Telophase in mitosis Black & White Stock Photos
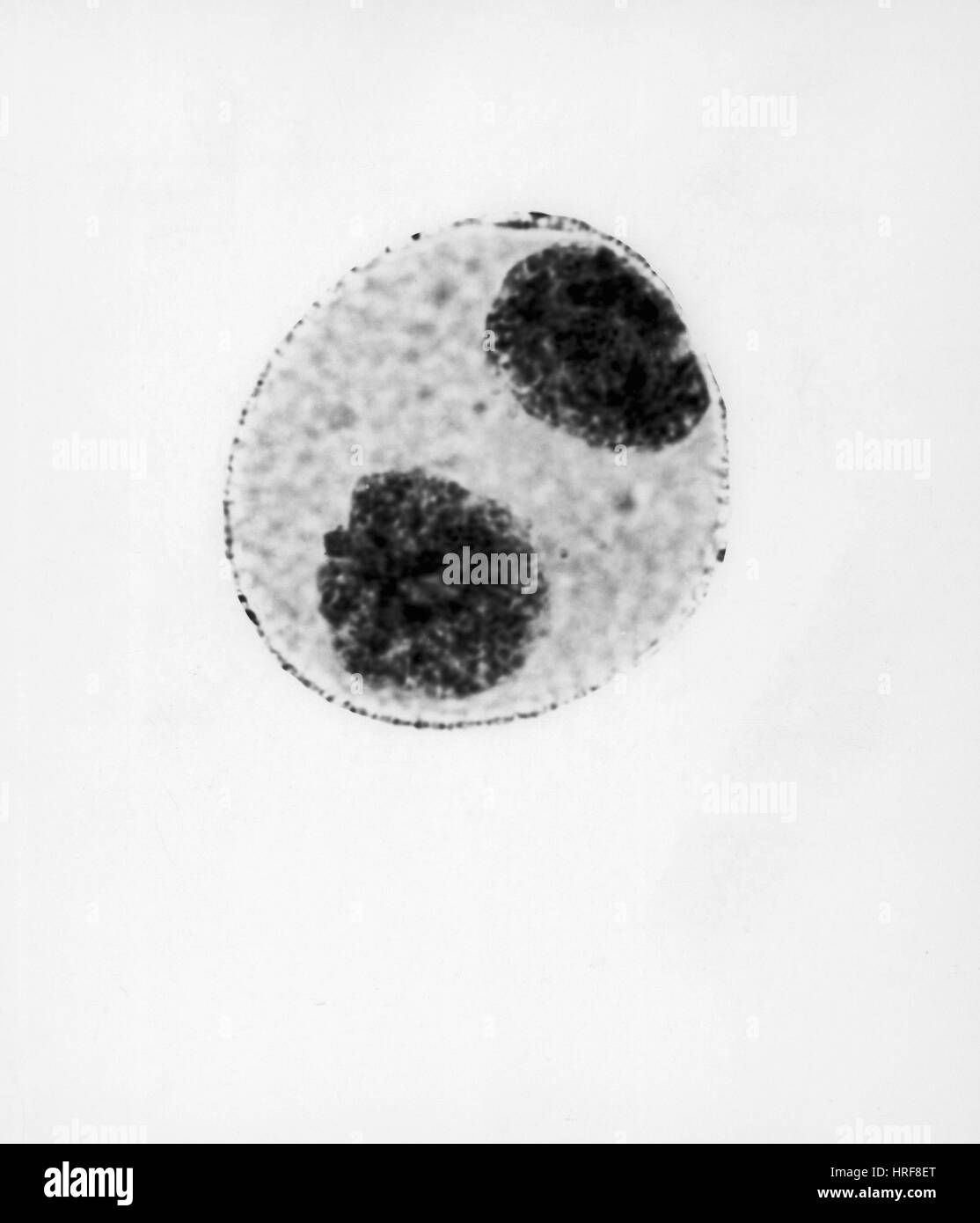 Telophase of Mitosis in Trillium Cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-telophase-of-mitosis-in-trillium-cell-134945632.html
Telophase of Mitosis in Trillium Cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-telophase-of-mitosis-in-trillium-cell-134945632.htmlRMHRF8ET–Telophase of Mitosis in Trillium Cell
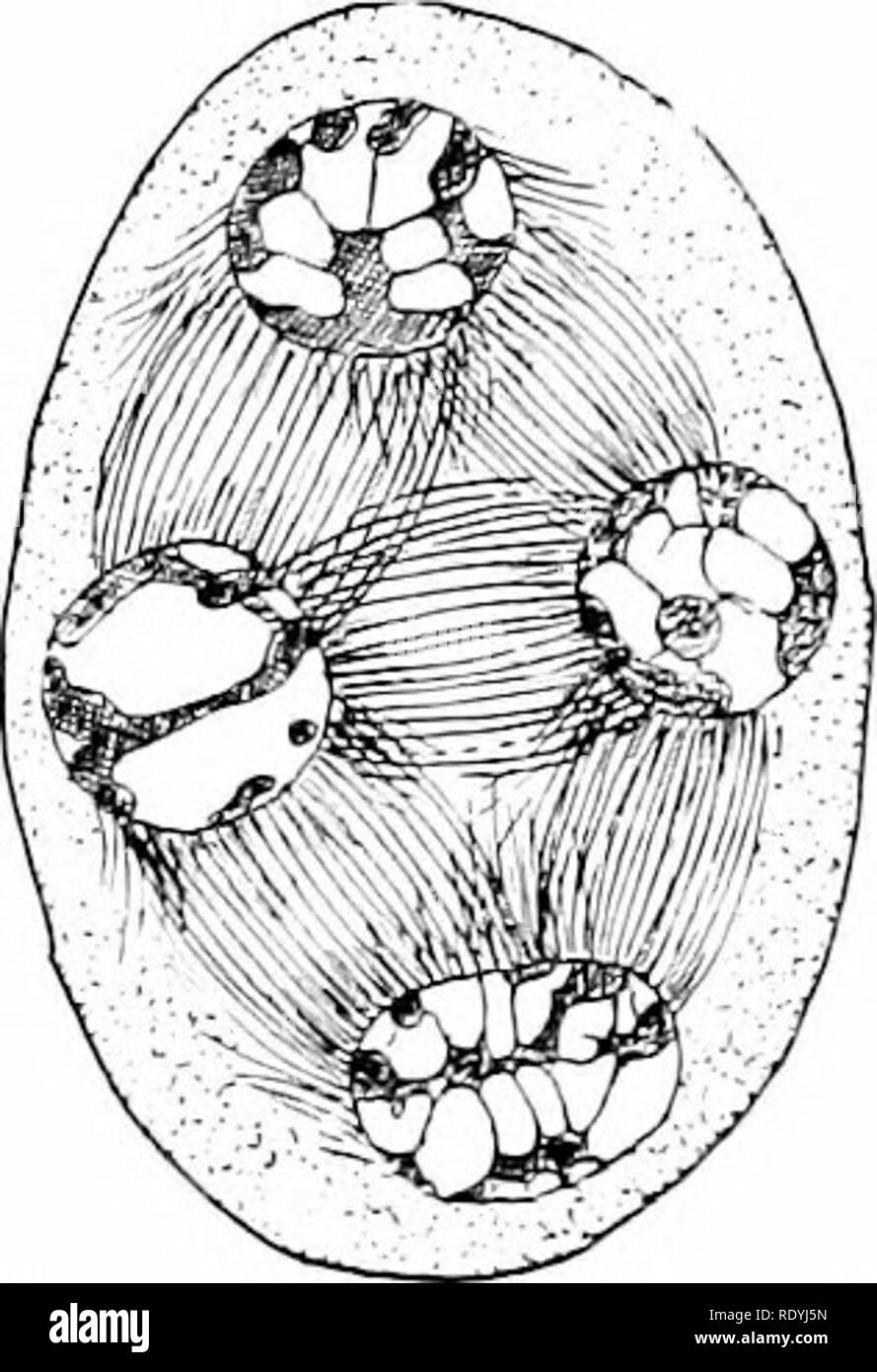 . Morphology of angiosperms (Morphology of spermatophytes. Part II). Angiosperms; Plant morphology. C Fm. 55.—Podophyllumpeltatum. Mitosis in pollen mother-cell. A, telophase of first division; £, late anaphase of second division; C, telophase of second division; the nuclei of the four microspores are formed, but the cell walls, as is characteristic of simultaneous division, have not yet appeared.—After Mottieb.2" besides, the enlargement and consequent readjustment of the spores soon break up the row (Fig. 58). The first record of the occurrence of a tetrad in Asclepias seems to have bee Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-angiosperms-morphology-of-spermatophytes-part-ii-angiosperms-plant-morphology-c-fm-55podophyllumpeltatum-mitosis-in-pollen-mother-cell-a-telophase-of-first-division-late-anaphase-of-second-division-c-telophase-of-second-division-the-nuclei-of-the-four-microspores-are-formed-but-the-cell-walls-as-is-characteristic-of-simultaneous-division-have-not-yet-appearedafter-mottieb2quot-besides-the-enlargement-and-consequent-readjustment-of-the-spores-soon-break-up-the-row-fig-58-the-first-record-of-the-occurrence-of-a-tetrad-in-asclepias-seems-to-have-bee-image232332289.html
. Morphology of angiosperms (Morphology of spermatophytes. Part II). Angiosperms; Plant morphology. C Fm. 55.—Podophyllumpeltatum. Mitosis in pollen mother-cell. A, telophase of first division; £, late anaphase of second division; C, telophase of second division; the nuclei of the four microspores are formed, but the cell walls, as is characteristic of simultaneous division, have not yet appeared.—After Mottieb.2" besides, the enlargement and consequent readjustment of the spores soon break up the row (Fig. 58). The first record of the occurrence of a tetrad in Asclepias seems to have bee Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-angiosperms-morphology-of-spermatophytes-part-ii-angiosperms-plant-morphology-c-fm-55podophyllumpeltatum-mitosis-in-pollen-mother-cell-a-telophase-of-first-division-late-anaphase-of-second-division-c-telophase-of-second-division-the-nuclei-of-the-four-microspores-are-formed-but-the-cell-walls-as-is-characteristic-of-simultaneous-division-have-not-yet-appearedafter-mottieb2quot-besides-the-enlargement-and-consequent-readjustment-of-the-spores-soon-break-up-the-row-fig-58-the-first-record-of-the-occurrence-of-a-tetrad-in-asclepias-seems-to-have-bee-image232332289.htmlRMRDYJ5N–. Morphology of angiosperms (Morphology of spermatophytes. Part II). Angiosperms; Plant morphology. C Fm. 55.—Podophyllumpeltatum. Mitosis in pollen mother-cell. A, telophase of first division; £, late anaphase of second division; C, telophase of second division; the nuclei of the four microspores are formed, but the cell walls, as is characteristic of simultaneous division, have not yet appeared.—After Mottieb.2" besides, the enlargement and consequent readjustment of the spores soon break up the row (Fig. 58). The first record of the occurrence of a tetrad in Asclepias seems to have bee
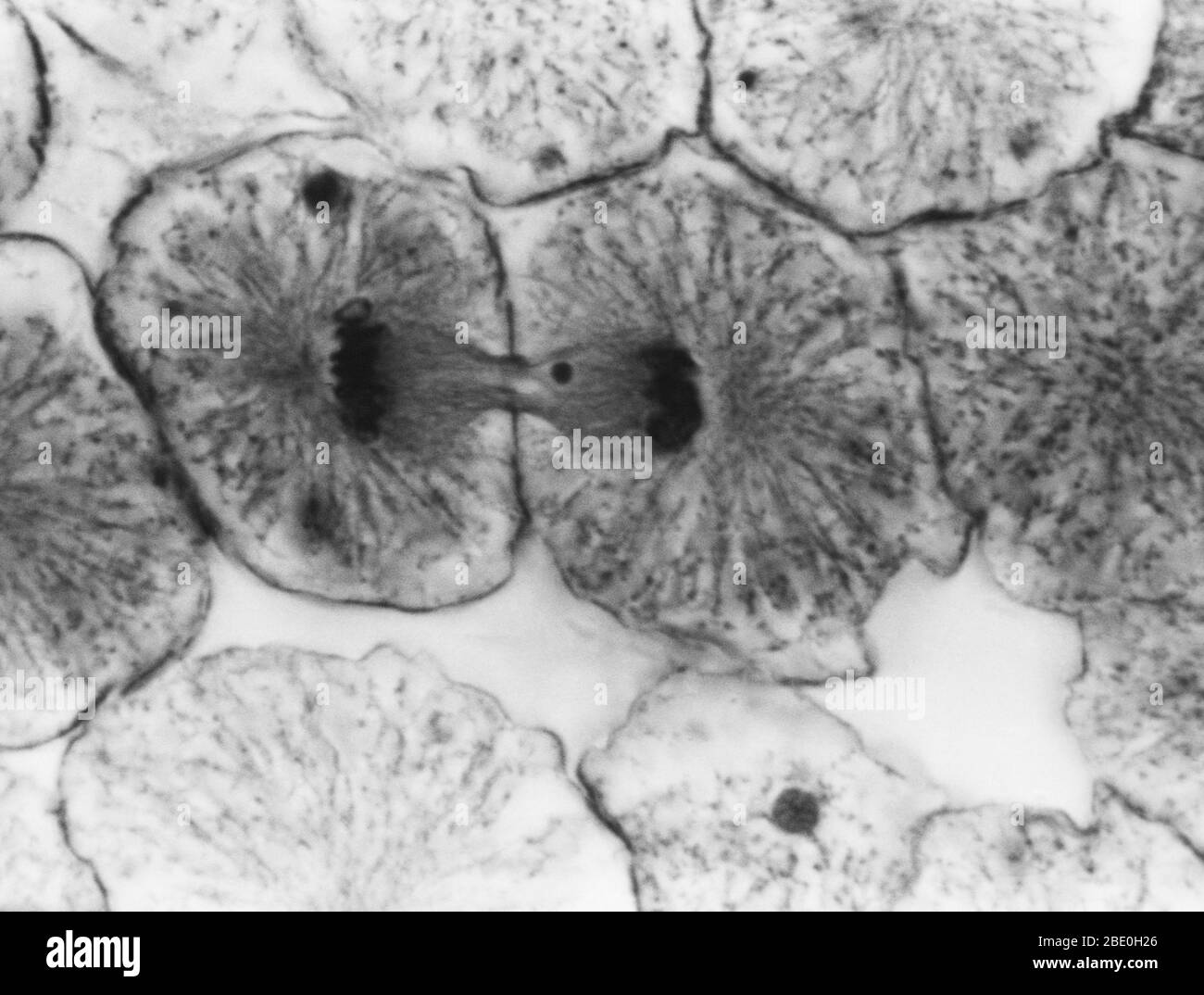 Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, telophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized e Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-telophase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-e-image352825934.html
Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, telophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized e Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-telophase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-e-image352825934.htmlRM2BE0H26–Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, telophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized e
 . Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. Figs. 350-352.—Pinus Laricio: three stages in the formation of the proembryo; fig. 350, four nuclei (two shown) at base of fertilized egg, showing the fibers which had been mistaken for a wall; X225; fig. 351, division of the nuclei shown in previous figure, indicating that no wall is formed at the four-nucleate stage; X355; fig. 352, late telophase of the mitosis the anaphase of which is shown in the previous figure; the transverse walls are nearly complete and the vertical walls, formed on the radiating fibers which are already beco Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-figs-350-352pinus-laricio-three-stages-in-the-formation-of-the-proembryo-fig-350-four-nuclei-two-shown-at-base-of-fertilized-egg-showing-the-fibers-which-had-been-mistaken-for-a-wall-x225-fig-351-division-of-the-nuclei-shown-in-previous-figure-indicating-that-no-wall-is-formed-at-the-four-nucleate-stage-x355-fig-352-late-telophase-of-the-mitosis-the-anaphase-of-which-is-shown-in-the-previous-figure-the-transverse-walls-are-nearly-complete-and-the-vertical-walls-formed-on-the-radiating-fibers-which-are-already-beco-image216417539.html
. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. Figs. 350-352.—Pinus Laricio: three stages in the formation of the proembryo; fig. 350, four nuclei (two shown) at base of fertilized egg, showing the fibers which had been mistaken for a wall; X225; fig. 351, division of the nuclei shown in previous figure, indicating that no wall is formed at the four-nucleate stage; X355; fig. 352, late telophase of the mitosis the anaphase of which is shown in the previous figure; the transverse walls are nearly complete and the vertical walls, formed on the radiating fibers which are already beco Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-figs-350-352pinus-laricio-three-stages-in-the-formation-of-the-proembryo-fig-350-four-nuclei-two-shown-at-base-of-fertilized-egg-showing-the-fibers-which-had-been-mistaken-for-a-wall-x225-fig-351-division-of-the-nuclei-shown-in-previous-figure-indicating-that-no-wall-is-formed-at-the-four-nucleate-stage-x355-fig-352-late-telophase-of-the-mitosis-the-anaphase-of-which-is-shown-in-the-previous-figure-the-transverse-walls-are-nearly-complete-and-the-vertical-walls-formed-on-the-radiating-fibers-which-are-already-beco-image216417539.htmlRMPG2JNR–. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. Figs. 350-352.—Pinus Laricio: three stages in the formation of the proembryo; fig. 350, four nuclei (two shown) at base of fertilized egg, showing the fibers which had been mistaken for a wall; X225; fig. 351, division of the nuclei shown in previous figure, indicating that no wall is formed at the four-nucleate stage; X355; fig. 352, late telophase of the mitosis the anaphase of which is shown in the previous figure; the transverse walls are nearly complete and the vertical walls, formed on the radiating fibers which are already beco
 . Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. Figs. 350-352.—Pinus Laricio: three stages in the formation of the proembryo; fig. 350, four nuclei (two shown) at base of fertilized egg, showing the fibers which had been mistaken for a wall; X225; fig. 351, division of the nuclei shown in previous figure, indicating that no wall is formed at the four-nucleate stage; X355; fig. 352, late telophase of the mitosis the anaphase of which is shown in the previous figure; the transverse walls are nearly complete and the vertical walls, formed on the radiating fibers which are already beco Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-figs-350-352pinus-laricio-three-stages-in-the-formation-of-the-proembryo-fig-350-four-nuclei-two-shown-at-base-of-fertilized-egg-showing-the-fibers-which-had-been-mistaken-for-a-wall-x225-fig-351-division-of-the-nuclei-shown-in-previous-figure-indicating-that-no-wall-is-formed-at-the-four-nucleate-stage-x355-fig-352-late-telophase-of-the-mitosis-the-anaphase-of-which-is-shown-in-the-previous-figure-the-transverse-walls-are-nearly-complete-and-the-vertical-walls-formed-on-the-radiating-fibers-which-are-already-beco-image232103345.html
. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. Figs. 350-352.—Pinus Laricio: three stages in the formation of the proembryo; fig. 350, four nuclei (two shown) at base of fertilized egg, showing the fibers which had been mistaken for a wall; X225; fig. 351, division of the nuclei shown in previous figure, indicating that no wall is formed at the four-nucleate stage; X355; fig. 352, late telophase of the mitosis the anaphase of which is shown in the previous figure; the transverse walls are nearly complete and the vertical walls, formed on the radiating fibers which are already beco Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-figs-350-352pinus-laricio-three-stages-in-the-formation-of-the-proembryo-fig-350-four-nuclei-two-shown-at-base-of-fertilized-egg-showing-the-fibers-which-had-been-mistaken-for-a-wall-x225-fig-351-division-of-the-nuclei-shown-in-previous-figure-indicating-that-no-wall-is-formed-at-the-four-nucleate-stage-x355-fig-352-late-telophase-of-the-mitosis-the-anaphase-of-which-is-shown-in-the-previous-figure-the-transverse-walls-are-nearly-complete-and-the-vertical-walls-formed-on-the-radiating-fibers-which-are-already-beco-image232103345.htmlRMRDH655–. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. Figs. 350-352.—Pinus Laricio: three stages in the formation of the proembryo; fig. 350, four nuclei (two shown) at base of fertilized egg, showing the fibers which had been mistaken for a wall; X225; fig. 351, division of the nuclei shown in previous figure, indicating that no wall is formed at the four-nucleate stage; X355; fig. 352, late telophase of the mitosis the anaphase of which is shown in the previous figure; the transverse walls are nearly complete and the vertical walls, formed on the radiating fibers which are already beco
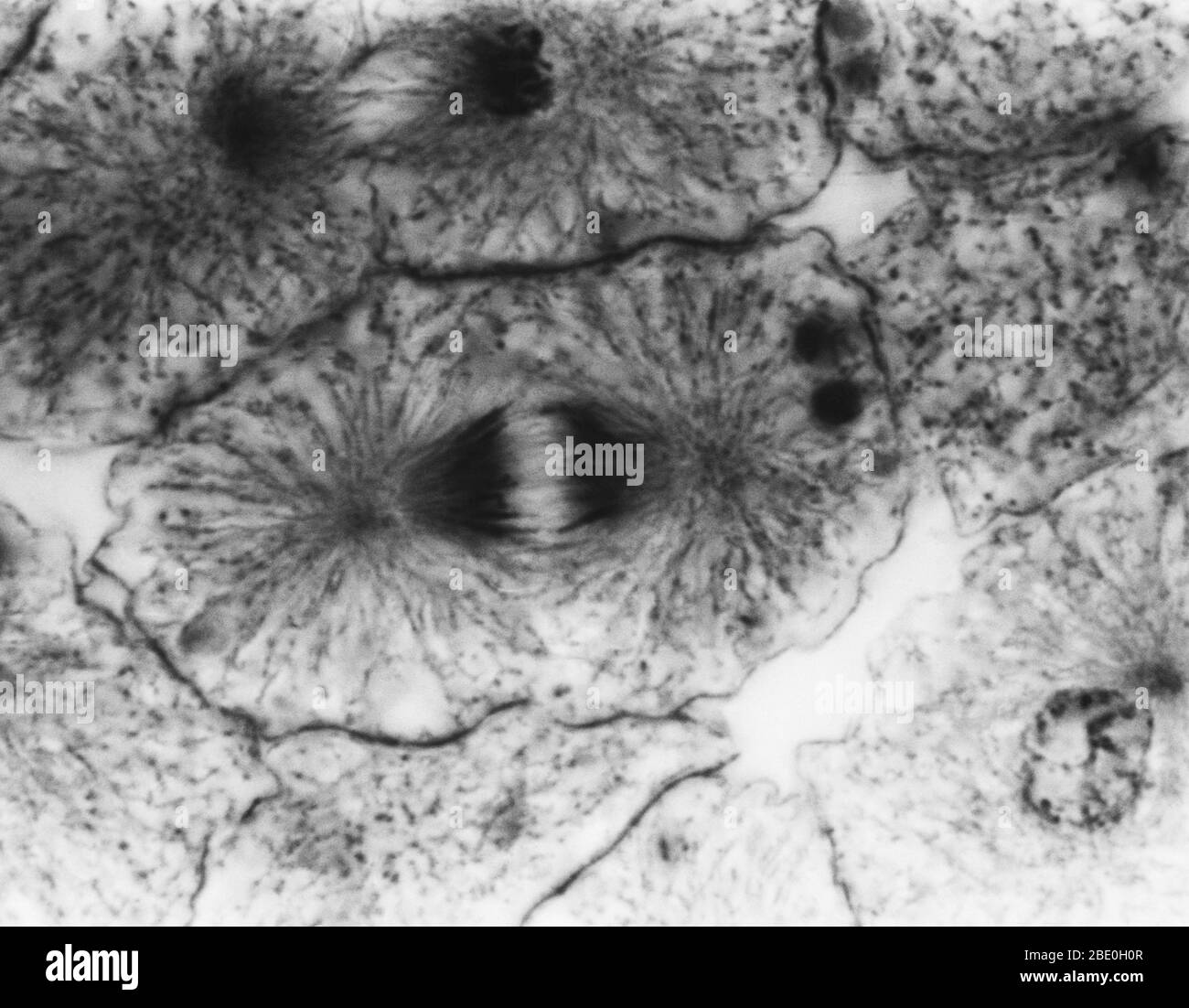 Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, early telophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertili Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-early-telophase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertili-image352825895.html
Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, early telophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertili Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-early-telophase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertili-image352825895.htmlRM2BE0H0R–Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, early telophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertili
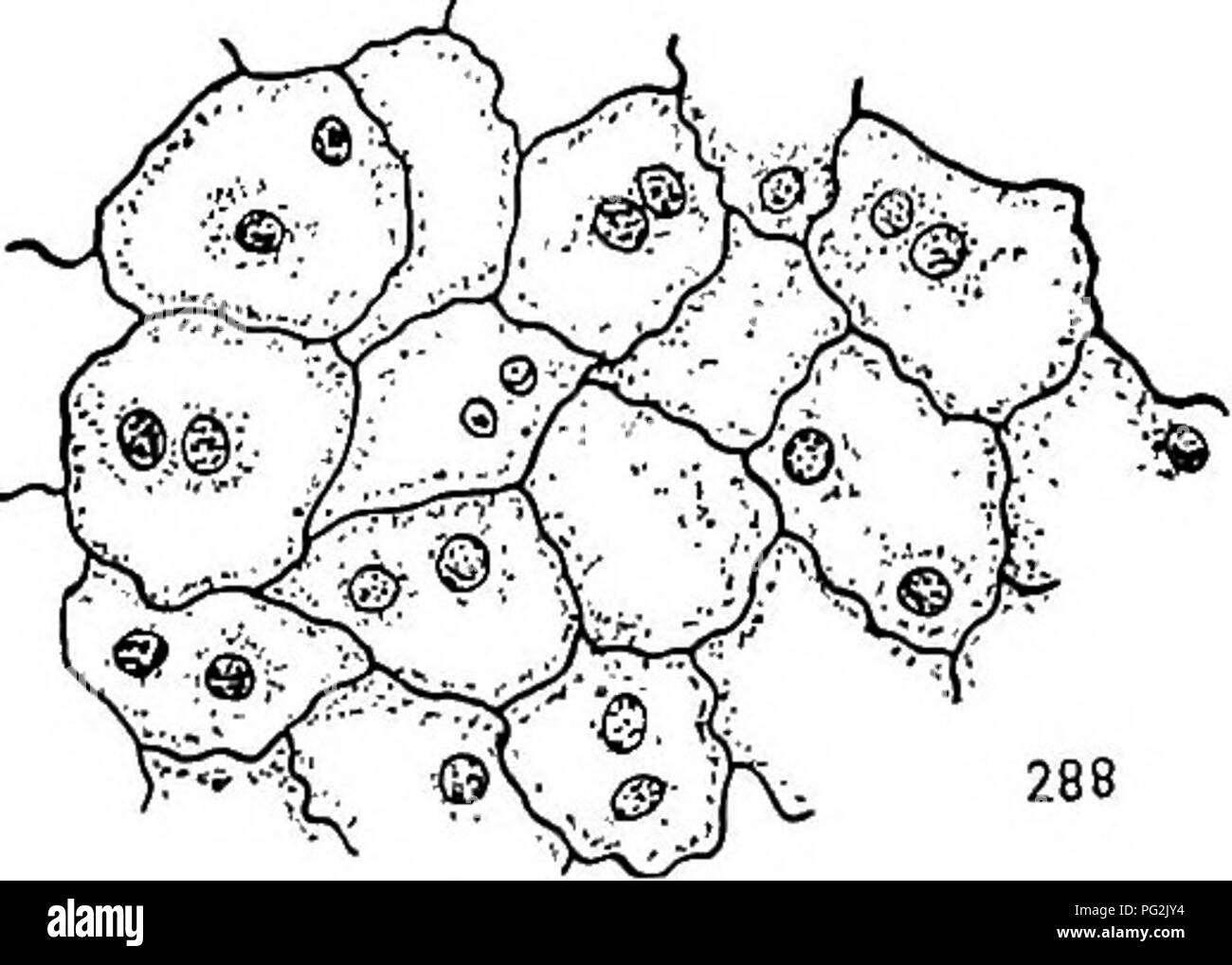 . Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. 286 287. Figs. 285-288.—Cryptomeria japonica: development of the endosperm; fig. 285, longitudinal section of upper portion of endosperm showing multinucleate condition and also that the walls are incomplete; May 26, 1902; X23S; fig. 286, telophase of the mitosis which is to result in the formation of a binucleate cell like those shown in fig. 288; May 29, 1903; XijOoo; fig. 287, a later stage in the same mitosis, the two daughter nuclei completely inclosed by the kinoplasmic fibrils; X 1,000; fig. 288, portion of the endosperm soon a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-286-287-figs-285-288cryptomeria-japonica-development-of-the-endosperm-fig-285-longitudinal-section-of-upper-portion-of-endosperm-showing-multinucleate-condition-and-also-that-the-walls-are-incomplete-may-26-1902-x23s-fig-286-telophase-of-the-mitosis-which-is-to-result-in-the-formation-of-a-binucleate-cell-like-those-shown-in-fig-288-may-29-1903-xijooo-fig-287-a-later-stage-in-the-same-mitosis-the-two-daughter-nuclei-completely-inclosed-by-the-kinoplasmic-fibrils-x-1000-fig-288-portion-of-the-endosperm-soon-a-image216417688.html
. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. 286 287. Figs. 285-288.—Cryptomeria japonica: development of the endosperm; fig. 285, longitudinal section of upper portion of endosperm showing multinucleate condition and also that the walls are incomplete; May 26, 1902; X23S; fig. 286, telophase of the mitosis which is to result in the formation of a binucleate cell like those shown in fig. 288; May 29, 1903; XijOoo; fig. 287, a later stage in the same mitosis, the two daughter nuclei completely inclosed by the kinoplasmic fibrils; X 1,000; fig. 288, portion of the endosperm soon a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-286-287-figs-285-288cryptomeria-japonica-development-of-the-endosperm-fig-285-longitudinal-section-of-upper-portion-of-endosperm-showing-multinucleate-condition-and-also-that-the-walls-are-incomplete-may-26-1902-x23s-fig-286-telophase-of-the-mitosis-which-is-to-result-in-the-formation-of-a-binucleate-cell-like-those-shown-in-fig-288-may-29-1903-xijooo-fig-287-a-later-stage-in-the-same-mitosis-the-two-daughter-nuclei-completely-inclosed-by-the-kinoplasmic-fibrils-x-1000-fig-288-portion-of-the-endosperm-soon-a-image216417688.htmlRMPG2JY4–. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. 286 287. Figs. 285-288.—Cryptomeria japonica: development of the endosperm; fig. 285, longitudinal section of upper portion of endosperm showing multinucleate condition and also that the walls are incomplete; May 26, 1902; X23S; fig. 286, telophase of the mitosis which is to result in the formation of a binucleate cell like those shown in fig. 288; May 29, 1903; XijOoo; fig. 287, a later stage in the same mitosis, the two daughter nuclei completely inclosed by the kinoplasmic fibrils; X 1,000; fig. 288, portion of the endosperm soon a
![. Studies on the plant cell. pt.1-8. Plant cells and tissues. Nos. 4SI-45Z-] STUDIES ON THE PLANT CELL. 579- which lie at a considerable distance from the structure (Fig. xob). The latter cannot then be said to occupy the position of centro- somes in relation to this spindle. Meanwhile important changes, which are best known for Zamia, take place in the blepharoplast. In this type the structure forms a hollow sphere which breaks up into segments and finally into granules as mitosis proceeds.. The radiations disappear without holding any apparent relation to the spindle. During telophase each o Stock Photo . Studies on the plant cell. pt.1-8. Plant cells and tissues. Nos. 4SI-45Z-] STUDIES ON THE PLANT CELL. 579- which lie at a considerable distance from the structure (Fig. xob). The latter cannot then be said to occupy the position of centro- somes in relation to this spindle. Meanwhile important changes, which are best known for Zamia, take place in the blepharoplast. In this type the structure forms a hollow sphere which breaks up into segments and finally into granules as mitosis proceeds.. The radiations disappear without holding any apparent relation to the spindle. During telophase each o Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/RE0KB5/studies-on-the-plant-cell-pt1-8-plant-cells-and-tissues-nos-4si-45z-studies-on-the-plant-cell-579-which-lie-at-a-considerable-distance-from-the-structure-fig-xob-the-latter-cannot-then-be-said-to-occupy-the-position-of-centro-somes-in-relation-to-this-spindle-meanwhile-important-changes-which-are-best-known-for-zamia-take-place-in-the-blepharoplast-in-this-type-the-structure-forms-a-hollow-sphere-which-breaks-up-into-segments-and-finally-into-granules-as-mitosis-proceeds-the-radiations-disappear-without-holding-any-apparent-relation-to-the-spindle-during-telophase-each-o-RE0KB5.jpg) . Studies on the plant cell. pt.1-8. Plant cells and tissues. Nos. 4SI-45Z-] STUDIES ON THE PLANT CELL. 579- which lie at a considerable distance from the structure (Fig. xob). The latter cannot then be said to occupy the position of centro- somes in relation to this spindle. Meanwhile important changes, which are best known for Zamia, take place in the blepharoplast. In this type the structure forms a hollow sphere which breaks up into segments and finally into granules as mitosis proceeds.. The radiations disappear without holding any apparent relation to the spindle. During telophase each o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/studies-on-the-plant-cell-pt1-8-plant-cells-and-tissues-nos-4si-45z-studies-on-the-plant-cell-579-which-lie-at-a-considerable-distance-from-the-structure-fig-xob-the-latter-cannot-then-be-said-to-occupy-the-position-of-centro-somes-in-relation-to-this-spindle-meanwhile-important-changes-which-are-best-known-for-zamia-take-place-in-the-blepharoplast-in-this-type-the-structure-forms-a-hollow-sphere-which-breaks-up-into-segments-and-finally-into-granules-as-mitosis-proceeds-the-radiations-disappear-without-holding-any-apparent-relation-to-the-spindle-during-telophase-each-o-image232355177.html
