626690825.html
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor-illustration-image626690825.htmlRF2YBG6F5–Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632133.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632133.htmlRF2J9K42D–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
 Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor-illustration-image626690844.html
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor-illustration-image626690844.htmlRF2YBG6FT–Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration.
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632137.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632137.htmlRF2J9K42H–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
 Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor-illustration-image626690786.html
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor-illustration-image626690786.htmlRF2YBG6DP–Monoamine oxidase inhibitor, illustration.
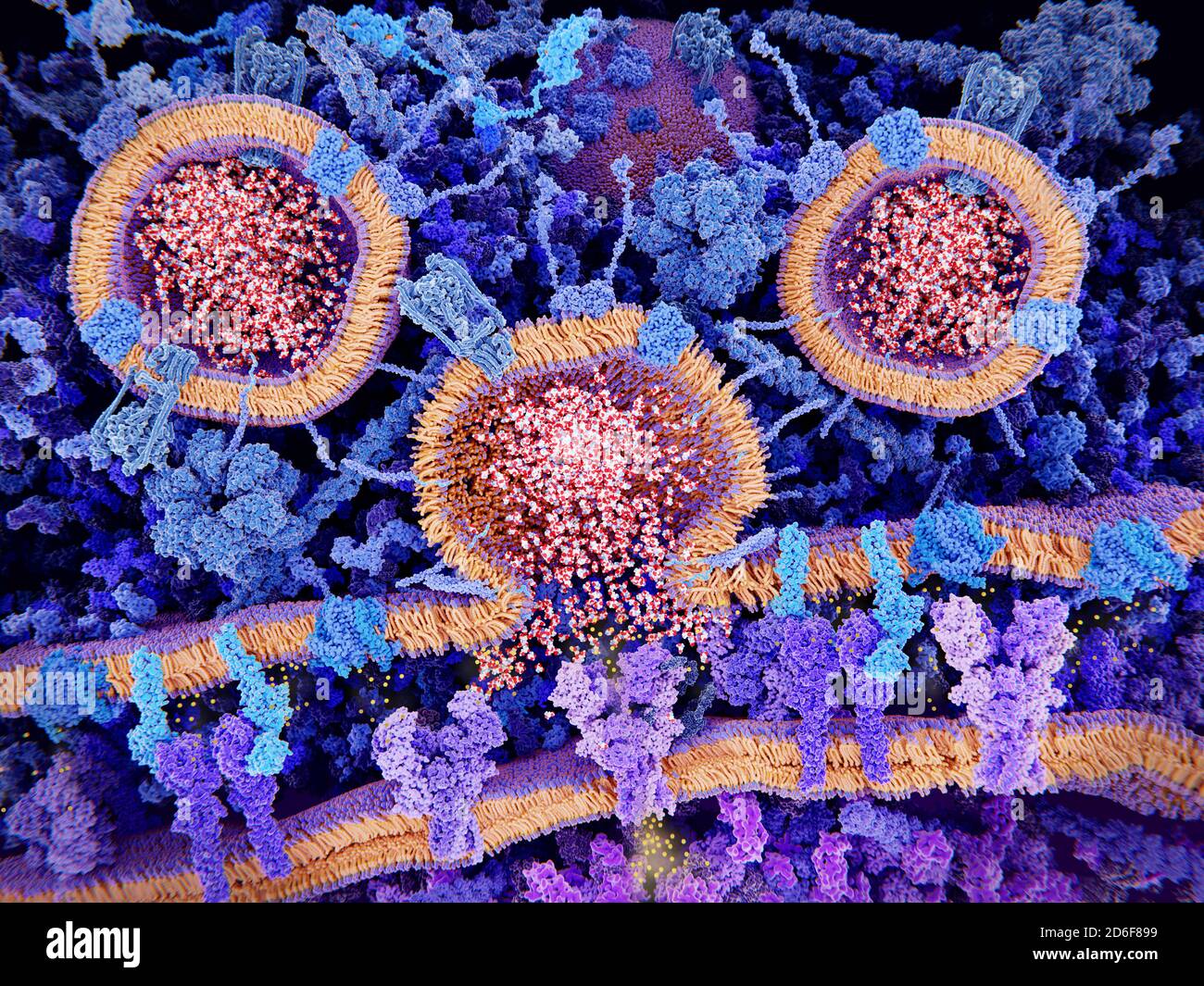 Excitatory synapse, illustration. A synapse is a junction between two neurons (nerve cells). An excitatory synapse increases the likelihood of an acti Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/excitatory-synapse-illustration-a-synapse-is-a-junction-between-two-neurons-nerve-cells-an-excitatory-synapse-increases-the-likelihood-of-an-acti-image382651845.html
Excitatory synapse, illustration. A synapse is a junction between two neurons (nerve cells). An excitatory synapse increases the likelihood of an acti Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/excitatory-synapse-illustration-a-synapse-is-a-junction-between-two-neurons-nerve-cells-an-excitatory-synapse-increases-the-likelihood-of-an-acti-image382651845.htmlRF2D6F899–Excitatory synapse, illustration. A synapse is a junction between two neurons (nerve cells). An excitatory synapse increases the likelihood of an acti
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632141.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632141.htmlRF2J9K42N–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
