Quick filters:
Tem plant cell Stock Photos and Images
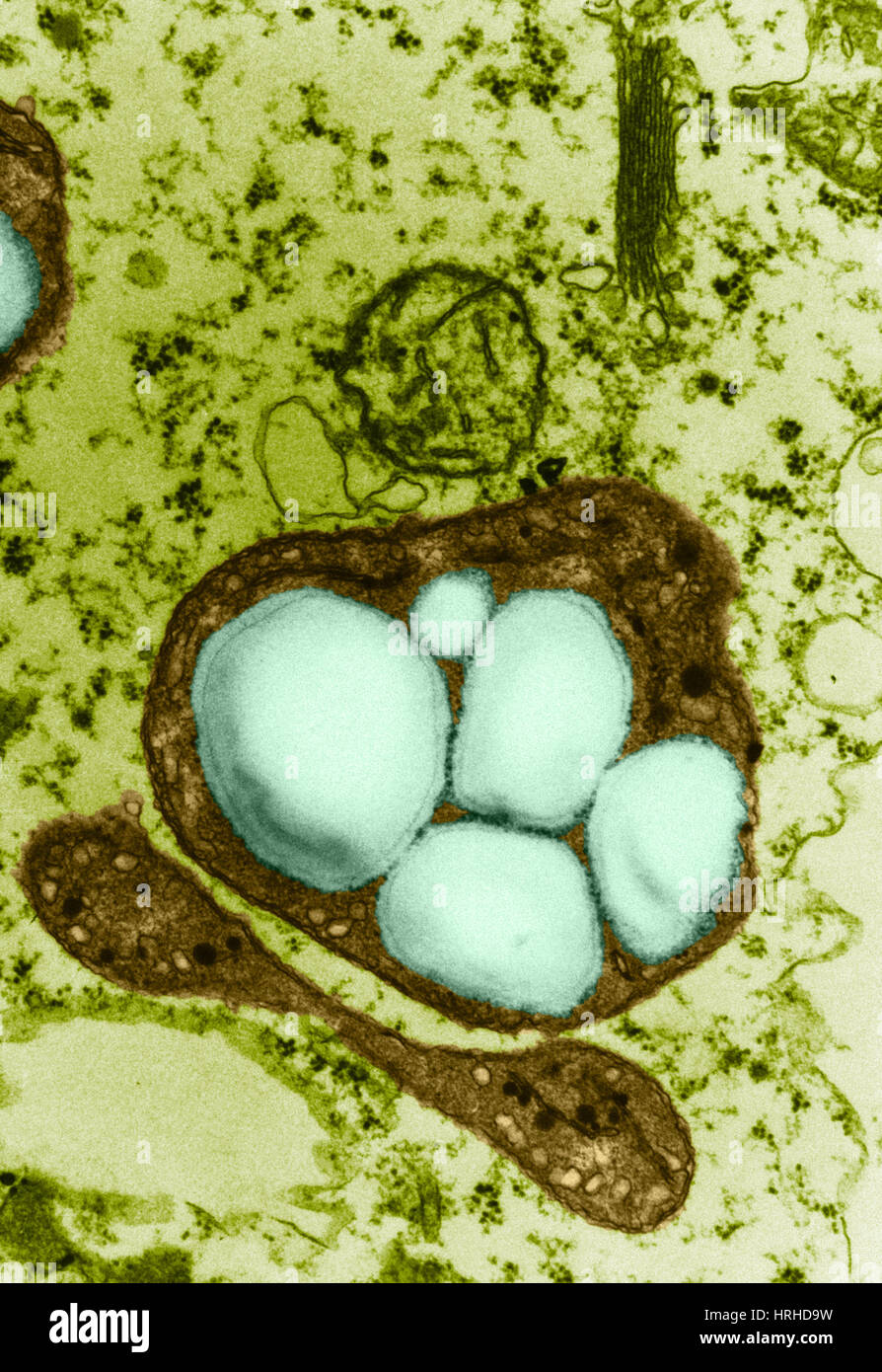
 Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134944077.html
Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134944077.htmlRMHRF6F9–Plant Cell TEM
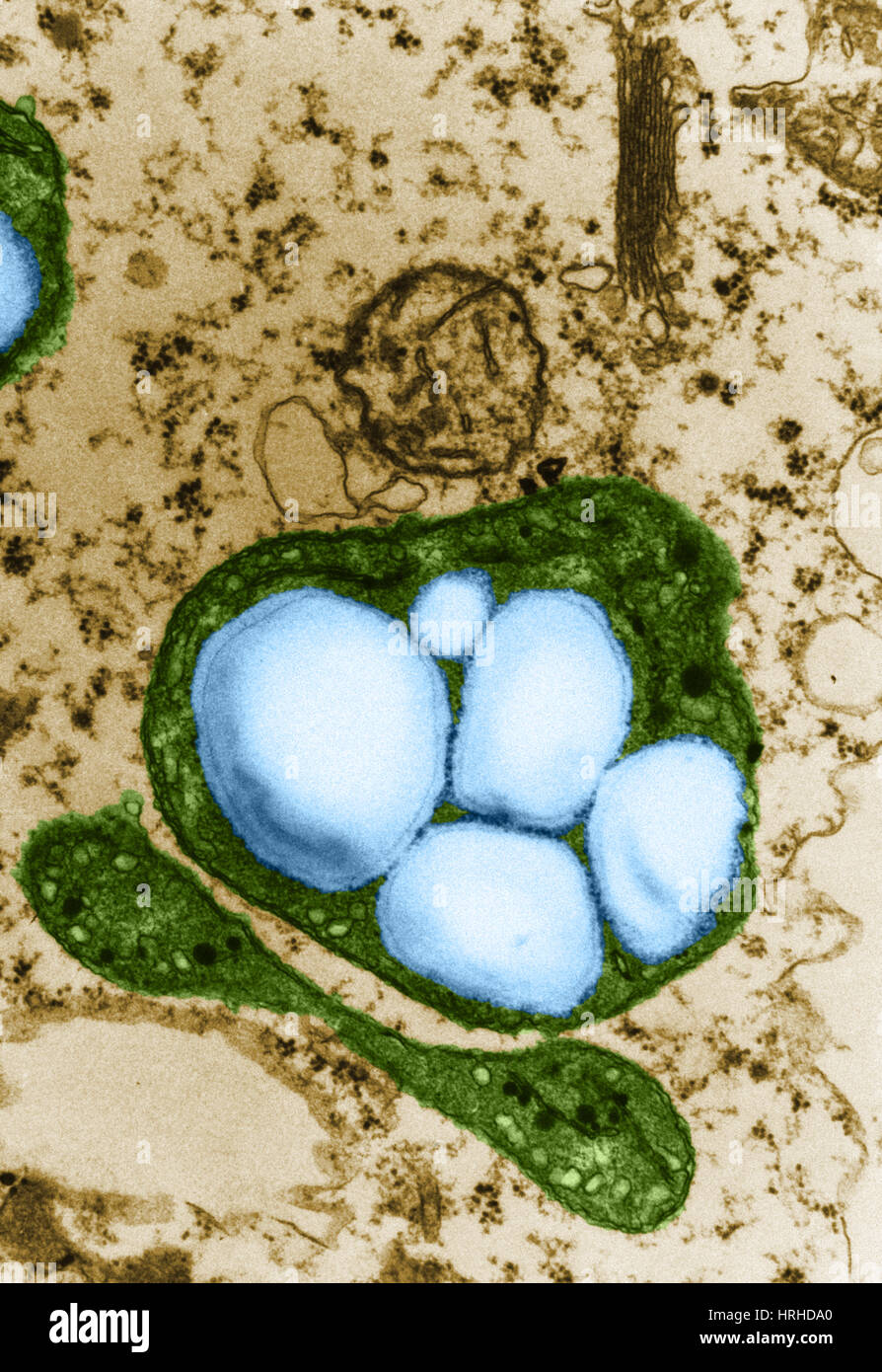
 TEM of Begonia spp. leaf showing a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tem-of-begonia-spp-leaf-showing-a-chloroplast-image65487630.html
TEM of Begonia spp. leaf showing a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/tem-of-begonia-spp-leaf-showing-a-chloroplast-image65487630.htmlRFDPF63X–TEM of Begonia spp. leaf showing a chloroplast
 Ultrastructural details of the mumps virions grown in a Vero cell culture, revealed in the transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image, 1977. Image courtesy Centers for Disease Control (CDC) / A. Harrison and F. A. Murphy. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/ultrastructural-details-of-the-mumps-virions-grown-in-a-vero-cell-culture-revealed-in-the-transmission-electron-microscopic-tem-image-1977-image-courtesy-centers-for-disease-control-cdc-a-harrison-and-f-a-murphy-image216120179.html
Ultrastructural details of the mumps virions grown in a Vero cell culture, revealed in the transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image, 1977. Image courtesy Centers for Disease Control (CDC) / A. Harrison and F. A. Murphy. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/ultrastructural-details-of-the-mumps-virions-grown-in-a-vero-cell-culture-revealed-in-the-transmission-electron-microscopic-tem-image-1977-image-courtesy-centers-for-disease-control-cdc-a-harrison-and-f-a-murphy-image216120179.htmlRMPFH3DR–Ultrastructural details of the mumps virions grown in a Vero cell culture, revealed in the transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image, 1977. Image courtesy Centers for Disease Control (CDC) / A. Harrison and F. A. Murphy. ()
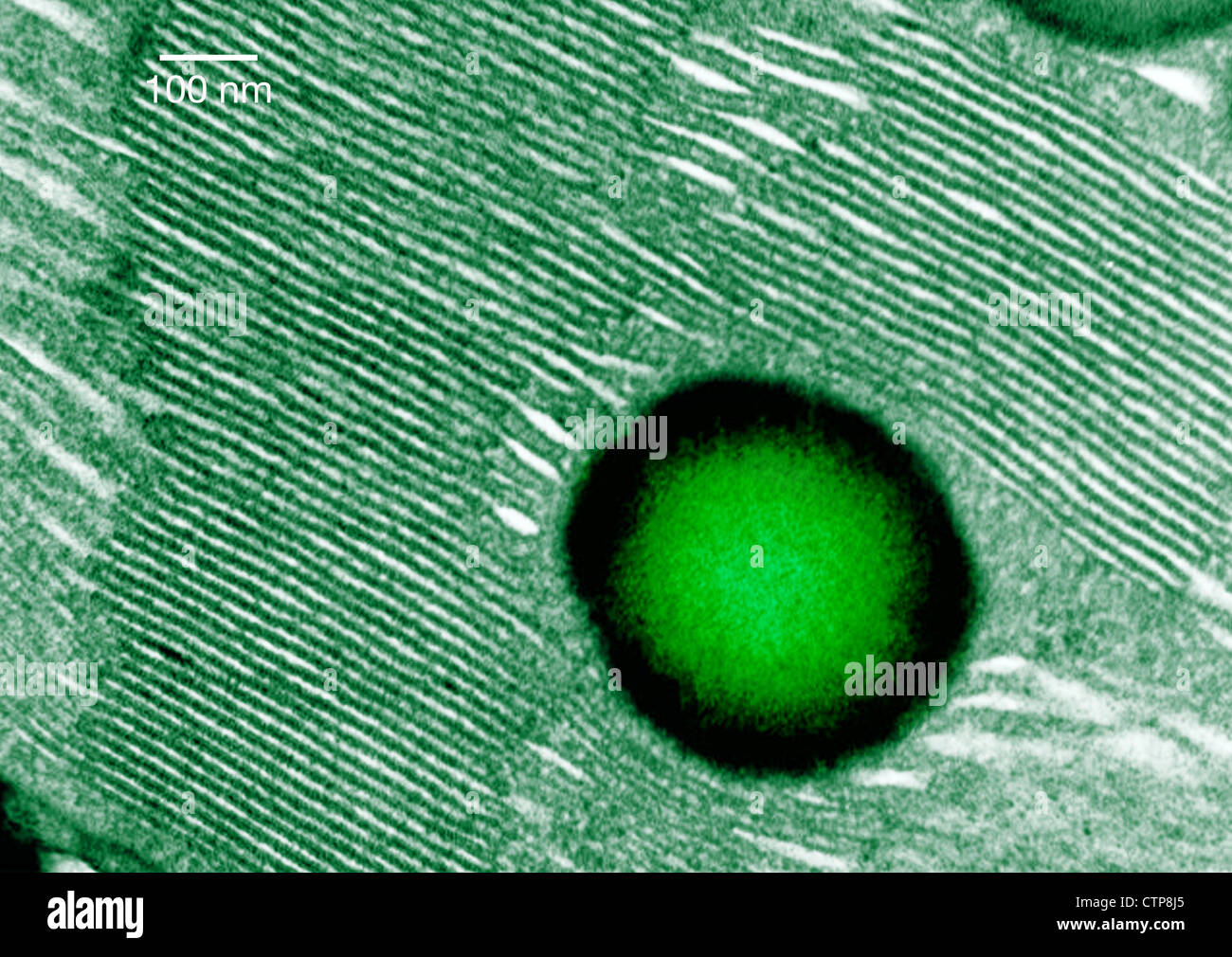 Transmission electron microscope image of a thin section cut from Begonia spp. leaf, showing a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-microscope-image-of-a-thin-section-cut-from-49662205.html
Transmission electron microscope image of a thin section cut from Begonia spp. leaf, showing a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-microscope-image-of-a-thin-section-cut-from-49662205.htmlRMCTP8J5–Transmission electron microscope image of a thin section cut from Begonia spp. leaf, showing a chloroplast
 Highly magnified, digitally colorized scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image, showing ultrastructural details at the site of interaction of numerous yellow colored, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) viral particles, located on the surface of a Vero E6 cell, which had been colorized blue, 2014. MERs is in the same family as the novel coronavirus which began to infect patients in Wuhan, China in early 2020. Courtesy National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)/CDC. Image produced in 2014. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/highly-magnified-digitally-colorized-scanning-electron-microscopic-sem-image-showing-ultrastructural-details-at-the-site-of-interaction-of-numerous-yellow-colored-middle-east-respiratory-syndrome-coronavirus-mers-cov-viral-particles-located-on-the-surface-of-a-vero-e6-cell-which-had-been-colorized-blue-2014-mers-is-in-the-same-family-as-the-novel-coronavirus-which-began-to-infect-patients-in-wuhan-china-in-early-2020-courtesy-national-institute-of-allergy-and-infectious-diseases-niaidcdc-image-produced-in-2014-image342265505.html
Highly magnified, digitally colorized scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image, showing ultrastructural details at the site of interaction of numerous yellow colored, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) viral particles, located on the surface of a Vero E6 cell, which had been colorized blue, 2014. MERs is in the same family as the novel coronavirus which began to infect patients in Wuhan, China in early 2020. Courtesy National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)/CDC. Image produced in 2014. () Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/highly-magnified-digitally-colorized-scanning-electron-microscopic-sem-image-showing-ultrastructural-details-at-the-site-of-interaction-of-numerous-yellow-colored-middle-east-respiratory-syndrome-coronavirus-mers-cov-viral-particles-located-on-the-surface-of-a-vero-e6-cell-which-had-been-colorized-blue-2014-mers-is-in-the-same-family-as-the-novel-coronavirus-which-began-to-infect-patients-in-wuhan-china-in-early-2020-courtesy-national-institute-of-allergy-and-infectious-diseases-niaidcdc-image-produced-in-2014-image342265505.htmlRM2ATRF41–Highly magnified, digitally colorized scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image, showing ultrastructural details at the site of interaction of numerous yellow colored, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) viral particles, located on the surface of a Vero E6 cell, which had been colorized blue, 2014. MERs is in the same family as the novel coronavirus which began to infect patients in Wuhan, China in early 2020. Courtesy National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)/CDC. Image produced in 2014. ()
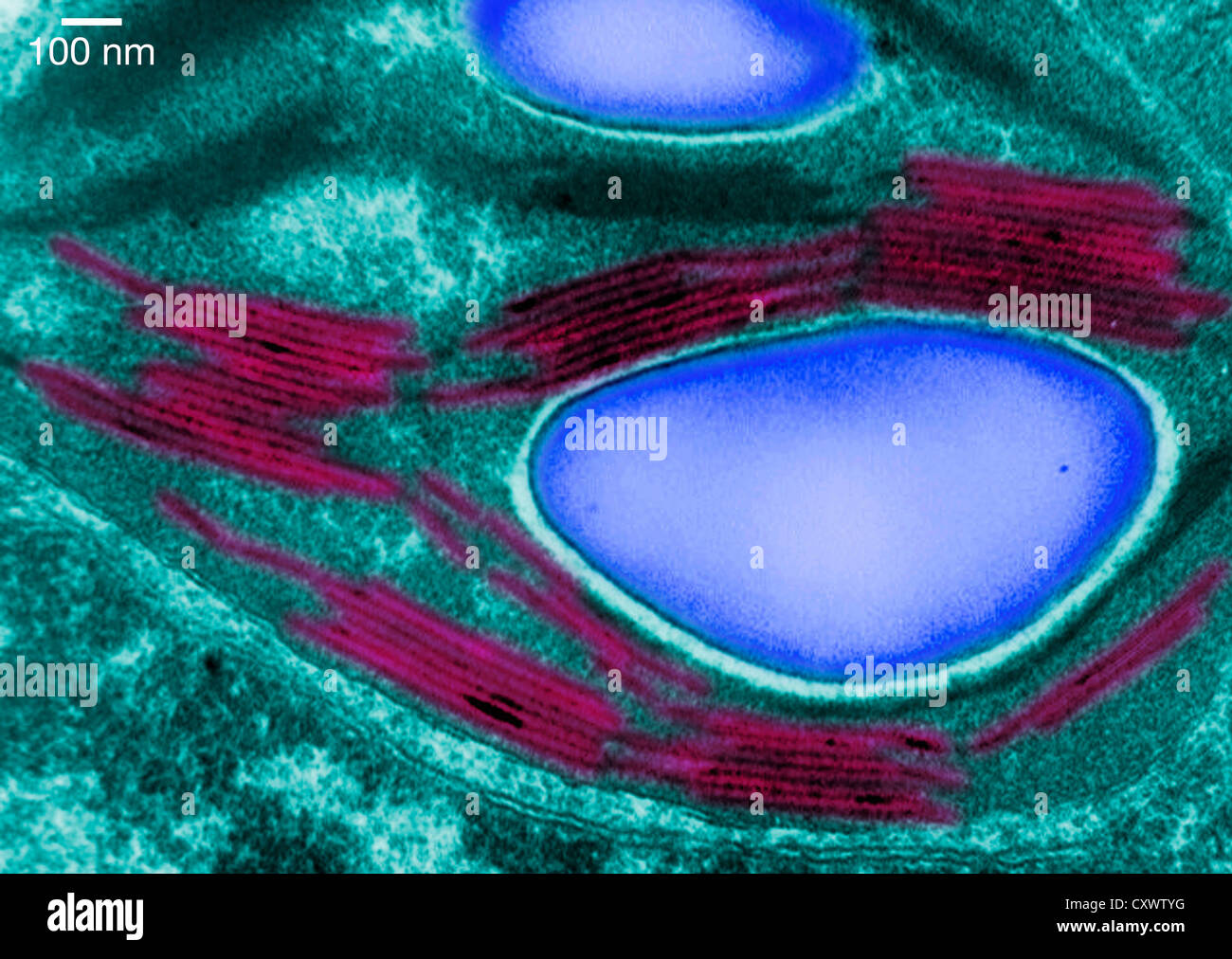 Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970180.html
Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970180.htmlRFCXWTYG–Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast
 Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970177.html
Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970177.htmlRFCXWTYD–Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast
 Archive image from page 174 of The cytoplasm of the plant. The cytoplasm of the plant cell cytoplasmofplant00guil Year: 1941 Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-174-of-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-cytoplasmofplant00guil-year-1941-chapter-xiv-159-the-vacuolar-system-or-alcohol-is-stained-deeply-red-by-aniline-blue-or-violet-basic-dyes-as-well-as-by-haematein-it-consequently-shows-a-whole-series-of-histochemical-reactions-which-are-very-well-known-and-are-very-different-from-those-of-the-chondriosomes-it-is-therefore-well-established-that-there-does-not-exist-the-slightest-relation-between-the-chondriome-and-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-they-are-two-independent-systems-which-are-coexistent-in-t-image259467175.html
Archive image from page 174 of The cytoplasm of the plant. The cytoplasm of the plant cell cytoplasmofplant00guil Year: 1941 Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-174-of-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-cytoplasmofplant00guil-year-1941-chapter-xiv-159-the-vacuolar-system-or-alcohol-is-stained-deeply-red-by-aniline-blue-or-violet-basic-dyes-as-well-as-by-haematein-it-consequently-shows-a-whole-series-of-histochemical-reactions-which-are-very-well-known-and-are-very-different-from-those-of-the-chondriosomes-it-is-therefore-well-established-that-there-does-not-exist-the-slightest-relation-between-the-chondriome-and-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-they-are-two-independent-systems-which-are-coexistent-in-t-image259467175.htmlRMW23N0R–Archive image from page 174 of The cytoplasm of the plant. The cytoplasm of the plant cell cytoplasmofplant00guil Year: 1941 Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in t
 Micrograph of onion cells, close-up Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/micrograph-of-onion-cells-close-up-image216183779.html
Micrograph of onion cells, close-up Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/micrograph-of-onion-cells-close-up-image216183779.htmlRMPFM0H7–Micrograph of onion cells, close-up
 . Botany of the living plant. Botany; Plants. SYNTHESIS, STORAGE AND BREAKDOWN 135 By a suitable elaboration of this arrangement the amount of carbon dioxide evolved could be determined and an index of the rate of respiration so ob- tained. It could be shown that respiration quickens with increasing tem- perature until levels are reached at which the cell-structure is adversely affected ; also that actively-growing material such as germinating seeds respire more quickly than mature or dormant parts of plants. This observation is indicative of a close connection between respiration and growth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/botany-of-the-living-plant-botany-plants-synthesis-storage-and-breakdown-135-by-a-suitable-elaboration-of-this-arrangement-the-amount-of-carbon-dioxide-evolved-could-be-determined-and-an-index-of-the-rate-of-respiration-so-ob-tained-it-could-be-shown-that-respiration-quickens-with-increasing-tem-perature-until-levels-are-reached-at-which-the-cell-structure-is-adversely-affected-also-that-actively-growing-material-such-as-germinating-seeds-respire-more-quickly-than-mature-or-dormant-parts-of-plants-this-observation-is-indicative-of-a-close-connection-between-respiration-and-growth-image234362741.html
. Botany of the living plant. Botany; Plants. SYNTHESIS, STORAGE AND BREAKDOWN 135 By a suitable elaboration of this arrangement the amount of carbon dioxide evolved could be determined and an index of the rate of respiration so ob- tained. It could be shown that respiration quickens with increasing tem- perature until levels are reached at which the cell-structure is adversely affected ; also that actively-growing material such as germinating seeds respire more quickly than mature or dormant parts of plants. This observation is indicative of a close connection between respiration and growth. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/botany-of-the-living-plant-botany-plants-synthesis-storage-and-breakdown-135-by-a-suitable-elaboration-of-this-arrangement-the-amount-of-carbon-dioxide-evolved-could-be-determined-and-an-index-of-the-rate-of-respiration-so-ob-tained-it-could-be-shown-that-respiration-quickens-with-increasing-tem-perature-until-levels-are-reached-at-which-the-cell-structure-is-adversely-affected-also-that-actively-growing-material-such-as-germinating-seeds-respire-more-quickly-than-mature-or-dormant-parts-of-plants-this-observation-is-indicative-of-a-close-connection-between-respiration-and-growth-image234362741.htmlRMRH841W–. Botany of the living plant. Botany; Plants. SYNTHESIS, STORAGE AND BREAKDOWN 135 By a suitable elaboration of this arrangement the amount of carbon dioxide evolved could be determined and an index of the rate of respiration so ob- tained. It could be shown that respiration quickens with increasing tem- perature until levels are reached at which the cell-structure is adversely affected ; also that actively-growing material such as germinating seeds respire more quickly than mature or dormant parts of plants. This observation is indicative of a close connection between respiration and growth.