. Studies on the plant cell. pt.1-8. Plant cells and tissues. Nos. 4SI-45Z-] STUDIES ON THE PLANT CELL. 579- which lie at a considerable distance from the structure (Fig. xob). The latter cannot then be said to occupy the position of centro- somes in relation to this spindle. Meanwhile important changes, which are best known for Zamia, take place in the blepharoplast. In this type the structure forms a hollow sphere which breaks up into segments and finally into granules as mitosis proceeds.. The radiations disappear without holding any apparent relation to the spindle. During telophase each o Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/studies-on-the-plant-cell-pt1-8-plant-cells-and-tissues-nos-4si-45z-studies-on-the-plant-cell-579-which-lie-at-a-considerable-distance-from-the-structure-fig-xob-the-latter-cannot-then-be-said-to-occupy-the-position-of-centro-somes-in-relation-to-this-spindle-meanwhile-important-changes-which-are-best-known-for-zamia-take-place-in-the-blepharoplast-in-this-type-the-structure-forms-a-hollow-sphere-which-breaks-up-into-segments-and-finally-into-granules-as-mitosis-proceeds-the-radiations-disappear-without-holding-any-apparent-relation-to-the-spindle-during-telophase-each-o-image232355177.htmlRMRE0KB5–. Studies on the plant cell. pt.1-8. Plant cells and tissues. Nos. 4SI-45Z-] STUDIES ON THE PLANT CELL. 579- which lie at a considerable distance from the structure (Fig. xob). The latter cannot then be said to occupy the position of centro- somes in relation to this spindle. Meanwhile important changes, which are best known for Zamia, take place in the blepharoplast. In this type the structure forms a hollow sphere which breaks up into segments and finally into granules as mitosis proceeds.. The radiations disappear without holding any apparent relation to the spindle. During telophase each o
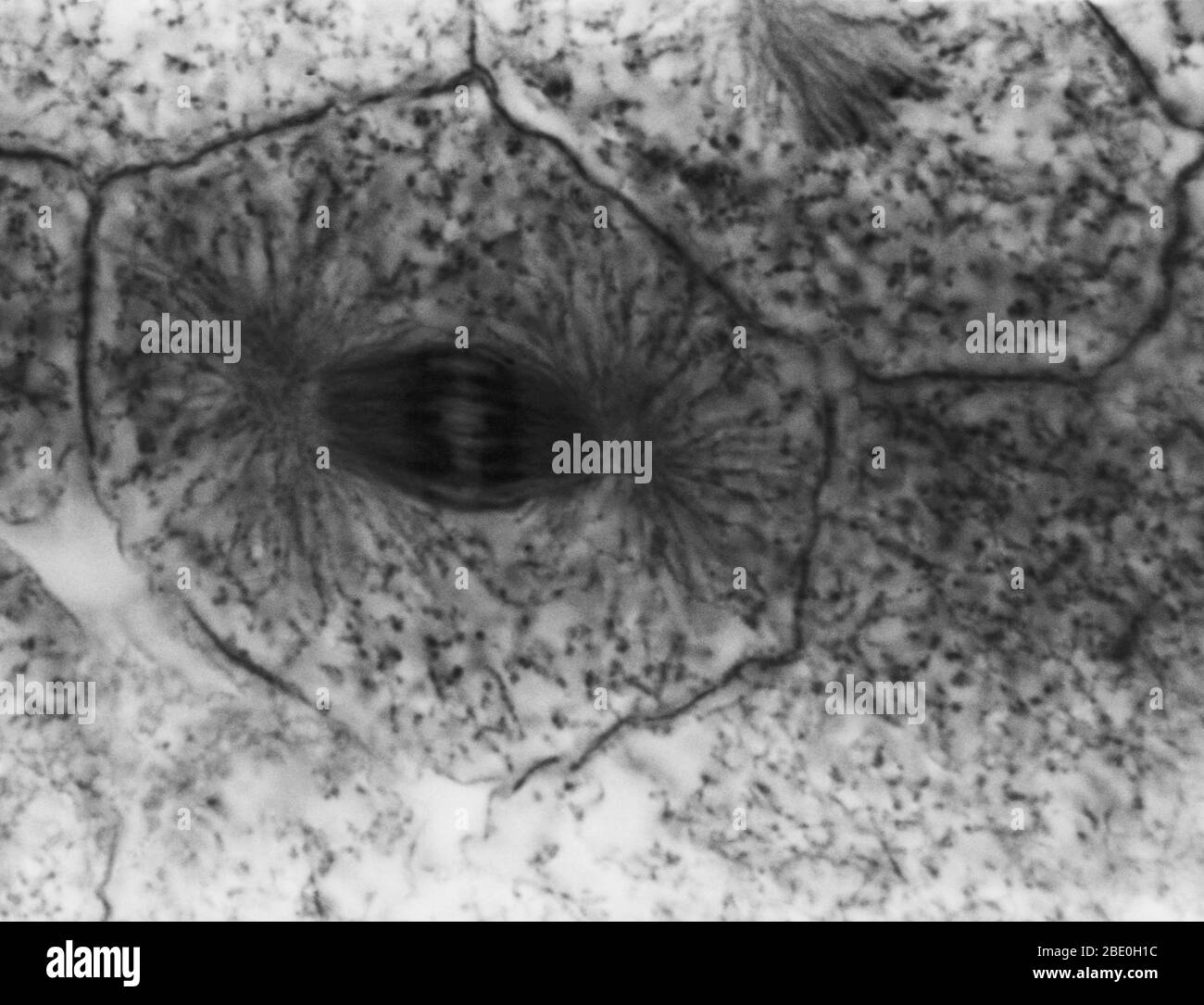 Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, anaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-anaphase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-egg-image352825912.html
Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, anaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-anaphase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-egg-image352825912.htmlRM2BE0H1C–Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, anaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg
 . Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. 286 287. Figs. 285-288.—Cryptomeria japonica: development of the endosperm; fig. 285, longitudinal section of upper portion of endosperm showing multinucleate condition and also that the walls are incomplete; May 26, 1902; X23S; fig. 286, telophase of the mitosis which is to result in the formation of a binucleate cell like those shown in fig. 288; May 29, 1903; XijOoo; fig. 287, a later stage in the same mitosis, the two daughter nuclei completely inclosed by the kinoplasmic fibrils; X 1,000; fig. 288, portion of the endosperm soon a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-286-287-figs-285-288cryptomeria-japonica-development-of-the-endosperm-fig-285-longitudinal-section-of-upper-portion-of-endosperm-showing-multinucleate-condition-and-also-that-the-walls-are-incomplete-may-26-1902-x23s-fig-286-telophase-of-the-mitosis-which-is-to-result-in-the-formation-of-a-binucleate-cell-like-those-shown-in-fig-288-may-29-1903-xijooo-fig-287-a-later-stage-in-the-same-mitosis-the-two-daughter-nuclei-completely-inclosed-by-the-kinoplasmic-fibrils-x-1000-fig-288-portion-of-the-endosperm-soon-a-image232103442.html
. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. 286 287. Figs. 285-288.—Cryptomeria japonica: development of the endosperm; fig. 285, longitudinal section of upper portion of endosperm showing multinucleate condition and also that the walls are incomplete; May 26, 1902; X23S; fig. 286, telophase of the mitosis which is to result in the formation of a binucleate cell like those shown in fig. 288; May 29, 1903; XijOoo; fig. 287, a later stage in the same mitosis, the two daughter nuclei completely inclosed by the kinoplasmic fibrils; X 1,000; fig. 288, portion of the endosperm soon a Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/morphology-of-gymnosperms-gymnosperms-plant-morphology-286-287-figs-285-288cryptomeria-japonica-development-of-the-endosperm-fig-285-longitudinal-section-of-upper-portion-of-endosperm-showing-multinucleate-condition-and-also-that-the-walls-are-incomplete-may-26-1902-x23s-fig-286-telophase-of-the-mitosis-which-is-to-result-in-the-formation-of-a-binucleate-cell-like-those-shown-in-fig-288-may-29-1903-xijooo-fig-287-a-later-stage-in-the-same-mitosis-the-two-daughter-nuclei-completely-inclosed-by-the-kinoplasmic-fibrils-x-1000-fig-288-portion-of-the-endosperm-soon-a-image232103442.htmlRMRDH68J–. Morphology of gymnosperms. Gymnosperms; Plant morphology. 286 287. Figs. 285-288.—Cryptomeria japonica: development of the endosperm; fig. 285, longitudinal section of upper portion of endosperm showing multinucleate condition and also that the walls are incomplete; May 26, 1902; X23S; fig. 286, telophase of the mitosis which is to result in the formation of a binucleate cell like those shown in fig. 288; May 29, 1903; XijOoo; fig. 287, a later stage in the same mitosis, the two daughter nuclei completely inclosed by the kinoplasmic fibrils; X 1,000; fig. 288, portion of the endosperm soon a
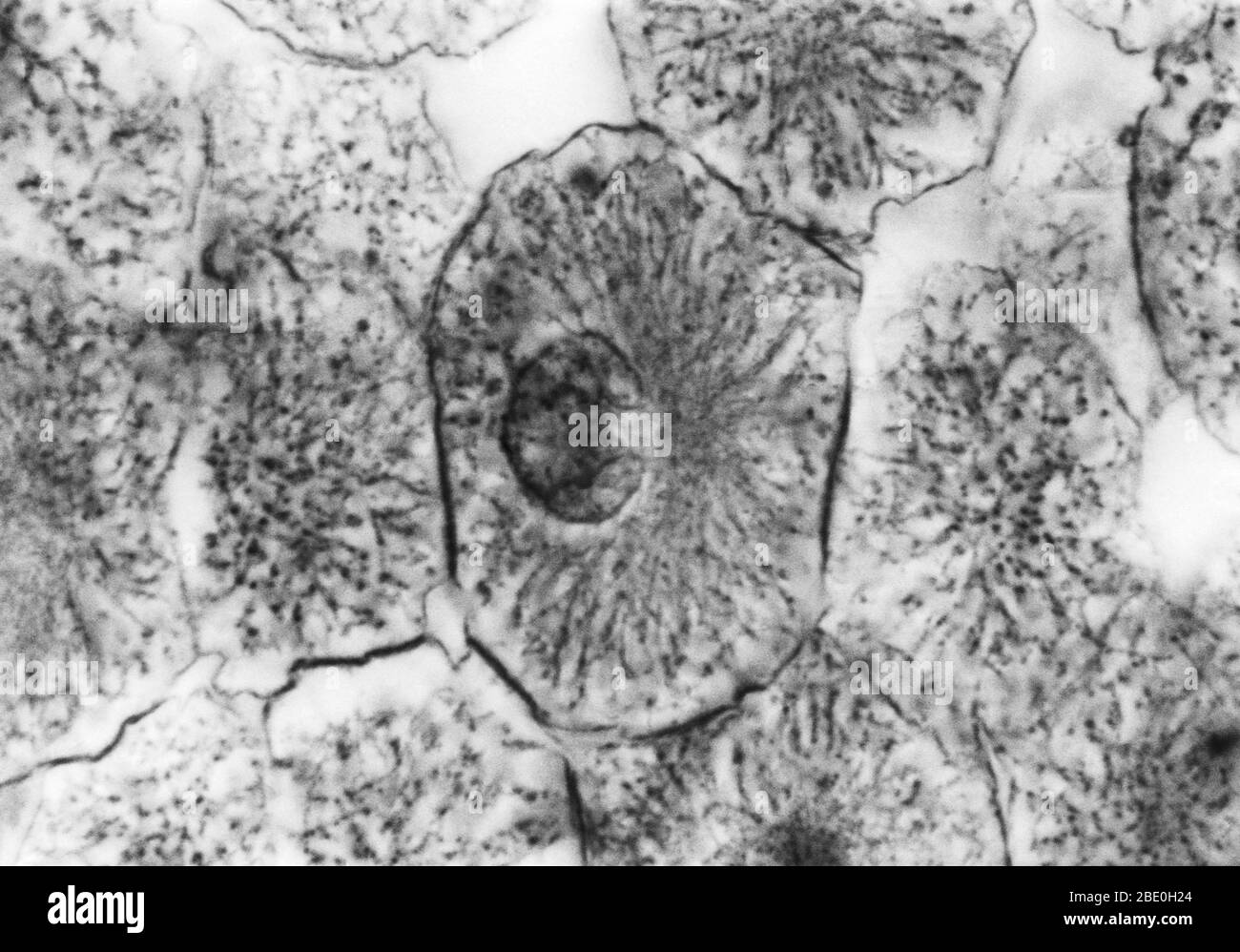 Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, prophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-prophase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-egg-image352825932.html
Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, prophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-prophase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-egg-image352825932.htmlRM2BE0H24–Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, prophase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg
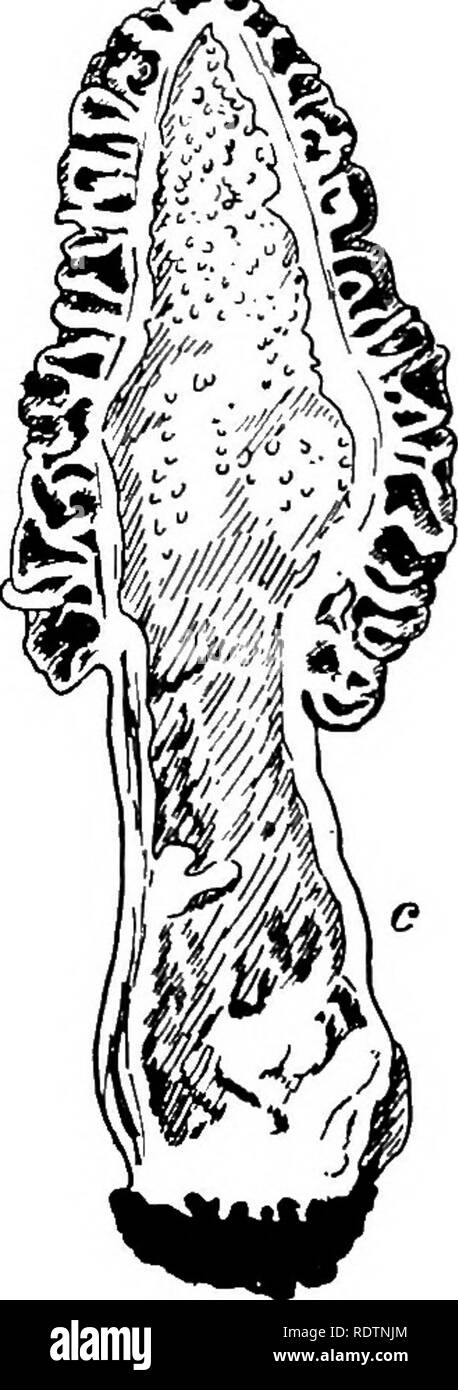 . Fungi, ascomycetes, ustilaginales, uredinales. Fungi. ^<#s^. Fig. 90. u. Helvetia crispa (Scop.) Fr.; b. and c. Morchella vulgaris Pers.; after Boudier. nuclear divisions, and finds two chromosomes in the vegetative and four in the fertile hyphae. Four again appear in the first and second (meiotic) divisions in the ascus, after the second fusion has taken place, and two are recorded in the telophase of the third division, and in the mitosis in the spore. The ripe spore normally contains eight nuclei. In both species, after an ascus has arisen from the penultimate cell of a hypha, the term Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fungi-ascomycetes-ustilaginales-uredinales-fungi-lts-fig-90-u-helvetia-crispa-scop-fr-b-and-c-morchella-vulgaris-pers-after-boudier-nuclear-divisions-and-finds-two-chromosomes-in-the-vegetative-and-four-in-the-fertile-hyphae-four-again-appear-in-the-first-and-second-meiotic-divisions-in-the-ascus-after-the-second-fusion-has-taken-place-and-two-are-recorded-in-the-telophase-of-the-third-division-and-in-the-mitosis-in-the-spore-the-ripe-spore-normally-contains-eight-nuclei-in-both-species-after-an-ascus-has-arisen-from-the-penultimate-cell-of-a-hypha-the-term-image232269148.html