 Excitatory synapse, illustration. A synapse is a junction between two neurons (nerve cells). An excitatory synapse increases the likelihood of an acti Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/excitatory-synapse-illustration-a-synapse-is-a-junction-between-two-neurons-nerve-cells-an-excitatory-synapse-increases-the-likelihood-of-an-acti-image382651855.html
Excitatory synapse, illustration. A synapse is a junction between two neurons (nerve cells). An excitatory synapse increases the likelihood of an acti Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/excitatory-synapse-illustration-a-synapse-is-a-junction-between-two-neurons-nerve-cells-an-excitatory-synapse-increases-the-likelihood-of-an-acti-image382651855.htmlRF2D6F89K–Excitatory synapse, illustration. A synapse is a junction between two neurons (nerve cells). An excitatory synapse increases the likelihood of an acti
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632140.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632140.htmlRF2J9K42M–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632132.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-neural-network-image470632132.htmlRF2J9K42C–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Neural network
 Planets and exoplanets of unexplored galaxies. Sci-Fi. New worlds to discover. Colonization and exploration of nebulae and galaxies. Planet and rings. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/planets-and-exoplanets-of-unexplored-galaxies-sci-fi-new-worlds-to-discover-colonization-and-exploration-of-nebulae-and-galaxies-planet-and-rings-image471155333.html
Planets and exoplanets of unexplored galaxies. Sci-Fi. New worlds to discover. Colonization and exploration of nebulae and galaxies. Planet and rings. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/planets-and-exoplanets-of-unexplored-galaxies-sci-fi-new-worlds-to-discover-colonization-and-exploration-of-nebulae-and-galaxies-planet-and-rings-image471155333.htmlRF2JAEYC5–Planets and exoplanets of unexplored galaxies. Sci-Fi. New worlds to discover. Colonization and exploration of nebulae and galaxies. Planet and rings.
