Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria, computer illustration. K. pneumoniae are Gram-negative, encapsulated, non-motile, enteric, rod prokaryote. This specie
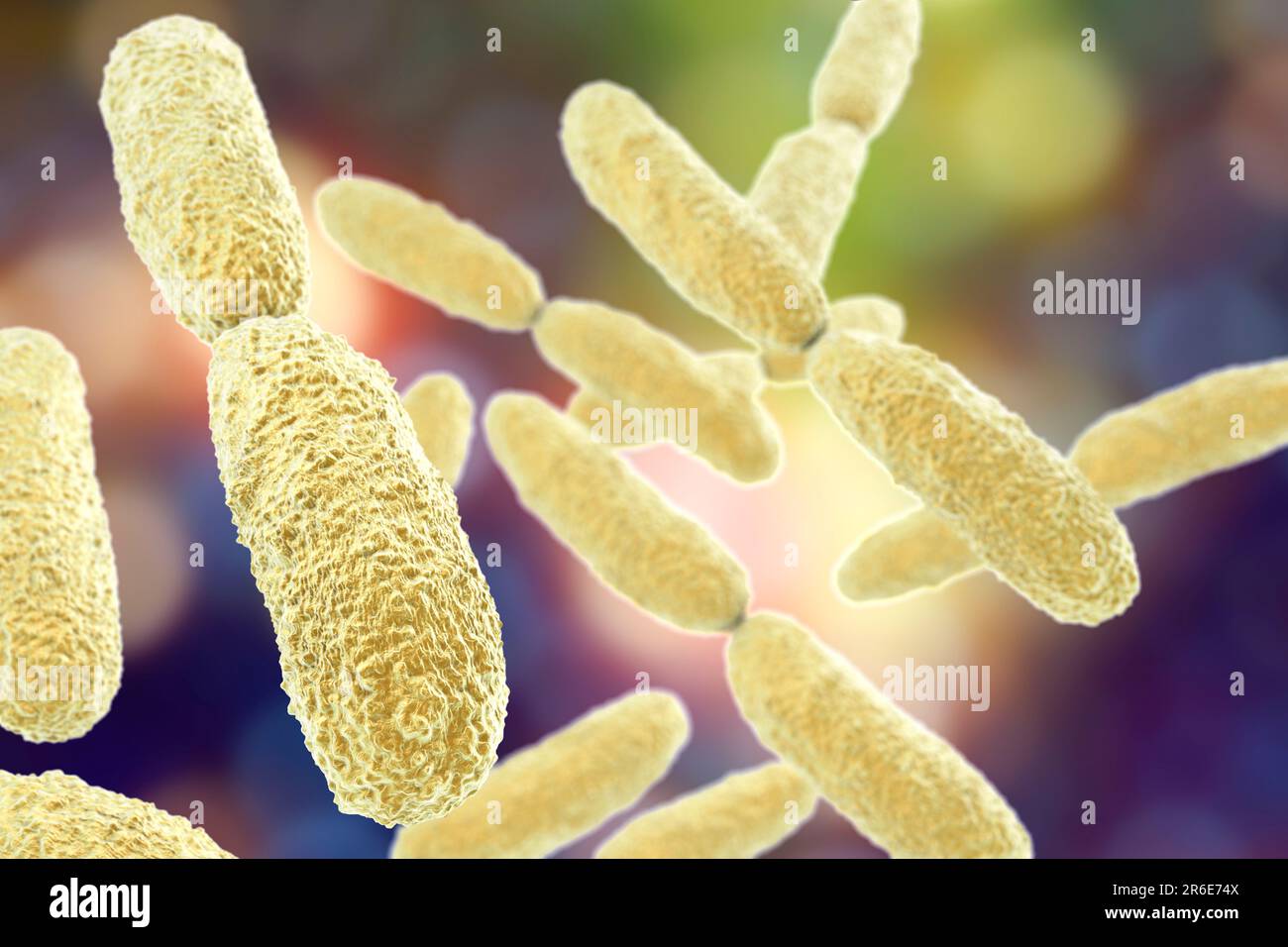
Image details
Contributor:
Dr_Microbe / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2R6E74XFile size:
68.7 MB (1.2 MB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
6000 x 4000 px | 50.8 x 33.9 cm | 20 x 13.3 inches | 300dpiMore information:
Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria, computer illustration. K. pneumoniae are Gram-negative, encapsulated, non-motile, enteric, rod prokaryote. This species causes Friedlander's pneumonia and urinary tract infections. K. pneumoniae pathogenicity can be attributed to its production of a heat-stable enterotoxin. This bacterium has antibiotic resistance properties. Klebsiella species may contain resistance plasmids(R-plasmids) which confer resistance to such antibiotics as ampicillin and carbenicillin. The R-plasmids can be transferred to other enteric bacteria not necessarily of the same species. Bacillary pneumonia is rare in healthy humans and usually occurs in infants, the elderly, alcoholics, and debilitated or immunocompromised hosts.