. Text book of vertebrate zoology. Vertebrates; Anatomy, Comparative. NERVOUS SYSTEM. 59 IV. Trochlearis (or Patheticus). V. Trigeminal (or Trifacial). VI. Abducens. VII. Facial. VIII. Auditory. IX. Glossopharyngeal. X. Vagus (or Pneumogastric). XI. Spinal Accessory (or Accessory of Willis). XII. Hypoglossal. As has been described, the spinal nerves contain both sen- sory and motor roots. The cranial nerves present some dif- ferences from this. Thus nerves I., II., and VIII. are purely. Fig. 61. Diagram of cranial nerves (shark), a, alveolaris; b, buccalis; c, cerebrum; cb, cerebellum; cl, cho
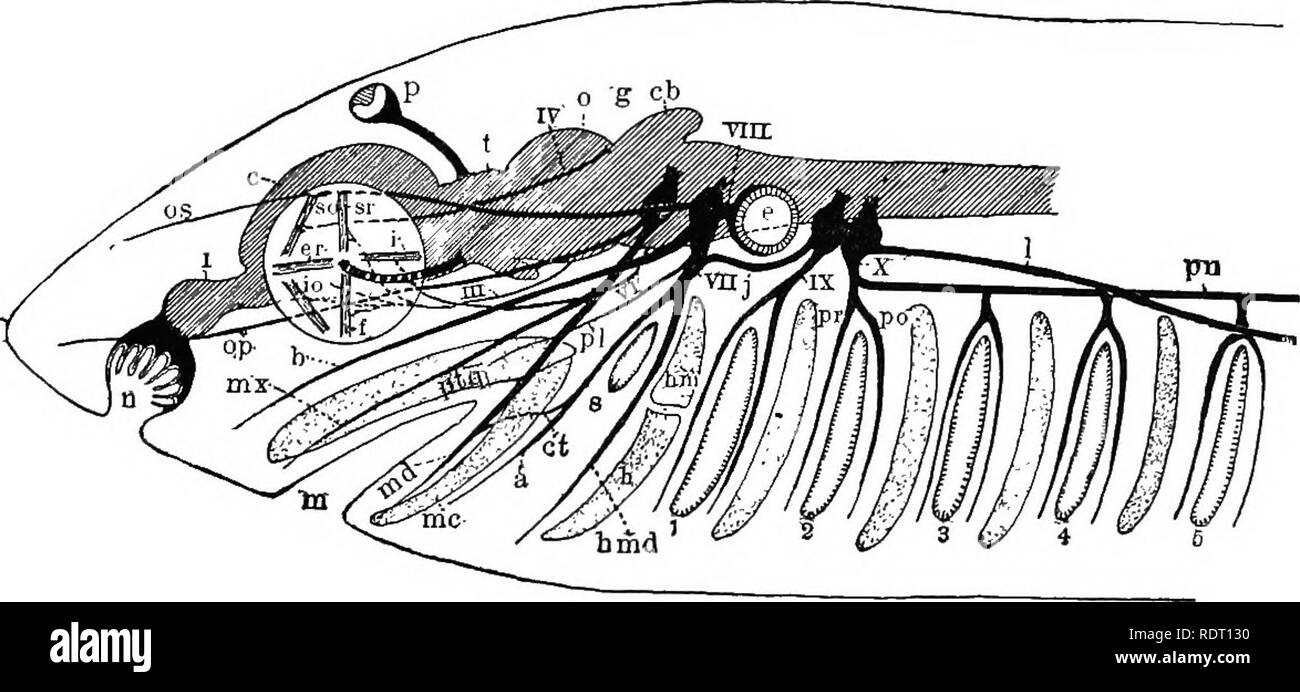
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RDT130File size:
7.1 MB (353.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
2322 x 1076 px | 39.3 x 18.2 cm | 15.5 x 7.2 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Text book of vertebrate zoology. Vertebrates; Anatomy, Comparative. NERVOUS SYSTEM. 59 IV. Trochlearis (or Patheticus). V. Trigeminal (or Trifacial). VI. Abducens. VII. Facial. VIII. Auditory. IX. Glossopharyngeal. X. Vagus (or Pneumogastric). XI. Spinal Accessory (or Accessory of Willis). XII. Hypoglossal. As has been described, the spinal nerves contain both sen- sory and motor roots. The cranial nerves present some dif- ferences from this. Thus nerves I., II., and VIII. are purely. Fig. 61. Diagram of cranial nerves (shark), a, alveolaris; b, buccalis; c, cerebrum; cb, cerebellum; cl, chorda tympani; e, ear; er, external rectus muscle; f, inferior rectus muscle; g, Gasserian ganglion; h, hyoid cartilage; hm, hyoman- dibular cartilage ; hnui, hyomandibular nerve ; ;', internal rectus muscle; io, inferior â oblique muscle ; j, Jacobson's commissure; /, lateralis branch of vagus; ni, mouth; //;r, Meckel's cartilage; vid^ mandibularis; vix, maxillaris superior; ;/, nose; 0, optic lobes (mesencephalon); op, ophthalmicus profundus; w, ophthalmicus super- ficialis; /, pinealis; pi, palatine; po, post-trematic branch; pn, intestinal (pneu- mogastric) branch of vagus ; /;-, pre-trematic branch ; ptq, pterygoquadrate cartilage ; s, spiracle; so, superior oblique muscle; sr, superior rectus muscle; /, thalamen- cephalon ; I-X, cranial nerves; 1-5, gill clefts. sensory; III., IV., and VI. are solely motor; while the others are mixed, i.e., contain both motor and sensory fibres. Both the olfactory and the optic nerves are usually regarded as differing from all other cranial nerves in that they arise as. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Kingsley, J. S. (John Sterling), 1854-1929. New York, H. Holt and Company