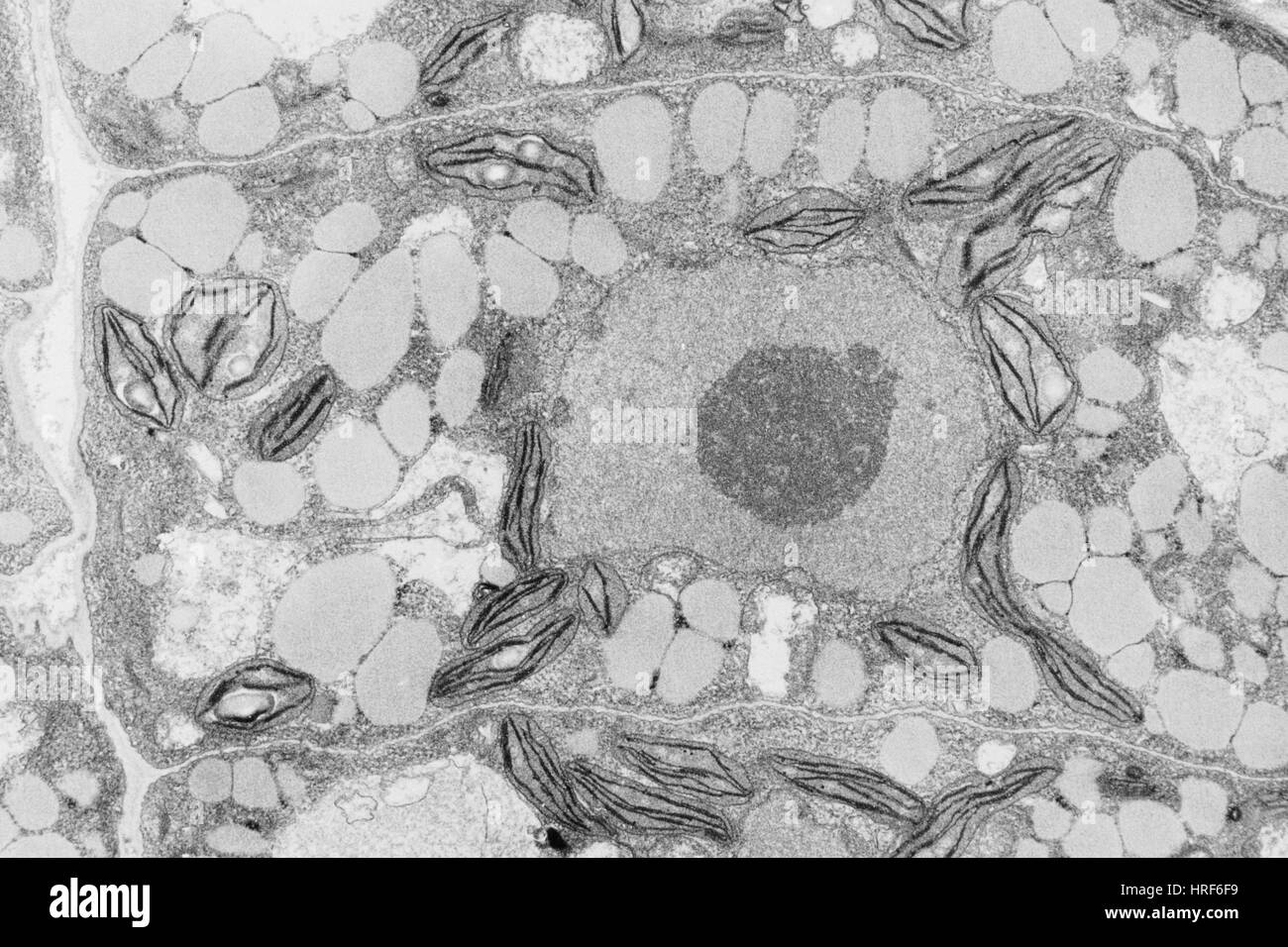
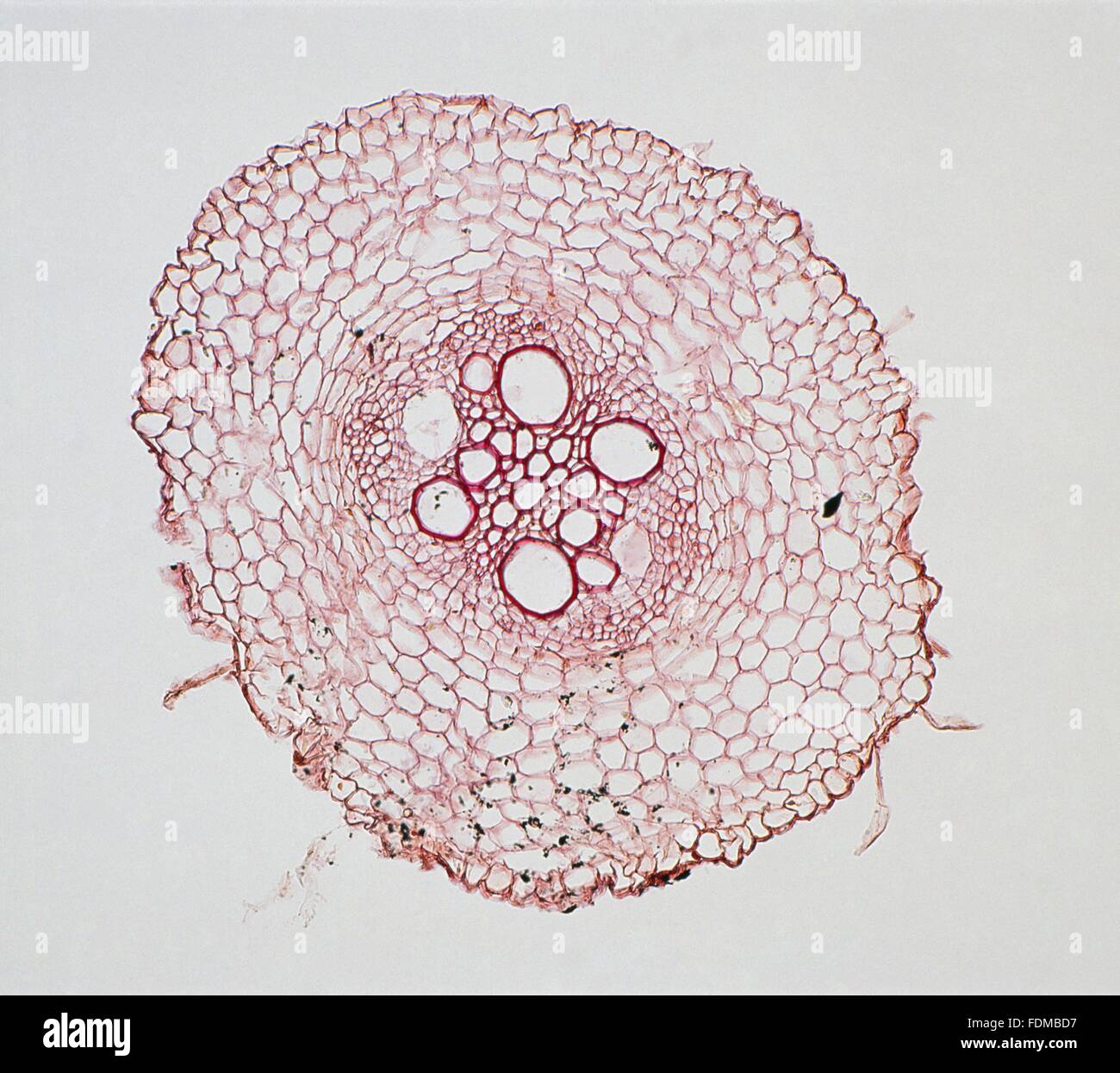 Micrograph of cross-section through a monocotyledonous root (maize) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-micrograph-of-cross-section-through-a-monocotyledonous-root-maize-94490403.html
Micrograph of cross-section through a monocotyledonous root (maize) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-micrograph-of-cross-section-through-a-monocotyledonous-root-maize-94490403.htmlRMFDMBD7–Micrograph of cross-section through a monocotyledonous root (maize)
 . The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in the cell. There is between the young stages of the vacuo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-159-the-vacuolar-system-or-alcohol-is-stained-deeply-red-by-aniline-blue-or-violet-basic-dyes-as-well-as-by-haematein-it-consequently-shows-a-whole-series-of-histochemical-reactions-which-are-very-well-known-and-are-very-different-from-those-of-the-chondriosomes-it-is-therefore-well-established-that-there-does-not-exist-the-slightest-relation-between-the-chondriome-and-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-they-are-two-independent-systems-which-are-coexistent-in-the-cell-there-is-between-the-young-stages-of-the-vacuo-image216167278.html
. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in the cell. There is between the young stages of the vacuo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-159-the-vacuolar-system-or-alcohol-is-stained-deeply-red-by-aniline-blue-or-violet-basic-dyes-as-well-as-by-haematein-it-consequently-shows-a-whole-series-of-histochemical-reactions-which-are-very-well-known-and-are-very-different-from-those-of-the-chondriosomes-it-is-therefore-well-established-that-there-does-not-exist-the-slightest-relation-between-the-chondriome-and-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-they-are-two-independent-systems-which-are-coexistent-in-the-cell-there-is-between-the-young-stages-of-the-vacuo-image216167278.htmlRMPFK7FX–. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in the cell. There is between the young stages of the vacuo
 Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image327404996.html
Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image327404996.htmlRF2A0JGBG–Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design.
 Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image330454525.html
Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image330454525.htmlRF2A5HE39–Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design.
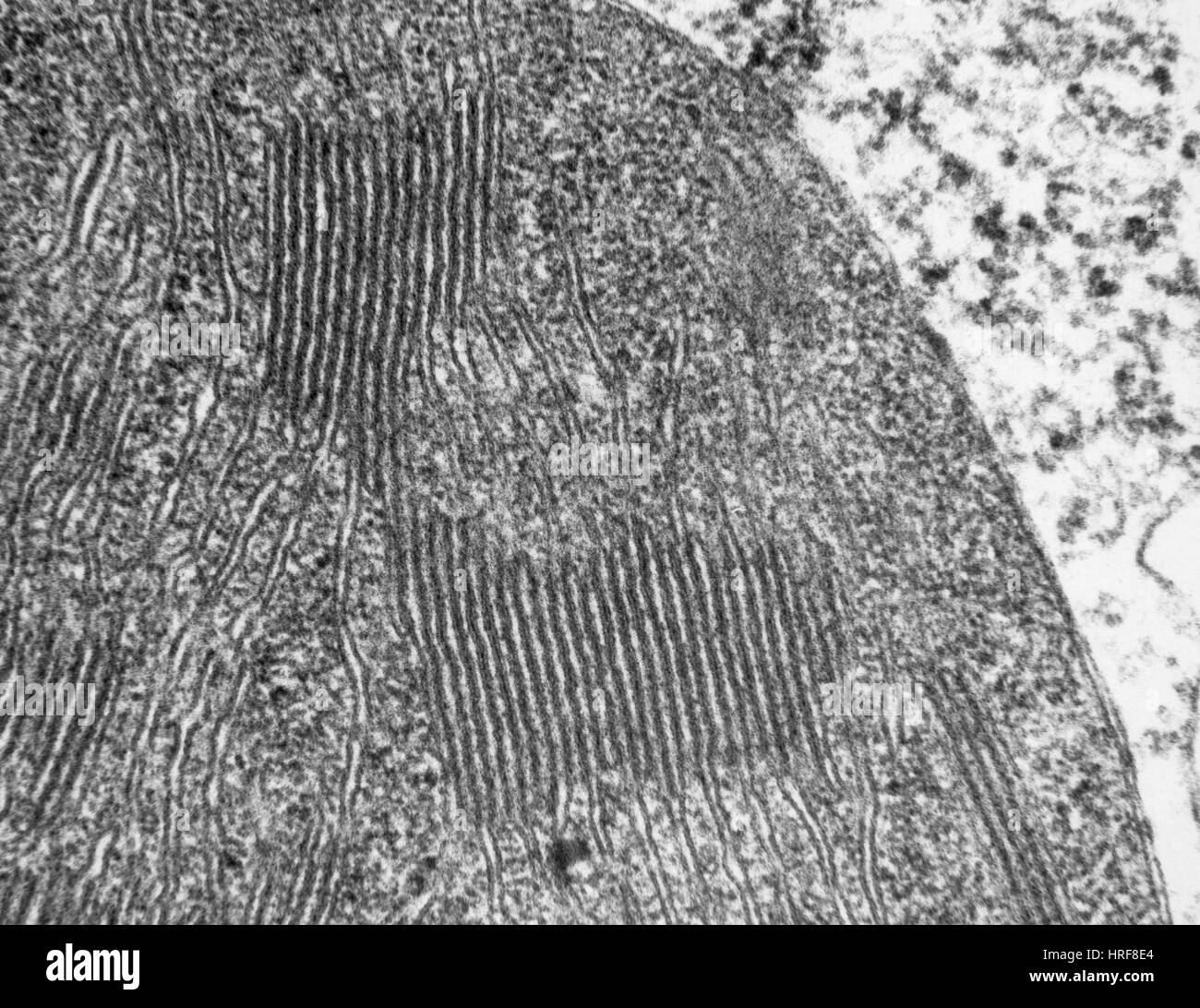 Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-134945612.html
Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-134945612.htmlRMHRF8E4–Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM
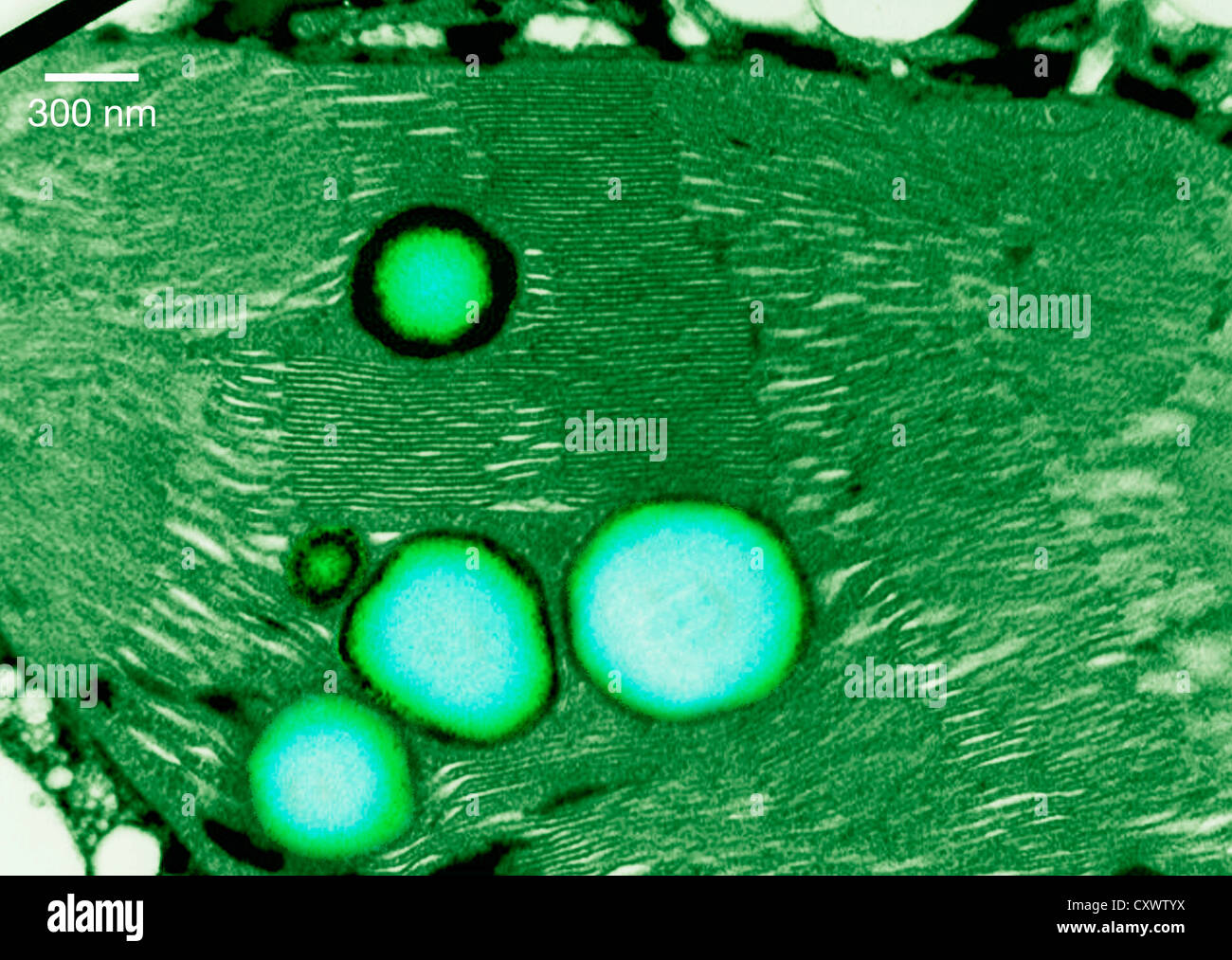 Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970190.html
Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970190.htmlRFCXWTYX–Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast
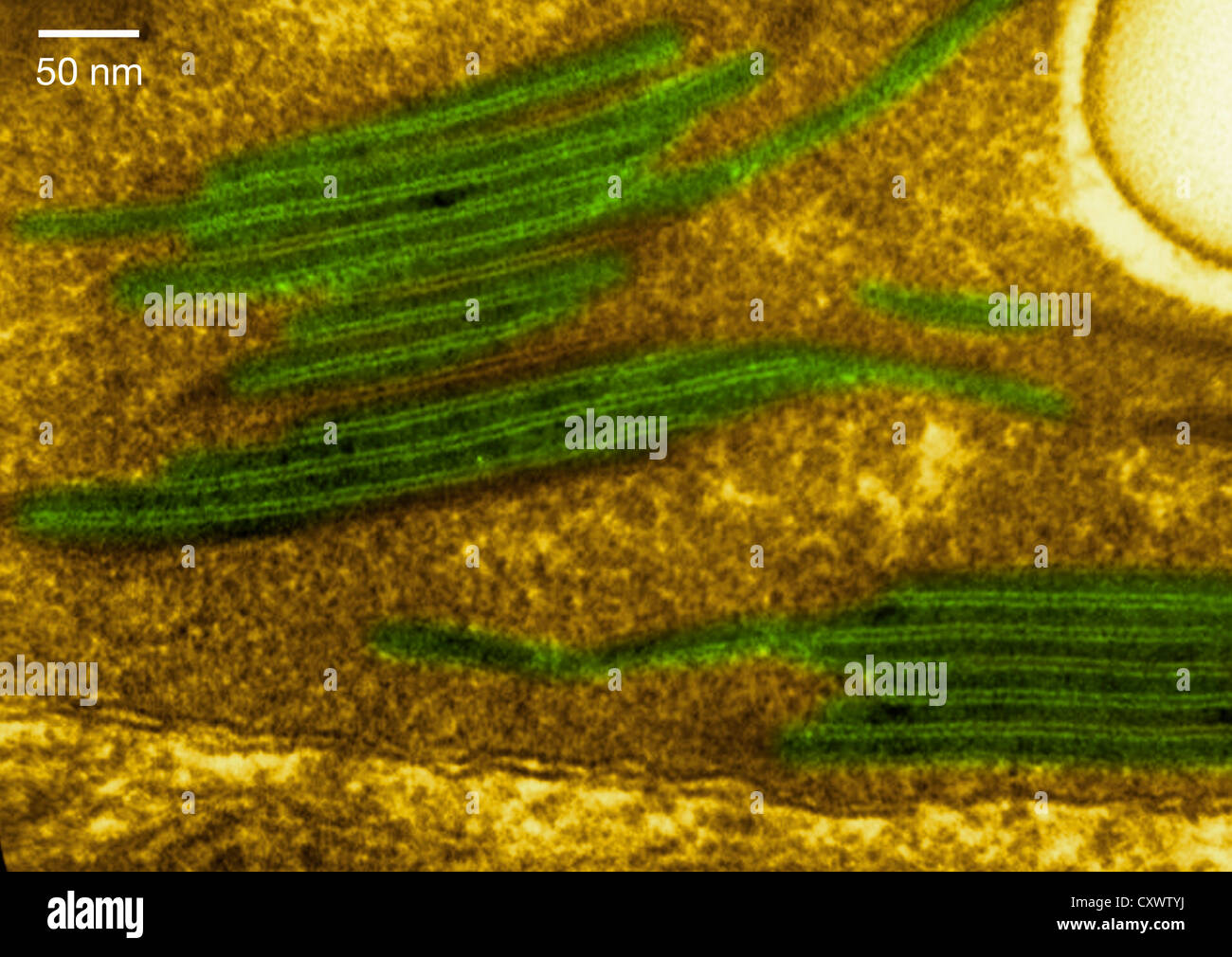 High magnification micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-high-magnification-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970182.html
High magnification micrograph of a chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-high-magnification-micrograph-of-a-chloroplast-50970182.htmlRFCXWTYJ–High magnification micrograph of a chloroplast
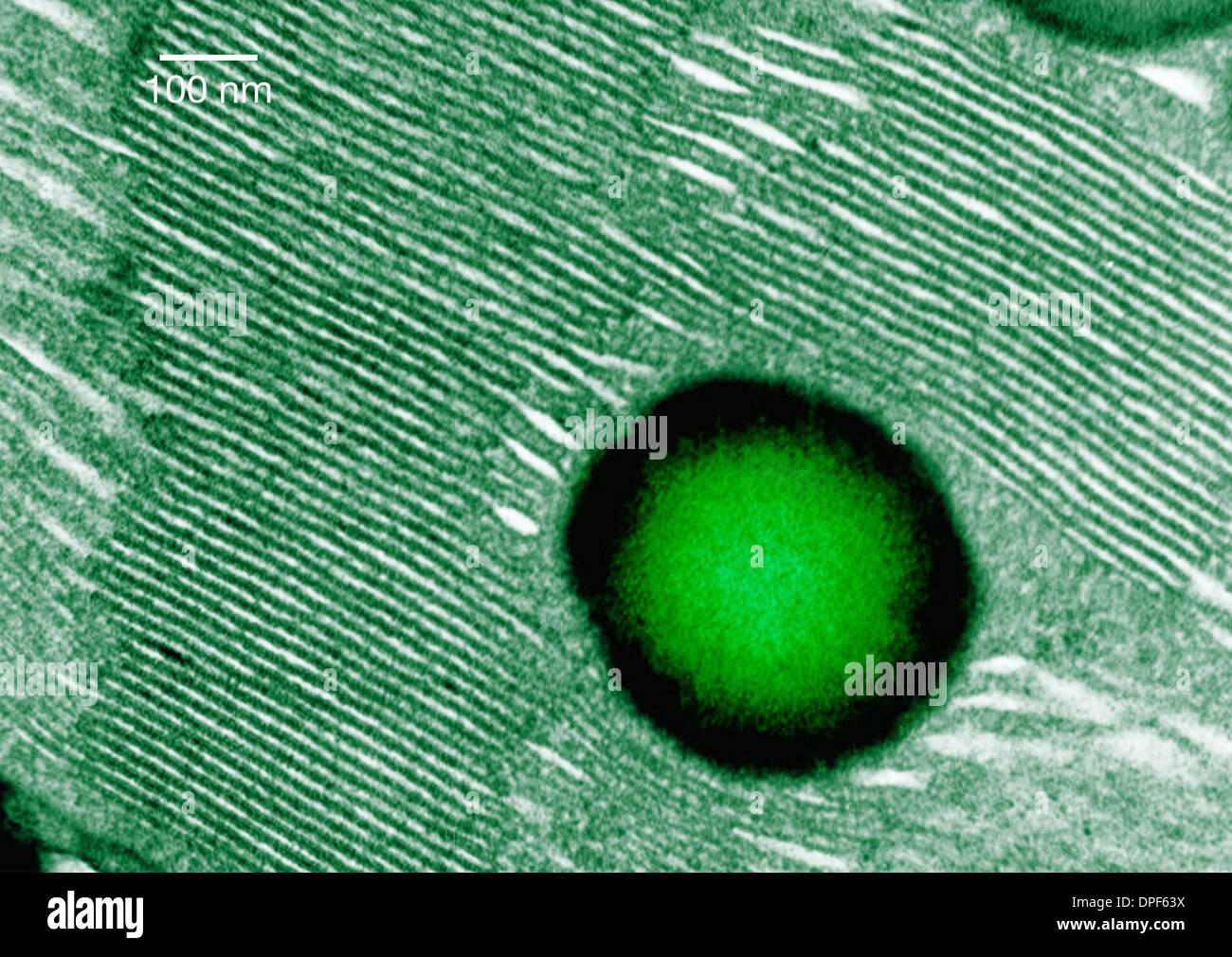
 Scanning electron micrograph of algae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-algae-50970172.html
Scanning electron micrograph of algae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-algae-50970172.htmlRFCXWTY8–Scanning electron micrograph of algae
 Archive image from page 161 of The cytoplasm of the plant. The cytoplasm of the plant cell cytoplasmofplant00guil Year: 1941 Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â â¢MsV 4f' 3 ii >i Mi# Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-161-of-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-cytoplasmofplant00guil-year-1941-chapter-xiv-development-of-the-vacuolar-system-first-stages-in-development-the-starting-point-of-the-recent-discoveries-on-the-question-of-the-development-of-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-was-an-observation-made-by-us-on-the-mode-of-formation-of-anthocyanin-pigment-in-teeth-of-leaflets-from-the-rose-bud-we-noticed-that-the-pigment-begins-to-form-at-the-extremity-of-the-tooth-in-examining-a-tooth-from-tip-to-base-all-the-phases-in-a-msv-4f-3-ii-gti-mi-image259463031.html
Archive image from page 161 of The cytoplasm of the plant. The cytoplasm of the plant cell cytoplasmofplant00guil Year: 1941 Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â â¢MsV 4f' 3 ii >i Mi# Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/archive-image-from-page-161-of-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-cytoplasmofplant00guil-year-1941-chapter-xiv-development-of-the-vacuolar-system-first-stages-in-development-the-starting-point-of-the-recent-discoveries-on-the-question-of-the-development-of-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-was-an-observation-made-by-us-on-the-mode-of-formation-of-anthocyanin-pigment-in-teeth-of-leaflets-from-the-rose-bud-we-noticed-that-the-pigment-begins-to-form-at-the-extremity-of-the-tooth-in-examining-a-tooth-from-tip-to-base-all-the-phases-in-a-msv-4f-3-ii-gti-mi-image259463031.htmlRMW23FMR–Archive image from page 161 of The cytoplasm of the plant. The cytoplasm of the plant cell cytoplasmofplant00guil Year: 1941 Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â â¢MsV 4f' 3 ii >i Mi#
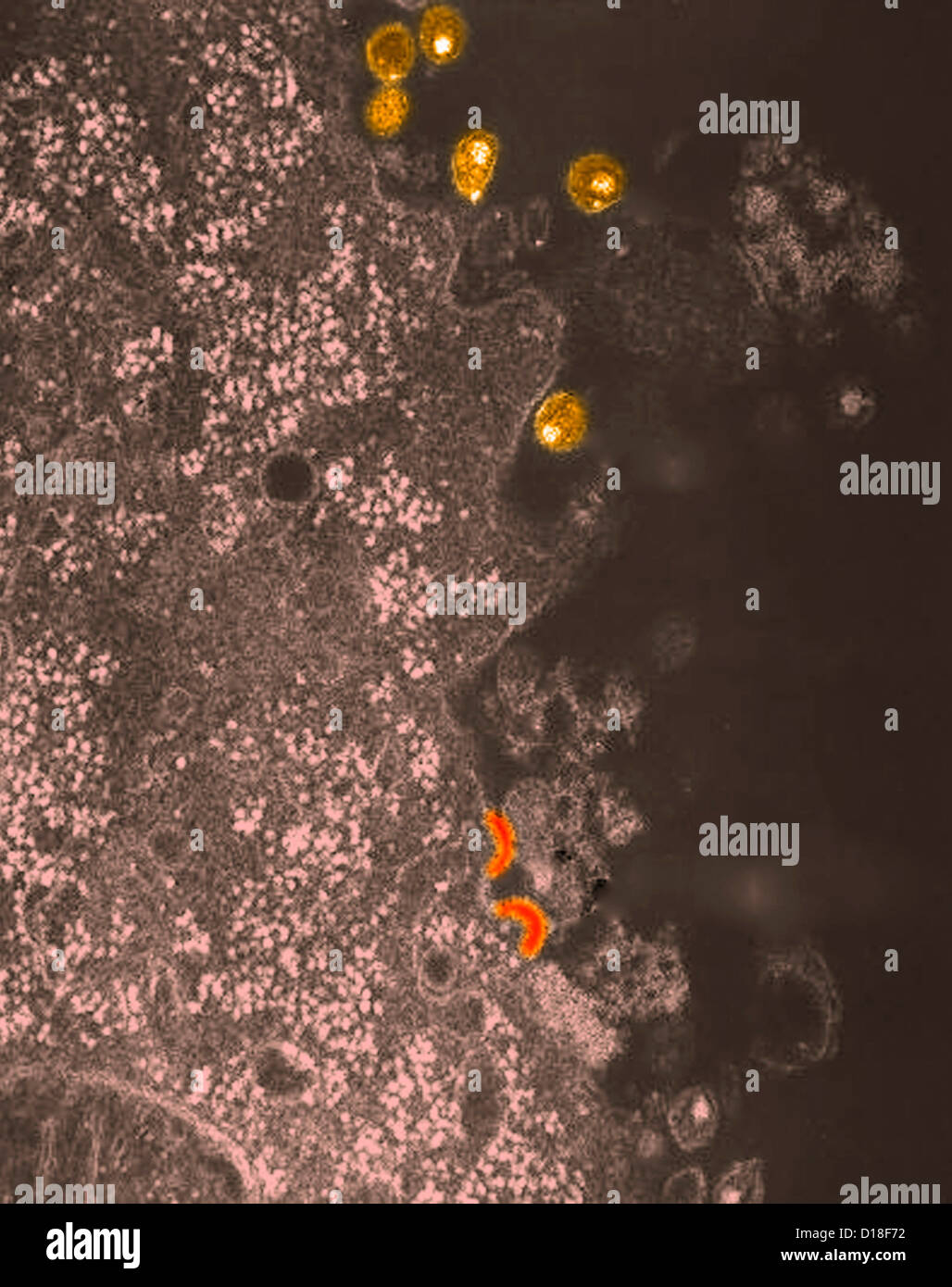 Electron micrograph of HIV virus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-hiv-virus-52433334.html
Electron micrograph of HIV virus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-hiv-virus-52433334.htmlRFD18F72–Electron micrograph of HIV virus
 . The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in the cell. There is between the young stages of the vacuo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-159-the-vacuolar-system-or-alcohol-is-stained-deeply-red-by-aniline-blue-or-violet-basic-dyes-as-well-as-by-haematein-it-consequently-shows-a-whole-series-of-histochemical-reactions-which-are-very-well-known-and-are-very-different-from-those-of-the-chondriosomes-it-is-therefore-well-established-that-there-does-not-exist-the-slightest-relation-between-the-chondriome-and-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-they-are-two-independent-systems-which-are-coexistent-in-the-cell-there-is-between-the-young-stages-of-the-vacuo-image231803592.html
. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in the cell. There is between the young stages of the vacuo Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-159-the-vacuolar-system-or-alcohol-is-stained-deeply-red-by-aniline-blue-or-violet-basic-dyes-as-well-as-by-haematein-it-consequently-shows-a-whole-series-of-histochemical-reactions-which-are-very-well-known-and-are-very-different-from-those-of-the-chondriosomes-it-is-therefore-well-established-that-there-does-not-exist-the-slightest-relation-between-the-chondriome-and-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-they-are-two-independent-systems-which-are-coexistent-in-the-cell-there-is-between-the-young-stages-of-the-vacuo-image231803592.htmlRMRD3FRM–. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV — 159 The Vacuolar System or alcohol, is stained deeply red by aniline blue or violet basic dyes, as well as by haematein. It consequently shows a whole series of histochemical reactions which are very well known and are very different from those of the chondriosomes. It is, therefore, well established that there does not exist the slightest relation between the chondriome and the vacuolar sys- tem; they are two independent systems which are coexistent in the cell. There is between the young stages of the vacuo
 . The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids axe by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swifte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-natural-history-of-the-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-axe-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-of-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asunder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swifte-image216390257.html
. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids axe by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swifte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-natural-history-of-the-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-axe-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-of-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asunder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swifte-image216390257.htmlRMPG1BYD–. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids axe by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swifte
 Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image330454676.html
Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image330454676.htmlRF2A5HE8M–Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design.
 Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image327404890.html
Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heavy-high-voltage-electric-power-transmission-cell-tower-radio-antenna-broadcast-steel-beam-tower-cellular-antenna-industrial-energy-power-design-image327404890.htmlRF2A0JG7P–Heavy High Voltage Electric Power Transmission Cell Tower radio Antenna. Broadcast Steel beam tower cellular antenna. Industrial energy power design.
 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134944073.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134944073.htmlRMHRF6F5–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
 Scanning electron micrograph of algae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-algae-50970181.html
Scanning electron micrograph of algae Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-scanning-electron-micrograph-of-algae-50970181.htmlRFCXWTYH–Scanning electron micrograph of algae
 Electron micrograph of HIV virus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-hiv-virus-52433364.html
Electron micrograph of HIV virus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-electron-micrograph-of-hiv-virus-52433364.htmlRFD18F84–Electron micrograph of HIV virus
 . The natural history of the farm : a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature . Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swif Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-natural-history-of-the-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-are-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-of-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asunder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swif-image232097592.html
. The natural history of the farm : a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature . Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swif Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-natural-history-of-the-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-are-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-of-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asunder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swif-image232097592.htmlRMRDGXRM–. The natural history of the farm : a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature . Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swif
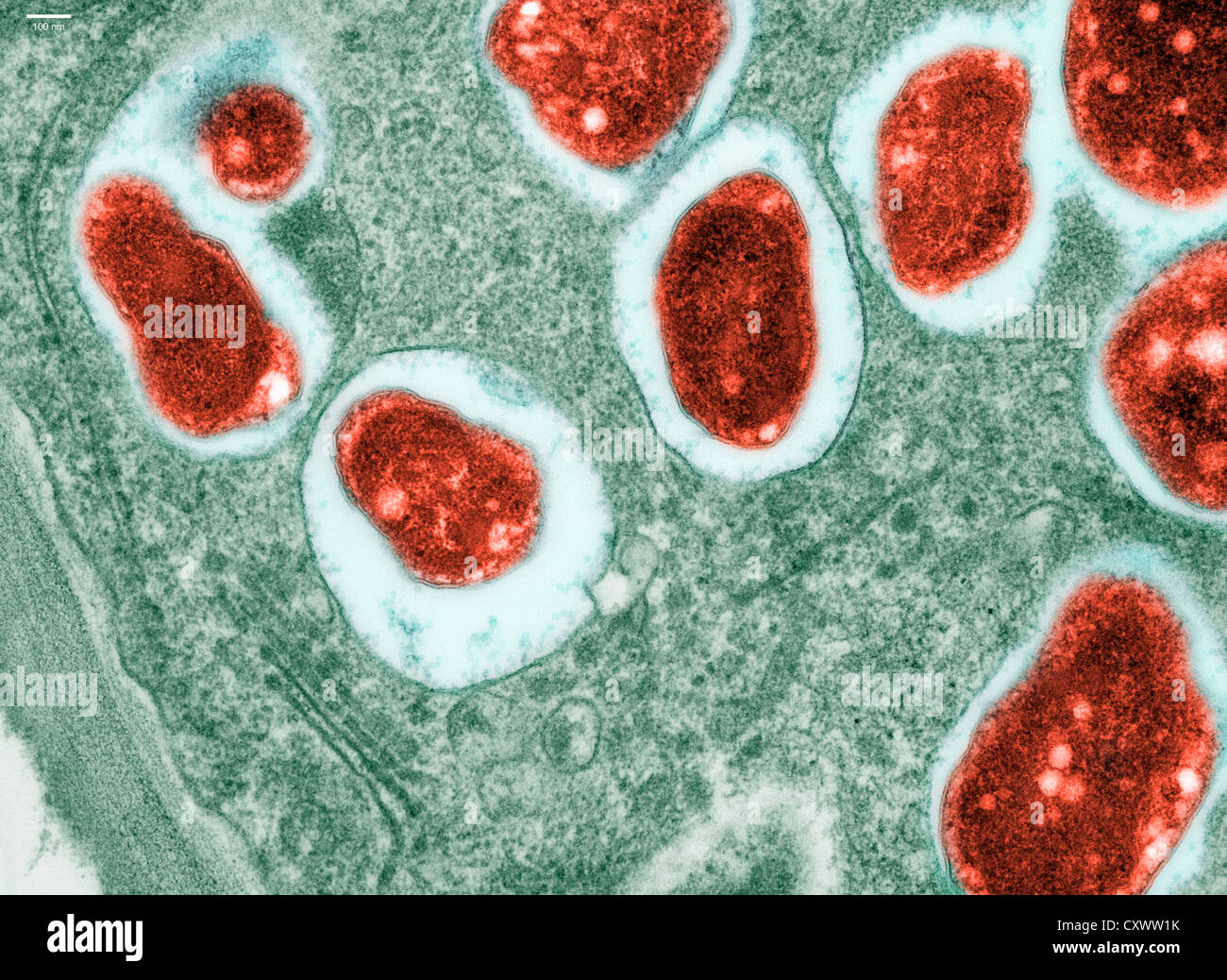 Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970239.html
Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970239.htmlRFCXWW1K–Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root
 . The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 HISTORY OF FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower o f stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asimder. Such plants are the algae: and these abound in the swiftest waters. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-history-of-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-are-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-o-f-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asimder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swiftest-waters-image216450690.html
. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 HISTORY OF FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower o f stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asimder. Such plants are the algae: and these abound in the swiftest waters. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-history-of-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-are-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-o-f-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asimder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swiftest-waters-image216450690.htmlRMPG451P–. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 HISTORY OF FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower o f stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asimder. Such plants are the algae: and these abound in the swiftest waters.
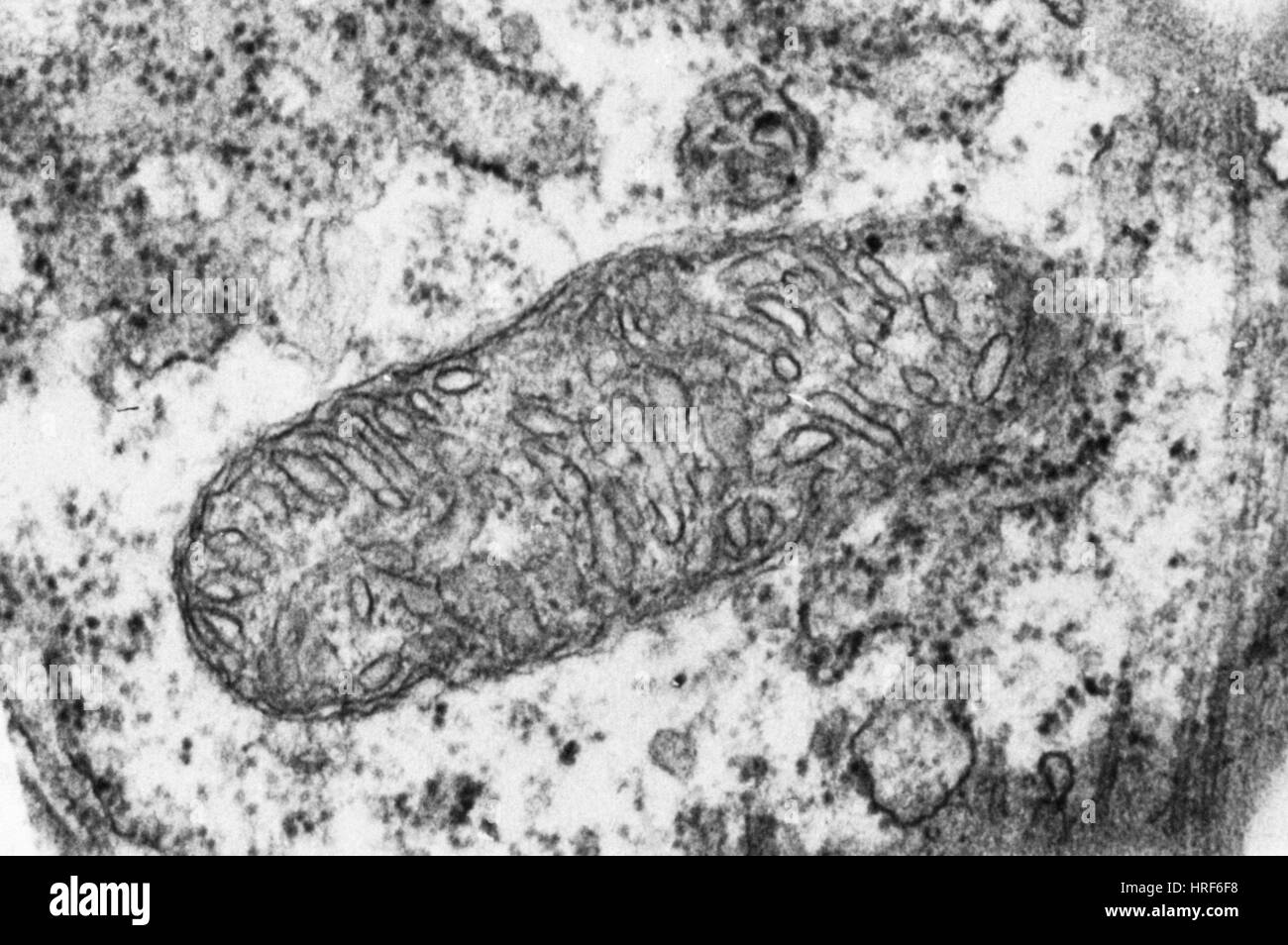 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134944076.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134944076.htmlRMHRF6F8–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
 . The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids axe by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swifte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-natural-history-of-the-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-axe-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-of-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asunder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swifte-image232005735.html
. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids axe by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swifte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-natural-history-of-the-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-axe-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-of-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asunder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swifte-image232005735.htmlRMRDCNK3–. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 NATURAL HISTORY OF THE FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids axe by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower of stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asunder. Such plants are the algae; and these abound in the swifte
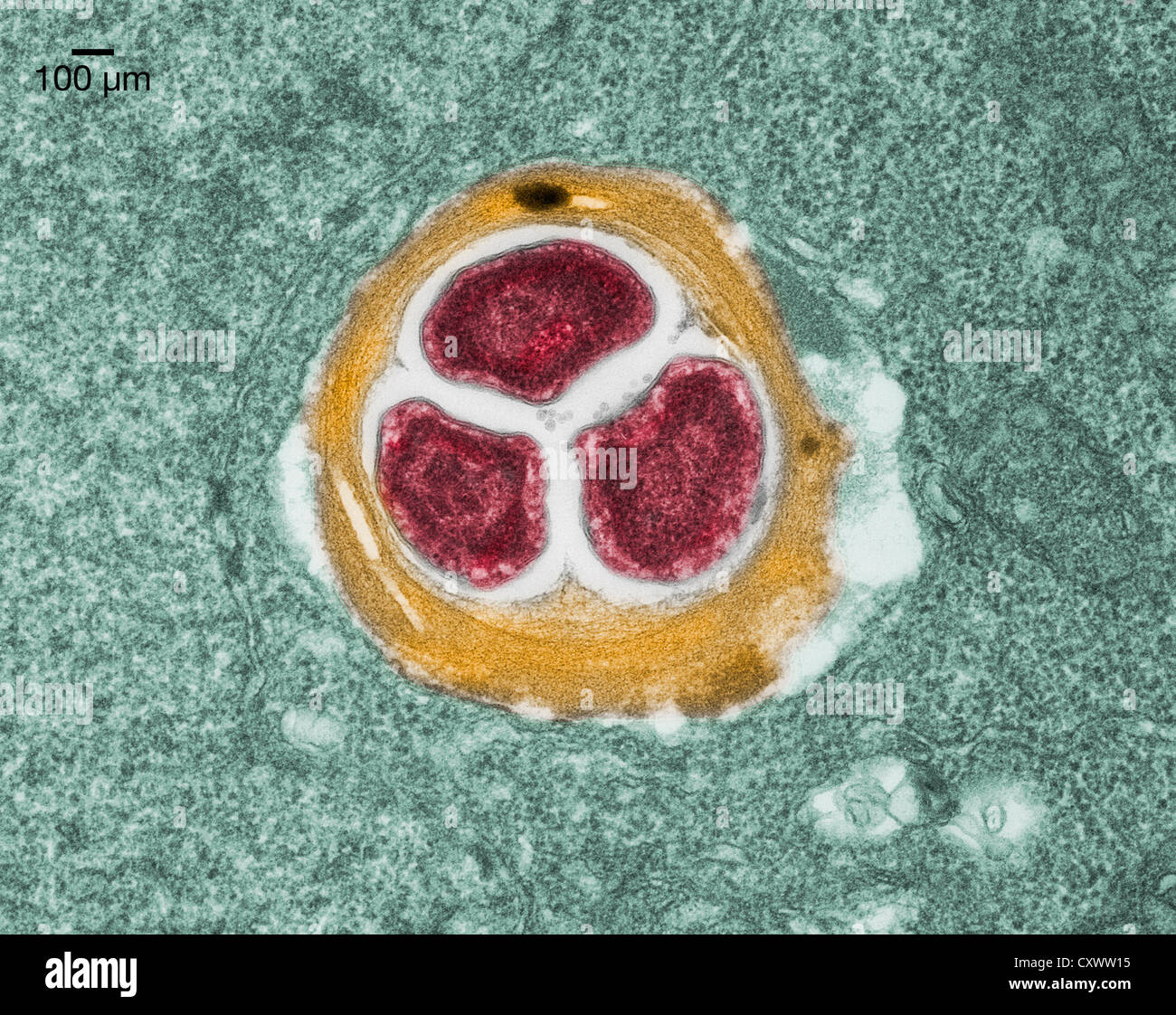 Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970225.html
Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970225.htmlRFCXWW15–Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root
 . The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â ^â¢M^sV 4f'^ 3 ii^ ^>i ^Mi!^#. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned pa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-development-of-the-vacuolar-system-first-stages-in-development-the-starting-point-of-the-recent-discoveries-on-the-question-of-the-development-of-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-was-an-observation-made-by-us-on-the-mode-of-formation-of-anthocyanin-pigment-in-teeth-of-leaflets-from-the-rose-bud-we-noticed-that-the-pigment-begins-to-form-at-the-extremity-of-the-tooth-in-examining-a-tooth-from-tip-to-base-all-the-phases-in-a-msv-4f-3-ii-gti-mi!-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-pa-image216167307.html
. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â ^â¢M^sV 4f'^ 3 ii^ ^>i ^Mi!^#. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned pa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-development-of-the-vacuolar-system-first-stages-in-development-the-starting-point-of-the-recent-discoveries-on-the-question-of-the-development-of-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-was-an-observation-made-by-us-on-the-mode-of-formation-of-anthocyanin-pigment-in-teeth-of-leaflets-from-the-rose-bud-we-noticed-that-the-pigment-begins-to-form-at-the-extremity-of-the-tooth-in-examining-a-tooth-from-tip-to-base-all-the-phases-in-a-msv-4f-3-ii-gti-mi!-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-pa-image216167307.htmlRMPFK7GY–. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â ^â¢M^sV 4f'^ 3 ii^ ^>i ^Mi!^#. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned pa
 Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-134945620.html
Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-134945620.htmlRMHRF8EC–Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM
 . The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 HISTORY OF FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower o f stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asimder. Such plants are the algae: and these abound in the swiftest waters. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-history-of-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-are-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-o-f-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asimder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swiftest-waters-image232034607.html
. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 HISTORY OF FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower o f stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asimder. Such plants are the algae: and these abound in the swiftest waters. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-natural-history-of-the-farm-a-guide-to-the-practical-study-of-the-sources-of-our-living-in-wild-nature-natural-history-34-history-of-farm-the-plant-life-of-the-stream-the-rapids-are-by-no-means-destitute-of-life-given-natural-waters-a-tem-perature-above-freezing-light-and-air-plants-will-grow-any-where-here-they-must-be-such-plants-as-can-withstand-the-shower-o-f-stones-that-every-flood-brings-down-upon-them-they-must-be-simply-organized-plants-that-are-not-killed-when-their-cell-masses-are-broken-asimder-such-plants-are-the-algae-and-these-abound-in-the-swiftest-waters-image232034607.htmlRMRDE2E7–. The natural history of the farm; a guide to the practical study of the sources of our living in wild nature. Natural history. 34 HISTORY OF FARM. THE PLANT LIFE OF THE STREAM The rapids are by no means destitute of life. Given natural waters, a tem- perature above freezing, light and air, plants will grow any- where: here, they must be such plants as can withstand the shower o f stones that every flood brings down upon them. They must be simply organized plants, that are not killed when their cell masses are broken asimder. Such plants are the algae: and these abound in the swiftest waters.
 Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970251.html
Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970251.htmlRFCXWW23–Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root
 Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-134945447.html
Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-134945447.htmlRMHRF887–Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM
 . Elementary biology; an introduction to the science of life. Biology. NEW ORGANISMS 293 340. Spores. The cells of yeast change their behavior when the yeast is growing in a solution that is gradually evaporat- ing, or when the food in the solution is gradualh' being used up, or when it is exposed to an ex- treme change in tem- perature. It is often found under such un- favorable conditions that the yeast plant will produce peculiar kinds of cells (see Fig. 124). A special cell like those described in the yeast (that is, a cell capable of continu- ing the growth of the plant from which it is d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elementary-biology-an-introduction-to-the-science-of-life-biology-new-organisms-293-340-spores-the-cells-of-yeast-change-their-behavior-when-the-yeast-is-growing-in-a-solution-that-is-gradually-evaporat-ing-or-when-the-food-in-the-solution-is-gradualh-being-used-up-or-when-it-is-exposed-to-an-ex-treme-change-in-tem-perature-it-is-often-found-under-such-un-favorable-conditions-that-the-yeast-plant-will-produce-peculiar-kinds-of-cells-see-fig-124-a-special-cell-like-those-described-in-the-yeast-that-is-a-cell-capable-of-continu-ing-the-growth-of-the-plant-from-which-it-is-d-image231775987.html
. Elementary biology; an introduction to the science of life. Biology. NEW ORGANISMS 293 340. Spores. The cells of yeast change their behavior when the yeast is growing in a solution that is gradually evaporat- ing, or when the food in the solution is gradualh' being used up, or when it is exposed to an ex- treme change in tem- perature. It is often found under such un- favorable conditions that the yeast plant will produce peculiar kinds of cells (see Fig. 124). A special cell like those described in the yeast (that is, a cell capable of continu- ing the growth of the plant from which it is d Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/elementary-biology-an-introduction-to-the-science-of-life-biology-new-organisms-293-340-spores-the-cells-of-yeast-change-their-behavior-when-the-yeast-is-growing-in-a-solution-that-is-gradually-evaporat-ing-or-when-the-food-in-the-solution-is-gradualh-being-used-up-or-when-it-is-exposed-to-an-ex-treme-change-in-tem-perature-it-is-often-found-under-such-un-favorable-conditions-that-the-yeast-plant-will-produce-peculiar-kinds-of-cells-see-fig-124-a-special-cell-like-those-described-in-the-yeast-that-is-a-cell-capable-of-continu-ing-the-growth-of-the-plant-from-which-it-is-d-image231775987.htmlRMRD28HR–. Elementary biology; an introduction to the science of life. Biology. NEW ORGANISMS 293 340. Spores. The cells of yeast change their behavior when the yeast is growing in a solution that is gradually evaporat- ing, or when the food in the solution is gradualh' being used up, or when it is exposed to an ex- treme change in tem- perature. It is often found under such un- favorable conditions that the yeast plant will produce peculiar kinds of cells (see Fig. 124). A special cell like those described in the yeast (that is, a cell capable of continu- ing the growth of the plant from which it is d
 Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970237.html
Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-transmission-electron-micrograph-of-soy-bean-root-50970237.htmlRFCXWW1H–Transmission electron micrograph of soy bean root
 Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-135018961.html
Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-135018961.htmlRMHRJJ1N–Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM
 . Plant anatomy from the standpoint of the development and functions of the tissues, and handbook of micro-technic. Plant anatomy. 15° CONSTRUCTION OF PLANT'S FOOD the temperature must fall almost or quite to o° C; and cool- temperate, arctic and alpine plants continue photosynthesizing until they become frozen. In regard to the maximum tem- perature, plants in general cease photosynthesizing after long exposure to approximately 38° C. Photosynthesis in the Lower Plants.—In the simpler Algae where each individual consists of a single cell, a chain of cells forming a filament, or a thin lamina Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plant-anatomy-from-the-standpoint-of-the-development-and-functions-of-the-tissues-and-handbook-of-micro-technic-plant-anatomy-15-construction-of-plants-food-the-temperature-must-fall-almost-or-quite-to-o-c-and-cool-temperate-arctic-and-alpine-plants-continue-photosynthesizing-until-they-become-frozen-in-regard-to-the-maximum-tem-perature-plants-in-general-cease-photosynthesizing-after-long-exposure-to-approximately-38-c-photosynthesis-in-the-lower-plantsin-the-simpler-algae-where-each-individual-consists-of-a-single-cell-a-chain-of-cells-forming-a-filament-or-a-thin-lamina-image232411129.html
. Plant anatomy from the standpoint of the development and functions of the tissues, and handbook of micro-technic. Plant anatomy. 15° CONSTRUCTION OF PLANT'S FOOD the temperature must fall almost or quite to o° C; and cool- temperate, arctic and alpine plants continue photosynthesizing until they become frozen. In regard to the maximum tem- perature, plants in general cease photosynthesizing after long exposure to approximately 38° C. Photosynthesis in the Lower Plants.—In the simpler Algae where each individual consists of a single cell, a chain of cells forming a filament, or a thin lamina Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/plant-anatomy-from-the-standpoint-of-the-development-and-functions-of-the-tissues-and-handbook-of-micro-technic-plant-anatomy-15-construction-of-plants-food-the-temperature-must-fall-almost-or-quite-to-o-c-and-cool-temperate-arctic-and-alpine-plants-continue-photosynthesizing-until-they-become-frozen-in-regard-to-the-maximum-tem-perature-plants-in-general-cease-photosynthesizing-after-long-exposure-to-approximately-38-c-photosynthesis-in-the-lower-plantsin-the-simpler-algae-where-each-individual-consists-of-a-single-cell-a-chain-of-cells-forming-a-filament-or-a-thin-lamina-image232411129.htmlRMRE36ND–. Plant anatomy from the standpoint of the development and functions of the tissues, and handbook of micro-technic. Plant anatomy. 15° CONSTRUCTION OF PLANT'S FOOD the temperature must fall almost or quite to o° C; and cool- temperate, arctic and alpine plants continue photosynthesizing until they become frozen. In regard to the maximum tem- perature, plants in general cease photosynthesizing after long exposure to approximately 38° C. Photosynthesis in the Lower Plants.—In the simpler Algae where each individual consists of a single cell, a chain of cells forming a filament, or a thin lamina
 Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-134945479.html
Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-134945479.htmlRMHRF89B–Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM
 . The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â ^â¢M^sV 4f'^ 3 ii^ ^>i ^Mi!^#. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned pa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-development-of-the-vacuolar-system-first-stages-in-development-the-starting-point-of-the-recent-discoveries-on-the-question-of-the-development-of-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-was-an-observation-made-by-us-on-the-mode-of-formation-of-anthocyanin-pigment-in-teeth-of-leaflets-from-the-rose-bud-we-noticed-that-the-pigment-begins-to-form-at-the-extremity-of-the-tooth-in-examining-a-tooth-from-tip-to-base-all-the-phases-in-a-msv-4f-3-ii-gti-mi!-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-pa-image231803626.html
. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â ^â¢M^sV 4f'^ 3 ii^ ^>i ^Mi!^#. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned pa Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cytoplasm-of-the-plant-cell-plant-cells-and-tissues-protoplasm-chapter-xiv-development-of-the-vacuolar-system-first-stages-in-development-the-starting-point-of-the-recent-discoveries-on-the-question-of-the-development-of-the-vacuolar-sys-tem-was-an-observation-made-by-us-on-the-mode-of-formation-of-anthocyanin-pigment-in-teeth-of-leaflets-from-the-rose-bud-we-noticed-that-the-pigment-begins-to-form-at-the-extremity-of-the-tooth-in-examining-a-tooth-from-tip-to-base-all-the-phases-in-a-msv-4f-3-ii-gti-mi!-please-note-that-these-images-are-extracted-from-scanned-pa-image231803626.htmlRMRD3FTX–. The cytoplasm of the plant cell. Plant cells and tissues; Protoplasm. Chapter XIV DEVELOPMENT OF THE VACUOLAR SYSTEM First stages in development:- The starting point of the recent discoveries on the question of the development of the vacuolar sys- tem was an observation made by us on the mode of formation of anthocyanin pigment in teeth of leaflets from the rose bud. We noticed that the pigment begins to form at the extremity of the tooth. In examining a tooth from tip to base, all the phases in A â ^â¢M^sV 4f'^ 3 ii^ ^>i ^Mi!^#. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned pa
 Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134944075.html
Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134944075.htmlRMHRF6F7–Plasma Membrane TEM
 Onion Root Cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-onion-root-cell-134943570.html
Onion Root Cell Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-onion-root-cell-134943570.htmlRMHRF5W6–Onion Root Cell
 Tomato Chloroplast (TEM) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-134945481.html
Tomato Chloroplast (TEM) Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-134945481.htmlRMHRF89D–Tomato Chloroplast (TEM)
 Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135021974.html
Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135021974.htmlRMHRJNWA–Tomato Chloroplast, TEM
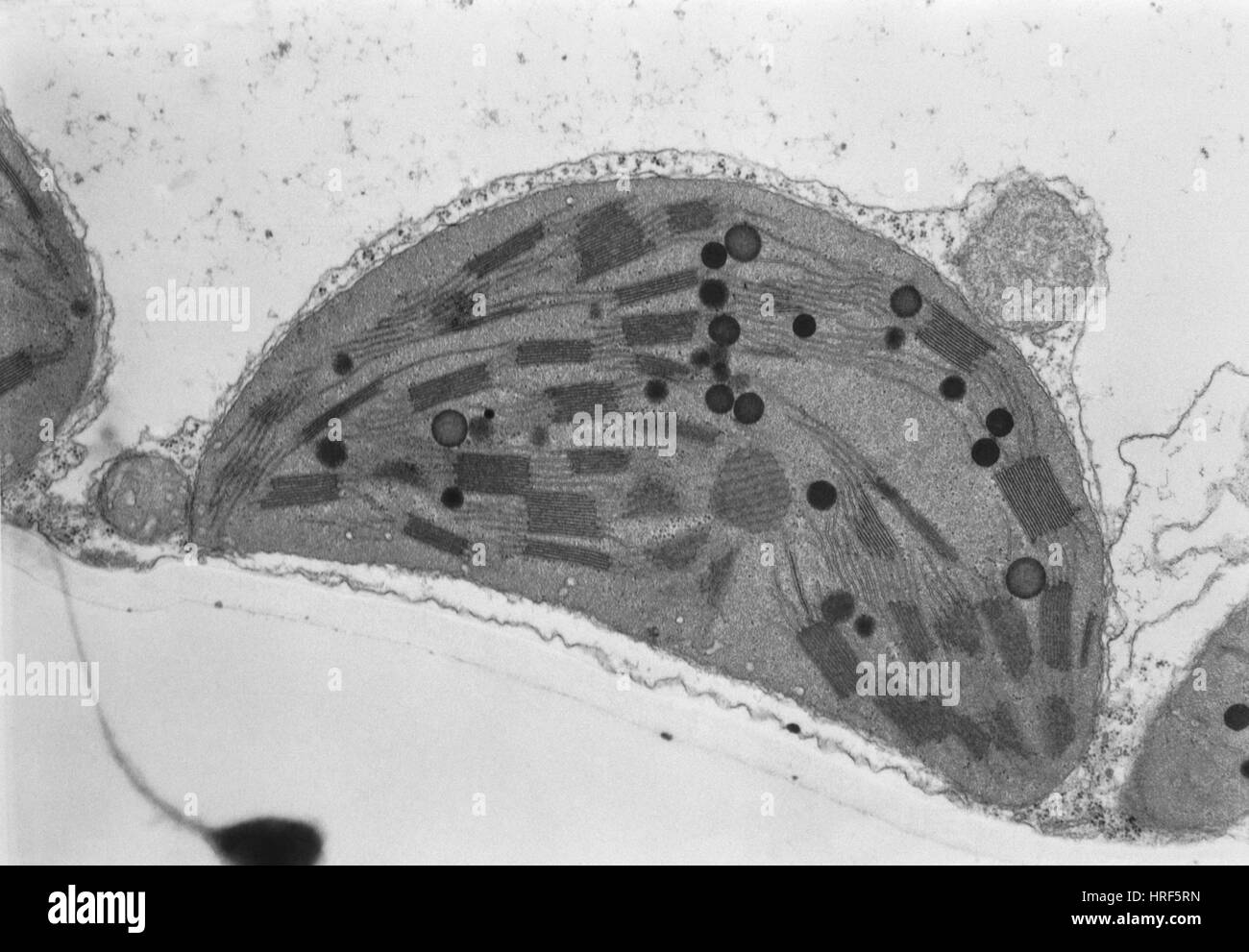 Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134943529.html
Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134943529.htmlRMHRF5RN–Chloroplast TEM
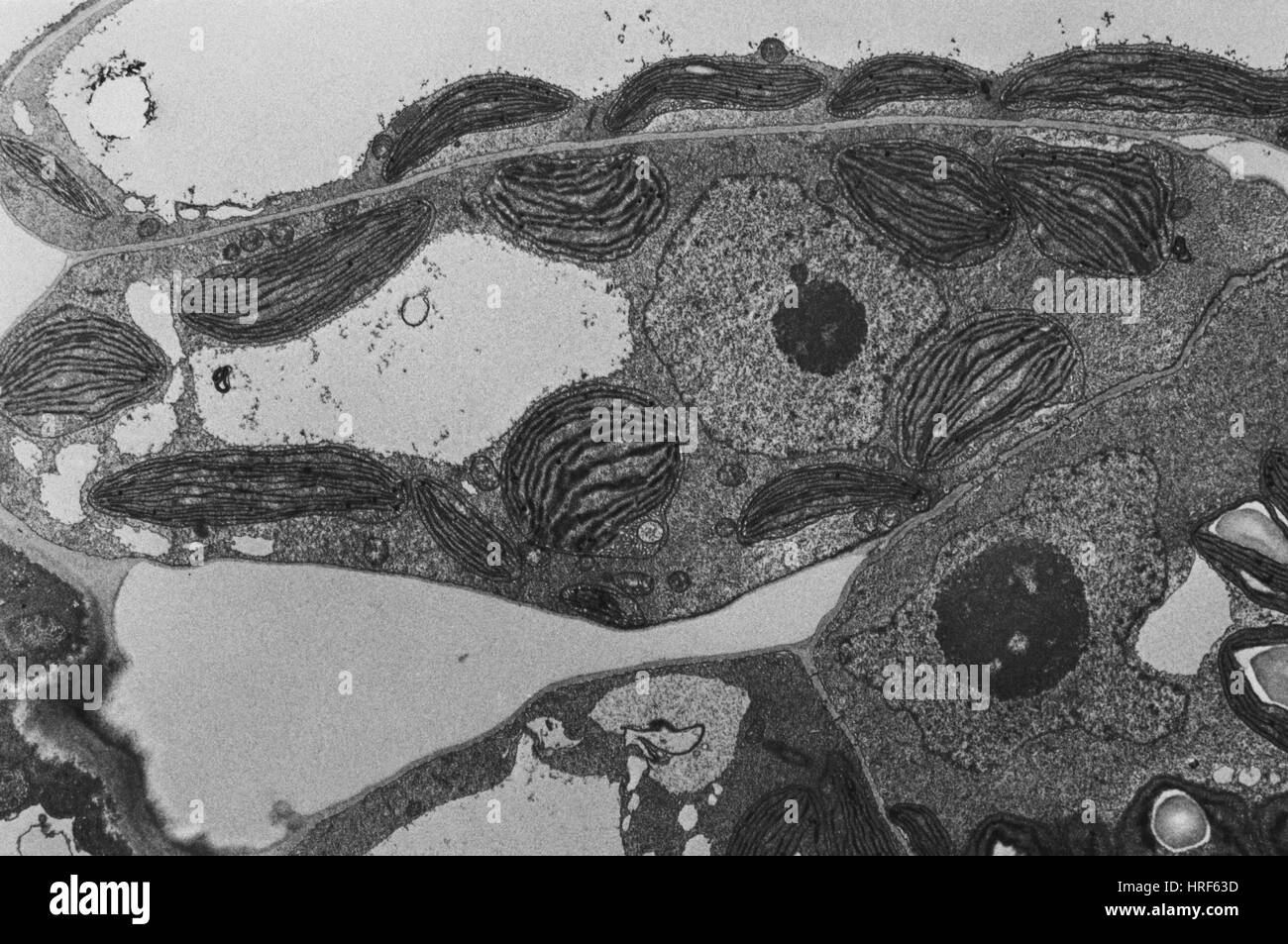 Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134943745.html
Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134943745.htmlRMHRF63D–Chloroplasts TEM
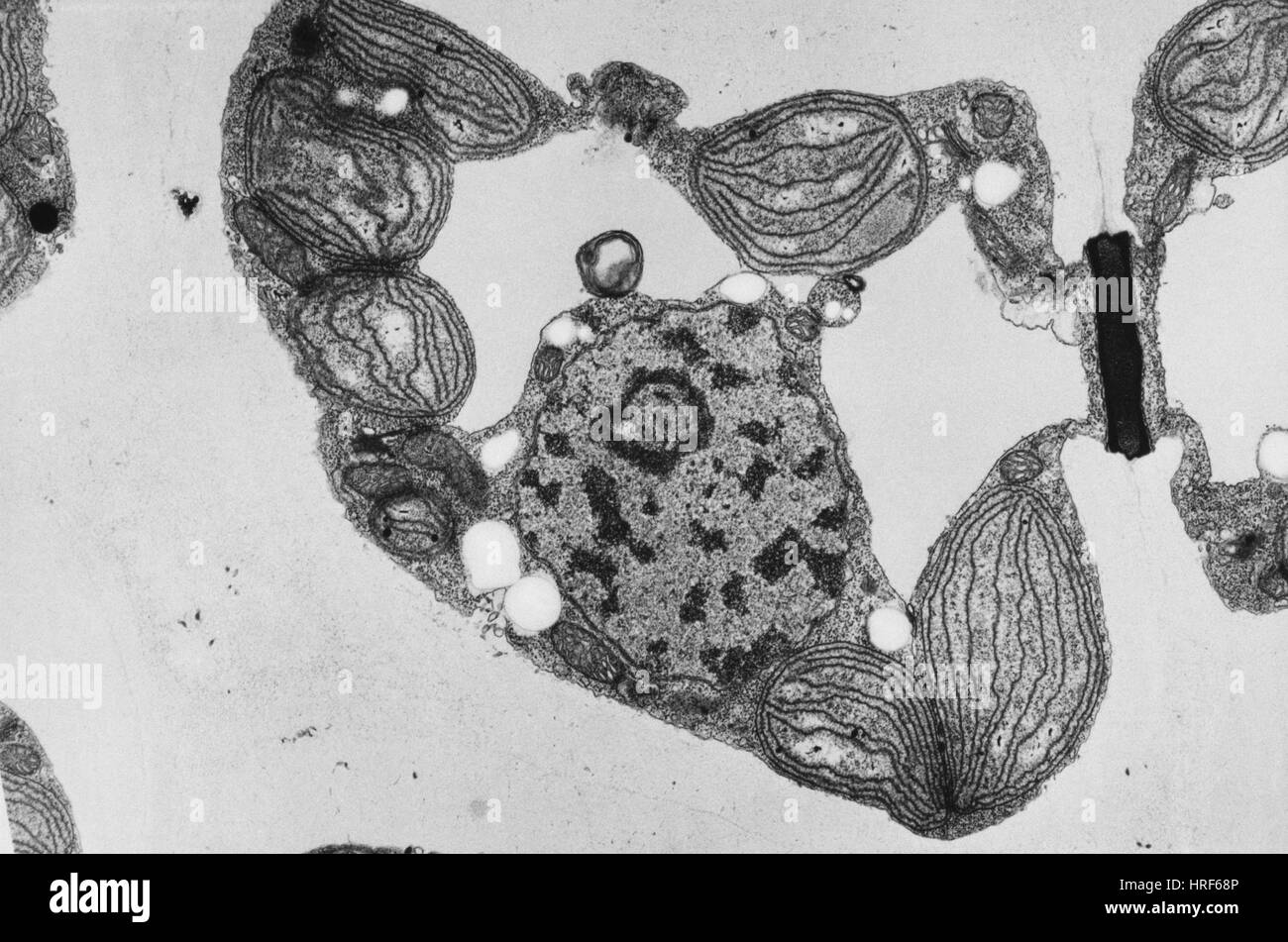 Red Algae TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-red-algae-tem-134943894.html
Red Algae TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-red-algae-tem-134943894.htmlRMHRF68P–Red Algae TEM
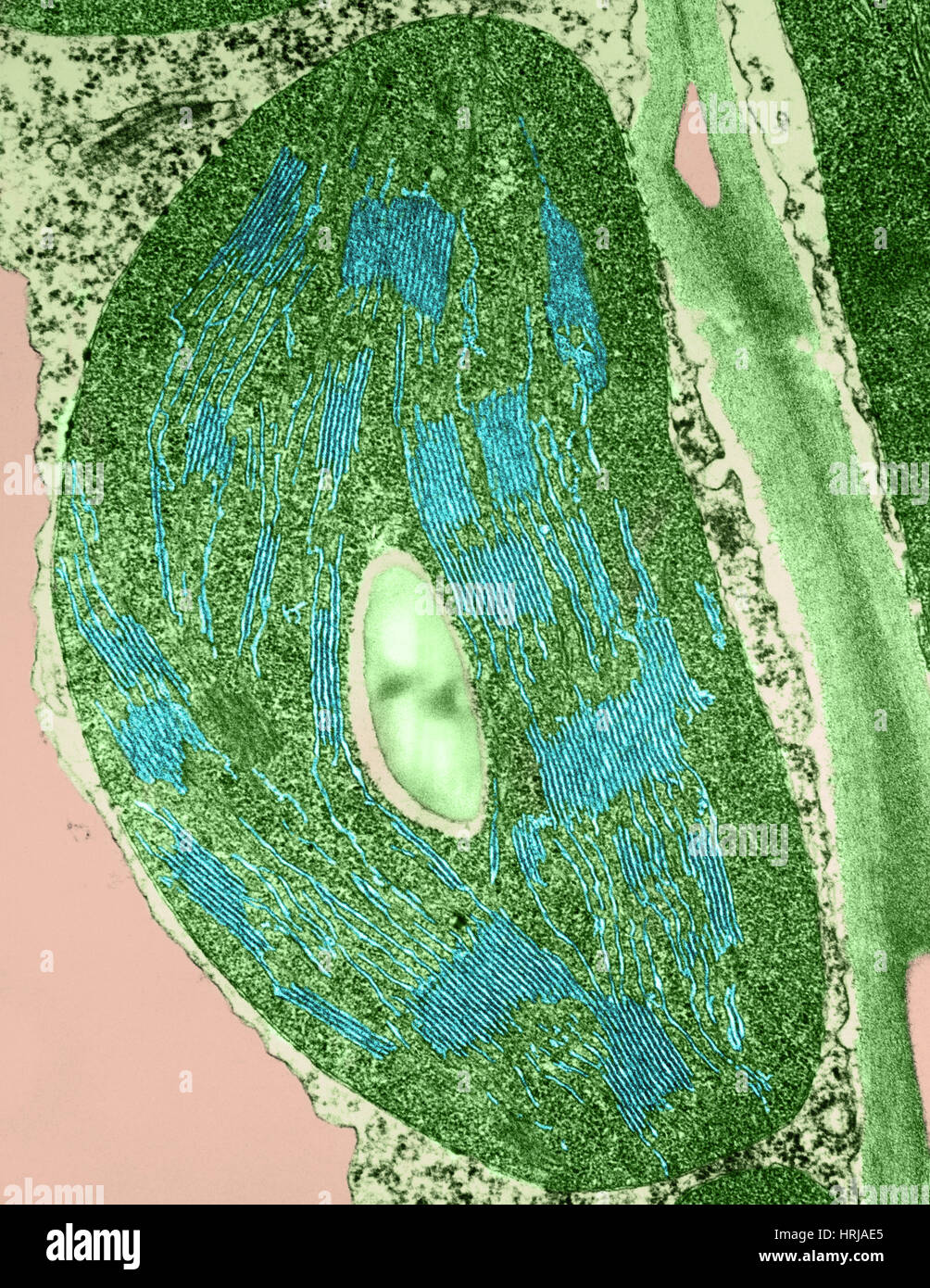 Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135013037.html
Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135013037.htmlRMHRJAE5–Tomato Chloroplast, TEM
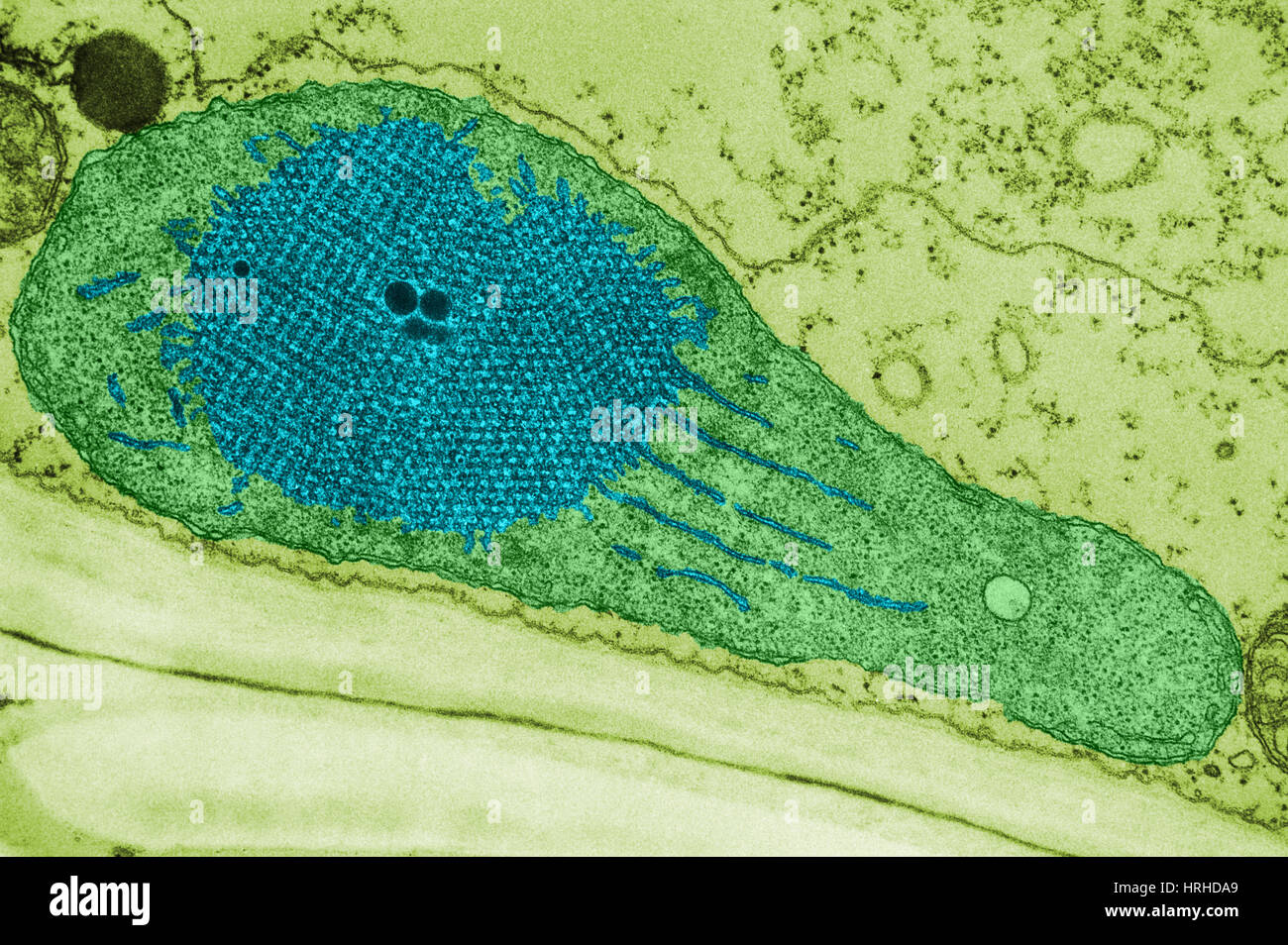 Developing Chloroplast and Etioplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-developing-chloroplast-and-etioplast-tem-134993329.html
Developing Chloroplast and Etioplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-developing-chloroplast-and-etioplast-tem-134993329.htmlRMHRHDA9–Developing Chloroplast and Etioplast TEM
 Corn Leaf Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-leaf-chloroplast-tem-135017544.html
Corn Leaf Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-leaf-chloroplast-tem-135017544.htmlRMHRJG74–Corn Leaf Chloroplast, TEM
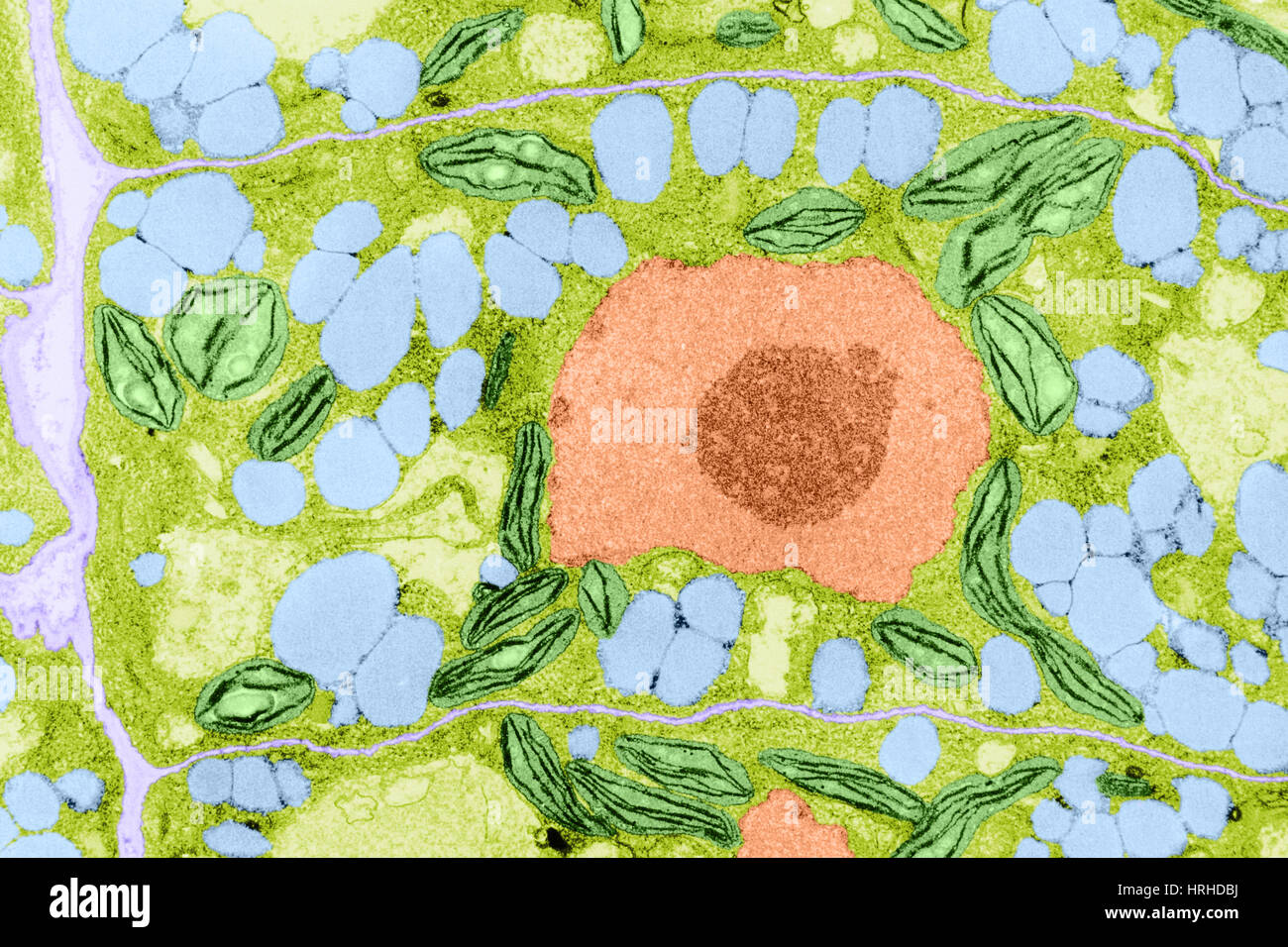 Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134993366.html
Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134993366.htmlRMHRHDBJ–Plant Cell TEM
 Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134993363.html
Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134993363.htmlRMHRHDBF–Plant Cell TEM
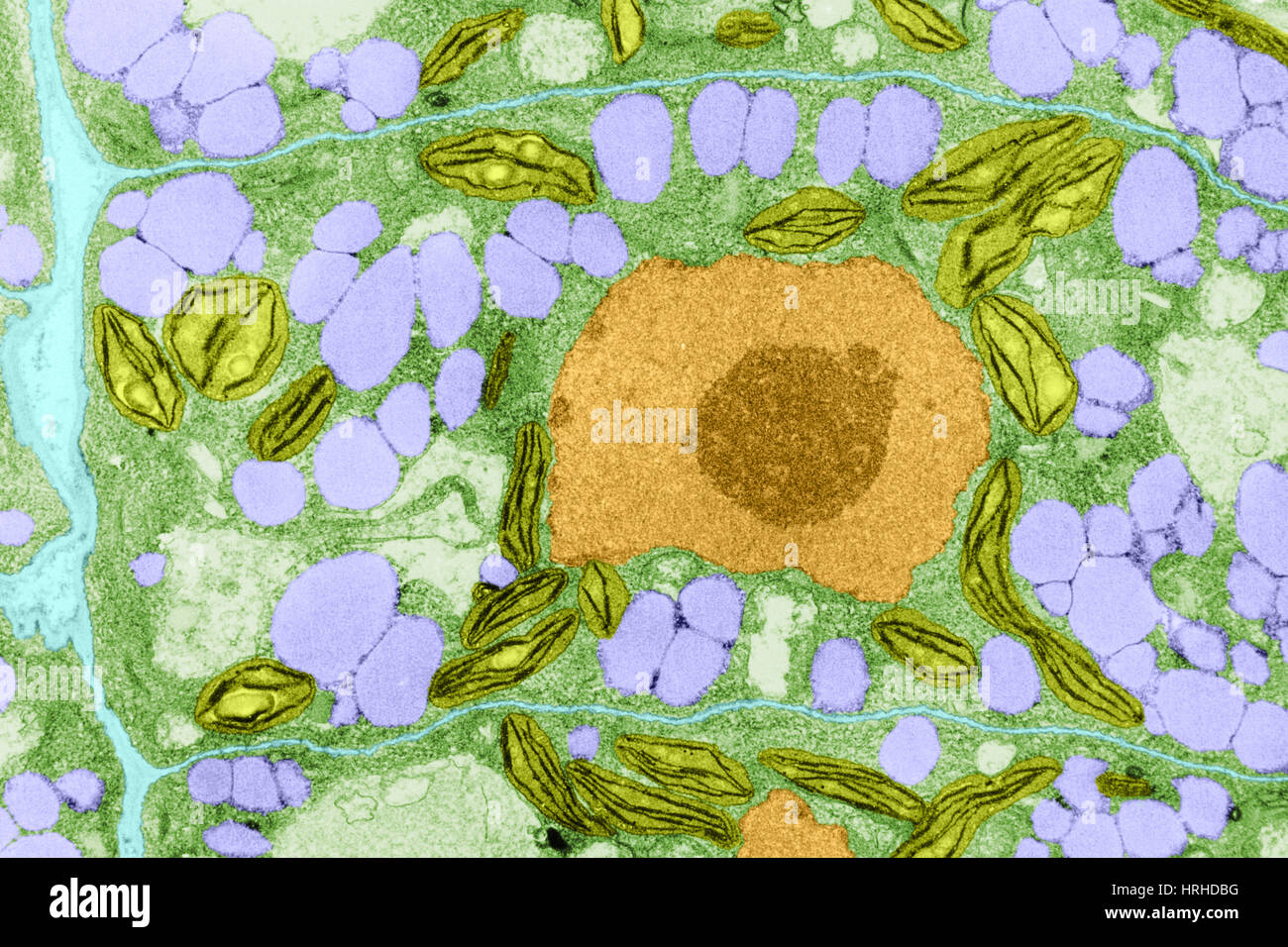 Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134993364.html
Plant Cell TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-cell-tem-134993364.htmlRMHRHDBG–Plant Cell TEM
 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134992479.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134992479.htmlRMHRHC7Y–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134992483.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134992483.htmlRMHRHC83–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