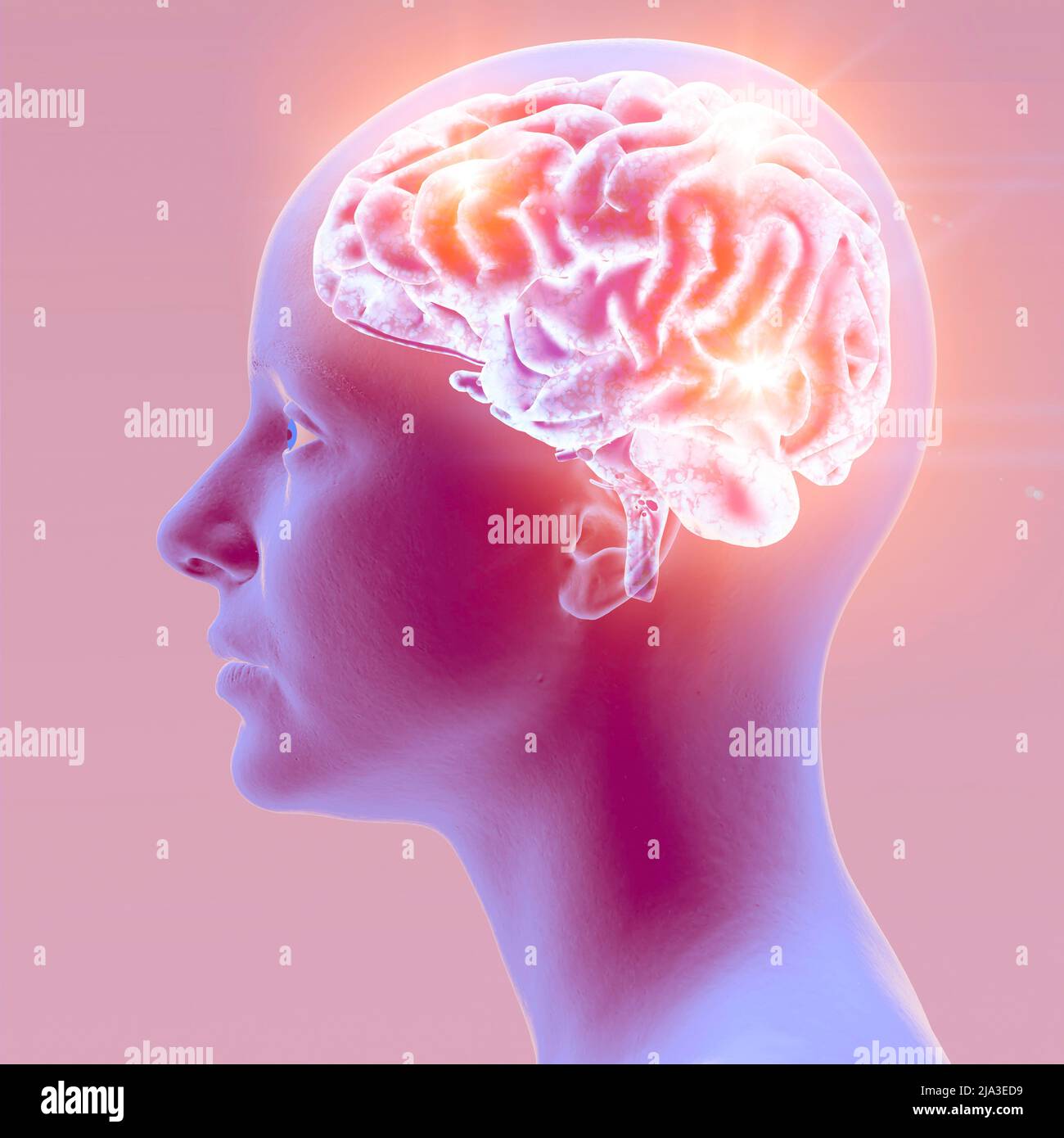 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470903701.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470903701.htmlRF2JA3ED9–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470906665.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470906665.htmlRF2JA3J75–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view
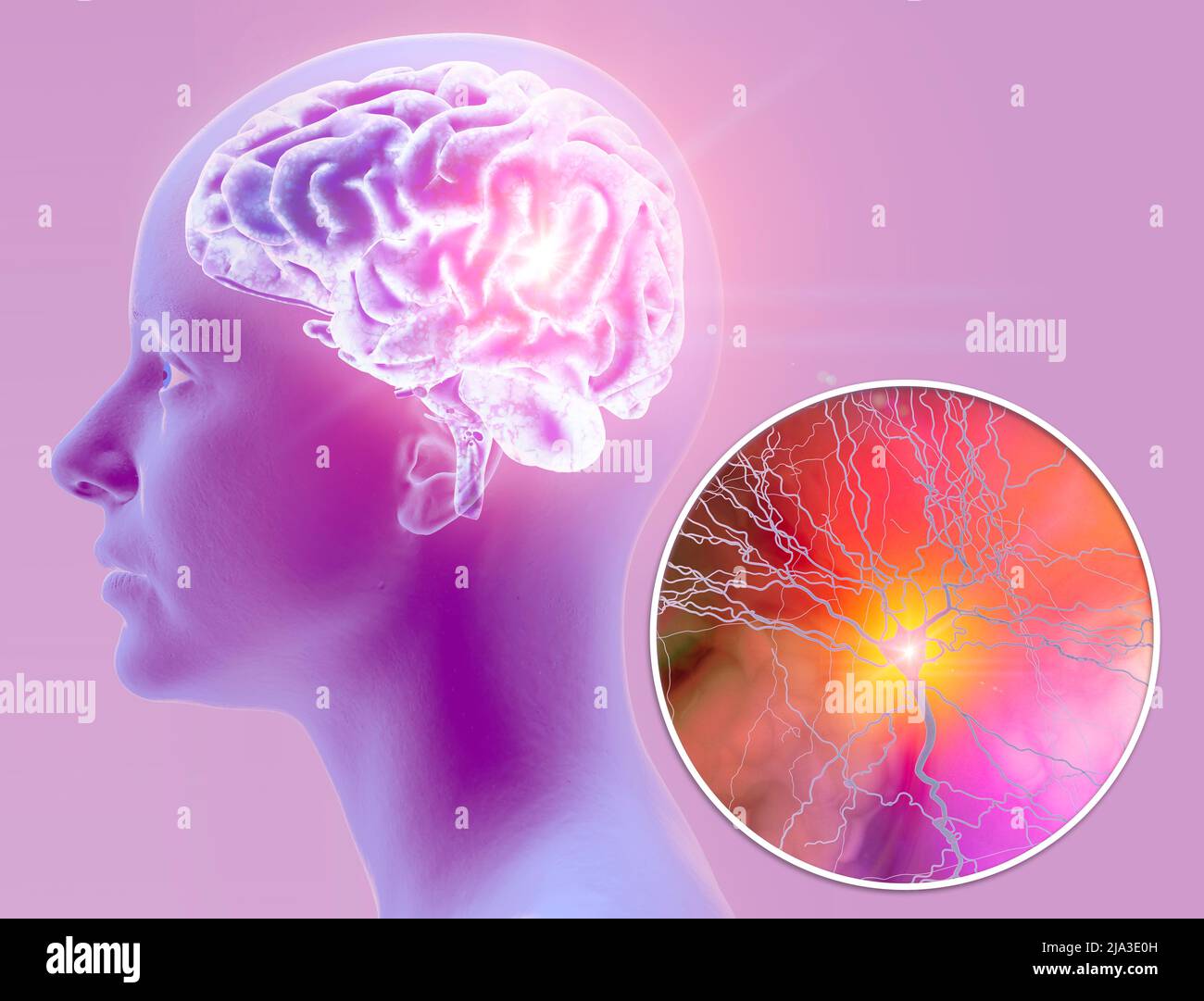 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470903345.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470903345.htmlRF2JA3E0H–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470855094.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-brain-face-side-view-image470855094.htmlRF2JA18DA–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Brain. Face side view
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185210225.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185210225.htmlRFMN91EW–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185211515.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185211515.htmlRFMN934Y–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