. Fungi, ascomycetes, ustilaginales, uredinales. Fungi. ^<#s^. Fig. 90. u. Helvetia crispa (Scop.) Fr.; b. and c. Morchella vulgaris Pers.; after Boudier. nuclear divisions, and finds two chromosomes in the vegetative and four in the fertile hyphae. Four again appear in the first and second (meiotic) divisions in the ascus, after the second fusion has taken place, and two are recorded in the telophase of the third division, and in the mitosis in the spore. The ripe spore normally contains eight nuclei. In both species, after an ascus has arisen from the penultimate cell of a hypha, the term Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/fungi-ascomycetes-ustilaginales-uredinales-fungi-lts-fig-90-u-helvetia-crispa-scop-fr-b-and-c-morchella-vulgaris-pers-after-boudier-nuclear-divisions-and-finds-two-chromosomes-in-the-vegetative-and-four-in-the-fertile-hyphae-four-again-appear-in-the-first-and-second-meiotic-divisions-in-the-ascus-after-the-second-fusion-has-taken-place-and-two-are-recorded-in-the-telophase-of-the-third-division-and-in-the-mitosis-in-the-spore-the-ripe-spore-normally-contains-eight-nuclei-in-both-species-after-an-ascus-has-arisen-from-the-penultimate-cell-of-a-hypha-the-term-image232269148.htmlRMRDTNJM–. Fungi, ascomycetes, ustilaginales, uredinales. Fungi. ^<#s^. Fig. 90. u. Helvetia crispa (Scop.) Fr.; b. and c. Morchella vulgaris Pers.; after Boudier. nuclear divisions, and finds two chromosomes in the vegetative and four in the fertile hyphae. Four again appear in the first and second (meiotic) divisions in the ascus, after the second fusion has taken place, and two are recorded in the telophase of the third division, and in the mitosis in the spore. The ripe spore normally contains eight nuclei. In both species, after an ascus has arisen from the penultimate cell of a hypha, the term
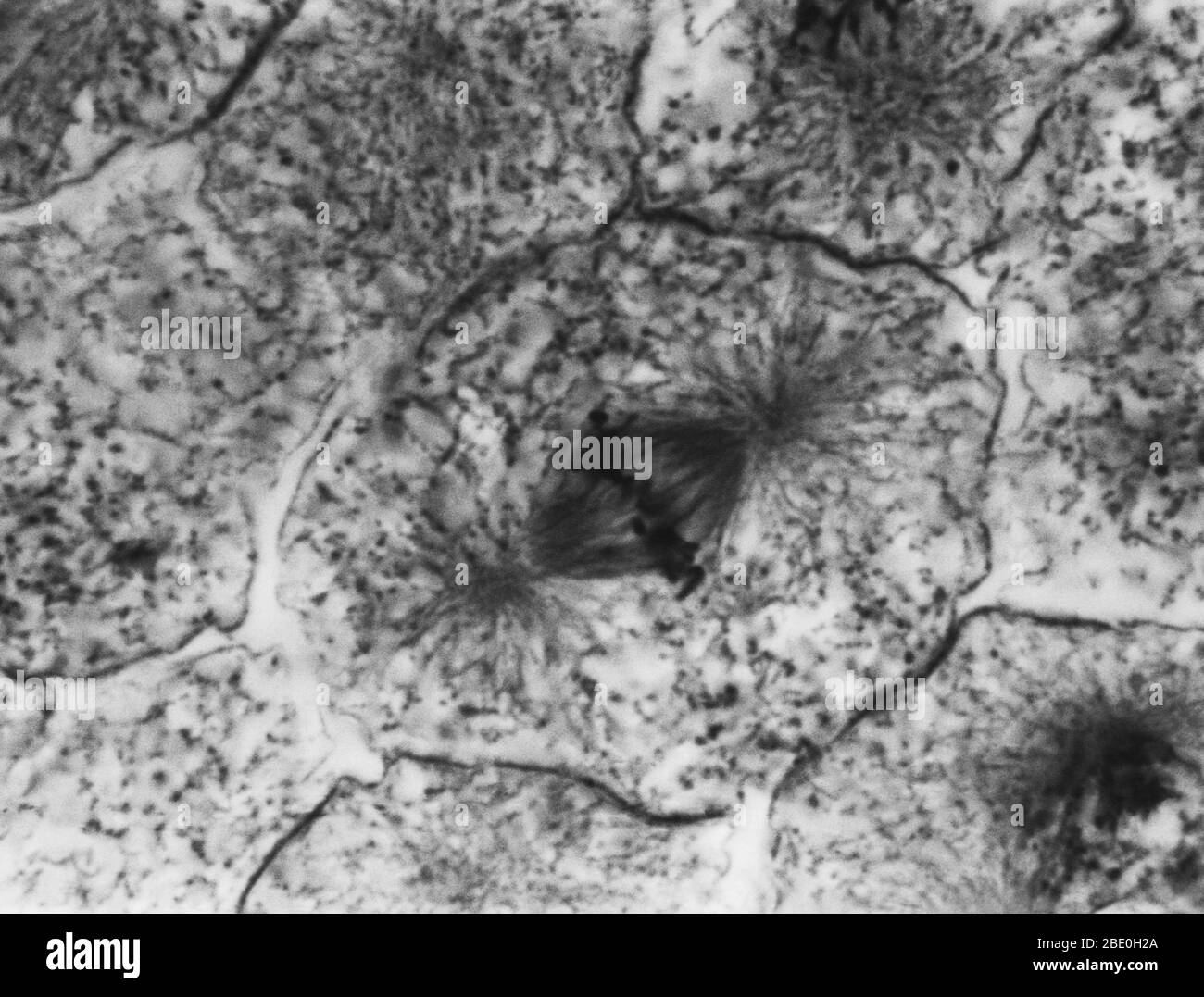 Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, metaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized eg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-metaphase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-eg-image352825938.html
Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, metaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized eg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-metaphase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertilized-eg-image352825938.htmlRM2BE0H2A–Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, metaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized eg
![. The plant cell, its modifications and vital processes; a manual for students. Plant physiology; Plant anatomy; Plant cells and tissues. 6 '' ,--. 1 Ml" ^1' iti ^K' ^^ 1 ^1- ^t' .,-i^ .:ja i sUowins Various Hinses in Mitosis). ]>I,ATES I. illitlll. (FlH't icro-ruplii 1, 2, 3, and 4 sliow the spireme stage ; ^ r, r, and 7, tlie monaster stage seen from tlie side , s'lii'il 9 tlie secondary chromosomes separating; 1(1 11 and 12, later stages of the metaphase; l' Vi Hrt h: nd cell), U, 16, and 16, end-stages (telophase). of Caltha.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanne Stock Photo . The plant cell, its modifications and vital processes; a manual for students. Plant physiology; Plant anatomy; Plant cells and tissues. 6 '' ,--. 1 Ml" ^1' iti ^K' ^^ 1 ^1- ^t' .,-i^ .:ja i sUowins Various Hinses in Mitosis). ]>I,ATES I. illitlll. (FlH't icro-ruplii 1, 2, 3, and 4 sliow the spireme stage ; ^ r, r, and 7, tlie monaster stage seen from tlie side , s'lii'il 9 tlie secondary chromosomes separating; 1(1 11 and 12, later stages of the metaphase; l' Vi Hrt h: nd cell), U, 16, and 16, end-stages (telophase). of Caltha.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanne Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/RDYCHX/the-plant-cell-its-modifications-and-vital-processes-a-manual-for-students-plant-physiology-plant-anatomy-plant-cells-and-tissues-6-1-mlquot-1-iti-k-1-1-t-i-ja-i-suowins-various-hinses-in-mitosis-gtiates-i-illitlll-flht-icro-ruplii-1-2-3-and-4-sliow-the-spireme-stage-r-r-and-7-tlie-monaster-stage-seen-from-tlie-side-sliiil-9-tlie-secondary-chromosomes-separating-11-11-and-12-later-stages-of-the-metaphase-l-vi-hrt-h-nd-cell-u-16-and-16-end-stages-telophase-of-caltha-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanne-RDYCHX.jpg) . The plant cell, its modifications and vital processes; a manual for students. Plant physiology; Plant anatomy; Plant cells and tissues. 