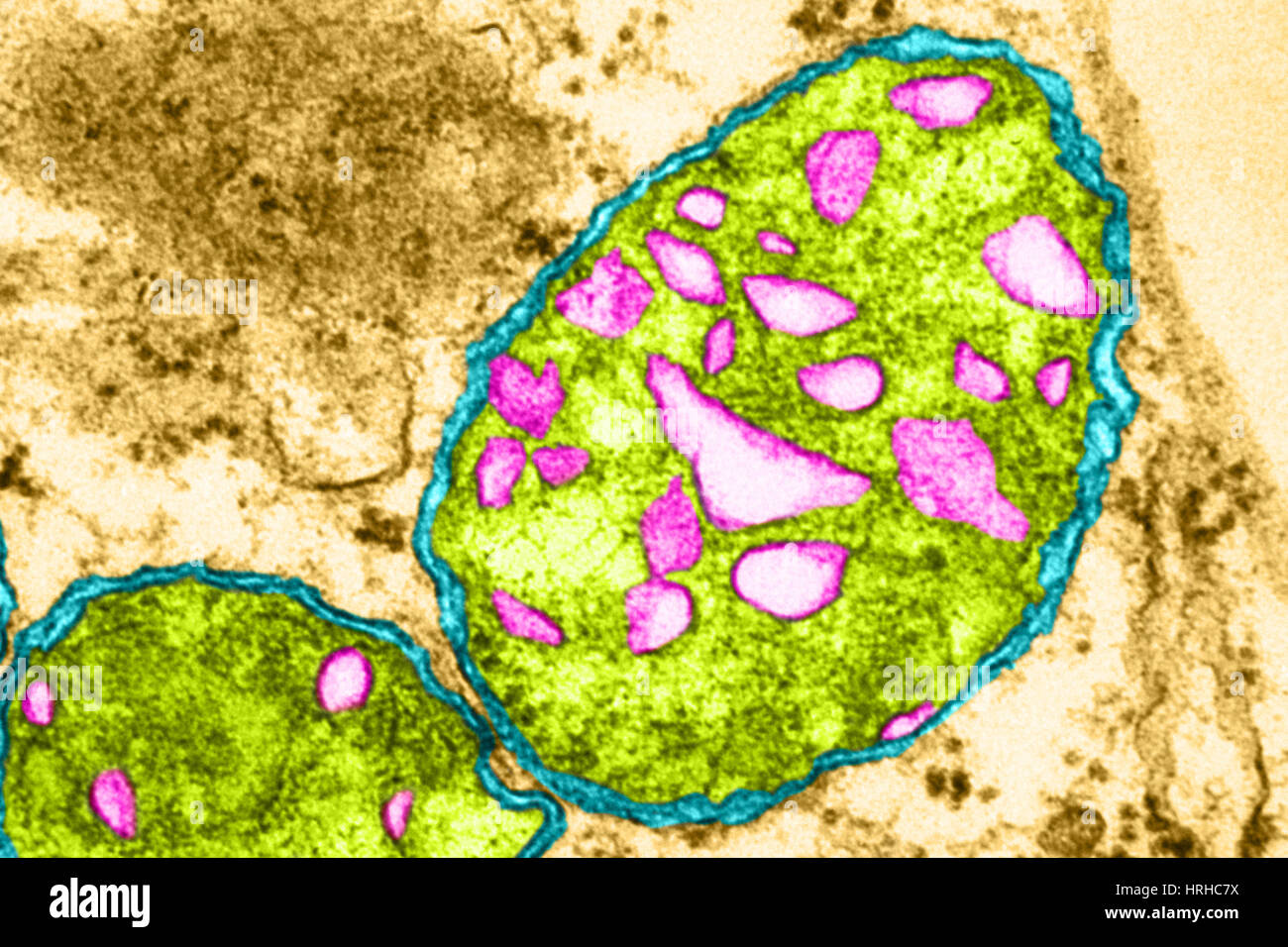 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134992478.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134992478.htmlRMHRHC7X–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
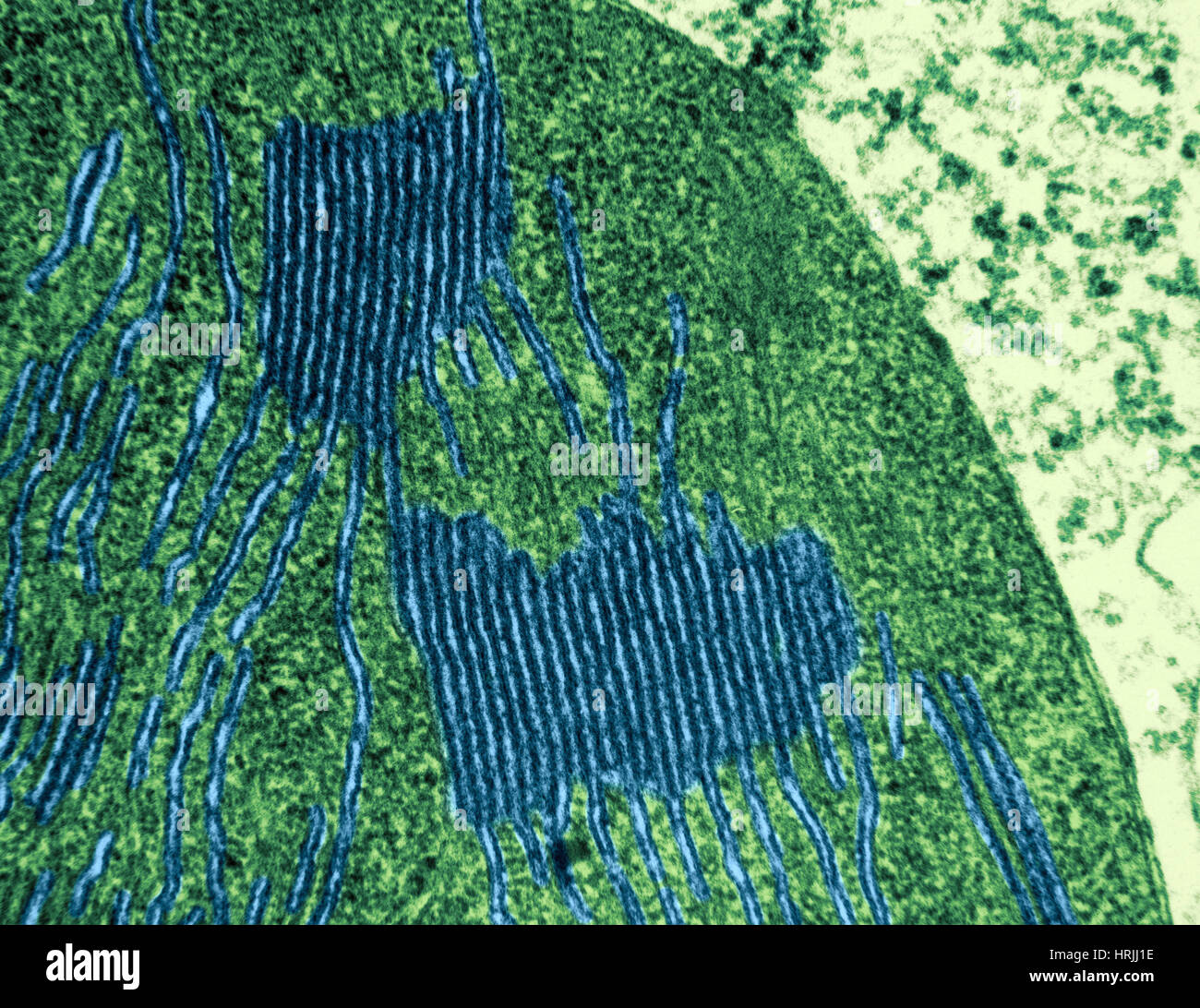 Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-135018954.html
Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-135018954.htmlRMHRJJ1E–Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM
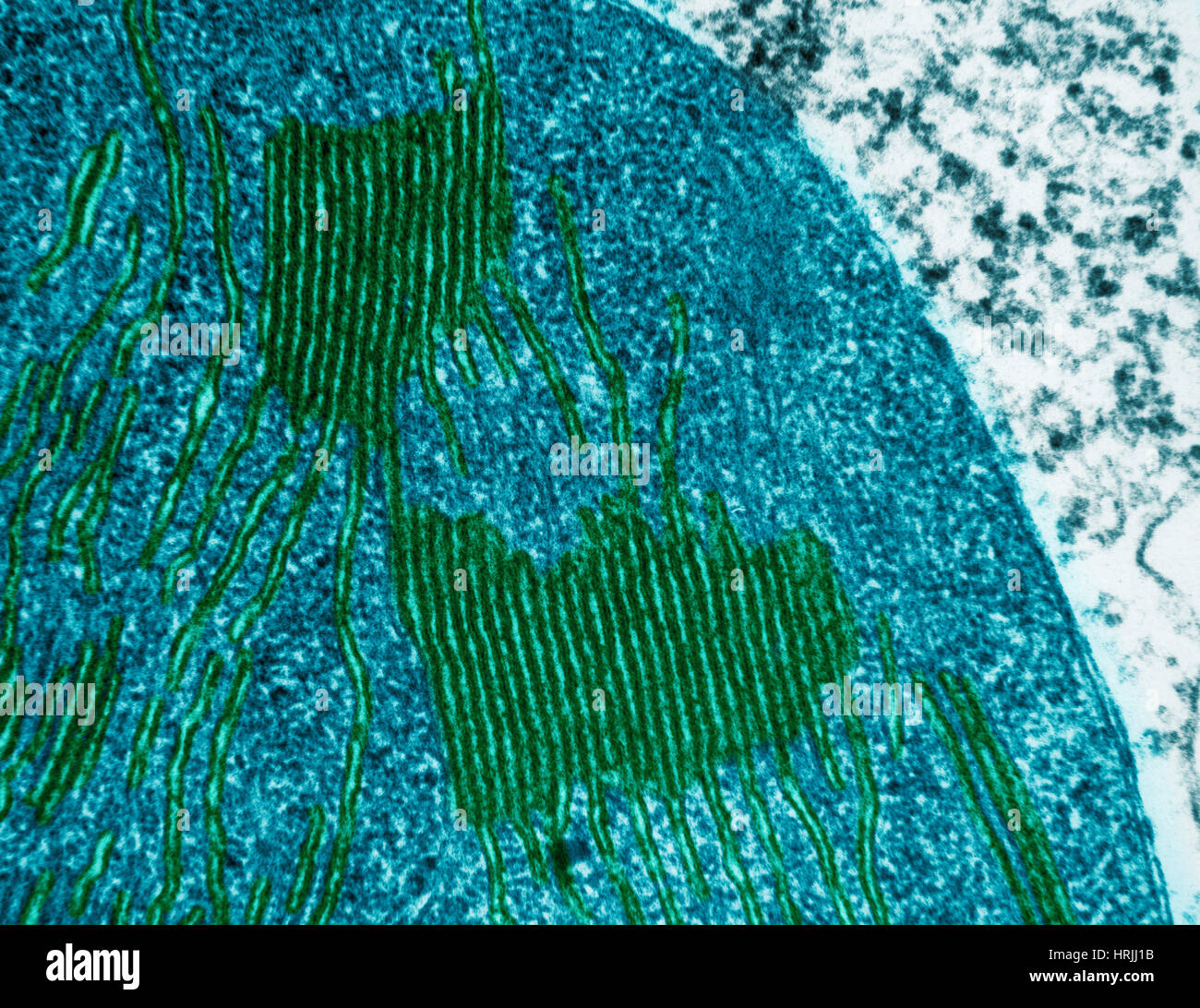 Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-135018951.html
Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-135018951.htmlRMHRJJ1B–Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM
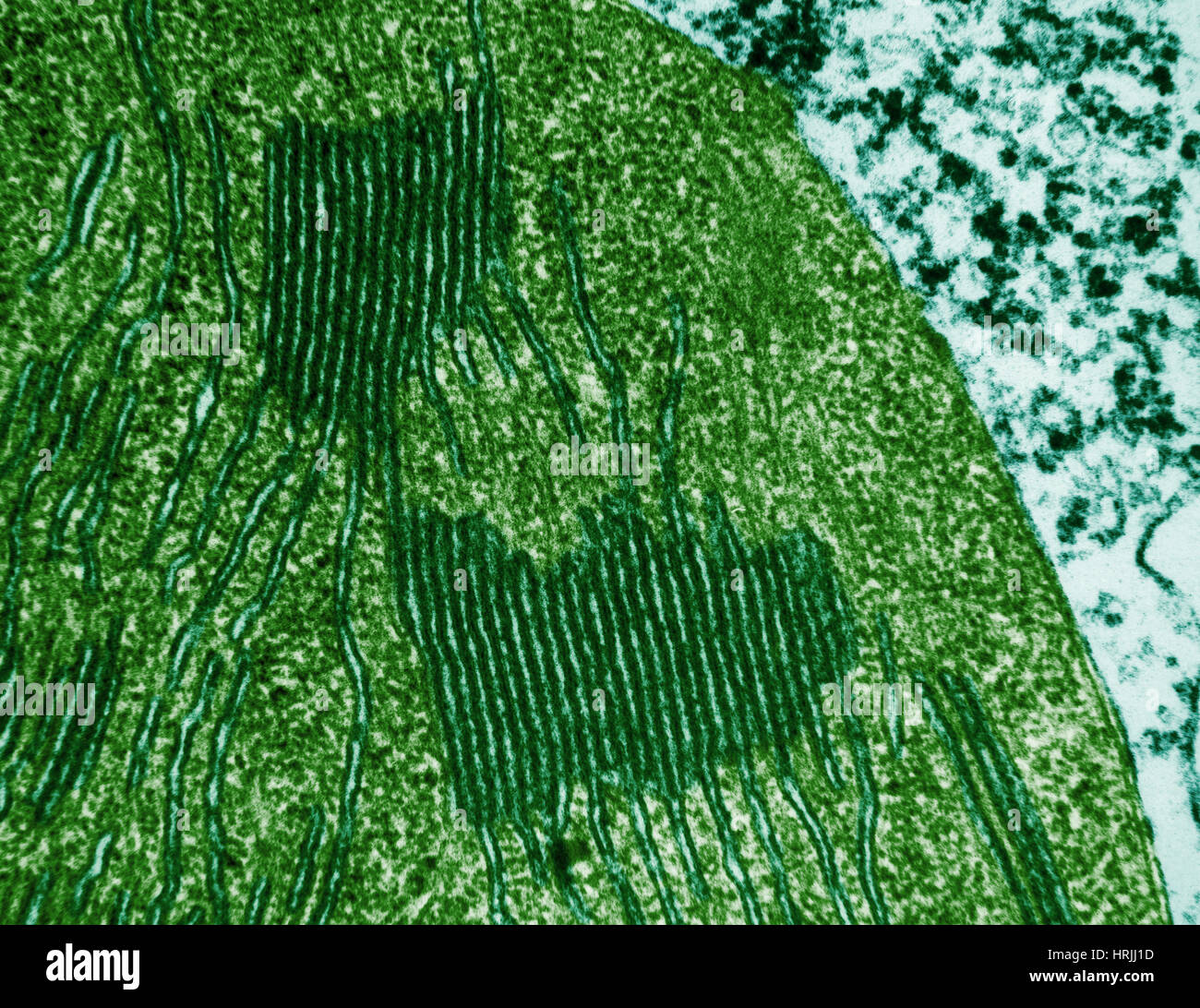 Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-135018953.html
Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-in-tomato-leaf-cell-tem-135018953.htmlRMHRJJ1D–Chloroplasts in Tomato Leaf Cell, TEM
 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134993359.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134993359.htmlRMHRHDBB–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134993356.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134993356.htmlRMHRHDB8–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
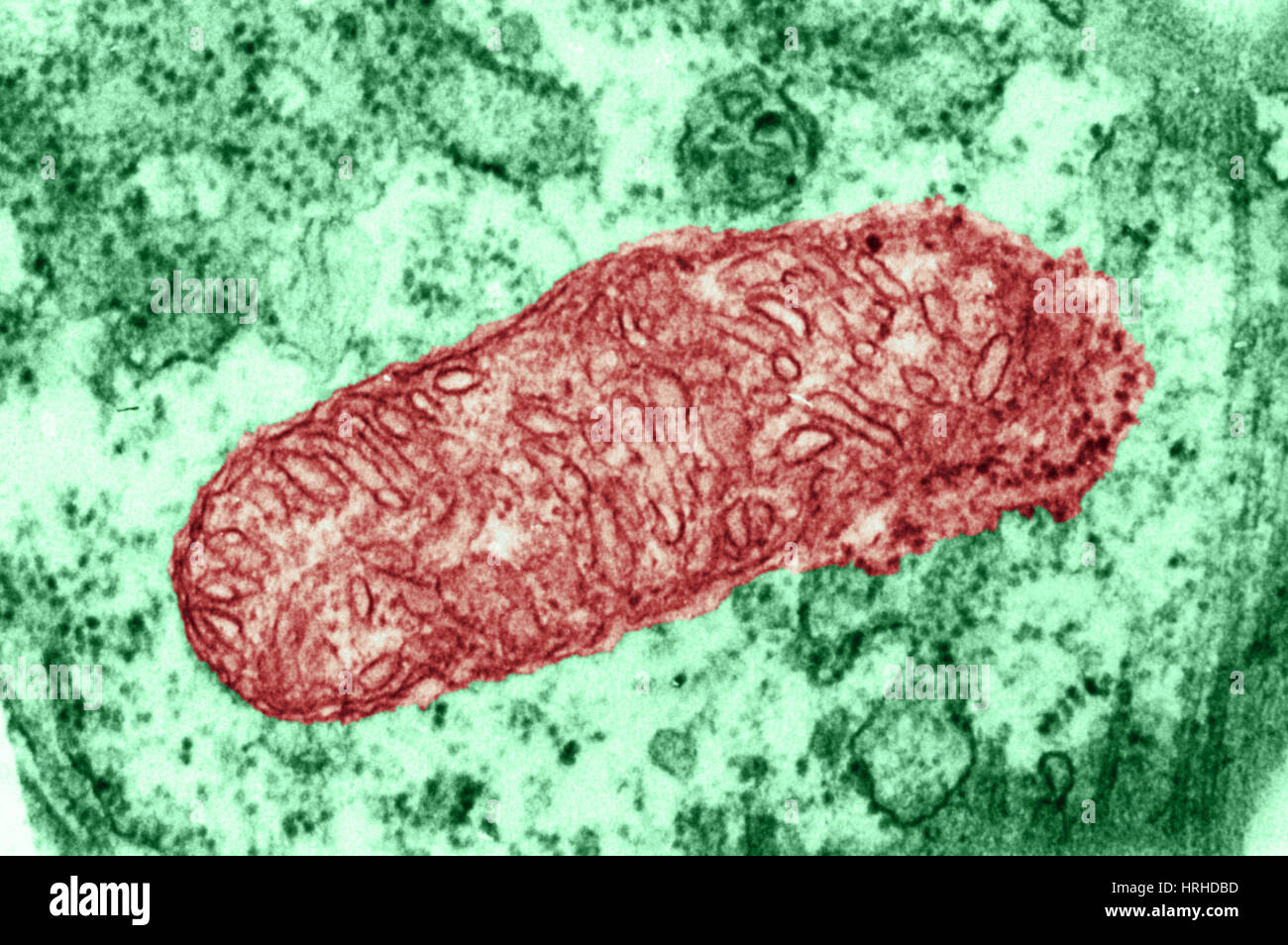 Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134993361.html
Plant Mitochondrion TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plant-mitochondrion-tem-134993361.htmlRMHRHDBD–Plant Mitochondrion TEM
 Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-135018959.html
Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-135018959.htmlRMHRJJ1K–Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM
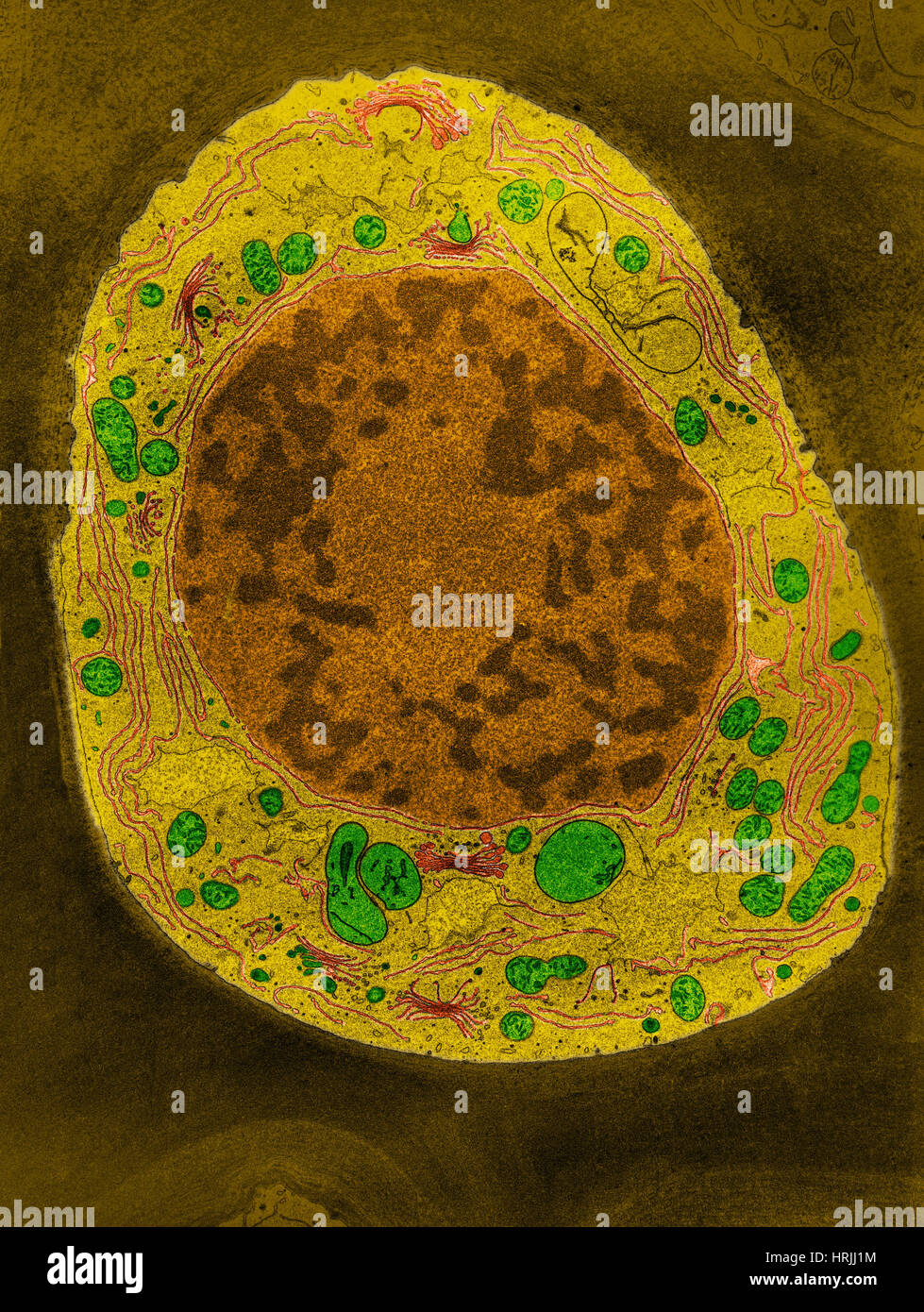 Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-135018960.html
Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-corn-root-tip-cell-tem-135018960.htmlRMHRJJ1M–Corn Root Tip Cell, TEM
 Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-135018950.html
Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-135018950.htmlRMHRJJ1A–Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM
 Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-135018947.html
Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-135018947.htmlRMHRJJ17–Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM
 Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-135018949.html
Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-in-corn-leaf-cell-tem-135018949.htmlRMHRJJ19–Chloroplast in Corn Leaf Cell, TEM
 Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134992468.html
Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134992468.htmlRMHRHC7G–Chloroplasts TEM
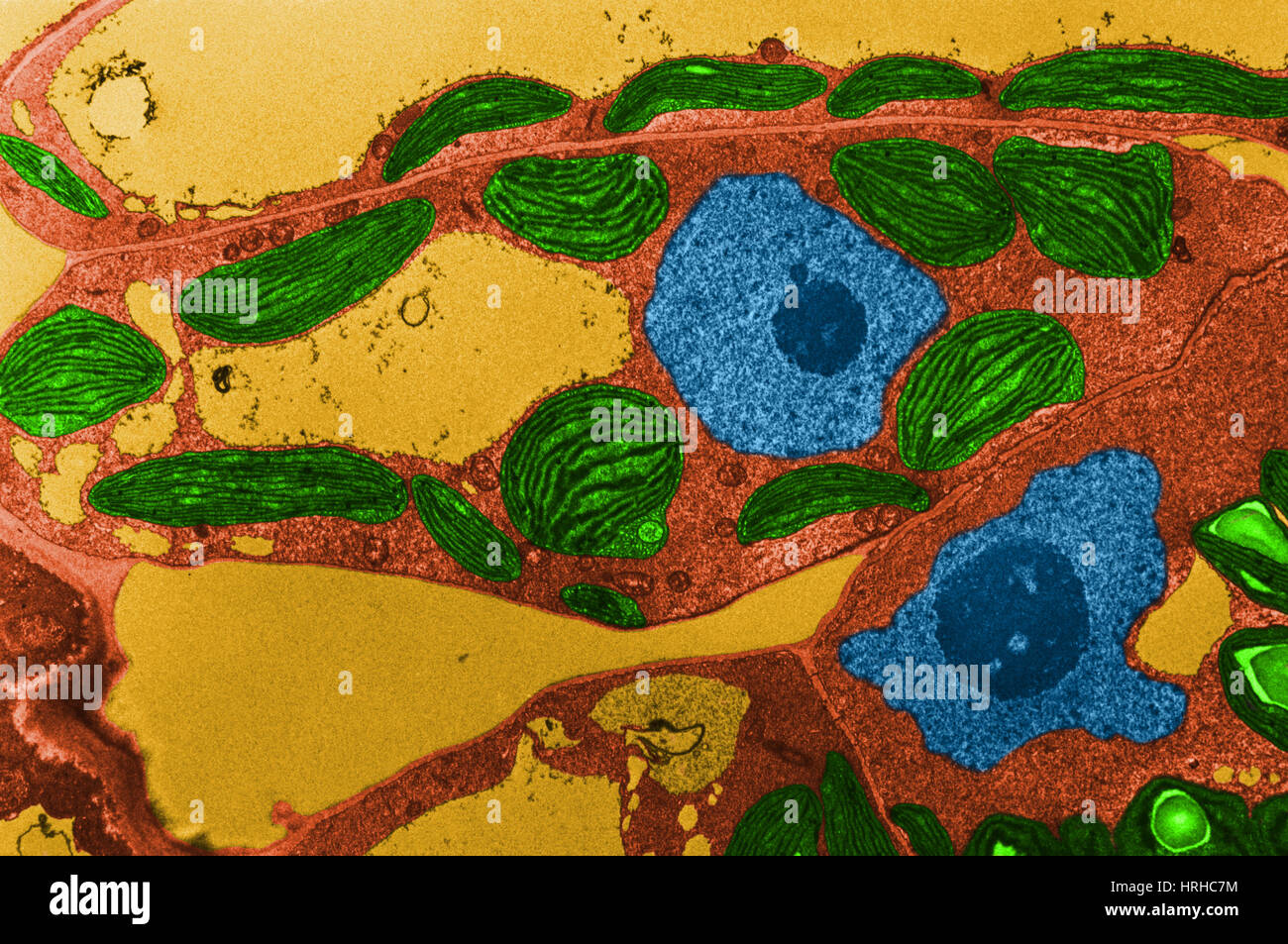 Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134992472.html
Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134992472.htmlRMHRHC7M–Chloroplasts TEM
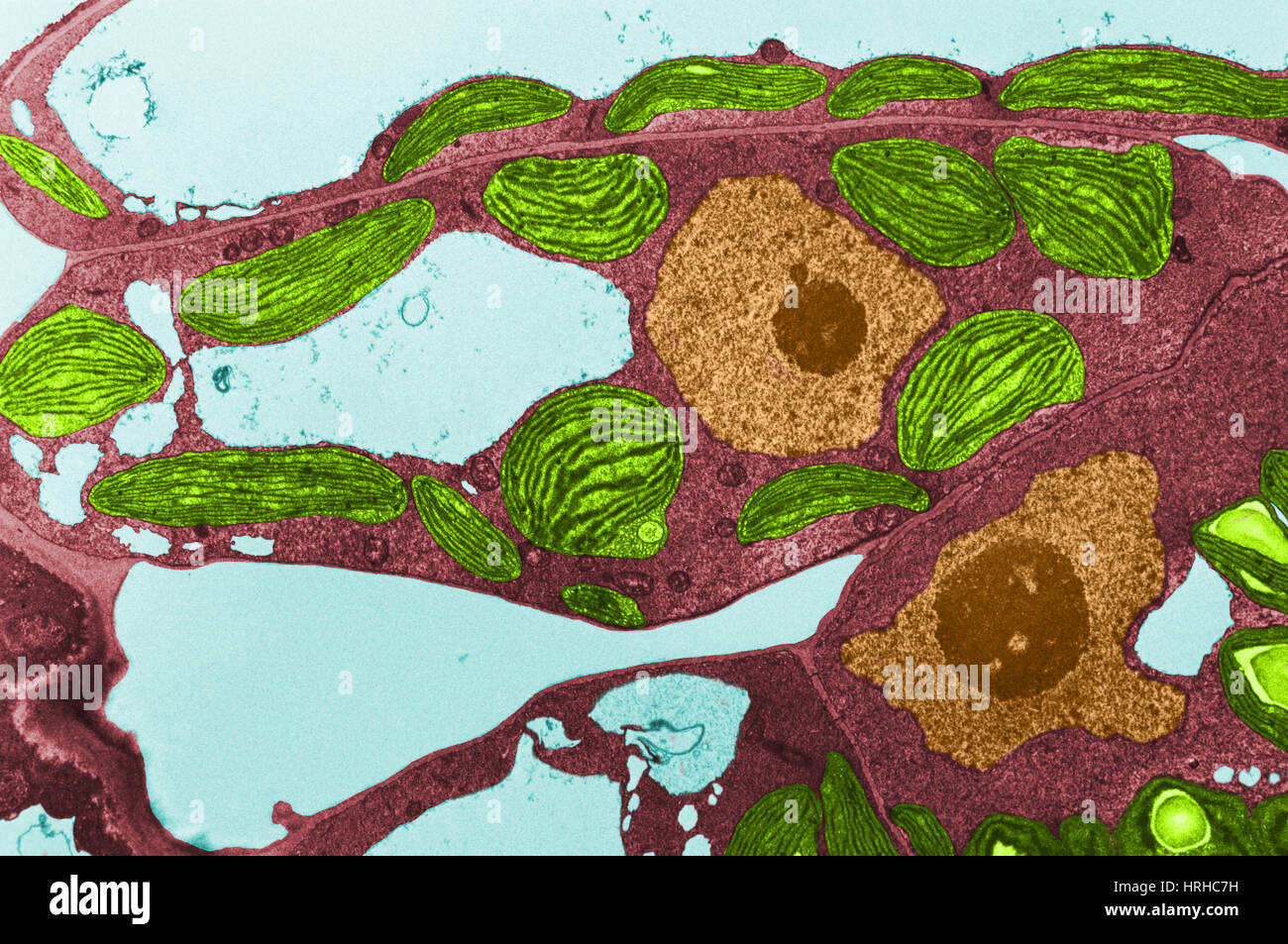 Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134992469.html
Chloroplasts TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplasts-tem-134992469.htmlRMHRHC7H–Chloroplasts TEM
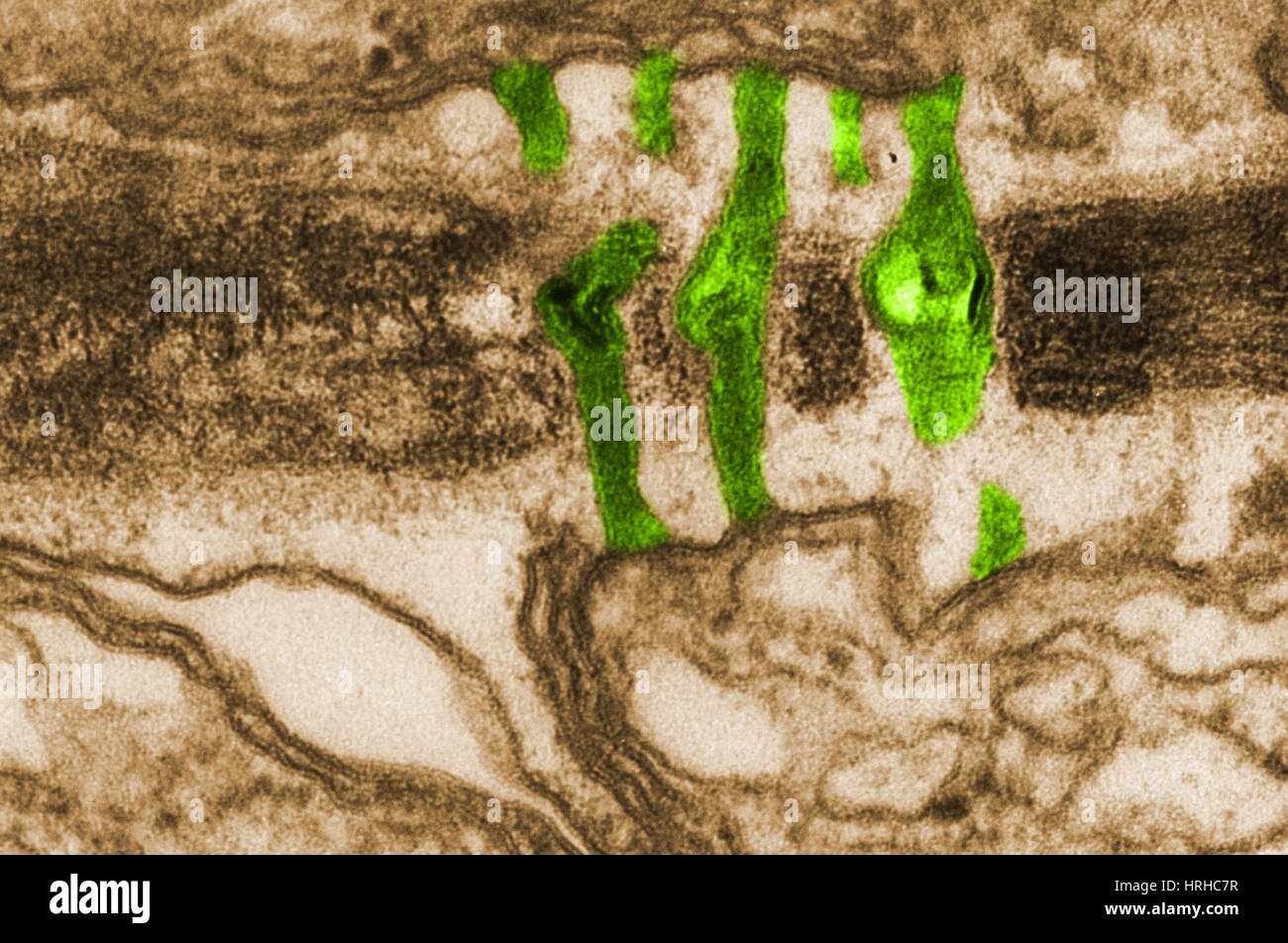 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134992475.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134992475.htmlRMHRHC7R–Plasmodesmata TEM
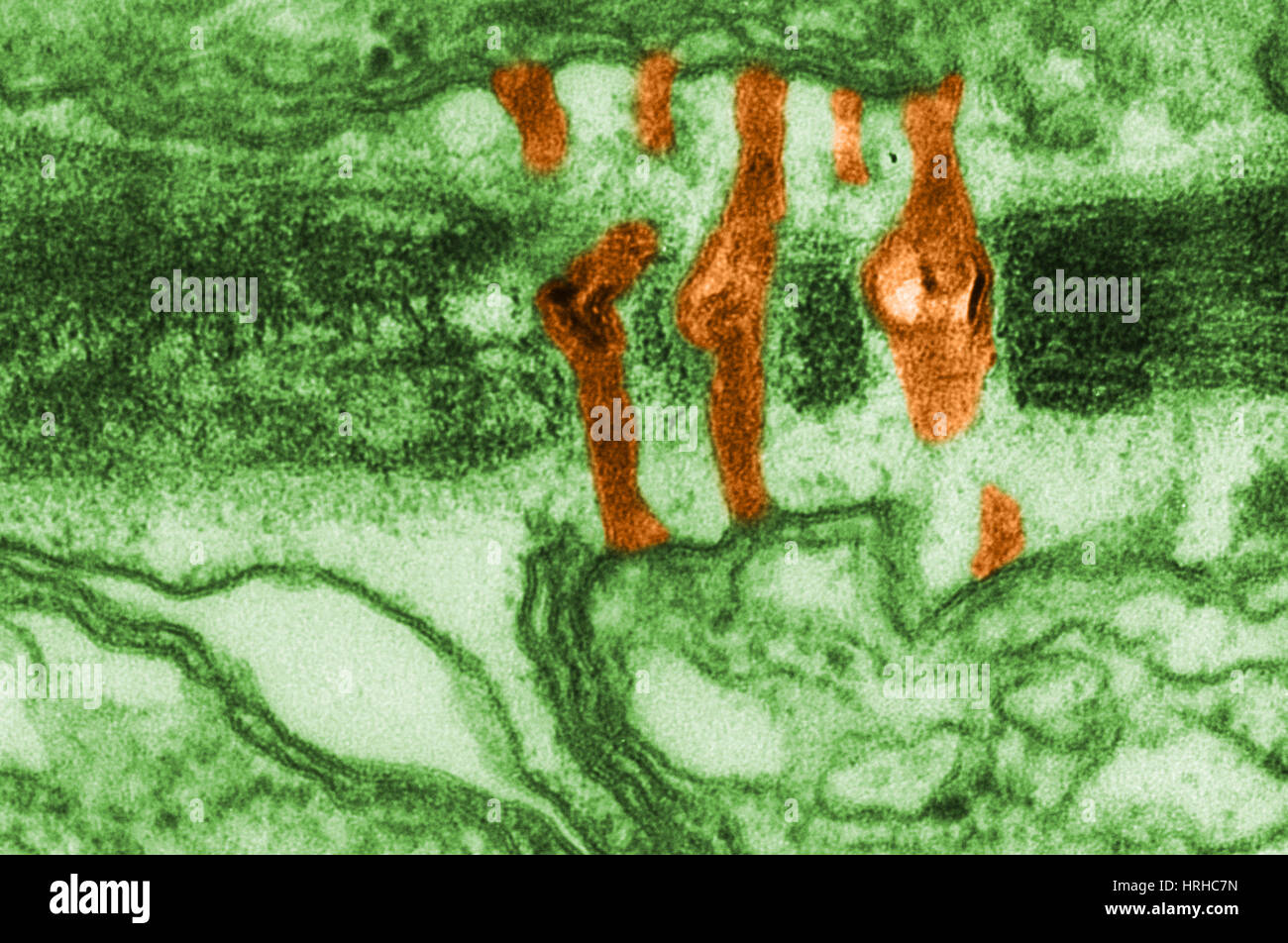 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134992473.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134992473.htmlRMHRHC7N–Plasmodesmata TEM
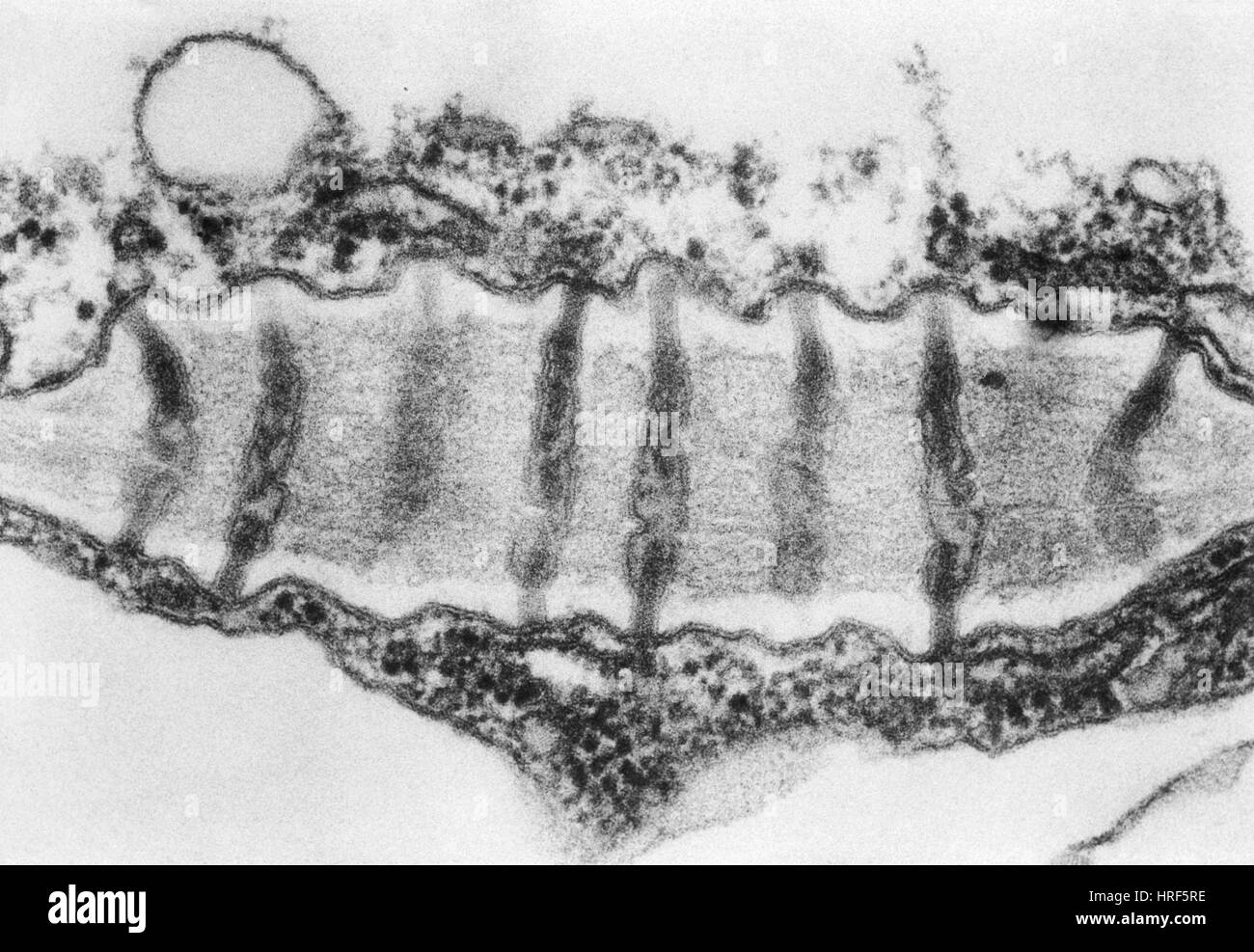 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134943522.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134943522.htmlRMHRF5RE–Plasmodesmata TEM
 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134992476.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134992476.htmlRMHRHC7T–Plasmodesmata TEM
 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134943872.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134943872.htmlRMHRF680–Plasmodesmata TEM
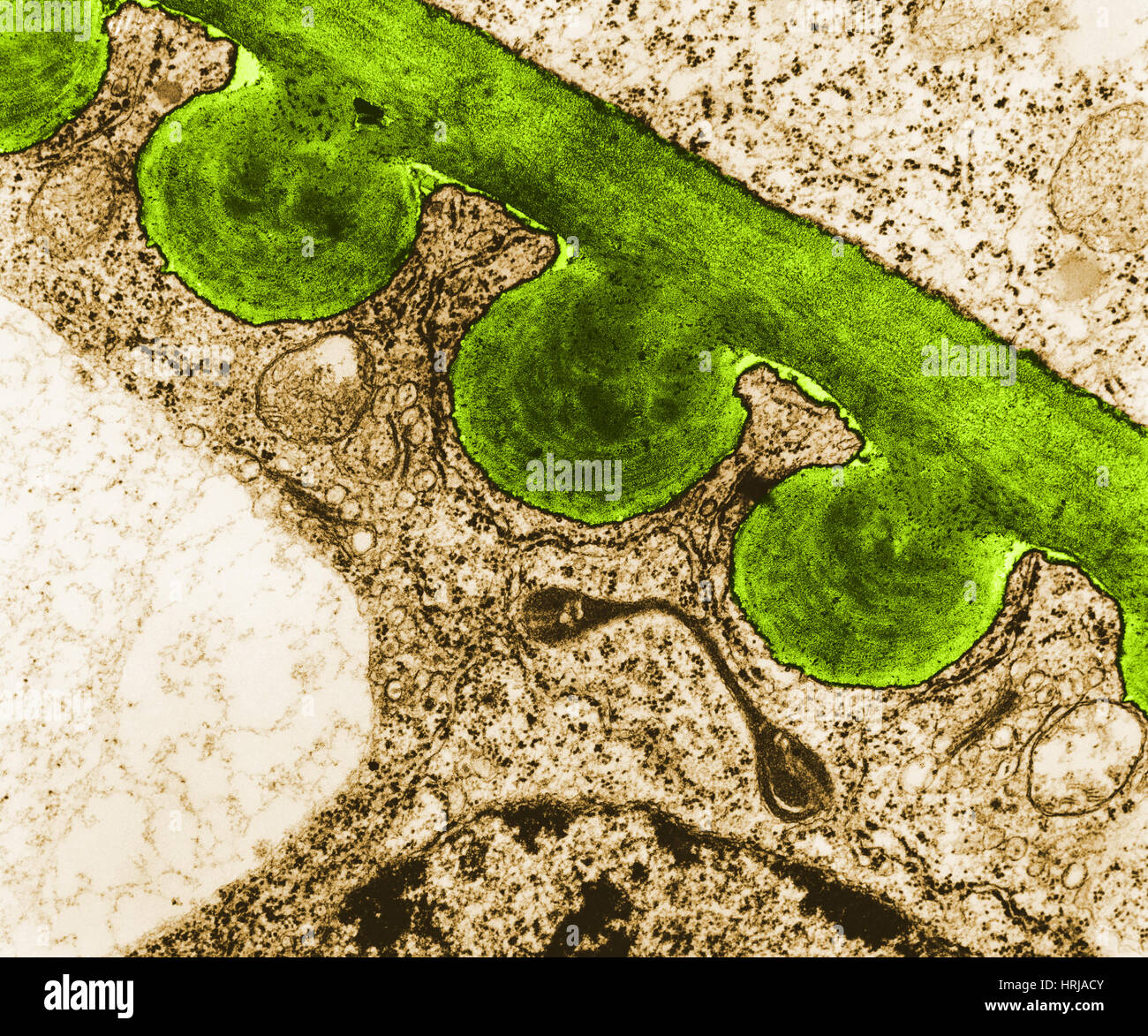 Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135013003.html
Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135013003.htmlRMHRJACY–Tomato Chloroplast, TEM
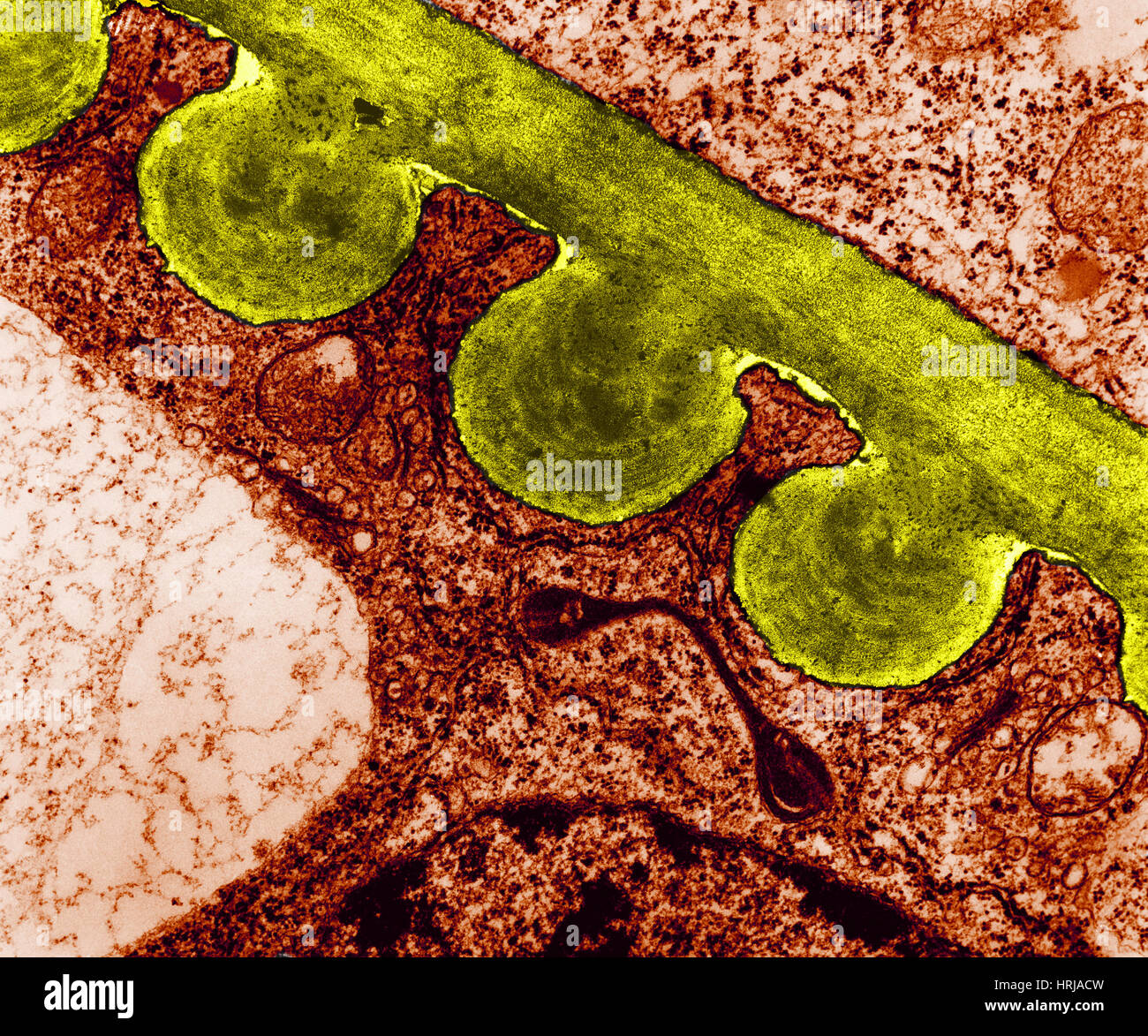 Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135013001.html
Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135013001.htmlRMHRJACW–Tomato Chloroplast, TEM
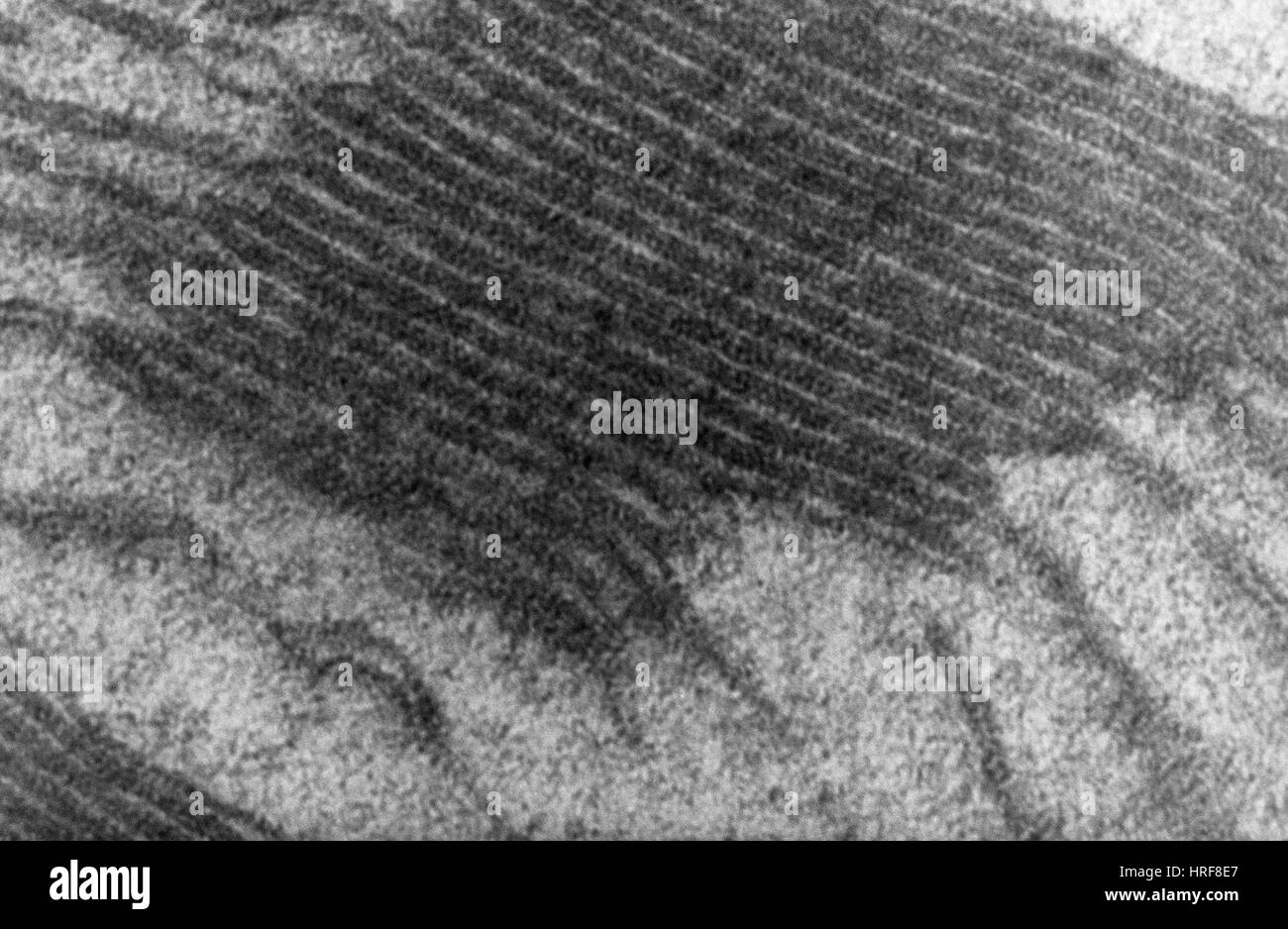 Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134945615.html
Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134945615.htmlRMHRF8E7–Chloroplast, TEM
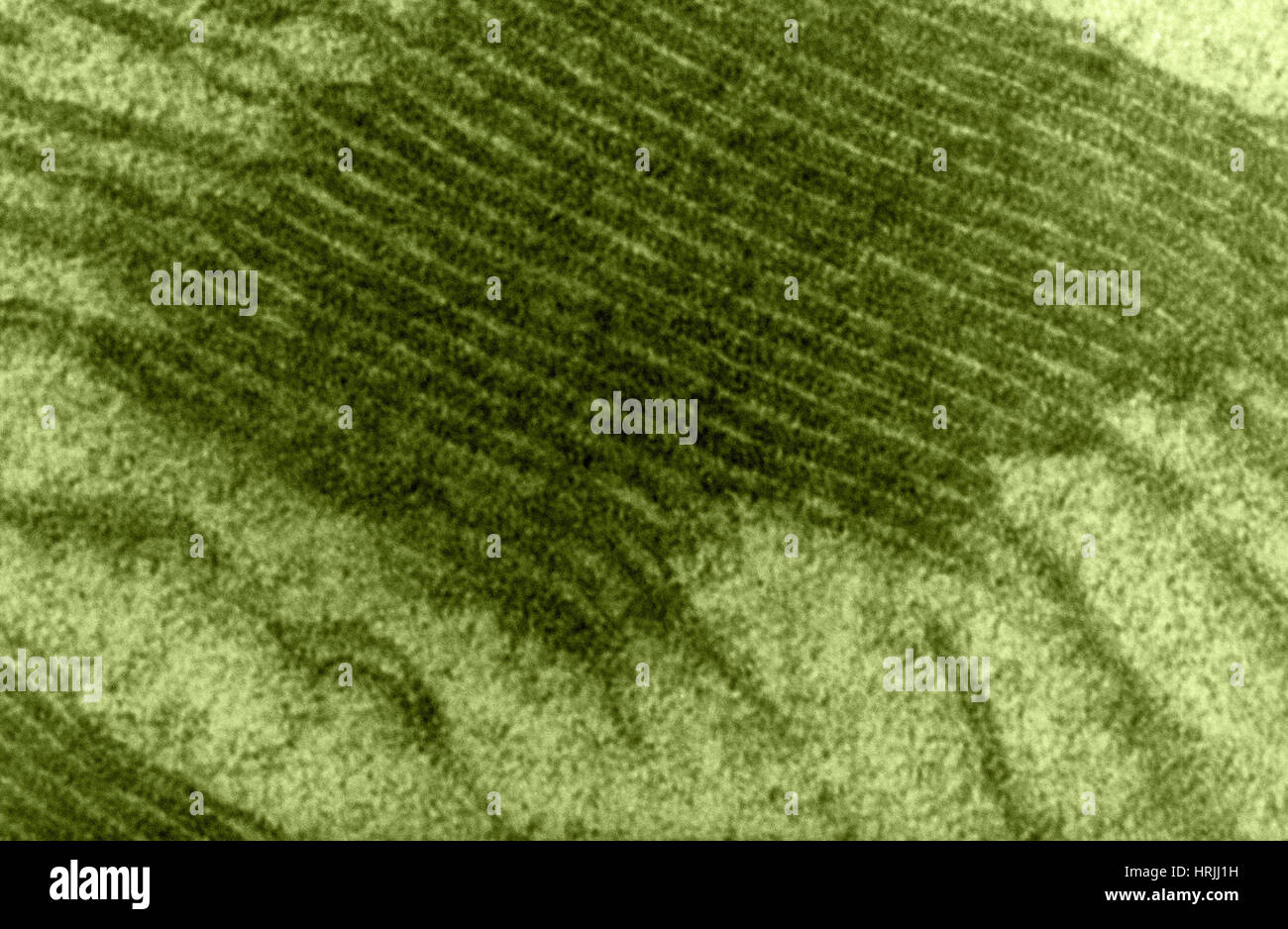 Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-135018957.html
Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-135018957.htmlRMHRJJ1H–Chloroplast, TEM
 Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-135018956.html
Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-135018956.htmlRMHRJJ1G–Chloroplast, TEM
 Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-135018955.html
Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-135018955.htmlRMHRJJ1F–Chloroplast, TEM
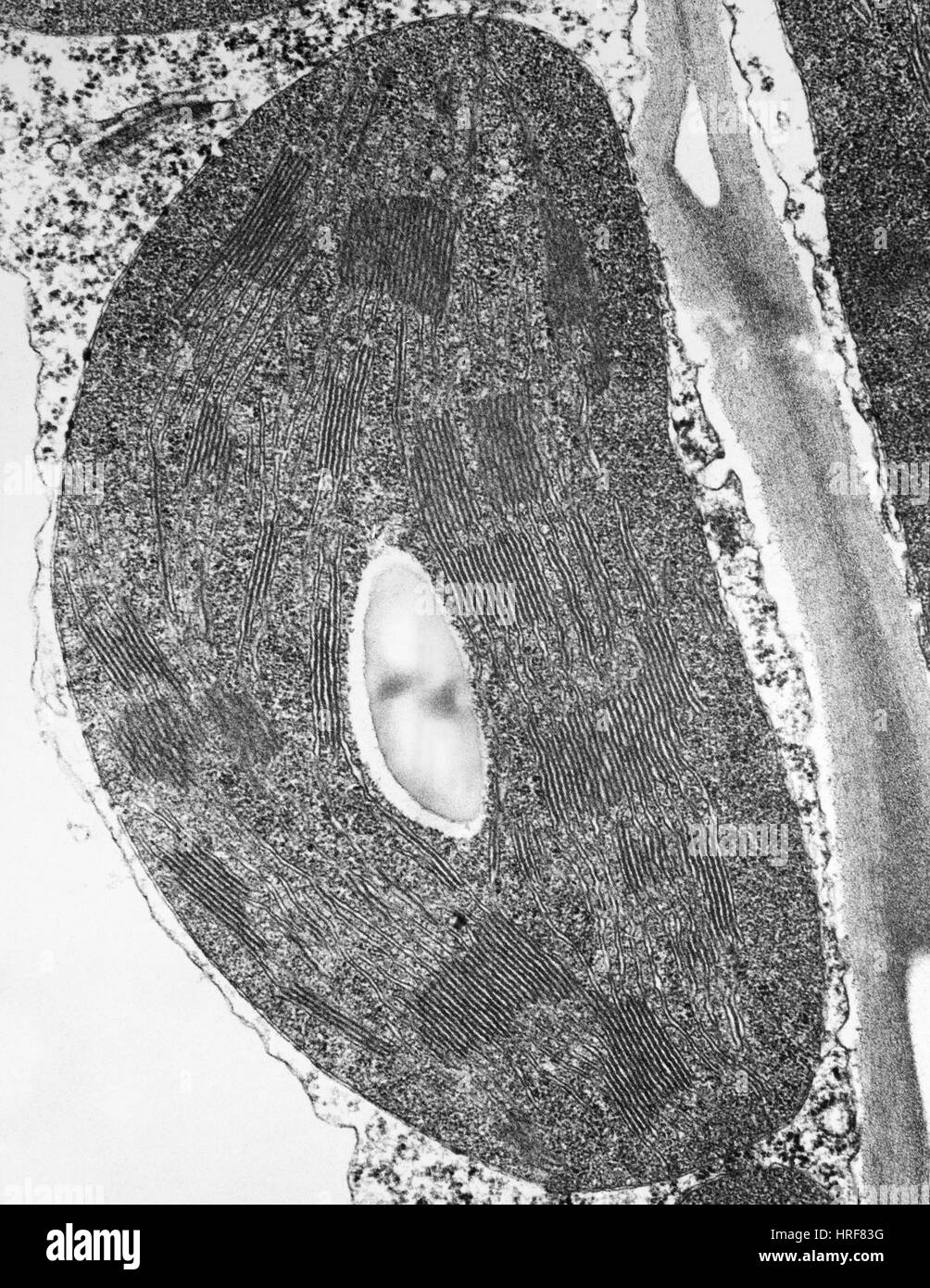 Tomato Chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-134945316.html
Tomato Chloroplast Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-134945316.htmlRMHRF83G–Tomato Chloroplast
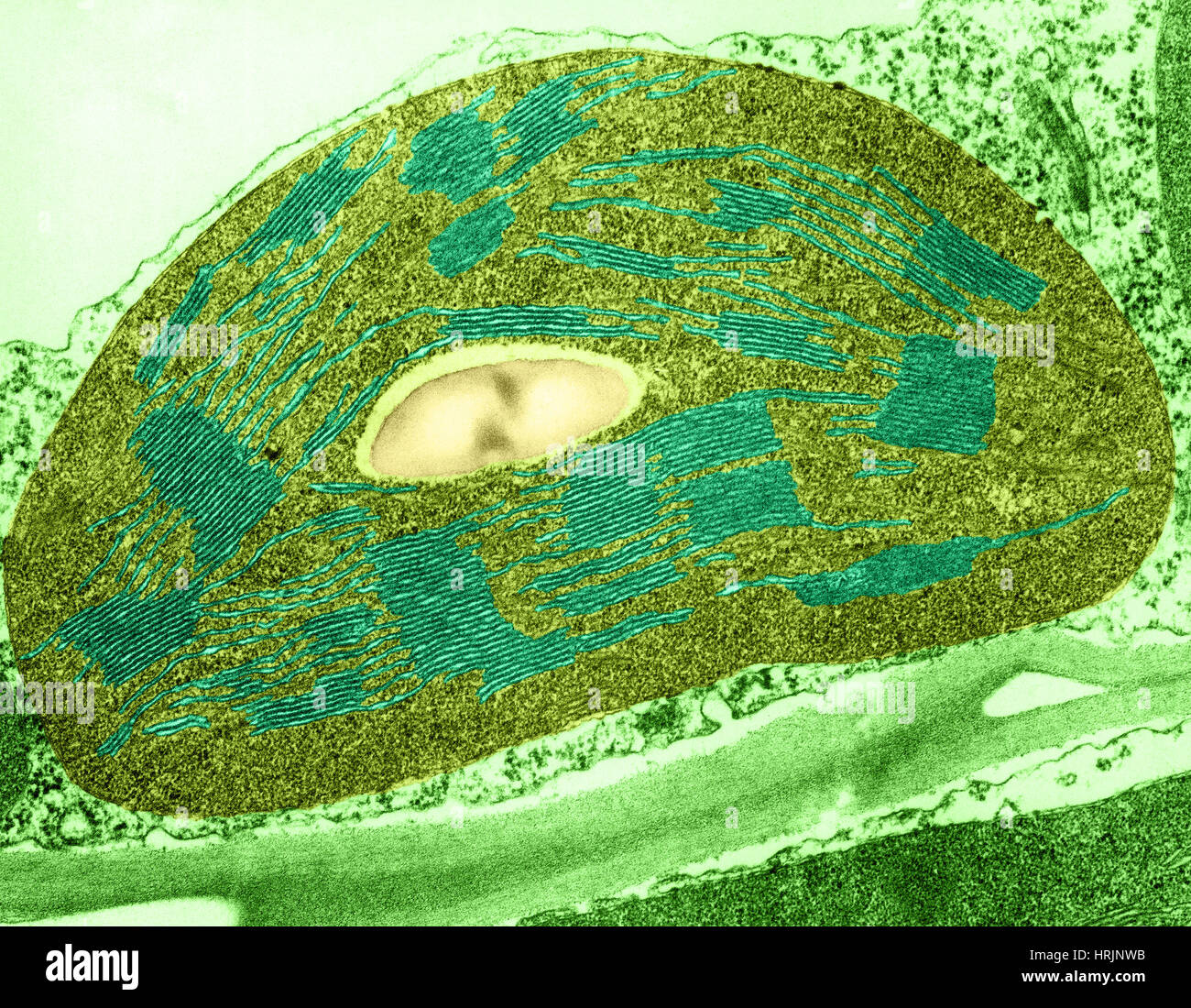 Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135021975.html
Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135021975.htmlRMHRJNWB–Tomato Chloroplast, TEM
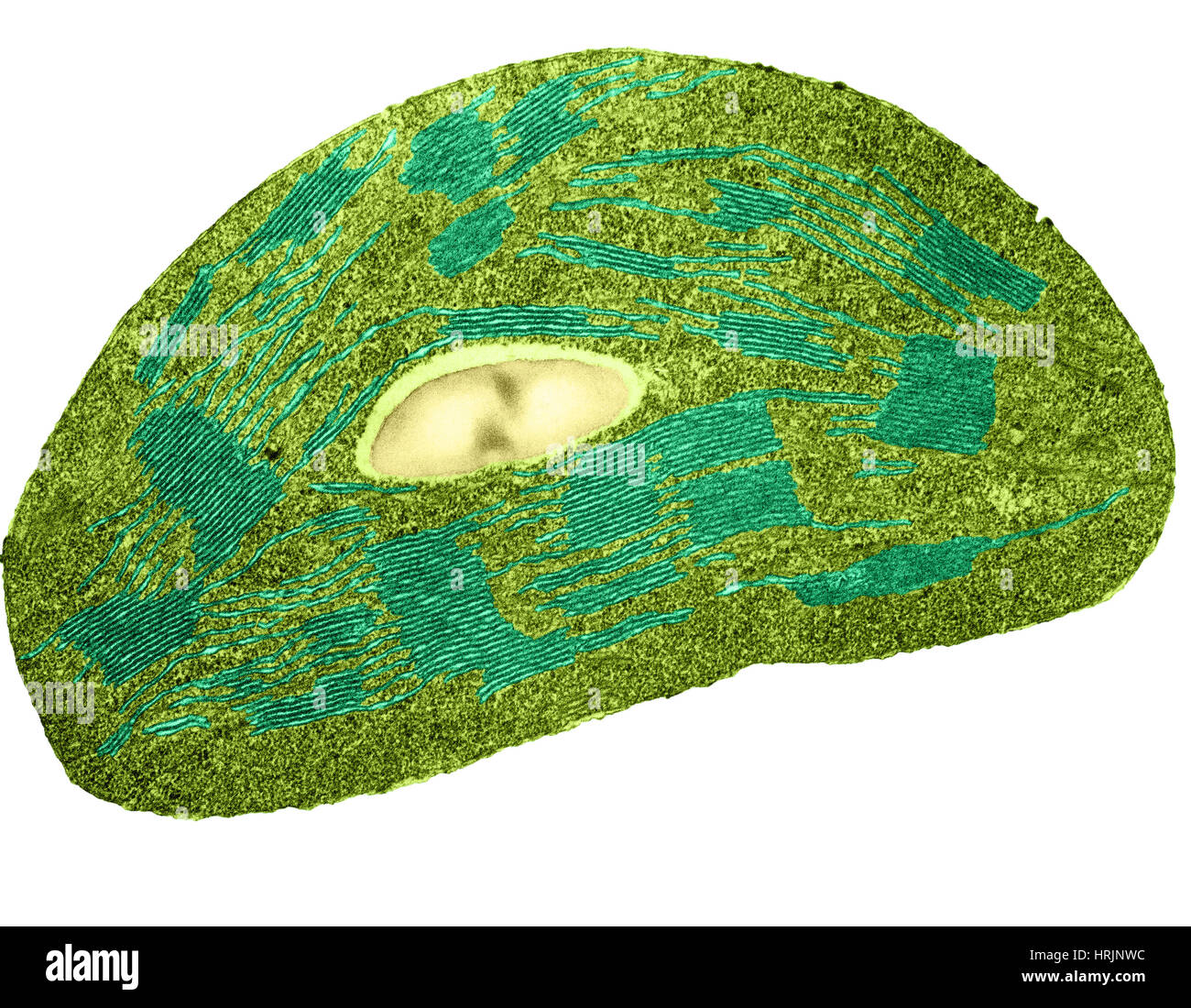 Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135021976.html
Tomato Chloroplast, TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tomato-chloroplast-tem-135021976.htmlRMHRJNWC–Tomato Chloroplast, TEM
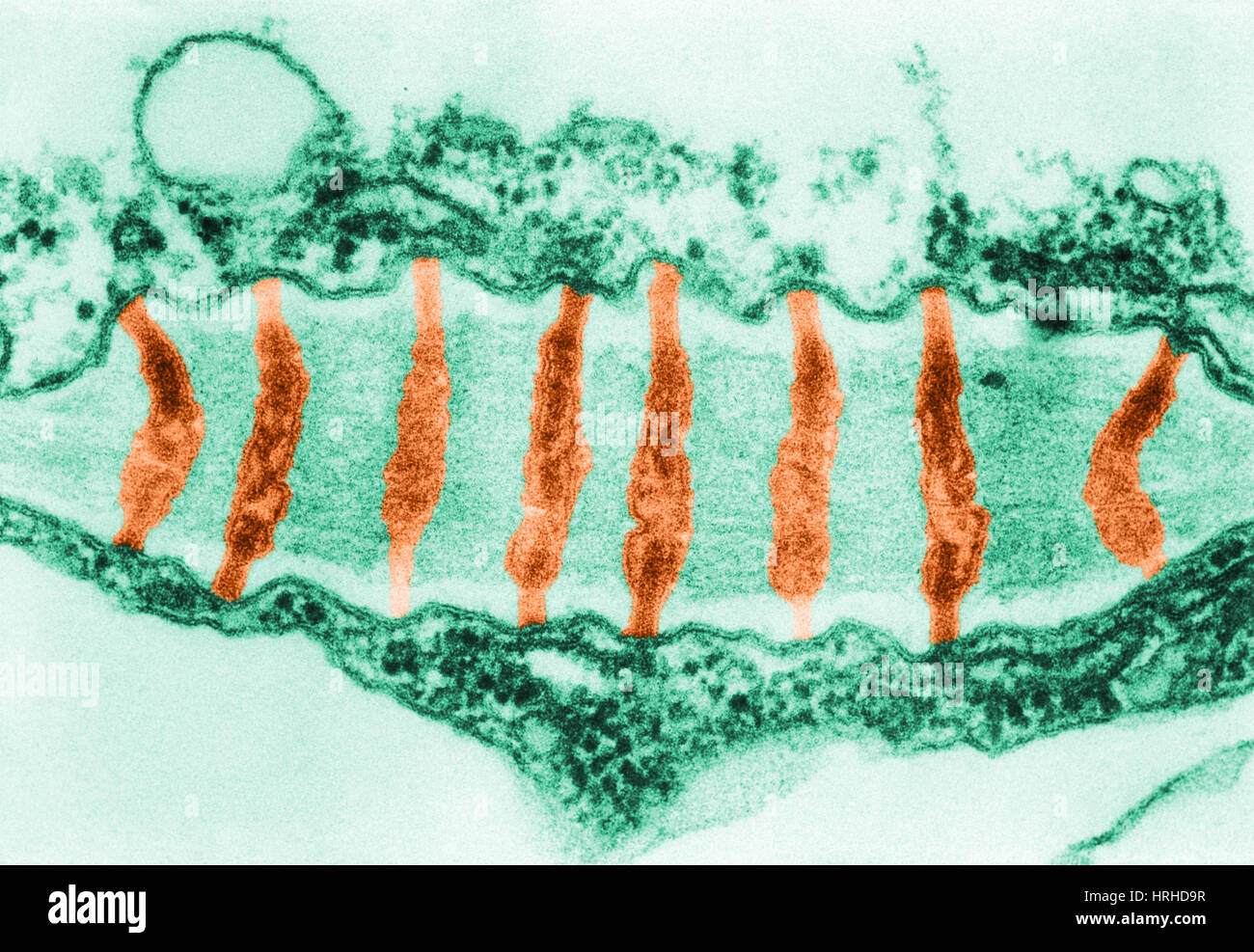 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134993315.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134993315.htmlRMHRHD9R–Plasmodesmata TEM
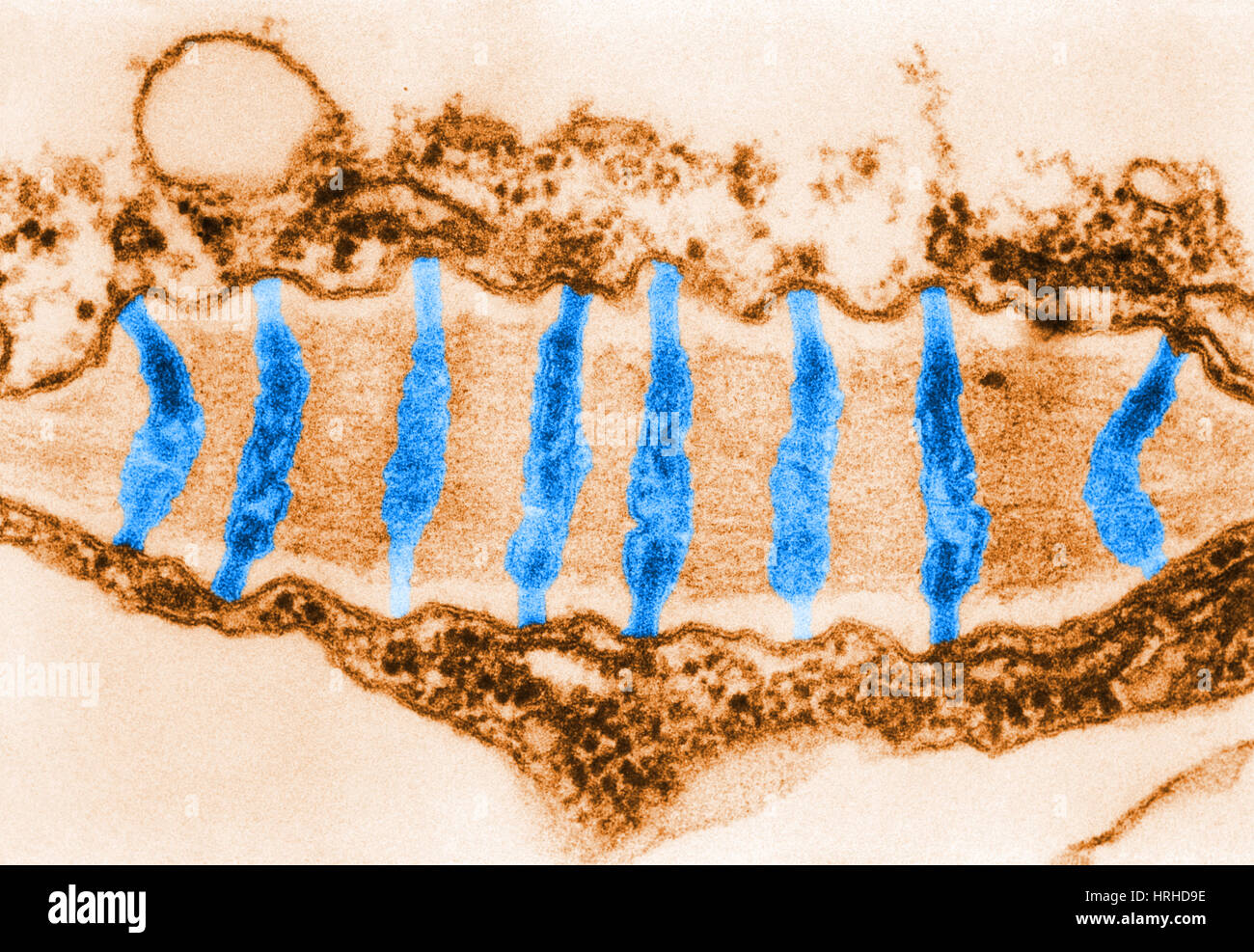 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134993306.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134993306.htmlRMHRHD9E–Plasmodesmata TEM
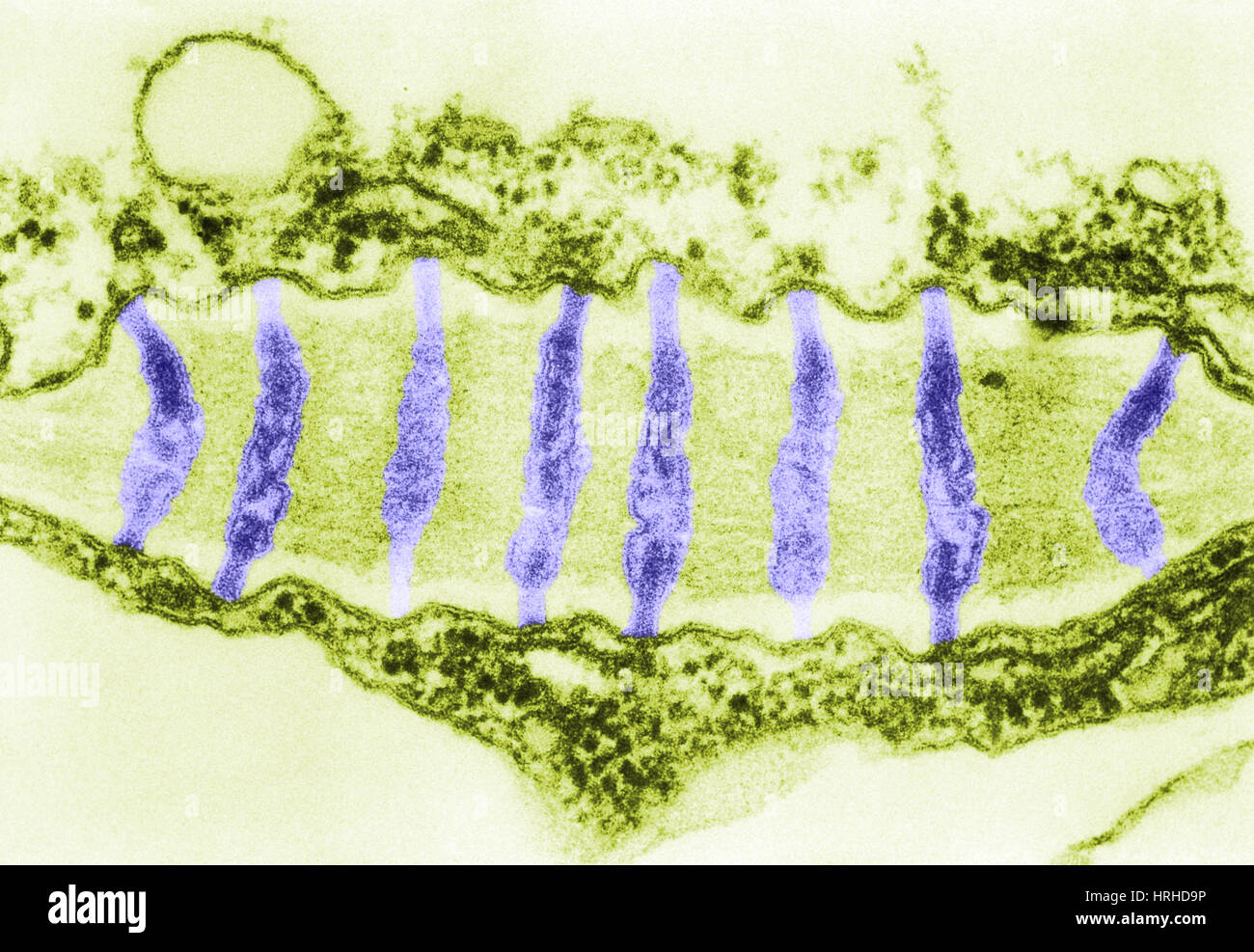 Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134993314.html
Plasmodesmata TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasmodesmata-tem-134993314.htmlRMHRHD9P–Plasmodesmata TEM
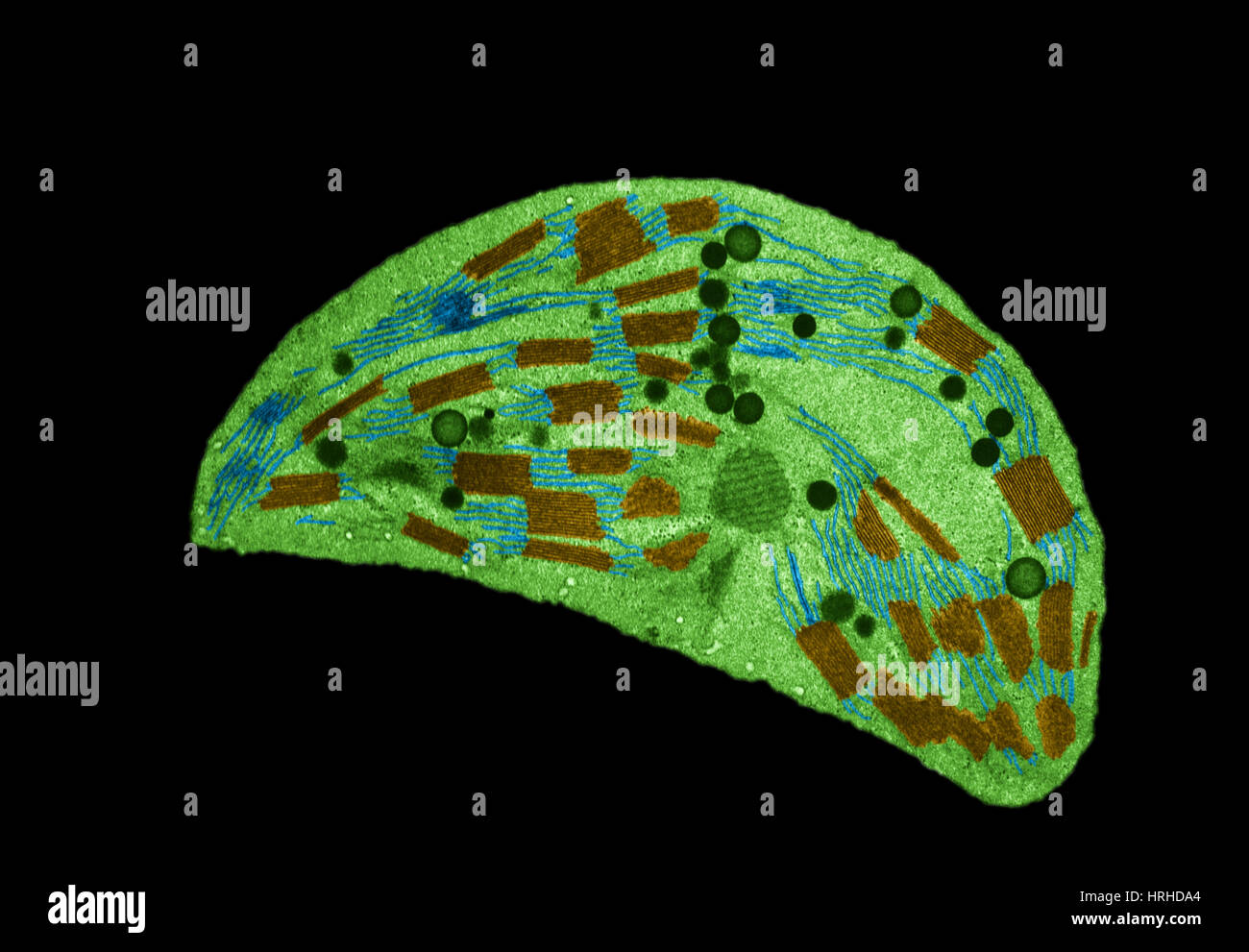 Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134993324.html
Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134993324.htmlRMHRHDA4–Chloroplast TEM
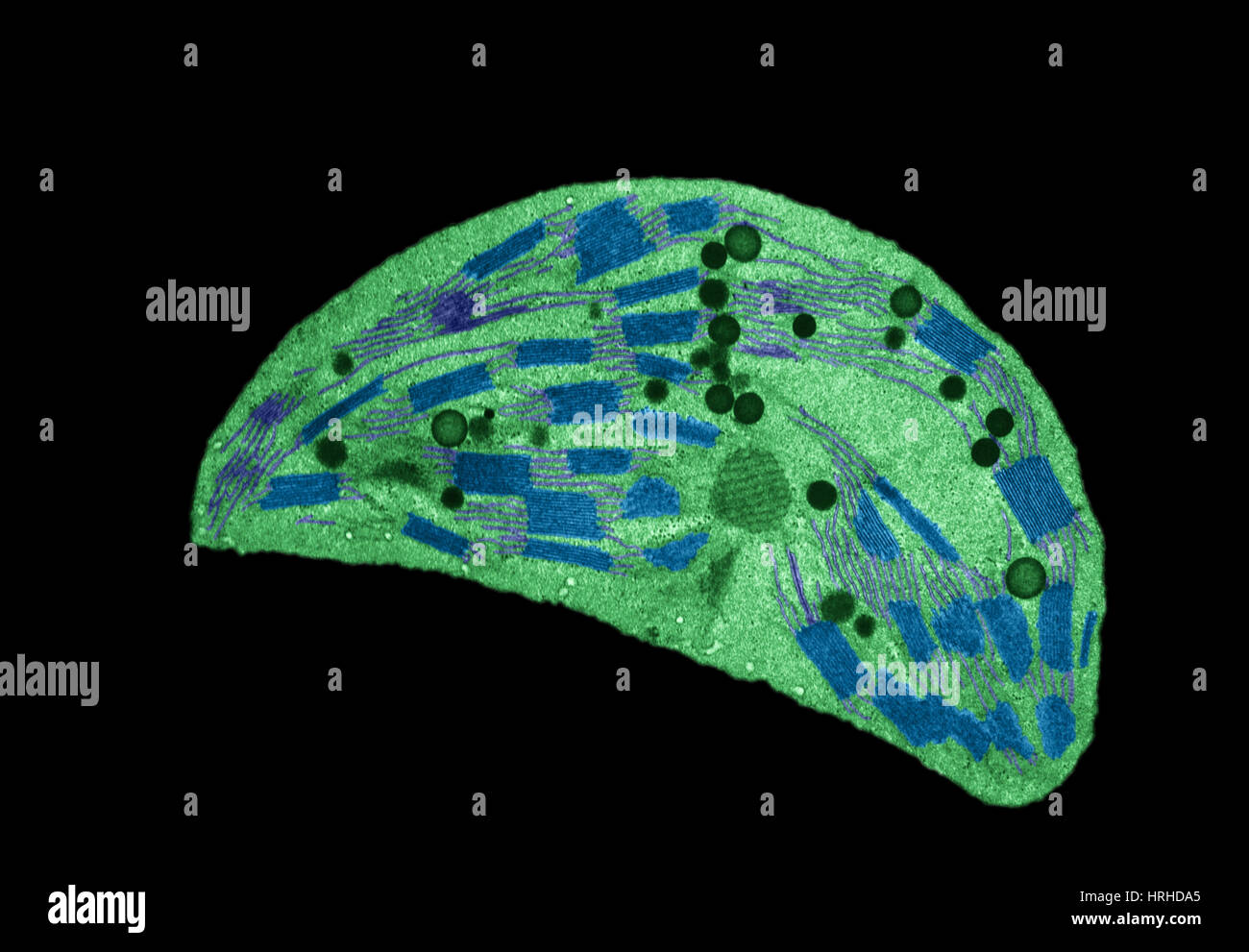 Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134993325.html
Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134993325.htmlRMHRHDA5–Chloroplast TEM
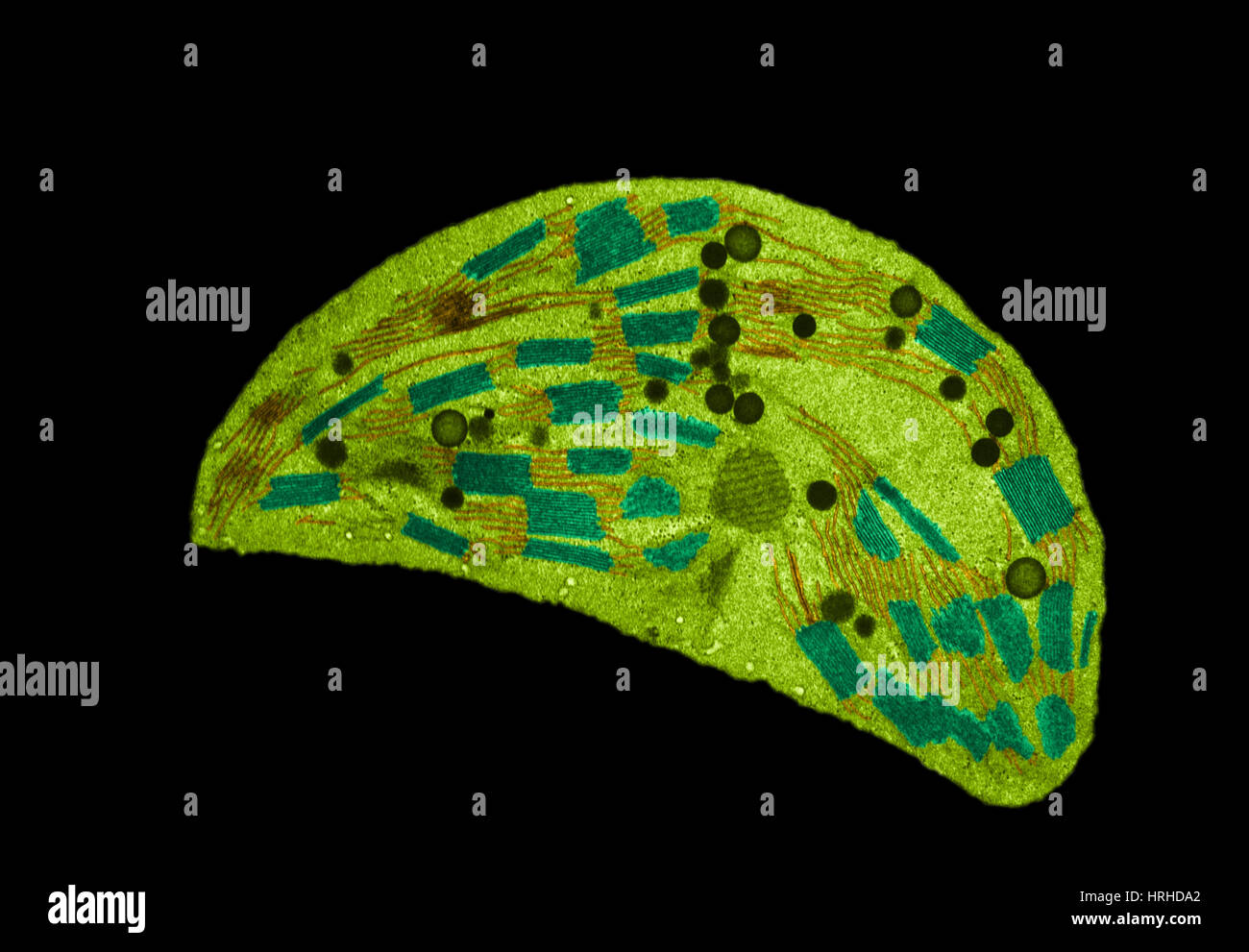 Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134993322.html
Chloroplast TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-chloroplast-tem-134993322.htmlRMHRHDA2–Chloroplast TEM
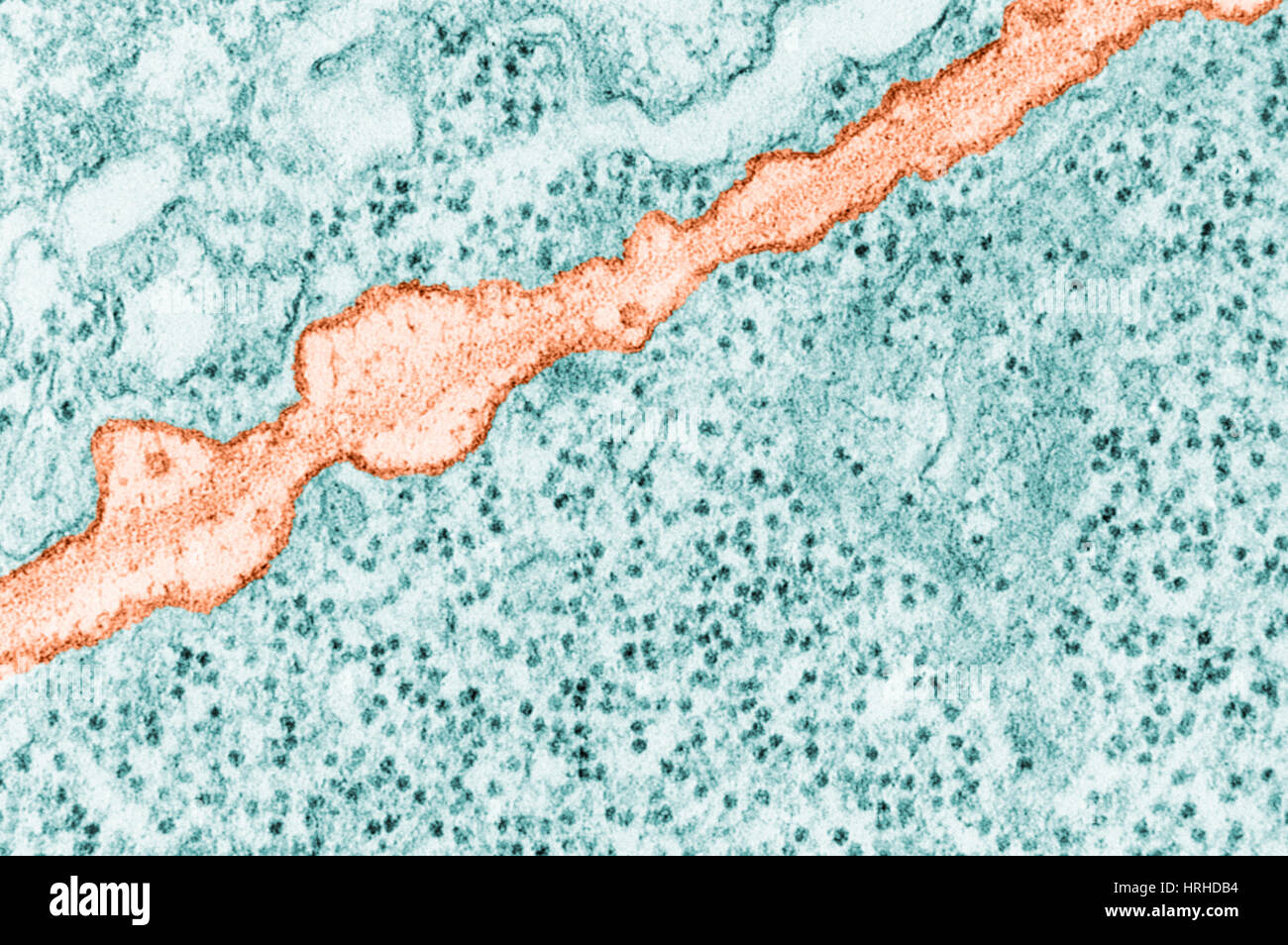 Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134993352.html
Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134993352.htmlRMHRHDB4–Plasma Membrane TEM
 Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134993355.html
Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134993355.htmlRMHRHDB7–Plasma Membrane TEM
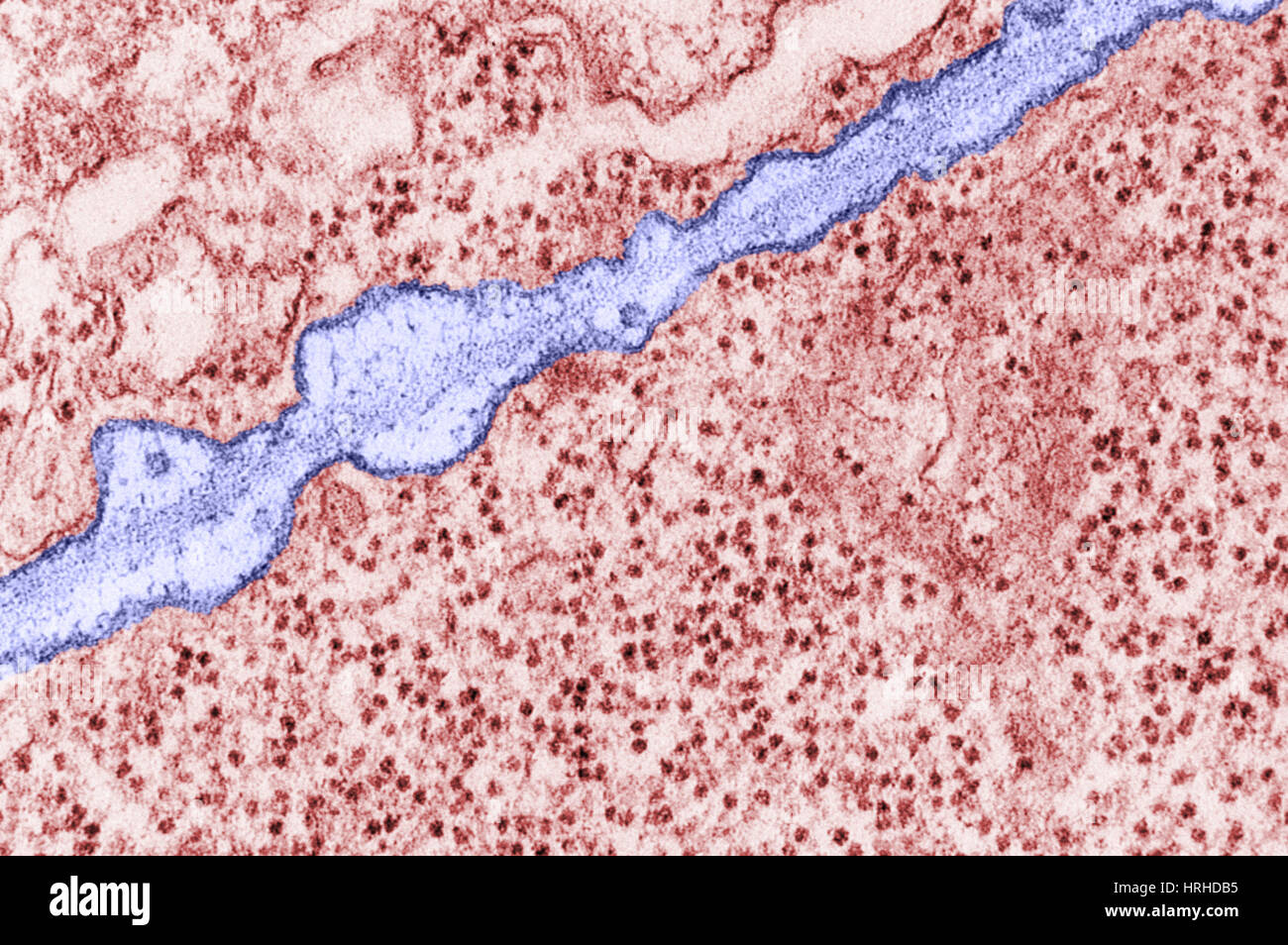 Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134993353.html
Plasma Membrane TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plasma-membrane-tem-134993353.htmlRMHRHDB5–Plasma Membrane TEM
 Plastid with Starch Granules TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plastid-with-starch-granules-tem-134993319.html
Plastid with Starch Granules TEM Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-plastid-with-starch-granules-tem-134993319.htmlRMHRHD9Y–Plastid with Starch Granules TEM