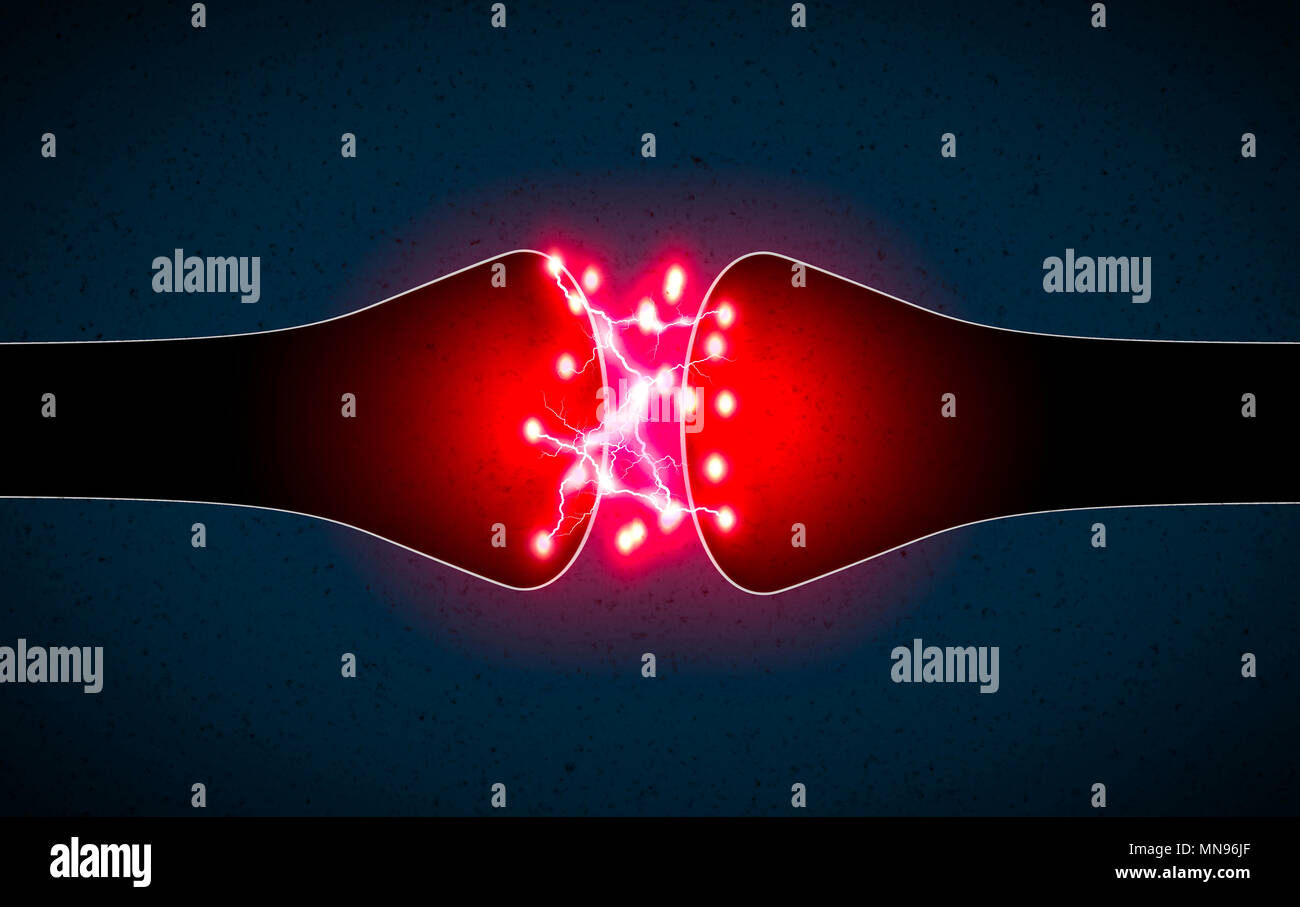 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185214247.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185214247.htmlRFMN96JF–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185214248.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185214248.htmlRFMN96JG–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185215763.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185215763.htmlRFMN98GK–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185259516.html
Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-is-a-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-or-to-the-target-efferent-cell-image185259516.htmlRFMNB8B8–Synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788044.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image470788044.htmlRF2J9X6XM–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 How the brain works. Synapses and neurons. Connections. Take care of your brain, stimuli and ideas. Degenerative diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/how-the-brain-works-synapses-and-neurons-connections-take-care-of-your-brain-stimuli-and-ideas-degenerative-diseases-parkinsons-and-alzheimers-image470471291.html
How the brain works. Synapses and neurons. Connections. Take care of your brain, stimuli and ideas. Degenerative diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/how-the-brain-works-synapses-and-neurons-connections-take-care-of-your-brain-stimuli-and-ideas-degenerative-diseases-parkinsons-and-alzheimers-image470471291.htmlRF2J9BPX3–How the brain works. Synapses and neurons. Connections. Take care of your brain, stimuli and ideas. Degenerative diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-image361616747.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-image361616747.htmlRF2C091RR–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image354131911.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image354131911.htmlRF2BG42T7–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain
 Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image354215944.html
Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/synapse-connections-structure-that-permits-a-neuron-or-nerve-cell-to-pass-an-electrical-or-chemical-signal-to-another-neuron-nervous-system-brain-image354215944.htmlRF2BG7X1C–Synapse connections. Structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Nervous system. Brain