6 '' ,--. 1 Ml" ^1' iti ^K' ^^ 1 ^1- ^t' .,-i^ .:ja i sUowins Various Hinses in Mitosis). ]>I,ATES I. illitlll. (FlH't icro-ruplii 1, 2, 3, and 4 sliow the spireme stage ; ^ r, r, and 7, tlie monaster stage seen from tlie side , s'lii'il 9 tlie secondary chromosomes separating; 1(1 11 and 12, later stages of the metaphase; l' Vi Hrt h: nd cell), U, 16, and 16, end-stages (telophase). of Caltha.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanne Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-plant-cell-its-modifications-and-vital-processes-a-manual-for-students-plant-physiology-plant-anatomy-plant-cells-and-tissues-6-1-mlquot-1-iti-k-1-1-t-i-ja-i-suowins-various-hinses-in-mitosis-gtiates-i-illitlll-flht-icro-ruplii-1-2-3-and-4-sliow-the-spireme-stage-r-r-and-7-tlie-monaster-stage-seen-from-tlie-side-sliiil-9-tlie-secondary-chromosomes-separating-11-11-and-12-later-stages-of-the-metaphase-l-vi-hrt-h-nd-cell-u-16-and-16-end-stages-telophase-of-caltha-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanne-image232327926.html
. The plant cell, its modifications and vital processes; a manual for students. Plant physiology; Plant anatomy; Plant cells and tissues. 6 '' ,--. 1 Ml" ^1' iti ^K' ^^ 1 ^1- ^t' .,-i^ .:ja i sUowins Various Hinses in Mitosis). ]>I,ATES I. illitlll. (FlH't icro-ruplii 1, 2, 3, and 4 sliow the spireme stage ; ^ r, r, and 7, tlie monaster stage seen from tlie side , s'lii'il 9 tlie secondary chromosomes separating; 1(1 11 and 12, later stages of the metaphase; l' Vi Hrt h: nd cell), U, 16, and 16, end-stages (telophase). of Caltha.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanne Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-plant-cell-its-modifications-and-vital-processes-a-manual-for-students-plant-physiology-plant-anatomy-plant-cells-and-tissues-6-1-mlquot-1-iti-k-1-1-t-i-ja-i-suowins-various-hinses-in-mitosis-gtiates-i-illitlll-flht-icro-ruplii-1-2-3-and-4-sliow-the-spireme-stage-r-r-and-7-tlie-monaster-stage-seen-from-tlie-side-sliiil-9-tlie-secondary-chromosomes-separating-11-11-and-12-later-stages-of-the-metaphase-l-vi-hrt-h-nd-cell-u-16-and-16-end-stages-telophase-of-caltha-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanne-image232327926.htmlRMRDYCHX–. The plant cell, its modifications and vital processes; a manual for students. Plant physiology; Plant anatomy; Plant cells and tissues. 6 '' ,--. 1 Ml" ^1' iti ^K' ^^ 1 ^1- ^t' .,-i^ .:ja i sUowins Various Hinses in Mitosis). ]>I,ATES I. illitlll. (FlH't icro-ruplii 1, 2, 3, and 4 sliow the spireme stage ; ^ r, r, and 7, tlie monaster stage seen from tlie side , s'lii'il 9 tlie secondary chromosomes separating; 1(1 11 and 12, later stages of the metaphase; l' Vi Hrt h: nd cell), U, 16, and 16, end-stages (telophase). of Caltha.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanne
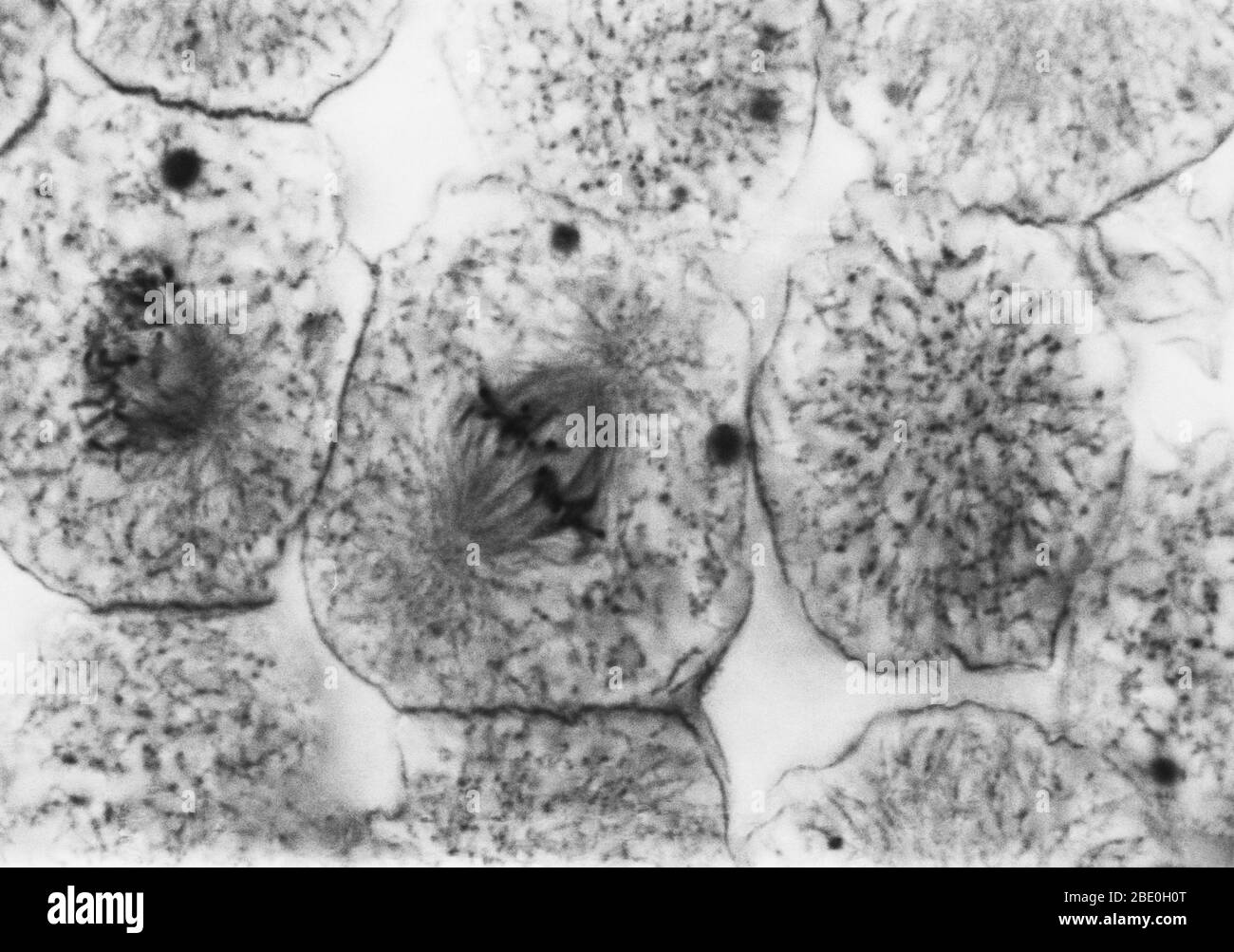 Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, early metaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertili Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-early-metaphase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertili-image352825896.html
Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, early metaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertili Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/light-micrograph-showing-mitosis-in-whitefish-blastula-early-metaphase-no-magnification-given-mitosis-the-usual-method-of-cell-division-characterized-typically-by-the-resolving-of-the-chromatin-of-the-nucleus-into-a-threadlike-form-which-condenses-into-chromosomes-each-of-which-separates-longitudinally-into-two-parts-one-part-of-each-chromosome-being-retained-in-each-of-two-new-cells-resulting-from-the-original-cell-the-four-main-phases-of-mitosis-are-prophase-metaphase-anaphase-and-telophase-blastula-an-animal-embryo-at-the-stage-immediately-following-the-division-of-the-fertili-image352825896.htmlRM2BE0H0T–Light micrograph showing mitosis in whitefish blastula, early metaphase. No magnification given. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertili